The Spectator
in three volumes: translations and index
for:
A New Edition
Reproducing the Original Text
Both as First Issued
and as Corrected by its Authors
with Introduction, Notes, and Index
edited by Henry Morley
1891
The Spectator
in three volumes: volume 1
A New Edition
Reproducing the Original Text
Both as First Issued
and as Corrected by its Authors
with Introduction, Notes, and Index
edited by Henry Morley
1891
Table of Contents / [Volume 3 link: Index]
- No. 1 – Thursday, March 1, 1711 – Addison
- No. 2 – Friday, March 2, 1711 – Steele
- No. 3 – Saturday, March 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 4 – Monday, March 5, 1711 – Steele
- No. 5 – Tuesday, March 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 6 – Wednesday, March 7, 1711 – Steele
- No. 7 – Thursday, March 8, 1711 – Addison
- No. 8 – Friday, March 9, 1711 – Addison
- No. 9 – Saturday, March 10, 1711 – Addison
- No. 10 – Monday, March 12, 1711 – Addison
- No. 11 – Tuesday, March 13, 1711 – Steele
- No. 12 – Wednesday, March 14, 1711 – Addison
- No. 13 – Thursday, March 15, 1711 – Addison
- No. 14 – Friday, March 16, 1711 – Steele
- No. 15 – Saturday, March 17, 1711 – Addison
- No. 16 – Monday, March 19, 1711 – Addison
- No. 17 – Tuesday, March 20, 1711 – Steele
- No. 18 – Wednesday, March 21, 1711 – Addison
- No. 19 – Thursday, March 22, 1711 – Steele
- No. 20 – Friday, March 23, 1711 – Steele
- No. 21 – Saturday, March 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 22 – Monday, March 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 23 – Tuesday, March 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 24 – Wednesday, March 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 25 – Thursday, March 29, 1711 – Addison
- No. 26 – Friday, March 30, 1711 – Addison
- No. 27 – Saturday, March 31, 1711 – Steele
- No. 28 – Monday, April 2, 1711 – Addison
- No. 29 – Tuesday, April 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 30 – Wednesday, April 4, 1711 – Steele
- No. 31 – Thursday, April 5, 1711 – Addison
- No. 32 – Friday, April 6, 1711 – Steele
- No. 33 – Saturday, April 7, 1711 – Steele
- No. 34 – Monday, April 9, 1711 – Addison
- No. 35 – Tuesday, April 10, 1711 – Addison
- No. 36 – Wednesday, April 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 37 – Thursday, April 12, 1711 – Addison
- No. 38 – Friday, April 13, 1711 – Steele
- No. 39 – Saturday, April 14, 1711 – Addison
- No. 40 – Monday, April 16, 1711 – Addison
- No. 41 – Tuesday, April 17, 1711 – Steele
- No. 42 – Wednesday, April 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 43 – Thursday, April 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 44 – Friday, April 20, 1711 – Addison
- No. 45 – Saturday, April 21, 1711 – Addison
- No. 46 – Monday, April 23, 1711 – Addison
- No. 47 – Tuesday, April 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 48 – Wednesday, April 25, 1711 – Steele
- No. 49 – Thursday, April 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 50 – Friday, April 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 51 – Saturday, April 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 52 – Monday, April 30, 1711 – Steele
- No. 53 – Tuesday, May 1, 1711 – Steele
- No. 54 – Wednesday, May 2, 1711 – Steele
- No. 55 – Thursday, May 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 56 – Friday, May 4, 1711 – Addison
- No. 57 – Saturday, May 5, 1711 – Addison
- No. 58 – Monday, May 7, 1711 – Addison
- No. 59 – Tuesday, May 8, 1711 – Addison
- No. 60 – Wednesday, May 9, 1711 – Addison
- No. 61 – Thursday, May 10, 1711 – Addison
- No. 62 – Friday, May 11, 1711 – Addison
- No. 63 – Saturday, May 12, 1711 – Addison
- No. 64 – Monday, May 14, 1711 – Steele
- No. 65 – Tuesday, May 15, 1711 – Steele
- No. 66 – Wednesday, May 16, 1711 – Steele
- No. 67 – Thursday, May 17, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 68 – Friday, May 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 69 – Saturday, May 19, 1711 – Addison
- No. 70 – Monday, May 21, 1711 – Addison
- No. 71 – Tuesday, May 22, 1711 – Steele
- No. 72 – Wednesday, May 23, 1711 – Addison
- No. 73 – Thursday, May 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 74 – Friday, May 25, 1711 – Addison
- No. 75 – Saturday, May 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 76 – Monday, May 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 77 – Tuesday, May 29, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 78 – Wednesday, May 30, 1711 – Steele
- No. 79 – Thursday, May 31, 1711 – Steele
- No. 80 – Friday, June 1, 1711 – Steele
- No. 81 – Saturday, June 2, 1711 – Addison
- No. 82 – Monday, June 4, 1711 – Steele
- No. 83 – Tuesday, June 5, 1711 – Addison
- No. 84 – Wednesday, June 6, 1711 – Steele
- No. 85 – Thursday, June 7, 1711 – Addison
- No. 86 – Friday, June 8, 1711 – Addison
- No. 87 – Saturday, June 9, 1711 – Steele
- No. 88 – Monday, June 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 89 – Tuesday, June 12, 1711 – Addison
- No. 90 – Wednesday, June 13, 1711 – Addison
- No. 91 – Thursday, June 14, 1711 – Steele
- No. 92 – Friday, June 15, 1711 – Addison
- No. 93 – Saturday, June 16, 1711 – Addison
- No. 94 – Monday, June 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 95 – Tuesday, June 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 96 – Wednesday, June 20, 1711 – Steele
- No. 97 – Thursday, June 21, 1711 – Steele
- No. 98 – Friday, June 22, 1711 – Addison
- No. 99 – Saturday, June 23, 1711 – Addison
- No. 100 – Monday, June 24, 1711 – Steele
- No. 101 – Tuesday, June 26, 1711 – Addison
- No. 102 – Wednesday, June 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 103 – Thursday, June 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 104 – Friday, June 29, 1711 – Steele
- No. 105 – Saturday, June 30, 1711 – Addison
- No. 106 – Monday, July 2, 1711 – Addison
- No. 107 – Tuesday, July 3, 1711 – Steele
- No. 108 – Wednesday, July 4, 1711 – Addison
- No. 109 – Thursday, July 5, 1711 – Steele
- No. 110 – Friday, July 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 111 – Saturday, July 7, 1711 – Addison
- No. 112 – Monday, July 9, 1711 – Addison
- No. 113 – Tuesday, July 10, 1711 – Steele
- No. 114 – Wednesday, July 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 115 – Thursday, July 12, 1711 – Addison
- No. 116 – Friday, July 13, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 117 – Saturday, July 14, 1711 – Addison
- No. 118 – Monday, July 16, 1711 – Steele
- No. 119 – Tuesday, July 17, 1711 – Addison
- No. 120 – Wednesday, July 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 121 – Thursday, July 19, 1711 – Addison
- No. 122 – Friday, July 20, 1711 – Addison
- No. 123 – Saturday, July 21, 1711 – Addison
- No. 124 – Monday, July 23, 1711 – Addison
- No. 125 – Tuesday, July 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 126 – Wednesday, July 25, 1711 – Addison
- No. 127 – Thursday, July 26, 1711 – Addison
- No. 128 – Friday, July 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 129 – Saturday, July 28, 1711 – Addison
- No. 130 – Monday, July 30, 1711 – Addison
- No. 131 – Tuesday, July 31, 1711 – Addison
- No. 132 – Wednesday, August 1, 1711 – Steele
- No. 133 – Thursday, August 2, 1711 – Steele
- No. 134 – Friday, August 3, 1711 – Steele
- No. 135 – Saturday, August 4, 1711 – Addison
- No. 136 – Monday, August 6, 1711 – Steele
- No. 137 – Tuesday, August 7, 1711 – Steele
- No. 138 – Wednesday, August 8, 1711 – Steele
- No. 139 – Thursday, August 9, 1711 – Steele
- No. 140 – Friday, August 10, 1711 – Steele
- No. 141 – Saturday, August 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 142 – Monday, August 13, 1711 – Steele
- No. 143 – Tuesday, August 14, 1711 – Steele
- No. 144 – Wednesday, August 15, 1711 – Steele
- No. 145 – Thursday, August 16, 1711 – Steele
- No. 146 – Friday, August 17, 1711 – Steele
- No. 147 – Saturday, August 18, 1711 – Steele
- No. 148 – Monday, August 20, 1711 – Steele
- No. 149 – Tuesday, August 21, 1711 – Steele
- No. 150 – Wednesday, August 22, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 151 – Thursday, August 23, 1711 – Steele
- No. 152 – Friday, August 24, 1711 – Steele
- No. 153 – Saturday, August 25, 1711 – Steele
- No. 154 – Monday, August 27, 1711 – Steele
- No. 155 – Tuesday, August 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 156 – Wednesday, August 29, 1711 – Steele
- No. 157 – Thursday, August 30, 1711 – Steele
- No. 158 – Friday, August 31, 1711 – Steele
- No. 159 – Saturday, September 1, 1711 – Addison
- No. 160 – Monday, September 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 161 – Tuesday, September 4, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 162 – Wednesday, September 5, 1711 – Addison
- No. 163 – Thursday, September 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 164 – Friday, September 7, 1711 – Addison
- No. 165 – Saturday, September 8, 1711 – Addison
- No. 166 – Monday, September 10, 1711 – Addison
- No. 167 – Tuesday, September 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 168 – Wednesday, September 12, 1711 – Steele
- No. 169 – Thursday, September 13, 1711 – Addison
- No. 170 – Friday, September 14, 1711 – Addison
- No. 171 – Saturday, September 15, 1711 – Addison
- No. 172 – Monday, September 17, 1711 – Steele
- No. 173 – Tuesday, September 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 174 – Wednesday, September 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 175 – Thursday, September 20, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 176 – Friday, September 21, 1711 – Steele
- No. 177 – Saturday, September 22, 1711 – Addison
- No. 178 – Monday, September 24, 1711 – Steele
- No. 179 – Tuesday, September 25, 1711 – Addison
- No. 180 – Wednesday, September 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 181 – Thursday, September 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 182 – Friday, September 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 183 – Saturday, September 29, 1711 – Addison
- No. 184 – Monday, October 1, 1711 – Addison
- No. 185 – Tuesday, October 2, 1711 – Addison
- No. 186 – Wednesday, October 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 187 – Thursday, October 4, 1711 – Steele
- No. 188 – Friday, October 5, 1711 – Steele
- No. 189 – Saturday, October 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 190 – Monday, October 8, 1711 – Steele
- No. 191 – Tuesday, October 9, 1711 – Addison
- No. 192 – Wednesday, October 10, 1711 – Steele
- No. 193 – Thursday, October 11, 1711 – Steele
- No. 194 – Friday, October 12, 1711 – Steele
- No. 195 – Saturday, October 13, 1711 – Addison
- No. 196 – Monday, October 15, 1711 – Steele
- No. 197 – Tuesday, October 16, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 198 – Wednesday, October 17, 1711 – Addison
- No. 199 – Thursday, October 18, 1711 – Steele
- No. 200 – Friday, October 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 201 – Saturday, October 20, 1711 – Addison
- No. 202 – Monday, October 22, 1711 – Steele
List of Original Advertisements Included
Each In Three Vols., Price 10s. 6d.
Charles Knight's
Shakspere.
Napier's
History of the Peninsular War. with Maps and Plans.
Longfellow's
Works — poems — prose — Dante.
Boswell's
Life Of Johnson. with Illustrations.
Motley's
Rise Of The Dutch Republic.
Byron's
Poetical Works.
When Richard Steele, in number 555 of his
Spectator
, signed its last
paper and named those who had most helped him 'to keep up the spirit of
so long and approved a performance,' he gave chief honour to one who had
on his page, as in his heart, no name but Friend. This was
'the
gentleman of whose assistance I formerly boasted in the Preface and
concluding Leaf of my Tatlers. I am indeed much more proud of his
long-continued Friendship, than I should be of the fame of being thought
the author of any writings which he himself is capable of producing. I
remember when I finished the Tender Husband, I told him there was
nothing I so ardently wished, as that we might some time or other
publish a work, written by us both, which should bear the name of The
Monument, in Memory of our Friendship.'
Why he refers to such a wish,
his next words show. The seven volumes of the
Spectator
, then
complete, were to his mind The Monument, and of the Friendship it
commemorates he wrote,
'I heartily wish what I have done here were as
honorary to that sacred name as learning, wit, and humanity render those
pieces which I have taught the reader how to distinguish for his.'
So
wrote Steele; and the
Spectator
will bear witness how religiously his
friendship was returned. In number 453, when, paraphrasing David's
Hymn
on Gratitude
, the 'rising soul' of Addison surveyed the mercies of his
God, was it not Steele whom he felt near to him at the Mercy-seat as he
wrote
Thy bounteous hand with worldly bliss
Has made my cup run o'er,
And in a kind and faithful Friend
Has doubled all my store?
The
Spectator
, Steele-and-Addison's
Spectator
, is a monument
befitting the most memorable friendship in our history. Steele was its
projector, founder, editor, and he was writer of that part of it which
took the widest grasp upon the hearts of men. His sympathies were with
all England. Defoe and he, with eyes upon the future, were the truest
leaders of their time. It was the firm hand of his friend Steele that
helped Addison up to the place in literature which became him. It was
Steele who caused the nice critical taste which Addison might have spent
only in accordance with the fleeting fashions of his time, to be
inspired with all Addison's religious earnestness, and to be enlivened
with the free play of that sportive humour, delicately whimsical and
gaily wise, which made his conversation the delight of the few men with
whom he sat at ease. It was Steele who drew his friend towards the days
to come, and made his gifts the wealth of a whole people. Steele said in
one of the later numbers of his
Spectator
, No. 532, to which he
prefixed a motto that assigned to himself only the part of whetstone to
the wit of others,
'I claim to myself the merit of having extorted excellent productions
from a person of the greatest abilities, who would not have let them
appear by any other means.'
There were those who argued that he was too careless of his own fame in
unselfish labour for the exaltation of his friend, and, no doubt, his
rare generosity of temper has been often misinterpreted. But for that
Addison is not answerable. And why should Steele have defined his own
merits? He knew his countrymen, and was in too genuine accord with the
spirit of a time then distant but now come, to doubt that, when he was
dead, his whole life's work would speak truth for him to posterity.
The friendship of which this work is the monument remained unbroken from
boyhood until death. Addison and Steele were schoolboys together at the
Charterhouse. Addison was a dean's son, and a private boarder; Steele,
fatherless, and a boy on the foundation. They were of like age. The
register of Steele's baptism, corroborated by the entry made on his
admission to the Charterhouse (which also implies that he was baptized
on the day of his birth) is March 12, 1671, Old Style; New Style, 1672.
Addison was born on May-day, 1672. Thus there was a difference of only
seven weeks.
Steele's father according to the register, also named Richard, was an
attorney in Dublin. Steele seems to draw from experience — although he is
not writing as of himself or bound to any truth of personal detail — when
in No. 181 of the
Tatler
he speaks of his father as having died when
he was not quite five years of age, and of his mother as 'a very
beautiful woman, of a noble spirit.' The first Duke of Ormond is
referred to by Steele in his Dedication to the
Lying Lover
as the
patron of his infancy; and it was by this nobleman that a place was
found for him, when in his thirteenth year, among the foundation boys at
the Charterhouse, where he first met with Joseph Addison. Addison, who
was at school at Lichfield in 1683-4-5, went to the Charterhouse in
1686, and left in 1687, when he was entered of Queen's College, Oxford.
Steele went to Oxford two years later, matriculating at Christ Church,
March 13, 1689-90, the year in which Addison was elected a Demy of
Magdalene. A letter of introduction from Steele, dated April 2, 1711,
refers to the administration of the will of 'my uncle Gascoigne, to
whose bounty I owe a liberal education.' This only representative of the
family ties into which Steele was born, an 'uncle' whose surname is not
that of Steele's mother before marriage, appears, therefore, to have
died just before or at the time when the
Spectator
undertook to
publish a sheetful of thoughts every morning, and — Addison here speaking
for him — looked forward to
'leaving his country, when he was summoned out of it, with the secret
satisfaction of thinking that he had not lived in vain.'
To Steele's warm heart Addison's friendship stood for all home blessings
he had missed. The sister's playful grace, the brother's love, the
mother's sympathy and simple faith in God, the father's guidance, where
were these for Steele, if not in his friend Addison?
Addison's father was a dean; his mother was the sister of a bishop; and
his ambition as a schoolboy, or his father's ambition for him, was only
that he should be one day a prosperous and pious dignitary of the
Church. But there was in him, as in Steele, the genius which shaped
their lives to its own uses, and made them both what they are to us now.
Joseph Addison was born into a home which the steadfast labour of his
father, Lancelot, had made prosperous and happy. Lancelot Addison had
earned success. His father, Joseph's grandfather, had been also a
clergyman, but he was one of those Westmoreland clergy of whose
simplicity and poverty many a joke has been made. Lancelot got his
education as a poor child in the Appleby Grammar School; but he made his
own way when at College; was too avowed a Royalist to satisfy the
Commonwealth, and got, for his zeal, at the Restoration, small reward in
a chaplaincy to the garrison at Dunkirk. This was changed, for the
worse, to a position of the same sort at Tangier, where he remained
eight years. He lost that office by misadventure, and would have been
left destitute if Mr. Joseph Williamson had not given him a living of
£120 a-year at Milston in Wiltshire. Upon this Lancelot Addison married
Jane Gulstone, who was the daughter of a Doctor of Divinity, and whose
brother became Bishop of Bristol. In the little Wiltshire parsonage
Joseph Addison and his younger brothers and sisters were born. The
essayist was named Joseph after his father's patron, afterwards Sir
Joseph Williamson, a friend high in office. While the children grew, the
father worked. He showed his ability and loyalty in books on West
Barbary, and Mahomet, and the State of the Jews; and he became one of
the King's chaplains in ordinary at a time when his patron Joseph
Williamson was Secretary of State. Joseph Addison was then but three
years old. Soon afterwards the busy father became Archdeacon of
Salisbury, and he was made Dean of Lichfield in 1683, when his boy
Joseph had reached the age of 11. When Archdeacon of Salisbury, the Rev.
Lancelot Addison sent Joseph to school at Salisbury; and when his father
became Dean of Lichfield, Joseph was sent to school at Lichfield, as
before said, in the years 1683-4-5. And then he was sent as a private
pupil to the Charterhouse. The friendship he there formed with Steele
was ratified by the approval of the Dean. The desolate boy with the warm
heart, bright intellect, and noble aspirations, was carried home by his
friend, at holiday times, into the Lichfield Deanery, where, Steele
wrote afterwards to Congreve in a Dedication of the
Drummer
,
'were
things of this nature to be exposed to public view, I could show under
the Dean's own hand, in the warmest terms, his blessing on the
friendship between his son and me; nor had he a child who did not prefer
me in the first place of kindness and esteem, as their father loved me
like one of them.'
Addison had two brothers, of whom one traded and
became Governor of Fort George in India, and the other became, like
himself, a Fellow of Magdalene College, Oxford. Of his three sisters two
died young, the other married twice, her first husband being a French
refugee minister who became a Prebendary of Westminster. Of this sister
of Addison's, Swift said she was 'a sort of wit, very like him. I was
not fond of her.'
In the latter years of the seventeenth century, when Steele and Addison
were students at Oxford, most English writers were submissive to the new
strength of the critical genius of France. But the English nation had
then newly accomplished the great Revolution that secured its liberties,
was thinking for itself, and calling forth the energies of writers who
spoke for the people and looked to the people for approval and support.
A new period was then opening, of popular influence on English
literature. They were the young days of the influence now full grown,
then slowly getting strength and winning the best minds away from an
imported Latin style adapted to the taste of patrons who sought credit
for nice critical discrimination. In 1690 Addison had been three years,
Steele one year, at Oxford. Boileau was then living, fifty-four years
old; and Western Europe was submissive to his sway as the great monarch
of literary criticism. Boileau was still living when Steele published
his
Tatler
, and died in the year of the establishment of the
Spectator
. Boileau, a true-hearted man, of genius and sense, advanced
his countrymen from the nice weighing of words by the Précieuses and the
grammarians, and by the French Academy, child of the intercourse between
those ladies and gentlemen. He brought ridicule on the inane politeness
of a style then in its decrepitude, and bade the writers of his time
find models in the Latin writers who, like Virgil and Horace, had
brought natural thought and speech to their perfection. In the preceding
labour for the rectifying of the language, preference had been given to
French words of Latin origin. French being one of those languages in
which Latin is the chief constituent, this was but a fair following of
the desire to make it run pure from its source.
If the English critics
who, in Charles the Second's time, submitted to French law, had seen its
spirit, instead of paying blind obedience to the letter, they also would
have looked back to the chief source of their language. Finding this to
be not Latin but Saxon, they would have sought to give it strength and
harmony, by doing then what, in the course of nature, we have learnt
again to do, now that the patronage of literature has gone from the
cultivated noble who appreciates in much accordance with the fashion of
his time, and passed into the holding of the English people. Addison and
Steele lived in the transition time between these periods. They were
born into one of them and — Steele immediately, Addison through Steele's
influence upon him — they were trusty guides into the other. Thus the
Spectator
is not merely the best example of their skill. It represents
also, perhaps best represents, a wholesome Revolution in our Literature.
The essential character of English Literature was no more changed than
characters of Englishmen were altered by the Declaration of Right which
Prince William of Orange had accepted with the English Crown, when
Addison had lately left and Steele was leaving Charterhouse for Oxford.
Yet change there was, and Steele saw to the heart of it, even in his
College days.
Oxford, in times not long past, had inclined to faith in divine right of
kings. Addison's father, a church dignitary who had been a Royalist
during the Civil War, laid stress upon obedience to authority in Church
and State. When modern literature was discussed or studied at Oxford
there would be the strongest disposition to maintain the commonly
accepted authority of French critics, who were really men of great
ability, correcting bad taste in their predecessors, and conciliating
scholars by their own devout acceptance of the purest Latin authors as
the types of a good style or proper method in the treatment of a
subject. Young Addison found nothing new to him in the temper of his
University, and was influenced, as in his youth every one must and
should be, by the prevalent tone of opinion in cultivated men. But he
had, and felt that he had, wit and genius of his own. His sensitive mind
was simply and thoroughly religious, generous in its instincts, and
strengthened in its nobler part by close communion with the mind of his
friend Steele.
May we not think of the two friends together in a College
chamber, Addison of slender frame, with features wanting neither in
dignity nor in refinement, Steele of robust make, with the radiant
'short face' of the
Spectator
, by right of which he claimed for that
worthy his admission to the Ugly Club. Addison reads Dryden, in praise
of whom he wrote his earliest known verse; or reads endeavours of his
own, which his friend Steele warmly applauds. They dream together of the
future; Addison sage, but speculative, and Steele practical, if rash.
Each is disposed to find God in the ways of life, and both avoid that
outward show of irreligion, which, after the recent Civil Wars, remains
yet common in the country, as reaction from an ostentatious piety which
laid on burdens of restraint; a natural reaction which had been
intensified by the base influence of a profligate King. Addison, bred
among the preachers, has a little of the preacher's abstract tone, when
talk between the friends draws them at times into direct expression of
the sacred sense of life which made them one.
Apart also from the mere
accidents of his childhood, a speculative turn in Addison is naturally
stronger than in Steele. He relishes analysis of thought. Steele came as
a boy from the rough world of shame and sorrow; his great, kindly heart
is most open to the realities of life, the state and prospects of his
country, direct personal sympathies; actual wrongs, actual remedies.
Addison is sensitive, and has among strangers the reserve of speech and
aspect which will pass often for coldness and pride, but is, indeed, the
shape taken by modesty in thoughtful men whose instinct it is to
speculate and analyze, and who become self-conscious, not through
conceit, but because they cannot help turning their speculations also on
themselves. Steele wholly comes out of himself as his heart hastens to
meet his friend. He lives in his surroundings, and, in friendly
intercourse, fixes his whole thought on the worth of his companion.
Never abating a jot of his ideal of a true and perfect life, or ceasing
to uphold the good because he cannot live to the full height of his own
argument, he is too frank to conceal the least or greatest of his own
shortcomings. Delight and strength of a friendship like that between
Steele and Addison are to be found, as many find them, in the charm and
use of a compact where characters differ so much that one lays open as
it were a fresh world to the other, and each draws from the other aid of
forces which the friendship makes his own. But the deep foundations of
this friendship were laid in the religious earnestness that was alike in
both; and in religious earnestness are laid also the foundations of this
book, its Monument.
Both Addison and Steele wrote verse at College. From each of them we
have a poem written at nearly the same age: Addison's in April, 1694,
Steele's early in 1695. Addison drew from literature a metrical 'Account
of the Greatest English Poets.' Steele drew from life the grief of
England at the death of William's Queen, which happened on the 28th of
December, 1694.
Addison, writing in that year, and at the age of about 23, for a College
friend,
A short account of all the Muse-possest,
That, down from Chaucer's days to Dryden's times
Have spent their noble rage in British rhymes,
was so far under the influence of French critical authority, as accepted
by most cultivators of polite literature at Oxford and wherever
authority was much respected, that from 'An Account of the Greatest
English Poets' he omitted Shakespeare. Of Chaucer he then knew no better
than to say, what might have been said in France, that
... age has rusted what the Poet writ,
Worn out his language, and obscured his wit:
In vain he jests in his unpolish'd strain,
And tries to make his readers laugh in vain.
Old Spenser next, warm'd with poetic rage,
In ancient tales amused a barb'rous age;
But now the mystic tale, that pleased of yore,
Can charm an understanding age no more.
It cost Addison some trouble to break loose from the critical cobweb of
an age of periwigs and patches, that accounted itself 'understanding,'
and the grand epoch of our Elizabethan literature, 'barbarous.' Rymer,
one of his critics, had said, that
'in the neighing of an horse, or in the growling of a mastiff, there
is a meaning, there is as lively expression, and, may I say, more
humanity than many times in the tragical flights of Shakespeare.'
Addison, with a genius of his own helped to free movement by the
sympathies of Steele, did break through the cobwebs of the critics; but
he carried off a little of their web upon his wings. We see it when in
the
Spectator
he meets the prejudices of an 'understanding age,'
and partly satisfies his own, by finding reason for his admiration of
Chevy Chase
and the
Babes in the Wood
, in their great
similarity to works of Virgil. We see it also in some of the criticisms
which accompany his admirable working out of the resolve to justify his
true natural admiration of the poetry of Milton, by showing that
Paradise Lost
was planned after the manner of the ancients, and
supreme even in its obedience to the laws of Aristotle. In his
Spectator
papers on Imagination he but half escapes from the
conventions of his time, which detested the wildness of a mountain pass,
thought Salisbury Plain one of the finest prospects in England, planned
parks with circles and straight lines of trees, despised our old
cathedrals for their 'Gothic' art, and saw perfection in the Roman
architecture, and the round dome of St. Paul's. Yet in these and all
such papers of his we find that Addison had broken through the weaker
prejudices of the day, opposing them with sound natural thought of his
own. Among cultivated readers, lesser moulders of opinion, there can be
no doubt that his genius was only the more serviceable in amendment of
the tastes of his own time, for friendly understanding and a partial
sharing of ideas for which it gave itself no little credit.
It is noticeable, however, that in his Account of the Greatest English
Poets, young Addison gave a fifth part of the piece to expression of the
admiration he felt even then for Milton. That his appreciation became
critical, and, although limited, based on a sense of poetry which
brought him near to Milton, Addison proved in the
Spectator
by
his eighteen Saturday papers upon
Paradise Lost
. But it was from
the religious side that he first entered into the perception of its
grandeur. His sympathy with its high purpose caused him to praise, in
the same pages that commended
Paradise Lost
to his countrymen,
another 'epic,' Blackmore's
Creation
, a dull metrical treatise
against atheism, as a work which deserved to be looked upon as
'one of the most useful and noble productions of our English verse.
The reader,' he added, of a piece which shared certainly with
Salisbury Plain the charms of flatness and extent of space, 'the
reader cannot but be pleased to find the depths of philosophy
enlivened with all the charms of poetry, and to see so great a
strength of reason amidst so beautiful a redundancy of the
imagination.'
The same strong sympathy with Blackmore's purpose in it blinded Dr.
Johnson also to the failure of this poem, which is Blackmore's best.
From its religious side, then, it may be that Addison, when a student at
Oxford, first took his impressions of the poetry of Milton. At Oxford he
accepted the opinion of France on Milton's art, but honestly declared,
in spite of that, unchecked enthusiasm:
Whate'er his pen describes I more than see,
Whilst every verse, arrayed in majesty,
Bold and sublime, my whole attention draws,
And seems above the critic's nicer laws.
This chief place among English poets Addison assigned to Milton, with
his mind fresh from the influences of a father who had openly contemned
the Commonwealth, and by whom he had been trained so to regard Milton's
service of it that of this he wrote:
Oh, had the Poet ne'er profaned his pen,
To varnish o'er the guilt of faithless men;
His other works might have deserved applause
But now the language can't support the cause,
While the clean current, tho' serene and bright,
Betrays a bottom odious to the sight.
If we turn now to the verse written by Steele in his young Oxford days,
and within twelve months of the date of Addison's lines upon English
poets, we have what Steele called
The Procession.
It is the procession
of those who followed to the grave the good Queen Mary, dead of
small-pox, at the age of 32. Steele shared his friend Addison's delight
in Milton, and had not, indeed, got beyond the sixth number of the
Tatler
before he compared the natural beauty and innocence of Milton's
Adam and Eve with Dryden's treatment of their love. But the one man for
whom Steele felt most enthusiasm was not to be sought through books, he
was a living moulder of the future of the nation. Eagerly intent upon
King William, the hero of the Revolution that secured our liberties, the
young patriot found in him also the hero of his verse. Keen sense of the
realities about him into which Steele had been born, spoke through the
very first lines of this poem:
The days of man are doom'd to pain and strife,
Quiet and ease are foreign to our life;
No satisfaction is, below, sincere,
Pleasure itself has something that's severe.
Britain had rejoiced in the high fortune of King William, and now a
mourning world attended his wife to the tomb. The poor were her first
and deepest mourners, poor from many causes; and then Steele pictured,
with warm sympathy, form after form of human suffering. Among those
mourning poor were mothers who, in the despair of want, would have
stabbed infants sobbing for their food,
But in the thought they stopp'd, their locks they tore,
Threw down the steel, and cruelly forbore.
The innocents their parents' love forgive,
Smile at their fate, nor know they are to live.
To the mysteries of such distress the dead queen penetrated, by her
'cunning to be good.' After the poor, marched the House of Commons in
the funeral procession. Steele gave only two lines to it:
With dread concern, the awful Senate came,
Their grief, as all their passions, is the same.
The next Assembly dissipates our fears,
The stately, mourning throng of British Peers.
A factious intemperance then characterized debates of the Commons, while
the House of Lords stood in the front of the Revolution, and secured the
permanency of its best issues. Steele describes, as they pass, Ormond,
Somers, Villars, who leads the horse of the dead queen, that 'heaves
into big sighs when he would neigh' — the verse has in it crudity as well
as warmth of youth — and then follow the funeral chariot, the jewelled
mourners, and the ladies of the court,
Their clouded beauties speak man's gaudy strife,
The glittering miseries of human life.
I yet see, Steele adds, this queen passing to her coronation in the
place whither she now is carried to her grave. On the way, through
acclamations of her people, to receive her crown,
She unconcerned and careless all the while
Rewards their loud applauses with a smile,
With easy Majesty and humble State
Smiles at the trifle Power, and knows its date.
But now
What hands commit the beauteous, good, and just,
The dearer part of William, to the dust?
In her his vital heat, his glory lies,
In her the Monarch lived, in her he dies.
...
No form of state makes the Great Man forego
The task due to her love and to his woe;
Since his kind frame can't the large suffering bear
In pity to his People, he's not here:
For to the mighty loss we now receive
The next affliction were to see him grieve.
If we look from these serious strains of their youth to the literary
expression of the gayer side of character in the two friends, we find
Addison sheltering his taste for playful writing behind a Roman Wall of
hexameter. For among his Latin poems in the Oxford
Musæ
Anglicanæ
are eighty or ninety lines of resonant Latin verse upon
'Machinæ Gesticulantes,
anglice
A Puppet-show.' Steele, taking
life as he found it, and expressing mirth in his own way of
conversation, wrote an English comedy, and took the word of a College
friend that it was valueless. There were two paths in life then open to
an English writer. One was the smooth and level way of patronage; the
other a rough up-hill track for men who struggled in the service of the
people. The way of patronage was honourable. The age had been made so
very discerning by the Romans and the French that a true understanding
of the beauties of literature was confined to the select few who had
been taught what to admire. Fine writing was beyond the rude
appreciation of the multitude. Had, therefore, the reading public been
much larger than it was, men of fastidious taste, who paid as much
deference to polite opinion as Addison did in his youth, could have
expected only audience fit but few, and would have been without
encouragement to the pursuit of letters unless patronage rewarded merit.
The other way had charms only for the stout-hearted pioneer who foresaw
where the road was to be made that now is the great highway of our
literature. Addison went out into the world by the way of his time;
Steele by the way of ours.
Addison, after the campaign of 1695, offered to the King the homage of a
paper of verses on the capture of Namur, and presented them through Sir
John Somers, then Lord Keeper of the Great Seal. To Lord Somers he sent
with them a flattering dedicatory address. Somers, who was esteemed a
man of taste, was not unwilling to 'receive the present of a muse
unknown.' He asked Addison to call upon him, and became his patron.
Charles Montagu, afterwards Earl of Halifax, critic and wit himself,
shone also among the statesmen who were known patrons of letters. Also
to him, who was a prince of patrons 'fed with soft dedication all day
long,' Addison introduced himself. To him, in 1697, as it was part of
his public fame to be a Latin scholar, Addison, also a skilful Latinist,
addressed, in Latin, a paper of verses on the Peace of Ryswick. With
Somers and Montagu for patrons, the young man of genius who wished to
thrive might fairly commit himself to the service of the Church, for
which he had been bred by his father; but Addison's tact and refinement
promised to be serviceable to the State, and so it was that, as Steele
tells us, Montagu made Addison a layman.
'His arguments were founded upon the general pravity and corruption of
men of business, who wanted liberal education. And I remember, as if I
had read the letter yesterday, that my Lord ended with a compliment,
that, however he might be represented as no friend to the Church, he
never would do it any other injury than keeping Mr. Addison out of
it.'
To the good offices of Montagu and Somers, Addison was indebted,
therefore, in 1699, for a travelling allowance of £300 a year. The grant
was for his support while qualifying himself on the continent by study
of modern languages, and otherwise, for diplomatic service. It dropped
at the King's death, in the spring of 1702, and Addison was cast upon
his own resources; but he throve, and lived to become an Under-Secretary
of State in days that made Prior an Ambassador, and rewarded with
official incomes Congreve, Rowe, Hughes, Philips, Stepney, and others.
Throughout his honourable career prudence dictated to Addison more or
less of dependence on the friendship of the strong. An honest friend of
the popular cause, he was more ready to sell than give his pen to it;
although the utmost reward would at no time have tempted him to throw
his conscience into the bargain. The good word of Halifax obtained him
from Godolphin, in 1704, the Government order for a poem on the Battle
of Blenheim, with immediate earnest of payment for it in the office of a
Commissioner of Appeal in the Excise worth £200 a year. For this
substantial reason Addison wrote the
Campaign
; and upon its
success, he obtained the further reward of an Irish Under-secretaryship.
The
Campaign
is not a great poem. Reams of
Campaigns
would
not have made Addison's name, what it now is, a household word among his
countrymen. The 'Remarks on several Parts of Italy, &c.,' in which
Addison followed up the success of his
Campaign
with notes of
foreign travel, represent him visiting Italy as 'Virgil's Italy,' the
land of the great writers in Latin, and finding scenery or customs of
the people eloquent of them at every turn. He crammed his pages with
quotation from Virgil and Horace, Ovid and Tibullus, Propertius, Lucan,
Juvenal and Martial, Lucretius, Statius, Claudian, Silius Italicus,
Ausonius, Seneca, Phædrus, and gave even to his 'understanding age' an
overdose of its own physic for all ills of literature. He could not see
a pyramid of jugglers standing on each other's shoulders, without
observing how it explained a passage in Claudian which shows that the
Venetians were not the inventors of this trick. But Addison's short
original accounts of cities and states that he saw are pleasant as well
as sensible, and here and there, as in the space he gives to a report of
St. Anthony's sermon to the fishes, or his short account of a visit to
the opera at Venice, there are indications of the humour that was
veiled, not crushed, under a sense of classical propriety. In his
account of the political state of Naples and in other passages, there is
mild suggestion also of the love of liberty, a part of the fine nature
of Addison which had been slightly warmed by contact with the generous
enthusiasm of Steele. In his poetical letter to Halifax written during
his travels Addison gave the sum of his prose volume when he told how he
felt himself
... on classic ground.
For here the Muse so oft her harp hath strung,
That not a mountain rears its head unsung;
Renown'd in verse each shady thicket grows,
And ev'ry stream in heav'nly numbers flows.
But he was writing to a statesman of the Revolution, who was his
political patron, just then out of office, and propriety suggested such
personal compliment as calling the Boyne a Tiber, and Halifax an
improvement upon Virgil; while his heart was in the closing emphasis,
also proper to the occasion, which dwelt on the liberty that gives their
smile to the barren rocks and bleak mountains of Britannia's isle, while
for Italy, rich in the unexhausted stores of nature, proud Oppression in
her valleys reigns, and tyranny usurps her happy plains. Addison's were
formal raptures, and he knew them to be so, when he wrote,
I bridle in my struggling Muse with pain,
That longs to launch into a bolder strain.
Richard Steele was not content with learning to be bold. Eager, at that
turning point of her national life, to serve England with strength of
arm, at least, if not with the good brains which he was neither
encouraged nor disposed to value highly, Steele's patriotism impelled
him to make his start in the world, not by the way of patronage, but by
enlisting himself as a private in the Coldstream Guards. By so doing he
knew that he offended a relation, and lost a bequest. As he said of
himself afterwards,
'when he mounted a war-horse, with a great sword in his hand, and
planted himself behind King William III against Louis XIV, he lost the
succession to a very good estate in the county of Wexford, in Ireland,
from the same humour which he has preserved, ever since, of preferring
the state of his mind to that of his fortune.'
Steele entered the Duke of Ormond's regiment, and had reasons for
enlistment. James Butler, the first Duke, whom his father served, had
sent him to the Charterhouse. That first Duke had been Chancellor of the
University at Oxford, and when he died, on the 21st of July, 1688, nine
months before Steele entered to Christchurch, his grandson, another
James Butler, succeeded to the Dukedom. This second Duke of Ormond was
also placed by the University of Oxford in his grandfather's office of
Chancellor. He went with King William to Holland in 1691, shared the
defeat of William in the battle of Steinkirk in August, 1692, and was
taken prisoner in July, 1693, when King William was defeated at Landen.
These defeats encouraged the friends of the Stuarts, and in 1694,
Bristol, Exeter and Boston adhered to King James. Troops were raised in
the North of England to assist his cause. In 1696 there was the
conspiracy of Sir George Barclay to seize William on the 15th of
February. Captain Charnock, one of the conspirators, had been a Fellow
of Magdalene. On the 23rd of February the plot was laid before
Parliament. There was high excitement throughout the country. Loyal
Associations were formed. The Chancellor of the University of Oxford was
a fellow-soldier of the King's, and desired to draw strength to his
regiment from the enthusiasm of the time. Steele's heart was with the
cause of the Revolution, and he owed also to the Ormonds a kind of
family allegiance. What was more natural than that he should be among
those young Oxford men who were tempted to enlist in the Chancellor's
own regiment for the defence of liberty? Lord Cutts, the Colonel of the
Regiment, made Steele his Secretary, and got him an Ensign's commission.
It was then that he wrote his first book, the
Christian Hero
, of which
the modest account given by Steele himself long afterwards, when put on
his defence by the injurious violence of faction, is as follows:
'He first became an author when an Ensign of the Guards, a way of life
exposed to much irregularity; and being thoroughly convinced of many
things, of which he often repented, and which he more often repeated,
he writ, for his own private use, a little book called the Christian
Hero, with a design principally to fix upon his own mind a strong
impression of virtue and religion, in opposition to a stronger
propensity towards unwarrantable pleasures. This secret admiration was
too weak; he therefore printed the book with his name, in hopes that a
standing testimony against himself, and the eyes of the world (that is
to say, of his acquaintance) upon him in a new light, would make him
ashamed of understanding and seeming to feel what was virtuous, and
living so contrary a life.'
Among his brother soldiers, and fresh from the Oxford worship of old
classical models, the religious feeling that accompanies all true
refinement, and that was indeed part of the English nature in him as in
Addison, prompted Steele to write this book, in which he opposed to the
fashionable classicism of his day a sound reflection that the heroism of
Cato or Brutus had far less in it of true strength, and far less
adaptation to the needs of life, than the unfashionable Christian
Heroism set forth by the Sermon on the Mount.
According to the second title of this book it is 'an Argument, proving
that no Principles but those of Religion are sufficient to make a Great
Man.' It is addressed to Lord Cutts in a dedication dated from the
Tower-Yard, March 23, 1701, and is in four chapters, of which the first
treats of the heroism of the ancient world, the second connects man with
his Creator, by the Bible Story and the Life and Death of Christ, the
third defines the Christian as set forth by the character and teaching
of St. Paul, applying the definition practically to the daily life of
Steele's own time. In the last chapter he descends from the
consideration of those bright incentives to a higher life, and treats of
the ordinary passions and interests of men, the common springs of action
(of which, he says, the chief are Fame and Conscience) which he declares
to be best used and improved when joined with religion; and here all
culminates in a final strain of patriotism, closing with the character
of King William, 'that of a glorious captain, and (what he much more
values than the most splendid titles) that of a sincere and honest man.'
This was the character of William which, when, in days of meaner public
strife, Steele quoted it years afterwards in the
Spectator
, he broke
off painfully and abruptly with a
... Fuit Ilium, et ingens
Gloria.
Steele's
Christian Hero
obtained many readers. Its fifth edition was
appended to the first collection of the
Tatler
into volumes, at the
time of the establishment of the
Spectator
. The old bent of the
English mind was strong in Steele, and he gave unostentatiously a lively
wit to the true service of religion, without having spoken or written to
the last day of his life a word of mere religious cant. One officer
thrust a duel on him for his zeal in seeking to make peace between him
and another comrade. Steele, as an officer, then, or soon afterwards,
made a Captain of Fusiliers, could not refuse to fight, but stood on the
defensive; yet in parrying a thrust his sword pierced his antagonist,
and the danger in which he lay quickened that abiding detestation of the
practice of duelling, which caused Steele to attack it in his plays, in
his
Tatler
, in his
Spectator
, with persistent energy.
Of the
Christian Hero
his companions felt, and he himself saw, that
the book was too didactic. It was indeed plain truth out of Steele's
heart, but an air of superiority, freely allowed only to the
professional man teaching rules of his own art, belongs to a too
didactic manner. Nothing was more repugnant to Steele's nature than the
sense of this. He had defined the Christian as 'one who is always a
benefactor, with the mien of a receiver.' And that was his own
character, which was, to a fault, more ready to give than to receive,
more prompt to ascribe honour to others than to claim it for himself. To
right himself, Steele wrote a light-hearted comedy,
The Funeral
, or
Grief à la Mode
; but at the core even of that lay the great
earnestness of his censure against the mockery and mummery of grief that
should be sacred; and he blended with this, in the character of Lawyer
Puzzle, a protest against mockery of truth and justice by the
intricacies of the law. The liveliness of this comedy made Steele
popular with the wits; and the inevitable touches of the author's
patriotism brought on him also the notice of the Whigs. Party men might,
perhaps, already feel something of the unbending independence that was
in Steele himself, as in this play he made old Lord Brumpton teach it to
his son:
'But be them honest, firm, impartial;
Let neither love, nor hate, nor faction move thee;
Distinguish words from things, and men from crimes.'
King William, perhaps, had he lived, could fairly have recognized in
Steele the social form of that sound mind which in Defoe was solitary.
In a later day it was to Steele a proud recollection that his name, to
be provided for, 'was in the last table-book ever worn by the glorious
and immortal William III.'
The
Funeral
, first acted with great success in 1702, was followed in
the next year by
The Tender Husband
, to which Addison contributed some
touches, for which Addison wrote a Prologue, and which Steele dedicated
to Addison, who would 'be surprised,' he said, 'in the midst of a daily
and familiar conversation, with an address which bears so distant an air
as a public dedication.' Addison and his friend were then thirty-one
years old. Close friends when boys, they are close friends now in the
prime of manhood. It was after they had blended wits over the writing of
this comedy that Steele expressed his wish for a work, written by both,
which should serve as
The Monument
to their most happy friendship. When
Addison and Steele were amused together with the writing of this comedy,
Addison, having lost his immediate prospect of political employment, and
his salary too, by King William's death in the preceding year, had come
home from his travels. On his way home he had received, in September, at
the Hague, news of his father's death. He wrote from the Hague, to Mr.
Wyche,
'At my first arrival I received the news of my father's death, and
ever since have been engaged in so much noise and company, that it was
impossible for me to think of rhyming in it.'
As his father's eldest son, he had, on his return to England, family
affairs to arrange, and probably some money to receive. Though attached
to a party that lost power at the accession of Queen Anne, and waiting
for new employment, Addison — who had declined the Duke of Somerset's
over-condescending offer of a hundred a year and all expenses as
travelling tutor to his son, the Marquis of Hertford — was able, while
lodging poorly in the Haymarket, to associate in London with the men by
whose friendship he hoped to rise, and was, with Steele, admitted into
the select society of wits, and men of fashion who affected wit and took
wits for their comrades, in the Kitcat Club. When in 1704 Marlborough's
victory at Blenheim revived the Whig influence, the suggestion of
Halifax to Lord Treasurer Godolphin caused Addison to be applied to for
his poem of the
Campaign
. It was after the appearance of this
poem that Steele's play was printed, with the dedication to his friend,
in which he said,
'I look upon my intimacy with you as one of the most valuable
enjoyments of my life. At the same time I make the town no ill
compliment for their kind acceptance of this comedy, in acknowledging
that it has so far raised my opinion of it, as to make me think it no
improper memorial of an inviolable Friendship. I should not offer it
to you as such, had I not been very careful to avoid everything that
might look ill-natured, immoral, or prejudicial to what the better
part of mankind hold sacred and honourable.'
This was the common ground between the friends. Collier's
Short View of
the Profaneness and Immorality of the English Stage
had been published
in 1698; it attacked a real evil, if not always in the right way, and
Congreve's reply to it had been a failure. Steele's comedies with all
their gaiety and humour were wholly free from the garnish of oaths and
unwholesome expletives which his contemporaries seemed to think
essential to stage emphasis. Each comedy of his was based on
seriousness, as all sound English wit has been since there have been
writers in England. The gay manner did not conceal all the earnest
thoughts that might jar with the humour of the town; and thus Steele was
able to claim, by right of his third play, 'the honour of being the only
English dramatist who had had a piece damned for its piety.'
This was the
Lying Lover
, produced in 1704, an adaptation from
Corneille in which we must allow that Steele's earnestness in upholding
truth and right did cause him to spoil the comedy. The play was
afterwards re-adapted by Foote as the
Liar
, and in its last form, with
another change or two, has been revived at times with great success. It
is worth while to note how Steele dealt with the story of this piece.
Its original is a play by Alarcon, which Corneille at first supposed to
have been a play by Lope de Vega. Alarcon, or, to give him his full
style, Don Juan Ruiz de Alarcon y Mendoza, was a Mexican-born Spaniard
of a noble family which had distinguished itself in Mexico from the time
of the conquest, and took its name of Alarcon from a village in New
Castile. The poet was a humpbacked dwarf, a thorough, but rather
haughty, Spanish gentleman, poet and wit, who wrote in an unusually pure
Spanish style; a man of the world, too, who came to Spain in or about
the year 1622, and held the very well-paid office of reporter to the
Royal Council of the Indies. When Alarcon, in 1634, was chosen by the
Court to write a festival drama, and, at the same time, publishing the
second part of his dramatic works, vehemently reclaimed plays for which,
under disguised names, some of his contemporaries had taken credit to
themselves, there was an angry combination against him, in which Lope de
Vega, Gongora, and Quevedo were found taking part. All that Alarcon
wrote was thoroughly his own, but editors of the 17th century boldly
passed over his claims to honour, and distributed his best works among
plays of other famous writers, chiefly those of Rojas and Lope de Vega.
This was what deceived Corneille, and caused him to believe and say that
Alarcon's
la Verdad sospechosa
, on which, in 1642, he founded his
Menteur
, was a work of Lope de Vega's. Afterwards Corneille learnt how
there had been in this matter lying among editors. He gave to
Alarcon the honour due, and thenceforth it is chiefly by this play that Alarcon has been remembered out of Spain. In Spain, when
in 1852 Don Juan Hartzenbusch edited Alarcon's comedies for the
Biblioteca de Autores Españoles
, he had to remark on the unjust neglect of that good author in Spain also, where the poets and men of letters had long wished in vain for a complete edition of his works. Lope de Vega, it may be added, was really the author of a sequel to
la Verdad sospechosa
, which Corneille adapted also as a sequel to his
Menteur
, but it was even poorer than such sequels usually are.
The
Lying Lover
in Alarcon's play is a Don Garcia fresh from
his studies in Salamanca, and Steele's Latine first appears there as a Tristan, the gracioso of old Spanish comedy. The two ladies are
a Jacinta and Lucrecia. Alarcon has in his light and graceful play no less than three heavy fathers, of a Spanish type, one of whom, the father of Lucrecia, brings about Don Garcia's punishment by threatening to kill him if he will not marry his daughter; and so the Liar is punished for his romancing by a marriage with the girl he does not care for, and not marrying the girl he loves.
Corneille was merciful, and in the fifth act bred in his
Menteur
a new fancy for Lucrece, so that the marriage at cross purposes was rather agreeable to him.
Steele, in adapting the
Menteur
as his
Lying Lover
, altered the close in sharp accordance with that 'just regard to a reforming age,'
which caused him (adapting a line in his 'Procession' then unprinted)
to write in his Prologue to it, 'Pleasure must still have
something that's severe.' Having translated Corneille's translations of Garcia and Tristan (Dorante and Cliton) into Young
Bookwit and Latine, he transformed the servant into a college friend, mumming as servant because, since 'a prating servant is necessary in intrigues,' the two had 'cast lots who should be the other's footman for the present expedition.' Then he adapted the French couplets into pleasant prose comedy, giving with a light touch the romancing of feats of war and of an entertainment on the river, but at last he turned desperately serious, and sent his Young Bookwit to Newgate on a charge of killing the gentleman — here
called Lovemore — who was at last to win the hand of the lady whom the Liar loved. In his last act, opening in Newgate, Steele started with blank verse, and although Lovemore of course was not dead,
and Young Bookwit got at last more than a shadow of a promise
the other lady in reward for his repentance, the changes in construction
of the play took it beyond the bounds of comedy, and were, in fact,
excellent morality but not good art. And this is what Steele means when
he says that he had his play damned for its piety.
With that strong regard for the drama which cannot well be wanting to
the man who has an artist's vivid sense of life, Steele never withdrew
his good will from the players, never neglected to praise a good play,
and, I may add, took every fair occasion of suggesting to the town the
subtlety of Shakespeare's genius. But he now ceased to write comedies,
until towards the close of his life he produced with a remarkable
success his other play, the
Conscious Lovers
. And of that, by the way,
Fielding made his Parson Adams say that
Cato
and the
Conscious
Lovers
were the only plays he ever heard of, fit for a Christian to
read, 'and, I must own, in the latter there are some things almost
solemn enough for a sermon.'
Perhaps it was about this time that Addison wrote his comedy of the
Drummer
, which had been long in his possession when Steele, who had
become a partner in the management of Drury Lane Theatre, drew it from
obscurity, suggested a few changes in it, and produced it — not openly as
Addison's — upon the stage. The published edition of it was recommended
also by a preface from Steele in which he says that he liked this
author's play the better
'for the want of those studied similies and
repartees which we, who have writ before him, have thrown into our
plays, to indulge and gain upon a false taste that has prevailed for
many years in the British theatre. I believe the author would have
condescended to fall into this way a little more than he has, had he
before the writing of it been often present at theatrical
representations. I was confirmed in my thoughts of the play by the
opinion of better judges to whom it was communicated, who observed that
the scenes were drawn after Molière's manner, and that an easy and
natural vein of humour ran through the whole. I do not question but the
reader will discover this, and see many beauties that escaped the
audience; the touches being too delicate for every taste in a popular
assembly. My brother-sharers' (in the Drury Lane patent) 'were of
opinion, at the first reading of it, that it was like a picture in which
the strokes were not strong enough to appear at a distance. As it is not
in the common way of writing, the approbation was at first doubtful, but
has risen every time it has been acted, and has given an opportunity in
several of its parts for as just and good actions as ever I saw on the stage.'
Addison's comedy was not produced till 1715, the year after his
unsuccessful attempt to revive the
Spectator
, which produced what
is called the eighth volume of that work. The play, not known to be his,
was so ill spoken of that he kept the authorship a secret to the last,
and Tickell omitted it from the collection of his patron's works. But
Steele knew what was due to his friend, and in 1722 manfully republished
the piece as Addison's, with a dedication to Congreve and censure of
Tickell for suppressing it. If it be true that the
Drummer
made
no figure on the stage though excellently acted, 'when I observe this,'
said Steele, 'I say a much harder thing of this than of the comedy.'
Addison's Drummer is a gentleman who, to forward his suit to a soldier's
widow, masquerades as the drumbeating ghost of her husband in her
country house, and terrifies a self-confident, free-thinking town
exquisite, another suitor, who believes himself brought face to face
with the spirit world, in which he professes that he can't believe. 'For
my part, child, I have made myself easy in those points.' The character
of a free-thinking exquisite is drawn from life without exaggeration,
but with more than a touch of the bitter contempt Addison felt for the
atheistic coxcomb, with whom he was too ready to confound the sincere
questioner of orthodox opinion. The only passages of his in the
Spectator
that border on intolerance are those in which he deals
with the free-thinker; but it should not be forgotten that the commonest
type of free-thinker in Queen Anne's time was not a thoughtful man who
battled openly with doubt and made an independent search for truth, but
an idler who repudiated thought and formed his character upon tradition
of the Court of Charles the Second. And throughout the
Spectator
we may find a Christian under-tone in Addison's intolerance of
infidelity, which is entirely wanting when the moralist is Eustace
Budgell. Two or three persons in the comedy of the
Drummer
give
opportunity for good character-painting in the actor, and on a healthy
stage, before an audience able to discriminate light touches of humour
and to enjoy unstrained although well-marked expression of varieties of
character, the
Drummer
would not fail to be a welcome
entertainment.
But our sketch now stands at the year 1705, when Steele had ceased for a
time to write comedies. Addison's
Campaign
had brought him fame,
and perhaps helped him to pay, as he now did, his College debts, with
interest. His
Remarks on Italy
, now published, were, as Tickell
says, 'at first but indifferently relished by the bulk of readers;' and
his
Drummer
probably was written and locked in his desk. There
were now such days of intercourse as Steele looked back to when with
undying friendship he wrote in the preface to that edition of the
Drummer
produced by him after Addison's death:
'He was above all men in that talent we call humour, and enjoyed it in
such perfection, that I have often reflected, after a night spent with
him apart from all the world, that I had had the pleasure of
conversing with an intimate acquaintance of Terence and Catullus, who
had all their wit and nature, heightened with humour more exquisite
and delightful than any other man ever possessed.' And again in the
same Preface, Steele dwelt upon 'that smiling mirth, that delicate
satire and genteel raillery, which appeared in Mr. Addison when he was
free from that remarkable bashfulness which is a cloak that hides and
muffles merit; and his abilities were covered only by modesty, which
doubles the beauties which are seen, and gives credit and esteem to
all that are concealed.'
Addison had the self-consciousness of a sensitive and speculative mind.
This, with a shy manner among those with whom he was not intimate,
passed for cold self-assertion. The 'little senate' of his intimate
friends was drawn to him by its knowledge of the real warmth of his
nature. And his friendships, like his religion, influenced his judgment.
His geniality that wore a philosophic cloak before the world, caused him
to abandon himself in the
Spectator
, even more unreservedly than
Steele would have done, to iterated efforts for the help of a friend
like Ambrose Philips, whose poems to eminent babies, 'little subject,
little wit,' gave rise to the name of Namby-pamby. Addison's quietness
with strangers was against a rapid widening of his circle of familiar
friends, and must have made the great-hearted friendship of Steele as
much to him as his could be to Steele. In very truth it 'doubled all his
store.' Steele's heart was open to enjoyment of all kindly intercourse
with men. In after years, as expression of thought in the literature of
nations gained freedom and sincerity, two types of literature were
formed from the types of mind which Addison and Steele may be said to
have in some measure represented. Each sought advance towards a better
light, one part by dwelling on the individual duties and
responsibilities of man, and his relation to the infinite; the other by
especial study of man's social ties and liberties, and his relation to
the commonwealth of which he is a member. Goethe, for instance, inclined
to one study; Schiller to the other; and every free mind will incline
probably to one or other of these centres of opinion. Addison was a cold
politician because he was most himself when analyzing principles of
thought, and humours, passions, duties of the individual. Steele, on the
contrary, braved ruin for his convictions as a politician, because his
social nature turned his earnestness into concern for the well-being of
his country, and he lived in times when it was not yet certain that the
newly-secured liberties were also finally secured. The party was strong
that desired to re-establish ancient tyrannies, and the Queen herself
was hardly on the side of freedom.
In 1706, the date of the union between England and Scotland, Whig
influence had been strengthened by the elections of the preceding year,
and Addison was, early in 1706, made Under-Secretary of State to Sir
Charles Hedges, a Tory, who was superseded before the end of the year by
Marlborough's son-in-law, the Earl of Sunderland, a Whig under whom
Addison, of course, remained in office, and who was, thenceforth, his
active patron. In the same year the opera of
Rosamond
was produced,
with Addison's libretto. It was but the third, or indeed the second,
year of operas in England, for we can hardly reckon as forming a year of
opera the Italian intermezzi and interludes of singing and dancing,
performed under Clayton's direction, at York Buildings, in 1703. In
1705, Clayton's
Arsinoe
, adapted and translated from the Italian, was
produced at Drury Lane. Buononcini's
Camilla
was given at the house in
the Haymarket, and sung in two languages, the heroine's part being in
English and the hero's in Italian. Thomas Clayton, a second-rate
musician, but a man with literary tastes, who had been introducer of the
opera to London, argued that the words of an opera should be not only
English, but the best of English, and that English music ought to
illustrate good home-grown literature. Addison and Steele agreed
heartily in this. Addison was persuaded to write words for an opera by
Clayton — his
Rosamond
— and Steele was persuaded afterwards to
speculate in some sort of partnership with Clayton's efforts to set
English poetry to music in the entertainments at York Buildings, though
his friend Hughes warned him candidly that Clayton was not much of a
musician.
Rosamond
was a failure of Clayton's and not a success of
Addison's. There is poor jesting got by the poet from a comic Sir
Trusty, who keeps Rosamond's bower, and has a scolding wife. But there
is a happy compliment to Marlborough in giving to King Henry a vision at
Woodstock of the glory to come for England, and in a scenic realization
of it by the rising of Blenheim Palace, the nation's gift to
Marlborough, upon the scene of the Fair Rosamond story. Indeed there can
be no doubt that it was for the sake of the scene at Woodstock, and the
opportunity thus to be made, that Rosamond was chosen for the subject of
the opera. Addison made Queen Eleanor give Rosamond a narcotic instead
of a poison, and thus he achieved the desired happy ending to an opera.
|
Believe your Rosamond alive. |
| King. |
O happy day! O pleasing view!
My Queen forgives — |
| Queen. |
— My lord is true. |
| King. |
No more I'll change. |
| Queen. |
No more I'll grieve. |
| Both. |
But ever thus united live. |
That is to say, for three days, the extent of the life of the opera. But
the literary Under-Secretary had saved his political dignity with the
stage tribute to Marlborough, which backed the closet praise in the
Campaign
.
In May, 1707, Steele received the office of Gazetteer, until then worth
£60, but presently endowed by Harley with a salary of £300 a year. At
about the same time he was made one of the gentlemen ushers to Queen
Anne's husband, Prince George of Denmark. In the same year Steele
married. Of his most private life before this date little is known. He
had been married to a lady from Barbadoes, who died in a few months.
From days referred to in the
Christian Hero
he derived a daughter of
whom he took fatherly care. In 1707 Steele, aged about 35, married Miss
(or, as ladies come of age were then called, Mrs.) Mary Scurlock, aged
29. It was a marriage of affection on both sides. Steele had from his
first wife an estate in Barbadoes, which produced, after payment of the
interest on its encumbrances, £670 a year. His appointment as Gazetteer,
less the £45 tax on it, was worth £255 a year, and his appointment on
the Prince Consort's household another hundred. Thus the income upon
which Steele married was rather more than a thousand a year, and Miss
Scurlock's mother had an estate of about £330 a year. Mary Scurlock had
been a friend of Steele's first wife, for before marriage she recalls
Steele to her mother's mind by saying, 'It is the survivor of the person
to whose funeral I went in my illness.'
'Let us make our regards to each other,' Steele wrote just before
marriage, 'mutual and unchangeable, that whilst the world around us is
enchanted with the false satisfactions of vagrant desires, our persons
may be shrines to each other, and sacred to conjugal faith, unreserved
confidence, and heavenly society.'
There remains also a prayer written by Steele before first taking the
sacrament with his wife, after marriage. There are also letters and
little notes written by Steele to his wife, treasured by her love, and
printed by a remorseless antiquary, blind to the sentence in one of the
first of them:
'I beg of you to shew my letters to no one living, but let us be
contented with one another's thoughts upon our words and actions,
without the intervention of other people, who cannot judge of so
delicate a circumstance as the commerce between man and wife.'
But they are printed for the frivolous to laugh at and the wise to
honour. They show that even in his most thoughtless or most anxious
moments the social wit, the busy patriot, remembered his 'dear Prue,'
and was her lover to the end. Soon after marriage, Steele took his wife
to a boarding-school in the suburbs, where they saw a young lady for
whom Steele showed an affection that caused Mrs. Steele to ask, whether
she was not his daughter. He said that she was. 'Then,' said Mrs.
Steele, 'I beg she may be mine too.' Thenceforth she lived in their home
as Miss Ousley, and was treated as a daughter by Steele's wife. Surely
this was a woman who deserved the love that never swerved from her. True
husband and true friend, he playfully called Addison her rival. In the
Spectator
there is a paper of Steele's (No. 142) representing some of
his own love-letters as telling what a man said and should be able to
say of his wife after forty years of marriage. Seven years after
marriage he signs himself, 'Yours more than you can imagine, or I
express.' He dedicates to her a volume of the
Lady's Library
, and
writes of her ministrations to him:
'if there are such beings as guardian angels, thus are they employed.
I will no more believe one of them more good in its inclinations than
I can conceive it more charming in its form than my wife.'
In the year before her death he was signing his letters with 'God bless
you!' and 'Dear Prue, eternally yours.' That Steele made it a duty of
his literary life to contend against the frivolous and vicious ridicule
of the ties of marriage common in his day, and to maintain their sacred
honour and their happiness, readers of the
Spectator
cannot fail to
find.
Steele, on his marriage in 1707, took a house in Bury Street, St.
James's, and in the following year went to a house at Hampton, which he
called in jest the Hovel. Addison had lent him a thousand pounds for
costs of furnishing and other immediate needs. This was repaid within a
year, and when, at the same time, his wife's mother was proposing a
settlement of her money beneficial to himself, Steele replied that he
was far from desiring, if he should survive his wife, 'to turn the
current of the estate out of the channel it would have been in, had I
never come into the family.' Liberal always of his own to others, he was
sometimes without a guinea, and perplexed by debt. But he defrauded no
man. When he followed his Prue to the grave he was in no man's debt,
though he left all his countrymen his debtors, and he left more than
their mother's fortune to his two surviving children. One died of
consumption a year afterwards, the other married one of the Welsh
Judges, afterwards Lord Trevor.
The friendship — equal friendship — between Steele and Addison was as
unbroken as the love between Steele and his wife. Petty tales may have
been invented or misread. In days of malicious personality Steele braved
the worst of party spite, and little enough even slander found to throw
against him. Nobody in their lifetime doubted the equal strength and
sincerity of the relationship between the two friends. Steele was no
follower of Addison's. Throughout life he went his own way, leading
rather than following; first as a playwright; first in conception and
execution of the scheme of the
Tatler
,
Spectator
, and
Guardian
;
following his own sense of duty against Addison's sense of expediency in
passing from the
Guardian
to the
Englishman
, and so to energetic
movement upon perilous paths as a political writer, whose whole heart
was with what he took to be the people's cause.
When Swift had been writing to Addison that he thought Steele 'the
vilest of mankind,' in writing of this to Swift, Steele complained that
the
Examiner
, — in which Swift had a busy hand, — said Addison had
'bridled him in point of politics,' adding,
'This was ill hinted both in relation to him and me. I know no party;
but the truth of the question is what I will support as well as I can,
when any man I honour is attacked.'
John Forster, whose keen insight into the essentials of literature led
him to write an essay upon each of the two great founders of the latest
period of English literature, Defoe and Steele, has pointed out in his
masterly essay upon Steele that Swift denies having spoken of Steele as
bridled by his friend, and does so in a way that frankly admits Steele's
right to be jealous of the imputation. Mr. Forster justly adds that
throughout Swift's intimate speech to Stella,
'whether his humours be sarcastic or polite, the friendship of Steele
and Addison is for ever suggesting some annoyance to himself, some
mortification, some regret, but never once the doubt that it was not
intimate and sincere, or that into it entered anything inconsistent
with a perfect equality.'
Six months after Addison's death Steele wrote (in No. 12 of the
Theatre
, and I am again quoting facts cited by John Forster),
'that there never was a more strict friendship than between himself
and Addison, nor had they ever any difference but what proceeded from
their different way of pursuing the same thing; the one waited and
stemmed the torrent, while the other too often plunged into it; but
though they thus had lived for some years past, shunning each other,
they still preserved the most passionate concern for their mutual
welfare; and when they met they were as unreserved as boys, and talked
of the greatest affairs, upon which they saw where they differed,
without pressing (what they knew impossible) to convert each other.'
As to the substance or worth of what thus divided them, Steele only adds
the significant expression of his hope that, if his family is the worse,
his country may be the better, 'for the mortification
he
has
undergone.'
Such, then, was the Friendship of which the
Spectator
is the abiding
Monument. The
Spectator
was a modified continuation of the
Tatler
,
and the
Tatler
was suggested by a portion of Defoe's
Review
. The
Spectator
belongs to the first days of a period when the people at
large extended their reading power into departments of knowledge
formerly unsought by them, and their favour was found generally to be
more desirable than that of the most princely patron. This period should
date from the day in 1703 when the key turned upon Defoe in Newgate, the
year of the production of Steele's
Tender Husband
, and the time when
Addison was in Holland on the way home from his continental travels.
Defoe was then forty-two years old, Addison and Steele being about
eleven years younger.
In the following year, 1704, the year of Blenheim — Defoe issued, on the
19th of February, No. 1 of 'A Weekly Review of the Affairs of France:
Purg'd from the Errors and Partiality of
News-Writers
and
Petty-Statesmen
, of all Sides,' and in the introductory sketch of its
plan, said:
'After our Serious Matters are over, we shall at the end of every
Paper, Present you with a little Diversion, as anything occurs to make
the World Merry; and whether Friend or Foe, one Party or another, if
anything happens so scandalous as to require an open Reproof, the
World may meet with it there.'
Here is the first 'little Diversion'; the germ of
Tatlers
and
Spectators
which in after years amused and edified the town.
Mercure Scandale:
or,
Advice from the Scandalous Club.
Translated out of French.
This Society is a Corporation long since established in Paris,
and we cannot compleat our Advices from France, without entertaining
the World with everything we meet with from that Country.
And, tho Corresponding with the Queens Enemies is prohibited;
yet since the Matter will be so honest, as only to tell the
World of what everybody will own to be scandalous, we reckon we
shall be welcome.
This Corporation has been set up some months, and opend
their first Sessions about last Bartholomew Fair; but having not
yet obtaind a Patent, they have never, till now, made their Resolves
publick.
The Business of this Society is to censure the Actions of Men,
not of Parties, and in particular, those Actions which are made
publick so by their Authors, as to be, in their own Nature, an
Appeal to the general Approbation.
They do not design to expose Persons but things; and of them,
none but such as more than ordinarily deserve it; they who would
not be censurd by this Assembly, are desired to act with caution
enough, not to fall under their Hands; for they resolve to treat
Vice, and Villanous Actions, with the utmost Severity.
The First considerable Matter that came before this Society, was
about Bartholomew Fair; but the Debates being long, they were
at last adjourned to the next Fair, when we suppose it will be
decided; so being not willing to trouble the World with anything
twice over, we refer that to next August.
On the 10th of September last, there was a long Hearing, before
the Club, of a Fellow that said he had killd the Duke of Bavaria.
Now as David punishd the Man that said he had killd King Saul,
whether it was so or no, twas thought this Fellow ought to be
delivered up to Justice, tho the Duke of Bavaria was alive.
Upon the whole, twas voted a scandalous Thing, That News.
Writers shoud kill Kings and Princes, and bring them to life again
at pleasure; and to make an Example of this Fellow, he was dismissd,
upon Condition he should go to the Queens-bench once a
Day, and bear Fuller, his Brother of the Faculty, company two
hours for fourteen Days together; which cruel Punishment was
executed with the utmost Severity.
The Club has had a great deal of trouble about the News-Writers,
who have been continually brought before them for their
ridiculous Stories, and imposing upon Mankind; and tho the
Proceedings have been pretty tedious, we must give you the
trouble of a few of them in our next.
The addition to the heading, 'Translated out of French,' appears only in
No. 1, and the first title
Mercure Scandale
(adopted from a French
book published about 1681) having been much criticized for its grammar
and on other grounds, was dropped in No. 18. Thenceforth Defoe's
pleasant comment upon passing follies appeared under the single head of
Advice from the Scandalous Club.
Still the verbal Critics exercised
their wits upon the title.
'We have been so often on the Defence of our Title,' says Defoe, in
No. 38, 'that the world begins to think Our Society wants
Employment ... If Scandalous must signify nothing but Personal
Scandal, respecting the Subject of which it is predicated; we desire
those gentlemen to answer for us how Post-Man or Post-Boy can
signify a News-Paper, the Post Man or Post Boy being in all my reading
properly and strictly applicable, not to the Paper, but to the Person
bringing or carrying the News? Mercury also is, if I understand it, by
a Transmutation of Meaning, from a God turned into a Book — From hence
our Club thinks they have not fair Play, in being deny'd the Privilege
of making an Allegory as well as other People.'
In No. 46 Defoe made, in one change more, a whimsical half concession of
a syllable, by putting a sign of contraction in its place, and
thenceforth calling this part of his Review,
Advice from the Scandal
Club
. Nothing can be more evident than the family likeness between this
forefather of the
Tatler
and
Spectator
and its more familiar
descendants. There is a trick of voice common to all, and some papers of
Defoe's might have been written for the
Spectator
. Take the little
allegory, for instance, in No. 45, which tells of a desponding young
Lady brought before the Society, as found by Rosamond's Pond in the Park
in a strange condition, taken by the mob for a lunatic, and whose
clothes were all out of fashion, but whose face, when it was seen,
astonished the whole society by its extraordinary sweetness and majesty.
She told how she had been brought to despair, and her name proved to
be — Modesty. In letters, questions, and comments also which might be
taken from Defoe's
Monthly Supplementary Journal
to the
Advice from the
Scandal Club
, we catch a likeness to the spirit of the
Tatler
and
Spectator
now and then exact. Some censured Defoe for not confining
himself to the weightier part of his purpose in establishing the
Review
. He replied, in the Introduction to his first
Monthly
Supplement
, that many men
'care but for a little reading at a time,' and said, 'thus we wheedle
them in, if it may be allow'd that Expression, to the Knowledge of the
World, who rather than take more Pains, would be content with their
Ignorance, and search into nothing.'
Single-minded, quick-witted, and prompt to act on the first suggestion
of a higher point of usefulness to which he might attain, Steele saw the
mind of the people ready for a new sort of relation to its writers, and
he followed the lead of Defoe. But though he turned from the more
frivolous temper of the enfeebled playhouse audience, to commune in free
air with the country at large, he took fresh care for the restraint of
his deep earnestness within the bounds of a cheerful, unpretending
influence. Drop by drop it should fall, and its strength lie in its
persistence. He would bring what wit he had out of the playhouse, and
speak his mind, like Defoe, to the people themselves every post-day. But
he would affect no pedantry of moralizing, he would appeal to no
passions, he would profess himself only 'a Tatler.' Might he not use, he
thought, modestly distrustful of the charm of his own mind, some of the
news obtained by virtue of the office of Gazetteer that Harley had given
him, to bring weight and acceptance to writing of his which he valued
only for the use to which it could be put. For, as he himself truly says
in the
Tatler
,
'wit, if a man had it, unless it be directed to some useful end, is
but a wanton, frivolous quality; all that one should value himself
upon in this kind is that he had some honourable intention in it.'
Swift, not then a deserter to the Tories, was a friend of Steele's, who,
when the first
Tatler
appeared, had been amusing the town at the
expense of John Partridge, astrologer and almanac-maker, with
'Predictions for the year 1708,' professing to be written by Isaac
Bickerstaff, Esq. The first prediction was of the death of Partridge,
'on the 29th of March next, about eleven at night, of a raging fever.'
Swift answered himself, and also published in due time
'The Accomplishment of the first of Mr. Bickerstaff's Predictions:
being an account of the death of Mr. Partridge, the almanack-maker,
upon the 29th instant.'
Other wits kept up the joke, and, in his next year's almanac (that for
1709), Partridge advertised that,
'whereas it has been industriously given out by Isaac Bickerstaff,
Esq., and others, to prevent the sale of this year's almanack, that
John Partridge is dead, this may inform all his loving countrymen that
he is still living, in health, and they are knaves that reported it
otherwise.'
Steele gave additional lightness to the touch of his
Tatler
, which
first appeared on the 12th of April, 1709, by writing in the name of
Isaac Bickerstaff, and carrying on the jest, that was to his serious
mind a blow dealt against prevailing superstition. Referring in his
first
Tatler
to this advertisement of Partridge's, he said of it,
'I have in another place, and in a paper by itself, sufficiently
convinced this man that he is dead; and if he has any shame, I do not
doubt but that by this time he owns it to all his acquaintance. For
though the legs and arms and whole body of that man may still appear
and perform their animal functions, yet since, as I have elsewhere
observed, his art is gone, the man is gone.'
To Steele, indeed, the truth was absolute, that a man is but what he can
do.
In this spirit, then, Steele began the
Tatler
, simply considering that
his paper was to be published 'for the use of the good people of
England,' and professing at the outset that he was an author writing for
the public, who expected from the public payment for his work, and that
he preferred this course to gambling for the patronage of men in office.
Having pleasantly shown the sordid spirit that underlies the
mountebank's sublime professions of disinterestedness,
'we have a contempt,' he says, 'for such paltry barterers, and have
therefore all along informed the public that we intend to give them
our advices for our own sakes, and are labouring to make our
lucubrations come to some price in money, for our more convenient
support in the service of the public. It is certain that many other
schemes have been proposed to me, as a friend offered to show me in a
treatise he had writ, which he called, The whole Art of Life; or, The
Introduction to Great Men, illustrated in a Pack of Cards. But being
a novice at all manner of play, I declined the offer.'
Addison took these cards, and played an honest game with them
successfully. When, at the end of 1708, the Earl of Sunderland,
Marlborough's son-in-law, lost his secretaryship, Addison lost his place
as under-secretary; but he did not object to go to Ireland as chief
secretary to Lord Wharton, the new Lord-lieutenant, an active party man,
a leader on the turf with reputation for indulgence after business hours
according to the fashion of the court of Charles II.
Lord Wharton took to Ireland Clayton to write him musical
entertainments, and a train of parasites of quality. He was a great
borough-monger, and is said at one critical time to have returned thirty
members. He had no difficulty, therefore, in finding Addison a seat, and
made him in that year, 1709, M.P. for Malmesbury. Addison only once
attempted to speak in the House of Commons, and then, embarrassed by
encouraging applause that welcomed him he stammered and sat down. But
when, having laid his political cards down for a time, and at ease in
his own home, pen in hand, he brought his sound mind and quick humour to
the aid of his friend Steele, he came with him into direct relation with
the English people. Addison never gave posterity a chance of knowing
what was in him till, following Steele's lead, he wrote those papers in
Tatler
,
Spectator
, and
Guardian
, wherein alone his genius abides
with us, and will abide with English readers to the end. The
Tatler
,
the
Spectator
, and the
Guardian
were, all of them, Steele's, begun
and ended by him at his sole discretion. In these three journals Steele
was answerable for 510 papers; Addison for 369. Swift wrote two papers,
and sent about a dozen fragments. Congreve wrote one article in the
Tatler
; Pope wrote thrice for the
Spectator
, and eight times for the
Guardian
. Addison, who was in Ireland when the
Tatler
first
appeared, only guessed the authorship by an expression in an early
number; and it was not until eighty numbers had been issued, and the
character of the new paper was formed and established, that Addison, on
his return to London, joined the friend who, with his usual complete
absence of the vanity of self-assertion, finally ascribed to the ally he
dearly loved, the honours of success.
It was the kind of success Steele had desired — a widely-diffused
influence for good. The
Tatlers
were penny papers published three
times a week, and issued also for another halfpenny with a blank
half-sheet for transmission by post, when any written scraps of the
day's gossip that friend might send to friend could be included. It was
through these, and the daily
Spectators
which succeeded them, that the
people of England really learnt to read. The few leaves of sound reason
and fancy were but a light tax on uncultivated powers of attention.
Exquisite grace and true kindliness, here associated with familiar ways
and common incidents of everyday life, gave many an honest man fresh
sense of the best happiness that lies in common duties honestly
performed, and a fresh energy, free as Christianity itself from
malice — for so both Steele and Addison meant that it should be — in
opposing themselves to the frivolities and small frauds on the
conscience by which manliness is undermined.
A pamphlet by John Gay —
The Present State of Wit, in a Letter to a
Friend in the Country
— was dated May 3, 1711, about two months after
the
Spectator
had replaced the
Tatler
. And thus Gay represents the
best talk of the town about these papers:
"Before I proceed further in the account of our weekly papers, it will
be necessary to inform you that at the beginning of the winter, to the
infinite surprise of all the Town, Mr. Steele flung up his Tatler,
and instead of Isaac Bickerstaff, Esquire, subscribed himself Richard
Steele to the last of those papers, after a handsome compliment to the
Town for their kind acceptance of his endeavours to divert them.
The chief reason he thought fit to give for his leaving off writing
was, that having been so long looked on in all public places and
companies as the Author of those papers, he found that his most
intimate friends and acquaintance were in pain to speak or act before
him.
The Town was very far from being satisfied with this reason, and most
people judged the true cause to be, either
- That he was quite spent, and wanted matter to continue his
undertaking any longer; or
- That he laid it down as a sort of submission to, and composition
with, the Government for some past offences; or, lastly,
- That he had a mind to vary his Shape, and appear again in some new
light.
However that were, his disappearance seemed to be bewailed as some
general calamity. Every one wanted so agreeable an amusement, and the
Coffee-houses began to be sensible that the Esquire's Lucubrations
alone had brought them more customers than all their other newspapers
put together.
It must indeed be confessed that never man threw up his pen, under
stronger temptations to have employed it longer. His reputation was at
a greater height, than I believe ever any living author's was before
him. It is reasonable to suppose that his gains were proportionably
considerable. Every one read him with pleasure and good-will; and the
Tories, in respect to his other good qualities, had almost forgiven
his unaccountable imprudence in declaring against them.
Lastly, it was highly improbable that, if he threw off a Character,
the ideas of which were so strongly impressed in every one's mind,
however finely he might write in any new form, that he should meet
with the same reception.
To give you my own thoughts of this gentleman's writings I shall, in
the first place, observe, that there is a noble difference between him
and all the rest of our gallant and polite authors. The latter have
endeavoured to please the Age by falling in with them, and encouraging
them in their fashionable vices and false notions of things. It would
have been a jest, some time since, for a man to have asserted that
anything witty could be said in praise of a married state, or that
Devotion and Virtue were any way necessary to the character of a Fine
Gentleman. Bickerstaff ventured to tell the Town that they were a
parcel of fops, fools, and coquettes; but in such a manner as even
pleased them, and made them more than half inclined to believe that he
spoke truth.
Instead of complying with the false sentiments or vicious tastes of
the Age — either in morality, criticism, or good breeding — he has
boldly assured them that they were altogether in the wrong; and
commanded them, with an authority which perfectly well became him, to
surrender themselves to his arguments for Virtue and Good Sense.
It is incredible to conceive the effect his writings have had on the
Town; how many thousand follies they have either quite banished or
given a very great check to; how much countenance they have added to
Virtue and Religion; how many people they have rendered happy, by
shewing them it was their own fault if they were not so; and, lastly,
how entirely they have convinced our young fops and young fellows of
the value and advantages of Learning.
He has indeed rescued it out of the hands of pedants and fools, and
discovered the true method of making it amiable and lovely to all
mankind. In the dress he gives it, it is a most welcome guest at
tea-tables and assemblies, and is relished and caressed by the
merchants on the Change. Accordingly there is not a Lady at Court, nor
a Banker in Lombard Street, who is not verily persuaded that Captain
Steele is the greatest scholar and best Casuist of any man in England.
Lastly, his writings have set all our Wits and men of letters on a new
way of thinking, of which they had little or no notion before: and,
although we cannot say that any of them have come up to the beauties
of the original, I think we may venture to affirm, that every one of
them writes and thinks much more justly than they did some time since.
The vast variety of subjects which Mr. Steele has treated of, in so
different manners, and yet all so perfectly well, made the World
believe that it was impossible they should all come from the same
hand. This set every one upon guessing who was the Esquire's friend?
and most people at first fancied it must be Doctor Swift; but it is
now no longer a secret, that his only great and constant assistant was
Mr. Addison.
This is that excellent friend to whom Mr. Steele owes so much; and who
refuses to have his name set before those pieces, which the greatest
pens in England would be proud to own. Indeed, they could hardly add
to this Gentleman's reputation: whose works in Latin and English
poetry long since convinced the World, that he was the greatest Master
in Europe in those two languages.
I am assured, from good hands, that all the visions, and other tracts
of that way of writing, with a very great number of the most exquisite
pieces of wit and raillery through the Lucubrations are entirely of
this Gentleman's composing: which may, in some measure, account for
that different Genius, which appears in the winter papers, from those
of the summer; at which time, as the Examiner often hinted, this
friend of Mr. Steele was in Ireland.
Mr. Steele confesses in his last Volume of the Tatlers that he is
obliged to Dr. Swift for his Town Shower, and the Description of
the Morn, with some other hints received from him in private
conversation.
I have also heard that several of those Letters, which came as from
unknown hands, were written by Mr. Henley: which is an answer to your
query, 'Who those friends are whom Mr. Steele speaks of in his last
Tatler?'
But to proceed with my account of our other papers. The expiration of
Bickerstaff's Lucubrations was attended with much the same
consequences as the death of Meliboeus's Ox in Virgil: as the latter
engendered swarms of bees, the former immediately produced whole
swarms of little satirical scribblers.
One of these authors called himself the Growler, and assured us
that, to make amends for Mr. Steele's silence, he was resolved to
growl at us weekly, as long as we should think fit to give him any
encouragement. Another Gentleman, with more modesty, called his paper
the Whisperer; and a third, to please the Ladies, christened his the
Tell tale.
At the same-time came out several Tatlers; each of which, with equal
truth and wit, assured us that he was the genuine Isaac Bickerstaff.
It may be observed that when the Esquire laid down his pen; though
he could not but foresee that several scribblers would soon snatch it
up, which he might (one would think) easily have prevented: he scorned
to take any further care about it, but left the field fairly open to
any worthy successor. Immediately, some of our Wits were for forming
themselves into a Club, headed by one Mr. Harrison, and trying how
they could shoot in this Bow of Ulysses; but soon found that this sort
of writing requires so fine and particular a manner of thinking, with
so exact a knowledge of the World, as must make them utterly despair
of success.
They seemed indeed at first to think that what was only the garnish of
the former Tatlers, was that which recommended them; and not those
Substantial Entertainments which they everywhere abound in. According
they were continually talking of their Maid, Night Cap,
Spectacles, and Charles Lillie. However there were, now and then,
some faint endeavours at Humour and sparks of Wit: which the Town, for
want of better entertainment, was content to hunt after through a heap
of impertinences; but even those are, at present, become wholly
invisible and quite swallowed up in the blaze of the Spectator.
You may remember, I told you before, that one cause assigned for the
laying down the Tatler was, Want of Matter; and, indeed, this was
the prevailing opinion in Town: when we were surprised all at once by
a paper called the Spectator, which was promised to be continued
every day; and was written in so excellent a style, with so nice a
judgment, and such a noble profusion of wit and humour, that it was
not difficult to determine it could come from no other hands but those
which had penned the Lucubrations.
This immediately alarmed these gentlemen, who, as it is said Mr.
Steele phrases it, had 'the Censorship in Commission.' They found the
new Spectator came on like a torrent, and swept away all before him.
They despaired ever to equal him in wit, humour, or learning; which
had been their true and certain way of opposing him: and therefore
rather chose to fall on the Author; and to call out for help to all
good Christians, by assuring them again and again that they were the
First, Original, True, and undisputed Isaac Bickerstaff.
Meanwhile, the Spectator, whom we regard as our Shelter from that
flood of false wit and impertinence which was breaking in upon us, is
in every one's hands; and a constant for our morning conversation at
tea-tables and coffee-houses. We had at first, indeed, no manner of
notion how a diurnal paper could be continued in the spirit and style
of our present Spectators: but, to our no small surprise, we find
them still rising upon us, and can only wonder from whence so
prodigious a run of Wit and Learning can proceed; since some of our
best judges seem to think that they have hitherto, in general,
outshone even the Esquire's first Tatlers.
Most people fancy, from their frequency, that they must be composed by
a Society: I withal assign the first places to Mr. Steele and his
Friend.
So far John Gay, whose discussion of the
Tatlers
and
Spectators
appeared when only fifty-five numbers of the
Spectator
had been
published.
There was high strife of faction; and there was real peril to the
country by a possible turn of affairs after Queen Anne's death, that
another Stuart restoration, in the name of divine right of kings, would
leave rights of the people to be reconquered in civil war. The chiefs of
either party were appealing to the people, and engaging all the wit they
could secure to fight on their side in the war of pamphlets. Steele's
heart was in the momentous issue. Both he and Addison had it in mind
while they were blending their calm playfulness with all the clamour of
the press. The spirit in which these friends worked, young Pope must
have felt; for after Addison had helped him in his first approach to
fame by giving honour in the
Spectator
to his
Essay on Criticism,
and when he was thankful for that service, he contributed to the
Spectator
his
Messiah
. Such offering clearly showed how Pope
interpreted the labour of the essayists.
In the fens of Lincolnshire the antiquary Maurice Johnson collected his
neighbours of Spalding.
'Taking care,' it is said, 'not to alarm the
country gentlemen by any premature mention of antiquities, he
endeavoured at first to allure them into the more flowery paths of
literature. In 1709 a few of them were brought together every post-day
at the coffee-house in the Abbey Yard; and after one of the party had
read aloud the last published number of the Tatler, they proceeded to
talk over the subject among themselves.'
Even in distant Perthshire
'the gentlemen met after church on Sunday to
discuss the news of the week; the Spectators were read as regularly as
the Journal.'
So the political draught of bitterness came sweetened
with the wisdom of good-humour. The good-humour of the essayists touched
with a light and kindly hand every form of affectation, and placed
every-day life in the light in which it would be seen by a natural and
honest man. A sense of the essentials of life was assumed everywhere for
the reader, who was asked only to smile charitably at its vanities.
Steele looked through all shams to the natural heart of the Englishman,
appealed to that, and found it easily enough, even under the disguise of
the young gentleman cited in the 77th
Tatler
,
'so ambitious to be
thought worse than he is that in his degree of understanding he sets up
for a free-thinker, and talks atheistically in coffee-houses all day,
though every morning and evening, it can be proved upon him, he
regularly at home says his prayers.'
But as public events led nearer to the prospect of a Jacobite triumph
that would have again brought Englishmen against each other sword to
sword, there was no voice of warning more fearless than Richard
Steele's. He changed the
Spectator
for the
Guardian
, that was to be,
in its plan, more free to guard the people's rights, and, standing
forward more distinctly as a politician, he became member for
Stockbridge. In place of the
Guardian
, which he had dropped when he
felt the plan of that journal unequal to the right and full expression
of his mind, Steele took for a periodical the name of
Englishman
, and
under that name fought, with then unexampled abstinence from
personality, against the principles upheld by Swift in his
Examiner
.
Then, when the Peace of Utrecht alarmed English patriots, Steele in a
bold pamphlet on
The Crisis
expressed his dread of arbitrary power and
a Jacobite succession with a boldness that cost him his seat in
Parliament, as he had before sacrificed to plain speaking his place of
Gazetteer.
Of the later history of Steele and Addison a few words will suffice.
This is not an account of their lives, but an endeavour to show why
Englishmen must always have a living interest in the
Spectator
, their
joint production. Steele's
Spectator
ended with the seventh volume.
The members of the Club were all disposed of, and the journal formally
wound up; but by the suggestion of a future ceremony of opening the
Spectator's
mouth, a way was made for Addison, whenever he pleased, to
connect with the famous series an attempt of his own for its revival. A
year and a half later Addison made this attempt, producing his new
journal with the old name and, as far as his contributions went, not
less than the old wit and earnestness, three times a week instead of
daily. But he kept it alive only until the completion of one volume.
Addison had not Steele's popular tact as an editor. He preached, and he
suffered drier men to preach, while in his jest he now and then wrote
what he seems to have been unwilling to acknowledge. His eighth volume
contains excellent matter, but the subjects are not always well chosen or varied judiciously, and one understands why the
Spectator
took a firmer hold upon society when the two friends in the
full strength of their life, aged about forty, worked together and
embraced between them a wide range of human thought and feeling. It
should be remembered also that Queen Anne died while Addison's eighth
volume was appearing, and the change in the Whig position brought him
other occupation of his time.
In April, 1713, in the interval between the completion of the true
Spectator
and the appearance of the supplementary volume, Addison's
tragedy of
Cato
, planned at College; begun during his foreign travels,
retouched in England, and at last completed, was produced at Drury Lane.
Addison had not considered it a stage play, but when it was urged that
the time was proper for animating the public with the sentiments of
Cato, he assented to its production. Apart from its real merit the play
had the advantage of being applauded by the Whigs, who saw in it a Whig
political ideal, and by the Tories, who desired to show that they were
as warm friends of liberty as any Whig could be.
Upon the death of Queen Anne Addison acted for a short time as secretary
to the Regency, and when George I appointed Addison's patron, the Earl
of Sunderland, to the Lord-lieutenancy of Ireland, Sunderland took
Addison with him as chief secretary. Sunderland resigned in ten months,
and thus Addison's secretaryship came to an end in August, 1716. Addison
was also employed to meet the Rebellion of 1715 by writing the
Freeholder
. He wrote under this title fifty-five papers, which were
published twice a week between December, 1715, and June, 1716; and he
was rewarded with the post of Commissioner for Trade and Colonies. In
August, 1716, he married the Countess Dowager of Warwick, mother to the
young Earl of Warwick, of whose education he seems to have had some
charge in 1708. Addison settled upon the Countess £4000 in lieu of an
estate which she gave up for his sake. Henceforth he lived chiefly at
Holland House. In April, 1717, Lord Sunderland became Secretary of
State, and still mindful of Marlborough's illustrious supporter, he made
Addison his colleague. Eleven months later, ill health obliged Addison
to resign the seals; and his death followed, June 17, 1719, at the age
of 47.
Steele's political difficulties ended at the death of Queen Anne. The
return of the Whigs to power on the accession of George I brought him
the office of Surveyor of the Royal Stables at Hampton Court; he was
also first in the Commission of the peace for Middlesex, and was made
one of the deputy lieutenants of the county. At the request of the
managers Steele's name was included in the new patent required at Drury
Lane by the royal company of comedians upon the accession of a new
sovereign. Steele also was returned as M.P. for Boroughbridge, in
Yorkshire, was writer of the Address to the king presented by the
Lord-lieutenant and the deputy lieutenants of Middlesex, and being
knighted on that occasion, with two other of the deputies, became in the
spring of the year, 1714, Sir Richard Steele. Very few weeks after the
death of his wife, in December, 1718, Sunderland, at a time when he had
Addison for colleague, brought in a bill for preventing any future
creations of peers, except when an existing peerage should become
extinct. Steele, who looked upon this as an infringement alike of the
privileges of the crown and of the rights of the subject, opposed the
bill in Parliament, and started in March, 1719, a paper called the
Plebeian
, in which he argued against a measure tending, he said, to
the formation of an oligarchy. Addison replied in the
Old Whig
, and
this, which occurred within a year of the close of Addison's life, was
the main subject of political difference between them. The bill,
strongly opposed, was dropped for that session, and reintroduced (after
Addison's death) in the December following, to be thrown out by the
House of Commons.
Steele's argument against the government brought on him the hostility of
the Duke of Newcastle, then Lord Chamberlain; and it was partly to
defend himself and his brother patentees against hostile action
threatened by the Duke, that Steele, in January, 1720, started his paper
called the
Theatre
. But he was dispossessed of his government of the
theatre, to which a salary of £600 a-year had been attached, and
suffered by the persecution of the court until Walpole's return to
power. Steele was then restored to his office, and in the following
year, 1722, produced his most successful comedy,
The Conscious Lovers
.
After this time his health declined; his spirits were depressed. He left
London for Bath. His only surviving son, Eugene, born while the
Spectator
was being issued, and to whom Prince Eugene had stood
godfather, died at the age of eleven or twelve in November, 1723. The
younger also of his two daughters was marked for death by consumption.
He was broken in health and fortune when, in 1726, he had an attack of
palsy which was the prelude to his death. He died Sept. 1, 1729, at
Carmarthen, where he had been boarding with a mercer who was his agent
and receiver of rents. There is a pleasant record that
'he retained his cheerful sweetness of temper to the last; and
would often be carried out, of a summer's evening, where the
country lads and lasses were assembled at their rural sports, — and,
with his pencil, gave an order on his agent, the mercer, for a new
gown to the best dancer.'
Two editions of the
Spectator
, the tenth and eleventh, were published
by Tonson in the year of Steele's death. These and the next edition,
dated 1739, were without the translations of the mottos, which appear,
however, in the edition of 1744. Notes were first added by Dr. Percy,
the editor of the
Reliques of Ancient Poetry
, and Dr. Calder. Dr. John
Calder, a native of Aberdeen, bred to the dissenting ministry, was for
some time keeper of Dr. Williams's Library in Redcross Street. He was a
candidate for the office given to Dr. Abraham Rees, of editor and
general super-intendent of the new issue of
Chambers's Cyclopædia
,
undertaken by the booksellers in 1776, and he supplied to it some new
articles. The Duke of Northumberland warmly patronized Dr. Calder, and
made him his companion in London and at Alnwick Castle as Private
Literary Secretary. Dr. Thomas Percy, who had constituted himself cousin
and retainer to the Percy of Northumberland, obtained his bishopric of
Dromore in 1782, in the following year lost his only son, and suffered
from that failure in eyesight, which resulted in a total blindness.
Having become intimately acquainted with Dr. Calder when at
Northumberland House and Alnwick, Percy intrusted to him the notes he
had collected for illustrating the
Tatler
,
Spectator
, and
Guardian
. These were after-wards used, with additions by Dr. Calder,
in the various editions of those works, especially in the six-volume
edition of the
Tatler
, published by John Nichols in 1786, where
Percy's notes have a P. attached to them, and Dr. Calder's are signed
'Annotator.' The
Tatler
was annotated fully, and the annotated
Tatler
has supplied some pieces of information given in the present
edition of the
Spectator
. Percy actually edited two volumes for R.
Tonson in 1764, but the work was stopped by the death of the bookseller,
and the other six were added to them in 1789. They were slightly
annotated, both as regards the number and the value of the notes; but
Percy and Calder lived when
Spectator
traditions were yet fresh, and
oral information was accessible as to points of personal allusion or as
to the authorship of a few papers or letters which but for them might
have remained anonymous. Their notes are those of which the substance
has run through all subsequent editions. Little, if anything, was added
to them by Bisset or Chalmers; the energies of those editors having been
chiefly directed to the preserving or multiplying of corruptions of the
text. Percy, when telling Tonson that he had completed two volumes of
the
Spectator
, said that he had corrected 'innumerable corruptions'
which had then crept in, and could have come only by misprint. Since
that time not only have misprints been preserved and multiplied, but
punctuation has been deliberately modernized, to the destruction of the
freshness of the original style, and editors of another 'understanding
age' have also taken upon themselves by many a little touch to correct
Addison's style or grammar.
This volume reprints for the first time in the present century the text
of the
Spectator
as its authors left it. A good recent edition
contains in the first 18 papers, which are a fair sample of the whole,
88 petty variations from the proper text (at that rate, in the whole
work more than 3000) apart from the recasting of the punctuation, which
is counted as a defect only in two instances, where it has changed the
sense. Chalmers's text, of 1817, was hardly better, and about two-thirds
of the whole number of corruptions had already appeared in Bisset's
edition of 1793, from which they were transferred. Thus Bisset as well
as Chalmers in the Dedication to Vol. I turned the 'polite
parts
of
learning' into the 'polite
arts
of learning,' and when the silent
gentleman tells us that many to whom his person is well known speak of
him 'very currently by Mr. What-d'ye-call him,' Bisset before Chalmers
rounded the sentence into 'very correctly by
the appellation
of Mr.
What-d'ye-call him.' But it seems to have been Chalmers who first
undertook to correct, in the next paper, Addison's grammar, by turning
'have laughed
to have seen
' into 'have laughed
to see
' and
transformed a treaty '
with
London and Wise,' — a firm now of historical
repute, — for the supply of flowers to the opera, into a treaty
'
between
London and Wise,' which most people would take to be a very
different matter. If the present edition has its own share of misprints
and oversights, at least it inherits none; and it contains no wilful
alteration of the text.
The papers as they first appeared in the daily issue of a penny (and
after the stamp was imposed two-penny) folio half-sheet, have been
closely compared with the first issue in guinea octavos, for which they
were revised, and with the last edition that appeared before the death
of Steele.
The original text is here given
precisely
as it was left
after revision by its authors; and there is shown at the same time
the
amount and character of the revision
.
- Sentences added in the reprint are
printed in brown without any appended note.
- Sentences
omitted, or words altered, are shown by printing the revised version in brown,
and giving the text as it stood in the original daily issue as a foot-note1.
Thus the reader has here both
the original texts of the
Spectator
. The
Essays
, as revised by their
authors for permanent use, form the main text of the present volume. But
if the words or passages in brackets be omitted; the words or passages
in corresponding foot-notes, — where there are such foot-notes, — being
substituted for them; the text becomes throughout that of the
Spectator
as it first came out in daily numbers.
- As the few
differences between good spelling in Queen Anne's time and good spelling
now are never of a kind to obscure the sense of a word, or lessen the
enjoyment of the reader, it has been thought better to make the
reproduction perfect, and thus show not only what Steele and Addison
wrote, but how they spelt,
- while restoring to their style the proper
harmony of their own methods of punctuating,
- and their way of sometimes
getting emphasis by turning to account the use of Capitals, which in
their hands was not wholly conventional.
- The original folio numbers have
been followed also in the use of italics
- and other little details of the disposition of the type; for
example, in the reproduction of those rows of single inverted commas,
which distinguish what a correspondent called the parts 'laced down the
side with little c's.' [This last detail of formatting has not been
reproduced in this file. html Ed.]
- The translation of the mottos and Latin quotations, which Steele and
Addison deliberately abstained from giving, and which, as they were
since added, impede and sometimes confound and contradict the text, are
here placed in a body at the end, for those who want them.
Again and
again the essayists indulge in banter on the mystery of the Latin and
Greek mottos; and what confusion must enter into the mind of the unwary
reader who finds Pope's
Homer
quoted at the head of a
Spectator
long
before Addison's word of applause to the young poet's
Essay on
Criticism.
- The mottos then are placed in an Appendix.
- There is a short
Appendix also of advertisements taken from the original number of the
Spectator, and a few others, where they seem to illustrate some point
in the text, will be found among the notes.
In the large number of notes
here added to a revision of those bequeathed to us by Percy and Calder,
the object has been to give information which may contribute to some
nearer acquaintance with the writers of the book, and enjoyment of
allusions to past manners and events.
- Finally, from the General Index
to the Spectators, &c., published as a separate volume in 1760, there
has been taken what was serviceable, and additions have been made to it
with a desire to secure for this edition of the Spectator the
advantages of being handy for reference as well as true to the real
text.
H. M.
"Sentences omitted, or words altered;" not, of course, the
immaterial variations of spelling into which compositors slipped in the
printing office. In the
Athenaeum
of May 12, 1877, is an answer to
misapprehensions on this head by the editor of a Clarendon Press volume
of
Selections from Addison
.
Contents
To The Right Honourable
John Lord Sommers,
Baron Of Evesham1.
My Lord,
I should not act the Part of an impartial Spectator, if I Dedicated the
following Papers to one who is not of the most consummate and most
acknowledged Merit.
None but a person of a finished Character can be the proper Patron of a
Work, which endeavours to Cultivate and Polish Human Life, by promoting
Virtue and Knowledge, and by recommending whatsoever may be either
Useful or Ornamental to Society.
I know that the Homage I now pay You, is offering a kind of Violence to
one who is as solicitous to shun Applause, as he is assiduous to deserve
it. But, my Lord, this is perhaps the only Particular in which your
Prudence will be always disappointed.
While Justice, Candour, Equanimity, a Zeal for the Good of your Country,
and the most persuasive Eloquence in bringing over others to it, are
valuable Distinctions, You are not to expect that the Publick will so
far comply with your Inclinations, as to forbear celebrating such
extraordinary Qualities. It is in vain that You have endeavoured to
conceal your Share of Merit, in the many National Services which You
have effected. Do what You will, the present Age will be talking of your
Virtues, tho' Posterity alone will do them Justice.
Other Men pass through Oppositions and contending Interests in the ways
of Ambition, but Your Great Abilities have been invited to Power, and
importuned to accept of Advancement. Nor is it strange that this should
happen to your Lordship, who could bring into the Service of Your
Sovereign the Arts and Policies of Ancient
Greece
and
Rome
; as well
as the most exact knowledge of our own Constitution in particular, and
of the interests of
Europe
in general; to which I must also add, a
certain Dignity in Yourself, that (to say the least of it) has been
always equal to those great Honours which have been conferred upon You.
It is very well known how much the Church owed to You in the most
dangerous Day it ever saw, that of the Arraignment of its Prelates; and
how far the Civil Power, in the Late and present Reign, has been
indebted to your Counsels and Wisdom.
But to enumerate the great Advantages which the publick has received
from your Administration, would be a more proper Work for an History,
than an Address of this Nature.
Your Lordship appears as great in your Private Life, as in the most
Important Offices which You have born. I would therefore rather chuse to
speak of the Pleasure You afford all who are admitted into your
Conversation, of Your Elegant Taste in all the Polite Parts of Learning,
of Your great Humanity and Complacency of Manners, and of the surprising
Influence which is peculiar to You in making every one who Converses
with your Lordship prefer You to himself, without thinking the less
meanly of his own Talents. But if I should take notice of all that might
be observed in your Lordship, I should have nothing new to say upon any
other Character of Distinction.
I am,
My Lord,
Your Lordship's
Most Obedient,
Most Devoted
Humble Servant,
The Spectator.
In 1695, when a student at Oxford, aged 23, Joseph Addison
had dedicated 'to the Right Honourable Sir George Somers, Lord Keeper of
the Great Seal,' a poem written in honour of King William III after his
capture of Namur in sight of the whole French Army under Villeroi. This
was Addison's first bid for success in Literature; and the twenty-seven
lines in which he then asked Somers to 'receive the present of a Muse
unknown,' were honourably meant to be what Dr. Johnson called 'a kind of
rhyming introduction to Lord Somers.' If you, he said to Somers then —
'If you, well pleas'd, shall smile upon my lays,
Secure of fame, my voice I'll boldly raise,
For next to what you write, is what you praise.'
Somers did smile, and at once held out to Addison his helping hand.
Mindful of this, and of substantial friendship during the last seventeen
years, Addison joined Steele in dedicating to his earliest patron the
first volume of the
Essays
which include his best security of fame.
At that time, John Somers, aged 61, and retired from political life, was
weak in health and high in honours earned by desert only. He was the son
of an attorney at Worcester, rich enough to give him a liberal education
at his City Grammar School and at Trinity College, Oxford, where he was
entered as a Gentleman Commoner. He left the University, without taking
a degree, to practise law. Having a strong bent towards Literature as
well as a keen, manly interest in the vital questions which concerned
the liberties of England under Charles the Second, he distinguished
himself by political tracts which maintained constitutional rights. He
rose at the bar to honour and popularity, especially after his pleading
as junior counsel for Sancroft, Archbishop of Canterbury, and the Six
Bishops, Lloyd, Turner, Lake, Ken, White, and Trelawney, who signed the
petition against the King's order for reading in all churches a
Declaration for Liberty of Conscience, which they said 'was founded upon
such a dispensing power as hath been often declared illegal in
Parliament.' Somers earned the gratitude of a people openly and loudly
triumphing in the acquittal of the Seven Bishops. He was active also in
co-operation with those who were planning the expulsion of the Stuarts
and the bringing over of the Prince of Orange. During the Interregnum
he, and at the same time also Charles Montague, afterwards Lord Halifax,
first entered Parliament. He was at the conference with the Lords upon
the question of declaring the Throne vacant. As Chairman of the
Committee appointed for the purpose, it was Somers who drew up the
Declaration of Right, which, in placing the Prince and Princess of
Orange on the throne, set forth the grounds of the Revolution and
asserted against royal encroachment the ancient rights and liberties of
England. For these services and for his rare ability as a constitutional
lawyer, King William, in the first year of his reign, made Somers
Solicitor-General. In 1692 he became Attorney-General as Sir John
Somers, and soon afterwards, in March 1692-3, the Great Seal, which had
been four years in Commission, was delivered to his keeping, with a
patent entitling him to a pension of £2000 a year from the day he
quitted office. He was then also sworn in as Privy Councillor. In April
1697 Somers as Lord Keeper delivered up the Great Seal, and received it
back with the higher title of Lord Chancellor. He was at the same time
created Baron Somers of Evesham; Crown property was also given to him to
support his dignity. One use that he made of his influence was to
procure young Addison a pension, that he might be forwarded in service
of the State. Party spirit among his political opponents ran high
against Somers. At the close of 1699 they had a majority in the Commons,
and deprived him of office, but they failed before the Lords in an
impeachment against him. In Queen Anne's reign, between 1708 and 1710,
the constitutional statesman, long infirm of health, who had been in
retirement serving Science as President of the Royal Society, was
serving the State as President of the Council. But in 1712, when Addison
addressed to him this Dedication of the first Volume of the first
reprint of
the Spectator
, he had withdrawn from public life, and four
years afterwards he died of a stroke of apoplexy.
Of Somers as a patron Lord Macaulay wrote:
'He had traversed the whole
vast range of polite literature, ancient and modern. He was at once a
munificent and a severely judicious patron of genius and learning. Locke
owed opulence to Somers. By Somers Addison was drawn forth from a cell
in a college. In distant countries the name of Somers was mentioned with
respect and gratitude by great scholars and poets who had never seen his
face. He was the benefactor of Leclerc. He was the friend of Filicaja.
Neither political nor religious differences prevented him from extending
his powerful protection to merit. Hickes, the fiercest and most
intolerant of all the non-jurors, obtained, by the influence of Somers,
permission to study Teutonic antiquities in freedom and safety. Vertue,
a Strict Roman Catholic, was raised, by the discriminating and liberal
patronage of Somers, from poverty and obscurity to the first rank among
the engravers of the age.'
Contents
|
Thursday, March 1, 1711 |
Addison |
Non fumum ex fulgore, sed ex fumo dare lucem
Cogitat, ut speciosa dehinc miracula promat.
Hor.

I have observed, that a Reader seldom peruses a Book with Pleasure 'till
he knows whether the Writer of it be a black or a fair Man, of a mild or
cholerick Disposition, Married or a Batchelor, with other Particulars of
the like nature, that conduce very much to the right Understanding of an
Author. To gratify this Curiosity, which is so natural to a Reader, I
design this Paper, and my next, as Prefatory Discourses to my following
Writings, and shall give some Account in them of the several persons
that are engaged in this Work. As the chief trouble of Compiling,
Digesting, and Correcting will fall to my Share, I must do myself the
Justice to open the Work with my own History.
was born to a small Hereditary Estate, which
according to the
tradition of the village where it lies,
was bounded by the same
Hedges and Ditches in
William
the Conqueror's Time that it is at
present, and has been delivered down from Father to Son whole and
entire, without the Loss or Acquisition of a single Field or Meadow,
during the Space of six hundred
. There
runs
a Story in the
Family, that when my Mother was gone with Child of me about three
Months, she dreamt that she was brought to Bed of a Judge. Whether this
might proceed from a Law-suit which was then depending in the Family, or
my Father's being a Justice of the Peace, I cannot determine; for I am
not so vain as to think it presaged any Dignity that I should arrive at
in my future Life, though that was the Interpretation which the
Neighbourhood put upon it. The Gravity of my Behaviour at my very first
Appearance in the World, and all the Time that I sucked, seemed to
favour my Mother's Dream: For, as she has often told me, I threw away my
Rattle before I was two Months old, and would not make use of my Coral
till they had taken away the Bells from it.
As for the rest of my Infancy, there being nothing in it remarkable, I
shall pass it over in Silence. I find that, during my Nonage, I had the
reputation of a very sullen Youth, but was always a Favourite of my
School-master, who used to say,
that my parts were solid, and would
wear well
. I had not been long at the University, before I
distinguished myself by a most profound Silence: For, during the Space
of eight Years, excepting in the publick Exercises of the College, I
scarce uttered the Quantity of an hundred Words; and indeed do not
remember that I ever spoke three Sentences together in my whole Life.
Whilst I was in this Learned Body, I applied myself with so much
Diligence to my Studies, that there are very few celebrated Books,
either in the Learned or the Modern Tongues, which I am not acquainted
with.
Upon the Death of my Father I was resolved to travel into Foreign
Countries, and therefore left the University, with the Character of an
odd unaccountable Fellow, that had a great deal of Learning, if I would
but show it.
insatiable Thirst after Knowledge carried me into all
the Countries of
Europe
,
in which
there was any thing new or
strange to be seen; nay, to such a Degree was my curiosity raised, that
having read the controversies of some great Men concerning the
Antiquities of
Egypt
, I made a Voyage to
Grand Cairo
, on
purpose to take the Measure of a Pyramid; and, as soon as I had set my
self right in that Particular, returned to my Native Country with great
Satisfaction
.
I have passed my latter Years in this City, where I am frequently seen
in most publick Places, tho' there are not above half a dozen of my
select Friends that know me; of whom my next Paper shall give a more
particular Account.
is no place of
general
Resort wherein I
do not often make my appearance; sometimes I am seen thrusting my Head
into a Round of Politicians at
Will's
and listning with great
Attention to the Narratives that are made in those little Circular
Audiences.
I smoak a Pipe at
Child's
; and, while I
seem attentive to nothing but the
Post-Man
, over-hear the
Conversation of every Table in the Room.
appear on
Sunday
nights at
St. James's
Coffee House
, and sometimes join the
little Committee of Politicks in the Inner-Room, as one who comes there
to hear and improve.
Face is likewise very well known at the
Grecian
,
the
Cocoa-Tree
,
and in the Theaters both of
Drury
Lane
and the
Hay-Market
.
I
been taken for a Merchant upon
the
Exchange
for above these ten Years, and sometimes pass for a
Jew
in the Assembly of Stock-jobbers at
Jonathan's
.
In short,
where-ever I see a Cluster of People, I always mix with them, tho' I
never open my Lips but in my own Club.
Thus I live in the World, rather as a Spectator of Mankind, than as one
of the Species; by which means I have made my self a Speculative
Statesman, Soldier, Merchant, and Artizan, without ever medling with any
Practical Part in Life. I am very well versed in the Theory of an
Husband, or a Father, and can discern the Errors in the Œconomy,
Business, and Diversion of others, better than those who are engaged in
them; as Standers-by discover Blots, which are apt to escape those who
are in the Game. I never espoused any Party with Violence, and am
resolved to observe an exact Neutrality between the Whigs and Tories,
unless I shall be forc'd to declare myself by the Hostilities of either
side. In short, I have acted in all the parts of my Life as a Looker-on,
which is the Character I intend to preserve in this Paper.
I have given the Reader just so much of my History and Character, as to
let him see I am not altogether unqualified for the Business I have
undertaken. As for other Particulars in my Life and Adventures, I shall
insert them in following Papers, as I shall see occasion. In the mean
time, when I consider how much I have seen, read, and heard, I begin to
blame my own Taciturnity; and since I have neither Time nor Inclination
to communicate the Fulness of my Heart in Speech, I am resolved to do it
in Writing; and to Print my self out, if possible, before I Die. I have
been often told by my Friends that it is Pity so many useful Discoveries
which I have made, should be in the Possession of a Silent Man. For this
Reason therefore, I shall publish a Sheet full of Thoughts every
Morning, for the Benefit of my Contemporaries; and if I can any way
contribute to the Diversion or Improvement of the Country in which I
live, I shall leave it, when I am summoned out of it, with the secret
Satisfaction of thinking that I have not Lived in vain.
are three very material Points which I have not spoken to in this
Paper, and which, for several important Reasons, I must keep to my self,
at least for some Time: I mean, an Account of my Name, my Age, and my
Lodgings. I must confess I would gratify my Reader in any thing that is
reasonable; but as for these three Particulars, though I am sensible
they might tend very much to the Embellishment of my Paper, I cannot yet
come to a Resolution of communicating them to the Publick. They would
indeed draw me out of that Obscurity which I have enjoyed for many
Years, and expose me in Publick Places to several Salutes and
Civilities, which have been always very disagreeable to me; for the
greatest
pain
I can suffer,
is
the being talked to, and being
stared at. It is for this Reason likewise, that I keep my Complexion and
Dress, as very great Secrets; tho' it is not impossible, but I may make
Discoveries of both in the Progress of the Work I have undertaken.
After having been thus particular upon my self, I shall in to-Morrow's
Paper give an Account of those Gentlemen who are concerned with me in
this Work. For, as I have before intimated, a Plan of it is laid and
concerted (as all other Matters of Importance are) in a Club.
,
as my Friends have engaged me to stand in the Front, those who have a
mind to correspond with me, may direct their Letters
To the Spectator
,
at Mr.
Buckley's
, in
Little Britain
. For
must further acquaint
the Reader, that tho' our Club meets only on
Tuesdays
and
Thursdays
,
we have appointed a Committee to sit every Night, for the Inspection of
all such Papers as may contribute to the Advancement of the Public Weal.
C.
I find by the writings of the family,
goes
where
This is said to allude to a description of the Pyramids of
Egypt, by John Greaves, a Persian scholar and Savilian Professor of
Astronomy at Oxford, who studied the principle of weights and measures
in the Roman Foot and the Denarius, and whose visit to the Pyramids in
1638, by aid of his patron Laud, was described in his
Pyramidographia
.
That work had been published in 1646, sixty-five years before the
appearance of the
Spectator
, and Greaves died in 1652. But in
1706 appeared a tract, ascribed to him by its title-page, and popular
enough to have been reprinted in 1727 and 1745, entitled,
The Origine
and Antiquity of our English Weights and Measures discovered by their
near agreement with such Standards that are now found in one of the
Egyptian Pyramids.
It based its arguments on measurements in the
Pyramidographia
, and gave to Professor Greaves, in Addison's time, the
same position with regard to Egypt that has been taken in our time by
the Astronomer-Royal for Scotland, Professor Piazzi Smyth.
publick
Will's
Coffee House, which had been known
successively as the
Red Cow
and the
Rose
before it took a
permanent name from Will Urwin, its proprietor, was the corner house on
the north side of Russell Street, at the end of Bow Street, now No. 21.
Dryden's use of this Coffee House caused the wits of the town to resort
there, and after Dryden's death, in 1700, it remained for some years the
Wits' Coffee House. There the strong interest in current politics took
chiefly the form of satire, epigram, or entertaining narrative. Its
credit was already declining in the days of the
Spectator
; wit
going out and card-play coming in.
Child's
Coffee House was in St. Paul's Churchyard.
Neighbourhood to the Cathedral and Doctors' Commons made it a place of
resort for the Clergy. The College of Physicians had been first
established in Linacre's House, No. 5, Knightrider Street, Doctors'
Commons, whence it had removed to Amen Corner, and thence in 1674 to the
adjacent Warwick Lane. The Royal Society, until its removal in 1711 to
Crane Court, Fleet Street, had its rooms further east, at Gresham
College. Physicians, therefore, and philosophers, as well as the clergy,
used
Child's
as a convenient place of resort.
The
Postman
, established and edited by M. Fonvive, a
learned and grave French Protestant, who was said to make £600 a year by
it, was a penny paper in the highest repute, Fonvive having secured for
his weekly chronicle of foreign news a good correspondence in Italy,
Spain, Portugal, Germany, Flanders, Holland. John Dunton, the
bookseller, in his
Life and Errors,
published in 1705, thus
characterized the chief newspapers of the day:
'the Observator is
best to towel the Jacks, the Review is best to promote peace, the
Flying Post is best for the Scotch news, the Postboy is
best for the English and Spanish news, the Daily Courant is the
best critic, the English Post is the best collector, the
London Gazette has the best authority, and the Postman is
the best for everything.'
St. James's
Coffee House was the last house but one
on the south-west corner of St. James's Street; closed about 1806. On
its site is now a pile of buildings looking down Pall Mall. Near St.
James's Palace, it was a place of resort for Whig officers of the Guards
and men of fashion. It was famous also in Queen Anne's reign, and long
after, as the house most favoured Whig statesmen and members of Parliament, who could there privately
discuss their party tactics.
The
Grecian
Coffee House was in Devereux Court, Strand,
and named from a Greek, Constantine, who kept it. Close to the Temple,
it was a place of resort for the lawyers. Constantine's Greek had
tempted also Greek scholars to the house, learned Professors and Fellows
of the Royal Society. Here, it is said, two friends quarrelled so
bitterly over a Greek accent that they went out into Devereux Court and
fought a duel, in which one was killed on the spot.
The
Cocoa Tree
was a Chocolate House in St. James's
Street, used by Tory statesmen and men of fashion as exclusively as
St.
James's
Coffee House, in the same street, was used by Whigs of the same
class. It afterwards became a Tory club.
Drury Lane had a theatre in Shakespeare's time, 'the
Phoenix,' called also 'the Cockpit.' It was destroyed in 1617 by a
Puritan mob, re-built, and occupied again till the stoppage of
stage-plays in 1648. In that theatre Marlowe's
Jew of Malta,
Massinger's
New Way to Pay Old Debts,
and other pieces of good
literature, were first produced. Its players under James I were 'the
Queen's servants.' In 1656 Davenant broke through the restriction upon
stage-plays, and took actors and musicians to 'the Cockpit,' from
Aldersgate Street. After the Restoration, Davenant having obtained a
patent, occupied, in Portugal Row, the Lincoln's Inn Theatre, and
afterwards one on the site of Dorset House, west of Whitefriars, the
last theatre to which people went in boats. Sir William Davenant, under
the patronage of the Duke of York, called his the Duke's Players. Thomas
Killigrew then had 'the Cockpit' in Drury Lane, his company being that
of the King's Players, and it was Killigrew who, dissatisfied with the
old 'Cockpit,' opened, in 1663, the first
Drury Lane Theatre
, nearly
upon the site now occupied by D.L. No. 4. The original theatre, burnt in
1671-2, was rebuilt by Sir Christopher Wren, and opened in 1674 with a
Prologue
by Dryden. That (D.L. No. 2) was the house visited by
the
Spectator
. It required rebuilding in 1741 (D.L. No. 3); and was burnt
down, and again rebuilt, in 1809, as we now have it (D.L. No. 4). There
was no Covent Garden Theatre till after
the Spectator's
time, in 1733,
when that house was first opened by Rich, the harlequin, under the
patent granted to the Duke's Company.
In 1711 the other great house was the theatre in the Haymarket, recently
built by Sir John Vanbrugh, author of
The Provoked Wife,
and architect
of Blenheim. This
Haymarket Theatre
, on the site of that known as 'Her
Majesty's,' was designed and opened by Vanbrugh in 1706, thirty persons
of quality having subscribed a hundred pounds each towards the cost of
it. He and Congreve were to write the plays, and Betterton was to take
charge of their performance. The speculation was a failure; partly
because the fields and meadows of the west end of the town cut off the
poorer playgoers of the City, who could not afford coach-hire; partly
because the house was too large, and its architecture swallowed up the
voices of the actors. Vanbrugh and Congreve opened their grand west-end
theatre with concession to the new taste of the fashionable for Italian
Opera. They began with a translated opera set to Italian music, which
ran only for three nights. Sir John Vanbrugh then produced his comedy of
The Confederacy,
with less success than it deserved. In a few months
Congreve abandoned his share in the undertaking. Vanbrugh proceeded to
adapt for his new house three plays of Molière. Then Vanbrugh, still
failing, let the Haymarket to Mr. Owen Swiney, a trusted agent of the
manager of
Drury Lane
, who was to allow him to draw what actors he
pleased from
Drury Lane
and divide profits. The recruited actors in
the
Haymarket
had better success. The secret league between the two
theatres was broken. In 1707 the
Haymarket
was supported by a
subscription headed by Lord Halifax. But presently a new joint patentee
brought energy into the counsels of
Drury Lane
. Amicable restoration
was made to the Theatre Royal of the actors under Swiney at the
Haymarket
; and to compensate Swiney for his loss of profit, it was
agreed that while
Drury Lane
confined itself to the acting of plays,
he should profit by the new taste for Italian music, and devote the
house in the
Haymarket
to opera. Swiney was content. The famous singer
Nicolini had come over, and the town was impatient to hear him. This
compact held for a short time. It was broken then by quarrels behind the
scenes. In 1709 Wilks, Dogget, Cibber, and Mrs. Oldfield treated with
Swiney to be sharers with him in the
Haymarket
as heads of a dramatic
company. They contracted the width of the theatre, brought down its
enormously high ceiling, thus made the words of the plays audible, and
had the town to themselves, till a lawyer, Mr. William Collier, M.P. for
Truro, in spite of the counter-attraction of the trial of Sacheverell,
obtained a license to open
Drury Lane
, and produced an actress who
drew money to Charles Shadwell's comedy,
The Fair Quaker of Deal.
At
the close of the season Collier agreed with Swiney and his
actor-colleagues to give up to them
Drury Lane
with its actors, take
in exchange the
Haymarket
with its singers, and be sole Director of
the Opera; the actors to pay Collier two hundred a year for the use of
his license, and to close their house on the Wednesdays when an opera
was played.
This was the relative position of
Drury Lane
and the
Haymarket
theatres when the
Spectator
first appeared.
Drury Lane
had entered
upon a long season of greater prosperity than it had enjoyed for thirty
years before. Collier, not finding the
Haymarket
as prosperous as it
was fashionable, was planning a change of place with Swiney, and he so
contrived, by lawyer's wit and court influence, that in the winter
following 1711 Collier was at Drury Lane with a new license for himself,
Wilks, Dogget, and Cibber; while Swiney, transferred to the Opera, was
suffering a ruin that caused him to go abroad, and be for twenty years
afterwards an exile from his country.
Jonathan's
Coffee House, in Change Alley, was the place
of resort for stock-jobbers. It was to
Garraway's
, also in Change
Alley, that people of quality on business in the City, or the wealthy
and reputable citizens, preferred to go.
pains ... are.
The Spectator
in its first daily issue was
'Printed for
Sam. Buckley, at the Dolphin in Little Britain; and sold by A.
Baldwin in Warwick Lane.'
The initials appended to the papers in their daily issue
were placed, in a corner of the page, after the printer's name.
Contents
|
Friday, March 2, 1711 |
Steele |
... Ast Alii sex
Et plures uno conclamant ore.
Juv.

first of our Society is a Gentleman of
Worcestershire
, of antient
Descent, a Baronet, his Name Sir
Roger De Coverly.
His great
Grandfather was Inventor of that famous Country-Dance which is call'd
after him. All who know that Shire are very well acquainted with the
Parts and Merits of Sir
Roger
. He is a Gentleman that is very singular
in his Behaviour, but his Singularities proceed from his good Sense, and
are Contradictions to the Manners of the World, only as he thinks the
World is in the wrong. However, this Humour creates him no Enemies, for
he does nothing with Sourness or Obstinacy; and his being unconfined to
Modes and Forms, makes him but the readier and more capable to please
and oblige all who know him.
he is in town he lives in
Soho
Square
: It is said, he keeps himself a Batchelour by reason he
was crossed in Love by a perverse beautiful Widow of the next County to
him.
this Disappointment, Sir
Roger
was what you call a fine
Gentleman, had often supped with my Lord
Rochester
and Sir
George Etherege
, fought a Duel upon his first coming to Town,
and kick'd Bully
Dawson
in a publick Coffee-house for calling
him Youngster. But being ill-used by the above-mentioned Widow, he was
very serious for a Year and a half; and tho' his Temper being naturally
jovial, he at last got over it, he grew careless of himself and never
dressed afterwards; he continues to wear a Coat and Doublet of the same
Cut that were in Fashion at the Time of his Repulse, which, in his merry
Humours, he tells us, has been in and out twelve Times since he first
wore it. 'Tis said Sir
Roger
grew humble in his Desires after he had
forgot this cruel Beauty, insomuch that it is reported he has frequently
offended in Point of Chastity with Beggars and Gypsies: but this is
look'd upon by his Friends rather as Matter of Raillery than Truth. He
is now in his Fifty-sixth Year, cheerful, gay, and hearty, keeps a good
House in both Town and Country; a great Lover of Mankind; but there is
such a mirthful Cast in his Behaviour, that he is rather beloved than
esteemed. His Tenants grow rich, his Servants look satisfied, all the
young Women profess Love to him, and the young Men are glad of his
Company: When he comes into a House he calls the Servants by their
Names, and talks all the way Up Stairs to a Visit. I must not omit that
Sir
Roger
is a Justice of the
Quorum
; that he fills the chair at a
Quarter-Session with great Abilities, and three Months ago, gained
universal Applause by explaining a Passage in the Game-Act.
The Gentleman next in Esteem and Authority among us, is another
Batchelour, who is a Member of the
Inner Temple
: a Man of great
Probity, Wit, and Understanding; but he has chosen his Place of
Residence rather to obey the Direction of an old humoursome Father, than
in pursuit of his own Inclinations. He was plac'd there to study the
Laws of the Land, and is the most learned of any of the House in those
of the Stage.
Aristotle
and
Longinus
are much better understood by
him than
Littleton
or
Cooke
. The Father sends up every Post
Questions relating to Marriage-Articles, Leases, and Tenures, in the
Neighbourhood; all which Questions he agrees with an Attorney to answer
and take care of in the Lump. He is studying the Passions themselves,
when he should be inquiring into the Debates among Men which arise from
them. He knows the Argument of each of the Orations of
Demosthenes
and
Tully
, but not one Case in the Reports of our own Courts. No one ever
took him for a Fool, but none, except his intimate Friends, know he has
a great deal of Wit. This Turn makes him at once both disinterested and
agreeable: As few of his Thoughts are drawn from Business, they are most
of them fit for Conversation. His Taste of Books is a little too just
for the Age he lives in; he has read all, but Approves of very few. His
Familiarity with the Customs, Manners, Actions, and Writings of the
Antients, makes him a very delicate Observer of what occurs to him in
the present World.
is an excellent Critick, and the Time of the Play
is his Hour of Business; exactly at five he passes through
New Inn
,
crosses through
Russel Court
; and takes a turn at
Will's
till the
play begins; he has his shoes rubb'd and his Perriwig powder'd at the
Barber's as you go into the Rose
— It is for the Good of the Audience
when he is at a Play, for the Actors have an Ambition to please him.
The Person of next Consideration is Sir
Andrew Freeport
, a Merchant of
great Eminence in the City of
London
: A Person of indefatigable
Industry, strong Reason, and great Experience. His Notions of Trade are
noble and generous, and (as every rich Man has usually some sly Way of
Jesting, which would make no great Figure were he not a rich Man) he
calls the Sea the
British Common
. He is acquainted with Commerce
in all its Parts, and will tell you that it is a stupid and barbarous
Way to extend Dominion by Arms; for true Power is to be got by Arts and
Industry. He will often argue, that if this Part of our Trade were well
cultivated, we should gain from one Nation; and if another, from
another. I have heard him prove that Diligence makes more lasting
Acquisitions than Valour, and that Sloth has ruin'd more Nations than
the Sword. He abounds in several frugal Maxims, amongst which the
greatest Favourite is, 'A Penny saved is a Penny got.' A General Trader
of good Sense is pleasanter Company than a general Scholar; and Sir
Andrew
having a natural unaffected Eloquence, the Perspicuity of his
Discourse gives the same Pleasure that Wit would in another Man. He has
made his Fortunes himself; and says that
England
may be richer
than other Kingdoms, by as plain Methods as he himself is richer than
other Men; tho' at the same Time I can say this of him, that there is
not a point in the Compass, but blows home a Ship in which he is an
Owner.
to Sir
Andrew
in the Club-room sits Captain
Sentry
, a Gentleman
of great Courage, good Understanding, but Invincible Modesty. He is one
of those that deserve very well, but are very awkward at putting their
Talents within the Observation of such as should take notice of them. He
was some Years a Captain, and behaved himself with great Gallantry in
several Engagements, and at several Sieges; but having a small Estate of
his own, and being next Heir to Sir
Roger
, he has quitted a Way of Life
in which no Man can rise suitably to his Merit, who is not something of
a Courtier, as well as a Soldier. I have heard him often lament, that in
a Profession where Merit is placed in so conspicuous a View, Impudence
should get the better of Modesty. When he has talked to this Purpose, I
never heard him make a sour Expression, but frankly confess that he left
the World, because he was not fit for it. A strict Honesty and an even
regular Behaviour, are in themselves Obstacles to him that must press
through Crowds who endeavour at the same End with himself, the Favour of
a Commander. He will, however, in this Way of Talk, excuse Generals, for
not disposing according to Men's Desert, or enquiring into it: For, says
he, that great Man who has a Mind to help me, has as many to break
through to come at me, as I have to come at him: Therefore he will
conclude, that the Man who would make a Figure, especially in a military
Way, must get over all false Modesty, and assist his Patron against the
Importunity of other Pretenders, by a proper Assurance in his own
Vindication. He says it is a civil Cowardice to be backward in asserting
what you ought to expect, as it is a military Fear to be slow in
attacking when it is your Duty. With this Candour does the Gentleman
speak of himself and others. The same Frankness runs through all his
Conversation. The military Part of his Life has furnished him with many
Adventures, in the Relation of which he is very agreeable to the
Company; for he is never over-bearing, though accustomed to command Men
in the utmost Degree below him; nor ever too obsequious, from an Habit
of obeying Men highly above him.
that our Society may not appear a Set of Humourists unacquainted
with the Gallantries and Pleasures of the Age, we have among us the
gallant
Will. Honeycomb
, a Gentleman who, according to his Years,
should be in the Decline of his Life, but having ever been very careful
of his Person, and always had a very easy Fortune, Time has made but
very little Impression, either by Wrinkles on his Forehead, or Traces in
his Brain. His Person is well turned, and of a good Height. He is very
ready at that sort of Discourse with which Men usually entertain Women.
He has all his Life dressed very well, and remembers Habits as others do
Men. He can smile when one speaks to him, and laughs easily. He knows
the History of every Mode, and can inform you from which of the French
King's Wenches our Wives and Daughters had this Manner of curling their
Hair, that Way of placing their Hoods; whose Frailty was covered by such
a Sort of Petticoat, and whose Vanity to show her Foot made that Part of
the Dress so short in such a Year. In a Word, all his Conversation and
Knowledge has been in the female World: As other Men of his Age will
take Notice to you what such a Minister said upon such and such an
Occasion, he will tell you when the Duke of
Monmouth
danced at Court
such a Woman was then smitten, another was taken with him at the Head of
his Troop in the
Park
. In all these important Relations, he has ever
about the same Time received a kind Glance, or a Blow of a Fan, from
some celebrated Beauty, Mother of the present Lord such-a-one. If you
speak of a young Commoner that said a lively thing in the House, he
starts up,
'He has good Blood in his Veins, Tom Mirabell begot him, the Rogue
cheated me in that Affair; that young Fellow's Mother used me more
like a Dog than any Woman I ever made Advances to.'
This Way of Talking of his, very much enlivens the Conversation among us
of a more sedate Turn; and I find there is not one of the Company but
myself, who rarely speak at all, but speaks of him as of that Sort of
Man, who is usually called a well-bred fine Gentleman. To conclude his
Character, where Women are not concerned, he is an honest worthy Man.
I cannot tell whether I am to account him whom I am next to speak of, as
one of our Company; for he visits us but seldom, but when he does, it
adds to every Man else a new Enjoyment of himself. He is a Clergyman, a
very philosophick Man, of general Learning, great Sanctity of Life, and
the most exact good Breeding. He has the Misfortune to be of a very weak
Constitution, and consequently cannot accept of such Cares and Business
as Preferments in his Function would oblige him to: He is therefore
among Divines what a Chamber-Counsellor is among Lawyers. The Probity of
his Mind, and the Integrity of his Life, create him Followers, as being
eloquent or loud advances others. He seldom introduces the Subject he
speaks upon; but we are so far gone in Years, that he observes when he
is among us, an Earnestness to have him fall on some divine Topick,
which he always treats with much Authority, as one who has no Interests
in this World, as one who is hastening to the Object of all his Wishes,
and conceives Hope from his Decays and Infirmities.
are my
ordinary Companions.
R.
The character of Sir Roger de Coverley is said to have been
drawn from Sir John Pakington, of Worcestershire, a Tory, whose name,
family, and politics are represented by a statesman of the present time.
The name, on this its first appearance in the
Spectator
, is spelt
Coverly; also in the first reprint.
Soho Square
was then a new and most fashionable part
of the town. It was built in 1681. The Duke of Monmouth lived in the
centre house, facing the statue. Originally the square was called King
Square. Pennant mentions, on Pegg's authority, a tradition that, on the
death of Monmouth, his admirers changed the name to Soho, the word of
the day at the field of Sedgemoor. But the ground upon which the Square
stands was called Soho as early as the year 1632. 'So ho' was the old
call in hunting when a hare was found.
John Wilmot, Earl of Rochester, b. 1648, d. 1680. His
licentious wit made him a favourite of Charles II. His strength was
exhausted by licentious living at the age of one and thirty. His chief
work is a poem upon 'Nothing.' He died repentant of his wasted life, in
which, as he told Burnet, he had 'for five years been continually
drunk,' or so much affected by frequent drunkenness as in no instance to
be master of himself.
Sir George Etherege, b. 1636, d. 1694. 'Gentle George' and
'Easy Etherege,' a wit and friend of the wits of the Restoration. He
bought his knighthood to enable him to marry a rich widow who required a
title, and died of a broken neck, by tumbling down-stairs when he was
drunk and lighting guests to their apartments. His three comedies,
The
Comical Revenge, She Would if she Could,
and
The Man of Mode, or Sir
Fopling Flutter,
excellent embodiments of the court humour of his time,
were collected and printed in 8vo in 1704, and reprinted, with addition
of five poems, in 1715.
Bully Dawson, a swaggering sharper of Whitefriars, is said
to have been sketched by Shadwell in the Captain Hackum of his comedy
called
The Squire of Alsatia.
The
Rose
Tavern was on the east side of Brydges Street,
near Drury Lane Theatre, much favoured by the looser sort of play-goers.
Garrick, when he enlarged the Theatre, made the
Rose
Tavern a part of
it.
Captain Sentry was by some supposed to have been drawn from
Colonel Kempenfelt, the father of the Admiral who went down with the
Royal George
.
Will. Honeycomb was by some found in a Colonel Cleland.
Steele's signature was
R
till No. 91; then
T
, and
occasionally
R
, till No. 134; then always
T
.
Addison signed
C
till No.
85, when he first used
L
; and was
L
or
C
till No. 265, then
L
, till he
first used
I
in No. 372. Once or twice using
L
, he was
I
till No. 405,
which he signed
O
, and by this letter he held, except for a return to
C
(with a single use of
O
), from 433 to 477.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 1, 1711 |
Addison |
Quoi quisque ferè studio devinctus adhæret:
Aut quibus in rebus multùm sumus antè morati:
Atque in quâ ratione fuit contenta magis mens;
In somnis eadem plerumque videmur obire.
Lucr. L. 4.

one of my late Rambles, or rather Speculations, I looked into the
great Hall where the Bank
is kept, and was not a little pleased to
see the Directors, Secretaries, and Clerks, with all the other Members
of that wealthy Corporation, ranged in their several Stations, according
to the Parts they act in that just and regular Œconomy. This revived in
my Memory the many Discourses which I had both read and heard,
concerning the Decay of Publick Credit, with the Methods of restoring
it, and which, in my Opinion, have always been defective, because they
have always been made with an Eye to separate Interests and Party
Principles.
The Thoughts of the Day gave my Mind Employment for the whole Night, so
that I fell insensibly into a kind of Methodical Dream, which disposed
all my Contemplations into a Vision or Allegory, or what else the Reader
shall please to call it.
Methoughts I returned to the Great Hall, where I had been the Morning
before, but to my Surprize, instead of the Company that I left there, I
saw, towards the Upper-end of the Hall, a beautiful Virgin seated on a
Throne of Gold. Her Name (as they told me) was
Publick Credit
. The
Walls, instead of being adorned with Pictures and Maps, were hung with
many Acts of Parliament written in Golden Letters.
the Upper end of
the Hall was the
Magna Charta
, with the Act of Uniformity
on
the right Hand, and the Act of Toleration
on the left. At the Lower
end of the Hall was the Act of Settlement
, which was placed full in
the Eye of the Virgin that sat upon the Throne. Both the Sides of the
Hall were covered with such Acts of Parliament as had been made for the
Establishment of Publick Funds. The Lady seemed to set an unspeakable
Value upon these several Pieces of Furniture, insomuch that she often
refreshed her Eye with them, and often smiled with a Secret Pleasure, as
she looked upon them; but at the same time showed a very particular
Uneasiness, if she saw any thing approaching that might hurt them. She
appeared indeed infinitely timorous in all her Behaviour: And, whether
it was from the Delicacy of her Constitution, or that she was troubled
with the Vapours, as I was afterwards told by one who I found was none
of her Well-wishers, she changed Colour, and startled at everything she
heard. She was likewise (as I afterwards found) a greater Valetudinarian
than any I had ever met with, even in her own Sex, and subject to such
Momentary Consumptions, that in the twinkling of an Eye, she would fall
away from the most florid Complexion, and the most healthful State of
Body, and wither into a Skeleton. Her Recoveries were often as sudden as
her Decays, insomuch that she would revive in a Moment out of a wasting
Distemper, into a Habit of the highest Health and Vigour.
I had very soon an Opportunity of observing these quick Turns and
Changes in her Constitution. There sat at her Feet a Couple of
Secretaries, who received every Hour Letters from all Parts of the
World; which the one or the other of them was perpetually reading to
her; and according to the News she heard, to which she was exceedingly
attentive, she changed Colour, and discovered many Symptoms of Health or
Sickness.
Behind the Throne was a prodigious Heap of Bags of Mony, which were
piled upon one another so high that they touched the Ceiling. The Floor
on her right Hand, and on her left, was covered with vast Sums of Gold
that rose up in Pyramids on either side of her: But this I did not so
much wonder at, when I heard, upon Enquiry, that she had the same Virtue
in her Touch, which the Poets tell us a
Lydian
King was formerly
possessed of; and that she could convert whatever she pleased into that
precious Metal.
After a little Dizziness, and confused Hurry of Thought, which a Man
often meets with in a Dream, methoughts the Hall was alarm'd, the Doors
flew open, and there entered half a dozen of the most hideous Phantoms
that I had ever seen (even in a Dream) before that Time. They came in
two by two, though match'd in the most dissociable Manner, and mingled
together in a kind of Dance.
would be tedious to describe their
Habits and Persons; for which Reason I shall only inform my Reader that
the first Couple were Tyranny and Anarchy, the second were Bigotry and
Atheism, the third the Genius of a Common-Wealth, and a young Man of
about twenty-two Years of Age
, whose Name I could not learn. He had
a Sword in his right Hand, which in the Dance he often brandished at the
Act of Settlement; and a Citizen, who stood by me, whispered in my Ear,
that he saw a Spunge in his left Hand.
Dance of so many jarring
Natures put me in mind of the Sun, Moon, and Earth, in the
Rehearsal
, that danced together for no other end but to
eclipse one another.
The Reader will easily suppose, by what has been before said, that the
Lady on the Throne would have been almost frightened to Distraction, had
she seen but any one of these Spectres; what then must have been her
Condition when she saw them all in a Body? She fainted and dyed away at
the sight.
Et neq; jam color est misto candore rubori;
Nec Vigor, et Vires, et quæ modò visa placebant;
Nec Corpus remanet ...
Ov. Met. Lib. 3.
There was as great a Change in the Hill of Mony Bags, and the Heaps of
Mony, the former shrinking, and falling into so many empty Bags, that I
now found not above a tenth part of them had been filled with Mony. The
rest that took up the same Space, and made the same Figure as the Bags
that were really filled with Mony, had been blown up with Air, and
called into my Memory the Bags full of Wind, which Homer tells us his
Hero received as a present from Æolus. The great Heaps of Gold, on
either side of the Throne, now appeared to be only Heaps of Paper, or
little Piles of notched Sticks, bound up together in Bundles, like
Bath-Faggots.
Whilst I was lamenting this sudden Desolation that had been made before
me, the whole Scene vanished: In the Room of the frightful Spectres,
there now entered a second Dance of Apparitions very agreeably matched
together, and made up of very amiable Phantoms.
first Pair was
Liberty, with Monarchy at her right Hand: The Second was Moderation
leading in Religion; and the third a Person whom I had never seen
,
with the genius of
Great Britain
.
their first Entrance the
Lady reviv'd, the Bags swell'd to their former Bulk, the Piles of
Faggots and Heaps of Paper changed into Pyramids of Guineas
: And for
my own part I was so transported with Joy, that I awaked, tho' I must
confess I would fain have fallen asleep again to have closed my Vision,
if I could have done it.
The Bank of England was then only 17 years old. It was
founded in 1694, and grew out of a loan of £1,200,000 for the public
service, for which the lenders — so low was the public credit — were to
have 8 per cent. interest, four thousand a year for expense of
management, and a charter for 10 years, afterwards renewed from time to
time, as the 'Governor and Company of the Bank of England.'
Magna Charta Libertatum
, the Great Charter of Liberties
obtained by the barons of King John, June 16, 1215, not only asserted
rights of the subject against despotic power of the king, but included
among them right of insurrection against royal authority unlawfully
exerted.
The Act of Uniformity, passed May 19, 1662, withheld
promotion in the Church from all who had not received episcopal
ordination, and required of all clergy assent to the contents of the
Prayer Book on pain of being deprived of their spiritual promotion. It
forbade all changes in matters of belief otherwise than by the king in
Parliament. While it barred the unconstitutional exercise of a
dispensing power by the king, and kept the settlement of its faith out
of the hands of the clergy and in those of the people, it was so
contrived also according to the temper of the majority that it served as
a test act for the English Hierarchy, and cast out of the Church, as
Nonconformists, those best members of its Puritan clergy, about two
thousand in number, whose faith was sincere enough to make them
sacrifice their livings to their sense of truth.
The Act of Toleration, with which Addison balances the Act
of Uniformity, was passed in the first year of William and Mary, and
confirmed in the 10th year of Queen Anne, the year in which this
Essay
was written. By it all persons dissenting from the Church of England,
except Roman Catholics and persons denying the Trinity, were relieved
from such acts against Nonconformity as restrained their religious
liberty and right of public worship, on condition that they took the
oaths of allegiance and supremacy, subscribed a declaration against
transubstantiation, and, if dissenting ministers, subscribed also to
certain of the Thirty-Nine Articles.
The Act of Settlement was that which, at the Revolution,
excluded the Stuarts and settled the succession to the throne of princes
who have since governed England upon the principle there laid down, not
of divine right, but of an original contract between prince and people,
the breaking of which by the prince may lawfully entail forfeiture of
the crown.
James Stuart, son of James II, born June 10, 1688, was
then in the 23rd year of his age.
The
Rehearsal
was a witty burlesque upon the heroic
dramas of Davenant, Dryden, and others, written by George Villiers, duke
of Buckingham, the Zimri of Dryden's 'Absalom and Achitophel,' 'that
life of pleasure and that soul of whim,' who, after running through a
fortune of £50,000 a year, died, says Pope, 'in the worst inn's worst
room.' His
Rehearsal
, written in 1663-4, was first acted in 1671.
In the last act the poet Bayes, who is showing and explaining a
Rehearsal of his play to Smith and Johnson, introduces an Eclipse which,
as he explains, being nothing else but an interposition, &c.
'Well, Sir, then what do I, but make the earth, sun, and moon, come
out upon the stage, and dance the hey' ... 'Come, come out, eclipse,
to the tune of Tom Tyler.'
Enter Luna.
Luna: Orbis, O Orbis! Come to me, thou little rogue, Orbis!
Enter the Earth.
Orb.: Who calls Terra-firma pray?
...
Enter Sol, to the tune of Robin Hood, &c.
While they dance Bayes cries, mightily taken with his device,
'Now the
Earth's before the Moon; now the Moon's before the Sun: there's the
Eclipse again.'
The elector of Hanover, who, in 1714, became King George
I.
In the year after the foundation of the Bank of England,
Mr. Charles Montague, — made in 1700 Baron and by George I, Earl of
Halifax, then (in 1695) Chancellor of the Exchequer, — restored the
silver currency to a just standard. The process of recoinage caused for
a time scarcity of coin and stoppage of trade. The paper of the Bank of
England fell to 20 per cent. discount. Montague then collected and paid
public debts from taxes imposed for the purpose and invented (in 1696),
to relieve the want of currency, the issue of Exchequer bills. Public
credit revived, the Bank capital increased, the currency sufficed, and.
says Earl Russell in his Essay on the English Government and
Constitution,
'from this time loans were made of a vast increasing amount with great
facility, and generally at a low interest, by which the nation were
enabled to resist their enemies. The French wondered at the prodigious
efforts that were made by so small a power, and the abundance with
which money was poured into its treasury... Books were written,
projects drawn up, edicts prepared, which were to give to France the
same facilities as her rival; every plan that fiscal ingenuity could
strike out, every calculation that laborious arithmetic could form,
was proposed, and tried, and found wanting; and for this simple
reason, that in all their projects drawn up in imitation of England,
one little element was omitted, videlicet, her free constitution.'
That is what Addison means by his allegory.
Contents
|
Monday, March 5, 1711 |
Steele |
.. Egregii Mortalem altique silenti!
Hor.

An Author, when he first appears in the World, is very apt to believe it
has nothing to think of but his Performances. With a good Share of this
Vanity in my Heart, I made it my Business these three Days to listen
after my own Fame; and, as I have sometimes met with Circumstances which
did not displease me, I have been encountered by others which gave me
much Mortification. It is incredible to think how empty I have in this
time observed some Part of the Species to be, what mere Blanks they are
when they first come abroad in the Morning, how utterly they are at a
Stand, until they are set a going by some Paragraph in a News-Paper:
Such Persons are very acceptable to a young Author, for they desire no
more
in anything
but to be new, to be agreeable. If I found
Consolation among such, I was as much disquieted by the Incapacity of
others. These are Mortals who have a certain Curiosity without Power of
Reflection, and perused my Papers like Spectators rather than Readers.
But there is so little Pleasure in Enquiries that so nearly concern our
selves (it being the worst Way in the World to Fame, to be too anxious
about it), that upon the whole I resolv'd for the future to go on in my
ordinary Way; and without too much Fear or Hope about the Business of
Reputation, to be very careful of the Design of my Actions, but very
negligent of the Consequences of them.
It is an endless and frivolous Pursuit to act by any other Rule than the
Care of satisfying our own Minds in what we do. One would think a silent
Man, who concerned himself with no one breathing, should be very liable
to Misinterpretations; and yet I remember I was once taken up for a
Jesuit, for no other reason but my profound Taciturnity. It is from this
Misfortune, that to be out of Harm's Way, I have ever since affected
Crowds. He who comes into Assemblies only to gratify his Curiosity, and
not to make a Figure, enjoys the Pleasures of Retirement in a more
exquisite Degree, than he possibly could in his Closet; the Lover, the
Ambitious, and the Miser, are followed thither by a worse Crowd than any
they can withdraw from. To be exempt from the Passions with which others
are tormented, is the only pleasing Solitude. I can very justly say with
the antient Sage,
I am never less alone than when alone
. As I am
insignificant to the Company in publick Places, and as it is visible I
do not come thither as most do, to shew my self; I gratify the Vanity of
all who pretend to make an Appearance, and often have as kind Looks from
well-dressed Gentlemen and Ladies, as a Poet would bestow upon one of
his Audience.
are so many Gratifications attend this publick sort
of Obscurity, that some little Distastes I daily receive have lost their
Anguish; and I
did the other day,
without the least Displeasure
overhear one say of me,
That strange Fellow,
and another answer,
I
have known the Fellow's Face for these twelve Years, and so must you;
but I believe you are the first ever asked who he was.
There are, I
must confess, many to whom my Person is as well known as that of their
nearest Relations, who give themselves no further Trouble about calling
me by my Name or Quality, but speak of me very currently by Mr
what-d-ye-call-him
.
To make up for these trivial Disadvantages, I have the high Satisfaction
of beholding all Nature with an unprejudiced Eye; and having nothing to
do with Men's Passions or Interests, I can with the greater Sagacity
consider their Talents, Manners, Failings, and Merits.
It is remarkable, that those who want any one Sense, possess the others
with greater Force and Vivacity. Thus my Want of, or rather Resignation
of Speech, gives me all the Advantages of a dumb Man. I have, methinks,
a more than ordinary Penetration in Seeing; and flatter my self that I
have looked into the Highest and Lowest of Mankind, and make shrewd
Guesses, without being admitted to their Conversation, at the inmost
Thoughts and Reflections of all whom I behold. It is from hence that
good or ill Fortune has no manner of Force towards affecting my
Judgment. I see Men flourishing in Courts, and languishing in Jayls,
without being prejudiced from their Circumstances to their Favour or
Disadvantage; but from their inward Manner of bearing their Condition,
often pity the Prosperous and admire the Unhappy.
Those who converse with the Dumb, know from the Turn of their Eyes and
the Changes of their Countenance their Sentiments of the Objects before
them. I have indulged my Silence to such an Extravagance, that the few
who are intimate with me, answer my Smiles with concurrent Sentences,
and argue to the very Point I shak'd my Head at without my speaking.
Will. Honeycomb
was very entertaining the other Night at a Play to a
Gentleman who sat on his right Hand, while I was at his Left.
Gentleman believed
Will
. was talking to himself, when upon my looking
with great Approbation at a
young thing
in a Box before us, he
said,
'I am quite of another Opinion: She has, I will allow, a very
pleasing Aspect, but, methinks, that Simplicity in her Countenance is
rather childish than innocent.'
When I observed her a second time, he said,
'I grant her Dress is very becoming, but perhaps the Merit of
Choice is owing to her Mother; for though,' continued he, 'I allow a
Beauty to be as much to be commended for the Elegance of her Dress, as a
Wit for that of his Language; yet if she has stolen the Colour of her
Ribbands from another, or had Advice about her Trimmings, I shall not
allow her the Praise of Dress, any more than I would call a Plagiary an
Author.'
When I threw my Eye towards the next Woman to her,
Will
. spoke
what I looked,
according to his romantic imagination
, in the following
Manner.
'Behold, you who dare, that charming Virgin. Behold the Beauty of her
Person chastised by the Innocence of her Thoughts. Chastity,
Good-Nature, and Affability, are the Graces that play in her
Countenance; she knows she is handsome, but she knows she is good.
Conscious Beauty adorned with conscious Virtue! What a Spirit is there
in those Eyes! What a Bloom in that Person! How is the whole Woman
expressed in her Appearance! Her Air has the Beauty of Motion, and her
Look the Force of Language.'
It was Prudence to turn away my Eyes from this Object, and therefore I
turned them to the thoughtless Creatures who make up the Lump of that
Sex, and move a knowing Eye no more than the Portraitures of
insignificant People by ordinary Painters, which are but Pictures of
Pictures.
Thus the working of my own Mind, is the general Entertainment of my
Life; I never enter into the Commerce of Discourse with any but my
particular Friends, and not in Publick even with them. Such an Habit has
perhaps raised in me uncommon Reflections; but this Effect I cannot
communicate but by my Writings. As my Pleasures are almost wholly
confined to those of the Sight, I take it for a peculiar Happiness that
I have always had an easy and familiar Admittance to the fair Sex. If I
never praised or flattered, I never belyed or contradicted them. As
these compose half the World, and are by the just Complaisance and
Gallantry of our Nation the more powerful Part of our People, I shall
dedicate a considerable Share of these my Speculations to their Service,
and shall lead the young through all the becoming Duties of Virginity,
Marriage, and Widowhood. When it is a Woman's Day, in my
Works
, I shall
endeavour at a Stile and Air suitable to their Understanding. When I say
this, I must be understood to mean, that I shall not lower but exalt the
Subjects I treat upon. Discourse for their Entertainment, is not to be
debased but refined. A Man may appear learned without talking Sentences;
as in his ordinary Gesture he discovers he can dance, tho' he does not
cut Capers. In a Word, I shall take it for the greatest Glory of my
Work, if among reasonable Women this Paper may furnish
Tea-Table Talk
.
In order to it, I shall treat on Matters which relate to Females as they
are concern'd to approach or fly from the other Sex, or as they are tyed
to them by Blood, Interest, or Affection. Upon this Occasion I think it
but reasonable to declare, that whatever Skill I may have in
Speculation, I shall never betray what the Eyes of Lovers say to each
other in my Presence. At the same Time I shall not think my self obliged
by this Promise, to conceal any false Protestations which I observe made
by Glances in publick Assemblies; but endeavour to make both Sexes
appear in their Conduct what they are in their Hearts. By this Means
Love, during the Time of my Speculations, shall be carried on with the
same Sincerity as any other Affair of less Consideration. As this is the
greatest Concern, Men shall be from henceforth liable to the greatest
Reproach for Misbehaviour in it. Falsehood in Love shall hereafter bear
a blacker Aspect than Infidelity in Friendship or Villany in Business.
For this great and good End, all Breaches against that noble Passion,
the Cement of Society, shall be severely examined. But this and all
other Matters loosely hinted at now and in my former Papers, shall have
their proper Place in my following Discourses: The present writing is
only to admonish the World, that they shall not find me an idle but a
very busy Spectator.
can
blooming Beauty
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 6, 1711 |
Addison |
Spectatum admissi risum teneatis?
Hor.

An Opera may be allowed to be extravagantly lavish in its Decorations,
as its only Design is to gratify the Senses, and keep up an indolent
Attention in the Audience. Common Sense however requires that there
should be nothing in the Scenes and Machines which may appear Childish
and Absurd. How would the Wits of King
Charles's
time have laughed to
have seen
Nicolini
exposed to a Tempest in Robes of Ermin, and sailing
in an open Boat upon a Sea of Paste-Board? What a Field of Raillery
would they have been let into, had they been entertain'd with painted
Dragons spitting Wild-fire, enchanted Chariots drawn by
Flanders
Mares, and real Cascades in artificial Land-skips? A little Skill in
Criticism would inform us that Shadows and Realities ought not to be
mix'd together in the same Piece; and that Scenes, which are designed as
the Representations of Nature, should be filled with Resemblances, and
not with the Things themselves. If one would represent a wide Champain
Country filled with Herds and Flocks, it would be ridiculous to draw the
Country only upon the Scenes, and to crowd several Parts of the Stage
with Sheep and Oxen. This is joining together Inconsistencies, and
making the Decoration partly Real, and partly Imaginary. I would
recommend what I have here said, to the Directors, as well as to the
Admirers, of our Modern Opera.
As I was walking
in
the Streets about a Fortnight ago, I saw an
ordinary Fellow carrying a Cage full of little Birds upon his Shoulder;
and as I was wondering with my self what Use he would put them to, he
was met very luckily by an Acquaintance, who had the same Curiosity.
Upon his asking him what he had upon his Shoulder, he told him, that he
had been buying Sparrows for the Opera. Sparrows for the Opera, says his
Friend, licking his lips, what are they to be roasted? No, no, says the
other, they are to enter towards the end of the first Act, and to fly
about the Stage.
strange Dialogue awakened my Curiosity so far that I immediately
bought the Opera, by which means I perceived the Sparrows were to act
the part of Singing Birds in a delightful Grove: though, upon a nearer
Enquiry I found the Sparrows put the same Trick upon the Audience, that
Sir
Martin Mar-all
practised upon his Mistress; for, though they
flew in Sight, the Musick proceeded from a Consort of Flagellets and
Bird-calls which was planted behind the Scenes. At the same time I made
this Discovery, I found by the Discourse of the Actors, that there were
great Designs on foot for the Improvement of the Opera; that it had been
proposed to break down a part of the Wall, and to surprize the Audience
with a Party of an hundred Horse, and that there was actually a Project
of bringing the
New River
into the House, to be employed in Jetteaus
and Water-works. This Project, as I have since heard, is post-poned
'till the Summer-Season; when it is thought the Coolness that proceeds
from Fountains and Cascades will be more acceptable and refreshing to
People of Quality.
the mean time, to find out a more agreeable
Entertainment for the Winter-Season, the Opera of
Rinaldo
is
filled with Thunder and Lightning, Illuminations, and Fireworks; which
the Audience may look upon without catching Cold, and indeed without
much Danger of being burnt; for there are several Engines filled with
Water, and ready to play at a Minute's Warning, in case any such
Accident should happen. However, as I have a very great Friendship for
the Owner of this Theater, I hope that he has been wise enough to
insure
his House before he would let this Opera be acted in it.
It is no wonder, that those Scenes should be very surprizing, which were
contrived by two Poets of different Nations, and raised by two Magicians
of different Sexes.
Armida
(as we are told in the Argument) was an
Amazonian
Enchantress, and poor Seignior
Cassani
(as we learn from
the
Persons represented
) a Christian Conjuror (
Mago Christiano
). I
must confess I am very much puzzled to find how an
Amazon
should be
versed in the Black Art, or how a
good
Christian
for such is the part of the magician
should deal with the Devil.
To consider the Poets after the Conjurers, I shall give you a Taste of
the
Italian
, from the first Lines of his Preface.
Eccoti, benigno
Lettore, un Parto di poche Sere, che se ben nato di Notte, non è però
aborto di Tenebre, mà si farà conoscere Figlio d'Apollo con qualche
Raggio di Parnasso.
Behold, gentle Reader, the Birth of a few Evenings,
which, tho' it be the Offspring of the Night, is not the Abortive of
Darkness, but will make it self known to be the Son of Apollo, with a
certain Ray of Parnassus.
afterwards proceeds to call Minheer
Hendel
, the
Orpheus
of our Age, and to acquaint us, in the same
Sublimity of Stile, that he Composed this Opera in a Fortnight. Such are
the Wits, to whose Tastes we so ambitiously conform our selves. The
Truth of it is, the finest Writers among the Modern
Italians
express
themselves in such a florid form of Words, and such tedious
Circumlocutions, as are used by none but Pedants in our own Country; and
at the same time, fill their Writings with such poor Imaginations and
Conceits, as our Youths are ashamed of, before they have been Two Years
at the University. Some may be apt to think that it is the difference of
Genius which produces this difference in the Works of the two Nations;
but to show there is nothing in this, if we look into the Writings of
the old
Italians
, such as
Cicero
and
Virgil
, we
shall find that the
English
Writers, in their way of thinking and
expressing themselves, resemble those Authors much more than the modern
Italians
pretend to do. And as for the Poet himself from whom the
Dreams of this Opera are taken, I must entirely agree with Monsieur
Boileau
, that one Verse in
Virgil
is worth all the
Clincant
or Tinsel of
Tasso
.
But to return to the Sparrows; there have been so many Flights of them
let loose in this Opera, that it is feared the House will never get rid
of them; and that in other Plays, they may make their Entrance in very
wrong and improper Scenes, so as to be seen flying in a Lady's
Bed-Chamber, or perching upon a King's Throne; besides the
Inconveniences which the Heads of the Audience may sometimes suffer from
them. I am credibly informed, that there was once a Design of casting
into an Opera the Story of
Whittington
and his Cat, and that in
order to it, there had been got together a great Quantity of Mice; but
Mr.
Rich
, the Proprietor of the Play-House, very prudently
considered that it would be impossible for the Cat to kill them all, and
that consequently the Princes of his Stage might be as much infested
with Mice, as the Prince of the Island was before the Cat's arrival upon
it; for which Reason he would not permit it to be Acted in his House.
indeed I cannot blame him; for, as he said very well upon that
Occasion, I do not hear that any of the Performers in our Opera, pretend
to equal the famous Pied Piper, who made all the Mice of a great Town in
Germany
follow his Musick, and by that means cleared the
Place of those little Noxious Animals.
I dismiss this Paper, I must inform my Reader, that I hear there
is a Treaty on Foot with
London
and
Wise
(who will be
appointed Gardeners of the Play-House,) to furnish the Opera of
Rinaldo
and
Armida
with an Orange-Grove; and that the next time it
is Acted, the Singing Birds will be Personated by Tom-Tits: The
undertakers being resolved to spare neither Pains nor Mony, for the
Gratification of the Audience.
C.
Dryden's play of
Sir Martin Mar-all
was produced in 1666.
It was entered at Stationers' Hall as by the duke of Newcastle, but
Dryden finished it. In Act 5 the foolish Sir Martin appears at a window
with a lute, as if playing and singing to Millicent, his mistress, while
his man Warner plays and sings. Absorbed in looking at the lady, Sir
Martin foolishly goes on opening and shutting his mouth and fumbling on
the lute after the man's song, a version of Voiture's
L'Amour sous sa
Loi
, is done. To which Millicent says,
'A pretty-humoured song — but stay, methinks he plays and sings still,
and yet we cannot hear him — Play louder, Sir Martin, that we may have
the Fruits on't.'
Handel had been met in Hanover by English noblemen who
invited him to England, and their invitation was accepted by permission
of the elector, afterwards George I, to whom he was then Chapel-master.
Immediately upon Handel's arrival in England, in 1710, Aaron Hill, who
was directing the Haymarket Theatre, bespoke of him an opera, the
subject being of Hill's own devising and sketching, on the story of
Rinaldo and Armida in Tasso's
Jerusalem Delivered
. G. Rossi wrote the
Italian words.
Rinaldo
, brought out in 1711, on the 24th of February,
had a run of fifteen nights, and is accounted one of the best of the 35
operas composed by Handel for the English stage. Two airs in it,
Cara
sposa
and
Lascia ch'io pianga
(the latter still admired as one of the
purest expressions of his genius), made a great impression. In the same
season the Haymarket produced
Hamlet
as an opera by Gasparini, called
Ambleto
, with an overture that had four movements ending in a jig. But
as was Gasparini so was Handel in the ears of Addison and Steele. They
recognized in music only the sensual pleasure that it gave, and the
words set to music for the opera, whatever the composer, were then, as
they have since been, almost without exception, insults to the
intellect.
Addison's spelling, which is as good as ours, represents
what was the true and then usual pronunciation of the name of Haendel.
The Pied Piper of Hamelin (i.e. Hameln).
'Hamelin town's in Brunswick,
By famous Hanover city;
The river Weser, deep and wide,
Washes its wall on the southern side.'
The old story has been annexed to English literature by the genius of
Robert Browning.
Evelyn, in the preface to his translation of Quintinye's
Complete Gardener
(1701), says that the nursery of Messrs. London
and Wise far surpassed all the others in England put together. It
exceeded 100 acres in extent. George London was chief gardener first to
William and Mary, then to Queen Anne. London and Wise's nursery belonged
at this time to a gardener named Swinhoe, but kept the name in which it
had become famous.
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 7, 1711 |
Steele |
Credebant hoc grande Nefas, et Morte piandum,
Si Juvenis Vetulo non assurrexerat ....
Juv.

I know no Evil under the Sun so great as the Abuse of the Understanding,
and yet there is no one Vice more common. It has diffus'd itself through
both Sexes, and all Qualities of Mankind; and there is hardly that
Person to be found, who is not more concerned for the Reputation of Wit
and Sense, than Honesty and Virtue. But this unhappy Affectation of
being Wise rather than Honest, Witty than Good-natur'd, is the Source of
most of the ill Habits of Life. Such false Impressions are owing to the
abandon'd Writings of Men of Wit, and the awkward Imitation of the rest
of Mankind.
For this Reason, Sir
Roger
was saying last Night, that he was of Opinion
that none but Men of fine Parts deserve to be hanged. The Reflections of
such Men are so delicate upon all Occurrences which they are concern'd
in, that they should be expos'd to more than ordinary Infamy and
Punishment, for offending against such quick Admonitions as their own
Souls give them, and blunting the fine Edge of their Minds in such a
Manner, that they are no more shock'd at Vice and Folly, than Men of
slower Capacities. There is no greater Monster in Being, than a very ill
Man of great Parts: He lives like a Man in a Palsy, with one Side of him
dead. While perhaps he enjoys the Satisfaction of Luxury, of Wealth, of
Ambition, he has lost the Taste of Good-will, of Friendship, of
Innocence.
Scarecrow
, the Beggar in
Lincoln's-Inn-Fields
, who
disabled himself in his Right Leg, and asks Alms all Day to get himself
a warm Supper and a Trull at Night, is not half so despicable a Wretch
as such a Man of Sense. The Beggar has no Relish above Sensations; he
finds Rest more agreeable than Motion; and while he has a warm Fire and
his Doxy, never reflects that he deserves to be whipped. Every Man who
terminates his Satisfaction and Enjoyments within the Supply of his own
Necessities and Passions, is, says Sir Roger, in my Eye as poor a Rogue
as
Scarecrow
. But, continued he, for the loss of publick and private
Virtue we are beholden to your Men of Parts forsooth; it is with them no
matter what is done, so it is done with an Air. But to me who am so
whimsical in a corrupt Age as to act according to Nature and Reason, a
selfish Man in the most shining Circumstance and Equipage, appears in
the same Condition with the Fellow above-mentioned, but more
contemptible in Proportion to what more he robs the Publick of and
enjoys above him. I lay it down therefore for a Rule, That the whole Man
is to move together; that every Action of any Importance is to have a
Prospect of publick Good; and that the general Tendency of our
indifferent Actions ought to be agreeable to the Dictates of Reason, of
Religion, of good Breeding; without this, a Man, as I have before
hinted, is hopping instead of walking, he is not in his entire and
proper Motion.
While the honest Knight was thus bewildering himself in good Starts, I
look'd intentively upon him, which made him I thought collect his Mind a
little. What I aim at, says he, is, to represent, That I am of Opinion,
to polish our Understandings and neglect our Manners is of all things
the most inexcusable. Reason should govern Passion, but instead of that,
you see, it is often subservient to it; and, as unaccountable as one
would think it, a wise Man is not always a good Man. This Degeneracy is
not only the Guilt of particular Persons, but also at some times of a
whole People; and perhaps it may appear upon Examination, that the most
polite Ages are the least virtuous. This may be attributed to the Folly
of admitting Wit and Learning as Merit in themselves, without
considering the Application of them. By this Means it becomes a Rule not
so much to regard what we do, as how we do it. But this false Beauty
will not pass upon Men of honest Minds and true Taste. Sir
Richard
Blackmore
says, with as much good Sense as Virtue,
It is a mighty
Dishonour and Shame to employ excellent Faculties and abundance of Wit,
to humour and please Men in their Vices and Follies. The great Enemy of
Mankind, notwithstanding his Wit and Angelick Faculties, is the most
odious Being in the whole Creation
.
goes on soon after to say very
generously, That he undertook the writing of his Poem
to rescue the
Muses out of the Hands of Ravishers
, to restore them to their sweet and
chaste Mansions, and to engage them in an
Employment suitable to their
Dignity
. This certainly ought to be the Purpose of every man who
appears in Publick; and whoever does not proceed upon that Foundation,
injures his Country as fast as he succeeds in his Studies. When Modesty
ceases to be the chief Ornament of one Sex, and Integrity of the other,
Society is upon a wrong Basis, and we shall be ever after without Rules
to guide our Judgment in what is really becoming and ornamental. Nature
and Reason direct one thing, Passion and Humour another: To follow the
Dictates of the two latter, is going into a Road that is both endless
and intricate; when we pursue the other, our Passage is delightful, and
what we aim at easily attainable.
I do not doubt but
England
is at present as polite a Nation as any in
the World; but any Man who thinks can easily see, that the Affectation
of being gay and in fashion has very near eaten up our good Sense and
our Religion. Is there anything so just, as that Mode and Gallantry
should be built upon exerting ourselves in what is proper and agreeable
to the Institutions of Justice and Piety among us? And yet is there
anything more common, than that we run in perfect Contradiction to them?
All which is supported by no other Pretension, than that it is done with
what we call a good Grace.
Nothing ought to be held laudable or becoming, but what Nature it self
should prompt us to think so. Respect to all kind of Superiours is
founded methinks upon Instinct; and yet what is so ridiculous as Age? I
make this abrupt Transition to the Mention of this Vice more than any
other, in order to introduce a little Story, which I think a pretty
Instance that the most polite Age is in danger of being the most
vicious.
'It happen'd at Athens, during a publick Representation of some Play
exhibited in honour of the Common-wealth that an old Gentleman came
too late for a Place suitable to his Age and Quality. Many of the
young Gentlemen who observed the Difficulty and Confusion he was in,
made Signs to him that they would accommodate him if he came where
they sate: The good Man bustled through the Crowd accordingly; but
when he came to the Seats to which he was invited, the Jest was to sit
close, and expose him, as he stood out of Countenance, to the whole
Audience. The Frolick went round all the Athenian Benches. But on
those Occasions there were also particular Places assigned for
Foreigners: When the good Man skulked towards the Boxes appointed for
the Lacedemonians, that honest People, more virtuous than polite,
rose up all to a Man, and with the greatest Respect received him among
them. The Athenians being suddenly touched with a Sense of the
Spartan Virtue, and their own Degeneracy, gave a Thunder of
Applause; and the old Man cry'd out, The Athenians understand what
is good, but the Lacedemonians practise it.'
R.
Richard Blackmore, born about 1650, d. 1729, had been
knighted in 1697, when he was made physician in ordinary to King
William. He was a thorough Whig, earnestly religious, and given to the
production of heroic poems. Steele shared his principles and honoured
his sincerity. When this essay was written, Blackmore was finishing his
best poem, the
Creation
, in seven Books, designed to prove from nature
the existence of a God. It had a long and earnest preface of
expostulation with the atheism and mocking spirit that were the legacy
to his time of the Court of the Restoration. The citations in the text
express the purport of what Blackmore had written in his then
unpublished but expected work, but do not quote from it literally.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 8, 1711 |
Addison |
Somnia, terrores magicos, miracula, Sagas,
Nocturnos lemures, portentaque Thessala rides?
Hor.

Going Yesterday to Dine with an old Acquaintance, I had the Misfortune
to find his whole Family very much dejected. Upon asking him the
Occasion of it, he told me that his Wife had dreamt a strange Dream the
Night before, which they were afraid portended some Misfortune to
themselves or to their Children. At her coming into the Room, I observed
a settled Melancholy in her Countenance, which I should have been
troubled for, had I not heard from whence it proceeded. We were no
sooner sat down, but, after having looked upon me a little while,
My
dear, says she, turning to her husband, you may now see the Stranger
that was in the Candle last Night.
Soon after this, as they began to
talk of Family Affairs, a little Boy at the lower end of the Table told
her, that he was to go into Join-hand on
Thursday
:
Thursday, says she,
no, Child, if it please God, you shall not begin upon Childermas-day;
tell your Writing-Master that Friday will be soon enough.
I was
reflecting with my self on the Odness of her Fancy, and wondering that
any body would establish it as a Rule to lose a Day in every Week. In
the midst of these my Musings she desired me to reach her a little Salt
upon the Point of my Knife, which I did in such a Trepidation and hurry
of Obedience, that I let it drop by the way; at which she immediately
startled, and said it fell towards her. Upon this I looked very blank;
and, observing the Concern of the whole Table, began to consider my
self, with some Confusion, as a Person that had brought a Disaster upon
the Family. The Lady however recovering her self, after a little space,
said to her Husband with a Sigh,
My Dear, Misfortunes never come Single.
My Friend, I found, acted but an under Part at his Table, and
being a Man of more Goodnature than Understanding, thinks himself
obliged to fall in with all the Passions and Humours of his Yoke-fellow:
Do not you remember, Child, says she,
that the Pidgeon-House fell the
very Afternoon that our careless Wench spilt the Salt upon the Table?
Yes, says he,
my Dear, and the next Post brought us an Account of the
Battel of Almanza
1.
The Reader may guess at the figure I made, after
having done all this Mischief.
dispatched my Dinner as soon as I
could, with my usual Taciturnity; when, to my utter Confusion, the Lady
seeing me
quitting
my Knife and Fork, and laying them across one
another upon my Plate, desired me that I would humour her so far as to
take them out of that Figure, and place them side by side. What the
Absurdity was which I had committed I did not know, but I suppose there
was some traditionary Superstition in it; and therefore, in obedience to
the Lady of the House, I disposed of my Knife and Fork in two parallel
Lines, which is the figure I shall always lay them in for the future,
though I do not know any Reason for it.
It is not difficult for a Man to see that a Person has conceived an
Aversion to him. For my own part, I quickly found, by the Lady's Looks,
that she regarded me as a very odd kind of Fellow, with an unfortunate
Aspect: For which Reason I took my leave immediately after Dinner, and
withdrew to my own Lodgings. Upon my Return home, I fell into a profound
Contemplation on the Evils that attend these superstitious Follies of
Mankind; how they subject us to imaginary Afflictions, and additional
Sorrows, that do not properly come within our Lot. As if the natural
Calamities of Life were not sufficient for it, we turn the most
indifferent Circumstances into Misfortunes, and suffer as much from
trifling Accidents, as from real Evils. I have known the shooting of a
Star spoil a Night's Rest; and have seen a Man in Love grow pale and
lose his Appetite, upon the plucking of a Merry-thought. A Screech-Owl
at Midnight has alarmed a Family, more than a Band of Robbers; nay, the
Voice of a Cricket hath struck more Terrour, than the Roaring of a Lion.
is nothing so inconsiderable
which
may not appear dreadful
to an Imagination that is filled with Omens and Prognosticks. A Rusty
Nail, or a Crooked Pin, shoot up into Prodigies.
I remember I was once in a mixt Assembly, that was full of Noise and
Mirth, when on a sudden an old Woman unluckily observed there were
thirteen of us in Company.
Remark struck a pannick Terror into
several
who
were present, insomuch that one or two of the Ladies
were going to leave the Room; but a Friend of mine, taking notice that
one of our female Companions was big with Child, affirm'd there were
fourteen in the Room, and that, instead of portending one of the Company
should die, it plainly foretold one of them should be born. Had not my
Friend found this Expedient to break the Omen, I question not but half
the Women in the Company would have fallen sick that very Night.
An old Maid, that is troubled with the Vapours, produces infinite
Disturbances of this kind among her Friends and Neighbours. I know a
Maiden Aunt, of a great Family, who is one of these Antiquated
Sybils
,
that forebodes and prophesies from one end of the Year to the other. She
is always seeing Apparitions, and hearing Death-Watches; and was the
other Day almost frighted out of her Wits by the great House-Dog, that
howled in the Stable at a time when she lay ill of the Tooth-ach. Such
an extravagant Cast of Mind engages Multitudes of People, not only in
impertinent Terrors, but in supernumerary Duties of Life, and arises
from that Fear and Ignorance which are natural to the Soul of Man. The
Horrour with which we entertain the Thoughts of Death (or indeed of any
future Evil), and the Uncertainty of its Approach, fill a melancholy
Mind with innumerable Apprehensions and Suspicions, and consequently
dispose it to the Observation of such groundless Prodigies and
Predictions. For as it is the chief Concern of Wise-Men, to retrench the
Evils of Life by the Reasonings of Philosophy; it is the Employment of
Fools, to multiply them by the Sentiments of Superstition.
For my own part, I should be very much troubled were I endowed with this
Divining Quality, though it should inform me truly of every thing that
can befall me. I would not anticipate the Relish of any Happiness, nor
feel the Weight of any Misery, before it actually arrives.
I know but one way of fortifying my Soul against these gloomy Presages
and Terrours of Mind, and that is, by securing to my self the Friendship
and Protection of that Being, who disposes of Events, and governs
Futurity. He sees, at one View, the whole Thread of my Existence, not
only that Part of it which I have already passed through, but that which
runs forward into all the Depths of Eternity. When I lay me down to
Sleep, I recommend my self to his Care; when I awake, I give my self up
to his Direction. Amidst all the Evils that threaten me, I will look up
to him for Help, and question not but he will either avert them, or turn
them to my Advantage. Though I know neither the Time nor the Manner of
the Death I am to die, I am not at all sollicitous about it, because I
am sure that he knows them both, and that he will not fail to comfort
and support me under them.
C.
: Fought April 25 (O.S. 14), 1707, between the English, under
Lord Galway, a Frenchman, with Portuguese, Dutch, and Spanish allies,
and a superior force of French and Spaniards, under an Englishman, the
Duke of Berwick, natural son of James II. Deserted by many of the
foreign troops, the English were defeated.
cleaning
that
that
Contents
|
Friday, March 9, 1711 |
Addison |
At Venus obscuro gradientes ære sepsit,
Et multo Nebulæ circum Dea fudit amictu,
Cernere ne quis eos ...
Virg.

shall here communicate to the World a couple of Letters, which I
believe will give the Reader as good an Entertainment as any that I am
able to furnish
him
with, and therefore shall make no Apology for
them.
'To the Spectator, &c.
Sir,
I am one of the Directors of the Society for the Reformation of
Manners, and therefore think myself a proper Person for your
Correspondence. I have thoroughly examined the present State of
Religion in Great-Britain, and am able to acquaint you with the
predominant Vice of every Market-Town in the whole Island. I can tell
you the Progress that Virtue has made in all our Cities, Boroughs, and
Corporations; and know as well the evil Practices that are committed
in Berwick or Exeter, as what is done in my own Family. In a Word,
Sir, I have my Correspondents in the remotest Parts of the Nation, who
send me up punctual Accounts from time to time of all the little
Irregularities that fall under their Notice in their several Districts
and Divisions.
I am no less acquainted with the particular Quarters and Regions of
this great Town, than with the different Parts and Distributions of
the whole Nation. I can describe every Parish by its Impieties, and
can tell you in which of our Streets Lewdness prevails, which Gaming
has taken the Possession of, and where Drunkenness has got the better
of them both. When I am disposed to raise a Fine for the Poor, I know
the Lanes and Allies that are inhabited by common Swearers. When I
would encourage the Hospital of Bridewell, and improve the Hempen
Manufacture, I am very well acquainted with all the Haunts and Resorts
of Female Night-walkers.
After this short Account of my self, I must let you know, that the
Design of this Paper is to give you Information of a certain irregular
Assembly which I think falls very properly under your Observation,
especially since the Persons it is composed of are Criminals too
considerable for the Animadversions of our Society. I mean, Sir, the
Midnight Masque, which has of late been frequently held in one of the
most conspicuous Parts of the Town, and which I hear will be continued
with Additions and Improvements. As all the Persons who compose this
lawless Assembly are masqued, we dare not attack any of them in our
Way, lest we should send a Woman of Quality to Bridewell, or a Peer
of Great-Britain to the Counter: Besides, that their Numbers are
so very great, that I am afraid they would be able to rout our whole
Fraternity, tho' we were accompanied with all our Guard of Constables.
Both these Reasons which secure them from our Authority, make them
obnoxious to yours; as both their Disguise and their Numbers will give
no particular Person Reason to think himself affronted by you.
If we are rightly inform'd, the Rules that are observed by this new
Society are wonderfully contriv'd for the Advancement of Cuckoldom.
The Women either come by themselves, or are introduced by Friends, who
are obliged to quit them upon their first Entrance, to the
Conversation of any Body that addresses himself to them. There are
several Rooms where the Parties may retire, and, if they please, show
their Faces by Consent. Whispers, Squeezes, Nods, and Embraces, are
the innocent Freedoms of the Place. In short, the whole Design of this
libidinous Assembly seems to terminate in Assignations and Intrigues;
and I hope you will take effectual Methods, by your publick Advice and
Admonitions, to prevent such a promiscuous Multitude of both Sexes
from meeting together in so clandestine a Manner.'
I am,
Your humble Servant,
And Fellow Labourer,
T. B.
Not long after the Perusal of this Letter I received another upon the
same Subject; which by the Date and Stile of it, I take to be written by
some young Templer.
Middle Temple, 1710-11.
Sir,
When a Man has been guilty of any Vice or Folly, I think the best
Attonement he can make for it is to warn others not to fall into the
like. In order to this I must acquaint you, that some Time in
February last I went to the Tuesday's Masquerade. Upon my first
going in I was attacked by half a Dozen female Quakers, who seemed
willing to adopt me for a Brother; but, upon a nearer Examination, I
found they were a Sisterhood of Coquets, disguised in that precise
Habit. I was soon after taken out to dance, and, as I fancied, by a
Woman of the first Quality, for she was very tall, and moved
gracefully. As soon as the Minuet was over, we ogled one another
through our Masques; and as I am very well read in
Waller, I
repeated to her the four following Verses out of his poem to
Vandike.
'The heedless Lover does not know
Whose Eyes they are that wound him so;
But confounded with thy Art,
Enquires her Name that has his Heart.'
I pronounced these Words with such a languishing Air, that I had some
Reason to conclude I had made a Conquest. She told me that she hoped
my Face was not akin to my Tongue; and looking upon her Watch, I
accidentally discovered the Figure of a Coronet on the back Part of
it. I was so transported with the Thought of such an Amour, that I
plied her from one Room to another with all the Gallantries I could
invent; and at length brought things to so happy an Issue, that she
gave me a private Meeting the next Day, without Page or Footman, Coach
or Equipage. My Heart danced in Raptures; but I had not lived in this
golden Dream above three Days, before I found good Reason to wish that
I had continued true to my Landress. I have since heard by a very
great Accident, that this fine Lady does not live far from
Covent-Garden, and that I am not the first Cully whom she has passed
herself upon for a Countess.
Thus, Sir, you see how I have mistaken a
Cloud for a
Juno; and if
you can make any use of this Adventure for the Benefit of those who
may possibly be as vain young Coxcombs as my self, I do most heartily
give you Leave.'
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble admirer,
B. L.
design to visit the next Masquerade my self, in the same Habit I wore
at
Grand Cairo
; and till then shall suspend my Judgment of this
Midnight Entertainment.
C.
them
See
Contents
|
Saturday, March 10, 1711 |
Addison |
Tigris agit rabidâ cum tigride pacem
Perpetuam, sævis inter se convenit ursis.
Juv.

Man is said to be a Sociable Animal, and, as an Instance of it, we may
observe, that we take all Occasions and Pretences of forming ourselves
into those little Nocturnal Assemblies, which are commonly known by the
name of
Clubs
. When a Sett of Men find themselves agree in any
Particular, tho' never so trivial, they establish themselves into a kind
of Fraternity, and meet once or twice a Week, upon the Account of such a
Fantastick-Resemblance. I know a considerable Market-town, in which
there was a Club of Fat-Men, that did not come together (as you may well
suppose) to entertain one another with Sprightliness and Wit, but to
keep one another in Countenance: The Room, where the Club met, was
something of the largest, and had two Entrances, the one by a Door of a
moderate Size, and the other by a Pair of Folding-Doors. If a Candidate
for this Corpulent Club could make his Entrance through the first he was
looked upon as unqualified; but if he stuck in the Passage, and could
not force his Way through it, the Folding-Doors were immediately thrown
open for his Reception, and he was saluted as a Brother. I have heard
that this Club, though it consisted but of fifteen Persons, weighed
above three Tun.
In Opposition to this Society, there sprung up another composed of
Scare-Crows and Skeletons, who being very meagre and envious, did all
they could to thwart the Designs of their Bulky Brethren, whom they
represented as Men of Dangerous Principles; till at length they worked
them out of the Favour of the People, and consequently out of the
Magistracy. These Factions tore the Corporation in Pieces for several
Years, till at length they came to this Accommodation; that the two
Bailiffs of the Town should be annually chosen out of the two Clubs; by
which Means the principal Magistrates are at this Day coupled like
Rabbets, one fat and one lean.
Every one has heard of the Club, or rather the Confederacy, of the
Kings
. This grand Alliance was formed a little after the Return of
King
Charles
the Second, and admitted into it Men of all Qualities and
Professions, provided they agreed in this Sir-name of
King
, which, as
they imagined, sufficiently declared the Owners of it to be altogether
untainted with Republican and Anti-Monarchical Principles.
A Christian Name has likewise been often used as a Badge of Distinction,
and made the Occasion of a Club. That of the
Georges
, which used to
meet at the Sign of the
George
, on St.
George's
day, and swear
Before George
, is still fresh in every one's Memory.
There are at present in several Parts of this City what they call
Street-Clubs
, in which the chief Inhabitants of the Street converse
together every Night. I remember, upon my enquiring after Lodgings in
Ormond-Street
, the Landlord, to recommend that Quarter of the Town,
told me there was at that time a very good Club in it; he also told me,
upon further Discourse with him, that two or three noisy Country
Squires, who were settled there the Year before, had considerably sunk
the Price of House-Rent; and that the Club (to prevent the like
Inconveniencies for the future) had thoughts of taking every House that
became vacant into their own Hands, till they had found a Tenant for it,
of a Sociable Nature and good Conversation.
The
Hum-Drum
Club, of which I was formerly an unworthy Member, was
made up of very honest Gentlemen, of peaceable Dispositions, that used
to sit together, smoak their Pipes, and say nothing 'till Midnight. The
Mum
Club (as I am informed) is an Institution of the same Nature, and
as great an Enemy to Noise.
After these two innocent Societies, I cannot forbear mentioning a very
mischievous one, that was erected in the Reign of King
Charles
the
Second: I mean
the Club of Duellists
, in which none was to be admitted
that had not fought his Man. The President of it was said to have killed
half a dozen in single Combat; and as for the other Members, they took
their Seats according to the number of their Slain. There was likewise a
Side-Table for such as had only drawn Blood, and shown a laudable
Ambition of taking the first Opportunity to qualify themselves for the
first Table. This Club, consisting only of Men of Honour, did not
continue long, most of the Members of it being put to the Sword, or
hanged, a little after its Institution.
Our Modern celebrated Clubs are founded upon Eating and Drinking, which
are Points wherein most Men agree, and in which the Learned and
Illiterate, the Dull and the Airy, the Philosopher and the Buffoon, can
all of them bear a Part.
Kit-Cat
it self is said to have taken
its Original from a Mutton-Pye. The
Beef-Steak
and October
Clubs, are neither of them averse to Eating and Drinking, if we may form
a Judgment of them from their respective Titles.
When Men are thus knit together, by Love of Society, not a Spirit of
Faction, and do not meet to censure or annoy those that are absent, but
to enjoy one another: When they are thus combined for their own
Improvement, or for the Good of others, or at least to relax themselves
from the Business of the Day, by an innocent and chearful Conversation,
there may be something very useful in these little Institutions and
Establishments.
I cannot forbear concluding this Paper with a Scheme of Laws that I met
with upon a Wall in a little Ale-house: How I came thither I may inform
my Reader at a more convenient time. These Laws were enacted by a Knot
of Artizans and Mechanicks, who used to meet every Night; and as there
is something in them, which gives us a pretty Picture of low Life, I
shall transcribe them Word for Word.
Rules to be observed in the Two-penny Club,
erected in this Place,
for the Preservation of Friendship and good Neighbourhood.
- Every Member at his first coming in shall lay down his Two Pence.
- Every Member shall fill his Pipe out of his own Box.
- If any Member absents himself he shall forfeit a Penny for the
Use of the Club, unless in case of Sickness or Imprisonment.
- If any Member swears or curses, his Neighbour may give him a Kick
upon the Shins.
- If any Member tells Stories in the Club that are not true, he shall
forfeit for every third Lie an Half-Penny.
- If any Member strikes another wrongfully, he shall pay his Club
for him.
- If any Member brings his Wife into the Club, he shall pay for
whatever she drinks or smoaks.
- If any Member's Wife comes to fetch him Home from the Club, she
shall speak to him without the Door.
- If any Member calls another Cuckold, he shall be turned out of the
Club.
- None shall be admitted into the Club that is of the same Trade with
any Member of it.
- None of the Club shall have his Cloaths or Shoes made or mended,
but by a Brother Member.
- No Non-juror shall be capable of being a Member.
Morality of this little Club is guarded by such wholesome Laws and
Penalties, that I question not but my Reader will be as well pleased
with them, as he would have been with the
Leges Convivales
of
Ben.
Johnson
, the Regulations of an old
Roman
Club cited by
Lipsius
,
or the rules of a
Symposium
in an ancient
Greek
author.
C.
The
Kit-Cat
Club met at a famous Mutton-Pie house in
Shire Lane, by Temple Bar. The house was kept by Christopher Cat, after
whom his pies were called Kit-Cats. The club originated in the
hospitality of Jacob Tonson, the bookseller, who, once a week, was host
at the house in Shire Lane to a gathering of writers. In an occasional
poem on the
Kit-Cat Club
, attributed to Sir Richard Blackmore, Jacob is
read backwards into
Bocaj
, and we are told
One Night in Seven at this convenient Seat
Indulgent Bocaj did the Muses treat;
Their Drink was gen'rous Wine and Kit-Cat's Pyes their Meat.
Hence did th' Assembly's Title first arise,
And Kit-Cat Wits spring first from Kit-Cat's Pyes.
About the year 1700 this gathering of wits produced a club in which the
great Whig chiefs were associated with foremost Whig writers, Tonson
being Secretary. It was as much literary as political, and its 'toasting
glasses,' each inscribed with lines to a reigning beauty, caused
Arbuthnot to derive its name from 'its pell mell pack of toasts'
'Of old Cats and young Kits.'
Tonson built a room for the Club at Barn Elms to which each member gave
his portrait by Sir Godfrey Kneller, who was himself a member. The
pictures were on a new-sized canvas adapted to the height of the walls,
whence the name 'kit-cat' came to be applied generally to three-quarter
length portraits.
The
Beef-Steak
Club, founded in Queen Anne's time, first
of its name, took a gridiron for badge, and had cheery Dick Estcourt the
actor for its providore. It met at a tavern in the Old Jewry that had
old repute for broiled steaks and 'the true British quintessence of malt
and hops.'
The
October
Club was of a hundred and fifty Tory
squires, Parliament men, who met at the Bell Tavern, in King Street,
Westminster, and there nourished patriotism with October ale. The
portrait of Queen Anne that used to hang in its Club room is now in the
Town Council-chamber at Salisbury.
In Four and Twenty Latin sentences engraven in marble over
the chimney, in the Apollo or Old Devil Tavern at Temple Bar; that being
his club room.
Contents
|
Monday, March 12, 1711 |
Addison |
Non aliter quàm qui adverso vix flumine lembum
Remigiis subigit: si brachia fortè remisit,
Atque illum in præceps prono rapit alveus amni.
Virg.

It is with much Satisfaction that I hear this great City inquiring Day
by Day after these my Papers, and receiving my Morning Lectures with a
becoming Seriousness and Attention. My Publisher tells me, that there
are already Three Thousand of them distributed every Day: So that if I
allow Twenty Readers to every Paper, which I look upon as a modest
Computation, I may reckon about Threescore thousand Disciples in
London
and
Westminster
, who I hope will take care to distinguish
themselves from the thoughtless Herd of their ignorant and unattentive
Brethren. Since I have raised to myself so great an Audience, I shall
spare no Pains to make their Instruction agreeable, and their Diversion
useful. For which Reasons I shall endeavour to enliven Morality with
Wit, and to temper Wit with Morality, that my Readers may, if possible,
both Ways find their account in the Speculation of the Day. And to the
End that their Virtue and Discretion may not be short transient
intermitting Starts of Thought, I have resolved to refresh their
Memories from Day to Day, till I have recovered them out of that
desperate State of Vice and Folly, into which the Age is fallen. The
Mind that lies fallow but a single Day, sprouts up in Follies that are
only to be killed by a constant and assiduous Culture. It was said of
Socrates
, that he brought Philosophy down from Heaven, to inhabit
among Men; and I shall be ambitious to have it said of me, that I have
brought Philosophy out of Closets and Libraries, Schools and Colleges,
to dwell in Clubs and Assemblies, at Tea-tables, and in Coffee-houses.
I would therefore in a very particular Manner recommend these my
Speculations to all well-regulated Families, that set apart an Hour in
every Morning for Tea and Bread and Butter; and would earnestly advise
them for their Good to order this Paper to be punctually served up, and
to be looked upon as a Part of the Tea Equipage.
Sir
Francis Bacon
observes, that a well-written Book, compared with
its Rivals and Antagonists, is like
Moses's
Serpent, that immediately
swallow'd up and devoured those of the
Ægyptians
. I shall not be so
vain as to think, that where the
Spectator
appears, the other publick
Prints will vanish; but shall leave it to my Readers Consideration,
whether, Is it not much better to be let into the Knowledge of
ones-self, than to hear what passes in
Muscovy
or
Poland
; and to
amuse our selves with such Writings as tend to the wearing out of
Ignorance, Passion, and Prejudice, than such as naturally conduce to
inflame Hatreds, and make Enmities irreconcileable.
In the next Place, I would recommend this Paper to the daily Perusal of
those Gentlemen whom I cannot but consider as my good Brothers and
Allies, I mean the Fraternity of Spectators who live in the World
without having any thing to do in it; and either by the Affluence of
their Fortunes, or Laziness of their Dispositions, have no other
Business with the rest of Mankind but to look upon them. Under this
Class of Men are comprehended all contemplative Tradesmen, titular
Physicians, Fellows of the Royal Society, Templers that are not given to
be contentious, and Statesmen that are out of business. In short, every
one that considers the World as a Theatre, and desires to form a right
Judgment of those who are the Actors on it.
There is another Set of Men that I must likewise lay a Claim to, whom I
have lately called the Blanks of Society, as being altogether
unfurnish'd with Ideas, till the Business and Conversation of the Day
has supplied them. I have often considered these poor Souls with an Eye
of great Commiseration, when I have heard them asking the first Man they
have met with, whether there was any News stirring? and by that Means
gathering together Materials for thinking. These needy Persons do not
know what to talk of, till about twelve a Clock in the Morning; for by
that Time they are pretty good Judges of the Weather, know which Way the
Wind sits, and whether the Dutch Mail be come in. As they lie at the
Mercy of the first Man they meet, and are grave or impertinent all the
Day long, according to the Notions which they have imbibed in the
Morning, I would earnestly entreat them not to stir out of their
Chambers till they have read this Paper, and do promise them that I will
daily instil into them such sound and wholesome Sentiments, as shall
have a good Effect on their Conversation for the ensuing twelve Hours.
But there are none to whom this Paper will be more useful than to the
female World. I have often thought there has not been sufficient Pains
taken in finding out proper Employments and Diversions for the Fair
ones. Their Amusements seem contrived for them rather as they are Women,
than as they are reasonable Creatures; and are more adapted to the Sex,
than to the Species. The Toilet is their great Scene of Business, and
the right adjusting of their Hair the principal Employment of their
Lives. The sorting of a Suit of Ribbons is reckoned a very good
Morning's Work; and if they make an Excursion to a Mercer's or a
Toy-shop, so great a Fatigue makes them unfit for any thing else all the
Day after. Their more serious Occupations are Sowing and Embroidery, and
their greatest Drudgery the Preparation of Jellies and Sweetmeats. This,
I say, is the State of ordinary Women; tho' I know there are Multitudes
of those of a more elevated Life and Conversation, that move in an
exalted Sphere of Knowledge and Virtue, that join all the Beauties of
the Mind to the Ornaments of Dress, and inspire a kind of Awe and
Respect, as well as Love, into their Male-Beholders. I hope to encrease
the Number of these by publishing this daily Paper, which I shall always
endeavour to make an innocent if not an improving Entertainment, and by
that Means at least divert the Minds of my female Readers from greater
Trifles. At the same Time, as I would fain give some finishing Touches
to those which are already the most beautiful Pieces in humane Nature, I
shall endeavour to point out all those Imperfections that are the
Blemishes, as well as those Virtues which are the Embellishments, of the
Sex. In the mean while I hope these my gentle Readers, who have so much
Time on their Hands, will not grudge throwing away a Quarter of an Hour
in a Day on this Paper, since they may do it without any Hindrance to
Business.
I know several of my Friends and Well-wishers are in great Pain for me,
lest I should not be able to keep up the Spirit of a Paper which I
oblige myself to furnish every Day: But to make them easy in this
Particular, I will promise them faithfully to give it over as soon as I
grow dull. This I know will be Matter of great Raillery to the small
Wits; who will frequently put me in mind of my Promise, desire me to
keep my Word, assure me that it is high Time to give over, with many
other little Pleasantries of the like Nature, which men of a little
smart Genius cannot forbear throwing out against their best Friends,
when they have such a Handle given them of being witty. But let them
remember, that I do hereby enter my Caveat against this Piece of
Raillery.
C.
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 13, 1711 |
Steele |
Dat veniam corvis, vexat censura columbas.
Juv.

Arietta is visited by all Persons of both Sexes, who may have any
Pretence to Wit and Gallantry. She is in that time of Life which is
neither affected with the Follies of Youth or Infirmities of Age; and
her Conversation is so mixed with Gaiety and Prudence, that she is
agreeable both to the Young and the Old. Her Behaviour is very frank,
without being in the least blameable; and as she is out of the Tract of
any amorous or ambitious Pursuits of her own, her Visitants entertain
her with Accounts of themselves very freely, whether they concern their
Passions or their Interests. I made her a Visit this Afternoon, having
been formerly introduced to the Honour of her Acquaintance, by my friend
Will. Honeycomb
, who has prevailed upon her to admit me sometimes into
her Assembly, as a civil, inoffensive Man. I found her accompanied with
one Person only, a Common-Place Talker, who, upon my Entrance, rose, and
after a very slight Civility sat down again; then turning to
Arietta
,
pursued his Discourse, which I found was upon the old Topick, of
Constancy in Love. He went on with great Facility in repeating what he
talks every Day of his Life; and, with the Ornaments of insignificant
Laughs and Gestures, enforced his Arguments by Quotations out of Plays
and Songs, which allude to the Perjuries of the Fair, and the general
Levity of Women. Methought he strove to shine more than ordinarily in
his Talkative Way, that he might insult my Silence, and distinguish
himself before a Woman of
Arietta's
Taste and Understanding.
had
often an Inclination to interrupt him, but could find no Opportunity,
'till the Larum ceased of its self; which it did not 'till he had
repeated and murdered the celebrated Story of the
Ephesian
Matron
.
Arietta
seemed to regard this Piece of Raillery as an Outrage done to
her Sex; as indeed I have always observed that Women, whether out of a
nicer Regard to their Honour, or what other Reason I cannot tell, are
more sensibly touched with those general Aspersions, which are cast upon
their Sex, than Men are by what is said of theirs.
When she had a little recovered her self from the serious Anger she was
in, she replied in the following manner.
Sir, when I consider, how perfectly new all you have said on this
Subject is, and that the Story you have given us is not quite two
thousand Years Old, I cannot but think it a Piece of Presumption to
dispute with you: But your Quotations put me in Mind of the Fable of
the Lion and the Man. The Man walking with that noble Animal, showed
him, in the Ostentation of Human Superiority, a Sign of a Man killing
a Lion. Upon which the Lion said very justly,
We Lions are none of us
Painters, else we could show a hundred Men killed by Lions, for one
Lion killed by a Man. You Men are Writers, and can represent us Women
as Unbecoming as you please in your Works, while we are unable to
return the Injury. You have twice or thrice observed in your
Discourse, that Hypocrisy is the very Foundation of our Education; and
that an Ability to dissemble our affections, is a professed Part of
our Breeding. These, and such other Reflections, are sprinkled up and
down the Writings of all Ages, by Authors, who leave behind them
Memorials of their Resentment against the Scorn of particular Women,
in Invectives against the whole Sex. Such a Writer, I doubt not, was
the celebrated
Petronius, who invented the pleasant Aggravations of
the Frailty of the
Ephesian Lady; but when we consider this Question
between the Sexes, which has been either a Point of Dispute or
Raillery ever since there were Men and Women, let us take Facts from
plain People, and from such as have not either Ambition or Capacity to
embellish their Narrations with any Beauties of Imagination.
I was the
other Day amusing myself with
Ligon's Account of
Barbadoes; and,
in Answer to your well-wrought Tale, I will give you (as it dwells
upon my Memory) out of that honest Traveller, in his fifty fifth page,
the History of
Inkle and
Yarico2.
Mr.
Thomas Inkle of
London, aged twenty Years, embarked in the
Downs, on the good Ship called the
Achilles, bound for the
West
Indies, on the 16th of June 1647, in order to improve his Fortune by
Trade and Merchandize. Our Adventurer was the third Son of an eminent
Citizen, who had taken particular Care to instill into his Mind an
early Love of Gain, by making him a perfect Master of Numbers, and
consequently giving him a quick View of Loss and Advantage, and
preventing the natural Impulses of his Passions, by Prepossession
towards his Interests. With a Mind thus turned, young
Inkle had a
Person every way agreeable, a ruddy Vigour in his Countenance,
Strength in his Limbs, with Ringlets of fair Hair loosely flowing on
his Shoulders. It happened, in the Course of the Voyage, that the
Achilles, in some Distress, put into a Creek on the Main of
America, in search of Provisions. The Youth, who is the Hero of my
Story, among others, went ashore on this Occasion. From their first
Landing they were observed by a Party of
Indians, who hid themselves
in the Woods for that Purpose. The
English unadvisedly marched a
great distance from the Shore into the Country, and were intercepted
by the Natives, who slew the greatest Number of them. Our Adventurer
escaped among others, by flying into a Forest. Upon his coming into a
remote and pathless Part of the Wood, he threw himself
tired and
breathless on a little Hillock, when an
Indian Maid rushed from
a Thicket behind him: After the first Surprize, they appeared mutually
agreeable to each other. If the
European was highly charmed
with the Limbs, Features, and wild Graces of the Naked
American; the
American was no less taken with the Dress,
Complexion, and Shape of an
European, covered from Head to
Foot. The
Indian grew immediately enamoured of him, and
consequently sollicitous for his Preservation: She therefore conveyed
him to a Cave, where she gave him a Delicious Repast of Fruits, and
led him to a Stream to slake his Thirst. In the midst of these good
Offices, she would sometimes play with his Hair, and delight in the
Opposition of its Colour to that of her Fingers: Then open his Bosome,
then laugh at him for covering it. She was, it seems, a Person of
Distinction, for she every day came to him in a different Dress, of
the most beautiful Shells, Bugles, and Bredes. She likewise brought
him a great many Spoils, which her other Lovers had presented to her;
so that his Cave was richly adorned with all the spotted Skins of
Beasts, and most Party-coloured Feathers of Fowls, which that World
afforded. To make his Confinement more tolerable, she would carry him
in the Dusk of the Evening, or by the favour of Moon-light, to
unfrequented Groves, and Solitudes, and show him where to lye down in
Safety, and sleep amidst the Falls of Waters, and Melody of
Nightingales. Her Part was to watch and hold him in her Arms, for fear
of her Country-men, and wake on Occasions to consult his Safety. In
this manner did the Lovers pass away their Time, till they had learn'd
a Language of their own, in which the Voyager communicated to his
Mistress, how happy he should be to have her in his Country, where she
should be Cloathed in such Silks as his Wastecoat was made of, and be
carried in Houses drawn by Horses, without being exposed to Wind or
Weather. All this he promised her the Enjoyment of, without such Fears
and Alarms as they were there tormented with. In this tender
Correspondence these Lovers lived for several Months, when
Yarico, instructed by her Lover, discovered a Vessel on the
Coast, to which she made Signals, and in the Night, with the utmost
Joy and Satisfaction accompanied him to a Ships-Crew of his
Country-Men, bound for
Barbadoes. When a Vessel from the Main
arrives in that Island, it seems the Planters come down to the Shoar,
where there is an immediate Market of the
Indians and other Slaves,
as with us of Horses and Oxen.
To be short, Mr.
Thomas Inkle, now coming into
English
Territories, began seriously to reflect upon his loss of Time, and to
weigh with himself how many Days Interest of his Mony he had lost
during his Stay with
Yarico. This Thought made the Young Man very
pensive, and careful what Account he should be able to give his
Friends of his Voyage. Upon which Considerations, the prudent and
frugal young Man sold
Yarico to a
Barbadian Merchant;
notwithstanding that the poor Girl, to incline him to commiserate her
Condition, told him that she was with Child by him: But he only made
use of that Information, to rise in his Demands upon the Purchaser.
I was so touch'd with this Story, (which I think should be always a
Counterpart to the
Ephesian
Matron) that I left the Room with Tears in
my Eyes; which a Woman of
Arietta's
good Sense, did, I am sure, take
for greater Applause, than any Compliments I could make her.
R.
Told in the prose
Satyricon
ascribed to Petronius, whom
Nero called his Arbiter of Elegance. The tale was known in the Middle
Ages from the stories of the
Seven Wise Masters
. She went down into
the vault with her husband's corpse, resolved to weep to death or die of
famine; but was tempted to share the supper of a soldier who was
watching seven bodies hanging upon trees, and that very night, in the
grave of her husband and in her funeral garments, married her new and
stranger guest.
A True and Exact History of the Island of Barbadoes. By
Richard Ligon, Gent.,
fol. 1673. The first edition had appeared in
1657. Steele's beautiful story is elaborated from the following short
passage in the page he cites. After telling that he had an Indian slave
woman 'of excellent shape and colour,' who would not be wooed by any
means to wear clothes, Mr. Ligon says:
'This Indian dwelling near the Sea Coast, upon the Main, an
English ship put in to a Bay, and sent some of her Men a shoar, to
try what victuals or water they could find, for in some distress they
were: But the Indians perceiving them to go up so far into the
Country, as they were sure they could not make a safe retreat,
intercepted them in their return, and fell upon them, chasing them
into a Wood, and being dispersed there, some were taken, and some
kill'd: But a young man amongst them straggling from the rest, was met
by this Indian maid, who upon the first sight fell in love with him,
and hid him close from her Countrymen (the Indians) in a Cave, and
there fed him, till they could safely go down to the shoar, where the
ship lay at anchor, expecting the return of their friends. But at
last, seeing them upon the shoar, sent the long-Boat for them, took
them aboard, and brought them away. But the youth, when he came ashoar
in the Barbadoes, forgot the kindness of the poor maid, that had
ventured her life for his safety, and sold her for a slave, who was as
free born as he: And so poor Yarico for her love, lost her liberty.'
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 14, 1711 |
Addison |
... Veteres avias tibi de pulmone revello.
Per.

At my coming to
London
, it was some time before I could settle my self
in a House to my likeing. I was forced to quit my first Lodgings, by
reason of an officious Land-lady, that would be asking every Morning how
I had slept. I then fell into an honest Family, and lived very happily
for above a Week; when my Land-lord, who was a jolly good-natur'd Man,
took it into his head that I wanted Company, and therefore would
frequently come into my Chamber to keep me from being alone. This I bore
for Two or Three Days; but telling me one Day that he was afraid I was
melancholy, I thought it was high time for me to be gone, and
accordingly took new Lodgings that very Night. About a Week after, I
found my jolly Land-lord, who, as I said before was an honest hearty
Man, had put me into an Advertisement of the
Daily Courant
, in the
following Words.
Whereas a melancholy Man left his Lodgings on Thursday
last in the Afternoon, and was afterwards seen going towards Islington;
If any one can give Notice of him to R. B., Fishmonger in the
Strand, he shall be very well rewarded for his Pains.
As I am the best
Man in the World to keep my own Counsel, and my Land-lord the Fishmonger
not knowing my Name, this Accident of my Life was never discovered to
this very Day.
I am now settled with a Widow-woman, who has a great many Children, and
complies with my Humour in everything. I do not remember that we have
exchang'd a Word together these Five Years; my Coffee comes into my
Chamber every Morning without asking for it; if I want Fire I point to
my Chimney, if Water, to my Bason: Upon which my Land-lady nods, as much
as to say she takes my Meaning, and immediately obeys my Signals. She
has likewise model'd her Family so well, that when her little Boy offers
to pull me by the Coat or prattle in my Face, his eldest Sister
immediately calls him off and bids him not disturb the Gentleman. At my
first entering into the Family, I was troubled with the Civility of
their rising up to me every time I came into the Room; but my Land-lady
observing, that upon these Occasions I always cried Pish and went out
again, has forbidden any such Ceremony to be used in the House; so that
at present I walk into the Kitchin or Parlour without being taken notice
of, or giving any Interruption to the Business or Discourse of the
Family. The Maid will ask her Mistress (tho' I am by) whether the
Gentleman is ready to go to Dinner, as the Mistress (who is indeed an
excellent Housewife) scolds at the Servants as heartily before my Face
as behind my Back. In short, I move up and down the House and enter into
all Companies, with the same Liberty as a Cat or any other domestick
Animal, and am as little suspected of telling anything that I hear or
see.
I remember last Winter there were several young Girls of the
Neighbourhood sitting about the Fire with my Land-lady's Daughters, and
telling Stories of Spirits and Apparitions. Upon my opening the Door the
young Women broke off their Discourse, but my Land-lady's Daughters
telling them that it was no Body but the Gentleman (for that is the Name
which I go by in the Neighbourhood as well as in the Family), they went
on without minding me. I seated myself by the Candle that stood on a
Table at one End of the Room; and pretending to read a Book that I took
out of my Pocket, heard several dreadful Stories of Ghosts as pale as
Ashes that had stood at the Feet of a Bed, or walked over a Churchyard
by Moonlight: And of others that had been conjured into the
Red-Sea
,
for disturbing People's Rest, and drawing their Curtains at Midnight;
with many other old Women's Fables of the like Nature. As one Spirit
raised another, I observed that at the End of every Story the whole
Company closed their Ranks and crouded about the Fire: I took Notice in
particular of a little Boy, who was so attentive to every Story, that I
am mistaken if he ventures to go to bed by himself this Twelvemonth.
Indeed they talked so long, that the Imaginations of the whole Assembly
were manifestly crazed, and I am sure will be the worse for it as long
as they live. I heard one of the Girls, that had looked upon me over her
Shoulder, asking the Company how long I had been in the Room, and
whether I did not look paler than I used to do.
put me under some
Apprehensions that I should be forced to explain my self if I did not
retire; for which Reason I took the Candle in my Hand, and went up into
my Chamber, not without wondering at this unaccountable Weakness in
reasonable Creatures,
that they should
love to astonish and terrify
one another.
Were I a Father, I should take a particular Care to
preserve my Children from these little Horrours of Imagination, which
they are apt to contract when they are young, and are not able to shake
off when they are in Years. I have known a Soldier that has enter'd a
Breach, affrighted at his own Shadow; and look pale upon a little
scratching at his Door, who the Day before had march'd up against a
Battery of Cannon. There are Instances of Persons, who have been
terrify'd, even to Distraction, at the Figure of a Tree or the shaking
of a Bull-rush. The Truth of it is, I look upon a sound Imagination as
the greatest Blessing of Life, next to a clear Judgment and a good
Conscience. In the mean Time, since there are very few whose Minds are
not more or less subject to these dreadful Thoughts and Apprehensions,
we ought to arm our selves against them by the Dictates of Reason and
Religion,
to pull the old Woman out of our Hearts
(as
Persius
expresses it in the
Motto
of my Paper), and extinguish those impertinent
Notions which we imbibed at a Time that we were not able to judge of
their Absurdity. Or if we believe, as many wise and good Men have done,
that there are such Phantoms and Apparitions as those I have been
speaking of, let us endeavour to establish to our selves an Interest in
him who holds the Reins of the whole Creation in his Hand, and moderates
them after such a Manner, that it is impossible for one Being to break
loose upon another without his Knowledge and Permission.
For my own Part, I am apt to join in Opinion with those who believe that
all the Regions of Nature swarm with Spirits; and that we have
Multitudes of Spectators on all our Actions, when we think our selves
most alone: But instead of terrifying my self with such a Notion, I am
wonderfully pleased to think that I am always engaged with such an
innumerable Society in searching out the Wonders of the Creation, and
joining in the same Consort of Praise and Adoration.
Milton
has
described this mixed Communion of Men and Spirits
in Paradise; and had doubtless his Eye upon a Verse in old
Hesiod
,
which is almost Word for Word the same with his third Line in the
following Passage.
Nor think, though Men were none,
That Heav'n would want Spectators, God want praise:
Millions of spiritual Creatures walk the Earth
Unseen, both when we wake and when we sleep;
All these with ceaseless Praise his Works behold
Both Day and Night. How often from the Steep
Of echoing Hill or Thicket, have we heard
Celestial Voices to the midnight Air,
Sole, or responsive each to others Note,
Singing their great Creator: Oft in bands,
While they keep Watch, or nightly Rounding walk,
With heav'nly Touch of instrumental Sounds,
In full harmonick Number join'd, their Songs
Divide the Night, and lift our Thoughts to Heav'n.
C.
who
Paradise Lost
, B. IV, lines 675-688.
In Bk. I of the
Works and Days
, description of the
Golden Age, when the good after death
Yet still held state on earth, and guardians were
Of all best mortals still surviving there,
Observ'd works just and unjust, clad in air,
And gliding undiscovered everywhere.
Chapman's Translation.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 15, 1711 |
Addison |
Dic mi hi si fueris tu leo qualis eris?
Mart.

is nothing that of late Years has afforded Matter of greater
Amusement to the Town than Signior
Nicolini's
Combat with a Lion in
the
Hay-Market
` which has been very often exhibited to the general
Satisfaction of most of the Nobility and Gentry in the Kingdom of
Great
Britain
. Upon the first Rumour of this intended Combat, it was
confidently affirmed, and is still believed by many in both Galleries,
that there would be a tame Lion sent from the Tower every Opera Night,
in order to be killed by
Hydaspes
; this Report, tho' altogether
groundless, so universally prevailed in the upper Regions of the
Play-House, that some of the most refined Politicians in those Parts of
the Audience, gave it out in Whisper, that the Lion was a Cousin-German
of the Tyger who made his Appearance in King
William's
days, and that
the Stage would be supplied with Lions at the public Expence, during the
whole Session. Many likewise were the Conjectures of the Treatment which
this Lion was to meet with from the hands of Signior
Nicolini
; some
supposed that he was to Subdue him in
Recitativo
, as
Orpheus
used to
serve the wild Beasts in his time, and afterwards to knock him on the
head; some fancied that the Lion would not pretend to lay his Paws upon
the Hero, by Reason of the received Opinion, that a Lion will not hurt a
Virgin. Several, who pretended to have seen the Opera in
Italy
, had
informed their Friends, that the Lion was to act a part in
High Dutch
,
and roar twice or thrice to a thorough Base, before he fell at the Feet
of
Hydaspes
. To clear up a Matter that was so variously reported, I
have made it my Business to examine whether this pretended Lion is
really the Savage he appears to be, or only a Counterfeit.
But before I communicate my Discoveries, I must acquaint the Reader,
that upon my walking behind the Scenes last Winter, as I was thinking on
something else, I accidentally jostled against a monstrous Animal that
extreamly startled me, and, upon my nearer Survey of it, appeared to be
a Lion-Rampant. The Lion, seeing me very much surprized, told me, in a
gentle Voice, that I might come by him if I pleased:
For (says
he) I do not intend to hurt anybody.
I thanked him very kindly,
and passed by him. And in a little time after saw him leap upon the
Stage, and act his Part with very great Applause. It has been observed
by several, that the Lion has changed his manner of Acting twice or
thrice since his first Appearance; which will not seem strange, when I
acquaint my Reader that the Lion has been changed upon the Audience
three several times. The first Lion was a Candle-snuffer, who being a
Fellow of a testy, cholerick Temper over-did his Part, and would not
suffer himself to be killed so easily as he ought to have done; besides,
it was observ'd of him, that he grew more surly every time he came out
of the Lion; and having dropt some Words in ordinary Conversation, as if
he had not fought his best, and that he suffered himself to be thrown
upon his Back in the Scuffle, and that he would wrestle with Mr
Nicolini
for what he pleased, out of his Lion's Skin, it was
thought proper to discard him: And it is verily believed to this Day,
that had he been brought upon the Stage another time, he would certainly
have done Mischief. Besides, it was objected against the first Lion,
that he reared himself so high upon his hinder Paws, and walked in so
erect a Posture, that he looked more like an old Man than a Lion. The
second Lion was a Taylor by Trade, who belonged to the Play-House, and
had the Character of a mild and peaceable Man in his Profession. If the
former was too furious, this was too sheepish, for his Part; insomuch
that after a short modest Walk upon the Stage, he would fall at the
first Touch of
Hydaspes
, without grappling with him, and giving
him an Opportunity of showing his Variety of
Italian
Tripps: It
is said, indeed, that he once gave him a Ripp in his flesh-colour
Doublet, but this was only to make work for himself, in his private
Character of a Taylor.
must not omit that it was this second Lion
who
treated me with so much Humanity behind the Scenes. The Acting Lion
at present is, as I am informed, a Country Gentleman, who does it for
his Diversion, but desires his Name may be concealed. He says very
handsomely in his own Excuse, that he does not Act for Gain, that he
indulges an innocent Pleasure in it, and that it is better to pass away
an Evening in this manner, than in Gaming and Drinking: But at the same
time says, with a very agreeable Raillery upon himself, that if his name
should be known, the ill-natured World might call him,
The Ass in the
Lion's skin
. This Gentleman's Temper is made out of such a happy
Mixture of the Mild and the Cholerick, that he out-does both his
predecessors, and has drawn together greater Audiences than have been
known in the Memory of Man.
I must not conclude my Narrative, without taking Notice of a groundless
Report that has been raised, to a Gentleman's Disadvantage, of whom I
must declare my self an Admirer; namely, that Signior
Nicolini
and the
Lion have been seen sitting peaceably by one another, and smoking a Pipe
together, behind the Scenes; by which their common Enemies would
insinuate, it is but a sham Combat which they represent upon the Stage:
But upon Enquiry I find, that if any such Correspondence has passed
between them, it was not till the Combat was over, when the Lion was to
be looked upon as dead, according to the received Rules of the
Drama
.
Besides, this is what is practised every day in
Westminster-Hall
,
where nothing is more usual than to see a Couple of Lawyers, who have
been rearing each other to pieces in the Court, embracing one another as
soon as they are out of it.
I would not be thought, in any part of this Relation, to reflect upon
Signior
Nicolini
, who, in Acting this Part only complies with the
wretched Taste of his Audience; he knows very well, that the Lion has
many more Admirers than himself; as they say of the famous
Equestrian
Statue on the
Pont-Neuf
at
Paris
, that more People go to see the
Horse, than the King who sits upon it. On the contrary, it gives me a
just Indignation, to see a Person whose Action gives new Majesty to
Kings, Resolution to Heroes, and Softness to Lovers, thus sinking from
the Greatness of his Behaviour, and degraded into the Character of the
London
Prentice. I have often wished that our Tragœdians would copy
after this great Master in Action. Could they make the same use of their
Arms and Legs, and inform their Faces with as significant Looks and
Passions, how glorious would an
English
Tragedy appear with that
Action which is capable of giving a Dignity to the forced Thoughts, cold
Conceits, and unnatural Expressions of an
Italian
Opera. In the mean
time, I have related this Combat of the Lion, to show what are at
present the reigning Entertainments of the Politer Part of
Great
Britain
.
Audiences have often been reproached by Writers for the Coarseness of
their Taste, but our present Grievance does not seem to be the Want of a
good Taste, but of Common Sense.
C.
The famous Neapolitan actor and singer, Cavalier Nicolino
Grimaldi, commonly called Nicolini, had made his first appearance in an
opera called
Pyrrhus and Demetrius,
which was the last attempt to
combine English with Italian. His voice was a soprano, but afterwards
descended into a fine contralto, and he seems to have been the finest
actor of his day. Prices of seats at the opera were raised on his coming
from 7s. 6d. to 10s. for pit and boxes, and from 10s. 6d. to 15s. for
boxes on the stage. When this paper was written he had appeared also in
a new opera on
Almahide
, and proceeded to those encounters with the
lion in the opera of
Hydaspes
, by a Roman composer, Francesco Mancini,
first produced May 23, 1710, which the
Spectator
has made memorable.
It had been performed 21 times in 1710, and was now reproduced and
repeated four times. Nicolini, as Hydaspes in this opera, thrown naked
into an amphitheatre to be devoured by a lion, is so inspired with
courage by the presence of his mistress among the spectators that (says
Mr Sutherland Edwards in his
History of the Opera
)
'after appealing to the monster in a minor key, and telling him that
he may tear his bosom, but cannot touch his heart, he attacks him in
the relative major, and strangles him.'
that
Contents
|
Friday, March 16, 1711 |
Steele |
... Teque his, Infelix, exue monstris.
Ovid.

I was reflecting this Morning upon the Spirit and Humour of the publick
Diversions Five and twenty Years ago, and those of the present Time; and
lamented to my self, that though in those Days they neglected their
Morality, they kept up their Good Sense; but that the
beau Monde
,
at present, is only grown more childish, not more innocent, than the
former. While I was in this Train of Thought, an odd Fellow, whose Face
I have often seen at the Play-house, gave me the following Letter with
these words, Sir,
The Lyon presents his humble Service to you, and
desired me to give this into your own Hands.
From my Den in the Hay-market, March 15.
Sir
'I have read all your Papers, and have stifled my Resentment against
your Reflections upon Operas, till that of this Day, wherein you
plainly insinuate, that Signior Grimaldi and my self have a
Correspondence more friendly than is consistent with the Valour of his
Character, or the Fierceness of mine. I desire you would, for your own
Sake, forbear such Intimations for the future; and must say it is a
great Piece of Ill-nature in you, to show so great an Esteem for a
Foreigner, and to discourage a Lyon that is your own
Country-man.
I take notice of your Fable of the Lyon and Man, but am so equally
concerned in that Matter, that I shall not be offended to which soever
of the Animals the Superiority is given. You have misrepresented me,
in saying that I am a Country-Gentleman, who act only for my
Diversion; whereas, had I still the same Woods to range in which I
once had when I was a Fox-hunter, I should not resign my Manhood for a
Maintenance; and assure you, as low as my Circumstances are at
present, I am so much a Man of Honour, that I would scorn to be any
Beast for Bread but a Lyon.
Yours, &c.
I had no sooner ended this, than one of my Land-lady's Children brought
me in several others, with some of which I shall make up my present
Paper, they all having a Tendency to the same Subject,
viz
. the
Elegance of our present Diversions.
Covent Garden, March 13.
Sir,
'I Have been for twenty Years Under-Sexton of this Parish of St.
Paul's, Covent-Garden, and have not missed tolling in to Prayers six
times in all those Years; which Office I have performed to my great
Satisfaction, till this Fortnight last past, during which Time I find
my Congregation take the Warning of my Bell, Morning and Evening, to
go to a Puppett-show set forth by one Powell, under the Piazzas.
By this Means, I have not only lost my two Customers, whom I used to
place for six Pence a Piece over against Mrs Rachel Eyebright, but
Mrs Rachel herself is gone thither also. There now appear among us
none but a few ordinary People, who come to Church only to say their
Prayers, so that I have no Work worth speaking of but on Sundays. I
have placed my Son at the Piazzas, to acquaint the Ladies that the
Bell rings for Church, and that it stands on the other side of the
Garden; but they only laugh at the Child.
I desire you would lay this before all the World, that I may not be
made such a Tool for the Future, and that Punchinello may chuse Hours
less canonical. As things are now, Mr Powell has a full
Congregation, while we have a very thin House; which if you can
Remedy, you will very much oblige,
Sir, Yours, &c.'
following Epistle I find is from the Undertaker of the Masquerade
.
Sir,
'I Have observed the Rules of my Masque so carefully (in not enquiring
into Persons), that I cannot tell whether you were one of the Company
or not last Tuesday; but if you were not and still design to come, I
desire you would, for your own Entertainment, please to admonish the
Town, that all Persons indifferently are not fit for this Sort of
Diversion. I could wish, Sir, you could make them understand, that it
is a kind of acting to go in Masquerade, and a Man should be able to
say or do things proper for the Dress in which he appears. We have now
and then Rakes in the Habit of Roman Senators, and grave Politicians
in the Dress of Rakes. The Misfortune of the thing is, that People
dress themselves in what they have a Mind to be, and not what they are
fit for. There is not a Girl in the Town, but let her have her Will in
going to a Masque, and she shall dress as a Shepherdess. But let me
beg of them to read the Arcadia, or some other good Romance, before
they appear in any such Character at my House. The last Day we
presented, every Body was so rashly habited, that when they came to
speak to each other, a Nymph with a Crook had not a Word to say but in
the pert Stile of the Pit Bawdry; and a Man in the Habit of a
Philosopher was speechless, till an occasion offered of expressing
himself in the Refuse of the Tyring-Rooms. We had a Judge that danced
a Minuet, with a Quaker for his Partner, while half a dozen Harlequins
stood by as Spectators: A Turk drank me off two Bottles of Wine, and
a Jew eat me up half a Ham of Bacon. If I can bring my Design to
bear, and make the Maskers preserve their Characters in my Assemblies,
I hope you will allow there is a Foundation laid for more elegant and
improving Gallantries than any the Town at present affords; and
consequently that you will give your Approbation to the Endeavours of,
Sir, Your most obedient humble servant.'
I am very glad the following Epistle obliges me to mention Mr
Powell
a
second Time in the same Paper; for indeed there cannot be too great
Encouragement given to his Skill in Motions, provided he is under proper
Restrictions.
Sir,
'The Opera at the
Hay-Market, and that under the little
Piazza in
Covent-Garden, being at present the Two leading Diversions of the
Town; and Mr
Powell professing in his Advertisements to set up
Whittington and his Cat against
Rinaldo and Armida, my Curiosity
led me the Beginning of last Week to view both these Performances, and
make my Observations upon them.
First therefore, I cannot but observe that Mr
Powell wisely
forbearing to give his Company a Bill of Fare before-hand, every Scene
is new and unexpected; whereas it is certain, that the Undertakers of
the
Hay-Market, having raised too great an Expectation in their
printed Opera, very much disappointed their Audience on the Stage.
The King of
Jerusalem is obliged to come from the City on foot,
instead of being drawn in a triumphant Chariot by white Horses, as my
Opera-Book had promised me; and thus, while I expected
Armida's
Dragons should rush forward towards
Argantes, I found the Hero was
obliged to go to
Armida, and hand her out of her Coach. We had also
but a very short Allowance of Thunder and Lightning; tho' I cannot in
this Place omit doing Justice to the Boy who had the Direction of the
Two painted Dragons, and made them spit Fire and Smoke: He flash'd out
his Rosin in such just Proportions, and in such due Time, that I could
not forbear conceiving Hopes of his being one Day a most excellent
Player. I saw, indeed, but Two things wanting to render his whole
Action compleat, I mean the keeping his Head a little lower, and
hiding his Candle.
I observe that Mr
Powell and the Undertakers had both the same
Thought, and I think, much about the same time, of introducing Animals
on their several Stages, though indeed with very different Success.
The Sparrows and Chaffinches at the
Hay-Market fly as yet very
irregularly over the Stage; and instead of perching on the Trees and
performing their Parts, these young Actors either get into the
Galleries or put out the Candles; whereas Mr
Powell has so well
disciplined his Pig, that in the first Scene he and Punch dance a
Minuet together.
I am informed however, that Mr
Powell resolves to
excell his Adversaries in their own Way; and introduce Larks in his
next Opera of
Susanna, or
Innocence betrayed, which will be
exhibited next Week with a Pair of new Elders
2.
The Moral of Mr
Powell's Drama is violated I confess by Punch's
national Reflections on the
French, and King
Harry's laying his
Leg upon his Queen's Lap in too ludicrous a manner before so great an
Assembly.
As to the Mechanism and Scenary, every thing, indeed, was uniform,
and of a Piece, and the Scenes were managed very dexterously; which
calls on me to take Notice, that at the
Hay-Market the Undertakers
forgetting to change their Side-Scenes, we were presented with a
Prospect of the Ocean in the midst of a delightful Grove; and tho' the
Gentlemen on the Stage had very much contributed to the Beauty of the
Grove, by walking up and down between the Trees, I must own I was not
a little astonished to see a well-dressed young Fellow in a
full-bottomed Wigg, appear in the Midst of the Sea, and without any
visible Concern taking Snuff.
I shall only observe one thing further, in which both Dramas agree;
which is, that by the Squeak of their Voices the Heroes of each are
Eunuchs; and as the Wit in both Pieces are equal, I must prefer the
Performance of Mr
Powell, because it is in our own Language.
'
I am, &c.'
Masquerades took rank as a leading pleasure of the town
under the management of John James Heidegger, son of a Zurich clergyman,
who came to England in 1708, at the age of 50, as a Swiss negotiator. He
entered as a private in the Guards, and attached himself to the service
of the fashionable world, which called him 'the Swiss Count,' and
readily accepted him as leader. In 1709 he made five hundred guineas by
furnishing the spectacle for Motteux's opera of
Tomyris, Queen of
Scythia
. When these papers were written he was thriving upon the
Masquerades, which he brought into fashion and made so much a rage of
the town that moralists and satirists protested, and the clergy preached
against them. A sermon preached against them by the Bishop of London,
January 6th, 1724, led to an order that no more should take place than
the six subscribed for at the beginning of the month. Nevertheless they
held their ground afterwards by connivance of the government. In 1728,
Heidegger was called in to nurse the Opera, which throve by his bold
puffing. He died, in 1749, at the age of 90, claiming chief honour to
the Swiss for ingenuity.
'I was born,' he said, 'a Swiss, and came to England without a
farthing, where I have found means to gain, £5000 a-year, — and to
spend it. Now I defy the ablest Englishman to go to Switzerland and
either gain that income or spend it there.'
The
History of Susanna
had been an established puppet
play for more than two generations. An old copy of verses on Bartholomew
Fair in the year 1665, describing the penny and twopenny puppet plays,
or, as they had been called in and since Queen Elizabeth's time,
'motions,' says
Their Sights are so rich, is able to bewitch
The heart of a very fine man-a;
Here's 'Patient Grisel' here, and 'Fair Rosamond' there,
And 'the History of Susanna.'
Pepys tells of the crowd waiting, in 1667, to see Lady Castlemaine come
out from the puppet play of
Patient Grisel.
Powell mentioned in this essay was a deformed cripple whose
Puppet-Show, called Punch's Theatre, owed its pre-eminence to his own
power of satire. This he delivered chiefly through Punch, the clown of
the puppets, who appeared in all plays with so little respect to
dramatic rule that Steele in the
Tatler
(for May 17, 1709) represents a
correspondent at Bath, telling how, of two ladies, Prudentia and
Florimel, who would lead the fashion, Prudentia caused Eve in the
Puppet-Show of
the Creation of the World
to be
'made the most like
Florimel that ever was seen,' and 'when we came to Noah's Flood in the
show, Punch and his wife were introduced dancing in the ark.'
Of the
fanatics called French Prophets, who used to assemble in Moorfields in
Queen Anne's reign, Lord Chesterfield remembered that
'the then
Ministry, who loved a little persecution well enough, was, however, so
wise as not to disturb their madness, and only ordered one Powell, the
master of a famous Puppet-Show, to make Punch turn Prophet; which he did
so well, that it soon put an end to the prophets and their prophecies.
The obscure Dr Sacheverell's fortune was made by a parliamentary
prosecution' (from Feb. 27 to March 23, 1709-10) 'much about the same
time the French Prophets were totally extinguished by a Puppet-Show'
(Misc. Works, ed. Maty., Vol. II, p. 523, 555).
This was the Powell who played in Covent Garden during the time of
week-day evening service, and who, taking up Addison's joke against the
opera from
, produced
Whittington and his Cat
as a rival to
Rinaldo and Armida
. [See also a note to
Contents
On the first of April will be performed at the Play-house in the
Hay-market, an Opera call'd
The Cruelty of Atreus.
N. B. The Scene wherein Thyestes eats his own Children,
is
to be performed by the famous Mr Psalmanazar1,
lately arrived
from Formosa;
The whole Supper being set to Kettle-drums.
R.
George Psalmanazar, who never told his real name and
precise birthplace, was an impostor from Languedoc, and 31 years old in
1711. He had been educated in a Jesuit college, where he heard stories
of the Jesuit missions in Japan and Formosa, which suggested to him how
he might thrive abroad as an interesting native. He enlisted as a
soldier, and had in his character of Japanese only a small notoriety
until, at Sluys, a dishonest young chaplain of Brigadier Lauder's Scotch
regiment, saw through the trick and favoured it, that he might recommend
himself to the Bishop of London for promotion. He professed to have
converted Psalmanazar, baptized him, with the Brigadier for godfather,
got his discharge from the regiment, and launched him upon London under
the patronage of Bishop Compton. Here Psalmanazar, who on his arrival
was between nineteen and twenty years old, became famous in the
religious world. He supported his fraud by invention of a language and
letters, and of a Formosan religion. To oblige the Bishop he translated
the church catechism into 'Formosan,' and he published in 1704 'an
historical and geographical Description of Formosa,' of which a second
edition appeared in the following year. It contained numerous plates of
imaginary scenes and persons. His gross and puerile absurdities in print
and conversation — such as his statements that the Formosans sacrificed
eighteen thousand male infants every year, and that the Japanese studied
Greek as a learned tongue, — excited a distrust that would have been
fatal to the success of his fraud, even with the credulous, if he had
not forced himself to give colour to his story by acting the savage in
men's eyes. But he must really, it was thought, be a savage who fed upon
roots, herbs, and raw flesh. He made, however, so little by the
imposture, that he at last confessed himself a cheat, and got his living
as a well-conducted bookseller's hack for many years before his death,
in 1763, aged 84. In 1711, when this jest was penned, he had not yet
publicly eaten his own children, i.e. swallowed his words and declared
his writings forgeries. In 1716 there was a subscription of £20 or £30 a
year raised for him as a Formosan convert. It was in 1728 that he began
to write that formal confession of his fraud, which he left for
publication after his death, and whereby he made his great public
appearance as Thyestes.
This jest against Psalmanazar was expunged from the first reprint of the
Spectator
in 1712, and did not reappear in the lifetime of Steele
or Addison, or until long after it had been amply justified.
|
Saturday, March 17, 1711 |
Addison |
Parva leves capiunt animos ...
Ovid.

When I was in
France
, I used to gaze with great Astonishment at
the Splendid Equipages and Party-coloured Habits, of that Fantastick
Nation. I was one Day in particular contemplating a Lady that sate in a
Coach adorned with gilded
Cupids
, and finely painted with the
Loves of
Venus
and
Adonis
. The Coach was drawn by six
milk-white Horses, and loaden behind with the same Number of powder'd
Foot-men. Just before the Lady were a Couple of beautiful Pages, that
were stuck among the Harness, and by their gay Dresses, and smiling
Features, looked like the elder Brothers of the little Boys that were
carved and painted in every Corner of the Coach.
The Lady was the unfortunate
Cleanthe
, who afterwards gave an
Occasion to a pretty melancholy Novel. She had, for several Years,
received the Addresses of a Gentleman, whom, after a long and intimate
Acquaintance, she forsook, upon the Account of this shining Equipage
which had been offered to her by one of great Riches, but a Crazy
Constitution. The Circumstances in which I saw her, were, it seems, the
Disguises only of a broken Heart, and a kind of Pageantry to cover
Distress; for in two Months after, she was carried to her Grave with the
same Pomp and Magnificence: being sent thither partly by the Loss of one
Lover, and partly by the Possession of another.
I have often reflected with my self on this unaccountable Humour in
Woman-kind, of being smitten with every thing that is showy and
superficial; and on the numberless Evils that befall the Sex, from this
light, fantastical Disposition. I my self remember a young Lady that was
very warmly sollicited by a Couple of importunate Rivals, who, for
several Months together, did all they could to recommend themselves, by
Complacency of Behaviour, and Agreeableness of Conversation. At length,
when the Competition was doubtful, and the Lady undetermined in her
Choice, one of the young Lovers very luckily bethought himself of adding
a supernumerary Lace to his Liveries, which had so good an Effect that
he married her the very Week after.
The usual Conversation of ordinary Women, very much cherishes this
Natural Weakness of being taken with Outside and Appearance. Talk of a
new-married Couple, and you immediately hear whether they keep their
Coach and six, or eat in Plate: Mention the Name of an absent Lady, and
it is ten to one but you learn something of her Gown and Petticoat. A
Ball is a great Help to Discourse, and a Birth-Day furnishes
Conversation for a Twelve-month after. A Furbelow of precious Stones, an
Hat buttoned with a Diamond, a Brocade Waistcoat or Petticoat, are
standing Topicks. In short, they consider only the Drapery of the
Species, and never cast away a Thought on those Ornaments of the Mind,
that make Persons Illustrious in themselves, and Useful to others. When
Women are thus perpetually dazling one anothers Imaginations, and
filling their Heads with nothing but Colours, it is no Wonder that they
are more attentive to the superficial Parts of Life, than the solid and
substantial Blessings of it. A Girl, who has been trained up in this
kind of Conversation, is in danger of every Embroidered Coat that comes
in her Way. A Pair of fringed Gloves may be her Ruin. In a word, Lace
and Ribbons, Silver and Gold Galloons, with the like glittering
Gew-Gaws, are so many Lures to Women of weak Minds or low Educations,
and, when artificially displayed, are able to fetch down the most airy
Coquet from the wildest of her Flights and Rambles.
True Happiness is of a retired Nature, and an Enemy to Pomp and Noise;
it arises, in the first place, from the Enjoyment of ones self; and, in
the next, from the Friendship and Conversation of a few select
Companions. It loves Shade and Solitude, and naturally haunts Groves and
Fountains, Fields and Meadows: In short, it feels every thing it wants
within itself, and receives no Addition from Multitudes of Witnesses and
Spectators. On the contrary, false Happiness loves to be in a Crowd, and
to draw the Eyes of the World upon her. She does not receive any
Satisfaction from the Applauses which she gives her self, but from the
Admiration which she raises in others. She flourishes in Courts and
Palaces, Theatres and Assemblies, and has no Existence but when she is
looked upon.
Aurelia
, tho' a Woman of Great Quality, delights in the Privacy of a
Country Life, and passes away a great part of her Time in her own Walks
and Gardens. Her Husband, who is her Bosom Friend and Companion in her
Solitudes, has been in Love with her ever since he knew her. They both
abound with good Sense, consummate Virtue, and a mutual Esteem; and are
a perpetual Entertainment to one another. Their Family is under so
regular an Œconomy, in its Hours of Devotion and Repast, Employment and
Diversion, that it looks like a little Common-Wealth within it self.
They often go into Company, that they may return with the greater
Delight to one another; and sometimes live in Town not to enjoy it so
properly as to grow weary of it, that they may renew in themselves the
Relish of a Country Life. By this means they are Happy in each other,
beloved by their Children, adored by their Servants, and are become the
Envy, or rather the Delight, of all that know them.
How different to this is the Life of
Fulvia
! she considers her Husband
as her Steward, and looks upon Discretion and good House-Wifery, as
little domestick Virtues, unbecoming a Woman of Quality. She thinks Life
lost in her own Family, and fancies herself out of the World, when she
is not in the Ring, the Play-House, or the Drawing-Room: She lives in a
perpetual Motion of Body and Restlessness of Thought, and is never easie
in any one Place, when she thinks there is more Company in another. The
missing of an Opera the first Night, would be more afflicting to her
than the Death of a Child. She pities all the valuable Part of her own
Sex, and calls every Woman of a prudent modest retired Life, a
poor-spirited, unpolished Creature. What a Mortification would it be to
Fulvia
, if she knew that her setting her self to View, is but exposing
her self, and that she grows Contemptible by being Conspicuous.
I cannot conclude my Paper, without observing that
Virgil
has very
finely touched upon this Female Passion for Dress and Show, in the
Character of
Camilla
; who, tho' she seems to have shaken off all the
other Weaknesses of her Sex, is still described as a Woman in this
Particular.
Poet tells us, that, after having made a great Slaughter
of the Enemy, she unfortunately cast her Eye on a
Trojan
who
wore
an embroidered Tunick, a beautiful Coat of Mail, with a Mantle of the
finest Purple.
A Golden Bow
, says he,
Hung upon his Shoulder; his
Garment was buckled with a Golden Clasp, and his Head was covered with
an Helmet of the same shining Mettle
. The
Amazon
immediately singled
out this well-dressed Warrior, being seized with a Woman's Longing for
the pretty Trappings that he was adorned with:
... Totumque incauta per agmen
Fæmineo prædæ et spoliorum ardebat amore.
This heedless Pursuit after these glittering Trifles, the Poet (by a
nice concealed Moral) represents to have been the Destruction of his
Female Hero.
C.
that
Contents
|
Monday, March 19, 1711 |
Addison |
Quid verum atque decens curo et rogo, et omnis in hoc sum.
Hor.

have receiv'd a Letter, desiring me to be very satyrical upon the
little Muff that is now in Fashion; another informs me of a Pair of
silver Garters buckled below the Knee, that have been lately seen at the
Rainbow Coffee-house in
Fleet-street
; a third sends me an heavy
Complaint against fringed Gloves. To be brief, there is scarce an
Ornament of either Sex which one or other of my Correspondents has not
inveighed against with some Bitterness, and recommended to my
Observation. I must therefore, once for all inform my Readers, that it
is not my Intention to sink the Dignity of this my Paper with
Reflections upon Red-heels or Top-knots, but rather to enter into the
Passions of Mankind, and to correct those depraved Sentiments that give
Birth to all those little Extravagancies which appear in their outward
Dress and Behaviour. Foppish and fantastick Ornaments are only
Indications of Vice, not criminal in themselves. Extinguish Vanity in
the Mind, and you naturally retrench the little Superfluities of
Garniture and Equipage. The Blossoms will fall of themselves, when the
Root that nourishes them is destroyed.
I shall therefore, as I have said, apply my Remedies to the first Seeds
and Principles of an affected Dress, without descending to the Dress it
self; though at the same time I must own, that I have Thoughts of
creating an Officer under me to be entituled,
The Censor of small
Wares
, and of allotting him one Day in a Week for the Execution of such
his Office. An Operator of this Nature might act under me with the same
Regard as a Surgeon to a Physician; the one might be employ'd in healing
those Blotches and Tumours which break out in the Body, while the other
is sweetning the Blood and rectifying the Constitution.
speak truly,
the young People of both Sexes are so wonderfully apt to shoot out into
long Swords or sweeping Trains, bushy Head-dresses or full-bottom'd
Perriwigs, with several other Incumbrances of Dress, that they stand in
need of being pruned very frequently
lest they should
be oppressed
with Ornaments, and over-run with the Luxuriency of their Habits. I am
much in doubt, whether I should give the Preference to a Quaker that is
trimmed close and almost cut to the Quick, or to a Beau that is loaden
with such a Redundance of Excrescencies. I must therefore desire my
Correspondents to let me know how they approve my Project, and whether
they think the erecting of such a petty Censorship may not turn to the
Emolument of the Publick; for I would not do any thing of this Nature
rashly and without Advice.
There is another Set of Correspondents to whom I must address my self,
in the second Place; I mean such as fill their Letters with private
Scandal, and black Accounts of particular Persons and Families.
world is so full of Ill-nature, that I have Lampoons sent me by People
who
cannot spell, and Satyrs compos'd by those who scarce know how
to write. By the last Post in particular I receiv'd a Packet of Scandal
that is not legible; and have a whole Bundle of Letters in Womens Hands
that are full of Blots and Calumnies, insomuch that when I see the Name
Cælia, Phillis, Pastora
, or the like, at the Bottom of a Scrawl, I
conclude on course that it brings me some Account of a fallen Virgin, a
faithless Wife, or an amorous Widow. I must therefore inform these my
Correspondents, that it is not my Design to be a Publisher of Intreagues
and Cuckoldoms, or to bring little infamous Stories out of their present
lurking Holes into broad Day light. If I attack the Vicious, I shall
only set upon them in a Body: and will not be provoked by the worst
Usage that I can receive from others, to make an Example of any
particular Criminal.
short, I have so much of a Drawcansir
in me,
that I shall pass over a single Foe to charge whole Armies. It is not
Lais
or
Silenus
, but the Harlot and the Drunkard, whom I shall
endeavour to expose; and shall consider the Crime as it appears in a
Species, not as it is circumstanced in an Individual. I think it was
Caligula
who wished the whole City of
Rome
had but one Neck, that he
might behead them at a Blow. I shall do out of Humanity what that
Emperor would have done in the Cruelty of his Temper, and aim every
Stroak at a collective Body of Offenders. At the same Time I am very
sensible, that nothing spreads a Paper like private Calumny and
Defamation; but as my Speculations are not under this Necessity, they
are not exposed to this Temptation.
In the next Place I must apply my self to my Party-Correspondents, who
are continually teazing me to take Notice of one anothers Proceedings.
How often am I asked by both Sides, if it is possible for me to be an
unconcerned Spectator of the Rogueries that are committed by the Party
which is opposite to him that writes the Letter. About two Days since I
was reproached with an old Grecian Law, that forbids any Man to stand as
a Neuter or a Looker-on in the Divisions of his Country.
, as I
am very sensible
my
Paper would lose its whole Effect, should it
run into the Outrages of a Party, I shall take Care to keep clear of
every thing
which
looks that Way.
I can any way asswage private
Inflammations, or allay publick Ferments, I shall apply my self to it
with my utmost Endeavours; but will never let my Heart reproach me with
having done any thing towards
encreasing
those Feuds and
Animosities that extinguish Religion, deface Government, and make a
Nation miserable.
What I have said under the three foregoing Heads, will, I am afraid,
very much retrench the Number of my Correspondents: I shall therefore
acquaint my Reader, that if he has started any Hint which he is not able
to pursue, if he has met with any surprizing Story which he does not
know how to tell, if he has discovered any epidemical Vice which has
escaped my Observation, or has heard of any uncommon Virtue which he
would desire to publish; in short, if he has any Materials that can
furnish out an innocent Diversion, I shall promise him my best
Assistance in the working of them up for a publick Entertainment.
This Paper my Reader will find was intended for an answer to a Multitude
of Correspondents; but I hope he will pardon me if I single out one of
them in particular, who has made me so very humble a Request, that I
cannot forbear complying with it.
To the Spectator.
March 15, 1710-11.
Sir,
'I Am at present so unfortunate, as to have nothing to do
but to mind my own Business; and therefore beg of you that
you will be pleased to put me into some small Post under you.
I observe that you have appointed your Printer and Publisher
to receive Letters and Advertisements for the City of London,
and shall think my self very much honoured by you, if you
will appoint me to take in Letters and Advertisements for the
City of Westminster and the Dutchy of Lancaster. Tho' I
cannot promise to fill such an Employment with sufficient
Abilities, I will endeavour to make up with Industry and
Fidelity what I want in Parts and Genius. I am,
Sir,
Your most obedient servant,
Charles Lillie.'
C.
The
Rainbow
, near the Inner Temple Gate, in Fleet Street,
was the second Coffee-house opened in London. It was opened about 1656,
by a barber named James Farr, part of the house still being occupied by
the bookseller's shop which had been there for at least twenty years
before. Farr also, at first, combined his coffee trade with the business
of barber, which he had been carrying on under the same roof. Farr was
made rich by his Coffee-house, which soon monopolized the
Rainbow
. Its
repute was high in the
Spectator's
time; and afterwards, when
coffee-houses became taverns, it lived on as a reputable tavern till the
present day.
that they may not
that
Drawcansir
in the Duke of Buckingham's
Rehearsal
parodies the heroic drama of the Restoration, as by turning the lines in
Dryden's
Tyrannic Love,
Spite of myself, I'll stay, fight, love, despair;
And all this I can do, because I dare,
into
I drink, I huff, I strut, look big and stare;
And all this I can do, because I dare.
When, in the last act, a Battle is fought between Foot and great
Hobby-Horses
'At last, Drawcansir comes in and Kills them all on both Sides,'
explaining himself in lines that begin,
Others may boast a single man to kill;
But I the blood of thousands daily spill.
that my
that
the encreasing
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 20, 1711 |
Steele |
... Tetrum ante Omnia vultum.
Juv.

Since our Persons are not of our own Making, when they are such as
appear Defective or Uncomely, it is, methinks, an honest and laudable
Fortitude to dare to be Ugly; at least to keep our selves from being
abashed with a Consciousness of Imperfections which we cannot help, and
in which there is no Guilt. I would not defend an haggard Beau, for
passing away much time at a Glass, and giving Softnesses and Languishing
Graces to Deformity. All I intend is, that we ought to be contented with
our Countenance and Shape, so far, as never to give our selves an
uneasie Reflection on that Subject. It is to the ordinary People, who
are not accustomed to make very proper Remarks on any Occasion, matter
of great Jest, if a Man enters with a prominent Pair of Shoulders into
an Assembly, or is distinguished by an Expansion of Mouth, or Obliquity
of Aspect. It is happy for a Man, that has any of these Oddnesses about
him, if he can be as merry upon himself, as others are apt to be upon
that Occasion: When he can possess himself with such a Chearfulness,
Women and Children, who were at first frighted at him, will afterwards
be as much pleased with him. As it is barbarous in others to railly him
for natural Defects, it is extreamly agreeable when he can Jest upon
himself for them.
Maintenon's
first Husband was an Hero in this Kind, and has
drawn many Pleasantries from the Irregularity of his Shape, which he
describes as very much resembling the Letter Z
. He diverts himself
likewise by representing to his Reader the Make of an Engine and Pully,
with which he used to take off his Hat. When there happens to be any
thing ridiculous in a Visage, and the Owner of it thinks it an Aspect of
Dignity, he must be of very great Quality to be exempt from Raillery:
The best Expedient therefore is to be pleasant upon himself. Prince
Harry
and
Falstaffe
, in
Shakespear
, have carried
the Ridicule upon Fat and Lean as far as it will go.
Falstaffe
is
Humourously called
Woolsack
,
Bed-presser
, and
Hill of
Flesh
; Harry a
Starveling
, an
Elves-Skin
, a
Sheath
, a
Bowcase
, and a
Tuck
. There is, in several
incidents of the Conversation between them, the Jest still kept up upon
the Person. Great Tenderness and Sensibility in this Point is one of the
greatest Weaknesses of Self-love; for my own part, I am a little unhappy
in the Mold of my Face, which is not quite so long as it is broad:
Whether this might not partly arise from my opening my Mouth much
seldomer than other People, and by Consequence not so much lengthning
the Fibres of my Visage, I am not at leisure to determine. However it
be, I have been often put out of Countenance by the Shortness of my
Face, and was formerly at great Pains in concealing it by wearing a
Periwigg with an high Foretop, and letting my Beard grow. But now I have
thoroughly got over this Delicacy, and could be contented it were much
shorter, provided it might qualify me for a Member of the Merry Club,
which the following Letter gives me an Account of. I have received it
from
Oxford
, and as it abounds with the Spirit of Mirth and good
Humour, which is natural to that Place, I shall set it down Word for
Word as it came to me.
'
Most Profound Sir,
Having been very well entertained, in the last of your Speculations
that I have yet seen, by your Specimen upon Clubs, which I therefore
hope you will continue, I shall take the Liberty to furnish you with a
brief Account of such a one as perhaps you have not seen in all your
Travels, unless it was your Fortune to touch upon some of the woody
Parts of the
African Continent, in your Voyage to or from
Grand Cairo. There have arose in this University (long since
you left us without saying any thing) several of these inferior
Hebdomadal Societies, as
the Punning Club,
the Witty
Club, and amongst the rest, the
Handsom Club; as a
Burlesque upon which, a certain merry Species, that seem to have come
into the World in Masquerade, for some Years last past have associated
themselves together, and assumed the name of the
Ugly Club:
This ill-favoured Fraternity consists of a President and twelve
Fellows; the Choice of which is not confin'd by Patent to any
particular Foundation (as
St. John's Men would have the World
believe, and have therefore erected a separate Society within
themselves) but Liberty is left to elect from any School in
Great
Britain, provided the Candidates be within the Rules of the Club,
as set forth in a Table entituled
The Act of Deformity. A
Clause or two of which I shall transmit to you.
- That no Person whatsoever shall be admitted without a visible
Quearity in his Aspect, or peculiar Cast of Countenance; of which the
President and Officers for the time being are to determine, and the
President to have the casting Voice.
- That a singular Regard be had, upon Examination, to the Gibbosity
of the Gentlemen that offer themselves, as Founders Kinsmen, or to the
Obliquity of their Figure, in what sort soever.
- That if the Quantity of any Man's Nose be eminently
miscalculated, whether as to Length or Breadth, he shall have a just
Pretence to be elected.
'
Lastly, That if there shall be two or more Competitors for the
same Vacancy,
cæteris paribus, he that has the thickest Skin to
have the Preference.
Every fresh Member, upon his first Night, is to entertain the Company
with a Dish of Codfish, and a Speech in praise of
Æsop2; whose
portraiture they have in full Proportion, or rather Disproportion,
over the Chimney; and their Design is, as soon as their Funds are
sufficient, to purchase the Heads of
Thersites, Duns Scotus, Scarron,
Hudibras, and the old Gentleman in
Oldham3, with all the
celebrated ill Faces of Antiquity, as Furniture for the Club Room.
As they have always been profess'd Admirers of the other Sex, so they
unanimously declare that they will give all possible Encouragement to
such as will take the Benefit of the Statute, tho' none yet have
appeared to do it.
The worthy President, who is their most devoted Champion, has lately
shown me two Copies of Verses composed by a Gentleman of his Society;
the first, a Congratulatory Ode inscrib'd to Mrs.
Touchwood, upon
the loss of her two Fore-teeth; the other, a Panegyrick upon Mrs.
Andirons left Shoulder. Mrs.
Vizard (he says) since the Small Pox,
is grown tolerably ugly, and a top Toast in the Club; but I never hear
him so lavish of his fine things, as upon old
Nell Trot, who
constantly officiates at their Table; her he even adores, and extolls
as the very Counterpart of Mother
Shipton; in short,
Nell (says
he) is one of the Extraordinary Works of Nature; but as for
Complexion, Shape, and Features, so valued by others, they are all
meer Outside and Symmetry, which is his Aversion. Give me leave to
add, that the President is a facetious, pleasant Gentleman, and never
more so, than when he has got (as he calls 'em) his dear Mummers about
him; and he often protests it does him good to meet a Fellow with a
right genuine Grimmace in his Air, (which is so agreeable in the
generality of the
French Nation;) and as an Instance of his
Sincerity in this particular, he gave me a sight of a List in his
Pocket-book of all of this Class, who for these five Years have fallen
under his Observation, with himself at the Head of 'em, and in the
Rear (as one of a promising and improving Aspect),
Sir, Your Obliged and Humble Servant,
Alexander Carbuncle.
[Sidenote: Oxford, March 12, 1710.]
R.
Abbé Paul Scarron, the burlesque writer, high in court
favour, was deformed from birth, and at the age of 27 lost the use of
all his limbs. In 1651, when 41 years old, Scarron married Frances
d'Aubigné, afterwards Madame de Maintenon; her age was then 16, and she
lived with Scarron until his death, which occurred when she was 25 years
old and left her very poor. Scarron's comparison of himself to the
letter Z is in his address 'To the Reader who has Never seen Me,'
prefixed to his
Relation Véritable de tout ce qui s'est passé en
l'autre Monde, au combat des Parques et des Poëtes, sur la Mort de
Voiture.
This was illustrated with a burlesque plate representing
himself as seen from the back of his chair, and surrounded by a
wondering and mocking world. His back, he said, was turned to the
public, because the convex of his back is more convenient than the
concave of his stomach for receiving the inscription of his name and
age.
The Life of Æsop
, ascribed to Planudes Maximus, a monk of
Constantinople in the fourteenth century, and usually prefixed to the
Fables, says that he was
'the most deformed of all men of his age, for
he had a pointed head, flat nostrils, a short neck, thick lips, was
black, pot-bellied, bow-legged, and hump-backed; perhaps even uglier
than Homer's Thersites.'
The description of Thersites in the second book of the
Iliad is thus translated by Professor Blackie:
The most
Ill-favoured wight was he, I ween, of all the Grecian host.
With hideous squint the railer leered: on one foot he was lame;
Forward before his narrow chest his hunching shoulders came;
Slanting and sharp his forehead rose, with shreds of meagre hair.
Controversies between the Scotists and Thomists, followers of the
teaching of Duns Scotus and Thomas Aquinas, caused Thomist perversion of
the name of Duns into its use as Dunce and tradition of the subtle
Doctor's extreme personal ugliness. Doctor Subtilis was translated The
Lath Doctor.
Scarron we have just spoken of. Hudibras's outward gifts are described
in Part I., Canto i., lines 240-296 of the poem.
His beard
In cut and dye so like a tile
A sudden view it would beguile:
The upper part thereof was whey;
The nether, orange mix'd with grey.
This hairy meteor, &c.
The 'old Gentleman in
Oldham
' is Loyola, as described in Oldham's
third satire on the Jesuits, when
Summon'd together, all th' officious band
The orders of their bedrid, chief attend.
Raised on his pillow he greets them, and, says Oldham,
Like Delphic Hag of old, by Fiend possest,
He swells, wild Frenzy heaves his panting breast,
His bristling hairs stick up, his eyeballs glow,
And from his mouth long strakes of drivel flow.
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 21, 1711 |
Addison |
Equitis quoque jam migravit ab aure voluptas
Omnis ad incertos oculos et gaudia vana.
Hor.

is my Design in this Paper to deliver down to Posterity a faithful
Account of the Italian Opera, and of the gradual Progress which it has
made upon the English Stage: For there is no Question but our great
Grand-children will be very curious to know the Reason why their
Fore-fathers used to sit together like an Audience of Foreigners in
their own Country, and to hear whole Plays acted before them in a Tongue
which they did not understand.
Arsinoe
was the first Opera that gave us a Taste of Italian
Musick.
great Success this Opera met with, produced some Attempts of
forming Pieces upon Italian Plans,
which
should give a more
natural and reasonable Entertainment than what can be met with in the
elaborate Trifles of that Nation.
alarm'd the Poetasters and
Fidlers of the Town, who were used to deal in a more ordinary Kind of
Ware; and therefore laid down an establish'd Rule, which is receiv'd as
such to this
Day
,
That nothing is capable of being well set to
Musick, that is not Nonsense.
Maxim was no sooner receiv'd, but we immediately fell to
translating the Italian Operas; and as there was no great Danger of
hurting the Sense of those extraordinary Pieces, our Authors would often
make Words of their own
which
were entirely foreign to the Meaning
of the Passages
they
pretended to translate; their chief Care
being to make the Numbers of the English Verse answer to those of the
Italian, that both of them might go to the same Tune. Thus the famous
Song in
Camilla
,
Barbara si t' intendo, &c.
Barbarous Woman, yes, I know your Meaning,
which expresses the Resentments of an angry Lover, was translated into
that English lamentation:
Frail are a Lovers Hopes, &c.
And it was pleasant enough to see the most refined Persons of the
British Nation dying away and languishing to Notes that were filled with
a Spirit of Rage and Indignation.
happen'd also very frequently,
where the Sense was rightly translated, the necessary Transposition of
Words
which
were drawn out of the Phrase of one Tongue into that
of another, made the Musick appear very absurd in one Tongue that was
very natural in the other. I remember an Italian verse that ran thus
Word for Word,
And turned my Rage, into Pity;
which the English for Rhime sake translated,
And into Pity turn'd my Rage.
By this Means the soft Notes that were adapted to Pity in the Italian,
fell upon the word Rage in the English; and the angry Sounds that were
turn'd to Rage in the Original, were made to express Pity in the
Translation.
oftentimes happen'd likewise, that the finest Notes in
the Air fell upon the most insignificant Words in the Sentence. I have
known the Word
And
pursu'd through the whole Gamut, have been
entertained with many a melodious
The
, and have heard the most
beautiful Graces Quavers and Divisions bestowed upon
Then, For,
and
From;
to the eternal Honour of our English Particles
.
The next Step to our Refinement, was the introducing of Italian Actors
into our Opera; who sung their Parts in their own Language, at the same
Time that our Countrymen perform'd theirs in our native Tongue. The King
or Hero of the Play generally spoke in Italian, and his Slaves answered
him in English: The Lover frequently made his Court, and gained the
Heart of his Princess in a Language which she did not understand. One
would have thought it very difficult to have carry'd on Dialogues after
this Manner, without an Interpreter between the Persons that convers'd
together; but this was the State of the English Stage for about three
Years.
At length the Audience grew tir'd of understanding Half the Opera, and
therefore to ease themselves Entirely of the Fatigue of Thinking, have
so order'd it at Present that the whole Opera is performed in an unknown
Tongue.
no longer understand the Language of our own Stage; insomuch
that I have often been afraid, when I have seen our Italian Performers
chattering in the Vehemence of Action, that they have been calling us
Names, and abusing us among themselves; but I hope, since we do put such
an entire Confidence in them, they will not talk against us before our
Faces, though they may do it with the same Safety as if it
were
`
behind our Backs. In the mean Time I cannot forbear thinking how
naturally an Historian, who writes Two or Three hundred Years hence, and
does not know the Taste of his wise Fore-fathers, will make the
following Reflection,
In the Beginning of the Eighteenth Century, the
Italian Tongue was so well understood in England, that Operas
were acted on the publick Stage in that Language.
One scarce knows how to be serious in the Confutation of an Absurdity
that shews itself at the first Sight. It does not want any great Measure
of Sense to see the Ridicule of this monstrous Practice; but what makes
it the more astonishing, it is not the Taste of the Rabble, but of
Persons of the greatest Politeness, which has establish'd it.
If the Italians have a Genius for Musick above the English, the English
have a Genius for other Performances of a much higher Nature, and
capable of giving the Mind a much nobler Entertainment.
one think
it was possible (at a Time when an Author lived that was able to write
the
Phædra
and
Hippolitus
for a People to be so
stupidly fond of the Italian Opera, as scarce to give a Third Days
Hearing to that admirable Tragedy? Musick is certainly a very agreeable
Entertainment, but if it would take the entire Possession of our Ears,
if it would make us incapable of hearing Sense, if it would exclude Arts
that have a much greater Tendency to the Refinement of humane Nature: I
must confess I would allow it no better Quarter than
Plato
has
done, who banishes it out of his Common-wealth.
At present, our Notions of Musick are so very uncertain, that we do not
know what it is we like, only, in general, we are transported with any
thing that is not English: so if it be of a foreign Growth, let it be
Italian, French, or High-Dutch, it is the same thing. In short, our
English Musick is quite rooted out, and nothing yet planted in its
stead.
When a Royal Palace is burnt to the Ground, every Man is at Liberty to
present his Plan for a new one; and tho' it be but indifferently put
together, it may furnish several Hints that may be of Use to a good
Architect. I shall take the same Liberty in a following Paper, of giving
my Opinion upon the Subject of Musick, which I shall lay down only in a
problematical Manner to be considered by those who are Masters in the
Art.
C.
Arsinoe
was produced at Drury Lane in 1705, with Mrs.
Tofts in the chief character, and her Italian rival, Margarita de
l'Epine, singing Italian songs before and after the Opera. The drama was
an Italian opera translated into English, and set to new music by Thomas
Clayton, formerly band master to William III.
and other numbers from time to time advertised
The Passion of Sappho,
and Feast of Alexander: Set to Musick by Mr. Thomas Clayton, as it is
performed at his house in York Buildings.
It was the same Clayton who
set to music Addison's unsuccessful opera of
Rosamond
, written as an
experiment in substituting homegrown literature for the fashionable
nonsense illustrated by Italian music. Thomas Clayton's music to
Rosamond
was described as 'a jargon of sounds.'
Camilla
, composed by
Marco Antonio Buononcini, and said to contain beautiful music, was
produced at Sir John Vanbrugh's Haymarket opera in 1705, and sung half
in English, half in Italian; Mrs. Tofts singing the part of the
Amazonian heroine in English, and Valentini that of the hero in Italian.
that
very day
that
which they
that
It was fifty years after this that Churchill wrote of
Mossop in the
Rosciad
,
In monosyllables his thunders roll,
He, she, it, and, we, ye, they, fright the soul.
was
The Tragedy of
Phædra and Hippolitus
, acted without
success in 1707, was the one play written by Mr. Edmund Smith, a
merchant's son who had been educated at Westminster School and Christ
Church, Oxford, and who had ended a dissolute life at the age of 42 (in
1710), very shortly before this paper was written. Addison's regard for
the play is warmed by friendship for the unhappy writer. He had, indeed,
written the
Prologue
to it, and struck therein also his note of war
against the follies of Italian Opera.
Had Valentini, musically coy,
Shunned Phædra's Arms, and scorn'd the puffer'd Joy,
It had not moved your Wonder to have seen
An Eunich fly from an enamour'd Queen;
How would it please, should she in English speak,
And could Hippolitus reply in Greek!
The
Epilogue
to this play was by Prior. Edmund Smith's relation to
Addison is shown by the fact that, in dedicating the printed edition of
his
Phædra
and
Hippolitus
to Lord Halifax, he speaks of Addison's lines
on the
Peace of Ryswick
as 'the best Latin Poem since the
Æneid
.'
Contents
|
Thursday, March 22, 1711 |
Steele |
Dii benefecerunt, inopis me quodque pusilli
Finxerunt animi, rarî et perpauca loquentis.
Hor.

Observing one Person behold another, who was an utter Stranger to him,
with a Cast of his Eye which, methought, expressed an Emotion of Heart
very different from what could be raised by an Object so agreeable as
the Gentleman he looked at, I began to consider, not without some secret
Sorrow, the Condition of an Envious Man. Some have fancied that Envy has
a certain Magical Force in it, and that the Eyes of the Envious have by
their Fascination blasted the Enjoyments of the Happy.
Francis
Bacon
says
, Some have been so curious as to remark the Times and
Seasons when the Stroke of an Envious Eye is most effectually
pernicious, and have observed that it has been when the Person envied
has been in any Circumstance of Glory and Triumph. At such a time the
Mind of the Prosperous Man goes, as it were, abroad, among things
without him, and is more exposed to the Malignity. But I shall not dwell
upon Speculations so abstracted as this, or repeat the many excellent
Things which one might collect out of Authors upon this miserable
Affection; but keeping in the road of common Life, consider the Envious
Man with relation to these three Heads, His Pains, His Reliefs, and His
Happiness.
The Envious Man is in Pain upon all Occasions which ought to give him
Pleasure. The Relish of his Life is inverted, and the Objects which
administer the highest Satisfaction to those who are exempt from this
Passion, give the quickest Pangs to Persons who are subject to it. All
the Perfections of their Fellow-Creatures are odious: Youth, Beauty,
Valour and Wisdom are Provocations of their Displeasure. What a Wretched
and Apostate State is this! To be offended with Excellence, and to hate
a Man because we Approve him! The Condition of the Envious Man is the
most Emphatically miserable; he is not only incapable of rejoicing in
another's Merit or Success, but lives in a World wherein all Mankind are
in a Plot against his Quiet, by studying their own Happiness and
Advantage.
Will. Prosper
is an honest Tale-bearer, he makes it
his business to join in Conversation with Envious Men. He points to such
an handsom Young Fellow, and whispers that he is secretly married to a
Great Fortune: When they doubt, he adds Circumstances to prove it; and
never fails to aggravate their Distress, by assuring 'em that to his
knowledge he has an Uncle will leave him some Thousands.
Will.
has many Arts of this kind to torture this sort of Temper, and delights
in it. When he finds them change colour, and say faintly They wish such
a Piece of News is true, he has the Malice to speak some good or other
of every Man of their Acquaintance.
The Reliefs of the Envious Man are those little Blemishes and
Imperfections, that discover themselves in an Illustrious Character. It
is matter of great Consolation to an Envious Person, when a Man of Known
Honour does a thing Unworthy himself: Or when any Action which was well
executed, upon better Information appears so alter'd in its
Circumstances, that the Fame of it is divided among many, instead of
being attributed to One. This is a secret Satisfaction to these
Malignants; for the Person whom they before could not but admire, they
fancy is nearer their own Condition as soon as his Merit is shared among
others. I remember some Years ago there came out an Excellent Poem,
without the Name of the Author. The little Wits, who were incapable of
Writing it, began to pull in Pieces the supposed Writer. When that would
not do, they took great Pains to suppress the Opinion that it was his.
That again failed. The next Refuge was to say it was overlook'd by one
Man, and many Pages wholly written by another. An honest Fellow, who
sate among a Cluster of them in debate on this Subject, cryed out,
Gentlemen, if you are sure none of you yourselves had an hand in it,
you are but where you were, whoever writ it.
But the most usual Succour
to the Envious, in cases of nameless Merit in this kind, is to keep the
Property, if possible, unfixed, and by that means to hinder the
Reputation of it from falling upon any particular Person. You see an
Envious Man clear up his Countenance, if in the Relation of any Man's
Great Happiness in one Point, you mention his Uneasiness in another.
When he hears such a one is very rich he turns Pale, but recovers when
you add that he has many Children. In a Word, the only sure Way to an
Envious Man's Favour, is not to deserve it.
But if we consider the Envious Man in Delight, it is like reading the
Seat of a Giant in a Romance; the Magnificence of his House consists in
the many Limbs of Men whom he has slain. If any who promised themselves
Success in any Uncommon Undertaking miscarry in the Attempt, or he that
aimed at what would have been Useful and Laudable, meets with Contempt
and Derision, the Envious Man, under the Colour of hating Vainglory, can
smile with an inward Wantonness of Heart at the ill Effect it may have
upon an honest Ambition for the future.
Having throughly considered the Nature of this Passion, I have made it
my Study how to avoid the Envy that may acrue to me from these my
Speculations; and if I am not mistaken in my self, I think I have a
Genius to escape it.
hearing in a Coffee-house one of my Papers
commended, I immediately apprehended the Envy that would spring from
that Applause; and therefore gave a Description of my Face the next Day
; being resolved as I grow in Reputation for Wit, to resign my
Pretensions to Beauty. This, I hope, may give some Ease to those unhappy
Gentlemen, who do me the Honour to torment themselves upon the Account
of this my Paper. As their Case is very deplorable, and deserves
Compassion, I shall sometimes be dull, in Pity to them, and will from
time to time administer Consolations to them by further Discoveries of
my Person. In the meanwhile, if any one says the
Spectator
has Wit, it
may be some Relief to them, to think that he does not show it in
Company. And if any one praises his Morality they may comfort themselves
by considering that his Face is none of the longest.
R.
We see likewise, the Scripture calleth Envy an Evil Eye: And the
Astrologers call the evil influences of the stars, Evil Aspects; so
that still there seemeth to be acknowledged, in the act of envy, an
ejaculation or irradiation of the eye. Nay some have been so curious
as to note that the times when the stroke or percussion of an envious
eye doth most hurt, are, when the party envied is beheld in glory or
triumph; for that sets an edge upon Envy; And besides, at such times,
the spirits of the persons envied do come forth most into the outward
parts, and so meet the blow.
Bacon's Essays: IX Of Envy
.
In
.
Contents
|
Friday, March 23, 1711 |
Steele |
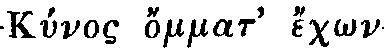

Hom.
Among the other hardy Undertakings which I have proposed to my self,
that of the Correction of Impudence is what I have very much at Heart.
This in a particular Manner is my Province as
Spectator
; for it is
generally an Offence committed by the Eyes, and that against such as the
Offenders would perhaps never have an Opportunity of injuring any other
Way. The following Letter is a Complaint of a Young Lady, who sets forth
a Trespass of this Kind with that Command of herself as befits Beauty
and Innocence, and yet with so much Spirit as sufficiently expresses her
Indignation. The whole Transaction is performed with the Eyes; and the
Crime is no less than employing them in such a Manner, as to divert the
Eyes of others from the best use they can make of them, even looking up
to Heaven.
'Sir,
There never was (I believe) an acceptable Man, but had some awkward
Imitators. Ever since the Spectator appear'd, have I remarked a kind
of Men, whom I choose to call Starers, that without any Regard
to Time, Place, or Modesty, disturb a large Company with their
impertinent Eyes. Spectators make up a proper Assembly for a
Puppet-Show or a Bear-Garden; but devout Supplicants and attentive
Hearers, are the Audience one ought to expect in Churches. I am, Sir,
Member of a small pious congregation near one of the North Gates of
this City; much the greater Part of us indeed are Females, and used to
behave our selves in a regular attentive Manner, till very lately one
whole Isle has been disturbed with one of these monstrous
Starers: He's the Head taller than any one in the Church; but
for the greater Advantage of exposing himself, stands upon a Hassock,
and commands the whole Congregation, to the great Annoyance of the
devoutest part of the Auditory; for what with Blushing, Confusion, and
Vexation, we can neither mind the Prayers nor Sermon. Your
Animadversion upon this Insolence would be a great favour to,
Sir,
Your most humble servant,
S. C.
I have frequently seen of this Sort of Fellows; and do not think there
can be a greater Aggravation of an Offence, than that it is committed
where the Criminal is protected by the Sacredness of the Place which he
violates. Many Reflections of this Sort might be very justly made upon
this Kind of Behaviour, but a
Starer
is not usually a Person to
be convinced by the Reason of the thing; and a Fellow that is capable of
showing an impudent Front before a whole Congregation, and can bear
being a publick Spectacle, is not so easily rebuked as to amend by
Admonitions. If therefore my Correspondent does not inform me, that
within Seven Days after this Date the Barbarian does not at least stand
upon his own Legs only, without an Eminence, my friend
Will. Prosper
has
promised to take an Hassock opposite to him, and stare against him in
Defence of the Ladies. I have given him Directions, according to the
most exact Rules of Opticks, to place himself in such a Manner that he
shall meet his Eyes wherever he throws them: I have Hopes that when
Will
. confronts him, and all the Ladies, in whose Behalf he engages him,
cast kind Looks and Wishes of Success at their Champion, he will have
some Shame, and feel a little of the Pain he has so often put others to,
of being out of Countenance.
It has indeed been Time out of Mind generally remarked, and as often
lamented, that this Family of
Starers
have infested publick
Assemblies: And I know no other Way to obviate so great an Evil, except,
in the Case of fixing their Eyes upon Women, some Male Friend will take
the Part of such as are under the Oppression of Impudence, and encounter
the Eyes of the
Starers
wherever they meet them. While we suffer
our Women to be thus impudently attacked, they have no Defence, but in
the End to cast yielding Glances at the
Starers
: And in this
Case, a Man who has no Sense of Shame has the same Advantage over his
Mistress, as he who has no Regard for his own Life has over his
Adversary. While the Generality of the World are fetter'd by Rules, and
move by proper and just Methods, he who has no Respect to any of them,
carries away the Reward due to that Propriety of Behaviour, with no
other Merit but that of having neglected it.
I take an impudent Fellow to be a sort of Out-law in Good-Breeding, and
therefore what is said of him no Nation or Person can be concerned for:
For this Reason one may be free upon him. I have put my self to great
Pains in considering this prevailing Quality which we call Impudence,
and have taken Notice that it exerts it self in a different Manner,
according to the different Soils wherein such Subjects of these
Dominions as are Masters of it were born. Impudence in an Englishman is
sullen and insolent, in a Scotchman it is untractable and rapacious, in
an Irishman absurd and fawning: As the Course of the World now runs, the
impudent Englishman behaves like a surly Landlord, the Scot, like an
ill-received Guest, and the Irishman, like a Stranger who knows he is
not welcome. There is seldom anything entertaining either in the
Impudence of a South or North Briton; but that of an Irishman is always
comick. A true and genuine Impudence is ever the Effect of Ignorance,
without the least Sense of it. The best and most successful
Starers
now in this Town are of that Nation: They have usually the Advantage of
the Stature mentioned in the above Letter of my Correspondent, and
generally take their Stands in the Eye of Women of Fortune; insomuch
that I have known one of them, three Months after he came from Plough,
with a tolerable good Air lead out a Woman from a Play, which one of our
own Breed, after four years at
Oxford
and two at the
Temple
, would
have been afraid to look at.
I cannot tell how to account for it, but these People have usually the
Preference to our own Fools, in the Opinion of the sillier Part of
Womankind. Perhaps it is that an English Coxcomb is seldom so obsequious
as an Irish one; and when the Design of pleasing is visible, an
Absurdity in the Way toward it is easily forgiven.
But those who are downright impudent, and go on without Reflection that
they are such, are more to be tolerated, than a Set of Fellows among us
who profess Impudence with an Air of Humour, and think to carry off the
most inexcusable of all Faults in the World, with no other Apology than
saying in a gay Tone,
I put an impudent Face upon the Matter
. No, no
Man shall be allowed the Advantages of Impudence, who is conscious that
he is such: If he knows he is impudent, he may as well be otherwise; and
it shall be expected that he blush, when he sees he makes another do it:
For nothing can attone for the want of Modesty, without which Beauty is
ungraceful, and Wit detestable.
R.
Contents
|
Saturday, March 24, 17111 |
Addison |
Locus est et phiribus Umbris.
Hor.

I am sometimes very much troubled, when I reflect upon the three great
Professions of Divinity, Law, and Physick; how they are each of them
over-burdened with Practitioners, and filled with Multitudes of
Ingenious Gentlemen that starve one another.
We may divide the Clergy into Generals, Field-Officers, and Subalterns.
Among the first we may reckon Bishops, Deans, and Arch-Deacons. Among
the second are Doctors of Divinity, Prebendaries, and all that wear
Scarfs. The rest are comprehended under the Subalterns. As for the first
Class, our Constitution preserves it from any Redundancy of Incumbents,
notwithstanding Competitors are numberless. Upon a strict Calculation,
it is found that there has been a great Exceeding of late Years in the
Second Division, several Brevets having been granted for the converting
of Subalterns into Scarf-Officers; insomuch that within my Memory the
price of Lute-string is raised above two Pence in a Yard. As for the
Subalterns, they are not to be numbred. Should our Clergy once enter
into the corrupt Practice of the Laity, by the splitting of their
Free-holds, they would be able to carry most of the Elections in
England
.
Body of the Law is no less encumbered with superfluous Members, that
are like
Virgil's
Army, which he tells us was so crouded
,
many of them had not Room to use their Weapons. This prodigious Society
of Men may be divided into the Litigious and Peaceable. Under the first
are comprehended all those who are carried down in Coach-fulls to
Westminster-Hall
every Morning in Term-time.
Martial's
description
of this Species of Lawyers is full of Humour:
Iras et verba locant.
Men that hire out their Words and Anger; that are more or less
passionate according as they are paid for it, and allow their Client a
quantity of Wrath proportionable to the Fee which they receive from him.
I must, however, observe to the Reader, that above three Parts of those
whom I reckon among the Litigious, are such as are only quarrelsome in
their Hearts, and have no Opportunity of showing their Passion at the
Bar. Nevertheless, as they do not know what Strifes may arise, they
appear at the Hall every Day, that they may show themselves in a
Readiness to enter the Lists, whenever there shall be Occasion for them.
The Peaceable Lawyers are, in the first place, many of the Benchers of
the several Inns of Court, who seem to be the Dignitaries of the Law,
and are endowed with those Qualifications of Mind that accomplish a Man
rather for a Ruler, than a Pleader.
Men live peaceably in their
Habitations, Eating once a Day, and Dancing once a Year
, for the
Honour of their Respective Societies.
Another numberless Branch of Peaceable Lawyers, are those young Men who
being placed at the Inns of Court in order to study the Laws of their
Country, frequent the Play-House more than
Westminster-Hall
, and are
seen in all publick Assemblies, except in a Court of Justice. I shall
say nothing of those Silent and Busie Multitudes that are employed
within Doors in the drawing up of Writings and Conveyances; nor of those
greater Numbers that palliate their want of Business with a Pretence to
such Chamber-Practice.
If, in the third place, we look into the Profession of Physick, we shall
find a most formidable Body of Men: The Sight of them is enough to make
a Man serious, for we may lay it down as a Maxim, that When a Nation
abounds in Physicians, it grows thin of People.
William Temple
is
very much puzzled to find a Reason why the Northern Hive, as he calls
it, does not send out such prodigious Swarms, and over-run the World
with
Goths
and
Vandals
, as it did formerly
; but had that
Excellent Author observed that there were no Students in Physick among
the Subjects of
Thor
and
Woden
, and that this Science very much
flourishes in the North at present, he might have found a better
Solution for this Difficulty, than any of those he has made use of. This
Body of Men, in our own Country, may be described like the
British
Army in
Cæsar's
time: Some of them slay in Chariots, and some on Foot.
If the Infantry do less Execution than the Charioteers, it is, because
they cannot be carried so soon into all Quarters of the Town, and
dispatch so much Business in so short a Time. Besides this Body of
Regular Troops, there are Stragglers, who, without being duly listed and
enrolled, do infinite Mischief to those who are so unlucky as to fall
into their Hands.
There are, besides the above-mentioned, innumerable Retainers to
Physick, who, for want of other Patients, amuse themselves with the
stifling of Cats in an Air Pump, cutting up Dogs alive, or impaling of
Insects upon the point of a Needle for Microscopical Observations;
besides those that are employed in the gathering of Weeds, and the Chase
of Butterflies: Not to mention the Cockle-shell-Merchants and
Spider-catchers.
When I consider how each of these Professions are crouded with
Multitudes that seek their Livelihood in them, and how many Men of Merit
there are in each of them, who may be rather said to be of the Science,
than the Profession; I very much wonder at the Humour of Parents, who
will not rather chuse to place their Sons in a way of Life where an
honest Industry cannot but thrive, than in Stations where the greatest
Probity, Learning and Good Sense may miscarry. How many
Men are Country-Curates, that might have made themselves Aldermen of
London
by a right Improvement of a smaller Sum of Mony than what is
usually laid out upon a learned Education? A sober, frugal Person, of
slender Parts and a slow Apprehension, might have thrived in Trade, tho'
he starves upon Physick; as a Man would be well enough pleased to buy
Silks of one, whom he would not venture to feel his Pulse.
Vagellius
is careful, studious and obliging, but withal a little thick-skull'd; he
has not a single Client, but might have had abundance of Customers. The
Misfortune is, that Parents take a Liking to a particular Profession,
and therefore desire their Sons may be of it. Whereas, in so great an
Affair of Life, they should consider the Genius and Abilities of their
Children, more than their own Inclinations.
It is the great Advantage of a trading Nation, that there are very few
in it so dull and heavy, who may not be placed in Stations of Life which
may give them an Opportunity of making their Fortunes. A well-regulated
Commerce is not, like Law, Physick or Divinity, to be overstocked with
Hands; but, on the contrary, flourishes by Multitudes, and gives
Employment to all its Professors. Fleets of Merchantmen are so many
Squadrons of floating Shops, that vend our Wares and Manufactures in all
the Markets of the World, and find out Chapmen under both the Tropicks.
C.
At this time, and until the establishment of New Style,
from 1752, the legal year began in England on the 25th of March, while
legally in Scotland, and by common usage throughout the whole kingdom,
the customary year began on the 1st of January. The
Spectator
dated its years, according to custom, from the first of January; and so
wrote its first date March 1, 1711. But we have seen letters in it dated
in a way often adopted to avoid confusion (1710-11) which gave both the
legal and the customary reckoning. March 24 being the last day of the
legal year 1710, in the following papers, until December 31, the year is
1711 both by law and custom. Then again until March 24, while usage will
be recognizing a new year, 1712, it will be still for England (but not
for Scotland) 1711 to the lawyers. The reform initiated by Pope Gregory
XIII in 1582, and not accepted for England and Ireland until 1751, had
been adopted by Scotland from the 1st of January, 1600.
[This reform was necessary to make up for the inadequate shortness of the previous calendar (relative to the solar year), which had resulted in some months' discrepancy by the eighteenth century.]
that
In Dugdale's
Origines Juridiciales
we read how in the
Middle Temple, on All Saints' Day, when the judges and serjeants who had
belonged to the Inn were feasted,
'the music being begun, the Master of
the Revels was twice called. At the second call, the Reader with the
white staff advanced, and began to lead the measures, followed by the
barristers and students in order; and when one measure was ended, the
Reader at the cupboard called for another.'
See Sir W. Temple's
Essay on Heroic Virtue
, Section 4.
'This part of Scythia, in its whole Northern extent, I take to have been
the vast Hive out of which issued so many mighty swarms of barbarous
nations,' &c. And again, 'Each of these countries was like a mighty
hive, which, by the vigour of propagation and health of climate, growing
too full of people, threw out some new swarm at certain periods of time,
that took wing and sought out some new abode, expelling or subduing the
old inhabitants, and seating themselves in their rooms, if they liked
the conditions of place and commodities of life they met with; if not,
going on till they found some other more agreeable to their present
humours and dispositions.' He attributes their successes and their rapid
propagation to the greater vigour of life in the northern climates; and
the only reason he gives for the absence of like effects during the
continued presence of like causes is, that Christianity abated their
enthusiasm and allayed 'the restless humour of perpetual wars and
actions.'
Contents
|
Monday, March 26, 1711 |
Steele |
Quodcunque ostendis mihi sic incredulus odi.
Hor.

The word
Spectator
being most usually understood as one of the
Audience at Publick Representations in our Theatres, I seldom fail of
many Letters relating to Plays and Operas. But, indeed, there are such
monstrous things done in both, that if one had not been an Eye-witness
of them, one could not believe that such Matters had really been
exhibited. There is very little which concerns human Life, or is a
Picture of Nature, that is regarded by the greater Part of the Company.
The Understanding is dismissed from our Entertainments. Our Mirth is the
Laughter of Fools, and our Admiration the Wonder of Idiots; else such
improbable, monstrous, and incoherent Dreams could not go off as they
do, not only without the utmost Scorn and Contempt, but even with the
loudest Applause and Approbation.
the Letters of my Correspondents
will represent this Affair in a more lively Manner than any Discourse of
my own; I
shall therefore
give them to my Reader with only this
Preparation, that they all come from Players,
and that the business of
Playing is now so managed that you are not to be surprised when I say
one or two of
them
are rational, others sensitive and vegetative
Actors, and others wholly inanimate. I shall not place these as I have
named them, but as they have Precedence in the Opinion of their
Audiences.
"Mr.
Spectator,
Your having been so humble as to take Notice of the Epistles of other
Animals, emboldens me, who am the wild Boar that was killed by Mrs.
Tofts3, to represent to you, That I think I was hardly used
in not having the Part of the Lion in
Hydaspes given to me. It
would have been but a natural Step for me to have personated that
noble Creature, after having behaved my self to Satisfaction in the
Part above-mention'd: But that of a Lion, is too great a Character for
one that never trod the Stage before but upon two Legs. As for the
little Resistance which I made, I hope it may be excused, when it is
considered that the Dart was thrown at me by so fair an Hand. I must
confess I had but just put on my Brutality; and
Camilla's
charms were such, that b-holding her erect Mien, hearing her charming
Voice, and astonished with her graceful Motion, I could not keep up to
my assumed Fierceness, but died like a Man.
I am Sir,
Your most humble Servan.,
Thomas Prone."
Mr. Spectator,
This is to let you understand, that the Play-House is a Representation
of the World in nothing so much as in this Particular, That no one
rises in it according to his Merit.
I have acted several Parts of
Household-stuff with great Applause for many Years: I am one of the
Men in the Hangings in the
Emperour of the Moon4; I have
twice performed the third Chair in an English Opera; and have
rehearsed the Pump in the
Fortune-Hunters5. I am now grown
old, and hope you will recommend me so effectually, as that I may say
something before I go off the Stage: In which you will do a great Act
of Charity to
Your most humble servant,
William Serene."
"
Mr. Spectator,
Understanding that Mr.
Serene has writ to you, and desired to
be raised from dumb and still Parts; I desire, if you give him Motion
or Speech, that you would advance me in my Way, and let me keep on in
what I humbly presume I am a Master, to wit, in representing human and
still Life together. I have several times acted one of the finest
Flower-pots in the same Opera wherein Mr.
Serene is a Chair;
therefore, upon his promotion, request that I may succeed him in the
Hangings, with my Hand in the Orange-Trees.
Your humble servant,
Ralph Simple."
Drury Lane, March 24, 1710-11.
Sir,
I saw your Friend the Templar this Evening in the Pit, and thought he
looked very little pleased with the Representation of the mad Scene of
the
Pilgrim. I wish, Sir, you would do us the Favour to
animadvert frequently upon the false Taste the Town is in, with
Relation to Plays as well as Operas. It certainly requires a Degree of
Understanding to play justly; but such is our Condition, that we are
to suspend our Reason to perform our Parts. As to Scenes of Madness,
you know, Sir, there are noble Instances of this Kind in
Shakespear; but then it is the Disturbance of a noble Mind,
from generous and humane Resentments: It is like that Grief which we
have for the decease of our Friends: It is no Diminution, but a
Recommendation of humane Nature, that in such Incidents Passion gets
the better of Reason; and all we can think to comfort ourselves, is
impotent against half what we feel. I will not mention that we had an
Idiot in the Scene, and all the Sense it is represented to have, is
that of Lust. As for my self, who have long taken Pains in personating
the Passions, I have to Night acted only an Appetite: The part I
play'd is Thirst, but it is represented as written rather by a Drayman
than a Poet.
I come in with a Tub about me, that Tub hung with
Quart-pots; with a full Gallon at my Mouth
6. I
am ashamed to tell
you that I pleased very much, and this was introduced as a Madness;
but sure it was not humane Madness, for a Mule or an
ass7 may
have been as dry as ever I was in my Life.
I am, Sir, Your most obedient And humble servant."
"From the
Savoy in the
Strand.
Mr.
Spectator,
If you can read it with dry Eyes, I give you this trouble to acquaint
you, that I am the unfortunate King
Latinus, and believe I am the
first Prince that dated from this Palace since
John of
Gaunt. Such
is the Uncertainty of all human Greatness, that I who lately never
moved without a Guard, am now pressed as a common Soldier, and am to
sail with the first fair Wind against my Brother
Lewis of
France.
It is a very hard thing to put off a Character which one has appeared
in with Applause: This I experienced since the Loss of my Diadem; for,
upon quarrelling with another Recruit, I spoke my Indignation out of
my Part in
recitativo:
...
Most audacious Slave,
Dar'st thou an angry Monarch's Fury brave?
8
The Words were no sooner out of my Mouth, when a Serjeant knock'd me
down, and ask'd me if I had a Mind to Mutiny, in talking things no
Body understood. You see, Sir, my unhappy Circumstances; and if by
your Mediation you can procure a Subsidy for a Prince (who never
failed to make all that beheld him merry at his Appearance) you will
merit the Thanks of
Your friend,
The King of
Latium."
therefore shall
whom
In the opera of Camilla:
| Camilla. |
That Dorinda's my Name. |
| Linco. |
Well, I know't, I'll take care. |
| Camilla. |
And my Life scarce of late — |
| Linco. |
You need not repeat. |
| Prenesto. |
Help me! oh help me! |
|
A wild Boar struck by Prenesto. |
| Huntsman. |
Let's try to assist him. |
| Linco. |
Ye Gods, what Alarm! |
| Huntsman. |
Quick run to his aid. |
|
Enter Prenesto: The Boar pursuing him. |
| Prenesto. |
O Heav'ns! who defends me? |
| Camilla. |
My Arm. |
|
She throws a Dart, and kills the Boar. |
| Linco. |
Dorinda of nothing afraid,
She's sprightly and gay, a valiant Maid,
And as bright as the Day. |
| Camilla. |
Take Courage, Hunter, the Savage is dead. |
Katherine Tofts, the daughter of a person in the family of Bishop
Burnet, had great natural charms of voice, person, and manner. Playing
with Nicolini, singing English to his Italian, she was the first of our
prime donne in
Italian Opera. Mrs. Tofts had made much money when
in 1709 she quitted the stage with disordered intellect; her voice being
then unbroken, and her beauty in the height of its bloom. Having
recovered health, she married Mr. Joseph Smith, a rich patron of arts
and collector of books and engravings, with whom she went to Venice,
when he was sent thither as English Consul. Her madness afterwards
returned, she lived, therefore, says Sir J. Hawkins,
'sequestered from the world in a remote part of the house, and had a
large garden to range in, in which she would frequently walk, singing
and giving way to that innocent frenzy which had seized her in the
earlier part of her life.'
She identified herself with the great princesses whose loves and sorrows
she had represented in her youth, and died about the year 1760.
The
Emperor of the Moon
is a farce, from the French,
by Mrs. Aphra Behn, first acted in London in 1687. It was originally
Italian, and had run 80 nights in Paris as
Harlequin I'Empereur dans
le Monde de la Lune
. In Act II. sc. 3,
'The Front of the Scene is only a Curtain or Hangings to be drawn up
at Pleasure.'
Various gay masqueraders, interrupted by return of the Doctor, are
carried by Scaramouch behind the curtain. The Doctor enters in wrath,
vowing he has heard fiddles. Presently the curtain is drawn up and
discovers where Scaramouch has
'plac'd them all in the Hanging in which they make the Figures, where
they stand without Motion in Postures.'
Scaramouch professes that the noise was made by putting up this piece of
Tapestry,
'the best in Italy for the Rareness of the Figures, sir.'
While the Doctor is admiring the new tapestry, said to have been sent
him as a gift, Harlequin, who is
'placed on a Tree in the Hangings, hits him on the 'Head with his
Truncheon.'
The place of a particular figure in the picture, with a hand on a tree,
is that supposed to be aspired to by the
Spectator's
next
correspondent.
'The Fortune Hunters, or Two Fools Well Met,'
a
Comedy first produced in 1685, was the only work of James Carlile, a
player who quitted the stage to serve King William III in the Irish
Wars, and was killed at the battle of Aghrim. The crowning joke of the
second Act of
the Fortune Hunters
is the return at night of Mr.
Spruce, an Exchange man, drunk and musical, to the garden-door of his
house, when Mrs. Spruce is just taking leave of young Wealthy. Wealthy
hides behind the pump. The drunken husband, who has been in a gutter,
goes to the pump to clean himself, and seizes a man's arm instead of a
pump-handle. He works it as a pump-handle, and complains that ' the
pump's dry;' upon which Young Wealthy empties a bottle of orange-flower
water into his face.
In the third act of Fletcher's comedy of the
Pilgrim
,
Pedro, the Pilgrim, a noble gentleman, has shown to him the interior of
a Spanish mad-house, and discovers in it his mistress Alinda, who,
disguised in a boy's dress, was found in the town the night before a
little crazed, distracted, and so sent thither. The scene here shows
various shapes of madness,
Some of pity
That it would make ye melt to see their passions,
And some as light again.
One is an English madman who cries,
Give me some drink,
Fill me a thousand pots and froth 'em, froth 'em!
Upon which a keeper says:
Those English are so malt-mad, there's no meddling with 'em.
When they've a fruitful year of barley there,
All the whole Island's thus.
We read in the text how they had produced on the stage of Drury Lane
that madman on the previous Saturday night; this Essay appearing on the
breakfast tables upon Monday morning.
horse
King Latinus to Turnus in Act II., sc. 10, of the opera of
Camilla
. Posterity will never know in whose person 'Latinus, king of
Latium and of the Volscians,' abdicated his crown at the opera to take
the Queen of England's shilling. It is the only character to which, in
the opera book, no name of a performer is attached. It is a part of
sixty or seventy lines in tyrant's vein; but all recitative. The King of
Latium was not once called upon for a song.
Contents
For the Good of the Publick.
Within two Doors of the Masquerade lives an eminent Italian Chirurgeon,
arriv'd from the Carnaval at Venice,
of great Experience in private Cures.
Accommodations are provided, and Persons admitted in their masquing Habits.
He has cur'd since his coming thither, in less than a Fortnight,
Four Scaramouches,
a Mountebank Doctor,
Two Turkish Bassas,
Three Nuns,
and a Morris Dancer.
"Venienti occurrite morbo."
N. B. Any Person may agree by the Great,
and be kept in
Repair by the Year.
The Doctor draws Teeth
without pulling
off your Mask.
R.
|
Tuesday, March 27, 17111 |
Addison |
Savit atrox Volscens, nec teli conspicit usquam
Auctorem nec quo se ardens immittere possit.
Vir.

There is nothing that more betrays a base, ungenerous Spirit, than the
giving of secret Stabs to a Man's Reputation. Lampoons and Satyrs, that
are written with Wit and Spirit, are like poison'd Darts, which not only
inflict a Wound, but make it incurable. For this Reason I am very much
troubled when I see the Talents of Humour and Ridicule in the Possession
of an ill-natured Man. There cannot be a greater Gratification to a
barbarous and inhuman Wit, than to stir up Sorrow in the Heart of a
private Person, to raise Uneasiness among near Relations, and to expose
whole Families to Derision, at the same time that he remains unseen and
undiscovered. If, besides the Accomplishments of being Witty and
Ill-natured, a Man is vicious into the bargain, he is one of the most
mischievous Creatures that can enter into a Civil Society. His Satyr
will then chiefly fall upon those who ought to be the most exempt from
it. Virtue, Merit, and every thing that is Praise-worthy, will be made
the Subject of Ridicule and Buffoonry. It is impossible to enumerate the
Evils which arise from these Arrows that fly in the dark, and I know no
other Excuse that is or can be made for them, than that the Wounds they
give are only Imaginary, and produce nothing more than a secret Shame or
Sorrow in the Mind of the suffering Person. It must indeed be confess'd,
that a Lampoon or a Satyr do not carry in them Robbery or Murder; but at
the same time, how many are there that would not rather lose a
considerable Sum of Mony, or even Life it self, than be set up as a Mark
of Infamy and Derision? And in this Case a Man should consider, that an
Injury is not to be measured by the Notions of him that gives, but of
him that receives it.
Those who can put the best Countenance upon the Outrages of this nature
which are offered them, are not without their secret Anguish. I have
often observed a Passage in
Socrates's
Behaviour at his Death, in
a Light wherein none of the Criticks have considered it. That excellent
Man, entertaining his Friends a little before he drank the Bowl of
Poison with a Discourse on the Immortality of the Soul, at his entering
upon it says, that he does not believe any the most Comick Genius can
censure him for talking upon such a Subject at such a Time.
passage, I think, evidently glances upon
Aristophanes
, who writ a
Comedy on purpose to ridicule the Discourses of that Divine Philosopher
: It has been observed by many Writers, that
Socrates
was so
little moved at this piece of Buffoonry, that he was several times
present at its being acted upon the Stage, and never expressed the least
Resentment of it. But, with Submission, I think the Remark I have here
made shows us, that this unworthy Treatment made an impression upon his
Mind, though he had been too wise to discover it.
Julius Cæsar
was Lampoon'd by
Catullus
, he invited
him to a Supper, and treated him with such a generous Civility, that he
made the Poet his friend ever after
. Cardinal
Mazarine
gave
the same kind of Treatment to the learned
Quillet
, who had
reflected upon his Eminence in a famous Latin Poem. The Cardinal sent
for him, and, after some kind Expostulations upon what he had written,
assured him of his Esteem, and dismissed him with a Promise of the next
good Abby that should fall, which he accordingly conferr'd upon him in a
few Months after.
had so good an Effect upon the Author, that he
dedicated the second Edition of his Book to the Cardinal, after having
expunged the Passages which had given him offence
.
Sextus Quintus
was not of so generous and forgiving a Temper. Upon his
being made Pope, the statue of
Pasquin
was one Night dressed in a very
dirty Shirt, with an Excuse written under it, that he was forced to wear
foul Linnen, because his Laundress was made a Princess. This was a
Reflection upon the Pope's Sister, who, before the Promotion of her
Brother, was in those mean Circumstances that
Pasquin
represented her.
As this Pasquinade made a great noise in
Rome
, the Pope offered a
Considerable Sum of Mony to any Person that should discover the Author
of it.
Author, relying upon his Holiness's Generosity, as also on
some private Overtures which he had received from him, made the
Discovery himself; upon which the Pope gave him the Reward he had
promised, but at the same time, to disable the Satyrist for the future,
ordered his Tongue to be cut out, and both his Hands to be chopped off
.
Aretine
is too trite an instance. Everyone knows that all the Kings of Europe were his tributaries. Nay, there
is a Letter of his extant, in which he makes his Boasts that he had laid
the Sophi of
Persia
under Contribution.
Though in the various Examples which I have here drawn together, these
several great Men behaved themselves very differently towards the Wits
of the Age who had reproached them, they all of them plainly showed that
they were very sensible of their Reproaches, and consequently that they
received them as very great Injuries. For my own part, I would never
trust a Man that I thought was capable of giving these secret Wounds,
and cannot but think that he would hurt the Person, whose Reputation he
thus assaults, in his Body or in his Fortune, could he do it with the
same Security. There is indeed something very barbarous and inhuman in
the ordinary Scriblers of Lampoons. An Innocent young Lady shall be
exposed, for an unhappy Feature. A Father of a Family turn'd to
Ridicule, for some domestick Calamity. A Wife be made uneasy all her
Life, for a misinterpreted Word or Action. Nay, a good, a temperate, and
a just Man, shall be put out of Countenance, by the Representation of
those Qualities that should do him Honour. So pernicious a thing is Wit,
when it is not tempered with Virtue and Humanity.
I have indeed heard of heedless, inconsiderate Writers, that without any
Malice have sacrificed the Reputation of their Friends and Acquaintance
to a certain Levity of Temper, and a silly Ambition of distinguishing
themselves by a Spirit of Raillery and Satyr: As if it were not
infinitely more honourable to be a Good-natured Man than a Wit. Where
there is this little petulant Humour in an Author, he is often very
mischievous without designing to be so. For which Reason I always lay it
down as a Rule, that an indiscreet Man is more hurtful than an
ill-natured one; for as the former will only attack his Enemies, and
those he wishes ill to, the other injures indifferently both Friends and
Foes.
cannot forbear, on this occasion, transcribing a Fable out of
Sir
Roger l'Estrange
, which accidentally lies before me.
'A company of Waggish Boys were watching of Frogs at the side of a
Pond, and still as any of 'em put up their Heads, they'd be pelting
them down again with Stones. Children (says one of the Frogs),
you never consider that though this may be Play to you, 'tis Death
to us.'
this Week is in a manner set apart and dedicated to Serious Thoughts
, I shall indulge my self in such Speculations as may not be
altogether unsuitable to the Season; and in the mean time, as the
settling in our selves a Charitable Frame of Mind is a Work very proper
for the Time, I have in this Paper endeavoured to expose that particular
Breach of Charity which has been generally over-looked by Divines,
because they are but few who can be guilty of it.
C.
At the top of this paper in a 12mo copy of the
Spectator
,
published in 1712, and annotated by a contemporary Spanish merchant, is
written, 'The character of Dr Swift.' This proves that the writer of the
note had an ill opinion of Dr Swift and a weak sense of the purport of
what he read. Swift, of course, understood what he read. At this time he
was fretting under the sense of a chill in friendship between himself
and Addison, but was enjoying his
Spectators
. A week before this
date, on the 16th of March, he wrote,
'Have you seen the Spectators yet, a paper that comes out every
day? It is written by Mr. Steele, who seems to have gathered new life
and have a new fund of wit; it is in the same nature as his
Tatlers, and they have all of them had something pretty. I
believe Addison and he club.'
Then he adds a complaint of the chill in their friendship. A month after
the date of this paper Swift wrote in his journal,
'The Spectator is written by Steele with Addison's help; 'tis
often very pretty.'
Later in the year, in June and September, he records dinner and supper
with his friends of old time, and says of Addison,
'I yet know no man half so agreeable to me as he is.'
Plato's Phædon
, § 40. The ridicule of Socrates in
The Clouds
of Aristophanes includes the accusation that he
displaced Zeus and put in his place Dinos, — Rotation. When Socrates, at
the point of death, assents to the request that he should show grounds
for his faith
'that when the man is dead, the soul exists and retains thought and
power,' Plato represents him as suggesting: Not the sharpest censor
'could say that in now discussing such matters, I am dealing with what
does not concern me.'
The bitter attack upon Cæsar and his parasite Mamurra was not withdrawn,
but remains to us as No. 29 of the
Poems
of Catullus. The doubtful
authority for Cæsar's answer to it is the statement in the
Life of Julius
Cæsar
by Suetonius that, on the day of its appearance, Catullus apologized
and was invited to supper; Cæsar abiding also by his old familiar friendship
with the poet's father. This is the attack said to be referred to in one of
Cicero's
letters
to Atticus (the last of Bk. XIII), in which he tells how
Cæsar was
'after the eighth hour in the bath; then he heard De Mamurrâ;
did not change countenance; was anointed; lay down; took an emetic.'
Claude Quillet published a Latin poem in four books,
entitled '
Callipædia
, seu de pulchræ prolis habendâ ratione,'
at Leyden, under the name of Calvidius Lætus, in 1655. In discussing
unions harmonious and inharmonious he digressed into an invective
against marriages of Powers, when not in accordance with certain
conditions; and complained that France entered into such unions prolific
only of ill, witness her gift of sovereign power to a Sicilian stranger.
'Trinacriis devectus ab oris advena.'
Mazarin, though born at Rome, was of Sicilian family. In the second
edition, published at Paris in 1656, dedicated to the cardinal Mazarin, the
passages complained of were omitted for the reason and with the result told
in the text; the poet getting 'une jolie Abbaye de 400 pistoles,' which he
enjoyed until his death (aged 59) in 1661.
Pasquino is the name of a torso, perhaps of Menelaus
supporting the dead body of Patroclus, in the Piazza di Pasquino in
Rome, at the corner of the Braschi Palace. To this modern Romans affixed
their scoffs at persons or laws open to ridicule or censure. The name of
the statue is accounted for by the tradition that there was in Rome, at
the beginning of the 16th century, a cobbler or tailor named Pasquino,
whose humour for sharp satire made his stall a place of common resort
for the idle, who would jest together at the passers-by. After
Pasquino's death his stall was removed, and in digging up its floor
there was found the broken statue of a gladiator. In this, when it was
set up, the gossips who still gathered there to exercise their wit,
declared that Pasquino lived again. There was a statue opposite to it
called Marforio — perhaps because it had been brought from the Forum of
Mars — with which the statue of Pasquin used to hold witty conversation;
questions affixed to one receiving soon afterwards salted answers on the
other. It was in answer to Marforio's question, Why he wore a dirty
shirt? that Pasquin's statue gave the answer cited in the text, when, in
1585, Pope Sixtus V had brought to Rome, and lodged there in great
state, his sister Camilla, who had been a laundress and was married to a
carpenter. The Pope's bait for catching the offender was promise of life
and a thousand doubloons if he declared himself, death on the gallows if
his name were disclosed by another.
The satirist Pietro d'Arezzo (Aretino), the most famous
among twenty of the name, was in his youth banished from Arezzo for
satire of the Indulgence trade of Leo XI. But he throve instead of
suffering by his audacity of bitterness, and rose to honour as the
Scourge of Princes,
il Flagello de' Principi
. Under Clement VII
he was at Rome in the Pope's service. Francis I of France gave him a
gold chain. Emperor Charles V gave him a pension of 200 scudi. He died
in 1557, aged 66, called by himself and his compatriots, though his wit
often was beastly, Aretino 'the divine.'
From the
Fables of Æsop and other eminent Mythologists,
with 'Morals and Reflections. By Sir Roger l'Estrange.
The vol.
contains Fables of Æsop, Barlandus, Anianus, Abstemius, Poggio the
Florentine, Miscellany from a Common School Book, and a Supplement of
Fables out of several authors, in which last section is that of the
Boys
and Frogs
, which Addison has copied out verbatim. Sir R. l'Estrange had
died in 1704, aged 88.
Easter Day in 1711 fell on the 1st of April.
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Accurrit quidam notus mihi nomine tantum;
Arreptaque manu, Quid agis dulcissime rerum?
Hor.

There are in this Town a great Number of insignificant People, who are
by no means fit for the better sort of Conversation, and yet have an
impertinent Ambition of appearing with those to whom they are not
welcome. If you walk in the
Park
, one of them will certainly joyn
with you, though you are in Company with Ladies; if you drink a Bottle,
they will find your Haunts.
makes
such Fellows
the more
burdensome is, that they neither offend nor please so far as to be taken
Notice of for either. It is, I presume, for this Reason that my
Correspondents are willing by my Means to be rid of them. The two
following Letters are writ by Persons who suffer by such Impertinence. A
worthy old Batchelour, who sets in for his Dose of Claret every Night at
such an Hour, is teized by a Swarm of them; who because they are sure of
Room and good Fire, have taken it in their Heads to keep a sort of Club
in his Company; tho' the sober Gentleman himself is an utter Enemy to
such Meetings.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The Aversion I for some Years have had to Clubs in general, gave me a
perfect Relish for your Speculation on that Subject; but I have since
been extremely mortified, by the malicious World's ranking me amongst
the Supporters of such impertinent Assemblies. I beg Leave to state my
Case fairly; and that done, I shall expect Redress from your judicious
Pen.
I am, Sir, a Batchelour of some standing, and a Traveller; my
Business, to consult my own Humour, which I gratify without
controuling other People's; I have a Room and a whole Bed to myself;
and I have a Dog, a Fiddle, and a Gun; they please me, and injure no
Creature alive. My chief Meal is a Supper, which I always make at a
Tavern. I am constant to an Hour, and not ill-humour'd; for which
Reasons, tho' I invite no Body, I have no sooner supp'd, than I have a
Crowd about me of that sort of good Company that know not whither else
to go. It is true every Man pays his Share, yet as they are Intruders,
I have an undoubted Right to be the only Speaker, or at least the
loudest; which I maintain, and that to the great Emolument of my
Audience. I sometimes tell them their own in pretty free Language; and
sometimes divert them with merry Tales, according as I am in Humour. I
am one of those who live in Taverns to a great Age, by a sort of
regular Intemperance; I never go to Bed drunk, but always flustered; I
wear away very gently; am apt to be peevish, but never angry. Mr.
Spectator, if you have kept various Company, you know there is in
every Tavern in Town some old Humourist or other, who is Master of the
House as much as he that keeps it. The Drawers are all in Awe of him;
and all the Customers who frequent his Company, yield him a sort of
comical Obedience. I do not know but I may be such a Fellow as this my
self. But I appeal to you, whether this is to be called a Club,
because so many Impertinents will break in upon me, and come without
Appointment?
Clinch of Barnet2 has a nightly Meeting, and
shows to every one that will come in and pay; but then he is the only
Actor. Why should People miscall things?
If his is allowed to be a Consort, why mayn't mine be a Lecture?
However, Sir, I submit it to you, and am,
Sir,
Your most obedient, Etc.
Tho. Kimbow.'
Good Sir,
'You and I were press'd against each other last Winter in a Crowd, in
which uneasy Posture we suffer'd together for almost Half an Hour. I
thank you for all your Civilities ever since, in being of my
Acquaintance wherever you meet me. But the other Day you pulled off
your Hat to me in the
Park, when I was walking with my Mistress: She
did not like your Air, and said she wonder'd what strange Fellows I
was acquainted with. Dear Sir, consider it is as much as my Life is
Worth, if she should think we were intimate; therefore I earnestly
intreat you for the Future to take no Manner of Notice of,
Sir,
Your obliged humble Servant,
Will. Fashion.'
A like
Impertinence
also very troublesome to the superior and
more intelligent Part of the fair Sex. It is, it seems, a great
Inconvenience, that those of the meanest Capacities will pretend to make
Visits, tho' indeed they are qualify'd rather to add to the Furniture of
the House (by filling an empty Chair) than to the Conversation they come
into when they visit. A Friend of mine hopes for Redress in this Case,
by the Publication of her Letter in my Paper; which she thinks those she
would be rid of will take to themselves. It seems to be written with an
Eye to one of those pert giddy unthinking Girls, who, upon the
Recommendation only of an agreeable Person and a fashionable Air, take
themselves to be upon a Level with Women of the greatest Merit.
Madam,
'I take this Way to acquaint you with what common Rules and Forms
would never permit me to tell you otherwise; to wit, that you and I,
tho' Equals in Quality and Fortune, are by no Means suitable
Companions. You are, 'tis true, very pretty, can dance, and make a
very good Figure in a publick Assembly; but alass, Madam, you must go
no further; Distance and Silence are your best Recommendations;
therefore let me beg of you never to make me any more Visits. You come
in a literal Sense to see one, for you have nothing to say. I do not
say this that I would by any Means lose your Acquaintance; but I would
keep it up with the Strictest Forms of good Breeding. Let us pay
Visits, but never see one another: If you will be so good as to deny
your self always to me, I shall return the Obligation by giving the
same Orders to my Servants. When Accident makes us meet at a third
Place, we may mutually lament the Misfortune of never finding one
another at home, go in the same Party to a Benefit-Play, and smile at
each other and put down Glasses as we pass in our Coaches. Thus we may
enjoy as much of each others Friendship as we are capable: For there
are some People who are to be known only by Sight, with which sort of
Friendship I hope you will always honour,
Madam,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
Mary Tuesday.
P.S. I subscribe my self by the Name of the Day I keep, that my
supernumerary Friends may know who I am.
these People
Clinch of Barnet, whose place of performance was at the
corner of Bartholomew Lane, behind the Royal Exchange, imitated,
according to his own advertisement,
'the Horses, the Huntsmen and a Pack of Hounds, a Sham Doctor, an old
Woman, the Bells, the Flute, the Double Curtell (or bassoon) and the
Organ, — all with his own Natural Voice, to the greatest perfection.'
The price of admission was a shilling.
This
Contents
To prevent all Mistakes that may happen
among Gentlemen of
the other End of the Town,
who come but once a Week to St.
James's
Coffee-house,
either by miscalling the Servants,
or requiring
such things from them as are not properly within their
respective Provinces;
this is to give Notice, that Kidney,
Keeper of
the Book-Debts of the outlying Customers,
and Observer of those
who go off without paying,
having resigned that Employment,
is succeeded by John Sowton;
to whose Place of Enterer of Messages
and first Coffee-Grinder,
William Bird
is promoted;
and Samuel
Burdock
comes as Shooe-Cleaner
in the Room of the said Bird.
R.
|
Thursday, March 29, 1711 |
Addison |
... Ægrescitque medendo.
Vir.

The following Letter will explain it self, and needs no Apology.
Sir,
'I am one of that sickly Tribe who are commonly known by the Name of
Valetudinarians, and do confess to you, that I first contracted
this ill Habit of Body, or rather of Mind, by the Study of Physick. I
no sooner began to peruse Books of this Nature, but I found my Pulse
was irregular, and scarce ever read the Account of any Disease that I
did not fancy my self afflicted with.
Dr.
Sydenham's learned
Treatise of Fevers1 threw me into a lingring Hectick, which hung
upon me all the while I was reading that excellent Piece. I then
applied my self to the Study of several Authors, who have written upon
Phthisical Distempers, and by that means fell into a Consumption, till
at length, growing very fat, I was in a manner shamed out of that
Imagination. Not long after this I found in my self all the Symptoms
of the Gout, except Pain, but was cured of it by a Treatise upon the
Gravel, written by a very Ingenious Author, who (as it is usual for
Physicians to convert one Distemper into another) eased me of the Gout
by giving me the Stone.
I at length studied my self into a
Complication of Distempers; but accidentally taking into my Hand that
Ingenious Discourse written by
Sanctorius2, I was resolved to
direct my self by a Scheme of Rules, which I had collected from his
Observations. The Learned World are very well acquainted with that
Gentleman's Invention; who, for the better carrying on of his
Experiments, contrived a certain Mathematical Chair, which was so
Artifically hung upon Springs, that it would weigh any thing as well
as a Pair of Scales. By this means he discovered how many Ounces of
his Food pass'd by Perspiration, what quantity of it was turned into
Nourishment, and how much went away by the other Channels and
Distributions of Nature.
Having provided myself with this Chair, I used to Study, Eat, Drink,
and Sleep in it; insomuch that I may be said, for these three last
Years, to have lived in a Pair of Scales. I compute my self, when I am
in full Health, to be precisely Two Hundred Weight, falling short of
it about a Pound after a Day's Fast, and exceeding it as much after a
very full Meal; so that it is my continual Employment, to trim the
Ballance between these two Volatile Pounds in my Constitution.
In my
ordinary Meals I fetch my self up to two Hundred Weight and
a half
pound3; and if after having dined I find my self fall short of it,
I drink just so much Small Beer, or eat such a quantity of Bread, as
is sufficient to make me weight. In my greatest Excesses I do not
transgress more than the other half Pound; which, for my Healths sake,
I do the first
Monday in every Month. As soon as I find my self duly
poised after Dinner, I walk till I have perspired five Ounces and four
Scruples; and when I discover, by my Chair, that I am so far reduced,
I fall to my Books, and Study away three Ounces more. As for the
remaining Parts of the Pound, I keep no account of them. I do not dine
and sup by the Clock, but by my Chair, for when that informs me my
Pound of Food is exhausted I conclude my self to be hungry, and lay in
another with all Diligence. In my Days of Abstinence I lose a Pound
and an half, and on solemn Fasts am two Pound lighter than on other
Days in the Year.
I allow my self, one Night with another, a Quarter of a Pound of Sleep
within a few Grains more or less; and if upon my rising I find that I
have not consumed my whole quantity, I take out the rest in my Chair.
Upon an exact Calculation of what I expended and received the last
Year, which I always register in a Book, I find the Medium to be two
hundred weight, so that I cannot discover that I am impaired one Ounce
in my Health during a whole Twelvemonth. And yet, Sir, notwithstanding
this my great care to ballast my self equally every Day, and to keep
my Body in its proper Poise, so it is that I find my self in a sick
and languishing Condition. My Complexion is grown very sallow, my
Pulse low, and my Body Hydropical. Let me therefore beg you, Sir, to
consider me as your Patient, and to give me more certain Rules to walk
by than those I have already observed, and you will very much oblige
Your Humble Servant.'
Letter puts me in mind of an
Italian
Epitaph written on the
Monument of a Valetudinarian;
Stavo ben, ma per star Meglio, sto
qui
: Which it is impossible to translate
. The Fear of Death often
proves mortal, and sets People on Methods to save their Lives, which
infallibly destroy them. This is a Reflection made by some Historians,
upon observing that there are many more thousands killed in a Flight
than in a Battel, and may be applied to those Multitudes of Imaginary
Sick Persons that break their Constitutions by Physick, and throw
themselves into the Arms of Death, by endeavouring to escape it. This
Method is not only dangerous, but below the Practice of a Reasonable
Creature. To consult the Preservation of Life, as the only End of it, To
make our Health our Business, To engage in no Action that is not part of
a Regimen, or course of Physick, are Purposes so abject, so mean, so
unworthy human Nature, that a generous Soul would rather die than submit
to them. Besides that a continual Anxiety for Life vitiates all the
Relishes of it, and casts a Gloom over the whole Face of Nature; as it
is impossible we should take Delight in any thing that we are every
Moment afraid of losing.
I do not mean, by what I have here said, that I think any one to blame
for taking due Care of their Health. On the contrary, as Cheerfulness of
Mind, and Capacity for Business, are in a great measure the Effects of a
well-tempered Constitution, a Man cannot be at too much Pains to
cultivate and preserve it. But this Care, which we are prompted to, not
only by common Sense, but by Duty and Instinct, should never engage us
in groundless Fears, melancholly Apprehensions and imaginary Distempers,
which are natural to every Man who is more anxious to live than how to
live. In short, the Preservation of Life should be only a secondary
Concern, and the Direction of it our Principal. If we have this Frame of
Mind, we shall take the best Means to preserve Life, without being
over-sollicitous about the Event; and shall arrive at that Point of
Felicity which
Martial
has mentioned as the Perfection of Happiness,
of neither fearing nor wishing for Death.
In answer to the Gentleman, who tempers his Health by Ounces and by
Scruples, and instead of complying with those natural Sollicitations of
Hunger and Thirst, Drowsiness or Love of Exercise, governs himself by
the Prescriptions of his Chair, I shall tell him a short Fable.
Jupiter
, says the Mythologist, to reward the Piety of a certain
Country-man, promised to give him whatever he would ask. The Country-man
desired that he might have the Management of the Weather in his own
Estate: He obtained his Request, and immediately distributed Rain, Snow,
and Sunshine, among his several Fields, as he thought the Nature of the
Soil required. At the end of the Year, when he expected to see a more
than ordinary Crop, his Harvest fell infinitely short of that of his
Neighbours: Upon which (says the fable) he desired
Jupiter
to take the
Weather again into his own Hands, or that otherwise he should utterly
ruin himself.
C.
Dr. Thomas Sydenham died in 1689, aged 65. He was the
friend of Boyle and Locke, and has sometimes been called the English
Hippocrates; though brethren of an older school endeavoured, but in
vain, to banish him as a heretic out of the College of Physicians. His
Methodus Curandi Febres
was first published in 1666.
Sanctorius, a Professor of Medicine at Padua, who died in
1636, aged 75, was the first to discover the insensible perspiration,
and he discriminated the amount of loss by it in experiments upon
himself by means of his Statical Chair. His observations were published
at Venice in 1614, in his
Ars de Static Medicind
, and led to the
increased use of Sudorifics. A translation of Sanctorius by Dr. John
Quincy appeared in 1712, the year after the publication of this essay.
The
Art of Static Medicine
was also translated into French by M. Le
Breton, in 1722. Dr. John Quincy became well known as the author of a
Complete Dispensatory
(1719, &c.).
an half
The old English reading is:
'I was well; I would be better; and here I am.'
Contents
|
Friday, March 30, 1711 |
Addison |
Pallida mors aequo pulsat pede pauperum tabernas
Regumque turres, O beate Sexti,
Vitæ summa brevis spem nos vetat inchoare longam.
Jam te premet nox, fabulæque manes,
Et domus exilis Plutonia.
Hor.

When I am in a serious Humour, I very often walk by my self in
Westminster
Abbey; where the Gloominess of the Place, and the Use to
which it is applied, with the Solemnity of the Building, and the
Condition of the People who lye in it, are apt to fill the Mind with a
kind of Melancholy, or rather Thoughtfulness, that is not disagreeable.
I Yesterday pass'd a whole Afternoon in the Church-yard, the Cloysters,
and the Church, amusing myself with the Tomb-stones and Inscriptions
that I met with in those several Regions of the Dead. Most of them
recorded nothing else of the buried Person, but that he was born upon
one Day and died upon another: The whole History of his Life, being
comprehended in those two Circumstances, that are common to all Mankind.
I could not but look upon these Registers of Existence, whether of Brass
or Marble, as a kind of Satyr upon the departed Persons; who had left no
other Memorial of them, but that they were born and that they died. They
put me in mind of several Persons mentioned in the Battles of Heroic
Poems, who have sounding Names given them, for no other Reason but that
they may be killed, and are celebrated for nothing but being knocked on
the Head.
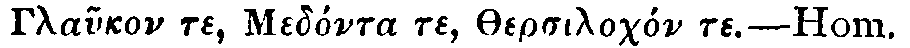 Glaucumque, Medontaque, Thersilochumque
Glaucumque, Medontaque, Thersilochumque. – Virg.
The Life of these Men is finely described in Holy Writ by
the Path of
an Arrow
which is immediately closed up and lost. Upon my going into
the Church, I entertain'd my self with the digging of a Grave; and saw
in every Shovel-full of it that was thrown up, the Fragment of a Bone or
Skull intermixt with a kind of fresh mouldering Earth that some time or
other had a Place in the Composition of an humane Body. Upon this, I
began to consider with my self, what innumerable Multitudes of People
lay confus'd together under the Pavement of that ancient Cathedral; how
Men and Women, Friends and Enemies, Priests and Soldiers, Monks and
Prebendaries, were crumbled amongst one another, and blended together in
the same common Mass; how Beauty, Strength, and Youth, with Old-age,
Weakness, and Deformity, lay undistinguish'd in the same promiscuous
Heap of Matter.
having thus surveyed this great Magazine of Mortality, as it were
in the Lump, I examined it more particularly by the Accounts which I
found on several of the Monuments
which
are raised in every
Quarter of that ancient Fabrick.
of them were covered with such
extravagant Epitaphs, that, if it were possible for the dead Person to
be acquainted with them, he would blush at the Praises which his Friends
have
bestowed upon him. There are others so excessively modest,
that they deliver the Character of the Person departed in Greek or
Hebrew, and by that Means are not understood once in a Twelve-month.
the poetical Quarter, I found there were Poets
who
had no
Monuments, and Monuments
which had
no Poets.
observed indeed
that the present War
had filled the Church with many of these
uninhabited Monuments, which had been erected to the Memory of Persons
whose Bodies were perhaps buried in the Plains of
Blenheim
, or in
the Bosom of the Ocean.
I could not but be very much delighted with several modern Epitaphs,
which are written with great Elegance of Expression and Justness of
Thought, and therefore do Honour to the Living as well as to the Dead.
As a Foreigner is very apt to conceive an Idea of the Ignorance or
Politeness of a Nation from the Turn of their publick Monuments and
Inscriptions, they should be submitted to the Perusal of Men of Learning
and Genius before they are put in Execution.
Cloudesly
Shovel's
Monument has very often given me great Offence: Instead of
the brave rough English Admiral, which was the distinguishing Character
of that plain gallant Man
, he is represented on his Tomb by the
Figure of a Beau, dress'd in a long Perriwig, and reposing himself upon
Velvet Cushions under a Canopy of State, The Inscription is answerable
to the Monument; for, instead of celebrating the many remarkable Actions
he had performed in the service of his Country, it acquaints us only
with the Manner of his Death, in which it was impossible for him to reap
any Honour. The
Dutch
, whom we are apt to despise for want of
Genius, shew an infinitely greater Taste of Antiquity and Politeness in
their Buildings and Works of this Nature, than what we meet with in those
of our own Country. The Monuments of their Admirals, which have been
erected at the publick Expence, represent them like themselves; and are
adorned with rostral Crowns and naval Ornaments, with beautiful Festoons
of
Seaweed
, Shells, and Coral.
But to return to our Subject. I have left the Repository of our English
Kings for the Contemplation of another Day, when I shall find my Mind
disposed for so serious an Amusement. I know that Entertainments of this
Nature, are apt to raise dark and dismal Thoughts in timorous Minds and
gloomy Imaginations; but for my own Part, though I am always serious, I
do not know what it is to be melancholy; and can, therefore, take a View
of Nature in her deep and solemn Scenes, with the same Pleasure as in
her most gay and delightful ones. By this Means I can improve my self
with those Objects, which others consider with Terror. When I look upon
the Tombs of the Great, every Emotion of Envy dies in me; when I read
the Epitaphs of the Beautiful, every inordinate Desire goes out; when I
meet with the Grief of Parents upon a Tombstone, my Heart melts with
Compassion; when I see the Tomb of the Parents themselves, I consider
the Vanity of grieving for those whom we must quickly follow: When I see
Kings lying by those who deposed them, when I consider rival Wits placed
Side by Side, or the holy Men that divided the World with their Contests
and Disputes, I reflect with Sorrow and Astonishment on the little
Competitions, Factions and Debates of Mankind. When I read the several
Dates of the Tombs, of some that dy'd Yesterday, and some six hundred
Years ago, I consider that great Day when we shall all of us be
Contemporaries, and make our Appearance together.
C.
that
had
that
that
At the close of the reign of William III the exiled James
II died, and France proclaimed his son as King of England. William III
thus was enabled to take England with him into the European War of the
Spanish Succession. The accession of Queen Anne did not check the
movement, and, on the 4th of May, 1702, war was declared against France
and Spain by England, the Empire, and Holland. The war then begun had
lasted throughout the Queen's reign, and continued, after the writing of
the
Spectator
Essays, until the signing of the Peace of Utrecht
on the 11th of April, 1713, which was not a year and a half before the
Queen's death, on the 1st of August, 1714. In this war Marlborough had
among his victories, Blenheim, 1704, Ramilies, 1706, Oudenarde, 1708,
Malplaquet, 1709. At sea Sir George Rooke had defeated the French fleet
off Vigo, in October, 1702, and in a bloody battle off Malaga, in
August, 1704, after his capture of Gibraltar.
Sir Cloudesly Shovel, a brave man of humble birth, who,
from a cabin boy, became, through merit, an admiral, died by the wreck
of his fleet on the Scilly Islands as he was returning from an
unsuccessful attack on Toulon. His body was cast on the shore, robbed of
a ring by some fishermen, and buried in the sand. The ring discovering
his quality, he was disinterred, and brought home for burial in
Westminster Abbey.
Contents
|
Saturday, March 31, 1711 |
Steele |
Ut nox longa, quibus Mentitur arnica, diesque
Longa videtur opus debentibus, ut piger Annus
Pupillis, quos dura premit Custodia matrum,
Sic mihi Tarda fluunt ingrataque Tempora, quæ spem
Consiliumque morantur agendi Gnaviter, id quod
Æquè pauperibus prodest, Locupletibus aquè,
Æquè neglectum pueris senibusque nocebit.
Hor.

There is scarce a thinking Man in the World, who is involved in the
Business of it, but lives under a secret Impatience of the Hurry and
Fatigue he suffers, and has formed a Resolution to fix himself, one time
or other, in such a State as is suitable to the End of his Being. You
hear Men every Day in Conversation profess, that all the Honour, Power,
and Riches which they propose to themselves, cannot give Satisfaction
enough to reward them for half the Anxiety they undergo in the Pursuit,
or Possession of them. While Men are in this Temper (which happens very
frequently) how inconsistent are they with themselves? They are wearied
with the Toil they bear, but cannot find in their Hearts to relinquish
it; Retirement is what they want, but they cannot betake themselves to
it; While they pant after Shade and Covert, they still affect to appear
in the most glittering Scenes of Life: But sure this is but just as
reasonable as if a Man should call for more Lights, when he has a mind
to go to Sleep.
Since then it is certain that our own Hearts deceive us in the Love of
the World, and that we cannot command our selves enough to resign it,
tho' we every Day wish our selves disengaged from its Allurements; let
us not stand upon a Formal taking of Leave, but wean our selves from
them, while we are in the midst of them.
It is certainly the general Intention of the greater Part of Mankind to
accomplish this Work, and live according to their own Approbation, as
soon as they possibly can: But since the Duration of Life is so
incertain, and that has been a common Topick of Discourse ever since
there was such a thing as Life it self, how is it possible that we
should defer a Moment the beginning to Live according to the Rules of
Reason?
The Man of Business has ever some one Point to carry, and then he tells
himself he'll bid adieu to all the Vanity of Ambition: The Man of
Pleasure resolves to take his leave at least, and part civilly with his
Mistress: But the Ambitious Man is entangled every Moment in a fresh
Pursuit, and the Lover sees new Charms in the Object he fancy'd he could
abandon. It is, therefore, a fantastical way of thinking, when we
promise our selves an Alteration in our Conduct from change of Place,
and difference of Circumstances; the same Passions will attend us
where-ever we are, till they are Conquered, and we can never live to our
Satisfaction in the deepest Retirement, unless we are capable of living
so in some measure amidst the Noise and Business of the World.
I have ever thought Men were better known, by what could be observed of
them from a Perusal of their private Letters, than any other way.
Friend, the Clergyman
, the other Day, upon serious Discourse with
him concerning the Danger of Procrastination, gave me the following
Letters from Persons with whom he lives in great Friendship and
Intimacy, according to the good Breeding and good Sense of his
Character. The first is from a Man of Business, who is his Convert; The
second from one of whom he conceives good Hopes; The third from one who
is in no State at all, but carried one way and another by starts.
Sir,
'I know not with what Words to express to you the Sense I have of the
high Obligation you have laid upon me, in the Penance you enjoined me
of doing some Good or other, to a Person of Worth, every Day I live.
The Station I am in furnishes me with daily Opportunities of this
kind: and the Noble Principle with which you have inspired me, of
Benevolence to all I have to deal with, quickens my Application in
every thing I undertake. When I relieve Merit from Discountenance,
when I assist a Friendless Person, when I produce conceal'd Worth, I
am displeas'd with my self, for having design'd to leave the World in
order to be Virtuous. I am sorry you decline the Occasions which the
Condition I am in might afford me of enlarging your Fortunes; but know
I contribute more to your Satisfaction, when I acknowledge I am the
better Man, from the Influence and Authority you have over,
Sir,
Your
most Oblig'd and Most Humble, Servant,
R. O.'
Sir,
'I am intirely convinced of the Truth of what you were pleas'd to say
to me, when I was last with you alone. You told me then of the silly
way I was in; but you told me so, as I saw you loved me, otherwise I
could not obey your Commands in letting you know my Thoughts so
sincerely as I do at present. I know
the Creature for whom I resign
so much of my Character is all that you said of her; but then the
Trifler has something in her so undesigning and harmless, that her
Guilt in one kind disappears by the Comparison of her Innocence in
another. Will you, Virtuous Men, allow no alteration of Offences?
Must
Dear
Chloe2 be called by the hard Name you pious People give to
common Women? I keep the solemn Promise I made you, in writing to you
the State of my Mind, after your kind Admonition; and will endeavour
to get the better of this Fondness, which makes me so much her humble
Servant, that I am almost asham'd to Subscribe my self
Yours,
T. D.'
Sir,
'There is no State of Life so Anxious as that of a Man who does not
live according to the Dictates of his own Reason. It will seem odd to
you, when I assure you that my Love of Retirement first of all brought
me to Court; but this will be no Riddle, when I acquaint you that I
placed my self here with a Design of getting so much Mony as might
enable me to Purchase a handsome Retreat in the Country. At present my
Circumstances enable me, and my Duty prompts me, to pass away the
remaining Part of my Life in such a Retirement as I at first proposed
to my self; but to my great Misfortune I have intirely lost the Relish
of it, and shou'd now return to the Country with greater Reluctance
than I at first came to Court. I am so unhappy, as to know that what I
am fond of are Trifles, and that what I neglect is of the greatest
Importance: In short, I find a Contest in my own Mind between Reason
and Fashion. I remember you once told me, that I might live in the
World, and out of it, at the same time. Let me beg of you to explain
this Paradox more at large to me, that I may conform my Life, if
possible, both to my Duty and my Inclination.
I am,
Your most humble Servant,
R.B.'
R.
See the close of
.
blank left
Contents
|
Monday, April 2, 1711 |
Addison |
... Neque semper arcum
Tendit Apollo.
Hor.

I shall here present my Reader with a Letter from a Projector,
concerning a new Office which he thinks may very much contribute to the
Embellishment of the City, and to the driving Barbarity out of
Streets.
I consider it as a Satyr upon Projectors in general, and a
lively Picture of the whole Art of Modern Criticism.
Sir,
'
Observing that you have Thoughts of creating certain Officers under
you for the Inspection of several petty Enormities which you your self
cannot attend to; and finding daily Absurdities hung out upon the
Sign-Posts of this City
2, to the great Scandal of Foreigners, as
well as those of our own Country, who are curious Spectators of the
same: I do humbly propose, that you would be pleased to make me your
Superintendant of all such Figures and Devices, as are or shall be
made use of on this Occasion; with full Powers to rectify or expunge
whatever I shall find irregular or defective. For want of such an
Officer, there is nothing like sound Literature and good Sense to be
met with in those Objects, that are everywhere thrusting themselves
out to the Eye, and endeavouring to become visible. Our streets are
filled with blue Boars, black Swans, and red Lions; not to mention
flying Pigs, and Hogs in Armour, with many other Creatures more
extraordinary than any in the desarts of
Africk. Strange! that
one who has all the Birds and Beasts in Nature to chuse out of, should
live at the Sign of an
Ens Rationis!
My first Task, therefore, should be, like that of
Hercules, to
clear the City from Monsters. In the second Place, I would forbid,
that Creatures of jarring and incongruous Natures should be joined
together in the same Sign; such as the Bell and the Neats-tongue, the
Dog and Gridiron.
The Fox and Goose may be supposed to have met, but
what has the Fox and the Seven Stars to do together? and when did the
Lamb
3 and Dolphin ever meet, except upon a Sign-Post? As for the
Cat and Fiddle, there is a Conceit in it, and therefore, I do not
intend that anything I have here said should affect it. I must however
observe to you upon this Subject, that it is usual for a young
Tradesman, at his first setting up, to add to his own Sign that of the
Master whom he serv'd; as the Husband, after Marriage, gives a Place
to his Mistress's Arms in his own Coat. This I take to have given Rise
to many of those Absurdities which are committed over our Heads, and,
as I am inform'd, first occasioned the three Nuns and a Hare, which we
see so frequently joined together. I would, therefore, establish
certain Rules, for the determining how far one Tradesman may
give the Sign of another, and in what Cases he may be allowed
to quarter it with his own.
In the third place, I would enjoin every Shop to make use of a Sign
which bears some Affinity to the Wares in which it deals. What can be
more inconsistent, than to see a Bawd at the Sign of the Angel, or a
Taylor at the Lion? A Cook should not live at the Boot, nor a
Shoemaker at the roasted Pig; and yet, for want of this Regulation, I
have seen a Goat set up before the Door of a Perfumer, and the French
King's Head at a Sword-Cutler's.
An ingenious Foreigner observes, that several of those Gentlemen who
value themselves upon their Families, and overlook such as are bred to
Trade, bear the Tools of their Fore-fathers in their Coats of Arms. I
will not examine how true this is in Fact: But though it may not be
necessary for Posterity thus to set up the Sign of their Fore-fathers;
I think it highly proper for those who actually profess the Trade, to
shew some such Marks of it before their Doors.
When the Name gives an Occasion for an ingenious Sign-post, I would
likewise advise the Owner to take that Opportunity of letting the
World know who he is.
It would have been ridiculous for the ingenious
Mrs.
Salmon4 to have lived at the Sign of the Trout; for
which Reason she has erected before her House the Figure of the Fish
that is her Namesake. Mr.
Bell has likewise distinguished
himself by a Device of the same Nature: And here, Sir, I must beg
Leave to observe to you, that this particular Figure of a Bell has
given Occasion to several Pieces of Wit in this Kind.
A Man of your
Reading must know, that
Abel Drugger gained great Applause by
it in the Time of
Ben Johnson5. Our
Apocryphal Heathen God
6 is also represented by this Figure; which, in conjunction with the
Dragon, make a very handsome picture in several of our Streets. As for
the Bell-Savage, which is the Sign of a savage Man standing by a Bell,
I was formerly very much puzzled upon the Conceit of it, till I
accidentally fell into the reading of an old Romance translated out of
the French; which gives an Account of a very beautiful Woman who was
found in a Wilderness, and is called in the French
la belle
Sauvage; and is everywhere translated by our Countrymen the
Bell-Savage. This Piece of Philology will, I hope, convince you that I
have made Sign posts my Study, and consequently qualified my self for
the Employment which I sollicit at your Hands. But before I conclude
my Letter, I must communicate to you another Remark, which I have made
upon the Subject with which I am now entertaining you, namely, that I
can give a shrewd Guess at the Humour of the Inhabitant by the Sign
that hangs before his Door. A surly cholerick Fellow generally makes
Choice of a Bear; as Men of milder Dispositions, frequently live at
the Lamb. Seeing a Punch-Bowl painted upon a Sign near
Charing
Cross, and very curiously garnished, with a couple of Angels hovering
over it and squeezing a Lemmon into it, I had the Curiosity to ask
after the Master of the House, and found upon Inquiry, as I had
guessed by the little
Agréemens upon his Sign, that he was a
Frenchman. I know, Sir, it is not requisite for me to enlarge upon
these Hints to a Gentleman of your great Abilities; so humbly
recommending my self to your Favour and Patronage,
I remain, &c.
I shall add to the foregoing Letter, another which came to me by the
same Penny-Post.
From my own Apartment near Charing-Cross.
Honoured Sir,
'Having heard that this Nation is a great Encourager of Ingenuity, I
have brought with me a Rope-dancer that was caught in one of the Woods
belonging to the Great Mogul. He is by Birth a Monkey; but
swings upon a Rope, takes a pipe of Tobacco, and drinks a Glass of
Ale, like any reasonable Creature. He gives great Satisfaction to the
Quality; and if they will make a Subscription for him, I will send for
a Brother of his out of Holland, that is a very good Tumbler,
and also for another of the same Family, whom I design for my
Merry-Andrew, as being an excellent mimick, and the greatest Drole in
the Country where he now is. I hope to have this Entertainment in a
Readiness for the next Winter; and doubt not but it will please more
than the Opera or Puppet-Show. I will not say that a Monkey is a
better Man than some of the Opera Heroes; but certainly he is a better
Representative of a Man, than the most artificial Composition of Wood
and Wire. If you will be pleased to give me a good Word in your paper,
you shall be every Night a Spectator at my Show for nothing.
I am, &c.
C.
It is as follows.
In the
Spectator's
time numbering of houses was so
rare that in Hatton's
New View of London
, published in 1708,
special mention is made of the fact that
'in Prescott Street, Goodman's
Fields, instead of signs the houses are distinguished by numbers, as the
staircases in the Inns of Court and Chancery.'
sheep
The sign before her Waxwork Exhibition, in Fleet Street,
near Temple Bar, was
the Golden Salmon
. She had very recently removed
to this house from her old establishment in St. Martin's le Grand.
Ben Jonson's Alchemist having taken gold from Abel Drugger,
the Tobacco Man, for the device of a sign — 'a good lucky one, a thriving
sign' — will give him nothing so commonplace as a sign copied from the
constellation he was born under, but says:
| Subtle |
He shall have a bel, that's Abel;
And by it standing one whose name is Dee
In a rug grown, there's D and rug, that's Drug:
And right anenst him a dog snarling er,
There's Drugger, Abel Drugger. That's his sign.
And here's now mystery and hieroglyphic. |
| Face |
Abel, thou art made. |
| Drugger |
Sir, I do thank his worship. |
Bel, in the apocryphal addition to the
Book of Daniel
,
called
the History of the Destruction of Bel and the Dragon.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 3, 1711 |
Addison |
... Sermo linguâ concinnus utrâque
Suavior: ut Chio nota si commista Falerni est.
Hor.

There is nothing that
has
more startled our
English
Audience, than
the
Italian Recitativo
at its first Entrance upon the Stage. People
were wonderfully surprized to hear Generals singing the Word of Command,
and Ladies delivering Messages in Musick. Our Country-men could not
forbear laughing when they heard a Lover chanting out a Billet-doux, and
even the Superscription of a Letter set to a Tune. The Famous Blunder in
an old Play of
Enter a King and two Fidlers Solus
, was now no longer
an Absurdity, when it was impossible for a Hero in a Desart, or a
Princess in her Closet, to speak anything unaccompanied with Musical
Instruments.
But however this
Italian
method of acting in
Recitativo
might appear
at first hearing, I cannot but think it much more just than that which
prevailed in our
English
Opera before this Innovation: The Transition
from an Air to Recitative Musick being more natural than the passing
from a Song to plain and ordinary Speaking, which was the common Method
in
Purcell's
Operas.
The only Fault I find in our present Practice, is the making use of
Italian Recitative
with
English
Words.
go to the Bottom of this Matter, I must observe, that the Tone, or
(as the
French
call it) the Accent of every Nation in their ordinary
Speech is altogether different from that of every other People, as we
may see even in the
Welsh
and
Scotch
,
who
border so near upon
us. By the Tone or Accent, I do not mean the Pronunciation of each
particular Word, but the Sound of the whole Sentence. Thus it is very
common for an
English
Gentleman, when he hears a
French
Tragedy, to
complain that the Actors all of them speak in a Tone; and therefore he
very wisely prefers his own Country-men, not considering that a
Foreigner complains of the same Tone in an
English
Actor.
For this Reason, the Recitative Musick in every Language, should be as
different as the Tone or Accent of each Language; for otherwise, what
may properly express a Passion in one Language, will not do it in
another. Every one who has been long in
Italy
knows very well, that
the Cadences in the
Recitativo
bear a remote Affinity to the Tone
of their Voices in ordinary Conversation, or to speak more properly, are
only the Accents of their Language made more Musical and Tuneful.
the Notes of Interrogation, or Admiration, in the
Italian
Musick (if one may so call them) which resemble their Accents in
Discourse on such Occasions, are not unlike the ordinary Tones of an
English
Voice when we are angry; insomuch that I have often seen
our Audiences extreamly mistaken as to what has been doing upon the
Stage, and expecting to see the Hero knock down his Messenger, when he
has been
asking
him a Question, or fancying that he quarrels with
his Friend, when he only bids him Good-morrow.
this Reason the
Italian
Artists cannot agree with our
English
Musicians in admiring
Purcell's
Compositions
,
and thinking his Tunes so wonderfully adapted to his Words, because both
Nations do not always express the same Passions by the same Sounds.
I am therefore humbly of Opinion, that an
English
Composer should
not follow the
Italian
Recitative too servilely, but make use of
many gentle Deviations from it, in Compliance with his own Native
Language. He may Copy out of it all the lulling Softness and
Dying
Falls
(as
Shakespear
calls them), but should still remember
that he ought to accommodate himself to an
English
Audience, and
by humouring the Tone of our Voices in ordinary Conversation, have the
same Regard to the Accent of his own Language, as those Persons had to
theirs whom he professes to imitate. It is observed, that several of the
singing Birds of our own Country learn to sweeten their Voices, and
mellow the Harshness of their natural Notes, by practising under those
that come from warmer Climates. In the same manner, I would allow the
Italian
Opera to lend our
English
Musick as much as may grace
and soften it, but never entirely to annihilate and destroy it. Let the
Infusion be as strong as you please, but still let the Subject Matter of
it be
English
.
A Composer should fit his Musick to the Genius of the People, and
consider that the Delicacy of Hearing, and Taste of Harmony, has been
formed upon those Sounds which every Country abounds with: In short,
that Musick is of a Relative Nature, and what is Harmony to one Ear, may
be Dissonance to another.
The same Observations which I have made upon the Recitative part of
Musick may be applied to all our Songs and Airs in general.
Baptist Lully
acted like a Man of Sense in this
Particular. He found the
French
Musick extreamly defective, and very
often barbarous: However, knowing the Genius of the People, the Humour
of their Language, and the prejudiced Ears
he
had to deal with he
did not pretend to extirpate the
French
Musick, and plant the
Italian
in its stead; but only to Cultivate and Civilize it with
innumerable Graces and Modulations which he borrow'd from the
Italian
.
By this means the
French
Musick is now perfect in its kind; and when
you say it is not so good as the
Italian
, you only mean that it does
not please you so well; for there is
scarce
a
Frenchman
who
would not wonder to hear you give the
Italian
such a Preference. The
Musick of the
French
is indeed very properly adapted to their
Pronunciation and Accent, as their whole Opera wonderfully favours the
Genius of such a gay airy People. The Chorus in which that Opera
abounds, gives the Parterre frequent Opportunities of joining in Consort
with the Stage. This Inclination of the Audience to Sing along with the
Actors, so prevails with them, that I have sometimes known the Performer
on the Stage do no more in a Celebrated Song, than the Clerk of a Parish
Church, who serves only to raise the Psalm, and is afterwards drown'd in
the Musick of the Congregation. Every Actor that comes on the Stage is a
Beau. The Queens and Heroines are so Painted, that they appear as Ruddy
and Cherry-cheek'd as Milk-maids. The Shepherds are all Embroider'd, and
acquit themselves in a Ball better than our
English
Dancing Masters. I
have seen a couple of Rivers appear in red Stockings; and
Alpheus
,
instead of having his Head covered with Sedge and Bull-Rushes, making
Love in a fair full-bottomed Perriwig, and a Plume of Feathers; but with
a Voice so full of Shakes and Quavers that I should have thought the
Murmurs of a Country Brook the much more agreeable Musick.
I remember the last Opera I saw in that merry Nation was the Rape of
Proserpine
, where
Pluto
, to make the more tempting Figure, puts
himself in a
French
Equipage, and brings
Ascalaphus
along with him
as his
Valet de Chambre
. This is what we call Folly and Impertinence;
but what the
French
look upon as Gay and Polite.
I shall add no more to what I have here offer'd, than that Musick,
Architecture, and Painting, as well as Poetry, and Oratory, are to
deduce their Laws and Rules from the general Sense and Taste of Mankind,
and not from the Principles of those Arts themselves; or, in other
Words, the Taste is not to conform to the Art, but the Art to the Taste.
Music is not design'd to please only Chromatick Ears, but all that are
capable ef distinguishing harsh from disagreeable Notes. A Man of an
ordinary Ear is a Judge whether a Passion is express'd in proper Sounds,
and whether the Melody of those Sounds be more or less pleasing.
C.
: that
only asking
Henry Purcell died of consumption in 1695, aged 37.
'He was,' says Mr. Hullah, in his Lectures on the History of Modern
Music, 'the first Englishman to demonstrate the possibility of a
national opera. No Englishman of the last century succeeded in
following Purcell's lead into this domain of art; none, indeed, would
seem to have understood in what his excellence consisted, or how his
success was attained. His dramatic music exhibits the same qualities
which had already made the success of Lulli. ... For some years after
Purcell's death his compositions, of whatever kind, were the chief, if
not the only, music heard in England. His reign might have lasted
longer, but for the advent of a musician who, though not perhaps more
highly gifted, had enjoyed immeasurably greater opportunities of
cultivating his gifts,'
Handel, who had also the advantage of being born thirty years later.
John Baptist Lulli, a Florentine, died in 1687, aged 53. In
his youth he was an under-scullion in the kitchen of Madame de
Montpensier, niece to Louis XIV. The discovery of his musical genius led
to his becoming the King's Superintendent of Music, and one of the most
influential composers that has ever lived. He composed the occasional
music for Molière's comedies, besides about twenty lyric tragedies;
which succeeded beyond all others in France, not only because of his
dramatic genius, which enabled him to give to the persons of these
operas a musical language fitted to their characters and expressive of
the situations in which they were placed; but also, says Mr. Hullah,
because
'Lulli being the first modern composer who caught the French ear, was
the means, to a great extent, of forming the modern French taste.'
His operas kept the stage for more than a century.
that he
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 4, 17111 |
Steele |
Si, Mimnermus uti censet, sine amore Focisque
Nil est Fucundum; vivas in amore Focisque.
Hor.

One common Calamity makes Men extremely affect each other, tho' they
differ in every other Particular. The Passion of Love is the most
general Concern among Men; and I am glad to hear by my last Advices from
Oxford
, that there are
a Set of Sighers in that University, who have erected themselves into a
Society in honour of that tender Passion. These Gentlemen are of that
Sort of Inamoratos, who are not so very much lost to common Sense, but
that they understand the Folly they are guilty of; and for that Reason
separate themselves from all other Company, because they will enjoy the
Pleasure of talking incoherently, without being ridiculous to any but
each other. When a Man comes into the Club, he is not obliged to make
any Introduction to his Discourse, but at once, as he is seating himself
in his Chair, speaks in the Thread of his own Thoughts, 'She gave me a
very obliging Glance, She Never look'd so well in her Life as this
Evening,' or the like Reflection, without Regard to any other Members of
the Society; for in this Assembly they do not meet to talk to each
other, but every Man claims the full Liberty of talking to himself.
Instead of Snuff-boxes and Canes, which are the usual Helps to Discourse
with other young Fellows, these have each some Piece of Ribbon, a broken
Fan, or an old Girdle, which they play with while they talk of the fair
Person remember'd by each respective Token. According to the
Representation of the Matter from my Letters, the Company appear like so
many Players rehearsing behind the Scenes; one is sighing and lamenting
his Destiny in beseeching Terms, another declaring he will break his
Chain, and another in dumb-Show, striving to express his Passion by his
Gesture. It is very ordinary in the Assembly for one of a sudden to rise
and make a Discourse concerning his Passion in general, and describe the
Temper of his Mind in such a Manner, as that the whole Company shall
join in the Description, and feel the Force of it. In this Case, if any
Man has declared the Violence of his Flame in more pathetick Terms, he
is made President for that Night, out of respect to his superior
Passion.
We had some Years ago in this Town a Set of People who met and dressed
like Lovers, and were distinguished by the Name of the
Fringe-Glove
Club
; but they were Persons of such moderate Intellects even before
they were impaired by their Passion, that their Irregularities could not
furnish sufficient Variety of Folly to afford daily new Impertinencies;
by which Means that Institution dropp'd. These Fellows could express
their Passion in nothing but their Dress; but the
Oxonians
are
Fantastical now they are Lovers, in proportion to their Learning and
Understanding before they became such. The Thoughts of the ancient Poets
on this agreeable Phrenzy, are translated in honour of some modern
Beauty; and
Chloris
is won to Day, by the same Compliment that
was made to
Lesbia
a thousand Years ago. But as far as I can
learn, the Patron of the Club is the renowned Don
Quixote
. The
Adventures of that gentle Knight are frequently mention'd in the
Society, under the colour of Laughing at the Passion and themselves: But
at the same Time, tho' they are sensible of the Extravagancies of that
unhappy Warrior, they do not observe, that to turn all the Reading of
the best and wisest Writings into Rhapsodies of Love, is a Phrenzy no
less diverting than that of the aforesaid accomplish'd
Spaniard
.
A Gentleman who, I hope, will continue his Correspondence, is lately
admitted into the Fraternity, and sent me the following Letter.
Sir,
'Since I find you take Notice of Clubs, I beg Leave to give you an
Account of one in
Oxford, which you have no where mention'd,
and perhaps never heard of. We distinguish our selves by the Title of
the
Amorous Club, are all Votaries of
Cupid, and
Admirers of the Fair Sex. The Reason that we are so little known in
the World, is the Secrecy which we are obliged to live under in the
University. Our Constitution runs counter to that of the Place wherein
we live: For in Love there are no Doctors, and we all profess so high
Passion, that we admit of no Graduates in it. Our Presidentship is
bestow'd according to the Dignity of Passion; our Number is unlimited;
and our Statutes are like those of the Druids, recorded in our own
Breasts only, and explained by the Majority of the Company. A
Mistress, and a Poem in her Praise, will introduce any Candidate:
Without the latter no one can be admitted; for he that is not in love
enough to rhime, is unqualified for our Society. To speak
disrespectfully of any Woman, is Expulsion from our gentle Society. As
we are at present all of us Gown-men, instead of duelling when we are
Rivals, we drink together the Health of our Mistress. The Manner of
doing this sometimes indeed creates Debates; on such Occasions we have
Recourse to the Rules of Love among the Antients.
Nævia sex Cyathis, septem Justina bibatur.
This Method of a Glass to every Letter of her Name,
occasioned the other Night a Dispute of some Warmth.
A young Student, who is in Love with Mrs.
Elizabeth Dimple,
was so unreasonable as to begin her Health under the Name of
Elizabetha; which so exasperated the Club, that by common
Consent we retrenched it to
Betty. We look upon a Man as
no Company, that does not sigh five times in a Quarter of an
Hour; and look upon a Member as very absurd, that is so
much himself as to make a direct Answer to a Question. In
fine, the whole Assembly is made up of absent Men, that is,
of such Persons as have lost their Locality, and whose Minds
and Bodies never keep Company with one another. As I am
an unfortunate Member of this distracted Society, you cannot
expect a very regular Account of it; for which Reason, I hope
you will pardon me that I so abruptly subscribe my self,
Sir,
Your most obedient,
humble Servant,
T. B.
I forgot to tell you, that
Albina, who has six Votaries in this
Club, is one of your Readers.'
R.
To this number of the
Spectator
was added in the original
daily issue an announcement of six places at which were to be sold
Compleat Setts of this Paper for the Month of March.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 5, 1711 |
Addison |
Sit mihi fas audita loqui!
Vir.

Last Night, upon my going into a Coffee-House not far from the
Hay-Market
Theatre, I diverted my self for above half an Hour
with overhearing the Discourse of one, who, by the Shabbiness of his
Dress, the Extravagance of his Conceptions, and the Hurry of his Speech,
I discovered to be of that Species who are generally distinguished by
the Title of Projectors. This Gentleman, for I found he was treated as
such by his Audience, was entertaining a whole Table of Listners with
the Project of an Opera, which he told us had not cost him above two or
three Mornings in the Contrivance, and which he was ready to put in
Execution, provided he might find his Account in it. He said, that he
had observed the great Trouble and Inconvenience which Ladies were at,
in travelling up and down to the several Shows that are exhibited in
different Quarters of the Town. The dancing Monkies are in one place;
the Puppet-Show in another; the Opera in a third; not to mention the
Lions, that are almost a whole Day's Journey from the Politer Part of
the Town. By this means People of Figure are forced to lose half the
Winter after their coming to Town, before they have seen all the strange
Sights about it. In order to remedy this great Inconvenience, our
Projector drew out of his Pocket the Scheme of an Opera, Entitled,
The Expedition of Alexander the Great
; in which he had disposed
of all the remarkable Shows about Town, among the Scenes and Decorations
of his Piece. The Thought, he confessed, was not originally his own, but
that he had taken the Hint of it from several Performances which he had
seen upon our Stage: In one of which there was a Rary-Show; in another,
a Ladder-dance; and in others a Posture-man, a moving Picture, with many
Curiosities of the like nature.
This
Expedition of Alexander
opens with his consulting the oracle
at
Delphos
, in which the dumb Conjuror, who has been visited by
so many Persons of Quality of late Years, is to be introduced as telling
him his Fortune; At the same time
Clench
of
Barnet
is
represented in another Corner of the Temple, as ringing the Bells of
Delphos
, for joy of his arrival.
Tent of
Darius
is to
be Peopled by the Ingenious Mrs.
Salmon
, where Alexander is
to fall in Love with a Piece of Wax-Work, that represents the beautiful
Statira
.
Alexander comes into that Country, in which
Quintus Curtius
tells us the Dogs were so exceeding fierce that
they would not loose their hold, tho' they were cut to pieces Limb by
Limb, and that they would hang upon their Prey by their Teeth when they
had nothing but a Mouth left, there is to be a scene of
Hockley in
the Hole
, in which is to be represented all the Diversions of
that Place, the Bull-baiting only excepted, which cannot possibly be
exhibited in the Theatre, by Reason of the Lowness of the Roof. The
several Woods in
Asia
, which
Alexander
must be supposed to
pass through, will give the Audience a Sight of Monkies dancing upon
Ropes, with many other Pleasantries of that ludicrous Species. At the
same time, if there chance to be any Strange Animals in Town, whether
Birds or Beasts, they may be either let loose among the Woods, or driven
across the Stage by some of the Country People of
Asia
.
the last
great Battel, Pinkethman
is to personate King
Porus
upon an
Elephant
, and is to be encountered by
Powell
representing
Alexander
the Great upon a Dromedary, which nevertheless Mr.
Powell
is desired to call by the Name of
Bucephalus
.
the Close of this
great decisive Battel, when the two Kings are thoroughly reconciled, to
shew the mutual Friendship and good Correspondence that reigns between
them, they both of them go together to a Puppet-Show, in which the
ingenious Mr.
Powell, junior
may have an Opportunity of displaying
his whole Art of Machinery, for the Diversion of the two Monarchs. Some
at the Table urged that a Puppet-Show was not a suitable Entertainment
for
Alexander
the Great; and that it might be introduced more
properly, if we suppose the Conqueror touched upon that part of
India
which is said to be inhabited by the Pigmies. But this Objection was
looked upon as frivolous, and the Proposal immediately over-ruled.
Projector further added, that after the Reconciliation of these two
Kings they might invite one another to Dinner, and either of them
entertain his Guest with the
German Artist
, Mr.
Pinkethman's
Heathen
Gods
, or any of the like Diversions, which shall then chance to be in vogue.
This Project was receiv'd with very great Applause by the whole Table.
which the Undertaker told us, that he had not yet communicated to
us above half his Design; for that
Alexander
being a
Greek
, it was
his Intention that the whole Opera should be acted in that Language,
which was a Tongue he was sure would wonderfully please the Ladies,
especially when it was a little raised and rounded by the
Ionick
Dialect; and could not but be
acceptable
to the whole Audience,
because there are fewer of them who understand
Greek
than
Italian
.
The only Difficulty that remained, was, how to get Performers, unless we
could persuade some Gentlemen of the Universities to learn to sing, in
order to qualify themselves for the Stage; but this Objection soon
vanished, when the Projector informed us that the
Greeks
were at
present the only Musicians in the
Turkish
Empire, and that it would be
very easy for our Factory at
Smyrna
to furnish us every Year with a
Colony of Musicians, by the Opportunity of the
Turkey
Fleet; besides,
says he, if we want any single Voice for any lower Part in the Opera,
Lawrence
can learn to speak
Greek
, as well as he does
Italian
, in a Fortnight's time.
The Projector having thus settled Matters, to the good liking of all
that heard him, he left his Seat at the Table, and planted himself
before the Fire, where I had unluckily taken my Stand for the
Convenience of over-hearing what he said. Whether he had observed me to
be more attentive than ordinary, I cannot tell, but he had not stood by
me above a Quarter of a Minute, but he turned short upon me on a sudden,
and catching me by a Button of my Coat, attacked me very abruptly after
the following manner.
Besides, Sir, I have heard of a very extraordinary
Genius for Musick that lives in Switzerland, who has so strong a
Spring in his Fingers, that he can make the Board of an Organ sound like
a Drum, and if I could but procure a Subscription of about Ten Thousand
Pound every Winter, I would undertake to fetch him over, and oblige him
by Articles to set every thing that should be sung upon the
English Stage.
this he looked full in my Face, expecting I
would make an Answer, when by good Luck, a Gentleman that had entered
the Coffee-house since the Projector applied himself to me, hearing him
talk of his
Swiss
Compositions, cry'd out with a kind of Laugh,
Is our Musick then to receive further Improvements from
Switzerland!8
This alarmed the Projector, who immediately let
go my Button, and turned about to answer him. I took the Opportunity of
the Diversion, which seemed to be made in favour of me, and laying down
my Penny upon the Bar, retired with some Precipitation.
C.
An advertisement of Mrs. Salmon's wax-work in the
Tatler
for Nov. 30, 1710, specifies among other attractions the
Turkish Seraglio in wax-work, the Fatal Sisters that spin, reel, and cut
the thread of man's life,
'an Old Woman flying from Time, who shakes his
head and hour-glass with sorrow at seeing age so unwilling to die.
Nothing but life can exceed the motions of the heads, hands, eyes, &c.,
of these figures, &c.'
Hockley-in-the-Hole, memorable for its Bear Garden, was on
the outskirt of the town, by Clerkenwell Green; with Mutton Lane on the
East and the fields on the West. By Town's End Lane (called Coppice Row
since the levelling of the coppice-crowned knoll over which it ran)
through Pickled-Egg Walk (now Crawford's Passage) one came to
Hockley-in-the-Hole or Hockley Hole, now Ray Street. The leveller has
been at work upon the eminences that surrounded it. In Hockley Hole,
dealers in rags and old iron congregated. This gave it the name of Rag
Street, euphonized into Ray Street since 1774. In the
Spectator's
time its Bear Garden, upon the site of which there are now metal works,
was a famous resort of the lowest classes. 'You must go to
Hockley-in-the-Hole, child, to learn valour,' says Mr. Peachum to Filch
in the
Beggar's Opera
.
William Penkethman was a low comedian dear to the gallery
at Drury Lane as 'Pinkey,' very popular also as a Booth Manager at
Bartholomew Fair. Though a sour critic described him as
'the Flower of
Bartholomew Fair and the Idol of the Rabble; a Fellow that overdoes
everything, and spoils many a Part with his own Stuff,'
the
Spectator
has in another paper given honourable fame to his skill as a comedian.
Here there is but the whimsical suggestion of a favourite showman and
low comedian mounted on an elephant to play King Porus.
George Powell, who in 1711 and 1712 appeared in such
characters as Falstaff, Lear, and Cortez in
the Indian Emperor,
now
and then also played the part of the favourite stage hero, Alexander the
Great in Lee's
Rival Queens
. He was a good actor, spoilt by
intemperance, who came on the stage sometimes warm with Nantz brandy,
and courted his heroines so furiously that Sir John Vanbrugh said they
were almost in danger of being conquered on the spot. His last new part
of any note was in 1713, Portius in Addison's
Cato
. He lived on for a
few wretched years, lost to the public, but much sought by sheriff's
officers.
'Powell junior' of the Puppet Show (see
, p. 59,
ante
) was a more prosperous man than his namesake of Drury Lane. In De
Foe's
Groans of Great Britain
, published in 1813, we read:
'
I was the other Day at a Coffee-House when the following
Advertisement was thrown in.
At Punch's Theatre in the Little
Piazza, Covent-Garden, this present Evening will be performed an
Entertainment, called, The History of Sir Richard Whittington,
shewing his Rise from a Scullion to be Lord-Mayor of London, with the
Comical Humours of Old Madge, the jolly Chamber-Maid, and the
Representation of the Sea, and the Court of Great Britain, concluding
with the Court of Aldermen, and Whittington Lord-Mayor, honoured
with the Presence of K. Hen. VIII and his Queen Anna Bullen, with
other diverting Decorations proper to the Play, beginning at 6
o'clock. Note, No money to be returned after the Entertainment is
begun. Boxes, 2s. Pit, 1s. Vivat Regina.
On enquiring into the Matter, I find this has long been a noble
Diversion of our Quality and Gentry; and that Mr. Powell, by
Subscriptions and full Houses, has gathered such Wealth as is ten
times sufficient to buy all the Poets in England; that he seldom goes
out without his Chair, and thrives on this incredible Folly to that
degree, that, were he a Freeman, he might hope that some future
Puppet-Show might celebrate his being Lord Mayor, as he has done Sir
R. Whittington.'
'Mr. Penkethman's Wonderful Invention call'd the Pantheon: or, the
Temple of the Heathen Gods. The Work of several Years, and great
Expense, is now perfected; being a most surprising and magnificent
Machine, consisting of 5 several curious Pictures, the Painting and
contrivance whereof is beyond Expression Admirable. The Figures, which
are above 100, and move their Heads, Legs, Arms, and Fingers, so
exactly to what they perform, and setting one Foot before another,
like living Creatures, that it justly deserves to be esteem'd the
greatest Wonder of the Age. To be seen from 10 in the Morning till 10
at Night, in the Little Piazza, Covent Garden, in the same House where
Punch's Opera is. Price 1s. 6d., 1s., and the lowest, 6d.'
This Advertisement was published in
and a few following numbers of
the
Spectator
.
wonderfully acceptable
The satire is against Heidegger. See
, p. 56,
ante
.
Contents
|
Friday, April 6, 1711 |
Steele |
Nil illi larvâ aut tragicis opus esse Cothurnis.
Hor.

The late Discourse concerning the Statutes of the
Ugly-Club
,
having been so well received at
Oxford
, that, contrary to the
strict Rules of the Society, they have been so partial as to take my own
Testimonial, and admit me into that select Body; I could not restrain
the Vanity of publishing to the World the Honour which is done me. It is
no small Satisfaction, that I have given Occasion for the President's
shewing both his Invention and Reading to such Advantage as my
Correspondent reports he did: But it is not to be doubted there were
many very proper Hums and Pauses in his Harangue, which lose their
Ugliness in the Narration, and which my Correspondent (begging his
Pardon) has no very good Talent at representing. I very much approve of
the Contempt the Society has of Beauty: Nothing ought to be laudable in
a Man, in which his Will is not concerned; therefore our Society can
follow Nature, and where she has thought fit, as it were, to mock
herself, we can do so too, and be merry upon the Occasion.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Your making publick the late Trouble I gave you, you will find to
have been the Occasion of this: Who should I meet at the Coffee-house
Door t'other Night, but my old Friend Mr. President? I saw somewhat
had pleased him; and as soon as he had cast his Eye upon me,
"Oho, Doctor, rare News from London, (says he); the Spectator
has made honourable Mention of the Club (Man) and published to the
World his sincere Desire to be a Member, with a recommendatory
Description of his Phiz: And tho' our Constitution has made no
particular Provision for short Faces, yet, his being an
extraordinary Case, I believe we shall find an Hole for him to creep
in at; for I assure you he is not against the Canon; and if his
Sides are as compact as his Joles, he need not disguise himself to
make one of us."
I presently called for the Paper to see how you looked in Print; and
after we had regaled our selves a while upon the pleasant Image of our
Proselite, Mr. President told me I should be his Stranger at the next
Night's Club: Where we were no sooner come, and Pipes brought, but Mr.
President began an Harangue upon your Introduction to my Epistle;
setting forth with no less Volubility of Speech than Strength of
Reason,
"That a Speculation of this Nature was what had been long and
much wanted; and that he doubted not but it would be of inestimable
Value to the Publick, in reconciling even of Bodies and Souls; in
composing and quieting the Minds of Men under all corporal
Redundancies, Deficiencies, and Irregularities whatsoever; and making
every one sit down content in his own Carcase, though it were not
perhaps so mathematically put together as he could wish." And again,
"How that for want of a due Consideration of what you first advance,
viz. that our Faces are not of our own choosing, People had
been transported beyond all good Breeding, and hurried themselves into
unaccountable and fatal Extravagancies: As, how many impartial
Looking-Glasses had been censured and calumniated, nay, and sometimes
shivered into ten thousand Splinters, only for a fair Representation
of the Truth? How many Headstrings and Garters had been made
accessory, and actually forfeited, only because Folks must needs
quarrel with their own Shadows? And who (continues he) but is deeply
sensible, that one great Source of the Uneasiness and Misery of human
Life, especially amongst those of Distinction, arises from nothing in
the World else, but too severe a Contemplation of an indefeasible
Contexture of our external Parts, or certain natural and invincible
Disposition to be fat or lean? When a little more of Mr.
Spectator's
Philosophy would take off all this; and in the mean time let them
observe, that there's not one of their Grievances of this Sort, but
perhaps in some Ages of the World has been highly in vogue; and may be
so again, nay, in some Country or other ten to one is so at this Day.
My Lady
Ample is the most miserable Woman in the World, purely
of her own making: She even grudges her self Meat and Drink, for fear
she should thrive by them; and is constantly crying out, In a Quarter
of a Year more I shall be quite out of all manner of Shape! Now
the1 Lady's Misfortune
seems to be only this, that she is planted
in a wrong Soil; for, go but t'other Side of the Water, it's a Jest at
Harlem to talk of a Shape under eighteen Stone. These wise
Traders regulate their Beauties as they do their Butter, by the Pound;
and Miss
Cross, when she first arrived in the
Low-Countries, was not computed to be so handsom as Madam
Van Brisket by near half a Tun. On the other hand, there's
'Squire
Lath, a proper Gentleman of Fifteen hundred Pound
per Annum, as well as of an unblameable Life and Conversation;
yet would not I be the Esquire for half his Estate; for if it was as
much more, he'd freely pare with it all for a pair of Legs to his
Mind: Whereas in the Reign of our first King
Edward of glorious
Memory, nothing more modish than a Brace of your fine taper
Supporters; and his Majesty without an Inch of Calf, managed Affairs
in Peace and War as laudably as the bravest and most politick of his
Ancestors; and was as terrible to his Neighbours under the Royal Name
of
Long-shanks, as
Coeur de Lion to the
Saracens
before him. If we look farther back into History we shall find, that
Alexander the Great wore his Head a little over the left
Shoulder; and then not a Soul stirred out 'till he had adjusted his
Neck-bone; the whole Nobility addressed the Prince and each other
obliquely, and all Matters of Importance were concerted and carried on
in the
Macedonian Court with their Polls on one Side.
For about
the first Century nothing made more Noise in the World than
Roman Noses, and then not a Word of them till they revived
again in Eighty eight
2. Nor is it so very long since
Richard
the Third set up half the Backs of the Nation; and high Shoulders, as
well as high Noses, were the Top of the Fashion. But to come to our
selves, Gentlemen, tho' I find by my quinquennial Observations that we
shall never get Ladies enough to make a Party in our own Country, yet
might we meet with better Success among some of our Allies. And what
think you if our Board sate for a
Dutch Piece? Truly I am of
Opinion, that as odd as we appear in Flesh and Blood, we should be no
such strange Things in Metzo-Tinto. But this Project may rest 'till
our Number is compleat; and this being our Election Night, give me
leave to propose Mr.
Spectator: You see his Inclinations, and perhaps
we may not have his Fellow."
I found most of them (as it is usual in all such Cases) were prepared;
but one of the Seniors (whom by the by Mr. President had taken all
this Pains to bring over) sate still, and cocking his Chin, which
seemed only to be levelled at his Nose, very gravely declared,
"That
in case he had had sufficient Knowledge of you, no Man should have
been more willing to have served you; but that he, for his part, had
always had regard to his own Conscience, as well as other Peoples
Merit; and he did not know but that you might be a handsome Fellow;
for as for your own Certificate, it was every Body's Business to speak
for themselves."
Mr. President immediately retorted,
"A handsome
Fellow! why he is a Wit (Sir) and you know the Proverb;"
and to ease
the old Gentleman of his Scruples, cried,
"That for Matter of Merit it
was all one, you might wear a Mask."
This threw him into a Pause, and
he looked, desirous of three Days to consider on it; but Mr. President
improved the Thought, and followed him up with an old Story,
"That
Wits were privileged to wear what Masks they pleased in all Ages; and
that a Vizard had been the constant Crown of their Labours, which was
generally presented them by the Hand of some Satyr, and sometimes of
Apollo himself:"
For the Truth of which he appealed to the
Frontispiece of several Books, and particularly to the
English
Juvenal3, to which he referred him; and only added,
"That such
Authors were the
Larvati4 or
Larvâ donati of the
Ancients."
This cleared up all, and in the Conclusion you were chose
Probationer; and Mr. President put round your Health as such,
protesting,
"That tho' indeed he talked of a Vizard, he did not
believe all the while you had any more Occasion for it than the
Cat-a-mountain;"
so that all you have to do now is to pay your Fees,
which here are very reasonable if you are not imposed upon; and you
may stile your self
Informis Societatis Socius: Which I am
desired to acquaint you with; and upon the same I beg you to accept of
the Congratulation of,
Sir,
Your oblig'd humble Servant,
R. A. C.
Oxford March 21.
this
At the coming of William III.
The third edition of Dryden's
Satires of Juvenal and
Persius
, published in 1702, was the first 'adorn'd with Sculptures.' The
Frontispiece represents at full length Juvenal receiving a mask of Satyr
from Apollo's hand, and hovered over by a Cupid who will bind the Head
to its Vizard with a Laurel Crown.
Larvati were bewitched persons; from Larva, of which the
original meaning is a ghost or spectre; the derived meanings are, a Mask
and a Skeleton.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 7, 1711 |
Steele |
Fervidus tecum Puer, et solutis
Gratiæ zonis, properentque Nymphæ,
Et parum comis sine te Juventas,
Mercuriusque.
Hor.
ad Venerem.

A friend of mine has two Daughters, whom I will call
Lætitia
and
Daphne
; The Former is one of the Greatest Beauties of the Age in
which she lives, the Latter no way remarkable for any Charms in her
Person. Upon this one Circumstance of their Outward Form, the Good and
Ill of their Life seems to turn.
Lætitia
has not, from her very
Childhood, heard any thing else but Commendations of her Features and
Complexion, by which means she is no other than Nature made her, a very
beautiful Outside. The Consciousness of her Charms has rendered her
insupportably Vain and Insolent, towards all who have to do with her.
Daphne
, who was almost Twenty before one civil Thing had ever
been said to her, found her self obliged to acquire some Accomplishments
to make up for the want of those Attractions which she saw in her
Sister. Poor
Daphne
was seldom submitted to in a Debate wherein
she was concerned; her Discourse had nothing to recommend it but the
good Sense of it, and she was always under a Necessity to have very well
considered what she was to say before she uttered it; while
Lætitia
was listened to with Partiality, and Approbation sate in
the Countenances of those she conversed with, before she communicated
what she had to say. These Causes have produced suitable Effects, and
Lætitia
is as insipid a Companion, as
Daphne
is an
agreeable one.
Lætitia
, confident of Favour, has studied no Arts
to please;
Daphne
, despairing of any Inclination towards her
Person, has depended only on her Merit.
Lætitia
has always
something in her Air that is sullen, grave and disconsolate.
Daphne
has a Countenance that appears chearful, open and
unconcerned. A young Gentleman saw
Lætitia
this Winter at a
Play, and became her Captive. His Fortune was such, that he wanted very
little Introduction to speak his Sentiments to her Father. The Lover was
admitted with the utmost Freedom into the Family, where a constrained
Behaviour, severe Looks, and distant Civilities, were the highest
Favours he could obtain of
Lætitia
; while
Daphne
used him
with the good Humour, Familiarity, and Innocence of a Sister: Insomuch
that he would often say to her,
Dear
Daphne;
wert thou but as
Handsome as Lætitia!
— She received such Language with that
ingenuous and pleasing Mirth, which is natural to a Woman without
Design. He still Sighed in vain for
Lætitia
, but found certain
Relief in the agreeable Conversation of
Daphne
. At length,
heartily tired with the haughty Impertinence of
Lætitia
, and
charmed with repeated Instances of good Humour he had observed in
Daphne
, he one Day told the latter, that he had something to say
to her he hoped she would be pleased with. —
Faith Daphne,
continued he,
I am in Love with thee, and despise thy Sister
sincerely
. The Manner of his declaring himself gave his Mistress
occasion for a very hearty Laughter. —
Nay,
says he,
I knew you
would Laugh at me, but I'll ask your Father.
He did so; the Father
received his Intelligence with no less Joy than Surprize, and was very
glad he had now no Care left but for his
Beauty
, which he thought
he could carry to Market at his Leisure. I do not know any thing that
has pleased me so much a great while, as this Conquest of my Friend
Daphne's
. All her Acquaintance congratulate her upon her Chance.
Medley, and laugh at that premeditating Murderer her Sister. As it is an
Argument of a light Mind, to think the worse of our selves for the
Imperfections of our Persons, it is equally below us to value our selves
upon the Advantages of them. The Female World seem to be almost
incorrigibly gone astray in this Particular; for which Reason, I shall
recommend the following Extract out of a Friend's Letter to the
Profess'd Beauties, who are a People almost as unsufferable as the
Profess'd Wits.
Monsieur St.
Evremont1 has concluded one of his Essays, with
affirming that the last Sighs of a Handsome Woman are not so much for
the loss of her Life, as of her Beauty. Perhaps this Raillery is pursued
too far, yet it is turn'd upon a very obvious Remark, that Woman's
strongest Passion is for her own Beauty, and that she values it as her
Favourite Distinction. From hence it is that all Arts, which pretend to
improve or preserve it, meet with so general a Reception among the Sex.
To say nothing of many False Helps and Contraband Wares of Beauty, which
are daily vended in this great Mart, there is not a Maiden-Gentlewoman,
of a good Family in any County of
South-Britain, who has not
heard of the Virtues of
May-Dew, or is unfurnished with some
Receipt or other in Favour of her Complexion; and I have known a
Physician of Learning and Sense, after Eight Years Study in the
University, and a Course of Travels into most Countries of
Europe, owe the first raising of his Fortunes to a Cosmetick
Wash.
This has given me Occasion to consider how so Universal a Disposition in
Womankind, which springs from a laudable Motive, the Desire of Pleasing,
and proceeds upon an Opinion, not altogether groundless, that Nature may
be helped by Art, may be turn'd to their Advantage. And, methinks, it
would be an acceptable Service to take them out of the Hands of Quacks
and Pretenders, and to prevent their imposing upon themselves, by
discovering to them the true Secret and Art of improving Beauty.
In order to this, before I touch upon it directly, it will be necessary
to lay down a few Preliminary Maxims,
viz.
- That no Woman can be Handsome by the Force of Features alone, any more
than she can be Witty only by the Help of Speech.
- That Pride destroys all Symmetry and Grace, and Affectation is a more
terrible Enemy to fine Faces than the Small-Pox.
- That no Woman is capable of being Beautiful, who is not incapable of
being False.
- And, That what would be Odious in a Friend, is Deformity in a Mistress.
From these few Principles, thus laid down, it will be easie to prove,
that the true Art of assisting Beauty consists in Embellishing the whole
Person by the proper Ornaments of virtuous and commendable Qualities.
By
this Help alone it is that those who are the Favourite Work of Nature,
or, as Mr.
Dryden expresses it, the Porcelain Clay of human
Kind
2, become animated, and are in a Capacity of exerting their
Charms: And those who seem to have been neglected by her, like Models
wrought in haste, are capable, in a great measure, of finishing what She
has left imperfect.
It is, methinks, a low and degrading Idea of that Sex, which was created
to refine the Joys, and soften the Cares of Humanity, by the most
agreeable Participation, to consider them meerly as Objects of Sight.
This is abridging them of their natural Extent of Power, to put them
upon a Level with their Pictures at
Kneller's. How much nobler is
the Contemplation of Beauty heighten'd by Virtue, and commanding our
Esteem and Love, while it draws our Observation? How faint and
spiritless are the Charms of a Coquet, when compar'd with the real
Loveliness of
Sophronia's Innocence, Piety, good Humour and
Truth; Virtues which add a new Softness to her Sex, and even beautify
her Beauty! That Agreeableness, which must otherwise have appeared no
longer in the modest Virgin, is now preserv'd in the tender Mother, the
prudent Friend, and the faithful Wife. Colours, artfully spread upon
Canvas, may entertain the Eye, but not affect the Heart; and she, who
takes no care to add to the natural Graces of her Person any excelling
Qualities, may be allowed still to amuse, as a Picture, but not to
triumph as a Beauty.
When
Adam is introduced by
Milton describing
Eve in
Paradise, and relating to the Angel the Impressions he felt upon seeing
her at her first Creation, he does not represent her like a
Grecian
Venus by her Shape or Features, but by the Lustre of her Mind which
shone in them, and gave them their Power of charming.
Grace was in all her Steps, Heaven in her Eye,
In all her Gestures Dignity and Love.
Without this irradiating Power the proudest Fair One ought to know,
whatever her Glass may tell her to the contrary, that her most perfect
Features are Uninform'd and Dead.
I cannot better close this Moral, than by a short Epitaph written by
Ben Johnson, with a Spirit which nothing could inspire but such
an Object as I have been describing.
Underneath this Stone doth lie
As much Virtue as cou'd die,
Which when alive did Vigour give
To as much Beauty as cou'd live
3.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
R. B.
R.
Charles de St. Denis, Sieur de St. Evremond, died in 1703,
aged 95, and was buried in Westminster Abbey. His military and
diplomatic career in France was closed in 1661, when his condemnations
of Mazarin, although the Cardinal was then dead, obliged him to fly from
the wrath of the French Court to Holland and afterwards to England,
where Charles II granted him a pension of £300 a-year. At Charles's
death the pension lapsed, and St. Evremond declined the post of cabinet
secretary to James II. After the Revolution he had William III for
friend, and when, at last, he was invited back, in his old age, to
France, he chose to stay and die among his English friends. In a second
volume of
Miscellany Essays by Monsieur de St. Evremont,
done into
English by Mr. Brown (1694), an Essay
Of the Pleasure that Women take
in their Beauty
ends (p. 135) with the thought quoted by Steele.
In
Don Sebastian, King of Portugal,
act I, says Muley
Moloch, Emperor of Barbary,
Ay; There look like the Workmanship of Heav'n:
This is the Porcelain Clay of Human Kind.
The lines are in the Epitaph
on Elizabeth L.H.
'One name was Elizabeth,
The other, let it sleep in death.'
But Steele, quoting from memory, altered the words to his purpose. Ben
Johnson's lines were:
Underneath this stone doth lie,
As much Beauty as could die,
Which in Life did Harbour give
To more Virtue than doth live.
Contents
|
Monday, April 9, 1711 |
Addison |
... parcit
Cognatis maculis similis fera ...
Juv.

The Club of which I am a Member, is very luckily composed of such
persons as are engaged in different Ways of Life, and disputed as it
were out of the most conspicuous Classes of Mankind: By this Means I am
furnished with the greatest Variety of Hints and Materials, and know
every thing that passes in the different Quarters and Divisions, not
only of this great City, but of the whole Kingdom. My Readers too have
the Satisfaction to find, that there is no Rank or Degree among them who
have not their Representative in this Club, and that there is always
some Body present who will take Care of their respective Interests, that
nothing may be written or published to the Prejudice or Infringement of
their just Rights and Privileges.
I last Night sat very late in company with this select Body of Friends,
who entertain'd me with several Remarks which they and others had made
upon these my Speculations, as also with the various Success which they
had met with among their several Ranks and Degrees of Readers.
Will.
Honeycomb
told me, in the softest Manner he could, That there were some
Ladies (but for your Comfort, says
Will
., they are not those of the most
Wit) that were offended at the Liberties I had taken with the Opera and
the Puppet-Show: That some of them were likewise very much surpriz'd,
that I should think such serious Points as the Dress and Equipage of
Persons of Quality, proper Subjects for Raillery.
He was going on, when Sir
Andrew Freeport
took him up short, and told
him, That the Papers he hinted at had done great Good in the City, and
that all their Wives and Daughters were the better for them: And further
added, That the whole City thought themselves very much obliged to me
for declaring my generous Intentions to scourge Vice and Folly as they
appear in a Multitude, without condescending to be a Publisher of
particular Intrigues and Cuckoldoms. In short, says Sir
Andrew
, if you
avoid that foolish beaten Road of falling upon Aldermen and Citizens,
and employ your Pen upon the Vanity and Luxury of Courts, your Paper
must needs be of general Use.
Upon this my Friend the
Templar
told Sir
Andrew
, That he wondered to
hear a Man of his Sense talk after that Manner; that the City had always
been the Province for Satyr; and that the Wits of King
Charles's
Time jested upon nothing else during his whole Reign. He then shewed, by
the Examples of
Horace, Juvenal, Boileau
, and the best Writers of
every Age, that the Follies of the Stage and Court had never been
accounted too sacred for Ridicule, how great so-ever the Persons might
be that patronized them. But after all, says he, I think your Raillery
has made too great an Excursion, in attacking several Persons of the
Inns of Court; and I do not believe you can shew me any Precedent for
your Behaviour in that Particular.
My good Friend Sir
Roger De Coverley
, who had said nothing all this
while, began his Speech with a Pish! and told us. That he wondered to
see so many Men of Sense so very serious upon Fooleries. Let our good
Friend, says he, attack every one that deserves it: I would only advise
you, Mr.
Spectator
, applying himself to me, to take Care how you meddle
with Country Squires: They are the Ornaments of the
English
Nation;
Men of good Heads and sound Bodies! and let me tell you, some of them
take it ill of you that you mention Fox-hunters with so little Respect.
Captain
Sentry
spoke very sparingly on this Occasion. What he said was
only to commend my Prudence in not touching upon the Army, and advised
me to continue to act discreetly in that Point.
By this Time I found every subject of my Speculations was taken away
from me by one or other of the Club; and began to think my self in the
Condition of the good Man that had one Wife who took a Dislike to his
grey Hairs, and another to his black, till by their picking out what
each of them had an Aversion to, they left his Head altogether bald and
naked.
While I was thus musing with my self, my worthy Friend the Clergy-man,
who, very luckily for me, was at the Club that Night, undertook my
Cause. He told us, That he wondered any Order of Persons should think
themselves too considerable to be advis'd: That it was not Quality, but
Innocence which exempted Men from Reproof; That Vice and Folly ought to
be attacked where-ever they could be met with, and especially when they
were placed in high and conspicuous Stations of Life. He further added,
That my Paper would only serve to aggravate the Pains of Poverty, if it
chiefly expos'd those who are already depressed, and in some measure
turn'd into Ridicule, by the Meanness of their Conditions and
Circumstances. He afterwards proceeded to take Notice of the great Use
this Paper might be of to the Publick, by reprehending those Vices which
are too trivial for the Chastisement of the Law, and too fantastical for
the Cognizance of the Pulpit. He then advised me to prosecute my
Undertaking with Chearfulness; and assured me, that whoever might be
displeased with me, I should be approved by all those whose Praises do
Honour to the Persons on whom they are bestowed.
The whole Club pays a particular Deference to the Discourse of this
Gentleman, and are drawn into what he says as much by the candid and
ingenuous Manner with which he delivers himself, as by the Strength of
Argument and Force of Reason which he makes use of.
Will. Honeycomb
immediately agreed, that what he had said was right; and that for his
Part, he would not insist upon the Quarter which he had demanded for the
Ladies. Sir
Andrew
gave up the City with the same Frankness. The
Templar
would not stand out; and was followed by Sir
Roger
and the
Captain
: Who
all agreed that I should be at Liberty to carry the War into what
Quarter I pleased; provided I continued to combat with Criminals in a
Body, and to assault the Vice without hurting the Person.
This Debate, which was held for the Good of Mankind, put me in Mind of
that which the
Roman
Triumvirate were formerly engaged in, for
their Destruction. Every Man at first stood hard for his Friend, till
they found that by this Means they should spoil their Proscription: And
at length, making a Sacrifice of all their Acquaintance and Relations,
furnished out a very decent Execution.
Having thus taken my Resolution to march on boldly in the Cause of
Virtue and good Sense, and to annoy their Adversaries in whatever Degree
or Rank of Men they may be found: I shall be deaf for the future to all
the Remonstrances that shall be made to me on this Account. If
Punch
grow extravagant, I shall reprimand him very freely: If the
Stage becomes a Nursery of Folly and Impertinence, I shall not be afraid
to animadvert upon it. In short, If I meet with any thing in City,
Court, or Country, that shocks Modesty or good Manners, I shall use my
utmost Endeavours to make an Example of it. I must however intreat every
particular Person, who does me the Honour to be a Reader of this Paper,
never to think himself, or any one of his Friends or Enemies, aimed at
in what is said: For I promise him, never to draw a faulty Character
which does not fit at least a Thousand People; or to publish a single
Paper, that is not written in the Spirit of Benevolence and with a Love
to Mankind.
C.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 10, 1711 |
Addison |
Risu inepto res ineptior milla est.
Mart.

Among all kinds of Writing, there is none in which Authors are more apt
to miscarry than in Works of Humour, as there is none in which they are
more ambitious to excell. It is not an Imagination that teems with
Monsters, an Head that is filled with extravagant Conceptions, which is
capable of furnishing the World with Diversions of this nature; and yet
if we look into the Productions of several Writers, who set up for Men
of Humour, what wild irregular Fancies, what unnatural Distortions of
Thought, do we meet with? If they speak Nonsense, they believe they are
talking Humour; and when they have drawn together a Scheme of absurd,
inconsistent Ideas, they are not able to read it over to themselves
without laughing. These poor Gentlemen endeavour to gain themselves the
Reputation of Wits and Humourists, by such monstrous Conceits as almost
qualify them for
Bedlam;
not considering that Humour should always lye
under the Check of Reason, and that it requires the Direction of the
nicest Judgment, by so much the more as it indulges it self in the most
boundless Freedoms.
is a kind of Nature that is to be observed in
this sort of Compositions, as well as in all other, and a certain
Regularity of Thought
which
must discover the Writer to be a Man
of Sense, at the same time that he appears altogether given up to
Caprice: For my part, when I read the delirious Mirth of an unskilful
Author, I cannot be so barbarous as to divert my self with it, but am
rather apt to pity the Man, than to laugh at any thing he writes.
deceased Mr.
Shadwell
, who had himself a great deal of the Talent,
which I am treating of, represents an empty Rake, in one of his Plays,
as very much surprized to hear one say that breaking of Windows was not
Humour
; and I question not but several
English
Readers will be as
much startled to hear me affirm, that many of those raving incoherent
Pieces, which are often spread among us, under odd Chimerical Titles,
are rather the Offsprings of a Distempered Brain, than Works of Humour.
It is indeed much easier to describe what is not Humour, than what is;
and very difficult to define it otherwise than as
Cowley
has done Wit,
by Negatives. Were I to give my own Notions of it, I would deliver them
after
Plato's
manner, in a kind of Allegory, and by supposing Humour
to be a Person, deduce to him all his Qualifications, according to the
following Genealogy.
Truth
was the Founder of the Family, and the Father
of
Good Sense
.
Good Sense
was the Father of
Wit
, who married a Lady of a
Collateral Line called
Mirth
, by whom he had Issue
Humour
.
Humour
therefore being the youngest of this Illustrious Family, and descended
from Parents of such different Dispositions, is very various and unequal
in his Temper; sometimes you see him putting on grave Looks and a solemn
Habit, sometimes airy in his Behaviour and fantastick in his Dress:
Insomuch that at different times he appears as serious as a Judge, and
as jocular as a
Merry-Andrew
. But as he has a great deal of the Mother
in his Constitution, whatever Mood he is in, he never fails to make his
Company laugh.
since there
is an Impostor
abroad, who
takes upon him
the Name of this young Gentleman, and would willingly pass for him in
the World; to the end that well-meaning Persons may not be imposed upon
by
Cheats
, I would desire my Readers, when they meet with
this
Pretender,
to look into his Parentage, and to examine him strictly,
whether or no he be remotely allied to
Truth
, and lineally descended
from
Good Sense
; if not, they may conclude him a Counterfeit.
may
likewise distinguish him by a loud and excessive Laughter, in which he
seldom gets his Company to join with him. For, as
True Humour
generally
looks serious, whilst every Body laughs
about him
;
False Humour
is
always laughing, whilst every Body about him looks serious. I shall only
add, if he has not in him a Mixture of both Parents, that is, if he
would pass for the Offspring of
Wit
without
Mirth
, or
Mirth
without
Wit
,
you may conclude him to be altogether Spurious, and a Cheat.
The Impostor, of whom I am speaking, descends Originally from
Falsehood
,
who was the Mother of
Nonsense
, who was brought to Bed of a Son called
Frenzy
, who Married one of the Daughters of
Folly
, commonly known by the
Name of
Laughter
, on whom he begot that Monstrous Infant of which I have
been here speaking. I shall set down at length the Genealogical Table of
False Humour
, and, at the same time, place under it the Genealogy of
True Humour
, that the Reader may at one View behold their different
Pedigrees and Relations.
| Falsehood |
Truth |
| | |
| |
| Nonsense |
Good Sense |
| | |
| |
| Frenzy=Laughter |
Wit=Mirth |
| | |
| |
| False Humour |
Humour |
I might extend the Allegory, by mentioning several of the Children of
False Humour
, who are more in Number than the Sands of the Sea, and
might in particular enumerate the many Sons and Daughters which he has
begot in this Island. But as this would be a very invidious Task, I
shall only observe in general, that
False Humour
differs from the
True
,
as a Monkey does from a Man.
- He is exceedingly given to little Apish Tricks and
Buffooneries.
- He so much delights in Mimickry, that it is all one to him
whether he exposes by it Vice and Folly, Luxury and Avarice; or, on
the contrary, Virtue and Wisdom, Pain and Poverty.
- He is wonderfully unlucky, insomuch that he will bite the
Hand that feeds him, and endeavour to ridicule both Friends and Foes
indifferently. For having but small Talents, he must be merry where he
can, not where he should.
- Being entirely void of Reason, he pursues no Point either
of Morality or Instruction, but is ludicrous only for the sake of
being so.
- Being incapable of any thing but Mock-Representations, his
Ridicule is always Personal, and aimed at the Vicious Man, or the
Writer; not at the Vice, or at the Writing.
I have here only pointed at the whole Species of False Humourists; but
as one of my principal Designs in this Paper is to beat down that
malignant Spirit, which discovers it self in the Writings of the present
Age, I shall not scruple, for the future, to single out any of the small
Wits, that infest the World with such Compositions as are ill-natured,
immoral and absurd. This is the only Exception which I shall make to the
general Rule I have prescribed my self, of
attacking Multitudes
: Since
every honest Man ought to look upon himself as in a Natural State of War
with the Libeller and Lampooner, and to annoy them where-ever they fall
in his way. This is but retaliating upon them, and treating them as they
treat others.
C.
that
Wit, in the town sense, is talked of to satiety in
Shadwell's plays; and window-breaking by the street rioters called
'Scowrers,' who are the heroes of an entire play of his, named after
them, is represented to the life by a street scene in the third act of
his
Woman Captain.
are several Impostors
take upon them
Counterfeits
any of these Pretenders
that is about him
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 11, 1711 |
Steele |
... Immania monstra
Perferimus ...
Virg.

I shall not put my self to any further Pains for this Day's
Entertainment, than barely to publish the Letters and Titles of
Petitions from the Play-house, with the Minutes I have made upon the
Latter for my Conduct in relation to them.
Drury-Lane, April
1 the 9th.
'
Upon reading the Project which is set forth in one of your late
Papers
2, of making an Alliance between all the Bulls, Bears,
Elephants, and Lions, which are separately exposed to publick View in
the Cities of
London and
Westminster; together with the other
Wonders, Shows, and Monsters, whereof you made respective Mention in
the said Speculation; We, the chief Actors of this Playhouse, met and
sat upon the said Design. It is with great Delight that We expect the
Execution of this Work; and in order to contribute to it, We have
given Warning to all our Ghosts to get their Livelihoods where they
can, and not to appear among us after Day-break of the 16th Instant.
We are resolved to take this Opportunity to part with every thing
which does not contribute to the Representation of humane Life; and
shall make a free Gift of all animated Utensils to your Projector. The
Hangings you formerly mentioned are run away; as are likewise a Set of
Chairs, each of which was met upon two Legs going through the
Rose
Tavern at Two this Morning. We hope, Sir, you will give proper Notice
to the Town that we are endeavouring at these Regulations; and that we
intend for the future to show no Monsters, but Men who are converted
into such by their own Industry and Affectation. If you will please to
be at the House to-night, you will see me do my Endeavour to show some
unnatural Appearances which are in vogue among the Polite and
Well-bred. I am to represent, in the Character of a fine Lady Dancing,
all the Distortions which are frequently taken for Graces in Mien and
Gesture. This, Sir, is a Specimen of the Method we shall take to
expose the Monsters which come within the Notice of a regular Theatre;
and we desire nothing more gross may be admitted by you Spectators for
the future. We have cashiered three Companies of Theatrical Guards,
and design our Kings shall for the future make Love and sit in Council
without an Army: and wait only your Direction, whether you will have
them reinforce King
Porus or join the Troops of
Macedon. Mr.
Penkethman resolves to consult his
Pantheon of Heathen Gods in
Opposition to the Oracle of
Delphos, and doubts not but he shall
turn the Fortunes of
Porus when he personates him. I am desired by
the Company to inform you, that they submit to your Censures; and
shall have you in greater Veneration than
Hercules was in of old, if
you can drive Monsters from the Theatre; and think your Merit will be
as much greater than his, as to convince is more than to conquer.
I am, Sir,
Your most obedient Servant,
T.D.
Sir,
When I acquaint you with the great and unexpected Vicissitudes of
my Fortune, I doubt not but I shall obtain your Pity and Favour.
I
have for many Years last past been Thunderer to the Play-house; and
have not only made as much Noise out of the Clouds as any Predecessor
of mine in the Theatre that ever bore that Character, but also have
descended and spoke on the Stage as the bold Thunder in
The
Rehearsal.
3
When they got me down thus low, they thought fit to degrade me
further, and make me a Ghost. I was contented with this for these two
last Winters; but they carry their Tyranny still further, and not
satisfied that I am banished from above Ground, they have given me to
understand that I am wholly to depart their Dominions, and taken from
me even my subterraneous Employment. Now, Sir, what I desire of you
is, that if your Undertaker thinks fit to use Fire-Arms (as other
Authors have done) in the Time of
Alexander, I may be a Cannon
against
Porus, or else provide for me in the Burning of
Persepolis, or what other Method you shall think fit.
Salmoneus of Covent-Garden.'
The Petition of all the Devils of the Play-house in behalf of themselves
and Families, setting forth their Expulsion from thence, with
Certificates of their good Life and Conversation, and praying Relief.
- The Merit of this Petition referred to Mr. Chr. Rich, who made them
Devils.
The Petition of the Grave-digger in
Hamlet
, to command the Pioneers in
the Expedition of
Alexander
.
Petition of
William Bullock
, to be
Hephestion
to
Penkethman the
Great.
The caricature here, and in following lines, is of a passage in Sir
Robert Stapylton's Slighted Maid: 'I am the Evening, dark as Night,'
&c.
In the Spectator's time the Rehearsal was an acted play, in which
Penkethman had the part of the gentleman Usher, and Bullock was one of
the two Kings of Brentford; Thunder was Johnson, who played also the
Grave-digger in Hamlet and other reputable parts.
March
was written by an oversight left in the first reprint
uncorrected.
.
Mr. Bayes, the poet, in the Duke of Buckingham's
Rehearsal
, after showing how he has planned a Thunder and Lightning
Prologue for his play, says,
|
Come out, Thunder and Lightning. |
|
Enter Thunder and Lightning.. |
| Thun |
I am the bold Thunder. |
| Bayes |
Mr. Cartwright, prithee speak that a little louder, and with a
hoarse voice. I am the bold Thunder: pshaw! Speak it me in a voice
that thunders it out indeed: I am the bold Thunder. |
| Thun |
I am the bold Thunder. |
| Light |
The brisk Lightning, I. |
William Bullock was a good and popular comedian, whom some
preferred to Penkethman, because he spoke no more than was set down for
him, and did not overact his parts. He was now with Penkethman, now with
Cibber and others, joint-manager of a theatrical booth at Bartholomew
Fair. When this essay was written Bullock and Penkethman were acting
together in a play called
Injured Love
, produced at Drury Lane on the
7th of April, Bullock as 'Sir Bookish Outside,' Penkethman as 'Tipple,'
a Servant. Penkethman, Bullock and Dogget were in those days Macbeth's
three witches. Bullock had a son on the stage capable of courtly parts,
who really had played Hephestion in
the Rival Queens
, in a theatre
opened by Penkethman at Greenwich in the preceding summer.
Contents
A Widow Gentlewoman,
wellborn both by Father and Mother's Side,
being
the Daughter of Thomas Prater,
once an eminent Practitioner in the
Law,
and of Letitia Tattle,
a Family well known in all Parts of this
Kingdom,
having been reduc'd by Misfortunes to wait on several great
Persons,
and for some time to be Teacher at a Boarding-School of young
Ladies;
giveth Notice to the Publick,
That she hath lately taken a House
near Bloomsbury-Square,
commodiously situated next the Fields in a
good Air;
where she teaches all sorts of Birds of the loquacious Kinds,
as Parrots, Starlings, Magpies, and others,
to imitate human Voices in
greater Perfection than ever yet was practis'd.
They are not only
instructed to pronounce Words distinctly, and in a proper Tone and
Accent,
but to speak the Language with great Purity and Volubility of
Tongue,
together with all the fashionable Phrases and Compliments now in
use either at Tea-Tables or visiting Days.
Those that have good Voices
may be taught to sing the newest Opera-Airs,
and, if requir'd, to speak
either Italian
or French,
paying something extraordinary above the
common Rates.
They whose Friends are not able to pay the full Prices may
be taken as Half-boarders.
She teaches such as are design'd for the
Diversion of the Publick,
and to act in enchanted Woods on the Theatres,
by the Great.
As she has often observ'd with much Concern how indecent
an Education is usually given these innocent Creatures,
which in some
Measure is owing to their being plac'd in Rooms next the Street,
where,
to the great Offence of chaste and tender Ears,
they learn Ribaldry,
obscene Songs, and immodest Expressions from Passengers and idle People,
and also to cry Fish and Card-matches, with other useless Parts of
Learning to Birds who have rich Friends,
she has fitted up proper and
neat Apartments for them in the back Part of her said House;
where she
suffers none to approach them but her self, and a Servant Maid who is
deaf and dumb,
and whom she provided on purpose to prepare their Food
and cleanse their Cages;
having found by long Experience how hard a
thing it is for those to keep Silence who have the Use of Speech,
and
the Dangers her Scholars are expos'd to by the strong Impressions that
are made by harsh Sounds and vulgar Dialects.
In short, if they are
Birds of any Parts or Capacity,
she will undertake to render them so
accomplish'd in the Compass of a Twelve-month,
that they shall be fit
Conversation for such Ladies as love to chuse their Friends and
Companions out of this Species.
R.
|
Thursday, April 12, 1711 |
Addison |
... Non illa colo calathisve Minervæ
Fœmineas assueta manus ...
Virg.

Some Months ago, my Friend Sir Roger, being in the Country, enclosed a
Letter to me, directed to a certain Lady whom I shall here call by the
Name of
Leonora
, and as it contained Matters of Consequence, desired
me to deliver it to her with my own Hand. Accordingly I waited upon her
Ladyship pretty early in the Morning, and was desired by her Woman to
walk into her Lady's Library, till such time as she was in a Readiness
to receive me. The very Sound of a
Lady's Library
gave me a great
Curiosity to see it; and as it was some time before the Lady came to me,
I had an Opportunity of turning over a great many of her Books, which
were ranged together in a very beautiful Order. At the End of the
Folios
(which were finely bound and gilt) were great Jars of
China
placed one above another in a very noble
Piece of Architecture.
Quartos
were separated from the
Octavos
by a Pile of smaller
Vessels, which rose in a
delightful
Pyramid. The
Octavos
were
bounded by Tea Dishes of all Shapes Colours and Sizes, which were so
disposed on a wooden Frame, that they looked like one continued Pillar
indented with the finest Strokes of Sculpture, and stained with the
greatest Variety of Dyes. That Part of the Library which was designed
for the Reception of Plays and Pamphlets, and other loose Papers, was
enclosed in a kind of Square, consisting of one of the prettiest
Grotesque Works that ever I saw, and made up of Scaramouches, Lions,
Monkies, Mandarines, Trees, Shells, and a thousand other odd Figures in
China
Ware. In the midst of the Room was a little Japan Table, with a
Quire of gilt Paper upon it, and on the Paper a Silver Snuff-box made in
the Shape of a little Book. I found there were several other Counterfeit
Books upon the upper Shelves, which were carved in Wood, and served only
to fill up the Number, like Fagots in the muster of a Regiment. I was
wonderfully pleased with such a mixt kind of Furniture, as seemed very
suitable both to the Lady and the Scholar, and did not know at first
whether I should fancy my self in a Grotto, or in a Library.
Upon my looking into the Books, I found there were some few which the
Lady had bought for her own use, but that most of them had been got
together, either because she had heard them praised, or because she had
seen the Authors of them.
several that I examin'd, I very well
remember these that follow
.
- Ogleby's Virgil.
- Dryden's Juvenal.
- Cassandra.
- Cleopatra.
- Astræa.
- Sir Isaac Newton's Works.
- The Grand Cyrus: With a Pin stuck in one of the middle Leaves.
- Pembroke's Arcadia.
- Locke of Human Understanding: With a Paper of Patches in it.
- A Spelling-Book.
- A Dictionary for the Explanation of hard Words.
- Sherlock upon Death.
- The fifteen Comforts of Matrimony.
- Sir William Temptle's Essays.
- Father Malbranche's Search after Truth, translated into English.
- A Book of Novels.
- The Academy of Compliments.
- Culpepper's Midwifry.
- The Ladies Calling.
- Tales in Verse by Mr. Durfey: Bound in Red Leather, gilt on the Back, and doubled down in several Places.
- All the Classick Authors in Wood.
- A set of Elzevers by the same Hand.
- Clelia: Which opened of it self in the Place that describes two Lovers in a Bower.
- Baker's Chronicle.
- Advice to a Daughter.
- The New Atalantis, with a Key to it.
- Mr. Steel's Christian Heroe.
- A Prayer Book: With a Bottle of Hungary Water by the side of it.
- Dr. Sacheverell's Speech.
- Fielding's Tryal.
- Seneca's Morals.
- Taylor's holy Living and Dying.
- La ferte's Instructions for Country Dances.
I was taking a Catalogue in my Pocket-Book of these, and several other
Authors, when
Leonora
entred, and upon my presenting her with the
Letter from the Knight, told me, with an unspeakable Grace, that she
hoped Sir
Roger
was in good Health: I answered
Yes
, for I hate
long Speeches, and after a Bow or two retired.
Leonora
was formerly a celebrated Beauty, and is still a very
lovely Woman. She has been a Widow for two or three Years, and being
unfortunate in her first Marriage, has taken a Resolution never to
venture upon a second. She has no Children to take care of, and leaves
the Management of her Estate to my good Friend Sir
Roger
. But as the
Mind naturally sinks into a kind of Lethargy, and falls asleep, that is
not agitated by some Favourite Pleasures and Pursuits,
Leonora
has turned all the Passions of her Sex into a Love of Books and
Retirement. She converses chiefly with Men (as she has often said
herself), but it is only in their Writings; and admits of very few Male-Visitants, except my Friend Sir
Roger
, whom she hears with great
Pleasure, and without Scandal. As her Reading has lain very much among
Romances, it has given her a very particular Turn of Thinking, and
discovers it self even in her House, her Gardens, and her Furniture. Sir
Roger
has entertained me an Hour together with a Description of her
Country-Seat, which is situated in a kind of Wilderness, about an
hundred Miles distant from
London
, and looks like a little
Enchanted Palace. The Rocks about her are shaped into Artificial
Grottoes covered with Wood-Bines and Jessamines. The Woods are cut into
shady Walks, twisted into Bowers, and filled with Cages of Turtles. The
Springs are made to run among Pebbles, and by that means taught to
Murmur very agreeably. They are likewise collected into a Beautiful Lake
that is Inhabited by a Couple of Swans, and empties it self by a little
Rivulet which runs through a Green Meadow, and is known in the Family by
the Name of
The Purling Stream
. The Knight likewise tells me, that
this Lady preserves her Game better than any of the Gentlemen in the
Country, not (says Sir
Roger
) that she sets so great a Value upon her
Partridges and Pheasants, as upon her Larks and Nightingales. For she
says that every Bird which is killed in her Ground, will spoil a
Consort, and that she shall certainly miss him the next Year.
When I think how odly this Lady is improved by Learning, I look upon her
with a Mixture of Admiration and Pity.
these Innocent
Entertainments which she has formed to her self, how much more Valuable
does she appear than those of her Sex,
who
employ themselves in
Diversions that are less Reasonable, tho' more in Fashion? What
Improvements would a Woman have made, who is so Susceptible of
Impressions from what she reads, had she been guided to such Books as
have a Tendency to enlighten the Understanding and rectify the Passions,
as well as to those which are of little more use than to divert the
Imagination?
But the manner of a Lady's Employing her self usefully in Reading shall
be the Subject of another Paper, in which I design to recommend such
particular Books as may be proper for the Improvement of the Sex. And as
this is a Subject of a very nice Nature, I shall desire my
Correspondents to give me their Thoughts upon it.
C.
very delightful
John Ogilby, or Ogilvy, who died in 1676, aged 76, was
originally a dancing-master, then Deputy Master of the Revels in Dublin;
then, after the outbreak of the Irish Rebellion, a student of Latin and
Greek in Cambridge. Finally, he settled down as a cosmographer. He
produced translations of both Virgil and Homer into English verse. His
Virgil
, published in 1649, was handsomely printed and the first
which gave the entire works in English, nearly half a century before
Dryden's which appeared in 1697.
The translation of
Juvenal
and
Persius
by Dryden, with
help of his two sons, and of Congreve, Creech, Tate, and others, was
first published in 1693. Dryden translated
Satires
1, 3, 6, 10, and 16
of Juvenal, and the whole of Persius. His
Essay on Satire
was prefixed.
Cassandra
and
Cleopatra
were romances from the French of
Gautier de Costes, Seigneur de la Calprenède, who died in 1663. He
published
Cassandra
in 10 volumes in 1642,
Cleopatra
in 12
volumes in 1656, besides other romances. The custom was to publish these
romances a volume at a time. A pretty and rich widow smitten with the
Cleopatra
while it was appearing, married La Calprenède upon
condition that he finished it, and his promise to do so was formally
inserted in the marriage contract. The English translations of these
French Romances were always in folio.
Cassandra
, translated by
Sir Charles Cotterell, was published in 1652;
Cleopatra
in 1668,
translated by Robert Loveday.
Astræa
was a pastoral Romance of
the days of Henri IV by Honoré D'Urfe, which had been translated by
John Pyper in 1620, and was again translated by a Person 'of Quality' in
1657. It was of the same school as Sir Philip Sydney's
Arcadia
,
first published after his death by his sister Mary, Countess of
Pembroke, in 1590, and from her, for whom, indeed, it had been written,
called
the Countess of Pembroke's Arcadia
.
Sir Isaac Newton was living in the
Spectator's
time. He died in
1727, aged 85. John Locke had died in 1704. His
Essay on the Human
Understanding
was first published in 1690. Sir William Temple had
died in 1699, aged 71.
The
Grand Cyrus
, by Magdeleine de Scudéri, was the most famous of
the French Romances of its day. The authoress, who died in 1701, aged
94, was called the Sappho of her time. Cardinal Mazarin left her a
pension by his will, and she had a pension of two thousand livres from
the king. Her
Grand Cyrus
, published in 10 volumes in 1650, was
translated (in one volume, folio) in 1653.
Clelia
, presently
afterwards included in the list of Leonora's books, was another very
popular romance by the same authoress, published in 10 volumes, a few
years later, immediately translated into English by John Davies, and
printed in the usual folio form.
Dr. William Sherlock, who after some scruple about taking the oaths to
King William, did so, and was made Dean of St. Paul's, published his
very popular
Practical Discourse concerning Death
, in 1689. He
died in 1707.
Father Nicolas Malebranche, in the
Spectator's
time, was living
in enjoyment of his reputation as one of the best French writers and
philosophers. The foundations of his fame had been laid by his
Recherche de la Vérité
, of which the first volume appeared in
1673. An English translation of it, by Thomas Taylor, was published (in
folio) in 1694. He died in 1715, Aged 77.
Thomas D'Urfey was a licentious writer of plays and songs, whose tunes
Charles II would hum as he leant on their writer's shoulder. His
New
Poems, with Songs
appeared in 1690. He died in 1723, aged 95.
The
New Atalantis
was a scandalous book by Mary de la Rivière
Manley, a daughter of Sir Roger Manley, governor of Guernsey. She began
her career as the victim of a false marriage, deserted and left to
support herself; became a busy writer and a woman of intrigue, who was
living in the
Spectator's
time, and died in 1724, in the house of
Alderman Barber, with whom she was then living. Her
New
Atalantis
, published in 1709, was entitled
Secret Memoirs and
Manners of several Persons of Quality of both sexes, from the New
Atalantis, an Island in the Mediterranean.
Under feigned names it
especially attacked members of Whig families, and led to proceedings for
libel.
La Ferte was a dancing master of the days of the
Spectator
, who
in Nos.
and
advertised his School 'in Compton Street, Soho, over
against St. Ann's Church Back-door,' adding that, 'at the desire of
several gentlemen in the City,' he taught dancing on Tuesdays and
Thursdays in the neighhourhood of the Royal Exchange.
that
Contents
|
Friday, April 13, 1711 |
Steele |
Cupias non placuisse nimis.
Mart.

A Late Conversation which I fell into, gave me an Opportunity of
observing a great deal of Beauty in a very handsome Woman, and as much
Wit in an ingenious Man, turned into Deformity in the one, and Absurdity
in the other, by the meer Force of Affectation. The Fair One had
something in her Person upon which her Thoughts were fixed, that she
attempted to shew to Advantage in every Look, Word, and Gesture. The
Gentleman was as diligent to do Justice to his fine Parts, as the Lady
to her beauteous Form: You might see his Imagination on the Stretch to
find out something uncommon, and what they call bright, to entertain
her; while she writhed her self into as many different Postures to
engage him. When she laughed, her Lips were to sever at a greater
Distance than ordinary to shew her Teeth: Her Fan was to point to
somewhat at a Distance, that in the Reach she may discover the Roundness
of her Arm; then she is utterly mistaken in what she saw, falls back,
smiles at her own Folly, and is so wholly discomposed, that her Tucker
is to be adjusted, her Bosom exposed, and the whole Woman put into new
Airs and Graces. While she was doing all this, the Gallant had Time to
think of something very pleasant to say next to her, or make some unkind
Observation on some other Lady to feed her Vanity. These unhappy Effects
of Affectation, naturally led me to look into that strange State of Mind
which so generally discolours the Behaviour of most People we meet with.
learned Dr.
Burnet
, in his Theory of the Earth, takes Occasion
to observe, That every Thought is attended with Consciousness and
Representativeness; the Mind has nothing presented to it but what is
immediately followed by a Reflection or Conscience, which tells you
whether that which was so presented is graceful or unbecoming. This Act
of the Mind discovers it self in the Gesture, by a proper Behaviour in
those whose Consciousness goes no further than to direct them in the
just Progress of their present Thought or Action; but betrays an
Interruption in every second Thought, when the Consciousness is employed
in too fondly approving a Man's own Conceptions; which sort of
Consciousness is what we call Affectation.
As the Love of Praise is implanted in our Bosoms as a strong Incentive
to worthy Actions, it is a very difficult Task to get above a Desire of
it for things that should be wholly indifferent. Women, whose Hearts are
fixed upon the Pleasure they have in the Consciousness that they are the
Objects of Love and Admiration, are ever changing the Air of their
Countenances, and altering the Attitude of their Bodies, to strike the
Hearts of their Beholders with new Sense of their Beauty. The dressing
Part of our Sex, whose Minds are the same with the sillyer Part of the
other, are exactly in the like uneasy Condition to be regarded for a
well-tied Cravat, an Hat cocked with an unusual Briskness, a very
well-chosen Coat, or other Instances of Merit, which they are impatient
to see unobserved.
But this apparent Affectation, arising from an ill-governed
Consciousness, is not so much to be wonder'd at in such loose and
trivial Minds as these: But when you see it reign in Characters of Worth
and Distinction, it is what you cannot but lament, not without some
Indignation. It creeps into the Heart of the wise Man, as well as that
of the Coxcomb. When you see a Man of Sense look about for Applause, and
discover an itching Inclination to be commended; lay Traps for a little
Incense, even from those whose Opinion he values in nothing but his own
Favour; Who is safe against this Weakness? or who knows whether he is
guilty of it or not? The best Way to get clear of such a light Fondness
for Applause, is to take all possible Care to throw off the Love of it
upon Occasions that are not in themselves laudable; but, as it appears,
we hope for no Praise from them. Of this Nature are all Graces in Mens
Persons, Dress and bodily Deportment; which will naturally be winning
and attractive if we think not of them, but lose their Force in
proportion to our Endeavour to make them such.
When our Consciousness turns upon the main Design of Life, and our
Thoughts are employed upon the chief Purpose either in Business or
Pleasure, we shall never betray an Affectation, for we cannot be guilty
of it: But when we give the Passion for Praise an unbridled Liberty, our
Pleasure in little Perfections, robs us of what is due to us for great
Virtues and worthy Qualities. How many excellent Speeches and honest
Actions are lost, for want of being indifferent where we ought? Men are
oppressed with regard to their Way of speaking and acting; instead of
having their Thought bent upon what they should do or say, and by that
Means bury a Capacity for great things, by their fear of failing in
indifferent things. This, perhaps, cannot be called Affectation; but it
has some Tincture of it, at least so far, as that their Fear of erring
in a thing of no Consequence, argues they would be too much pleased in
performing it.
It is only from a thorough Disregard to himself in such Particulars,
that a Man can act with a laudable Sufficiency: His Heart is fixed upon
one Point in view; and he commits no Errors, because he thinks nothing
an Error but what deviates from that Intention.
The wild Havock Affectation makes in that Part of the World which should
be most polite, is visible where ever we turn our Eyes: It pushes Men
not only into Impertinencies in Conversation, but also in their
premeditated Speeches. At the Bar it torments the Bench, whose Business
it is to cut off all Superfluities in what is spoken before it by the
Practitioner; as well as several little Pieces of Injustice which arise
from the Law it self.
have seen it make a Man run from the Purpose
before a Judge, who was, when at the Bar himself, so close and logical a
Pleader, that with all the Pomp of Eloquence in his Power, he never
spoke a Word too much
.
It might be born even here, but it often ascends the Pulpit it self; and
the Declaimer, in that sacred Place, is frequently so impertinently
witty, speaks of the last Day it self with so many quaint Phrases, that
there is no Man who understands Raillery, but must resolve to sin no
more: Nay, you may behold him sometimes in Prayer for a proper Delivery
of the great Truths he is to utter, humble himself with so very well
turned Phrase, and mention his own Unworthiness in a Way so very
becoming, that the Air of the pretty Gentleman is preserved, under the
Lowliness of the Preacher.
I shall end this with a short Letter I writ the other Day to a very
witty Man, over-run with the Fault I am speaking of.
Dear Sir,
'I Spent some Time with you the other Day, and must take the Liberty
of a Friend to tell you of the unsufferable Affectation you are guilty
of in all you say and do. When I gave you an Hint of it, you asked me
whether a Man is to be cold to what his Friends think of him? No; but
Praise is not to be the Entertainment of every Moment: He that hopes
for it must be able to suspend the Possession of it till proper
Periods of Life, or Death it self. If you would not rather be
commended than be Praiseworthy, contemn little Merits; and allow no
Man to be so free with you, as to praise you to your Face. Your Vanity
by this Means will want its Food. At the same time your Passion for
Esteem will be more fully gratified; Men will praise you in their
Actions: Where you now receive one Compliment, you will then receive
twenty Civilities. Till then you will never have of either, further
than
Sir,
Your humble Servant.'
R.
Dr. Thomas Burnet, who produced in 1681 the
Telluris
Theoria Sacra,
translated in 1690 as
the Sacred Theory of the Earth,
was living in the
Spectator's
time. He died in 1715, aged 80. He
was for 30 years Master of the Charter-house, and set himself against
James II in refusing to admit a Roman Catholic as a Poor Brother.
Burnet's
Theory
, a romance that passed for science in its day, was
opposed in 1696 by Whiston in his
New Theory of the Earth
(one all for
Fire, the other all for Water), and the new Romance was Science even in
the eyes of Locke. Addison, from Oxford in 1699, addressed a Latin ode
to Burnet.
Lord Cowper.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 14, 1711 |
Addison |
Multa fero, ut placem genus irritabile vatum,
Cum scribo.
Hor.

As a perfect Tragedy is the Noblest Production of Human Nature, so it is
capable of giving the Mind one of the most delightful and most improving
Entertainments.
virtuous Man (says
Seneca
) struggling with
Misfortunes, is such a Spectacle as Gods might look upon with Pleasure
: And such a Pleasure it is which one meets with in the Representation
of a well-written Tragedy. Diversions of this kind wear out of our
Thoughts every thing that is mean and little. They cherish and cultivate
that Humanity which is the Ornament of our Nature. They soften
Insolence, sooth Affliction, and subdue the Mind to the Dispensations of
Providence.
It is no Wonder therefore that in all the polite Nations of the World,
this part of the
Drama
has met with publick Encouragement.
The modern Tragedy excels that of
Greece
and
Rome
, in the
Intricacy and Disposition of the Fable; but, what a Christian Writer
would be ashamed to own, falls infinitely short of it in the Moral Part
of the Performance.
I
may
shew more at large hereafter; and in the mean time,
that I may contribute something towards the Improvement of the
English
Tragedy, I shall take notice, in this and in other
following Papers, of some particular Parts in it that seem liable to
Exception.
Aristotle
observes,
the
Iambick
Verse in the
Greek
Tongue was the most proper for Tragedy: Because at the same
time that it lifted up the Discourse from Prose, it was that which
approached nearer to it than any other kind of Verse. For, says he, we
may observe that Men in Ordinary Discourse very often speak
Iambicks
, without taking notice of it. We may make the same
Observation of our
English
Blank Verse, which often enters into
our Common Discourse, though we do not attend to it, and is such a due
Medium between Rhyme and Prose, that it seems wonderfully adapted to
Tragedy. I am therefore very much offended when I see a Play in Rhyme,
which is as absurd in
English
, as a Tragedy of
Hexameters
would have been in
Greek
or
Latin
. The Solæcism is, I
think, still greater, in those Plays that have some Scenes in Rhyme and
some in Blank Verse, which are to be looked upon as two several
Languages; or where we see some particular Similies dignifyed with
Rhyme, at the same time that everything about them lyes in Blank Verse.
I would not however debar the Poet from concluding his Tragedy, or, if
he pleases, every Act of it, with two or three Couplets, which may have
the same Effect as an Air in the
Italian
Opera after a long
Recitativo
, and give the Actor a graceful
Exit
. Besides
that we see a Diversity of Numbers in some Parts of the Old Tragedy, in
order to hinder the Ear from being tired with the same continued
Modulation of Voice. For the same Reason I do not dislike the Speeches
in our
English
Tragedy that close with an
Hemistick
, or
half Verse, notwithstanding the Person who speaks after it begins a new
Verse, without filling up the preceding one; Nor with abrupt Pauses and
Breakings-off in the middle of a Verse, when they humour any Passion
that is expressed by it.
Since I am upon this Subject, I must observe that our
English
Poets have succeeded much better in the Style, than in the Sentiments of
their Tragedies. Their Language is very often Noble and Sonorous, but
the Sense either very trifling or very common.
the contrary, in the
Ancient Tragedies, and indeed in those of
Corneille
and
Racine
tho' the Expressions are very great, it is the Thought
that bears them up and swells them. For my own part, I prefer a noble
Sentiment that is depressed with homely Language, infinitely before a
vulgar one that is blown up with all the Sound and Energy of Expression.
Whether this Defect in our Tragedies may arise from Want of Genius,
Knowledge, or Experience in the Writers, or from their Compliance with
the vicious Taste of their Readers, who are better Judges of the
Language than of the Sentiments, and consequently relish the one more
than the other, I cannot determine. But I believe it might rectify the
Conduct both of the one and of the other, if the Writer laid down the
whole Contexture of his Dialogue in plain
English
, before he
turned it into Blank Verse; and if the Reader, after the Perusal of a
Scene, would consider the naked Thought of every Speech in it, when
divested of all its Tragick Ornaments. By this means, without being
imposed upon by Words, we may judge impartially of the Thought, and
consider whether it be natural or great enough for the Person that
utters it, whether it deserves to shine in such a Blaze of Eloquence, or
shew itself in such a Variety of Lights as are generally made use of by
the Writers of our
English
Tragedy.
I must in the next place observe, that when our Thoughts are great and
just, they are often obscured by the sounding Phrases, hard Metaphors,
and forced Expressions in which they are cloathed.
Shakespear
is often
very Faulty in this Particular.
is a fine Observation in
Aristotle
to this purpose, which I have never seen quoted. The
Expression, says he, ought to be very much laboured in the unactive
Parts of the Fable, as in Descriptions, Similitudes, Narrations, and the
like; in which the Opinions, Manners and Passions of Men are not
represented; for these (namely the Opinions, Manners and Passions) are
apt to be obscured by Pompous Phrases, and Elaborate Expressions
.
Horace
, who copied most of his Criticisms after
Aristotle
, seems to
have had his Eye on the foregoing Rule in the following Verses:
Et Tragicus plerumque dolet Sermone pedestri,
Telephus et Peleus, cum pauper et exul uterque,
Projicit ampullas et sesquipedalia verba,
Si curat cor Spectantis tetigisse querelâ.
Tragedians too lay by their State, to grieve.
Peleus and Telephus, Exit'd and Poor,
Forget their Swelling and Gigantick Words.
(Ld. Roscommon.)
our Modern
English
Poets, there is none who was better turned
for Tragedy than
Lee
; if instead of favouring the Impetuosity of
his Genius, he had restrained it, and kept it within its proper Bounds.
His Thoughts are wonderfully suited to Tragedy, but frequently lost in
such a Cloud of Words, that it is hard to see the Beauty of them: There
is an infinite Fire in his Works, but so involved in Smoak, that it does
not appear in half its Lustre. He frequently succeeds in the Passionate
Parts of the Tragedy, but more particularly where he slackens his
Efforts, and eases the Style of those Epithets and Metaphors, in which
he so much abounds. What can be more Natural, more Soft, or more
Passionate, than that Line in
Statira's
Speech, where she
describes the Charms of
Alexander's
Conversation?
Then he would talk: Good Gods! how he would talk!
That unexpected Break in the Line, and turning the Description of his
Manner of Talking into an Admiration of it, is inexpressibly Beautiful,
and wonderfully suited, to the fond Character of the Person that speaks
it. There is a Simplicity in the Words, that outshines the utmost Pride
of Expression.
Otway
has
Nature in the Language of his Tragedy, and
therefore shines in the Passionate Parts, more than any of our
English
Poets. As there is something Familiar and Domestick in
the Fable of his Tragedy, more than in those of any other Poet, he has
little Pomp, but great Force in his Expressions. For which Reason,
though he has admirably succeeded in the tender and melting Part of his
Tragedies, he sometimes falls into too great a Familiarity of Phrase in
those Parts, which, by
Aristotle's
Rule, ought to have been
raised and supported by the Dignity of Expression.
It has been observed by others, that this Poet has founded his Tragedy
of
Venice Preserved
on so wrong a Plot, that the greatest
Characters in it are those of Rebels and Traitors. Had the Hero of his
Play discovered the same good Qualities in the Defence of his Country,
that he showed for its Ruin and Subversion, the Audience could not
enough pity and admire him: But as he is now represented, we can only
say of him what the
Roman
Historian says of
Catiline
, that
his Fall would have been Glorious (
si pro Patriâ sic concidisset
)
had he so fallen in the Service of his Country.
C.
From Seneca on
Providence
:
"De Providentiâ, sive Quare Bonis Viris Mala Accidant cum sit
Providentia' § 2,
'Ecce spectaculum dignum, ad quod respiciat intentus operi suo Deus:
ecce par Deo dignum, vir fortis cum malâ fortunâ compositus, utique si
et provocavit."
So also Minutius Felix,
Adversus Gentes:
"Quam pulchrum spectaculum Deo, cum Christianus cum dolore
congueditur? cum adversus minas, et supplicia, et tormenta componitur?
cum libertatem suam adversus reges ac Principes erigit.'
Epictetus also bids the endangered man remember that he has been sent by
God as an athlete into the arena.
shall
Poetics
, Part I. § 7. Also in the
Rhetoric
, bk III. ch. i.
These chiefs of the French tragic drama died, Corneille in
1684, and his brother Thomas in 1708; Racine in 1699.
It is the last sentence in Part III of the
Poetics
.
Nathaniel Lee died in 1692 of injury received during a
drunken frolic. Disappointed of a fellowship at Cambridge, he turned
actor; failed upon the stage, but prospered as a writer for it. His
career as a dramatist began with
Nero
, in 1675, and he wrote in all
eleven plays. His most successful play was the
Rival Queens
, or the
Death of Alexander the Great, produced in 1677. Next to it in success,
and superior in merit, was his
Theodosius
, or the Force of Love,
produced in 1680. He took part with Dryden in writing the very
successful adaptation of
Œdipus
, produced in 1679, as an English
Tragedy based upon Sophocles and Seneca. During two years of his life
Lee was a lunatic in Bedlam.
Thomas Otway died of want in 1685, at the age of 34. Like
Lee, he left college for the stage, attempted as an actor, then turned
dramatist, and produced his first tragedy,
Alcibiades
, in 1675,
the year in which Lee produced also his first tragedy,
Nero
.
Otway's second play,
Don Carlos
, was very successful, but his
best were, the
Orphan
, produced in 1680, remarkable for its
departure from the kings and queens of tragedy for pathos founded upon
incidents in middle life, and
Venice Preserved
, produced in 1682.
Contents
|
Monday, April 16, 1711 |
Addison |
Ac ne forte putes, me, que facere ipse recusem,
Cum recte tractant alii, laudare maligne;
Ille per extentum funem mihi fosse videtur
Ire Poeta, meum qui pectus inaniter angit,
Irritat, mulcet, falsis terroribus implet,
Ut magus; et modo me Thebis, modo ponit Athenis.
Hor.

The
English
Writers of Tragedy are possessed with a Notion, that
when they represent a virtuous or innocent Person in Distress, they
ought not to leave him till they have delivered him out of his Troubles,
or made him triumph over his Enemies. This Error they have been led into
by a ridiculous Doctrine in modern Criticism, that they are obliged to
an equal Distribution of Rewards and Punishments, and an impartial
Execution of poetical Justice. Who were the first that established this
Rule I know not; but I am sure it has no Foundation in Nature, in
Reason, or in the Practice of the Ancients. We find that Good and Evil
happen alike to all Men on this side the Grave; and as the principal
Design of Tragedy is to raise Commiseration and Terror in the Minds of
the Audience, we shall defeat this great End, if we always make Virtue
and Innocence happy and successful. Whatever Crosses and Disappointments
a good Man suffers in the Body of the Tragedy, they will make but small
Impression on our Minds, when we know that in the last Act he is to
arrive at the End of his Wishes and Desires. When we see him engaged in
the Depth of his Afflictions, we are apt to comfort our selves, because
we are sure he will find his Way out of them: and that his Grief, how
great soever it may be at present, will soon terminate in Gladness. For
this Reason the ancient Writers of Tragedy treated Men in their Plays,
as they are dealt with in the World, by making Virtue sometimes happy
and sometimes miserable, as they found it in the Fable which they made
choice of, or as it might affect their Audience in the most agreeable
Manner.
Aristotle
the Tragedies that were written in
either of these Kinds, and observes, That those which ended unhappily
had always pleased the People, and carried away the Prize in the publick
Disputes of the Stage, from those that ended happily
. Terror and
Commiseration leave a pleasing Anguish in the Mind; and fix the Audience
in such a serious Composure of Thought as is much more lasting and
delightful than any little transient Starts of Joy and Satisfaction.
Accordingly, we find, that more of our English Tragedies have succeeded,
in which the Favourites of the Audience sink under their Calamities,
than those in which they recover themselves out of them.
best Plays
of this Kind are
The Orphan, Venice Preserved, Alexander the Great,
Theodosius, All for Love, Œdipus, Oroonoko, Othello
, &c.
King Lear
is an admirable Tragedy of the same Kind, as
Shakespear
wrote it; but as it is reformed according to the
chymerical Notion of Poetical Justice, in my humble Opinion it has lost
half its Beauty.
the same time I must allow, that there are very
noble Tragedies which have been framed upon the other Plan, and have
ended happily; as indeed most of the good Tragedies, which have been
written since the starting of the above-mentioned Criticism, have taken
this Turn: As
The Mourning Bride, Tamerlane, Ulysses, Phædra
and
Hippolitus
, with most of Mr.
Dryden's
. I must also
allow, that many of
Shakespear's
, and several of the celebrated
Tragedies of Antiquity, are cast in the same Form. I do not therefore
dispute against this Way of writing Tragedies, but against the Criticism
that would establish this as the only Method; and by that Means would
very much cramp the
English
Tragedy, and perhaps give a wrong
Bent to the Genius of our Writers.
The Tragi-Comedy, which is the Product of the
English
Theatre, is
one of the most monstrous Inventions that ever entered into a Poet's
Thoughts. An Author might as well think of weaving the Adventures of
Æneas
and
Hudibras
into one Poem, as of writing such a
motly Piece of Mirth and Sorrow. But the Absurdity of these Performances
is so very visible, that I shall not insist upon it.
The same Objections which are made to Tragi-Comedy, may in some Measure
be applied to all Tragedies that have a double Plot in them; which are
likewise more frequent upon the
English
Stage, than upon any
other: For though the Grief of the Audience, in such Performances, be
not changed into another Passion, as in Tragi-Comedies; it is diverted
upon another Object, which weakens their Concern for the principal
Action, and breaks the Tide of Sorrow, by throwing it into different
Channels. This Inconvenience, however, may in a great Measure be cured,
if not wholly removed, by the skilful Choice of an Under-Plot, which may
bear such a near Relation to the principal Design, as to contribute
towards the Completion of it, and be concluded by the same Catastrophe.
There is also another Particular, which may be reckoned among the
Blemishes, or rather the false Beauties, of our
English
Tragedy: I
mean those particular Speeches, which are commonly known by the Name of
Rants
. The warm and passionate Parts of a Tragedy, are always the
most taking with the Audience; for which Reason we often see the Players
pronouncing, in all the Violence of Action, several Parts of the Tragedy
which the Author writ with great Temper, and designed that they should
have been so acted. I have seen
Powell
very often raise himself a
loud Clap by this Artifice. The Poets that were acquainted with this
Secret, have given frequent Occasion for such Emotions in the Actor, by
adding Vehemence to Words where there was no Passion, or inflaming a
real Passion into Fustian. This hath filled the Mouths of our Heroes
with Bombast; and given them such Sentiments, as proceed rather from a
Swelling than a Greatness of Mind. Unnatural Exclamations, Curses, Vows,
Blasphemies, a Defiance of Mankind, and an Outraging of the Gods,
frequently pass upon the Audience for tow'ring Thoughts, and have
accordingly met with infinite Applause.
I shall here add a Remark, which I am afraid our Tragick Writers may
make an ill use of. As our Heroes are generally Lovers, their Swelling
and Blustring upon the Stage very much recommends them to the fair Part
of their Audience. The Ladies are wonderfully pleased to see a Man
insulting Kings, or affronting the Gods, in one Scene, and throwing
himself at the Feet of his Mistress in another. Let him behave himself
insolently towards the Men, and abjectly towards the Fair One, and it is
ten to one but he proves a Favourite of the Boxes.
Dryden
and
Lee
, in several of their Tragedies, have practised this Secret
with good Success.
But to shew how a Rant pleases beyond the most just and natural Thought
that is not pronounced with Vehemence, I would desire the Reader when he
sees the Tragedy of
Œdipus
, to observe how quietly the Hero is
dismissed at the End of the third Act, after having pronounced the
following Lines, in which the Thought is very natural, and apt to move
Compassion;
To you, good Gods, I make my last Appeal;
Or clear my Virtues, or my Crimes reveal.
If in the Maze of Fate I blindly run,
And backward trod those Paths I sought to shun;
Impute my Errors to your own Decree:
My Hands are guilty, but my Heart is free.
us then observe with what Thunder-claps of Applause he leaves the
Stage, after the Impieties and Execrations at the End of the fourth Act
; and you will wonder to see an Audience so cursed and so pleased at
the same time;
O that as oft have at Athens seen,
[Where, by the Way, there was no Stage till many Years after
Œdipus
.]
The Stage arise, and the big Clouds descend;
So now, in very Deed, I might behold
This pond'rous Globe, and all yen marble Roof,
Meet like the Hands of Jove, and crush Mankind.
For all the Elements, &c.
Here Aristotle is not quite accurately quoted. What he says
of the tragedies which end unhappily is, that Euripides was right in
preferring them,
'and as the strongest proof of it we find that upon the stage, and in
the dramatic contests, such tragedies, if they succeed, have always
the most tragic effect.'
Poetics
, Part II. § 12.
Of the two plays in this list, besides
Othello
,
which have not been mentioned in the preceding notes,
All for
Love
, produced in 1678, was Dryden's
Antony and Cleopatra
,
Oroonoko
, first acted in, 1678, was a tragedy by Thomas
Southerne, which included comic scenes. Southerne, who held a commission
in the army, was living in the
Spectator's
time, and died in
1746, aged 86. It was in his best play,
Isabella
, or the Fatal
Marriage, that Mrs. Siddons, in 1782, made her first appearance on the
London stage.
Congreve's
Mourning Bride
was first acted in 1697;
Rowe's
Tamerlane
(with a hero planned in complement to William
III) in 1702; Rowe's
Ulysses
in 1706; Edmund Smith's
Phædra
and
Hippolitus
in 1707.
The third Act of
Œdipus
was by Dryden, the fourth
by Lee. Dryden wrote also the first Act, the rest was Lee's.
Contents
Having spoken of Mr. Powell,
as sometimes raising himself Applause from the ill Taste of an Audience;
I must do him the Justice to own,
that he is excellently formed for a Tragoedian,
and, when he pleases, deserves the Admiration of the best Judges;
as I doubt not but he will in the Conquest of Mexico,
which is acted for his own Benefit To-morrow Night.
C.
|
Tuesday, April 17, 1711 |
Steele |
Tu non inventa reperta es.
Ovid

Compassion for the Gentleman who writes the following Letter, should not
prevail upon me to fall upon the Fair Sex, if it were not that I find
they are frequently Fairer than they ought to be. Such Impostures are
not to be tolerated in Civil Society; and I think his Misfortune ought
to be made publick, as a Warning for other Men always to Examine into
what they Admire.
Sir,
Supposing you to be a Person of general Knowledge, I make my
Application to you on a very particular Occasion. I have a great Mind
to be rid of my Wife, and hope, when you consider my Case, you will be
of Opinion I have very just Pretensions to a Divorce. I am a mere Man
of the Town, and have very little Improvement, but what I have got
from Plays.
I remember in
The Silent Woman the Learned Dr.
Cutberd, or Dr.
Otter (I forget which) makes one of the
Causes of Separation to be
Error Personæ, when a Man marries
a Woman, and finds her not to be the same Woman whom he intended to
marry, but another
1. If that be Law, it is, I presume, exactly my
Case. For you are to know, Mr.
Spectator, that there are Women who do
not let their Husbands see their Faces till they are married.
Not to keep you in suspence, I mean plainly, that Part of the Sex who
paint. They are some of them so Exquisitely skilful this Way, that
give them but a Tolerable Pair of Eyes to set up with, and they will
make Bosoms, Lips, Cheeks, and Eye-brows, by their own Industry. As
for my Dear, never Man was so Enamour'd as I was of her fair Forehead,
Neck, and Arms, as well as the bright Jett of her Hair; but to my
great Astonishment, I find they were all the Effects of Art: Her Skin
is so Tarnished with this Practice, that when she first wakes in a
Morning, she scarce seems young enough to be the Mother of her whom I
carried to Bed the Night before. I shall take the Liberty to part with
her by the first Opportunity, unless her Father will make her Portion
suitable to her real, not her assumed, Countenance. This I thought fit
to let him and her know by your Means.
I am, Sir,
Your most obedient,
humble Servant.
I cannot tell what the Law, or the Parents of the Lady, will do for this
Injured Gentleman, but must allow he has very much Justice on his Side.
I have indeed very long observed this Evil, and distinguished those of
our Women who wear their own, from those in borrowed Complexions, by the
Picts
and the
British
. There does not need any great
Discernment to judge which are which. The
British
have a lively,
animated Aspect; The
Picts
, tho' never so Beautiful, have dead,
uninformed Countenances. The Muscles of a real Face sometimes swell with
soft Passion, sudden Surprize, and are flushed with agreeable
Confusions, according as the Objects before them, or the Ideas presented
to them, affect their Imagination. But the
Picts
behold all
things with the same Air, whether they are Joyful or Sad; the same fixed
Insensibility appears upon all Occasions. A
Pict
, tho' she takes
all that Pains to invite the Approach of Lovers, is obliged to keep them
at a certain Distance; a Sigh in a Languishing Lover, if fetched too
near her, would dissolve a Feature; and a Kiss snatched by a Forward
one, might transfer the Complexion of the Mistress to the Admirer. It is
hard to speak of these false Fair Ones, without saying something
uncomplaisant, but I would only recommend to them to consider how they
like coming into a Room new Painted; they may assure themselves, the
near Approach of a Lady who uses this Practice is much more offensive.
Will. Honeycomb
told us, one Day, an Adventure he once had with a
Pict
. This Lady had Wit, as well as Beauty, at Will; and made it
her Business to gain Hearts, for no other Reason, but to rally the
Torments of her Lovers. She would make great Advances to insnare Men,
but without any manner of Scruple break off when there was no
Provocation. Her Ill-Nature and Vanity made my Friend very easily Proof
against the Charms of her Wit and Conversation; but her beauteous Form,
instead of being blemished by her Falshood and Inconstancy, every Day
increased upon him, and she had new Attractions every time he saw her.
When she observed
Will
. irrevocably her Slave, she began to use him as
such, and after many Steps towards such a Cruelty, she at last utterly
banished him. The unhappy Lover strove in vain, by servile Epistles, to
revoke his Doom; till at length he was forced to the last Refuge, a
round Sum of Money to her Maid. This corrupt Attendant placed him early
in the Morning behind the Hangings in her Mistress's Dressing-Room. He
stood very conveniently to observe, without being seen. The
Pict
begins the Face she designed to wear that Day, and I have heard him
protest she had worked a full half Hour before he knew her to be the
same Woman. As soon as he saw the Dawn of that Complexion, for which he
had so long languished, he thought fit to break from his Concealment,
repeating that of
Cowley
:
Th' adorning Thee, with so much Art,
Is but a barbarous Skill;
'Tis like the Pois'ning of a Dart,
Too apt before to kill
2.
The
Pict
stood before him in the utmost Confusion, with the prettiest
Smirk imaginable on the finished side of her Face, pale as Ashes on the
other.
Honeycomb
seized all her Gallypots and Washes, and carried off
his Han kerchief full of Brushes, Scraps of
Spanish
Wool, and Phials
of Unguents. The Lady went into the Country, the Lover was cured.
It is certain no Faith ought to be kept with Cheats, and an Oath made to
a
Pict
is of it self void. I would therefore exhort all the
British
Ladies to single them out, nor do I know any but
Lindamira
, who should
be Exempt from Discovery; for her own Complexion is so delicate, that
she ought to be allowed the covering it with Paint, as a Punishment for
choosing to be the worst Piece of Art extant, instead of the Masterpiece
of Nature. As for my part, who have no Expectations from Women, and
consider them only as they are Part of the Species, I do not half so
much fear offending a Beauty, as a Woman of Sense; I shall therefore
produce several Faces which have been in Publick this many Years, and
never appeared. It will be a very pretty Entertainment in the Playhouse
(when I have abolished this Custom) to see so many Ladies, when they
first lay it down,
incog.
, in their own Faces.
In the mean time, as a Pattern for improving their Charms, let the Sex
study the agreeable
Statira
. Her Features are enlivened with the
Chearfulness of her Mind, and good Humour gives an Alacrity to her Eyes.
She is Graceful without affecting an Air, and Unconcerned without
appearing Careless. Her having no manner of Art in her Mind, makes her
want none in her Person.
How like is this Lady, and how unlike is a
Pict
, to that Description
Dr.
Donne
gives of his Mistress?
Her pure and eloquent Blood
Spoke in her Cheeks, and so distinctly wrought,
That one would almost say her Body thought
3.
Ben Jonson's
Epicœne
, or the Silent Woman, kept the
stage in the
Spectator's
time, and was altered by G. Colman for Drury
Lane, in 1776. Cutbeard in the play is a barber, and Thomas Otter a Land
and Sea Captain.
Tom Otter's bull, bear, and horse is known all over
England, in rerum naturâ.
In the fifth act Morose, who has
married a Silent Woman and discovered her tongue after marriage, is
played upon by the introduction of Otter, disguised as a Divine, and
Cutbeard, as a Canon Lawyer, to explain to him
for how many causes a man may have divortium legitimum, a
lawful divorce.
Cutbeard, in opening with burlesque pedantry a budget of twelve
impediments which make the bond null, is thus supported by Otter:
| Cutb. |
The first is impedimentum erroris. |
| Otter. |
Of which there are several species. |
| Cutb |
Ay, as error personæ. |
| Otter |
If you contract yourself to one person, thinking her another. |
This is fourth of five stanzas to
The Waiting-Maid,
in
the collection of poems called
The Mistress
.
Donne's
Funeral Elegies
, on occasion of the untimely death
of Mistress Elizabeth Drury.
Of the Progress of the Soul,
Second
Anniversary. It is the strain not of a mourning lover, but of a mourning
friend. Sir Robert Drury was so cordial a friend that he gave to Donne
and his wife a lodging rent free in his own large house in Drury Lane,
'and was also,' says Isaac Walton, 'a cherisher of his studies, and
such a friend as sympathized with him and his, in all their joys and
sorrows.'
The lines quoted by Steele show that the sympathy was mutual;
but the poetry in them is a flash out of the clouds of a dull context.
It is hardly worth noticing that Steele, quoting from memory, puts
'would' for 'might' in the last line. Sir Robert's daughter Elizabeth,
who, it is said, was to have been the wife of Prince Henry, eldest son
of James I, died at the age of fifteen in 1610.
Contents
A young Gentlewoman of about Nineteen Years of Age
(bred in the Family of a Person of Quality lately deceased,)
who Paints the finest Flesh-colour,
wants a Place,
and is to be heard of at the House of
Minheer Grotesque
a Dutch Painter in Barbican.
N.B.
She is also well-skilled in the Drapery-part,
and puts on Hoods and mixes Ribbons
so as to suit the Colours of the Face
with great Art and Success.
R.
|
Wednesday, April 18, 1711 |
Addison |
Garganum inugire putes nemus aut mare Thuscum,
Tanto cum strepitu ludi spectantur; et artes,
Divitiæque peregrina, quibus oblitus actor
Cum stetit in Scena, concurrit dextera lævæ.
Dixit adhuc aliquid? Nil sane. Quid placet ergo?
Lana Tarentino violas imitata veneno.
Hor.

Aristotle
has
, That ordinary Writers in Tragedy endeavour
to raise Terror and Pity in their Audience, not by proper Sentiments and
Expressions, but by the Dresses and Decorations of the Stage. There is
something of this kind very ridiculous in the
English
Theatre. When
the Author has a mind to terrify us, it thunders; When he would make us
melancholy, the Stage is darkened. But among all our Tragick Artifices,
I am the most offended at those which are made use of to inspire us with
magnificent Ideas of the Persons that speak. The ordinary Method of
making an Hero, is to clap a huge Plume of Feathers upon his Head, which
rises so very high, that there is often a greater Length from his Chin
to the Top of his Head, than to the sole of his Foot. One would believe,
that we thought a great Man and a tall Man the same thing. This very
much embarrasses the Actor, who is forced to hold his Neck extremely
stiff and steady all the while he speaks; and notwithstanding any
Anxieties which he pretends for his Mistress, his Country, or his
Friends, one may see by his Action, that his greatest Care and Concern
is to keep the Plume of Feathers from falling off his Head. For my own
part, when I see a Man uttering his Complaints under such a Mountain of
Feathers, I am apt to look upon him rather as an unfortunate Lunatick,
than a distressed Hero. As these superfluous Ornaments upon the Head
make a great Man, a Princess generally receives her Grandeur from those
additional Incumbrances that fall into her Tail: I mean the broad
sweeping Train that follows her in all her Motions, and finds constant
Employment for a Boy who stands behind her to open and spread it to
Advantage. I do not know how others are affected at this Sight, but, I
must confess, my Eyes are wholly taken up with the Page's Part; and as
for the Queen, I am not so attentive to any thing she speaks, as to the
right adjusting of her Train, lest it should chance to trip up her
Heels, or incommode her, as she walks to and fro upon the Stage. It is,
in my Opinion, a very odd Spectacle, to see a Queen venting her Passion
in a disordered Motion, and a little Boy taking care all the while that
they do not ruffle the Tail of her Gown. The Parts that the two Persons
act on the Stage at the same Time, are very different: The Princess is
afraid lest she should incur the Displeasure of the King her Father, or
lose the Hero her Lover, whilst her Attendant is only concerned lest she
should entangle her Feet in her Petticoat.
We are told, That an ancient Tragick Poet, to move the Pity of his
Audience for his exiled Kings and distressed Heroes, used to make the
Actors represent them in Dresses and Cloaths that were thread-bare and
decayed. This Artifice for moving Pity, seems as ill-contrived, as that
we have been speaking of to inspire us with a great Idea of the Persons
introduced upon the Stage. In short, I would have our Conceptions raised
by the Dignity of Thought and Sublimity of Expression, rather than by a
Train of Robes or a Plume of Feathers.
Another mechanical Method of making great Men, and adding Dignity to
Kings and Queens, is to accompany them with Halberts and Battle-axes.
Two or three Shifters of Scenes, with the two Candle-snuffers, make up a
compleat Body of Guards upon the
English
Stage; and by the Addition of
a few Porters dressed in Red Coats, can represent above a Dozen Legions.
I have sometimes seen a Couple of Armies drawn up together upon the
Stage, when the Poet has been disposed to do Honour to his Generals. It
is impossible for the Reader's Imagination to multiply twenty Men into
such prodigious Multitudes, or to fancy that two or three hundred
thousand Soldiers are fighting in a Room of forty or fifty Yards in
Compass. Incidents of such a Nature should be told, not represented.
Non tamen intus
Digna geri promes in scenam: multaque tolles
Ex oculis, qua mox narret facundia prœsens.
Hor.
Yet there are things improper for a Scene,
Which Men of Judgment only will relate.
(L. Roscom.)
I should therefore, in this Particular, recommend to my Countrymen the
Example of the
French
Stage, where the Kings and Queens always appear
unattended, and leave their Guards behind the Scenes. I should likewise
be glad if we imitated the
French
in banishing from our Stage the
Noise of Drums, Trumpets, and Huzzas; which is sometimes so very great,
that when there is a Battle in the
Hay-Market
Theatre, one may hear it
as far as
Charing-Cross
.
I have here only touched upon those Particulars which are made use of to
raise and aggrandize Persons in Tragedy; and shall shew in another Paper
the several Expedients which are practised by Authors of a vulgar Genius
to move Terror, Pity, or Admiration, in their Hearers.
The Tailor and the Painter often contribute to the Success of a Tragedy
more than the Poet. Scenes affect ordinary Minds as much as Speeches;
and our Actors are very sensible, that a well-dressed Play his sometimes
brought them as full Audiences, as a well-written one. The
Italians
have a very good Phrase to express this Art of imposing upon the
Spectators by Appearances: They call it the
Fourberia della Scena, The
Knavery or trickish Part of the Drama
. But however the Show and Outside
of the Tragedy may work upon the Vulgar, the more understanding Part of
the Audience immediately see through it and despise it.
A good Poet will give the Reader a more lively Idea of an Army or a
Battle in a Description, than if he actually saw them drawn up in
Squadrons and Battalions, or engaged in the Confusion of a Fight. Our
Minds should be opened to great Conceptions and inflamed with glorious
Sentiments by what the Actor speaks, more than by what he appears. Can
all the Trappings or Equipage of a King or Hero give
Brutus
half that
Pomp and Majesty which he receives from a few Lines in
Shakespear
?
C.
Poetics
, Part II. § 13.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 19, 1711 |
Steele |
Ha tibi erunt artes; pacisque imponere morem,
Parcere Subjectis, et debellare Superbos.
Virg.

There are Crowds of Men, whose great Misfortune it is that they were not
bound to Mechanick Arts or Trades; it being absolutely necessary for
them to be led by some continual Task or Employment. These are such as
we commonly call dull Fellows; Persons, who for want of something to do,
out of a certain Vacancy of Thought, rather than Curiosity, are ever
meddling with things for which they are unfit. I cannot give you a
Notion of them better than by presenting you with a Letter from a
Gentleman, who belongs to a Society of this Order of Men, residing at
Oxford
.
Oxford, April 13, 1711.
Four a Clock in the Morning.
Sir,
'In some of your late Speculations, I find some Sketches towards an
History of Clubs: But you seem to me to shew them in somewhat too
ludicrous a Light. I have well weighed that Matter, and think, that
the most important Negotiations may best be carried on in such
Assemblies. I shall therefore, for the Good of Mankind, (which, I
trust, you and I are equally concerned for) propose an Institution of
that Nature for Example sake.
I must confess, the Design and Transactions of too many Clubs are
trifling, and manifestly of no consequence to the Nation or Publick
Weal: Those I'll give you up. But you must do me then the Justice to
own, that nothing can be more useful or laudable than the Scheme we go
upon. To avoid Nicknames and Witticisms, we call ourselves
The
Hebdomadal Meeting: Our President continues for a Year at least, and
sometimes four or five: We are all Grave, Serious, Designing Men, in
our Way: We think it our Duty, as far as in us lies, to take care the
Constitution receives no Harm, —
Ne quid detrimenti Res capiat
publica — To censure Doctrines or Facts, Persons or Things, which we
don't like; To settle the Nation at home, and to carry on the War
abroad, where and in what manner we see fit: If other People are not
of our Opinion, we can't help that. 'Twere better they were. Moreover,
we now and then condescend to direct, in some measure, the little
Affairs of our own University.
Verily,
Mr.
Spectator, we are much offended at the Act for importing
French Wines
1: A Bottle or two of good solid Edifying Port, at
honest
George's, made a Night chearful, and threw off Reserve. But
this plaguy
French Claret will not only cost us more Mony, but do us
less Good: Had we been aware of it, before it had gone too far, I must
tell you, we would have petitioned to be heard upon that Subject. But
let that pass.
I must let you know likewise, good Sir, that we look upon a certain
Northern Prince's March, in Conjunction with Infidels
2, to be
palpably against our Goodwill and Liking; and, for all Monsieur
Palmquist
3, a most dangerous Innovation; and we are by no means yet
sure, that some People are not at the Bottom on't. At least, my own
private Letters leave room for a Politician well versed in matters of
this Nature, to suspect as much, as a penetrating Friend of mine tells
me.
We think we have at last done the business with the Malecontents in
Hungary, and shall clap up a Peace there
4.
What the Neutrality Army
5 is to do, or what the Army in
Flanders,
and what two or three other Princes, is not yet fully determined among
us; and we wait impatiently for the coming in of the next
Dyer's6
who, you must know, is our Authentick Intelligence, our
Aristotle in
Politics. And 'tis indeed but fit there should be some
Dernier Resort,
the Absolute Decider of all Controversies.
We were lately informed, that the Gallant Train'd Bands had patroll'd
all Night long about the Streets of
London: We indeed could not
imagine any Occasion for it, we guessed not a Tittle on't aforehand,
we were in nothing of the Secret; and that City Tradesmen, or their
Apprentices, should do Duty, or work, during the Holidays, we thought
absolutely impossible: But
Dyer being positive in it, and some
Letters from other People, who had talked with some who had it from
those who should know, giving some Countenance to it, the Chairman
reported from the Committee, appointed to examine into that Affair,
That 'twas Possible there might be something in't. I have much more to
say to you, but my two good Friends and Neighbours,
Dominick and
Slyboots, are just come in, and the Coffee's ready. I am, in the
mean time,
Mr.
Spectator,
Your Admirer, and
Humble Servant,
Abraham Froth.
You may observe the Turn of their Minds tends only to Novelty, and not
Satisfaction in any thing. It would be Disappointment to them, to come
to Certainty in any thing, for that would gravel them, and put an end to
their Enquiries, which dull Fellows do not make for Information, but for
Exercise. I do not know but this may be a very good way of accounting
for what we frequently see, to wit, that dull Fellows prove very good
Men of Business. Business relieves them from their own natural
Heaviness, by furnishing them with what to do; whereas Business to
Mercurial Men, is an Interruption from their real Existence and
Happiness. Tho' the dull Part of Mankind are harmless in their
Amusements, it were to be wished they had no vacant Time, because they
usually undertake something that makes their Wants conspicuous, by their
manner of supplying them. You shall seldom find a dull Fellow of good
Education, but (if he happens to have any Leisure upon his Hands,) will
turn his Head to one of those two Amusements, for all Fools of Eminence,
Politicks or Poetry. The former of these Arts, is the Study of all dull
People in general; but when Dulness is lodged in a Person of a quick
Animal Life, it generally exerts it self in Poetry. One might here
mention a few Military Writers, who give great Entertainment to the Age,
by reason that the Stupidity of their Heads is quickened by the Alacrity
of their Hearts. This Constitution in a dull Fellow, gives Vigour to
Nonsense, and makes the Puddle boil, which would otherwise stagnate.
British Prince
, that Celebrated Poem, which was written in the Reign
of King Charles the Second, and deservedly called by the Wits of that
Age
Incomparable
, was the Effect of such an happy Genius as we are
speaking of. From among many other Disticks no less to be quoted on this
Account, I cannot but recite the two following Lines.
A painted Vest Prince Voltager had on,
Which from a Naked Pict his Grandsire won.
Here if the Poet had not been Vivacious, as well as Stupid, he could
not
, in the Warmth and Hurry of Nonsense,
have
been capable of
forgetting that neither Prince
Voltager
, nor his Grandfather, could
strip a Naked Man of his Doublet; but a Fool of a colder Constitution,
would have staid to have Flea'd the
Pict
, and made Buff of his Skin,
for the Wearing of the Conqueror.
To bring these Observations to some useful Purpose of Life, what I would
propose should be, that we imitated those wise Nations, wherein every
Man learns some Handycraft-Work. Would it not employ a Beau prettily
enough, if instead of eternally playing with a Snuff-box, he spent some
part of his Time in making one? Such a Method as this, would very much
conduce to the Publick Emolument, by making every Man living good for
something; for there would then be no one Member of Human Society, but
would have some little Pretension for some Degree in it; like him who
came to
Will's
Coffee-house, upon the Merit of having writ a Posie of
a Ring.
R.
Like the chopping in two of the
Respublica
in the
quotation just above of the well-known Roman formula by which consuls
were to see
ne quid Respublica detrimenti capiat
, this is a jest on
the ignorance of the political wiseacres. Port wine had been forced on
England in 1703 in place of Claret, and the drinking of it made an act
of patriotism, — which then meant hostility to France, — by the Methuen
treaty, so named from its negotiator, Paul Methuen, the English Minister
at Lisbon. It is the shortest treaty upon record, having only two
clauses, one providing that Portugal should admit British cloths; the
other that England should admit Portuguese wines at one-third less duty
than those of France. This lasted until 1831, and so the English were
made Port wine drinkers. Abraham Froth and his friends of the
Hebdomadal Meeting
, all 'Grave, Serious, Designing Men in their Way'
have a confused notion in 1711 of the Methuen Treaty of 1703 as 'the Act
for importing French wines,' with which they are much offended. The
slowness and confusion of their ideas upon a piece of policy then so
familiar, gives point to the whimsical solemnity of their 'Had we been
aware,' &c.
The subject of Mr. Froth's profound comment is now the
memorable March of Charles XII of Sweden to the Ukraine, ending on the
8th of July, 1709, in the decisive battle of Pultowa, that established
the fortune of Czar Peter the Great, and put an end to the preponderance
of Sweden in northern Europe. Charles had seemed to be on his way to
Moscow, when he turned south and marched through desolation to the
Ukraine, whither he was tempted by Ivan Mazeppa, a Hetman of the
Cossacks, who, though 80 years old, was ambitious of independence to be
won for him by the prowess of Charles XII. Instead of 30,000 men Mazeppa
brought to the King of Sweden only himself as a fugitive with 40 or 50
attendants; but in the spring of 1809 he procured for the wayworn and
part shoeless army of Charles the alliance of the Saporogue Cossacks.
Although doubled by these and by Wallachians, the army was in all but
20,000 strong with which he then determined to besiege Pullowa; and
there, after two months' siege, he ventured to give battle to a
relieving army of 60,000 Russians. Of his 20,000 men, 9000 were left on
that battle-field, and 3000 made prisoners. Of the rest — all that
survived of 54,000 Swedes with whom he had quitted Saxony to cross the
steppes of Russia, and of 16,000 sent to him as reinforcement
afterwards — part perished, and they who were left surrendered on
capitulation, Charles himself having taken refuge at Bender in
Bessarabia with the Turks, Mr. Froth's Infidels.
Perhaps Monsieur Palmquist is the form in which these
'Grave, Serious, Designing Men in their Way' have picked up the name of
Charles's brave general, Count Poniatowski, to whom he owed his escape
after the battle of Pultowa, and who won over Turkey to support his
failing fortunes. The Turks, his subsequent friends, are the 'Infidels'
before-mentioned, the wise politicians being apparently under the
impression that they had marched with the Swedes out of Saxony.
Here Mr. Froth and his friends were truer prophets than
anyone knew when this number of the
Spectator
appeared, on the 19th of
April. The news had not reached England of the death of the Emperor
Joseph I on the 17th of April. During his reign, and throughout the
war, the Hungarians, desiring independence, had been fighting on the
side of France. The Archduke Charles, now become Emperor, was ready to
give the Hungarians such privileges, especially in matters of religion,
as restored their friendship.
After Pultowa, Frederick IV of Denmark, Augustus II of
Poland, and Czar Peter, formed an alliance against Sweden; and in the
course of 1710 the Emperor of Germany, Great Britain, and the
States-General concluded two treaties guaranteeing the neutrality of all
the States of the Empire. This suggests to Mr. Froth and his friends the
idea that there is a 'Neutrality Army' operating somewhere.
Dyer was a Jacobite printer, whose News-letter was twice in
trouble for 'misrepresenting the proceedings of the House,' and who, in
1703, had given occasion for a proclamation against 'printing and
spreading false 'news.'
'
The British Princes
, an Heroick Poem,' by the Hon.
Edward Howard, was published in 1669. The author produced also five
plays, and a volume of Poems and Essays, with a Paraphrase on Cicero's
Lælius
in Heroic Verse. The Earls of Rochester and Dorset devoted some
verses to jest both on
The British Princes
and on Edward Howard's
Plays. Even Dr. Sprat had his rhymed joke with the rest, in lines to a
Person of Honour 'upon his Incomparable, Incomprehensible Poem, intitled
The British Princes
.' Edward Howard did not print the nonsense here
ascribed to him. It was a burlesque of his lines:
'A vest as admir'd Vortiger had on,
Which from this Island's foes his Grandsire won.'
Contents
|
Friday, April 20, 1711 |
Addison |
Tu, quid ego et populus mecum desideret, audi.
Hor.

the several Artifices which are put in Practice by the Poets to
fill the Minds of
an
Audience with Terror, the first Place is due
to Thunder and Lightning, which are often made use of at the Descending
of a God, or the Rising of a Ghost, at the Vanishing of a Devil, or at
the Death of a Tyrant. I have known a Bell introduced into several
Tragedies with good Effect; and have seen the whole Assembly in a very
great Alarm all the while it has been ringing. But there is nothing
which delights and terrifies our
English
Theatre so much as a
Ghost, especially when he appears in a bloody Shirt. A Spectre has very
often saved a Play, though he has done nothing but stalked across the
Stage, or rose through a Cleft of it, and sunk again without speaking
one Word. There may be a proper Season for these several Terrors; and
when they only come in as Aids and Assistances to the Poet, they are not
only to be excused, but to be applauded.
the sounding of the Clock
in
Venice Preserved
, makes the Hearts of the whole Audience
quake; and conveys a stronger Terror to the Mind than it is possible for
Words to do. The Appearance of the Ghost in
Hamlet
is a
Master-piece in its kind, and wrought up with all the Circumstances that
can create either Attention or Horror. The Mind of the Reader is
wonderfully prepared for his Reception by the Discourses that precede
it: His Dumb Behaviour at his first Entrance, strikes the Imagination
very strongly; but every time he enters, he is still more terrifying.
Who can read the Speech with which young
Hamlet
accosts him,
without trembling?
| Hor. |
Look, my Lord, it comes! |
| Ham. |
Angels and Ministers of Grace defend us!
Be thou a Spirit of Health, or Goblin damn'd;
Bring with thee Airs from Heav'n, or Blasts from Hell;
Be thy Events wicked or charitable;
Thou com'st in such a questionable Shape
That I will speak to thee. I'll call thee Hamlet,
King, Father, Royal Dane: Oh! Oh! Answer me,
Let me not burst in Ignorance; but tell
Why thy canoniz'd Bones, hearsed in Death,
Have burst their Cearments? Why the Sepulchre,
Wherein we saw thee quietly inurn'd,
Hath op'd his ponderous and marble Jaws
To cast thee up again? What may this mean?
That thou dead Coarse again in compleat Steel
Revisit'st thus the Glimpses of the Moon,
Making Night hideous? |
I do not therefore find Fault with the Artifices above-mentioned when
they are introduced with Skill, and accompanied by proportionable
Sentiments and Expressions in the Writing.
For the moving of Pity, our principal Machine is the Handkerchief; and
indeed in our common Tragedies, we should not know very often that the
Persons are in Distress by any thing they say, if they did not from time
to time apply their Handkerchiefs to their Eyes. Far be it from me to
think of banishing this Instrument of Sorrow from the Stage; I know a
Tragedy could not subsist without it: All that I would contend for, is,
to keep it from being misapplied. In a Word, I would have the Actor's
Tongue sympathize with his Eyes.
A disconsolate Mother, with a Child in her Hand, has frequently drawn
Compassion from the Audience, and has therefore gained a place in
several Tragedies. A Modern Writer, that observed how this had took in
other Plays, being resolved to double the Distress, and melt his
Audience twice as much as those before him had done, brought a Princess
upon the Stage with a little Boy in one Hand and a Girl in the other.
This too had a very good Effect. A third Poet, being resolved to
out-write all his Predecessors, a few Years ago introduced three
Children, with great Success: And as I am informed, a young Gentleman,
who is fully determined to break the most obdurate Hearts, has a Tragedy
by him, where the first Person that appears upon the Stage, is an
afflicted Widow in her mourning Weeds, with half a Dozen fatherless
Children attending her, like those that usually hang about the Figure of
Charity. Thus several Incidents that are beautiful in a good Writer,
become ridiculous by falling into the Hands of a bad one.
But among all our Methods of moving Pity or Terror, there is none so
absurd and barbarous, and what more exposes us to the Contempt and
Ridicule of our Neighbours, than that dreadful butchering of one
another, which is so very frequent upon the
English
Stage.
delight
in seeing Men stabbed, poysoned, racked, or impaled, is certainly the
Sign of a cruel Temper: And as this is often practised before the
British
Audience, several
French
Criticks, who think these are
grateful Spectacles to us, take occasion from them to represent us as a
People that delight in Blood
. It is indeed very odd, to see our
Stage strowed with Carcasses in the last Scene of a Tragedy; and to
observe in the Ward-robe of a Play-house several Daggers, Poniards,
Wheels, Bowls for Poison, and many other Instruments of Death. Murders
and Executions are always transacted behind the Scenes in the
French
Theatre; which in general is very agreeable to the Manners of a polite
and civilized People: But as there are no Exceptions to this Rule on the
French
Stage, it leads them into Absurdities almost as ridiculous as
that which falls under our present Censure. I remember in the famous
Play of
Corneille
, written upon the Subject of the
Horatii
and
Curiatii
; the fierce young hero who had overcome the
Curiatii
one
after another, (instead of being congratulated by his Sister for his
Victory, being upbraided by her for having slain her Lover,) in the
Height of his Passion and Resentment kills her. If any thing could
extenuate so brutal an Action, it would be the doing of it on a sudden,
before the Sentiments of Nature, Reason, or Manhood could take Place in
him. However, to avoid
publick Blood-shed
, as soon as his Passion is
wrought to its Height, he follows his Sister the whole length of the
Stage, and forbears killing her till they are both withdrawn behind the
Scenes. I must confess, had he murder'd her before the Audience, the
Indecency might have been greater; but as it is, it appears very
unnatural, and looks like killing in cold Blood. To give my Opinion upon
this Case; the Fact ought not to have been represented, but to have been
told, if there was any Occasion for it.
It may not be unacceptable to the Reader, to see how
Sophocles
has
conducted a Tragedy under the like delicate Circumstances.
Orestes
was
in the same Condition with
Hamlet
in
Shakespear
, his Mother having
murdered his Father, and taken possession of his Kingdom in Conspiracy
with her Adulterer. That young Prince therefore, being determined to
revenge his Father's Death upon those who filled his Throne, conveys
himself by a beautiful Stratagem into his Mother's Apartment with a
Resolution to kill her. But because such a Spectacle would have been too
shocking to the Audience, this dreadful Resolution is executed behind
the Scenes: The Mother is heard calling out to her Son for Mercy; and
the Son answering her, that she shewed no Mercy to his Father; after
which she shrieks out that she is wounded, and by what follows we find
that she is slain. I do not remember that in any of our Plays there are
Speeches made behind the Scenes, though there are other Instances of
this Nature to be met with in those of the Ancients: And I believe my
Reader will agree with me, that there is something infinitely more
affecting in this dreadful Dialogue between the Mother and her Son
behind the Scenes, than could have been in anything transacted before
the Audience.
Orestes
immediately after meets the Usurper at the
Entrance of his Palace; and by a very happy Thought of the Poet avoids
killing him before the Audience, by telling him that he should live some
Time in his present Bitterness of Soul before he would dispatch him; and
by
ordering him to retire into that Part of the Palace where he had
slain his Father, whose Murther he would revenge in the very same Place
where it was committed. By this means the Poet observes that Decency,
which
Horace
afterwards established by a Rule, of forbearing to commit
Parricides or unnatural Murthers before the Audience.
Nec coram populo natos Medea trucidet.
Let not Medea draw her murth'ring Knife,
And spill her Children's Blood upon the Stage.
The
French
have therefore refin'd too much upon
Horace's
Rule, who
never designed to banish all Kinds of Death from the Stage; but only
such as had too much Horror in them, and which would have a better
Effect upon the Audience when transacted behind the Scenes. I would
therefore recommend to my Countrymen the Practice of the ancient Poets,
who were very sparing of their publick Executions, and rather chose to
perform them behind the Scenes, if it could be done with as great an
Effect upon the Audience. At the same time I must observe, that though
the devoted Persons of the Tragedy were seldom slain before the
Audience, which has generally something ridiculous in it, their Bodies
were often produced after their Death, which has always in it something
melancholy or terrifying; so that the killing on the Stage does not seem
to have been avoided only as an Indecency, but also as an Improbability.
Nec pueros coram populo Medea
trucidet;
Aut humana palam coquat exta nefarius Atreus;
Aut in avem Progne
vertatur, Cadmus
in anguem,
Quodcunque ostendis mihi sic, incredulus odi.
Hor.
Medea
must not draw her murth'ring Knife,
Nor Atreus
there his horrid Feast prepare.
Cadmus
and Progne's
Metamorphosis,
(She to a Swallow turn'd, he to a Snake)
And whatsoever contradicts my Sense,
I hate to see, and never can believe.
(Ld.
Roscommon.)
4
I have now gone through the several Dramatick Inventions which are made
use of by
the
Ignorant Poets to supply the Place of Tragedy, and by
the
Skilful to improve it; some of which I could wish entirely
rejected, and the rest to be used with Caution. It would be an endless
Task to consider Comedy in the same Light, and to mention the
innumerable Shifts that small Wits put in practice to raise a Laugh.
Bullock
in
short Coat, and
Norris
in a long one, seldom
fail of this Effect
. In ordinary Comedies, a broad and a narrow
brim'd Hat are different Characters. Sometimes the Wit of the Scene lies
in a Shoulder-belt, and Sometimes in a Pair of Whiskers.
Lover running
about the Stage, with his Head peeping out of a Barrel, was thought a
very good Jest in King
Charles
the Second's time; and invented by
one of the first Wits of that Age
. But
Ridicule is not so
delicate as Compassion, and
because
the Objects that make us laugh
are infinitely more numerous than those that make us weep, there is a
much greater Latitude for comick than tragick Artifices, and by
Consequence a much greater Indulgence to be allowed them.
C.
the
In Act V The toll of the passing bell for Pierre in the
parting scene between Jaffier and Belvidera.
Thus Rene Rapin, — whom Dryden declared alone
'sufficient,
were all other critics lost, to teach anew the rules of writing,'
said
in his
Reflections on Aristotle's Treatise of Poetry,
translated by
Rymer in 1694,
The English, our Neighbours, love Blood in their Sports,
by the quality of their Temperament: These are Insulaires, separated
from the rest of men; we are more humane ... The English have more of
Genius for Tragedy than other People, as well by the Spirit of their
Nation, which delights in Cruelty, as also by the Character of their
Language, which is proper for Great Expressions.'
The Earl of Roscommon, who died in 1684, aged about 50,
besides his
Essay on Translated Verse,
produced, in 1680, a
Translation of
Horace's Art of Poetry
into English Blank Verse,
with Remarks. Of his
Essay
, Dryden said:
'The Muse's Empire is restored again
In Charles his reign, and by Roscommon's pen.'
Of Bullock see note, p. 138,
ante
. Norris had at one
time, by his acting of Dicky in Farquhar's
Trip to the Jubilee,
acquired the name of Jubilee Dicky.
Sir George Etherege. It was his first play,
The Comical
Revenge, or Love in a Tub
, produced in 1664, which introduced him to
the society of Rochester, Buckingham, &c.
as
Contents
|
Saturday, April 21, 1711 |
Addison |
Natio Comæda est.
Juv.

is nothing which I more desire than a safe and honourable Peace
, tho' at the same time I am very apprehensive of many ill
Consequences that may attend it. I do not mean in regard to our
Politicks, but to our Manners. What an Inundation of Ribbons and
Brocades will break in upon us? What Peals of Laughter and Impertinence
shall we be exposed to? For the Prevention of these great Evils, I could
heartily wish that there was an Act of Parliament for Prohibiting the
Importation of
French
Fopperies.
The Female Inhabitants of our Island have already received very strong
Impressions from this ludicrous Nation, tho' by the Length of the War
(as there is no Evil which has not some Good attending it) they are
pretty well worn out and forgotten. I remember the time when some of our
well-bred Country-Women kept their
Valet de Chambre
, because,
forsooth, a Man was much more handy about them than one of their own
Sex. I myself have seen one of these Male
Abigails
tripping about
the Room with a Looking-glass in his Hand, and combing his Lady's Hair a
whole Morning together. Whether or no there was any Truth in the Story
of a Lady's being got with Child by one of these her Handmaids I cannot
tell, but I think at present the whole Race of them is extinct in our
own Country.
the Time that several of our Sex were taken into this kind of
Service, the Ladies likewise brought up the Fashion of receiving Visits
in their Beds
. It was then look'd upon as a piece of Ill Breeding,
for a Woman to refuse to see a Man, because she was not stirring; and a
Porter would have been thought unfit for his Place, that could have made
so awkward an Excuse. As I love to see every thing that is new, I once
prevailed upon my Friend
Will. Honeycomb
to carry me along with him to
one of these Travelled Ladies, desiring him, at the same time, to
present me as a Foreigner who could not speak
English
, that so I
might not be obliged to bear a Part in the Discourse. The Lady, tho'
willing to appear undrest, had put on her best Looks, and painted her
self for our Reception. Her Hair appeared in a very nice Disorder, as
the Night-Gown which was thrown upon her Shoulders was ruffled with
great Care. For my part, I am so shocked with every thing which looks
immodest in the Fair Sex, that I could not forbear taking off my Eye
from her when she moved in her Bed, and was in the greatest Confusion
imaginable every time she stired a Leg or an Arm. As the Coquets, who
introduced this Custom, grew old, they left it off by Degrees; well
knowing that a Woman of Threescore may kick and tumble her Heart out,
without making any Impressions.
Sempronia
is at present the most profest Admirer of the
French
Nation, but is so modest as to admit her Visitants no
further than her Toilet. It is a very odd Sight that beautiful Creature
makes, when she is talking Politicks with her Tresses flowing about her
Shoulders, and examining that Face in the Glass, which does such
Execution upon all the Male Standers-by. How prettily does she divide
her Discourse between her Woman and her Visitants? What sprightly
Transitions does she make from an Opera or a Sermon, to an Ivory Comb or
a Pincushion? How have I been pleased to see her interrupted in an
Account of her Travels, by a Message to her Footman; and holding her
Tongue, in the midst of a Moral Reflexion, by applying the Tip of it to
a Patch?
There is nothing which exposes a Woman to greater dangers, than that
Gaiety and Airiness of Temper, which are natural to most of the Sex. It
should be therefore the Concern of every wise and virtuous Woman, to
keep this Sprightliness from degenerating into Levity. On the contrary,
the whole Discourse and Behaviour of the
French
is to make the
Sex more Fantastical, or (as they are pleased to term it,)
more
awakened
, than is consistent either with Virtue or Discretion. To
speak Loud in Publick Assemblies, to let every one hear you talk of
Things that should only be mentioned in Private or in Whisper, are
looked upon as Parts of a refined Education. At the same time, a Blush
is unfashionable, and Silence more ill-bred than any thing that can be
spoken. In short, Discretion and Modesty, which in all other Ages and
Countries have been regarded as the greatest Ornaments of the Fair Sex,
are considered as the Ingredients of narrow Conversation, and Family
Behaviour.
Some Years ago I was at the Tragedy of
Macbeth
, and unfortunately
placed myself under a Woman of Quality that is since Dead; who, as I
found by the Noise she made, was newly returned from
France
. A
little before the rising of the Curtain, she broke out into a loud
Soliloquy,
When will the dear Witches enter?
and immediately upon
their first Appearance, asked a Lady that sat three Boxes from her, on
her Right-hand, if those Witches were not charming Creatures.
little
after, as
Betterton
was in one of the finest Speeches of the Play, she
shook her Fan at another Lady, who sat as far on the Left hand, and told
her with a Whisper, that might be heard all over the Pit, We must not
expect to see
Balloon
to-night
. Not long after, calling out to a
young Baronet by his Name, who sat three Seats before me, she asked him
whether
Macbeth's
Wife was still alive; and before he could give an
Answer, fell a talking of the Ghost of
Banquo
. She had by this time
formed a little Audience to herself, and fixed the Attention of all
about her. But as I had a mind to hear the Play, I got out of the Sphere
of her Impertinence, and planted myself in one of the remotest Corners
of the Pit.
This pretty Childishness of Behaviour is one of the most refined Parts
of Coquetry, and is not to be attained in Perfection, by Ladies that do
not Travel for their Improvement. A natural and unconstrained Behaviour
has something in it so agreeable, that it is no Wonder to see People
endeavouring after it. But at the same time, it is so very hard to hit,
when it is not Born with us, that People often make themselves
Ridiculous in attempting it.
very ingenious
French
Author
tells us, that the Ladies of the
Court of
France
, in his Time, thought it Ill-breeding, and a kind of
Female Pedantry, to pronounce an hard Word right; for which Reason they
took frequent occasion to use hard Words, that they might shew a
Politeness in murdering them. He further adds, that a Lady of some
Quality at Court, having accidentally made use of an hard Word in a
proper Place, and pronounced it right, the whole Assembly was out of
Countenance for her.
I must however be so just to own, that there are many Ladies who have
Travelled several Thousand of Miles without being the worse for it, and
have brought Home with them all the Modesty, Discretion and good Sense
that they went abroad with.
on the contrary, there are great Numbers
of
Travelled
Ladies,
who
have lived all their Days within the
Smoke of
London
. I
known a Woman that never was out of the Parish
of St.
James's
,
betray
as many Foreign Fopperies in her
Carriage, as she could have Gleaned up in half the Countries of
Europe
.
C.
At this date the news would just have reached England of
the death of the Emperor Joseph and accession of Archduke Charles to the
German crown. The Archduke's claim to the crown of Spain had been
supported as that of a younger brother of the House of Austria, in whose
person the two crowns of Germany and Spain were not likely to be united.
When, therefore, Charles became head of the German empire, the war of
the Spanish succession changed its aspect altogether, and the English
looked for peace. That of 1711 was, in fact, Marlborough's last
campaign; peace negotiations were at the same time going on between
France and England, and preliminaries were signed in London in October
of this year, 1711. England was accused of betraying the allied cause;
but the changed political conditions led to her withdrawal from it, and
her withdrawal compelled the assent of the allies to the general peace
made by the Treaty of Utrecht, which, after tedious negotiations, was
not signed until the 11th of April, 1713, the continuous issue of the
Spectator
having ended, with Vol. VII., in December, 1712.
The custom was copied from the French
Précieuses
, at
a time when
courir les ruelles
(to take the run of the bedsides)
was a Parisian phrase for fashionable morning calls upon the ladies. The
ruelle
is the little path between the bedside and the wall.
Balloon
was a game like tennis played with a foot-ball;
but the word may be applied here to a person. It had not the-sense which
now first occurs to the mind of a modern reader. Air balloons are not
older than 1783.
Describing perhaps one form of reaction against the verbal
pedantry and
Phébus
of the
Précieuses
.
that
with
Contents
|
Monday, April 23, 1711 |
Addison |
Non bene junctarum discordia semina rerum.
Ovid.

When I want Materials for this Paper, it is my Custom to go abroad in
quest of Game; and when I meet any proper Subject, I take the first
Opportunity of setting down an Hint of it upon Paper. At the same time I
look into the Letters of my Correspondents, and if I find any thing
suggested in them that may afford Matter of Speculation, I likewise
enter a Minute of it in my Collection of Materials. By this means I
frequently carry about me a whole Sheetful of Hints, that would look
like a Rhapsody of Nonsense to any Body but myself: There is nothing in
them but Obscurity and Confusion, Raving and Inconsistency. In short,
they are my Speculations in the first Principles, that (like the World
in its Chaos) are void of all Light, Distinction, and Order.
a Week since there happened to me a very odd Accident, by Reason
of one of these my Papers of Minutes which I had accidentally dropped at
Lloyd's
Coffee-house, where the Auctions are usually kept. Before
I missed it, there were a Cluster of People who had found it, and were
diverting themselves with it at one End of the Coffee-house: It had
raised so much Laughter among them before I had observed what they were
about, that I had not the Courage to own it. The Boy of the
Coffee-house, when they had done with it, carried it about in his Hand,
asking every Body if they had dropped a written Paper; but no Body
challenging it, he was ordered by those merry Gentlemen who had before
perused it, to get up into the Auction Pulpit, and read it to the whole
Room, that if any one would own it they might. The Boy accordingly
mounted the Pulpit, and with a very audible Voice read as follows.
Minutes
Sir
Roger de Coverly's Country
Seat — Yes, for I hate long
Speeches — Query, if a good Christian may be a
Conjurer —
Childermas-day, Saltseller, House-Dog, Screech-owl,
Cricket — Mr.
Thomas Inkle of London, in the good Ship called
The
Achilles.
Yarico — Ægrescitique medendo — Ghosts — The Lady's
Library — Lion by Trade a Taylor — Dromedary called
Bucephalus — Equipage the Lady's
summum bonum —
Charles Lillie to
be taken notice of
2 — Short Face a Relief to Envy — Redundancies in
the three Professions — King
Latinus a Recruit — Jew devouring an Ham
of Bacon —
Westminster Abbey —
Grand Cairo — Procrastination —
April
Fools — Blue Boars, Red Lions, Hogs in Armour — Enter a King and two
Fidlers
solus — Admission into the Ugly Club — Beauty, how
improveable — Families of true and false Humour — The Parrot's
School-Mistress — Face half
Pict half
British — no Man to be an Hero
of Tragedy under Six foot — Club of Sighers — Letters from Flower-Pots,
Elbow-Chairs, Tapestry-Figures, Lion, Thunder — The Bell rings to the
Puppet-Show — Old-Woman with a Beard married to a smock-faced Boy — My
next Coat to be turned up with Blue — Fable of Tongs and
Gridiron — Flower Dyers — The Soldier's Prayer — Thank ye for nothing,
says the Gally-Pot —
Pactolus in Stockings, with golden Clocks to
them — Bamboos, Cudgels, Drumsticks — Slip of my Landlady's eldest
Daughter — The black Mare with a Star in her Forehead — The Barber's
Pole —
Will. Honeycomb's Coat-pocket —
Cæsar's Behaviour and my
own in Parallel Circumstances — Poem in Patch-work —
Nulli gravis est
percussus Achilles — The Female Conventicler — The Ogle Master.
The reading of this Paper made the whole Coffee-house very merry; some
of them concluded it was written by a Madman, and others by some Body
that had been taking Notes out of the
Spectator
. One who had the
Appearance of a very substantial Citizen, told us, with several politick
Winks and Nods, that he wished there was no more in the Paper than what
was expressed in it: That for his part, he looked upon the Dromedary,
the Gridiron, and the Barber's Pole, to signify something more than what
is usually meant by those Words; and that he thought the Coffee-man
could not do better than to carry the Paper to one of the Secretaries of
State. He further added, that he did not like the Name of the outlandish
Man with the golden Clock in his Stockings.
young
Oxford
Scholar
, who chanced to be with his Uncle at the Coffee-house,
discover'd to us who this
Pactolus
was; and by that means turned
the whole Scheme of this worthy Citizen into Ridicule. While they were
making their several Conjectures upon this innocent Paper, I reach'd out
my Arm to the Boy, as he was coming out of the Pulpit, to give it me;
which he did accordingly. This drew the Eyes of the whole Company upon
me; but after having cast a cursory Glance over it, and shook my Head
twice or thrice at the reading of it, I twisted it into a kind of Match,
and litt my Pipe with it. My profound Silence, together with the
Steadiness of my Countenance, and the Gravity of my Behaviour during
this whole Transaction, raised a very loud Laugh on all Sides of me; but
as I had escaped all Suspicion of being the Author, I was very well
satisfied, and applying myself to my Pipe, and the
Post-man
, took
no
further
Notice of any thing that passed about me.
My Reader will find, that I have already made use of above half the
Contents of the foregoing Paper; and will easily Suppose, that those
Subjects which are yet untouched were such Provisions as I had made for
his future Entertainment. But as I have been unluckily prevented by this
Accident, I shall only give him the Letters which relate to the two last
Hints.
first of them I should not have published, were I not
informed that there is many a Husband who suffers very much in his
private Affairs by the indiscreet Zeal of such a Partner as is hereafter
mentioned; to whom I may apply the barbarous Inscription quoted by the
Bishop of
Salisbury
in his Travels
;
Dum nimia pia est,
facta est impia
.
Sir,
'I am one of those unhappy Men that are plagued with a Gospel-Gossip,
so common among Dissenters (especially Friends). Lectures in the
Morning, Church-Meetings at Noon, and Preparation Sermons at Night,
take up so much of her Time, 'tis very rare she knows what we have for
Dinner, unless when the Preacher is to be at it. With him come a
Tribe, all Brothers and Sisters it seems; while others, really such,
are deemed no Relations. If at any time I have her Company alone, she
is a meer Sermon Popgun, repeating and discharging Texts, Proofs, and
Applications so perpetually, that however weary I may go to bed, the
Noise in my Head will not let me sleep till towards Morning. The
Misery of my Case, and great Numbers of such Sufferers, plead your
Pity and speedy Relief, otherwise must expect, in a little time, to be
lectured, preached, and prayed into Want, unless the Happiness of
being sooner talked to Death prevent it.
I am, &c.
R. G.
The second Letter relating to the Ogling Master, runs thus.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am an Irish Gentleman, that have travelled many Years for my
Improvement; during which time I have accomplished myself in the whole
Art of Ogling, as it is at present practised in all the polite Nations
of Europe. Being thus qualified, I intend, by the Advice of my
Friends, to set up for an Ogling-Master. I teach the Church Ogle in
the Morning, and the Play-house Ogle by Candle-light. I have also
brought over with me a new flying Ogle fit for the Ring; which I teach
in the Dusk of the Evening, or in any Hour of the Day by darkning one
of my Windows. I have a Manuscript by me called The Compleat Ogler,
which I shall be ready to show you upon any Occasion. In the mean
time, I beg you will publish the Substance of this Letter in an
Advertisement, and you will very much oblige,
Yours, &c.
Lloyd's Coffee House
was first established in Lombard
Street, at the corner of Abchurch Lane. Pains were taken to get early
Ship news at Lloyd's, and the house was used by underwriters and
insurers of Ships' cargoes. It was found also to be a convenient place
for sales. A poem called
The Wealthy Shopkeeper
, printed in 1700, says
of him,
Now to Lloyd's Coffee-house he never fails,
To read the Letters, and attend the Sales.
It was afterwards removed to Pope's Head Alley, as 'the New Lloyd's
Coffee House;' again removed in 1774 to a corner of the Old Royal
Exchange; and in the building of the new Exchange was provided with the
rooms now known as 'Lloyd's Subscription Rooms,' an institution which
forms part of our commercial system.
Charles Lillie, the perfumer in the Strand, at the corner
of Beaufort Buildings — where the business of a perfumer is at this day
carried on — appears in the
,
, and subsequent numbers of the
Spectator
, together with Mrs. Baldwin of Warwick Lane, as a chief
agent for the sale of the Paper. To the line which had run
'London:
Printed for Sam. Buckley, at the Dolphin in Little Britain; and
Sold by A. Baldwin in Warwick-Lane; where Advertisements are taken
in;'
there was then appended:
'as also by Charles Lillie, Perfumer, at
the Corner of Beaufort-Buildings in the Strand'.
Nine other agents,
of whom complete sets could be had, were occasionally set forth together
with these two in an advertisement; but only these are in the colophon.
Oxonian
Gilbert Burnet, author of the
History of the Reformation,
and
History of his own Time,
was Bishop of Salisbury from 1689 to his
death in 1715. Addison here quotes:
'Some Letters containing an Account
of what seemed most remarkable in Travelling through Switzerland, Italy,
some parts of Germany, &c., in the Years 1685 and 1686. Written by G.
Burnet, D.D., to the Honourable R. B.'
In the first letter, which is
from Zurich, Dr. Burnet speaks of many Inscriptions at Lyons of the late
and barbarous ages, as
Bonum Memoriam
, and
Epitaphium
hunc
. Of 23 Inscriptions in the Garden of the Fathers of Mercy, he
quotes one which must be towards the barbarous age, as appears by the
false Latin in '
Nimia
' He quotes it because he has 'made a little
reflection on it,' which is, that its subject, Sutia Anthis, to whose
memory her husband Cecalius Calistis dedicates the inscription which
says
'quædum Nimia pia fuit, facta est Impia'
(who while she was too pious, was made impious),
must have been publicly accused of Impiety, or
her husband would not have recorded it in such a manner; that to the
Pagans Christianity was Atheism and Impiety; and that here, therefore,
is a Pagan husband's testimony to the better faith, that the Piety of
his wife made her a Christian.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 24, 1711 |
Addison |
Ride si sapis.
Mart.

.
Hobbs
, in his
Discourse of Human Nature
, which, in my humble
Opinion, is much the best of all his Works, after some very curious
Observations upon Laughter, concludes thus:
'The Passion of Laughter is
nothing else but sudden Glory arising from some sudden Conception of
some Eminency in ourselves by Comparison with the Infirmity of others,
or with our own formerly: For Men laugh at the Follies of themselves
past, when they come suddenly to Remembrance, except they bring with
them any present Dishonour.'
According to this Author, therefore, when we hear a Man laugh
excessively, instead of saying he is very Merry, we ought to tell him he
is very Proud. And, indeed, if we look into the bottom of this Matter,
we shall meet with many Observations to confirm us in his Opinion. Every
one laughs at some Body that is in an inferior State of Folly to
himself. It was formerly the Custom for every great House in
England
to keep a tame Fool dressed in Petticoats, that the Heir of the Family
might have an Opportunity of joking upon him, and diverting himself with
his Absurdities. For the same Reason Idiots are still in Request in most
of the Courts of
Germany
, where there is not a Prince of any great
Magnificence, who has not two or three dressed, distinguished,
undisputed Fools in his Retinue, whom the rest of the Courtiers are
always breaking their Jests upon.
The
Dutch
, who are more famous for their Industry and Application,
than for Wit and Humour, hang up in several of their Streets what they
call the Sign of the
Gaper
, that is, the Head of an Idiot dressed in a
Cap and Bells, and gaping in a most immoderate manner: This is a
standing Jest at
Amsterdam
.
Thus every one diverts himself with some Person or other that is below
him in Point of Understanding, and triumphs in the Superiority of his
Genius, whilst he has such Objects of Derision before his Eyes.
.
Dennis
has very well expressed this in a Couple of humourous Lines,
which are part of a Translation of a
Satire
in Monsieur Boileau
.
Thus one Fool lolls his Tongue out at another,
And shakes his empty Noddle at his Brother.
Mr.
Hobbs's
Reflection gives us the Reason why the insignificant
People above-mentioned are Stirrers up of Laughter among Men of a gross
Taste: But as the more understanding Part of Mankind do not find their
Risibility affected by such ordinary Objects, it may be worth the while
to examine into the several Provocatives of Laughter in Men of superior
Sense and Knowledge.
In the first Place I must observe, that there is a Set of merry Drolls,
whom the common People of all Countries admire, and seem to love so
well,
that they could eat them
, according to the old Proverb: I mean
those circumforaneous Wits whom every Nation calls by the Name of that
Dish of Meat which it loves best. In
Holland
they are termed
Pickled
Herrings
; in
France, Jean Pottages
; in
Italy, Maccaronies
; and in
Great Britain, Jack Puddings
. These merry Wags, from whatsoever Food
they receive their Titles, that they may make their Audiences laugh,
always appear in a Fool's Coat, and commit such Blunders and Mistakes in
every Step they take, and every Word they utter, as those who listen to
them would be ashamed of.
But this little Triumph of the Understanding, under the Disguise of
Laughter, is no where more visible than in that Custom which prevails
every where among us on the first Day of the present Month, when every
Body takes it in his Head to make as many Fools as he can. In proportion
as there are more Follies discovered, so there is more Laughter raised
on this Day than on any other in the whole Year. A Neighbour of mine,
who is a Haberdasher by Trade, and a very shallow conceited Fellow,
makes his Boasts that for these ten Years successively he has not made
less than an hundred
April
Fools. My Landlady had a falling out with
him about a Fortnight ago, for sending every one of her Children upon
some
Sleeveless Errand
, as she terms it. Her eldest Son went to buy an
Halfpenny worth of Inkle at a Shoe-maker's; the eldest Daughter was
dispatch'd half a Mile to see a Monster; and, in short, the whole Family
of innocent Children made
April
Fools. Nay, my Landlady herself did
not escape him. This empty Fellow has laughed upon these Conceits ever
since.
This Art of Wit is well enough, when confined to one Day in a
Twelvemonth; but there is an ingenious Tribe of Men sprung up of late
Years, who are for making
April
Fools every Day in the Year. These
Gentlemen are commonly distinguished by the Name of
Biters
; a Race of
Men that are perpetually employed in laughing at those Mistakes which
are of their own Production.
Thus we see, in proportion as one Man is more refined than another, he
chooses his Fool out of a lower or higher Class of Mankind: or, to speak
in a more Philosophical Language, That secret Elation and Pride of
Heart, which is generally called Laughter, arises in him from his
comparing himself with an Object below him, whether it so happens that
it be a Natural or an Artificial Fool. It is indeed very possible, that
the Persons we laugh at may in the main of their Characters be much
wiser Men than ourselves; but if they would have us laugh at them, they
must fall short of us in those Respects which stir up this Passion.
I am afraid I shall appear too Abstracted in my Speculations, if I shew
that when a Man of Wit makes us laugh, it is by betraying some Oddness
or Infirmity in his own Character, or in the Representation which he
makes of others; and that when we laugh at a Brute or even
at
an
inanimate thing, it is at some Action or Incident that bears a remote
Analogy to any Blunder or Absurdity in reasonable Creatures.
But to come into common Life: I shall pass by the Consideration of those
Stage Coxcombs that are able to shake a whole Audience, and take notice
of a particular sort of Men who are such Provokers of Mirth in
Conversation, that it is impossible for a Club or Merry-meeting to
subsist without them; I mean, those honest Gentlemen that are always
exposed to the Wit and Raillery of their Well-wishers and Companions;
that are pelted by Men, Women, and Children, Friends and Foes, and, in a
word, stand as
Butts
in Conversation, for every one to shoot at that
pleases. I know several of these
Butts
, who are Men of Wit and Sense,
though by some odd Turn of Humour, some unlucky Cast in their Person or
Behaviour, they have always the Misfortune to make the Company merry.
The Truth of it is, a Man is not qualified for a
Butt
, who has not a
good deal of Wit and Vivacity, even in the ridiculous side of his
Character. A stupid
Butt
is only fit for the Conversation of ordinary
People: Men of Wit require one that will give them Play, and bestir
himself in the absurd Part of his Behaviour. A
Butt
with these
Accomplishments frequently gets the Laugh of his side, and turns the
Ridicule upon him that attacks him.
John Falstaff
was an Hero of
this Species, and gives a good Description of himself in his Capacity of
a
Butt
, after the following manner;
Men of all Sorts
(says that
merry Knight)
take a pride to gird at me. The Brain of Man is not able
to invent any thing that tends to Laughter more than I invent, or is
invented on me. I am not only Witty in my self, but the Cause that Wit
is in other Men
.
C.
Chap. ix. § 13. Thomas Hobbes's
Human Nature
was
published in 1650. He died in 1679, aged 91.
Boileau's 4th satire. John Dennis was at this time a
leading critic of the French school, to whom Pope afterwards attached
lasting ridicule. He died in 1734, aged 77.
Henry IV Part II
Act I § 2.
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 25, 1711 |
Steele |
... Per multas aditum sibi sæpe figuras
Repperit ...
Ovid

My Correspondents take it ill if I do not, from Time to Time let them
know I have received their Letters. The most effectual Way will be to
publish some of them that are upon important Subjects; which I shall
introduce with a Letter of my own that I writ a Fortnight ago to a
Fraternity who thought fit to make me an honorary Member.
To the President and Fellows of the
Ugly Club.
May it please your Deformities,
I have received the Notification of the Honour you have done me, in
admitting me into your Society. I acknowledge my Want of Merit, and
for that Reason shall endeavour at all Times to make up my own
Failures, by introducing and recommending to the Club Persons of more
undoubted Qualifications than I can pretend to. I shall next Week come
down in the Stage-Coach, in order to take my Seat at the Board; and
shall bring with me a Candidate of each Sex. The Persons I shall
present to you, are an old Beau and a modern
Pict. If they are not
so eminently gifted by Nature as our Assembly expects, give me Leave
to say their acquired Ugliness is greater than any that has ever
appeared before you. The Beau has varied his Dress every Day of his
Life for these thirty Years last past, and still added to the
Deformity he was born with. The
Pict has still greater Merit towards
us; and has, ever since she came to Years of Discretion, deserted the
handsome Party, and taken all possible Pains to acquire the Face in
which I shall present her to your Consideration and Favour.
I desire to know whether you admit People of Quality.
I am, Gentlemen,
Your most obliged
Humble Servant,
The Spectator.
April 7.
Mr.
Spectator,
To shew you there are among us of the vain weak Sex, some that have
Honesty and Fortitude enough to dare to be ugly, and willing to be
thought so; I apply my self to you, to beg your Interest and
Recommendation to the Ugly Club. If my own Word will not be taken,
(tho' in this Case a Woman's may) I can bring credible Witness of my
Qualifications for their Company, whether they insist upon Hair,
Forehead, Eyes, Cheeks, or Chin; to which I must add, that I find it
easier to lean to my left Side than my right. I hope I am in all
respects agreeable: And for Humour and Mirth, I'll keep up to the
President himself. All the Favour I'll pretend to is, that as I am the
first Woman has appeared desirous of good Company and agreeable
Conversation, I may take and keep the upper End of the Table. And
indeed I think they want a Carver, which I can be after as ugly a
Manner as they can wish. I desire your Thoughts of my Claim as soon as
you can. Add to my Features the Length of my Face, which is full half
Yard; tho' I never knew the Reason of it till you gave one for the
Shortness of yours. If I knew a Name ugly enough to belong to the
above-described Face, I would feign one; but, to my unspeakable
Misfortune, my Name is the only disagreeable Prettiness about me; so
prithee make one for me that signifies all the Deformity in the World:
You understand Latin, but be sure bring it in with my being in the
Sincerity of my Heart,
Your most frightful Admirer,
and Servant,
Hecatissa.
Mr.
Spectator,
I Read your Discourse upon Affectation, and from the Remarks made in
it examined my own Heart so strictly, that I thought I had found out
its most secret Avenues, with a Resolution to be aware of you for the
future. But alas! to my Sorrow I now understand, that I have several
Follies which I do not know the Root of. I am an old Fellow, and
extremely troubled with the Gout; but having always a strong Vanity
towards being pleasing in the Eyes of Women, I never have a Moment's
Ease, but I am mounted in high-heel'd Shoes with a glased Wax-leather
Instep. Two Days after a severe Fit I was invited to a Friend's House
in the City, where I believed I should see Ladies; and with my usual
Complaisance crippled my self to wait upon them: A very sumptuous
Table, agreeable Company, and kind Reception, were but so many
importunate Additions to the Torment I was in. A Gentleman of the
Family observed my Condition; and soon after the Queen's Health, he,
in the Presence of the whole Company, with his own Hand degraded me
into an old Pair of his own Shoes. This operation, before fine Ladies,
to me (who am by Nature a Coxcomb) was suffered with the same
Reluctance as they admit the Help of Men in their greatest Extremity.
The Return of Ease made me forgive the rough Obligation laid upon me,
which at that time relieved my Body from a Distemper, and will my Mind
for ever from a Folly. For the Charity received I return my Thanks
this Way.
Your most humble Servant.
Epping, April 18.
Sir,
We have your Papers here the Morning they come out, and we have been
very well entertained with your last, upon the false Ornaments of
Persons who represent Heroes in a Tragedy. What made your Speculation
come very seasonably amongst us is, that we have now at this Place a
Company of Strolers, who are very far from offending in the
impertinent Splendor of the Drama. They are so far from falling into
these false Gallantries, that the Stage is here in its Original
Situation of a Cart.
Alexander the Great was acted by a Fellow
in a Paper Cravat.
The next Day, the Earl of Essex
1 seemed to have
no Distress but his Poverty: And my Lord Foppington
2 the same
Morning wanted any better means to shew himself a Fop, than by wearing
Stockings of different Colours. In a Word, tho' they have had a full
Barn for many Days together, our Itinerants are still so wretchedly
poor, that without you can prevail to send us the Furniture you forbid
at the Play-house, the Heroes appear only like sturdy Beggars, and the
Heroines Gipsies.
We have had but one Part which was performed and
dressed with Propriety, and that was Justice Clodpate
3:
This was so
well done that it offended Mr. Justice Overdo
4; who, in the midst
of our whole Audience, was (like Quixote in the Puppet-Show) so
highly provok'd, that he told them, If they would move compassion, it
should be in their own Persons, and not in the Characters of
distressed Princes and Potentates: He told them, If they were so good
at finding the way to People's Hearts, they should do it at the End of
Bridges or Church-Porches, in their proper Vocation of Beggars. This,
the Justice says, they must expect, since they could not be contented
to act Heathen Warriors, and such Fellows as
Alexander, but
must presume to make a Mockery of one of the
Quorum.
Your Servant.
R.
In
The Unhappy Favourite
, or the Earl of Essex, a
Tragedy of John Banks, first acted in 1682.
Lord Foppington is in Colley Cibber's
Careless
Husband
, first acted in 1794.
Justice Clodpate is in the Shadwell's
Epsons Wells
,
first acted in 1676.
Adam Overdo is the Justice of the Peace, who in Ben
Jonson's
Bartholomew Fair
goes disguised
'for the good of the
Republic in the Fair and the weeding out of enormity.'
Contents
|
Thursday, April 26, 1711 |
Steele |
... Hominem pagina nostra sapit.
Mart.

It is very natural for a Man who is not turned for Mirthful Meetings of
Men, or Assemblies of the fair Sex, to delight in that sort of
Conversation which we find in Coffee-houses. Here a Man, of my Temper,
is in his Element; for if he cannot talk, he can still be more agreeable
to his Company, as well as pleased in himself, in being only an Hearer.
It is a Secret known but to few, yet of no small use in the Conduct of
Life, that when you fall into a Man's Conversation, the first thing you
should consider is, whether he has a greater Inclination to hear you, or
that you should hear him. The latter is the more general Desire, and I
know very able Flatterers that never speak a Word in Praise of the
Persons from whom they obtain daily Favours, but still practise a
skilful Attention to whatever is uttered by those with whom they
converse. We are very Curious to observe the Behaviour of Great Men and
their Clients; but the same Passions and Interests move Men in lower
Spheres; and I (that have nothing else to do but make Observations) see
in every Parish, Street, Lane, and Alley of this Populous City, a little
Potentate that has his Court, and his Flatterers who lay Snares for his
Affection and Favour, by the same Arts that are practised upon Men in
higher Stations.
In the Place I most usually frequent, Men differ rather in the Time of
Day in which they make a Figure, than in any real Greatness above one
another. I, who am at the Coffee-house at Six in a Morning, know that my
Friend
Beaver
the Haberdasher has a Levy of more undissembled
Friends and Admirers, than most of the Courtiers or Generals of
Great-Britain
. Every Man about him has, perhaps, a News-Paper in
his Hand; but none can pretend to guess what Step will be taken in any
one Court of
Europe
, 'till Mr.
Beaver
has thrown down his
Pipe, and declares what Measures the Allies must enter into upon this
new Posture of Affairs. Our Coffee-house is near one of the Inns of
Court, and
Beaver
has the Audience and Admiration of his
Neighbours from Six 'till within a Quarter of Eight, at which time he is
interrupted by the Students of the House; some of whom are ready dress'd
for
Westminster
, at Eight in a Morning, with Faces as busie as if
they were retained in every Cause there; and others come in their
Night-Gowns to saunter away their Time, as if they never designed to go
thither.
do not know that I meet, in any of my Walks, Objects which
move both my Spleen and Laughter so effectually, as these young Fellows
at the
Grecian, Squire's, Searle's
, and all other
Coffee-houses adjacent to the Law, who rise early for no other purpose
but to publish their Laziness. One would think these young
Virtuoso's
take a gay Cap and Slippers, with a Scarf and
Party-coloured Gown, to be Ensigns of Dignity; for the vain Things
approach each other with an Air, which shews they regard one another for
their Vestments. I have observed, that the Superiority among these
proceeds from an Opinion of Gallantry and Fashion: The Gentleman in the
Strawberry Sash, who presides so much over the rest, has, it seems,
subscribed to every Opera this last Winter, and is supposed to receive
Favours from one of the Actresses.
When the Day grows too busie for these Gentlemen to enjoy any longer the
Pleasures of their
Deshabilé
, with any manner of Confidence, they
give place to Men who have Business or good Sense in their Faces, and
come to the Coffee-house either to transact Affairs or enjoy
Conversation. The Persons to whose Behaviour and Discourse I have most
regard, are such as are between these two sorts of Men: Such as have not
Spirits too Active to be happy and well pleased in a private Condition,
nor Complexions too warm to make them neglect the Duties and Relations
of Life. Of these sort of Men consist the worthier Part of Mankind; of
these are all good Fathers, generous Brothers, sincere Friends, and
faithful Subjects. Their Entertainments are derived rather from Reason
than Imagination: Which is the Cause that there is no Impatience or
Instability in their Speech or Action. You see in their Countenances
they are at home, and in quiet Possession of the present Instant, as it
passes, without desiring to quicken it by gratifying any Passion, or
prosecuting any new Design. These are the Men formed for Society, and
those little Communities which we express by the Word
Neighbourhoods
.
The Coffee-house is the Place of Rendezvous to all that live near it,
who are thus turned to relish calm and ordinary Life.
Eubulus
presides over the middle Hours of the Day, when this Assembly of Men
meet together. He enjoys a great Fortune handsomely, without launching
into Expence; and exerts many noble and useful Qualities, without
appearing in any publick Employment. His Wisdom and Knowledge are
serviceable to all that think fit to make use of them; and he does the
office of a Council, a Judge, an Executor, and a Friend to all his
Acquaintance, not only without the Profits which attend such Offices,
but also without the Deference and Homage which are usually paid to
them. The giving of Thanks is displeasing to him. The greatest Gratitude
you can shew him is to let him see you are the better Man for his
Services; and that you are as ready to oblige others, as he is to oblige
you.
In the private Exigencies of his Friends he lends, at legal Value,
considerable Sums, which he might highly increase by rolling in the
Publick Stocks. He does not consider in whose Hands his Mony will
improve most, but where it will do most Good.
Eubulus
has so great an Authority in his little Diurnal Audience, that
when he shakes his Head at any Piece of publick News, they all of them
appear dejected; and on the contrary, go home to their Dinners with a
good Stomach and cheerful Aspect, when
Eubulus
seems to intimate that
Things go well. Nay, their Veneration towards him is so great, that when
they are in other Company they speak and act after him; are Wise in his
Sentences, and are no sooner sat down at their own Tables, but they hope
or fear, rejoice or despond as they saw him do at the Coffee-house. In a
word, every Man is
Eubulus
as soon as his Back is turned.
Having here given an Account of the several Reigns that succeed each
other from Day-break till Dinner-time, I shall mention the Monarchs of
the Afternoon on another Occasion, and shut up the whole Series of them
with the History of
Tom
the Tyrant; who, as first Minister of the
Coffee-house, takes the Government upon him between the Hours of Eleven
and Twelve at Night, and gives his Orders in the most Arbitrary manner
to the Servants below him, as to the Disposition of Liquors, Coal and
Cinders.
R.
The
Grecian
(see
, p. 7,
ante
,) was by
the Temple;
Squire's
, by Gray's Inn;
Serle's
, by Lincoln's
Inn.
Squire's
, a roomy, red-brick house, adjoined the gate of
Gray's Inn, in Fulwood's Rents, Holborn, then leading to Gray's Inn
Walks, which lay open to the country. Squire, the establisher of this
coffee-house, died in 1717.
Serle's
was near Will's, which stood
at the corner of Serle Street and Portugal Street, Lincoln's Inn.
Contents
|
Friday, April 27, 17111 |
Addison |
Nunquam aliud Natura, aliud Sapientia dixit.
Juv.

the four
Indian
Kings were in this Country about a Twelvemonth
ago
, I often mixed with the Rabble, and followed them a whole Day
together, being wonderfully struck with the Sight of every thing that is
new or uncommon. I have, since their Departure, employed a Friend to
make many Inquiries of their Landlord the Upholsterer, relating to their
Manners and Conversation, as also concerning the Remarks which they made
in this Country: For, next to the forming a right Notion of such
Strangers, I should be desirous of learning what Ideas they have
conceived of us.
The Upholsterer finding my Friend very inquisitive about these his
Lodgers, brought him some time since a little Bundle of Papers, which he
assured him were written by King
Sa Ga Yean Qua Rash Tow
, and, as he
supposes, left behind by some Mistake. These Papers are now translated,
and contain abundance of very odd Observations, which I find this little
Fraternity of Kings made during their Stay in the Isle of
Great
Britain
. I shall present my Reader with a short Specimen of them in
this Paper, and may perhaps communicate more to him hereafter. In the
Article of
London
are the following Words, which without doubt are
meant of the Church of St.
Paul
.
'On the most rising Part of the Town there stands a huge House, big
enough to contain the whole Nation of which I am King. Our good
Brother
E Tow O Koam, King of the
Rivers, is of opinion it was
made by the Hands of that great God to whom it is consecrated. The
Kings of
Granajah and of the
Six Nations believe that it was
created with the Earth, and produced on the same Day with the Sun and
Moon. But for my own Part, by the best Information that I could get of
this Matter, I am apt to think that this prodigious Pile was fashioned
into the Shape it now bears by several Tools and Instruments of which
they have a wonderful Variety in this Country. It was probably at
first an huge mis-shapen Rock that grew upon the Top of the Hill,
which the Natives of the Country (after having cut it into a kind of
regular Figure) bored and hollowed with incredible Pains and Industry,
till they had wrought in it all those beautiful Vaults and Caverns
into which it is divided at this Day.
As soon as this Rock was thus
curiously scooped to their Liking, a prodigious Number of Hands must
have been employed in chipping the Outside of it, which is now as
smooth as
the Surface of a Pebble3; and is in several Places hewn
out into Pillars that stand like the Trunks of so many Trees bound
about the Top with Garlands of Leaves. It is probable that when this
great Work was begun, which must have been many Hundred Years ago,
there was some Religion among this People; for they give it the Name
of a Temple, and have a Tradition that it was designed for Men to pay
their Devotions in.
And indeed, there are several Reasons which make
us think that the Natives of this Country had formerly among them some
sort of Worship; for they set apart every seventh Day as sacred: But
upon my going into one of
these4 holy Houses on that Day, I could
not observe any Circumstance of Devotion in their Behaviour: There was
indeed a Man in Black who was mounted above the rest, and seemed to
utter something with a great deal of Vehemence; but as for those
underneath him, instead of paying their Worship to the Deity of the
Place, they were most of them bowing and curtisying to one another,
and a considerable Number of them fast asleep.
The Queen of the Country appointed two Men to attend us, that had
enough of our Language to make themselves understood in some few
Particulars. But we soon perceived these two were great Enemies to one
another, and did not always agree in the same Story. We could make a
Shift to gather out of one of them, that this Island was very much
infested with a monstrous Kind of Animals, in the Shape of Men, called
Whigs; and he often told us, that he hoped we should meet with
none of them in our Way, for that if we did, they would be apt to
knock us down for being Kings.
Our other Interpreter used to talk very much of a kind of Animal
called a
Tory, that was as great a Monster as the
Whig,
and would treat us as ill for being Foreigners. These two Creatures,
it seems, are born with a secret Antipathy to one another, and engage
when they meet as naturally as the Elephant and the Rhinoceros. But as
we saw none of either of these Species, we are apt to think that our
Guides deceived us with Misrepresentations and Fictions, and amused us
with an Account of such Monsters as are not really in their Country.
These Particulars we made a shift to pick out from the Discourse of
our Interpreters; which we put together as well as we could, being
able to understand but here and there a Word of what they said, and
afterwards making up the Meaning of it among ourselves. The Men of the
Country are very cunning and ingenious in handicraft Works; but withal
so very idle, that we often saw young lusty raw-boned Fellows carried
up and down the Streets in little covered Rooms by a Couple of
Porters, who are hired for that Service. Their Dress is likewise very
barbarous, for they almost strangle themselves about the Neck, and
bind their Bodies with many Ligatures, that we are apt to think are
the Occasion of several Distempers among them which our Country is
entirely free from. Instead of those beautiful Feathers with which we
adorn our Heads, they often buy up a monstrous Bush of Hair, which
covers their Heads, and falls down in a large Fleece below the Middle
of their Backs; with which they walk up and down the Streets, and are
as proud of it as if it was of their own growth.
We were invited to one of their publick Diversions, where we hoped to
have seen the great Men of their Country running down a Stag or
pitching a Bar, that we might have discovered who were the
Persons of
the greatest Abilities among them5; but instead of that, they
conveyed us into a huge Room lighted up with abundance of Candles,
where this lazy People sat still above three Hours to see several
Feats of Ingenuity performed by others, who it seems were paid for it.
As for the Women of the Country, not being able to talk with them, we
could only make our Remarks upon them at a Distance. They let the Hair
of their Heads grow to a great Length; but as the Men make a great
Show with Heads of Hair that are not of their own, the Women, who they
say have very fine Heads of Hair, tie it up in a Knot, and cover it
from being seen. The Women look like Angels, and would be more
beautiful than the Sun, were it not for little black Spots that are
apt to break out in their Faces, and sometimes rise in very odd
Figures.
I have observed that those little Blemishes wear off very
soon; but when they disappear in one Part of the Face, they are very
apt to break out in another, insomuch that I have seen a Spot upon the
Forehead in the Afternoon, which was upon the Chin in the Morning
6.'
The Author then proceeds to shew the Absurdity of Breeches and
Petticoats, with many other curious Observations, which I shall reserve
for another Occasion. I cannot however conclude this Paper without
taking notice, That amidst these wild Remarks there now and then appears
something very reasonable. I cannot likewise forbear observing, That we
are all guilty in some Measure of the same narrow way of Thinking, which
we meet with in this Abstract of the
Indian
Journal; when we
fancy the Customs, Dress, and Manners of other Countries are ridiculous
and extravagant, if they do not resemble those of our own.
C.
Swift writes to Stella, in his Journal, 28th April,
1711:
'The Spectator is written by Steele, with Addison's help; 'tis often
very pretty. Yesterday it was made of a noble hint I gave him long ago
for his Tatlers, about an Indian, supposed to write his travels into
England. I repent he ever had it. I intended to have written a book on
that subject. I believe he has spent it all in one paper, and all the
under hints there are mine too; but I never see him or Addison.'
The paper, it will be noticed, was not written by Steele.
The four kings Te Yee Neen Ho Ga Prow, Sa Ga Yean Qua Rash
Tow, E Tow O Koam, and Oh Nee Yeath Ton Now Prow, were chiefs of the
Iroquois Indians who had been persuaded by adjacent British colonists to
come and pay their respects to Queen Anne, and see for themselves the
untruth of the assertion made among them by the Jesuits, that the
English and all other nations were vassals to the French king. They were
said also to have been told that the Saviour was born in France and
crucified in England.
polished Marble
those
Men of the greatest Perfections in their Country
There was, among other fancies, a patch cut to the pattern
of a coach and horses. Suckling, in verses
upon the Black Spots worn by
my Lady D. E.,
had called them her
... Mourning weeds for Hearts forlorn,
Which, though you must not love, you could not scorn,
Contents
|
Saturday, April 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Torquet ab Obscenis jam nunc Sermonibus Aurem.
Hor.

Mr. Spectator,
'My Fortune, Quality, and Person are such as render me as Conspicuous
as any Young Woman in Town. It is in my Power to enjoy it in all its
Vanities, but I have, from a very careful Education, contracted a
great Aversion to the forward Air and Fashion which is practised in
all Publick Places and Assemblies. I attribute this very much to the
Stile and Manners of our Plays: I was last Night at the
Funeral, where a Confident Lover in the Play, speaking of his
Mistress, cries out:
Oh that Harriot!
to fold these Arms
about the Waste of that Beauteous strugling, and at last yielding
Fair!1
Such an Image as this ought, by no means, to be
presented to a Chaste and Regular Audience. I expect your Opinion of
this Sentence, and recommend to your Consideration, as a
Spectator,
the conduct of the Stage at present with Relation to Chastity and
Modesty.
I am, Sir,
Your Constant Reader
and Well-wisher.
Complaint of this Young Lady is so just, that the Offence is
great
enough to have displeased Persons who cannot pretend to that
Delicacy and Modesty, of which she is Mistress. But there is a great
deal to be said in Behalf of an Author: If the Audience would but
consider the Difficulty of keeping up a sprightly Dialogue for five Acts
together, they would allow a Writer, when he wants Wit, and can't please
any otherwise, to help it out with a little Smuttiness. I will answer
for the Poets, that no one ever writ Bawdy for any other Reason but
Dearth of Invention.
the Author cannot strike out of himself any
more of that which he has superior to those who make up the Bulk of his
Audience, his natural Recourse is to that which he has in common with
them; and a Description which gratifies a sensual Appetite will please,
when the Author has nothing
about him to delight
a refined
Imagination. It is to such a Poverty we must impute this and all other
Sentences in Plays, which are of this Kind, and which are commonly
termed Luscious Expressions.
This Expedient, to supply the Deficiencies of Wit, has been used more or
less, by most of the Authors who have succeeded on the Stage; tho' I
know but one who has professedly writ a Play upon the Basis of the
Desire of Multiplying our Species, and that is the Polite Sir
George
Etherege;
if I understand what the Lady would be at, in the Play
called
She would if She could.
Other Poets have, here and there,
given an Intimation that there is this Design, under all the Disguises
and Affectations which a Lady may put on; but no Author, except this,
has made sure Work of it, and put the Imaginations of the Audience upon
this one Purpose, from the Beginning to the End of the Comedy. It has
always fared accordingly; for whether it be, that all who go to this
Piece would if they could, or that the Innocents go to it, to guess only
what
She would if She could
, the Play has always been well
received.
It lifts an heavy empty Sentence, when there is added to it a lascivious
Gesture of Body; and when it is too low to be raised even by that, a
flat Meaning is enlivened by making it a double one. Writers, who want
Genius
, never fail of keeping this Secret in reserve, to create a
Laugh, or raise a Clap. I, who know nothing of Women but from seeing
Plays, can give great Guesses at the whole Structure of the fair Sex, by
being innocently placed in the Pit, and insulted by the Petticoats of
their Dancers; the Advantages of whose pretty Persons are a great Help
to a dull Play. When a Poet flags in writing Lusciously, a pretty Girl
can move Lasciviously, and have the same good Consequence for the
Author.
Poets in this Case use their Audiences, as dull Parasites
do their Patrons; when they cannot longer divert
them
with their
Wit or Humour, they bait
their
Ears
something which is
agreeable to
their
Temper, though below
their
Understanding.
Apicius
cannot resist being pleased, if you give him an Account of a
delicious Meal; or
Clodius
, if you describe a Wanton Beauty: Tho' at
the same time, if you do not awake those Inclinations in them, no Men
are better Judges of what is just and delicate in Conversation. But as I
have before observed, it is easier to talk to the Man, than to the Man
of Sense.
It is remarkable, that the Writers of least Learning are best skilled in
the luscious Way.
Poetesses of the Age have done Wonders in this
kind; and we are obliged to the Lady who writ
Ibrahim
, for
introducing a preparatory Scene to the very Action, when the Emperor
throws his Handkerchief as a Signal for his Mistress to follow him into
the most retired Part of the Seraglio. It must be confessed his
Turkish
Majesty went off with a good Air, but, methought, we made but
a sad Figure who waited without.
ingenious Gentlewoman, in this
piece of Bawdry, refined upon an Author of the same Sex
, who, in the
Rover
, makes a Country Squire strip to his Holland Drawers. For
Blunt
is disappointed, and the Emperor is understood to go on to the
utmost. The Pleasantry of stripping almost Naked has been since
practised (where indeed it should have begun) very successfully at
Bartholomew
Fair.
It is not here to be omitted, that in one of the above-mentioned Female
Compositions, the
Rover
is very frequently sent on the same Errand; as
I take it, above once every Act. This is not wholly unnatural; for, they
say, the Men-Authors draw themselves in their chief Characters, and the
Women-Writers may be allowed the same Liberty. Thus, as the Male Wit
gives his Hero a [good] Fortune, the Female gives her Heroin a great
Gallant, at the End of the Play. But, indeed, there is hardly a Play one
can go to, but the Hero or fine Gentleman of it struts off upon the same
account, and leaves us to consider what good Office he has put us to, or
to employ our selves as we please. To be plain, a Man who frequents
Plays would have a very respectful Notion of himself, were he to
recollect how often he has been used as a Pimp to ravishing Tyrants, or
successful Rakes. When the Actors make their
Exit
on this good
Occasion, the Ladies are sure to have an examining Glance from the Pit,
to see how they relish what passes; and a few lewd Fools are very ready
to employ their Talents upon the Composure or Freedom of their Looks.
Such Incidents as these make some Ladies wholly absent themselves from
the Play-House; and others never miss the first Day of a Play, lest it
should prove too luscious to admit their going with any Countenance to
it on the second.
If Men of Wit, who think fit to write for the Stage, instead of this
pitiful way of giving Delight, would turn their Thoughts upon raising it
from good natural Impulses as are in the Audience, but are choked up by
Vice and Luxury, they would not only please, but befriend us at the same
time. If a Man had a mind to be new in his way of Writing, might not he
who is now represented as a fine Gentleman, tho' he betrays the Honour
and Bed of his Neighbour and Friend, and lies with half the Women in the
Play, and is at last rewarded with her of the best Character in it; I
say, upon giving the Comedy another Cast, might not such a one divert
the Audience quite as well, if at the Catastrophe he were found out for
a Traitor, and met with Contempt accordingly? There is seldom a Person
devoted to above one Darling Vice at a time, so that there is room
enough to catch at Men's Hearts to their Good and Advantage, if the
Poets will attempt it with the Honesty which becomes their Characters.
There is no Man who loves his Bottle or his Mistress, in a manner so
very abandoned, as not to be capable of relishing an agreeable
Character, that is no way a Slave to either of those Pursuits. A Man
that is Temperate, Generous, Valiant, Chaste, Faithful and Honest, may,
at the same time, have Wit, Humour, Mirth, Good-breeding, and Gallantry.
While he exerts these latter Qualities, twenty Occasions might be
invented to shew he is Master of the other noble Virtues. Such
Characters would smite and reprove the Heart of a Man of Sense, when he
is given up to his Pleasures. He would see he has been mistaken all this
while, and be convinced that a sound Constitution and an innocent Mind
are the true Ingredients for becoming and enjoying Life. All Men of true
Taste would call a Man of Wit, who should turn his Ambition this way, a
Friend and Benefactor to his Country; but I am at a loss what Name they
would give him, who makes use of his Capacity for contrary Purposes.
R.
The Play is by Steele himself, the writer of this Essay. Steele's Plays
were as pure as his
Spectator
Essays, absolutely discarding the
customary way of enforcing feeble dialogues by the spurious force of
oaths, and aiming at a wholesome influence upon his audience. The
passage here recanted was a climax of passion in one of the lovers of
two sisters, Act II., sc. I, and was thus retrenched in subsequent
editions:
| Campley. |
Oh that Harriot! to embrace that beauteous – |
| Lord Hardy. |
Ay, Tom; but methinks your Head runs too much on
the Wedding Night only, to make your Happiness lasting; mine is fixt on
the married State; I expect my Felicity from Lady Sharlot, in her Friendship,
her Constancy, her Piety, her household Cares, her maternal Tenderness
— You think not of any excellence of your Mistress that is more than
skin deep. |
gross
else to gratifie
him
his
his
his
Mary Pix, whose Tragedy of
Ibrahim XII, Emperor of the
Turks
, was first acted in 1696.
Mrs. Aphra Behn, whose
Rover, or the Banished Cavaliers
,
is a Comedy in two Parts; first acted, Part I in 1677, Part II in
1681.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 2, 1711 |
Addison |
Omnes ut Tecum meritis pro Talibus annos
Exigat, et pulchra faciat Te prole parentem.
Virg.

An ingenious Correspondent, like a sprightly Wife, will always have the
last Word. I did not think my last Letter to the deformed Fraternity
would have occasioned any Answer, especially since I had promised them
so sudden a Visit: But as they think they cannot shew too great a
Veneration for my Person, they have already sent me up an Answer. As to
the Proposal of a Marriage between my self and the matchless
Hecatissa
, I have but one Objection to it; which is, That all the
Society will expect to be acquainted with her; and who can be sure of
keeping a Woman's Heart long, where she may have so much Choice? I am
the more alarmed at this, because the Lady seems particularly smitten
with Men of their Make.
I believe I shall set my Heart upon her; and think never the worse of my
Mistress for an Epigram a smart Fellow writ, as he thought, against her;
it does but the more recommend her to me. At the same time I cannot but
discover that his Malice is stolen from
Martial
.
Tacta places, Audit a places, si non videare
Tota places, neutro, si videare, places.
Whilst in the Dark on thy soft Hand I hung,
And heard the tempting Siren in thy Tongue,
What Flames, what Darts, what Anguish I endured!
But when the Candle entered I was cur'd.
'Your Letter to us we have received, as a signal Mark of your Favour
and brotherly Affection. We shall be heartily glad to see your short
Face in
Oxford: And since the Wisdom of our Legislature has been
immortalized in your Speculations, and our personal Deformities in
some sort by you recorded to all Posterity; we hold ourselves in
Gratitude bound to receive with the highest Respect, all such Persons
as for their extraordinary Merit you shall think fit, from Time to
Time, to recommend unto the Board. As for the Pictish Damsel, we have
an easy Chair prepared at the upper End of the Table; which we doubt
not but she will grace with a very hideous Aspect, and much better
become the Seat in the native and unaffected Uncomeliness of her
Person, than with all the superficial Airs of the Pencil, which (as
you have very ingeniously observed) vanish with a Breath, and the most
innocent Adorer may deface the Shrine with a Salutation, and in the
literal Sense of our Poets, snatch and imprint his balmy Kisses, and
devour her melting Lips: In short, the only Faces of the Pictish Kind
that will endure the Weather, must be of Dr.
Carbuncle's Die; tho'
his, in truth, has cost him a World the Painting; but then he boasts
with
Zeuxes, In eternitatem pingo; and oft jocosely tells the Fair
Ones, would they acquire Colours that would stand kissing, they must
no longer Paint but Drink for a Complexion: A Maxim that in this our
Age has been pursued with no ill Success; and has been as admirable in
its Effects, as the famous Cosmetick mentioned in the
Post-man, and
invented by the renowned
British Hippocrates of the Pestle and
Mortar; making the Party, after a due Course, rosy, hale and airy; and
the best and most approved Receipt now extant for the Fever of the
Spirits. But to return to our Female Candidate, who, I understand, is
returned to herself, and will no longer hang out false Colours; as she
is the first of her Sex that has done us so great an Honour, she will
certainly, in a very short Time, both in Prose and Verse, be a Lady of
the most celebrated Deformity now living; and meet with Admirers here
as frightful as herself. But being a long-headed Gentlewoman, I am apt
to imagine she has some further Design than you have yet penetrated;
and perhaps has more mind to the
Spectator than any of his Fraternity,
as the Person of all the World she could like for a Paramour: And if
so, really I cannot but applaud her Choice; and should be glad, if it
might lie in my Power, to effect an amicable Accommodation betwixt two
Faces of such different Extremes, as the only possible Expedient to
mend the Breed, and rectify the Physiognomy of the Family on both
Sides. And again, as she is a Lady of very fluent Elocution, you need
not fear that your first Child will be born dumb, which otherwise you
might have some Reason to be apprehensive of.
To be plain with you, I
can see nothing shocking in it; for tho she has not a Face like a
John-Apple, yet as a late Friend of mine, who at Sixty-five ventured
on a Lass of Fifteen, very frequently, in the remaining five Years of
his Life, gave me to understand, That, as old as he then seemed, when
they were first married he and his Spouse
could1 make but
Fourscore; so may Madam
Hecatissa very justly allege hereafter,
That, as long-visaged as she may then be thought, upon their
Wedding-day Mr.
Spectator and she had but Half an Ell of Face betwixt
them: And this my very worthy Predecessor, Mr. Sergeant
Chin, always
maintained to be no more than the true oval Proportion between Man and
Wife. But as this may be a new thing to you, who have hitherto had no
Expectations from Women, I shall allow you what Time you think fit to
consider on't; not without some Hope of seeing at last your Thoughts
hereupon subjoin'd to mine, and which is an Honour much desired by,
Sir,
Your assured Friend,
and most humble Servant,
Hugh
Gobling2, Præses.'
The following Letter has not much in it, but as it is written in my own
Praise I cannot for my Heart suppress it.
Sir,
'You proposed, in your Spectator of last Tuesday, Mr. Hobbs's
Hypothesis for solving that very odd Phænomenon of Laughter. You have
made the Hypothesis valuable by espousing it your self; for had it
continued Mr. Hobbs's, no Body would have minded it. Now here this
perplexed Case arises. A certain Company laughed very heartily upon
the Reading of that very Paper of yours: And the Truth on it is, he
must be a Man of more than ordinary Constancy that could stand it out
against so much Comedy, and not do as we did. Now there are few Men in
the World so far lost to all good Sense, as to look upon you to be a
Man in a State of Folly inferior to himself. Pray then how do you
justify your Hypothesis of Laughter?
Thursday, the 26th of
the Month of Fools.
Your most humble,
Q. R.'
Sir,
'In answer to your Letter, I must desire you to recollect yourself;
and you will find, that when you did me the Honour to be so merry over
my Paper, you laughed at the Idiot, the German Courtier, the Gaper,
the Merry-Andrew, the Haberdasher, the Biter, the Butt, and not at
Your humble Servant,
The Spectator.'
could both
Goblin
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 1, 1711 |
Steele |
... Aliquando bonus dormitat Homerus.
Hor.

My Correspondents grow so numerous, that I cannot avoid frequently
inserting their Applications to me.
Mr
Spectator,
'I am glad I can inform you, that your Endeavours to adorn that Sex,
which is the fairest Part of the visible Creation, are well received,
and like to prove not unsuccessful. The Triumph of
Daphne over her
Sister
Letitia has been the Subject of Conversation at Several
Tea-Tables where I have been present; and I have observed the fair
Circle not a little pleased to find you considering them as reasonable
Creatures, and endeavouring to banish that
Mahometan Custom which
had too much prevailed even in this Island, of treating Women as if
they had no Souls. I must do them the Justice to say, that there seems
to be nothing wanting to the finishing of these lovely Pieces of Human
Nature, besides the turning and applying their Ambition properly, and
the keeping them up to a Sense of what is their true Merit.
Epictetus, that
plain honest Philosopher, as little as he had of
Gallantry, appears to have understood them, as well as the polite St.
Evremont, and has hit this Point very luckily
1.
When young
Women, says he,
arrive at a certain Age, they hear themselves called
Mistresses, and are made to believe that their only Business is to
please the Men; they immediately begin to dress, and place all their
Hopes in the adorning of their Persons; it is therefore, continues
he,
worth the while to endeavour by all means to make them sensible
that the Honour paid to them is only, upon account of their
conducting themselves with Virtue, Modesty, and Discretion.
Now to pursue the Matter yet further, and to render your Cares for
the Improvement of the Fair Ones more effectual, I would propose a new
method, like those Applications which are said to convey their virtues
by Sympathy; and that is, in order to embellish the Mistress, you
should give a new Education to the Lover, and teach the Men not to be
any longer dazzled by false Charms and unreal Beauty. I cannot but
think that if our Sex knew always how to place their Esteem justly,
the other would not be so often wanting to themselves in deserving it.
For as the being enamoured with a Woman of Sense and Virtue is an
Improvement to a Man's Understanding and Morals, and the Passion is
ennobled by the Object which inspires it; so on the other side, the
appearing amiable to a Man of a wise and elegant Mind, carries in it
self no small Degree of Merit and Accomplishment. I conclude
therefore, that one way to make the Women yet more agreeable is, to
make the Men more virtuous.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
R. B.'
April 26.
Sir,
'Yours of
Saturday last I read, not without some Resentment; but I
will suppose when you say you expect an Inundation of Ribbons and
Brocades, and to see many new Vanities which the Women will fall into
upon a Peace with
France, that you intend only the unthinking Part
of our Sex: And what Methods can reduce them to Reason is hard to
imagine.
But, Sir, there are others yet, that your Instructions might be of
great Use to, who, after their best Endeavours, are sometimes at a
loss to acquit themselves to a Censorious World: I am far from
thinking you can altogether disapprove of Conversation between Ladies
and Gentlemen, regulated by the Rules of Honour and Prudence; and have
thought it an Observation not ill made, that where that was wholly
denied, the Women lost their Wit, and the Men their Good-manners. 'Tis
sure, from those improper Liberties you mentioned, that a sort of
undistinguishing People shall banish from their Drawing-Rooms the
best-bred Men in the World, and condemn those that do not. Your
stating this Point might, I think, be of good use, as well as much
oblige,
Sir,
Your Admirer, and
most humble Servant,
Anna Bella.'
No Answer to this, till
Anna Bella
sends a Description of those she
calls the Best-bred Men in the World
.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am a Gentleman who for many Years last past have been well known to
be truly Splenatick, and that my Spleen arises from having contracted
so great a Delicacy, by reading the best Authors, and keeping the most
refined Company, that I cannot bear the least Impropriety of Language,
or Rusticity of Behaviour. Now, Sir, I have ever looked upon this as a
wise Distemper; but by late Observations find that every heavy Wretch,
who has nothing to say, excuses his Dulness by complaining of the
Spleen. Nay, I saw, the other Day, two Fellows in a Tavern Kitchen set
up for it, call for a Pint and Pipes, and only by Guzling Liquor to
each other's Health, and wafting Smoke in each other's Face, pretend
to throw off the Spleen. I appeal to you, whether these Dishonours are
to be done to the Distemper of the Great and the Polite. I beseech
you, Sir, to inform these Fellows that they have not the Spleen,
because they cannot talk without the help of a Glass at their Mouths,
or convey their Meaning to each other without the Interposition of
Clouds. If you will not do this with all Speed, I assure you, for my
part, I will wholly quit the Disease, and for the future be merry with
the Vulgar.
I am, Sir,
Your humble Servant.'
Sir,
'This is to let you understand, that I am a reformed Starer, and
conceived a Detestation for that Practice from what you have writ upon
the Subject. But as you have been very severe upon the Behaviour of us
Men at Divine Service, I hope you will not be so apparently partial to
the Women, as to let them go wholly unobserved. If they do everything
that is possible to attract our Eyes, are we more culpable than they
for looking at them? I happened last Sunday to be shut into a Pew,
which was full of young Ladies in the Bloom of Youth and Beauty. When
the Service began, I had not Room to kneel at the Confession, but as I
stood kept my eyes from wandring as well as I was able, till one of
the young Ladies, who is a Peeper, resolved to bring down my Looks,
and fix my Devotion on her self. You are to know, Sir, that a Peeper
works with her Hands, Eyes, and Fan; one of which is continually in
Motion, while she thinks she is not actually the Admiration of some
Ogler or Starer in the Congregation. As I stood utterly at a loss how
to behave my self, surrounded as I was, this Peeper so placed her self
as to be kneeling just before me. She displayed the most beautiful
Bosom imaginable, which heaved and fell with some Fervour, while a
delicate well-shaped Arm held a Fan over her Face. It was not in
Nature to command ones Eyes from this Object; I could not avoid taking
notice also of her Fan, which had on it various Figures, very improper
to behold on that Occasion. There lay in the Body of the Piece a
Venus, under a Purple Canopy furled with curious Wreaths of Drapery,
half naked, attended with a Train of Cupids, who were busied in
Fanning her as she slept. Behind her was drawn a Satyr peeping over
the silken Fence, and threatening to break through it. I frequently
offered to turn my Sight another way, but was still detained by the
Fascination of the Peeper's Eyes, who had long practised a Skill in
them, to recal the parting Glances of her Beholders. You see my
Complaint, and hope you will take these mischievous People, the
Peepers, into your Consideration: I doubt not but you will think a
Peeper as much more pernicious than a Starer, as an Ambuscade is more
to be feared than an open Assault.
I am, Sir,
Your most Obedient Servant.'
This Peeper using both Fan and Eyes to be considered as a
Pict,
and
proceed accordingly.
King
Latinus to the
Spectator, Greeting.
'
Tho' some may think we descend from our Imperial Dignity, in holding
Correspondence with a private
Litterato2; yet as we have great
Respect to all good Intentions for our Service, we do not esteem it
beneath us to return you our Royal Thanks for what you published in
our Behalf, while under Confinement in the Inchanted Castle of the
Savoy, and for your Mention of a Subsidy for a Prince in Misfortune.
This your timely Zeal has inclined the Hearts of divers to be aiding
unto us, if we could propose the Means. We have taken their Good will
into Consideration, and have contrived a Method which will be easy to
those who shall give the Aid, and not unacceptable to us who receive
it. A Consort of Musick shall be prepared at
Haberdashers-Hall for
Wednesday the Second of
May, and we will honour the said
Entertainment with our own Presence, where each Person shall be
assessed but at two Shillings and six Pence. What we expect from you
is, that you publish these our Royal Intentions, with Injunction that
they be read at all Tea-Tables within the Cities of
London and
Westminster; and so we bid you heartily Farewell.
Latinus, King of the
Volscians.'
Given at our Court in Vinegar-Yard,
Story the Third from the Earth.
April 28, 1711.
R.
Epictetus his Morals, with Simplicius his Comment,
was
translated by George Stanhope in 1694. The citation above is a free
rendering of the sense of cap. 62 of the Morals.
Litterati
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 2, 1711 |
Steele |
... Sirenua nos exercet inertia.
Hor.

The following Letter being the first that I have received from the
learned University of
Cambridge
, I could not but do my self the Honour
of publishing it. It gives an Account of a new Sect of Philosophers
which has arose in that famous Residence of Learning; and is, perhaps,
the only Sect this Age is likely to produce.
Cambridge, April 26.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Believing you to be an universal Encourager of liberal Arts and
Sciences, and glad of any Information from the learned World, I
thought an Account of a Sect of Philosophers very frequent among us,
but not taken Notice of, as far as I can remember, by any Writers
either ancient or modern, would not be unacceptable to you. The
Philosophers of this Sect are in the Language of our University called
Lowngers. I am of Opinion, that, as in many other things, so
likewise in this, the Ancients have been defective;
viz. in
mentioning no Philosophers of this Sort. Some indeed will affirm that
they are a kind of Peripateticks, because we see them continually
walking about. But I would have these Gentlemen consider, that tho'
the ancient Peripateticks walked much, yet they wrote much also;
(witness, to the Sorrow of this Sect,
Aristotle and others): Whereas
it is notorious that most of our Professors never lay out a Farthing
either in Pen, Ink, or Paper. Others are for deriving them from
Diogenes, because several of the leading Men of the Sect have a
great deal of the cynical Humour in them, and delight much in
Sun-shine. But then again,
Diogenes was content to have his constant
Habitation in a narrow Tub; whilst our Philosophers are so far from
being of his Opinion, that it's Death to them to be confined within
the Limits of a good handsome convenient Chamber but for half an Hour.
Others there are, who from the Clearness of their Heads deduce the
Pedigree of
Lowngers from that great Man (I think it was either
Plato or
Socrates1) who after all his Study and Learning
professed, That all he then knew was, that he knew nothing. You easily
see this is but a shallow Argument, and may be soon confuted.
I have with great Pains and Industry made my Observations from time to
time upon these Sages; and having now all Materials ready, am
compiling a Treatise, wherein I shall set forth the Rise and Progress
of this famous Sect, together with their Maxims, Austerities, Manner
of living, &c. Having prevailed with a Friend who designs shortly to
publish a new Edition of
Diogenes Laertius, to add this Treatise of
mine by way of Supplement; I shall now, to let the World see what may
be expected from me (first begging Mr.
Spectator's Leave that the
World may see it) briefly touch upon some of my chief Observations,
and then subscribe my self your humble Servant. In the first Place I
shall give you two or three of their Maxims: The fundamental one, upon
which their whole System is built, is this, viz. That Time being an
implacable Enemy to and Destroyer of all things, ought to be paid in
his own Coin, and be destroyed and murdered without Mercy by all the
Ways that can be invented. Another favourite Saying of theirs is, That
Business was designed only for Knaves, and Study for Blockheads. A
third seems to be a ludicrous one, but has a great Effect upon their
Lives; and is this, That the Devil is at Home. Now for their Manner of
Living: And here I have a large Field to expatiate in; but I shall
reserve Particulars for my intended Discourse, and now only mention
one or two of their principal Exercises. The elder Proficients employ
themselves in inspecting
mores hominum multorum, in getting
acquainted with all the Signs and Windows in the Town. Some are
arrived at so great Knowledge, that they can tell every time any
Butcher kills a Calf, every time any old Woman's Cat is in the Straw;
and a thousand other Matters as important. One ancient Philosopher
contemplates two or three Hours every Day over a Sun-Dial; and is true
to the Dial,
...
As the Dial to the Sun,
Although it be not shone upon
2.
Our younger Students are content to carry their Speculations as yet no
farther than Bowling-greens, Billiard-Tables, and such like Places.
This may serve for a Sketch of my Design; in which I hope I shall have
your Encouragement.
I am,
Sir,
Yours
3.
I must be so just as to observe I have formerly seen of this Sect at our
other University; tho' not distinguished by the Appellation which the
learned Historian, my Correspondent, reports they bear at
Cambridge
.
They were ever looked upon as a People that impaired themselves more by
their strict Application to the Rules of their Order, than any other
Students whatever. Others seldom hurt themselves any further than to
gain weak Eyes and sometimes Head-Aches; but these Philosophers are
seized all over with a general Inability, Indolence, and Weariness, and
a certain Impatience of the Place they are in, with an Heaviness in
removing to another.
The
Lowngers
are satisfied with being merely Part of the Number of
Mankind, without distinguishing themselves from amongst them. They may
be said rather to suffer their Time to pass, than to spend it, without
Regard to the past, or Prospect of the future. All they know of Life is
only the present Instant, and do not taste even that. When one of this
Order happens to be a Man of Fortune, the Expence of his Time is
transferr'd to his Coach and Horses, and his Life is to be measured by
their Motion, not his own Enjoyments or Sufferings. The chief
Entertainment one of these Philosophers can possibly propose to himself,
is to get a Relish of Dress: This, methinks, might diversifie the Person
he is weary of (his own dear self) to himself. I have known these two
Amusements make one of these Philosophers make a tolerable Figure in the
World; with a variety of Dresses in publick Assemblies in Town, and
quick Motion of his Horses out of it, now to
Bath
, now to
Tunbridge
, then to
Newmarket
, and then to
London
,
he has in Process of Time brought it to pass, that his Coach and his
Horses have been mentioned in all those Places. When the
Lowngers
leave an Academick Life, and instead of this more elegant way of
appearing in the polite World, retire to the Seats of their Ancestors,
they usually join a Pack of Dogs, and employ their Days in defending
their Poultry from Foxes: I do not know any other Method that any of
this Order has ever taken to make a Noise in the World; but I shall
enquire into such about this Town as have arrived at the Dignity of
being
Lowngers
by the Force of natural Parts, without having ever
seen an University; and send my Correspondent, for the Embellishment of
his Book, the Names and History of those who pass their Lives without
any Incidents at all; and how they shift Coffee-houses and
Chocolate-houses from Hour to Hour, to get over the insupportable Labour
of doing nothing.
R.
Socrates in his
Apology
, or
Defence
before his Judges, as
reported by Plato. The oracle having said that there was none wiser than
he, he had sought to confute the oracle, and found the wise man of the
world foolish through belief in his own wisdom.
'When I left him I reasoned thus with myself, I am wiser than this
man, for neither of us appears to know anything great and good; but he
fancies he knows something, although he knows nothing, whereas I, as I
do not know anything, do not fancy that I do.'
True as Dial to the Sun,
Although it be not shined upon.
Hudibras
. Part III. c. 2.
This Letter may be by Laurence Eusden. See Note to
.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 3, 1711 |
Addison |
... Intus, et in jecore ægro
Nascuntur Domini ...
Pers.

Most of the Trades, Professions, and Ways of Living among Mankind, take
their Original either from the Love of Pleasure or the Fear of Want. The
former, when it becomes too violent, degenerates into
Luxury
, and
the latter into
Avarice
. As these two Principles of Action draw
different Ways,
Persius
has given us a very humourous Account of
a young Fellow who was rouzed out of his Bed, in order to be sent upon a
long Voyage, by
Avarice
, and afterwards over-persuaded and kept
at Home by
Luxury
. I shall set down at length the Pleadings of
these two imaginary Persons, as they are in the Original with Mr.
Dryden's
Translation of them.
Mane, piger, stertis: surge, inquit Avaritia; eja
Surge. Negas, Instat, surge inquit. Non queo. Surge.
Et quid agam? Rogitas? Saperdas advehe Ponto,
Castoreum, stuppas, hebenum, thus, lubrica Coa.
Tolle recens primus piper è siliente camelo.
Verte aliquid; jura. Sed Jupiter Audiet. Eheu!
Baro, regustatum digito terebrare salinum
Contentus perages, si vivere cum Jove tendis.
Jam pueris pellem succinctus et ænophorum aptas;
Ocyus ad Navem. Nil obstat quin trabe vasta
Ægæum rapias, nisi solers Luxuria ante
Seductum moneat; quo deinde, insane ruis? Quo?
Quid tibi vis? Calido sub pectore mascula bilis
Intumuit, quam non extinxerit urna cicutæ?
Tun' mare transilias? Tibi torta cannabe fulto
Cœna sit in transtro? Veientanúmque rubellum
Exhalet vapida læsum pice sessilis obba?
Quid petis? Ut nummi, quos hic quincunce modesto
Nutrieras, pergant avidos sudare deunces?
Indulge genio: carpamus dulcia; nostrum est
Quod vivis; cinis, et manes, et fabula fies.
Vive memor lethi: fugit hora. Hoc quod loquor, inde est.
En quid agis? Duplici in diversum scinderis hamo.
Hunccine, an hunc sequeris! — —
Whether alone, or in thy Harlot's Lap,
When thou wouldst take a lazy Morning's Nap;
Up, up, says Avarice; thou snor'st again,
Stretchest thy Limbs, and yawn'st, but all in vain.
The rugged Tyrant no Denial takes;
At his Command th' unwilling Sluggard wakes.
What must I do? he cries; What? says his Lord:
Why rise, make ready, and go streight Aboard:
With Fish, from Euxine Seas, thy Vessel freight;
Flax, Castor, Coan Wines, the precious Weight
Of Pepper and Sabean Incense, take
With thy own Hands, from the tir'd Camel's Back,
And with Post-haste thy running Markets make.
Be sure to turn the Penny; Lye and Swear,
'Tis wholsome Sin: But Jove, thou say'st, will hear.
Swear, Fool, or Starve; for the Dilemma's even:
A Tradesman thou! and hope to go to Heav'n?
Resolv'd for Sea, the Slaves thy Baggage pack,
Each saddled with his Burden on his Back.
Nothing retards thy Voyage, now; but He,
That soft voluptuous Prince, call'd Luxury;
And he may ask this civil Question; Friend,
What dost thou make a Shipboard? To what End?
Art thou of Bethlem's noble College free?
Stark, staring mad, that thou wouldst tempt the Sea?
Cubb'd in a Cabbin, on a Mattress laid,
On a brown George, with lousy Swobbers fed;
Dead Wine, that stinks of the Borachio, sup
From a foul Jack, or greasy Maple Cup!
Say, wouldst thou bear all this, to raise the Store,
From Six i'th' Hundred to Six Hundred more?
Indulge, and to thy Genius freely give:
For, not to live at Ease, is not, to live:
Death stalks behind thee, and each flying Hour
Does some loose Remnant of thy Life devour.
Live, while thou liv'st; for Death will make us all,
A Name, a Nothing but an Old Wife's Tale.
Speak, wilt thou Avarice or Pleasure choose
To be thy Lord? Take one, and one refuse.
When a Government flourishes in Conquests, and is secure from foreign
Attacks, it naturally falls into all the Pleasures of Luxury; and as
these Pleasures are very expensive, they put those who are addicted to
them upon raising fresh Supplies of Mony, by all the Methods of
Rapaciousness and Corruption; so that Avarice and Luxury very often
become one complicated Principle of Action, in those whose Hearts are
wholly set upon Ease, Magnificence, and Pleasure.
most Elegant and
Correct of all the
Latin
Historians observes, that in his time,
when the most formidable States of the World were subdued by the
Romans
, the Republick sunk into those two Vices of a quite
different Nature, Luxury and Avarice
: And accordingly describes
Catiline
as one who coveted the Wealth of other Men, at the same
time that he squander'd away his own. This Observation on the
Commonwealth, when it was in its height of Power and Riches, holds good
of all Governments that are settled in a State of Ease and Prosperity.
At such times Men naturally endeavour to outshine one another in Pomp
and Splendor, and having no Fears to alarm them from abroad, indulge
themselves in the Enjoyment of all the Pleasures they can get into their
Possession; which naturally produces Avarice, and an immoderate Pursuit
after Wealth and Riches.
As I was humouring my self in the Speculation of these two great
Principles of Action, I could not forbear throwing my Thoughts into a
little kind of Allegory or Fable, with which I shall here present my
Reader.
There were two very powerful Tyrants engaged in a perpetual War against
each other: The Name of the first was
Luxury
, and of the second
Avarice
. The Aim of each of them was no less than Universal
Monarchy over the Hearts of Mankind.
Luxury
had many Generals
under him, who did him great Service, as
Pleasure
,
Mirth
,
Pomp
and
Fashion
.
Avarice
was likewise very strong
in his Officers, being faithfully served by
Hunger
,
Industry
,
Care
and
Watchfulness
: He had likewise a
Privy-Counsellor who was always at his Elbow, and whispering something
or other in his Ear: The Name of this Privy-Counsellor was
Poverty
. As
Avarice
conducted himself by the Counsels of
Poverty
, his Antagonist was entirely guided by the Dictates and
Advice of
Plenty
, who was his first Counsellor and Minister of
State, that concerted all his Measures for him, and never departed out
of his Sight. While these two great Rivals were thus contending for
Empire, their Conquests were very various.
Luxury
got Possession
of one Heart, and
Avarice
of another. The Father of a Family would
often range himself under the Banners of
Avarice
, and the Son under
those of
Luxury
. The Wife and Husband would often declare themselves
on the two different Parties; nay, the same Person would very often side
with one in his Youth, and revolt to the other in his old Age. Indeed
the Wise Men of the World stood
Neuter
; but alas! their Numbers were
not considerable. At length, when these two Potentates had wearied
themselves with waging War upon one another, they agreed upon an
Interview, at which neither of their Counsellors were to be present. It
is said that
Luxury
began the Parley, and after having represented the
endless State of War in which they were engaged, told his Enemy, with a
Frankness of Heart which is natural to him, that he believed they two
should be very good Friends, were it not for the Instigations of
Poverty
, that pernicious Counsellor, who made an ill use of his Ear,
and filled him with groundless Apprehensions and Prejudices. To this
Avarice
replied, that he looked upon
Plenty
(the first Minister of
his Antagonist) to be a much more destructive Counsellor than
Poverty
,
for that he was perpetually suggesting Pleasures, banishing all the
necessary Cautions against Want, and consequently undermining those
Principles on which the Government of
Avarice
was founded. At last, in
order to an Accommodation, they agreed upon this Preliminary; That each
of them should immediately dismiss his Privy-Counsellor. When things
were thus far adjusted towards a Peace, all other differences were soon
accommodated, insomuch that for the future they resolved to live as good
Friends and Confederates, and to share between them whatever Conquests
were made on either side. For this Reason, we now find
Luxury
and
Avarice
taking Possession of the same Heart, and dividing the same
Person between them. To which I shall only add, that since the
discarding of the Counsellors above-mentioned,
Avarice
supplies
Luxury
in the room of
Plenty
, as
Luxury
prompts
Avarice
in the
place of
Poverty
.
C.
Alieni appetens, sui profusus.
Sallust.
Contents
|
Friday, May 4, 1711 |
Addison |
Felices errore suo ...
Lucan.

The
Americans
believe that all Creatures have Souls, not only Men and
Women, but Brutes, Vegetables, nay even the most inanimate things, as
Stocks and Stones. They believe the same of all the Works of Art, as of
Knives, Boats, Looking-glasses: And that as any of these things perish,
their Souls go into another World, which is inhabited by the Ghosts of
Men and Women. For this Reason they always place by the Corpse of their
dead Friend a Bow and Arrows, that he may make use of the Souls of them
in the other World, as he did of their wooden Bodies in this. How absurd
soever such an Opinion as this may appear, our
European
Philosophers
have maintained several Notions altogether as improbable. Some of
Plato's
followers in particular, when they talk of the World of Ideas,
entertain us with Substances and Beings no less extravagant and
chimerical. Many
Aristotelians
have likewise spoken as unintelligibly
of their substantial Forms.
shall only instance
Albertus Magnus
, who
in his Dissertation upon the Loadstone observing that Fire will destroy
its magnetick Vertues, tells us that he took particular Notice of one as
it lay glowing amidst an Heap of burning Coals, and that he perceived a
certain blue Vapour to arise from it, which he believed might be the
substantial Form
, that is, in our
West-Indian
Phrase, the
Soul
of
the Loadstone
.
There is a Tradition among the
Americans
, that one of their Countrymen
descended in a Vision to the great Repository of Souls, or, as we call
it here, to the other World; and that upon his Return he gave his
Friends a distinct Account of every thing he saw among those Regions of
the Dead.
Friend of mine, whom I have formerly mentioned, prevailed
upon one of the Interpreters of the
Indian
Kings
, to inquire of
them, if possible, what Tradition they have among them of this Matter:
Which, as well as he could learn by those many Questions which he asked
them at several times, was in Substance as follows.
The Visionary, whose Name was
Marraton
, after having travelled for a
long Space under an hollow Mountain, arrived at length on the Confines
of this World of Spirits; but could not enter it by reason of a thick
Forest made up of Bushes, Brambles and pointed Thorns, so perplexed and
interwoven with one another, that it was impossible to find a Passage
through it. Whilst he was looking about for some Track or Path-way that
might be worn in any Part of it, he saw an huge Lion crouched under the
Side of it, who kept his Eye upon him in the same Posture as when he
watches for his Prey. The
Indian
immediately started back, whilst
the Lion rose with a Spring, and leaped towards him. Being wholly
destitute of all other Weapons, he stooped down to take up an huge Stone
in his Hand; but to his infinite Surprize grasped nothing, and found the
supposed Stone to be only the Apparition of one. If he was disappointed
on this Side, he was as much pleased on the other, when he found the
Lion, which had seized on his left Shoulder, had no Power to hurt him,
and was only the Ghost of that ravenous Creature which it appeared to
be. He no sooner got rid of his impotent Enemy, but he marched up to the
Wood, and after having surveyed it for some Time, endeavoured to press
into one Part of it that was a little thinner than the rest; when again,
to his great Surprize, he found the Bushes made no Resistance, but that
he walked through Briars and Brambles with the same Ease as through the
open Air; and, in short, that the whole Wood was nothing else but a Wood
of Shades. He immediately concluded, that this huge Thicket of Thorns
and Brakes was designed as a kind of Fence or quick-set Hedge to the
Ghosts it inclosed; and that probably their soft Substances might be
torn by these subtle Points and Prickles, which were too weak to make
any Impressions in Flesh and Blood. With this Thought he resolved to
travel through this intricate Wood; when by Degrees he felt a Gale of
Perfumes breathing upon him, that grew stronger and sweeter in
Proportion as he advanced. He had not proceeded much further when he
observed the Thorns and Briars to end, and give place to a thousand
beautiful green Trees covered with Blossoms of the finest Scents and
Colours, that formed a Wilderness of Sweets, and were a kind of Lining
to those ragged Scenes which he had before passed through. As he was
coming out of this delightful Part of the Wood, and entering upon the
Plains it inclosed, he saw several Horsemen rushing by him, and a little
while after heard the Cry of a Pack of Dogs. He had not listned long
before he saw the Apparition of a milk-white Steed, with a young Man on
the Back of it, advancing upon full Stretch after the Souls of about an
hundred Beagles that were hunting down the Ghost of an Hare, which ran
away before them with an unspeakable Swiftness. As the Man on the
milk-white Steed came by him, he looked upon him very attentively, and
found him to be the young Prince
Nicharagua
, who died about Half a
Year before, and, by reason of his great Vertues, was at that time
lamented over all the Western Parts of
America
.
had no sooner got out of the Wood, but he was entertained with such a
Landskip of flowry Plains, green Meadows, running Streams, sunny Hills,
and shady Vales, as were not to be
represented
by his own
Expressions, nor, as he said, by the Conceptions of others.
happy
Region was peopled with innumerable Swarms of Spirits, who applied
themselves to Exercises and Diversions according as their Fancies led
them. Some of them were tossing the Figure of a Colt; others were
pitching the Shadow of a Bar; others were breaking the Apparition of
a
Horse; and Multitudes employing themselves upon ingenious
Handicrafts with the Souls of
departed Utensils
; for that is the Name
which in the
Indian
Language they give their Tools when they are burnt
or broken. As he travelled through this delightful Scene, he was very
often tempted to pluck the Flowers that rose every where about him in
the greatest Variety and Profusion, having never seen several of them in
his own Country: But he quickly found that though they were Objects of
his Sight, they were not liable to his Touch. He at length came to the
Side of a great River, and being a good Fisherman himself stood upon the
Banks of it some time to look upon an Angler that had taken a great many
Shapes of Fishes, which lay flouncing up and down by him.
I should have told my Reader, that this
Indian
had been formerly
married to one of the greatest Beauties of his Country, by whom he had
several Children. This Couple were so famous for their Love and
Constancy to one another, that the
Indians
to this Day, when they give
a married Man Joy of his Wife, wish that they may live together like
Marraton
and
Yaratilda
.
Marraton
had not stood long by the
Fisherman when he saw the Shadow of his beloved
Yaratilda
, who had for
some time fixed her Eye upon him, before he discovered her. Her Arms
were stretched out towards him, Floods of Tears ran down her Eyes; her
Looks, her Hands, her Voice called him over to her; and at the same time
seemed to tell him that the River was impassable. Who can describe the
Passion made up of Joy, Sorrow, Love, Desire, Astonishment, that rose in
the Indian upon the Sight of his dear
Yaratilda
? He could express it
by nothing but his Tears, which ran like a River down his Cheeks as he
looked upon her. He had not stood in this Posture long, before he
plunged into the Stream that lay before him; and finding it to be
nothing but the Phantom of a River, walked on the Bottom of it till he
arose on the other Side. At his Approach
Yaratilda
flew into his Arms,
whilst
Marraton
wished himself disencumbered of that Body which kept
her from his Embraces. After many Questions and Endearments on both
Sides, she conducted him to a Bower which she had dressed with her own
Hands with all the Ornaments that could be met with in those blooming
Regions. She had made it gay beyond Imagination, and was every day
adding something new to it. As
Marraton
stood astonished at the
unspeakable Beauty of her Habitation, and ravished with the Fragrancy
that came from every Part of it,
Yaratilda
told him that she was
preparing this Bower for his Reception, as well knowing that his Piety
to his God, and his faithful Dealing towards Men, would certainly bring
him to that happy Place whenever his Life should be at an End. She then
brought two of her Children to him, who died some Years before, and
resided with her in the same delightful Bower, advising him to breed up
those others which were still with him in such a Manner, that they might
hereafter all of them meet together in this happy Place.
Tradition tells us further, that he had afterwards a Sight of those
dismal Habitations which are the Portion of ill Men after Death; and
mentions several Molten Seas of Gold, in which were plunged the Souls of
barbarous
Europeans
,
who
put to the Sword so many Thousands of
poor
Indians
for the sake of that precious Metal: But having already
touched upon the chief Points of this Tradition, and exceeded the
Measure of my Paper, I shall not give any further Account of it.
C.
Albertus Magnus, a learned Dominican who resigned, for love
of study, his bishopric of Ratisbon, died at Cologne in 1280. In alchemy
a distinction was made between stone and spirit, as between body and
soul, substance and accident. The evaporable parts were called, in
alchemy, spirit and soul and accident.
See
described
an
that
Contents
|
Saturday, May 5, 1711 |
Addison |
Quem præstare potest mulier galeata pudorem,
Quæ fugit à Sexu!
Juv.

the Wife of
Hector
, in
Homer's Iliads
, discourses
with her Husband about the Battel in which he was going to engage, the
Hero, desiring her to leave that Matter to his Care, bids her go to her
Maids and mind her Spinning
: by which the Poet intimates, that Men
and Women ought to busy themselves in their proper Spheres, and on such
Matters only as are suitable to their respective Sex.
I am at this time acquainted with a young Gentleman, who has passed a
great Part of his Life in the Nursery, and, upon Occasion, can make a
Caudle or a Sack-Posset better than any Man in
England
. He is
likewise a wonderful Critick in Cambrick and Muslins, and will talk an
Hour together upon a Sweet-meat. He entertains his Mother every Night
with Observations that he makes both in Town and Court: As what Lady
shews the nicest Fancy in her Dress; what Man of Quality wears the
fairest Whig; who has the finest Linnen, who the prettiest Snuff-box,
with many other the like curious Remarks that may be made in good
Company.
On the other hand I have very frequently the Opportunity of seeing a
Rural
Andromache
, who came up to Town last Winter, and is one of
the greatest Fox-hunters in the Country. She talks of Hounds and Horses,
and makes nothing of leaping over a Six-bar Gate. If a Man tells her a
waggish Story, she gives him a Push with her Hand in jest, and calls him
an impudent Dog; and if her Servant neglects his Business, threatens to
kick him out of the House. I have heard her, in her Wrath, call a
Substantial Trades-man a Lousy Cur; and remember one Day, when she could
not think of the Name of a Person, she described him in a large Company
of Men and Ladies, by the Fellow with the Broad Shoulders.
If those Speeches and Actions, which in their own Nature are
indifferent, appear ridiculous when they proceed from a wrong Sex, the
Faults and Imperfections of one Sex transplanted into another, appear
black and monstrous. As for the Men, I shall not in this Paper any
further concern my self about them: but as I would fain contribute to
make Womankind, which is the most beautiful Part of the Creation,
entirely amiable, and wear out all those little Spots and Blemishes that
are apt to rise among the Charms which Nature has poured out upon them,
I shall dedicate this Paper to their Service. The Spot which I would
here endeavour to clear them of, is that Party-Rage which of late Years
is very much crept into their Conversation. This is, in its Nature, a
Male Vice, and made up of many angry and cruel Passions that are
altogether repugnant to the Softness, the Modesty, and those other
endearing Qualities which are natural to the Fair Sex. Women were formed
to temper Mankind, and sooth them into Tenderness and Compassion, not to
set an Edge upon their Minds, and blow up in them those Passions which
are too apt to rise of their own Accord. When I have seen a pretty Mouth
uttering Calumnies and Invectives, what would not I have given to have
stopt it? How have I been troubled to see some of the finest Features in
the World grow pale, and tremble with Party-Rage?
Camilla
is one of
the greatest Beauties in the
British
Nation, and yet values her self
more upon being the
Virago
of one Party, than upon being the Toast of
both. The Dear Creature, about a Week ago, encountered the fierce and
beautiful
Penthesilea
across a Tea-Table; but in the Height of her
Anger, as her Hand chanced to shake with the Earnestness of the Dispute,
she scalded her Fingers, and spilt a Dish of Tea upon her Petticoat. Had
not this Accident broke off the Debate, no Body knows where it would
have ended.
There is one Consideration which I would earnestly recommend to all my
Female Readers, and which, I hope, will have some weight with them. In
short, it is this, that there is nothing so bad for the Face as
Party-Zeal. It gives an ill-natured Cast to the Eye, and a disagreeable
Sourness to the Look; besides, that it makes the Lines too strong, and
flushes them worse than Brandy. I have seen a Woman's Face break out in
Heats, as she has been talking against a great Lord, whom she had never
seen in her Life; and indeed never knew a Party-Woman that kept her
Beauty for a Twelvemonth. I would therefore advise all my Female
Readers, as they value their Complexions, to let alone all Disputes of
this Nature; though, at the same time, I would give free Liberty to all
superannuated motherly Partizans to be as violent as they please, since
there will be no Danger either of their spoiling their Faces, or of
their gaining Converts.
For my own
, I think a Man makes an odious and despicable
Figure, that is violent in a Party: but a Woman is too sincere to
mitigate the Fury of her Principles with Temper and Discretion, and to
act with that Caution and Reservedness which are requisite in our Sex.
this unnatural Zeal gets into them, it throws them into ten
thousand Heats and Extravagancies; their generous
Souls
set no
Bounds to their Love or to their Hatred; and whether a Whig or Tory, a
Lap-Dog or a Gallant, an Opera or a Puppet-Show, be the Object of it,
the Passion, while it reigns, engrosses the whole Woman.
remember when Dr.
Titus Oates
was in all his Glory, I
accompanied my Friend
Will.
Honeycomb
in a Visit to a Lady of his
Acquaintance: We were no sooner sat down, but upon casting my Eyes about
the Room, I found in almost every Corner of it a Print that represented
the Doctor in all Magnitudes and Dimensions. A little after, as the Lady
was discoursing my Friend, and held her Snuff-box in her Hand, who
should I see in the Lid of it but the Doctor. It was not long after
this, when she had Occasion for her Handkerchief, which upon the first
opening discovered among the Plaits of it the Figure of the Doctor. Upon
this my Friend
Will
., who loves Raillery, told her, That if he was in
Mr.
Truelove's
Place (for that was the Name for her Husband) she
should be made as uneasy by a Handkerchief as ever
Othello
was.
I am
afraid,
said she,
Mr.
Honeycomb
,
5 you are a Tory; tell me truly,
are you a Friend to the Doctor or not? Will
., instead of making her a
Reply, smiled in her Face (for indeed she was very pretty) and told her
that one of her Patches was dropping off. She immediately adjusted it,
and looking a little seriously,
Well
, says she,
I'll be hang'd if
you and your silent Friend there are not against the Doctor in your
Hearts, I suspected as much by his saying nothing
. Upon this she took
her Fan into her Hand, and upon the opening of it again displayed to us
the Figure of the Doctor, who was placed with great Gravity among the
Sticks of it. In a word, I found that the Doctor had taken Possession of
her Thoughts, her Discourse, and most of her Furniture; but finding my
self pressed too close by her Question, I winked upon my Friend to take
his Leave, which he did accordingly.
C.
Hector's parting from Andromache, at the close of Book VI:
No more — but hasten to thy tasks at home,
There guide the spindle, and direct the loom;
Me glory summons to the martial scene,
The field of combat is the sphere for men.
Not a new paragraph in the first issue.
"Souls (I mean those of ordinary Women).: This, however, was
cancelled by an Erratum in the next number.
Addison was six years old when Titus Oates began his
'Popish Plot' disclosures. Under a name which called up recollections of
the vilest trading upon theological intolerance, he here glances at Dr.
Henry Sacheverell, whose trial (Feb. 27-March 20, 1710) for his sermons
in praise of the divine right of kings and contempt of the Whigs, and
his sentence of suspension for three years, had caused him to be admired
enthusiastically by all party politicians who were of his own way of
thinking. The change of person pleasantly puts 'Tory' for 'Whig,' and
avoids party heat by implying a suggestion that excesses are not all on
one side. Sacheverell had been a College friend of Addison's. He is the
'dearest Harry' for whom, at the age of 22, Addison wrote his metrical
'Account of the greatest English Poets' which omitted Shakespeare from
the list.
Honycombe
Contents
|
Monday, May 7, 1711 |
Addison |
Ut pictura poesis erit ...
Hor.

Nothing is so much admired, and so little understood, as Wit. No Author
that I know of has written professedly upon it; and as for those who
make any Mention of it, they only treat on the Subject as it has
accidentally fallen in their Way, and that too in little short
Reflections, or in general declamatory Flourishes, without entering into
the Bottom of the Matter. I hope therefore I shall perform an acceptable
Work to my Countrymen, if I treat at large upon this Subject; which I
shall endeavour to do in a Manner suitable to it, that I may not incur
the Censure which a famous Critick bestows upon one who had written a
Treatise upon
the Sublime
in a low groveling Stile. I intend to
lay aside a whole Week for this Undertaking, that the Scheme of my
Thoughts may not be broken and interrupted; and I dare promise my self,
if my Readers will give me a Week's Attention, that this great City will
be very much changed for the better by next
Saturday
Night. I
shall endeavour to make what I say intelligible to ordinary Capacities;
but if my Readers meet with any Paper that in some Parts of it may be a
little out of their Reach, I would not have them discouraged, for they
may assure themselves the next shall be much clearer.
As the great and only End of these my Speculations is to banish Vice and
Ignorance out of the Territories of
Great-Britain
, I shall
endeavour as much as possible to establish among us a Taste of polite
Writing. It is with this View that I have endeavoured to set my Readers
right in several Points relating to Operas and Tragedies; and shall from
time to time impart my Notions of Comedy, as I think they may tend to
its Refinement and Perfection. I find by my Bookseller that these Papers
of Criticism, with that upon Humour, have met with a more kind Reception
than indeed I could have hoped for from such Subjects; for which Reason
I shall enter upon my present Undertaking with greater Chearfulness.
In this, and one or two following Papers, I shall trace out the History
of false Wit, and distinguish the several Kinds of it as they have
prevailed in different Ages of the World. This I think the more
necessary at present, because I observed there were Attempts on foot
last Winter to revive some of those antiquated Modes of Wit that have
been long exploded out of the Commonwealth of Letters. There were
several Satyrs and Panegyricks handed about in Acrostick, by which Means
some of the most arrant undisputed Blockheads about the Town began to
entertain ambitious Thoughts, and to set up for polite Authors. I shall
therefore describe at length those many Arts of false Wit, in which a
Writer does not show himself a Man of a beautiful Genius, but of great
Industry.
The first Species of false Wit which I have met with is very venerable
for its Antiquity, and has produced several Pieces which have lived very
near as long as the
Iliad
it self: I mean those short Poems
printed among the minor
Greek
Poets, which resemble the Figure of
an Egg, a Pair of Wings, an Ax, a Shepherd's Pipe, and an Altar.
As
the first, it is a little oval Poem, and may not improperly
be called a Scholar's Egg. I would endeavour to hatch it, or, in more
intelligible Language, to translate it into
English
, did not I
find the Interpretation of it very difficult; for the Author seems to
have been more intent upon the Figure of his Poem, than upon the Sense
of it.
The Pair of Wings consist of twelve Verses, or rather Feathers, every
Verse decreasing gradually in its Measure according to its Situation in
the Wing. The subject of it (as in the rest of the Poems which follow)
bears some remote Affinity with the Figure, for it describes a God of
Love, who is always painted with Wings.
The Ax methinks would have been a good Figure for a Lampoon, had the
Edge of it consisted of the most satyrical Parts of the Work; but as it
is in the Original, I take it to have been nothing else but the Posy of
an Ax which was consecrated to
Minerva
, and was thought to have
been the same that
Epeus
made use of in the building of the
Trojan
Horse; which is a Hint I shall leave to the Consideration
of the Criticks. I am apt to think that the Posy was written originally
upon the Ax, like those which our modern Cutlers inscribe upon their
Knives; and that therefore the Posy still remains in its ancient Shape,
tho' the Ax it self is lost.
Shepherd's Pipe may be said to be full of Musick, for it is composed
of nine different Kinds of Verses, which by their several Lengths
resemble the nine Stops of the old musical Instrument,
that
is
likewise the Subject of the Poem
.
The Altar is inscribed with the Epitaph of
Troilus
the Son of
Hecuba
; which, by the way, makes me believe, that these false Pieces
of Wit are much more ancient than the Authors to whom they are generally
ascribed; at least I will never be perswaded, that so fine a Writer as
Theocritus
could have been the Author of any such simple Works.
It was impossible for a Man to succeed in these Performances who was not
a kind of Painter, or at least a Designer: He was first of all to draw
the Out-line of the Subject which he intended to write upon, and
afterwards conform the Description to the Figure of his Subject. The
Poetry was to contract or dilate itself according to the Mould in which
it was cast. In a word, the Verses were to be cramped or extended to the
Dimensions of the Frame that was prepared for them; and to undergo the
Fate of those Persons whom the Tyrant
Procrustes
used to lodge in his
Iron Bed; if they were too short, he stretched them on a Rack, and if
they were too long, chopped off a Part of their Legs, till they fitted
the Couch which he had prepared for them.
Mr.
Dryden
hints at this obsolete kind of Wit in one of the following
Verses,
in his Mac Flecno
; which an
English
Reader cannot
understand, who does not know that there are those little Poems
abovementioned in the Shape of Wings and Altars.
... Chuse for thy Command
Some peaceful Province in Acrostick Land;
There may'st thou Wings display, and Altars raise,
And torture one poor Word a thousand Ways.
Fashion of false Wit was revived by several Poets of the last Age,
and in particular may be met with among
Mr. Herbert's
Poems; and,
if I am not mistaken, in the Translation of
Du Bartas
.
— I do not
remember any other kind of Work among the Moderns which more resembles
the Performances I have mentioned, than that famous Picture of King
Charles
the First, which has the whole Book of
Psalms
written in the Lines of the Face and the Hair of the Head. When I was
last at
Oxford
I perused one of the Whiskers; and was reading the
other, but could not go so far in it as I would have done, by reason of
the Impatience of my Friends and Fellow-Travellers, who all of them
pressed to see such a Piece of Curiosity. I have since heard, that there
is now an eminent Writing-Master in Town, who has transcribed all the
Old Testament
in a full-bottomed Periwig; and if the Fashion
should introduce the thick kind of Wigs which were in Vogue some few
Years ago, he promises to add two or three supernumerary Locks that
shall contain all the
Apocrypha
. He designed this Wig originally
for King
William
, having disposed of the two Books of
Kings
in the two Forks of the Foretop; but that glorious Monarch
dying before the Wig was finished, there is a Space left in it for the
Face of any one that has a mind to purchase it.
But to return to our ancient Poems in Picture, I would humbly propose,
for the Benefit of our modern Smatterers in Poetry, that they would
imitate their Brethren among the Ancients in those ingenious Devices. I
have communicated this Thought to a young Poetical Lover of my
Acquaintance, who intends to present his Mistress with a Copy of Verses
made in the Shape of her Fan; and, if he tells me true, has already
finished the three first Sticks of it. He has likewise promised me to
get the Measure of his Mistress's Marriage-Finger, with a Design to make
a Posy in the Fashion of a Ring, which shall exactly fit it. It is so
very easy to enlarge upon a good Hint, that I do not question but my
ingenious Readers will apply what I have said to many other Particulars;
and that we shall see the Town filled in a very little time with
Poetical Tippets, Handkerchiefs, Snuff-Boxes, and the like Female
Ornaments.
shall therefore conclude with a Word of Advice to those
admirable
English
Authors who call themselves Pindarick Writers
,
that they would apply themselves to this kind of Wit without Loss of
Time, as being provided better than any other Poets with Verses of all
Sizes and Dimensions.
C.
Not a new paragraph in the first issue.
which
The
Syrinx
of Theocritus consists of twenty verses, so
arranged that the length of each pair is less than that of the pair
before, and the whole resembles the ten reeds of the mouth organ or Pan
pipes
. The Egg is, by tradition, called Anacreon's.
Simmias of Rhodes, who lived about B.C. 324, is said to have been the
inventor of shaped verses. Butler in his
Character of a Small Poet
said of Edward Benlowes:
'As for Altars and Pyramids in poetry, he has outdone all men that
way; for he has made a gridiron and a frying-pan in verse, that
besides the likeness in shape, the very tone and sound of the words
did perfectly represent the noise that is made by those utensils.'
But a devout earnestness gave elevation to George Herbert's
ingenious conceits. Joshua Sylvester's dedication to King James the
First of his translation of the Divine Weeks and Works of Du Bartas has
not this divine soul in its oddly-fashioned frame. It begins with a
sonnet on the Royal Anagram 'James Stuart: A just Master;' celebrates
his Majesty in French and Italian, and then fills six pages with verse
built in his Majesty's honour, in the form of bases and capitals of
columns, inscribed each with the name of one of the Muses. Puttenham's
Art of Poetry,
published in 1589, book II., ch. ii. contains the fullest
account of the mysteries and varieties of this sort of versification.
When the tyranny of French criticism had imprisoned nearly
all our poetry in the heroic couplet, outside exercise was allowed only
to those who undertook to serve under Pindar.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 8, 1711 |
Addison |
Operose Nihil agunt.
Seneca.

There is nothing more certain than that every Man would be a Wit if he
could, and notwithstanding Pedants of a pretended Depth and Solidity are
apt to decry the Writings of a polite Author, as
Flash
and
Froth
,
they all of them shew upon Occasion that they would spare no pains to
arrive at the Character of those whom they seem to despise. For this
Reason we often find them endeavouring at Works of Fancy, which cost
them infinite Pangs in the Production. The Truth of it is, a Man had
better be a Gally-Slave than a Wit, were one to gain that Title by those
Elaborate Trifles which have been the Inventions of such Authors as were
often Masters of great Learning but no Genius.
In my last Paper I mentioned some of these false Wits among the
Ancients, and in this shall give the Reader two or three other Species
of them, that flourished in the same early Ages of the World.
first
I shall produce are the
Lipogrammiatists
or
Letter-droppers
of
Antiquity, that would take an Exception, without any Reason, against
some particular Letter in the Alphabet, so as not to admit it once into
a whole Poem. One
Tryphiodorus
was a great Master in this kind of
Writing. He composed an
Odyssey
or Epick Poem on the Adventures of
Ulysses
, consisting of four and twenty Books, having entirely banished
the Letter
A
from his first Book, which was called
Alpha
(as
Lucus
a non Lucendo
) because there was not an
Alpha
in it. His second Book
was inscribed
Beta
for the same Reason. In short, the Poet excluded
the whole four and twenty Letters in their Turns, and shewed them, one
after another, that he could do his Business without them.
It must have been very pleasant to have seen this Poet avoiding the
reprobate Letter, as much as another would a false Quantity, and making
his Escape from it through the several
Greek
Dialects, when he was
pressed with it in any particular Syllable. For the most apt and elegant
Word in the whole Language was rejected, like a Diamond with a Flaw in
it, if it appeared blemished with a wrong Letter. I shall only observe
upon this Head, that if the Work I have here mentioned had been now
extant, the
Odyssey
of
Tryphiodorus
, in all probability, would have
been oftner quoted by our learned Pedants, than the
Odyssey
of
Homer
. What a perpetual Fund would it have been of obsolete Words and
Phrases, unusual Barbarisms and Rusticities, absurd Spellings and
complicated Dialects? I make no question but it would have been looked
upon as one of the most valuable Treasuries of the
Greek
Tongue.
find likewise among the Ancients that ingenious kind of Conceit, which
the Moderns distinguish by the Name of a
Rebus
, that does not sink
a Letter but a whole Word, by substituting a Picture in its Place. When
Cæsar
was one of the Masters of the
Roman
Mint, he placed the
Figure of an Elephant upon the Reverse of the Publick Mony; the Word
Cæsar
signifying an Elephant in the
Punick
Language. This was
artificially contrived by
Cæsar
, because it was not lawful for a
private Man to stamp his own Figure upon the Coin of the Commonwealth.
Cicero
,
was so called from the Founder of his Family, that was
marked on the Nose with a little Wen like a Vetch (which is
Cicer
in
Latin
) instead of
Marcus Tullius Cicero
, order'd the Words
Marcus
Tullius
with the Figure of a Vetch at the End of them to be inscribed
on a publick Monument
. This was done probably to shew that he was
neither ashamed of his Name or Family, notwithstanding the Envy of his
Competitors had often reproached him with both. In the same manner we
read of a famous Building that was marked in several Parts of it with
the Figures of a Frog and a Lizard: Those Words in
Greek
having been
the Names of the Architects, who by the Laws of their Country were never
permitted to inscribe their own Names upon their Works. For the same
Reason it is thought, that the Forelock of the Horse in the Antique
Equestrian Statue of
Marcus Aurelius
, represents at a Distance the
Shape of an Owl, to intimate the Country of the Statuary, who, in all
probability, was an
Athenian
. This kind of Wit was very much in Vogue
among our own Countrymen about an Age or two ago, who did not practise
it for any oblique Reason, as the Ancients abovementioned, but purely
for the sake of being Witty. Among innumerable Instances that may be
given of this Nature, I shall produce the Device of one Mr
Newberry
,
as I find it mentioned by our learned
Cambden
in his Remains. Mr
Newberry
, to represent his Name by a Picture, hung up at his Door the
Sign of a Yew-Tree, that had several Berries upon it, and in the midst
of them a great golden
N
hung upon a Bough of the Tree, which by the
Help of a little false Spelling made up the Word
N-ew-berry
.
I shall conclude this Topick with a
Rebus
, which has been lately hewn
out in Free-stone, and erected over two of the Portals of
Blenheim
House, being the Figure of a monstrous Lion tearing to Pieces a little
Cock. For the better understanding of which Device, I must acquaint my
English
Reader that a Cock has the Misfortune to be called in
Latin
by the same Word that signifies a
Frenchman
, as a Lion is the Emblem
of the
English
Nation. Such a Device in so noble a Pile of Building
looks like a Punn in an Heroick Poem; and I am very sorry the truly
ingenious Architect would suffer the Statuary to blemish his excellent
Plan with so poor a Conceit: But I hope what I have said will gain
Quarter for the Cock, and deliver him out of the Lion's Paw.
I find likewise in ancient Times the Conceit of making an Eccho talk
sensibly, and give rational Answers. If this could be excusable in any
Writer, it would be in
Ovid
, where he introduces the Eccho as a Nymph,
before she was worn away into nothing but a Voice.
learned
Erasmus
, tho' a Man of Wit and Genius, has composed a Dialogue
upon this silly kind of Device, and made use of an Eccho who seems to
have been a very extraordinary Linguist, for she answers the Person she
talks with in
Latin, Greek
, and
Hebrew
, according as she found the
Syllables which she was to repeat in any one of those learned Languages.
Hudibras
, in Ridicule of this false kind of Wit, has described
Bruin
bewailing the Loss of his Bear to a solitary Eccho, who is of
great used to the Poet in several Disticks, as she does not only repeat
after him, but helps out his Verse, and furnishes him with
Rhymes
.
He rag'd, and kept as heavy a Coil as
Stout Hercules for loss of Hylas;
Forcing the Valleys to repeat
The Accents of his sad Regret;
He beat his Breast, and tore his Hair,
For Loss of his dear Crony Bear,
That Eccho from the hollow Ground
His Doleful Wailings did resound
More wistfully, but many times,
Then in small Poets Splay-foot Rhymes,
That make her, in her rueful Stories
To answer to Introgatories,
And most unconscionably depose
Things of which She nothing knows:
And when she has said all she can say,
'Tis wrested to the Lover's Fancy.
Quoth he, O whither, wicked Bruin,
Art thou fled to my — Eccho, Ruin?
I thought th' hadst scorn'd to budge a Step
for Fear. (Quoth Eccho) Marry guep.
Am not I here to take thy Part!
Then what has quell'd thy stubborn Heart?
Have these Bones rattled, and this Head
So often in thy Quarrel bled?
Nor did I ever winch or grudge it,
For thy dear Sake. (Quoth she) Mum budget.
Think'st thou 'twill not be laid i' th' Dish.
Thou turn'dst thy Back? Quoth Eccho, Pish.
To run from those th' hadst overcome
Thus cowardly? Quoth Eccho, Mum.
But what a-vengeance makes thee fly
From me too, as thine Enemy?
Or if thou hadst not Thought of me,
Nor what I have endur'd for Thee,
Yet Shame and Honour might prevail
To keep thee thus for turning tail;
For who will grudge to spend his Blood in
His Honour's Cause? Quoth she, A Pudding.
From
, I omit,
, a letter. In
modern literature there is a Pugna Porcorum (pig-fight) of which every
word begins with a p, and there are Spanish odes from which all vowels
but one are omitted. The earliest writer of Lipogrammatic verse is said
to have been the Greek poet Lasus, born in Achaia 538 B.C. Lope de Vega
wrote five novels, each with one of the five vowels excluded from it.
This French name for an enigmatical device is said to be
derived from the custom of the priests of Picardy at carnival time to
set up ingenious jests upon current affairs, 'de
rebus
quæ geruntur.'
Addison takes these illustrations from the chapter on
Rebus or Name devises,
in that pleasant old book, Camden's
Remains
,
which he presently cites. The next chapter in the
Remains
is upon
Anagrams.
Colloquia Familiaria
, under the title Echo. The dialogue
is ingeniously contrived between a youth and Echo.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 9, 1711 |
Addison |
Hoc est quod palles? Cur quis non prandeat, Hoc est?
Per.
Sat. 3.

Several kinds of false Wit that vanished in the refined Ages of the
World, discovered themselves again in the Times of Monkish Ignorance.
As the Monks were the Masters of all that little Learning which was then
extant, and had their whole Lives entirely disengaged from Business, it
is no wonder that several of them, who wanted Genius for higher
Performances, employed many Hours in the Composition of such Tricks in
Writing as required much Time and little Capacity. I have seen half the
Æneid
turned into
Latin
Rhymes by one of the
Beaux Esprits
of
that dark Age; who says in his Preface to it, that the
Æneid
wanted
nothing but the Sweets of Rhyme to make it the most perfect Work in its
Kind. I have likewise seen an Hymn in Hexameters to the Virgin
Mary,
which filled a whole Book, tho' it consisted but of the eight following
Words.
Tot, tibi, sunt, Virgo, dotes, quot, sidera, Cælo.
Thou hast as many Virtues, O Virgin, as there are Stars in Heaven.
Poet rung the
changes
upon these eight several Words, and by
that Means made his Verses almost as numerous as the Virtues and the
Stars which they celebrated. It is no wonder that Men who had so much
Time upon their Hands did not only restore all the antiquated Pieces of
false Wit, but enriched the World with Inventions of their own.
was
to this Age that we owe the Production of Anagrams
, which is nothing
else but a Transmutation of one Word into another, or the turning of the
same Set of Letters into different Words; which may change Night into
Day, or Black into White, if Chance, who is the Goddess that presides
over these Sorts of Composition, shall so direct. I remember a witty
Author, in Allusion to this kind of Writing, calls his Rival, who (it
seems) was distorted, and had his Limbs set in Places that did not
properly belong to them,
The Anagram of a Man
.
When the Anagrammatist takes a Name to work upon, he considers it at
first as a Mine not broken up, which will not shew the treasure it
contains till he shall have spent many Hours in the Search of it: For
it is his Business to find out one Word that conceals it self in
another, and to examine the Letters in all the Variety of Stations in
which they can possibly be ranged. I have heard of a Gentleman who, when
this Kind of Wit was in fashion, endeavoured to gain his Mistress's
Heart by it.
was one of the finest Women of her Age, and
known
by the Name of the Lady
Mary Boon
. The Lover not being able to
make any thing of
Mary
, by certain Liberties indulged to this
kind of Writing, converted it into
Moll
; and after having shut
himself up for half a Year, with indefatigable Industry produced an
Anagram. Upon the presenting it to his Mistress, who was a little vexed
in her Heart to see herself degraded into
Moll Boon
, she told
him, to his infinite Surprise, that he had mistaken her Sirname, for
that it was not
Boon
but
Bohun
.
... Ibi omnis
Effusus labor ...
The lover was thunder-struck with his Misfortune, insomuch that in a
little time after he lost his Senses, which indeed had been very much
impaired by that continual Application he had given to his Anagram.
Acrostick
was probably invented about the same time with the
Anagram, tho' it is impossible to decide whether the Inventor of the one
of the other
were
the greater Blockhead. The
Simple
Acrostick is nothing but the Name or Title of a Person or Thing made out
of the initial Letters of several Verses, and by that Means written,
after the Manner of the
Chinese
, in a perpendicular Line. But
besides these there are
Compound
Acrosticks, where the principal
Letters stand two or three deep. I have seen some of them where the
Verses have not only been edged by a Name at each Extremity, but have
had the same Name running down like a Seam through the Middle of the
Poem.
is another near Relation of the Anagrams and Acrosticks, which is
commonly
called
a Chronogram.
kind of Wit appears very often
on many modern Medals, especially those of
Germany
, when they
represent in the Inscription the Year in which they were coined. Thus we
see on a Medal of
Gustavus Adolphus
the following Words, CHRISTVS
DUX ERGO TRIVMPHVS. If you take the pains to pick the Figures out of the
several Words, and range them in their proper Order, you will find they
amount to MDCXVVVII, or 1627, the Year in which the Medal was stamped:
For as some of the Letters distinguish themselves from the rest, and
overtop their Fellows, they are to be considered in a double Capacity,
both as Letters and as Figures. Your laborious
German
Wits will turn
over a whole Dictionary for one of these ingenious Devices. A Man would
think they were searching after an apt classical Term, but instead of
that they are looking out a Word that has an L, and M, or a D in it.
When therefore we meet with any of these Inscriptions, we are not so
much to look in 'em for the Thought, as for the Year of the Lord.
Boutz Rimez
were the Favourites of the
French
Nation for a whole Age together, and that at a Time when it abounded in
Wit and Learning. They were a List of Words that rhyme to one another,
drawn up by another Hand, and given to a Poet, who was to make a Poem to
the Rhymes in the same Order that they were placed upon the List: The
more uncommon the Rhymes were, the more extraordinary was the Genius of
the Poet that could accommodate his Verses to them. I do not know any
greater Instance of the Decay of Wit and Learning among the
French
(which generally follows the Declension of Empire) than
the endeavouring to restore this foolish Kind of Wit. If the Reader will
be at the trouble to see Examples of it, let him look into the new
Mercure Galant
; where the Author every Month gives a List of
Rhymes to be filled up by the Ingenious, in order to be communicated to
the Publick in the
Mercure
for the succeeding Month. That for the
Month of
November
last
, which now lies before me, is as follows.
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Lauriers |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Guerriers |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Musette |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Lisette |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Cesars |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Etendars |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Houlette |
| - - - - - - - - - - - - |
Folette |
One would be amazed to see so learned a Man as
Menage
talking
seriously on this Kind of Trifle in the following Passage.
Monsieur de la Chambre has told me that he never knew what he was
going to write when he took his Pen into his Hand; but that one
Sentence always produced another. For my own part, I never knew what I
should write next when I was making Verses. In the first place I got
all my Rhymes together, and was afterwards perhaps three or four
Months in filling them up. I one Day shewed Monsieur Gombaud a
Composition of this Nature, in which among others I had made use of
the four following Rhymes, Amaryllis, Phillis, Marne, Arne, desiring
him to give me his Opinion of it. He told me immediately, that my
Verses were good for nothing. And upon my asking his Reason, he said,
Because the Rhymes are too common; and for that Reason easy to be put
into Verse. Marry, says I, if it be so, I am very well rewarded for
all the Pains I have been at. But by Monsieur Gombaud's Leave,
notwithstanding the Severity of the Criticism, the Verses were good.
Vid
.
Menagiana
.
far the learned
Menage,
whom I have translated
Word for Word
.
The first Occasion of these
Bouts Rimez
made them in some manner
excusable, as they were Tasks which the
French
Ladies used to impose
on their Lovers.
when a grave Author, like him above-mentioned,
tasked himself, could there be anything more ridiculous? Or would not
one be apt to believe that the Author played
booty
, and did not
make his List of Rhymes till he had finished his Poem?
shall only add, that this Piece of false Wit has been finely ridiculed
by Monsieur
Sarasin,
in a Poem intituled,
La Defaite des Bouts-Rimez,
The Rout of the Bouts-Rimez.
I must subjoin to this last kind of Wit the double Rhymes, which are
used in Doggerel Poetry, and generally applauded by ignorant Readers.
the Thought of the Couplet in such Compositions is good, the Rhyme adds
little
to it; and if bad, it will not be in the Power of the
Rhyme to recommend it. I am afraid that great Numbers of those who
admire the incomparable
Hudibras
, do it more on account of these
Doggerel Rhymes than of the Parts that really deserve admiration. I am
sure I have heard the
Pulpit, Drum Ecclesiastick,
Was beat with fist instead of a Stick,
and
There was an ancient sage Philosopher
Who had read Alexander Ross over,
more frequently quoted, than the finest Pieces of Wit in the whole Poem.
C.
chymes
This is an error.
meant in old Greek
what it now means. Lycophron, who lived B.C. 280, and wrote a Greek poem
on Cassandra, was famous for his Anagrams, of which two survive. The
Cabalists had a branch of their study called Themuru, changing, which
made mystical anagrams of sacred names.
was called
The invention of Acrostics is attributed to Porphyrius Optatianus, a writer of the 4th century. But the arguments of the Comedies of Plautus are in form of acrostics, and acrostics occur in the original Hebrew of the
Book of Psalms.
was
known by the name of
The Chronogram was popular also, especially among the
Germans, for inscriptions upon marble or in books. More than once, also,
in Germany and Belgium a poem was written in a hundred hexameters, each
yielding a chronogram of the date it was to celebrate.
Bouts rimés are said to have been suggested to the wits of
Paris by the complaint of a verse turner named Dulot, who grieved one
day over the loss of three hundred sonnets; and when surprise was
expressed at the large number, said they were the 'rhymed ends,' that
only wanted filling up.
Menagiana
, vol. I. p. 174, ed. Amst. 1713. The
Menagiana
were published in 4 volumes, in 1695 and 1696. Gilles Menage died at
Paris in 1692, aged 79. He was a scholar and man of the world, who had a
retentive memory, and, says Bayle,
'could say a thousand good things in a thousand pleasing ways.'
The repertory here quoted from is the best of
the numerous collections of 'ana.'
double
Jean François Sarasin, whose works were first collected by
Menage, and published in 1656, two years after his death. His defeat of
the Bouts-Rimés, has for first title
Dulot Vaincu
is in four cantos,
and was written in four or five days.
nothing
Contents
|
Thursday, May 10, 1711 |
Addison |
Non equidem studeo, bullalis ut mihi nugis
Pagina turgescal, dare pondus idonea fumo.
Pers.

There is no kind of false Wit which has been so recommended by the
Practice of all Ages, as that which consists in a Jingle of Words, and
is comprehended under the general Name of
Punning
. It is indeed
impossible to kill a Weed, which the Soil has a natural Disposition to
produce. The Seeds of Punning are in the Minds of all Men, and tho' they
may be subdued by Reason, Reflection and good Sense, they will be very
apt to shoot up in the greatest Genius, that is not broken and
cultivated by the Rules of Art. Imitation is natural to us, and when it
does not raise the Mind to Poetry, Painting, Musick, or other more noble
Arts, it often breaks out in Punns and Quibbles.
Aristotle
, in the Eleventh Chapter of his Book of Rhetorick, describes
two or three kinds of Punns, which he calls Paragrams, among the
Beauties of good Writing, and produces Instances of them out of some of
the greatest Authors in the
Greek
Tongue.
Cicero
has sprinkled
several of his Works with Punns, and in his Book where he lays down the
Rules of Oratory, quotes abundance of Sayings as Pieces of Wit, which
also upon Examination prove arrant Punns. But the Age in which
the
Punn
chiefly flourished, was the Reign of King
James
the First.
That learned Monarch was himself a tolerable Punnster, and made very few
Bishops or Privy-Counsellors that had not some time or other signalized
themselves by a Clinch, or a
Conundrum
. It was therefore in this
Age that the Punn appeared with Pomp and Dignity. It had before been
admitted into merry Speeches and ludicrous Compositions, but was now
delivered with great Gravity from the Pulpit, or pronounced in the most
solemn manner at the Council-Table. The greatest Authors, in their most
serious Works, made frequent use of Punns. The Sermons of Bishop
Andrews
, and the Tragedies of
Shakespear
, are full of
them. The Sinner was punned into Repentance by the former, as in the
latter nothing is more usual than to see a Hero weeping and quibbling
for a dozen Lines together.
I must add to these great Authorities, which seem to have given a kind
of Sanction to this Piece of false Wit, that all the Writers of
Rhetorick have treated of Punning with very great Respect, and divided
the several kinds of it into hard Names, that are reckoned among the
Figures of Speech, and recommended as Ornaments in Discourse. I remember
a Country School-master of my Acquaintance told me once, that he had
been in Company with a Gentleman whom he looked upon to be the greatest
Paragrammatist
among the Moderns. Upon Inquiry, I found my
learned Friend had dined that Day with Mr.
Swan
, the famous
Punnster; and desiring him to give me some Account of Mr.
Swan's
Conversation, he told me that he generally talked in the
Paranomasia
, that he sometimes gave into the
Plocè
, but
that in his humble Opinion he shined most in the
Antanaclasis
.
I must not here omit, that a famous University of this Land was formerly
very much infested with Punns; but whether or no this might not arise
from the Fens and Marshes in which it was situated, and which are now
drained, I must leave to the Determination of more skilful Naturalists.
After this short History of Punning, one would wonder how it should be
so entirely banished out of the Learned World, as it is at present,
especially since it had found a Place in the Writings of the most
ancient Polite Authors. To account for this, we must consider, that the
first Race of Authors, who were the great Heroes in Writing, were
destitute of all Rules and Arts of Criticism; and for that Reason,
though they excel later Writers in Greatness of Genius, they fall short
of them in Accuracy and Correctness. The Moderns cannot reach their
Beauties, but can avoid their Imperfections. When the World was
furnished with these Authors of the first Eminence, there grew up
another Set of Writers, who gained themselves a Reputation by the
Remarks which they made on the Works of those who preceded them. It was
one of the Employments of these Secondary Authors, to distinguish the
several kinds of Wit by Terms of Art, and to consider them as more or
less perfect, according as they were founded in Truth. It is no wonder
therefore, that even such Authors as
Isocrates, Plato
, and
Cicero
,
should have such little Blemishes as are not to be met with in Authors
of a much inferior Character, who have written since those several
Blemishes were discovered.
do not find that there was a proper
Separation made between Punns and
true
Wit by any of the Ancient
Authors, except
Quintilian
and
Longinus
. But when this Distinction
was once settled, it was very natural for all Men of Sense to agree in
it. As for the Revival of this false Wit, it happened about the time of
the Revival of Letters; but as soon as it was once detected, it
immediately vanished and disappeared. At the same time there is no
question, but as it has sunk in one Age and rose in another, it will
again recover it self in some distant Period of Time, as Pedantry and
Ignorance shall prevail upon Wit and Sense. And, to speak the Truth, I
do very much apprehend, by some of the last Winter's Productions, which
had their Sets of Admirers, that our Posterity will in a few Years
degenerate into a Race of Punnsters: At least, a Man may be very
excusable for any Apprehensions of this kind, that has seen
Acrosticks
handed about the Town with great Secrecy and Applause; to which I must
also add a little Epigram called the
Witches Prayer
, that fell into
Verse when it was read either backward or forward, excepting only that
it Cursed one way and Blessed the other. When one sees there are
actually such Pains-takers among our
British
Wits, who can tell what
it may end in? If we must Lash one another, let it be with the manly
Strokes of Wit and Satyr; for I am of the old Philosopher's Opinion,
That if I must suffer from one or the other, I would rather it should be
from the Paw of a Lion, than the Hoof of an Ass. I do not speak this out
of any Spirit of Party. There is a most crying Dulness on both Sides. I
have seen Tory
Acrosticks
and Whig
Anagrams
, and do not quarrel with
either of them, because they are
Whigs
or
Tories
, but because they
are
Anagrams
and
Acrosticks
.
But to return to Punning. Having pursued the History of a Punn, from its
Original to its Downfal, I shall here define it to be a Conceit arising
from the use of two Words that agree in the Sound, but differ in the
Sense. The only way therefore to try a Piece of Wit, is to translate it
into a different Language: If it bears the Test, you may pronounce it
true; but if it vanishes in the Experiment, you may conclude it to have
been a Punn. In short, one may say of a Punn, as the Countryman
described his Nightingale, that it is
vox et præterea nihil,
a Sound,
and nothing but a Sound. On the contrary, one may represent true Wit by
the Description which
Aristinetus
makes of a fine Woman; when she is
dressed
she is Beautiful, when she is
undressed
she is Beautiful; or
as
Mercerus
has translated it [more Emphatically]
Induitur, formosa est: Exuitur, ipsa forma est.
C.
fine
Contents
|
Friday, May 11, 1711 |
Addison |
Scribendi rectè sapere est et principium et fons.
Hor.

Mr.
Lock
has an admirable Reflexion upon the Difference of Wit and
Judgment, whereby he endeavours to shew the Reason why they are not
always the Talents of the same Person. His Words are as follows:
And
hence, perhaps, may be given some Reason of that common Observation,
That Men who have a great deal of Wit and prompt Memories, have not
always the clearest Judgment, or deepest Reason. For Wit lying most in
the Assemblage of Ideas, and putting those together with Quickness and
Variety, wherein can be found any Resemblance or Congruity, thereby to
make up pleasant Pictures and agreeable Visions in the Fancy; Judgment,
on the contrary, lies quite on the other Side, In separating carefully
one from another, Ideas wherein can be found the least Difference,
thereby to avoid being misled by Similitude, and by Affinity to take one
thing for another. This is a way of proceeding quite contrary to
Metaphor and Allusion; wherein, for the most part, lies that
Entertainment and Pleasantry of Wit which strikes so lively on the
Fancy, and is therefore so acceptable to all People.1
This is, I think, the best and most Philosophical Account that I have
ever met with of Wit, which generally, though not always, consists in
such a Resemblance and Congruity of Ideas as this Author mentions. I
shall only add to it, by way of Explanation, That every Resemblance of
Ideas is not that which we call Wit, unless it be such an one that gives
Delight
and
Surprise
to the Reader: These two Properties
seem essential to Wit, more particularly the last of them. In order
therefore that the Resemblance in the Ideas be Wit, it is necessary that
the Ideas should not lie too near one another in the Nature of things;
for where the Likeness is obvious, it gives no Surprize. To compare one
Man's Singing to that of another, or to represent the Whiteness of any
Object by that of Milk and Snow, or the Variety of its Colours by those
of the Rainbow, cannot be called Wit, unless besides this obvious
Resemblance, there be some further Congruity discovered in the two Ideas
that is capable of giving the Reader some Surprize. Thus when a Poet
tells us, the Bosom of his Mistress is as white as Snow, there is no Wit
in the Comparison; but when he adds, with a Sigh, that it is as cold
too, it then grows into Wit. Every Reader's Memory may supply him with
innumerable Instances of the same Nature. For this Reason, the
Similitudes in Heroick Poets, who endeavour rather to fill the Mind with
great Conceptions, than to divert it with such as are new and
surprizing, have seldom any thing in them that can be called Wit. Mr.
Lock's
Account of Wit, with this short Explanation, comprehends
most of the Species of Wit, as Metaphors, Similitudes, Allegories,
Ænigmas, Mottos, Parables, Fables, Dreams, Visions, dramatick Writings,
Burlesque, and all the Methods of Allusion: As there are many other
Pieces of Wit, (how remote soever they may appear at first sight, from
the foregoing Description) which upon Examination will be found to agree
with it.
As
true Wit
generally consists in this Resemblance and Congruity
of Ideas,
false Wit
chiefly consists in the Resemblance and
Congruity sometimes of single Letters, as in Anagrams, Chronograms,
Lipograms, and Acrosticks: Sometimes of Syllables, as in Ecchos and
Doggerel Rhymes: Sometimes of Words, as in Punns and Quibbles; and
sometimes of whole Sentences or Poems, cast into the Figures of
Eggs,
Axes
, or
Altars
: Nay, some carry the Notion of Wit so far, as
to ascribe it even to external Mimickry; and to look upon a Man as an
ingenious Person, that can resemble the Tone, Posture, or Face of
another.
As
true Wit
consists in the Resemblance of Ideas, and
false
Wit
in the Resemblance of Words, according to the foregoing
Instances; there is another kind of Wit which consists partly in the
Resemblance of Ideas, and partly in the Resemblance of Words; which for
Distinction Sake I shall call
mixt Wit
. This kind of Wit is that which
abounds in
Cowley
, more than in any Author that ever wrote. Mr.
Waller
has likewise a great deal of it. Mr.
Dryden
is very sparing
in it.
Milton
had a Genius much above it.
Spencer
is in the same
Class with
Milton
. The
Italians
, even in their Epic Poetry, are full
of it. Monsieur
Boileau
, who formed himself upon the Ancient Poets,
has every where rejected it with Scorn. If we look after mixt Wit among
the
Greek
Writers, we shall find it no where but in the
Epigrammatists. There are indeed some Strokes of it in the little Poem
ascribed to Musœus, which by that, as well as many other Marks, betrays
it self to be a modern Composition. If we look into the
Latin
Writers,
we find none of this mixt Wit in
Virgil, Lucretius
, or
Catullus
;
very little in
Horace
, but a great deal of it in
Ovid
, and scarce
any thing else in
Martial
.
Out of the innumerable Branches of
mixt Wit
, I shall choose one
Instance which may be met with in all the Writers of this Class. The
Passion of Love in its Nature has been thought to resemble Fire; for
which Reason the Words Fire and Flame are made use of to signify Love.
The witty Poets therefore have taken an Advantage from the doubtful
Meaning of the Word Fire, to make an infinite Number of Witticisms.
Cowley
observing the cold Regard of his Mistress's Eyes, and at the
same Time their Power of producing Love in him, considers them as
Burning-Glasses made of Ice; and finding himself able to live in the
greatest Extremities of Love, concludes the Torrid Zone to be habitable.
When his Mistress has read his Letter written in Juice of Lemmon by
holding it to the Fire, he desires her to read it over a second time by
Love's Flames. When she weeps, he wishes it were inward Heat that
distilled those Drops from the Limbeck. When she is absent he is beyond
eighty, that is, thirty Degrees nearer the Pole than when she is with
him. His ambitious Love is a Fire that naturally mounts upwards; his
happy Love is the Beams of Heaven, and his unhappy Love Flames of Hell.
When it does not let him sleep, it is a Flame that sends up no Smoak;
when it is opposed by Counsel and Advice, it is a Fire that rages the
more by the Wind's blowing upon it. Upon the dying of a Tree in which he
had cut his Loves, he observes that his written Flames had burnt up and
withered the Tree. When he resolves to give over his Passion, he tells
us that one burnt like him for ever dreads the Fire. His Heart is an
Ætna
, that instead of
Vulcan's
Shop incloses
Cupid's
Forge in it.
His endeavouring to drown his Love in Wine, is throwing Oil upon the
Fire. He would insinuate to his Mistress, that the Fire of Love, like
that of the Sun (which produces so many living Creatures) should not
only warm but beget. Love in another Place cooks Pleasure at his Fire.
Sometimes the Poet's Heart is frozen in every Breast, and sometimes
scorched in every Eye. Sometimes he is drowned in Tears, and burnt in
Love, like a Ship set on Fire in the Middle of the Sea.
The Reader may observe in every one of these Instances, that the Poet
mixes the Qualities of Fire with those of Love; and in the same Sentence
speaking of it both as a Passion and as real Fire, surprizes the Reader
with those seeming Resemblances or Contradictions that make up all the
Wit in this kind of Writing. Mixt Wit therefore is a Composition of Punn
and true Wit, and is more or less perfect as the Resemblance lies in the
Ideas or in the Words: Its Foundations are laid partly in Falsehood and
partly in Truth: Reason puts in her Claim for one Half of it, and
Extravagance for the other. The only Province therefore for this kind of
Wit, is Epigram, or those little occasional Poems that in their own
Nature are nothing else but a Tissue of Epigrams. I cannot conclude this
Head of
mixt Wit
, without owning that the admirable Poet out of whom I
have taken the Examples of it, had as much true Wit as any Author that
ever writ; and indeed all other Talents of an extraordinary Genius.
It may be expected, since I am upon this Subject, that I should take
notice of Mr.
Dryden's
Definition of Wit; which, with all the
Deference that is due to the Judgment of so great a Man, is not so
properly a Definition of Wit, as of good writing in general.
, as he
defines it, is
'a Propriety of Words and Thoughts adapted to the Subject.'
2
this be a true Definition of Wit, I am apt to think
that
Euclid
was
the greatest Wit that ever set Pen to Paper: It
is certain that never was a greater Propriety of Words and Thoughts
adapted to the Subject, than what that Author has made use of in his
Elements. I shall only appeal to my Reader, if this Definition agrees
with any Notion he has of Wit: If it be a true one I am sure Mr.
Dryden
was not only a better Poet, but a greater Wit than Mr.
Cowley
; and
Virgil
a much more facetious Man than either
Ovid
or
Martial
.
Bouhours
,
I look upon to be the most penetrating of all the
French
Criticks, has taken pains to shew, that it is impossible
for any Thought to be beautiful which is not just, and has not its
Foundation in the Nature of things: That the Basis of all Wit is Truth;
and that no Thought can be valuable, of which good Sense is not the
Ground-work
.
Boileau
has endeavoured to inculcate the same
Notions in several Parts of his Writings, both in Prose and Verse
.
This is that natural Way of Writing, that beautiful Simplicity, which we
so much admire in the Compositions of the Ancients; and which no Body
deviates from, but those who want Strength of Genius to make a Thought
shine in its own natural Beauties. Poets who want this Strength of
Genius to give that Majestick Simplicity to Nature, which we so much
admire in the Works of the Ancients, are forced to hunt after foreign
Ornaments, and not to let any Piece of Wit of what kind soever escape
them. I look upon these writers as
Goths
in Poetry, who, like
those in Architecture, not being able to come up to the beautiful
Simplicity of the old
Greeks and Romans
, have endeavoured to
supply its place with all the Extravagancies of an irregular Fancy.
.
Dryden
makes a very handsome Observation, on
Ovid
's writing a Letter
from
Dido
to
Æneas
, in the following Words
.
'Ovid' says he,
(speaking of Virgil's Fiction of Dido and Æneas) 'takes it up
after him, even in the same Age, and makes an Ancient Heroine of
Virgil's new-created Dido; dictates a Letter for her just before her
Death to the ungrateful Fugitive; and, very unluckily for himself, is
for measuring a Sword with a Man so much superior in Force to him on the
same Subject. I think I may be Judge of this, because I have translated
both. The famous Author of the Art of Love has nothing of his own; he
borrows all from a greater Master in his own Profession, and, which is
worse, improves nothing which he finds: Nature fails him, and being
forced to his old Shift, he has Recourse to Witticism. This passes
indeed with his soft Admirers, and gives him the Preference to Virgil
in their Esteem.'
Were not I supported by so great an Authority as that of Mr.
Dryden
, I
should not venture to observe, That the Taste of most of our
English
Poets, as well as Readers, is extremely
Gothick
.
quotes Monsieur
Segrais
for a threefold Distinction of the Readers of Poetry: In
the first of which he comprehends the Rabble of Readers, whom he does
not treat as such with regard to their Quality, but to their Numbers and
Coarseness of their Taste. His Words are as follow:
'Segrais has
distinguished the Readers of Poetry, according to their Capacity of
judging, into three Classes. [He might have said the same of Writers
too, if he had pleased.] In the lowest Form he places those whom he
calls Les Petits Esprits, such things as are our Upper-Gallery
Audience in a Play-house; who like nothing but the Husk and Rind of Wit,
prefer a Quibble, a Conceit, an Epigram, before solid Sense and elegant
Expression: These are Mob Readers. If Virgil and Martial
stood for Parliament-Men, we know already who would carry it. But though
they make the greatest Appearance in the Field, and cry the loudest, the
best on't is they are but a sort of French Huguenots, or
Dutch Boors, brought over in Herds, but not Naturalized; who have
not Lands of two Pounds per Annum in Parnassus, and
therefore are not privileged to poll. Their Authors are of the same
Level, fit to represent them on a Mountebank's Stage, or to be Masters
of the Ceremonies in a Bear-garden: Yet these are they who have the most
Admirers. But it often happens, to their Mortification, that as their
Readers improve their Stock of Sense, (as they may by reading better
Books, and by Conversation with Men of Judgment) they soon forsake
them.'
must not dismiss this Subject without
observing that as Mr.
Lock
in the Passage above-mentioned has discovered the most
fruitful Source of Wit, so there is another of a quite contrary Nature
to it, which does likewise branch it self out into several kinds. For
not only the
Resemblance
, but the
Opposition
of Ideas,
does very often produce Wit; as I could shew in several little Points,
Turns and Antitheses, that I may possibly enlarge upon in some future
Speculation.
C.
Essay concerning Human Understanding
, Bk II. ch. II (p. 68
of ed. 1690; the first).
'If Wit has truly been defined as a Propriety of Thoughts and Words,
then that definition will extend to all sorts of Poetry ... Propriety
of Thought is that Fancy which arises naturally from the Subject, or
which the Poet adapts to it. Propriety of Words is the cloathing of
these Thoughts with such Expressions as are naturally proper to them.'
Dryden's Preface to
Albion and Albanius
.
is
Dominique Bouhours, a learned and accomplished Jesuit, who
died in 1702, aged 75, was a Professor of the Humanities, in Paris, till
the headaches by which he was tormented until death compelled him to
resign his chair. He was afterwards tutor to the two young Princes of
Longueville, and to the son of the minister Colbert. His best book was
translated into English in 1705, as
'The Art of Criticism: or the Method of making a Right Judgment upon
Subjects of Wit and Learning. Translated from the best Edition of the
French, of the Famous Father Bouhours, by a Person of Quality.
In Four Dialogues.'
Here he says:
'Truth is the first Quality, and, as it were, the foundation of
Thought; the fairest is the faultiest, or, rather, those which pass
for the fairest, are not really so, if they want this Foundation.... I
do not understand your Doctrine, replies Philanthus, and I can scarce
persuade myself that a witty Thought should be always founded on
Truth: On the contrary, I am of the opinion of a famous Critic (i.e.
Vavassor in his book on Epigrams) that Falsehood gives it often all
its Grace, and is, as it were, the Soul of it,'
&c., pp, 6, 7, and the following.
As in the lines
Tout doit tendre au Bon Sens: mais pour y parvenir
Le chemin est glissant et penible a tenir.
Art. Poétique,
chant 1.
And again,
Aux dépens du Bon Sens gardez de plaisanter.
Art. Poétique
, chant 3.
Dedication of his translation of the
Æneid
to Lord
Normanby, near the middle; when speaking of the anachronism that made
Dido and Æneas contemporaries.
Jean Regnauld de Segrais, b. 1624, d. 1701, was of Caen,
where he was trained by Jesuits for the Church, but took to Literature,
and sought thereby to support four brothers and two sisters, reduced to
want by the dissipations of his father. He wrote, as a youth, odes,
songs, a tragedy, and part of a romance. Attracting, at the age of 20,
the attention of a noble patron, he became, in 1647, and remained for
the next 24 years, attached to the household of Mlle. de Montpensier. He
was a favoured guest among the
Précieuses
of the
Hotel Rambouillet
,
and was styled, for his acquired air of
bon ton
, the Voiture of Caen.
In 1671 he was received by Mlle. de La Fayette. In 1676 he married a
rich wife, at Caen, his native town, where he settled and revived the
local 'Academy.' Among his works were translations into French verse of
the
Æneid
and
Georgics
. In the dedication of his own translation of the
Æneid
by an elaborate essay to Lord Normanby, Dryden refers much, and
with high respect, to the dissertation prefixed by Segrais to his French
version, and towards the end (on p. 80 where the essay occupies 100
pages), writes as above quoted. The first parenthesis is part of the
quotation.
"would not break the thread of this discourse without;" and
an
Erratum
appended to the next Number says, 'for
without
read
with
.'
Contents
|
Saturday, May 12, 1711 |
Addison |
Humano capiti cervicem pictor equinam
Jungere si velit et varías inducere plumas
Undique collatis membris, ut turpiter atrum
Desinat in piscem mulier formosa supernè;
Spectatum admissi risum teneatis amici?
Credite, Pisones, isti tabulæ fore librum
Persimilem, cujus, velut ægri somnia, vanæ
Finguntur species ...
Hor.

It is very hard for the Mind to disengage it self from a Subject in
which it has been long employed. The Thoughts will be rising of themselves from time to time, tho' we give
them no Encouragement; as the Tossings and Fluctuations of the Sea
continue several Hours after the Winds are laid.
It is to this that I impute my last Night's Dream or Vision, which
formed into one continued Allegory the several Schemes of Wit, whether
False, Mixed, or True, that have been the Subject of my late Papers.
Methoughts I was transported into a Country that was filled with
Prodigies and Enchantments, governed by the Goddess of
Falsehood
,
entitled
the Region of False Wit
. There is nothing in the Fields, the
Woods, and the Rivers, that appeared natural. Several of the Trees
blossomed in Leaf-Gold, some of them produced Bone-Lace, and some of
them precious Stones. The Fountains bubbled in an Opera Tune, and were
filled with Stags, Wild-Boars, and Mermaids, that lived among the
Waters; at the same time that Dolphins and several kinds of Fish played
upon the Banks or took their Pastime in the Meadows. The Birds had many
of them golden Beaks, and human Voices.
Flowers perfumed the Air
with Smells of Incense, Amber-greese, and Pulvillios
; and were so
interwoven with one another, that they grew up in Pieces of Embroidery.
The Winds were filled with Sighs and Messages of distant Lovers. As I
was walking to and fro in this enchanted Wilderness, I could not forbear
breaking out into Soliloquies upon the several Wonders which lay before
me, when, to my great Surprize, I found there were artificial Ecchoes in
every Walk, that by Repetitions of certain Words which I spoke, agreed
with me, or contradicted me, in every thing I said. In the midst of my
Conversation with these invisible Companions, I discovered in the Centre
of a very dark Grove a monstrous Fabrick built after the
Gothick
manner, and covered with innumerable Devices in that barbarous kind of
Sculpture. I immediately went up to it, and found it to be a kind of
Heathen Temple consecrated to the God of
Dullness
. Upon my
Entrance I saw the Deity of the Place dressed in the Habit of a Monk,
with a Book in one Hand and a Rattle in the other. Upon his right Hand
was
Industry
, with a Lamp burning before her; and on his left
Caprice
, with a Monkey sitting on her Shoulder. Before his Feet
there stood an
Altar
of a very odd Make, which, as I afterwards
found, was shaped in that manner to comply with the Inscription that
surrounded it. Upon the Altar there lay several Offerings of
Axes,
Wings
, and
Eggs
, cut in Paper, and inscribed with Verses. The
Temple was filled with Votaries, who applied themselves to different
Diversions, as their Fancies directed them. In one part of it I saw a
Regiment of
Anagrams
, who were continually in motion, turning to the
Right or to the Left, facing about, doubling their Ranks, shifting their
Stations, and throwing themselves into all the Figures and
Countermarches of the most changeable and perplexed Exercise.
Not far from these was a Body of
Acrosticks
, made up of very
disproportioned Persons. It was disposed into three Columns, the
Officers planting themselves in a Line on the left Hand of each Column.
The Officers were all of them at least Six Foot high, and made three
Rows of very proper Men; but the Common Soldiers, who filled up the
Spaces between the Officers, were such Dwarfs, Cripples, and Scarecrows,
that one could hardly look upon them without laughing. There were behind
the
Acrosticks
two or three Files of
Chronograms
, which
differed only from the former, as their Officers were equipped (like the
Figure of Time) with an Hour-glass in one Hand, and a Scythe in the
other, and took their Posts promiscuously among the private Men whom
they commanded.
In the Body of the Temple, and before the very Face of the Deity,
methought I saw the Phantom of
Tryphiodorus
the
Lipogrammatist
, engaged in a Ball with four and twenty Persons,
who pursued him by Turns thro' all the Intricacies and Labyrinths of a
Country Dance, without being able to overtake him.
Observing several to be very busie at the Western End of the
Temple
, I inquired into what they were doing, and found there was
in that Quarter the great Magazine of
Rebus's
. These were several
Things of the most different Natures tied up in Bundles, and thrown upon
one another in heaps like Faggots. You might behold an Anchor, a
Night-rail, and a Hobby-horse bound up together. One of the Workmen
seeing me very much surprized, told me, there was an infinite deal of
Wit in several of those Bundles, and that he would explain them to me if
I pleased; I thanked him for his Civility, but told him I was in very
great haste at that time. As I was going out of the Temple, I observed
in one Corner of it a Cluster of Men and Women laughing very heartily,
and diverting themselves at a Game of
Crambo
. I heard several
Double Rhymes
as I passed by them, which raised a great deal of
Mirth.
Not far from these was another Set of merry People engaged at a
Diversion, in which the whole Jest was to mistake one Person for
another. To give Occasion for these ludicrous Mistakes, they were
divided into Pairs, every Pair being covered from Head to Foot with the
same kind of Dress, though perhaps there was not the least Resemblance
in their Faces. By this means an old Man was sometimes mistaken for a
Boy, a Woman for a Man, and a Black-a-moor for an
European
, which
very often produced great Peals of Laughter. These I guessed to be a
Party of
Punns
. But being very desirous to get out of this World
of Magick, which had almost turned my Brain, I left the Temple, and
crossed over the Fields that lay about it with all the Speed I could
make. I was not gone far before I heard the Sound of Trumpets and
Alarms, which seemed to proclaim the March of an Enemy; and, as I
afterwards found, was in reality what I apprehended it. There appeared
at a great Distance a very shining Light, and, in the midst of it, a
Person of a most beautiful Aspect; her Name was
Truth
. On her right Hand
there marched a Male Deity, who bore several Quivers on his
Shoulders, — and grasped several Arrows in his Hand. His Name was
Wit
. The Approach of these two Enemies filled all the Territories
of
False Wit
with an unspeakable Consternation, insomuch that the
Goddess of those Regions appeared in Person upon her Frontiers, with the
several inferior Deities, and the different Bodies of Forces which I had
before seen in the Temple, who were now drawn up in Array, and prepared
to give their Foes a warm Reception. As the March of the Enemy was very
slow, it gave time to the several Inhabitants who bordered upon the
Regions
of
Falsehood
to draw their Forces into a Body, with a
Design to stand upon their Guard as Neuters, and attend the Issue of the
Combat.
I must here inform my Reader, that the Frontiers of the Enchanted
Region, which I have before described, were inhabited by the Species of
Mixed Wit
, who made a very odd Appearance when they were mustered
together in an Army. There were Men whose Bodies were stuck full of
Darts, and Women whose Eyes were Burning-glasses: Men that had Hearts of
Fire, and Women that had Breasts of Snow. It would be endless to
describe several Monsters of the like Nature, that composed this great
Army; which immediately fell asunder and divided itself into two Parts,
the one half throwing themselves behind the Banners of
Truth
, and the
others behind those of
Falsehood
.
The Goddess of
Falsehood
was of a Gigantick Stature, and advanced some
Paces before the Front of her Army: but as the dazling Light, which
flowed from
Truth
, began to shine upon her, she faded insensibly;
insomuch that in a little Space she looked rather like an huge Phantom,
than a real Substance. At length, as the Goddess of
Truth
approached
still nearer to her, she fell away entirely, and vanished amidst the
Brightness of her Presence; so that there did not remain the least Trace
or Impression of her Figure in the Place where she had been seen.
As at the rising of the Sun the Constellations grow thin, and the Stars
go out one after another, till the whole Hemisphere is extinguished;
such was the vanishing of the Goddess: And not only of the Goddess her
self, but of the whole Army that attended her, which sympathized with
their Leader, and shrunk into Nothing, in proportion as the Goddess
disappeared. At the same time the whole Temple sunk, the Fish betook
themselves to the Streams, and the wild Beasts to the Woods: The
Fountains recovered their Murmurs, the Birds their Voices, the Trees
their Leaves, the Flowers their Scents, and the whole Face of Nature its
true and genuine Appearance. Tho' I still continued asleep, I fancied my
self as it were awakened out of a Dream, when I saw this Region of
Prodigies restored to Woods and Rivers, Fields and Meadows.
Upon the removal of that wild Scene of Wonders, which had very much
disturbed my Imagination, I took a full Survey of the Persons of
Wit
and
Truth
; for indeed it was impossible to look upon the first, without
seeing the other at the same time. There was behind them a strong and
compact Body of Figures. The Genius of
Heroic Poetry
appeared
with a Sword in her Hand, and a Lawrel on her Head.
Tragedy
was
crowned with Cypress, and covered with Robes dipped in Blood.
Satyr
had Smiles in her Look, and a Dagger under her Garment.
Rhetorick
was known by her Thunderbolt; and
Comedy
by her
Mask. After several other Figures,
Epigram
marched up in the
Rear, who had been posted there at the Beginning of the Expedition, that
he might not revolt to the Enemy, whom he was suspected to favour in his
Heart. I was very much awed and delighted with the Appearance of the God
of
Wit
; there was something so amiable and yet so piercing in his
Looks, as inspired me at once with Love and Terror. As I was gazing on
him, to my unspeakable Joy, he took a Quiver of Arrows from his
Shoulder, in order to make me a Present of it; but as I was reaching out
my Hand to receive it of him, I knocked it against a Chair, and by that
means awaked.
C.
Scent bags. Ital. Polviglio; from Pulvillus, a little
cushion.
Contents
|
Monday, May 14, 1711 |
Steele |
... Hic vivimus Ambitiosa
Paupertate omnes ...
Juv.

The most improper things we commit in the Conduct of our Lives, we are
led into by the Force of Fashion. Instances might be given, in which a
prevailing Custom makes us act against the Rules of Nature, Law and
common Sense: but at present I shall confine my Consideration of the
Effect it has upon Men's Minds, by looking into our Behaviour when it is
the Fashion to go into Mourning. The Custom of representing the Grief we
have for the Loss of the Dead by our Habits, certainly had its Rise from
the real Sorrow of such as were too much distressed to take the proper
Care they ought of their Dress. By Degrees it prevailed, that such as
had this inward Oppression upon their Minds, made an Apology for not
joining with the rest of the World in their ordinary Diversions, by a
Dress suited to their Condition. This therefore was at first assumed by
such only as were under real Distress; to whom it was a Relief that they
had nothing about them so light and gay as to be irksome to the Gloom
and Melancholy of their inward Reflections, or that might misrepresent
them to others. In process of Time this laudable Distinction of the
Sorrowful was lost, and Mourning is now worn by Heirs and Widows.
see nothing but Magnificence and Solemnity in the Equipage of the
Relict, and an Air
of
Release from Servitude in the Pomp of a Son
who has lost a wealthy Father. This Fashion of Sorrow is now become a
generous Part of the Ceremonial between Princes and Sovereigns, who in
the Language of all Nations are stiled Brothers to each other, and put
on the Purple upon the Death of any Potentate with whom they live in
Amity. Courtiers, and all who wish themselves such, are immediately
seized with Grief from Head to Foot upon this Disaster to their Prince;
so that one may know by the very Buckles of a Gentleman-Usher, what
Degree of Friendship any deceased Monarch maintained with the Court to
which he belongs. A good Courtier's Habit and Behaviour is
hieroglyphical on these Occasions: He deals much in Whispers, and you
may see he dresses according to the best Intelligence.
The general Affectation among Men, of appearing greater than they are,
makes the whole World run into the Habit of the Court. You see the Lady,
who the Day before was as various as a Rainbow, upon the Time appointed
for beginning to mourn, as dark as a Cloud. This Humour does not prevail
only on those whose Fortunes can support any Change in their Equipage,
not on those only whose Incomes demand the Wantonness of new
Appearances; but on such also who have just enough to cloath them. An
old Acquaintance of mine, of Ninety Pounds a Year, who has naturally the
Vanity of being a Man of Fashion deep at his Heart, is very much put to
it to bear the Mortality of Princes.
made a new black Suit upon the
Death of the King of
Spain
, he turned it for the King of
Portugal
,
and he now keeps his Chamber while it is scouring for the Emperor
.
He is a good Œconomist in his Extravagance, and makes only a fresh
black Button upon his Iron-gray Suit for any Potentate of small
Territories; he indeed adds his Crape Hatband for a Prince whose
Exploits he has admired in the
Gazette.
But whatever Compliments may
be made on these Occasions, the true Mourners are the Mercers, Silkmen,
Lacemen and Milliners. A Prince of merciful and royal Disposition would
reflect with great Anxiety upon the Prospect of his Death, if he
considered what Numbers would be reduced to Misery by that Accident
only: He would think it of Moment enough to direct, that in the
Notification of his Departure, the Honour done to him might be
restrained to those of the Houshold of the Prince to whom it should be
signified. He would think a general Mourning to be in a less Degree the
same Ceremony which is practised in barbarous Nations, of killing their
Slaves to attend the Obsequies of their Kings.
I had been wonderfully at a Loss for many Months together, to guess at
the Character of a Man who came now and then to our Coffee-house: He
ever ended a News-paper with this Reflection,
Well, I see all the
Foreign Princes are in good Health
. If you asked, Pray, Sir, what says
the
Postman
from
Vienna
? he answered,
Make us thankful, the
German
Princes are all well
: What does he say from
Barcelona
?
He does not
speak but that the Country agrees very well with the new Queen
. After
very much Enquiry, I found this Man of universal Loyalty was a wholesale
Dealer in Silks and Ribbons: His Way is, it seems, if he hires a Weaver,
or Workman, to have it inserted in his Articles,
'That all this shall be
well and truly performed, provided no foreign Potentate shall depart
this Life within the Time above-mentioned.'
It happens in all publick
Mournings, that the many Trades which depend upon our Habits, are during
that Folly either pinched with present Want, or terrified with the
apparent Approach of it. All the Atonement which Men can make for wanton
Expences (which is a sort of insulting the Scarcity under which others
labour) is, that the Superfluities of the Wealthy give Supplies to the
Necessities of the Poor: but instead of any other Good arising from the
Affectation of being in courtly Habits of Mourning, all Order seems to
be destroyed by it; and the true Honour which one Court does to another
on that Occasion, loses its Force and Efficacy. When a foreign Minister
beholds the Court of a Nation (which flourishes in Riches and Plenty)
lay aside, upon the Loss of his Master, all Marks of Splendor and
Magnificence, though the Head of such a joyful People, he will conceive
greater Idea of the Honour done his Master, than when he sees the
Generality of the People in the same Habit. When one is afraid to ask
the Wife of a Tradesman whom she has lost of her Family; and after some
Preparation endeavours to know whom she mourns for; how ridiculous is it
to hear her explain her self, That we have lost one of the House of
Austria
! Princes are elevated so highly above the rest of Mankind,
that it is a presumptuous Distinction to take a Part in Honours done to
their Memories, except we have Authority for it, by being related in a
particular Manner to the Court which pays that Veneration to their
Friendship, and seems to express on such an Occasion the Sense of the
Uncertainty of human Life in general, by assuming the Habit of Sorrow
though in the full possession of Triumph and Royalty.
R.
of a
The death of Charles II of Spain, which gave occasion for
the general war of the Spanish succession, took place in 1700. John V,
King of Portugal, died in 1706, and the Emperor Joseph I died on the
17th of April, 1711, less than a month before this paper was written.
The black suit that was now 'scouring for the Emperor' was, therefore,
more than ten years old, and had been turned five years ago.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 15, 1711 |
Steele |
... Demetri teque Tigelli
Discipularum inter jubeo plorare cathedras.
Hor.

After having at large explained what Wit is, and described the false
Appearances of it, all that Labour seems but an useless Enquiry, without
some Time be spent in considering the Application of it. The Seat of
Wit, when one speaks as a Man of the Town and the World, is the
Play-house; I shall therefore fill this Paper with Reflections upon the
Use of it in that Place. The Application of Wit in the Theatre has as
strong an Effect upon the Manners of our Gentlemen, as the Taste of it
has upon the Writings of our Authors. It may, perhaps, look like a very
presumptuous Work, though not Foreign from the Duty of a
Spectator
, to
tax the Writings of such as have long had the general Applause of a
Nation; But I shall always make Reason, Truth, and Nature the Measures
of Praise and Dispraise; if those are for me, the Generality of Opinion
is of no Consequence against me; if they are against me, the general
Opinion cannot long support me.
Without further Preface, I am going to look into some of our most
applauded Plays, and see whether they deserve the Figure they at present
bear in the Imagination of Men, or not.
In reflecting upon these Works, I shall chiefly dwell upon that for
which each respective Play is most celebrated.
present Paper shall
be employed upon Sir
Fopling Flutter
. The received Character of
this Play is, That it is the Pattern of Genteel Comedy.
Dorimant
and
Harriot
are the Characters of greatest Consequence, and if these are
Low and Mean, the Reputation of the Play is very Unjust.
I will take for granted, that a fine Gentleman should be honest in his
Actions, and refined in his Language. Instead of this, our Hero in this
Piece is a direct Knave in his Designs, and a Clown in his Language.
Bellair
is his Admirer and Friend; in return for which, because he is
forsooth a greater Wit than his said Friend, he thinks it reasonable to
persuade him to marry a young Lady, whose Virtue, he thinks, will last
no longer than till she is a Wife, and then she cannot but fall to his
Share, as he is an irresistible fine Gentleman. The Falshood to Mrs.
Loveit
, and the Barbarity of Triumphing over her Anguish for losing
him, is another Instance of his Honesty, as well as his Good-nature. As
to his fine Language; he calls the Orange-Woman, who, it seems, is
inclined to grow Fat,
An Over-grown Jade, with a Flasket of Guts before
her
; and salutes her with a pretty Phrase of
How now, Double Tripe
?
Upon the mention of a Country Gentlewoman, whom he knows nothing of, (no
one can imagine why) he
will lay his Life she is some awkward
ill-fashioned Country Toad, who not having above four Dozen of Hairs on
her Head, has adorned her Baldness with a large white Fruz, that she may
look Sparkishly in the Forefront of the King's Box at an old Play
.
Unnatural Mixture of senseless Common-Place!
As to the Generosity of his Temper, he tells his poor Footman,
If he
did not wait better
— he would turn him away, in the insolent Phrase
of,
I'll uncase you
.
Now for Mrs.
Harriot
: She laughs at Obedience to an absent
Mother, whose Tenderness
Busie
describes to be very exquisite,
for
that she is so pleased with finding
Harriot
again, that she
cannot chide her for being out of the way
. This Witty Daughter, and
fine Lady, has so little Respect for this good Woman, that she Ridicules
her Air in taking Leave, and cries,
In what Struggle is my poor
Mother yonder? See, see, her Head tottering, her Eyes staring, and her
under Lip trembling
. But all this is atoned for, because
she has
more Wit than is usual in her Sex, and as much Malice, tho' she is as
Wild as you would wish her and has a Demureness in her Looks that makes
it so surprising!
Then to recommend her as a fit Spouse for his
Hero, the Poet makes her speak her Sense of Marriage very ingeniously:
I think
, says she,
I might be brought to endure him, and that
is all a reasonable Woman should expect in an Husband
. It is,
methinks, unnatural that we are not made to understand how she that was
bred under a silly pious old Mother, that would never trust her out of
her sight, came to be so Polite.
It cannot be denied, but that the Negligence of every thing, which
engages the Attention of the sober and valuable Part of Mankind, appears
very well drawn in this Piece: But it is denied, that it is necessary to
the Character of a Fine Gentleman, that he should in that manner trample
upon all Order and Decency. As for the Character of
Dorimant
, it
is more of a Coxcomb than that of
Fopling
. He says of one of his
Companions, that a good Correspondence between them is their mutual
Interest. Speaking of that Friend, he declares, their being much
together
makes the Women think the better of his Understanding, and
judge more favourably of my Reputation. It makes him pass upon some for
a Man of very good Sense, and me upon others for a very civil
Person
.
This whole celebrated Piece is a perfect Contradiction to good Manners,
good Sense, and common Honesty; and as there is nothing in it but what
is built upon the Ruin of Virtue and Innocence, according to the Notion
of Merit in this Comedy, I take the Shoemaker to be, in reality, the
Fine Gentleman of the Play: For it seems he is an Atheist, if we may
depend upon his Character as given by the Orange-Woman, who is her self
far from being the lowest in the Play. She says of a Fine Man who is
Dorimant's
Companion, There
is not such another Heathen in the Town,
except the Shoemaker
. His Pretension to be the Hero of the
Drama
appears still more in his own Description of his way of Living with his
Lady.
There is
, says he,
never a Man in Town lives more like a
Gentleman with his Wife than I do; I never mind her Motions; she never
enquires into mine. We speak to one another civilly, hate one another
heartily; and because it is Vulgar to Lye and Soak together, we have
each of us our several Settle-Bed
. That of
Soaking together
is as
good as if
Dorimant
had spoken it himself; and, I think, since he puts
Human Nature in as ugly a Form as the Circumstances will bear, and is a
staunch Unbeliever, he is very much Wronged in having no part of the
good Fortune bestowed in the last Act.
To speak plainly of this whole Work, I think nothing but being lost to a
sense of Innocence and Virtue can make any one see this Comedy, without
observing more frequent Occasion to move Sorrow and Indignation, than
Mirth and Laughter.
the same time I allow it to be Nature, but it is
Nature in its utmost Corruption and Degeneracy
.
R.
The Man of Mode
, or
Sir Fopling Flutter
, by Sir George
Etherege, produced in 1676. Etherege painted accurately the life and
morals of the Restoration, and is said to have represented himself in
Bellair; Beau Hewit, the son of a Herefordshire Baronet, in Sir Fopling;
and to have formed Dorimant upon the model of the Earl of Rochester.
To this number of the
Spectator
is appended the first
advertisement of Pope's
Essay on Criticism
.
This Day is publish'd An Essay on Criticism.
Printed for W. Lewis in Russell street Covent-Garden;
and Sold by W. Taylor, at the Ship in Pater Noster Row;
T. Osborn, in Gray's Inn near the Walks;
T. Graves, in St. James's Street;
and T. Morphew, near Stationers-Hall.
Price 1s.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 16, 1711 |
Steele |
Motus doceri gaudet Ionicos
Matura Virgo, et fingitur artubus
Jam nunc, et incestos amores
De Tenero meditatur Ungui.
Hor.

The two following Letters are upon a Subject of very great Importance,
tho' expressed without an Air of Gravity.
To the
Spectator.
Sir,
I Take the Freedom of asking your Advice in behalf of a Young
Country Kinswoman of mine who is lately come to Town, and under my
Care for her Education. She is very pretty, but you can't imagine how
unformed a Creature it is. She comes to my Hands just as Nature left
her, half-finished, and without any acquired Improvements. When I look
on her I often think of the
Belle Sauvage mentioned in one of your
Papers. Dear
Mr.
Spectator, help me to make her comprehend the
visible Graces of Speech, and the dumb Eloquence of Motion; for she is
at present a perfect Stranger to both. She knows no Way to express her
self but by her Tongue, and that always to signify her Meaning. Her
Eyes serve her yet only to see with, and she is utterly a Foreigner to
the Language of Looks and Glances. In this I fancy you could help her
better than any Body. I have bestowed two Months in teaching her to
Sigh when she is not concerned, and to Smile when she is not pleased;
and am ashamed to own she makes little or no Improvement. Then she is
no more able now to walk, than she was to go at a Year old. By Walking
you will easily know I mean that regular but easy Motion, which gives
our Persons so irresistible a Grace as if we moved to Musick, and is a
kind of disengaged Figure, or, if I may so speak, recitative Dancing.
But the want of this I cannot blame in her, for I find she has no Ear,
and means nothing by Walking but to change her Place. I could pardon
too her Blushing, if she knew how to carry her self in it, and if it
did not manifestly injure her Complexion.
They tell me you are a Person who have seen the World, and are a Judge
of fine Breeding; which makes me ambitious of some Instructions from
you for her Improvement: Which when you have favoured me with, I shall
further advise with you about the Disposal of this fair Forrester in
Marriage; for I will make it no Secret to you, that her Person and
Education are to be her Fortune.
I am,
Sir,
Your very humble Servant
Celimene.
Sir, Being employed by
Celimene to make up and send to you her
Letter, I make bold to recommend the Case therein mentioned to your
Consideration, because she and I happen to differ a little in our
Notions. I, who am a rough Man, am afraid the young Girl is in a fair
Way to be spoiled:
Therefore pray, Mr.
Spectator, let us have your
Opinion of this fine thing called
Fine Breeding; for I am afraid it
differs too much from that plain thing called
Good Breeding.
Your most humble Servant1.
The general Mistake among us in the Educating our Children, is, That
in our Daughters we take care of their Persons and neglect their
Minds: in our Sons we are so intent upon adorning their Minds, that we
wholly neglect their Bodies. It is from this that you shall see a
young Lady celebrated and admired in all the Assemblies about Town,
when her elder Brother is afraid to come into a Room. From this ill
Management it arises, That we frequently observe a Man's Life is half
spent before he is taken notice of; and a Woman in the Prime of her
Years is out of Fashion and neglected. The Boy I shall consider upon
some other Occasion, and at present stick to the Girl: And I am the
more inclined to this, because I have several Letters which complain
to me that my Female Readers have not understood me for some Days last
past, and take themselves to be unconcerned in the present Turn of my
Writings. When a Girl is safely brought from her Nurse, before she is
capable of forming one simple Notion of any thing in Life, she is
delivered to the Hands of her Dancing-Master; and with a Collar round
her Neck, the pretty wild Thing is taught a fantastical Gravity of
Behaviour, and forced to a particular Way of holding her Head, heaving
her Breast, and moving with her whole Body; and all this under Pain of
never having an Husband, if she steps, looks, or moves awry. This
gives the young Lady wonderful Workings of Imagination, what is to
pass between her and this Husband that she is every Moment told of,
and for whom she seems to be educated. Thus her Fancy is engaged to
turn all her Endeavours to the Ornament of her Person, as what must
determine her Good and Ill in this Life; and she naturally thinks, if
she is tall enough, she is wise enough for any thing for which her
Education makes her think she is designed. To make her an agreeable
Person is the main Purpose of her Parents; to that is all their Cost,
to that all their Care directed; and from this general Folly of
Parents we owe our present numerous Race of Coquets. These Reflections
puzzle me, when I think of giving my advice on the Subject of managing
the wild Thing mentioned in the Letter of my Correspondent. But sure
there is a middle Way to be followed; the Management of a young Lady's
Person is not to be overlooked, but the Erudition of her Mind is much
more to be regarded. According as this is managed, you will see the
Mind follow the Appetites of the Body, or the Body express the Virtues
of the Mind.
Cleomira
dances with all the Elegance of Motion imaginable; but
her Eyes are so chastised with the Simplicity and Innocence of her
Thoughts, that she raises in her Beholders Admiration and good Will,
but no loose Hope or wild Imagination. The true Art in this Case is,
To make the Mind and Body improve together; and if possible, to make
Gesture follow Thought, and not let Thought be employed upon Gesture
R.
John Hughes is the author of these two letters, and,
Chalmers thinks, also of the letters signed R. B. in Nos.
and
. He
was in 1711 thirty-two years old. John Hughes, the son of a citizen of
London, was born at Marlborough, educated at the private school of a
Dissenting minister, where he had Isaac Watts for schoolfellow, delicate
of health, zealous for poetry and music, and provided for by having
obtained, early in life, a situation in the Ordnance Office. He died of
consumption at the age of 40, February 17, 1719-20, on the night of the
first production of his Tragedy of
The Siege of Damascus
. Verse of his
was in his lifetime set to music by Purcell and Handel. In 1712 an opera
of
Calypso and Telemachus
, to which Hughes wrote the words, was
produced with success at the Haymarket. In translations, in original
verse, and especially in prose, he merited the pleasant little
reputation that he earned; but his means were small until, not two years
before his death, Lord Cowper gave him the well-paid office of Secretary
to the Commissioners of the Peace. Steele has drawn the character of his
friend Hughes as that of a religious man exempt from every sensual vice,
an invalid who could take pleasure in seeing the innocent happiness of
the healthy, who was never peevish or sour, and who employed his
intervals of ease in drawing and designing, or in music and poetry.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 17, 1711 |
Budgell1 |
Saltare elegantius quam necesse est probæ.
Sal.

, in one of his
Dialogues
, introduces a Philosopher chiding his
Friend for his being a Lover of Dancing, and a Frequenter of Balls
.
The other undertakes the Defence of his Favourite Diversion, which, he
says, was at first invented by the Goddess
Rhea
, and preserved the
Life of
Jupiter
himself, from the Cruelty of his Father
Saturn.
He
proceeds to shew, that it had been Approved by the greatest Men in all
Ages; that
Homer
calls
Merion
a
Fine Dancer;
and says, That the
graceful Mien and great Agility which he had acquired by that Exercise,
distinguished him above the rest in the Armies, both of
Greeks
and
Trojans
.
He adds, that
Pyrrhus
gained more Reputation by Inventing the Dance
which is called after his Name, than by all his other Actions: That the
Lacedæmonians
, who were the bravest People in
Greece
, gave
great Encouragement to this Diversion, and made their
Hormus
(a
Dance much resembling the
French Brawl
) famous over all
Asia
: That there were still extant some
Thessalian
Statues
erected to the Honour of their best Dancers: And that he wondered how
his Brother Philosopher could declare himself against the Opinions of
those two Persons, whom he professed so much to admire,
Homer
and
Hesiod
; the latter of which compares Valour and Dancing together;
and says, That
the Gods have bestowed Fortitude on some Men, and on
others a Disposition for Dancing
.
Lastly, he puts him in mind that
Socrates
, (who, in the Judgment
of
Apollo
, was the wisest of Men) was not only a professed
Admirer of this Exercise in others, but learned it himself when he was
an old Man.
The Morose Philosopher is so much affected by these, and some other
Authorities, that he becomes a Convert to his Friend, and desires he
would take him with him when he went to his next Ball.
I love to shelter my self under the Examples of Great Men; and, I think,
I have sufficiently shewed that it is not below the Dignity of these my
Speculations to take notice of the following Letter, which, I suppose,
is sent me by some substantial Tradesman about
Change
.
Sir,
'I am a Man in Years, and by an honest Industry in the World have
acquired enough to give my Children a liberal Education, tho' I was an
utter Stranger to it my self. My eldest Daughter, a Girl of Sixteen,
has for some time been under the Tuition of Monsieur
Rigadoon,
a Dancing-Master in the City; and I was prevailed upon by her and her
Mother to go last Night to one of his Balls. I must own to you, Sir,
that having never been at any such Place before, I was very much
pleased and surprized with that Part of his Entertainment which he
called
French Dancing. There were several young Men and Women,
whose Limbs seemed to have no other Motion, but purely what the Musick
gave them. After this Part was over, they began a Diversion which they
call
Country Dancing, and wherein there were also some things
not disagreeable, and divers
Emblematical Figures, Compos'd, as
I guess, by Wise Men, for the Instruction of Youth.
Among the rest, I observed one, which, I think, they call
Hunt the
Squirrel, in which while the Woman flies the Man pursues her; but
as soon as she turns, he runs away, and she is obliged to follow.
The Moral of this Dance does, I think, very aptly recommend Modesty
and Discretion to the Female Sex.
But as the best Institutions are liable to Corruptions, so, Sir, I
must acquaint you, that very great Abuses are crept into this
Entertainment. I was amazed to see my Girl handed by, and handing
young Fellows with so much Familiarity; and I could not have thought
it had been in the Child. They very often made use of a most impudent
and lascivious Step called
Setting, which I know not how to describe
to you, but by telling you that it is the very reverse of
Back to
Back.
At last an impudent young Dog bid the Fidlers play a Dance
called
Mol Patley3, and after having made two or three Capers, ran
to his Partner, locked his Arms in hers, and whisked her round
cleverly above Ground in such manner, that I, who sat upon one of the
lowest Benches, saw further above her Shoe than I can think fit to
acquaint you with. I could no longer endure these Enormities;
wherefore just as my Girl was going to be made a Whirligig, I ran in,
seized on the Child, and carried her home.
Sir, I am not yet old enough to be a Fool. I suppose this Diversion
might be at first invented to keep up a good Understanding between
young Men and Women, and so far I am not against it; but I shall never
allow of these things. I know not what you will say to this Case at
present, but am sure that had you been with me you would have seen
matter of great Speculation.
I am
Yours, &c.
I must confess I am afraid that my Correspondent had too much Reason to
be a little out of Humour at the Treatment of his Daughter, but I
conclude that he would have been much more so, had he seen one of those
kissing Dances
in which
Will. Honeycomb
assures me they are obliged to
dwell almost a Minute on the Fair One's Lips, or they will be too quick
for the Musick, and dance quite out of Time.
am not able however to give my final Sentence against this Diversion;
and am of Mr.
Cowley's
Opinion
, that so much of Dancing at least
as belongs to the Behaviour and an handsome Carriage of the Body, is
extreamly useful, if not absolutely necessary.
We generally form such Ideas of People at first Sight, as we are hardly
ever persuaded to lay aside afterwards: For this Reason, a Man would
wish to have nothing disagreeable or uncomely in his Approaches, and to
be able to enter a Room with a good Grace.
I might add, that a moderate Knowledge in the little Rules of
Good-breeding gives a Man some Assurance, and makes him easie in all
Companies. For want of this, I have seen a Professor of a Liberal
Science at a Loss to salute a Lady; and a most excellent Mathematician
not able to determine whether he should stand or sit while my Lord drank
to him.
It is the proper Business of a Dancing-Master to regulate these Matters;
tho' I take it to be a just Observation, that unless you add something
of your own to what these fine Gentlemen teach you, and which they are
wholly ignorant of themselves, you will much sooner get the Character of
an Affected Fop, than of a Well-bred Man.
As for
Country Dancing
, it must indeed be confessed, that the great
Familiarities between the two Sexes on this Occasion may sometimes
produce very dangerous Consequences; and I have often thought that few
Ladies Hearts are so obdurate as not to be melted by the Charms of
Musick, the Force of Motion, and an handsome young Fellow who is
continually playing before their Eyes, and convincing them that he has
the perfect Use of all his Limbs.
But as this kind of Dance is the particular Invention of our own
Country, and as every one is more or less a Proficient in it, I would
not Discountenance it; but rather suppose it may be practised innocently
by others, as well as myself, who am often Partner to my Landlady's
Eldest Daughter.
Postscript
Having heard a good Character of the Collection of Pictures which is to
be Exposed to Sale on
Friday
next; and concluding from the following
Letter, that the Person who Collected them is a Man of no unelegant
Taste, I will be so much his Friend as to Publish it, provided the
Reader will only look upon it as filling up the Place of an
Advertisement.
From the three Chairs in the Piazza, Covent-Garden.
May 16, 1711.
Sir
'As you are Spectator, I think we, who make it our Business to exhibit
any thing to publick View, ought to apply our selves to you for your
Approbation. I have travelled Europe to furnish out a Show for you,
and have brought with me what has been admired in every Country
through which I passed. You have declared in many Papers, that your
greatest Delights are those of the Eye, which I do not doubt but I
shall gratifie with as Beautiful Objects as yours ever beheld. If
Castles, Forests, Ruins, Fine Women, and Graceful Men, can please you,
I dare promise you much Satisfaction, if you will Appear at my Auction
on Friday next. A Sight is, I suppose, as grateful to a Spectator,
as a Treat to another Person, and therefore I hope you will pardon
this Invitation from,
Sir,
Your most Obedient
Humble Servant,
J. Graham.
Eustace Budgell, the contributor of this and of about three
dozen other papers to the
Spectator
, was, in 1711, twenty-six years
old, and by the death of his father, Gilbert Budgell, D.D., obtained, in
this year, encumbered by some debt, an income of £950. He was first
cousin to Addison, their mothers being two daughters of Dr. Nathaniel
Gulstone, and sisters to Dr. Gulstone, bishop of Bristol. He had been
sent in 1700 to Christ Church, Oxford, where he spent several years.
When, in 1709, Addison went to Dublin as secretary to Lord Wharton, in
his Irish administration, he took with him his cousin Budgell as a
private secretary. During Addison's first stay in Ireland Budgell lived
with him, and paid careful attention to his duties. To this relationship
and friendship Budgell was indebted for the insertion of papers of his
in the
Spectator
. Addison not only gratified his literary ambition,
but helped him to advancement in his service of the government. On the
accession of George I. Budgell was appointed Secretary to the Lords
Justices of Ireland and Deputy Clerk of the Council; was chosen also
Honorary Bencher of the Dublin Inns of Court and obtained a seat in the
Irish Parliament. In 1717, when Addison became Secretary of State for
Ireland, he appointed Eustace Budgell to the post of Accountant and
Comptroller-General of the Irish Revenue, which was worth nearly £400
a-year. In 1718, anger at being passed over in an appointment caused
Budgell to charge the Duke of Bolton, the newly-arrived Lord-Lieutenant,
with folly and imbecility. For this he was removed from his Irish
appointments. He then ruined his hope of patronage in England, lost
three-fourths of his fortune in the South Sea Bubble, and spent the
other fourth in a fruitless attempt to get into Parliament. While
struggling to earn bread as a writer, he took part in the publication of
Dr. Matthew Tindal's
Christianity as Old as the Creation
, and when, in
1733, Tindal died, a Will was found which, to the exclusion of a
favourite nephew, left £2100 (nearly all the property) to Budgell. The
authenticity of the Will was successfully contested, and thereby Budgell
disgraced. He retorted on Pope for some criticism upon this which he
attributed to him, and Pope wrote in the prologue to his Satires,
Let Budgell charge low Grub-street on my quill,
And write whate'er he please, — except my Will.
At last, in May, 1737, Eustace Budgell filled his pockets with stones,
hired a boat, and drowned himself by jumping from it as it passed under
London Bridge. There was left on his writing-table at home a slip of
paper upon which he had written,
'What Cato did, and Addison approved, cannot be wrong.'
The Dialogue
Of Dancing
between Lucian and Crato is here
quoted from a translation then just published in four volumes,
'of the
Works of Lucian, translated from the Greek by several Eminent Hands,
1711.'
The dialogue is in Vol. III, pp. 402-432, translated 'by Mr.
Savage of the Middle Temple.'
Moll Peatley
was a popular and vigorous dance, dating, at
least, from 1622.
In his scheme of a College and School, published in 1661,
as
a Proposition for the Advancement of Experimental Philosophy,
among
the ideas for training boys in the school is this, that
'in foul weather it would not be amiss for them to learn to Dance,
that is, to learn just so much (for all beyond is superfluous, if not
worse) as may give them a graceful comportment of their bodies.'
Contents
|
Friday, May 18, 1711 |
Addison |
Nos duo turba sumus ...
Ovid.

One would think that the larger the Company is, in which we are engaged,
the greater Variety of Thoughts and Subjects would be started in
Discourse; but instead of this, we find that Conversation is never so
much straightened and confined as in numerous Assemblies. When a
Multitude meet together upon any Subject of Discourse, their Debates are
taken up chiefly with Forms and general Positions; nay, if we come into
a more contracted Assembly of Men and Women, the Talk generally runs
upon the Weather, Fashions, News, and the like publick Topicks. In
Proportion as Conversation gets into Clubs and Knots of Friends, it
descends into Particulars, and grows more free and communicative: But
the most open, instructive, and unreserved Discourse, is that which
passes between two Persons who are familiar and intimate Friends. On
these Occasions, a Man gives a Loose to every Passion and every Thought
that is uppermost, discovers his most retired Opinions of Persons and
Things, tries the Beauty and Strength of his Sentiments, and exposes his
whole Soul to the Examination of his Friend.
Tully
was the first who observed, that Friendship improves Happiness
and abates Misery, by the doubling of our Joy and dividing of our Grief;
a Thought in which he hath been followed by all the Essayers upon
Friendship, that have written since his Time. Sir
Francis Bacon
has
finely described other Advantages, or, as he calls them, Fruits of
Friendship; and indeed there is no Subject of Morality which has been
better handled and more exhausted than this. Among the several fine
things which have been spoken of it, I shall beg leave to quote some out
of a very ancient Author, whose Book would be regarded by our Modern
Wits as one of the most shining Tracts of Morality that is extant, if it
appeared under the Name of a
Confucius
, or of any celebrated
Grecian
Philosopher: I mean the little Apocryphal Treatise entitled,
The Wisdom
of the Son of
Sirach. How finely has he described the Art of making
Friends, by an obliging and affable Behaviour? And laid down that
Precept which a late excellent Author has delivered as his own,
'
That we
should have many Well-wishers, but few 'Friends.'
Sweet Language will
multiply Friends; and a fair-speaking Tongue will increase kind
Greetings. Be in Peace with many, nevertheless have but one Counsellor
of a thousand1.
With what Prudence does he caution us in the Choice
of our Friends? And with what Strokes of Nature (I could almost say of
Humour) has he described the Behaviour of a treacherous and
self-interested Friend?
If thou wouldst get a Friend, prove him first,
and be not hasty to credit him: For some Man is a Friend for his own
Occasion, and will not abide in the Day of thy Trouble. And there is a
Friend, who being turned to Enmity and Strife will discover thy
Reproach.
Again,
Some Friend is a Companion at the Table, and will not
continue in the Day of thy Affliction: But in thy Prosperity he will be
as thy self, and will be bold over thy Servants. If thou be brought low
he will be against thee, and hide himself from thy Face.2
What can
be more strong and pointed than the following Verse?
Separate thy self
from thine Enemies, and take heed of thy Friends.
In the next Words he
particularizes one of those Fruits of Friendship which is described at
length by the two famous Authors above-mentioned, and falls into a
general Elogium of Friendship, which is very just as well as very
sublime.
A faithful Friend is a strong Defence; and he that hath found
such an one, hath found a Treasure. Nothing doth countervail a faithful
Friend, and his Excellency is unvaluable. A faithful Friend is the
Medicine of Life; and they that fear the Lord shall find him. Whoso
feareth the Lord shall direct his Friendship aright; for as he is, so
shall his Neighbour (that is, his Friend)
be also.3
I do not
remember to have met with any Saying that has pleased me more than that
of a Friend's being the Medicine of Life, to express the Efficacy of
Friendship in healing the Pains and Anguish which naturally cleave to
our Existence in this World; and am Wonderfully pleased with the Turn in
the last Sentence, That a virtuous Man shall as a Blessing meet with a
Friend who is as virtuous as himself. There is another Saying in the
same Author, which would have been very much admired in an Heathen
Writer;
Forsake not an old Friend, for the new is not comparable to
him: A new Friend is as new Wine; When it is old thou shalt drink it
with Pleasure.4
With what Strength of Allusion and Force of Thought,
has he described the Breaches and Violations of Friendship?
Whoso
casteth a Stone at the Birds frayeth them away; and he that upbraideth
his Friend, breaketh Friendship. Tho' thou drawest a Sword at a Friend
yet despair not, for there may be a returning to Favour: If thou hast
opened thy Mouth against thy Friend fear not, for there may be a
Reconciliation; except for Upbraiding, or Pride, or disclosing of
Secrets, or a treacherous Wound; for, for these things every Friend will
depart.5
We may observe in this and several other Precepts in this
Author, those little familiar Instances and Illustrations, which are so
much admired in the moral Writings of
Horace
and
Epictetus
. There
are very beautiful Instances of this Nature in the following Passages,
which are likewise written upon the same Subject:
Whoso discovereth
Secrets, loseth his Credit, and shall never find a Friend to his Mind.
Love thy Friend, and be faithful unto him; but if thou bewrayest his
Secrets, follow no more after him: For as a Man hath destroyed his
Enemy, so hast thou lost the Love of thy Friend; as one that letteth a
Bird go out of his Hand, so hast thou let thy Friend go, and shalt not
get him again: Follow after him no mere, for he is too far off; he is as
a Roe escaped out of the Snare. As for a Wound it may be bound up, and
after reviling there may be Reconciliation; but he that bewrayeth
Secrets, is without Hope.6
the several Qualifications of a good Friend, this wise Man has
very justly singled out Constancy and Faithfulness as the principal: To
these, others have added Virtue, Knowledge, Discretion, Equality in Age
and Fortune, and as
Cicero
calls it,
Morum Comitas
, a Pleasantness
of Temper
. If I were to give my Opinion upon such an exhausted
Subject, I should join to these other Qualifications a
certain.Æquability or Evenness of Behaviour. A Man often contracts a
Friendship with one whom perhaps he does not find out till after a
Year's Conversation; when on a sudden some latent ill Humour breaks out
upon him, which he never discovered or suspected at his first entering
into an Intimacy with him. There are several Persons who in some certain
Periods of their Lives are inexpressibly agreeable, and in others as
odious and detestable.
Martial
has given us a very pretty Picture of
one of this Species in the following Epigram:
Difficilis, facilis, jucundus, acerbus es idem,
Nec tecum possum vivere, nec sine te.
In all thy Humours, whether grave or mellow,
Thou'rt such a touchy, testy, pleasant Fellow;
Hast so much Wit, and Mirth, and Spleen about thee,
There is no living with thee, nor without thee.
It is very unlucky for a Man to be entangled in a Friendship with one,
who by these Changes and Vicissitudes of Humour is sometimes amiable and
sometimes odious: And as most Men are at some Times in an admirable
Frame and Disposition of Mind, it should be one of the greatest Tasks of
Wisdom to keep our selves well when we are so, and never to go out of
that which is the agreeable Part of our Character.
C.
Ecclesiasticus
vii. 5, 6.
Ecclesiasticus
vi. 7, and following verses.
Ecclesiasticus
vi. 15-18.
Ecclesiasticus
ix. 10.
Ecclesiasticus
ix, 20-22.
Ecclesiasticus
xxvii. 16, &c.
Cicero
de Amicitiâ
, and in the
De Officiis
he says
(Bk.II.),
'difficile dicta est, quantopere conciliet animos hominum comitas,
affabilitasque sermonia.'
Contents
|
Saturday, May 19, 1711 |
Addison |
Hic segetes, illic veniunt felicius uvæ:
Arborei fœtus alibi, atque injussa virescunt
Gramina. Nonne vides, croceos ut Tmolus odores,
India mittit ebur, molles sua thura Sabæi?
At Chalybes nudi ferrum, virosaque Pontus
Castorea, Eliadum palmas Epirus equarum?
Continuo has leges æternaque fœdera certis
Imposuit Natura locis ...
Virg.

There is no Place in the Town which I so much love to frequent as the
Royal-Exchange
. It gives me a secret Satisfaction, and in some
measure, gratifies my Vanity, as I am an
Englishman
, to see so rich an
Assembly of Countrymen and Foreigners consulting together upon the
private Business of Mankind, and making this Metropolis a kind of
Emporium
for the whole Earth. I must confess I look upon High-Change
to be a great Council, in which all considerable Nations have their
Representatives. Factors in the Trading World are what Ambassadors are
in the Politick World; they negotiate Affairs, conclude Treaties, and
maintain a good Correspondence between those wealthy Societies of Men
that are divided from one another by Seas and Oceans, or live on the
different Extremities of a Continent. I have often been pleased to hear
Disputes adjusted between an Inhabitant of
Japan
and an Alderman of
London
, or to see a Subject of the
Great Mogul
entering into a
League with one of the
Czar of Muscovy
. I am infinitely delighted in
mixing with these several Ministers of Commerce, as they are
distinguished by their different Walks and different Languages:
Sometimes I am justled among a Body of
Armenians
; Sometimes I am lost
in a Crowd of
Jews
; and sometimes make one in a Groupe of
Dutchmen
.
I am a
Dane
,
Swede
, or
Frenchman
at different times; or rather
fancy my self like the old Philosopher, who upon being asked what
Countryman he was, replied, That he was a Citizen of the World.
Though I very frequently visit this busie Multitude of People, I am
known to no Body there but my Friend, Sir
Andrew
, who often smiles upon
me as he sees me bustling in the Crowd, but at the same time connives at
my Presence without taking any further Notice of me.
is indeed a
Merchant of
Egypt
, who just knows me by sight, having formerly
remitted me some Mony to
Grand Cairo
; but as I am not versed in
the Modern
Coptick
, our Conferences go no further than a Bow and a
Grimace.
This grand Scene of Business gives me an infinite Variety of solid and
substantial Entertainments. As I am a great Lover of Mankind, my Heart
naturally overflows with Pleasure at the sight of a prosperous and happy
Multitude, insomuch that at many publick Solemnities I cannot forbear
expressing my Joy with Tears that have stolen down my Cheeks. For this
Reason I am wonderfully delighted to see such a Body of Men thriving in
their own private Fortunes, and at the same time promoting the Publick
Stock; or in other Words, raising Estates for their own Families, by
bringing into their Country whatever is wanting, and carrying out of it
whatever is superfluous.
Nature seems to have taken a particular Care to disseminate her
Blessings among the different Regions of the World, with an Eye to this
mutual Intercourse and Traffick among Mankind, that the Natives of the
several Parts of the Globe might have a kind of Dependance upon one
another, and be united together by their common Interest. Almost every
Degree
produces something peculiar to it. The Food often grows in one
Country, and the Sauce in another. The Fruits of
Portugal
are
corrected by the Products of
Barbadoes:
The Infusion of a
China
Plant sweetned with the Pith of an
Indian
Cane. The
Philippick
Islands give a Flavour to our
European
Bowls. The single Dress of a
Woman of Quality is often the Product of a hundred Climates. The Muff
and the Fan come together from the different Ends of the Earth. The
Scarf is sent from the Torrid Zone, and the Tippet from beneath the
Pole. The Brocade Petticoat rises out of the Mines of
Peru
, and the
Diamond Necklace out of the Bowels of
Indostan
.
If we consider our own Country in its natural Prospect, without any of
the Benefits and Advantages of Commerce, what a barren uncomfortable
Spot of Earth falls to our Share!
Historians tell us, that no
Fruit grows Originally among us, besides Hips and Haws, Acorns and
Pig-Nutts, with other Delicates of the like Nature; That our Climate of
itself, and without the Assistances of Art, can make no further Advances
towards a Plumb than to a Sloe, and carries an Apple to no greater a
Perfection than a Crab: That
our
Melons, our Peaches, our Figs,
our Apricots, and Cherries, are Strangers among us, imported in
different Ages, and naturalized in our
English
Gardens; and that they
would all degenerate and fall away into the Trash of our own Country, if
they were wholly neglected by the Planter, and left to the Mercy of our
Sun and Soil. Nor has Traffick more enriched our Vegetable World, than
it has improved the whole Face of Nature among us. Our Ships are laden
with the Harvest of every Climate: Our Tables are stored with Spices,
and Oils, and Wines: Our Rooms are filled with Pyramids of
China
, and
adorned with the Workmanship of
Japan
: Our Morning's Draught comes to
us from the remotest Corners of the Earth: We repair our Bodies by the
Drugs of
America
, and repose ourselves under
Indian
Canopies. My
Friend Sir
Andrew
calls the Vineyards of
France
our Gardens; the
Spice-Islands our Hot-beds; the
Persians
our Silk-Weavers, and the
Chinese
our Potters. Nature indeed furnishes us with the bare
Necessaries of Life, but Traffick gives us greater Variety of what is
Useful, and at the same time supplies us with every thing that is
Convenient and Ornamental.
is it the least Part of this our
Happiness, that whilst we enjoy the remotest Products of the North and
South, we are free from those Extremities of Weather
which
give
them Birth; That our Eyes are refreshed with the green Fields of
Britain
, at the same time that our Palates are feasted with Fruits
that rise between the Tropicks.
For these Reasons there are no more useful Members in a Commonwealth
than Merchants. They knit Mankind together in a mutual Intercourse of
good Offices, distribute the Gifts of Nature, find Work for the Poor,
add Wealth to the Rich, and Magnificence to the Great. Our
English
Merchant converts the Tin of his own Country into Gold, and exchanges
his Wool for Rubies. The
Mahometans
are clothed in our
British
Manufacture, and the Inhabitants of the frozen Zone warmed with the
Fleeces of our Sheep.
When I have been upon the
'Change
, I have often fancied one of our old
Kings standing in Person, where he is represented in Effigy, and looking
down upon the wealthy Concourse of People with which that Place is every
Day filled. In this Case, how would he be surprized to hear all the
Languages of
Europe
spoken in this little Spot of his former
Dominions, and to see so many private Men, who in his Time would have
been the Vassals of some powerful Baron, negotiating like Princes for
greater Sums of Mony than were formerly to be met with in the Royal
Treasury! Trade, without enlarging the
British
Territories, has given
us a kind of additional Empire: It has multiplied the Number of the
Rich, made our Landed Estates infinitely more Valuable than they were
formerly, and added to them an Accession of other Estates as Valuable as
the Lands themselves.
C.
A reference to the
Spectator's
voyage to Grand Cairo
mentioned in
"these Fruits, in their present State, as well as our"
that
Contents
|
Monday, May 21, 1711 |
Addison |
Interdum vulgus rectum videt.
Hor.

When I travelled, I took a particular Delight in hearing the Songs and
Fables that are come from Father to Son, and are most in Vogue among the
common People of the Countries through which I passed; for it is
impossible that any thing should be universally tasted and approved by a
Multitude, tho' they are only the Rabble of a Nation, which hath not in
it some peculiar Aptness to please and gratify the Mind of Man. Human
Nature is the same in all reasonable Creatures; and whatever falls in
with it, will meet with Admirers amongst Readers of all Qualities and
.
Molière
, as we are told by Monsieur
Boileau
, used to
read all his Comedies to
an
old Woman
who
was his
Housekeeper, as she sat with him at her Work by the Chimney-Corner; and
could foretel the Success of his Play in the Theatre, from the Reception
it met at his Fire-side: For he tells us the Audience always followed
the old Woman, and never failed to laugh in the same Place
.
I know nothing which more shews the essential and inherent Perfection of
Simplicity of Thought, above that which I call the Gothick Manner in
Writing, than this, that the first pleases all Kinds of Palates, and the
latter only such as have formed to themselves a wrong artificial Taste
upon little fanciful Authors and Writers of Epigram.
Homer
,
Virgil
,
or
Milton
, so far as the Language of their Poems is understood, will
please a Reader of plain common Sense, who would neither relish nor
comprehend an Epigram of
Martial
, or a Poem of
Cowley
: So, on the
contrary, an ordinary Song or Ballad that is the Delight of the common
People, cannot fail to please all such Readers as are not unqualified
for the Entertainment by their Affectation or Ignorance; and the Reason
is plain, because the same Paintings of Nature which recommend it to the
most ordinary Reader, will appear Beautiful to the most refined.
The old Song of
Chevey Chase
is the favourite Ballad of the common
People of
England
; and
Ben Johnson
used to say he had rather have
been the Author of it than of all his Works.
Philip Sidney
in his
Discourse of Poetry
speaks of it in the following Words;
I never
heard the old Song of Piercy and Douglas, that I found not my Heart
more moved than with a Trumpet; and yet it is sung by some blind Crowder
with no rougher Voice than rude Stile; which being so evil apparelled in
the Dust and Cobweb of that uncivil Age, what would it work trimmed in
the gorgeous Eloquence of Pindar?
For my own part I am so professed an
Admirer of this antiquated Song, that I shall give my Reader a Critick
upon it, without any further Apology for so doing.
The greatest Modern Criticks have laid it down as a Rule, that an
Heroick Poem should be founded upon some important Precept of Morality,
adapted to the Constitution of the Country in which the Poet writes.
Homer
and
Virgil
have formed their Plans in this View. As
Greece
was a Collection of many Governments, who suffered very much among
themselves, and gave the
Persian
Emperor, who was their common Enemy,
many Advantages over them by their mutual Jealousies and Animosities,
Homer
, in order to establish among them an Union, which was so
necessary for their Safety, grounds his Poem upon the Discords of the
several
Grecian
Princes who were engaged in a Confederacy against an
Asiatick
Prince, and the several Advantages which the Enemy gained by
such their Discords.
the Time the Poem we are now treating of was
written, the Dissentions of the Barons, who were then so many petty
Princes, ran very high, whether they quarrelled among themselves, or
with their Neighbours, and produced unspeakable Calamities to the
Country
: The Poet, to deter Men from such unnatural Contentions,
describes a bloody Battle and dreadful Scene of Death, occasioned by the
mutual Feuds which reigned in the Families of an
English
and
Scotch
Nobleman: That he designed this for the Instruction of his Poem, we may
learn from his four last Lines, in which, after the Example of the
modern Tragedians, he draws from it a Precept for the Benefit of his
Readers.
God save the King, and bless the Land
In Plenty, Joy, and Peace;
And grant henceforth that foul Debate
'Twixt Noblemen may cease.
The next Point observed by the greatest Heroic Poets, hath been to
celebrate Persons and Actions which do Honour to their Country: Thus
Virgil's
Hero was the Founder of
Rome
,
Homer's
a Prince of
Greece
; and for this Reason
Valerius Flaccus
and
Statius
, who were
both
Romans
, might be justly derided for having chosen the Expedition
of the
Golden Fleece
, and the
Wars of Thebes
for the Subjects of
their Epic Writings.
The Poet before us has not only found out an Hero in his own Country,
but raises the Reputation of it by several beautiful Incidents.
English
are the first
who
take the Field, and the last
who
quit it. The
English
bring only Fifteen hundred to the Battle, the
Scotch
Two thousand. The
English
keep the Field with Fifty three:
The
Scotch
retire with Fifty five: All the rest on each side being
slain in Battle.
the most remarkable Circumstance of this kind, is
the different Manner in which the
Scotch
and
English
Kings
receive
the News of this Fight, and of the great Men's Deaths who commanded
in it.
This News was brought to Edinburgh,
Where Scotland's King did reign,
That brave Earl Douglas suddenly
Was with an Arrow slain.
O heavy News, King James did say,
Scotland can Witness be,
I have not any Captain more
Of such Account as he.
Like Tydings to King Henry came
Within as short a Space,
That Piercy of Northumberland
Was slain in Chevy-Chase.
Now God be with him, said our King,
Sith 'twill no better be,
I trust I have within my Realm
Five hundred as good as he.
Yet shall not Scot nor Scotland say
But I will Vengeance take,
And be revenged on them all
For brave Lord Piercy's Sake.
This Vow full well the King performed
After on Humble-down,
In one Day fifty Knights were slain,
With Lords of great Renown.
And of the rest of small Account
Did many Thousands dye, &c.
At the same time that our Poet shews a laudable Partiality to his
Countrymen, he represents the
Scots
after a Manner not unbecoming so
bold and brave a People.
Earl Douglas on a milk-white Steed,
Most like a Baron bold,
Rode foremost of the Company
Whose Armour shone like Gold.
His Sentiments and Actions are every Way suitable to an Hero.
of us
two, says he, must dye: I am an Earl as well as your self, so that you
can have no Pretence for refusing the Combat: However, says he, 'tis
Pity, and indeed would be a Sin, that so many innocent Men should perish
for our sakes, rather let you and I end our Quarrel
in single Fight.
Ere thus I will out-braved be,
One of us two shall dye;
I know thee well, an Earl thou art,
Lord Piercy, so am I.
But trust me, Piercy, Pity it were,
And great Offence, to kill
Any of these our harmless Men,
For they have done no Ill.
Let thou and I the Battle try,
And set our Men aside;
Accurst be he, Lord Piercy said,
By whom this is deny'd.
When these brave Men had distinguished themselves in the Battle and a
single Combat with each other, in the Midst of a generous Parly, full of
heroic Sentiments, the
Scotch
Earl falls; and with his dying Words
encourages his Men to revenge his Death, representing to them, as the
most bitter Circumstance of it, that his Rival saw him fall.
With that there came an Arrow keen
Out of an English Bow,
Which struck Earl Douglas to the Heart
A deep and deadly Blow.
Who never spoke more Words than these,
Fight on, my merry Men all,
For why, my Life is at an End,
Lord Piercy sees my Fall.
Merry Men
, in the Language of those Times, is no more than a cheerful
Word for Companions and Fellow-Soldiers. A Passage in the Eleventh Book
of
Virgil's Æneid
is very much to be admired, where
Camilla
in her
last Agonies instead of weeping over the Wound she had received, as one
might have expected from a Warrior of her Sex, considers only (like the
Hero of whom we are now speaking) how the Battle should be continued
after her Death.
Tum sic exspirans, &c.
A gathering Mist overclouds her chearful Eyes;
And from her Cheeks the rosie Colour flies.
Then turns to her, whom, of her Female Train,
She trusted most, and thus she speaks with Pain.
Acca, 'tis past! He swims before my Sight,
Inexorable Death; and claims his Right.
Bear my last Words to Turnus, fly with Speed,
And bid him timely to my Charge succeed;
Repel the Trojans, and the Town relieve:
Farewel ...
Turnus
did not die in so heroic a Manner; tho' our Poet seems to
have had his Eye upon
Turnus's
Speech in the last Verse,
Lord Piercy sees my Fall.
... Vicisti, et victum tendere palmas
Ausonii videre ...
Earl
Piercy's
Lamentation over his Enemy is generous, beautiful,
and passionate; I must only caution the Reader not to let the Simplicity
of the Stile, which one may well pardon in so old a Poet, prejudice him
against the Greatness of the Thought.
Then leaving Life, Earl Piercy took
The dead Man by the Hand,
And said, Earl Douglas, for thy Life
Would I had lost my Land.
O Christ! my very heart doth bleed
With Sorrow for thy Sake;
For sure a more renowned Knight
Mischance did never take.
That beautiful Line,
Taking the dead Man by the Hand
, will put
the Reader in mind of
Æneas's
Behaviour towards
Lausus
,
whom he himself had slain as he came to the Rescue of his aged Father.
At vero ut vultum vidit morientis, et ora,
Ora modis Anchisiades, pallentia miris;
Ingemuit, miserans graviter, dextramque tetendit, &c.
The pious Prince beheld young Lausus dead;
He grieved, he wept; then grasped his Hand, and said,
Poor hapless Youth! What Praises can be paid
To worth so great ...
I shall take another Opportunity to consider the other Part of this old
Song.
a little
that
Besides the old woman, Molière is said to have relied on
the children of the Comedians, read his pieces to them, and corrected
passages at which they did not show themselves to be amused.
Defence of Poesy.
The author of
Chevy Chase
was not contemporary with the
dissensions of the Barons, even if the ballad of the
Hunting of the
Cheviot
was a celebration of the Battle of Otterbourne, fought in 1388,
some 30 miles from Newcastle. The battle of Chevy Chase, between the
Percy and the Douglas, was fought in Teviotdale, and the ballad which
moved Philip Sidney's heart was written in the fifteenth century. It may
have referred to a Battle of Pepperden, fought near the Cheviot Hills,
between the Earl of Northumberland and Earl William Douglas of Angus, in
1436. The ballad quoted by Addison is not that of which Sidney spoke,
but a version of it, written after Sidney's death, and after the best
plays of Shakespeare had been written.
that
that
received
by a single Combat.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 22, 1711 |
Steele |
... Scribere jussit Amor.
Ovid.

The entire Conquest of our Passions is so difficult a Work, that they
who despair of it should think of a less difficult Task, and only
attempt to Regulate them. But there is a third thing which may
contribute not only to the Ease, but also to the Pleasure of our Life;
and that is refining our Passions to a greater Elegance, than we receive
them from Nature. When the Passion is Love, this Work is performed in
innocent, though rude and uncultivated Minds, by the mere Force and
Dignity of the Object. There are Forms which naturally create Respect in
the Beholders, and at once Inflame and Chastise the Imagination. Such an
Impression as this gives an immediate Ambition to deserve, in order to
please. This Cause and Effect are beautifully described by Mr.
Dryden
in the Fable of
Cymon
and
Iphigenia
. After
he has represented
Cymon
so stupid, that
He Whistled as he went, for want of Thought,
he makes him fall into the following Scene, and shews its Influence upon
him so excellently, that it appears as Natural as Wonderful.
It happen'd on a Summer's Holiday,
That to the Greenwood-shade he took his Way;
His Quarter-staff, which he cou'd ne'er forsake,
Hung half before, and half behind his Back.
He trudg'd along unknowing what he sought,
And whistled as he went, for want of Thought.
By Chance conducted, or by Thirst constrain'd,
The deep recesses of the Grove he gain'd;
Where in a Plain, defended by the Wood,
Crept thro' the matted Grass a Crystal Flood,
By which an Alabaster Fountain stood:
And on the Margin of the Fount was laid,
(Attended by her Slaves) a sleeping Maid,
Like Dian,
and her Nymphs, when, tir'd with Sport,
To rest by cool Eurotas
they resort:
The Dame herself the Goddess well expressed,
Not more distinguished by her Purple Vest,
Than by the charming Features of her Face,
And even in Slumber a superior Grace:
Her comely Limbs composed with decent Care,
Her Body shaded with a slight Cymarr;
Her Bosom to the View was only bare:1
...
The fanning Wind upon her Bosom blows,
To meet the fanning Wind the Bosom rose;
The fanning Wind and purling Streams continue her Repose.
The Fool of Nature stood with stupid Eyes
And gaping Mouth, that testify'd Surprize,
Fix'd on her Face, nor could remove his Sight,
New as he was to Love, and Novice in Delight:
Long mute he stood, and leaning on his Staff,
His Wonder witness'd with an Idiot Laugh;
Then would have spoke, but by his glimmering Sense
First found his want of Words, and fear'd Offence:
Doubted for what he was he should be known,
By his Clown-Accent, and his Country Tone.
lest this fine Description should be excepted against, as the
Creation of that great Master, Mr.
Dryden
, and not an Account of
what has really ever happened in the World; I shall give you,
verbatim
, the Epistle of an enamoured Footman in the Country to
his Mistress
. Their Sirnames shall not be inserted, because their
Passion demands a greater Respect than is due to their Quality.
James
is Servant in a great Family, and Elizabeth waits upon the
Daughter of one as numerous, some Miles off of her Lover.
James
,
before he beheld
Betty
, was vain of his Strength, a rough
Wrestler, and quarrelsome Cudgel-Player;
Betty
a Publick Dancer
at Maypoles, a Romp at Stool-Ball: He always following idle Women, she
playing among the Peasants: He a Country Bully, she a Country Coquet.
But Love has made her constantly in her Mistress's Chamber, where the
young Lady gratifies a secret Passion of her own, by making
Betty
talk of
James
; and
James
is become a constant Waiter near
his Master's Apartment, in reading, as well as he can, Romances. I
cannot learn who
Molly
is, who it seems walked Ten Mile to carry
the angry Message, which gave Occasion to what follows.
To Elizabeth ...
My Dear Betty, May 14, 1711.
Remember your bleeding Lover,
who lies bleeding at the ...
Where two beginning Paps were scarcely spy'd,
For yet their Places were but signify'd.
Wounds Cupid made with the Arrows he borrowed at the Eyes of
Venus, which is your sweet Person.
Nay more, with the Token you sent me for my Love and Service offered
to your sweet Person; which was your base Respects to my ill
Conditions; when alas! there is no ill Conditions in me, but quite
contrary; all Love and Purity, especially to your sweet Person; but
all this I take as a Jest.
But the sad and dismal News which Molly brought me, struck me
to the Heart, which was, it seems, and is your ill Conditions for my
Love and Respects to you.
For she told me, if I came Forty times to you, you would not speak
with me, which Words I am sure is a great Grief to me.
Now, my Dear, if I may not be permitted to your sweet Company, and to
have the Happiness of speaking with your sweet Person, I beg the
Favour of you to accept of this my secret Mind and Thoughts, which
hath so long lodged in my Breast; the which if you do not accept, I
believe will go nigh to break my Heart.
For indeed, my Dear, I Love you above all the Beauties I ever saw in
all my Life.
The young Gentleman, and my Masters Daughter, the Londoner that
is come down to marry her, sat in the Arbour most part of last Night.
Oh! dear Betty, must the Nightingales sing to those who marry
for Mony, and not to us true Lovers! Oh my dear Betty, that we
could meet this Night where we used to do in the Wood!
Now, my Dear, if I may not have the Blessing of kissing your sweet
Lips, I beg I may have the Happiness of kissing your fair Hand, with a
few Lines from your dear self, presented by whom you please or think
fit. I believe, if Time would permit me, I could write all Day; but
the Time being short, and Paper little, no more from your
never-failing Lover till Death, James ...
Poor James! Since his Time and Paper were so short; I, that have more
than I can use well of both, will put the Sentiments of his kind Letter
(the Stile of which seems to be confused with Scraps he had got in
hearing and reading what he did not understand) into what he meant to
express.
Dear Creature, Can you then neglect him who has forgot all his
Recreations and Enjoyments, to pine away his Life in thinking of you?
When I do so, you appear more amiable to me than Venus does in
the most beautiful Description that ever was made of her. All this
Kindness you return with an Accusation, that I do not love you: But
the contrary is so manifest, that I cannot think you in earnest. But
the Certainty given me in your Message by Molly, that you do
not love me, is what robs me of all Comfort. She says you will not see
me: If you can have so much Cruelty, at least write to me, that I may
kiss the Impression made by your fair Hand. I love you above all
things, and, in my Condition, what you look upon with Indifference is
to me the most exquisite Pleasure or Pain. Our young Lady, and a fine
Gentleman from London, who are to marry for mercenary Ends,
walk about our Gardens, and hear the Voice of Evening Nightingales, as
if for Fashion-sake they courted those Solitudes, because they have
heard Lovers do so. Oh Betty! could I hear these Rivulets
murmur, and Birds sing while you stood near me, how little sensible
should I be that we are both Servants, that there is anything on Earth
above us. Oh! I could write to you as long as I love you, till Death
it self.
James.
N.B.
By the Words
Ill-Conditions
, James means in a Woman
Coquetry
, in a Man
Inconstancy
.
R.
The next couplet Steele omits:
James Hirst, a servant to the Hon. Edward Wortley (who was
familiar with Steele, and a close friend of Addison's), by mistake gave
to his master, with a parcel of letters, one that he had himself written
to his sweetheart. Mr. Wortley opened it, read it, and would not return
it.
'No, James,' he said, 'you shall be a great man. This letter must
appear in the Spectator.'
And so it did. The end of the love story is
that Betty died when on the point of marriage to James, who, out of
love to her, married her sister.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 23, 1711 |
Addison |
... Genus immortale manet, multosque per annos
Stat fortuna Domus, et avi numerantur avorum.
Virg.

Having already given my Reader an Account of several extraordinary Clubs
both ancient and modern, I did not design to have troubled him with any
more Narratives of this Nature; but I have lately received Information
of a Club which I can call neither ancient nor modern, that I dare say
will be no less surprising to my Reader than it was to my self; for
which Reason I shall communicate it to the Publick as one of the
greatest Curiosities in its kind.
A Friend of mine complaining of a Tradesman who is related to him, after
having represented him as a very idle worthless Fellow, who neglected
his Family, and spent most of his Time over a Bottle, told me, to
conclude his Character, that he was a Member of the
Everlasting
Club
. So very odd a Title raised my Curiosity to enquire into the
Nature of a Club that had such a sounding Name; upon which my Friend
gave me the following Account.
Everlasting Club consists of a hundred Members, who divide the whole
twenty four Hours among them in such a Manner, that the Club sits Day
and Night from one end of the Year to
another
, no Party presuming
to rise till they are relieved by those who are in course to succeed
them.
this means a Member of the Everlasting Club never wants
Company; for tho' he is not upon Duty himself, he is sure to find some
who
are; so that if he be disposed to take a Whet, a Nooning, an
Evening's Draught, or a Bottle after Midnight, he goes to the Club and
finds a Knot of Friends to his Mind.
is a Maxim in this Club That the Steward never dies; for as they
succeed one another by way of Rotation, no Man is to quit the great
Elbow-chair
which
stands at the upper End of the Table, 'till his
Successor is in a Readiness to fill it; insomuch that there has not been
a
Sede vacante
in the Memory of Man.
Club was instituted towards the End (or, as some of them say, about
the Middle) of the Civil Wars, and continued without Interruption till
the Time of the
Great Fire
, which burnt them out and dispersed
them for several Weeks. The Steward at that time maintained his Post
till he had like to have been blown up with a neighbouring-House, (which
was demolished in order to stop the Fire;) and would not leave the Chair
at last, till he had emptied all the Bottles upon the Table, and
received repeated Directions from the Club to withdraw himself.
Steward is frequently talked of in the Club, and looked upon by every
Member of it as a greater Man, than the famous Captain
mentioned in my
Lord Clarendon, who
was burnt in his Ship because he would
not quit it without Orders. It is said that towards the close of 1700,
being the great Year of Jubilee, the Club had it under Consideration
whether they should break up or continue their Session; but after many
Speeches and Debates it was at length agreed to sit out the other
Century. This Resolution passed in a general Club
Nemine
Contradicente
.
Having given this short Account of the Institution and Continuation of
the Everlasting Club, I should here endeavour to say something of the
Manners and Characters of its several Members, which I shall do
according to the best Lights I have received in this Matter.
It appears by their Books in general, that, since their first
Institution, they have smoked fifty Tun of Tobacco; drank thirty
thousand Butts of Ale, One thousand Hogsheads of Red Port, Two hundred
Barrels of Brandy, and a Kilderkin of small Beer. There has been
likewise a great Consumption of Cards. It is also said, that they
observe the law in
Ben. Johnson's
Club, which orders the Fire to
be always kept in (
focus perennis esto
) as well for the
Convenience of lighting their Pipes, as to cure the Dampness of the
Club-Room.
have an old Woman in the nature of a Vestal, whose
Business it is to cherish and perpetuate the Fire
which
burns from
Generation to Generation, and has seen the Glass-house Fires in and out
above an Hundred Times.
The Everlasting Club treats all other Clubs with an Eye of Contempt, and
talks even of the Kit-Cat and October as of a couple of Upstarts.
ordinary Discourse (as much as I have been able to learn of it) turns
altogether upon such Adventures as have passed in their own Assembly; of
Members who have taken the Glass in their Turns for a Week together,
without stirring out of their Club; of others
who
have smoaked an
Hundred Pipes at a Sitting; of others
who
have not missed their
Morning's Draught for Twenty Years together: Sometimes they speak in
Raptures of a Run of Ale in King Charles's Reign; and sometimes reflect
with Astonishment upon Games at Whisk,
which
have been
miraculously recovered by Members of the Society, when in all human
Probability the Case was desperate.
They delight in several old Catches, which they sing at all Hours to
encourage one another to moisten their Clay, and grow immortal by
drinking; with many other edifying Exhortations of the like Nature.
There are four general Clubs held in a Year, at which Times they fill up
Vacancies, appoint Waiters, confirm the old Fire-Maker or elect a new
one, settle Contributions for Coals, Pipes, Tobacco, and other
Necessaries.
The Senior Member has out-lived the whole Club twice over, and has been
drunk with the Grandfathers of some of the present sitting Members.
C.
The other
(several): that
Of London in 1666.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 24, 1711 |
Addison |
... O Dea certé!
Virg.

It is very strange to consider, that a Creature like Man, who is
sensible of so many Weaknesses and Imperfections, should be actuated by
a Love of Fame: That Vice and Ignorance, Imperfection and Misery should
contend for Praise, and endeavour as much as possible to make themselves
Objects of Admiration.
But notwithstanding Man's Essential Perfection is but very little, his
Comparative Perfection may be very considerable. If he looks upon
himself in an abstracted Light, he has not much to boast of; but if he
considers himself with regard to it in others, he may find Occasion of
glorying, if not in his own Virtues at least in the Absence of another's
Imperfections. This gives a different Turn to the Reflections of the
Wise Man and the Fool. The first endeavours to shine in himself, and the
last to outshine others. The first is humbled by the Sense of his own
Infirmities, the last is lifted up by the Discovery of those which he
observes in other men. The Wise Man considers what he wants, and the
Fool what he abounds in. The Wise Man is happy when he gains his own
Approbation, and the Fool when he Recommends himself to the Applause of
those about him.
however unreasonable and absurd this Passion for Admiration may
appear in such a Creature as Man, it is not wholly to be discouraged;
since it often produces very good Effects, not only as it restrains him
from doing any thing
which
is mean and contemptible, but as it
pushes him to Actions
which
are great and glorious. The Principle
may be defective or faulty, but the Consequences it produces are so
good, that, for the Benefit of Mankind, it ought not to be extinguished.
is observed by Cicero
, — that men of the greatest and the most
shining Parts are the most actuated by Ambition; and if we look into the
two Sexes, I believe we shall find this Principle of Action stronger in
Women than in Men.
The Passion for Praise, which is so very vehement in the Fair Sex,
produces excellent Effects in Women of Sense, who desire to be admired
for that only which deserves Admiration:
And I think we may observe, without a Compliment to them, that many of
them do not only live in a more uniform Course of Virtue, but with an
infinitely greater Regard to their Honour, than what we find in the
Generality of our own Sex. How many Instances have we of Chastity,
Fidelity, Devotion? How many Ladies distinguish themselves by the
Education of their Children, Care of their Families, and Love of their
Husbands, which are the great Qualities and Atchievements of Womankind:
As the making of War, the carrying on of Traffic, the Administration of
Justice, are those by which Men grow famous, and get themselves a Name.
But as this Passion for Admiration, when it works according to Reason,
improves the beautiful Part of our Species in every thing that is
Laudable; so nothing is more Destructive to them when it is governed by
Vanity and Folly. What I have therefore here to say, only regards the
vain Part of the Sex, whom for certain Reasons, which the Reader will
hereafter see at large, I shall distinguish by the Name of
Idols
.
An
Idol
is wholly taken up in the Adorning of her Person. You see
in every Posture of her Body, Air of her Face, and Motion of her Head,
that it is her Business and Employment to gain Adorers. For this Reason
your
Idols
appear in all publick Places and Assemblies, in order
to seduce Men to their Worship. The Play-house is very frequently filled
with
Idols
; several of them are carried in Procession every
Evening about the Ring, and several of them set up their Worship even in
Churches. They are to be accosted in the Language proper to the Deity.
Life and Death are in their Power: Joys of Heaven and Pains of Hell are
at their Disposal: Paradise is in their Arms, and Eternity in every
Moment that you are present with them. Raptures, Transports, and
Ecstacies are the Rewards which they confer: Sighs and Tears, Prayers
and broken Hearts, are the Offerings which are paid to them. Their
Smiles make Men happy; their Frowns drive them to Despair. I shall only
add under this Head, that
Ovid's
Book of the
Art of Love
is a
kind of Heathen Ritual, which contains all the forms of Worship which
are made use of to an
Idol
.
would be as difficult a Task to reckon up these different kinds of
Idols
, as
Milton's
was
to number those that were known
in
Canaan
, and the Lands adjoining. Most of them are worshipped,
like
Moloch
, in
Fire and Flames
. Some of them, like
Baal
, love to see their Votaries cut and slashed, and shedding
their Blood for them. Some of them, like the
Idol
in the
Apocrypha
,
must have Treats and Collations prepared for them every Night. It has
indeed been known, that some of them have been used by their incensed
Worshippers like the
Chinese Idols
, who are Whipped and Scourged when
they refuse to comply with the Prayers that are offered to them.
I must here observe, that those Idolaters who devote themselves to the
Idols
I am here speaking of, differ very much from all other kinds of
Idolaters. For as others fall out because they Worship different
Idols
, these Idolaters quarrel because they Worship the same.
The Intention therefore of the
Idol
is quite contrary to the wishes of
the Idolater; as the one desires to confine the Idol to himself, the
whole Business and Ambition of the other is to multiply Adorers.
Humour of an
Idol
is prettily described in a Tale of
Chaucer
; He
represents one of them sitting at a Table with three of her Votaries
about her, who are all of them courting her Favour, and paying their
Adorations: She smiled upon one, drank to another, and trod upon the
other's Foot which was under the Table. Now which of these three, says
the old Bard, do you think was the Favourite? In troth, says he, not one
of all the three
.
The Behaviour of this old
Idol
in
Chaucer
, puts me in mind of the
Beautiful
Clarinda
, one of the greatest
Idols
among the Moderns. She
is Worshipped once a Week by Candle-light, in the midst of a large
Congregation generally called an Assembly. Some of the gayest Youths in
the Nation endeavour to plant themselves in her Eye, whilst she sits in
form with multitudes of Tapers burning about her. To encourage the Zeal
of her Idolaters, she bestows a Mark of her Favour upon every one of
them, before they go out of her Presence. She asks a Question of one,
tells a Story to another, glances an Ogle upon a third, takes a Pinch of
Snuff from the fourth, lets her Fan drop by accident to give the fifth
an Occasion of taking it up. In short, every one goes away satisfied
with his Success, and encouraged to renew his Devotions on the same
Canonical Hour that Day Sevennight.
An
Idol
may be Undeified by many accidental Causes. Marriage in
particular is a kind of Counter-
Apotheosis
, or a Deification inverted.
When a Man becomes familiar with his Goddess, she quickly sinks into a
Woman.
Old Age is likewise a great Decayer of your
Idol
: The Truth of it is,
there is not a more unhappy Being than a Superannuated
Idol
,
especially when she has contracted such Airs and Behaviour as are only
Graceful when her Worshippers are about her.
Considering therefore that in these and many other Cases the
Woman
generally outlives the
Idol
, I must return to the Moral of this Paper,
and desire my fair Readers to give a proper Direction to their Passion
for being admired; In order to which, they must endeavour to make
themselves the Objects of a reasonable and lasting Admiration. This is
not to be hoped for from Beauty, or Dress, or Fashion, but from those
inward Ornaments which are not to be defaced by Time or Sickness, and
which appear most amiable to those who are most acquainted with them.
C.
that
Tuscul. Quæst.
Lib. v. § 243.
Paradise Lost
, Bk. I.
The story is in
The Remedy of Love
Stanzas 5-10.
Contents
|
Friday, May 25, 1711 |
Addison |
... Pendent opera interrupta ...
Virg.

my last
Monday's
Paper I gave some general Instances of those
beautiful Strokes which please the Reader in the old Song of
Chevey-Chase
; I shall here, according to my Promise, be more
particular, and shew that the Sentiments in that Ballad are extremely
natural and poetical, and full of
the
majestick Simplicity which
we admire in the greatest of the ancient Poets: For which Reason I shall
quote several Passages of it, in which the Thought is altogether the
same with what we meet in several Passages of the
Æneid
; not that I
would infer from thence, that the Poet (whoever he was) proposed to
himself any Imitation of those Passages, but that he was directed to
them in general by the same Kind of Poetical Genius, and by the same
Copyings after Nature.
Had this old Song been filled with Epigrammatical Turns and Points of
Wit, it might perhaps have pleased the wrong Taste of some Readers; but
it would never have become the Delight of the common People, nor have
warmed the Heart of Sir
Philip Sidney
like the Sound of a Trumpet; it
is only Nature that can have this Effect, and please those Tastes which
are the most unprejudiced or the most refined.
must however beg leave
to dissent from so great an Authority as that of Sir
Philip Sidney
, in
the Judgment which he has passed as to the rude Stile and evil Apparel
of this antiquated Song; for there are several Parts in it where not
only the Thought but the Language is majestick, and the Numbers
sonorous;
at least, the
Apparel
is much more
gorgeous
than many
of the Poets made use of in Queen
Elizabeth's
Time, as the Reader will
see in several of the following Quotations.
What can be greater than either the Thought or the Expression in that
Stanza,
To drive the Deer with Hound and Horn
Earl Piercy took his Way;
The Child may rue that was unborn
The Hunting of that Day!
way of considering the Misfortunes which this Battle would bring
upon Posterity, not only on those who were born immediately after the
Battle and lost their Fathers in it, but on those also who perished
in future Battles
which took their rise
from this Quarrel of
the two Earls, is wonderfully beautiful, and conformable to the Way of
Thinking among the ancient Poets.
Audiet pugnas vilio parentum
Rara juventus.
Hor.
What can be more sounding and poetical, resemble more the majestic
Simplicity of the Ancients, than the following Stanzas?
The stout Earl of Northumberland
A Vow to God did make,
His Pleasure in the Scotish Woods
Three Summers Days to take.
With fifteen hundred Bowmen bold,
All chosen Men of Might,
Who knew full well, in time of Need,
To aim their Shafts aright.
The Hounds ran swiftly thro' the Woods
The nimble Deer to take,
And with their Cries the Hills and Dales
An Eccho shrill did make.
... Vocat ingenti Clamore Cithseron
Taygetique canes, domitrixque Epidaurus equorum:
Et vox assensu nemorum ingeminata remugit.
Lo, yonder doth Earl Dowglas come,
His Men in Armour bright;
Full twenty Hundred Scottish Spears,
All marching in our Sight.
All Men of pleasant Tividale,
Fast by the River Tweed, etc.
The Country of the
Scotch
Warriors, described in these two last
Verses, has a fine romantick Situation, and affords a couple of smooth
Words for Verse. If the Reader compares the forgoing six Lines of the
Song with the following Latin Verses, he will see how much they are
written in the Spirit of
Virgil
.
Adversi campo apparent, hastasque reductis
Protendunt longe dextris; et spicula vibrant;
Quique altum Preneste viri, quique arva Gabinæ
Junonis, gelidumque Anienem, et roscida rivis
Hernica saxa colunt: ... qui rosea rura Velini,
Qui Terticæ horrentes rupes, montemque Severum,
Casperiamque colunt, Forulosque et flumen Himellæ:
Qui Tiberim Fabarimque bibunt ...
But to proceed.
Earl Dowglas on a milk-white Steed,
Most like a Baron bold,
Rode foremost of the Company,
Whose Armour shone like Gold.
Turnus ut antevolans tardum precesserat agmen, &c. Vidisti, quo Turnus
equo, quibus ibat in armis Aureus ...
Our English Archers bent their Bows
Their Hearts were good and true;
At the first Flight of Arrows sent,
Full threescore Scots they slew.
They clos'd full fast on ev'ry side,
No Slackness there was found.
And many a gallant Gentleman
Lay gasping on the Ground.
With that there came an Arrow keen
Out of an English Bow,
Which struck Earl Dowglas to the Heart
A deep and deadly Blow.
Æneas was wounded after the same Manner by an unknown Hand in the midst
of a Parly.
Has inter voces, media inter talia verba,
Ecce viro stridens alis allapsa sagitta est,
Incertum quâ pulsa manu ...
But of all the descriptive Parts of this Song, there are none more
beautiful than the four following Stanzas which have a great Force and
Spirit in them, and are filled with very natural Circumstances. The
Thought in the third Stanza was never touched by any other Poet, and is
such an one as would have shined in
Homer
or in
Virgil
.
So thus did both those Nobles die,
Whose Courage none could stain:
An English Archer then perceived
The noble Earl was slain.
He had a Bow bent in his Hand,
Made of a trusty Tree,
An Arrow of a Cloth-yard long
Unto the Head drew he.
Against Sir Hugh Montgomery
So right his Shaft he set,
The Gray-goose Wing that was thereon
In his Heart-Blood was wet.
This Fight did last from Break of Day
Till setting of the Sun;
For when they rung the Evening Bell
The Battle scarce was done.
One may observe likewise, that in the Catalogue of the Slain the Author
has followed the Example of the greatest ancient Poets, not only in
giving a long List of the Dead, but by diversifying it with little
Characters of particular Persons.
And with Earl Dowglas there was slain
Sir Hugh Montgomery,
Sir Charles Carrel, that from the Field
One Foot would never fly:
Sir Charles Murrel of Ratcliff too,
His Sister's Son was he;
Sir David Lamb, so well esteem'd,
Yet saved could not be.
The familiar Sound in these Names destroys the Majesty of the
Description; for this Reason I do not mention this Part of the Poem but
to shew the natural Cast of Thought which appears in it, as the two last
Verses look almost like a Translation of
Virgil
.
... Cadit et Ripheus justissimus unus
Qui fuit in Teucris et servantissimus æqui,
Diis aliter visum est ...
the Catalogue of the
English
who
fell,
Witherington's
Behaviour is in the same manner particularized very artfully, as the
Reader is prepared for it by that Account which is given of him in the
Beginning of the Battle
; though I am satisfied your little Buffoon
Readers (who have seen that Passage ridiculed in Hudibras) will not be
able to take the Beauty of it: For which Reason I dare not so much as
quote it.
Then stept a gallant Squire forth,
Witherington was his Name,
Who said, I would not have it told
To Henry our King for Shame,
That e'er my Captain fought on Foot,
And I stood looking on.
We meet with the same Heroic Sentiments in
Virgil
.
Non pudet, O Rutuli, cunctis pro talibus unam
Objectare animam? numerone an viribus æqui
Non sumus ... ?
What can be more natural or more moving than the Circumstances in which
he describes the Behaviour of those Women who had lost their Husbands on
this fatal Day?
Next Day did many Widows come
Their Husbands to bewail;
They washed their Wounds in brinish Tears,
But all would not prevail.
Their Bodies bath'd in purple Blood,
They bore with them away;
They kiss'd them dead a thousand Times,
When they were clad in Clay.
Thus we see how the Thoughts of this Poem, which naturally arise from
the Subject, are always simple, and sometimes exquisitely noble; that
the Language is often very sounding, and that the whole is written with
a true poetical Spirit.
If this Song had been written in the
Gothic
Manner, which is the
Delight of all our little Wits, whether Writers or Readers, it would not
have hit the Taste of so many Ages, and have pleased the Readers of all
Ranks and Conditions. I shall only beg Pardon for such a Profusion of
Latin
Quotations; which I should not have made use of, but that I
feared my own Judgment would have looked too singular on such a Subject,
had not I supported it by the Practice and Authority of
Virgil
.
C.
that
very sonorous;
should perish
should arise
that
Contents
|
Saturday, May 26, 1711 |
Steele |
Omnis Aristippum decuit color, et status, et res.
Hor.

It was with some Mortification that I suffered the Raillery of a Fine
Lady of my Acquaintance, for calling, in one of my Papers,
Dorimant
a
Clown. She was so unmerciful as to take Advantage of my invincible
Taciturnity, and on that occasion, with great Freedom to consider the
Air, the Height, the Face, the Gesture of him who could pretend to judge
so arrogantly of Gallantry. She is full of Motion, Janty and lively in
her Impertinence, and one of those that commonly pass, among the
Ignorant, for Persons who have a great deal of Humour. She had the Play
of Sir
Fopling
in her Hand, and after she had said it was happy for
her there was not so charming a Creature as
Dorimant
now living, she
began with a Theatrical Air and Tone of Voice to Read, by way of Triumph
over me, some of his Speeches.
'Tis she, that lovely Hair, that easy
Shape, those wanton Eyes, and all those melting Charms about her Mouth,
which
Medley
spoke of; I'll follow the Lottery, and put in for a Prize
with my Friend
Bellair.
In Love the Victors from the Vanquish'd fly;
They fly that wound, and they pursue that dye,
Then turning over the Leaves, she reads alternately, and speaks,
And you and Loveit to her Cost shall find
I fathom all the Depths of Womankind.
Oh the Fine Gentleman! But here, continues she, is the Passage I admire
most, where he begins to Teize
Loveit
, and mimick Sir
Fopling
: Oh
the pretty Satyr, in his resolving to be a Coxcomb to please, since
Noise and Nonsense have such powerful Charms!
I, that I may Successful prove,
Transform my self to what you love.
Then how like a Man of the Town, so Wild and Gay is that
The Wife will find a Diff'rence in our Fate,
You wed a Woman, I a good Estate.
It would have been a very wild Endeavour for a Man of my Temper to offer
any Opposition to so nimble a Speaker as my Fair Enemy is; but her
Discourse gave me very many Reflections, when I had left her Company.
Among others, I could not but consider, with some Attention, the false
Impressions the generality (the Fair Sex more especially) have of what
should be intended, when they say a
Fine Gentleman
; and could not help
revolving that Subject in my Thoughts, and settling, as it were, an Idea
of that Character in my own Imagination.
No Man ought to have the Esteem of the rest of the World, for any
Actions which are disagreeable to those Maxims which prevail, as the
Standards of Behaviour, in the Country wherein he lives. What is
opposite to the eternal Rules of Reason and good Sense, must be excluded
from any Place in the Carriage of a Well-bred Man. I did not, I confess,
explain myself enough on this Subject, when I called
Dorimant
a Clown,
and made it an Instance of it, that he called the
Orange Wench
,
Double Tripe
: I should have shewed, that Humanity obliges a Gentleman
to give no Part of Humankind Reproach, for what they, whom they
Reproach, may possibly have in Common with the most Virtuous and Worthy
amongst us. When a Gentleman speaks Coarsly, he has dressed himself
Clean to no purpose: The Cloathing of our Minds certainly ought to be
regarded before that of our Bodies. To betray in a Man's Talk a
corrupted Imagination, is a much greater Offence against the
Conversation of Gentlemen, than any Negligence of Dress imaginable. But
this Sense of the Matter is so far from being received among People even
of Condition, that
Vocifer
passes for a fine Gentleman. He is Loud,
Haughty, Gentle, Soft, Lewd, and Obsequious by turns, just as a little
Understanding and great Impudence prompt him at the present Moment. He
passes among the silly Part of our Women for a Man of Wit, because he is
generally in Doubt. He contradicts with a Shrug, and confutes with a
certain Sufficiency, in professing such and such a Thing is above his
Capacity. What makes his Character the pleasanter is, that he is a
professed Deluder of Women; and because the empty Coxcomb has no Regard
to any thing that is of it self Sacred and Inviolable, I have heard an
unmarried Lady of Fortune say, It is pity so fine a Gentleman as
Vocifer
is so great an Atheist. The Crowds of such inconsiderable
Creatures that infest all Places of Assembling, every Reader will have
in his Eye from his own Observation; but would it not be worth
considering what sort of Figure a Man who formed himself upon those
Principles among us, which are agreeable to the Dictates of Honour and
Religion, would make in the familiar and ordinary Occurrences of Life?
I hardly have observed any one fill his several Duties of Life better
than
Ignotus
. All the under Parts of his Behaviour and such as are
exposed to common Observation, have their Rise in him from great and
noble Motives. A firm and unshaken Expectation of another Life, makes
him become this; Humanity and Good-nature, fortified by the Sense of
Virtue, has the same Effect upon him, as the Neglect of all Goodness has
upon many others. Being firmly established in all Matters of Importance,
that certain Inattention which makes Men's Actions look easie appears in
him with greater Beauty: By a thorough Contempt of little Excellencies,
he is perfectly Master of them. This Temper of Mind leaves him under no
Necessity of Studying his Air, and he has this peculiar Distinction,
that his Negligence is unaffected.
He that can work himself into a Pleasure in considering this Being as an
uncertain one, and think to reap an Advantage by its Discontinuance, is
in a fair way of doing all things with a graceful Unconcern, and
Gentleman-like Ease. Such a one does not behold his Life as a short,
transient, perplexing State, made up of trifling Pleasures, and great
Anxieties; but sees it in quite another Light; his Griefs are Momentary,
and his Joys Immortal. Reflection upon Death is not a gloomy and sad
Thought of Resigning every Thing that he Delights in, but it is a short
Night followed by an endless Day. What I would here contend for is, that
the more Virtuous the Man is, the nearer he will naturally be to the
Character of Genteel and Agreeable. A Man whose Fortune is Plentiful,
shews an Ease in his Countenance, and Confidence in his Behaviour, which
he that is under Wants and Difficulties cannot assume. It is thus with
the State of the Mind; he that governs his Thoughts with the everlasting
Rules of Reason and Sense, must have something so inexpressibly Graceful
in his Words and Actions, that every Circumstance must become him. The
Change of Persons or Things around him do not at all alter his
Situation, but he looks disinterested in the Occurrences with which
others are distracted, because the greatest Purpose of his Life is to
maintain an Indifference both to it and all its Enjoyments. In a word,
to be a Fine Gentleman, is to be a Generous and a Brave Man. What can
make a Man so much in constant Good-humour and Shine, as we call it,
than to be supported by what can never fail him, and to believe that
whatever happens to him was the best thing that could possibly befal
him, or else he on whom it depends would not have permitted it to have
befallen him at all?
R.
Contents
|
Monday, May 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Ut tu Fortunam, sic nos te, Celse, feremus.
Hor.

There is nothing so common as to find a Man whom in the general
Observations of his Carriage you take to be of an uniform Temper,
subject to such unaccountable Starts of Humour and Passion, that he is
as much unlike himself and differs as much from the Man you at first
thought him, as any two distinct Persons can differ from each other.
This proceeds from the Want of forming some Law of Life to our selves,
or fixing some Notion of things in general, which may affect us in such
Manner as to create proper Habits both in our Minds and Bodies. The
Negligence of this, leaves us exposed not only to an unbecoming Levity
in our usual Conversation, but also to the same Instability in our
Friendships, Interests, and Alliances. A Man who is but a mere Spectator
of what passes around him, and not engaged in Commerces of any
Consideration, is but an ill Judge of the secret Motions of the Heart of
Man, and by what Degrees it is actuated to make such visible Alterations
in the same Person: But at the same Time, when a Man is no way concerned
in the Effects of such Inconsistences in the Behaviour of Men of the
World, the Speculation must be in the utmost Degree both diverting and
instructive; yet to enjoy such Observations in the highest Relish, he
ought to be placed in a Post of Direction, and have the dealing of their
Fortunes to them. I have therefore been wonderfully diverted with some
Pieces of secret History, which an Antiquary, my very good Friend, lent
me as a Curiosity.
are memoirs of the private Life of
Pharamond
of France
.
'Pharamond, says my Author, was a Prince of
infinite Humanity and Generosity, and at the same time the most pleasant
and facetious Companion of his Time. He had a peculiar Taste in him
(which would have been unlucky in any Prince but himself,) he thought
there could be no exquisite Pleasure in Conversation but among Equals;
and would pleasantly bewail himself that he always lived in a Crowd, but
was the only man in France that never could get into Company.
This Turn of Mind made him delight in Midnight Rambles, attended only
with one Person of his Bed-chamber: He would in these Excursions get
acquainted with Men (whose Temper he had a Mind to try) and recommend
them privately to the particular Observation of his first Minister. He
generally found himself neglected by his new Acquaintance as soon as
they had Hopes of growing great; and used on such Occasions to remark,
That it was a great Injustice to tax Princes of forgetting themselves in
their high Fortunes, when there were so few that could with Constancy
bear the Favour of their very Creatures.'
My Author in these loose Hints
has one Passage that gives us a very lively Idea of the uncommon Genius
of
Pharamond
. He met with one Man whom he had put to all the usual
Proofs he made of those he had a mind to know thoroughly, and found him
for his Purpose: In Discourse with him one Day, he gave him Opportunity
of saying how much would satisfy all his Wishes. The Prince immediately
revealed himself, doubled the Sum, and spoke to him in this manner.
'Sir, You have twice what you desired, by the Favour of Pharamond;
but look to it, that you are satisfied with it, for 'tis the last you
shall ever receive. I from this Moment consider you as mine; and to make
you truly so, I give you my Royal Word you shall never be greater or
less than you are at present. Answer me not, (concluded the Prince
smiling) but enjoy the Fortune I have put you in, which is above my own
Condition; for you have hereafter nothing to hope or to fear.'
His Majesty having thus well chosen and bought a Friend and Companion,
he enjoyed alternately all the Pleasures of an agreeable private Man and
a great and powerful Monarch: He gave himself, with his Companion, the
Name of the merry Tyrant; for he punished his Courtiers for their
Insolence and Folly, not by any Act of Publick Disfavour, but by
humorously practising upon their Imaginations. If he observed a Man
untractable to his Inferiors, he would find an Opportunity to take some
favourable Notice of him, and render him insupportable. He knew all his
own Looks, Words and Actions had their Interpretations; and his Friend
Monsieur
Eucrate
(for so he was called) having a great Soul without
Ambition, he could communicate all his Thoughts to him, and fear no
artful Use would be made of that Freedom. It was no small Delight when
they were in private to reflect upon all which had passed in publick.
Pharamond
would often, to satisfy a vain Fool of Power in his Country,
talk to him in a full Court, and with one Whisper make him despise all
his old Friends and Acquaintance. He was come to that Knowledge of Men
by long Observation, that he would profess altering the whole Mass of
Blood in some Tempers, by thrice speaking to them. As Fortune was in his
Power, he gave himself constant Entertainment in managing the mere
Followers of it with the Treatment they deserved. He would, by a skilful
Cast of his Eye and half a Smile, make two Fellows who hated, embrace
and fall upon each other's Neck with as much Eagerness, as if they
followed their real Inclinations, and intended to stifle one another.
When he was in high good Humour, he would lay the Scene with
Eucrate
,
and on a publick Night exercise tho Passions of his whole Court. He was
pleased to see an haughty Beauty watch the Looks of the Man she had long
despised, from Observation of his being taken notice of by
Pharamond
;
and the Lover conceive higher Hopes, than to follow the Woman he was
dying for the Day before. In a Court where Men speak Affection in the
strongest Terms, and Dislike in the faintest, it was a comical Mixture
of Incidents to see Disguises thrown aside in one Case and encreased on
the other, according as Favour or Disgrace attended the respective
Objects of Men's Approbation or Disesteem.
Pharamond
in his Mirth upon
the Meanness of Mankind used to say,
'As he could take away a Man's Five
Senses, he could give him an Hundred. The Man in Disgrace shall
immediately lose all his natural Endowments, and he that finds Favour
have the Attributes of an Angel.' He would carry it so far as to say,
'It should not be only so in the Opinion of the lower Part of his Court,
but the Men themselves shall think thus meanly or greatly of themselves,
as they are out or in the good Graces of a Court.'
A Monarch who had Wit and Humour like
Pharamond
, must have Pleasures
which no Man else can ever have Opportunity of enjoying. He gave Fortune
to none but those whom he knew could receive it without Transport: He
made a noble and generous Use of his Observations; and did not regard
his Ministers as they were agreeable to himself, but as they were useful
to his Kingdom: By this means the King appeared in every Officer of
State; and no Man had a Participation of the Power, who had not a
Similitude of the Virtue of
Pharamond
.
R.
Pharamond, or
Faramond
, was the subject of one of
the romances of M. de Costes de la Calprenède, published at Paris (12
vols.) in 1661. It was translated into English (folio) by J. Phillips in
1677.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 29, 1711 |
Budgell |
Non convivere licet, nec urbe tota
Quisquam est tam propè tam proculque nobis.
Mart.

My Friend
Will Honeycomb
is one of those Sort of Men who are very often
absent in Conversation, and what the
French
call
a reveur
and
a
distrait
. A little before our Club-time last Night we were walking
together in
Somerset
Garden, where
Will.
, had picked up a small Pebble
of so odd a Make, that he said he would present it to a Friend of his,
an eminent
Virtuoso
. After we had walked some time, I made a full stop
with my Face towards the West, which
Will.
, knowing to be my usual Method
of asking what's a Clock, in an Afternoon, immediately pulled out his
Watch, and told me we had seven Minutes good. We took a turn or two
more, when, to my great Surprize, I saw him squirr away his Watch a
considerable way into the
Thames
, and with great Sedateness in his
Looks put up the Pebble, he had before found, in his Fob. As I have
naturally an Aversion to much Speaking, and do not love to be the
Messenger of ill News, especially when it comes too late to be useful, I
left him to be convinced of his Mistake in due time, and continued my
Walk, reflecting on these little Absences and Distractions in Mankind,
and resolving to make them the Subject of a future Speculation.
was the more confirmed in my Design, when I considered that they were
very often Blemishes in the Characters of Men of excellent Sense; and
helped to keep up the Reputation of that Latin Proverb
, which Mr.
Dryden
has Translated in the following Lines:
Great Wit to Madness sure is near ally'd,
And thin Partitions do their Bounds divide.
My Reader does, I hope, perceive, that I distinguish a Man who is
Absent
, because he thinks of something else, from one who is
Absent
,
because he thinks of nothing at all: The latter is too innocent a
Creature to be taken notice of; but the Distractions of the former may,
I believe, be generally accounted for from one of these Reasons.
Either their Minds are wholly fixed on some particular Science, which is
often the Case of Mathematicians and other learned Men; or are wholly
taken up with some Violent Passion, such as Anger, Fear, or Love, which
ties the Mind to some distant Object; or, lastly, these Distractions
proceed from a certain Vivacity and Fickleness in a Man's Temper, which
while it raises up infinite Numbers of
Ideas
in the Mind, is
continually pushing it on, without allowing it to rest on any particular
Image. Nothing therefore is more unnatural than the Thoughts and
Conceptions of such a Man, which are seldom occasioned either by the
Company he is in, or any of those Objects which are placed before him.
While you fancy he is admiring a beautiful Woman, 'tis an even Wager
that he is solving a Proposition in
Euclid
; and while you may imagine
he is reading the
Paris
Gazette, it is far from being impossible, that
he is pulling down and rebuilding the Front of his Country-house.
At the same time that I am endeavouring to expose this Weakness in
others, I shall readily confess that I once laboured under the same
Infirmity myself. The Method I took to conquer it was a firm Resolution
to learn something from whatever I was obliged to see or hear. There is
a way of Thinking if a Man can attain to it, by which he may strike
somewhat out of any thing. I can at present observe those Starts of good
Sense and Struggles of unimproved Reason in the Conversation of a Clown,
with as much Satisfaction as the most shining Periods of the most
finished Orator; and can make a shift to command my Attention at a
Puppet-Show
or an
Opera
, as well as at
Hamlet
or
Othello
. I
always make one of the Company I am in; for though I say little myself,
my Attention to others, and those Nods of Approbation which I never
bestow unmerited, sufficiently shew that I am among them. Whereas
Will.
Honeycomb
, tho' a Fellow of good Sense, is every Day doing and saying an
hundred Things which he afterwards confesses, with a well-bred
Frankness, were somewhat
mal a propos
, and undesigned.
I chanced the other Day to go into a Coffee-house, where
Will
, was
standing in the midst of several Auditors whom he had gathered round
him, and was giving them an Account of the Person and Character of
Moll
Hinton
. My Appearance before him just put him in mind of me, without
making him reflect that I was actually present. So that keeping his Eyes
full upon me, to the great Surprize of his Audience, he broke off his
first Harangue, and proceeded thus:
'Why now there's my Friend
(mentioning me by my Name) he is a Fellow that thinks a great deal, but
never opens his Mouth; I warrant you he is now thrusting his short Face
into some Coffee-house about 'Change. I was his Bail in the time of
the Popish-Plot, when he was taken up for a Jesuit.'
If he had looked
on me a little longer, he had certainly described me so particularly,
without ever considering what led him into it, that the whole Company
must necessarily have found me out; for which Reason, remembering the
old Proverb,
Out of Sight out of Mind
, I left the Room; and upon
meeting him an Hour afterwards, was asked by him, with a great deal of
Good-humour, in what Part of the World I had lived, that he had not seen
me these three Days.
Bruyère
has given us the Character of
an absent
Man
,
with a great deal of Humour, which he has pushed to an agreeable
Extravagance; with the Heads of it I shall conclude my present Paper.
'Menalcas (says that excellent Author) comes down in a Morning,
opens his Door to go out, but shuts it again, because he perceives
that he has his Night-cap on; and examining himself further finds that
he is but half-shaved, that he has stuck his Sword on his right Side,
that his Stockings are about his Heels, and that his Shirt is over his
Breeches. When he is dressed he goes to Court, comes into the
Drawing-room, and walking bolt-upright under a Branch of Candlesticks
his Wig is caught up by one of them, and hangs dangling in the Air.
All the Courtiers fall a laughing, but Menalcas laughs louder than
any of them, and looks about for the Person that is the Jest of the
Company. Coming down to the Court-gate he finds a Coach, which taking
for his own, he whips into it; and the Coachman drives off, not
doubting but he carries his Master. As soon as he stops, Menalcas
throws himself out of the Coach, crosses the Court, ascends the
Staircase, and runs thro' all the Chambers with the greatest
Familiarity, reposes himself on a Couch, and fancies himself at home.
The Master of the House at last comes in, Menalcas rises to receive
him, and desires him to sit down; he talks, muses, and then talks
again. The Gentleman of the House is tired and amazed; Menalcas is
no less so, but is every Moment in Hopes that his impertinent Guest
will at last end his tedious Visit. Night comes on, when Menalcas is
hardly undeceived.
When he is playing at Backgammon, he calls for a full Glass of Wine
and Water; 'tis his turn to throw, he has the Box in one Hand and his
Glass in the other, and being extremely dry, and unwilling to lose
Time, he swallows down both the Dice, and at the same time throws his
Wine into the Tables. He writes a Letter, and flings the Sand into the
Ink-bottle; he writes a second, and mistakes the Superscription: A
Nobleman receives one of them, and upon opening it reads as follows:
I would have you, honest Jack, immediately upon the Receipt of this,
take in Hay enough to serve me the Winter. His Farmer receives the
other and is amazed to see in it, My Lord, I received your Grace's
Commands with an entire Submission to — If he is at an Entertainment,
you may see the Pieces of Bread continually multiplying round his
Plate: 'Tis true the rest of the Company want it, as well as their
Knives and Forks, which Menalcas does not let them keep long.
Sometimes in a Morning he puts his whole Family in an hurry, and at
last goes out without being able to stay for his Coach or Dinner, and
for that Day you may see him in every Part of the Town, except the
very Place where he had appointed to be upon a Business of Importance.
You would often take him for every thing that he is not; for a Fellow
quite stupid, for he hears nothing; for a Fool, for he talks to
himself, and has an hundred Grimaces and Motions with his Head, which
are altogether involuntary; for a proud Man, for he looks full upon
you, and takes no notice of your saluting him: The Truth on't is, his
Eyes are open, but he makes no use of them, and neither sees you, nor
any Man, nor any thing else: He came once from his Country-house, and
his own Footman undertook to rob him, and succeeded: They held a
Flambeau to his Throat, and bid him deliver his Purse; he did so, and
coming home told his Friends he had been robbed; they desired to know
the Particulars, Ask my Servants, says Menalcas, for they were with
me.
X.
Seneca
de Tranquill. Anim
. cap. xv.
'Nullum magnum ingenium sine mixturâ dementiæ'
Dryden's lines are in Part I of
Absalom and Achitophel
.
Caractères
, Chap. xi. de l'Homme. La Bruyère's Menalque was
identified with a M. de Brancas, brother of the Duke de Villars. The
adventure of the wig is said really to have happened to him at a
reception by the Queen-Mother. He was said also on his wedding-day to
have forgotten that he had been married. He went abroad as usual, and
only remembered the ceremony of the morning upon finding the changed
state of his household when, as usual, he came home in the evening.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 30, 1711 |
Steele |
Cum Talis sis, Utinam noster esses!
The following Letters are so pleasant, that I doubt not but the Reader
will be as much diverted with them as I was. I have nothing to do in
this Day's Entertainment, but taking the Sentence from the End of the
Cambridge
Letter, and placing it at the Front of my Paper; to shew the
Author I wish him my Companion with as much Earnestness as he invites me
to be his.
Sir,
'I Send you the inclosed, to be inserted (if you think them worthy of
it) in your
Spectators; in which so surprizing a Genius appears, that
it is no Wonder if all Mankind endeavours to get somewhat into a Paper
which will always live.
As to the
Cambridge Affair, the Humour was really carried on in the
Way I described it. However, you have a full Commission to put out or
in, and to do whatever you think fit with it.
I have already had the
Satisfaction of seeing you take that Liberty with some things I have
before sent you
1.
Go on, Sir, and prosper. You have the best Wishes of
Sir, Your very Affectionate,
and Obliged Humble Servant.
Cambridge.
Mr, Spectator,
'You well know it is of great Consequence to clear Titles, and it is
of Importance that it be done in the proper Season; On which Account
this is to assure you, that the
Club Of Ugly Faces was instituted
originally at
Cambridge in the merry Reign of King
Charles II. As
in great Bodies of Men it is not difficult to find Members enough for
such a Club, so (I remember) it was then feared, upon their Intention
of dining together, that the Hall belonging to
Clarehall, (the
ugliest
then in the Town, tho'
now the neatest) would not be large
enough
Handsomely to hold the Company. Invitations were made to great
Numbers, but very few accepted them without much Difficulty.
One
pleaded that being at
London in a Bookseller's Shop, a Lady going by
with a great Belly longed to kiss him.
He had certainly been excused,
but that Evidence appeared, That indeed one in
London did pretend
she longed to kiss him, but that it was only a
Pickpocket, who
during his kissing her stole away all his Money.
Another would have
got off by a Dimple in his Chin; but it was proved upon
him, that he
had, by coming into a Room, made a Woman miscarry, and frightened two
Children into Fits. A
Third alledged, That he was taken by a Lady for
another Gentleman, who was one of the handsomest in the University;
But upon Enquiry it was found that the Lady had actually lost one Eye,
and the other was very much upon the Decline. A
Fourth produced
Letters out of the Country in his Vindication, in which a Gentleman
offered him his Daughter, who had lately fallen in Love with him, with
a good Fortune: But it was made appear that the young Lady was
amorous, and had like to have run away with her Father's Coachman, so
that it was supposed, that her Pretence of falling in Love with him
was only in order to be well married. It was pleasant to hear the
several Excuses which were made, insomuch that some made as much
Interest to be excused as they would from serving Sheriff; however at
last the Society was formed, and proper Officers were appointed; and
the Day was fix'd for the Entertainment, which was in
Venison
Season. A pleasant
Fellow of King's College (commonly called
Crab
from his sour Look, and the only Man who did not pretend to get off)
was nominated for Chaplain; and nothing was wanting but some one to
sit in the Elbow-Chair, by way of
President, at the upper end of the
Table; and there the Business stuck, for there was no Contention for
Superiority
there. This Affair made so great a Noise, that the King,
who was then at
Newmarket, heard of it, and was pleased merrily and
graciously to say,
He could not Be There himself, but he would Send
them a Brace of Bucks.
I would desire you, Sir, to set this Affair in a true Light, that
Posterity may not be misled in so important a Point: For when
the
wise Man who shall write your true History shall acquaint the World,
That you had a
Diploma sent from the
Ugly Club at Oxford, and that
by vertue of it you were admitted into it, what a learned Work will
there be among
future Criticks about the Original of that Club,
which both Universities will contend so warmly for? And perhaps some
hardy
Cantabrigian Author may then boldly affirm, that the Word
Oxford was an interpolation of some
Oxonian instead of
Cambridge. This Affair will be best adjusted in your Life-time; but
I hope your Affection to your
Mother will not make you partial to your
Aunt.
To tell you, Sir, my own Opinion: Tho' I cannot find any ancient
Records of any Acts of the
Society of the Ugly Faces, considered in a
publick Capacity; yet in a
private one they have certainly
Antiquity on their Side. I am perswaded they will hardly give Place to
the
Lowngers, and the
Lowngers are of the same Standing with the
University itself.
Tho' we well know, Sir, you want no Motives to do Justice, yet I am
commission'd to tell you, that you are invited to be admitted
ad
eundem at
Cambridge; and I believe I may venture safely to deliver
this as the Wish of our Whole University.'
To Mr.
Spectator.
The humble Petition of Who and Which.
Sheweth,
'
That your Petitioners being in a forlorn and destitute Condition,
know not to whom we should apply ourselves for Relief, because there
is hardly any Man alive who hath not injured us. Nay, we speak it with
Sorrow, even You your self, whom we should suspect of such a Practice
the last of all Mankind, can hardly acquit your self of having given
us some Cause of Complaint. We are descended of ancient Families, and
kept up our Dignity and Honour many Years, till the Jack-sprat THAT
supplanted us. How often have we found ourselves slighted by the
Clergy in their Pulpits, and the Lawyers at the Bar? Nay, how often
have we heard in one of the most polite and august Assemblies in the
Universe, to our great Mortification, these Words,
That That that
noble Lord urged; which if one of us had had Justice done, would
have sounded nobler thus,
That Which that noble Lord urged.
Senates themselves, the Guardians of
British Liberty, have
degraded us, and preferred
That to us; and yet no Decree was ever
given against us. In the very Acts of Parliament, in which the utmost
Right should be done to every
Body,
Word and
Thing, we find our selves often either not used, or used one
instead of another. In the first and best Prayer Children are taught,
they learn to misuse us:
Our Father Which art in Heaven,
should be,
Our Father Who art in Heaven; and even a
Convocation after long Debates, refused to consent to an Alteration of
it. In our
general Confession we say, —
Spare thou them, O
God, Which confess their Faults, which ought to be,
Who confess
their Faults. What Hopes then have we of having Justice done so,
when the Makers of our very Prayers and Laws, and the most learned in
all Faculties, seem to be in a Confederacy against us, and our Enemies
themselves must be our Judges.'
The
Spanish Proverb says,
Il sabio muda consejo, il necio no;
i. e.
A wise Man changes his Mind, a Fool never will.
So
that we think You, Sir, a very proper Person to address to, since we
know you to be capable of being convinced, and changing your Judgment.
You are well able to settle this Affair, and to you we submit our Cause.
We desire you to assign the Butts and Bounds of each of us; and that for
the future we may both enjoy our own. We would desire to be heard by our
Counsel, but that we fear in their very Pleadings they would betray our
Cause: Besides, we have been oppressed so many Years, that we can appear
no other way, but
in forma pauperis. All which considered, we hope you
will be pleased to do that which to Right and Justice shall appertain.
And your Petitioners, &c.
R.
This letter is probably by Laurence Eusden, and the
preceding letter by the same hand would be the account of the Loungers
in
Laurence Eusden, son of Dr. Eusden, Rector of Spalsworth, in
Yorkshire, was educated at Trinity College, Cambridge, took orders, and
became Chaplain to Lord Willoughby de Broke. He obtained the patronage
of Lord Halifax by a Latin version of his Lordship's poem on the Battle
of the Boyne, in 1718. By the influence of the Duke of Newcastle, then
Lord Chamberlain, he was made Poet-laureate, upon the death of Rowe.
Eusden died, rector of Conington, Lincolnshire, in 1730, and his death
was hastened by intemperance. Of the laurel left for Cibber Pope wrote
in the Dunciad,
Know, Eusden thirsts no more for sack or praise;
He sleeps among the dull of ancient days.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 31, 1711 |
Steele |
Oderunt peccare boni virtutis amore.
Hor.

I have received very many Letters of late from my Female Correspondents,
most of whom are very angry with me for Abridging their Pleasures, and
looking severely upon Things, in themselves, indifferent. But I think
they are extremely Unjust to me in this Imputation: All that I contend
for is, that those Excellencies, which are to be regarded but in the
second Place, should not precede more weighty Considerations. The Heart
of Man deceives him in spite of the Lectures of half a Life spent in
Discourses on the Subjection of Passion; and I do not know why one may
not think the Heart of Woman as Unfaithful to itself. If we grant an
Equality in the Faculties of both Sexes, the Minds of Women are less
cultivated with Precepts, and consequently may, without Disrespect to
them, be accounted more liable to Illusion in Cases wherein natural
Inclination is out of the Interests of Virtue. I shall take up my
present Time in commenting upon a Billet or two which came from Ladies,
and from thence leave the Reader to judge whether I am in the right or
not, in thinking it is possible Fine Women may be mistaken.
The following Address seems to have no other Design in it, but to tell
me the Writer will do what she pleases for all me.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am Young, and very much inclin'd to follow the Paths of Innocence:
but at the same time, as I have a plentiful Fortune, and of Quality, I
am unwilling to resign the Pleasures of Distinction, some little
Satisfaction in being Admired in general, and much greater in being
beloved by a Gentleman, whom I design to make my Husband. But I have a
mind to put off entering into Matrimony till another Winter is over my
Head, which, (whatever, musty Sir, you may think of the Matter) I
design to pass away in hearing Music, going to Plays, Visiting, and
all other Satisfactions which Fortune and Youth, protected by
Innocence and Virtue, can procure for, '
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
M. T.
'My Lover does not know I like him, therefore having no Engagements
upon me, I think to stay and know whether I may not like any one else
better.'
I have heard
Will. Honeycomb
say,
A Woman seldom writes her Mind but in her Postscript.
I think this Gentlewoman has sufficiently
discovered hers in this. I'll lay what Wager she pleases against her
present Favourite, and can tell her that she will Like Ten more before
she is fixed, and then will take the worst Man she ever liked in her
Life. There is no end of Affection taken in at the Eyes only; and you
may as well satisfie those Eyes with seeing, as controul any Passion
received by them only. It is from loving by Sight that Coxcombs so
frequently succeed with Women, and very often a Young Lady is bestowed
by her Parents to a Man who weds her as Innocence itself, tho' she has,
in her own Heart, given her Approbation of a different Man in every
Assembly she was in the whole Year before. What is wanting among Women,
as well as among Men, is the Love of laudable Things, and not to rest
only in the Forbearance of such as are Reproachful.
How far removed from a Woman of this light Imagination is
Eudosia!
Eudosia
has all the Arts of Life and good Breeding with so much
Ease, that the Virtue of her Conduct looks more like an Instinct than
Choice. It is as little difficult to her to think justly of Persons and
Things, as it is to a Woman of different Accomplishments, to move ill or
look awkward. That which was, at first, the Effect of Instruction, is
grown into an Habit; and it would be as hard for
Eudosia
to
indulge a wrong Suggestion of Thought, as it would be for
Flavia
the fine Dancer to come into a Room with an unbecoming Air.
But the Misapprehensions People themselves have of their own State of
Mind, is laid down with much discerning in the following Letter, which
is but an Extract of a kind Epistle from my charming mistress
Hecatissa
, who is above the Vanity of external Beauty, and is
the best Judge of the Perfections of the Mind.
Mr.
Spectator,
"I Write this to acquaint you, that very many Ladies, as well as
myself, spend many Hours more than we used at the Glass, for want of
the Female Library of which you promised us a Catalogue. I hope, Sir,
in the Choice of Authors for us, you will have a particular Regard to
Books of Devotion. What they are, and how many, must be your chief
Care; for upon the Propriety of such Writings depends a great deal. I
have known those among us who think, if they every Morning and Evening
spend an Hour in their Closet, and read over so many Prayers in six or
seven Books of Devotion, all equally nonsensical, with a sort of
Warmth, (that might as well be raised by a Glass of Wine, or a Drachm
of Citron) they may all the rest of their time go on in whatever their
particular Passion leads them to. The beauteous
Philautia, who is
(in your Language) an
Idol, is one of these Votaries; she has a very
pretty furnished Closet, to which she retires at her appointed Hours:
This is her Dressing-room, as well as Chapel; she has constantly
before her a large Looking-glass, and upon the Table, according to a
very witty Author,
Together lye her Prayer-book and Paint,
At once t' improve the Sinner and the Saint.
It must be a good Scene, if one could be present at it, to see this
Idol by turns lift up her Eyes to Heaven, and steal Glances at her
own dear Person. It cannot but be a pleasing Conflict between Vanity
and Humiliation. When you are upon this Subject, choose Books which
elevate the Mind above the World, and give a pleasing Indifference to
little things in it. For want of such Instructions, I am apt to
believe so many People take it in their Heads to be sullen, cross and
angry, under pretence of being abstracted from the Affairs of this
Life, when at the same time they betray their Fondness for them by
doing their Duty as a Task, and pouting and reading good Books for a
Week together. Much of this I take to proceed from the Indiscretion of
the Books themselves, whose very Titles of Weekly Preparations, and
such limited Godliness, lead People of ordinary Capacities into great
Errors, and raise in them a Mechanical Religion, entirely distinct
from Morality. I know a Lady so given up to this sort of Devotion,
that tho' she employs six or eight Hours of the twenty-four at Cards,
she never misses one constant Hour of Prayer, for which time another
holds her Cards, to which she returns with no little Anxiousness till
two or three in the Morning. All these Acts are but empty Shows, and,
as it were, Compliments made to Virtue; the Mind is all the while
untouched with any true Pleasure in the Pursuit of it. From hence I
presume it arises that so many People call themselves Virtuous, from
no other Pretence to it but an Absence of Ill. There is
Dulcianara
is the most insolent of all Creatures to her Friends and Domesticks,
upon no other Pretence in Nature but that (as her silly Phrase is) no
one can say Black is her Eye. She has no Secrets, forsooth, which
should make her afraid to speak her Mind, and therefore she is
impertinently Blunt to all her Acquaintance, and unseasonably
Imperious to all her Family. Dear Sir, be pleased to put such Books in
our Hands, as may make our Virtue more inward, and convince some of us
that in a Mind truly virtuous the Scorn of Vice is always accompanied
with the Pity of it. This and other things are impatiently expected
from you by our whole Sex; among the rest by,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,'
B.
Contents
|
Friday, June 1, 1711 |
Steele |
Cœlum non animum mutant qui trans mare currunt.
Hor.

In the Year 1688, and on the same Day of that Year, were born in
Cheapside, London
, two Females of exquisite Feature and Shape; the one
we shall call
Brunetta
, the other
Phillis
. A close Intimacy between
their Parents made each of them the first Acquaintance the other knew in
the World: They played, dressed Babies, acted Visitings, learned to
Dance and make Curtesies, together. They were inseparable Companions in
all the little Entertainments their tender Years were capable of: Which
innocent Happiness continued till the Beginning of their fifteenth Year,
when it happened that Mrs.
Phillis
had an Head-dress on which became
her so very well, that instead of being beheld any more with Pleasure
for their Amity to each other, the Eyes of the Neighbourhood were turned
to remark them with Comparison of their Beauty. They now no longer
enjoyed the Ease of Mind and pleasing Indolence in which they were
formerly happy, but all their Words and Actions were misinterpreted by
each other, and every Excellence in their Speech and Behaviour was
looked upon as an Act of Emulation to surpass the other. These
Beginnings of Disinclination soon improved into a Formality of
Behaviour; a general Coldness, and by natural Steps into an
irreconcilable Hatred.
These two Rivals for the Reputation of Beauty, were in their Stature,
Countenance and Mien so very much alike, that if you were speaking of
them in their Absence, the Words in which you described the one must
give you an Idea of the other. They were hardly distinguishable, you
would think, when they were apart, tho' extremely different when
together. What made their Enmity the more entertaining to all the rest
of their Sex was, that in Detraction from each other neither could fall
upon Terms which did not hit herself as much as her Adversary. Their
Nights grew restless with Meditation of new Dresses to outvie each
other, and inventing new Devices to recal Admirers, who observed the
Charms of the one rather than those of the other on the last Meeting.
Their Colours failed at each other's Appearance, flushed with Pleasure
at the Report of a Disadvantage, and their Countenances withered upon
Instances of Applause. The Decencies to which Women are obliged, made
these Virgins stifle their Resentment so far as not to break into open
Violences, while they equally suffered the Torments of a regulated
Anger. Their Mothers, as it is usual, engaged in the Quarrel, and
supported the several Pretensions of the Daughters with all that
ill-chosen Sort of Expence which is common with People of plentiful
Fortunes and mean Taste. The Girls preceded their Parents like Queens of
May
, in all the gaudy Colours imaginable, on every
Sunday
to Church,
and were exposed to the Examination of the Audience for Superiority of
Beauty.
During this constant Straggle it happened, that
Phillis
one Day at
publick Prayers smote the Heart of a gay
West-Indian
, who appear'd in
all the Colours which can affect an Eye that could not distinguish
between being fine and tawdry. This
American
in a Summer-Island Suit
was too shining and too gay to be resisted by
Phillis
, and too intent
upon her Charms to be diverted by any of the laboured Attractions of
Brunetta
. Soon after,
Brunetta
had the Mortification to see her
Rival disposed of in a wealthy Marriage, while she was only addressed to
in a Manner that shewed she was the Admiration of all Men, but the
Choice of none.
Phillis
was carried to the Habitation of her Spouse in
Barbadoes
:
Brunetta
had the Ill-nature to inquire for her by every
Opportunity, and had the Misfortune to hear of her being attended by
numerous Slaves, fanned into Slumbers by successive Hands of them, and
carried from Place to Place in all the Pomp of barbarous Magnificence.
Brunetta
could not endure these repeated Advices, but employed all her
Arts and Charms in laying Baits for any of Condition of the same Island,
out of a mere Ambition to confront her once more before she died. She at
last succeeded in her Design, and was taken to Wife by a Gentleman whose
Estate was contiguous to that of her Enemy's Husband. It would be
endless to enumerate the many Occasions on which these irreconcileable
Beauties laboured to excel each other; but in process of Time it
happened that a Ship put into the Island consigned to a Friend of
Phillis
, who had Directions to give her the Refusal of all Goods
for Apparel, before
Brunetta
could be alarmed of their Arrival.
He did so, and
Phillis
was dressed in a few Days in a Brocade
more gorgeous and costly than had ever before appeared in that Latitude.
Brunetta
languished at the Sight, and could by no means come up
to the Bravery of her Antagonist. She communicated her Anguish of Mind
to a faithful Friend, who by an Interest in the Wife of
Phillis's
Merchant, procured a Remnant of the same Silk for
Brunetta
.
Phillis
took pains to appear in all public Places where she was
sure to meet
Brunetta
;
Brunetta
was now prepared for the
Insult, and came to a public Ball in a plain black Silk Mantua, attended
by a beautiful Negro Girl in a Petticoat of the same Brocade with which
Phillis
was attired. This drew the Attention of the whole
Company, upon which the unhappy
Phillis
swooned away, and was
immediately convey'd to her House. As soon as she came to herself she
fled from her Husband's House, went on board a Ship in the Road, and is
now landed in inconsolable Despair at
Plymouth
.
Postscript
.
After the above melancholy Narration, it may perhaps be a Relief to the
Reader to peruse the following Expostulation.
To Mr. Spectator.
The just Remonstrance of affronted That.
'Tho' I deny not the Petition of Mr.
Who and
Which, yet
You should not suffer them to be rude and call honest People Names:
For that bears very hard on some of those Rules of Decency, which You
are justly famous for establishing. They may find fault, and correct
Speeches in the Senate and at the Bar: But let them try to get
themselves so
often and with so much
Eloquence
repeated in a Sentence, as a great Orator doth frequently introduce
me.
My Lords! (says he) with humble Submission,
That that I say is
this; that,
That that that Gentleman has advanced, is not
That, that he should have proved to your Lordships. Let those two
questionary Petitioners try to do thus with their
Who's and their
Whiches.
What great advantage was I of to Mr.
Dryden in his
Indian
Emperor,
You force me still to answer You in That,
to furnish out a Rhyme to
Morat? And what a poor Figure would Mr.
Bayes have made without his
Egad and all That? How can a judicious
Man distinguish one thing from another, without saying
This here, or
That there? And how can a sober Man without using the
Expletives
of Oaths (in which indeed the Rakes and Bullies have a great advantage
over others) make a Discourse of any tolerable Length, without
That
is; and if he be a very grave Man indeed, without
That is to say?
And how instructive as well as entertaining are those usual
Expressions in the Mouths of great Men,
Such Things as That and
The
like of That.
I am not against reforming the Corruptions of Speech You mention, and
own there are proper Seasons for the Introduction of other Words
besides
That; but I scorn as much to supply the Place of a
Who or
a
Which at every Turn, as they are
unequal always to fill mine;
And I expect good Language and civil Treatment, and hope to receive it
for the future:
That, that I shall only add is, that I am,
Yours,
That.'
R.
Contents
To The Right Honourable
Charles Lord Hallifax1.
My Lord,
Similitude of Manners and Studies is usually mentioned as one of the
strongest motives to Affection and Esteem; but the passionate Veneration
I have for your Lordship, I think, flows from an Admiration of Qualities
in You, of which, in the whole course of these Papers I have
acknowledged myself incapable. While I busy myself as a Stranger upon
Earth, and can pretend to no other than being a Looker-on, You are
conspicuous in the Busy and Polite world, both in the World of Men, and
that of Letters; While I am silent and unobserv'd in publick Meetings,
You are admired by all that approach You as the Life and Genius of the
Conversation. What an happy Conjunction of different Talents meets in
him whose whole Discourse is at once animated by the Strength and Force
of Reason, and adorned with all the Graces and Embellishments of Wit:
When Learning irradiates common Life, it is then in its highest Use and
Perfection; and it is to such as Your Lordship, that the Sciences owe
the Esteem which they have with the active Part of Mankind. Knowledge of
Books in recluse Men, is like that sort of Lanthorn which hides him who
carries it, and serves only to pass through secret and gloomy Paths of
his own; but in the Possession of a Man of Business, it is as a Torch in
the Hand of one who is willing and able to shew those, who are
bewildered, the Way which leads to their Prosperity and Welfare. A
generous Concern for your Country, and a Passion for every thing which
is truly Great and Noble, are what actuate all Your Life and Actions;
and I hope You will forgive me that I have an Ambition this Book may be
placed in the Library of so good a Judge of what is valuable, in that
Library where the Choice is such, that it will not be a Disparagement to
be the meanest Author in it. Forgive me, my Lord, for taking this
Occasion of telling all the World how ardently I Love and Honour You;
and that I am, with the utmost Gratitude for all Your Favours,
My Lord,
Your Lordship's
Most Obliged,
Most Obedient, and
Most Humble Servant,
The Spectator.
When the
Spectators
were reissued in volumes, Vol. I. ended
with No. 80, and to the second volume, containing the next 89 numbers,
this Dedication was prefixed.
Charles Montague, at the time of the dedication fifty years old, and
within four years of the end of his life, was born, in 1661, at Horton,
in Northamptonshire. His father was a younger son of the first Earl of
Manchester. He was educated at Westminster School and at Trinity
College, Cambridge.
Apt for wit and verse, he joined with his friend Prior in writing a
burlesque on Dryden's
Hind and Panther
, 'Transversed to the Story of
the Country and the City Mouse.' In Parliament in James the Second's
reign, he joined in the invitation of William of Orange, and rose
rapidly, a self-made man, after the Revolution. In 1691 he was a Lord of
the Treasury; in April, 1694, he became Chancellor of the Exchequer, and
in May, 1697, First Lord of the Treasury, retaining the Chancellorship
and holding both offices till near the close of 1699. Of his dealing
with the currency, see note on p. 19. In 1700 he was made Baron Halifax,
and had secured the office of Auditor of the Exchequer, which was worth
at least £4000 a year, and in war time twice as much. The Tories, on
coming to power, made two unsuccessful attempts to fix on him charges of
fraud. In October, 1714, George I. made him Earl of Halifax and Viscount
Sunbury. Then also he again became Prime Minister. He was married, but
died childless, in May, 1715. In 1699, when Somers and Halifax were the
great chiefs of the Whig Ministry, they joined in befriending Addison,
then 27 years old, who had pleased Somers with a piece of English verse
and Montague with Latin lines upon the Peace of Ryswick.
Now, therefore, having dedicated the First volume of the
Spectator
to
Somers, it is to Halifax that Steele and he inscribe the Second.
Of the defect in Charles Montague's character, Lord Macaulay writes
that, when at the height of his fortune,
"He became proud even to insolence. Old companions ... hardly knew
their friend Charles in the great man who could not forget for one
moment that he was First Lord of the Treasury, that he was Chancellor
of the Exchequer, that he had been a Regent of the kingdom, that he
had founded the Bank of England, and the new East India Company, that
he had restored the Currency, that he had invented the Exchequer
Bills, that he had planned the General Mortgage, and that he had been
pronounced, by a solemn vote of the Commons, to have deserved all the
favours which he had received from the Crown. It was said that
admiration of himself and contempt of others were indicated by all his
gestures, and written in all the lines of his face."
Contents
|
Saturday, June 2, 1711 |
Addison |
Qualis ubi audito venantum murmure Tigris
Horruit in maculas ...
Statins.

About the Middle of last Winter I went to see an Opera at the Theatre in
the
Hay-Market
, where I could not but take notice of two Parties
of very fine Women, that had placed themselves in the opposite
Side-Boxes, and seemed drawn up in a kind of Battle-Array one against
another. After a short Survey of them, I found they were Patch'd
differently; the Faces on one Hand, being spotted on the right Side of
the Forehead, and those upon the other on the Left. I quickly perceived
that they cast hostile Glances upon one another; and that their Patches
were placed in those different Situations, as Party-Signals to
distinguish Friends from Foes. In the Middle-Boxes, between these two
opposite Bodies, were several Ladies who Patched indifferently on both
Sides of their Faces, and seem'd to sit there with no other Intention
but to see the Opera. Upon Inquiry I found, that the Body of
Amazons
on my Right Hand, were Whigs, and those on my Left,
Tories; And that those who had placed themselves in the Middle Boxes
were a Neutral Party, whose Faces had not yet declared themselves. These
last, however, as I afterwards found, diminished daily, and took their
Party with one Side or the other; insomuch that I observed in several of
them, the Patches, which were before dispersed equally, are now all gone
over to the Whig or Tory Side of the Face. The Censorious say, That the
Men, whose Hearts are aimed at, are very often the Occasions that one
Part of the Face is thus dishonoured, and lies under a kind of Disgrace,
while the other is so much Set off and Adorned by the Owner; and that
the Patches turn to the Right or to the Left, according to the
Principles of the Man who is most in Favour. But whatever may be the
Motives of a few fantastical Coquets, who do not Patch for the Publick
Good so much as for their own private Advantage, it is certain, that
there are several Women of Honour who patch out of Principle, and with
an Eye to the Interest of their Country. Nay, I am informed that some of
them adhere so stedfastly to their Party, and are so far from
sacrificing their Zeal for the Publick to their Passion for any
particular Person, that in a late Draught of Marriage-Articles a Lady
has stipulated with her Husband, That, whatever his Opinions are, she
shall be at liberty to Patch on which Side she pleases.
I must here take notice, that
Rosalinda
, a famous Whig Partizan,
has most unfortunately a very beautiful Mole on the Tory Part of her
Forehead; which being very conspicuous, has occasioned many Mistakes,
and given an Handle to her Enemies to misrepresent her Face, as tho' it
had Revolted from the Whig Interest. But, whatever this natural Patch
may seem to intimate, it is well known that her Notions of Government
are still the same. This unlucky Mole, however, has mis-led several
Coxcombs; and like the hanging out of false Colours, made some of them
converse with
Rosalinda
in what they thought the Spirit of her
Party, when on a sudden she has given them an unexpected Fire, that has
sunk them all at once. If
Rosalinda
is unfortunate in her Mole,
Nigranilla
is as unhappy in a Pimple, which forces her, against
her Inclinations, to Patch on the Whig Side.
I am told that many virtuous Matrons, who formerly have been taught to
believe that this artificial Spotting of the Face was unlawful, are now
reconciled by a Zeal for their Cause, to what they could not be prompted
by a Concern for their Beauty.
way of declaring War upon one
another, puts me in mind of what is reported of the Tigress, that
several Spots rise in her Skin when she is angry, or as Mr.
Cowley
has imitated the Verses that stand as the Motto on this
Paper,
...
She swells with angry Pride,
And calls forth all her Spots on ev'ry Side1.
When I was in the Theatre the Time above-mentioned, I had the Curiosity
to count the Patches on both Sides, and found the Tory Patches to be
about Twenty stronger than the Whig; but to make amends for this small
Inequality, I the next Morning found the whole Puppet-Show filled with
Faces spotted after the Whiggish Manner. Whether or no the Ladies had
retreated hither in order to rally their Forces I cannot tell; but the
next Night they came in so great a Body to the Opera, that they
out-number'd the Enemy.
This Account of Party Patches, will, I am afraid, appear improbable to
those who live at a Distance from the fashionable World: but as it is a
Distinction of a very singular Nature, and what perhaps may never meet
with a Parallel, I think I should not have discharged the Office of a
faithful
Spectator
, had I not recorded it.
I have, in former Papers, endeavoured to expose this Party-Rage in
Women, as it only serves to aggravate the Hatreds and Animosities that
reign among Men, and in a great measure deprive the Fair Sex of those
peculiar Charms with which Nature has endowed them.
When the
Romans
and
Sabines
were at War, and just upon the Point of
giving Battel, the Women, who were allied to both of them, interposed
with so many Tears and Intreaties, that they prevented the mutual
Slaughter which threatned both Parties, and united them together in a
firm and lasting Peace.
I would recommend this noble Example to our
British
Ladies, at a Time
when their Country is torn with so many unnatural Divisions, that if
they continue, it will be a Misfortune to be born in it. The
Greeks
thought it so improper for Women to interest themselves in Competitions
and Contentions, that for this Reason, among others, they forbad them,
under Pain of Death, to be present at the
Olympick
Games,
notwithstanding these were the publick Diversions of all
Greece
.
our
English
Women excel those of all Nations in Beauty, they should
endeavour to outshine them in all other Accomplishments
proper
to
the Sex, and to distinguish themselves as tender Mothers, and faithful
Wives, rather than as furious Partizans. Female Virtues are of a
Domestick Turn. The Family is the proper Province for Private Women to
shine in. If they must be shewing their Zeal for the Publick, let it not
be against those who are perhaps of the same Family, or at least of the
same Religion or Nation, but against those who are the open, professed,
undoubted Enemies of their Faith, Liberty and Country. When the
Romans
were pressed with a Foreign Enemy, the Ladies voluntarily contributed
all their Rings and Jewels to assist the Government under a publick
Exigence, which appeared so laudable an Action in the Eyes of their
Countrymen, that from thenceforth it was permitted by a Law to pronounce
publick Orations at the Funeral of a Woman in Praise of the deceased
Person, which till that Time was peculiar to Men. Would our
English
Ladies, instead of sticking on a Patch against those of their own
Country, shew themselves so truly Publick-spirited as to sacrifice every
one her Necklace against the common Enemy, what Decrees ought not to be
made in Favour of them?
I am recollecting upon this Subject such Passages as occur to my
Memory out of ancient Authors, I cannot omit a Sentence in the
celebrated Funeral Oration of
Pericles
which he made in Honour of
those brave
Athenians
that were slain in a fight with the
Lacedæmonians
. After having addressed himself to the several Ranks
and Orders of his Countrymen, and shewn them how they should behave
themselves in the Publick Cause, he turns to the Female Part of his
Audience;
'And as for you (says he) I shall advise you in very few
Words: Aspire only to those Virtues that are peculiar to your Sex;
follow your natural Modesty, and think it your greatest Commendation not
to be talked of one way or other'.
C.
Davideis
, Bk III. But Cowley's Tiger is a Male.
that are proper
Thucydides, Bk II.
Contents
'
|
Monday, June 4, 1711 |
Steele |
... Caput domina venate sub hasta.
Juv.

under
Ludgate
the other Day, I heard a Voice bawling for
Charity, which I thought I had somewhere heard before. Coming near to
the Grate, the Prisoner called me by my Name, and desired I would throw
something into the Box: I was out of Countenance for him, and did as he
bid me, by putting in half a Crown. I went away, reflecting upon the
strange Constitution of some Men, and how meanly they behave themselves
in all Sorts of Conditions. The Person who begged of me is now, as I
take it, Fifty; I was well acquainted with him till about the Age of
Twenty-five; at which Time a good Estate fell to him by the Death of a
Relation. Upon coming to this unexpected good Fortune, he ran into all
the Extravagancies imaginable; was frequently in drunken Disputes, broke
Drawers Heads, talked and swore loud, was unmannerly to those above him,
and insolent to those below him. I could not but remark, that it was the
same Baseness of Spirit which worked in his Behaviour in both Fortunes:
The same little Mind was insolent in Riches, and shameless in Poverty.
This Accident made me muse upon the Circumstances of being in Debt in
general, and solve in my Mind what Tempers were most apt to fall into
this Error of Life, as well as the Misfortune it must needs be to
languish under such Pressures. As for my self, my natural Aversion to
that sort of Conversation which makes a Figure with the Generality of
Mankind, exempts me from any Temptations to Expence; and all my Business
lies within a very narrow Compass, which is only to give an honest Man,
who takes care of my Estate, proper Vouchers for his quarterly Payments
to me, and observe what Linnen my Laundress brings and takes away with
her once a Week: My Steward brings his Receipt ready for my Signing; and
I have a pretty Implement with the respective Names of Shirts, Cravats,
Handkerchiefs and Stockings, with proper Numbers to know how to reckon
with my Laundress. This being almost all the Business I have in the
World for the Care of my own Affairs, I am at full Leisure to observe
upon what others do, with relation to their Equipage and Œconomy.
When I walk the Street, and observe the Hurry about me in this Town,
Where with like Haste, tho' diff'rent Ways they run;
Some to undo, and some to be undone;2
I say, when I behold this vast Variety of Persons and Humours, with the
Pains they both take for the Accomplishment of the Ends mentioned in the
above Verse of
Denham,
I cannot much wonder at the Endeavour after
Gain, but am extremely astonished that Men can be so insensible of the
Danger of running into Debt. One would think it impossible a Man who is
given to contract Debts should know, that his Creditor has, from that
Moment in which he transgresses Payment, so much as that Demand comes to
in his Debtor's Honour, Liberty, and Fortune. One would think he did not
know, that his Creditor can say the worst thing imaginable of him, to
wit,
That he is unjust
, without Defamation; and can seize his Person,
without being guilty of an Assault. Yet such is the loose and abandoned
Turn of some Men's Minds, that they can live under these constant
Apprehensions, and still go on to encrease the Cause of them. Can there
be a more low and servile Condition, than to be ashamed, or afraid, to
see any one Man breathing? Yet he that is much in Debt, is in that
Condition with relation to twenty different People. There are indeed
Circumstances wherein Men of honest Natures may become liable to Debts,
by some unadvised Behaviour in any great Point of their Life, or
mortgaging a Man's Honesty as a Security for that of another, and the
like; but these Instances are so particular and circumstantiated, that
they cannot come within general Considerations: For one such Case as one
of these, there are ten, where a Man, to keep up a Farce of Retinue and
Grandeur within his own House, shall shrink at the Expectation of surly
Demands at his Doors. The Debtor is the Creditor's Criminal, and all the
Officers of Power and State, whom we behold make so great a Figure, are
no other than so many Persons in Authority to make good his Charge
against him. Human Society depends upon his having the Vengeance Law
allots him; and the Debtor owes his Liberty to his Neighbour, as much as
the Murderer does his Life to his Prince.
Our Gentry are, generally speaking, in Debt; and many Families have put
it into a kind of Method of being so from Generation to Generation. The
Father mortgages when his Son is very young: and the Boy is to marry as
soon as he is at Age, to redeem it, and find Portions for his Sisters.
This, forsooth, is no great Inconvenience to him; for he may wench, keep
a publick Table or feed Dogs, like a worthy
English
Gentleman, till he
has out-run half his Estate, and leave the same Incumbrance upon his
First-born, and so on, till one Man of more Vigour than ordinary goes
quite through the Estate, or some Man of Sense comes into it, and scorns
to have an Estate in Partnership, that is to say, liable to the Demand
or Insult of any Man living. There is my Friend Sir
Andrew.
, tho' for
many Years a great and general Trader, was never the Defendant in a
Law-Suit, in all the Perplexity of Business, and the Iniquity of Mankind
at present: No one had any Colour for the least Complaint against his
Dealings with him. This is certainly as uncommon, and in its Proportion
as laudable in a Citizen, as it is in a General never to have suffered a
Disadvantage in Fight. How different from this Gentleman is
Jack
Truepenny,
who has been an old Acquaintance of Sir
Andrew.
and my self
from Boys, but could never learn our Caution.
Jack
has a whorish
unresisting Good-nature, which makes him incapable of having a Property
in any thing. His Fortune, his Reputation, his Time and his Capacity,
are at any Man's Service that comes first. When he was at School, he was
whipped thrice a Week for Faults he took upon him to excuse others;
since he came into the Business of the World, he has been arrested twice
or thrice a Year for Debts he had nothing to do with, but as a Surety
for others; and I remember when a Friend of his had suffered in the Vice
of the Town, all the Physick his Friend took was conveyed to him by
Jack
, and inscribed, 'A Bolus or an Electuary for Mr.
Truepenny
.'
Jack
had a good Estate left him, which came to nothing; because he
believed all who pretended to Demands upon it. This Easiness and
Credulity destroy all the other Merit he has; and he has all his Life
been a Sacrifice to others, without ever receiving Thanks, or doing one
good Action.
I will end this Discourse with a Speech which I heard
Jack
make to one
of his Creditors, (of whom he deserved gentler Usage) after lying a
whole Night in Custody at his Suit.
Sir,
'Your Ingratitude for the many Kindnesses I have done you, shall not
make me unthankful for the Good you have done me, in letting me see
there is such a Man as you in the World. I am obliged to you for the
Diffidence I shall have all the rest of my Life: I shall hereafter
trust no Man so far as to be in his Debt.'
R.
Ludgate was originally built in 1215, by the Barons who
entered London, destroyed houses of Jews and erected this gate with
their ruins. It was first used as a prison in 1373, being then a free
prison, but soon losing that privilege. Sir Stephen Forster, who was
Lord Mayor in 1454, had been a prisoner at Ludgate and begged at the
grate, where he was seen by a rich widow who bought his liberty, took
him into her service, and eventually married him. To commemorate this he
enlarged the accommodation for the prisoners and added a chapel. The old
gate was taken down and rebuilt in 1586. That second gate was destroyed
in the Fire of London.
The gate which succeeded and was used, like its predecessors, as a
wretched prison for debtors, was pulled down in 1760, and the prisoners
removed, first to the London workhouse, afterwards to part of the
Giltspur Street Compter.
Sir John Denham's
Cooper's Hill.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 5, 1711 |
Addison |
... Animum pictura pascit inani.
Virg.

When the Weather hinders me from taking my Diversions without Doors, I
frequently make a little Party with two or three select Friends, to
visit any thing curious that may be seen under Covert. My principal
Entertainments of this Nature are Pictures, insomuch that when I have
found the Weather set in to be very bad, I have taken a whole Day's
Journey to see a Gallery that is furnished by the Hands of great
Masters. By this means, when the Heavens are filled with Clouds, when
the Earth swims in Rain, and all Nature wears a lowering Countenance, I
withdraw myself from these uncomfortable Scenes into the visionary
Worlds of Art; where I meet with shining Landskips, gilded Triumphs,
beautiful Faces, and all those other Objects that fill the mind with gay
Ideas, and disperse that Gloominess which is apt to hang upon it in
those dark disconsolate Seasons.
I was some Weeks ago in a Course of these Diversions; which had taken
such an entire Possession of my Imagination, that they formed in it a
short Morning's Dream, which I shall communicate to my Reader, rather as
the first Sketch and Outlines of a Vision, than as a finished Piece.
I dreamt that I was admitted into a long spacious Gallery, which had one
Side covered with Pieces of all the Famous Painters who are now living,
and the other with the Works of the greatest Masters that are dead.
On the side of the
Living
, I saw several Persons busy in Drawing,
Colouring, and Designing; on the side of the
Dead
Painters, I could
not discover more than one Person at Work, who was exceeding slow in his
Motions, and wonderfully nice in his Touches.
I was resolved to examine the several Artists that stood before me, and
accordingly applied my self to the side of the
Living
. The first I
observed at Work in this Part of the Gallery was
Vanity
, with his Hair
tied behind him in a Ribbon, and dressed like a
Frenchman
. All the
Faces he drew were very remarkable for their Smiles, and a certain
smirking Air which he bestowed indifferently on every Age and Degree of
either Sex. The
Toujours Gai
appeared even in his Judges, Bishops, and
Privy-Counsellors: In a word all his Men were
Petits Maitres
, and all
his Women
Coquets
. The Drapery of his Figures was extreamly
well-suited to his Faces, and was made up of all the glaring Colours
that could be mixt together; every Part of the Dress was in a Flutter,
and endeavoured to distinguish itself above the rest.
On the left Hand of
Vanity
stood a laborious Workman, who I found was
his humble Admirer, and copied after him. He was dressed like a
German
, and had a very hard Name, that sounded something like
Stupidity
.
The third Artist that I looked over was
Fantasque
, dressed like a
Venetian Scaramouch. He had an excellent Hand at a
Chimera
, and
dealt very much in Distortions and Grimaces: He would sometimes affright
himself with the Phantoms that flowed from his Pencil. In short, the
most elaborate of his Pieces was at best but a terrifying Dream; and one
could say nothing more of his finest Figures, than that they were
agreeable Monsters.
The fourth Person I examined was very remarkable for his hasty Hand,
which left his Pictures so unfinished, that the Beauty in the Picture
(which was designed to continue as a monument of it to Posterity) faded
sooner than in the Person after whom it was drawn.
made so much haste
to dispatch his Business, that he neither gave himself time to clean his
Pencils,
nor
mix his Colours. The Name of this expeditious Workman
was
Avarice
.
Not far from this Artist I saw another of a quite different Nature, who
was dressed in the Habit of a
Dutchman
, and known by the Name of
Industry
. His Figures were wonderfully laboured; If he drew the
Portraiture of a man, he did not omit a single Hair in his Face; if the
Figure of a Ship, there was not a Rope among the Tackle that escaped
him. He had likewise hung a great Part of the Wall with Night-pieces,
that seemed to shew themselves by the Candles which were lighted up in
several Parts of them; and were so inflamed by the Sun-shine which
accidentally fell upon them, that at first sight I could scarce forbear
crying out,
Fire
.
The five foregoing Artists were the most considerable on this Side the
Gallery; there were indeed several others whom I had not time to look
into. One of them, however, I could not forbear observing, who was very
busie in retouching the finest Pieces, tho' he produced no Originals of
his own. His Pencil aggravated every Feature that was before
over-charged, loaded every Defect, and poisoned every Colour it touched.
Though this workman did so much Mischief on the Side of the Living, he
never turned his Eye towards that of the Dead. His Name was
Envy
.
Having taken a cursory View of one Side of the Gallery, I turned my self
to that which was filled by the Works of those great Masters that were
dead; when immediately I fancied my self standing before a Multitude of
Spectators, and thousands of Eyes looking upon me at once; for all
before me appeared so like Men and Women, that I almost forgot they were
Pictures.
Raphael's
Figures stood in one Row,
Titian's
in another,
Guido Rheni's
in a third. One Part of the Wall was peopled by
Hannibal Carrache
, another by
Correggio
, and another by
Rubens
. To
be short, there was not a great Master among the Dead who had not
contributed to the Embellishment of this Side of the Gallery. The
Persons that owed their Being to these several Masters, appeared all of
them to be real and alive, and differed among one another only in the
Variety of their Shapes, Complexions, and Cloaths; so that they looked
like different Nations of the same Species.
Observing an old Man (who was the same Person I before mentioned, as the
only Artist that was at work on this Side of the Gallery) creeping up
and down from one Picture to another, and retouching all the fine Pieces
that stood before me, I could not but be very attentive to all his
Motions. I found his Pencil was so very light, that it worked
imperceptibly, and after a thousand Touches, scarce produced any visible
Effect in the Picture on which he was employed. However, as he busied
himself incessantly, and repeated Touch after Touch without Rest or
Intermission, he wore off insensibly every little disagreeable Gloss
that hung upon a Figure.
also added such a beautiful Brown to the
Shades, and Mellowness to the Colours, that he made every Picture appear
more perfect than when it came fresh from
the
Master's Pencil. I
could not forbear looking upon the Face of this ancient Workman, and
immediately, by the long Lock of Hair upon his Forehead, discovered him
to be
Time
.
Whether it were because the Thread of my Dream was at an End I cannot
tell, but upon my taking a Survey of this imaginary old Man, my Sleep
left me.
C.
or
its
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 6, 1711 |
Steele |
... Quis talia fando
Myrmidonum Dolopumve aut duri miles Ulyssei
Temperet a Lachrymis?
Virg.

over the old Manuscript wherein the private Actions of
Pharamond
are set down by way of Table-Book. I found many things
which gave me great Delight; and as human Life turns upon the same
Principles and Passions in all Ages, I thought it very proper to take
Minutes of what passed in that Age, for the Instruction of this. The
Antiquary, who lent me these Papers, gave me a Character of
Eucrate
,
the Favourite of
Pharamond
, extracted from an Author who lived in that
Court. The Account he gives both of the Prince and this his faithful
Friend, will not be improper to insert here, because I may have Occasion
to mention many of their Conversations, into which these Memorials of
them may give Light.
'
Pharamond, when he had a Mind to retire for an Hour or two from the
Hurry of Business and Fatigue of Ceremony, made a Signal to
Eucrate,
by putting his Hand to his Face, placing his Arm negligently on a
Window, or some such Action as appeared indifferent to all the rest of
the Company. Upon such Notice, unobserved by others, (for their entire
Intimacy was always a Secret)
Eucrate repaired to his own Apartment
to receive the King. There was a secret Access to this Part of the
Court, at which
Eucrate used to admit many whose mean Appearance in
the Eyes of the ordinary Waiters and Door-keepers made them be
repulsed from other Parts of the Palace. Such as these were let in
here by Order of
Eucrate, and had Audiences of
Pharamond. This
Entrance
Pharamond called
The Gate of the Unhappy, and the Tears
of the Afflicted who came before him, he would say were Bribes
received by
Eucrate; for
Eucrate had the most compassionate Spirit
of all Men living, except his generous Master, who was always kindled
at the least Affliction which was communicated to him. In the Regard
for the Miserable,
Eucrate took particular Care, that the common
Forms of Distress, and the idle Pretenders to Sorrow, about Courts,
who wanted only Supplies to Luxury, should never obtain Favour by his
Means: But the Distresses which arise from the many inexplicable
Occurrences that happen among Men, the unaccountable Alienation of
Parents from their Children, Cruelty of Husbands to Wives, Poverty
occasioned from Shipwreck or Fire, the falling out of Friends, or such
other terrible Disasters, to which the Life of Man is exposed; In
Cases of this Nature,
Eucrate was the Patron; and enjoyed this Part
of the Royal Favour so much without being envied, that it was never
inquired into by whose Means, what no one else cared for doing, was
brought about.
'One Evening when
Pharamond came into the Apartment of
Eucrate, he
found him extremely dejected; upon which he asked (with a Smile which
was natural to him)
"What, is there any one too miserable to be
relieved by Pharamond, that Eucrate is melancholy?
I fear there
is, answered the Favourite; a Person without, of a good Air, well
Dressed, and tho' a Man in the Strength of his Life, seems to faint
under some inconsolable Calamity: All his Features seem suffused with
Agony of Mind; but I can observe in him, that it is more inclined to
break away in Tears than Rage. I asked him what he would have; he said
he would speak to Pharamond. I desired his Business; he could hardly
say to me, Eucrate, carry me to the King, my Story is not to be told
twice, I fear I shall not be able to speak it at all."
Pharamond
commanded Eucrate to let him enter; he did so, and the Gentleman
approached the King with an Air which spoke
him under the greatest
Concern in what Manner to demean himself2. The King, who had a
quick Discerning, relieved him from the Oppression he was under; and
with the most beautiful Complacency said to him,
"Sir, do not add to
that Load of Sorrow I see in your Countenance, the Awe of my Presence:
Think you are speaking to your Friend; if the Circumstances of your
Distress will admit of it, you shall find me so."
To whom the
Stranger:
"Oh excellent
Pharamond, name not a Friend to the
unfortunate
Spinamont. I had one, but he is dead by my own Hand
3;
but, oh
Pharamond, tho' it was by the Hand of
Spinamont, it was by
the Guilt of
Pharamond. I come not, oh excellent Prince, to implore
your Pardon; I come to relate my Sorrow, a Sorrow too great for human
Life to support: From henceforth shall all Occurrences appear Dreams
or short Intervals of Amusement, from this one Affliction which has
seiz'd my very Being: Pardon me, oh
Pharamond, if my Griefs give me
Leave, that I lay before you, in the Anguish of a wounded Mind, that
you, good as you are, are guilty of the generous Blood spilt this Day
by this unhappy Hand: Oh that it had perished before that Instant!"
Here the Stranger paused, and recollecting his Mind, after some little
Meditation, he went on in a calmer Tone and Gesture as follows.
"There is an Authority due to Distress; and as none of human Race is
above the Reach of Sorrow, none should be above the Hearing the Voice
of it: I am sure Pharamond is not. Know then, that I have this
Morning unfortunately killed in a Duel, the Man whom of all Men living
I most loved. I command my self too much in your royal Presence, to
say, Pharamond, give me my Friend! Pharamond has taken him from
me! I will not say, shall the merciful Pharamond destroy his own
Subjects? Will the Father of his Country murder his People? But, the
merciful Pharamond does destroy his Subjects, the Father of his
Country does murder his People. Fortune is so much the Pursuit of
Mankind, that all Glory and Honour is in the Power of a Prince,
because he has the Distribution of their Fortunes. It is therefore the
Inadvertency, Negligence, or Guilt of Princes, to let any thing grow
into Custom which is against their Laws. A Court can make Fashion and
Duty walk together; it can never, without the Guilt of a Court,
happen, that it shall not be unfashionable to do what is unlawful. But
alas! in the Dominions of Pharamond, by the Force of a Tyrant
Custom, which is mis-named a Point of Honour, the Duellist kills his
Friend whom he loves; and the Judge condemns the Duellist, while he
approves his Behaviour. Shame is the greatest of all Evils; what avail
Laws, when Death only attends the Breach of them, and Shame Obedience
to them? As for me, oh Pharamond, were it possible to describe
the nameless Kinds of Compunctions and Tendernesses I feel, when I
reflect upon the little Accidents in our former Familiarity, my Mind
swells into Sorrow which cannot be resisted enough to be silent in the
Presence of Pharamond."
With that he fell into a Flood of
Tears, and wept aloud.
"Why should not Pharamond hear the
Anguish he only can relieve others from in Time to come? Let him hear
from me, what they feel who have given Death by the false Mercy of his
Administration, and form to himself the Vengeance call'd for by those
who have perished by his Negligence.'
R.
See
Steele uses the suggestion of the Romance of
Pharamond
whose
'whole Person,' says the romancer, 'was of so
excellent a composition, and his words so Great and so Noble that it was
very difficult to deny him reverence,'
to connect with a remote king his
ideas of the duty of a Court. Pharamond's friend Eucrate, whose name
means Power well used, is an invention of the Essayist, as well as the
incident and dialogue here given, for an immediate good purpose of his
own, which he pleasantly contrives in imitation of the style of the
romance. In the original, Pharamond is said to be
'
truly and wholly
charming, as well for the vivacity and delicateness of his spirit,
accompanied with a perfect knowledge of all Sciences, as for a sweetness
which is wholly particular to him, and a complacence which &c.... All
his inclinations are in such manner fixed upon virtue, that no
consideration nor passion can disturb him; and in those extremities into
which his ill fortune hath cast him, he hath never let pass any occasion
to do good.'
That is why Steele chose Pharamond for his king in this and
a preceding paper.
the utmost sense of his Majesty without the ability to
express it.
Spinamont is Mr. Thornhill, who, on the 9th of May, 1711,
killed in a duel Sir Cholmomleley Dering, Baronet, of Kent. Mr.
Thornhill was tried and acquitted; but two months afterwards,
assassinated by two men, who, as they stabbed him, bade him remember Sir
Cholmondeley Dering. Steele wrote often and well against duelling,
condemning it in the
Tatler
several times, in the
Spectator
several
times, in the
Guardian
several times, and even in one of his plays.
Contents
|
Thursday, June 7, 1711 |
Addison |
Interdum speciosa locis, morataque recte
Fabula nullius Veneris, sine pondere et Arte,
Valdius oblectat populum, meliusque moratur,
Quàm versus inopes rerum, nugæque canoræ.
Hor.

It is the Custom of the
Mahometans
, if they see any printed or
written Paper upon the Ground, to take it up and lay it aside carefully,
as not knowing but it may contain some Piece of their
Alcoran
. I
must confess I have so much of the
Mussulman
in me, That I cannot
forbear looking into every printed Paper which comes in my Way, under
whatsoever despicable Circumstances it may appear; for as no mortal
Author, in the ordinary Fate and Vicissitude of Things, knows to what
Use his Works may, some time or other, be applied, a Man may often meet
with very celebrated Names in a Paper of Tobacco. I have lighted my Pipe
more than once with the Writings of a Prelate; and know a Friend of
mine, who, for these several Years, has converted the Essays of a Man of
Quality into a kind of Fringe for his Candlesticks. I remember in
particular, after having read over a Poem of an Eminent Author on a
Victory, I met with several Fragments of it upon the next rejoicing Day,
which had been employ'd in Squibs and Crackers, and by that means
celebrated its Subject in a double Capacity. I once met with a Page of
Mr.
Baxter
under a
Christmas
Pye. Whether or no the
Pastry-Cook had made use of it through Chance or Waggery, for the
Defence of that superstitious
Viande
, I know not; but upon the
Perusal of it, I conceived so good an Idea of the Author's Piety, that I
bought the whole Book. I have often profited by these accidental
Readings, and have sometimes found very Curious Pieces, that are either
out of Print, or not to be met with in the Shops of our
London
Booksellers
. For this Reason, when my Friends take a Survey of my
Library, they are very much surprised to find, upon the Shelf of Folios,
two long Band-Boxes standing upright among my Books, till I let them see
that they are both of them lined with deep Erudition and abstruse
Literature. I might likewise mention a Paper-Kite, from which I have
received great Improvement; and a Hat-Case, which I would not exchange
for all the Beavers in
Great-Britain
. This my inquisitive Temper,
or rather impertinent Humour of prying into all Sorts of Writing, with
my natural Aversion to Loquacity, give me a good deal of Employment when
I enter any House in the Country; for I cannot for my Heart leave a
Room, before I have thoroughly studied the Walls of it, and examined the
several printed Papers which are usually pasted upon them. The last
Piece that I met with upon this Occasion gave me a most exquisite
Pleasure. My Reader will think I am not serious, when I acquaint him
that the Piece I am going to speak of was the old Ballad of the
Two
Children in the Wood
, which is one of the darling Songs of the
common People, and has been the Delight of most
Englishmen
in
some Part of their Age.
This Song is a plain simple Copy of Nature, destitute of the Helps and
Ornaments of Art. The Tale of it is a pretty Tragical Story, and pleases
for no other Reason but because it is a Copy of Nature. There is even a
despicable Simplicity in the Verse; and yet because the Sentiments
appear genuine and unaffected, they are able to move the Mind of the
most polite Reader with Inward Meltings of Humanity and Compassion.
Incidents grow out of the Subject, and are such as [are the most proper
to excite Pity; for
which Reason the whole Narration has something
in it very moving, notwithstanding the Author of it (whoever he was) has
deliver'd it in such an abject Phrase and Poorness of Expression, that
the quoting any part of it would look like a Design of turning it into
Ridicule. But though the Language is mean, the Thoughts
, as I have
before said,
from one end to the other are
natural
, and therefore
cannot fail to please those who are not Judges of Language, or those
who, notwithstanding they are Judges of Language, have a
true
and
unprejudiced Taste of Nature.
Condition, Speech, and Behaviour of
the dying Parents, with the Age, Innocence, and Distress of the
Children, are set forth in such tender Circumstances, that it is
impossible for a
Reader of common Humanity
not to be affected with
them. As for the Circumstance of the
Robin-red-breast
, it is
indeed a little Poetical Ornament; and to shew
the Genius of the Author
amidst all his Simplicity, it is just the same kind of Fiction
which one of the greatest of the
Latin
Poets has made use of upon
a parallel Occasion; I mean that Passage in
Horace
, where he
describes himself when he was a Child, fallen asleep in a desart Wood,
and covered with Leaves by the Turtles that took pity on him.
Me fabulosa Vulture in Apulo,
Altricis extra limen Apuliæ,
Ludo fatigatumque somno
Fronde novâ puerum palumbes
Texere ...
have heard that the late Lord
Dorset
, who had the greatest Wit
temper'd with the greatest
Candour,
and was one of the finest
Criticks as well as the best Poets of his Age, had a numerous collection
of old
English
Ballads, and took a particular Pleasure in the
Reading of them. I can affirm the same of Mr.
Dryden
, and know
several of the most refined Writers of our present Age who are of the
same Humour.
I might likewise refer my Reader to
Moliere's
Thoughts on this
Subject, as he has expressed them in the Character of the
Misanthrope
; but those only who are endowed with a true Greatness
of Soul and Genius can divest themselves of the little Images of
Ridicule, and admire Nature in her Simplicity and Nakedness.
for the
little conceited Wits of the Age, who can only shew their Judgment by
finding Fault, they cannot be supposed to admire these Productions
which
have nothing to recommend them but the Beauties of Nature,
when they do not know how to relish even those Compositions that, with
all the Beauties of Nature, have also the additional Advantages of Art
.
Virgil
himself would have touched upon, had the like
Story been told by that Divine Poet. For
wonderfully natural
genuine
goodnatured Reader
what a Genius the Author was Master of
Humanity
that
Addison had incurred much ridicule from the bad taste of
the time by his papers upon Chevy Chase, though he had gone some way to
meet it by endeavouring to satisfy the Dennises of 'that polite age,'
with authorities from Virgil. Among the jests was a burlesque criticism
of
Tom Thumb
. What Addison thought of the 'little images of Ridicule'
set up against him, the last paragraph of this Essay shows, but the
collation of texts shows that he did flinch a little. We now see how he
modified many expressions in the reprint of this Essay upon the
Babes
in the Wood
.
Contents
|
Friday, June 8, 1711 |
Addison |
Heu quam difficile est crimen non prodere vultu!
Ovid.

are several Arts which
all Men are in
some measure
Masters
of, without having been at the Pains of learning them. Every one
that speaks or reasons is a Grammarian and a Logician, tho' he may be
wholly unacquainted with the Rules of Grammar or Logick, as they are
delivered in Books and Systems. In the same Manner, every one is in some
Degree a Master of that Art which is generally distinguished by the Name
of Physiognomy; and naturally forms to himself the Character or Fortune
of a Stranger, from the Features and Lineaments of his Face.
are no
sooner presented to any one we never saw before, but we are immediately
struck with the Idea of a proud, a reserved, an affable, or a
good-natured Man; and upon our first going into a Company of
Strangers
, our Benevolence or Aversion, Awe or Contempt, rises naturally
towards several particular Persons before we have heard them speak a
single Word, or so much as know who they are.
Every Passion gives a particular Cast to the Countenance, and is apt to
discover itself in some Feature or other. I have seen an Eye curse for
half an Hour together, and an Eye-brow call a Man Scoundrel. Nothing is
more common than for Lovers to complain, resent, languish, despair, and
die in dumb Show. For my own part, I am so apt to frame a Notion of
every Man's Humour or Circumstances by his Looks, that I have sometimes
employed my self from
Charing-Cross
to the
Royal-Exchange
in drawing the Characters of those who have passed by me. When I see a
Man with a sour rivell'd Face, I cannot forbear pitying his Wife; and
when I meet with an open ingenuous Countenance, think on the Happiness
of his Friends, his Family, and Relations.
cannot recollect the Author of a famous Saying to a Stranger who stood
silent in his Company,
Speak that I may see thee:
But,
with Submission, I think we may be better known by our Looks than by our
Words; and that a Man's Speech is much more easily disguised than his
Countenance. In this Case, however, I think the Air of the whole Face is
much more expressive than the Lines of it: The Truth of it is, the Air
is generally nothing else but the inward Disposition of the Mind made
visible.
Those who have established Physiognomy into an Art, and laid down Rules
of judging Mens Tempers by their Faces, have regarded the Features much
more than the Air.
Martial
has a pretty Epigram on this Subject:
Crine ruber, niger ore, brevis pede, lumine lœsus:
Rem magnam prœstas, Zoile, si bonus es.
(Epig. 54, 1. 12)
Thy Beard and Head are of a diff'rent Dye;
Short of one Foot, distorted in an Eye:
With all these Tokens of a Knave compleat,
Should'st thou be honest, thou'rt a dev'lish Cheat.
have seen a very ingenious Author on this Subject,
who
founds
his Speculations on the Supposition, That as a Man hath in the Mould of
his Face a remote Likeness to that of an Ox, a Sheep, a Lion, an Hog, or
any other Creature; he hath the same Resemblance in the Frame of his
Mind, and is subject to those Passions which are predominant in the
Creature that appears in his Countenance
. Accordingly he gives the
Prints of several Faces that are of a different Mould, and by
a little
overcharging the Likeness, discovers the Figures of these several Kinds
of brutal Faces in human Features.
remember, in the Life of the famous
Prince of
Conde
the Writer observes,
the
Face of that
Prince was like the Face of an Eagle, and that the Prince was very well
pleased to be told so. In this Case therefore we may be sure, that he
had in his Mind some general implicit Notion of this Art of Physiognomy
which I have just now mentioned; and that when his Courtiers told him
his Face was made like an Eagle's, he understood them in the same manner
as if they had told him, there was something in his Looks which shewed
him to be strong, active, piercing, and of a royal Descent. Whether or
no the different Motions of the Animal Spirits, in different Passions,
may have any Effect on the Mould of the Face when the Lineaments are
pliable and tender, or whether the same kind of Souls require the same
kind of Habitations, I shall leave to the Consideration of the Curious.
In the mean Time I think nothing can be more glorious than for a Man to
give the Lie to his Face, and to be an honest, just, good-natured Man,
in spite of all those Marks and Signatures which Nature seems to have
set upon him for the Contrary. This very often happens among those, who,
instead of being exasperated by their own Looks, or envying the Looks of
others, apply themselves entirely to the cultivating of their Minds, and
getting those Beauties which are more lasting and more ornamental. I
have seen many an amiable Piece of Deformity; and have observed a
certain Chearfulness in as bad a System of Features as ever was clapped
together, which hath appeared more lovely than all the blooming Charms
of an insolent Beauty. There is a double Praise due to Virtue, when it
is lodged in a Body that seems to have been prepared for the Reception
of Vice; in many such Cases the Soul and the Body do not seem to be
Fellows.
Socrates
was an extraordinary Instance of this Nature.
chanced to be a great Physiognomist in his Time at
Athens
,
who had made strange Discoveries of Mens Tempers and Inclinations by
their outward Appearances.
Socrates's
Disciples, that they might
put this Artist to the Trial, carried him to their Master, whom he had
never seen before, and did not know
he was then in company with him
. After
short Examination of his Face, the Physiognomist
pronounced him the most lewd, libidinous, drunken old Fellow that he had
ever
met with
in his
whole
Life. Upon which the Disciples all
burst out a laughing, as thinking they had detected the Falshood and
Vanity of his Art. But
Socrates
told them, that the Principles of
his Art might be very true, notwithstanding his present Mistake; for
that he himself was naturally inclined to those particular Vices which
the Physiognomist had discovered in his Countenance, but that he had
conquered the strong Dispositions he was born with by the Dictates of
Philosophy.
are indeed told by an ancient Author, that
Socrates
very much
resembled
Silenus
in his Face
; which we find to have been
very rightly observed from the Statues and Busts of both,
that
are still extant; as well as on several antique Seals and precious
Stones, which are frequently enough to be met with in the Cabinets of
the Curious. But however Observations of this Nature may sometimes hold,
a wise Man should be particularly cautious how he gives credit to a
Man's outward Appearance.
is an irreparable Injustice
we
are
guilty of towards one another, when we are prejudiced by the Looks and
Features of those whom we do not know. How often do we conceive Hatred
against a Person of Worth, or fancy a Man to be proud and ill-natured by
his Aspect, whom we think we cannot esteem too much when we are
acquainted with his real Character?
.
Moore
, in his
admirable System of Ethicks, reckons this particular Inclination to take
a Prejudice against a Man for his Looks, among the smaller Vices in
Morality, and, if I remember, gives it the Name of a
Prosopolepsia
.
every Man is
Master
unknown Persons
Socrates. In Apul.
Flor
.
that
The idea is as old as Aristotle who, in treating of arguing
from signs in general, speaks under the head of Physiognomy of
conclusions drawn from natural signs, such as indications of the temper
proper to each class of animals in forms resembling them. The book
Addison refers to is Baptista della Porta '
De Humanâ
Physiognomiâ
'
Histoire du Louis de Bourbon II du Nom Prince de Condé,
Englished by Nahum Tate in 1693.
that the
Cicero,
Tusc. Quæst.
Bk. IV. near the close. Again
de Fato
, c. 5, he says that the physiognomist Zopyrus pronounced
Socrates stupid and dull, because the outline of his throat was not
concave, but full and obtuse.
who he was.
seen
Plato in the
Symposium
; where Alcibiades is made to
draw the parallel under the influence of wine and revelry. He compares
the person of Socrates to the sculptured figures of the Sileni and the
Mercuries in the streets of Athens, but owns the spell by which he was
held, in presence of Socrates, as by the flute of the Satyr Marsyas.
which
that we
Dr Henry More.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 9, 1711 |
Steele |
... Nimium ne crede colori.
Virg.

It has been the Purpose of several of my Speculations to bring People to
an unconcerned Behaviour, with relation to their Persons, whether
beautiful or defective. As the Secrets of the
Ugly Club
were
exposed to the Publick, that Men might see there were some noble Spirits
in the Age, who are not at all displeased with themselves upon
Considerations which they had no Choice in: so the Discourse concerning
Idols
tended to lessen the Value People put upon themselves from
personal Advantages, and Gifts of Nature. As to the latter Species of
Mankind, the Beauties, whether Male or Female, they are generally the
most untractable People of all others. You are so excessively perplexed
with the Particularities in their Behaviour, that, to be at Ease, one
would be apt to wish there were no such Creatures. They expect so great
Allowances, and give so little to others, that they who have to do with
them find in the main, a Man with a better Person than ordinary, and a
beautiful Woman, might be very happily changed for such to whom Nature
has been less liberal. The Handsome Fellow is usually so much a
Gentleman, and the Fine Woman has something so becoming, that there is
no enduring either of them. It has therefore been generally my Choice to
mix with chearful Ugly Creatures, rather than Gentlemen who are Graceful
enough to omit or do what they please; or Beauties who have Charms
enough to do and say what would be disobliging in any but themselves.
Diffidence and Presumption, upon account of our Persons, are equally
Faults; and both arise from the Want of knowing, or rather endeavouring
to know, our selves, and for what we ought to be valued or neglected.
But indeed, I did not imagine these little Considerations and Coquetries
could have the ill Consequences as I find they have by the following
Letters of my Correspondents, where it seems Beauty is thrown into the
Account, in Matters of Sale, to those who receive no Favour from the
Charmers.
June 4
Mr. Spectator,.
After I have assured you I am in every respect one of the Handsomest
young Girls about Town — I need be particular in nothing but the make
of my Face, which has the Misfortune to be exactly Oval. This I take
to proceed from a Temper that naturally inclines me both to speak and
hear.
With this Account you may wonder how I can have the Vanity to offer my
self as a Candidate, which I now do, to a Society, where the
Spectator
and
Hecatissa have been admitted with so much Applause. I don't
want to be put in mind how very Defective I am in every thing that is
Ugly: I am too sensible of my own Unworthiness in this Particular, and
therefore I only propose my self as a Foil to the Club.
You see how honest I have been to confess all my Imperfections, which
is a great deal to come from a Woman, and what I hope you will
encourage with the Favour of your Interest.
There can be no Objection made on the Side of the matchless
Hecatissa, since it is certain I shall be in no Danger of
giving her the least occasion of Jealousy: And then a Joint-Stool in
the very lowest Place at the Table, is all the Honour that is coveted
by
Your most Humble and Obedient Servant,
Rosalinda.
P.S. I have sacrificed my Necklace to put into the Publick Lottery
against the Common Enemy. And last
Saturday, about Three a
Clock in the Afternoon, I began to patch indifferently on both Sides
of my Face.
London, June 7, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Upon reading your late Dissertation concerning
Idols, I cannot
but complain to you that there are, in six or seven Places of this
City, Coffee-houses kept by Persons of that Sisterhood. These
Idols sit and receive all Day long the adoration of the Youth
within such and such Districts: I know, in particular, Goods are not
entered as they ought to be at the Custom-house, nor Law-Reports
perused at the Temple; by reason of one Beauty who detains the young
Merchants too long near
Change, and another Fair One who keeps
the Students at her House when they should be at Study. It would be
worth your while to see how the Idolaters alternately offer Incense to
their
Idols, and what Heart-burnings arise in those who wait
for their Turn to receive kind Aspects from those little Thrones,
which all the Company, but these Lovers, call the Bars. I saw a
Gentleman turn as pale as Ashes, because an
Idol turned the
Sugar in a Tea-Dish for his Rival, and carelessly called the Boy to
serve him, with a
Sirrah! Why don't you give the Gentleman the Box
to please himself? Certain it is, that a very hopeful young Man
was taken with Leads in his Pockets below Bridge, where he intended to
drown himself, because his
Idol would wash the Dish in which
she had but just
then1 drank Tea, before she would let him use it.
I am, Sir, a Person past being Amorous, and do not give this
Information out of Envy or Jealousy, but I am a real Sufferer by it.
These Lovers take any thing for Tea and Coffee; I saw one Yesterday
surfeit to make his Court; and all his Rivals, at the same time, loud
in the Commendation of Liquors that went against every body in the
Room that was not in Love. While these young Fellows resign their
Stomachs with their Hearts, and drink at the
Idol in this
manner, we who come to do Business, or talk Politicks, are utterly
poisoned: They have also Drams for those who are more enamoured than
ordinary; and it is very common for such as are too low in
Constitution to ogle the
Idol upon the Strength of Tea, to
fluster themselves with warmer Liquors: Thus all Pretenders advance,
as fast as they can, to a Feaver or a Diabetes. I must repeat to you,
that I do not look with an evil Eye upon the Profit of the
Idols, or the Diversion of the Lovers; what I hope from this
Remonstrance, is only that we plain People may not be served as if we
were Idolaters; but that from the time of publishing this in your
Paper, the
Idols would mix Ratsbane only for their Admirers, and
take more care of us who don't love them.
I am,
Sir,
Yours,
T.T.
2
R.
just before
This letter is ascribed to Laurence Eusden.
Contents
This to give Notice,
That the three Criticks
who last Sunday
settled the Characters
of my Lord Rochester
and Boileau,
in the Yard of a Coffee House in Fuller's Rents,
will meet this next Sunday
at the same Time and Place,
to finish the Merits of several Dramatick Writers:
And will also make an End of the Nature of True Sublime.
|
Monday, June 11, 1711 |
Steele |
Quid Domini facient, audent cum tulia Fures?
Virg.

May 30, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
I have no small Value for your Endeavours to lay before the World what
may escape their Observation, and yet highly conduces to their
Service. You have, I think, succeeded very well on many Subjects; and
seem to have been conversant in very different Scenes of Life. But in
the Considerations of Mankind, as a
Spectator, you should not omit
Circumstances which relate to the inferior Part of the World, any more
than those which concern the greater. There is one thing in particular
which I wonder you have not touched upon, and that is the general
Corruption of Manners in the Servants of
Great Britain. I am a Man
that have travelled and seen many Nations, but have for seven Years
last past resided constantly in
London, or within twenty Miles of
it: In this Time I have contracted a numerous Acquaintance among the
best Sort of People, and have hardly found one of them happy in their
Servants. This is matter of great Astonishment to Foreigners, and all
such as have visited Foreign Countries; especially since we cannot but
observe, That there is no Part of the World where Servants have those
Privileges and Advantages as in
England: They have no where else
such plentiful Diet, large Wages, or indulgent Liberty: There is no
Place wherein they labour less, and yet where they are so little
respectful, more wasteful, more negligent, or where they so frequently
change their Masters. To this I attribute, in a great measure, the
frequent Robberies and Losses which we suffer on the high Road and in
our own Houses. That indeed which gives me the present Thought of this
kind, is, that a careless Groom of mine has spoiled me the prettiest
Pad in the World with only riding him ten Miles, and I assure you, if
I were to make a Register of all the Horses I have known thus abused
by Negligence of Servants, the Number would mount a Regiment. I wish
you would give us your Observations, that we may know how to treat
these Rogues, or that we Masters may enter into Measures to reform
them. Pray give us a Speculation in general about Servants, and you
make me
Pray do not omit the Mention
of Grooms in particular.
Yours,
Philo-Britannicus
This honest Gentleman, who is so desirous that I should write a Satyr
upon Grooms, has a great deal of Reason for his Resentment; and I know
no Evil which touches all Mankind so much as this of the Misbehaviour of
Servants.
The Complaint of this Letter runs wholly upon Men-Servants; and I can
attribute the Licentiousness which has at present prevailed among them,
to nothing but what an hundred before me have ascribed it to, The Custom
of giving Board-Wages: This one Instance of false Œconomy is sufficient
to debauch the whole Nation of Servants, and makes them as it were but
for some part of their Time in that Quality. They are either attending
in Places where they meet and run into Clubs, or else, if they wait at
Taverns, they eat after their Masters, and reserve their Wages for other
Occasions. From hence it arises, that they are but in a lower Degree
what their Masters themselves are; and usually affect an Imitation of
their Manners: And you have in Liveries, Beaux, Fops, and Coxcombs, in
as high Perfection as among People that keep Equipages. It is a common
Humour among the Retinue of People of Quality, when they are in their
Revels, that is when they are out of their Masters Sight, to assume in a
humourous Way the Names and Titles of those whose Liveries they wear. By
which means Characters and Distinctions become so familiar to them, that
it is to this, among other Causes, one may impute a certain Insolence
among our Servants, that they take no Notice of any Gentleman though
they know him ever so well, except he is an Acquaintance of their
Master's.
My Obscurity and Taciturnity leave me at Liberty, without Scandal, to
dine, if I think fit, at a common Ordinary, in the meanest as well as
the most sumptuous House of Entertainment.
in the other Day at a
Victualling-House near the House of Peers, I heard the Maid come down
and tell the Landlady at the Bar, That my Lord Bishop swore he would
throw her out
a
Window, if she did not bring up more Mild Beer,
and that my Lord Duke would have a double Mug of Purle. My Surprize was
encreased, in hearing loud and rustick Voices speak and answer to each
other upon the publick Affairs, by the Names of the most Illustrious of
our Nobility; till of a sudden one came running in, and cry'd the House
was rising. Down came all the Company together, and away! The Alehouse
was immediately filled with Clamour, and scoring one Mug to the Marquis
of such a Place, Oyl and Vinegar to such an Earl, three Quarts to my new
Lord for wetting his Title, and so forth. It is a Thing too notorious to
mention the Crowds of Servants, and their Insolence, near the Courts of
Justice, and the Stairs towards the Supreme Assembly, where there is an
universal Mockery of all Order, such riotous Clamour and licentious
Confusion, that one would think the whole Nation lived in Jest, and
there were no such thing as Rule and Distinction among us.
The next Place of Resort, wherein the servile World are let loose, is at
the Entrance of
Hide-Park
, while the Gentry are at the Ring.
Hither People bring their Lacqueys out of State, and here it is that all
they say at their Tables, and act in their Houses, is communicated to
the whole Town. There are Men of Wit in all Conditions of Life; and
mixing with these People at their Diversions, I have heard Coquets and
Prudes as well rallied, and Insolence and Pride exposed, (allowing for
their want of Education) with as much Humour and good Sense, as in the
politest Companies.
is a general Observation, That all Dependants run
in some measure into the Manners and Behaviour of those whom they serve:
You shall frequently meet with Lovers and Men of Intrigue among the
Lacqueys, as well as at
White's
or in the Side-Boxes. I
remember some Years ago an Instance of this Kind. A Footman to a Captain
of the Guard used frequently, when his Master was out of the Way, to
carry on Amours and make Assignations in his Master's Cloaths. The
Fellow had a very good Person, and there are very many Women that think
no further than the Outside of a Gentleman: besides which, he was almost
as learned a Man as the Colonel himself: I say, thus qualified, the
Fellow could scrawl
Billets-doux
so well, and furnish a Conversation
on the common Topicks, that he had, as they call it, a great deal of
good Business on his Hands. It happened one Day, that coming down a
Tavern-Stairs in his Master's fine Guard-Coat, with a well-dress'd Woman
masked, he met the Colonel coming up with other Company; but with a
ready Assurance he quitted his Lady, came up to him, and said,
Sir, I
know you have too much Respect for yourself to cane me in this
honourable Habit: But you see there is a Lady in the Case, and I hope on
that Score also you will put off your Anger till I have told you all
another time.
After a little Pause the Colonel cleared up his
Countenance, and with an Air of Familiarity whispered his Man apart,
Sirrah, bring the Lady with you to ask Pardon for you;
then aloud,
Look to it
, Will,
I'll never forgive you else.
The Fellow went back
to his Mistress, and telling her with a loud Voice and an Oath, That was
the honestest Fellow in the World, convey'd her to an Hackney-Coach.
But the many Irregularities committed by Servants in the Places
above-mentioned, as well as in the Theatres, of which Masters are
generally the Occasions, are too various not to need being resumed on
another Occasion.
R.
of the
White's
, established as a chocolate-house in 1698,
had a polite character for gambling, and was a haunt of sharpers and gay
noblemen before it became a Club.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 12, 1711 |
Addison |
... Petite hinc juvenesque senesque
Finem animo certum, miserisque viatica canis.
Cras hoc fiet. Idem eras fiet. Quid? quasi magnum
Nempe diem donas? sed cum lux altera venit,
Jam cras hesternum consumpsimus; ecce aliud cras
Egerit hos annos, et semper paulum erit ultra.
Nam quamvis prope te, quamvis temone sub uno
Vertentem sese frustra sectabere canthum.
Per.

As my Correspondents upon the Subject of Love are very numerous, it is
my Design, if possible, to range them under several Heads, and address
my self to them at different Times. The first Branch of them, to whose
Service I shall Dedicate these Papers, are those that have to do with
Women of dilatory Tempers, who are for spinning out the Time of
Courtship to an immoderate Length, without being able either to close
with their Lovers, or to dismiss them. I have many Letters by me filled
with Complaints against, this sort of Women. In one of them no less a
Man than a Brother of the Coif tells me, that he began his Suit
Vicesimo nono Caroli secundi
, before he had been a Twelvemonth at
the
Temple;
that he prosecuted it for many Years after he was
called to the Bar; that at present he is a Sergeant at Law; and
notwithstanding he hoped that Matters would have been long since brought
to an Issue, the Fair One still
demurrs
. I am so well pleased
with this Gentleman's Phrase, that I shall distinguish this Sect of
Women by the Title of
Demurrers
. I find by another Letter from
one that calls himself
Thirsis
, that his Mistress has been
Demurring above these seven Years. But among all my Plaintiffs of this
Nature, I most pity the unfortunate
Philander
, a Man of a
constant Passion and plentiful Fortune, who sets forth that the timorous
and irresolute
Silvia
has demurred till she is past
Child-bearing.
Strephon
appears by his Letter to be a very
cholerick Lover, and irrevocably smitten with one that demurrs out of
Self-interest. He tells me with great Passion that she has bubbled him
out of his Youth; that she drilled him on to Five and Fifty, and that he
verily believes she will drop him in his old Age, if she can find her
Account in another. I shall conclude this Narrative with a Letter from
honest Sam Hopewell, a very pleasant Fellow, who it seems has at last
married a
Demurrer:
I must only premise, that Sam, who is a very
good Bottle-Companion, has been the Diversion of his Friends, upon
account of his Passion, ever since the Year One thousand Six hundred and
Eighty one.
Dear Sir,
'You know very well my Passion for Mrs. Martha, and what a
Dance she has led me: She took me at the Age of Two and Twenty, and
dodged with me above Thirty Years. I have loved her till she is grown
as Grey as a Cat, and am with much ado become the Master of her
Person, such as it is at present. She is however in my Eye a very
charming old Woman. We often lament that we did not marry sooner, but
she has no Body to blame for it but her self: You know very well that
she would never think of me whilst she had a Tooth in her Head. I have
put the Date of my Passion (Anno Amoris Trigesimo primo)
instead of a Posy, on my Wedding-Ring. I expect you should send me a
Congratulatory Letter, or, if you please, an Epithalamium, upon this
Occasion.
Mrs. Martha's and
Yours Eternally,
Sam Hopewell
In order to banish an Evil out of the World, that does not only produce
great Uneasiness to private Persons, but has also a very bad Influence
on the Publick, I shall endeavour to shew the Folly of
Demurrage
from
two or three Reflections which I earnestly recommend to the Thoughts of
my fair Readers.
First of all I would have them seriously think on the Shortness of their
Time. Life is not long enough for a Coquet to play all her Tricks in. A
timorous Woman drops into her Grave before she has done deliberating.
Were the Age of Man the same that it was before the Flood, a Lady might
sacrifice half a Century to a Scruple, and be two or three Ages in
demurring. Had she Nine Hundred Years good, she might hold out to the
Conversion of the
Jews
before she thought fit to be prevailed upon.
But, alas! she ought to play her Part in haste, when she considers that
she is suddenly to quit the Stage, and make Room for others.
In the second Place, I would desire my Female Readers to consider, that
as the Term of Life is short, that of Beauty is much shorter. The finest
Skin wrinkles in a few Years, and loses the Strength of its Colourings
so soon, that we have scarce Time to admire it. I might embellish this
Subject with Roses and Rain-bows, and several other ingenious Conceits,
which I may possibly reserve for another Opportunity.
There is a third Consideration which I would likewise recommend to a
Demurrer, and that is the great Danger of her falling in Love when she
is about Threescore, if she cannot satisfie her Doubts and Scruples
before that Time. There is a kind of
latter Spring
, that sometimes
gets into the Blood of an old Woman and turns her into a very odd sort
of an Animal. I would therefore have the Demurrer consider what a
strange Figure she will make, if she chances to get over all
Difficulties, and comes to a final Resolution, in that unseasonable Part
of her Life.
I would not however be understood, by any thing I have here said, to
discourage that natural Modesty in the Sex, which renders a Retreat from
the first Approaches of a Lover both fashionable and graceful: All that
I intend, is, to advise them, when they are prompted by Reason and
Inclination, to demurr only out of Form, and so far as Decency requires.
A virtuous Woman should reject the first Offer of Marriage, as a good
Man does that of a Bishoprick; but I would advise neither the one nor
the other to persist in refusing what they secretly approve. I would in
this Particular propose the Example of
Eve
to all her Daughters,
as
Milton
has represented her in the following Passage, which I
cannot forbear transcribing intire, tho' only the twelve last Lines are
to my present Purpose.
The Rib he form'd and fashion'd with his Hands;
Under his forming Hands a Creature grew,
Man-like, but diff'rent Sex; so lovely fair!
That what seem'd fair in all the World, seem'd now
Mean, or in her summ'd up, in her contain'd
And in her Looks; which from that time infus'd
Sweetness into my Heart, unfelt before:
And into all things from her Air inspir'd
The Spirit of Love and amorous Delight.
She disappear'd, and left me dark! I wak'd
To find her, or for ever to deplore
Her Loss, and other Pleasures all1 abjure;
When out of Hope, behold her, not far off,
Such as I saw her in my Dream, adorn'd
With what all Earth or Heaven could bestow
To make her amiable: On she came,
Led by her heav'nly Maker, though unseen,
And guided by his Voice, nor uninform'd
Of nuptial Sanctity and Marriage Rites:
Grace was in all her Steps, Heav'n in her Eye,
In every Gesture Dignity and Love.
I overjoyed, could not forbear aloud.
This Turn hath made Amends; thou hast fulfill'd
Thy Words, Creator bounteous and benign!
Giver of all things fair! but fairest this
Of all thy Gifts, nor enviest. I now see
Bone of my Bone, Flesh of my Flesh, my Self....
She heard me thus, and tho' divinely brought,
Yet Innocence and Virgin Modesty,
Her Virtue, and the Conscience of her Worth,
That would be woo'd, and not unsought be won,
Not obvious, not obtrusive, but retir'd
The more desirable; or, to say all,
Nature her self, tho' pure of sinful Thought,
Wrought in her so, that seeing me, she turn'd2.
I followed her: she what was Honour knew,
And with obsequious Majesty approved
My pleaded Reason. To the Nuptial Bower
I led her blushing like the Morn3 ...
to
fled;
P. L. Bk. VIII.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 13, 1711 |
Addison |
... Magnus sine viribus Ignis
Incassum furit
Virg.

is not, in my Opinion, a Consideration more effectual to
extinguish inordinate Desires in the Soul of Man, than the Notions of
Plato
and his Followers
upon that Subject. They tell us, that
every Passion which has been contracted by the Soul during her Residence
in the Body, remains with her in a separate State; and that the Soul in
the Body or out of the Body, differs no more than the Man does from
himself when he is in his House, or in open Air. When therefore the
obscene Passions in particular have once taken Root and spread
themselves in the Soul, they cleave to her inseparably, and remain in
her for ever, after the Body is cast off and thrown aside. As an
Argument to confirm this their Doctrine they observe, that a lewd Youth
who goes on in a continued Course of Voluptuousness, advances by Degrees
into a libidinous old Man; and that the Passion survives in the Mind
when it is altogether dead in the Body; nay, that the Desire grows more
violent, and (like all other Habits) gathers Strength by Age, at the
same time that it has no Power of executing its own Purposes. If, say
they, the Soul is the most subject to these Passions at a time when it
has the least Instigations from the Body, we may well suppose she will
still retain them when she is entirely divested of it. The very
Substance of the Soul is festered with them, the Gangrene is gone too
far to be ever cured; the Inflammation will rage to all Eternity.
In this therefore (say the
Platonists
) consists the Punishment of a
voluptuous Man after Death: He is tormented with Desires which it is
impossible for him to gratify, solicited by a Passion that has neither
Objects nor Organs adapted to it: He lives in a State of invincible
Desire and Impotence, and always burns in the Pursuit of what he always
despairs to possess. It is for this Reason (says
Plato
) that the
Souls of the Dead appear frequently in Cœmiteries, and hover about the
Places where their Bodies are buried, as still hankering after their old
brutal Pleasures, and desiring again to enter the Body that gave them an
Opportunity of fulfilling them.
Some of our most eminent Divines have made use of this
Platonick
Notion, so far as it regards the Subsistence of our Passions after
Death, with great Beauty and Strength of Reason.
Plato
indeed
carries the Thought very far, when he grafts upon it his Opinion of
Ghosts appearing in Places of Burial. Though, I must confess, if one did
believe that the departed Souls of Men and Women wandered up and down
these lower Regions, and entertained themselves with the Sight of their
Species, one could not devise a more Proper Hell for an impure Spirit
than that which
Plato
has touched upon.
The Ancients seem to have drawn such a State of Torments in the
Description of
Tantalus
, who was punished with the Rage of an
eternal Thirst, and set up to the Chin in Water that fled from his Lips
whenever he attempted to drink it.
Virgil
, who has cast the whole System of
Platonick
Philosophy, so far as it relates to the Soul of Man, in beautiful
Allegories, in the sixth Book of his
Æneid
gives us the
Punishment of a Voluptuary after Death, not unlike that which we are
here speaking of.
... Lucent genialibus altis
Aurea fulcra toris, epulæque ante ora paratæ
Regifico luxu: Furiarum maxima juxta
Accubat, et manibus prohibet contingere mensas;
Exurgitque facem attollens, atque intonat ore.
They lie below on Golden Beds display'd,
And genial Feasts with regal Pomp are made:
The Queen of Furies by their Side is set,
And snatches from their Mouths th' untasted Meat;
Which if they touch, her hissing Snakes she rears,
Tossing her Torch, and thund'ring in their Ears.
Dryd.
I may a little alleviate the Severity of this my Speculation (which
otherwise may lose me several of my polite Readers) I shall translate a
Story
that
has been quoted upon another Occasion by one of the
most learned Men of the present Age, as I find it in the Original.
Reader will see it is not foreign to my present Subject, and I dare say
will think it a lively Representation of a Person lying under the
Torments of such a kind of Tantalism, or
Platonick
Hell, as that
which we have now under Consideration. Monsieur
Pontignan
speaking of a Love-Adventure that happened to him in the Country, gives
the following Account of it
.
'When I was in the Country last Summer, I was often in Company with a
Couple of charming Women, who had all the Wit and Beauty one could
desire in Female Companions, with a Dash of Coquetry, that from time
to time gave me a great many agreeable Torments. I was, after my Way,
in Love with both of them, and had such frequent opportunities of
pleading my Passion to them when they were asunder, that I had Reason
to hope for particular Favours from each of them. As I was walking one
Evening in my Chamber with nothing about me but my Night gown, they
both came into my Room and told me, They had a very pleasant Trick to
put upon a Gentleman that was in the same House, provided I would bear
a Part in it. Upon this they told me such a plausible Story, that I
laughed at their Contrivance, and agreed to do whatever they should
require of me: They immediately began to swaddle me up in my
Night-Gown with long Pieces of Linnen, which they folded about me till
they had wrapt me in above an hundred Yards of Swathe: My Arms were
pressed to my Sides, and my Legs closed together by so many Wrappers
one over another, that I looked like an
Ægyptian Mummy. As I
stood bolt upright upon one End in this antique Figure, one of the
Ladies burst out a laughing, And now,
Pontignan, says she, we
intend to perform the Promise that we find you have extorted from each
of us. You have often asked the Favour of us, and I dare say you are a
better bred Cavalier than to refuse to go to Bed to two Ladies, that
desire it of you. After having stood a Fit of Laughter, I begged them
to uncase me, and do with me what they pleased. No, no, said they, we
like you very well as you are; and upon that ordered me to be carried
to one of their Houses, and put to Bed in all my Swaddles.
The Room
was lighted up on all Sides: and I was laid very decently between a
pair4 of Sheets, with my Head (which was indeed the only Part I
could move) upon a very high Pillow: This was no sooner done, but my
two Female Friends came into Bed to me in their finest Night-Clothes.
You may easily guess at the Condition of a Man that saw a Couple of
the most beautiful Women in the World undrest and abed with him,
without being able to stir Hand or Foot. I begged them to release me,
and struggled all I could to get loose, which I did with so much
Violence, that about Midnight they both leaped out of the Bed, crying
out they were undone. But seeing me safe, they took their Posts again,
and renewed their Raillery. Finding all my Prayers and Endeavours were
lost, I composed my self as well as I could, and told them, that if
they would not unbind me, I would fall asleep between them, and by
that means disgrace them for ever: But alas! this was impossible;
could I have been disposed to it, they would have prevented me by
several little ill-natured Caresses and Endearments which they
bestowed upon me. As much devoted as I am to Womankind, I would not
pass such another Night to be Master of the whole Sex. My Reader will
doubtless be curious to know what became of me the next Morning: Why
truly my Bed-fellows left me about an Hour before Day, and told me, if
I would be good and lie still, they would send somebody to take me up
as soon as it was time for me to rise: Accordingly about Nine a Clock
in the Morning an old Woman came to un-swathe me. I bore all this very
patiently, being resolved to take my Revenge of my Tormentors, and to
keep no Measures with them as soon as I was at Liberty; but upon
asking my old Woman what was become of the two Ladies, she told me she
believed they were by that Time within Sight of
Paris, for that they
went away in a Coach and six before five a clock in the Morning.
L.
Plato's doctrine of the soul and of its destiny is to be
found at the close of his
Republic
; also near the close of the
Phædon
, in a passage of the
Philebus
, and in another of the
Gorgias
. In § 131 of the
Phædon
is the passage here especially
referred to; which was the basis also of lines 461-475 of Milton's
Comus
. The last of our own Platonists was Henry More, one of whose
books Addison quoted four essays back (in
), and who died only
four and twenty years before these essays were written, after a long
contest in prose and verse, against besotting or obnubilating the soul
with 'the foul steam of earthly life.'
which
Paraphrased from the
Academe Galante
(Ed. 1708, p. 160).
couple
Contents
|
Thursday, June 14, 1711 |
Steele |
In furias ignemque ruunt, Amor omnibus Idem.
Virg.

Tho' the Subject I am now going upon would be much more properly the
Foundation of a Comedy, I cannot forbear inserting the Circumstances
which pleased me in the Account a young Lady gave me of the Loves of a
Family in Town, which shall be nameless; or rather for the better Sound
and Elevation of the History, instead of Mr. and Mrs. such-a-one, I
shall call them by feigned Names. Without further Preface, you are to
know, that within the Liberties of the City of
Westminster
lives the
Lady
Honoria
, a Widow about the Age of Forty, of a healthy
Constitution, gay Temper, and elegant Person. She dresses a little too
much like a Girl, affects a childish Fondness in the Tone of her Voice,
sometimes a pretty Sullenness in the leaning of her Head, and now and
then a Down-cast of her Eyes on her Fan: Neither her Imagination nor her
Health would ever give her to know that she is turned of Twenty; but
that in the midst of these pretty Softnesses, and Airs of Delicacy and
Attraction, she has a tall Daughter within a Fortnight of Fifteen, who
impertinently comes into the Room, and towers so much towards Woman,
that her Mother is always checked by her Presence, and every Charm of
Honoria
droops at the Entrance of
Flavia
. The agreeable
Flavia
would be what she is not, as well as her Mother
Honoria
; but all their
Beholders are more partial to an Affectation of what a Person is growing
up to, than of what has been already enjoyed, and is gone for ever. It
is therefore allowed to
Flavia
to look forward, but not to
Honoria
to look back.
Flavia
is no way dependent on her Mother with relation
to her Fortune, for which Reason they live almost upon an Equality in
Conversation; and as
Honoria
has given
Flavia
to understand, that it
is ill-bred to be always calling Mother,
Flavia
is as well pleased
never to be called Child. It happens by this means, that these Ladies
are generally Rivals in all Places where they appear; and the Words
Mother and Daughter never pass between them but out of Spite.
Flavia
one Night at a Play observing
Honoria
draw the Eyes of several in the
Pit, called to a Lady who sat by her, and bid her ask her Mother to lend
her her Snuff-Box for one Moment. Another Time, when a Lover of
Honoria
was on his Knees beseeching the Favour to kiss her Hand,
Flavia
rushing into the Room, kneeled down by him and asked Blessing.
Several of these contradictory Acts of Duty have raised between them
such a Coldness that they generally converse when they are in mixed
Company by way of talking at one another, and not to one another.
Honoria
is ever complaining of a certain Sufficiency in the young
Women of this Age, who assume to themselves an Authority of carrying all
things before them, as if they were Possessors of the Esteem of Mankind,
and all, who were but a Year before them in the World, were neglected or
deceased.
Flavia
, upon such a Provocation, is sure to observe, that
there are People who can resign nothing, and know not how to give up
what they know they cannot hold; that there are those who will not allow
Youth their Follies, not because they are themselves past them, but
because they love to continue in them. These Beauties Rival each other
on all Occasions, not that they have always had the same Lovers but each
has kept up a Vanity to shew the other the Charms of her Lover.
Dick
Crastin
and
Tom Tulip
, among many others, have of late been
Pretenders in this Family:
Dick
to
Honoria
,
Tom
to
Flavia
.
Dick
is the only surviving Beau of the last Age, and
Tom
almost the
only one that keeps up that Order of Men in this.
I wish I could repeat the little Circumstances of a Conversation of the
four Lovers with the Spirit in which the young Lady, I had my Account
from, represented it at a Visit where I had the Honour to be present;
but it seems
Dick Crastin
, the admirer of
Honoria
, and
Tom Tulip
,
the Pretender to
Flavia
, were purposely admitted together by the
Ladies, that each might shew the other that her Lover had the
Superiority in the Accomplishments of that sort of Creature whom the
sillier Part of Women call a fine Gentleman. As this Age has a much more
gross Taste in Courtship, as well as in every thing else, than the last
had, these Gentlemen are Instances of it in their different Manner of
Application.
Tulip
is ever making Allusions to the Vigour of his
Person, the sinewy Force of his Make; while
Crastin
professes a wary
Observation of the Turns of his Mistress's Mind.
Tulip
gives himself
the Air of a restless Ravisher,
Crastin
practises that of a skilful
Lover. Poetry is the inseparable Property of every Man in Love; and as
Men of Wit write Verses on those Occasions, the rest of the World repeat
the Verses of others. These Servants of the Ladies were used to imitate
their Manner of Conversation, and allude to one another, rather than
interchange Discourse in what they said when they met.
Tulip
the other
Day seized his Mistress's Hand, and repeated out of
Ovid's Art of Love
,
'Tis I can in soft Battles pass the Night,
Yet rise next Morning vigorous for the Fight,
Fresh as the Day, and active as the Light.
Upon hearing this,
Crastin
, with an Air of Deference, played
Honoria's
Fan, and repeated,
Sedley has that prevailing gentle Art,
That can with a resistless Charm impart
The loosest Wishes to the chastest Heart:
Raise such a Conflict, kindle such a Fire,
Between declining Virtue and Desire,
Till the poor vanquish'd Maid dissolves away
In Dreams all Night, in Sighs and Tears all Day.1
When
Crastin
had uttered these Verses with a Tenderness which at once
spoke Passion and Respect,
Honoria
cast a triumphant Glance at
Flavia
, as exulting in the Elegance of
Crastin's
Courtship, and upbraiding her with the Homeliness of
Tulip's
.
Tulip
understood the Reproach, and in Return began to applaud the
Wisdom of old amorous Gentlemen, who turned their Mistress's Imagination
as far as possible from what they had long themselves forgot, and ended
his Discourse with a sly Commendation of the Doctrine of
Platonick
Love; at the same time he ran over, with a laughing
Eye,
Crastin's
thin Legs, meagre Looks, and spare Body. The old
Gentleman immediately left the Room with some Disorder, and the
Conversation fell upon untimely Passion, After-Love, and unseasonable
Youth.
Tulip
sung, danced, moved before the Glass, led his
Mistress half a Minuet, hummed
Celia the Fair, in the bloom of Fifteen;
when there came a Servant with a Letter to him, which was as follows.
Sir,
'
I understand very well what you meant by your Mention of
Platonick Love. I shall be glad to meet you immediately in
Hide-Park, or behind
Montague-House, or attend you to
Barn-Elms
2, or any other fashionable Place that's fit for a
Gentleman to die in, that you shall appoint for,
Sir, Your most Humble Servant,
Richard Crastin.
Tulip's
Colour changed at the reading of this Epistle; for which
Reason his Mistress snatched it to read the Contents. While she was
doing so
Tulip
went away, and the Ladies now agreeing in a Common
Calamity, bewailed together the Danger of their Lovers. They immediately
undressed to go out, and took Hackneys to prevent Mischief: but, after
alarming all Parts of the Town,
Crastin
was found by his Widow in
his Pumps at
Hide-Park
, which Appointment
Tulip
never
kept, but made his Escape into the Country.
Flavia
tears her Hair
for his inglorious Safety, curses and despises her Charmer, is fallen in
Love with
Crastin
: Which is the first Part of the History of the
Rival Mother
.
R.
Rochester's
Imitations of Horace
, Sat. I. 10.
A famous duelling place under elm trees, in a meadow half
surrounded by the Thames.
Contents
|
Friday, June 15, 1711 |
Addison |
... Convivæ prope dissentire videntur,
Poscentes vario multum diversa palato;
Quid dem? Quid non dem?
Hor.

over the late Packets of Letters which have been sent to me, I
found the following one
.
Mr. Spectator,
'Your Paper is a Part of my Tea-Equipage; and my Servant knows my
Humour so well, that calling for my Breakfast this Morning (it being
past my usual Hour) she answer'd, the Spectator was not yet come in;
but that the Tea-Kettle boiled, and she expected it every Moment.
Having thus in part signified to you the Esteem and Veneration which I
have for you, I must put you in mind of the Catalogue of Books which
you have promised to recommend to our Sex; for I have deferred
furnishing my Closet with Authors, 'till I receive your Advice in this
Particular, being your daily Disciple and humble Servant,
Leonora.
In Answer to my fair Disciple, whom I am very proud of, I must acquaint
her and the rest of my Readers, that since I have called out for Help in
my Catalogue of a Lady's Library, I have received many Letters upon that
Head, some of which I shall give an Account of.
In the first Class I shall take notice of those which come to me from
eminent Booksellers, who every one of them mention with Respect the
Authors they have printed, and consequently have an Eye to their own
Advantage more than to that of the Ladies. One tells me, that he thinks
it absolutely necessary for Women to have true Notions of Right and
Equity, and that therefore they cannot peruse a better Book than
Dalton's Country Justice
: Another thinks they cannot be without
The Compleat Jockey
. A third observing the Curiosity and Desire
of prying into Secrets, which he tells me is natural to the fair Sex, is
of Opinion this female Inclination, if well directed, might turn very
much to their Advantage, and therefore recommends to me
Mr
. Mede
upon the Revelations
. A fourth lays it down as an unquestioned
Truth, that a Lady cannot be thoroughly accomplished who has not read
The Secret Treaties and Negotiations of Marshal
D'Estrades. Mr.
Jacob Tonson Jun.
is of Opinion, that
Bayle's Dictionary
might be of very great use to the Ladies, in order to make them general
Scholars. Another whose Name I have forgotten, thinks it highly proper
that every Woman with Child should read
Mr.
Wall's
History of
Infant Baptism
: As another is very importunate with me to recommend
to all my female Readers
The finishing Stroke: Being a Vindication of
the Patriarchal Scheme
, &c.
In the second Class I shall mention Books which are recommended by
Husbands, if I may believe the Writers of them. Whether or no they are
real Husbands or personated ones I cannot tell, but the Books they
recommend are as follow.
A Paraphrase on the History of
Susanna.
Rules to keep
Lent.
The Christian's Overthrow prevented. A
Dissuasive from the Play-house. The Virtues of Camphire, with Directions
to make Camphire Tea. The Pleasures of a Country Life. The Government of
the Tongue
. A Letter dated from
Cheapside
desires me that I
would advise all young Wives to make themselves Mistresses of
Wingate's Arithmetick
, and concludes with a Postscript, that he
hopes I will not forget
The Countess of
Kent's
Receipts
.
I may reckon the Ladies themselves as a third Class among these my
Correspondents and Privy-Counsellors. In a Letter from one of them, I am
advised to place
Pharamond
at the Head of my Catalogue, and, if I
think proper, to give the second place to
Cassandra
.
Coquetilla
begs me not to think of nailing Women upon their Knees
with Manuals of Devotion, nor of scorching their Faces with Books of
Housewifry.
Florella
desires to know if there are any Books
written against Prudes, and intreats me, if there are, to give them a
Place in my Library.
of all Sorts have their several Advocates:
All for Love
is mentioned in above fifteen Letters;
Sophonisba
, or
Hannibal's Overthrow
, in a Dozen;
The
Innocent Adultery
is likewise highly approved of;
Mithridates
King of Pontus
has many Friends;
Alexander the Great
and
Aurengzebe
have the same Number of Voices; but
Theodosius
,
or
The Force of Love
. carries it from all the rest
.
I should, in the last Place, mention such Books as have been proposed by
Men of Learning, and those who appear competent Judges of this Matter;
and must here take Occasion to thank
A. B
. whoever it is that
conceals himself under those two Letters, for his Advice upon this
Subject: But as I find the Work I have undertaken to be very difficult,
I shall defer the executing of it till I am further acquainted with the
Thoughts of my judicious Contemporaries, and have time to examine the
several Books they offer to me; being resolved, in an Affair of this
Moment, to proceed with the greatest Caution.
In the mean while, as I have taken the Ladies under my particular Care,
I shall make it my Business to find out in the best Authors ancient and
modern such Passages as may be for their use, and endeavour to
accommodate them as well as I can to their Taste; not questioning but
the valuable Part of the Sex will easily pardon me, if from Time to Time
I laugh at those little Vanities and Follies which appear in the
Behaviour of some of them, and which are more proper for Ridicule than a
serious Censure. Most Books being calculated for Male Readers, and
generally written with an Eye to Men of Learning, makes a Work of this
Nature the more necessary; besides, I am the more encouraged, because I
flatter myself that I see the Sex daily improving by these my
Speculations. My fair Readers are already deeper Scholars than the
Beaus. I could name some of them who could talk much better than several
Gentlemen that make a Figure at
Will's
; and as I frequently
receive Letters from the
fine Ladies
and
pretty Fellows
, I
cannot but observe that the former are superior to the others not only
in the Sense but in the Spelling. This cannot but have a good Effect
upon the Female World, and keep them from being charmed by those empty
Coxcombs that have hitherto been admired among the Women, tho' laugh'd
at among the Men.
I am credibly informed that
Tom Tattle
passes for an impertinent
Fellow, that
Will Trippet
begins to be smoaked, and that
Frank
Smoothly
himself is within a Month of a Coxcomb, in case I think fit
to continue this Paper. For my part, as it is my Business in some
measure to detect such as would lead astray weak Minds by their false
Pretences to Wit and Judgment, Humour and Gallantry, I shall not fail to
lend the best Lights I am able to the fair Sex for the Continuation of
these their Discoveries.
By Mrs. Perry, whose sister, Miss Shepheard, has letters in
two later numbers,
and
. These ladies were descended from Sir
Fleetwood Shepheard.
Michael Dalton's
Country Justice
was first published in
1618. Joseph Mede's
Clavis Apocalyptica
, published in 1627, and
translated by Richard More in 1643, was as popular in the Pulpit as
The
Country Justice
on the Bench. The negotiations of Count d'Estrades were
from 1637 to 1662. The translation of
Bayle's Dictionary
had been
published by Tonson in 1610. Dr. William Wall's
History of Infant
Baptism
, published in 1705, was in its third edition.
Aurungzebe
was
by Dryden.
Mithridates
and
Theodosius
were by Lee.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 16, 1711 |
Addison |
... Spatio brevi
Spem longam reseces: dum loquimur, fugerit Invida
Ætas: carpe Diem, quam minimum credula postero.
Hor.

all of us complain of the Shortness of Time, saith
Seneca
and yet have much more than we know what to do with. Our Lives, says he,
are spent either in doing nothing at all, or in doing nothing to the
Purpose, or in doing nothing that we ought to do: We are always
complaining our Days are few, and acting as though there would be no End
of them. That noble Philosopher has described our Inconsistency with our
selves in this Particular, by all those various Turns of Expression and
Thought which are peculiar to his Writings.
I often consider Mankind as wholly inconsistent with itself in a Point
that bears some Affinity to the former. Though we seem grieved at the
Shortness of Life in general, we are wishing every Period of it at an
end. The Minor longs to be at Age, then to be a Man of Business, then to
make up an Estate, then to arrive at Honours, then to retire. Thus
although the whole of Life is allowed by every one to be short, the
several Divisions of it appear long and tedious. We are for lengthening
our Span in general, but would fain contract the Parts of which it is
composed. The Usurer would be very well satisfied to have all the Time
annihilated that lies between the present Moment and next Quarter-day.
The Politician would be contented to lose three Years in his Life, could
he place things in the Posture which he fancies they will stand in after
such a Revolution of Time. The Lover would be glad to strike out of his
Existence all the Moments that are to pass away before the happy
Meeting. Thus, as fast as our Time runs, we should be very glad in most
Parts of our Lives that it ran much faster than it does. Several Hours
of the Day hang upon our Hands, nay we wish away whole Years: and travel
through Time as through a Country filled with many wild and empty
Wastes, which we would fain hurry over, that we may arrive at those
several little Settlements or imaginary Points of Rest which are
dispersed up and down in it.
If we divide the Life of most Men into twenty Parts, we shall find that
at least nineteen of them are meer Gaps and Chasms, which are neither
filled with Pleasure nor Business. I do not however include in this
Calculation the Life of those Men who are in a perpetual Hurry of
Affairs, but of those only who are not always engaged in Scenes of
Action; and I hope I shall not do an unacceptable Piece of Service to
these Persons, if I point out to them certain Methods for the filling up
their empty Spaces of Life. The Methods I shall propose to them are as
follow.
The first is the Exercise of Virtue, in the most general Acceptation of
the Word. That particular Scheme which comprehends the Social Virtues,
may give Employment to the most industrious Temper, and find a Man in
Business more than the most active Station of Life. To advise the
Ignorant, relieve the Needy, comfort the Afflicted, are Duties that fall
in our way almost every Day of our Lives. A Man has frequent
Opportunities of mitigating the Fierceness of a Party; of doing Justice
to the Character of a deserving Man; of softning the Envious, quieting
the Angry, and rectifying the Prejudiced; which are all of them
Employments suited to a reasonable Nature, and bring great Satisfaction
to the Person who can busy himself in them with Discretion.
There is another kind of Virtue that may find Employment for those
Retired Hours in which we are altogether left to our selves, and
destitute of Company and Conversation; I mean that Intercourse and
Communication which every reasonable Creature ought to maintain with the
great Author of his Being. The Man who lives under an habitual Sense of
the Divine Presence keeps up a perpetual Chearfulness of Temper, and
enjoys every Moment the Satisfaction of thinking himself in Company with
his dearest and best of Friends. The Time never lies heavy upon him: It
is impossible for him to be alone. His Thoughts and Passions are the
most busied at such Hours when those of other Men are the most unactive:
He no sooner steps out of the World but his Heart burns with Devotion,
swells with Hope, and triumphs in the Consciousness of that Presence
which every where surrounds him; or, on the contrary, pours out its
Fears, its Sorrows, its Apprehensions, to the great Supporter of its
Existence.
I have here only considered the Necessity of a Man's being Virtuous,
that he may have something to do; but if we consider further, that the
Exercise of Virtue is not only an Amusement for the time it lasts, but
that its Influence extends to those Parts of our Existence which lie
beyond the Grave, and that our whole Eternity is to take its Colour from
those Hours which we here employ in Virtue or in Vice, the Argument
redoubles upon us, for putting in Practice this Method of passing away
our Time.
When a Man has but a little Stock to improve, and has opportunities of
turning it all to good Account, what shall we think of him if he suffers
nineteen Parts of it to lie dead, and perhaps employs even the twentieth
to his Ruin or Disadvantage? But because the Mind cannot be always in
its Fervours, nor strained up to a Pitch of Virtue, it is necessary to
find out proper Employments for it in its Relaxations.
The next Method therefore that I would propose to fill up our Time,
should be useful and innocent Diversions. I must confess I think it is
below reasonable Creatures to be altogether conversant in such
Diversions as are meerly innocent, and have nothing else to recommend
them, but that there is no Hurt in them. Whether any kind of Gaming has
even thus much to say for it self, I shall not determine; but I think it
is very wonderful to see Persons of the best Sense passing away a dozen
Hours together in shuffling and dividing a Pack of Cards, with no other
Conversation but what is made up of a few Game Phrases, and no other
Ideas but those of black or red Spots ranged together in different
Figures. Would not a man laugh to hear any one of this Species
complaining that Life is short.
The
Stage
might be made a perpetual Source of the most noble and
useful Entertainments, were it under proper Regulations.
But the Mind never unbends itself so agreeably as in the Conversation of
a well chosen Friend. There is indeed no Blessing of Life that is any
way comparable to the Enjoyment of a discreet and virtuous Friend. It
eases and unloads the Mind, clears and improves the Understanding,
engenders Thoughts and Knowledge, animates Virtue and good Resolution,
sooths and allays the Passions, and finds Employment for most of the
vacant Hours of Life.
Next to such an Intimacy with a particular Person, one would endeavour
after a more general Conversation with such as are able to entertain and
improve those with whom they converse, which are Qualifications that
seldom go asunder.
There are many other useful Amusements of Life, which one would
endeavour to multiply, that one might on all Occasions have Recourse to
something rather than suffer the mind to lie idle, or run adrift with
any Passion that chances to rise in it.
A Man that has a Taste of Musick, Painting, or Architecture, is like one
that has another Sense when compared with such as have no Relish of
those Arts. The Florist, the Planter, the Gardiner, the Husbandman, when
they are only as Accomplishments to the Man of Fortune, are great
Reliefs to a Country Life, and many ways useful to those who are
possessed of them.
But of all the Diversions of Life, there is none so proper to fill up
its empty Spaces as the reading of useful and entertaining Authors. But
this I shall only touch upon, because it in some Measure interferes with
the third Method, which I shall propose in another Paper, for the
Employment of our dead unactive Hours, and which I shall only mention in
general to be the Pursuit of Knowledge.
Epist. 49
, and in his
De Brevitate Vita
.
Contents
|
Monday, June 18, 1711 |
Addison |
... Hoc est
Vivere bis, vita posse priore frui.
Mart.

The last Method which I proposed in my
Saturday's Paper
, for
filling up those empty Spaces of Life which are so tedious and
burdensome to idle People, is the employing ourselves in the Pursuit of
Knowledge.
remember
Mr. Boyle
speaking of a certain
Mineral, tells us, That a Man may consume his whole Life in the Study of
it, without arriving at the Knowledge of all its Qualities. The Truth of
it is, there is not a single Science, or any Branch of it, that might
not furnish a Man with Business for Life, though it were much longer
than it is.
I shall not here engage on those beaten Subjects of the Usefulness of
Knowledge, nor of the Pleasure and Perfection it gives the Mind, nor on
the Methods of attaining it, nor recommend any particular Branch of it,
all which have been the Topicks of many other Writers; but shall indulge
my self in a Speculation that is more uncommon, and may therefore
perhaps be more entertaining.
I have before shewn how the unemployed Parts of Life appear long and
tedious, and shall here endeavour to shew how those Parts of Life which
are exercised in Study, Reading, and the Pursuits of Knowledge, are long
but not tedious, and by that means discover a Method of lengthening our
Lives, and at the same time of turning all the Parts of them to our
Advantage.
.
Lock
observes
,
'That we get the Idea of Time, or Duration, by
reflecting on that Train of Ideas which succeed one another in our
Minds: That for this Reason, when we sleep soundly without dreaming, we
have no Perception of Time, or the Length of it whilst we sleep; and
that the Moment wherein we leave off to think, till the Moment we begin
to think again, seems to have no distance.'
To which the Author adds,
'And so I doubt not but it would be to a waking Man, if it were possible
for him to keep only one Idea in his Mind, without Variation, and the
Succession of others: And we see, that one who fixes his Thoughts very
intently on one thing, so as to take but little notice of the Succession
of Ideas that pass in his Mind whilst he is taken up with that earnest
Contemplation, lets slip out of his Account a good Part of that
Duration, and thinks that Time shorter than it is.'
We might carry this Thought further, and consider a Man as, on one Side,
shortening his Time by thinking on nothing, or but a few things; so, on
the other, as lengthening it, by employing his Thoughts on many
Subjects, or by entertaining a quick and constant Succession of Ideas.
Monsieur
Mallebranche
, in his
Enquiry after Truth
,
(which was published several Years before Mr.
Lock's Essay on Human
Understanding
) tells us, That it is possible some Creatures may think
Half an Hour as long as we do a thousand Years; or look upon that Space
of Duration which we call a Minute, as an Hour, a Week, a Month, or an
whole Age.
This Notion of Monsieur
Mallebranche
is capable of some little
Explanation from what I have quoted out of Mr.
Lock
; for if our Notion
of Time is produced by our reflecting on the Succession of Ideas in our
Mind, and this Succession may be infinitely accelerated or retarded, it
will follow, that different Beings may have different Notions of the
same Parts of Duration, according as their Ideas, which we suppose are
equally distinct in each of them, follow one another in a greater or
less Degree of Rapidity.
There is a famous Passage in the
Alcoran
, which looks as if
Mahomet
had been possessed of the Notion we are now speaking of.
is there
said
, That the Angel
Gabriel
took
Mahomet
Out of his Bed one
Morning to give him a Sight of all things in the Seven Heavens, in
Paradise, and in Hell, which the Prophet took a distinct View of; and
after having held ninety thousand Conferences with God, was brought back
again to his Bed. All this, says the
Alcoran
, was transacted in
so small a space of Time, that
Mahomet
at his Return found his
Bed still warm, and took up an Earthen Pitcher, (which was thrown down
at the very Instant that the Angel
Gabriel
carried him away)
before the Water was all spilt.
There is a very pretty Story in the
Turkish
Tales which relates
to this Passage of that famous Impostor, and bears some Affinity to the
Subject we are now upon. A Sultan of
Egypt
, who was an Infidel,
used to laugh at this Circumstance in
Mahomet's
Life, as what was
altogether impossible and absurd: But conversing one Day with a great
Doctor in the Law, who had the Gift of working Miracles, the Doctor told
him he would quickly convince him of the Truth of this Passage in the
History of Mahomet, if he would consent to do what he should desire of
him. Upon this the Sultan was directed to place himself by an huge Tub
of Water, which he did accordingly; and as he stood by the Tub amidst a
Circle of his great Men, the holy Man bid him plunge his Head into the
Water, and draw it up again: The King accordingly thrust his Head into
the Water, and at the same time found himself at the Foot of a Mountain
on a Sea-shore. The King immediately began to rage against his Doctor
for this Piece of Treachery and Witchcraft; but at length, knowing it
was in vain to be angry, he set himself to think on proper Methods for
getting a Livelihood in this strange Country: Accordingly he applied
himself to some People whom he saw at work in a Neighbouring Wood: these
People conducted him to a Town that stood at a little Distance from the
Wood, where, after some Adventures, he married a Woman of great Beauty
and Fortune. He lived with this Woman so long till he had by her seven
Sons and seven Daughters: He was afterwards reduced to great Want, and
forced to think of plying in the Streets as a Porter for his Livelihood.
One Day as he was walking alone by the Sea-side, being seized with many
melancholy Reflections upon his former and his present State of Life,
which had raised a Fit of Devotion in him, he threw off his Clothes with
a Design to wash himself, according to the Custom of the
Mahometans
, before he said his Prayers.
After his first Plunge into the Sea, he no sooner raised his Head above
the Water but he found himself standing by the Side of the Tub, with the
great Men of his Court about him, and the holy Man at his Side. He
immediately upbraided his Teacher for having sent him on such a Course
of Adventures, and betrayed him into so long a State of Misery and
Servitude; but was wonderfully surprised when he heard that the State he
talked of was only a Dream and Delusion; that he had not stirred from
the Place where he then stood; and that he had only dipped his Head into
the Water, and immediately taken it out again.
The
Mahometan
Doctor took this Occasion of instructing the
Sultan, that nothing was impossible with God; and that
He
, with
whom a Thousand Years are but as one Day, can, if he pleases, make a
single Day, nay a single Moment, appear to any of his Creatures as a
Thousand Years.
I shall leave my Reader to compare these Eastern Fables with the Notions
of those two great Philosophers whom I have quoted in this Paper; and
shall only, by way of Application, desire him to consider how we may
extend Life beyond its natural Dimensions, by applying our selves
diligently to the Pursuits of Knowledge.
The Hours of a wise Man are lengthened by his Ideas, as those of a Fool
are by his Passions: The Time of the one is long, because he does not
know what to do with it; so is that of the other, because he
distinguishes every Moment of it with useful or amusing Thought; or in
other Words, because the one is always wishing it away, and the other
always enjoying it.
How different is the View of past Life, in the Man who is grown old in
Knowledge and Wisdom, from that of him who is grown old in Ignorance and
Folly? The latter is like the Owner of a barren Country that fills his
Eye with the Prospect of naked Hills and Plains, which produce nothing
either profitable or ornamental; the other beholds a beautiful and
spacious Landskip divided into delightful Gardens, green Meadows,
fruitful Fields, and can scarce cast his Eye on a single Spot of his
Possessions, that is not covered with some beautiful Plant or Flower.
L.
Not of himself, but in
The Usefulness of Natural
Philosophy
(
Works
, ed. 1772, vol. ii. p. 11), Boyle quotes from the old
Alchemist, Basil Valentine, who said in his
Currus Triumphalis
Antimonii
'That the shortness of life makes it impossible for one man thoroughly
to learn Antimony, in which every day something of new is
discovered.'
Essay on the Human Understanding
, Bk II. ch. 14.
Two English Translations of Malebranche's
Search after
Truth
were published in 1694, one by T. Taylor of Magdalen College,
Oxford. Malebranche sets out with the argument that man has no innate
perception of Duration.
The Night Journey of Mahomet gives its Title to the 17th
Sura of the
Koran
, which assumes the believer's knowledge of the Visions
of Gabriel seen at the outset of the prophet's career, when he was
carried by night from Mecca to Jerusalem and thence through the seven
heavens to the throne of God on the back of Borak, accompanied by
Gabriel according to some traditions, and according to some in a vision.
Details of the origin of this story will be found in Muir, ii. 219,
Nöld, p. 102. Addison took it from the
Turkish Tales.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 19, 1711 |
Steele |
Curæ Leves loquuntur, Ingentes Stupent.1
Having read the two following Letters with much Pleasure, I cannot but
think the good Sense of them will be as agreeable to the Town as any
thing I could say either on the Topicks they treat of, or any other.
They both allude to former Papers of mine, and I do not question but the
first, which is upon inward Mourning, will be thought the Production of
a Man who is well acquainted with the generous Earnings of Distress in a
manly Temper, which is above the Relief of Tears. A Speculation of my
own on that Subject I shall defer till another Occasion.
The second Letter is from a Lady of a Mind as great as her
Understanding. There is perhaps something in the Beginning of it which I
ought in Modesty to conceal; but I have so much Esteem for this
Correspondent, that I will not alter a Tittle of what she writes, tho' I
am thus scrupulous at the Price of being Ridiculous.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I was very well pleased with your Discourse upon General Mourning,
and should be obliged to you if you would enter into the Matter more
deeply, and give us your Thoughts upon the common Sense the ordinary
People have of the Demonstrations of Grief, who prescribe Rules and
Fashions to the most solemn Affliction; such as the Loss of the
nearest Relations and dearest Friends. You cannot go to visit a sick
Friend, but some impertinent Waiter about him observes the Muscles of
your Face, as strictly as if they were Prognosticks of his Death or
Recovery. If he happens to be taken from you, you are immediately
surrounded with Numbers of these Spectators, who expect a melancholy
Shrug of your Shoulders, a Pathetical shake of your Head, and an
Expressive Distortion of your Face, to measure your Affection and
Value for the Deceased: But there is nothing, on these Occasions, so
much in their Favour as immoderate Weeping. As all their passions are
superficial, they imagine the Seat of Love and Friendship to be placed
visibly in the Eyes: They judge what Stock of Kindness you had for the
Living, by the Quantity of Tears you pour out for the Dead; so that if
one Body wants that Quantity of Salt-water another abounds with, he is
in great Danger of being thought insensible or ill-natured: They are
Strangers to Friendship, whose Grief happens not to be moist enough to
wet such a Parcel of Handkerchiefs. But Experience has told us,
nothing is so fallacious as this outward Sign of Sorrow; and the
natural History of our Bodies will teach us that this Flux of the
Eyes, this Faculty of Weeping, is peculiar only to some Constitutions.
We observe in the tender Bodies of Children, when crossed in their
little Wills and Expectations, how dissolvable they are into Tears. If
this were what Grief is in Men, Nature would not be able to support
them in the Excess of it for one Moment. Add to this Observation, how
quick is their Transition from this Passion to that of their Joy. I
won't say we see often, in the next tender Things to Children, Tears
shed without much Grieving. Thus it is common to shed Tears without
much Sorrow, and as common to suffer much Sorrow without shedding
Tears. Grief and Weeping are indeed frequent Companions, but, I
believe, never in their highest Excesses. As Laughter does not proceed
from profound Joy, so neither does Weeping from profound Sorrow. The
Sorrow which appears so easily at the Eyes, cannot have pierced deeply
into the Heart. The Heart distended with Grief, stops all the Passages
for Tears or Lamentations.
'Now, Sir, what I would incline you to in all this, is, that you would
inform the shallow Criticks and Observers upon Sorrow, that true
Affliction labours to be invisible, that it is a Stranger to Ceremony,
and that it bears in its own Nature a Dignity much above the little
Circumstances which are affected under the Notion of Decency. You must
know, Sir, I have lately lost a dear Friend, for whom I have not yet
shed a Tear, and for that Reason your Animadversions on that Subject
would be the more acceptable to',
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
B.D.
June
the 15
th.
Mr.
Spectator,
'As I hope there are but few who have so little Gratitude as not to
acknowledge the Usefulness of your Pen, and to esteem it a Publick
Benefit; so I am sensible, be that as it will, you must nevertheless
find the Secret and Incomparable Pleasure of doing Good, and be a
great Sharer in the Entertainment you give. I acknowledge our Sex to
be much obliged, and I hope improved, by your Labours, and even your
Intentions more particularly for our Service. If it be true, as 'tis
sometimes said, that our Sex have an Influence on the other, your
Paper may be a yet more general Good. Your directing us to Reading is
certainly the best Means to our Instruction; but I think, with you,
Caution in that Particular very useful, since the Improvement of our
Understandings may, or may not, be of Service to us, according as it
is managed. It has been thought we are not generally so Ignorant as
Ill-taught, or that our Sex does so often want Wit, Judgment, or
Knowledge, as the right Application of them: You are so well-bred, as
to say your fair Readers are already deeper Scholars than the Beaus,
and that you could name some of them that talk much better than
several Gentlemen that make a Figure at
Will's: This may
possibly be, and no great Compliment, in my Opinion, even supposing
your Comparison to reach
Tom's and the
Grecian: Surely
you are too wise to think That a Real Commendation of a Woman. Were it
not rather to be wished we improved in our own Sphere, and approved
our selves better Daughters, Wives, Mothers, and Friends?
I can't but agree with the Judicious Trader in
Cheapside
(though I am not at all prejudiced in his Favour) in recommending the
Study of Arithmetick; and must dissent even from the Authority which
you mention, when it advises the making our Sex Scholars. Indeed a
little more Philosophy, in order to the Subduing our Passions to our
Reason, might be sometimes serviceable, and a Treatise of that Nature
I should approve of, even in exchange for
Theodosius, or
The
Force of Love; but as I well know you want not Hints, I will
proceed no further than to recommend the Bishop of
Cambray's
Education of a Daughter, as 'tis translated into the only Language I
have any Knowledge of
2, tho' perhaps very much to its Disadvantage.
I have heard it objected against that Piece, that its Instructions are
not of general Use, but only fitted for a great Lady; but I confess I
am not of that Opinion; for I don't remember that there are any Rules
laid down for the Expences of a Woman, in which Particular only I
think a Gentlewoman ought to differ from a Lady of the best Fortune,
or highest Quality, and not in their Principles of Justice, Gratitude,
Sincerity, Prudence, or Modesty. I ought perhaps to make an Apology
for this long Epistle; but as I rather believe you a Friend to
Sincerity, than Ceremony, shall only assure you I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Annabella.
T.
Seneca. Citation omitted also in the early reprints.
Fenelon was then living. He died in 1715, aged 63.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 20, 1711 |
Steele |
... Amicum
Mancipium domino, et frugi ...
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
I have frequently read your Discourse upon Servants, and, as I am one
my self, have been much offended that in that Variety of Forms wherein
you considered the Bad, you found no Place to mention the Good. There
is however one Observation of yours I approve, which is, That there
are Men of Wit and good Sense among all Orders of Men; and that
Servants report most of the Good or Ill which is spoken of their
Masters. That there are Men of Sense who live in Servitude, I have the
Vanity to say I have felt to my woful Experience. You attribute very
justly the Source of our general Iniquity to Board-Wages, and the
Manner of living out of a domestick Way: But I cannot give you my
Thoughts on this Subject any way so well, as by a short account of my
own Life to this the Forty fifth Year of my Age; that is to say, from
my being first a Foot-boy at Fourteen, to my present Station of a
Nobleman's Porter in the Year of my Age above-mentioned. Know then,
that my Father was a poor Tenant to the Family of Sir
Stephen
Rackrent: Sir
Stephen put me to School, or rather made me
follow his Son
Harry to School, from my Ninth Year; and there,
tho' Sir
Stephen paid something for my Learning, I was used
like a Servant, and was forced to get what Scraps of Learning I could
by my own Industry, for the Schoolmaster took very little Notice of
me. My young Master was a Lad of very sprightly Parts; and my being
constantly about him, and loving him, was no small Advantage to me. My
Master loved me extreamly, and has often been whipped for not keeping
me at a Distance. He used always to say, That when he came to his
Estate I should have a Lease of my Father's Tenement for nothing. I
came up to Town with him to
Westminster School; at which time
he taught me at Night all he learnt; and put me to find out Words in
the Dictionary when he was about his Exercise. It was the Will of
Providence that Master
Harry was taken very ill of a Fever, of
which he died within Ten Days after his first falling sick. Here was
the first Sorrow I ever knew; and I assure you, Mr.
Spectator, I
remember the beautiful Action of the sweet Youth in his Fever, as
fresh as if it were Yesterday. If he wanted any thing, it must be
given him by
Tom: When I let any thing fall through the Grief I
was under, he would cry, Do not beat the poor Boy: Give him some more
Julep for me, no Body else shall give it me. He would strive to hide
his being so bad, when he saw I could not bear his being in so much
Danger, and comforted me, saying,
Tom, Tom, have a good Heart.
When I was holding a Cup at his Mouth, he fell into Convulsions; and
at this very Time I hear my dear Master's last Groan. I was quickly
turned out of the Room, and left to sob and beat my Head against the
Wall at my Leisure. The Grief I was in was inexpressible; and every
Body thought it would have cost me my Life. In a few Days my old Lady,
who was one of the Housewives of the World, thought of turning me out
of Doors, because I put her in mind of her Son. Sir
Stephen
proposed putting me to Prentice; but my Lady being an excellent
Manager, would not let her Husband throw away his Money in Acts of
Charity. I had sense enough to be under the utmost Indignation, to see
her discard with so little Concern, one her Son had loved so much; and
went out of the House to ramble wherever my Feet would carry me.
The third Day after I left Sir
Stephen's Family, I was
strolling up and down the Walks in the
Temple. A young
Gentleman of the House, who (as I heard him say afterwards) seeing me
half-starved and well-dressed, thought me an Equipage ready to his
Hand, after very little Inquiry more than
Did I want a Master?,
bid me follow him; I did so, and in a very little while thought myself
the happiest Creature in this World. My Time was taken up in carrying
Letters to Wenches, or Messages to young Ladies of my Master's
Acquaintance.
We rambled from Tavern to Tavern, to the Play-house, the
Mulberry-Garden
1, and all places of Resort; where my Master engaged
every Night in some new Amour, in which and Drinking he spent all his
Time when he had Money. During these Extravagancies I had the Pleasure
of lying on the Stairs of a Tavern half a Night, playing at Dice with
other Servants, and the like Idleness. When my Master was moneyless,
I was generally employ'd in transcribing amorous Pieces of Poetry, old
Songs, and new Lampoons. This Life held till my Master married, and he
had then the Prudence to turn me off, because I was in the Secret of
his Intreagues.
I was utterly at a loss what Course to take next; when at last I
applied my self to a Fellow-sufferer, one of his Mistresses, a Woman
of the Town. She happening at that time to be pretty full of Money,
cloathed me from Head to Foot, and knowing me to be a sharp Fellow,
employed me accordingly. Sometimes I was to go abroad with her, and
when she had pitched upon a young Fellow she thought for her Turn, I
was to be dropped as one she could not trust.
She would often cheapen
Goods at the
New Exchange2 and when she had a mind to be
attacked, she would send me away on an Errand. When an humble Servant
and she were beginning a Parley, I came immediately, and told her Sir
John was come home; then she would order another Coach to
prevent being dogged. The Lover makes Signs to me as I get behind the
Coach, I shake my Head it was impossible: I leave my Lady at the next
Turning, and follow the Cully to know how to fall in his Way on
another Occasion. Besides good Offices of this Nature, I writ all my
Mistress's Love-Letters; some from a Lady that saw such a Gentleman at
such a Place in such a coloured Coat, some shewing the Terrour she was
in of a jealous old Husband, others explaining that the Severity of
her Parents was such (tho' her Fortune was settled) that she was
willing to run away with such a one, tho' she knew he was but a
younger Brother. In a Word, my half Education and Love of idle Books,
made me outwrite all that made Love to her by way of Epistle; and as
she was extremely cunning, she did well enough in Company by a skilful
Affectation of the greatest Modesty. In the midst of all this I was
surprised with a Letter from her and a Ten Pound Note.
Honest Tom,
You will never see me more. I am married to a very cunning Country
Gentleman, who might possibly guess something if I kept you still;
therefore farewell.
When this Place was lost also in Marriage, I was resolved to go among
quite another People, for the future; and got in Butler to one of
those Families where there is a Coach kept, three or four Servants, a
clean House, and a good general Outside upon a small Estate. Here I
lived very comfortably for some Time,'till I unfortunately found my
Master, the very gravest Man alive, in the Garret with the
Chambermaid. I knew the World too well to think of staying there; and
the next Day pretended to have received a Letter out of the Country
that my Father was dying, and got my Discharge with a Bounty for my
Discretion.
The next I lived with was a peevish single man, whom I stayed with for
a Year and a Half. Most part of the Time I passed very easily; for
when I began to know him, I minded no more than he meant what he said;
so that one Day in a good Humour he said
I was the best man he ever
had, by my want of respect to him.
These, Sir, are the chief Occurrences of my Life; and I will not dwell
upon very many other Places I have been in, where I have been the
strangest Fellow in the World, where no Body in the World had such
Servants as they, where sure they were the unluckiest People in the
World in Servants; and so forth. All I mean by this Representation,
is, to shew you that we poor Servants are not (what you called us too
generally) all Rogues; but that we are what we are, according to the
Example of our Superiors. In the Family I am now in, I am guilty of no
one Sin but Lying; which I do with a grave Face in my Gown and Staff
every Day I live, and almost all Day long, in denying my Lord to
impertinent Suitors, and my Lady to unwelcome Visitants. But, Sir, I
am to let you know that I am, when I get abroad, a Leader of the
Servants: I am he that keep Time with beating my Cudgel against the
Boards in the Gallery at an Opera; I am he that am touched so properly
at a Tragedy, when the People of Quality are staring at one another
during the most important Incidents: When you hear in a Crowd a Cry in
the right Place, an Humm where the Point is touched in a Speech, or an
Hussa set up where it is the Voice of the People; you may conclude it
is begun or joined by,
T.
Sir,
Your more than Humble Servant,
Thomas Trusty
A place of open-air entertainment near Buckingham House.
Sir Charles Sedley named one of his plays after it.
In the Strand, between Durham Yard and York Buildings; in
the
Spectator's
time the fashionable mart for milliners. It was
taken down in 1737.
Contents
|
Thursday, June 21, 1711 |
Steele |
Projecere animas.
Virg.

Among the loose Papers which I have frequently spoken of heretofore, I
find a Conversation between
Pharamond
and
Eucrate
upon the
Subject of Duels, and the Copy of an Edict issued in Consequence of that
Discourse.
Eucrate
argued, that nothing but the most severe and vindictive
Punishments, such as placing the Bodies of the Offenders in Chains, and
putting them to Death by the most exquisite Torments, would be
sufficient to extirpate a Crime which had so long prevailed and was so
firmly fixed in the Opinion of the World as great and laudable; but the
King answered, That indeed Instances of Ignominy were necessary in the
Cure of this Evil; but considering that it prevailed only among such as
had a Nicety in their Sense of Honour, and that it often happened that a
Duel was fought to save Appearances to the World, when both Parties were
in their Hearts in Amity and Reconciliation to each other; it was
evident that turning the Mode another way would effectually put a Stop
to what had Being only as a Mode. That to such Persons, Poverty and
Shame were Torments sufficient, That he would not go further in
punishing in others Crimes which he was satisfied he himself was most
Guilty of, in that he might have prevented them by speaking his
Displeasure sooner. Besides which the King said, he was in general
averse to Tortures, which was putting Human Nature it self, rather than
the Criminal, to Disgrace; and that he would be sure not to use this
Means where the Crime was but an ill Effect arising from a laudable
Cause, the Fear of Shame. The King, at the same time, spoke with much
Grace upon the Subject of Mercy; and repented of many Acts of that kind
which had a magnificent Aspect in the doing, but dreadful Consequences
in the Example. Mercy to Particulars, he observed, was Cruelty in the
General: That though a Prince could not revive a Dead Man by taking the
Life of him who killed him, neither could he make Reparation to the next
that should die by the evil Example; or answer to himself for the
Partiality, in not pardoning the next as well as the former Offender.
'As for me, says Pharamond, I have conquer'd France, and yet have
given Laws to my People: The Laws are my Methods of Life; they are not
a Diminution but a Direction to my Power. I am still absolute to
distinguish the Innocent and the Virtuous, to give Honours to the
Brave and Generous: I am absolute in my Good-will: none can oppose my
Bounty, or prescribe Rules for my Favour. While I can, as I please,
reward the Good, I am under no Pain that I cannot pardon the Wicked:
For which Reason, continued Pharamond, I will effectually put a stop
to this Evil, by exposing no more the Tenderness of my Nature to the
Importunity of having the same Respect to those who are miserable by
their Fault, and those who are so by their Misfortune. Flatterers
(concluded the King smiling) repeat to us Princes, that we are
Heaven's Vice-regents; Let us be so, and let the only thing out of our
Power be to do Ill.'
Soon after the Evening wherein
Pharamond
and
Eucrate
had this
Conversation, the following Edict was Published.
'
Pharamond's Edict against Duels.
Pharamond,
King of the Gauls,
to all his loving Subjects
sendeth Greeting.
Whereas it has come to our Royal Notice and Observation, that in
contempt of all Laws Divine and Human, it is of late become a Custom
among the Nobility and Gentry of this our Kingdom, upon slight and
trivial, as well as great and urgent Provocations, to invite each
other into the Field, there by their own Hands, and of their own
Authority, to decide their Controversies by Combat; We have thought
fit to take the said Custom into our Royal Consideration, and find,
upon Enquiry into the usual Causes whereon such fatal Decisions have
arisen, that by this wicked Custom, maugre all the Precepts of our
Holy Religion, and the Rules of right Reason, the greatest Act of the
human Mind,
Forgiveness of Injuries, is become vile and
shameful; that the Rules of Good Society and Virtuous Conversation are
hereby inverted; that the Loose, the Vain, and the Impudent, insult
the Careful, the Discreet, and the Modest; that all Virtue is
suppressed, and all Vice supported, in the one Act of being capable to
dare to the Death. We have also further, with great Sorrow of Mind,
observed that this Dreadful Action, by long Impunity, (our Royal
Attention being employed upon Matters of more general Concern) is
become Honourable, and the Refusal to engage in it Ignominious. In
these our Royal Cares and Enquiries We are yet farther made to
understand, that the Persons of most Eminent Worth, and most hopeful
Abilities, accompanied with the strongest Passion for true Glory, are
such as are most liable to be involved in the Dangers arising from
this Licence. Now taking the said Premises into our serious
Consideration, and well weighing that all such Emergencies (wherein
the Mind is incapable of commanding it self, and where the Injury is
too sudden or too exquisite to be born) are particularly provided for
by Laws heretofore enacted; and that the Qualities of less Injuries,
like those of Ingratitude, are too nice and delicate to come under
General Rules; We do resolve to blot this Fashion, or Wantonness of
Anger, out of the Minds of Our Subjects, by Our Royal Resolutions
declared in this Edict, as follow.
No Person who either Sends or Accepts a Challenge, or the Posterity of
either, tho' no Death ensues thereupon, shall be, after the
Publication of this our Edict, capable of bearing Office in these our
Dominions.
The Person who shall prove the sending or receiving a Challenge, shall
receive to his own Use and Property, the whole Personal Estate of both
Parties: and their Real Estate shall be immediately vested in the next
Heir of the Offenders in as ample Manner as if the said Offenders were
actually Deceased.
In Cases where the Laws (which we have already granted to our
Subjects) admit of an Appeal for Blood; when the Criminal is condemned
by the said Appeal, He shall not only suffer Death, but his whole
Estate, Real, Mixed, and Personal, shall from the Hour of his Death be
vested in the next Heir of the Person whose Blood he spilt.
That it shall not hereafter be in our Royal Power, or that of our
Successors, to pardon the said Offences, or restore
the Offenders1
in their Estates, Honour, or Blood for ever.
Given at our Court at Blois,
the 8th of February, 420.
In the Second Year of our Reign.
T.
them
Contents
|
Friday, June 22, 1711 |
Addison |
Tanta est quarendi cura decoris.
Juv.

There is not so variable a thing in Nature as a Lady's Head-dress:
Within my own Memory I have known it rise and fall above thirty Degrees.
ten Years ago it shot up to a very great Height
, insomuch that
the Female Part of our Species were much taller than the Men.
Women
were of such an enormous Stature, that
we appeared as Grasshoppers
before them
. At present the whole Sex is in a manner dwarfed and
shrunk into a race of Beauties that seems almost another Species. I
remember several Ladies, who were once very near seven Foot high, that
at present want some inches of five: How they came to be thus curtailed
I cannot learn; whether the whole Sex be at present under any Penance
which we know nothing of, or whether they have cast their Head-dresses
in order to surprize us with something in that kind which shall be
entirely new; or whether some of the tallest of the Sex, being too
cunning for the rest, have contrived this Method to make themselves
appear sizeable, is still a Secret; tho' I find most are of Opinion,
they are at present like Trees new lopped and pruned, that will
certainly sprout up and flourish with greater Heads than before. For my
own part, as I do not love to be insulted by Women who are taller than
my self, I admire the Sex much more in their present Humiliation, which
has reduced them to their natural Dimensions, than when they had
extended their Persons and lengthened themselves out into formidable and
gigantick Figures. I am not for adding to the beautiful Edifices of
Nature, nor for raising any whimsical Superstructure upon her Plans: I
must therefore repeat it, that I am highly pleased with the Coiffure now
in Fashion, and think it shews the good Sense which at present very much
reigns among the valuable Part of the Sex. One may observe that Women in
all Ages have taken more Pains than Men to adorn the Outside of their
Heads; and indeed I very much admire, that those Female Architects, who
raise such wonderful Structures out of Ribbands, Lace, and Wire, have
not been recorded for their respective Inventions. It is certain there
has been as many Orders in these Kinds of Building, as in those which
have been made of Marble: Sometimes they rise in the Shape of a Pyramid,
sometimes like a Tower, and sometimes like a Steeple. In
Juvenal's
time the Building grew by several Orders and Stories,
as he has very humorously described it.
Tot premit ordinibus, tot adhuc compagibus altum
Ædificat caput: Andromachen a fronte videbis;
Post minor est: Altam credas.
Juv.
But I do not remember in any Part of my Reading, that the Head-dress
aspired to so great an Extravagance as in the fourteenth Century; when
it was built up in a couple of Cones or Spires, which stood so
excessively high on each Side of the Head, that a Woman, who was but a
Pigmie
without her Head-dress, appear'd like a
Colossus
upon putting it on.
Paradin
says,
'That these
old-fashioned Fontanges rose an Ell above the Head; that they were
pointed like Steeples, and had long loose Pieces of Crape fastened to
the Tops of them, which were curiously fringed and hung down their Backs
like Streamers.'
Women might possibly have carried this Gothick Building much higher,
had not a famous Monk,
Thomas Conecte
by Name, attacked it
with great Zeal and Resolution.
This holy Man travelled from Place to Place to preach down this
monstrous Commode; and succeeded so well in it, that as the Magicians
sacrificed their Books to the Flames upon the Preaching of an Apostle,
many of the Women threw down their Head-dresses in the Middle of his
Sermon, and made a Bonfire of them within Sight of the Pulpit. He was so
renowned as well for the Sanctity of his Life as his Manner of Preaching
that he had often a Congregation of twenty thousand People; the Men
placing themselves on the one Side of his Pulpit, and the Women on the
other, that appeared (to use the Similitude of an ingenious Writer) like
a Forest of Cedars with their Heads reaching to the Clouds. He so warmed
and animated the People against this monstrous Ornament, that it lay
under a kind of Persecution; and whenever it appeared in publick was
pelted down by the Rabble, who flung Stones at the Persons that wore it.
But notwithstanding this Prodigy vanished, while the Preacher was among
them, it began to appear again some Months after his Departure, or to
tell it in Monsieur
Paradin's
own Words,
'The Women that, like
Snails, in a Fright, had drawn in their Horns, shot them out again as
soon as the Danger was over.'
Extravagance of the Womens
Head-dresses in that Age is taken notice of by Monsieur
d'Argentré
in the History of
Bretagne
, and by other
Historians as well as the Person I have here quoted.
It is usually observed, that a good Reign is the only proper Time for
making of Laws against the Exorbitance of Power; in the same manner an
excessive Head-dress may be attacked the most effectually when the
Fashion is against it. I do therefore recommend this Paper to my Female
Readers by way of Prevention.
I would desire the Fair Sex to consider how impossible it is for them to
add any thing that can be ornamental to what is already the Master-piece
of Nature. The Head has the most beautiful Appearance, as well as the
highest Station, in a human Figure. Nature has laid out all her Art in
beautifying the Face; she has touched it with Vermilion, planted in it a
double Row of Ivory, made it the Seat of Smiles and Blushes, lighted it
up and enlivened it with the Brightness of the Eyes, hung it on each
Side with curious Organs of Sense, given it Airs and Graces that cannot
be described, and surrounded it with such a flowing Shade of Hair as
sets all its Beauties in the most agreeable Light: In short, she seems
to have designed the Head as the Cupola to the most glorious of her
Works; and when we load it with such a Pile of supernumerary Ornaments,
we destroy the Symmetry of the human Figure, and foolishly contrive to
call off the Eye from great and real Beauties, to childish Gewgaws,
Ribbands, and Bone-lace.
L.
The Commode, called by the French
Fontange
, worn on
their heads by ladies at the beginning of the 18th century, was a
structure of wire, which bore up the hair and the forepart of the lace
cap to a great height. The
Spectator
tells how completely and
suddenly the fashion was abandoned in his time.
Numbers
xiii 33.
Guillaume Paradin, a laborious writer of the 16th century,
born at Cuizeau, in the Bresse Chalonnoise, and still living in 1581,
wrote a great many books. The passages quoted by the
Spectator
are from his
Annales de Bourgoigne
, published in 1566.
Thomas Conecte, of Bretagne, was a Carmelite monk, who
became famous as a preacher in 1428. After reproving the vices of the
age in several parts of Europe, he came to Rome, where he reproved the
vices he saw at the Pope's court, and was, therefore, burnt as a heretic
in 1434.
Bertrand d'Argentré was a French lawyer, who died, aged 71,
in 1590. His
Histoire de Bretagne
was printed at Rennes in 1582.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 23, 1711 |
Addison |
... Turpi secernis Honestum.
Hor.

The Club, of which I have often declared my self a Member, were last
Night engaged in a Discourse upon that which passes for the chief Point
of Honour among Men and Women; and started a great many Hints upon the
Subject, which I thought were entirely new: I shall therefore methodize
the several Reflections that arose upon this Occasion, and present my
Reader with them for the Speculation of this Day; after having premised,
that if there is any thing in this Paper which seems to differ with any
Passage of last
Thursday's
, the Reader will consider this as the
Sentiments of the Club, and the other as my own private Thoughts, or
rather those of
Pharamond
.
The great Point of Honour in Men is Courage, and in Women Chastity. If a
Man loses his Honour in one Rencounter, it is not impossible for him to
regain it in another; a Slip in a Woman's Honour is irrecoverable. I can
give no Reason for fixing the Point of Honour to these two Qualities,
unless it be that each Sex sets the greatest Value on the Qualification
which renders them the most amiable in the Eyes of the contrary Sex. Had
Men chosen for themselves, without Regard to the Opinions of the Fair
Sex, I should believe the Choice would have fallen on Wisdom or Virtue;
or had Women determined their own Point of Honour, it is probable that
Wit or Good-Nature would have carried it against Chastity.
Nothing recommends a Man more to the Female Sex than Courage; whether it
be that they are pleased to see one who is a Terror to others fall like
a Slave at their Feet, or that this Quality supplies their own principal
Defect, in guarding them from Insults and avenging their Quarrels, or
that Courage is a natural Indication of a strong and sprightly
Constitution. On the other side, nothing makes a Woman more esteemed by
the opposite Sex than Chastity; whether it be that we always prize those
most who are hardest to come at, or that nothing besides Chastity, with
its collateral Attendants, Truth, Fidelity, and Constancy, gives the Man
a Property in the Person he loves, and consequently endears her to him
above all things.
I am very much pleased with a Passage in the Inscription on a Monument
erected in
Westminster Abbey
to the late Duke and Dutchess of
Newcastle:
'Her Name was Margaret Lucas, youngest Sister
to the Lord Lucas of Colchester; a noble Family, for all the
Brothers were valiant, and all the Sisters virtuous.
In Books of Chivalry, where the Point of Honour is strained to Madness,
the whole Story runs on Chastity and Courage. The Damsel is mounted on a
white Palfrey, as an Emblem of her Innocence; and, to avoid Scandal,
must have a Dwarf for her Page. She is not to think of a Man, 'till some
Misfortune has brought a Knight-Errant to her Relief. The Knight falls
in Love, and did not Gratitude restrain her from murdering her
Deliverer, would die at her Feet by her Disdain. However he must wait
some Years in the Desart, before her Virgin Heart can think of a
Surrender. The Knight goes off, attacks every thing he meets that is
bigger and stronger than himself, seeks all Opportunities of being
knock'd on the Head, and after seven Years Rambling returns to his
Mistress, whose Chastity has been attacked in the mean time by Giants
and Tyrants, and undergone as many Tryals as her Lover's Valour.
In
Spain
, where there are still great Remains of this Romantick
Humour, it is a transporting Favour for a Lady to cast an accidental
Glance on her Lover from a Window, tho' it be two or three Stories high;
as it is usual for the Lover to assert his Passion for his Mistress, in
single Combat with a mad Bull.
The great Violation of the Point of Honour from Man to Man, is giving
the Lie. One may tell another he Whores, Drinks, Blasphemes, and it may
pass unresented; but to say he Lies, tho' but in Jest, is an Affront
that nothing but Blood can expiate. The Reason perhaps may be, because
no other Vice implies a want of Courage so much as the making of a Lie;
and therefore telling a man he Lies, is touching him in the most
sensible Part of Honour, and indirectly calling him a Coward.
I cannot
omit under this Head what Herodotus tells us of the ancient
Persians, That from the Age of five Years to twenty they instruct
their Sons only in three things, to manage the Horse, to make use of the
Bow, and to speak Truth.
The placing the Point of Honour in this false kind of Courage, has given
Occasion to the very Refuse of Mankind, who have neither Virtue nor
common Sense, to set up for Men of Honour.
English
Peer
,
who has not been long dead, used to tell a pleasant Story of a
French
Gentleman that visited him early one Morning at
Paris
, and after great Professions of Respect, let him know that
he had it in his Power to oblige him; which in short, amounted to this,
that he believed he could tell his Lordship the Person's Name who
justled him as he came out from the Opera, but before he would proceed,
he begged his Lordship that he would not deny him the Honour of making
him his Second. The
English
Lord, to avoid being drawn into a
very foolish Affair, told him, that he was under Engagements for his two
next Duels to a Couple of particular Friends. Upon which the Gentleman
immediately withdrew, hoping his Lordship would not take it ill if he
medled no farther in an Affair from whence he himself was to receive no
Advantage.
The beating down this false Notion of Honour, in so vain and lively a
People as those of
France
, is deservedly looked upon as one of
the most glorious Parts of their present King's Reign. It is pity but
the Punishment of these mischievous Notions should have in it some
particular Circumstances of Shame and Infamy, that those who are Slaves
to them may see, that instead of advancing their Reputations they lead
them to Ignominy and Dishonour.
Death is not sufficient to deter Men who make it their Glory to despise
it, but if every one that fought a Duel were to stand in the Pillory, it
would quickly lessen the Number of these imaginary Men of Honour, and
put an end to so absurd a Practice.
When Honour is a Support to virtuous Principles, and runs parallel with
the Laws of God and our Country, it cannot be too much cherished and
encouraged: But when the Dictates of Honour are contrary to those of
Religion and Equity, they are the greatest Depravations of human Nature,
by giving wrong Ambitions and false Ideas of what is good and laudable;
and should therefore be exploded by all Governments, and driven out as
the Bane and Plague of Human Society.
L.
Percy said he had been told that this was William
Cavendish, first Duke of Devonshire, who died in 1707.
Contents
|
Monday, June 25, 1711 |
Steele |
Nil ego contulerim jucundo sanus amico.
Hor.

A man advanced in Years that thinks fit to look back upon his former
Life, and calls that only Life which was passed with Satisfaction and
Enjoyment, excluding all Parts which were not pleasant to him, will find
himself very young, if not in his Infancy. Sickness, Ill-humour, and
Idleness, will have robbed him of a great Share of that Space we
ordinarily call our Life. It is therefore the Duty of every Man that
would be true to himself, to obtain, if possible, a Disposition to be
pleased, and place himself in a constant Aptitude for the Satisfactions
of his Being. Instead of this, you hardly see a Man who is not uneasy in
proportion to his Advancement in the Arts of Life. An affected Delicacy
is the common Improvement we meet with in those who pretend to be
refined above others: They do not aim at true Pleasures themselves, but
turn their Thoughts upon observing the false Pleasures of other Men.
Such People are Valetudinarians in Society, and they should no more come
into Company than a sick Man should come into the Air: If a Man is too
weak to bear what is a Refreshment to Men in Health, he must still keep
his Chamber. When any one in Sir
Roger's
Company complains he is out of
Order, he immediately calls for some Posset-drink for him; for which
reason that sort of People who are ever bewailing their Constitution in
other Places are the Chearfullest imaginable when he is present.
It is a wonderful thing that so many, and they not reckoned absurd,
shall entertain those with whom they converse by giving them the History
of their Pains and Aches; and imagine such Narrations their Quota of the
Conversation. This is of all other the meanest Help to Discourse, and a
Man must not think at all, or think himself very insignificant, when he
finds an Account of his Head-ach answer'd by another's asking what News
in the last Mail? Mutual good Humour is a Dress we ought to appear in
whenever we meet, and we should make no mention of what concerns our
selves, without it be of Matters wherein our Friends ought to rejoyce:
But indeed there are Crowds of People who put themselves in no Method of
pleasing themselves or others; such are those whom we usually call
indolent Persons. Indolence is, methinks, an intermediate State between
Pleasure and Pain, and very much unbecoming any Part of our Life after
we are out of the Nurse's Arms. Such an Aversion to Labour creates a
constant Weariness, and one would think should make Existence it self a
Burthen. The indolent Man descends from the Dignity of his Nature, and
makes that Being which was Rational merely Vegetative: His Life consists
only in the meer Encrease and Decay of a Body, which, with relation to
the rest of the World, might as well have been uninformed, as the
Habitation of a reasonable Mind.
Of this kind is the Life of that extraordinary Couple
Harry Tersett
and his Lady.
Harry
was in the Days of his Celibacy one of those pert
Creatures who have much Vivacity and little Understanding; Mrs.
Rebecca
Quickly
, whom he married, had all that the Fire of Youth and a lively
Manner could do towards making an agreeable Woman. The two People of
seeming Merit fell into each other's Arms; and Passion being sated, and
no Reason or good Sense in either to succeed it, their Life is now at a
Stand; their Meals are insipid, and their Time tedious; their Fortune
has placed them above Care, and their Loss of Taste reduced them below
Diversion. When we talk of these as Instances of Inexistence, we do not
mean, that in order to live it is necessary we should always be in
Jovial Crews, or crowned with Chaplets of Roses, as the merry Fellows
among the Ancients are described; but it is intended by considering
these Contraries to Pleasure, Indolence, and too much Delicacy, to shew
that it is Prudence to preserve a Disposition in our selves to receive a
certain Delight in all we hear and see.
This portable Quality of good Humour seasons all the Parts and
Occurrences we meet with, in such a manner, that, there are no Moments
lost; but they all pass with so much Satisfaction, that the heaviest of
Loads (when it is a Load) that of Time, is never felt by us.
Varilas
has this Quality to the highest Perfection, and communicates it wherever
he appears: The Sad, the Merry, the Severe, the Melancholy, shew a new
Chearfulness when he comes amongst them. At the same time no one can
repeat any thing that
Varilas
has ever said that deserves Repetition;
but the Man has that innate Goodness of Temper, that he is welcome to
every Body, because every Man thinks he is so to him. He does not seem
to contribute any thing to the Mirth of the Company; and yet upon
Reflection you find it all happened by his being there. I thought it was
whimsically said of a Gentleman, That if
Varilas
had Wit, it would be
the best Wit in the World. It is certain, when a well-corrected lively
Imagination and good Breeding are added to a sweet Disposition, they
qualify it to be one of the greatest Blessings, as well as Pleasures of
Life.
Men would come into Company with ten times the Pleasure they do, if they
were sure of hearing nothing which should shock them, as well as
expected what would please them. When we know every Person that is
spoken of is represented by one who has no ill Will, and every thing
that is mentioned described by one that is apt to set it in the best
Light, the Entertainment must be delicate; because the Cook has nothing
brought to his Hand but what is the most excellent in its Kind.
Beautiful Pictures are the Entertainments of pure Minds, and Deformities
of the corrupted. It is a Degree towards the Life of Angels, when we
enjoy Conversation wherein there is nothing presented but in its
Excellence: and a Degree towards that of Dæmons, wherein nothing is
shewn but in its Degeneracy.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 26, 1711 |
Addison |
Romulus, et Liber pater, et cum Castore Pollux,
Post ingentia facta, Deorum in templa recepti;
Dum terras hominumque colunt genus, aspera bella
Componunt, agros assignant, oppida condunt;
Ploravere suis non respondere favorem
Speratum meritis: ...
Hor.

, says a late ingenious Author,
is the Tax a Man pays to the
Publick for being Eminent
. It is a Folly for an eminent Man to
think of escaping it, and a Weakness to be affected with it. All the
illustrious Persons of Antiquity, and indeed of every Age in the World,
have passed through this fiery Persecution. There is no Defence against
Reproach, but Obscurity; it is a kind of Concomitant to Greatness, as
Satyrs and Invectives were an essential Part of a
Roman
Triumph.
If Men of Eminence are exposed to Censure on one hand, they are as much
liable to Flattery on the other. If they receive Reproaches which are
not due to them, they likewise receive Praises which they do not
deserve. In a word, the Man in a high Post is never regarded with an
indifferent Eye, but always considered as a Friend or an Enemy. For this
Reason Persons in great Stations have seldom their true Characters drawn
till several Years after their Deaths. Their personal Friendships and
Enmities must cease, and the Parties they were engaged in be at an End,
before their Faults or their Virtues can have Justice done them. When
Writers have the least Opportunities of knowing the Truth they are in
the best Disposition to tell it.
It is therefore the Privilege of Posterity to adjust the Characters of
illustrious Persons, and to set Matters right between those Antagonists,
who by their Rivalry for Greatness divided a whole Age into Factions. We
can now allow
Cæsar
to be a great Man, without derogating from
Pompey
; and celebrate the Virtues of
Cato
, without
detracting from those of
Cæsar
. Every one that has been long dead
has a due Proportion of Praise allotted him, in which whilst he lived
his Friends were too profuse and his Enemies too sparing.
to Sir
Isaac Newton's
Calculations, the last Comet that
made its Appearance in 1680, imbib'd so much Heat by its Approaches to
the Sun, that it would have been two thousand times hotter than red hot
Iron, had it been a Globe of that Metal; and that supposing it as big as
the Earth, and at the same Distance from the Sun, it would be fifty
thousand Years in cooling, before it recovered its natural Temper
.
In the like manner, if an
Englishman
considers the great Ferment
into which our Political World is thrown at present, and how intensely
it is heated in all its Parts, he cannot suppose that it will cool again
in less than three hundred Years. In such a Tract of Time it is possible
that the Heats of the present Age may be extinguished, and our several
Classes of great Men represented under their proper Characters. Some
eminent Historian may then probably arise that will not write
recentibus odiis
(as
Tacitus
expresses it) with the
Passions and Prejudices of a contemporary Author, but make an impartial
Distribution of Fame among the Great Men of the present Age.
I cannot forbear entertaining my self very often with the Idea of such
an imaginary Historian describing the Reign of
Anne
the First,
and introducing it with a Preface to his Reader, that he is now entring
upon the most shining Part of the
English
Story. The great Rivals
in Fame will then be distinguished according to their respective Merits,
and shine in their proper Points of
. Such
an
one (says the
Historian) tho' variously represented by the Writers of his own Age,
appears to have been a Man of more than ordinary Abilities, great
Application and uncommon Integrity: Nor was such an one (tho' of an
opposite Party and Interest) inferior to him in any of these Respects.
The several Antagonists who now endeavour to depreciate one another, and
are celebrated or traduced by different Parties, will then have the same
Body of Admirers, and appear Illustrious in the Opinion of the whole
British
Nation. The deserving Man, who can now recommend himself
to the Esteem of but half his Countrymen, will then receive the
Approbations and Applauses of a whole Age.
Among the several Persons that flourish in this Glorious Reign, there is
no question but such a future Historian as the Person of whom I am
speaking, will make mention of the Men of Genius and Learning, who have
now any Figure in the
British
Nation. For my own part, I often
flatter my self with the honourable Mention which will then be made of
me; and have drawn up a Paragraph in my own Imagination, that I fancy
will not be altogether unlike what will be found in some Page or other
of this imaginary Historian.
It was under this Reign, says he, that the
Spectator publish'd those
little Diurnal Essays which are still extant. We know very little of the
Name or Person of this Author, except only that he was a Man of a very
short Face, extreamly addicted to Silence, and so great a Lover of
Knowledge, that he made a Voyage to
Grand Cairo for no other
Reason, but to take the Measure of a Pyramid. His chief Friend was one
Sir
Roger De Coverley, a whimsical Country Knight, and a
Templar
whose Name he has not transmitted to us. He lived as a Lodger at the
House of a Widow-Woman, and was a great Humourist in all Parts of his
Life. This is all we can affirm with any Certainty of his Person and
Character. As for his Speculations, notwithstanding the several obsolete
Words and obscure Phrases of the Age in which he lived, we still
understand enough of them to see the Diversions and Characters of the
English Nation in his Time: Not but that we are to make Allowance
for the Mirth and Humour of the Author, who has doubtless strained many
Representations of Things beyond the Truth.
For if we interpret his
Words in the literal Meaning, we must suppose that Women of the first
Quality used to pass away whole Mornings at a Puppet-Show: That they
attested their Principles by their
Patches: That an Audience
would sit out
an4 Evening to hear a Dramatical Performance written
in a Language which they did not understand: That Chairs and Flower-pots
were introduced as Actors upon the
British Stage: That a
promiscuous Assembly of Men and Women were allowed to meet at Midnight
in Masques within the Verge of the Court; with many Improbabilities of
the like Nature. We must therefore, in these and the like Cases, suppose
that these remote Hints and Allusions aimed at some certain Follies
which were then in Vogue, and which at present we have not any Notion
of. We may guess by several Passages in the
Speculations, that
there were Writers who endeavoured to detract from the Works of this
Author; but as nothing of this nature is come down to us, we cannot
guess at any Objections that could be made to his Paper. If we consider
his Style with that Indulgence which we must shew to old
English
Writers, or if we look into the Variety of his Subjects, with those
several Critical Dissertations, Moral Reflections,
The following Part of the Paragraph is so much to my Advantage, and
beyond any thing I can pretend to, that I hope my Reader will excuse me
for not inserting it.
L.
Swift.
In his
Principia
, published 1687, Newton says this
to show that the nuclei of Comets must consist of solid matter.
a
a whole
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 27, 1711 |
Addison |
... Lusus animo debent aliquando dari,
Ad cogitandum melior ut redeat sibi.
Phædr.

I do not know whether to call the following Letter a Satyr upon Coquets,
or a Representation of their several fantastical Accomplishments, or
what other Title to give it; but as it is I shall communicate it to the
Publick. It will sufficiently explain its own Intentions, so that I
shall give it my Reader at Length, without either Preface or Postscript.
Mr. Spectator,
'Women are armed with Fans as Men with Swords, and sometimes do more
Execution with them. To the end therefore that Ladies may be entire
Mistresses of the Weapon which they bear, I have erected an Academy
for the training up of young Women in the
Exercise of the Fan,
according to the most fashionable Airs and Motions that are now
practis'd at Court. The Ladies who
carry Fans under me are
drawn up twice a-day in my great Hall, where they are instructed in
the Use of their Arms, and
exercised by the following Words of
Command,
Handle your Fans,
Unfurl your fans.
Discharge your Fans,
Ground your Fans,
Recover your Fans,
Flutter your Fans.
By the right Observation of these few plain Words of Command, a Woman
of a tolerable Genius,
who1 will apply herself diligently to her
Exercise for the Space of but one half Year, shall be able to give her
Fan all the Graces that can possibly enter into that little modish
Machine.
But to the end that my Readers may form to themselves a right Notion
of this
Exercise, I beg leave to explain it to them in all its
Parts. When my Female Regiment is drawn up in Array, with every one
her Weapon in her Hand, upon my giving the Word to
handle their
Fans, each of them shakes her Fan at me with a Smile, then gives
her Right-hand Woman a Tap upon the Shoulder, then presses her Lips
with the Extremity of her Fan, then lets her Arms fall in an easy
Motion, and stands in a Readiness to receive the next Word of Command.
All this is done with a close Fan, and is generally learned in the
first Week.
The next Motion is that of
unfurling the Fan, in which
are2 comprehended several little Flirts and Vibrations, as also
gradual and deliberate Openings, with many voluntary Fallings asunder
in the Fan itself, that are seldom learned under a Month's Practice.
This Part of the
Exercise pleases the Spectators more than any
other, as it discovers on a sudden an infinite Number of
Cupids,
Garlands, Altars, Birds, Beasts, Rainbows, and the
like agreeable Figures, that display themselves to View, whilst every
one in the Regiment holds a Picture in her Hand.
Upon my giving the Word to
discharge their Fans, they give one
general Crack that may be heard at a considerable distance when the
Wind sits fair. This is one of the most difficult Parts of the
Exercise; but I have several Ladies with me, who at their first
Entrance could not give a Pop loud enough to be heard at the further
end of a Room, who can now
discharge a Fan in such a manner,
that it shall make a Report like a Pocket-Pistol. I have likewise
taken care (in order to hinder young Women from letting off their Fans
in wrong Places or unsuitable Occasions) to shew upon what Subject the
Crack of a Fan may come in properly: I have likewise invented a Fan,
with which a Girl of Sixteen, by the help of a little Wind which is
inclosed about one of the largest Sticks, can make as loud a Crack as
a Woman of Fifty with an ordinary Fan.
When the Fans are thus
discharged, the Word of Command in
course is to
ground their Fans. This teaches a Lady to quit her
Fan gracefully when she throws it aside in order to take up a Pack of
Cards, adjust a Curl of Hair, replace a falling Pin, or apply her self
to any other Matter of Importance. This Part of the
Exercise,
as it only consists in tossing a Fan with an Air upon a long Table
(which stands by for that Purpose) may be learned in two Days Time as
well as in a Twelvemonth.
When my Female Regiment is thus disarmed, I generally let them walk
about the Room for some Time; when on a sudden (like Ladies that look
upon their Watches after a long Visit) they all of them hasten to
their Arms, catch them up in a Hurry, and place themselves in their
proper Stations upon my calling out
Recover your Fans. This
Part of the
Exercise is not difficult, provided a Woman applies
her Thoughts to it.
The
Fluttering of the Fan is the last, and indeed the
Master-piece of the whole
Exercise; but if a Lady does not
mis-spend her Time, she may make herself Mistress of it in three
Months. I generally lay aside the Dog-days and the hot Time of the
Summer for the teaching this Part of the
Exercise; for as soon
as ever I pronounce
Flutter your Fans, the Place is fill'd with
so many Zephyrs and gentle Breezes as are very refreshing in that
Season of the Year, tho' they might be dangerous to Ladies of a tender
Constitution in any other.
There is an infinite Variety of Motions to be made use of in the
Flutter of a Fan. There is the angry Flutter, the modest
Flutter, the timorous Flutter, the confused Flutter, the merry
Flutter, and the amorous Flutter.
Not to be tedious, there is scarce
any Emotion in the Mind
which3 does not produce a suitable
Agitation in the Fan; insomuch, that if I only see the Fan of a
disciplin'd Lady, I know very well whether she laughs, frowns, or
blushes. I have seen a Fan so very angry, that it would have been
dangerous for the absent Lover
who3 provoked it to have come
within the Wind of it; and at other times so very languishing, that I
have been glad for the Lady's sake the Lover was at a sufficient
Distance from it. I need not add, that a Fan is either a Prude or
Coquet according to the Nature of the Person
who3 bears it. To
conclude my Letter, I must acquaint you that I have from my own
Observations compiled a little Treatise for the use of my Scholars,
entitled
The Passions of the Fan; which I will communicate to
you, if you think it may be of use to the Publick. I shall have a
general Review on
Thursday next; to which you shall be very
welcome if you will honour it with your Presence.
I am, &c.
P. S. I teach young Gentlemen the whole Art of Gallanting a
Fan.
N. B. I have several little plain Fans made for this Use, to
avoid Expence.'
L.
that
is
that
Contents
|
Thursday, June 28, 1711 |
Steele |
... Sibi quivis
Speret idem frusta sudet frustraque laboret
Ausus idem ...
Hor.

My Friend the Divine having been used with Words of Complaisance (which
he thinks could be properly applied to no one living, and I think could
be only spoken of him, and that in his Absence) was so extreamly
offended with the excessive way of speaking Civilities among us, that he
made a Discourse against it at the Club; which he concluded with this
Remark, That he had not heard one Compliment made in our Society since
its Commencement. Every one was pleased with his Conclusion; and as each
knew his good Will to the rest, he was convinced that the many
Professions of Kindness and Service, which we ordinarily meet with, are
not natural where the Heart is well inclined; but are a Prostitution of
Speech, seldom intended to mean Any Part of what they express, never to
mean All they express.
Reverend Friend, upon this Topick, pointed to
us two or three Paragraphs on this Subject in the first Sermon of the
first Volume of the late Arch-Bishop's Posthumous Works
. I do not
know that I ever read any thing that pleased me more, and as it is the
Praise of
Longinus
, that he Speaks of the Sublime in a Style
suitable to it, so one may say of this Author upon Sincerity, that he
abhors any Pomp of Rhetorick on this Occasion, and treats it with a more
than ordinary Simplicity, at once to be a Preacher and an Example. With
what Command of himself does he lay before us, in the Language and
Temper of his Profession, a Fault, which by the least Liberty and Warmth
of Expression would be the most lively Wit and Satyr? But his Heart was
better disposed, and the good Man chastised the great Wit in such a
manner, that he was able to speak as follows.
'... Amongst too many other Instances of the great Corruption and
Degeneracy of the Age wherein we live, the great and general Want of
Sincerity in Conversation is none of the least. The World is grown so
full of Dissimulation and Compliment, that Mens Words are hardly any
Signification of their Thoughts; and if any Man measure his Words by
his Heart, and speak as he thinks, and do not express more Kindness to
every Man, than Men usually have for any Man, he can hardly escape the
Censure of want of Breeding. The old English Plainness and
Sincerity, that generous Integrity of Nature, and Honesty of
Disposition, which always argues true Greatness of Mind and is usually
accompanied with undaunted Courage and Resolution, is in a great
measure lost amongst us: There hath been a long Endeavour to transform
us into Foreign Manners and Fashions, and to bring us to a servile
Imitation of none of the best of our Neighbours in some of the worst
of their Qualities. The Dialect of Conversation is now-a-days so
swelled with Vanity and Compliment, and so surfeited (as I may say) of
Expressions of Kindness and Respect, that if a Man that lived an Age
or two ago should return into the World again he would really want a
Dictionary to help him to understand his own Language, and to know the
true intrinsick Value of the Phrase in Fashion, and would hardly at
first believe at what a low Rate the highest Strains and Expressions
of Kindness imaginable do commonly pass in current Payment; and when
he should come to understand it, it would be a great while before he
could bring himself with a good Countenance and a good Conscience to
converse with Men upon equal Terms, and in their own way.
And in truth it is hard to say, whether it should more provoke our
Contempt or our Pity, to hear what solemn Expressions of Respect and
Kindness will pass between Men, almost upon no Occasion; how great
Honour and Esteem they will declare for one whom perhaps they never
saw before, and how entirely they are all on the sudden devoted to his
Service and Interest, for no Reason; how infinitely and eternally
obliged to him, for no Benefit; and how extreamly they will be
concerned for him, yea and afflicted too, for no Cause. I know it is
said, in Justification of this hollow kind of Conversation, that there
is no Harm, no real Deceit in Compliment, but the Matter is well
enough, so long as we understand one another; et Verba valent ut
Nummi: Words are like Money; and when the current Value of them is
generally understood, no Man is cheated by them. This is something, if
such Words were any thing; but being brought into the Account, they
are meer Cyphers. However, it is still a just Matter of Complaint,
that Sincerity and Plainness are out of Fashion, and that our Language
is running into a Lie; that Men have almost quite perverted the use of
Speech, and made Words to signifie nothing, that the greatest part of
the Conversation of Mankind is little else but driving a Trade of
Dissimulation; insomuch that it would make a Man heartily sick and
weary of the World, to see the little Sincerity that is in Use and
Practice among Men.
When the Vice is placed in this contemptible Light, he argues
unanswerably against it, in Words and Thoughts so natural, that any
Man who reads them would imagine he himself could have been the Author
of them.
If the Show of any thing be good for any thing, I am sure Sincerity is
better: for why does any Man dissemble, or seem to be that which he is
not, but because he thinks it good to have such a Quality as he
pretends to? For to counterfeit and dissemble, is to put on the
Appearance of some real Excellency. Now the best way in the World to
seem to be any thing, is really to be what he would seem to be.
Besides, that it is many times as troublesome to make good the
Pretence of a good Quality, as to have it; and if a Man have it not,
it is ten to one but he is discovered to want it; and then all his
Pains and Labour to seem to have it, is lost.
In another Part of the same Discourse he goes on to shew, that all
Artifice must naturally tend to the Disappointment of him that practises
it.
'Whatsoever Convenience may be thought to be in Falshood and
Dissimulation, it is soon over; but the Inconvenience of it is
perpetual, because it brings a Man under an everlasting Jealousie and
Suspicion, so that he is not believed when he speaks Truth, nor
trusted when perhaps he means honestly. When a Man hath once forfeited
the Reputation of his Integrity, he is set fast, and nothing will then
serve his Turn, neither Truth nor Falshood.'
R.
This sermon
on Sincerity,
from John i. 47, is the last
Tillotson preached. He preached it in 1694, on the 29th of July, and
died, in that year, on the 24th of November, at the age of 64. John
Tillotson was the son of a Yorkshire clothier, and was made Archbishop
of Canterbury in 1691, on the deprivation of William Sancroft for his
refusal to take the oaths to William and Mary.
Contents
|
Friday, June 29, 1711 |
Steele |
... Qualis equos Threissa fatigat
Harpalyce ...
Virg.

It would be a noble Improvement, or rather a Recovery of what we call
good Breeding, if nothing were to pass amongst us for agreeable which
was the least Transgression against that Rule of Life called Decorum, or
a Regard to Decency. This would command the Respect of Mankind, because
it carries in it Deference to their good Opinion, as Humility lodged in
a worthy Mind is always attended with a certain Homage, which no haughty
Soul, with all the Arts imaginable, will ever be able to purchase.
Tully
says, Virtue and Decency are so nearly related, that it is
difficult to separate them from each other but in our Imagination. As
the Beauty of the Body always accompanies the Health of it, so certainly
is Decency concomitant to Virtue: As Beauty of Body, with an agreeable
Carriage, pleases the Eye, and that Pleasure consists in that we observe
all the Parts with a certain Elegance are proportioned to each other; so
does Decency of Behaviour which appears in our Lives obtain the
Approbation of all with whom we converse, from the Order, Consistency,
and Moderation of our Words and Actions. This flows from the Reverence
we bear towards every good Man, and to the World in general; for to be
negligent of what any one thinks of you, does not only shew you arrogant
but abandoned. In all these Considerations we are to distinguish how one
Virtue differs from another; As it is the Part of Justice never to do
Violence, it is of Modesty never to commit Offence. In this last
Particular lies the whole Force of what is called Decency; to this
purpose that excellent Moralist above-mentioned talks of Decency; but
this Quality is more easily comprehended by an ordinary Capacity, than
expressed with all his Eloquence. This Decency of Behaviour is generally
transgressed among all Orders of Men; nay, the very Women, tho'
themselves created as it were for Ornament, are often very much mistaken
in this ornamental Part of Life. It would methinks be a short Rule for
Behaviour, if every young Lady in her Dress, Words, and Actions were
only to recommend her self as a Sister, Daughter, or Wife, and make
herself the more esteemed in one of those Characters. The Care of
themselves, with regard to the Families in which Women are born, is the
best Motive for their being courted to come into the Alliance of other
Houses. Nothing can promote this End more than a strict Preservation of
Decency. I should be glad if a certain Equestrian Order of Ladies, some
of whom one meets in an Evening at every Outlet of the Town, would take
this Subject into their serious Consideration;
order thereunto the
following Letter may not be wholly unworthy their Perusal
.
Mr. Spectator,
'Going lately to take the Air in one of the most beautiful Evenings
this Season has produced, as I was admiring the Serenity of the Sky,
the lively Colours of the Fields, and the Variety of the Landskip
every Way around me, my Eyes were suddenly called off from these
inanimate Objects by a little party of Horsemen I saw passing the
Road. The greater Part of them escaped my particular Observation, by
reason that my whole Attention was fixed on a very fair Youth who rode
in the midst of them, and seemed to have been dressed by some
Description in a Romance. His Features, Complexion, and Habit had a
remarkable Effeminacy, and a certain languishing Vanity appeared in
his Air: His Hair, well curl'd and powder'd, hung to a considerable
Length on his Shoulders, and was wantonly ty'd, as if by the Hands of
his Mistress, in a Scarlet Ribbon, which played like a Streamer behind
him: He had a Coat and Wastecoat of blue Camlet trimm'd and
embroidered with Silver; a Cravat of the finest Lace; and wore, in a
smart Cock, a little Beaver Hat edged with Silver, and made more
sprightly by a Feather. His Horse too, which was a Pacer, was adorned
after the same airy Manner, and seemed to share in the Vanity of the
Rider. As I was pitying the Luxury of this young Person, who appeared
to me to have been educated only as an Object of Sight, I perceived on
my nearer Approach, and as I turned my Eyes downward, a Part of the
Equipage I had not observed before, which was a Petticoat of the same
with the Coat and Wastecoat. After this Discovery, I looked again on
the Face of the fair Amazon who had thus deceived me, and
thought those Features which had before offended me by their Softness,
were now strengthened into as improper a Boldness; and tho' her Eyes
Nose and Mouth seemed to be formed with perfect Symmetry, I am not
certain whether she, who in Appearance was a very handsome Youth, may
not be in Reality a very indifferent Woman.
There is an Objection which naturally presents it self against these
occasional Perplexities and Mixtures of Dress, which is, that they
seem to break in upon that Propriety and Distinction of Appearance in
which the Beauty of different Characters is preserved; and if they
should be more frequent than they are at present, would look like
turning our publick Assemblies into a general Masquerade. The Model of
this Amazonian Hunting-Habit for Ladies, was, as I take it,
first imported from France, and well enough expresses the
Gaiety of a People who are taught to do any thing so it be with an
Assurance; but I cannot help thinking it sits awkwardly yet on our
English Modesty. The Petticoat is a kind of Incumbrance upon
it, and if the Amazons should think fit to go on in this
Plunder of our Sex's Ornaments, they ought to add to their Spoils, and
compleat their Triumph over us, by wearing the Breeches.
If it be natural to contract insensibly the Manners of those we
imitate, the Ladies who are pleased with assuming our Dresses will do
us more Honour than we deserve, but they will do it at their own
Expence. Why should the lovely Camilla deceive us in more
Shapes than her own, and affect to be represented in her Picture with
a Gun and a Spaniel, while her elder Brother, the Heir of a worthy
Family, is drawn in Silks like his Sister? The Dress and Air of a Man
are not well to be divided; and those who would not be content with
the Latter, ought never to think of assuming the Former. There is so
large a portion of natural Agreeableness among the Fair Sex of our
Island, that they seem betrayed into these romantick Habits without
having the same Occasion for them with their Inventors: All that needs
to be desired of them is, that they would be themselves, that
is, what Nature designed them; and to see their Mistake when they
depart from this, let them look upon a Man who affects the Softness
and Effeminacy of a Woman, to learn how their Sex must appear to us,
when approaching to the Resemblance of a Man.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant.
T.
The letter is by John Hughes.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 30, 1711 |
Addison |
... Id arbitror
Adprime in vita esse utile, ne quid nimis.
Ter. And.

My Friend
Will. Honeycomb
values himself very much upon what he calls
the Knowledge of Mankind, which has cost him many Disasters in his
Youth; for
Will
. reckons every Misfortune that he has met with among the
Women, and every Rencounter among the Men, as Parts of his Education,
and fancies he should never have been the Man he is, had not he broke
Windows, knocked down Constables, disturbed honest People with his
Midnight Serenades, and beat up a lewd Woman's Quarters, when he was a
young Fellow. The engaging in Adventures of this Nature
Will
. calls the
studying of Mankind; and terms this Knowledge of the Town, the Knowledge
of the World.
Will.
ingenuously confesses, that for half his Life his
Head ached every Morning with reading of Men over-night; and at present
comforts himself under certain Pains which he endures from time to time,
that without them he could not have been acquainted with the Gallantries
of the Age. This
Will.
looks upon as the Learning of a Gentleman, and
regards all other kinds of Science as the Accomplishments of one whom he
calls a Scholar, a Bookish Man, or a Philosopher.
For these Reasons
Will.
shines in mixt Company, where he has the
Discretion not to go out of his Depth, and has often a certain way of
making his real Ignorance appear a seeming one. Our Club however has
frequently caught him tripping, at which times they never spare him.
as
Will.
often insults us with the Knowledge of the Town, we sometimes
take our Revenge upon him by our Knowledge
of
Books.
He was last Week producing two or three Letters which he writ in his
Youth to a Coquet Lady. The Raillery of them was natural, and well
enough for a mere Man of the Town; but, very unluckily, several of the
Words were wrong spelt.
Will.
laught this off at first as well as he
could; but finding himself pushed on all sides, and especially by the
Templar
, he told us, with a little Passion, that he never liked
Pedantry in Spelling, and that he spelt like a Gentleman, and not like a
Scholar: Upon this
Will.
had recourse to his old Topick of shewing the
narrow-Spiritedness, the Pride, and Ignorance of Pedants; which he
carried so far, that upon my retiring to my Lodgings, I could not
forbear throwing together such Reflections as occurred to me upon that
Subject.
Man
who
has been brought up among Books, and is able to talk of
nothing else, is a very indifferent Companion, and what we call a
Pedant. But, methinks, we should enlarge the Title, and give it every
one that does not know how to think out of his Profession and particular
way of Life.
What is a greater Pedant than a meer Man of the Town? Bar him the
Play-houses, a Catalogue of the reigning Beauties, and an Account of a
few fashionable Distempers that have befallen him, and you strike him
dumb. How many a pretty Gentleman's Knowledge lies all within the Verge
of the Court? He will tell you the Names of the principal Favourites,
repeat the shrewd Sayings of a Man of Quality, whisper an Intreague that
is not yet blown upon by common Fame; or, if the Sphere of his
Observations is a little larger than ordinary, will perhaps enter into
all the Incidents, Turns, and Revolutions in a Game of Ombre. When he
has gone thus far he has shown you the whole Circle of his
Accomplishments, his Parts are drained, and he is disabled from any
further Conversation.
are these but rank Pedants? and yet these are
the Men
who
value themselves most on their Exemption from the
Pedantry of Colleges.
I might here mention the Military Pedant who always talks in a Camp, and
is storming Towns, making Lodgments and fighting Battles from one end of
the Year to the other. Every thing he speaks smells of Gunpowder; if you
take away his Artillery from him, he has not a Word to say for himself.
I might likewise mention the Law-Pedant, that is perpetually putting
Cases, repeating the Transactions of
Westminster-Hall
, wrangling
with you upon the most indifferent Circumstances of Life, and not to be
convinced of the Distance of a Place, or of the most trivial Point in
Conversation, but by dint of Argument. The State-Pedant is wrapt up in
News, and lost in Politicks. If you mention either of the Kings of
Spain
or
Poland
, he talks very notably; but if you go out
of the
Gazette
, you drop him. In short, a meer Courtier, a meer
Soldier, a meer Scholar, a meer any thing, is an insipid Pedantick
Character, and equally ridiculous.
all the Species of Pedants, which I have
mentioned
, the
Book-Pedant is much the most supportable; he has at least an exercised
Understanding, and a Head which is full though confused, so that a Man
who converses with him may often receive from him hints of things that
are worth knowing, and what he may possibly turn to his own Advantage,
tho' they are of little Use to the Owner. The worst kind of Pedants
among Learned Men, are such as are naturally endued with a very small
Share of common Sense, and have read a great number of Books without
Taste or Distinction.
The Truth of it is, Learning, like Travelling, and all other Methods of
Improvement, as it finishes good Sense, so it makes a silly Man ten
thousand times more insufferable, by supplying variety of Matter to his
Impertinence, and giving him an Opportunity of abounding in Absurdities.
Shallow Pedants cry up one another much more than Men of solid and
useful Learning. To read the Titles they give an Editor, or Collator of
a Manuscript, you would take him for the Glory of the Commonwealth of
Letters, and the Wonder of his Age, when perhaps upon Examination you
find that he has only Rectify'd a
Greek
Particle, or laid out a
whole Sentence in proper Commas.
They are obliged indeed to be thus lavish of their Praises, that they
may keep one another in Countenance; and it is no wonder if a great deal
of Knowledge, which is not capable of making a Man wise, has a natural
Tendency to make him Vain and Arrogant.
L.
in
that
that
above mentioned
Contents
|
Monday, July 2, 1711 |
Addison |
... Hinc tibi Copia
Manabit ad plenum, benigno
Ruris honorum opulenta cornu.
Hor.

Having often received an Invitation from my Friend Sir
Roger De Coverley
to pass away a Month with him in the Country, I last Week accompanied
him thither, and am settled with him for some time at his Country-house,
where I intend to form several of my ensuing Speculations. Sir
Roger
,
who is very well acquainted with my Humour, lets me rise and go to Bed
when I please, dine at his own Table or in my Chamber as I think fit,
sit still and say nothing without bidding me be merry. When the
Gentlemen of the Country come to see him, he only shews me at a
Distance: As I have been walking in his Fields I have observed them
stealing a Sight of me over an Hedge, and have heard the Knight desiring
them not to let me see them, for that I hated to be stared at.
I am the more at Ease in Sir
Roger
's Family, because it consists of
sober and staid Persons; for as the Knight is the best Master in the
World, he seldom changes his Servants; and as he is beloved by all about
him, his Servants never care for leaving him; by this means his
Domesticks are all in Years, and grown old with their Master. You would
take his Valet de Chambre for his Brother, his Butler is grey-headed,
his Groom is one of the gravest Men that I have ever seen, and his
Coachman has the Looks of a Privy-Counsellor. You see the Goodness of
the Master even in the old House-dog, and in a grey Pad that is kept in
the Stable with great Care and Tenderness out of Regard to his past
Services, tho' he has been useless for several Years.
I could not but observe with a great deal of Pleasure the Joy that
appeared in the Countenances of these ancient Domesticks upon my
Friend's Arrival at his Country-Seat. Some of them could not refrain
from Tears at the Sight of their old Master; every one of them press'd
forward to do something for him, and seemed discouraged if they were not
employed. At the same time the good old Knight, with a Mixture of the
Father and the Master of the Family, tempered the Enquiries after his
own Affairs with several kind Questions relating to themselves.
Humanity and good Nature engages every Body to him, so that when he is
pleasant upon any of them, all his Family are in good Humour, and none
so much as the Person whom he diverts himself with: On the contrary, if
he coughs, or betrays any Infirmity of old Age, it is easy for a
Stander-by to observe a secret Concern in the Looks of all his Servants
.
My worthy Friend has put me under the particular Care of his Butler, who
is a very prudent Man, and, as well as the rest of his Fellow-Servants,
wonderfully desirous of pleasing me, because they have often heard their
Master talk of me as of his particular Friend.
My chief Companion, when Sir
Roger
is diverting himself in the Woods or
the Fields, is a very venerable Man who is ever with Sir
Roger
, and has
lived at his House in the Nature of a Chaplain above thirty Years. This
Gentleman is a Person of good Sense and some Learning, of a very regular
Life and obliging Conversation: He heartily loves Sir
Roger
, and knows
that he is very much in the old Knight's Esteem, so that he lives in the
Family rather as a Relation than a Dependant.
I have observed in several of my Papers, that my Friend Sir
Roger
,
amidst all his good Qualities, is something of an Humourist; and that
his Virtues, as well as Imperfections, are as it were tinged by a
certain Extravagance, which makes them particularly
his
, and
distinguishes them from those of other Men. This Cast of Mind, as it is
generally very innocent in it self, so it renders his Conversation
highly agreeable, and more delightful than the same Degree of Sense and
Virtue would appear in their common and ordinary Colours. As I was
walking with him last Night, he asked me how I liked the good Man whom I
have just now mentioned? and without staying for my Answer told me, That
he was afraid of being insulted with Latin and Greek at his own Table;
for which Reason he desired a particular Friend of his at the University
to find him out a Clergyman rather of plain Sense than much Learning, of
a good Aspect, a clear Voice, a sociable Temper, and, if possible, a Man
that understood a little of Back-Gammon.
My
Friend, says Sir
Roger., found me out this Gentleman, who, besides
the Endowments
required2 of him, is, they tell me, a good
Scholar, tho' he does not shew it. I have given him the Parsonage of
the Parish; and because I know his Value have settled upon him a good
Annuity for Life. If he outlives me, he shall find that he was higher
in my Esteem than perhaps he thinks he is. He has now been with me
thirty Years; and tho' he does not know I have taken Notice of it, has
never in all that time asked anything of me for himself, tho' he is
every Day solliciting me for something in behalf of one or other of my
Tenants his Parishioners. There has not been a Law-suit in the Parish
since he has liv'd among them: If any Dispute arises they apply
themselves to him for the Decision; if they do not acquiesce in his
Judgment, which I think never happened above once or twice at most,
they appeal to me.
At his first settling with me, I made him a Present
of all the good Sermons
which3 have been printed in
English, and only begg'd of him that every
Sunday he
would pronounce one of them in the Pulpit. Accordingly, he has
digested them into such a Series, that they follow one another
naturally, and make a continued System of practical Divinity.
Sir
Roger
was going on in his Story, the Gentleman we were talking of
came up to us; and upon the Knight's asking him who preached to morrow
(for it was
Saturday
Night) told us, the Bishop of St.
Asaph
in the Morning, and Dr.
South
in the Afternoon. He
then shewed us his List of Preachers for the whole Year, where I saw
with a great deal of Pleasure Archbishop
Tillotson
, Bishop
Saunderson
, Doctor
Barrow
, Doctor
Calamy
, with
several living Authors who have published Discourses of Practical
Divinity. I no sooner saw this venerable Man in the Pulpit, but I very
much approved of my Friend's insisting upon the Qualifications of a good
Aspect and a clear Voice; for I was so charmed with the Gracefulness of
his Figure and Delivery, as well as with the Discourses he pronounced,
that I think I never passed any Time more to my Satisfaction. A Sermon
repeated after this Manner, is like the Composition of a Poet in the
Mouth of a graceful Actor.
I could heartily wish that more of our Country Clergy would follow this
Example; and instead of wasting their Spirits in laborious Compositions
of their own, would endeavour after a handsome Elocution, and all those
other Talents that are proper to enforce what has been penned by greater
Masters. This would not only be more easy to themselves, but more
edifying to the People.
L.
Thomas Tyers in his
Historical Essay on Mr. Addison
(1783) first named Sir John Pakington, of Westwood, Worcestershire, as
the original of Sir Roger de Coverley. But there is no real parallel.
Sir John, as Mr. W. H. Wills has pointed out in his delightful annotated
collection of the Sir Roger de Coverley papers, was twice married, a
barrister, Recorder of the City of Worcester, and M. P. for his native
county, in every Parliament but one, from his majority till his death.
The name of Roger of Coverley applied to a
contre-danse
(i.e. a
dance in which partners stand in opposite rows) Anglicised
Country-Dance, was ascribed to the house of Calverley in Yorkshire, by
an ingenious member thereof, Ralph Thoresby, who has left a MS. account
of the family written in 1717. Mr. Thoresby has it that Sir Roger of
Calverley in the time of Richard I had a harper who was the composer of
this tune; his evidence being, apparently, that persons of the name of
Harper had lands in the neighbourhood of Calverley. Mr. W. Chappell, who
repeats this statement in his
Popular Music of the Olden Time,
says
that in a MS. of the beginning of the last century, this tune is called
'Old Roger of Coverlay for evermore. A Lancashire Hornpipe.' In the
Dancing Master
of 1696. it is called ' Roger of Coverly.' Mr.
Chappell quotes also, in illustration of the familiar knowledge of this
tune and its name in Addison's time, from 'the History of Robert Powell,
the Puppet Showman (1715),' that
'upon the Preludis being ended, each party fell to bawling and calling
for particular tunes. The hobnail'd fellows, whose breeches and lungs
seem'd to be of the same leather, cried out for Cheshire Rounds,
Roger of Coverly,' &c.
I required
that
Archbishop Tillotson's
Sermons
appeared in 14 volumes,
small 8vo, published at intervals; the first in 1671; the second in
1678; the third in 1682; the fourth in 1694; and the others after his
death in that year. Robert Sanderson, who died in 1663, was a friend of
Laud and chaplain to Charles I, who made him Regius Professor of
Divinity at Oxford. At the Restoration he was made Bishop of Lincoln.
His fame was high for piety and learning. The best edition of his
Sermons was the eighth, published in 1687: Thirty-six Sermons, with Life
by Izaak Walton. Isaac Barrow, Theologian and Mathematician, Cambridge
Professor and Master of Trinity, died in 1677. His
Works
were edited by
Archbishop Tillotson, and include Sermons that must have been very much
to the mind of Sir Roger de Coverley,
Against Evil Speaking.
Edmund
Calamy, who died in 1666, was a Nonconformist, and one of the writers of
the Treatise against Episcopacy called, from the Initials of its
authors, Smeetymnuus, which Bishop Hall attacked and John Milton
defended. Calamy opposed the execution of Charles I and aided in
bringing about the Restoration. He became chaplain to Charles II, but
the Act of Uniformity again made him a seceder. His name, added to the
other three, gives breadth to the suggestion of Sir Roger's orthodoxy.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 3, 1711 |
Steele |
Æsopo ingentem statuam posuere Attici,
Servumque collocârunt Æterna in Basi,
Patere honoris scirent ut Cuncti viam.
Phæd.

The Reception, manner of Attendance, undisturbed Freedom and Quiet,
which I meet with here in the Country, has confirm'd me in the Opinion I
always had, that the general Corruption of Manners in Servants is owing
to the Conduct of Masters. The Aspect of every one in the Family carries
so much Satisfaction, that it appears he knows the happy Lot which has
befallen him in being a Member of it. There is one Particular which I
have seldom seen but at Sir
Roger
's; it is usual in all other Places,
that Servants fly from the Parts of the House through which their Master
is passing; on the contrary, here they industriously place themselves in
his way; and it is on both Sides, as it were, understood as a Visit,
when the Servants appear without calling. This proceeds from the humane
and equal Temper of the Man of the House, who also perfectly well knows
how to enjoy a great Estate, with such Œconomy as ever to be much
beforehand. This makes his own Mind untroubled, and consequently unapt
to vent peevish Expressions, or give passionate or inconsistent Orders
to those about him. Thus Respect and Love go together; and a certain
Chearfulness in Performance of their Duty is the particular Distinction
of the lower Part of this Family. When a Servant is called before his
Master, he does not come with an Expectation to hear himself rated for
some trivial Fault, threatned to be stripped, or used with any other
unbecoming Language, which mean Masters often give to worthy Servants;
but it is often to know, what Road he took that he came so readily back
according to Order; whether he passed by such a Ground, if the old Man
who rents it is in good Health: or whether he gave Sir
Roger
's Love to
him, or the like.
A Man who preserves a Respect, founded on his Benevolence to his
Dependants, lives rather like a Prince than a Master in his Family; his
Orders are received as Favours, rather than Duties; and the Distinction
of approaching him is Part of the Reward for executing what is commanded
by him.
There is another Circumstance in which my Friend excells in his
Management, which is the Manner of rewarding his Servants: He has ever
been of Opinion, that giving his cast Cloaths to be worn by Valets has a
very ill Effect upon little Minds, and creates a Silly Sense of Equality
between the Parties, in Persons affected only with outward things. I
have heard him often pleasant on this Occasion, and describe a young
Gentleman abusing his Man in that Coat, which a Month or two before was
the most pleasing Distinction he was conscious of in himself. He would
turn his Discourse still more pleasantly upon the Ladies Bounties of
this kind; and I have heard him say he knew a fine Woman, who
distributed Rewards and punishments in giving becoming or unbecoming
Dresses to her Maids.
But my good Friend is above these little Instances of Goodwill, in
bestowing only Trifles on his Servants; a good Servant to him is sure of
having it in his Choice very soon of being no Servant at all. As I
before observed, he is so good an Husband, and knows so thoroughly that
the Skill of the Purse is the Cardinal Virtue of this Life; I say, he
knows so well that Frugality is the Support of Generosity, that he can
often spare a large Fine when a Tenement falls, and give that Settlement
to a good Servant who has a Mind to go into the World, or make a
Stranger pay the Fine to that Servant, for his more comfortable
Maintenance, if he stays in his Service.
A Man of Honour and Generosity considers, it would be miserable to
himself to have no Will but that of another, tho' it were of the best
Person breathing, and for that Reason goes on as fast as he is able to
put his Servants into independent Livelihoods. The greatest Part of Sir
Roger
'S Estate is tenanted by Persons who have served himself or his
Ancestors. It was to me extreamly pleasant to observe the Visitants from
several Parts to welcome his Arrival into the Country: and all the
Difference that I could take notice of between the late Servants who
came to see him, and those who staid in the Family, was that these
latter were looked upon as finer Gentlemen and better Courtiers.
This Manumission and placing them in a way of Livelihood, I look upon as
only what is due to a good Servant, which Encouragement will make his
Successor be as diligent, as humble, and as ready as he was. There is
something wonderful in the Narrowness of those Minds, which can be
pleased, and be barren of Bounty to those who please them.
might, on this Occasion, recount the Sense that Great Persons in all
Ages have had of the Merit of their Dependants, and the Heroick Services
which Men have done their Masters in the Extremity of their Fortunes;
and shewn to their undone Patrons, that Fortune was all the Difference
between them; but as I design this my Speculation only
as a
gentle
Admonition to thankless Masters, I shall not go out of the Occurrences
of Common Life, but assert it as a general Observation, that I never
saw, but in Sir
Roger
'S Family, and one or two more, good Servants
treated as they ought to be. Sir
Roger
's Kindness extends to their
Children's Children, and this very Morning he sent his Coachman's
Grandson to Prentice. I shall conclude this Paper with an Account of a
Picture in his Gallery, where there are many which will deserve my
future Observation.
At the very upper end of this handsome Structure I saw the Portraiture
of two young Men standing in a River, the one naked, the other in a
Livery. The Person supported seemed half dead, but still so much alive
as to shew in his Face exquisite Joy and Love towards the other. I
thought the fainting Figure resembled my Friend Sir
Roger
; and looking
at the Butler, who stood by me, for an Account of it, he informed me
that the Person in the Livery was a Servant of Sir
Roger
's, who stood on
the Shore while his Master was swimming, and observing him taken with
some sudden Illness, and sink under Water, jumped in and saved him. He
told me Sir
Roger
took off the Dress he was in as soon as he came home,
and by a great Bounty at that time, followed by his Favour ever since,
had made him Master of that pretty Seat which we saw at a distance as we
came to this House. I remember'd indeed Sir
Roger
said there lived a
very worthy Gentleman, to whom he was highly obliged, without mentioning
anything further. Upon my looking a little dissatisfy'd at some Part of
the Picture my Attendant informed me that it was against Sir
Roger
'S
Will, and at the earnest Request of the Gentleman himself, that he was
drawn in the Habit in which he had saved his Master.
R.
a
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 4, 1711 |
Addison |
Gratis anhelans, multa agendo nihil agens.
Phæd.

As I was Yesterday Morning walking with Sir
Roger
before his House, a
Country-Fellow brought him a huge Fish, which, he told him, Mr.
William Wimble
had caught that very Morning; and that he
presented it, with his Service to him, and intended to come and dine
with him. At the same Time he delivered a Letter, which my Friend read
to me as soon as the Messenger left him.
Sir Roger,
'I desire you to accept of a Jack, which is the best I have caught
this Season. I intend to come and stay with you a Week, and see how
the Perch bite in the
Black River. I observed with some Concern, the
last time I saw you upon the Bowling-Green, that your Whip wanted a
Lash to it; I will bring half a dozen with me that I twisted last
Week, which I hope will serve you all the Time you are in the Country.
I have not been out of the Saddle for six Days last past, having been
at
Eaton with Sir
John's eldest Son. He takes to his Learning
hugely. I am,
Sir, Your Humble Servant
Will. Wimble
1.'
This extraordinary Letter, and Message that accompanied it, made me very
curious to know the Character and Quality of the Gentleman who sent
them; which I found to be as follows.
Will. Wimble
is younger Brother
to a Baronet, and descended of the ancient Family of the
Wimbles
. He
is now between Forty and Fifty; but being bred to no Business and born
to no Estate, he generally lives with his elder Brother as
Superintendant of his Game. He hunts a Pack of Dogs better than any Man
in the Country, and is very famous for finding out a Hare. He is
extreamly well versed in all the little Handicrafts of an idle Man: He
makes a
May-fly
to a Miracle; and furnishes the whole Country with
Angle-Rods. As he is a good-natur'd officious Fellow, and very much
esteem'd upon account of his Family, he is a welcome Guest at every
House, and keeps up a good Correspondence among all the Gentlemen about
him. He carries a Tulip-root in his Pocket from one to another, or
exchanges a Poppy between a Couple of Friends that live perhaps in the
opposite Sides of the County.
Will
. is a particular Favourite of all
the young Heirs, whom he frequently obliges with a Net that he has
weaved, or a Setting-dog that he has
made
himself: He now and then
presents a Pair of Garters of his own knitting to their Mothers or
Sisters; and raises a great deal of Mirth among them, by enquiring as
often as he meets them
how they wear
? These Gentleman-like
Manufactures and obliging little Humours, make
Will
. the Darling of
the Country.
Sir
Roger
was proceeding in the Character of him, when we saw him make
up to us with two or three Hazle-Twigs in his Hand that he had cut in
Sir
Roger
's Woods, as he came through them, in his Way to the House. I
was very much pleased to observe on one Side the hearty and sincere
Welcome with which Sir
Roger
received him, and on the other, the secret
Joy which his Guest discover'd at Sight of the good old Knight. After
the first Salutes were over,
Will.
desired Sir
Roger
to lend him one
of his Servants to carry a Set of Shuttlecocks he had with him in a
little Box to a Lady that lived about a Mile off, to whom it seems he
had promis'd such a Present for above this half Year.
Roger
's Back
was no sooner turned but honest
Will.
began
to tell me of a
large Cock-Pheasant that he had sprung in one of the neighbouring Woods,
with two or three other Adventures of the same Nature. Odd and uncommon
Characters are the Game that I look for, and most delight in; for which
Reason I was as much pleased with the Novelty of the Person that talked
to me, as he could be for his Life with the springing of a Pheasant, and
therefore listned to him with more than ordinary Attention.
In the midst of his Discourse the Bell rung to Dinner, where the
Gentleman I have been speaking of had the Pleasure of seeing the huge
Jack, he had caught, served up for the first Dish in a most sumptuous
Manner. Upon our sitting down to it he gave us a long Account how he had
hooked it, played with it, foiled it, and at length drew it out upon the
Bank, with several other Particulars that lasted all the first Course. A
Dish of Wild-fowl that came afterwards furnished Conversation for the
rest of the Dinner, which concluded with a late Invention of
Will's
for improving the Quail-Pipe.
Upon withdrawing into my Room after Dinner, I was secretly touched with
Compassion towards the honest Gentleman that had dined with us; and
could not but consider with a great deal of Concern, how so good an
Heart and such busy Hands were wholly employed in Trifles; that so much
Humanity should be so little beneficial to others, and so much Industry
so little advantageous to himself. The same Temper of Mind and
Application to Affairs might have recommended him to the publick Esteem,
and have raised his Fortune in another Station of Life. What Good to his
Country or himself might not a Trader or Merchant have done with such
useful tho' ordinary Qualifications?
Will. Wimble's
is the Case of many a younger Brother of a great
Family, who had rather see their Children starve like Gentlemen, than
thrive in a Trade or Profession that is beneath their Quality. This
Humour fills several Parts of
Europe
with Pride and Beggary. It is the
Happiness of a Trading Nation, like ours, that the younger Sons, tho'
uncapabie of any liberal Art or Profession, may be placed in such a Way
of Life, as may perhaps enable them to vie with the best of their
Family: Accordingly we find several Citizens that were launched into the
World with narrow Fortunes, rising by an honest Industry to greater
Estates than those of their elder Brothers. It is not improbable but
Will
, was formerly tried at Divinity, Law, or Physick; and that
finding his Genius did not lie that Way, his Parents gave him up at
length to his own Inventions. But certainly, however improper he might
have been for Studies of a higher Nature, he was perfectly well turned
for the Occupations of Trade and Commerce. As I think this is a Point
which cannot be too much inculcated, I shall desire my Reader to compare
what I have here written with what I have said in my
Speculation.
L.
Will Wimble has been identified with Mr. Thomas Morecraft,
younger son of a Yorkshire baronet. Mr. Morecraft in his early life
became known to Steele, by whom he was introduced to Addison. He
received help from Addison, and, after his death, went to Dublin, where
he died in 1741 at the house of his friend, the Bishop of Kildare. There
is no ground for this or any other attempt to find living persons in the
creations of the
Spectator
, although, because lifelike, they were, in
the usual way, attributed by readers to this or that individual, and so
gave occasion for the statement of Pudgell in the Preface to his
Theophrastus
that
'most of the characters in the Spectator were conspicuously known.'
The only original of Will Wimble, as Mr. Wills has pointed out, is Mr.
Thomas Gules of No. 256 in the
Tatler
.
begun
Contents
|
Thursday, July 5, 1711 |
Steele |
Abnormis sapiens ...
Hor.

I was this Morning walking in the Gallery, when Sir
Roger
entered at the
End opposite to me, and advancing towards me, said, he was glad to meet
me among his Relations the
De Coverleys
, and hoped I liked the
Conversation of so much good Company, who were as silent as myself. I
knew he alluded to the Pictures, and as he is a Gentleman who does not a
little value himself upon his ancient Descent, I expected he would give
me some Account of them. We were now arrived at the upper End of the
Gallery, when the Knight faced towards one of the Pictures, and as we
stood before it, he entered into the Matter, after his blunt way of
saying Things, as they occur to his Imagination, without regular
Introduction, or Care to preserve the Appearance of Chain of Thought.
'It is, said he, worth while to consider the Force of Dress; and how
the Persons of one Age differ from those of another, merely by that
only. One may observe also, that the general Fashion of one Age has
been followed by one particular Set of People in another, and by them
preserved from one Generation to another. Thus the vast jetting Coat
and small Bonnet, which was the Habit in
Harry the Seventh's Time,
is kept on in the Yeomen of the Guard; not without a good and politick
View, because they look a Foot taller, and a Foot and an half broader:
Besides that the Cap leaves the Face expanded, and consequently more
terrible, and fitter to stand at the Entrance of Palaces.
This Predecessor of ours, you see, is dressed after this manner, and
his Cheeks would be no larger than mine, were he in a Hat as I am.
He
was the last Man that won a Prize in the Tilt-Yard (which is now a
Common Street before
Whitehall1.) You see the broken Lance that
lies there by his right Foot; He shivered that Lance of his Adversary
all to Pieces; and bearing himself, look you, Sir, in this manner, at
the same time he came within the Target of the Gentleman who rode
against him, and taking him with incredible Force before him on the
Pommel of his Saddle, he in that manner rid the Turnament over, with
an Air that shewed he did it rather to perform the Rule of the Lists,
than expose his Enemy; however, it appeared he knew how to make use of
a Victory, and with a gentle Trot he marched up to a Gallery where
their Mistress sat (for they were Rivals) and let him down with
laudable Courtesy and pardonable Insolence. I don't know but it might
be exactly where the Coffee-house is now.
You are to know this my Ancestor was not only of a military Genius,
but fit also for the Arts of Peace, for he played on the Base-Viol as
well as any Gentlemen at Court; you see where his Viol hangs by his
Basket-hilt Sword. The Action at the Tilt-yard you may be sure won the
fair Lady, who was a Maid of Honour, and the greatest Beauty of her
Time; here she stands, the next Picture. You see, Sir, my Great Great
Great Grandmother has on the new-fashioned Petticoat, except that the
Modern is gather'd at the Waste; my Grandmother appears as if she
stood in a large Drum, whereas the Ladies now walk as if they were in
a Go-Cart.
For all this Lady was bred at Court, she became an
Excellent Country-Wife, she brought ten Children, and when I shew you
the Library, you shall see in her own Hand (allowing for the
Difference of the Language) the best Receipt now in
England both for
an Hasty-pudding and a White-pot
2.
If you please to fall back a little, because 'tis necessary to look at
the three next Pictures at one View; these are three Sisters. She on
the right Hand, who is so very beautiful, died a Maid; the next to
her, still handsomer, had the same Fate, against her Will; this homely
thing in the middle had both their Portions added to her own, and was
stolen by a neighbouring Gentleman, a Man of Stratagem and Resolution,
for he poisoned three Mastiffs to come at her, and knocked down two
Deer-stealers in carrying her off. Misfortunes happen in all Families:
The Theft of this Romp and so much Mony, was no great matter to our
Estate. But the next Heir that possessed it was this soft Gentleman,
whom you see there: Observe the small Buttons, the little Boots, the
Laces, the Slashes about his Cloaths, and above all the Posture he is
drawn in, (which to be sure was his own choosing;) you see he sits
with one Hand on a Desk writing, and looking as it were another way,
like an easy Writer, or a Sonneteer: He was one of those that had too
much Wit to know how to live in the World; he was a Man of no Justice,
but great good Manners; he ruined every Body that had any thing to do
with him, but never said a rude thing in his Life; the most indolent
Person in the World, he would sign a Deed that passed away half his
Estate with his Gloves on, but would not put on his Hat before a Lady
if it were to save his Country. He is said to be the first that made
Love by squeezing the Hand. He left the Estate with ten thousand
Pounds Debt upon it, but however by all Hands I have been informed
that he was every way the finest Gentleman in the World. That Debt lay
heavy on our House for one Generation, but it was retrieved by a Gift
from that honest Man you see there, a Citizen of our Name, but nothing
at all a-kin to us. I know Sir
Andrew. FREEPORT has said behind my
Back, that this Man was descended from one of the ten Children of the
Maid of Honour I shewed you above; but it was never made out. We
winked at the thing indeed, because Mony was wanting at that time.
Here I saw my Friend a little embarrassed, and turned my Face to the
next Portraiture.
Sir
Roger
went on with his Account of the Gallery in the following
Manner.
'This Man (pointing to him I looked at) I take to be the Honour of our
House. Sir Humphrey De Coverley; he was in his Dealings as punctual as
a Tradesman, and as generous as a Gentleman. He would have thought
himself as much undone by breaking his Word, as if it were to be
followed by Bankruptcy. He served his Country as Knight of this Shire
to his dying Day. He found it no easy matter to maintain an Integrity
in his Words and Actions, even in things that regarded the Offices
which were incumbent upon him, in the Care of his own Affairs and
Relations of Life, and therefore dreaded (tho' he had great Talents)
to go into Employments of State, where he must be exposed to the
Snares of Ambition. Innocence of Life and great Ability were the
distinguishing Parts of his Character; the latter, he had often
observed, had led to the Destruction of the former, and used
frequently to lament that Great and Good had not the same
Signification. He was an excellent Husbandman, but had resolved not to
exceed such a Degree of Wealth; all above it he bestowed in secret
Bounties many Years after the Sum he aimed at for his own Use was
attained. Yet he did not slacken his Industry, but to a decent old Age
spent the Life and Fortune which was superfluous to himself, in the
Service of his Friends and Neighbours.
Here we were called to Dinner, and Sir
Roger
ended the Discourse of this
Gentleman, by telling me, as we followed the Servant, that this his
Ancestor was a brave Man, and narrowly escaped being killed in the Civil
Wars;
'For,' said he, 'he was sent out of the Field upon a private Message,
the Day before the Battel of Worcester.'
The Whim of narrowly escaping by having been within a Day of Danger,
with other Matters above-mentioned, mixed with good Sense, left me at a
Loss whether I was more delighted with my Friend's Wisdom or Simplicity.
R.
When Henry VIII drained the site of St. James's Park he
formed, close to the Palace of Whitehall, a large Tilt-yard for noblemen
and others to exercise themselves in jousting, tourneying, and fighting
at the barriers. Houses afterwards were built on its ground, and one of
them became Jenny Man's "Tilt Yard Coffee House." The
Paymaster-General's office now stands on the site of it.
A kind of Custard.
Contents
|
Friday, July 6, 1711 |
Addison |
Horror ubique animos, simul ipsa silentia terrent.
Virg.

At a little distance from Sir
Roger
's House, among the Ruins of an old
Abby, there is a long Walk of aged Elms; which are shot up so very high,
that when one passes under them, the Rooks and Crows that rest upon the
Tops of them seem to be cawing in another Region. I am very much
delighted with this sort of Noise, which I consider as a kind of natural
Prayer to that Being who supplies the Wants of his whole Creation, and
who
, in the beautiful Language of the
Psalms
, feedeth the young
Ravens that call upon him.
like this
Retirement
the better,
because of an ill Report it lies under of being
haunted
; for which
Reason (as I have been told in the Family) no living Creature ever walks
in it besides the Chaplain. My good Friend the Butler desired me with a
very grave Face not to venture my self in it after Sun-set, for that one
of the Footmen had been almost frighted out of his Wits by a Spirit that
appear'd to him in the Shape of a black Horse without an Head; to which
he added, that about a Month ago one of the Maids coming home late that
way with a Pail of Milk upon her Head, heard such a Rustling among the
Bushes that she let it fall.
I was taking a Walk in this Place last Night between the Hours of Nine
and Ten, and could not but fancy it one of the most proper Scenes in the
World for a Ghost to appear in. The Ruins of the Abby are scattered up
and down on every Side, and half covered with Ivy and Elder-Bushes, the
Harbours of several solitary Birds which seldom make their Appearance
till the Dusk of the Evening. The Place was formerly a Churchyard, and
has still several Marks in it of Graves and Burying-Places. There is
such an Eccho among the old Ruins and Vaults, that if you stamp but a
little louder than ordinary, you hear the Sound repeated. At the same
time the Walk of Elms, with the Croaking of the Ravens which from time
to time are heard from the Tops of them, looks exceeding solemn and
venerable. These Objects naturally raise Seriousness and Attention; and
when Night heightens the Awfulness of the Place, and pours out her
supernumerary Horrors upon every thing in it, I do not at all wonder
that weak Minds fill it with Spectres and Apparitions.
Mr. Locke, in his Chapter of the Association of Ideas, has very curious
Remarks to shew how by the Prejudice of Education one Idea often
introduces into the Mind a whole Set that bear no Resemblance to one
another in the Nature of things. Among several Examples of this Kind, he
produces the following Instance.
The Ideas of Goblins and Sprights have
really no more to do with Darkness than Light: Yet let but a foolish
Maid inculcate these often on the Mind of a Child, and raise them there
together, possibly he shall never be able to separate them again so long
as he lives; but Darkness shall ever afterwards bring with it those
frightful Ideas, and they shall be so joined, that he can no more bear
the one than the other2.
As I was walking in this Solitude, where the Dusk of the Evening
conspired with so many other Occasions of Terrour, I observed a Cow
grazing not far from me, which an Imagination that is apt to
startle
,
might easily have construed into a black Horse without an Head: And I
dare say the poor Footman lost his Wits upon some such trivial Occasion.
My Friend Sir
Roger
has often told me with a great deal of Mirth, that
at his first coming to his Estate he found three Parts of his House
altogether useless; that the best Room in it had the Reputation of being
haunted, and by that means was locked up; that Noises had been heard in
his long Gallery, so that he could not get a Servant to enter it after
eight a Clock at Night; that the Door of one of his Chambers was nailed
up, because there went a Story in the Family that a Butler had formerly
hang'd himself in it; and that his Mother, who lived to a great Age, had
shut up half the Rooms in the House, in which either her Husband, a Son,
or Daughter had died.
Knight seeing his Habitation reduced
to
so small a Compass, and himself in a manner shut out of his own House,
upon the Death of his Mother ordered
all the Apartments
to be
flung open, and
exorcised
by his Chaplain, who lay in every Room one
after another, and by that Means dissipated the Fears which had so long
reigned in the Family.
I should not have been thus particular upon these ridiculous Horrours,
did I not find them so very much prevail in all Parts of the Country. At
the same time I think a Person who is thus terrify'd with the
Imagination of Ghosts and Spectres much more reasonable than one who,
contrary to the Reports of all Historians sacred and prophane, ancient
and modern, and to the Traditions of all Nations, thinks the Appearance
of Spirits fabulous and groundless: Could not I give myself up to this
general Testimony of Mankind, I should to the Relations of particular
Persons who are now living, and whom I cannot distrust in other Matters
of Fact. I might here add, that not only the Historians, to whom we may
join the Poets, but likewise the Philosophers of Antiquity have favoured
this Opinion.
Lucretius
himself, though by the Course of his
Philosophy he was obliged to maintain that the Soul did not exist
separate from the Body, makes no Doubt of the Reality of Apparitions,
and that Men have often appeared after their Death. This I think very
remarkable; he was so pressed with the Matter of Fact which he could not
have the Confidence to deny, that he was forced to account for it by one
of the most absurd unphilosophical Notions that was ever started.
tells us, That the Surfaces of all Bodies are perpetually flying off
from their respective Bodies, one after another; and that these Surfaces
or thin Cases that included each other whilst they were joined in the
Body like the Coats of an Onion, are sometimes seen entire when they are
separated from it; by which means we often behold the Shapes and Shadows
of Persons who are either dead or absent
.
I shall dismiss this Paper with a Story out of
Josephus
, not so much
for the sake of the Story it self as for the moral Reflections with
which the Author concludes it, and which I shall here set down in his
own Words.
'
Glaphyra the Daughter of King
Archelaus, after the Death of her
two first Husbands (being married to a third, who was Brother to her
first Husband, and so passionately in love with her that he turned off
his former Wife to make room for this Marriage) had a very odd kind of
Dream. She fancied that she saw her first Husband coming towards her,
and that she embraced him with great Tenderness; when in the midst of
the Pleasure which she expressed at the Sight of him, he reproached
her after the following manner:
Glaphyra, says he, thou hast made
good the old Saying, That Women are not to be trusted. Was not I the
Husband of thy Virginity? Have I not Children by thee? How couldst
thou forget our Loves so far as to enter into a second Marriage, and
after that into a third, nay to take for thy Husband a Man who has so
shamelessly crept into the Bed of his Brother? However, for the sake
of our passed Loves, I shall free thee from thy present Reproach, and
make thee mine for ever.
Glaphyra told
this Dream to several Women
of her Acquaintance, and died soon after.
6 I thought this Story
might not be impertinent in this Place, wherein I speak of those
Kings: Besides that, the Example deserves to be taken notice of as it
contains a most certain Proof of the Immortality of the Soul, and of
Divine Providence. If any Man thinks these Facts incredible, let him
enjoy his own Opinion to himself, but let him not endeavour to disturb
the Belief of others, who by Instances of this Nature are excited to
the Study of Virtue.'
L.
Walk
Essay on the Human Understanding
, Bk. II., ch. 33.
into
the Rooms
Lucret. iv. 34, &c.
Josephus,
Antiq. Jud
. lib. xvii. cap. 15, 415.
Contents
|
Saturday, July 7, 1711 |
Addison |
... Inter Silvas Academi quærere Verum.
Hor.

The Course of my last Speculation led me insensibly into a Subject upon
which I always meditate with great Delight, I mean the Immortality of
the Soul. I was yesterday walking alone in one of my Friend's Woods, and
lost my self in it very agreeably, as I was running over in my Mind the
several Arguments that establish this great Point, which is the Basis of
Morality, and the Source of all the pleasing Hopes and secret Joys that
can arise in the Heart of a reasonable Creature. I considered those
several Proofs, drawn;
- From the Nature of the Soul it self, and particularly its
Immateriality; which, tho' not absolutely necessary to the Eternity of
its Duration, has, I think, been evinced to almost a Demonstration.
- From its Passions and Sentiments, as particularly from its
Love of Existence, its Horrour of Annihilation, and its Hopes of
Immortality, with that secret Satisfaction which it finds in the
Practice of Virtue, and that Uneasiness which follows in it upon the
Commission of Vice.
- From the Nature of the Supreme Being, whose Justice,
Goodness, Wisdom and Veracity are all concerned in this great Point.
But among these and other excellent Arguments for the Immortality of the
Soul, there is one drawn from the perpetual Progress of the Soul to its
Perfection, without a Possibility of ever arriving at it; which is a
Hint that I do not remember to have seen opened and improved by others
who have written on this Subject, tho' it seems to me to carry a great
Weight with it. How can it enter into the Thoughts of Man, that the
Soul, which is capable of such immense Perfections, and of receiving new
Improvements to all Eternity, shall fall away into nothing almost as
soon as it is created? Are such Abilities made for no Purpose? A Brute
arrives at a Point of Perfection that he can never pass: In a few Years
he has all the Endowments he is capable of; and were he to live ten
thousand more, would be the same thing he is at present. Were a human
Soul thus at a stand in her Accomplishments, were her Faculties to be
full blown, and incapable of further Enlargements, I could imagine it
might fall away insensibly, and drop at once into a State of
Annihilation. But can we believe a thinking Being that is in a perpetual
Progress of Improvements, and travelling on from Perfection to
Perfection, after having just looked abroad into the Works of its
Creator, and made a few Discoveries of his infinite Goodness, Wisdom and
Power, must perish at her first setting out, and in the very beginning
of her Enquiries?
Man, considered in his present State, seems only sent into the World
to propagate his Kind
. He provides
himself with a Successor, and
immediately quits his Post to make room for him.
... Hares
Hæredem alterius, velut unda, supervenit undam.
He does not seem born to enjoy Life, but to deliver it down to others.
This is not surprising to consider in Animals, which are formed for our
Use, and can finish their Business in a short Life. The Silk-worm, after
having spun her Task, lays her Eggs and dies. But a Man can never have
taken in his full measure of Knowledge, has not time to subdue his
Passions, establish his Soul in Virtue, and come up to the Perfection of
his Nature, before he is hurried off the Stage. Would an infinitely wise
Being make such glorious Creatures for so mean a Purpose? Can he delight
in the Production of such abortive Intelligences, such short-lived
reasonable Beings? Would he give us Talents that are not to be exerted?
Capacities that are never to be gratified? How can we find that Wisdom
which shines through all his Works, in the Formation of Man, without
looking on this World as only a Nursery for the next, and believing that
the several Generations of rational Creatures, which rise up and
disappear in such quick Successions, are only to receive their first
Rudiments of Existence here, and afterwards to be transplanted into a
more friendly Climate, where they may spread and flourish to all
Eternity.
There is not, in my Opinion, a more pleasing and triumphant
Consideration in Religion than this of the perpetual Progress which the
Soul makes towards the Perfection of its Nature, without ever arriving
at a Period in it. To look upon the Soul as going on from Strength to
Strength, to consider that she is to shine for ever with new Accessions
of Glory, and brighten to all Eternity; that she will be still adding
Virtue to Virtue, and Knowledge to Knowledge; carries in it something
wonderfully agreeable to that Ambition which is natural to the Mind of
Man. Nay, it must be a Prospect pleasing to God himself, to see his
Creation for ever beautifying in his Eyes, and drawing nearer to him, by
greater Degrees of Resemblance.
Methinks this single Consideration, of the Progress of a finite Spirit
to Perfection, will be sufficient to extinguish all Envy in inferior
Natures, and all Contempt in superior. That Cherubim which now appears
as a God to a human Soul, knows very well that the Period will come
about in Eternity, when the human Soul shall be as perfect as he himself
now is: Nay, when she shall look down upon that Degree of Perfection, as
much as she now falls short of it. It is true the higher Nature still
advances, and by that means preserves his Distance and Superiority in
the Scale of Being; but he knows how high soever the Station is of which
he stands possessed at present, the inferior Nature will at length mount
up to it, and shine forth in the same Degree of Glory.
With what Astonishment and Veneration may we look into our own Souls,
where there are such hidden Stores of Virtue and Knowledge, such
inexhausted Sources of Perfection? We know not yet what we shall be, nor
will it ever enter into the Heart of Man to conceive the Glory that will
be always in Reserve for him.
Soul considered with its Creator, is
like one of those Mathematical Lines that may draw nearer to another for
all Eternity without a Possibility of touching it
: And can there be
a Thought so transporting, as to consider ourselves in these perpetual
Approaches to him, who is not only the Standard of Perfection but of
Happiness!
L.
,and provide
The Asymptotes of the Hyperbola.
Contents
|
Monday, July 9, 1711 |
Addison |
am always very well pleased with a Country
Sunday
; and think, if
keeping holy the Seventh Day
were
only a human Institution, it
would be the best Method that could have been thought of for the
polishing and civilizing of Mankind.
is certain the Country-People
would soon degenerate into a kind of Savages and Barbarians, were there
not such frequent Returns of a stated Time, in which the whole Village
meet together with their best Faces, and in their cleanliest
Habits
, to converse with one another upon indifferent Subjects, hear their
Duties explained to them, and join together in Adoration of the Supreme
Being.
Sunday
clears away the Rust of the whole Week, not only as it
refreshes in their Minds the Notions of Religion, but as it puts both
the Sexes upon appearing in their most agreeable Forms, and exerting all
such Qualities as are apt to give them a Figure in the Eye of the
Village. A Country-Fellow distinguishes himself as much in the
Church-yard
, as a Citizen does upon the
Change
, the whole
Parish-Politicks being generally discussed in that Place either after
Sermon or before the Bell rings.
My Friend Sir
Roger
, being a good Churchman, has beautified the Inside
of his Church with several Texts of his own chusing: He has likewise
given a handsome Pulpit-Cloth, and railed in the Communion-Table at his
own Expence.
has often told me, that at his coming to his Estate he
found
his Parishioners
very irregular; and that in order to make
them kneel and join in the Responses, he gave every one of them a
Hassock and a Common-prayer Book: and at the same time employed an
itinerant Singing-Master, who goes about the Country for that Purpose,
to instruct them rightly in the Tunes of the Psalms; upon which they now
very much value themselves, and indeed out-do most of the Country
Churches that I have ever heard.
As Sir
Roger
is Landlord to the whole Congregation, he keeps them in
very good Order, and will suffer no Body to sleep in it besides himself;
for if by chance he has been surprized into a short Nap at Sermon, upon
recovering out of it he stands up and looks about him, and if he sees
any Body else nodding, either wakes them himself, or sends his Servant
to them. Several other of the old Knight's Particularities break out
upon these Occasions: Sometimes he will be lengthening out a Verse in
the Singing-Psalms, half a Minute after the rest of the Congregation
have done with it; sometimes, when he is pleased with the Matter of his
Devotion, he pronounces
Amen
three or four times to the same Prayer;
and sometimes stands up when every Body else is upon their Knees, to
count the Congregation, or see if any of his Tenants are missing.
I was Yesterday very much surprised to hear my old Friend, in the Midst
of the Service, calling out to one
John Matthews
to mind what he was
about, and not disturb the Congregation. This
John Matthews
it seems
is remarkable for being an idle Fellow, and at that Time was kicking his
Heels for his Diversion. This Authority of the Knight, though exerted in
that odd Manner which accompanies him in all Circumstances of Life, has
a very good Effect upon the Parish, who are not polite enough to see any
thing ridiculous in his Behaviour; besides that the general good Sense
and Worthiness of his Character makes his Friends observe these little
Singularities as Foils that rather set off than blemish his good
Qualities.
As soon as the Sermon is finished, no Body presumes to stir till Sir
Roger
is gone out of the Church. The Knight walks down from his Seat in
the Chancel between a double Row of his Tenants, that stand bowing to
him on each Side; and every now and then enquires how such an one's
Wife, or Mother, or Son, or Father do, whom he does not see at Church;
which is understood as a secret Reprimand to the Person that is absent.
The Chaplain has often told me, that upon a Catechising-day, when Sir
Roger
has been pleased with a Boy that answers well, he has ordered a
Bible to be given him next Day for his Encouragement; and sometimes
accompanies it with a Flitch of Bacon to his Mother. Sir
Roger
has
likewise added five Pounds a Year to the Clerk's Place; and that he may
encourage the young Fellows to make themselves perfect in the
Church-Service, has promised upon the Death of the present Incumbent,
who is very old, to bestow it according to Merit.
The fair Understanding between Sir
Roger
and his Chaplain, and their
mutual Concurrence in doing Good, is the more remarkable, because the
very next Village is famous for the Differences and Contentions that
rise between the Parson and the 'Squire, who live in a perpetual State
of War. The Parson is always preaching at the 'Squire, and the 'Squire
to be revenged on the Parson never comes to Church. The 'Squire has made
all his Tenants Atheists and Tithe-Stealers; while the Parson instructs
them every
Sunday
in the Dignity of his Order, and insinuates to them
in almost every Sermon, that he is a better Man than his Patron. In
short, Matters are come to such an Extremity, that the 'Squire has not
said his Prayers either in publick or private this half Year; and that
the Parson threatens him, if he does not mend his Manners, to pray for
him in the Face of the whole Congregation.
Feuds of this Nature, though too frequent in the Country, are very fatal
to the ordinary People; who are so used to be dazled with Riches, that
they pay as much Deference to the Understanding of a Man of an Estate,
as of a Man of Learning; and are very hardly brought to regard any
Truth, how important soever it may be, that is preached to them, when
they know there are several Men of five hundred a Year who do not
believe it.
L.
had been
Dress
the Parish
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 10, 1711 |
Steele |
... Harent infixi pectore vultus.
Virg.

In my first Description of the Company in which I pass most of my Time,
it may be remembered that I mentioned a great Affliction which my Friend
Sir
Roger
had met with in his Youth; which was no less than a
Disappointment in Love. It happened this Evening, that we fell into a
very pleasing Walk at a Distance from his House: As soon as we came into
it,
'It is,
quoth the good Old Man, looking round him with a Smile, very
hard, that any Part of my Land should be settled upon one who has used
me so ill as the perverse Widow
1 did; and yet I am sure I could not
see a Sprig of any Bough of this whole Walk of Trees, but I should
reflect upon her and her Severity. She has certainly the finest Hand
of any Woman in the World. You are to know this was the Place wherein
I used to muse upon her; and by that Custom I can never come into it,
but the same tender Sentiments revive in my Mind, as if I had actually
walked with that Beautiful Creature under these Shades. I have been
Fool enough to carve her Name on the Bark of several of these Trees;
so unhappy is the Condition of Men in Love, to attempt the removing of
their Passion by the Methods which serve only to imprint it deeper.
She has certainly the finest Hand of any Woman in the World.'
Here followed a profound Silence; and I was not displeased to observe my
Friend falling so naturally into a Discourse, which I had ever before
taken Notice he industriously avoided. After a very long Pause he
entered upon an Account of this great Circumstance in his Life, with an
Air which I thought raised my Idea of him above what I had ever had
before; and gave me the Picture of that chearful Mind of his, before it
received that Stroke which has ever since affected his Words and
Actions. But he went on as follows.
'I came to my Estate in my Twenty Second Year, and resolved to follow
the Steps of the most Worthy of my Ancestors who have inhabited this
Spot of Earth before me, in all the Methods of Hospitality and good
Neighbourhood, for the sake of my Fame; and in Country Sports and
Recreations, for the sake of my Health. In my Twenty Third Year I was
obliged to serve as Sheriff of the County; and in my Servants,
Officers and whole Equipage, indulged the Pleasure of a young Man (who
did not think ill of his own Person) in taking that publick Occasion
of shewing my Figure and Behaviour to Advantage.
You may easily
imagine to yourself what Appearance I made, who am pretty tall,
rid2 well, and was very well dressed, at the Head of a whole County,
with Musick before me, a Feather in my Hat, and my Horse well Bitted.
I can assure you I was not a little pleased with the kind Looks and
Glances I had from all the Balconies and Windows as I rode to the Hall
where the Assizes were held. But when I came there, a Beautiful
Creature in a Widow's Habit sat in Court to hear the Event of a Cause
concerning her Dower. This commanding Creature (who was born for
Destruction of all who behold her) put on such a Resignation in her
Countenance, and bore the Whispers of all around the Court with such a
pretty Uneasiness, I warrant you, and then recovered her self from one
Eye to another, 'till she was perfectly confused by meeting something
so wistful in all she encountered, that at last, with a Murrain to
her, she cast her bewitching Eye upon me. I no sooner met it, but I
bowed like a great surprized Booby; and knowing her Cause to be the
first which came on, I cried, like a Captivated Calf as I was, Make
way for the Defendant's Witnesses. This sudden Partiality made all the
County immediately see the Sheriff also was become a Slave to the fine
Widow. During the Time her Cause was upon Tryal, she behaved herself,
I warrant you, with such a deep Attention to her Business, took
Opportunities to have little Billets handed to her Council, then would
be in such a pretty Confusion, occasioned, you must know, by acting
before so much Company, that not only I but the whole Court was
prejudiced in her Favour; and all that the next Heir to her Husband
had to urge, was thought so groundless and frivolous, that when it
came to her Council to reply, there was not half so much said as every
one besides in the Court thought he could have urged to her Advantage.
You must understand, Sir, this perverse Woman is one of those
unaccountable Creatures, that secretly rejoice in the Admiration of
Men, but indulge themselves in no further Consequences. Hence it is
that she has ever had a Train of Admirers, and she removes from her
Slaves in Town to those in the Country, according to the Seasons of
the Year. She is a reading Lady, and far gone in the Pleasures of
Friendship; She is always accompanied by a Confident, who is Witness
to her daily Protestations against our Sex, and consequently a Bar to
her first Steps towards Love, upon the Strength of her own Maxims and
Declarations.
However, I must needs say this accomplished Mistress of mine has
distinguished me above the rest, and has been known to declare Sir
Roger De Coverley was the Tamest and most Human of all the Brutes in
the Country. I was told she said so, by one who thought he rallied me;
but upon the Strength of this slender Encouragement, of being thought
least detestable, I made new Liveries, new paired my Coach-Horses,
sent them all to Town to be bitted, and taught to throw their Legs
well, and move all together, before I pretended to cross the Country
and wait upon her. As soon as I thought my Retinue suitable to the
Character of my Fortune and Youth, I set out from hence to make my
Addresses. The particular Skill of this Lady has ever been to inflame
your Wishes, and yet command Respect. To make her Mistress of this
Art, she has a greater Share of Knowledge, Wit, and good Sense, than
is usual even among Men of Merit. Then she is beautiful beyond the
Race of Women. If you won't let her go on with a certain Artifice with
her Eyes, and the Skill of Beauty, she will arm her self with her real
Charms, and strike you with Admiration instead of Desire. It is
certain that if you were to behold the whole Woman, there is that
Dignity in her Aspect, that Composure in her Motion, that Complacency
in her Manner, that if her Form makes you hope, her Merit makes you
fear. But then again, she is such a desperate Scholar, that no
Country-Gentleman can approach her without being a Jest. As I was
going to tell you, when I came to her House I was admitted to her
Presence with great Civility; at the same time she placed her self to
be first seen by me in such an Attitude, as I think you call the
Posture of a Picture, that she discovered new Charms, and I at last
came towards her with such an Awe as made me Speechless. This she no
sooner observed but she made her Advantage of it, and began a
Discourse to me concerning Love and Honour, as they both are followed
by Pretenders, and the real Votaries to them. When she
had discussed
these Points in a Discourse, which I verily believe was as learned as
the best Philosopher in
Europe could possibly make, she asked me
whether she was so happy as to fall in with my Sentiments on these
important Particulars. Her Confident sat by her, and upon my being in
the last Confusion and Silence, this malicious Aid of hers, turning to
her, says, I am very glad to observe Sir
Roger pauses upon this
Subject, and seems resolved to deliver all his Sentiments upon the
Matter when he pleases to speak. They both kept their Countenances,
and after I had sat half an Hour meditating how to behave before such
profound Casuists, I rose up and took my Leave. Chance has since that
time thrown me very often in her Way, and she as often has directed a
Discourse to me which I do not understand. This Barbarity has kept me
ever at a Distance from the most beautiful Object my Eyes ever beheld.
It is thus also she deals with all Mankind, and you must make Love to
her, as you would conquer the Sphinx, by posing her. But were she like
other Women, and that there were any talking to her, how constant must
the Pleasure of that Man be, who could converse with a Creature — But,
after all, you may be sure her Heart is fixed on some one or other;
and yet I have been credibly inform'd; but who can believe half that
is said! After she had done speaking to me, she put her Hand to her
Bosom, and adjusted her Tucker. Then she cast her Eyes a little down,
upon my beholding her too earnestly. They say she sings excellently:
her Voice in her ordinary Speech has something in it inexpressibly
sweet. You must know I dined with her at a publick Table the Day after
I first saw her, and she helped me to some Tansy in the Eye of all the
Gentlemen in the Country: She has certainly the finest Hand of any
Woman in the World. I can assure you, Sir, were you to behold her, you
would be in the same Condition; for as her Speech is Musick, her Form
is Angelick. But I find I grow irregular while I am talking of her;
but indeed it would be Stupidity to be unconcerned at such
Perfection. Oh the excellent Creature, she is as inimitable to all
Women, as she is inaccessible to all Men.'
I found my Friend begin to rave, and insensibly led him towards the
House, that we might be joined by some other Company; and am convinced
that the Widow is the secret Cause of all that Inconsistency which
appears in some Parts of my Friend's Discourse; tho' he has so much
Command of himself as not directly to mention her, yet according to that
of
Martial
, which one knows not how to render in
English, Dum facet
hanc loquitur
.
shall end this Paper with that whole Epigram
,
which represents with much Humour my honest Friend's Condition.
Quicquid agit Rufus nihil est nisi Nævia Rufo,
Si gaudet, si flet, si tacet, hanc loquitur:
Cœnat, propinat, poscit, negat, annuit, una est
Nævia; Si non sit Nævia mutus erit.
Scriberet hesterna Patri cum Luce Salutem,
Nævia lux, inquit, Nævia lumen, ave.
Let Rufus weep, rejoice, stand, sit, or walk,
Still he can nothing but of Nævia talk;
Let him eat, drink, ask Questions, or dispute,
Still he must speak of Nævia, or be mute.
He writ to his Father, ending with this Line,
I am, my Lovely Nævia, ever thine.
R.
Mrs Catherine Boevey, widow of William Boevey, Esq., who
was left a widow at the age of 22, and died in January, 1726, has one of
the three volumes of the
Lady's Library
dedicated to her by Steele in
terms that have been supposed to imply resemblance between her and the
'perverse widow;' as being both readers, &c. Mrs Boevey is said also to
have had a Confidant (Mary Pope) established in her household. But there
is time misspent in all these endeavours to reduce to tittle-tattle the
creations of a man of genius.
ride
Bk. I. Ep. 69.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 11, 1711 |
Steele |
... Paupertatis pudor et fuga ...
Hor.

Œconomy in our Affairs has the same Effect upon our Fortunes which Good
Breeding has upon our Conversations. There is a pretending Behaviour in
both Cases, which, instead of making Men esteemed, renders them both
miserable and contemptible. We had Yesterday at
Sir Roger's
a Set of
Country Gentlemen who dined with him; and after Dinner the Glass was
taken, by those who pleased, pretty plentifully. Among others I observed
a Person of a tolerable good Aspect, who seemed to be more greedy of
Liquor than any of the Company, and yet, methought, he did not taste it
with Delight. As he grew warm, he was suspicious of every thing that was
said; and as he advanced towards being fudled, his Humour grew worse. At
the same time his Bitterness seem'd to be rather an inward
Dissatisfaction in his own Mind, than any Dislike he had taken at the
Company. Upon hearing his Name, I knew him to be a Gentle man of a
considerable Fortune in this County, but greatly in Debt. What gives the
unhappy Man this Peevishness of Spirit is, that his Estate is dipped,
and is eating out with Usury; and yet he has not the Heart to sell any
Part of it. His proud Stomach, at the Cost of restless Nights, constant
Inquietudes, Danger of Affronts, and a thousand nameless Inconveniences,
preserves this Canker in his Fortune, rather than it shall be said he is
a Man of fewer Hundreds a Year than he has been commonly reputed. Thus
he endures the Torment of Poverty, to avoid the Name of being less rich.
If you go to his House you see great Plenty; but served in a Manner that
shews it is all unnatural, and that the Master's Mind is not at home.
There is a certain Waste and Carelessness in the Air of every thing, and
the whole appears but a covered Indigence, a magnificent Poverty. That
Neatness and Chearfulness, which attends the Table of him who lives
within Compass, is wanting, and exchanged for a Libertine Way of Service
in all about him.
This Gentleman's Conduct, tho' a very common way of Management, is as
ridiculous as that Officer's would be, who had but few Men under his
Command, and should take the Charge of an Extent of Country rather than
of a small Pass. To pay for, personate, and keep in a Man's Hands, a
greater Estate than he really has, is of all others the most
unpardonable Vanity, and must in the End reduce the Man who is guilty of
it to Dishonour. Yet if we look round us in any County of
Great
Britain
, we shall see many in this fatal Error; if that may be called
by so soft a Name, which proceeds from a false Shame of appearing what
they really are, when the contrary Behaviour would in a short Time
advance them to the Condition which they pretend to.
Laertes
has
hundred Pounds a Year; which is mortgaged for six
thousand Pounds; but it is impossible to convince him that if he sold as
much as would pay off that Debt, he would save four Shillings in the
Pound
, which he gives for the Vanity of being the reputed Master of
it.
Yet
if
Laertes
did this, he would, perhaps, be easier in his
own Fortune; but then
Irus
, a Fellow of Yesterday, who has but twelve
hundred a Year, would be his Equal. Rather than this shall be,
Laertes
goes on to bring well-born Beggars into the World, and every Twelvemonth
charges, his Estate with at least one Year's Rent more by the Birth of a
Child.
Laertes
and
Irus
are Neighbours, whose Way of living are an
Abomination to each other.
Irus
is moved by the Fear of Poverty, and
Laertes
by the Shame of it. Though the Motive of Action is of so near
Affinity in both, and may be resolved into this, 'That to each of them
Poverty is the greatest of all Evils,' yet are their Manners very widely
different. Shame of Poverty makes
Laertes
launch into unnecessary
Equipage, vain Expense, and lavish Entertainments; Fear of Poverty makes
Irus
allow himself only plain Necessaries, appear without a Servant,
sell his own Corn, attend his Labourers, and be himself a Labourer.
Shame of Poverty makes
Laertes
go every Day a step nearer to it; and
Fear of Poverty stirs up
Irus
to make every Day some further Progress
from it.
These different Motives produce the Excesses of which Men are guilty of
in the Negligence of and Provision for themselves. Usury, Stock-jobbing,
Extortion and Oppression, have their Seed in the Dread of Want; and
Vanity, Riot and Prodigality, from the Shame of it: But both these
Excesses are infinitely below the Pursuit of a reasonable Creature.
After we have taken Care to command so much as is necessary for
maintaining our selves in the Order of Men suitable to our Character,
the Care of Superfluities is a Vice no less extravagant, than the
Neglect of Necessaries would have been before.
it is that they are both out of Nature when she is followed with
Reason and good Sense. It is from this Reflection that I always read Mr.
Cowley
with the greatest Pleasure: His Magnanimity is as much above
that of other considerable Men as his Understanding; and it is a true
distinguishing Spirit in the elegant Author who published his Works
,
to dwell so much upon the Temper of his Mind and the Moderation of his
Desires: By this means he has render'd his Friend as amiable as famous.
That State of Life which bears the Face of Poverty with Mr.
Cowley's
great Vulgar
, is admirably described; and it is no small Satisfaction
to those of the same Turn of Desire, that he produces the Authority of
the wisest Men of the best Age of the World, to strengthen his Opinion
of the ordinary Pursuits of Mankind.
It would methinks be no ill Maxim of Life, if according to that Ancestor
of Sir
Roger
, whom I lately mentioned, every Man would point to himself
what Sum he would resolve not to exceed. He might by this means cheat
himself into a Tranquility on this Side of that Expectation, or convert
what he should get above it to nobler Uses than his own Pleasures or
Necessities. This Temper of Mind would exempt a Man from an ignorant
Envy of restless Men above him, and a more inexcusable Contempt of happy
Men below him. This would be sailing by some Compass, living with some
Design; but to be eternally bewildered in Prospects of Future Gain, and
putting on unnecessary Armour against improbable Blows of Fortune, is a
Mechanick Being which has not good Sense for its Direction, but is
carried on by a sort of acquired Instinct towards things below our
Consideration and unworthy our Esteem. It is possible that the
Tranquility I now enjoy at Sir
Roger's
may have created in me this Way
of Thinking, which is so abstracted from the common Relish of the World:
But as I am now in a pleasing Arbour surrounded with a beautiful
Landskip, I find no Inclination so strong as to continue in these
Mansions, so remote from the ostentatious Scenes of Life; and am at this
present Writing Philosopher enough to conclude with Mr.
Cowley
;
If e'er Ambition did my Fancy cheat,
With any Wish so mean as to be Great;
Continue, Heav'n, still from me to remove
The humble Blessings of that Life I love.4
The Land Tax.
But
Dr. Thomas Sprat, Bishop of Rochester, in his
Life of
Cowley
prefixed to an edition of the Poet's works. The temper of Cowley
here referred to is especially shown in his Essays, as in the opening
one
Of Liberty
, and in that
Of Greatness,
which is followed by the
paraphrase from Horace's
Odes
, Bk. III. Od. i, beginning with the
expression above quoted:
Hence, ye profane; I hate ye all;
Both the Great Vulgar and the Small.
From the Essay
Of Greatness.
Contents
|
Thursday, July 12, 1711 |
Addison |
... Ut sit Mens sana in Corpore sano.
Juv.

Bodily Labour is of two Kinds, either that which a Man submits to for
his Livelihood, or that which he undergoes for his Pleasure. The latter
of them generally changes the Name of Labour for that of Exercise, but
differs only from ordinary Labour as it rises from another Motive.
A Country Life abounds in both these kinds of Labour, and for that
Reason gives a Man a greater Stock of Health, and consequently a more
perfect Enjoyment of himself, than any other Way of Life. I consider the
Body as a System of Tubes and Glands, or to use a more Rustick Phrase, a
Bundle of Pipes and Strainers, fitted to one another after so wonderful
a Manner as to make a proper Engine for the Soul to work with. This
Description does not only comprehend the Bowels, Bones, Tendons, Veins,
Nerves and Arteries, but every Muscle and every Ligature, which is a
Composition of Fibres, that are so many imperceptible Tubes or Pipes
interwoven on all sides with invisible Glands or Strainers.
This general Idea of a Human Body, without considering it in its
Niceties of Anatomy, lets us see how absolutely necessary Labour is for
the right Preservation of it. There must be frequent Motions and
Agitations, to mix, digest, and separate the Juices contained in it, as
well as to clear and cleanse that Infinitude of Pipes and Strainers of
which it is composed, and to give their solid Parts a more firm and
lasting Tone. Labour or Exercise ferments the Humours, casts them into
their proper Channels, throws off Redundancies, and helps Nature in
those secret Distributions, without which the Body cannot subsist in its
Vigour, nor the Soul act with Chearfulness.
I might here mention the Effects which this has upon all the Faculties
of the Mind, by keeping the Understanding clear, the Imagination
untroubled, and refining those Spirits that are necessary for the proper
Exertion of our intellectual Faculties, during the present Laws of Union
between Soul and Body. It is to a Neglect in this Particular that we
must ascribe the Spleen, which is so frequent in Men of studious and
sedentary Tempers, as well as the Vapours to which those of the other
Sex are so often subject.
not Exercise been absolutely necessary for our Well-being, Nature
would not have made the Body so proper for it, by giving such an
Activity to the Limbs, and such a Pliancy to every Part as necessarily
produce those Compressions, Extentions, Contortions, Dilatations, and
all other kinds of
Motions
that are necessary for the Preservation
of such a System of Tubes and Glands as has been before mentioned. And
that we might not want Inducements to engage us in such an Exercise of
the Body as is proper for its Welfare, it is so ordered that nothing
valuable can be procured without it. Not to mention Riches and Honour,
even Food and Raiment are not to be come at without the Toil of the
Hands and Sweat of the Brows. Providence furnishes Materials, but
expects that we should work them up our selves. The Earth must be
laboured before it gives its Encrease, and when it is forced into its
several Products, how many Hands must they pass through before they are
fit for Use? Manufactures, Trade, and Agriculture, naturally employ more
than nineteen Parts of the Species in twenty; and as for those who are
not obliged to Labour, by the Condition in which they are born, they are
more miserable than the rest of Mankind, unless they indulge themselves
in that voluntary Labour which goes by the Name of Exercise.
My Friend Sir
Roger
has been an indefatigable Man in Business of this
kind, and has hung several Parts of his House with the Trophies of his
former Labours. The Walls of his great Hall are covered with the Horns
of several kinds of Deer that he has killed in the Chace, which he
thinks the most valuable Furniture of his House, as they afford him
frequent Topicks of Discourse, and shew that he has not been Idle. At
the lower End of the Hall, is a large Otter's Skin stuffed with Hay,
which his Mother ordered to be hung up in that manner, and the Knight
looks upon with great Satisfaction, because it seems he was but nine
Years old when his Dog killed him. A little Room adjoining to the Hall
is a kind of Arsenal filled with Guns of several Sizes and Inventions,
with which the Knight has made great Havock in the Woods, and destroyed
many thousands of Pheasants, Partridges and Wood-cocks. His Stable Doors
are patched with Noses that belonged to Foxes of the Knight's own
hunting down. Sir
Roger
shewed me one of them that for Distinction sake
has a Brass Nail struck through it, which cost him about fifteen Hours
riding, carried him through half a dozen Counties, killed him a Brace of
Geldings, and lost above half his Dogs. This the Knight looks upon as
one of the greatest Exploits of his Life. The perverse Widow, whom I
have given some Account of, was the Death of several Foxes; for Sir
Roger
has told me that in the Course of his Amours he patched the
Western Door of his Stable. Whenever the Widow was cruel, the Foxes were
sure to pay for it. In proportion as his Passion for the Widow abated
and old Age came on, he left off Fox-hunting; but a Hare is not yet safe
that Sits within ten Miles of his House.
There is no kind of Exercise which I would so recommend to my Readers of
both Sexes as this of Riding, as there is none which so much conduces to
Health, and is every way accommodated to the Body, according to the
Idea
which I have given of it.
Sydenham
is very lavish in its
Praises; and if the
English
Reader will see the Mechanical Effects of
it describ'd at length, he may find them in a Book published not many
Years since, under the Title of
Medicina Gymnastica
. For my own
part, when I am in Town, for want of these Opportunities, I exercise
myself an Hour every Morning upon a dumb Bell that is placed in a Corner
of my Room, and pleases me the more because it does every thing I
require of it in the most profound Silence. My Landlady and her
Daughters are so well acquainted with my Hours of Exercise, that they
never come into my Room to disturb me whilst I am ringing.
I was some Years younger than I am at present, I used to employ
myself in a more laborious Diversion, which I learned from a
Latin
Treatise of Exercises that is written with great Erudition
: It is
there called the
skiomachia
, or the fighting with a Man's own Shadow,
and consists in the brandishing of two short Sticks grasped in each
Hand, and loaden with Plugs of Lead at either End. This opens the Chest,
exercises the Limbs, and gives a Man all the Pleasure of Boxing, without
the Blows. I could wish that several Learned Men would lay out that Time
which they employ in Controversies and Disputes about nothing, in this
Method of fighting with their own Shadows. It might conduce very much to
evaporate the Spleen, which makes them uneasy to the Publick as well as
to themselves.
To conclude, As I am a Compound of Soul and Body, I consider myself as
obliged to a double Scheme of Duties; and I think I have not fulfilled
the Business of the Day when I do not thus employ the one in Labour and
Exercise, as well as the other in Study and Contemplation.
L.
Motion
Medicina Gymnastica, or, a Treatise concerning the Power of
Exercise.
By Francis Fuller, M.A.
Artis Gymnasticæ apud Antiquos ...
Libri VI. (Venice,
1569). By Hieronymus Mercurialis, who died at Forli, in 1606. He speaks
of the shadow-fighting in Lib. iv. cap. 5, and Lib. v. cap. 2.
Contents
|
Friday, July 13, 1711 |
Budgell |
... Vocat ingenti clamore Cithœron,
Taygetique canes ...
Virg.

Those who have searched into human Nature observe that nothing so much
shews the Nobleness of the Soul, as that its Felicity consists in
Action. Every Man has such an active Principle in him, that he will find
out something to employ himself upon in whatever Place or State of Life
he is posted. I have heard of a Gentleman who was under close
Confinement in the
Bastile
seven Years; during which Time he amused
himself in scattering a few small Pins about his Chamber, gathering them
up again, and placing them in different Figures on the Arm of a great
Chair. He often told his Friends afterwards, that unless he had found
out this Piece of Exercise, he verily believed he should have lost his
Senses.
After what has been said, I need not inform my Readers, that Sir
Roger
,
with whose Character I hope they are at present pretty well acquainted,
has in his Youth gone through the whole Course of those rural Diversions
which the Country abounds in; and which seem to be extreamly well suited
to that laborious Industry a Man may observe here in a far greater
Degree than in Towns and Cities. I have before hinted at some of my
Friend's Exploits: He has in his youthful Days taken forty Coveys of
Partridges in a Season; and tired many a Salmon with a Line consisting
but of a single Hair. The constant Thanks and good Wishes of the
Neighbourhood always attended him, on account of his remarkable Enmity
towards Foxes; having destroyed more of those Vermin in one Year, than
it was thought the whole Country could have produced. Indeed the Knight
does not scruple to own among his most intimate Friends that in order to
establish his Reputation this Way, he has secretly sent for great
Numbers of them out of other Counties, which he used to turn loose about
the Country by Night, that he might the better signalize himself in
their Destruction the next Day. His Hunting-Horses were the finest and
best managed in all these Parts: His Tenants are still full of the
Praises of a grey Stone-horse that unhappily staked himself several
Years since, and was buried with great Solemnity in the Orchard.
Roger
, being at present too old for Fox-hunting, to keep himself
in Action, has disposed of his Beagles and got a Pack of
Stop-Hounds
.
What these want in Speed, he endeavours to make amends for by the
Deepness of their Mouths and the Variety of their Notes, which are
suited in such manner to each other, that the whole Cry makes up a
compleat Consort
. He is so nice in this Particular that a Gentleman
having made him a Present of a very fine Hound the other Day, the Knight
returned it by the Servant with a great many Expressions of Civility;
but desired him to tell his Master, that the Dog he had sent was indeed
a most excellent
Base
, but that at present he only wanted a
Counter-Tenor
.
I believe my Friend had ever read
Shakespear
, I
should certainly conclude he had taken the Hint from
Theseus
in the
Midsummer Night's Dream
.
My Hounds are bred out of the Spartan Kind,
So flu'd, so sanded; and their Heads are hung
With Ears that sweep away the Morning Dew.
Crook-knee'd and dew-lap'd like Thessalian Bulls;
Slow in Pursuit, but match'd in Mouths like Bells,
Each under each: A Cry more tuneable
Was never hallowed to, nor chear'd with Horn.
Sir
Roger
is so keen at this Sport, that he has been out almost every
Day since I came down; and upon the Chaplain's offering to lend me his
easy Pad, I was prevailed on Yesterday Morning to make one of the
Company. I was extremely pleased, as we rid along, to observe the
general Benevolence of all the Neighbourhood towards my Friend. The
Farmers Sons thought themselves happy if they could open a Gate for the
good old Knight as he passed by; which he generally requited with a Nod
or a Smile, and a kind Enquiry after their Fathers and Uncles.
After we had rid about a Mile from Home, we came upon a large Heath, and
the Sports-men began to beat. They had done so for some time, when, as I
was at a little Distance from the rest of the Company, I saw a Hare pop
out from a small Furze-brake almost under my Horse's Feet. I marked the
Way she took, which I endeavoured to make the Company sensible of by
extending my Arm; but to no purpose, 'till Sir
Roger
, who knows that
none of my extraordinary Motions are insignificant, rode up to me, and
asked me
if Puss was gone that Way?
Upon my answering
Yes
, he
immediately called in the Dogs, and put them upon the Scent. As they
were going off, I heard one of the Country-Fellows muttering to his
Companion,
That 'twas a Wonder they had not lost all their Sport, for
want of the silent Gentleman's crying Stole Away.
This, with my Aversion to leaping Hedges, made me withdraw to a rising
Ground, from whence I could have the Picture of the whole Chace, without
the Fatigue of keeping in with the Hounds. The Hare immediately threw
them above a Mile behind her; but I was pleased to find, that instead of
running straight forwards, or in Hunter's Language,
Flying the
Country
, as I was afraid she might have done, she wheel'd about, and
described a sort of Circle round the Hill where I had taken my Station,
in such manner as gave me a very distinct View of the Sport. I could see
her first pass by, and the Dogs some time afterwards unravelling the
whole Track she had made, and following her thro' all her Doubles. I was
at the same time delighted in observing that Deference which the rest of
the Pack paid to each particular Hound, according to the Character he
had acquired amongst them: If they were at Fault, and an old Hound of
Reputation opened but once, he was immediately followed by the whole
Cry; while a raw Dog or one who was a noted
Liar
, might have yelped
his Heart out, without being taken Notice of.
The Hare now, after having squatted two or three Times, and been put up
again as often, came still nearer to the Place where she was at first
started. The Dogs pursued her, and these were followed by the jolly
Knight, who rode upon a white Gelding, encompassed by his Tenants and
Servants, and chearing his Hounds with all the Gaiety of Five and
Twenty. One of the Sportsmen rode up to me, and told me, that he was
sure the Chace was almost at an End, because the old Dogs, which had
hitherto lain behind, now headed the Pack. The Fellow was in the right.
Our Hare took a large Field just under us, followed by the full Cry
in
View
. I must confess the Brightness of the Weather, the Chearfulness of
everything around me, the
Chiding
of the Hounds, which was returned
upon us in a double Eccho, from two neighbouring Hills, with the
Hallowing of the Sportsmen, and the Sounding of the Horn, lifted my
Spirits into a most lively Pleasure, which I freely indulged because I
was sure it was
innocent
. If I was under any Concern, it was on the
Account of the poor Hare, that was now quite spent, and almost within
the Reach of her Enemies; when the Huntsman getting forward threw down
his Pole before the Dogs. They were now within eight Yards of that Game
which they had been pursuing for almost as many Hours; yet on the Signal
before-mentioned they all made a sudden Stand, and tho' they continued
opening as much as before, durst not once attempt to pass beyond the
Pole. At the same time Sir
Roger
rode forward, and alighting, took up
the Hare in his Arms; which he soon delivered up to one of his Servants
with an Order, if she could be kept alive, to let her go in his great
Orchard; where it seems he has several of these Prisoners of War, who
live together in a very comfortable Captivity. I was highly pleased to
see the Discipline of the Pack, and the Good-nature of the Knight, who
could not find in his heart to murther a Creature that had given him so
much Diversion.
As we were returning home, I remembred that Monsieur
Paschal
in his
most excellent Discourse on
the Misery of Man
, tells us, That
all our
Endeavours after Greatness proceed from nothing but a Desire of being
surrounded by a Multitude of Persons and Affairs that may hinder us from
looking into our selves, which is a View we cannot bear
. He afterwards
goes on to shew that our Love of Sports comes from the same Reason, and
is particularly severe upon
Hunting
,
What
, says he,
unless it be to
drown Thought, can make Men throw away so much Time and Pains upon a
silly Animal, which they might buy cheaper in the Market
? The foregoing
Reflection is certainly just, when a Man suffers his whole Mind to be
drawn into his Sports, and altogether loses himself in the Woods; but
does not affect those who propose a far more laudable End from this
Exercise, I mean,
The Preservation of Health, and keeping all the
Organs of the Soul in a Condition to execute her Orders
.
that
incomparable Person, whom I last quoted, been a little more indulgent to
himself in this Point, the World might probably have enjoyed him much
longer; whereas thro' too great an Application to his Studies in his
Youth, he contracted that ill Habit of Body, which, after a tedious
Sickness, carried him oft in the fortieth Year of his Age
; and the
whole History we have of his Life till that Time, is but one continued
Account of the behaviour of a noble Soul struggling under innumerable
Pains and Distempers.
For my own part I intend to Hunt twice a Week during my Stay with Sir
Roger
; and shall prescribe the moderate use of this Exercise to all my
Country Friends, as the best kind of Physick for mending a bad
Constitution, and preserving a good one.
cannot do this better, than in the following Lines out of Mr.
Dryden
.
The first Physicians by Debauch were made;
Excess began, and Sloth sustains the Trade.
By Chace our long-liv'd Fathers earn'd their Food;
Toil strung the Nerves, and purify'd the Blood;
But we their Sons, a pamper'd Race of Men,
Are dwindled down to threescore Years and ten.
Better to hunt in Fields for Health unbought,
Than fee the Doctor for a nauseous Draught.
The Wise for Cure on Exercise depend:
God never made his Work for Man to mend.
As to dogs, the difference is great between a hunt now and
a hunt in the
Spectator's
time. Since the early years of the last
century the modern foxhound has come into existence, while the beagle
and the deep-flewed southern hare-hound, nearly resembling the
bloodhound, with its sonorous note, has become almost extinct.
Absolutely extinct also is the old care to attune the voices of a pack.
Henry II, in his breeding of hounds, is said to have been careful not
only that they should be fleet, but also 'well-tongued and consonous;'
the same care in Elizabeth's time is, in the passage quoted by the
Spectator
, attributed by Shakespeare to Duke Theseus; and the paper
itself shows that care was taken to match the voices of a pack in the
reign also of Queen Anne. This has now been for some time absolutely
disregarded. In many important respects the pattern harrier of the
present day differs even from the harriers used at the beginning of the
present century.
Act IV. sc. 1.
Pascal, who wrote a treatise on Conic sections at the age
of 16, and had composed most of his mathematical works and made his
chief experiments in science by the age of 26, was in constant
suffering, by disease, from his 18th year until his death, in 1662, at
the age stated in the text. Expectation of an early death caused him to
pass from his scientific studies into the direct service of religion,
and gave, as the fruit of his later years, the Provincial Letters and
the
Pensées
.
Epistle
to his kinsman, J. Driden, Esq., of Chesterton.
Contents
|
Saturday, July 14, 1711 |
Addison |
... Ipsi sibi somnia fingunt.
Virg.

There are some Opinions in which a Man should stand Neuter, without
engaging his Assent to one side or the other. Such a hovering Faith as
this, which refuses to settle upon any Determination, is absolutely
necessary to a Mind that is careful to avoid Errors and Prepossessions.
When the Arguments press equally on both sides in Matters that are
indifferent to us, the safest Method is to give up our selves to
neither.
It is with this Temper of Mind that I consider the Subject of
Witchcraft. When I hear the Relations that are made from all Parts of
the World, not only from
Norway
and
Lapland
, from the
East
and
West Indies
, but from every particular Nation in
Europe
, I cannot forbear thinking that there is such an
Intercourse and Commerce with Evil Spirits, as that which we express by
the Name of Witch-craft. But when I consider that the ignorant and
credulous Parts of the World abound most in these Relations, and that
the Persons among us, who are supposed to engage in such an Infernal
Commerce, are People of a weak Understanding and a crazed Imagination,
and at the same time reflect upon the many Impostures and Delusions of
this Nature that have been detected in all Ages, I endeavour to suspend
my Belief till I hear more certain Accounts than any which have yet come
to my Knowledge. In short, when I consider the Question, whether there
are such Persons in the World as those we call Witches? my Mind is
divided between the two opposite Opinions; or rather (to speak my
Thoughts freely) I believe in general that there is, and has been such a
thing as Witch-craft; but at the same time can give no Credit to any
particular Instance of it.
I am engaged in this Speculation, by some Occurrences that I met with
Yesterday, which I shall give my Reader an Account of at large. As I was
walking with my Friend Sir
Roger
by the side of one of his Woods, an old
Woman applied herself to me for my Charity.
Dress and Figure put me
in mind of the following Description in
Otway
.
In a close Lane as I pursued my Journey,
I spy'd a wrinkled Hag, with Age grown double,
Picking dry Sticks, and mumbling to her self.
Her Eyes with scalding Rheum were gall'd and red,
Cold Palsy shook her Head; her Hands seem'd wither'd;
And on her crooked Shoulders had she wrap'd
The tatter'd Remnants of an old striped Hanging,
Which served to keep her Carcase from the Cold:
So there was nothing of a Piece about her.
Her lower Weeds were all o'er coarsly patch'd
With diff'rent-colour'd Rags, black, red, white, yellow,
And seem'd to speak Variety of Wretchedness.2
As I was musing on this Description, and comparing it with the Object
before me, the Knight told me,
that
very old Woman had the
Reputation of a Witch all over the Country, that her Lips were observed
to be always in Motion, and that there was not a Switch about her House
which her Neighbours did not believe had carried her several hundreds of
Miles. If she chanced to stumble, they always found Sticks or Straws
that lay in the Figure of a Cross before her. If she made any Mistake at
Church, and cryed
Amen
in a wrong Place, they never failed to
conclude that she was saying her Prayers backwards. There was not a Maid
in the Parish that would take a Pin of her, though she would offer a Bag
of Mony with it. She goes by the Name of
Moll White
, and has made
the Country ring with several imaginary Exploits which are palmed upon
her. If the Dairy Maid does not make her Butter come so soon as she
should have it,
Moll White
is at the Bottom of the Churn. If a
Horse sweats in the Stable,
Moll White
has been upon his Back. If
a Hare makes an unexpected escape from the Hounds, the Huntsman curses
Moll White
. Nay, (says Sir
Roger
) I have known the Master of the
Pack, upon such an Occasion, send one of his Servants to see if
Moll
White
had been out that Morning.
This Account raised my Curiosity so far, that I begged my Friend Sir
Roger
to go with me into her Hovel, which stood in a solitary Corner
under the side of the Wood. Upon our first entering Sir
Roger
winked to
me, and pointed at something that stood behind the Door, which, upon
looking that Way, I found to be an old Broom-staff. At the same time he
whispered me in the Ear to take notice of a Tabby Cat that sat in the
Chimney-Corner, which, as the old Knight told me, lay under as bad a
Report as
Moll White
her self; for besides that
Moll
is
said often to accompany her in the same Shape, the Cat is reported to
have spoken twice or thrice in her Life, and to have played several
Pranks above the Capacity of an ordinary Cat.
I was secretly concerned to see Human Nature in so much Wretchedness and
Disgrace, but at the same time could not forbear smiling to hear Sir
Roger
, who is a little puzzled about the old Woman, advising her as a
Justice of Peace to avoid all Communication with the Devil, and never to
hurt any of her Neighbours' Cattle. We concluded our Visit with a
Bounty, which was very acceptable.
In our Return home, Sir
Roger
told me, that old
Moll
had been
often brought before him for making Children spit Pins, and giving Maids
the Night-Mare; and that the Country People would be tossing her into a
Pond and trying Experiments with her every Day, if it was not for him
and his Chaplain.
have since found upon Enquiry, that Sir
Roger
was several times
staggered with the Reports that had been brought him concerning this old
Woman, and would frequently have bound her over to the County Sessions,
had not his Chaplain with much ado perswaded him to the contrary
.
I have been the more particular in this Account, because I hear there is
scarce a Village in
England
that has not a
Moll White
in
it. When an old Woman begins to doat, and grow chargeable to a Parish,
she is generally turned into a Witch, and fills the whole Country with
extravagant Fancies, imaginary Distempers and terrifying Dreams. In the
mean time, the poor Wretch that is the innocent Occasion of so many
Evils begins to be frighted at her self, and sometimes confesses secret
Commerce and Familiarities that her Imagination forms in a delirious old
Age. This frequently cuts off Charity from the greatest Objects of
Compassion, and inspires People with a Malevolence towards those poor
decrepid Parts of our Species, in whom Human Nature is defaced by
Infirmity and Dotage.
L.
Ottway
, which I could not forbear repeating on this
occasion.
Orphan
, Act II. Chamont to Monimia.
The knight told me, upon hearing the Description,
When this essay was written, charges were being laid
against one old woman, Jane Wenham, of Walkerne, a little village north
of Hertford, which led to her trial for witchcraft at assizes held in
the following year, 1712, when she was found guilty; and became
memorable as the last person who, in this country, was condemned to
capital punishment for that impossible offence. The judge got first a
reprieve and then a pardon. The lawyers had refused to draw up any
indictment against the poor old creature, except, in mockery, for
'conversing familiarly with the devil in form of a cat.' But of that
offence she was found guilty upon the testimony of sixteen witnesses,
three of whom were clergymen. One witness, Anne Thorne, testified that
every night the pins went from her pincushion into her mouth. Others
gave evidence that they had seen pins come jumping through the air into
Anne Thorne's mouth. Two swore that they had heard the prisoner, in the
shape of a cat, converse with the devil, he being also in form of a cat.
Anne Thorne swore that she was tormented exceedingly with cats, and that
all the cats had the face and voice of the witch. The vicar of Ardeley
had tested the poor ignorant creature with the Lord's Prayer, and
finding that she could not repeat it, had terrified her with his moral
tortures into some sort of confession. Such things, then, were said and
done, and such credulity was abetted even by educated men at the time
when this essay was written. Upon charges like those ridiculed in the
text, a woman actually was, a few months later, not only committed by
justices with a less judicious spiritual counsellor than Sir Roger's
chaplain, but actually found guilty at the assizes, and condemned to
death.
Contents
|
Monday, July 16, 1711 |
Steele |
... Haret lateri lethalis arundo.
Virg.

This agreeable Seat is surrounded with so many pleasing Walks, which are
struck out of a Wood, in the midst of which the House stands, that one
can hardly ever be weary of rambling from one Labyrinth of Delight to
another. To one used to live in a City the Charms of the Country are so
exquisite, that the Mind is lost in a certain Transport which raises us
above ordinary Life, and is yet not strong enough to be inconsistent
with Tranquility. This State of Mind was I in, ravished with the Murmur
of Waters, the Whisper of Breezes, the Singing of Birds; and whether I
looked up to the Heavens, down on the Earth, or turned to the Prospects
around me, still struck with new Sense of Pleasure; when I found by the
Voice of my Friend, who walked by me, that we had insensibly stroled
into the Grove sacred to the Widow.
This Woman, says he, is of all others the most unintelligible: she
either designs to marry, or she does not. What is the most perplexing
of all, is, that she doth not either say to her Lovers she has any
Resolution against that Condition of Life in general, or that she
banishes them; but conscious of her own Merit, she permits their
Addresses, without Fear of any ill Consequence, or want of Respect,
from their Rage or Despair. She has that in her Aspect, against which
it is impossible to offend. A Man whose Thoughts are constantly bent
upon so agreeable an Object, must be excused if the ordinary
Occurrences in Conversation are below his Attention. I call her indeed
perverse, but, alas! why do I call her so? Because her superior Merit
is such, that I cannot approach her without Awe, that my Heart is
checked by too much Esteem: I am angry that her Charms are not more
accessible, that I am more inclined to worship than salute her: How
often have I wished her unhappy that I might have an Opportunity of
serving her? and how often troubled in that very Imagination, at
giving her the Pain of being obliged? Well, I have led a miserable
Life in secret upon her Account; but fancy she would have condescended
to have some regard for me, if it had not been for that watchful
Animal her Confident.
Of all Persons under the Sun (continued he, calling me by my Name) be
sure to set a Mark upon Confidents: they are of all People the most
impertinent. What is most pleasant to observe in them, is, that they
assume to themselves the Merit of the Persons whom they have in their
Custody. Orestilla is a great Fortune, and in wonderful Danger
of Surprizes, therefore full of Suspicions of the least indifferent
thing, particularly careful of new Acquaintance, and of growing too
familiar with the old. Themista, her Favourite-Woman, is every
whit as careful of whom she speaks to, and what she says. Let the Ward
be a Beauty, her Confident shall treat you with an Air of Distance;
let her be a Fortune, and she assumes the suspicious Behaviour of her
Friend and Patroness. Thus it is that very many of our unmarried Women
of Distinction, are to all Intents and Purposes married, except the
Consideration of different Sexes. They are directly under the Conduct
of their Whisperer; and think they are in a State of Freedom, while
they can prate with one of these Attendants of all Men in general, and
still avoid the Man they most like. You do not see one Heiress in a
hundred whose Fate does not turn upon this Circumstance of choosing a
Confident. Thus it is that the Lady is addressed to, presented and
flattered, only by Proxy, in her Woman. In my Case, how is it possible
that–
Sir
Rodger
was proceeding in his Harangue, when we heard the Voice of
one speaking very importunately, and repeating these Words,
'What, not
one Smile?'
We followed the Sound till we came to a close Thicket, on
the other side of which we saw a young Woman sitting as it were in a
personated Sullenness just over a transparent Fountain. Opposite to her
stood Mr.
William
, Sir Roger's Master of the Game. The Knight
whispered me, 'Hist, these are Lovers.' The Huntsman looking earnestly
at the Shadow of the young Maiden in the Stream,
'Oh thou dear Picture, if thou couldst remain there in the Absence of
that fair Creature whom you represent in the Water, how willingly
could I stand here satisfied for ever, without troubling my dear
Betty herself with any Mention of her unfortunate
William, whom she is angry with: But alas! when she pleases to
be gone, thou wilt also vanish — Yet let me talk to thee while thou
dost stay. Tell my dearest Betty thou dost not more depend upon
her, than does her William? Her Absence will make away with me
as well as thee. If she offers to remove thee, I'll jump into these
Waves to lay hold on thee; her self, her own dear Person, I must never
embrace again — Still do you hear me without one Smile — It is too much
to bear — '
He had no sooner spoke these Words, but he made an Offer of throwing
himself into the Water: At which his Mistress started up, and at the
next Instant he jumped across the Fountain and met her in an Embrace.
She half recovering from her Fright, said in the most charming Voice
imaginable, and with a Tone of Complaint,
'I thought how well you would drown yourself. No, no, you won't drown
yourself till you have taken your leave of Susan Holliday.'
The Huntsman, with a Tenderness that spoke the most passionate Love, and
with his Cheek close to hers, whispered the softest Vows of Fidelity in
her Ear, and cried,
'Don't, my Dear, believe a Word Kate Willow says; she is
spiteful and makes Stories, because she loves to hear me talk to her
self for your sake.'
Look you there, quoth Sir Roger, do you see there, all Mischief comes
from Confidents! But let us not interrupt them; the Maid is honest,
and the Man dares not be otherwise, for he knows I loved her Father: I
will interpose in this matter, and hasten the Wedding. Kate
Willow is a witty mischievous Wench in the Neighbourhood, who was
a Beauty; and makes me hope I shall see the perverse Widow in her
Condition. She was so flippant with her Answers to all the honest
Fellows that came near her, and so very vain of her Beauty, that she
has valued herself upon her Charms till they are ceased. She therefore
now makes it her Business to prevent other young Women from being more
Discreet than she was herself: However, the saucy Thing said the other
Day well enough, 'Sir Roger and I must make a Match, for we are 'both
despised by those we loved:' The Hussy has a great deal of Power
wherever she comes, and has her Share of Cunning.
However, when I reflect upon this Woman, I do not know whether in the
main I am the worse for having loved her: Whenever she is recalled to
my Imagination my Youth returns, and I feel a forgotten Warmth in my
Veins. This Affliction in my Life has streaked all my Conduct with a
Softness, of which I should otherwise have been incapable. It is,
perhaps, to this dear Image in my Heart owing, that I am apt to
relent, that I easily forgive, and that many desirable things are
grown into my Temper, which I should not have arrived at by better
Motives than the Thought of being one Day hers. I am pretty well
satisfied such a Passion as I have had is never well cured; and
between you and me, I am often apt to imagine it has had some
whimsical Effect upon my Brain: For I frequently find, that in my most
serious Discourse I let fall some comical Familiarity of Speech or odd
Phrase that makes the Company laugh; However, I cannot but allow she
is a most excellent Woman. When she is in the Country I warrant she
does not run into Dairies, but reads upon the Nature of Plants; but
has a Glass Hive, and comes into the Garden out of Books to see them
work, and observe the Policies of their Commonwealth. She understands
every thing. I'd give ten Pounds to hear her argue with my Friend Sir
Look you there, quoth Sir Roger, do you see there, all Mischief comes
from Confidents! But let us not interrupt them; the Maid is honest,
and the Man dares not be otherwise, for he knows I loved her Father: I
will interpose in this matter, and hasten the Wedding. Kate
Willow is a witty mischievous Wench in the Neighbourhood, who was
a Beauty; and makes me hope I shall see the perverse Widow in her
Condition. She was so flippant with her Answers to all the honest
Fellows that came near her, and so very vain of her Beauty, that she
has valued herself upon her Charms till they are ceased. She therefore
now makes it her Business to prevent other young Women from being more
Discreet than she was herself: However, the saucy Thing said the other
Day well enough, 'Sir Roger and I must make a Match, for we are 'both
despised by those we loved:' The Hussy has a great deal of Power
wherever she comes, and has her Share of Cunning.
However, when I reflect upon this Woman, I do not know whether in the
main I am the worse for having loved her: Whenever she is recalled to
my Imagination my Youth returns, and I feel a forgotten Warmth in my
Veins. This Affliction in my Life has streaked all my Conduct with a
Softness, of which I should otherwise have been incapable. It is,
perhaps, to this dear Image in my Heart owing, that I am apt to
relent, that I easily forgive, and that many desirable things are
grown into my Temper, which I should not have arrived at by better
Motives than the Thought of being one Day hers. I am pretty well
satisfied such a Passion as I have had is never well cured; and
between you and me, I am often apt to imagine it has had some
whimsical Effect upon my Brain: For I frequently find, that in my most
serious Discourse I let fall some comical Familiarity of Speech or odd
Phrase that makes the Company laugh; However, I cannot but allow she
is a most excellent Woman. When she is in the Country I warrant she
does not run into Dairies, but reads upon the Nature of Plants; but
has a Glass Hive, and comes into the Garden out of Books to see them
work, and observe the Policies of their Commonwealth. She understands
every thing. I'd give ten Pounds to hear her argue with my Friend Sir
Andrew Freeport about Trade. No, no, for all she looks so innocent as
it were, take my Word for it she is no Fool.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 17, 1711 |
Addison |
Urbem quam dicunt Romam, Melibæe, putavi
Stultus ego huic nostræ similem ...
Virg.

The first and most obvious Reflections which arise in a Man who changes
the City for the Country, are upon the different Manners of the People
whom he meets with in those two different Scenes of Life. By Manners I
do not mean Morals, but Behaviour and Good Breeding, as they shew
themselves in the Town and in the Country.
And here, in the first place, I must observe a very great Revolution
that has happen'd in this Article of Good Breeding. Several obliging
Deferences, Condescensions and Submissions, with many outward Forms and
Ceremonies that accompany them, were first of all brought up among the
politer Part of Mankind, who lived in Courts and Cities, and
distinguished themselves from the Rustick part of the Species (who on
all Occasions acted bluntly and naturally) by such a mutual Complaisance
and Intercourse of Civilities. These Forms of Conversation by degrees
multiplied and grew troublesome; the Modish World found too great a
Constraint in them, and have therefore thrown most of them aside.
Conversation, like the
Romish
Religion, was so encumbered with Show
and Ceremony, that it stood in need of a Reformation to retrench its
Superfluities, and restore it to its natural good Sense and Beauty. At
present therefore an unconstrained Carriage, and a certain Openness of
Behaviour, are the Height of Good Breeding. The Fashionable World is
grown free and easie; our Manners sit more loose upon us: Nothing is so
modish as an agreeable Negligence. In a word, Good Breeding shews it
self most, where to an ordinary Eye it appears the least.
If after this we look on the People of Mode in the Country, we find in
them the Manners of the last Age. They have no sooner fetched themselves
up to the Fashion of the polite World, but the Town has dropped them,
and are nearer to the first State of Nature than to those Refinements
which formerly reign'd in the Court, and still prevail in the Country.
One may now know a Man that never conversed in the World, by his Excess
of Good Breeding. A polite Country 'Squire shall make you as many Bows
in half an Hour, as would serve a Courtier for a Week. There is
infinitely more to do about Place and Precedency in a Meeting of
Justices Wives, than in an Assembly of Dutchesses.
This Rural Politeness is very troublesome to a Man of my Temper, who
generally take the Chair that is next me, and walk first or last, in the
Front or in the Rear, as Chance directs. I have known my Friend Sir
Roger's Dinner almost cold before the Company could adjust the
Ceremonial, and be prevailed upon to sit down; and have heartily pitied
my old Friend, when I have seen him forced to pick and cull his Guests,
as they sat at the several Parts of his Table, that he might drink their
Healths according to their respective Ranks and Qualities. Honest
Will.
Wimble
, who I should have thought had been altogether uninfected with
Ceremony, gives me abundance of Trouble in this Particular. Though he
has been fishing all the Morning, he will not help himself at Dinner
'till I am served. When we are going out of the Hall, he runs behind me;
and last Night, as we were walking in the Fields, stopped short at a
Stile till I came up to it, and upon my making Signs to him to get over,
told me, with a serious Smile, that sure I believed they had no Manners
in the Country.
There has happened another Revolution in the Point of Good Breeding,
which relates to the Conversation among Men of Mode, and which I cannot
but look upon as very extraordinary. It was certainly one of the first
Distinctions of a well-bred Man, to express every thing that had the
most remote Appearance of being obscene, in modest Terms and distant
Phrases; whilst the Clown, who had no such Delicacy of Conception and
Expression, clothed his
Ideas
in those plain homely Terms that are the
most obvious and natural. This kind of Good Manners was perhaps carried
to an Excess, so as to make Conversation too stiff, formal and precise:
for which Reason (as Hypocrisy in one Age is generally succeeded by
Atheism in another) Conversation is in a great measure relapsed into the
first Extream; so that at present several of our Men of the Town, and
particularly those who have been polished in
France
, make use of the
most coarse uncivilized Words in our Language, and utter themselves
often in such a manner as a Clown would blush to hear.
This infamous Piece of Good Breeding, which reigns among the Coxcombs of
the Town, has not yet made its way into the Country; and as it is
impossible for such an irrational way of Conversation to last long among
a People that make any Profession of Religion, or Show of Modesty, if
the Country Gentlemen get into it they will certainly be left in the
Lurch. Their Good-breeding will come too late to them, and they will be
thought a Parcel of lewd Clowns, while they fancy themselves talking
together like Men of Wit and Pleasure.
As the two Points of Good Breeding, which I have hitherto insisted upon,
regard Behaviour and Conversation, there is a third which turns upon
Dress. In this too the Country are very much behind-hand. The Rural
Beaus are not yet got out of the Fashion that took place at the time of
the Revolution, but ride about the Country in red Coats and laced Hats,
while the Women in many Parts are still trying to outvie one another in
the Height of their Head-dresses.
But a Friend of mine, who is now upon the Western Circuit, having
promised to give me an Account of the several Modes and Fashions that
prevail in the different Parts of the Nation through which he passes, I
shall defer the enlarging upon this last Topick till I have received a
Letter from him, which I expect every Post.
L.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 18, 1711 |
Addison |
... Equidem credo, quia sit Divinitus illis
Ingenium ...
Virg.

My Friend Sir
Roger
is very often merry with me upon my passing so much
of my Time among his Poultry: He has caught me twice or thrice looking
after a Bird's Nest, and several times sitting an Hour or two together
near an Hen and Chickens. He tells me he believes I am personally
acquainted with every Fowl about his House; calls such a particular Cock
my Favourite, and frequently complains that his Ducks and Geese have
more of my Company than himself.
I must confess I am infinitely delighted with those Speculations of
Nature which are to be made in a Country-Life; and as my Reading has
very much lain among Books of natural History, I cannot forbear
recollecting upon this Occasion the several Remarks which I have met
with in Authors, and comparing them with what falls under my own
Observation: The Arguments for Providence drawn from the natural History
of Animals being in my Opinion demonstrative.
The Make of every Kind of Animal is different from that of every other
Kind; and yet there is not the least Turn in the Muscles or Twist in the
Fibres of any one, which does not render them more proper for that
particular Animal's Way of Life than any other Cast or Texture of them
would have been.
The most violent Appetites in all Creatures are
Lust
and
Hunger
: The
first is a perpetual Call upon them to propagate their Kind; the latter
to preserve themselves.
It is astonishing to consider the different Degrees of Care that descend
from the Parent to the Young, so far as is absolutely necessary for the
leaving a Posterity.
Creatures cast their Eggs as Chance directs
them, and think of them no farther, as Insects and several Kinds of
Fish: Others, of a nicer Frame, find out proper Beds to
deposite
them in, and there leave them; as the Serpent, the Crocodile, and
Ostrich: Others hatch their Eggs and tend the Birth, 'till it is able to
shift for it self.
What can we call the Principle which directs every different Kind of
Bird to observe a particular Plan in the Structure of its Nest, and
directs all of the same Species to work after the same Model? It cannot
be Imitation; for though you hatch a Crow under a Hen, and never let it
see any of the Works of its own Kind, the Nest it makes shall be the
same, to the laying of a Stick, with all the other Nests of the same
Species. It cannot be
Reason
; for were Animals indued with it to as
great a Degree as Man, their Buildings would be as different as ours,
according to the different Conveniences that they would propose to
themselves.
Is it not remarkable, that the same Temper of Weather, which raises this
genial Warmth in Animals, should cover the Trees with Leaves and the
Fields with Grass for their Security and Concealment, and produce such
infinite Swarms of Insects for the Support and Sustenance of their
respective Broods?
Is it not wonderful, that the Love of the Parent should be so violent
while it lasts; and that it should last no longer than is necessary for
the Preservation of the Young?
The Violence of this natural Love is exemplify'd by a very barbarous
Experiment; which I shall quote at Length, as I find it in an excellent
Author, and hope my Readers will pardon the mentioning such an Instance
of Cruelty, because there is nothing can so effectually shew the
Strength of that Principle in Animals of which I am here speaking. 'A
Person who was well skilled in Dissection opened a Bitch, and as she lay
in the most exquisite Tortures, offered her one of her young Puppies,
which she immediately fell a licking; and for the Time seemed insensible
of her own Pain: On the Removal, she kept her Eye fixt on it, and began
a wailing sort of Cry, which seemed rather to proceed from the Loss of
her young one, than the Sense of her own Torments.
But notwithstanding this natural Love in Brutes is much more violent and
intense than in rational Creatures, Providence has taken care that it
should be no longer troublesome to the Parent than it is useful to the
Young: for so soon as the Wants of the latter cease, the Mother
withdraws her Fondness, and leaves them to provide for themselves: and
what is a very remarkable Circumstance in this part of Instinct, we find
that the Love of the Parent may be lengthened out beyond its usual time,
if the Preservation of the Species requires it; as we may see in Birds
that drive away their Young as soon as they are able to get their
Livelihood, but continue to feed them if they are tied to the Nest, or
confined within a Cage, or by any other Means appear to be out of a
Condition of supplying their own Necessities.
This natural Love is not observed in animals to ascend from the Young to
the Parent, which is not at all necessary for the Continuance of the
Species: Nor indeed in reasonable Creatures does it rise in any
Proportion, as it spreads it self downwards; for in all Family
Affection, we find Protection granted and Favours bestowed, are greater
Motives to Love and Tenderness, than Safety, Benefits, or Life received.
One would wonder to hear Sceptical Men disputing for the Reason of
Animals, and telling us it is only our Pride and Prejudices that will
not allow them the Use of that Faculty.
Reason shews it self in all Occurrences of Life; whereas the Brute makes
no Discovery of such a Talent, but in what immediately regards his own
Preservation, or the Continuance of his Species. Animals in their
Generation are wiser than the Sons of Men; but their Wisdom is confined
to a few Particulars, and lies in a very narrow Compass. Take a Brute
out of his Instinct, and you find him wholly deprived of Understanding.
To use an Instance that comes often under Observation.
With what Caution does the Hen provide herself a Nest in Places
unfrequented, and free from Noise and Disturbance! When she has laid her
Eggs in such a Manner that she can cover them, what Care does she take
in turning them frequently, that all Parts may partake of the vital
Warmth? When she leaves them, to provide for her necessary Sustenance,
how punctually does she return before they have time to cool, and become
incapable of producing an Animal? In the Summer you see her giving her
self greater Freedoms, and quitting her Care for above two Hours
together; but in Winter, when the Rigour of the Season would chill the
Principles of Life, and destroy the young one, she grows more assiduous
in her Attendance, and stays away but half the Time. When the Birth
approaches, with how much Nicety and Attention does she help the Chick
to break its Prison? Not to take notice of her covering it from the
Injuries of the Weather, providing it proper Nourishment, and teaching
it to help it self; nor to mention her forsaking the Nest, if after the
usual Time of reckoning the young one does not make its Appearance. A
Chymical Operation could not be followed with greater Art or Diligence,
than is seen in the hatching of a Chick; tho' there are many other Birds
that shew an infinitely greater Sagacity in all the forementioned
Particulars.
But at the same time the Hen, that has all this seeming Ingenuity,
(which is indeed absolutely necessary for the Propagation of the
Species) considered in other respects, is without the least Glimmerings
of Thought or common Sense. She mistakes a Piece of Chalk for an Egg,
and sits upon it in the same manner: She is insensible of any Increase
or Diminution in the Number of those she lays: She does not distinguish
between her own and those of another Species; and when the Birth appears
of never so different a Bird, will cherish it for her own. In all these
Circumstances which do not carry an immediate Regard to the Subsistence
of her self or her Species, she is a very Ideot.
There is not, in my Opinion, any thing more mysterious in Nature than
this Instinct in Animals, which thus rises above Reason, and falls
infinitely short of it. It cannot be accounted for by any Properties in
Matter, and at the same time works after so odd a manner, that one
cannot think it the Faculty of an intellectual Being. For my own part, I
look upon it as upon the Principle of Gravitation in Bodies, which is
not to be explained by any known Qualities inherent in the Bodies
themselves, nor from any Laws of Mechanism, but, according to the best
Notions of the greatest Philosophers, is an immediate Impression from
the first Mover, and the Divine Energy acting in the Creatures.
L.
depose
Contents
|
Thursday, July 19, 1711 |
Addison |
... Jovis omnia plena.
Virg.

As I was walking this Morning in the great Yard that belongs to my
Friend's Country House, I was wonderfully pleased to see the different
Workings of Instinct in a Hen followed by a Brood of Ducks. The Young,
upon the sight of a Pond, immediately ran into it; while the Stepmother,
with all imaginable Anxiety, hovered about the Borders of it, to call
them out of an Element that appeared to her so dangerous and
destructive. As the different Principle which acted in these different
Animals cannot be termed Reason, so when we call it
Instinct
, we mean
something we have no Knowledge of. To me, as I hinted in my last Paper,
it seems the immediate Direction of Providence, and such an Operation of
the Supreme Being, as that which determines all the Portions of Matter
to their proper Centres.
modern Philosopher, quoted by Monsieur
Bayle
in his learned
Dissertation on the Souls of Brutes
, delivers
the same Opinion, tho' in a bolder Form of Words, where he says,
Deus
est Anima Brutorum
, God himself is the Soul of Brutes. Who can tell
what to call that seeming Sagacity in Animals, which directs them to
such Food as is proper for them, and makes them naturally avoid whatever
is noxious or unwholesome?
Tully
has observed that a Lamb no sooner
falls from its Mother, but immediately and of his own accord applies
itself to the Teat.
Dampier
,
his Travels
, tells us, that when
Seamen are thrown upon any of the unknown Coasts of
America
, they
never venture upon the Fruit of any Tree, how tempting soever it may
appear, unless they observe that it is marked with the Pecking of Birds;
but fall on without any Fear or Apprehension where the Birds have been
before them.
But notwithstanding Animals have nothing like the use of Reason, we find
in them all the lower Parts of our Nature, the Passions and Senses in
their greatest Strength and Perfection. And here it is worth our
Observation, that all Beasts and Birds of Prey are wonderfully subject
to Anger, Malice, Revenge, and all the other violent Passions that may
animate them in search of their proper Food; as those that are incapable
of defending themselves, or annoying others, or whose Safety lies
chiefly in their Flight, are suspicious, fearful and apprehensive of
every thing they see or hear; whilst others that are of Assistance and
Use to Man, have their Natures softened with something mild and
tractable, and by that means are qualified for a Domestick Life. In this
Case the Passions generally correspond with the Make of the Body. We do
not find the Fury of a Lion in so weak and defenceless an Animal as a
Lamb, nor the Meekness of a Lamb in a Creature so armed for Battel and
Assault as the Lion. In the same manner, we find that particular Animals
have a more or less exquisite Sharpness and Sagacity in those particular
Senses which most turn to their Advantage, and in which their Safety and
Welfare is the most concerned.
Nor must we here omit that great Variety of Arms with which Nature has
differently fortified the Bodies of several kind of Animals, such as
Claws, Hoofs, and Horns, Teeth, and Tusks, a Tail, a Sting, a Trunk, or
a
Proboscis
. It is likewise observed by Naturalists, that it must be
some hidden Principle distinct from what we call Reason, which instructs
Animals in the Use of these their Arms, and teaches them to manage them
to the best Advantage; because they naturally defend themselves with
that Part in which their Strength lies, before the Weapon be formed in
it; as is remarkable in Lambs, which tho' they are bred within Doors,
and never saw the Actions of their own Species, push at those who
approach them with their Foreheads, before the first budding of a Horn
appears.
shall add to these general Observations, an Instance which Mr.
Lock
has given us of Providence even in the Imperfections of a Creature which
seems the meanest and most despicable in the whole animal World.
We
may
, says he,
from the Make of an Oyster, or Cockle, conclude, that it
has not so many nor so quick Senses as a Man, or several other Animals:
Nor if it had, would it, in that State and Incapacity of transferring it
self from one Place to another, be bettered by them. What good would
Sight and Hearing do to a Creature, that cannot move it self to, or from
the Object, wherein at a distance it perceives Good or Evil? And would
not Quickness of Sensation be an Inconvenience to an Animal, that must
be still where Chance has once placed it; and there receive the Afflux
of colder or warmer, clean or foul Water, as it happens to come to it
.
shall add to this Instance out of Mr.
Lock
another out of the
learned Dr.
Moor
, who cites it from
Cardan
, in relation to
another Animal which Providence has left Defective, but at the same time
has shewn its Wisdom in the Formation of that Organ in which it seems
chiefly to have failed.
What is more obvious and ordinary than a Mole?
and yet what more palpable Argument of Providence than she? The Members
of her Body are so exactly fitted to her Nature and Manner of Life: For
her Dwelling being under Ground where nothing is to be seen, Nature has
so obscurely fitted her with Eyes, that Naturalists can hardly agree
whether she have any Sight at all or no. But for Amends, what she is
capable of for her Defence and Warning of Danger, she has very eminently
conferred upon her; for she is exceeding quick of hearing. And then her
short Tail and short Legs, but broad Fore-feet armed with sharp Claws,
we see by the Event to what Purpose they are, she so swiftly working her
self under Ground, and making her way so fast in the Earth as they that
behold it cannot but admire it. Her Legs therefore are short, that she
need dig no more than will serve the mere Thickness of her Body; and her
Fore-feet are broad that she may scoop away much Earth at a time; and
little or no Tail she has, because she courses it not on the Ground,
like the Rat or Mouse, of whose Kindred she is, but lives under the
Earth, and is fain to dig her self a Dwelling there. And she making her
way through so thick an Element, which will not yield easily, as the Air
or the Wafer, it had been dangerous to have drawn so long a Train behind
her; for her Enemy might fall upon her Rear, and fetch her out, before
she had compleated or got full Possession of her Works
.
cannot forbear mentioning Mr.
Boyle's
Remark upon this last
Creature, who I remember somewhere in his Works observes
, that
though the Mole be not totally blind (as it is commonly thought) she has
not Sight enough to distinguish particular Objects. Her Eye is said to
have but one Humour in it, which is supposed to give her the Idea of
Light, but of nothing else, and is so formed that this Idea is probably
painful to the Animal. Whenever she comes up into broad Day she might be
in Danger of being taken, unless she were thus affected by a Light
striking upon her Eye, and immediately warning her to bury herself in
her proper Element. More Sight would be useless to her, as none at all
might be fatal.
I have only instanced such Animals as seem the most imperfect Works of
Nature; and if Providence shews it self even in the Blemishes of these
Creatures, how much more does it discover it self in the several
Endowments which it has variously bestowed upon such Creatures as are
more or less finished and compleated in their several Faculties,
according to the condition of Life in which they are posted.
I could wish our Royal Society would compile a Body of Natural History,
the best that could be gather'd together from Books and Observations. If
the several Writers among them took each his particular Species, and
gave us a distinct Account of its Original, Birth and Education; its
Policies, Hostilities and Alliances, with the Frame and Texture of its
inward and outward Parts, and particularly those that distinguish it
from all other Animals, with their peculiar Aptitudes for the State of
Being in which Providence has placed them, it would be one of the best
Services their Studies could do Mankind, and not a little redound to the
Glory of the All-wise Contriver.
It is true, such a Natural History, after all the Disquisitions of the
Learned, would be infinitely Short and Defective. Seas and Desarts hide
Millions of Animals from our Observation. Innumerable Artifices and
Stratagems are acted in the
Howling Wilderness
and in the
Great
Deep
, that can never come to our Knowledge. Besides that there are
infinitely more Species of Creatures which are not to be seen without,
nor indeed with the help of the finest Glasses, than of such as are
bulky enough for the naked Eye to take hold of. However from the
Consideration of such Animals as lie within the Compass of our
Knowledge, we might easily form a Conclusion of the rest, that the same
Variety of Wisdom and Goodness runs through the whole Creation, and puts
every Creature in a Condition to provide for its Safety and Subsistence
in its proper Station.
Tully
has given us an admirable Sketch of Natural History, in his
second Book concerning the Nature of the Gods; and then in a Stile so
raised by Metaphors and Descriptions, that it lifts the Subject above
Raillery and Ridicule, which frequently fall on such nice Observations
when they pass through the Hands of an ordinary Writer.
L.
Bayle's Dictionary
, here quoted, first appeared in English
in 1710. Pierre Bayle himself had first produced it in two folio vols.
in 1695-6, and was engaged in controversies caused by it until his death
in 1706, at the age of 59. He was born at Carlat, educated at the
universities of Puylaurens and Toulouse, was professor of Philosophy
successively at Sedan and Rotterdam till 1693, when he was deprived for
scepticism. He is said to have worked fourteen hours a day for 40 years,
and has been called 'the Shakespeare of Dictionary Makers.'
Captain William Dampier's
Voyages round the World
appeared
in 3 vols., 1697-1709. The quotation is from vol. i. p. 39 (Ed. 1699,
the Fourth). Dampier was born in 1652, and died about 1712.
Essay on Human Understanding
, Bk. II. ch. 9, § 13.
Antidote against Atheism
, Bk. II. ch. 10, § 5.
Disquisition about the Final Causes of Natural Things,
Sect. 2.
Contents
|
Friday, July 20, 1711 |
Addison |
Comes jucundus in via pro vehiculo est.
Publ. Syr. Frag.

A man's first Care should be to avoid the Reproaches of his own Heart;
his next, to escape the Censures of the World: If the last interferes
with the former, it ought to be entirely neglected; but otherwise, there
cannot be a greater Satisfaction to an honest Mind, than to see those
Approbations which it gives it self seconded by the Applauses of the
Publick: A Man is more sure of his Conduct, when the Verdict which he
passes upon his own Behaviour is thus warranted and confirmed by the
Opinion of all that know him.
My worthy Friend Sir Roger is one of those who is not only at Peace
within himself, but beloved and esteemed by all about him. He receives a
suitable Tribute for his universal Benevolence to Mankind, in the
Returns of Affection and Good-will, which are paid him by every one that
lives within his Neighbourhood. I lately met with two or three odd
Instances of that general Respect which is shown to the good old Knight.
He would needs carry
Will. Wimble
and myself with him to the
County-Assizes: As we were upon the Road
Will. Wimble
joined a couple
of plain Men who rid before us, and conversed with them for some Time;
during which my Friend Sir Roger acquainted me with their Characters.
The first of them, says he, that has a Spaniel by his Side, is a Yeoman
of about an hundred Pounds a Year, an honest Man: He is just within the
Game-Act, and qualified to kill an Hare or a Pheasant: He knocks down a
Dinner with his Gun twice or thrice a Week; and by that means lives much
cheaper than those who have not so good an Estate as himself. He would
be a good Neighbour if he did not destroy so many Partridges: in short,
he is a very sensible Man; shoots flying; and has been several times
Foreman of the Petty-Jury.
The other that rides along with him is
Tom Touchy
, a Fellow famous for
taking the Law
of every Body. There is not one in the Town where he
lives that he has not sued at a Quarter-Sessions. The Rogue had once the
Impudence to go to Law with the
Widow
. His Head is full of Costs,
Damages, and Ejectments: He plagued a couple of honest Gentlemen so long
for a Trespass in breaking one of his Hedges, till he was forced to sell
the Ground it enclosed to defray the Charges of the Prosecution: His
Father left him fourscore Pounds a Year; but he has
cast
and been cast
so often, that he is not now worth thirty. I suppose he is going upon
the old Business of the Willow-Tree.
As Sir
Roger
was giving me this Account of Tom Touchy,
Will. Wimble
and his two Companions stopped short till we came up to them. After
having paid their Respects to Sir
Roger
,
Will
. told him that Mr.
Touchy
and he must appeal to him upon a Dispute that arose between
them.
Will
. it seems had been giving his Fellow-Traveller an Account
of his Angling one Day in such a Hole; when
Tom Touchy
, instead of
hearing out his Story, told him that Mr. such an One, if he pleased,
might
take the Law of him
for fishing in that Part of the River. My
Friend Sir
Roger
heard them both, upon a round Trot; and after having
paused some time told them, with the Air of a Man who would not give his
Judgment rashly, that
much might be said on both Sides
. They were
neither of them dissatisfied with the Knight's Determination, because
neither of them found himself in the Wrong by it: Upon which we made the
best of our Way to the Assizes.
The Court was sat before Sir
Roger
came; but notwithstanding all the
Justices had taken their Places upon the Bench, they made room for the
old Knight at the Head of them; who for his Reputation in the Country
took occasion to whisper in the Judge's Ear,
That he was glad his
Lordship had met with so much good Weather in his Circuit
. I was
listening to the Proceeding of the Court with much Attention, and
infinitely pleased with that great Appearance and Solemnity which so
properly accompanies such a publick Administration of our Laws; when,
after about an Hour's Sitting, I observed to my great Surprize, in the
Midst of a Trial, that my Friend Sir
Roger
was getting up to speak. I
was in some Pain for him, till I found he had acquitted himself of two
or three Sentences, with a Look of much Business and great Intrepidity.
Upon his first Rising the Court was hushed, and a general Whisper ran
among the Country People that Sir
Roger
was up
. The Speech he made was
so little to the Purpose, that I shall not trouble my Readers with an
Account of it; and I believe was not so much designed by the Knight
himself to inform the Court, as to give him a Figure in my Eye, and keep
up his Credit in the Country.
I was highly delighted, when the Court rose, to see the Gentlemen of the
Country gathering about my old Friend, and striving who should
compliment him most; at the same time that the ordinary People gazed
upon him at a distance, not a little admiring his Courage, that was not
afraid to speak to the Judge.
In our Return home we met with a very odd Accident; which I cannot
forbear relating, because it shews how desirous all who know Sir
Roger
are of giving him Marks of their Esteem. When we were arrived upon the
Verge of his Estate, we stopped at a little Inn to rest our selves and
our Horses. The Man of the House had it seems been formerly a Servant in
the Knight's Family; and to do Honour to his old Master, had some time
since, unknown to Sir
Roger
, put him up in a Sign-post before the Door;
so that
the Knight's Head
had hung out upon the Road about a Week
before he himself knew any thing of the Matter. As soon as Sir
Roger
was
acquainted with it, finding that his Servant's Indiscretion proceeded
wholly from Affection and Good-will, he only told him that he had made
him too high a Compliment; and when the Fellow seemed to think that
could hardly be, added with a more decisive Look, That it was too great
an Honour for any Man under a Duke; but told him at the same time, that
it might be altered with a very few Touches, and that he himself would
be at the Charge of it. Accordingly they got a Painter by the Knight's
Directions to add a pair of Whiskers to the Face, and by a little
Aggravation to the Features to change it into the
Saracen's Head
. I
should not have known this Story had not the Inn-keeper, upon Sir
Roger's
alighting, told him in my Hearing, That his Honour's Head was
brought back last Night with the Alterations that he had ordered to be
made in it. Upon this my Friend with his usual Chearfulness related the
Particulars above-mentioned, and ordered the Head to be brought into the
Room. I could not forbear discovering greater Expressions of Mirth than
ordinary upon the Appearance of this monstrous Face, under which,
notwithstanding it was made to frown and stare in a most extraordinary
manner, I could still discover a distant Resemblance of my old Friend.
Sir
Roger
, upon seeing me laugh, desired me to tell him truly if I
thought it possible for People to know him in that Disguise. I at first
kept my usual Silence; but upon the Knight's conjuring me to tell him
whether it was not still more like himself than a
Saracen
, I composed
my Countenance in the best manner I could, and replied,
That much might
be said on both Sides
.
These several Adventures, with the Knight's Behaviour in them, gave me
as pleasant a Day as ever I met with in any of my Travels.
L.
Contents
|
Saturday, July 21, 1711 |
Addison |
Doctrina sed vim promovet insitam,
Rectique cultus pectora roborant:
Utcunque defecere mores,
Dedecorant bene nata culpæ.
Hor.

As I was Yesterday taking the Air with my Friend Sir
Roger
, we were met
by a fresh-coloured ruddy young Man, who rid by us full speed, with a
couple of Servants behind him. Upon my Enquiry who he was, Sir
Roger
told me that he was a young Gentleman of a considerable Estate, who had
been educated by a tender Mother that lives not many Miles from the
Place where we were. She is a very good Lady, says my Friend, but took
so much care of her Son's Health, that she has made him good for
nothing. She quickly found that Reading was bad for his Eyes, and that
Writing made his Head ache. He was let loose among the Woods as soon as
he was able to ride on Horseback, or to carry a Gun upon his Shoulder.
To be brief, I found, by my Friend's Account of him, that he had got a
great Stock of Health, but nothing else; and that if it were a Man's
Business only to live, there would not be a more accomplished young
Fellow in the whole Country.
The Truth of it is, since my residing in these Parts I have seen and
heard innumerable Instances of young Heirs and elder Brothers, who
either from their own reflecting upon the Estates they are born to, and
therefore thinking all other Accomplishments unnecessary, or from
hearing these Notions frequently inculcated to them by the Flattery of
their Servants and Domesticks, or from the same foolish Thought
prevailing in those who have the Care of their Education, are of no
manner of use but to keep up their Families, and transmit their Lands
and Houses in a Line to Posterity.
This makes me often think on a Story I have heard of two Friends, which
I shall give my Reader at large, under feigned Names. The Moral of it
may, I hope, be useful, though there are some Circumstances which make
it rather appear like a Novel, than a true Story.
Eudoxus
and
Leontine
began the World with small Estates.
They were both of them Men of good Sense and great Virtue. They
prosecuted their Studies together in their earlier Years, and entered
into such a Friendship as lasted to the End of their Lives.
Eudoxus
, at his first setting out in the World, threw himself
into a Court, where by his natural Endowments and his acquired Abilities
he made his way from one Post to another, till at length he had raised a
very considerable Fortune.
Leontine
on the contrary sought all
Opportunities of improving his Mind by Study, Conversation, and Travel.
He was not only acquainted with all the Sciences, but with the most
eminent Professors of them throughout
Europe
. He knew perfectly
well the Interests of its Princes, with the Customs and Fashions of
their Courts, and could scarce meet with the Name of an extraordinary
Person in the
Gazette
whom he had not either talked to or seen.
In short, he had so well mixt and digested his Knowledge of Men and
Books, that he made one of the most accomplished Persons of his Age.
During the whole Course of his Studies and Travels he kept up a punctual
Correspondence with
Eudoxus
, who often made himself acceptable to
the principal Men about Court by the Intelligence which he received from
Leontine
.
they were both turn'd of Forty (an Age in which,
according to Mr. Cowley, there is no dallying with Life
) they determined, pursuant to the
Resolution they had taken in the beginning of their Lives, to retire,
and pass the Remainder of their Days in the Country. In order to this,
they both of them married much about the same time.
Leontine
,
with his own and his Wife's Fortune, bought a Farm of three hundred a
Year, which lay within the Neighbourhood of his Friend
Eudoxus
,
who had purchased an Estate of as many thousands. They were both of them
Fathers
about the same time,
Eudoxus
having a Son born to
him, and
Leontine
a Daughter; but to the unspeakable Grief of the
latter, his young Wife (in whom all his Happiness was wrapt up) died in
a few Days after the Birth of her Daughter. His Affliction would have
been insupportable, had not he been comforted by the daily Visits and
Conversations of his Friend. As they were one Day talking together with
their usual Intimacy,
Leontine
, considering how incapable he was of
giving his Daughter a proper education in his own House, and
Eudoxus
reflecting on the ordinary Behaviour of a Son who knows himself to be
the Heir of a great Estate, they both agreed upon an Exchange of
Children, namely that the Boy should be bred up with
Leontine
as his
Son, and that the Girl should live with
Eudoxus
as his Daughter, till
they were each of them arrived at Years of Discretion. The Wife of
Eudoxus
, knowing that her Son could not be so advantageously brought
up as under the Care of
Leontine
, and considering at the same time
that he would be perpetually under her own Eye, was by degrees prevailed
upon to fall in with the Project. She therefore took
Leonilla
, for
that was the Name of the Girl, and educated her as her own Daughter. The
two Friends on each side had wrought themselves to such an habitual
Tenderness for the Children who were under their Direction, that each of
them had the real Passion of a Father, where the Title was but
imaginary.
Florio
, the Name of the young Heir that lived with
Leontine
, though he had all the Duty and Affection imaginable for his
supposed Parent, was taught to rejoice at the Sight of
Eudoxus
, who
visited his Friend very frequently, and was dictated by his natural
Affection, as well as by the Rules of Prudence, to make himself esteemed
and beloved by
Florio
. The Boy was now old enough to know his supposed
Father's Circumstances, and that therefore he was to make his way in the
World by his own Industry. This Consideration grew stronger in him every
Day, and produced so good an Effect, that he applied himself with more
than ordinary Attention to the Pursuit of every thing which
Leontine
recommended to him. His natural Abilities, which were very good,
assisted by the Directions of so excellent a Counsellor, enabled him to
make a quicker Progress than ordinary through all the Parts of his
Education. Before he was twenty Years of Age, having finished his
Studies and Exercises with great Applause, he was removed from the
University to the Inns of Court, where there are very few that make
themselves considerable Proficients in the Studies of the Place, who
know they shall arrive at great Estates without them. This was not
Florio's
Case; he found that three hundred a Year was but a poor
Estate for
Leontine
and himself to live upon, so that he Studied
without Intermission till he gained a very good Insight into the
Constitution and Laws of his Country.
I should have told my Reader, that whilst
Florio
lived at the House of
his Foster-father, he was always an acceptable Guest in the Family of
Eudoxus
, where he became acquainted with
Leonilla
from her Infancy.
His Acquaintance with her by degrees grew into Love, which in a Mind
trained up in all the Sentiments of Honour and Virtue became a very
uneasy Passion. He despaired of gaining an Heiress of so great a
Fortune, and would rather have died than attempted it by any indirect
Methods.
Leonilla
, who was a Woman of the greatest Beauty joined with
the greatest Modesty, entertained at the same time a secret Passion for
Florio
, but conducted her self with so much Prudence that she never
gave him the least Intimation of it.
Florio
was now engaged in all
those Arts and Improvements that are proper to raise a Man's private
Fortune, and give him a Figure in his Country, but secretly tormented
with that Passion which burns with the greatest Fury in a virtuous and
noble Heart, when he received a sudden Summons from
Leontine
to repair
to him into the Country the next Day. For it seems
Eudoxus
was so
filled with the Report of his Son's Reputation, that he could no longer
withhold making himself known to him. The Morning after his Arrival at
the House of his supposed Father,
Leontine
told him that
Eudoxus
had
something of great Importance to communicate to him; upon which the good
Man embraced him, and wept.
Florio
was no sooner arrived at the great
House that stood in his Neighbourhood, but
Eudoxus
took him by the
Hand, after the first Salutes were over, and conducted him into his
Closet. He there opened to him the whole Secret of his Parentage and
Education, concluding after this manner:
I have no other way left of
acknowledging my Gratitude to
Leontine,
than by marrying you to his
Daughter. He shall not lose the Pleasure of being your Father by the
Discovery I have made to you.
Leonilla
too shall be still my Daughter;
her filial Piety, though misplaced, has been so exemplary that it
deserves the greatest Reward I can confer upon it. You shall have the
Pleasure of seeing a great Estate fall to you, which you would have lost
the Relish of had you known your self born to it. Continue only to
deserve it in the same manner you did before you were possessed of it. I
have left your Mother in the next Room. Her Heart yearns towards you.
She is making the same Discoveries to
Leonilla
which I have made to
your self. Florio
was so overwhelmed with this Profusion of Happiness,
that he was not able to make a Reply, but threw himself down at his
Father's Feet, and amidst a Flood of Tears, Kissed and embraced his
Knees, asking his Blessing, and expressing in dumb Show those Sentiments
of Love, Duty, and Gratitude that were too big for Utterance. To
conclude, the happy Pair were married, and half
Eudoxus's
Estate
settled upon them.
Leontine
and
Eudoxus
passed the
remainder of their Lives together; and received in the dutiful and
affectionate Behaviour of
Florio
and
Leonilla
the just
Recompence, as well as the natural Effects of that Care which they had
bestowed upon them in their Education.
L.
Essay
On the Danger of Procrastination
:
'There's no
fooling with Life when it is once turn'd beyond Forty.'
Contents
|
Monday, July 23, 1711 |
Addison |
A Man who publishes his Works in a Volume, has an infinite Advantage
over one who communicates his Writings to the World in loose Tracts and
single Pieces. We do not expect to meet with any thing in a bulky
Volume, till after some heavy Preamble, and several Words of Course, to
prepare the Reader for what follows: Nay, Authors have established it as
a kind of Rule, that a Man ought to be dull sometimes; as the most
severe Reader makes Allowances for many Rests and Nodding-places in a
Voluminous Writer. This gave Occasion to the famous Greek Proverb which
I have chosen for my Motto,
That a great Book is a great Evil.
On the contrary, those who publish their Thoughts in distinct Sheets,
and as it were by Piece-meal, have none of these Advantages. We must
immediately fall into our Subject, and treat every Part of it in a
lively Manner, or our Papers are thrown by as dull and insipid: Our
Matter must lie close together, and either be wholly new in itself, or
in the Turn it receives from our Expressions. Were the Books of our best
Authors thus to be retailed to the Publick, and every Page submitted to
the Taste of forty or fifty thousand Readers, I am afraid we should
complain of many flat Expressions, trivial Observations, beaten Topicks,
and common Thoughts, which go off very well in the Lump. At the same
Time, notwithstanding some Papers may be made up of broken Hints and
irregular Sketches, it is often expected that every Sheet should be a
kind of Treatise, and make out in Thought what it wants in Bulk: That a
Point of Humour should be worked up in all its Parts; and a Subject
touched upon in its most essential Articles, without the Repetitions,
Tautologies and Enlargements, that are indulged to longer Labours. The
ordinary Writers of Morality prescribe to their Readers after the
Galenick way; their Medicines are made up in large Quantities. An
Essay-Writer must practise in the Chymical Method, and give the Virtue
of a full Draught in a few Drops. Were all Books reduced thus to their
Quintessence, many a bulky Author would make his Appearance in a
Penny-Paper: There would be scarce such a thing in Nature as a Folio.
The Works of an Age would be contained on a few Shelves; not to mention
millions of Volumes that would be utterly annihilated.
I cannot think that the Difficulty of furnishing out separate Papers of
this Nature, has hindered Authors from communicating their Thoughts to
the World after such a Manner: Though I must confess I am amazed that
the Press should be only made use of in this Way by News-Writers, and
the Zealots of Parties; as if it were not more advantageous to Mankind,
to be instructed in Wisdom and Virtue, than in Politicks; and to be made
good Fathers, Husbands and Sons, than Counsellors and Statesmen. Had the
Philosophers and great Men of Antiquity, who took so much Pains in order
to instruct Mankind, and leave the World wiser and better than they
found it; had they, I say, been possessed of the Art of Printing, there
is no question but they would have made such an Advantage of it, in
dealing out their Lectures to the Publick. Our common Prints would be of
great Use were they thus calculated to diffuse good Sense through the
Bulk of a People, to clear up their Understandings, animate their Minds
with Virtue, dissipate the Sorrows of a heavy Heart, or unbend the Mind
from its more severe Employments with innocent Amusements.
Knowledge, instead of being bound up in Books and kept in Libraries and
Retirements, is thus obtruded upon the Publick; when it is canvassed in
every Assembly, and exposed upon every Table, I cannot forbear
reflecting upon that Passage in the
Proverbs
:
Wisdom crieth without,
she uttereth her Voice in the Streets: she crieth in the chief Place of
Concourse, in the Openings of the Gates. In the City she uttereth her
Words, saying, How long, ye simple ones, will ye love Simplicity? and
the Scorners delight in their Scorning? and Fools hate Knowledge?1
The many Letters which come to me from Persons of the best Sense in both
Sexes, (for I may pronounce their Characters from their Way of Writing)
do not at a little encourage me in the Prosecution of this my
Undertaking: Besides that my Book-seller tells me, the Demand for these
my Papers increases daily. It is at his Instance that I shall continue
my
rural Speculations
to the End of this Month; several having made up
separate Sets of them, as they have done before of those relating to
Wit, to Operas, to Points of Morality, or Subjects of Humour.
I am not at all mortified, when sometimes I see my
Works
thrown aside by
Men of no Taste nor Learning. There is a kind of Heaviness and Ignorance
that hangs upon the Minds of ordinary Men, which is too thick for
Knowledge to break through. Their Souls are not to be enlightened.
... Nox atra cava circumvolat umbra.
To these I must apply the Fable of the Mole, That after having consulted
many Oculists for the bettering of his Sight, was at last provided with
a good Pair of Spectacles; but upon his endeavouring to make use of
them, his Mother told him very prudently,
'That Spectacles, though they
might help the Eye of a Man, could be of no use to a Mole.'
It is not
therefore for the Benefit of Moles that I publish these my daily Essays.
But besides such as are Moles through Ignorance, there are others who
are Moles through Envy.
it is said in the
Latin
Proverb,
'That
one Man is a Wolf to another
; so generally speaking, one Author is a
Mole to another Author. It is impossible for them to discover Beauties
in one another's Works; they have Eyes only for Spots and Blemishes:
They can indeed see the Light as it is said of the Animals which are
their Namesakes, but the Idea of it is painful to them; they
immediately shut their Eyes upon it, and withdraw themselves into a
wilful Obscurity. I have already caught two or three of these dark
undermining Vermin, and intend to make a String of them, in order to
hang them up in one of my Papers, as an Example to all such voluntary
Moles.
C.
Proverbs
i 20-22.
"Homo homini Lupus." Plautus Asin. Act ii sc. 4.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 24, 1711 |
Addison |
Ne pueri, ne tanta animis assuescite bella:
Neu patriæ validas in viscera vertite vires.
Vir.

My worthy Friend Sir
Roger
, when we are talking of the Malice of
Parties, very frequently tells us an Accident that happened to him when
he was a School-boy, which was at a time when the Feuds ran high between
the Roundheads and Cavaliers. This worthy Knight, being then but a
Stripling, had occasion to enquire which was the Way to St.
Anne's
Lane, upon which the Person whom he spoke to, instead of
answering his Question, call'd him a young Popish Cur, and asked him who
had made
Anne
a Saint? The Boy, being in some Confusion, enquired
of the next he met, which was the Way to
Anne's
Lane; but was call'd a
prick-eared Cur for his Pains, and instead of being shewn the Way, was
told that she had been a Saint before he was born, and would be one
after he was hanged. Upon this, says Sir
Roger
, I did not think fit to
repeat the former Question, but going into every Lane of the
Neighbourhood, asked what they called the Name of that Lane. By which
ingenious Artifice he found out the place he enquired after, without
giving Offence to any Party. Sir
Roger
generally closes this Narrative
with Reflections on the Mischief that Parties do in the Country; how
they spoil good Neighbourhood, and make honest Gentlemen hate one
another; besides that they manifestly tend to the Prejudice of the
Land-Tax, and the Destruction of the Game.
There cannot a greater Judgment befal a Country than such a dreadful
Spirit of Division as rends a Government into two distinct People, and
makes them greater Strangers and more averse to one another, than if
they were actually two different Nations. The Effects of such a Division
are pernicious to the last degree, not only with regard to those
Advantages which they give the Common Enemy, but to those private Evils
which they produce in the Heart of almost every particular Person. This
Influence is very fatal both to Mens Morals and their Understandings; it
sinks the Virtue of a Nation, and not only so, but destroys even Common
Sense.
A furious Party Spirit, when it rages in its full Violence, exerts it
self in Civil War and Bloodshed; and when it is under its greatest
Restraints naturally breaks out in Falshood, Detraction, Calumny, and a
partial Administration of Justice. In a Word, it fills a Nation with
Spleen and Rancour, and extinguishes all the Seeds of Good-Nature,
Compassion and Humanity.
Plutarch
very finely, that a Man should not allow himself to hate
even his Enemies, because, says he, if you indulge this Passion in some
Occasions, it will rise of it self in others; if you hate your Enemies,
you will contract such a vicious Habit of Mind, as by degrees will break
out upon those who are your Friends, or those who are indifferent to
you
. I
here observe how admirably this Precept of Morality
(which derives the Malignity of Hatred from the Passion it self, and not
from its Object) answers to that great Rule which was dictated to the
World about an hundred Years before this Philosopher wrote
; but
instead of that, I shall only take notice, with a real Grief of Heart,
that the Minds of many good Men among us appear sowered with
Party-Principles, and alienated from one another in such a manner, as
seems to me altogether inconsistent with the Dictates either of Reason
or Religion. Zeal for a Publick Cause is apt to breed Passions in the
Hearts of virtuous Persons, to which the Regard of their own private
Interest would never have betrayed them.
If this Party-Spirit has so ill an Effect on our Morals, it has likewise
a very great one upon our Judgments. We often hear a poor insipid Paper
or Pamphlet cried up, and sometimes a noble Piece depreciated, by those
who are of a different Principle from the Author. One who is actuated by
this Spirit is almost under an Incapacity of discerning either real
Blemishes or Beauties. A Man of Merit in a different Principle,
is
like an Object seen in two different Mediums,
that
appears crooked or
broken, however streight and entire it may be in it self.
this
Reason there is scarce a Person of any Figure in
England
, who does not
go by two
contrary Characters,
as opposite to one another as Light
and Darkness.
and Learning suffer in
a
particular manner
from this strange Prejudice, which at present prevails amongst all Ranks
and Degrees in the
British
Nation. As Men formerly became eminent in
learned Societies by their Parts and Acquisitions, they now distinguish
themselves by the Warmth and Violence with which they espouse their
respective Parties. Books are valued upon the like Considerations: An
Abusive Scurrilous Style passes for Satyr, and a dull Scheme of Party
Notions is called fine Writing.
There is one Piece of Sophistry practised by both Sides, and that is the
taking any scandalous Story that has been ever whispered or invented of
a Private Man, for a known undoubted Truth, and raising suitable
Speculations upon it. Calumnies that have been never proved, or have
been often refuted, are the ordinary Postulatums of these infamous
Scriblers, upon which they proceed as upon first Principles granted by
all Men, though in their Hearts they know they are false, or at best
very doubtful. When they have laid these Foundations of Scurrility, it
is no wonder that their Superstructure is every way answerable to them.
If this shameless Practice of the present Age endures much longer,
Praise and Reproach will cease to be Motives of Action in good Men.
There are certain Periods of Time in all Governments when this inhuman
Spirit prevails.
Italy
was long torn in Pieces by the
Guelfes
and
Gibellines
, and
France
by those who were for and against the League:
But it is very unhappy for a Man to be born in such a stormy and
tempestuous Season.
is the restless Ambition of artful Men that thus
breaks a People into Factions, and draws several well-meaning
Persons
to their Interest by a Specious Concern for their Country.
How many honest Minds are filled with uncharitable and barbarous
Notions, out of their Zeal for the Publick Good? What Cruelties and
Outrages would they not commit against Men of an adverse Party, whom
they would honour and esteem, if instead of considering them as they are
represented, they knew them as they are? Thus are Persons of the
greatest Probity seduced into shameful Errors and Prejudices, and made
bad Men even by that noblest of Principles, the Love of their Country. I
cannot here forbear mentioning the famous
Spanish
Proverb,
If there
were neither Fools nor Knaves in the World, all People would be of one
Mind
.
For my own part, I could heartily wish that all honest Men would enter
into an Association, for the Support of one another against the
Endeavours of those whom they ought to look upon as their Common
Enemies, whatsoever Side they may belong to.
there such an honest
Body of Neutral
Forces, we should never see the worst of Men in
great Figures of Life, because they are useful to a Party; nor the best
unregarded, because they are above practising those Methods which would
be grateful to their Faction. We should then single every Criminal out
of the Herd, and hunt him down, however formidable and overgrown he
might appear: On the contrary, we should shelter distressed Innocence,
and defend Virtue, however beset with Contempt or Ridicule, Envy or
Defamation. In short, we should not any longer regard our Fellow
Subjects as Whigs or Tories, but should make the Man of Merit our
Friend, and the Villain our Enemy.
C.
Among his
Moral Essays
is that showing
How one shall be
helped by Enemies.
In his
Lives
, also, Plutarch applauds in Pericles
the noble sentiment which led him to think it his most excellent
attainment never to have given way to envy or anger, notwithstanding the
greatness of his power, nor to have nourished an implacable hatred
against his greatest foe. This, he says, was his only real title to the
name of Olympius.
Luke
vi. 27-32.
Characters altogether different
a very
People
Neutral Body of
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 25, 1711 |
Addison |
Tros Rutulusve fuat, nullo discrimine habebo.
Virg.

In my Yesterday's Paper I proposed, that the honest Men of all Parties
should enter into a kind of Association for the Defence of one another,
and
the
Confusion of their common Enemies. As it is designed this
neutral Body should act with a Regard to nothing but Truth and Equity,
and divest themselves of the little Heats and Prepossessions that cleave
to Parties of all Kinds, I have prepared for them the following Form of
an Association, which may express their Intentions in the most plain and
simple Manner.
We whose Names are hereunto subscribed do solemnly declare,
That we do in our Consciences believe two and two make four;
and that we shall adjudge any Man whatsoever to be our Enemy
who endeavours to persuade us to the contrary. We are likewise
ready to maintain, with the Hazard of all that is near and dear
to us, That six is less than seven in all Times and all Places,
and that ten will not be more three Years hence than it is at
present. We do also firmly declare, That it is our Resolution as
long as we live to call Black black, and White white. And we
shall upon all Occasions oppose such Persons that upon any Day
of the Year shall call Black white, or White black, with the utmost
Peril of our Lives and Fortunes.
Were there such a Combination of honest Men, who without any Regard to
Places would endeavour to extirpate all such furious Zealots as would
sacrifice one half of their Country to the Passion and Interest of the
other; as also such infamous Hypocrites, that are for promoting their
own Advantage, under Colour of the Publick Good; with all the profligate
immoral Retainers to each Side, that have nothing to recommend them but
an implicit Submission to their Leaders; we should soon see that furious
Party-Spirit extinguished, which may in time expose us to the Derision
and Contempt of all the Nations about us.
A Member of this Society, that would thus carefully employ himself in
making Room for Merit, by throwing down the worthless and depraved Part
of Mankind from those conspicuous Stations of Life to which they have
been sometimes advanced, and all this without any Regard to his private
Interest, would be no small Benefactor to his Country.
remember to have read in
Diodorus Siculus
an Account of a
very active little Animal, which I think he calls the
Ichneumon
,
that makes it the whole Business of his Life to break the Eggs of the
Crocodile, which he is always in search after. This instinct is the more
remarkable, because the
Ichneumon
never feeds upon the Eggs he
has broken, nor in any other Way finds his Account in them. Were it not
for the incessant Labours of this industrious Animal,
Ægypt
, says
the Historian, would be over-run with Crocodiles: for the
Ægyptians
are so far from destroying those pernicious Creatures,
that they worship them as Gods.
If we look into the Behaviour of ordinary Partizans, we shall find them
far from resembling this disinterested Animal; and rather acting after
the Example of the wild
Tartars
, who are ambitious of destroying
a Man of the most extraordinary Parts and Accomplishments, as thinking
that upon his Decease the same Talents, whatever Post they qualified him
for, enter of course into his Destroyer.
As in the whole Train of my Speculations, I have endeavoured as much as
I am able to extinguish that pernicious Spirit of Passion and Prejudice,
which rages with the same Violence in all Parties, I am still the more
desirous of doing some Good in this Particular, because I observe that
the Spirit of Party reigns more in the Country than in the Town. It here
contracts a kind of Brutality and rustick Fierceness, to which Men of a
politer Conversation are wholly Strangers. It extends it self even to
the Return of the Bow and the Hat; and at the same time that the Heads
of Parties preserve toward one another an outward Shew of Good-breeding,
and keep up a perpetual Intercourse of Civilities, their Tools that are
dispersed in these outlying Parts will not so much as mingle together at
a Cockmatch. This Humour fills the Country with several periodical
Meetings of Whig Jockies and Tory Fox-hunters; not to mention the
innumerable Curses, Frowns, and Whispers it produces at a
Quarter-Sessions.
I do not know whether I have observed in any of my former Papers, that
my Friends Sir
Roger De Coverley
and Sir
Andrew Freeport
are of
different Principles, the first of them inclined to the
landed
and the other to the
monyed
Interest. This Humour is so moderate
in each of them, that it proceeds no farther than to an agreeable
Raillery, which very often diverts the rest of the Club. I find however
that the Knight is a much stronger Tory in the Country than in Town,
which, as he has told me in my Ear, is absolutely necessary for the
keeping up his Interest. In all our Journey from
London
to his House
we did not so much as bait at a Whig Inn; or if by chance the Coachman
stopped at a wrong Place, one of Sir
Roger's
Servants would ride up to
his Master full speed, and whisper to him that the Master of the House
was against such an one in the last Election. This often betray'd us
into hard Beds and bad Chear; for we were not so inquisitive about the
Inn as the Inn-keeper; and, provided our Landlord's Principles were
sound, did not take any Notice of the Staleness of his Provisions. This
I found still the more inconvenient, because the better the Host was,
the worse generally were his Accommodations; the Fellow knowing very
well, that those who were his Friends would take up with coarse Diet and
an hard Lodging. For these Reasons, all the while I was upon the Road I
dreaded entering into an House of any one that Sir Roger had applauded
for an honest Man.
Since my Stay at Sir
Roger's
in the Country, I daily find more Instances
of this narrow Party-Humour. Being upon a Bowling-green at a
Neighbouring Market-Town the other Day, (for that is the Place where the
Gentlemen of one Side meet once a Week) I observed a Stranger among them
of a better Presence and genteeler Behaviour than ordinary; but was much
surprised, that notwithstanding he was a very fair
Bettor
, no
Body would take him up. But upon Enquiry I found, that he was one who
had given a disagreeable Vote in a former Parliament, for which Reason
there was not a Man upon that Bowling-green who would have so much
Correspondence with him as to Win his Money of him.
other Instances of this Nature, I must not omit one which
concerns
my self.
Will. Wimble
the other Day relating
several strange Stories that he had picked up no Body knows where of a
certain great Man; and upon my staring at him, as one that was surprised
to hear such things in the Country
which
had never been so much as
whispered in the Town,
Will
. stopped short in the Thread of his
Discourse, and after Dinner asked my Friend Sir
Roger
in his Ear
if he was sure that I was not a Fanatick.
It gives me a serious Concern to see such a Spirit of Dissention in the
Country; not only as it destroys Virtue and Common Sense, and renders us
in a Manner Barbarians towards one another, but as it perpetuates our
Animosities, widens our Breaches, and transmits our present Passions and
Prejudices to our Posterity. For my own Part, I am sometimes afraid that
I discover the Seeds of a Civil War in these our Divisions; and
therefore cannot but bewail, as in their first Principles, the Miseries
and Calamities of our Children.
C.
Bibliothecæ Historicæ
, Lib. i. § 87.
concerns to
that
Contents
|
Thursday, July 26, 1711 |
Addison |
Quantum est in rebus Inane?
Pers.

It is our Custom at Sir
Roger's
, upon the coming in of the Post, to sit
about a Pot of Coffee, and hear the old Knight read
Dyer's
Letter; which he does with his Spectacles upon his Nose, and in an
audible Voice, smiling very often at those little Strokes of Satyr which
are so frequent in the Writings of that Author. I afterwards communicate
to the Knight such Packets as I receive under the Quality of
Spectator
.
The following Letter chancing to please him more than ordinary, I shall
publish it at his Request.
Mr.
Spectator,
'You have diverted the Town almost a whole Month at the Expence of the
Country, it is now high time that you should give the Country their
Revenge. Since your withdrawing from this Place, the Fair Sex are run
into great Extravagancies. Their Petticoats, which began to heave and
swell before you left us, are now blown up into a most enormous
Concave, and rise every Day more and more: In short, Sir, since our
Women know themselves to be out of the Eye of the
Spectator, they will
be kept within no Compass. You praised them a little too soon, for the
Modesty of their Head-Dresses; for as the Humour of a sick Person is
often driven out of one Limb into another, their Superfluity of
Ornaments, instead of being entirely Banished, seems only fallen from
their Heads upon their lower Parts. What they have lost in Height they
make up in Breadth, and contrary to all Rules of Architecture widen
the Foundations at the same time that they shorten the Superstructure.
Were they, like
Spanish Jennets, to impregnate by the Wind, they
could not have thought on a more proper Invention. But as we do not
yet hear any particular Use in this Petticoat, or that it contains any
thing more than what was supposed to be in those of Scantier Make, we
are wonderfully at a loss about it.
The Women give out, in Defence of these wide Bottoms, that they are
Airy, and very proper for the Season; but this I look upon to be only
a Pretence, and a piece of Art, for it is well known we have not had a
more moderate Summer these many Years, so that it is certain the Heat
they complain of cannot be in the Weather: Besides, I would fain ask
these tender constitutioned Ladies, why they should require more
Cooling than their Mothers before them.
I find several Speculative Persons are of Opinion that our Sex has of
late Years been very sawcy, and that the Hoop Petticoat is made use of
to keep us at a Distance. It is most certain that a Woman's Honour
cannot be better entrenched than after this manner, in Circle within
Circle, amidst such a Variety of Out-works and Lines of
Circumvallation.
A Female who is thus invested in Whale-Bone is
sufficiently secured against the Approaches of an ill-bred Fellow, who
might as well think of Sir
George Etherege's way of making Love
in a Tub
1, as in the midst of so many Hoops.
Among these various Conjectures, there are Men of Superstitious
tempers, who look upon the Hoop Petticoat as a kind of Prodigy. Some
will have it that it portends the Downfal of the
French King,
and observe that the Farthingale appeared in
England a little
before the Ruin of the
Spanish Monarchy. Others are of Opinion
that it foretels Battle and Bloodshed, and believe it of the same
Prognostication as the Tail of a Blazing Star. For my part, I am apt
to think it is a Sign that Multitudes are coming into the World rather
than going out of it.
The first time I saw a Lady dressed in one of these Petticoats, I
could not forbear blaming her in my own Thoughts for walking abroad
when she was
so near her Time, but soon recovered myself out of
my Error, when I found all the Modish Part of the Sex as
far
gone as her self. It is generally thought some crafty Women have
thus betrayed their Companions into Hoops, that they might make them
accessory to their own Concealments, and by that means escape the
Censure of the World; as wary Generals have sometimes dressed two or
three Dozen of their Friends in their own Habit, that they might not
draw upon themselves any particular Attacks of the Enemy. The
strutting Petticoat smooths all Distinctions, levels the Mother with
the Daughter, and sets Maids and Matrons, Wives and Widows, upon the
same Bottom. In the mean while I cannot but be troubled to see so many
well-shaped innocent Virgins bloated up, and waddling up and down like
big-bellied Women.
Should this Fashion get among the ordinary People our publick Ways
would be so crowded that we should want Street-room. Several
Congregations of the best Fashion find themselves already very much
streightened, and if the Mode encrease I wish it may not drive many
ordinary Women into Meetings and Conventicles. Should our Sex at the
same time take it into their Heads to wear Trunk Breeches (as who
knows what their Indignation at this Female Treatment may drive them
to) a Man and his Wife would fill a whole Pew.
You know, Sir, it is recorded of Alexander the Great
2, that in his
Indian Expedition he buried several Suits of Armour, which by his
Direction were made much too big for any of his Soldiers, in order to
give Posterity an extraordinary Idea of him, and make them believe he
had commanded an Army of Giants. I am persuaded that if one of the
present Petticoats happen to be hung up in any Repository of
Curiosities, it will lead into the same Error the Generations that lie
some Removes from us: unless we can believe our Posterity will think
so disrespectfully of their Great Grand-Mothers, that they made
themselves Monstrous to appear Amiable.
When I survey this new-fashioned
Rotonda in all its Parts, I cannot
but think of the old Philosopher, who after having entered into an
Egyptian Temple, and looked about for the Idol of the Place, at
length discovered a little Black Monkey Enshrined in the midst of it,
upon which he could not forbear crying out, (to the great Scandal of
the Worshippers) What a magnificent Palace is here for such a
Ridiculous Inhabitant!
Though you have taken a Resolution, in one of your Papers, to avoid
descending to Particularities of Dress, I believe you will not think
it below you, on so extraordinary an Occasion, to Unhoop the Fair Sex,
and cure this fashionable Tympany that is got among them. I am apt to
think the Petticoat will shrink of its own accord at your first coming
to Town; at least a Touch of your Pen will make it contract it self,
like the sensitive Plant, and by that means oblige several who are
either terrified or astonished at this portentous Novelty, and among
the rest,
Your humble Servant, &c.
C.
Love in a Tub
, Act iv, sc, 6.
In Plutarch's
Life
of him.
Contents
|
Friday, July 27, 1711 |
Addison |
... Concordia discors.
Lucan.

Women in their Nature are much more gay and joyous than Men; whether it
be that their Blood is more refined, their Fibres more delicate, and
their animal Spirits more light and volatile; or whether, as some have
imagined, there may not be a kind of Sex in the very Soul, I shall not
pretend to determine. As Vivacity is the Gift of Women, Gravity is that
of Men. They should each of them therefore keep a Watch upon the
particular Biass which Nature has fixed in their Mind, that it may not
draw
too much, and lead them out of the Paths of Reason. This will
certainly happen, if the one in every Word and Action affects the
Character of being rigid and severe, and the other of being brisk and
airy. Men should beware of being captivated by a kind of savage
Philosophy, Women by a thoughtless Gallantry. Where these Precautions
are not observed, the Man often degenerates into a Cynick, the Woman
into a Coquet; the Man grows sullen and morose, the Woman impertinent
and fantastical.
By what I have said, we may conclude, Men and Women were made as
Counterparts to one another, that the Pains and Anxieties of the Husband
might be relieved by the Sprightliness and good Humour of the Wife. When
these are rightly tempered, Care and Chearfulness go Hand in Hand; and
the Family, like a Ship that is duly trimmed, wants neither Sail nor
Ballast.
Natural Historians observe, (for whilst I am in the Country I must fetch
my Allusions from thence) That only the Male Birds have Voices; That
their Songs begin a little before Breeding-time, and end a little after;
That whilst the Hen is covering her Eggs, the Male generally takes his
Stand upon a Neighbouring Bough within her Hearing; and by that means
amuses and diverts her with his Songs during the whole Time of her
Sitting.
This Contract among Birds lasts no longer than till a Brood of young
ones arises from it; so that in the feather'd Kind, the Cares and
Fatigues of the married State, if I may so call it, lie principally upon
the Female. On the contrary, as in our Species the Man and
the
Woman
are joined together for Life, and the main Burden rests upon the former,
Nature has given all the little Arts of Soothing and Blandishment to the
Female, that she may chear and animate her Companion in a constant and
assiduous Application to the making a Provision for his Family, and the
educating of their common Children. This however is not to be taken so
strictly, as if the same Duties were not often reciprocal, and incumbent
on both Parties; but only to set forth what seems to have been the
general Intention of Nature, in the different Inclinations and
Endowments which are bestowed on the different Sexes.
But whatever was the Reason that Man and Woman were made with this
Variety of Temper, if we observe the Conduct of the Fair Sex, we find
that they choose rather to associate themselves with a Person who
resembles them in that light and volatile Humour which is natural to
them, than to such as are qualified to moderate and counter-ballance it.
It has been an old Complaint, That the Coxcomb carries it with them
before the Man of Sense. When we see a Fellow loud and talkative, full
of insipid Life and Laughter, we may venture to pronounce him a female
Favourite: Noise and Flutter are such Accomplishments as they cannot
withstand. To be short, the Passion of an ordinary Woman for a Man is
nothing else but Self-love diverted upon another Object: She would have
the Lover a Woman in every thing but the Sex. I do not know a finer
Piece of Satyr on this Part of Womankind, than those lines of
Mr.
Dryden
,
Our thoughtless Sex is caught by outward Form,
And empty Noise, and loves it self in Man.
This is a Source of infinite Calamities to the Sex, as it frequently
joins them to Men, who in their own Thoughts are as fine Creatures as
themselves; or if they chance to be good-humoured, serve only to
dissipate their Fortunes, inflame their Follies, and aggravate their
Indiscretions.
The same female Levity is no less fatal to them after Mariage than
before: It represents to their Imaginations the faithful prudent Husband
as an honest tractable
and
domestick Animal; and turns their Thoughts
upon the fine gay Gentleman that laughs, sings, and dresses so much more
agreeably.
As this irregular Vivacity of Temper leads astray the Hearts of ordinary
Women in the Choice of their Lovers and the Treatment of their Husbands,
it operates with the same pernicious Influence towards their Children,
who are taught to accomplish themselves in all those sublime Perfections
that appear captivating in the Eye of their Mother. She admires in her
Son what she loved in her Gallant; and by that means contributes all she
can to perpetuate herself in a worthless Progeny.
The younger
Faustina
was a lively Instance of this sort of Women.
Notwithstanding she was married to
Marcus Aurelius
, one of the
greatest, wisest, and best of the
Roman
Emperors, she thought a
common Gladiator much the prettier Gentleman; and had taken such Care to
accomplish her Son
Commodus
according to her own Notions of a
fine Man, that when he ascended the Throne of his Father, he became the
most foolish and abandoned Tyrant that was ever placed at the Head of
the
Roman
Empire, signalizing himself in nothing but the fighting
of Prizes, and knocking out Men's Brains.
he had no Taste of true
Glory, we see him in several Medals and Statues
which
are still
extant of him, equipped like an
Hercules
with a Club and a Lion's
Skin.
I have been led into this Speculation by the Characters I have heard of
a Country Gentleman and his Lady, who do not live many Miles from Sir
Roger
. The Wife is an old Coquet, that is always hankering after the
Diversions of the Town; the Husband a morose Rustick, that frowns and
frets at the Name of it. The Wife is overrun with Affectation, the
Husband sunk into Brutality: The Lady cannot bear the Noise of the Larks
and Nightingales, hates your tedious Summer Days, and is sick at the
Sight of shady Woods and purling Streams; the Husband wonders how any
one can be pleased with the Fooleries of Plays and Operas, and rails
from Morning to Night at essenced Fops and tawdry Courtiers. The
Children are educated in these different Notions of their Parents. The
Sons follow the Father about his Grounds, while the Daughters read
Volumes of Love-Letters and Romances to their Mother. By this means it
comes to pass, that the Girls look upon their Father as a Clown, and the
Boys think their Mother no better than she should be.
How different are the Lives of
Aristus
and
Aspasia
? the
innocent Vivacity of the one is tempered and composed by the chearful
Gravity of the other. The Wife grows wise by the Discourses of the
Husband, and the Husband good-humour'd by the Conversations of the Wife.
Aristus
would
be so amiable were it not for his
Aspasia
, nor
Aspasia
so much
esteemed
were it not
for her
Aristus
. Their Virtues are blended in their Children, and
diffuse through the whole Family a perpetual Spirit of Benevolence,
Complacency, and Satisfaction.
C.
that
to be esteemed
Contents
|
Saturday, July 28, 1711 |
Addison |
Vertentem sese frustra sectabere canthum,
Cum rota posterior curras et in axe secundo.
Pers.

Great Masters in Painting never care for drawing People in the Fashion;
as very well knowing that the Headdress, or Periwig, that now prevails,
and gives a Grace to their Portraitures at present, will make a very odd
Figure, and perhaps look monstrous in the Eyes of Posterity. For this
Reason they often represent an illustrious Person in a
Roman
Habit, or in some other Dress that never varies. I could wish, for the
sake of my Country Friends, that there was such a kind of
everlasting
Drapery
to be made use of by all who live at a certain distance from
the Town, and that they would agree upon such Fashions as should never
be liable to Changes and Innovations.
want of this
standing
Dress
, a Man
who
takes a Journey into the Country is as much
surprised, as one
who
walks in a Gallery of old Family Pictures;
and finds as great a Variety of Garbs and Habits in the Persons he
converses with. Did they keep to one constant Dress they would sometimes
be in the Fashion, which they never are as Matters are managed at
present. If instead of running after the Mode, they would continue fixed
in one certain Habit, the Mode would some time or other overtake them,
as a Clock that stands still is sure to point right once in twelve
Hours: In this Case therefore I would advise them, as a Gentleman did
his Friend who was hunting about the whole Town after a rambling Fellow,
If you follow him you will never find him, but if you plant your self at
the Corner of any one Street, I'll engage it will not be long before you
see him.
I have already touched upon this Subject in a Speculation
which
shews how cruelly the Country are led astray in following the Town; and
equipped in a ridiculous Habit, when they fancy themselves in the Height
of the Mode. Since that Speculation I have received a Letter (which I
there hinted at) from a Gentleman who is now in the Western Circuit.
Mr.
Spectator,
'
Being a Lawyer of the
Middle-Temple,
a2 Cornishman
by Birth, I generally ride the Western Circuit for my health, and as I
am not interrupted with Clients, have leisure to make many
Observations that escape the Notice of my Fellow-Travellers.
One of the most fashionable Women I met with in all the Circuit was my
Landlady at
Stains, where I chanced to be on a Holiday. Her
Commode was not half a Foot high, and her Petticoat within some Yards
of a modish Circumference.
In the same Place I observed a young Fellow
with a tolerable Periwig, had it not been covered with a Hat that was
shaped in the
Ramillie Cock
3. As I proceeded in my Journey
I observed the Petticoat grew scantier and scantier, and about
threescore Miles from
London was so very unfashionable, that a
Woman might walk in it without any manner of Inconvenience.
Not far from
Salisbury I took notice of a Justice of Peace's
Lady
who4 was at least ten Years behindhand in her Dress, but at
the same time as fine as Hands could make her. She was flounced and
furbelowed from Head to Foot; every Ribbon was wrinkled, and every
Part of her Garments in Curl, so that she looked like one of those
Animals which in the Country we call a
Friezeland Hen.
Not many Miles beyond this Place I was informed that one of the last
Year's little Muffs had by some means or other straggled into those
Parts, and that all Women of Fashion were cutting their old Muffs in
two, or retrenching them, according to the little Model
which5
was got among them. I cannot believe the Report they have there, that
it was sent down frank'd by a Parliament-man in a little Packet; but
probably by next Winter this Fashion will be at the Height in the
Country, when it is quite out at
London.
The greatest Beau at our next Country Sessions was dressed in a most
monstrous Flaxen Periwig, that was made in King
William's Reign. The
Wearer of it goes, it seems, in his own Hair, when he is at home, and
lets his Wig lie in Buckle for a whole half Year, that he may put it
on upon Occasions to meet the Judges in it.
I must not here omit an Adventure
which5 happened to us in a
Country Church upon the Frontiers of
Cornwall. As we were in the
midst of the Service, a Lady who is the chief Woman of the Place, and
had passed the Winter at
London with her Husband, entered the
Congregation in a little Headdress, and a hoop'd Petticoat. The
People, who were wonderfully startled at such a Sight, all of them
rose up. Some stared at the prodigious Bottom, and some at the little
Top of this strange Dress.
In the mean time the Lady of the Manor
filled the
area6 of the Church, and walked up to her Pew with
an unspeakable Satisfaction, amidst the Whispers, Conjectures, and
Astonishments of the whole Congregation.
Upon our Way from hence we saw a young Fellow riding towards us full
Gallop, with a Bob Wig and a black Silken Bag tied to it. He stopt
short at the Coach, to ask us how far the Judges were behind us.
His
Stay was so very short, that we had only time to observe his new silk
Waistcoat,
which7 was unbutton'd in several Places to let us see
that he had a clean Shirt on, which was ruffled down to his middle.
From this Place, during our Progress through the most Western Parts of
the Kingdom, we fancied ourselves in King
Charles the Second's
Reign, the People having made very little Variations in their Dress
since that time.
The smartest of the Country Squires appear still in
the
Monmouth-Cock
8 and when they go a wooing (whether they have
any Post in the Militia or not) they generally put on a red Coat. We
were, indeed, very much surprized, at the Place we lay at last Night,
to meet with a Gentleman that had accoutered himself in a Night-Cap
Wig, a Coat with long Pockets, and slit Sleeves, and a pair of Shoes
with high Scollop Tops; but we soon found by his Conversation that he
was a Person who laughed at the Ignorance and Rusticity of the Country
People, and was resolved to live and die in the Mode.
Sir, If you think this Account of my Travels may be of any Advantage
to the Publick, I will next Year trouble you with such Occurrences as
I shall meet with in other Parts of
England. For I am informed there
are greater Curiosities in the Northern Circuit than in the Western;
and that a Fashion makes its Progress much slower into
Cumberland
than into
Cornwall. I
have heard in particular, that the
Steenkirk
9 arrived but two Months ago at
Newcastle, and that there
are several Commodes in those Parts which are worth taking a Journey
thither to see.
C.
that
and a
Fashion of 1706
that
that
whole Area
that
Of 1685.
Fashion of 1692-3.
Contents
|
Monday, July 30, 1711 |
Addison |
... Semperque recentes
Convectare juvat prædas, et vivere rapto.
Virg.

As I was Yesterday riding out in the Fields with my Friend Sir
Roger
, we
saw at a little Distance from us a Troop of Gypsies. Upon the first
Discovery of them, my Friend was in some doubt whether he should not
exert the Justice of the Peace upon such a Band of Lawless Vagrants; but
not having his Clerk with him, who is a necessary Counsellor on these
Occasions, and fearing that his Poultry might fare the worse for it, he
let the Thought drop: But at the same time gave me a particular Account
of the Mischiefs they do in the Country, in stealing People's Goods and
spoiling their Servants.
If a stray Piece of Linnen hangs upon an Hedge,
says Sir
Roger, they are sure to have it; if the Hog loses his Way in
the Fields, it is ten to one but he becomes their Prey; our Geese cannot
live in Peace for them; if a Man prosecutes them with Severity, his
Hen-roost is sure to pay for it: They generally straggle into these
Parts about this Time of the Year; and set the Heads of our
Servant-Maids so agog for Husbands, that we do not expect to have any
Business done as it should be whilst they are in the Country.
I have an
honest Dairy-maid
who1 crosses their Hands with a Piece of Silver
every Summer, and never fails being promised the handsomest young Fellow
in the Parish for her pains. Your Friend the Butler has been Fool enough
to be seduced by them; and, though he is sure to lose a Knife, a Fork,
or a Spoon every time his Fortune is told him, generally shuts himself
up in the Pantry with an old Gypsie for above half an Hour once in a
Twelvemonth. Sweet-hearts are the things they live upon, which they
bestow very plentifully upon all those that apply themselves to them.
You see now and then some handsome young Jades among them: The Sluts
have very often white Teeth and black Eyes.
Sir
Roger
observing that I listned with great Attention to his Account
of a People who were so entirely new to me, told me, That if I would
they should tell us our Fortunes. As I was very well pleased with the
Knight's Proposal, we rid up and communicated our Hands to them. A
Cassandra
of the Crew, after having examined my Lines very diligently,
told me, That I loved a pretty Maid in a Corner, that I was a good
Woman's Man, with some other Particulars which I do not think proper to
relate.
Friend Sir
Roger
alighted from his Horse, and exposing his
Palm to two or three that stood by him, they crumpled it into all
Shapes, and diligently scanned every Wrinkle that could be made in it;
when one of them,
who
was older and more Sun-burnt than the rest,
told him, That he had a Widow in his Line of Life: Upon which the Knight
cried, Go, go, you are an idle Baggage; and at the same time smiled upon
me. The Gypsie finding he was not displeased in his Heart, told him,
after a farther Enquiry into his Hand, that his True-love was constant,
and that she should dream of him to-night: My old Friend cried Pish, and
bid her go on. The Gypsie told him that he was a Batchelour, but would
not be so long; and that he was dearer to some Body than he thought: The
Knight still repeated, She was an idle Baggage, and bid her go on. Ah
Master, says the Gypsie, that roguish Leer of yours makes a pretty
Woman's Heart ake; you ha'n't that Simper about the Mouth for
Nothing — The uncouth Gibberish with which all this was uttered like the
Darkness of an Oracle, made us the more attentive to it. To be short,
the Knight left the Money with her that he had crossed her Hand with,
and got up again on his Horse.
As we were riding away, Sir
Roger
told me, that he knew several sensible
People who believed these Gypsies now and then foretold very strange
things; and for half an Hour together appeared more jocund than
ordinary. In the Height of his good-Humour, meeting a common Beggar upon
the Road who was no Conjurer, as he went to relieve him he found his
Pocket was picked: That being a Kind of Palmistry at which this Race of
Vermin are very dextrous.
might here entertain my Reader with Historical Remarks on this idle
profligate People,
who
infest all the Countries of
Europe
, and
live in the midst of Governments in a kind of Commonwealth by
themselves.
instead of entering into Observations of this Nature, I
shall fill the remaining Part of my Paper with a Story
which
is
still fresh in
Holland
, and was printed in one of our Monthly Accounts
about twenty Years ago.
'
As the
Trekschuyt, or Hackney-boat, which
carries Passengers from
Leyden to
Amsterdam, was putting off, a Boy
running along the
side5 of the Canal desired to be taken in; which
the Master of the Boat refused, because the Lad had not quite Money
enough to pay the usual Fare.
An eminent Merchant being pleased with the
Looks of the Boy, and secretly touched with Compassion towards him, paid
the Money for him
6, and ordered him to be taken on board. Upon
talking with him afterwards, he found that he could speak readily in
three or four Languages, and learned upon farther Examination that he
had been stoln away when he was a Child by a Gypsie, and had rambled
ever since with a Gang of those Strollers up and down several Parts of
Europe. It happened that the Merchant, whose Heart seems to have
inclined towards the Boy by a secret kind of Instinct, had himself lost
a Child some Years before. The Parents, after a long Search for him,
gave him for drowned in one of the Canals with which that Country
abounds; and the Mother was so afflicted at the Loss of a fine Boy, who
was her only Son, that she died for Grief of it.
Upon laying together
all Particulars, and examining the several Moles and Marks
by which
the Mother used to describe the Child
when7 he was first missing,
the Boy proved to be the Son of the Merchant whose Heart had so
unaccountably melted at the Sight of him.
The Lad was very well pleased
to find a Father
who8 was so rich, and likely to leave him a good
Estate; the Father on the other hand was not a little delighted to see a
Son return to him, whom he had given for lost, with such a Strength of
Constitution, Sharpness of Understanding, and Skill in Languages.'
Here
the printed Story leaves off; but if I may give credit to Reports, our
Linguist having received such extraordinary Rudiments towards a good
Education, was afterwards trained up in every thing that becomes a
Gentleman; wearing off by little and little all the vicious Habits and
Practises that he had been used to in the Course of his Peregrinations:
, it is said, that he has since been employed in foreign Courts upon
National Business, with great Reputation to himself and Honour to
those
who sent him
, and that he has visited several Countries as a
publick Minister, in which he formerly wander'd as a Gypsie.
C.
that
that
that
that
Sides
About three pence.
by when
that
his Country
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 31, 1711 |
Addison |
... Ipsæ rursum concedite Sylvæ.
Virg.

It is usual for a Man who loves Country Sports to preserve the Game in
his own Grounds, and divert himself upon those that belong to his
Neighbour.
Friend Sir
Roger
generally goes two or three Miles from
his House, and gets into the Frontiers of his Estate, before he beats
about in search of
a
Hare or Partridge, on purpose to spare his
own Fields, where he is always sure of finding Diversion, when the worst
comes to the worst. By this Means the Breed about his House has time to
encrease and multiply, besides that the Sport is the more agreeable
where the Game is the harder to come at, and
where it
does not lie so
thick as to produce any Perplexity or Confusion in the Pursuit. For
these Reasons the Country Gentleman, like the Fox, seldom preys near his
own Home.
In the same manner I have made a Month's Excursion out of the Town,
which is the great Field of Game for Sportsmen of my Species, to try my
Fortune in the Country, where I have started several Subjects, and
hunted them down, with some Pleasure to my self, and I hope to others. I
am here forced to use a great deal of Diligence before I can spring any
thing to my Mind, whereas in Town, whilst I am following one Character,
it is ten to one but I am crossed in my Way by another, and put up such
a Variety of odd Creatures in both Sexes, that they foil the Scent of
one another, and puzzle the Chace. My greatest Difficulty in the Country
is to find Sport, and in Town to chuse it. In the mean time, as I have
given a whole Month's Rest to the Cities of
London
and
Westminster
,
I promise my self abundance of new Game upon my return thither.
It is indeed high time for me to leave the Country, since I find the
whole Neighbourhood begin to grow very inquisitive after my Name and
Character. My Love of Solitude, Taciturnity, and particular way of Life,
having raised a great Curiosity in all these Parts.
The Notions which have been framed of me are various; some look upon me
as very proud,
some as very modest,
and some as very melancholy.
Will. Wimble
, as my Friend the Butler tells me, observing me very much
alone, and extreamly silent when I am in Company, is afraid I have
killed a Man. The Country People seem to suspect me for a Conjurer; and
some of them hearing of the Visit
which
I made to
Moll White
,
will needs have it that Sir
Roger
has brought down a Cunning Man with
him, to cure the old Woman, and free the Country from her Charms. So
that the Character which I go under in part of the Neighbourhood, is
what they here call a
White Witch
.
A Justice of Peace, who lives about five Miles off, and is not of Sir
Roger's
Party, has it seems said twice or thrice at his Table, that he
wishes Sir
Roger
does not harbour a Jesuit in his House, and that he
thinks the Gentlemen of the Country would do very well to make me give
some Account of my self.
On the other side, some of Sir
Roger's
Friends are afraid the old Knight
is impos'd upon by a designing Fellow, and as they have heard that he
converses very promiscuously when he is in Town, do not know but he has
brought down with him some discarded Whig, that is sullen, and says
nothing, because he is out of Place.
is the Variety of Opinions
which
are here entertained of me,
so that I pass among some for a disaffected Person, and among others for
a Popish Priest; among some for a Wizard, and among others for a
Murderer; and all this for no other Reason, that I can imagine, but
because I do not hoot and hollow and make a Noise. It is true my Friend
Sir
Roger
tells them,
That it is my way
, and that I am only a
Philosopher; but
this
will not satisfy them. They think there is
more in me than he discovers, and that I do not hold my Tongue for
nothing.
For these and other Reasons I shall set out for
London
to Morrow,
having found by Experience that the Country is not a Place for a Person
of my Temper, who does not love Jollity, and what they call
Good-Neighbourhood. A Man that is out of Humour when an unexpected Guest
breaks in upon him, and does not care for sacrificing an Afternoon to
every Chance-comer; that will be the Master of his own Time, and the
Pursuer of his own Inclinations makes but a very unsociable Figure in
this kind of Life. I shall therefore retire into the Town, if I may make
use of that Phrase, and get into the Crowd again as fast as I can, in
order to be alone. I can there raise what Speculations I please upon
others without being observed my self, and at the same time enjoy all
the Advantages of Company with all the Privileges of Solitude. In the
mean while, to finish the Month and conclude these my rural
Speculations, I shall here insert a Letter from my Friend
Will.
Honeycomb
, who has not lived a Month for these forty Years out of the
Smoke of
London
, and rallies me after his way upon my Country Life.
Dear Spec,
'I Suppose this Letter will find thee picking of Daisies, or smelling
to a Lock of Hay, or passing away thy time in some innocent Country
Diversion of the like Nature. I have however Orders from the Club to
summon thee up to Town, being all of us cursedly afraid thou wilt not
be able to relish our Company, after thy Conversations with Moll
White and Will. Wimble. Pr'ythee don't send us up any more Stories
of a Cock and a Bull, nor frighten the Town with Spirits and Witches.
Thy Speculations begin to smell confoundedly of Woods and Meadows. If
thou dost not come up quickly, we shall conclude that thou art in
Love with one of Sir Roger's Dairy-maids. Service to the Knight. Sir
Andrew is grown the Cock of the Club since he left us, and if he does
not return quickly will make every Mother's Son of us Commonwealth's
Men.
Dear Spec,
Thine Eternally,
Will. Honeycomb.
C.
an
that
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 1, 1711 |
Steel |
... Qui aut Tempus quid postulet non videt, aut plura loquitur, aut se
ostentat, aut eorum quibuscum est rationem non habet, is ineptus esse
dicitur.
Tull.

Having notified to my good Friend Sir
Roger
that I should set out for
London
the next Day, his Horses were ready at the appointed Hour in
the Evening; and attended by one of his Grooms, I arrived at the
County-Town at twilight, in order to be ready for the Stage-Coach the
Day following. As soon as we arrived at the Inn, the Servant who waited
upon me, inquir'd of the Chamberlain in my Hearing what Company he had
for the Coach?
Fellow answered, Mrs.
Betty Arable
, the great
Fortune, and the Widow her Mother; a recruiting Officer (who took a
Place because they were to go;) young Squire
Quickset
her Cousin
(that her Mother wished her to be married to;)
Ephraim
the Quaker
her Guardian; and a Gentleman that had studied himself dumb from Sir
Roger De Coverley's
. I observed by what he said of my self, that
according to his Office he dealt much in Intelligence; and doubted not
but there was some Foundation for his Reports of the rest of the
Company, as well as for the whimsical Account he gave of me. The next
Morning at Day-break we were all called; and I, who know my own natural
Shyness, and endeavour to be as little liable to be disputed with as
possible, dressed immediately, that I might make no one wait. The first
Preparation for our Setting-out was, that the Captain's Half-Pike was
placed near the Coach-man, and a Drum behind the Coach. In the mean Time
the Drummer, the Captain's Equipage, was very loud, that none of the
Captain's things should be placed so as to be spoiled; upon which his
Cloake-bag was fixed in the Seat of the Coach: And the Captain himself,
according to a frequent, tho' invidious Behaviour of Military Men,
ordered his Man to look sharp, that none but one of the Ladies should
have the Place he had taken fronting to the Coach-box.
We were in some little Time fixed in our Seats, and sat with that
Dislike which People not too good-natured usually conceive of each other
at first Sight. The Coach jumbled us insensibly into some sort of
Familiarity: and we had not moved above two Miles, when the Widow asked
the Captain what Success he had in his Recruiting? The Officer, with a
Frankness he believed very graceful, told her,
'That indeed he had but very little Luck, and had suffered much by
Desertion, therefore should be glad to end his Warfare in the Service
of her or her fair Daughter. In a Word, continued he, I am a Soldier,
and to be plain is my Character: You see me, Madam, young, sound, and
impudent; take me your self, Widow, or give me to her, I will be
wholly at your Disposal. I am a Soldier of Fortune, ha!'
This was followed by a vain Laugh of his own, and a deep Silence of all
the rest of the Company. I had nothing left for it but to fall fast
asleep, which I did with all Speed.
'Come, said he, resolve upon it, we will make a Wedding at the next
Town: We will wake this pleasant Companion who is fallen asleep, to be
the Brideman, and' (giving the Quaker a Clap on the Knee) he
concluded, 'This sly Saint, who, I'll warrant, understands what's what
as well as you or I, Widow, shall give the Bride as Father.'
The Quaker, who happened to be a Man of Smartness, answered,
'Friend, I take it in good Part that thou hast given me the Authority
of a Father over this comely and virtuous Child; and I must assure
thee, that if I have the giving her, I shall not bestow her on thee.
Thy Mirth, Friend, savoureth of Folly: Thou art a Person of a light
Mind; thy Drum is a Type of thee, it soundeth because it is empty.
Verily, it is not from thy Fullness, but thy Emptiness that thou hast
spoken this Day. Friend, Friend, we have hired this Coach in
Partnership with thee, to carry us to the great City; we cannot go any
other Way. This worthy Mother must hear thee if thou wilt needs utter
thy Follies; we cannot help it, Friend, I say: if thou wilt we must
hear thee: But if thou wert a Man of Understanding, thou wouldst not
take Advantage of thy courageous Countenance to abash us Children of
Peace. Thou art, thou sayest, a Soldier; give Quarter to us, who
cannot resist thee.
Why didst thou fleer at our Friend, who feigned
himself asleep? he
said2 nothing: but how dost thou know what he
containeth? If thou speakest improper things in the hearing of this
virtuous young Virgin, consider it is an Outrage against a distressed
Person that cannot get from thee: To speak indiscreetly what we are
obliged to hear, by being hasped up with thee in this publick Vehicle,
is in some Degree assaulting on the high Road.'
Here
Ephraim
paused, and the Captain with an happy and uncommon
Impudence (which can be convicted and support it self at the same time)
cries,
'
Faith, Friend, I thank thee; I should have been a little impertinent
if thou hadst not reprimanded me. Come, thou art, I see, a smoaky old
Fellow, and I'll be very orderly the ensuing Part of the Journey. I
was
going3 to give my self Airs, but, Ladies, I beg Pardon.'
The Captain was so little out of Humour, and our Company was so far from
being sowered by this little Ruffle, that
Ephraim
and he took a
particular Delight in being agreeable to each other for the future; and
assumed their different Provinces in the Conduct of the Company. Our
Reckonings, Apartments, and Accommodation, fell under
Ephraim:
and the Captain looked to all Disputes on the Road, as the good
Behaviour of our Coachman, and the Right we had of taking Place as going
to
London
of all Vehicles coming from thence. The Occurrences we
met with were ordinary, and very little happened which could entertain
by the Relation of them: But when I consider'd the Company we were in, I
took it for no small good Fortune that the whole Journey was not spent
in Impertinences, which to one Part of us might be an Entertainment, to
the other a Suffering.
What therefore
Ephraim
said when we were almost arriv'd at
London
, had to me an Air not only of good Understanding but good
Breeding. Upon the young Lady's expressing her Satisfaction in the
Journey, and declaring how delightful it had been to her,
Ephraim
declared himself as follows:
'There is no ordinary Part of humane Life which expresseth so much a
good Mind, and a right inward Man, as his Behaviour upon meeting with
Strangers, especially such as may seem the most unsuitable Companions
to him: Such a Man, when he falleth in the way with Persons of
Simplicity and Innocence, however knowing he may be in the Ways of
Men, will not vaunt himself thereof; but will the rather hide his
Superiority to them, that he may not be painful unto them.
My good Friend, (continued he, turning to the Officer) thee and I are
to part by and by, and peradventure we may never meet again: But be
advised by a plain Man; Modes and Apparel are but Trifles to the real
Man, therefore do not think such a Man as thy self terrible for thy
Garb, nor such a one as me contemptible for mine.
When two such as thee and I meet, with Affections as we ought to have
towards each other, thou should'st rejoice to see my peaceable
Demeanour, and I should be glad to see thy Strength and Ability to
protect me in it.'
The man who would not fight received the name of Ephraim
from the 9th verse of
Psalm
lxxviii, which says:
'The children of Ephraim, being armed and carrying bows, turned back
in the day of battle.'
sayeth
a going
Contents
|
Thursday, August 2, 1711 |
Steele |
Quis Desiderio sit pudor aut modus
Tam Chari capitis?
Hor.

There is a sort of Delight, which is alternately mixed with Terror and
Sorrow, in the Contemplation of Death. The Soul has its Curiosity more
than ordinarily awakened, when it turns its Thoughts upon the Conduct of
such who have behaved themselves with an Equal, a Resigned, a Chearful,
a Generous or Heroick Temper in that Extremity.
We are affected with these respective Manners of Behaviour, as we
secretly believe the Part of the Dying Person imitable by our selves, or
such as we imagine our selves more particularly capable of.
Men of exalted Minds march before us like Princes, and are, to the
Ordinary Race of Mankind, rather Subjects for their Admiration than
Example. However, there are no Ideas strike more forcibly upon our
Imaginations; than those which are raised from Reflections upon the
Exits of great and excellent Men. Innocent Men who have suffered as
Criminals, tho' they were Benefactors to Human Society, seem to be
Persons of the highest Distinction, among the vastly greater Number of
Human Race, the Dead. When the Iniquity of the Times brought
Socrates
to his Execution, how great and wonderful is it to
behold him, unsupported by any thing but the Testimony of his own
Conscience and Conjectures of Hereafter, receive the Poison with an Air
of Mirth and good Humour, and as if going on an agreeable Journey
bespeak some Deity to make it fortunate.
When
Phocion's
good Actions had met with the like Reward from his
Country, and he was led to Death with many others of his Friends, they
bewailing their Fate, he walking composedly towards the Place of
Execution, how gracefully does he support his Illustrious Character to
the very last Instant. One of the Rabble spitting at him as he passed,
with his usual Authority he called to know if no one was ready to teach
this Fellow how to behave himself. When a Poor-spirited Creature that
died at the same time for his Crimes bemoaned himself unmanfully, he
rebuked him with this Question, Is it no Consolation to such a Man as
thou art to die with
Phocion?
At the Instant when he was to die,
they asked him what commands he had for his Son, he answered, To forget
this Injury of the
Athenians. Niocles
, his Friend, under the same
Sentence, desired he might drink the Potion before him:
Phocion
said, because he never had denied him any thing he would not even this,
the most difficult Request he had ever made.
Instances
were very noble and great, and the Reflections of
those Sublime Spirits had made Death to them what it is really intended
to be by the Author of Nature, a Relief from a various Being ever
subject to Sorrows and Difficulties.
Epaminondas
, the
Theban
General, having received in Fight
a mortal Stab with a Sword, which was left in his Body, lay in that
Posture 'till he had Intelligence that his Troops
had
obtained the
Victory, and then permitted it to be drawn
out
, at which Instant he
expressed himself in this manner,
This is not the end of my Life, my
Fellow-Soldiers; it is now your Epaminondas is born, who dies in
so much Glory.
It were an endless Labour to collect the Accounts with which all Ages
have filled the World of Noble and Heroick Minds that have resigned this
Being, as if the Termination of Life were but an ordinary Occurrence of
it.
This common-place way of Thinking I fell into from an awkward Endeavour
to throw off a real and fresh Affliction, by turning over Books in a
melancholy Mood; but it is not easy to remove Griefs which touch the
Heart, by applying Remedies which only entertain the Imagination. As
therefore this Paper is to consist of any thing which concerns Human
Life, I cannot help letting the present Subject regard what has been the
last Object of my Eyes, tho' an Entertainment of Sorrow.
I went this Evening to visit a Friend, with a design to rally him, upon
a Story I had heard of his intending to steal a Marriage without the
Privity of us his intimate Friends and Acquaintance.
came into his
Apartment with that Intimacy which I have done for very many Years, and
walked directly into his Bed-chamber, where I found my Friend in the
Agonies of Death
. What could I do? The innocent Mirth in my Thoughts
struck upon me like the most flagitious Wickedness: I in vain called
upon him; he was senseless, and too far spent to have the least
Knowledge of my Sorrow, or any Pain in himself. Give me leave then to
transcribe my Soliloquy, as I stood by his Mother, dumb with the weight
of Grief for a Son who was her Honour and her Comfort, and never till
that Hour since his Birth had been an Occasion of a Moment's Sorrow to
her.
'How surprising is this Change! from the Possession of vigorous Life
and Strength, to be reduced in a few Hours to this fatal Extremity!
Those Lips which look so pale and livid, within these few Days gave
Delight to all who heard their Utterance: It was the Business, the
Purpose of his Being, next to Obeying him to whom he is going, to
please and instruct, and that for no other end but to please and
instruct. Kindness was the Motive of his Actions, and with all the
Capacity requisite for making a Figure in a contentious World,
Moderation, Good-Nature, Affability, Temperance and Chastity, were the
Arts of his Excellent Life. There as he lies in helpless Agony, no
Wise Man who knew him so well as I, but would resign all the World can
bestow to be so near the end of such a Life. Why does my Heart so
little obey my Reason as to lament thee, thou excellent Man. ...
Heaven receive him, or restore him ... Thy beloved Mother, thy obliged
Friends, thy helpless Servants, stand around thee without Distinction.
How much wouldst thou, hadst thou thy Senses, say to each of us.
But now that good Heart bursts, and he is at rest — with that Breath
expired a Soul who never indulged a Passion unfit for the Place he is
gone to: Where are now thy Plans of Justice, of Truth, of Honour? Of
what use the Volumes thou hast collated, the Arguments thou hast
invented, the Examples thou hast followed. Poor were the Expectations
of the Studious, the Modest and the Good, if the Reward of their
Labours were only to be expected from Man. No, my Friend, thy intended
Pleadings, thy intended good Offices to thy Friends, thy intended
Services to thy Country, are already performed (as to thy Concern in
them) in his Sight before whom the Past, Present, and Future appear at
one View. While others with thy Talents were tormented with Ambition,
with Vain-glory, with Envy, with Emulation, how well didst thou turn
thy Mind to its own Improvement in things out of the Power of Fortune,
in Probity, in Integrity, in the Practice and Study of Justice; how
silent thy Passage, how private thy Journey, how glorious thy End!
Many have I known more Famous, some more Knowing, not one so
Innocent.'
R.
From Plutarch's
Life of Phocion.
This friend was Stephen, son of Edmund Clay, haberdasher.
Stephen Clay was of the Inner Temple, and called to the bar in 1700.
Contents
|
Friday, August 3, 1711 |
Steele |
... Opiferque per Orbem
Dicor ...
Ovid.

During my Absence in the Country, several Packets have been left for me,
which were not forwarded to me, because I was expected every Day in
Town. The Author of the following Letter, dated from
Tower-Hill
,
having sometimes been entertained with some Learned Gentlemen in Plush
Doublets, who have vended their Wares from a Stage in that Place, has
pleasantly enough addressed Me, as no less a Sage in Morality, than
those are in Physick. To comply with his kind Inclination to make my
Cures famous, I shall give you his Testimonial of my great Abilities at
large in his own Words.
Sir,
'Your saying t'other Day there is something wonderful in the
Narrowness of those Minds which can be pleased, and be barren of
Bounty to those who please them, makes me in pain that I am not a Man
of Power: If I were, you should soon see how much I approve your
Speculations. In the mean time, I beg leave to supply that Inability
with the empty Tribute of an honest Mind, by telling you plainly I
love and thank you for your daily Refreshments. I constantly peruse
your Paper as I smoke my Morning's Pipe, (tho' I can't forbear reading
the Motto before I fill and light) and really it gives a grateful
Relish to every Whif; each Paragraph is freight either with useful or
delightful Notions, and I never fail of being highly diverted or
improved. The Variety of your Subjects surprizes me as much as a Box
of Pictures did formerly, in which there was only one Face, that by
pulling some Pieces of Isinglass over it, was changed into a grave
Senator or a Merry Andrew, a patch'd Lady or a Nun, a Beau or a
Black-a-moor, a Prude or a Coquet, a Country 'Squire or a Conjurer,
with many other different Representations very entertaining (as you
are) tho' still the same at the Bottom. This was a childish Amusement
when I was carried away with outward Appearance, but you make a deeper
Impression, and affect the secret Springs of the Mind; you charm the
Fancy, sooth the Passions, and insensibly lead the Reader to that
Sweetness of Temper that you so well describe; you rouse Generosity
with that Spirit, and inculcate Humanity with that Ease, that he must
be miserably Stupid that is not affected by you. I can't say indeed
that you have put Impertinence to Silence, or Vanity out of
Countenance; but methinks you have bid as fair for it, as any Man that
ever appeared upon a publick Stage; and offer an infallible Cure of
Vice and Folly, for the Price of One Penny. And since it is usual for
those who receive Benefit by such famous Operators, to publish an
Advertisement, that others may reap the same Advantage, I think my
self obliged to declare to all the World, that having for a long time
been splenatick, ill natured, froward, suspicious, and unsociable, by
the Application of your Medicines, taken only with half an Ounce of
right Virginia Tobacco, for six successive Mornings, I am become
open, obliging, officious, frank, and hospitable.
I am, Your Humble Servant, and great Admirer,
George Trusty.
Tower-hill,
July 5, 1711.
This careful Father and humble Petitioner hereafter mentioned, who are
under Difficulties about the just Management of Fans, will soon receive
proper Advertisements relating to the Professors in that behalf, with
their Places of Abode and Methods of Teaching.
July the 5th, 1711.
Sir,
'In your Spectator of June the 7th you Transcribe a Letter sent
to you from a new sort of Muster-master, who teaches Ladies the whole
Exercise of the Fan; I have a Daughter just come to Town, who tho' she
has always held a Fan in her Hand at proper Times, yet she knows no
more how to use it according to true Discipline, than an awkward
School-boy does to make use of his new Sword: I have sent for her on
purpose to learn the Exercise, she being already very well
accomplished in all other Arts which are necessary for a young Lady to
understand; my Request is, that you will speak to your Correspondent
on my behalf, and in your next Paper let me know what he expects,
either by the Month, or the Quarter, for teaching; and where he keeps
his Place of Rendezvous. I have a Son too, whom I would fain have
taught to gallant Fans, and should be glad to know what the Gentleman
will have for teaching them both, I finding Fans for Practice at my
own Expence. This Information will in the highest manner oblige,
Sir, Your most humble Servant,
William Wiseacre.
As soon as my Son is perfect in this Art (which I hope will be in a
Year's time, for the Boy is pretty apt,) I design he shall learn to
ride the great Horse, (altho' he is not yet above twenty Years old) if
his Mother, whose Darling he is, will venture him.
To the Spectator.
The humble Petition of Benjamin Easie, Gent.
Sheweth,
'That it was your Petitioner's Misfortune to walk to Hackney
Church last Sunday, where to his great Amazement he met with a Soldier
of your own training: she furls a Fan, recovers a Fan, and goes
through the whole Exercise of it to Admiration. This well-managed
Officer of yours has, to my Knowledge, been the Ruin of above five
young Gentlemen besides my self, and still goes on laying waste
wheresoever she comes, whereby the whole Village is in great danger.
Our humble Request is therefore that this bold Amazon be ordered
immediately to lay down her Arms, or that you would issue forth an
Order, that we who have been thus injured may meet at the Place of
General Rendezvous, and there be taught to manage our Snuff-Boxes in
such manner as we may be an equal Match for her:
And your Petitioner shall ever Pray, &c.
R.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 4, 1711 |
Addison |
Est brevitate opus, ut currat Sententia ...
Hor.

I have somewhere read of an eminent Person, who used in his private
Offices of Devotion to give Thanks to Heaven that he was born a
Frenchman:
For my own part, I look upon it as a peculiar Blessing
that I was Born an
Englishman
.
many other Reasons, I think
my self very happy in my Country, as the
Language
of it is
wonderfully adapted to a Man
who
is sparing of his Words, and an
Enemy to Loquacity.
As I have frequently reflected on my good Fortune in this Particular, I
shall communicate to the Publick my Speculations upon the,
English
Tongue, not doubting but they will be acceptable to all
my curious Readers.
The
English
delight in Silence more than any other
European
Nation, if the Remarks which are made on us by
Foreigners are true. Our Discourse is not kept up in Conversation, but
falls into more Pauses and Intervals than in our Neighbouring Countries;
as it is observed, that the Matter of our Writings is thrown much closer
together, and lies in a narrower Compass than is usual in the Works of
Foreign Authors: For, to favour our Natural Taciturnity, when we are
obliged to utter our Thoughts, we do it in the shortest way we are able,
and give as quick a Birth to our Conception as possible.
This Humour shows itself in several Remarks that we may make upon the
English
Language. As first of all by its abounding in
Monosyllables, which gives us an Opportunity of delivering our Thoughts
in few Sounds. This indeed takes off from the Elegance of our Tongue,
but at the same time expresses our Ideas in the readiest manner, and
consequently answers the first Design of Speech better than the
Multitude of Syllables, which make the Words of other Languages more
Tunable and Sonorous.
Sounds of our
English
Words are
commonly like those of String Musick, short and transient,
which
rise and perish upon a single Touch; those of other Languages are like
the Notes of Wind Instruments, sweet and swelling, and lengthen'd out
into variety of Modulation.
In the next place we may observe, that where the Words are not
Monosyllables, we often make them so, as much as lies in our Power, by
our Rapidity of Pronounciation; as it generally happens in most of our
long Words which are derived from the
Latin
, where we contract
the length of the Syllables that give them a grave and solemn Air in
their own Language, to make them more proper for Dispatch, and more
conformable to the Genius of our Tongue. This we may find in a multitude
of Words, as
Liberty, Conspiracy, Theatre, Orator
, &c.
The same natural Aversion to Loquacity has of late Years made a very
considerable Alteration in our Language, by closing in one Syllable the
Termination of our Præterperfect Tense, as in the Words,
drown'd,
walk' d, arriv'd
, for
drowned, walked, arrived
, which has
very much disfigured the Tongue, and turned a tenth part of our
smoothest Words into so many Clusters of Consonants. This is the more
remarkable, because the want of Vowels in our Language has been the
general Complaint of our politest Authors, who nevertheless are the Men
that have made these Retrenchments, and consequently very much increased
our former Scarcity.
Reflection on the Words that end in
ed
, I have heard in
Conversation from one of the greatest Genius's this Age has produced
. I think we may add to the foregoing Observation, the Change which
has happened in our Language, by the Abbreviation of several Words that
are terminated in
eth
, by substituting an
s
in the room
of the last Syllable, as in
drowns, walks, arrives
, and
innumerable other Words, which in the Pronunciation of our Forefathers
were
drowneth, walketh, arriveth
. This has wonderfully multiplied
a Letter which was before too frequent in the
English
Tongue, and
added to that
hissing
in our Language, which is taken so much
notice of by Foreigners; but at the same time humours our Taciturnity,
and eases us of many superfluous Syllables.
I might here observe, that the same single Letter on many Occasions does
the Office of a whole Word, and represents the
His
and
Her
of our Forefathers. There is no doubt but the Ear of a Foreigner, which
is the best Judge in this Case, would very much disapprove of such
Innovations, which indeed we do our selves in some measure, by retaining
the old Termination in Writing, and in all the solemn Offices of our
Religion.
As in the Instances I have given we have epitomized many of our
particular Words to the Detriment of our Tongue, so on other Occasions
we have drawn two Words into one, which has likewise very much untuned
our Language, and clogged it with Consonants, as
mayn't, can't,
shd'n't, wo'n't
, and the like, for
may not, can not, shall not,
will not
, &c.
It is perhaps this Humour of speaking no more than we needs must, which
has so miserably curtailed some of our Words, that in familiar Writings
and Conversations they often lose all but their first Syllables, as in
mob.
rep.
pos.
incog.
and the like; and as
all ridiculous Words make their first Entry into a Language by familiar
Phrases, I dare not answer for these that they will not in time be
looked upon as a part of our Tongue. We see some of our Poets have been
so indiscreet as to imitate
Hudibras's
Doggrel Expressions in
their serious Compositions, by throwing out the Signs of our
Substantives, which are essential to the English Language. Nay, this
Humour of shortning our Language had once run so far, that some of our
celebrated Authors, among whom we may reckon Sir
Roger E Estrange
in particular, began to prune their Words of all superfluous Letters, as
they termed them, in order to adjust the Spelling to the Pronunciation;
which would have confounded all our Etymologies, and have quite
destroyed our Tongue.
We may here likewise observe that our proper Names, when familiarized in
English, generally dwindle to Monosyllables, whereas in other modern
Languages they receive a softer Turn on this Occasion, by the Addition
of a new Syllable.
Nick
in
Italian
is
Nicolini
,
Jack
in French
Janot
; and so of the rest.
There is another Particular in our Language which is a great Instance of
our Frugality of Words, and that is the suppressing of several Particles
which must be produced in other Tongues to make a Sentence intelligible.
This often perplexes the best Writers, when they find the Relatives
whom, which, or they at their Mercy whether they may have Admission or
not; and will never be decided till we have something like an Academy,
that by the best Authorities and Rules drawn from the Analogy of
Languages shall settle all Controversies between Grammar and Idiom.
I have only considered our Language as it shows the Genius and natural
Temper of the
English
, which is modest, thoughtful and sincere,
and which perhaps may recommend the People, though it has spoiled the
Tongue. We might perhaps carry the same Thought into other Languages,
and deduce a greater Part of what is peculiar to them from the Genius of
the People who speak them. It is certain, the light talkative Humour of
the
French
has not a little infected their Tongue, which might be
shown by many Instances; as the Genius of the
Italians
, which is
so much addicted to Musick and Ceremony, has moulded all their Words and
Phrases to those particular Uses. The Stateliness and Gravity of the
Spaniards
shews itself to Perfection in the Solemnity of their
Language, and the blunt honest Humour of the
Germans
sounds
better in the Roughness of the High Dutch, than it would in a politer
Tongue.
C.
that
that
Swift.
Contents
|
Monday, August 6, 1711 |
Steele |
... Parthis mendacior ...
Hor.

According to the Request of this strange Fellow, I shall Print the
following Letter.
Mr.
Spectator,
I shall without any manner of Preface or Apology acquaint you, that I
am, and ever have been from my Youth upward, one of the greatest Liars
this Island has produced. I have read all the Moralists upon the
Subject, but could never find any Effect their Discourses had upon me,
but to add to my Misfortune by new Thoughts and Ideas, and making me
more ready in my Language, and capable of sometimes mixing seeming
Truths with my Improbabilities. With this strong Passion towards
Falshood in this kind, there does not live an honester Man or a
sincerer Friend; but my Imagination runs away with me, and whatever is
started I have such a Scene of Adventures appears in an Instant before
me, that I cannot help uttering them, tho', to my immediate Confusion,
I cannot but know I am liable to be detected by the first Man I meet.
Upon occasion of the mention of the Battel of
Pultowa, I could
not forbear giving an Account of a Kinsman of mine, a young Merchant
who was bred at
Mosco, that had too much Metal to attend Books
of Entries and Accounts, when there was so active a Scene in the
Country where he resided, and followed the Czar as a Volunteer: This
warm Youth, born at the Instant the thing was spoke of, was the Man
who unhorsed the
Swedish General, he was the Occasion that the
Muscovites kept their Fire in so soldier-like a manner, and
brought up those Troops which were covered from the Enemy at the
beginning of the Day;
besides this, he had at last the good Fortune to
be the Man who took Count
Piper1 With all this Fire I knew
my Cousin to be the Civilest Creature in the World. He never made any
impertinent Show of his Valour, and then he had an excellent Genius
for the World in every other kind.
I had Letters from him (here I felt
in my Pockets) that exactly spoke the Czar's Character, which I knew
perfectly
2 well; and I could not forbear concluding, that I lay
with his Imperial Majesty twice or thrice a Week all the while he
lodged at
Deptford3. What is worse than all this, it is
impossible to speak to me, but you give me some occasion of coming out
with one Lie or other, that has neither Wit, Humour, Prospect of
Interest, or any other Motive that I can think of in Nature. The other
Day, when one was commending an Eminent and Learned Divine, what
occasion in the World had I to say, Methinks he would look more
Venerable if he were not so fair a man? I remember the Company smiled.
I have seen the Gentleman since, and he is Coal-Black. I have
Intimations every Day in my Life that no Body believes me, yet I am
never the better. I was saying something the other Day to an old
Friend at
Will's Coffee-house, and he made me no manner of
Answer; but told me, that an Acquaintance of
Tully the Orator
having two or three times together said to him, without receiving any
Answer, That upon his Honour he was but that very Month forty Years of
Age; Tully answer'd, Surely you think me the most incredulous Man in
the World, if I don't believe what you have told me every Day this ten
Years. The Mischief of it is, I find myself wonderfully inclin'd to
have been present at every Occurrence that is spoken of before me;
this has led me into many Inconveniencies, but indeed they have been
the fewer, because I am no ill-natur'd Man, and never speak Things to
any Man's Disadvantage. I never directly defame, but I do what is as
bad in the Consequence, for I have often made a Man say such and such
a lively Expression, who was born a mere Elder Brother. When one has
said in my Hearing, Such a one is no wiser than he should be, I
immediately have reply'd, Now 'faith, I can't see that, he said a very
good Thing to my Lord such a one, upon such an Occasion, and the like.
Such an honest Dolt as this has been watch'd in every Expression he
uttered, upon my Recommendation of him, and consequently been subject
to the more Ridicule. I once endeavoured to cure my self of this
impertinent Quality, and resolved to hold my Tongue for seven Days
together; I did so, but then I had so many Winks and unnecessary
Distortions of my Face upon what any body else said, that I found I
only forbore the Expression, and that I still lied in my Heart to
every Man I met with. You are to know one Thing (which I believe
you'll say is a pity, considering the Use I should have made of it) I
never Travelled in my Life; but I do not know whether I could have
spoken of any Foreign Country with more Familiarity than I do at
present, in Company who are Strangers to me. I have cursed the Inns in
Germany; commended the Brothels at
Venice; the Freedom
of Conversation in
France; and tho' I never was out of this
dear Town, and fifty Miles about it, have been three Nights together
dogged by Bravoes for an Intreague with a Cardinal's Mistress at
Rome.
It were endless to give you Particulars of this kind, but I can assure
you, Mr.
Spectator, there are about Twenty or Thirty of us in this
Town, I mean by this Town the Cities of
London and
Westminster; I
say there are in Town a sufficient Number of us to make a Society
among our selves; and since we cannot be believed any longer, I beg of
you to print this my Letter, that we may meet together, and be under
such Regulation as there may be no Occasion for Belief or Confidence
among us. If you think fit, we might be called
The Historians, for
Liar is become a very harsh Word. And that a Member of the Society
may not hereafter be ill received by the rest of the World, I desire
you would explain a little this sort of Men, and not let us
Historians be ranked, as we are in the Imaginations of ordinary
People, among common Liars, Makebates, Impostors, and Incendiaries.
For your Instruction herein, you are to know that an Historian in
Conversation is only a Person of so pregnant a Fancy, that he cannot
be contented with ordinary Occurrences. I know a Man of Quality of our
Order, who is of the wrong Side of Forty-three, and has been of that
Age, according to
Tully's Jest, for some Years since, whose Vein is
upon the Romantick. Give him the least Occasion, and he will tell you
something so very particular that happen'd in such a Year, and in such
Company, where by the by was present such a one, who was afterwards
made such a thing. Out of all these Circumstances, in the best
Language in the World, he will join together with such probable
Incidents an Account that shews a Person of the deepest Penetration,
the honestest Mind, and withal something so Humble when he speaks of
himself, that you would Admire. Dear Sir, why should this be Lying!
There is nothing so instructive. He has withal the gravest Aspect;
something so very venerable and great! Another of these Historians is
a Young Man whom we would take in, tho' he extreamly wants Parts, as
People send Children (before they can learn any thing) to School, to
keep them out of Harm's way.
He tells things which have nothing at all
in them, and can neither please
nor4 displease, but merely take
up your Time to no manner of Purpose, no manner of Delight; but he is
Good-natured, and does it because he loves to be saying something to
you, and entertain you.
I could name you a Soldier that
hath5 done very great things
without Slaughter; he is prodigiously dull and slow of Head, but what
he can say is for ever false, so that we must have him.
Give me leave to tell you of one more who is a Lover; he is the most
afflicted Creature in the World, lest what happened between him and a
Great Beauty should ever be known. Yet again, he comforts himself.
Hang the Jade her Woman. If Mony can keep the Slut trusty I will
do it, though I mortgage every Acre; Anthony
and Cleopatra
for that; All for Love and the World well lost ...
Then, Sir, there is my little Merchant, honest
Indigo of the
Change, there's my Man for Loss and Gain, there's Tare and
Tret, there's lying all round the Globe; he has such a prodigious
Intelligence he knows all the
French are doing, or what we
intend or ought to intend, and has it from such Hands. But, alas,
whither am I running! While I complain, while I remonstrate to you,
even all this is a Lie, and there is not one such Person of Quality,
Lover, Soldier, or Merchant as I have now described in the whole
World, that I know of. But I will catch my self once in my Life, and
in spite of Nature speak one Truth, to wit that I am
Your Humble Servant, &c.
T.
Prime Minister of Charles XII.
exactly
In the Spring of 1698.
or
has
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 7, 1711 |
Steele |
At hæc etiam Servis semper libera fuerunt, timerent, gauderent, dolerent, suo
potius quam alterius arbitrio.
Tull.
Epist.

It is no small Concern to me, that I find so many Complaints from that
Part of Mankind whose Portion it is to live in Servitude, that those
whom they depend upon will not allow them to be even as happy as their
Condition will admit of. There are, as these unhappy Correspondents
inform me, Masters who are offended at a chearful Countenance, and think
a Servant is broke loose from them, if he does not preserve the utmost
Awe in their Presence. There is one who says, if he looks satisfied, his
Master asks him what makes him so pert this Morning; if a little sour,
Hark ye, Sirrah, are not you paid your Wages? The poor Creatures live in
the most extreme Misery together: The Master knows not how to preserve
Respect, nor the Servant how to give it. It seems this Person is of so
sullen a Nature, that he knows but little Satisfaction in the midst of a
plentiful Fortune, and secretly frets to see any Appearance of Content,
in one that lives upon the hundredth Part of his Income, who is unhappy
in the Possession of the Whole. Uneasy Persons, who cannot possess their
own Minds, vent their Spleen upon all who depend upon them: which, I
think, is expressed in a lively manner in the following Letters.
August 2, 1711.
Sir,
I have read your Spectator of the third of the last Month, and wish I
had the Happiness of being preferred to serve so good a Master as Sir
Roger. The Character of my Master is the very Reverse of that good and
gentle Knight's. All his Directions are given, and his Mind revealed,
by way of Contraries: As when any thing is to be remembered, with a
peculiar Cast of Face he cries, Be sure to forget now. If I am
to make haste back, Don't come these two Hours; be sure to call by
the Way upon some of your Companions. Then another excellent Way
of his is, if he sets me any thing to do, which he knows must
necessarily take up half a Day, he calls ten times in a Quarter of an
Hour to know whether I have done yet. This is his Manner; and the same
Perverseness runs through all his Actions, according as the
Circumstances vary. Besides all this, he is so suspicious, that he
submits himself to the Drudgery of a Spy. He is as unhappy himself as
he makes his Servants: He is constantly watching us, and we differ no
more in Pleasure and Liberty than as a Gaoler and a Prisoner. He lays
Traps for Faults, and no sooner makes a Discovery, but falls into such
Language, as I am more ashamed of for coming from him, than for being
directed to me. This, Sir, is a short Sketch of a Master I have served
upwards of nine Years; and tho' I have never wronged him, I confess my
Despair of pleasing him has very much abated my Endeavour to do it. If
you will give me leave to steal a Sentence out of my Master's
Clarendon, I shall tell you my Case in a Word, Being used
worse than I deserved, I cared less to deserve well than I had
done.
I am, Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Ralph Valet.
Dear Mr. Specter, I am the next thing to a Lady's Woman, and am under
both my Lady and her Woman. I am so used by them both, that I should
be very glad to see them in the Specter. My Lady her self is of no
Mind in the World, and for that Reason her Woman is of twenty Minds in
a Moment. My Lady is one that never knows what to do with her self;
she pulls on and puts off every thing she wears twenty times before
she resolves upon it for that Day. I stand at one end of the Room, and
reach things to her Woman. When my Lady asks for a thing, I hear and
have half brought it, when the Woman meets me in the middle of the
Room to receive it, and at that Instant she says No she will not have
it. Then I go back, and her Woman comes up to her, and by this time
she will have that and two or three things more in an Instant: The
Woman and I run to each other; I am loaded and delivering the things
to her, when my Lady says she wants none of all these things, and we
are the dullest Creatures in the World, and she the unhappiest Woman
living, for she shan't be dress'd in any time. Thus we stand not
knowing what to do, when our good Lady with all the Patience in the
World tells us as plain as she can speak, that she will have Temper
because we have no manner of Understanding; and begins again to dress,
and see if we can find out of our selves what we are to do. When she
is Dressed she goes to Dinner, and after she has disliked every thing
there, she calls for the Coach, then commands it in again, and then
she will not go out at all, and then will go too, and orders the
Chariot. Now, good Mr. Specter, I desire you would in the Behalf of
all who serve froward Ladies, give out in your Paper, that nothing can
be done without allowing Time for it, and that one cannot be back
again with what one was sent for, if one is called back before one can
go a Step for that they want. And if you please let them know that all
Mistresses are as like as all Servants.
I am
Your Loving Friend,
Patience Giddy.
These are great Calamities; but I met the other Day in the five Fields
towards
Chelsea
, a pleasanter Tyrant than either of the above
represented. A fat Fellow was puffing on in his open Waistcoat; a Boy of
fourteen in a Livery, carrying after him his Cloak, upper Coat, Hat,
Wig, and Sword. The poor Lad was ready to sink with the Weight, and
could not keep up with his Master, who turned back every half Furlong,
and wondered what made the lazy Young Dog lag behind.
There is something very unaccountable, that People cannot put themselves
in the Condition of the Persons below them, when they consider the
Commands they give. But there is nothing more common, than to see a
Fellow (who if he were reduced to it, would not be hired by any Man
living) lament that he is troubled with the most worthless Dogs in
Nature.
It would, perhaps, be running too far out of common Life to urge, that
he who is not Master of himself and his own Passions, cannot be a proper
Master of another. Æquanimity in a Man's own Words and Actions, will
easily diffuse it self through his whole Family.
Pamphilio
has
the happiest Household of any Man I know, and that proceeds from the
humane regard he has to them in their private Persons, as well as in
respect that they are his Servants. If there be any Occasion, wherein
they may in themselves be supposed to be unfit to attend their Master's
Concerns, by reason of an Attention to their own, he is so good as to
place himself in their Condition. I thought it very becoming in him,
when at Dinner the other Day he made an Apology for want of more
Attendants. He said,
One of my Footmen is gone to the Wedding of his
Sister, and the other I don't expect to Wait, because his Father died
but two Days ago
.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 8, 1711 |
Steele |
Utitur in re non Dubia testibus non necessariis.
Tull.

One meets now and then with Persons who are extreamly learned and knotty
in Expounding clear Cases.
Tully
tells
of an Author that
spent some Pages to prove that Generals could not perform the great
Enterprizes which have made them so illustrious, if they had not had
Men. He asserted also, it seems, that a Minister at home, no more than a
Commander abroad, could do any thing without other Men were his
Instruments and Assistants. On this Occasion he produces the Example of
Themistodes, Pericles, Cyrus
, and
Alexander
himself, whom
he denies to have been capable of effecting what they did, except they
had been followed by others. It is pleasant enough to see such Persons
contend without Opponents, and triumph without Victory.
The Author above-mentioned by the Orator, is placed for ever in a very
ridiculous Light, and we meet every Day in Conversation such as deserve
the same kind of Renown, for troubling those with whom they converse
with the like Certainties. The Persons that I have always thought to
deserve the highest Admiration in this kind are your ordinary
Story-tellers, who are most religiously careful of keeping to the Truth
in every particular Circumstance of a Narration, whether it concern the
main End or not. A Gentleman whom I had the Honour to be in Company with
the other Day, upon some Occasion that he was pleased to take, said, He
remembered a very pretty Repartee made by a very witty Man in King
Charles's
time upon the like Occasion. I remember (said he, upon
entring into the Tale) much about the time of
Oates's
Plot, that
a Cousin-German of mine and I were at the
Bear
in
Holborn:
No, I am out, it was at the
Cross
Keys, but
Jack Thompson
was there, for he was very great with the Gentleman who made the Answer.
But I am sure it was spoken some where thereabouts, for we drank a
Bottle in that Neighbourhood every Evening: But no matter for all that,
the thing is the same; but ...
He was going on to settle the Geography of the Jest when I left the
Room, wondering at this odd turn of Head which can play away its Words,
with uttering nothing to the Purpose, still observing its own
Impertinencies, and yet proceeding in them. I do not question but he
informed the rest of his Audience, who had more Patience than I, of the
Birth and Parentage, as well as the Collateral Alliances of his Family
who made the Repartee, and of him who provoked him to it.
It is no small Misfortune to any who have a just Value for their Time,
when this Quality of being so very Circumstantial, and careful to be
exact, happens to shew it self in a Man whose Quality obliges them to
attend his Proofs, that it is now Day, and the like. But this is
augmented when the same Genius gets into Authority, as it often does.
Nay I have known it more than once ascend the very Pulpit. One of this
sort taking it in his Head to be a great Admirer of Dr.
Tillotson
and Dr.
Beveridge
, never failed of proving out of these great
Authors Things which no Man living would have denied him upon his
own
single Authority. One Day resolving to come to the Point in hand, he
said, According to that excellent Divine, I will enter upon the Matter,
or in his Words, in the fifteenth Sermon of the Folio Edition, Page 160.
I shall briefly explain the Words, and then consider the Matter
contained in them
.
This honest Gentleman needed not, one would think, strain his Modesty so
far as to alter his Design of
Entring into the Matter
, to that of
Briefly explaining
. But so it was, that he would not even be
contented with that Authority, but added also the other Divine to
strengthen his Method, and told us, With the Pious and Learned Dr.
Beveridge
, Page 4th of his 9th Volume, I
shall endeavour to
make it as plain as I can from the Words which I have now read, wherein
for that Purpose we shall consider
... This Wiseacre was reckoned by
the Parish, who did not understand him, a most excellent Preacher; but
that he read too much, and was so Humble that he did not trust enough to
his own Parts.
Next to these ingenious Gentlemen, who argue for what no body can deny
them, are to be ranked a sort of People who do not indeed attempt to
prove insignificant things, but are ever labouring to raise Arguments
with you about Matters you will give up to them without the least
Controversy. One of these People told a Gentleman who said he saw Mr.
such a one go this Morning at nine a Clock towards the
Gravel-Pits
, Sir, I must beg your pardon for that, for tho' I am
very loath to have any Dispute with you, yet I must take the liberty to
tell you it was nine when I saw him at
St. James's
. When Men of
this Genius are pretty far gone in Learning they will put you to prove
that Snow is white, and when you are upon that Topick can say that there
is really no such thing as Colour in Nature; in a Word, they can turn
what little Knowledge they have into a ready Capacity of raising Doubts;
into a Capacity of being always frivolous and always unanswerable. It
was of two Disputants of this impertinent and laborious kind that the
Cynick said,
One of these Fellows is Milking a Ram, and the other
holds the Pail
.
On Rhetorical Invention
.
Contents
The Exercise of the Snuff-Box,
according to the most fashionable Airs and Motions,
in opposition to the Exercise of the Fan,
will be Taught with the best plain or perfumed Snuff,
at Charles Lillie's
Perfumer
at the Corner of Beaufort-Buildings in the Strand,
and Attendance given
for the Benefit of the young Merchants about the Exchange
for two Hours every Day at Noon, except Saturdays,
at a Toy-shop near Garraway's
Coffee-House.
There will be likewise Taught
The Ceremony of the Snuff-box,
or Rules for offering Snuff to a Stranger, a Friend, or a Mistress,
according to the Degrees of Familiarity or Distance;
with an Explanation of
the Careless, the Scornful, the Politick, and the Surly Pinch,
and the Gestures proper to each of them.
N. B.
The Undertaker does not question
but in a short time to have formed
a Body of Regular Snuff-Boxes
ready to meet and make head against
[all] the Regiment of Fans which have been
lately Disciplined, and are now in Motion.
T.
|
Thursday, August 9, 1711 |
Steele |
Vera Gloria radices agit, atque etiam propagatur: Ficta omnia celeriter, tanquam flosculi, decidunt, nec simulatum potest quidquam esse diuturnum.
Tull.

Of all the Affections which attend Human Life, the Love of Glory is the
most Ardent. According as this is Cultivated in Princes, it produces the
greatest Good or the greatest Evil. Where Sovereigns have it by
Impressions received from Education only, it creates an Ambitious rather
than a Noble Mind; where it is the natural Bent of the Prince's
Inclination, it prompts him to the Pursuit of Things truly Glorious. The
two greatest Men now in
Europe
(according to the common Acceptation of
the Word
Great
) are
Lewis
King of
France
, and
Peter
Emperor of
Russia
. As it is certain that all Fame does not arise from the
Practice of Virtue, it is, methinks, no unpleasing Amusement to examine
the Glory of these Potentates, and distinguish that which is empty,
perishing, and frivolous, from what is solid, lasting, and important.
Lewis
of
France
had
Infancy attended by Crafty and Worldly Men,
who made Extent of Territory the most glorious
Instance
of Power,
and mistook the spreading of Fame for the Acquisition of Honour. The
young Monarch's Heart was by such Conversation easily deluded into a
Fondness for Vain-glory, and upon these unjust Principles to form or
fall in with suitable Projects of Invasion, Rapine, Murder, and all the
Guilts that attend War when it is unjust. At the same time this Tyranny
was laid, Sciences and Arts were encouraged in the most generous Manner,
as if Men of higher Faculties were to be bribed to permit the Massacre
of the rest of the World. Every Superstructure which the Court of
France
built upon their first Designs, which were in themselves
vicious, was suitable to its false Foundation. The Ostentation of
Riches, the Vanity of Equipage, Shame of Poverty, and Ignorance of
Modesty, were the common Arts of Life: The generous Love of one Woman
was changed into Gallantry for all the Sex, and Friendships among Men
turned into Commerces of Interest, or mere Professions.
While these
were the Rules of Life, Perjuries in the Prince, and a general
Corruption of Manners in the Subject, were the Snares in which
France
has Entangled all her Neighbours.
With such false Colours have the
Eyes of
Lewis
been enchanted, from the Debauchery of his early Youth,
to the Superstition of his present old Age. Hence it is, that he has the
Patience to have Statues erected to his Prowess, his Valour, his
Fortitude; and in the Softnesses and Luxury of a Court, to be applauded
for Magnanimity and Enterprize in Military Atchievements.
Peter Alexiwitz
of
Russia
, when he came to Years of Manhood, though
he found himself Emperor of a vast and numerous People, Master of an
endless Territory, absolute Commander of the Lives and Fortunes of his
Subjects, in the midst of this unbounded Power and Greatness turned his
Thoughts upon Himself and People with Sorrow. Sordid Ignorance and a
Brute Manner of Life this Generous Prince beheld and contemned from the
Light of his own
Genius
. His Judgment suggested this to him, and his
Courage prompted him to amend it. In order to this he did not send to
the Nation from whence the rest of the World has borrowed its
Politeness, but himself left his Diadem to learn the true Way to Glory
and Honour, and Application to useful Arts, wherein to employ the
Laborious, the Simple, the Honest part of his People. Mechanick
Employments and Operations were very justly the first Objects of his
Favour and Observation. With this glorious Intention he travelled into
Foreign Nations in an obscure Manner, above receiving little Honours
where he sojourned, but prying into what was of more Consequence, their
Arts of Peace and of War. By this means has this great Prince laid the
Foundation of a great and lasting Fame, by personal Labour, personal
Knowledge, personal Valour. It would be Injury to any of Antiquity to
name them with him. Who, but himself, ever left a Throne to learn to sit
in it with more Grace? Who ever thought himself mean in Absolute
Power, 'till he had learned to use it?
If we consider this wonderful Person, it is Perplexity to know where to
begin his Encomium. Others may in a Metaphorical or Philosophick Sense
be said to command themselves, but this Emperor is also literally under
his own Command. How generous and how good was his entring his own Name
as a private Man in the Army he raised, that none in it might expect to
out-run the Steps with which he himself advanced! By such Measures this
god-like Prince learned to Conquer, learned to use his Conquests. How
terrible has he appeared in Battel, how gentle in Victory? Shall then
the base Arts of the
Frenchman
be held Polite, and the honest Labours
of the
Russian
Barbarous? No: Barbarity is the Ignorance of true
Honour, or placing any thing instead of it. The unjust Prince is Ignoble
and Barbarous, the good Prince only Renowned and Glorious.
Tho' Men may impose upon themselves what they please by their corrupt
Imaginations, Truth will ever keep its Station; and as Glory is nothing
else but the Shadow of Virtue, it will certainly disappear at the
Departure of Virtue. But how carefully ought the true Notions of it to
be preserved, and how industrious should we be to encourage any Impulses
towards it? The
Westminster
School-boy
said the other Day he
could not sleep or play for the Colours in the Hall
, ought to be
free from receiving a Blow for ever.
But let us consider what is truly Glorious according to the Author I
have to day quoted in the Front of my Paper.
Perfection of Glory, says
Tully
, consists in these three
Particulars:
That the People love us; that they have Confidence in
us; that being affected with a certain Admiration towards us, they think
we deserve Honour
.
This was spoken of Greatness in a Commonwealth: But if one were to form
a Notion of Consummate Glory under our Constitution, one must add to the
above-mentioned Felicities a certain necessary Inexistence, and
Disrelish of all the rest, without the Prince's Favour.
He should, methinks, have Riches, Power, Honour, Command, Glory; but
Riches, Power, Honour, Command and Glory should have no Charms, but as
accompanied with the Affection of his Prince. He should, methinks, be
Popular because a Favourite, and a Favourite because Popular.
Were it not to make the Character too imaginary, I would give him
Sovereignty over some Foreign Territory, and make him esteem that an
empty Addition without the kind Regards of his own Prince.
One may merely have an
Idea
of a Man thus composed and
circumstantiated, and if he were so made for Power without an Incapacity
of giving Jealousy, he would be also Glorious, without Possibility of
receiving Disgrace. This Humility and this Importance must make his
Glory immortal.
These Thoughts are apt to draw me beyond the usual Length of this Paper,
but if I could suppose such Rhapsodies cou'd outlive the common Fate of
ordinary things, I would say these Sketches and Faint Images of Glory
were drawn in
August, 1711,
when
John
Duke of
Marlborough
made that memorable March wherein he took the French
Lines without Bloodshed.
T.
Instances
The Colours taken at Blenheim hung in Westminster Hall.
Towards the close of the first
Philippic
.
Contents
|
Friday, August 10, 1711 |
Steele |
Animum curis nunc huc nunc dividit illuc.
Virg.

When I acquaint my Reader, that I have many other Letters not yet
acknowledged, I believe he will own, what I have a mind he should
believe, that I have no small Charge upon me, but am a Person of some
Consequence in this World. I shall therefore employ the present Hour
only in reading Petitions, in the Order as follows.
Mr. Spectator,
'I have lost so much Time already, that I desire, upon the Receipt
hereof, you would sit down immediately and give me your Answer. And I
would know of you whether a Pretender of mine really loves me.
As well as I can I will describe his Manners. When he sees me he is
always talking of Constancy, but vouchsafes to visit me but once a
Fortnight, and then is always in haste to be gone.
When I am sick, I hear, he says he is mightily concerned, but neither
comes nor sends, because, as he tells his Acquaintance with a Sigh, he
does not care to let me know all the Power I have over him, and how
impossible it is for him to live without me.
When he leaves the Town he writes once in six Weeks, desires to hear
from me, complains of the Torment of Absence, speaks of Flames,
Tortures, Languishings and Ecstasies. He has the Cant of an impatient
Lover, but keeps the Pace of a Lukewarm one.
You know I must not go faster than he does, and to move at this rate
is as tedious as counting a great Clock. But you are to know he is
rich, and my Mother says, As he is slow he is sure; He will love me
long, if he loves me little: But I appeal to you whether he loves at
all
Your Neglected, Humble Servant,
Lydia Novell.
All these Fellows who have Mony are extreamly sawcy and cold; Pray,
Sir, tell them of it.
Mr.Spectator,
'I have been delighted with nothing more through the whole Course of
your Writings than the Substantial Account you lately gave of Wit, and
I could wish you would take some other Opportunity to express further
the Corrupt Taste the Age is run into; which I am chiefly apt to
attribute to the Prevalency of a few popular Authors, whose Merit in
some respects has given a Sanction to their Faults in others.
Thus the Imitators of
Milton seem to place all the Excellency
of that sort of Writing either in the uncouth or antique Words, or
something else which was highly vicious, tho' pardonable, in that
Great Man.
The Admirers of what we call Point, or Turn, look upon it as the
particular Happiness to which
Cowley, Ovid and others owe their
Reputation, and therefore imitate them only in such Instances; what is
Just, Proper and Natural does not seem to be the Question with them,
but by what means a quaint Antithesis may be brought about, how one
Word may be made to look two Ways, and what will be the Consequence of
a forced Allusion.
Now tho' such Authors appear to me to resemble those who make
themselves fine, instead of being well dressed or graceful; yet the
Mischief is, that these Beauties in them, which I call Blemishes, are
thought to proceed from Luxuriance of Fancy and Overflowing of good
Sense: In one word, they have the Character of being too Witty; but if
you would acquaint the World they are not Witty at all, you would,
among many others, oblige,
Sir,
Your Most Benevolent Reader,
R. D.
Sir,
'I am a young Woman, and reckoned Pretty, therefore you'll pardon me
that I trouble you to decide a Wager between me and a Cousin of mine,
who is always contradicting one because he understands
Latin. Pray,
Sir. is
Dimpple spelt with a single or a double
P?'
I am, Sir,
Your very Humble Servant,
Betty Saunter.
Pray, Sir,
direct thus, To the kind Querist,
and leave it at;
Mr. Lillie's,
for I don't care to be known in the thing at all. I
am, Sir, again Your Humble Servant.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'I must needs tell you there are several of your Papers I do not much
like. You are often so Nice there is no enduring you, and so Learned
there is no understanding you. What have you to do with our
Petticoats?'
Your Humble Servant,
Parthenope.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Last Night as I was walking in the Park, I met a couple of Friends;
Prithee
Jack, says one of them, let us go drink a Glass of Wine, for
I am fit for nothing else. This put me upon reflecting on the many
Miscarriages which happen in Conversations over Wine, when Men go to
the Bottle to remove such Humours as it only stirs up and awakens.
This I could not attribute more to any thing than to the Humour of
putting Company upon others which Men do not like themselves. Pray,
Sir, declare in your Papers, that he who is a troublesome Companion to
himself, will not be an agreeable one to others. Let People reason
themselves into good-Humour, before they impose themselves upon their
Friends. Pray, Sir, be as Eloquent as you can upon this Subject, and
do Human Life so much Good, as to argue powerfully, that it is not
every one that can swallow who is fit to drink a Glass of Wine.'
Your most Humble Servant.
Sir,
'I this Morning cast my Eye upon your Paper concerning the Expence of
Time. You are very obliging to the Women, especially those who are not
Young and past Gallantry, by touching so gently upon Gaming: Therefore
I hope you do not think it wrong to employ a little leisure Time in
that Diversion; but I should be glad to hear you say something upon
the Behaviour of some of the Female Gamesters.
I have observed Ladies, who in all other respects are Gentle,
Good-humoured, and the very Pinks of good Breeding; who as soon as the
Ombre Table is called for, and set down to their Business, are
immediately Transmigrated into the veriest Wasps in Nature.
You must know I keep my Temper, and win their Mony; but am out of
Countenance to take it, it makes them so very uneasie. Be pleased,
dear Sir, to instruct them to lose with a better Grace, and you will
oblige'
Yours,
Rachel Basto.
Mr.
Spectator1,
'
Your Kindness to
Eleonora, in one of your Papers, has given me
Encouragement to do my self the Honour of writing to you. The great
Regard you have so often expressed for the Instruction and Improvement
of our Sex, will, I hope, in your own Opinion, sufficiently excuse me
from making any Apology for the Impertinence of this Letter. The great
Desire I have to embellish my Mind with some of those Graces which you
say are so becoming, and which you assert Reading helps us to, has
made me uneasie 'till I am put in a Capacity of attaining them: This,
Sir, I shall never think my self in, 'till you shall be pleased to
recommend some Author or Authors to my Perusal.
I thought indeed, when I first cast my Eye on
Eleonora's Letter,
that I should have had no occasion for requesting it of you; but to my
very great Concern, I found, on the Perusal of that
Spectator, I was
entirely disappointed, and am as much at a loss how to make use of my
Time for that end as ever. Pray, Sir, oblige me at least with one
Scene, as you were pleased to entertain
Eleonora with your Prologue.
I write to you not only my own Sentiments, but also those of several
others of my Acquaintance, who are as little pleased with the ordinary
manner of spending one's Time as my self: And if a fervent Desire
after Knowledge, and a great Sense of our present Ignorance, may be
thought a good Presage and Earnest of Improvement, you may look upon
your Time you shall bestow in answering this Request not thrown away
to no purpose. And I can't but add, that unless you have a particular
and more than ordinary Regard for
Eleonora, I have a better Title to
your Favour than she; since I do not content myself with Tea-table
Reading of your Papers, but it is my Entertainment very often when
alone in my Closet. To shew you I am capable of Improvement, and hate
Flattery, I acknowledge I do not like some of your Papers; but even
there I am readier to call in question my own shallow Understanding
than Mr.
Spector's profound Judgment.
I am, Sir,
your already (and in hopes of being more) your obliged Servant,
Parthenia.
This last Letter is written with so urgent and serious an Air, that I
cannot but think it incumbent upon me to comply with her Commands, which
I shall do very suddenly.
T.
This letter, signed
Parthenia
, was by Miss Shepheard,
sister of Mrs. Perry, who wrote the Letter in
, signed
Leonora
.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 11, 1711 |
Steele |
... Migravit ab Aure voluptas
Omnis ...
Hor.

In the present Emptiness of the Town, I have several Applications from
the lower Part of the Players, to admit Suffering to pass for Acting.
They in very obliging Terms desire me to let a Fall on the Ground, a
Stumble, or a good Slap on the Back, be reckoned a Jest. These Gambols I
shall tolerate for a Season, because I hope the Evil cannot continue
longer than till the People of Condition and Taste return to Town. The
Method, some time ago, was to entertain that Part of the Audience, who
have no Faculty above Eyesight, with Rope-dancers and Tumblers; which
was a way discreet enough, because it prevented Confusion, and
distinguished such as could show all the Postures which the Body is
capable of, from those who were to represent all the Passions to which
the Mind is subject. But tho' this was prudently settled, Corporeal and
Intellectual Actors ought to be kept at a still wider Distance than to
appear on the same Stage at all: For which Reason I must propose some
Methods for the Improvement of the Bear-Garden, by dismissing all Bodily
Actors to that Quarter.
In Cases of greater moment, where Men appear in Publick, the Consequence
and Importance of the thing can bear them out. And tho' a Pleader or
Preacher is Hoarse or Awkward, the Weight of the Matter commands Respect
and Attention; but in Theatrical Speaking, if the Performer is not
exactly proper and graceful, he is utterly ridiculous. In Cases where
there is little else expected, but the Pleasure of the Ears and Eyes,
the least Diminution of that Pleasure is the highest Offence. In Acting,
barely to perform the Part is not commendable, but to be the least out
is contemptible. To avoid these Difficulties and Delicacies, I am
informed, that while I was out of Town, the Actors have flown in the
Air, and played such Pranks, and run such Hazards, that none but the
Servants of the Fire-office, Tilers and Masons, could have been able to
perform the like. The Author of the following Letter, it seems, has been
of the Audience at one of these Entertainments, and has accordingly
complained to me upon it; but I think he has been to the utmost degree
Severe against what is exceptionable in the Play he mentions, without
dwelling so much as he might have done on the Author's most excellent
Talent of Humour. The pleasant Pictures he has drawn of Life, should
have been more kindly mentioned, at the same time that he banishes his
Witches, who are too dull Devils to be attacked with so much Warmth.
Mr.
Spectator1,
'
Upon a Report that
Moll White had followed you to Town, and was to
act a Part in the
Lancashire-Witches, I went last Week to see that
Play
2. It was my Fortune to sit next to a Country Justice of the
Peace, a Neighbour (as he said) of Sir
Roger's, who pretended to shew
her to us in one of the Dances. There was Witchcraft enough in the
Entertainment almost to incline me to believe him;
Ben Johnson was
almost lamed; young
Bullock narrowly saved his Neck; the Audience
was astonished, and an old Acquaintance of mine, a Person of Worth,
whom I would have bowed to in the Pit, at two Yards distance did not
know me.
If you were what the Country People reported you, a white Witch, I
could have wished you had been there to have exorcised that Rabble of
Broomsticks, with which we were haunted for above three Hours. I could
have allowed them to set
Clod in the Tree, to have scared the
Sportsmen, plagued the Justice, and employed honest
Teague with his
holy Water. This was the proper Use of them in Comedy, if the Author
had stopped here; but I cannot conceive what Relation the Sacrifice of
the Black Lamb, and the Ceremonies of their Worship to the Devil, have
to the Business of Mirth and Humour.
The Gentleman who writ this Play, and has drawn some Characters in it
very justly, appears to have been misled in his Witchcraft by an
unwary following the inimitable
Shakespear. The Incantations in
Mackbeth have a Solemnity admirably adapted to the Occasion of that
Tragedy, and fill the Mind with a suitable Horror; besides, that the
Witches are a Part of the Story it self, as we find it very
particularly related in
Hector Bœtius, from whom he seems to have
taken it. This therefore is a proper Machine where the Business is
dark, horrid, and bloody; but is extremely foreign from the Affair of
Comedy. Subjects of this kind, which are in themselves disagreeable,
can at no time become entertaining, but by passing through an
Imagination like
Shakespear's to form them;
for which Reason Mr.
Dryden would not allow even
Beaumont and
Fletcher capable of
imitating him.
But Shakespear's
Magick cou'd not copy'd be,
Within that Circle none durst walk but He3.
I should not, however, have troubled you with these Remarks, if there
were not something else in this Comedy, which wants to be exorcised more
than the Witches. I mean the Freedom of some Passages, which I should
have overlook'd, if I had not observed that those Jests can raise the
loudest Mirth, though they are painful to right Sense, and an Outrage
upon Modesty.
We must attribute such Liberties to the Taste of that Age, but indeed by
such Representations a Poet sacrifices the best Part of his Audience to
the worst; and, as one would think, neglects the Boxes, to write to the
Orange-Wenches.
I must not conclude till I have taken notice of the Moral with which
this Comedy ends. The two young Ladies having given a notable Example of
outwitting those who had a Right in the Disposal of them, and marrying
without Consent of Parents, one of the injur'd Parties, who is easily
reconciled, winds up all with this Remark,
... Design whate'er we will,
There is a Fate which over-rules us still.
We are to suppose that the Gallants are Men of Merit, but if they had
been Rakes the Excuse might have serv'd as well.
Hans Carvel's
Wife
4 was
of the same Principle, but has express'd it with a
Delicacy which shews she is not serious in her Excuse, but in a sort
of humorous Philosophy turns off the Thought of her Guilt, and says,
That if weak Women go astray,
Their Stars are more in fault than they.
This, no doubt, is a full Reparation, and dismisses the Audience with
very edifying Impressions.
These things fall under a Province you have partly pursued already,
and therefore demand your Animadversion, for the regulating so Noble
an Entertainment as that of the Stage. It were to be wished, that all
who write for it hereafter would raise their Genius, by the Ambition
of pleasing People of the best Understanding; and leave others who
shew nothing of the Human Species but Risibility, to seek their
Diversion at the Bear-Garden, or some other Privileg'd Place, where
Reason and Good-manners have no Right to disturb them.'
August 8, 1711.
I am, &c.
T.
This letter is by John Hughes.
Shadwell's Play of the
Lancashire Witches
was in the bill
of the Theatre advertised at the end of this number of the
Spectator
.
'By her Majesty's Company of Comedians.
At the Theatre Royal in Drury Lane, on Tuesday next, being the 14th
Day of August, will be presented, A comedy call'd the Lancashire
Witches, Written by the Ingenious Mr. Shadwell, late Poet Laureat.
Carefully Revis'd. With all the Original Decorations of Scenes,
Witche's Songs and Dances, proper to the Dramma. The Principal Parts
to be perform'd by Mr. Mills, Mr. Booth, Mr. Johnson, Mr. Bullock,
Sen., Mr. Norris, Mr. Pack, Mr. Bullock, Jun., Mrs. Elrington, Mrs.
Powel, Mrs. Bradshaw, Mrs. Cox. And the Witches by Mr. Burkhead, Mr.
Ryan, Mrs. Mills, and Mrs. Willis. It being the last time of Acting in
this Season.'
Prologue to Davenant and Dryden's version of the
Tempest
.
In Prior's Poem of
Hans Carvel
.
Contents
|
Monday, August 13, 1711 |
Steele |
... Irrupta tenet Copula ...
Hor.

following Letters being Genuine
, and the Images of a Worthy
Passion, I am willing to give the old Lady's Admonition to my self, and
the Representation of her own Happiness, a Place in my Writings.
August 9, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am now in the sixty seventh Year of my Age, and read you with
Approbation; but methinks you do not strike at the Root of the
greatest Evil in Life, which is the false Notion of Gallantry in Love.
It is, and has long been, upon a very ill Foot; but I, who have been a
Wife Forty Years, and was bred in a way that has made me ever since
very happy, see through the Folly of it. In a Word, Sir, when I was a
young Woman, all who avoided the Vices of the Age were very carefully
educated, and all fantastical Objects were turned out of our Sight.
The Tapestry Hangings, with the great and venerable Simplicity of the
Scripture Stories, had better Effects than now the Loves of
Venus and
Adonis or
Bacchus and
Ariadne in
your fine present Prints. The Gentleman I am married to made Love to
me in Rapture, but it was the Rapture of a Christian and a Man of
Honour, not a Romantick Hero or a Whining Coxcomb: This put our Life
upon a right Basis. To give you an Idea of our Regard one to another,
I inclose to you several of his Letters, writ Forty Years ago, when my
Lover; and one writ t'other Day, after so many Years Cohabitation.'
Your Servant,
Andromache.
August 7, 1671.
Madam,
'If my Vigilance and ten thousand Wishes for your Welfare and Repose
could have any force, you last Night slept in Security, and had
every good Angel in your Attendance. To have my Thoughts ever fixed
on you, to live in constant Fear of every Accident to which Human
Life is liable, and to send up my hourly Prayers to avert 'em from
you; I say, Madam, thus to think, and thus to suffer, is what I do
for Her who is in Pain at my Approach, and calls all my tender
Sorrow Impertinence. You are now before my Eyes, my Eyes that are
ready to flow with Tenderness, but cannot give relief to my gushing
Heart, that dictates what I am now Saying, and yearns to tell you
all its Achings. How art thou, oh my Soul, stoln from thy self! How
is all thy Attention broken! My Books are blank Paper, and my
Friends Intruders. I have no hope of Quiet but from your Pity; To
grant it, would make more for your Triumph. To give Pain is the
Tyranny, to make Happy the true Empire of Beauty. If you would
consider aright, you'd find an agreeable Change in dismissing the
Attendance of a Slave, to receive the Complaisance of a Companion. I
bear the former in hopes of the latter Condition: As I live in
Chains without murmuring at the Power which inflicts 'em, so I could
enjoy Freedom without forgetting the Mercy that gave it.'
Madam, I am
Your most devoted, most obedient Servant.
Tho' I made him no Declarations in his Favour, you see he had Hopes
of Me when he writ this in the Month following.
Madam, September 3, 1671.
'Before the Light this Morning dawned upon the Earth I awaked, and lay
in Expectation of its return, not that it cou'd give any new Sense of
Joy to me, but as I hoped it would bless you with its chearful Face,
after a Quiet which I wish'd you last Night. If my Prayers are heard,
the Day appeared with all the Influence of a Merciful Creator upon
your Person and Actions. Let others, my lovely Charmer, talk of a
blind Being that disposes their Hearts, I contemn their low Images of
Love. I have not a Thought which relates to you, that I cannot with
Confidence beseech the All-seeing Power to bless me in. May he direct
you in all your Steps, and reward your Innocence, your Sanctity of
Manners, your Prudent Youth, and becoming Piety, with the Continuance
of his Grace and Protection. This is an unusual Language to Ladies;
but you have a Mind elevated above the giddy Motions of a Sex insnared
by Flattery, and misled by a false and short Adoration into a solid
and long Contempt. Beauty, my fairest Creature, palls in the
Possession, but I love also your Mind; your Soul is as dear to me as
my own; and if the Advantages of a liberal Education, some Knowledge,
and as much Contempt of the World, join'd with the Endeavours towards
a Life of strict Virtue and Religion, can qualify me to raise new
Ideas in a Breast so well disposed as yours is, our Days will pass
away with Joy; and old Age, instead of introducing melancholy
Prospects of Decay, give us hope of Eternal Youth in a better Life. I
have but few Minutes from the Duty of my Employment to write in, and
without time to read over what I have writ, therefore beseech you to
pardon the first Hints of my Mind, which I have expressed in so little
Order.
I am, dearest Creature,
Your most Obedient,
most Devoted Servant.'
The two next were written after the Day of our Marriage was fixed.
September 25, 1671
Madam,
'It is the hardest thing in the World to be in Love, and yet attend
Business. As for me, all that speak to me find me out, and I must
lock myself up, or other People will do it for me. A Gentleman asked
me this Morning what News from Holland, and I answered, 'She's
Exquisitely handsome'. Another desir'd to know when I had been last
at Windsor, I reply'd, 'She designs to go with me'. Prethee, allow
me at least to kiss your Hand before the appointed Day, that my Mind
may be in some Composure. Methinks I could write a Volume to you,
but all the Language on Earth would fail in saying how much, and
with what dis-interested Passion,
I am ever Yours.
September 30, 1671.
Seven in the Morning.
Dear Creature,
Next to the Influence of Heav'n, I am to thank you that I see the
returning Day with Pleasure. To pass my Evenings in so sweet a
Conversation, and have the Esteem of a Woman of your Merit, has in
it a Particularity of Happiness no more to be express'd than
return'd. But I am, my Lovely Creature, contented to be on the
obliged Side, and to employ all my Days in new Endeavours to
convince you and all the World of the Sense I have of your
Condescension in Chusing,
Madam, Your Most Faithful,
Most Obedient Humble Servant.
He was, when he writ the following Letter, as agreeable and pleasant
a Man as any in England.
October 20, 1671.
Madam,
I Beg Pardon that my Paper is not Finer, but I am forced to write
from a Coffee-house where I am attending about Business. There is a
dirty Crowd of Busie Faces all around me talking of Mony, while all
my Ambition, all my Wealth is Love: Love which animates my Heart,
sweetens my Humour, enlarges my Soul, and affects every Action of my
Life. 'Tis to my lovely Charmer I owe that many noble Ideas are
continually affix'd to my Words and Actions: 'Tis the natural Effect
of that generous Passion to create in the Admirer some Similitude of
the Object admired; thus, my Dear, am I every Day to improve from so
sweet a Companion. Look up, my Fair One, to that Heaven which made
thee such, and join with me to implore its Influence on our tender
innocent Hours, and beseech the Author of Love to bless the Rites he
has ordained, and mingle with our Happiness a just Sense of our
transient Condition, and a Resignation to his Will, which only can
regulate our Minds to a steady Endeavour to please him and each
other.
I am, for Ever,
your Faithful Servant.
I will not trouble you with more Letters at this time, but if you
saw the poor withered Hand which sends you these Minutes, I am sure
you will smile to think that there is one who is so gallant as to
speak of it still as so welcome a Present, after forty Years
Possession of the Woman whom he writes to.
June 23, 1711.
Madam,
I Heartily beg your Pardon for my Omission to write Yesterday. It
was of no Failure of my tender Regard for you; but having been very
much perplexed in my Thoughts on the Subject of my last, made me
determine to suspend speaking of it 'till I came to myself. But, my
Lovely Creature, know it is not in the Power of Age, or Misfortune,
or any other Accident which hangs over Human Life, to take from me
the pleasing Esteem I have for you, or the Memory of the bright
Figure you appeared in when you gave your Hand and Heart to,
Madam,
Your most Grateful Husband,
and Obedient
Servant.
They are, after the first, with a few changes of phrase and
the alteration of date proper to the design of this paper, copies of
Steele's own love-letters addressed to Mrs. Scurlock, in August and
September, 1707; except the last, a recent one, written since marriage.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 14, 1711 |
Steele |
Non est vivere sed valere Vita.
Martial.

It is an unreasonable thing some Men expect of their Acquaintance. They
are ever complaining that they are out of Order, or Displeased, or they
know not how, and are so far from letting that be a Reason for retiring
to their own Homes, that they make it their Argument for coming into
Company. What has any body to do with Accounts of a Man's being
Indispos'd but his Physician? If a Man laments in Company, where the
rest are in Humour enough to enjoy themselves, he should not take it ill
if a Servant is ordered to present him with a Porringer of Cawdle or
Posset-drink, by way of Admonition that he go Home to Bed. That Part of
Life which we ordinarily understand by the Word Conversation, is an
Indulgence to the Sociable Part of our Make; and should incline us to
bring our Proportion of good Will or good Humour among the Friends we
meet with, and not to trouble them with Relations which must of
necessity oblige them to a real or feigned Affliction. Cares,
Distresses, Diseases, Uneasinesses, and Dislikes of our own, are by no
means to be obtruded upon our Friends. If we would consider how little
of this Vicissitude of Motion and Rest, which we call Life, is spent
with Satisfaction, we should be more tender of our Friends, than to
bring them little Sorrows which do not belong to them. There is no real
Life, but chearful Life; therefore Valetudinarians should be sworn
before they enter into Company, not to say a Word of themselves till the
Meeting breaks up.
is not here pretended, that we should be always
sitting
with Chaplets of Flowers round our Heads, or be crowned
with Roses, in order to make our Entertainment agreeable to us; but if
(as it is usually observed) they who resolve to be Merry, seldom are so;
it will be much more unlikely for us to be well-pleased, if they are
admitted who are always complaining they are sad. Whatever we do we
should keep up the Chearfulness of our Spirits, and never let them sink
below an Inclination at least to be well-pleased: The Way to this, is to
keep our Bodies in Exercise, our Minds at Ease. That insipid State
wherein neither are in Vigour, is not to be accounted any part of our
Portion of Being. When we are in the Satisfaction of some Innocent
Pleasure, or Pursuit of some laudable Design, we are in the Possession
of Life, of Human Life. Fortune will give us Disappointments enough, and
Nature is attended with Infirmities enough, without our adding to the
unhappy Side of our Account by our Spleen or ill Humour. Poor
Cottilus
, among so many real Evils, a Chronical Distemper and a
narrow Fortune, is never heard to complain: That equal Spirit of his,
which any Man may have, that, like him, will conquer Pride, Vanity and
Affectation, and follow Nature, is not to be broken, because it has no
Points to contend for. To be anxious for nothing but what Nature demands
as necessary, if it is not the Way to an Estate, is the Way to what Men
aim at by getting an Estate. This Temper will preserve Health in the
Body, as well as Tranquility in the Mind.
Cottilus
sees the World in a
Hurry, with the same Scorn that a Sober Person sees a Man Drunk. Had he
been contented with what he ought to have been, how could, says he, such
a one have met with such a Disappointment? If another had valued his
Mistress for what he ought to have lov'd her, he had not been in her
Power. If her Virtue had had a Part of his Passion, her Levity had been
his Cure; she could not then have been false and amiable at the same
time.
Since we cannot promise ourselves constant Health, let us endeavour at
such a Temper as may be our best Support in the Decay of it.
Uranius
has arrived at that Composure of Soul, and wrought himself up to such a
Neglect of every thing with which the Generality of Mankind is
enchanted, that nothing but acute Pains can give him Disturbance, and
against those too he will tell his intimate Friends he has a Secret
which gives him present Ease:
Uranius
is so thoroughly perswaded of
another Life, and endeavours so sincerely to secure an Interest in it,
that he looks upon Pain but as a quickening of his Pace to an Home,
where he shall be better provided for than in his present Apartment.
Instead of the melancholy Views which others are apt to give themselves,
he will tell you that he has forgot he is Mortal, nor will he think of
himself as such. He thinks at the Time of his Birth he entered into an
Eternal Being; and the short Article of Death he will not allow an
Interruption of Life, since that Moment is not of half the Duration as
is his ordinary Sleep. Thus is his Being one uniform and consistent
Series of chearful Diversions and moderate Cares, without Fear or Hope
of Futurity. Health to him is more than Pleasure to another Man, and
Sickness less affecting to him than Indisposition is to others.
I must confess, if one does not regard Life after this manner, none but
Ideots can pass it away with any tolerable Patience. Take a Fine Lady
who is of a Delicate Frame, and you may observe from the Hour she rises
a certain Weariness of all that passes about her. I know more than one
who is much too nice to be quite alive. They are sick of such strange
frightful People that they meet; one is so awkward, and another so
disagreeable, that it looks like a Penance to breathe the same Air with
them. You see this is so very true, that a great Part of Ceremony and
Good-breeding among Ladies turns upon their Uneasiness; and I'll
undertake, if the How-d'ye Servants of our Women were to make a Weekly
Bill of Sickness, as the Parish Clerks do of Mortality, you would not
find in an Account of seven Days, one in Thirty that was not downright
Sick or indisposed, or but a very little better than she was, and so
forth.
It is certain that to enjoy Life and Health as a constant Feast, we
should not think Pleasure necessary, but, if possible, to arrive at an
Equality of Mind. It is as mean to be overjoyed upon Occasions of
Good-Fortune, as to be dejected in Circumstances of Distress. Laughter
in one Condition is as unmanly as Weeping in the other. We should not
form our Minds to expect Transport on every Occasion, but know how to
make it Enjoyment to be out of Pain. Ambition, Envy, vagrant Desire, or
impertinent Mirth will take up our Minds, without we can possess our
selves in that Sobriety of Heart which is above all Pleasures, and can
be felt much better than described. But the ready Way, I believe, to the
right Enjoyment of Life, is by a Prospect towards another to have but a
very mean Opinion of it.
great Author of our Time has set this in an
excellent Light, when with a Philosophick Pity of Human Life, he spoke
of it in his
Theory of the Earth
, in the following manner.
For what is this Life but a Circulation of little mean Actions? We
lie down and rise again, dress and undress, feed and wax hungry, work or
play, and are weary, and then we lie down again, and the Circle returns.
We spend the Day in Trifles, and when the Night comes we throw our
selves into the Bed of Folly, amongst Dreams and broken Thoughts, and
wild Imaginations. Our Reason lies asleep by us, and we are for the Time
as arrant Brutes as those that sleep in the Stalls or in the Field. Are
not the Capacities of Man higher than these? And ought not his Ambition
and Expectations to be greater? Let us be Adventurers for another World:
'Tis at least a fair and noble Chance; and there is nothing in this
worth our Thoughts or our Passions. If we should be disappointed, we are
still no worse than the rest of our Fellow-Mortals; and if we succeed in
our Expectations, we are Eternally Happy.
sit
Ed. Amsterdam, 1699, p. 241.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 15, 1711 |
Steele |
... Nôris quam elegans formarum
Spectator siem.
Ter.

Beauty has been the Delight and Torment of the World ever since it
began. The Philosophers have felt its Influence so sensibly, that almost
every one of them has left us some Saying or other, which has intimated
that he too well knew the Power of it. One
has
us, that a
graceful Person is a more powerful Recommendation than the best Letter
that can be writ in your Favour. Another
desires the Possessor of it
to consider it as a meer Gift of Nature, and not any Perfection of his
own. A Third
calls it a short liv'd Tyranny; a Fourth
, a silent
Fraud, because it imposes upon us without the Help of Language; but I
think
Carneades
spoke as much like a Philosopher as any of them,
tho' more like a Lover, when he call'd it Royalty without Force. It is
not indeed to be denied, that there is something irresistible in a
Beauteous Form; the most Severe will not pretend, that they do not feel
an immediate Prepossession in Favour of the Handsome. No one denies them
the Privilege of being first heard, and being regarded before others in
Matters of ordinary Consideration. At the same time the Handsome should
consider that it is a Possession, as it were, foreign to them. No one
can give it himself, or preserve it when they have it. Yet so it is,
that People can bear any Quality in the World better than Beauty. It is
the Consolation of all who are naturally too much affected with the
Force of it, that a little Attention, if a Man can attend with Judgment,
will cure them. Handsome People usually are so fantastically pleas'd
with themselves, that if they do not kill at first Sight, as the Phrase
is, a second Interview disarms them of all their Power. But I shall make
this Paper rather a Warning-piece to give Notice where the Danger is,
than to propose Instructions how to avoid it when you have fallen in the
way of it. Handsome Men shall be the Subject of another Chapter, the
Women shall take up the present Discourse.
Amaryllis
, who has been in Town but one Winter, is extreamly
improved with the Arts of Good-Breeding, without leaving Nature. She has
not lost the Native Simplicity of her Aspect, to substitute that
Patience of being stared at, which is the usual Triumph and Distinction
of a Town Lady. In Publick Assemblies you meet her careless Eye
diverting itself with the Objects around her, insensible that she her
self is one of the brightest in the Place.
Dulcissa
is quite
of
another Make, she is almost a Beauty by
Nature, but more than one by Art. If it were possible for her to let her
Fan or any Limb about her rest, she would do some Part of the Execution
she meditates; but tho' she designs her self a Prey she will not stay to
be taken. No Painter can give you Words for the different Aspects of
Dulcissa
in half a Moment, whereever she appears: So little does
she accomplish what she takes so much pains for, to be gay and careless.
Merab
is attended with all the Charms of Woman and
Accomplishments of Man. It is not to be doubted but she has a great deal
of Wit, if she were not such a Beauty; and she would have more Beauty
had she not so much Wit. Affectation prevents her Excellencies from
walking together. If she has a Mind to speak such a Thing, it must be
done with such an Air of her Body; and if she has an Inclination to look
very careless, there is such a smart Thing to be said at the same Time,
that the Design of being admired destroys it self. Thus the unhappy
Merab
, tho' a Wit and Beauty, is allowed to be neither, because
she will always be both.
Albacinda
has the Skill as well as Power of pleasing. Her Form is
majestick, but her Aspect humble. All good Men should beware of the
Destroyer. She will speak to you like your Sister, till she has you
sure; but is the most vexatious of Tyrants when you are so. Her
Familiarity of Behaviour, her indifferent Questions, and general
Conversation, make the silly Part of her Votaries full of Hopes, while
the wise fly from her Power. She well knows she is too Beautiful and too
Witty to be indifferent to any who converse with her, and therefore
knows she does not lessen herself by Familiarity, but gains Occasions of
Admiration, by seeming Ignorance of her Perfections.
Eudosia
adds to the Height of her Stature a Nobility of Spirit
which still distinguishes her above the rest of her Sex. Beauty in
others is lovely, in others agreeable, in others attractive; but in
Eudosia
it is commanding: Love towards
Eudosia
is a
Sentiment like the Love of Glory. The Lovers of other Women are softened
into Fondness, the Admirers of
Eudosia
exalted into Ambition.
Eucratia
presents her self to the Imagination with a more kindly
Pleasure, and as she is Woman, her Praise is wholly Feminine. If we were
to form an Image of Dignity in a Man, we should give him Wisdom and
Valour, as being essential to the Character of Manhood. In like manner,
if you describe a right Woman in a laudable Sense, she should have
gentle Softness, tender Fear, and all those Parts of Life, which
distinguish her from the other Sex; with some Subordination to it, but
such an Inferiority that makes her still more lovely.
Eucratia
is
that Creature, she is all over Woman. Kindness is all her Art, and
Beauty all her Arms. Her Look, her Voice, her Gesture, and whole
Behaviour is truly Feminine. A Goodness mixed with Fear, gives a
Tincture to all her Behaviour. It would be Savage to offend her, and
Cruelty to use Art to gain her.
are beautiful, but
Eucratia
thou art Beauty!
Omnamante
is made for Deceit, she has an Aspect as Innocent as
the famed
Lucrece
, but a Mind as Wild as the more famed
Cleopatra
. Her Face speaks a Vestal, but her Heart a
Messalina
. Who that beheld
Omnamante's
negligent
unobserving Air, would believe that she hid under that regardless Manner
the witty Prostitute, the rapacious Wench, the prodigal Courtesan? She
can, when she pleases, adorn those Eyes with Tears like an Infant that
is chid! She can cast down that pretty Face in Confusion, while you rage
with Jealousy, and storm at her Perfidiousness; she can wipe her Eyes,
tremble and look frighted, till you think yourself a Brute for your
Rage, own yourself an Offender, beg Pardon, and make her new Presents.
I go too far in reporting only the Dangers in beholding the
Beauteous, which I design for the Instruction of the Fair as well as
their Beholders; and shall end this Rhapsody with mentioning what I
thought was well enough said of an Antient Sage to a Beautiful Youth,
whom he saw admiring his own Figure in Brass. What, said the
Philosopher
, could that Image of yours say for it self if it could
speak? It might say, (answered the Youth)
That it is very Beautiful.
And are not you ashamed
, reply'd the Cynick,
to value your self
upon that only of which a Piece of Brass is capable?
T.
Aristotle.
Plato.
Socrates.
Theophrastus.
Eudosia
Antisthenes. Quoted from Diogenes Laertius, Lib. vi. cap.
I.
Contents
|
Thursday, August 16, 1711 |
Steele |
Stultitiam patiuntur opes ...
Hor.

If the following Enormities are not amended upon the first Mention, I
desire further Notice from my Correspondents.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am obliged to you for your Discourse the other Day upon frivolous
Disputants, who with great Warmth, and Enumeration of many
Circumstances and Authorities, undertake to prove Matters which no
Body living denies. You cannot employ your self more usefully than in
adjusting the Laws of Disputation in Coffee-houses and accidental
Companies, as well as in more formal Debates. Among many other things
which your own Experience must suggest to you, it will be very
obliging if you please to take notice of Wagerers.
I will not here
repeat what
Hudibras says of such Disputants, which is so true,
that it is almost Proverbial
1; but shall only acquaint you with a
Set of young Fellows of the Inns of Court, whose Fathers have provided
for them so plentifully, that they need not be very anxious to get Law
into their Heads for the Service of their Country at the Bar; but are
of those who are sent (as the Phrase of Parents is) to the
Temple to know how to keep their own. One of these Gentlemen is
very loud and captious at a Coffee-house which I frequent, and being
in his Nature troubled with an Humour of Contradiction, though withal
excessive Ignorant, he has found a way to indulge this Temper, go on
in Idleness and Ignorance, and yet still give himself the Air of a
very learned and knowing Man, by the Strength of his Pocket. The
Misfortune of the thing is, I have, as it happens sometimes, a greater
Stock of Learning than of Mony. The Gentleman I am speaking of, takes
Advantage of the Narrowness of my Circumstances in such a manner, that
he has read all that I can pretend to, and runs me down with such a
positive Air, and with such powerful Arguments, that from a very
Learned Person I am thought a mere Pretender. Not long ago I was
relating that I had read such a Passage in
Tacitus, up starts
my young Gentleman in a full Company, and pulling out his Purse
offered to lay me ten Guineas, to be staked immediately in that
Gentleman's Hands, (pointing to one smoaking at another Table) that I
was utterly mistaken. I was Dumb for want of ten Guineas; he went on
unmercifully to Triumph over my Ignorance how to take him up, and told
the whole Room he had read
Tacitus twenty times over, and such
a remarkable Instance as that could not escape him. He has at this
time three considerable Wagers depending between him and some of his
Companions, who are rich enough to hold an Argument with him. He has
five Guineas upon Questions in Geography, two that the
Isle of
Wight is a Peninsula, and three Guineas to one that the World is
round. We have a Gentleman comes to our Coffee-house, who deals
mightily in Antique Scandal; my Disputant has laid him twenty Pieces
upon a Point of History, to wit, that
Cæsar never lay with
Cato's Sister, as is scandalously reported by some People.
There are several of this sort of Fellows in Town, who wager
themselves into Statesmen, Historians, Geographers, Mathematicians,
and every other Art, when the Persons with whom they talk have not
Wealth equal to their Learning. I beg of you to prevent, in these
Youngsters, this compendious Way to Wisdom, which costs other People
so much Time and Pains, and you will oblige
Your humble Servant.
Coffee-House near the Temple, Aug. 12, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Here's a young Gentleman that sings Opera-Tunes or Whistles in a full
House. Pray let him know that he has no Right to act here as if he
were in an empty Room. Be pleased to divide the Spaces of a Publick
Room, and certify Whistlers, Singers, and Common Orators, that are
heard further than their Portion of the Room comes
to, that the Law
is open, and that there is an Equity which will relieve us from such
as interrupt us in our Lawful Discourse, as much as against such as
stop us on the Road. I take these Persons, Mr.
Spectator, to be such
Trespassers as the Officer in your Stage-Coach, and of the same
Sentiment with Counsellor
Ephraim.
It is true the Young Man is
rich, and, as the Vulgar say,
needs2 not care for any Body; but
sure that is no Authority for him to go whistle where he pleases.
I am, Sir,
Your Most Humble Servant,
P.S. I have Chambers in the
Temple, and here are Students
that learn upon the Hautboy; pray desire the Benchers that all Lawyers
who are Proficients in Wind-Musick may lodge to the
Thames.
Mr.
Spectator,
We are a Company of young Women who pass our Time very much together,
and obliged by the mercenary Humour of the Men to be as Mercenarily
inclined as they are. There visits among us an old Batchelor whom each
of us has a Mind to. The Fellow is rich, and knows he may have any of
us, therefore is particular to none, but excessively ill-bred. His
Pleasantry consists in Romping, he snatches Kisses by Surprize, puts
his Hand in our Necks, tears our Fans, robs us of Ribbons, forces
Letters out of our Hands, looks into any of our Papers, and a thousand
other Rudenesses. Now what I'll desire of you is to acquaint him, by
Printing this, that if he does not marry one of us very suddenly, we
have all agreed, the next time he pretends to be merry, to affront
him, and use him like a Clown as he is. In the Name of the Sisterhood
I take my Leave of you, and am, as they all are,
Your Constant Reader and Well-wisher.
Mr.
Spectator,
I and several others of your Female Readers, have conformed our selves
to your Rules, even to our very Dress. There is not one of us but has
reduced our outward Petticoat to its ancient Sizable Circumference,
tho' indeed we retain still a Quilted one underneath, which makes us
not altogether unconformable to the Fashion; but 'tis on Condition,
Mr.
Spectator extends not his Censure so far. But we find you Men
secretly approve our Practice, by imitating our Pyramidical Form. The
Skirt of your fashionable Coats forms as large a Circumference as our
Petticoats; as these are set out with Whalebone, so are those with
Wire, to encrease and sustain the Bunch of Fold that hangs down on
each Side; and the Hat, I perceive, is decreased in just proportion to
our Head-dresses. We make a regular Figure, but I defy your
Mathematicks to give Name to the Form you appear in. Your Architecture
is mere
Gothick, and betrays a worse Genius than ours;
therefore if you are partial to your own Sex, I shall be less than I
am now
Your Humble Servant.
T.
I have heard old cunning Stagers
Say Fools for Arguments lay Wagers.
Hudibras, Part II. c. i.
need
Contents
|
Friday, August 17, 1711 |
Steele |
Nemo Vir Magnus sine aliquo Afflatu divino unquam fuit.
Tull.

We know the highest Pleasure our Minds are capable of enjoying with
Composure, when we read Sublime Thoughts communicated to us by Men of
great Genius and Eloquence. Such is the Entertainment we meet with in
the Philosophick Parts of
Cicero
's Writings. Truth and good Sense
have there so charming a Dress, that they could hardly be more agreeably
represented with the Addition of Poetical Fiction and the Power of
Numbers. This ancient Author, and a modern one, had fallen into my Hands
within these few Days; and the Impressions they have left upon me, have
at the present quite spoiled me for a merry Fellow. The Modern is that
admirable Writer the Author of
The Theory of the Earth
. The
Subjects with which I have lately been entertained in them both bear a
near Affinity; they are upon Enquiries into Hereafter, and the Thoughts
of the latter seem to me to be raised above those of the former in
proportion to his Advantages of Scripture and Revelation. If I had a
Mind to it, I could not at present talk of any thing else; therefore I
shall translate a Passage in the one, and transcribe a Paragraph out of
the other, for the Speculation of this
.
Cicero
tells us
,
that
Plato
reports
Socrates
, upon receiving his Sentence,
to have spoken to his Judges in the following manner.
I have great Hopes, oh my Judges, that it is infinitely to my
Advantage that I am sent to Death: For it is of necessity that one of
these two things must be the Consequence. Death must take away all
these Senses, or convey me to another Life. If all Sense is to be
taken away, and Death is no more than that profound Sleep without
Dreams, in which we are sometimes buried, oh Heavens! how desirable is
it to die? how many Days do we know in Life preferable to such a
State? But if it be true that Death is but a Passage to Places which
they who lived before us do now inhabit, how much still happier is it
to go from those who call themselves Judges, to appear before those
that really are such; before Minos, Rhadamanthus, Æacus, and
Triptolemus, and to meet Men who have lived with Justice and
Truth? Is this, do you think, no happy Journey? Do you think it
nothing to speak with Orpheus, Musceus, Homer, and
Hesiod? I would, indeed, suffer many Deaths to enjoy these
Things. With what particular Delight should I talk to Palamedes,
Ajax, and others, who like me have suffered by the Iniquity of
their Judges. I should examine the Wisdom of that great Prince, who
carried such mighty Forces against Troy; and argue with
Ulysses and Sisyphus, upon difficult Points, as I have
in Conversation here, without being in Danger of being condemned. But
let not those among you who have pronounced me an innocent Man be
afraid of Death. No Harm can arrive at a good Man whether dead or
living; his Affairs are always under the direction of the Gods; nor
will I believe the Fate which is allotted to me myself this Day to
have arrived by Chance; nor have I ought to say either against my
Judges or Accusers, but that they thought they did me an Injury ...
But I detain you too long, it is Time that I retire to Death, and you
to your Affairs of Life; which of us has the Better is known to the
Gods, but to no Mortal Man.
The Divine
Socrates
is here represented in a Figure worthy his
great Wisdom and Philosophy, worthy the greatest mere Man that ever
breathed. But the modern Discourse is written upon a Subject no less
than the Dissolution of Nature it self. Oh how glorious is the old Age
of that great Man, who has spent his Time in such Contemplations as has
made this Being, what only it should be, an Education for Heaven! He
has, according to the Lights of Reason and Revelation, which seemed to
him clearest, traced the Steps of Omnipotence: He has, with a Celestial
Ambition, as far as it is consistent with Humility and Devotion,
examined the Ways of Providence, from the Creation to the Dissolution of
the visible World. How pleasing must have been the Speculation, to
observe Nature and Providence move together, the Physical and Moral
World march the same Pace: To observe Paradise and eternal Spring the
Seat of Innocence, troubled Seasons and angry Skies the Portion of
Wickedness and Vice.
this admirable Author has reviewed all that
has past, or is to come, which relates to the habitable World, and run
through the whole Fate of it, how could a Guardian Angel, that had
attended it through all its Courses or Changes, speak more emphatically
at the End of his Charge, than does our Author when he makes, as it
were, a Funeral Oration over this Globe, looking to the Point where it
once stood
?
Let us only, if you please, to take leave of this Subject, reflect
upon this Occasion on the Vanity and transient Glory of this habitable
World. How by the Force of one Element breaking loose upon the rest,
all the Vanities of Nature, all the Works of Art, all the Labours of
Men, are reduced to Nothing. All that we admired and adored before as
great and magnificent, is obliterated or vanished; and another Form
and Face of things, plain, simple, and every where the same,
overspreads the whole Earth. Where are now the great Empires of the
World, and their great Imperial Cities? Their Pillars, Trophies, and
Monuments of Glory? Shew me where they stood, read the Inscription,
tell me the Victors Name. What Remains, what Impressions, what
Difference or Distinction, do you see in this Mass of Fire? Rome it
self, eternal Rome, the great City, the Empress of the World, whose
Domination and Superstition, ancient and modern, make a great Part of
the History of the Earth, what is become of her now? She laid her
Foundations deep, and her Palaces were strong and sumptuous; She
glorified her self, and lived deliciously, and said in her Heart, I sit
a Queen, and shall see no Sorrow: But her Hour is come, she is
wiped away from the Face of the Earth, and buried in everlasting
Oblivion. But it is not Cities only, and Works of Mens Hands, but the
everlasting Hills, the Mountains and Rocks of the Earth are melted as
Wax before the Sun, and their Place is no where found. Here
stood the Alps, the Load of the Earth, that covered many
Countries, and reached their Arms from the Ocean to the Black
Sea; this huge Mass of Stone is softned and dissolved as a tender
Cloud into Rain. Here stood the African Mountains, and
Atlas with his Top above the Clouds; there was frozen
Caucasus, and Taurus, and Imaus, and the
Mountains of Asia; and yonder towards the North, stood the
Riphaean Hills, cloathd in Ice and Snow. All these are
Vanished, dropt away as the Snow upon their Heads. Great and
Marvellous are thy Works, Just and True are thy Ways, thou King of
Saints! Hallelujah.
Tusculan Questions
, Bk. I.
Theory of the Earth
, Book III., ch. xii.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 18, 1711 |
Steele |
Pronuntiatio est Vocis et Vultus et Gestus moderatio cum venustate.
Tull.

Mr.
Spectator,
The well Reading of the Common Prayer is of so great Importance, and
so much neglected, that I take the Liberty to offer to your
Consideration some Particulars on that Subject: And what more worthy
your Observation than this? A thing so Publick, and of so high
Consequence. It is indeed wonderful, that the frequent Exercise of it
should not make the Performers of that Duty more expert in it. This
Inability, as I conceive, proceeds from the little Care that is taken
of their Reading, while Boys and at School, where when they are got
into
Latin, they are looked upon as above
English, the
Reading of which is wholly neglected, or at least read to very little
purpose, without any due Observations made to them of the proper
Accent and Manner of Reading; by this means they have acquired such
ill Habits as won't easily be removed. The only way that I know of to
remedy this, is to propose some Person of great Ability that way as a
Pattern for them; Example being most effectual to convince the
Learned, as well as instruct the Ignorant.
You must know, Sir, I've been a constant Frequenter of the Service of
the Church of
England for above these four Years last past, and
'till
Sunday was Seven-night never discovered, to so great a
Degree, the Excellency of the Common-Prayer. When being at St.
James's Garlick-Hill Church, I heard the Service read so
distinctly, so emphatically, and so fervently, that it was next to an
Impossibility to be unattentive. My Eyes and my Thoughts could not
wander as usual, but were confin'd to my Prayers: I then considered I
addressed my self to the Almighty, and not to a beautiful Face. And
when I reflected on my former Performances of that Duty, I found I had
run it over as a matter of Form, in comparison to the Manner in which
I then discharged it. My Mind was really affected, and fervent Wishes
accompanied my Words. The Confession was read with such a resigned
Humility, the Absolution with such a comfortable Authority, the
Thanksgivings with such a Religious Joy, as made me feel those
Affections of the Mind in a Manner I never did before.
To remedy
therefore the Grievance above complained of, I humbly propose, that
this excellent Reader
1, upon the next and every Annual Assembly of
the Clergy of
Sion-College, and all other Conventions, should
read Prayers before them. For then those that are afraid of stretching
their Mouths, and spoiling their soft Voice, will learn to Read with
Clearness, Loudness, and Strength. Others that affect a rakish
negligent Air by folding their Arms, and lolling on their Book, will
be taught a decent Behaviour, and comely Erection of Body. Those that
Read so fast as if impatient of their Work, may learn to speak
deliberately. There is another sort of Persons whom I call Pindarick
Readers, as being confined to no set measure; these pronounce five or
six Words with great Deliberation, and the five or six subsequent ones
with as great Celerity: The first part of a Sentence with a very
exalted Voice, and the latter part with a submissive one: Sometimes
again with one sort of a Tone, and immediately after with a very
different one. These Gentlemen will learn of my admired Reader an
Evenness of Voice and Delivery, and all who are innocent of these
Affectations, but read with such an Indifferency as if they did not
understand the Language, may then be informed of the Art of Reading
movingly and fervently, how to place the Emphasis, and give the proper
Accent to each Word, and how to vary the Voice according to the Nature
of the Sentence. There is certainly a very great Difference between
the Reading a Prayer and a Gazette, which I beg of you to inform a Set
of Readers, who affect, forsooth, a certain Gentleman-like Familiarity
of Tone, and mend the Language as they go on, crying instead of
Pardoneth and Absolveth, Pardons and Absolves. These are often pretty
Classical Scholars, and would think it an unpardonable Sin to read
Virgil or
Martial with so little Taste as they do Divine
Service.
This Indifferency seems to me to arise from the Endeavour of avoiding
the Imputation of Cant, and the false Notion of it. It will be proper
therefore to trace the Original and Signification of this Word. Cant
is, by some People, derived from one
Andrew Cant, who, they
say, was a Presbyterian Minister in some illiterate Part of
Scotland, who by Exercise and Use had obtained the Faculty,
alias Gift, of Talking in the Pulpit in such a Dialect, that
it's said he was understood by none but his own Congregation, and not
by all of them. Since
Mas. Cant's time, it has been understood
in a larger Sense, and signifies all sudden Exclamations, Whinings,
unusual Tones, and in fine all Praying and Preaching, like the
unlearned of the Presbyterians. But I hope a proper Elevation of
Voice, a due Emphasis and Accent, are not to come within this
Description. So that our Readers may still be as unlike the
Presbyterians as they please. The Dissenters (I mean such as I have
heard) do indeed elevate their Voices, but it is with sudden jumps
from the lower to the higher part of them; and that with so little
Sense or Skill, that their Elevation and Cadence is Bawling and
Muttering. They make use of an Emphasis, but so improperly, that it is
often placed on some very insignificant Particle, as upon
if,
or
and. Now if these Improprieties have so great an Effect on
the People, as we see they have, how great an Influence would the
Service of our Church, containing the best Prayers that ever were
composed, and that in Terms most affecting, most humble, and most
expressive of our Wants, and Dependance on the Object of our Worship,
dispos'd in most proper Order, and void of all Confusion; what
Influence, I say, would these Prayers have, were they delivered with a
due Emphasis, and apposite Rising and Variation of Voice, the Sentence
concluded with a gentle Cadence, and, in a word, with such an Accent
and Turn of Speech as is peculiar to Prayer?
As the matter of Worship is now managed, in Dissenting Congregations,
you find insignificant Words and Phrases raised by a lively Vehemence;
in our own Churches, the most exalted Sense depreciated, by a
dispassionate Indolence.
I remember to have heard Dr.
S —
e2 say in his Pulpit, of the Common-prayer, that,
at least, it was as perfect as any thing of Human Institution: If the
Gentlemen who err in this kind would please to recollect the many
Pleasantries they have read upon those who recite good Things with an
ill Grace, they would go on to think that what in that Case is only
Ridiculous, in themselves is Impious.
But leaving this to their own
Reflections, I shall conclude this Trouble with what
Cæsar said
upon the Irregularity of Tone in one who read before him,
Do you
read or sing? If you sing, you sing very ill3.
The Rec. Philip Stubbs, afterwards Archdeacon of St. Alban's.
Smalridge?
Si legis cantas; si cantas, male cantas.
The word Cant is rather from
cantare
, as a chanting whine, than from the
Andrew Cants, father and son, of Charles the Second's time.
Contents
|
Monday, August 20, 1711 |
Steele |
Exempta juvat spinis e pluribus una.
Hor.

My Correspondents assure me that the Enormities which they lately
complained of, and I published an Account of, are so far from being
amended, that new Evils arise every Day to interrupt their Conversation,
in Contempt of my Reproofs. My Friend who writes from the Coffee-house
near the
Temple
, informs me that the Gentleman who constantly
sings a Voluntary in spite of the whole Company, was more musical than
ordinary after reading my Paper; and has not been contented with that,
but has danced up to the Glass in the Middle of the Room, and practised
Minuet-steps to his own Humming. The incorrigible Creature has gone
still further, and in the open Coffee-house, with one Hand extended as
leading a Lady in it, he has danced both
French
and
Country-Dances, and admonished his supposed Partner by Smiles and Nods
to hold up her Head, and fall back, according to the respective Facings
and Evolutions of the Dance. Before this Gentleman began this his
Exercise, he was pleased to clear his Throat by coughing and spitting a
full half Hour; and as soon as he struck up, he appealed to an
Attorney's Clerk in the Room, whether he hit as he ought
Since you
from Death have saved me?
and then asked the young Fellow (pointing
to a Chancery-Bill under his Arm) whether that was an Opera-Score he
carried or not? Without staying for an Answer he fell into the Exercise
Above-mentioned, and practised his Airs to the full House who were
turned upon him, without the least Shame or Repentance for his former
Transgressions.
I am to the last Degree at a Loss what to do with this young Fellow,
except I declare him an Outlaw, and pronounce it penal for any one to
speak to him in the said House which he frequents, and direct that he be
obliged to drink his Tea and Coffee without Sugar, and not receive from
any Person whatsoever any thing above mere Necessaries.
As we in
England
are a sober People, and generally inclined
rather to a certain Bashfulness of Behaviour in Publick, it is amazing
whence some Fellows come whom one meets with in this Town; they do not
at all seem to be the Growth of our Island; the Pert, the Talkative, all
such as have no Sense of the Observations of others, are certainly of
foreign Extraction. As for my Part, I am as much surprised when I see a
talkative
Englishman
, as I should be to see the
Indian
Pine growing on one of our quick-set Hedges. Where these Creatures get
Sun enough, to make them such lively Animals and dull Men, is above my
Philosophy.
There are another Kind of Impertinents which a Man is perplexed with in
mixed Company, and those are your loud Speakers: These treat Mankind as
if we were all deaf; they do not express but declare themselves. Many of
these are guilty of this Outrage out of Vanity, because they think all
they say is well; or that they have their own Persons in such
Veneration, that they believe nothing which concerns them can be
insignificant to any Body else. For these Peoples sake, I have often
lamented that we cannot close our Ears with as much ease as we can our
Eyes: It is very uneasy that we must necessarily be under Persecution.
Next to these Bawlers, is a troublesome Creature who comes with the Air
of your Friend and your Intimate, and that is your Whisperer. There is
one of them at a Coffee-house which I my self frequent, who observing me
to be a Man pretty well made for Secrets, gets by me, and with a Whisper
tells me things which all the Town knows. It is no very hard matter to
guess at the Source of this Impertinence, which is nothing else but a
Method or Mechanick Art of being wise. You never see any frequent in it,
whom you can suppose to have anything in the World to do. These Persons
are worse than Bawlers, as much as a secret Enemy is more dangerous than
a declared one. I wish this my Coffee-house Friend would take this for
an Intimation, that I have not heard one Word he has told me for these
several Years; whereas he now thinks me the most trusty Repository of
his Secrets. The Whisperers have a pleasant way of ending the close
Conversation, with saying aloud,
Do not you think so?
Then whisper
again, and then aloud,
but you know that Person;
then whisper again.
The thing would be well enough, if they whisper'd to keep the Folly of
what they say among Friends; but alas, they do it to preserve the
Importance of their Thoughts. I am sure I could name you more than one
Person whom no Man living ever heard talk upon any Subject in Nature, or
ever saw in his whole Life with a Book in his Hand, that I know not how
can whisper something like Knowledge of what has and does pass in the
World; which you would think he learned from some familiar Spirit that
did not think him worthy to receive the whole Story. But in truth
Whisperers deal only in half Accounts of what they entertain you with. A
great Help to their Discourse is, 'That the Town says, and People begin
to talk very freely, and they had it from Persons too considerable to be
named, what they will tell you when things are riper.' My Friend has
winked upon me any Day since I came to Town last, and has communicated
to me as a Secret, that he designed in a very short Time to tell me a
Secret; but I shall know what he means, he now assures me, in less than
a Fortnight's Time.
But I must not omit the dearer Part of Mankind, I mean the Ladies, to
take up a whole Paper upon Grievances which concern the Men only; but
shall humbly propose, that we change Fools for an Experiment only. A
certain Set of Ladies complain they are frequently perplexed with a
Visitant who affects to be wiser than they are; which Character he hopes
to preserve by an obstinate Gravity, and great Guard against discovering
his Opinion upon any Occasion whatsoever. A painful Silence has hitherto
gained him no further Advantage, than that as he might, if he had
behaved himself with Freedom, been excepted against but as to this and
that Particular, he now offends in the whole. To relieve these Ladies,
my good Friends and Correspondents, I shall exchange my dancing Outlaw
for their dumb Visitant, and assign the silent Gentleman all the Haunts
of the Dancer; in order to which, I have sent them by the Penny-post the
following Letters for their Conduct in their new Conversations.
Sir,
I have, you may be sure, heard of your Irregularities without regard
to my Observations upon you; but shall not treat you with so much
Rigour as you deserve. If you will give yourself the Trouble to repair
to the Place mentioned in the Postscript to this Letter at Seven this
Evening, you will be conducted into a spacious Room well-lighted,
where there are Ladies and Musick. You will see a young Lady laughing
next the Window to the Street; you may take her out, for she loves you
as well as she does any Man, tho' she never saw you before. She never
thought in her Life, any more than your self. She will not be
surprised when you accost her, nor concerned when you leave her.
Hasten from a Place where you are laughed at, to one where you will be
admired. You are of no Consequence, therefore go where you will be
welcome for being so.
Your most Humble Servant.'
Sir,
'The Ladies whom you visit, think a wise Man the most impertinent
Creature living, therefore you cannot be offended that they are
displeased with you. Why will you take pains to appear wise, where you
would not be the more esteemed for being really so? Come to us; forget
the Gigglers; and let your Inclination go along with you whether you
speak or are silent; and let all such Women as are in a Clan or
Sisterhood, go their own way; there is no Room for you in that Company
who are of the common Taste of the Sex.'
For Women born to be controll'd
Stoop to the forward and the bold;
Affect the haughty, and the proud,
The gay, the frolick, and the loud.1
T.
Waller
Of Love.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 21, 1711 |
Steele |
Cui in manu sit quem esse dementem velit,
Quem sapere, quem sanari, quem in morbum injici,
Quem contra amari, quem accersiri, quem expeti.
Cæcil. apud Tull.

The following Letter and my Answer shall take up the present Speculation.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am the young Widow of a Country Gentleman who has left me Entire
Mistress of a large Fortune, which he agreed to as an Equivalent for
the Difference in our Years. In these Circumstances it is not
extraordinary to have a Crowd of Admirers; which I have abridged in my
own Thoughts, and reduced to a couple of Candidates only, both young,
and neither of them disagreeable in their Persons; according to the
common way of computing, in one the Estate more than deserves my
Fortune, and in the other my Fortune more than deserves the Estate.
When I consider the first, I own I am so far a Woman I cannot avoid
being delighted with the Thoughts of living great; but then he seems
to receive such a Degree of Courage from the Knowledge of what he has,
he looks as if he was going to confer an Obligation on me; and the
Readiness he accosts me with, makes me jealous I am only hearing a
Repetition of the same things he has said to a hundred Women before.
When I consider the other, I see myself approached with so much
Modesty and Respect, and such a Doubt of himself, as betrays methinks
an Affection within, and a Belief at the same time that he himself
would be the only Gainer by my Consent. What an unexceptionable
Husband could I make out of both! but since that's impossible, I beg
to be concluded by your Opinion; it is absolutely in your Power to
dispose of
Your most Obedient Servant,
Sylvia.
Madam,
You do me great Honour in your Application to me on this important
Occasion; I shall therefore talk to you with the Tenderness of a
Father, in Gratitude for your giving me the Authority of one. You do
not seem to make any great Distinction between these Gentlemen as to
their Persons; the whole Question lies upon their Circumstances and
Behaviour; If the one is less respectful because he is rich, and the
other more obsequious because he is not so, they are in that Point
moved by the same Principle, the Consideration of Fortune, and you
must place them in each others Circumstances before you can judge of
their Inclination. To avoid Confusion in discussing this Point, I will
call the richer Man
Strephon, and the other
Florio. If
you believe
Florio with
Strephon's Estate would behave
himself as he does now,
Florio is certainly your Man; but if
you think
Strephon, were he in
Florio's Condition, would
be as obsequious as
Florio is now, you ought for your own sake
to choose
Strephon; for where the Men are equal, there is no
doubt Riches ought to be a Reason for Preference. After this manner,
my dear Child, I would have you abstract them from their
Circumstances; for you are to take it for granted, that he who is very
humble only because he is poor, is the very same Man in Nature with
him who is haughty because he is rich.
When you have gone thus far, as to consider the Figure they make
towards you; you will please, my Dear, next to consider the Appearance
you make towards them. If they are Men of Discerning, they can observe
the Motives of your Heart; and
Florio can see when he is
disregarded only upon your Account of Fortune, which makes you to him
a mercenary Creature: and you are still the same thing to
Strephon, in taking him for his Wealth only: You are therefore
to consider whether you had rather oblige, than receive an Obligation.
The Marriage-Life is always an insipid, a vexatious, or an happy
Condition. The first is, when two People of no Genius or Taste for
themselves meet together, upon such a Settlement as has been thought
reasonable by Parents and Conveyancers from an exact Valuation of the
Land and Cash of both Parties: In this Case the young Lady's Person is
no more regarded, than the House and Improvements in Purchase of an
Estate: but she goes with her Fortune, rather than her Fortune with
her. These make up the Crowd or Vulgar of the Rich, and fill up the
Lumber of human Race, without Beneficence towards those below them, or
Respect towards those above them; and lead a despicable, independent
and useless Life, without Sense of the Laws of Kindness, Good-nature,
mutual Offices, and the elegant Satisfactions which flow from Reason
and Virtue.
The vexatious Life arises from a Conjunction of two People of quick
Taste and Resentment, put together for Reasons well known to their
Friends, in which especial Care is taken to avoid (what they think the
chief of Evils) Poverty, and insure to them Riches, with every Evil
besides. These good People live in a constant Constraint before
Company, and too great Familiarity alone; when they are within
Observation they fret at each other's Carriage and Behaviour; when
alone they revile each other's Person and Conduct: In Company they are
in a Purgatory, when only together in an Hell.
The happy Marriage is, where two Persons meet and voluntarily make
Choice of each other, without principally regarding or neglecting the
Circumstances of Fortune or Beauty. These may still love in spite of
Adversity or Sickness: The former we may in some measure defend our
selves from, the other is the Portion of our very Make. When you have
a true Notion of this sort of Passion, your Humour of living great
will vanish out of your Imagination, and you will find Love has
nothing to do with State. Solitude, with the Person beloved, has a
Pleasure, even in a Woman's Mind, beyond Show or Pomp. You are
therefore to consider which of your Lovers will like you best
undressed, which will bear with you most when out of Humour? and your
way to this is to ask your self, which of them you value most for his
own sake? and by that judge which gives the greater Instances of his
valuing you for your self only.
After you have expressed some Sense of the humble Approach of
Florio, and a little Disdain at
Strephon's Assurance in
his Address, you cry out,
What an unexceptionable Husband could I
make out of both? It would therefore methinks be a good way to
determine your self:
Take him in whom what you like is not
transferable to another; for if you choose otherwise, there is no
Hopes your Husband will ever have what you liked in his Rival; but
intrinsick Qualities in one Man may very probably purchase every thing
that is adventitious in
another1. In plainer Terms: he whom you
take for his personal Perfections will sooner arrive at the Gifts of
Fortune, than he whom you take for the sake of his Fortune attain to
Personal Perfections. If
Strephon is not as accomplished and
agreeable as
Florio, Marriage to you will never make him so;
but Marriage to you may make
Florio as rich as
Strephon?
Therefore to make a sure Purchase, employ Fortune upon Certainties,
but do not sacrifice Certainties to Fortune.
I am, Your most Obedient, Humble Servant.
any other.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 22, 1711 |
Budgell |
Nil habet infelix paupertas durius in se,
Quàm quod ridiculos homines facit ...
Juv.

As I was walking in my Chamber the Morning before I went last into the
Country, I heard the Hawkers with great Vehemence crying about a Paper,
entitled,
The ninety nine Plagues of an empty Purse
. I had indeed some
Time before observed, that the Orators of
Grub-street
had dealt very
much in
Plagues
. They have already published in the same Month,
The
Plagues of Matrimony, The Plagues of a single Life, The nineteen Plagues
of a Chambermaid, The Plagues of a Coachman, The Plagues of a Footman
,
and
The Plague of Plagues
. The success these several
Plagues
met
with, probably gave Occasion to the above-mentioned Poem on an
empty
Purse
. However that be, the same Noise so frequently repeated under my
Window, drew me insensibly to think on some of those Inconveniences and
Mortifications which usually attend on Poverty, and in short, gave Birth
to the present Speculation: For after my Fancy had run over the most
obvious and common Calamities which Men of mean Fortunes are liable to,
it descended to those little Insults and Contempts, which though they
may seem to dwindle into nothing when a Man offers to describe them, are
perhaps in themselves more cutting and insupportable than the former.
Juvenal
with a great deal of Humour and Reason tells us, that nothing
bore harder upon a poor Man in his Time, than the continual Ridicule
which his Habit and Dress afforded to the Beaus of
Rome
.
Quid, quod materiam præbet causasque jocorum
Omnibus hic idem? si fœda et scissa lacerna,
Si toga sordidula est, et rupta calceus alter
Pelle patet, vel si consuto vulnere crassum
Atque recens linam ostendit non una Cicatrix.
(Juv. Sat. 3.)
Add, that the Rich have still a Gibe in Store,
And will be monstrous witty on the Poor;
For the torn Surtout and the tatter'd Vest,
The Wretch and all his Wardrobe are a Jest:
The greasie Gown sully'd with often turning,
Gives a good Hint to say the Man's in Mourning;
Or if the Shoe be ript, or Patch is put,
He's wounded I see the Plaister on his Foot.
(Dryd.)
'Tis on this Occasion that he afterwards adds the Reflection which I
have chosen for my Motto.
Want is the Scorn of every wealthy Fool,
And Wit in Rags is turn'd to Ridicule.
(Dryd.)
It must be confess'd that few things make a Man appear more despicable
or more prejudice his Hearers against what he is going to offer, than an
awkward or pitiful Dress; insomuch that I fancy, had
Tully
himself
pronounced one of his Orations with a Blanket about his Shoulders, more
People would have laughed at his Dress than have admired his Eloquence.
This last Reflection made me wonder at a Set of Men, who, without being
subjected to it by the Unkindness of their Fortunes, are contented to
draw upon themselves the Ridicule of the World in this Particular; I
mean such as take it into their Heads, that the first regular Step to be
a Wit is to commence a Sloven. It is certain nothing has so much debased
that, which must have been otherwise so great a Character; and I know
not how to account for it, unless it may possibly be in Complaisance to
those narrow Minds who can have no Notion of the same Person's
possessing different Accomplishments; or that it is a sort of Sacrifice
which some Men are contented to make to Calumny, by allowing it to
fasten on one Part of their Character, while they are endeavouring to
establish another. Yet however unaccountable this foolish Custom is, I
am afraid it could plead a long Prescription; and probably gave too much
Occasion for the Vulgar Definition still remaining among us of an
Heathen Philosopher
.
I have seen the Speech of a
Terræ-filius
, spoken in King Charles II's
Reign; in which he describes two very eminent Men, who were perhaps the
greatest Scholars of their Age; and after having mentioned the entire
Friendship between them, concludes, That
they had but one Mind, one
Purse, one Chamber, and one Hat
. The Men of Business were also infected
with a Sort of Singularity little better than this. I have heard my
Father say, that a broad-brimm'd Hat, short Hair, and unfolded
Hankerchief, were in his time absolutely necessary to denote a
notable
Man;
and that he had known two or three, who aspired to the Character
of
very notable
, wear Shoestrings with great Success.
To the Honour of our present Age it must be allowed, that some of our
greatest Genius's for Wit and Business have almost entirely broke the
Neck of these Absurdities.
Victor
, after having dispatched the most important Affairs of the
Commonwealth, has appeared at an Assembly, where all the Ladies have
declared him the genteelest Man in the Company; and in
Atticus
, though
every way one of the greatest Genius's the Age has produced, one sees
nothing particular in his Dress or Carriage to denote his Pretensions to
Wit and Learning: so that at present a Man may venture to cock up his
Hat, and wear a fashionable Wig, without being taken for a Rake or a
Fool.
Medium between a Fop and a Sloven is what a Man of Sense would
endeavour to keep; yet I remember Mr.
Osbourn
advises his Son
to
appear in his Habit rather above than below his Fortune; and tells him,
that he will find an handsom Suit of Cloathes always procures some
additional Respect. I have indeed myself observed that my Banker bows
lowest to me when I wear my full-bottom'd Wig; and writes me
Mr.
or
Esq.
, accordingly as he sees me dressed.
I shall conclude this Paper with an Adventure which I was myself an
Eye-witness of very lately.
I happened the other Day to call in at a celebrated Coffee-house near
the
Temple
. I had not been there long when there came in an elderly
Man very meanly dressed, and sat down by me; he had a thread-bare loose
Coat on, which it was plain he wore to keep himself warm, and not to
favour his under Suit, which seemed to have been at least its
Contemporary: His short Wig and Hat were both answerable to the rest of
his Apparel. He was no sooner seated than he called for a Dish of Tea;
but as several Gentlemen in the Room wanted other things, the Boys of
the House did not think themselves at leisure to mind him.
could
observe the old Fellow was very uneasy at the Affront, and at his being
obliged to repeat his Commands several times to no purpose; 'till at
last one of the
lads
presented him with some stale Tea in a broken
Dish, accompanied with a Plate of brown Sugar; which so raised his
Indignation, that after several obliging Appellations of Dog and Rascal,
he asked him aloud before the whole Company,
Why he must be used with
less Respect than that Fop there?
pointing to a well-dressed young
Gentleman who was drinking Tea at the opposite Table.
Boy of the
House replied with a
great
deal of Pertness, That his Master had
two sorts of Customers, and that the Gentleman at the other Table had
given him many a Sixpence for wiping his Shoes. By this time the young
Templar
, who found his Honour concerned in the Dispute, and that the
Eyes of the whole Coffee-house were upon him, had thrown aside a Paper
he had in his Hand, and was coming towards us, while we at the Table
made what haste we could to get away from the impending Quarrel, but
were all of us surprised to see him as he approached nearer put on an
Air of Deference and Respect. To whom the old Man said,
Hark you,
Sirrah, I'll pay off your extravagant Bills once more; but will take
effectual Care for the future, that your Prodigality shall not spirit up
a Parcel of Rascals to insult your Father
.
Tho' I by no means approve either the Impudence of the Servants or the
Extravagance of the Son, I cannot but think the old Gentleman was in
some measure justly served for walking in Masquerade, I mean appearing
in a Dress so much beneath his Quality and Estate.
X.
Advice to a Son
, by Francis Osborn, Esq., Part I. sect. 23.
Rascals
good
Contents
|
Thursday, August 23, 1711 |
Steele |
Maximas Virtutes jacere omnes necesse est Voluptate dominante.
Tull.
de Fin.
I know no one Character that gives Reason a greater Shock, at the same
Time that it presents a good ridiculous Image to the Imagination, than
that of a Man of Wit and Pleasure about the Town. This Description of a
Man of Fashion, spoken by some with a Mixture of Scorn and Ridicule, by
others with great Gravity as a laudable Distinction, is in every Body's
Mouth that spends any Time in Conversation. My Friend
Will. Honeycomb
has this Expression very frequently; and I never could understand by the
Story which follows, upon his Mention of such a one, but that his Man of
Wit and Pleasure was either a Drunkard too old for Wenching, or a young
lewd Fellow with some Liveliness, who would converse with you, receive
kind Offices of you, and at the same time debauch your Sister, or lie
with your Wife. According to his Description, a Man of Wit, when he
could have Wenches for Crowns apiece which he liked quite as well, would
be so extravagant as to bribe Servants, make false Friendships, fight
Relations: I say, according to him, plain and simple Vice was too little
for a Man of Wit and Pleasure; but he would leave an easy and accessible
Wickedness, to come at the same thing with only the Addition of certain
Falshood and possible Murder.
Will
, thinks the Town grown very dull, in
that we do not hear so much as we used to do of these Coxcombs, whom
(without observing it) he describes as the most infamous Rogues in
Nature, with relation to Friendship, Love, or Conversation.
When Pleasure is made the chief Pursuit of Life, it will necessarily
follow that such Monsters as these will arise from a constant
Application to such Blandishments as naturally root out the Force of
Reason and Reflection, and substitute in their Place a general
Impatience of Thought, and a constant Pruiriency of inordinate Desire.
Pleasure, when it is a Man's chief Purpose, disappoints it self; and the
constant Application to it palls the Faculty of enjoying it, tho' it
leaves the Sense of our Inability for that we wish, with a Disrelish of
every thing else. Thus the intermediate Seasons of the Man of Pleasure
are more heavy than one would impose upon the vilest Criminal. Take him
when he is awaked too soon after a Debauch, or disappointed in following
a worthless Woman without Truth, and there is no Man living whose Being
is such a Weight or Vexation as his is. He is an utter Stranger to the
pleasing Reflections in the Evening of a well-spent Day, or the Gladness
of Heart or Quickness of Spirit in the Morning after profound Sleep or
indolent Slumbers. He is not to be at Ease any longer than he can keep
Reason and good Sense without his Curtains; otherwise he will be haunted
with the Reflection, that he could not believe such a one the Woman that
upon Trial he found her. What has he got by his Conquest, but to think
meanly of her for whom a Day or two before he had the highest Honour?
and of himself for, perhaps, wronging the Man whom of all Men living he
himself would least willingly have injured?
Pleasure seizes the whole Man who addicts himself to it, and will not
give him Leisure for any good Office in Life which contradicts the
Gaiety of the present Hour. You may indeed observe in People of Pleasure
a certain Complacency and Absence of all Severity, which the Habit of a
loose unconcerned Life gives them; but tell the Man of Pleasure your
secret Wants, Cares, or Sorrows, and you will find he has given up the
Delicacy of his Passions to the Cravings of his Appetites. He little
knows the perfect Joy he loses, for the disappointing Gratifications
which he pursues. He looks at Pleasure as she approaches, and comes to
him with the Recommendation of warm Wishes, gay Looks, and graceful
Motion; but he does not observe how she leaves his Presence with
Disorder, Impotence, down-cast Shame, and conscious Imperfection. She
makes our Youth inglorious, our Age shameful.
Will. Honeycomb
gives us twenty Intimations in an Evening of several
Hags whose Bloom was given up to his Arms; and would raise a Value to
himself for having had, as the Phrase is, very good Women.
Will.'s
good
Women are the Comfort of his Heart, and support him, I warrant, by the
Memory of past Interviews with Persons of their Condition. No, there is
not in the World an Occasion wherein Vice makes so phantastical a
Figure, as at the Meeting of two old People who have been Partners in
unwarrantable Pleasure. To tell a toothless old Lady that she once had a
good Set, or a defunct Wencher that he once was the admired Thing of the
Town, are Satires instead of Applauses; but on the other Side, consider
the old Age of those who have passed their Days in Labour, Industry, and
Virtue, their Decays make them but appear the more venerable, and the
Imperfections of their Bodies are beheld as a Misfortune to humane
Society that their Make is so little durable.
But to return more directly to my Man of Wit and Pleasure. In all Orders
of Men, wherever this is the chief Character, the Person who wears it is
a negligent Friend, Father, and Husband, and entails Poverty on his
unhappy Descendants. Mortgages Diseases, and Settlements are the
Legacies a Man of Wit and Pleasure leaves to his Family. All the poor
Rogues that make such lamentable Speeches after every Sessions at
Tyburn
, were, in their Way, Men of Wit and Pleasure, before they fell
into the Adventures which brought them thither.
Irresolution and Procrastination in all a Man's Affairs, are the natural
Effects of being addicted to Pleasure: Dishonour to the Gentleman and
Bankruptcy to the Trader, are the Portion of either whose chief Purpose
of Life is Delight. The chief Cause that this Pursuit has been in all
Ages received with so much Quarter from the soberer Part of Mankind, has
been that some Men of great Talents have sacrificed themselves to it:
The shining Qualities of such People have given a Beauty to whatever
they were engaged in, and a Mixture of Wit has recommended Madness. For
let any Man who knows what it is to have passed much Time in a Series of
Jollity, Mirth, Wit, or humourous Entertainments, look back at what he
was all that while a doing, and he will find that he has been at one
Instant sharp to some Man he is sorry to have offended, impertinent to
some one it was Cruelty to treat with such Freedom, ungracefully noisy
at such a Time, unskilfully open at such a Time, unmercifully calumnious
at such a Time; and from the whole Course of his applauded
Satisfactions, unable in the end to recollect any Circumstance which can
add to the Enjoyment of his own Mind alone, or which he would put his
Character upon with other Men. Thus it is with those who are best made
for becoming Pleasures; but how monstrous is it in the generality of
Mankind who pretend this Way, without Genius or Inclination towards it?
The Scene then is wild to an Extravagance: this is as if Fools should
mimick Madmen. Pleasure of this Kind is the intemperate Meals and loud
Jollities of the common Rate of Country Gentlemen, whose Practice and
Way of Enjoyment is to put an End as fast as they can to that little
Particle of Reason they have when they are sober: These Men of Wit and
Pleasure dispatch their Senses as fast as possible by drinking till they
cannot taste, smoaking till they cannot see, and roaring till they
cannot hear.
T
Contents
|
Friday, August 24, 1711 |
Steele |
There is no sort of People whose Conversation is so pleasant as that of
military Men, who derive their Courage and Magnanimity from Thought and
Reflection. The many Adventures which attend their Way of Life makes
their Conversation so full of Incidents, and gives them so frank an Air
in speaking of what they have been Witnesses of, that no Company can be
more amiable than that of Men of Sense who are Soldiers. There is a
certain irregular Way in their Narrations or Discourse, which has
something more warm and pleasing than we meet with among Men who are
used to adjust and methodize their Thoughts.
I was this Evening walking in the Fields with my Friend Captain
Sentry
,
and I could not, from the many Relations which I drew him into of what
passed when he was in the Service, forbear expressing my Wonder, that
the Fear of Death, which we, the rest of Mankind, arm ourselves against
with so much Contemplation, Reason and Philosophy, should appear so
little in Camps, that common Men march into open Breaches, meet opposite
Battalions, not only without Reluctance but with Alacrity. My Friend
answered what I said in the following manner:
'What you wonder at may very naturally be the Subject of Admiration to
all who are not conversant in Camps; but when a Man has spent some
time in that way of Life, he observes a certain Mechanick Courage
which the ordinary Race of Men become Masters of from acting always in
a Crowd: They see indeed many drop, but then they see many more alive;
they observe themselves escape very narrowly, and they do not know why
they should not again. Besides which general way of loose thinking,
they usually spend the other Part of their Time in Pleasures upon
which their Minds are so entirely bent, that short Labours or Dangers
are but a cheap purchase of Jollity, Triumph, Victory, fresh Quarters,
new Scenes, and uncommon Adventures.'
Such are the Thoughts of the Executive Part of an Army, and indeed of
the Gross of Mankind in general; but none of these Men of Mechanical
Courage have ever made any great Figure in the Profession of Arms. Those
who are formed for Command, are such as have reasoned themselves, out of
a Consideration of greater Good than Length of Days, into such a
Negligence of their Being, as to make it their first Position, That it
is one Day to be resigned; and since it is, in the Prosecution of worthy
Actions and Service of Mankind they can put it to habitual Hazard. The
Event of our Designs, say they, as it relates to others, is uncertain;
but as it relates to ourselves it must be prosperous, while we are in
the Pursuit of our Duty, and within the Terms upon which Providence has
ensured our Happiness, whether we die or live. All
that
Nature
prescribed must be good; and as Death is natural to us, it is Absurdity
to fear it. Fear loses its Purpose when we are sure it cannot preserve
us, and we should draw Resolution to meet it from the Impossibility to
escape it. Without a Resignation to the Necessity of dying, there can be
no Capacity in Man to attempt any thing that is glorious: but when they
have once attained to that Perfection, the Pleasures of a Life spent in
Martial Adventures, are as great as any of which the human Mind is
capable. The Force of Reason gives a certain Beauty, mixed with the
Conscience of well-doing and Thirst of Glory, to all which before was
terrible and ghastly to the Imagination. Add to this, that the
Fellowship of Danger, the common good of Mankind, the general Cause, and
the manifest Virtue you may observe in so many Men, who made no Figure
till that Day, are so many Incentives to destroy the little
Consideration of their own Persons. Such are the Heroick Part of
Soldiers who are qualified for Leaders: As to the rest whom I before
spoke of, I know not how it is, but they arrive at a certain Habit of
being void of Thought, insomuch that on occasion of the most imminent
Danger they are still in the same Indifference. Nay I remember an
Instance of a gay
French-man
, who was led on in Battle by a
superior Officer, (whose Conduct it was his Custom to speak of always
with Contempt and Raillery) and in the Beginning of the Action received
a Wound he was sensible was mortal;
Reflection on this Occasion was,
I wish I could live another Hour, to see how this blundering Coxcomb
will get clear of this Business.
I remember two young Fellows who rid in the same Squadron of a Troop of
Horse, who were ever together; they eat, they drank, they intreagued; in
a word, all their Passions and Affections seemed to tend the same Way,
and they appeared serviceable to each other in them. We were in the Dusk
of the Evening to march over a River, and the Troop these Gentlemen
belonged to were to be transported in a Ferry-boat, as fast as they
could. One of the Friends was now in the Boat, while the other was drawn
up with others by the Waterside waiting the Return of the Boat. A
Disorder happened in the Passage by an unruly Horse; and a Gentleman who
had the Rein of his Horse negligently under his Arm, was forced into the
Water by his Horse's Jumping over. The Friend on the Shore cry'd out,
Who's that is drowned trow? He was immediately answer'd, Your Friend,
Harry Thompson
. He very gravely reply'd,
Ay, he had a mad
Horse
. This short Epitaph from such a Familiar, without more Words,
gave me, at that Time under Twenty, a very moderate Opinion of the
Friendship of Companions. Thus is Affection and every other Motive of
Life in the Generality rooted out by the present busie Scene about them:
they lament no Man whose Capacity can be supplied by another; and where
Men converse without Delicacy, the next Man you meet will serve as well
as he whom you have lived with half your Life. To such the Devastation
of Countries, the Misery of Inhabitants, the Cries of the Pillaged, and
the silent Sorrow of the great Unfortunate, are ordinary Objects; their
Minds are bent upon the little Gratifications of their own Senses and
Appetites, forgetful of Compassion, insensible of Glory, avoiding only
Shame; their whole Hearts taken up with the trivial Hope of meeting and
being merry. These are the People who make up the Gross of the Soldiery:
But the fine Gentleman in that Band of Men is such a One as I have now
in my Eye, who is foremost in all Danger to which he is ordered. His
Officers are his Friends and Companions, as they are Men of Honour and
Gentlemen; the private Men his Brethren, as they are of his Species. He
is beloved of all that behold him: They wish him in Danger as he views
their Ranks, that they may have Occasions to save him at their own
Hazard. Mutual Love is the Order of the Files where he commands; every
Man afraid for himself and his Neighbour, not lest their Commander
should punish them, but lest he should be offended. Such is his Regiment
who knows Mankind, and feels their Distresses so far as to prevent them.
Just in distributing what is their Due, he would think himself below
their Tailor to wear a Snip of their Cloaths in
Lace upon his own; and below the most rapacious Agent, should he enjoy
a Farthing above his own Pay. Go on, brave Man, immortal Glory is thy
Fortune, and immortal Happiness thy Reward.
T.
which
This is told in the
Memoirs of Condé
of the Chevalier de
Flourilles, a lieutenant-general of his killed in 1674, at the Battle of
Senelf.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 25, 1711 |
Steele |
Habet natura ut aliarum omnium rerum sic vivendi modum; senectus autem peractio Ætatis est tanquam Fabulæ. Cujus defatigationem fugere debemus, præsertim adjunctâ Satietate.
Tull.
de Senec.
Of all the impertinent Wishes which we hear expressed in Conversation,
there is not one more unworthy a Gentleman or a Man of liberal
Education, than that of wishing one's self Younger. I have observed this
Wish is usually made upon Sight of some Object which gives the Idea of a
past Action, that it is no Dishonour to us that we cannot now repeat, or
else on what was in it self shameful when we performed it. It is a
certain Sign of a foolish or a dissolute Mind if we want our Youth again
only for the Strength of Bones and Sinews which we once were Masters of.
It is (as my Author has it) as absurd in an old Man to wish for the
Strength of a Youth, as it would be in a young Man to wish for the
Strength of a Bull or a Horse. These Wishes are both equally out of
Nature, which should direct in all things that are not contradictory to
Justice, Law, and Reason.
tho' every old Man has been
Young
,
and every young one hopes to be old, there seems to be a most unnatural
Misunderstanding between those two Stages of Life. The unhappy Want of
Commerce arises from the insolent Arrogance or Exultation in Youth, and
the irrational Despondence or Self-pity in Age. A young Man whose
Passion and Ambition is to be good and wise, and an old one who has no
Inclination to be lewd or debauched, are quite unconcerned in this
Speculation; but the Cocking young Fellow who treads upon the Toes of
his Elders, and the old Fool who envies the sawcy Pride he sees in him,
are the Objects of our present Contempt and Derision. Contempt and
Derision are harsh Words; but in what manner can one give Advice to a
Youth in the Pursuit and Possession of sensual Pleasures, or afford Pity
to an old Man in the Impotence and Desire of Enjoying them? When young
Men in publick Places betray in their Deportment an abandoned
Resignation to their Appetites, they give to sober Minds a Prospect of a
despicable Age, which, if not interrupted by Death in the midst of their
Follies, must certainly come. When an old Man bewails the Loss of such
Gratifications which are passed, he discovers a monstrous Inclination to
that which it is not in the Course of Providence to recal.
The State of an old Man, who is dissatisfy'd merely for his being such,
is the most out of all Measures of Reason and good Sense of any Being we
have any Account of from the highest Angel to the lowest Worm. How
miserable is the Contemplation to consider a libidinous old Man (while
all Created things, besides himself and Devils, are following the Order
of Providence) fretting at the Course of things, and being almost the
sole Malecontent in the Creation. But let us a little reflect upon what
he has lost by the number of Years: The Passions which he had in Youth
are not to be obeyed as they were then, but Reason is more powerful now
without the Disturbance of them. An old Gentleman t'other Day in
Discourse with a Friend of his (reflecting upon some Adventures they had
in Youth together) cry'd out,
Oh Jack, those were happy Days! That is
true
, reply'd his Friend,
but methinks we go about our Business
more quietly than we did then
. One would think it should be no small
Satisfaction to have gone so far in our Journey that the Heat of the Day
is over with us. When Life itself is a Feaver, as it is in licentious
Youth, the Pleasures of it are no other than the Dreams of a Man in that
Distemper, and it is as absurd to wish the Return of that Season of
Life, as for a Man in Health to be sorry for the Loss of gilded Palaces,
fairy Walks, and flowery Pastures, with which he remembers he was
entertained in the troubled Slumbers of a Fit of Sickness.
As to all the rational and worthy Pleasures of our Being, the Conscience
of a good Fame, the Contemplation of another Life, the Respect and
Commerce of honest Men, our Capacities for such Enjoyments are enlarged
by Years. While Health endures, the latter Part of Life, in the Eye of
Reason, is certainly the more eligible. The Memory of a well-spent Youth
gives a peaceable, unmixed, and elegant Pleasure to the Mind; and to
such who are so unfortunate as not to be able to look back on Youth with
Satisfaction, they may give themselves no little Consolation that they
are under no Temptation to repeat their Follies, and that they at
present despise them. It was prettily said,
'He that would be long an old Man, must begin early to be one:'
It is too late to resign a thing
after a Man is robbed of it; therefore it is necessary that before the
Arrival of Age we bid adieu to the Pursuits of Youth, otherwise sensual
Habits will live in our Imaginations when our Limbs cannot be
subservient to them. The poor Fellow who lost his Arm last Siege, will
tell you, he feels the Fingers that were buried in
Flanders
ake
every cold Morning at
Chelsea
.
The fond Humour of appearing in the gay and fashionable World, and being
applauded for trivial Excellencies, is what makes Youth have Age in
Contempt, and makes Age resign with so ill a Grace the Qualifications of
Youth: But this in both Sexes is inverting all things, and turning the
natural Course of our Minds, which should build their Approbations and
Dislikes upon what Nature and Reason dictate, into Chimera and
Confusion.
Age in a virtuous Person, of either Sex, carries in it an Authority
which makes it preferable to all the Pleasures of Youth. If to be
saluted, attended, and consulted with Deference, are Instances of
Pleasure, they are such as never fail a virtuous old Age. In the
Enumeration of the Imperfections and Advantages of the younger and later
Years of Man, they are so near in their Condition, that, methinks, it
should be incredible we see so little Commerce of Kindness between them.
If we consider Youth and Age with
Tully
, regarding the Affinity
to Death, Youth has many more Chances to be near it than Age; what Youth
can say more than an old Man, 'He shall live 'till Night?' Youth catches
Distempers more easily, its Sickness is more violent, and its Recovery
more doubtful. The Youth indeed hopes for many more Days, so cannot the
old Man. The Youth's Hopes are ill-grounded; for what is more foolish
than to place any Confidence upon an Uncertainty? But the old Man has
not Room so much as for Hope; he is still happier than the Youth, he has
already enjoyed what the other does but hope for: One wishes to live
long, the other has lived long. But alas, is there any thing in human
Life, the Duration of which can be called long? There is nothing which
must end to be valued for its Continuance. If Hours, Days, Months, and
Years pass away, it is no matter what Hour, what Day, what Month, or
what Year we die. The Applause of a good Actor is due to him at whatever
Scene of the Play he makes his Exit. It is thus in the Life of a Man of
Sense, a short Life is sufficient to manifest himself a Man of Honour
and Virtue; when he ceases to be such he has lived too long, and while
he is such, it is of no Consequence to him how long he shall be so,
provided he is so to his Life's End.
T.
a Young
Contents
|
Monday, August 27, 1711 |
Steele |
Nemo repente fuit turpissimus ...
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator,
'You are frequent in the mention of Matters which concern the feminine
World, and take upon you to be very severe against Men upon all those
Occasions:
But all this while I am afraid you have been very little
conversant with Women, or you would know the generality of them are
not so angry as you imagine at the general Vices
among1 us. I am
apt to believe (begging your Pardon) that you are still what I my self
was once, a queer modest Fellow; and therefore, for your Information,
shall give you a short Account of my self, and the Reasons why I was
forced to wench, drink, play, and do every thing which are necessary
to the Character of a Man of Wit and Pleasure, to be well with the
Ladies.
You are to know then that I was bred a Gentleman, and had the
finishing Part of my Education under a Man of great Probity, Wit, and
Learning, in one of our Universities. I will not deny but this made my
Behaviour and Mein bear in it a Figure of Thought rather than Action;
and a Man of a quite contrary Character, who never thought in his
Life, rallied me one Day upon it, and said, He believed I was still a
Virgin. There was a young Lady of Virtue present, and I was not
displeased to favour the Insinuation; but it had a quite contrary
Effect from what I expected. I was ever after treated with great
Coldness both by that Lady and all the rest of my Acquaintance.
In a
very little time I never came into a Room but I could hear a Whisper,
Here comes the Maid: A Girl of Humour would on some
Occasion2
say, Why, how do you know more than any of us? An Expression of that
kind was generally followed by a loud Laugh: In a word, for no other
Fault in the World than that they really thought me as innocent as
themselves, I became of no Consequence among them, and was received
always upon the Foot of a Jest. This made so strong an Impression upon
me, that I resolved to be as agreeable as the best of the Men who
laugh'd at me; but I observed it was Nonsense for me to be Impudent at
first among those who knew me: My Character for Modesty was so
notorious wherever I had hitherto appeared, that I resolved to shew my
new Face in new Quarters of the World.
My first Step I chose with
Judgment; for I went to
Astrop3, and came down among a Crowd of
Academicks, at one Dash, the impudentest Fellow they had ever seen in
their Lives. Flushed with this Success, I made Love and was happy.
Upon this Conquest I thought it would be unlike a Gentleman to stay
longer with my Mistress, and crossed the Country to
Bury: I could
give you a very good Account of my self at that Place also. At these
two ended my first Summer of Gallantry. The Winter following, you
would wonder at it, but I relapsed into Modesty upon coming among
People of Figure in
London, yet not so much but that the Ladies who
had formerly laughed at me, said, Bless us! how wonderfully that
Gentleman is improved?
Some Familiarities about the Play-houses
towards the End of the ensuing Winter, made me conceive new Hopes of
Adventures; and instead of returning the next Summer to
Astrop or
Bury4, I thought my self qualified to go to
Epsom, and followed
a young Woman, whose Relations were jealous of my Place in her Favour,
to
Scarborough. I carried my Point, and in my third Year aspired to
go to
Tunbridge, and in the Autumn of the same Year made my
Appearance at
Bath. I was now got into the Way of Talk proper for
Ladies, and was run into a vast Acquaintance among them, which I
always improved to the
best Advantage. In all this Course of Time,
and some Years following, I found a sober modest Man was always looked
upon by both Sexes as a precise unfashioned Fellow of no Life or
Spirit. It was ordinary for a Man who had been drunk in good Company,
or passed a Night with a Wench, to speak of it next Day before Women
for whom he had the greatest Respect. He was reproved, perhaps, with a
Blow of the Fan, or an Oh Fie, but the angry Lady still preserved an
apparent Approbation in her Countenance: He was called a strange
wicked Fellow, a sad Wretch; he shrugs his Shoulders, swears, receives
another Blow, swears again he did not know he swore, and all was well.
You might often see Men game in the Presence of Women, and throw at
once for more than they were worth, to recommend themselves as Men of
Spirit. I found by long Experience that the loosest Principles and
most abandoned Behaviour, carried all before them in Pretensions to
Women of Fortune. The Encouragement given to People of this Stamp,
made me soon throw off the remaining Impressions of a sober Education.
In the above-mentioned Places, as well as in Town, I always kept
Company with those who lived most at large; and in due Process of Time
I was a pretty Rake among the Men, and a very pretty Fellow among the
Women. I must confess, I had some melancholy Hours upon the Account of
the Narrowness of my Fortune, but my Conscience at the same time gave
me the Comfort that I had qualified my self for marrying a Fortune.
When I had lived in this manner for some time, and became thus
accomplished, I was now in the twenty seventh Year of my Age, and
about the Forty seventh of my Constitution, my Health and Estate
wasting very fast; when I happened to fall into the Company of a very
pretty young Lady in her own Disposal. I entertained the Company, as
we Men of Gallantry generally do, with the many Haps and Disasters,
Watchings under Windows, Escapes from jealous Husbands, and several
other Perils. The young Thing was wonderfully charmed with one that
knew the World so well, and talked so fine; with
Desdemona, all her
Lover said affected her;
it was strange,'twas wondrous strange. In a
word, I saw the Impression I had made upon her, and with a very little
Application the pretty Thing has married me. There is so much Charm in
her Innocence and Beauty, that I do now as much detest the Course I
have been in for many Years, as I ever did before I entred into it.
What I intend, Mr.
Spectator, by writing all this to you, is that you
would, before you go any further with your Panegyricks on the Fair
Sex, give them some Lectures upon their silly Approbations. It is that
I am weary of Vice, and that it was not my natural Way, that I am now
so far recovered as not to bring this believing dear Creature to
Contempt and Poverty for her Generosity to me. At the same time tell
the Youth of good Education of our Sex, that they take too little Care
of improving themselves in little things: A good Air at entring into a
Room, a proper Audacity in expressing himself with Gaiety and
Gracefulness, would make a young Gentleman of Virtue and Sense capable
of discountenancing the shallow impudent Rogues that shine among the
Women.
Mr.
Spectator, I don't doubt but you are a very sagacious Person, but
you are so great with
Tully of late, that I fear you will contemn
these Things as Matters of no Consequence: But believe me, Sir, they
are of the highest Importance to Human Life; and if you can do any
thing towards opening fair Eyes, you will lay an Obligation upon all
your Contemporaries who are Fathers, Husbands, or Brothers to Females.
Your most affectionate humble Servant,
Simon Honeycomb.
T.
amongst
Occasions
A small Spa, in Northamptonshire, upon the Oxford border.
From Astrop to Bath the scale of fashion rises.
Bury Fair and Epsom Wells gave titles to two of Shadwell's
Comedies.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 28, 1711 |
Steele |
... Hæ nugæ seria ducunt
In mala ...
Hor.

I have more than once taken Notice of an indecent Licence taken in
Discourse, wherein the Conversation on one Part is involuntary, and the
Effect of some necessary Circumstance. This happens in travelling
together in the same hired Coach, sitting near each other in any publick
Assembly, or the like. I have, upon making Observations of this sort,
received innumerable Messages from that Part of the Fair Sex whose Lot
in Life is to be of any Trade or publick Way of Life. They are all to a
Woman urgent with me to lay before the World the unhappy Circumstances
they are under, from the unreasonable Liberty which is taken in their
Presence, to talk on what Subject it is thought fit by every Coxcomb who
wants Understanding or Breeding. One or two of these Complaints I shall
set down.
Mr. Spectator,
'I Keep a Coffee-house, and am one of those whom you have thought fit
to mention as an Idol some time ago. I suffered a good deal of
Raillery upon that Occasion; but shall heartily forgive you, who are
the Cause of it, if you will do me Justice in another Point. What I
ask of you, is, to acquaint my Customers (who are otherwise very good
ones) that I am unavoidably hasped in my Bar, and cannot help hearing
the improper Discourses they are pleased to entertain me with. They
strive who shall say the most immodest Things in my Hearing: At the
same time half a dozen of them loll at the Bar staring just in my
Face, ready to interpret my Looks and Gestures according to their own
Imaginations. In this passive Condition I know not where to cast my
Eyes, place my Hands, or what to employ my self in: But this Confusion
is to be a Jest, and I hear them say in the End, with an Air of Mirth
and Subtlety, Let her alone, she knows as well as we, for all she
looks so. Good Mr. Spectator, persuade Gentlemen that it is out of all
Decency: Say it is possible a Woman may be modest and yet keep a
Publick-house. Be pleased to argue, that in truth the Affront is the
more unpardonable because I am oblig'd to suffer it, and cannot fly
from it. I do assure you, Sir, the Chearfulness of Life which would
arise from the honest Gain I have, is utterly lost to me, from the
endless, flat, impertinent Pleasantries which I hear from Morning to
Night. In a Word, it is too much for me to bear, and I desire you to
acquaint them, that I will keep Pen and Ink at the Bar, and write down
all they say to me, and send it to you for the Press. It is possible
when they see how empty what they speak, without the Advantage of an
impudent Countenance and Gesture, will appear, they may come to some
Sense of themselves, and the Insults they are guilty of towards me. I
am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
The Idol.
This Representation is so just, that it is hard to speak of it without
an Indignation which perhaps would appear too elevated to such as can be
guilty of this inhuman Treatment, where they see they affront a modest,
plain, and ingenuous Behaviour. This Correspondent is not the only
Sufferer in this kind, for I have long Letters both from the
Royal
and
New Exchange
on the same Subject. They tell me that a young Fop cannot
buy a Pair of Gloves, but he is at the same time straining for some
Ingenious Ribaldry to say to the young Woman who helps them on. It is no
small Addition to the Calamity, that the Rogues buy as hard as the
plainest and modestest Customers they have; besides which, they loll
upon their Counters half an Hour longer than they need, to drive away
other Customers, who are to share their Impertinencies with the
Milliner, or go to another Shop. Letters from
'Change-Alley
are full
of the same Evil, and the Girls tell me except I can chase some eminent
Merchants from their Shops they shall in a short time fail. It is very
unaccountable, that Men can have so little Deference to all Mankind who
pass by them, as to bear being seen toying by two's and three's at a
time, with no other Purpose but to appear gay enough to keep up a light
Conversation of Common-place Jests, to the Injury of her whose Credit is
certainly hurt by it, tho' their own may be strong enough to bear it.
When we come to have exact Accounts of these Conversations, it is not to
be doubted but that their Discourses will raise the usual Stile of
buying and selling: Instead of the plain downright lying, and asking and
bidding so unequally to what they will really give and take, we may hope
to have from these fine Folks an Exchange of Compliments. There must
certainly be a great deal of pleasant Difference between the Commerce of
Lovers, and that of all other Dealers, who are, in a kind, Adversaries.
A sealed Bond, or a Bank-Note, would be a pretty Gallantry to convey
unseen into the Hands of one whom a Director is charmed with; otherwise
the City-Loiterers are still more unreasonable than those at the other
End of the Town: At the
New Exchange
they are eloquent for want
of Cash, but in the City they ought with Cash to supply their want of
Eloquence.
If one might be serious on this prevailing Folly, one might observe,
that it is a melancholy thing, when the World is mercenary even to the
buying and selling our very Persons, that young Women, tho' they have
never so great Attractions from Nature, are never the nearer being
happily disposed of in Marriage; I say, it is very hard under this
Necessity, it shall not be possible for them to go into a way of Trade
for their Maintenance, but their very Excellencies and personal
Perfections shall be a Disadvantage to them, and subject them to be
treated as if they stood there to sell their Persons to Prostitution.
There cannot be a more melancholy Circumstance to one who has made any
Observation in the World, than one of those erring Creatures exposed to
Bankruptcy. When that happens, none of these toying Fools will do any
more than any other Man they meet to preserve her from Infamy, Insult,
and Distemper. A Woman is naturally more helpless than the other Sex;
and a Man of Honour and Sense should have this in his View in all Manner
of Commerce with her. Were this well weighed, Inconsideration, Ribaldry,
and Nonsense, would not be more natural to entertain Women with than
Men; and it would be as much Impertinence to go into a Shop of one of
these young Women without buying, as into that of any other Trader. I
shall end this Speculation with a Letter I have received from a pretty
Milliner in the City.
Mr. Spectator,
'I have read your Account of Beauties, and was not a little surprized
to find no Character of my self in it. I do assure you I have little
else to do but to give Audience as I am such. Here are Merchants of no
small Consideration, who call in as certainly as they go to
'Change, to say something of my roguish Eye: And here is one
who makes me once or twice a Week tumble over all my Goods, and then
owns it was only a Gallantry to see me act with these pretty Hands;
then lays out three Pence in a little Ribbon for his Wrist-bands, and
thinks he is a Man of great Vivacity. There is an ugly Thing not far
off me, whose Shop is frequented only by People of Business, that is
all Day long as busy as possible. Must I that am a Beauty be treated
with for nothing but my Beauty? Be pleased to assign Rates to my kind
Glances, or make all pay who come to see me, or I shall be undone by
my Admirers for want of Customers. Albacinda, Eudosia, and all the
rest would be used just as we are, if they were in our Condition;
therefore pray consider the Distress of us the lower Order of
Beauties, and I shall be
Your obliged humble Servant.
T.
In the first issue this is numbered by mistake 156. The
wrong numbering is continued to No. 163, when two successive papers are
numbered 163; there is no 164, and then two papers are numbered 165.
After this, at 166 the numbering falls right.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 29, 1711 |
Steele |
... Sed tu simul obligasti
Perfidum votis caput, enitescis
Pulchrior multo ...
Hor.

I do not think any thing could make a pleasanter Entertainment, than the
History of the reigning Favourites among the Women from Time to Time
about this Town: In such an Account we ought to have a faithful
Confession of each Lady for what she liked such and such a Man, and he
ought to tell us by what particular Action or Dress he believed he
should be most successful. As for my part, I have always made as easy a
Judgment when a Man dresses for the Ladies, as when he is equipped for
Hunting or Coursing. The Woman's Man is a Person in his Air and
Behaviour quite different from the rest of our Species: His Garb is more
loose and negligent, his Manner more soft and indolent; that is to say,
in both these Cases there is an apparent Endeavour to appear unconcerned
and careless. In catching Birds the Fowlers have a Method of imitating
their Voices to bring them to the Snare; and your Women's Men have
always a Similitude of the Creature they hope to betray, in their own
Conversation. A Woman's Man is very knowing in all that passes from one
Family to another, has little pretty Officiousnesses, is not at a loss
what is good for a Cold, and it is not amiss if he has a Bottle of
Spirits in his Pocket in case of any sudden Indisposition.
Curiosity having been my prevailing Passion, and indeed the sole
Entertainment of my Life, I have sometimes made it my business to
examine the Course of Intreagues as well as the Manners and
Accomplishments of such as have been most successful that Way. In all my
Observation, I never knew a Man of good Understanding a general
Favourite; some Singularity in his Behaviour, some Whim in his Way of
Life, and what would have made him ridiculous among the Men, has
recommended him to the other Sex. I should be very sorry to offend a
People so fortunate as these of whom I am speaking; but let any one look
over the old Beaux, and he will find the Man of Success was remarkable
for quarrelling impertinently for their Sakes, for dressing unlike the
rest of the World, or passing his Days in an insipid Assiduity about the
Fair Sex, to gain the Figure he made amongst them. Add to this that he
must have the Reputation of being well with other Women, to please any
one Woman of Gallantry; for you are to know, that there is a mighty
Ambition among the light Part of the Sex to gain Slaves from the
Dominion of others. My Friend
Will. Honeycomb
says it was a common Bite
with him to lay Suspicions that he was favoured by a Lady's Enemy, that
is some rival Beauty, to be well with herself. A little Spite is natural
to a great Beauty: and it is ordinary to snap up a disagreeable Fellow
lest another should have him. That impudent Toad
Bareface
fares
well among all the Ladies he converses with, for no other Reason in the
World but that he has the Skill to keep them from Explanation one with
another. Did they know there is not one who likes him in her Heart, each
would declare her Scorn of him the next Moment; but he is well received
by them because it is the Fashion, and Opposition to each other brings
them insensibly into an Imitation of each other. What adds to him the
greatest Grace is, the pleasant Thief, as they call him, is the most
inconstant Creature living, has a wonderful deal of Wit and Humour, and
never wants something to say; besides all which, he has a most spiteful
dangerous Tongue if you should provoke him.
To make a Woman's Man, he must not be a Man of Sense, or a Fool; the
Business is to entertain, and it is much better to have a Faculty of
arguing, than a Capacity of judging right. But the pleasantest of all
the Womens Equipage are your regular Visitants; these are Volunteers in
their Service, without Hopes of Pay or Preferment; It is enough that
they can lead out from a publick Place, that they are admitted on a
publick Day, and can be allowed to pass away part of that heavy Load,
their Time, in the Company of the Fair. But commend me above all others
to those who are known for your Ruiners of Ladies; these are the
choicest Spirits which our Age produces. We have several of these
irresistible Gentlemen among us when the Company is in Town. These
Fellows are accomplished with the Knowledge of the ordinary Occurrences
about Court and Town, have that sort of good Breeding which is exclusive
of all Morality, and consists only in being publickly decent, privately
dissolute.
It is wonderful how far a fond Opinion of herself can carry a Woman, to
make her have the least Regard to a professed known Woman's Man: But as
scarce one of all the Women who are in the Tour of Gallantries ever
hears any thing of what is the common Sense of sober Minds, but are
entertained with a continual Round of Flatteries, they cannot be
Mistresses of themselves enough to make Arguments for their own Conduct
from the Behaviour of these Men to others. It is so far otherwise, that
a general Fame for Falshood in this kind, is a Recommendation: and the
Coxcomb, loaded with the Favours of many others, is received like a
Victor that disdains his Trophies, to be a Victim to the present
Charmer.
If you see a Man more full of Gesture than ordinary in a publick
Assembly, if loud upon no Occasion, if negligent of the Company round
him, and yet laying wait for destroying by that Negligence, you may take
it for granted that he has ruined many a Fair One. The Woman's Man
expresses himself wholly in that Motion which we call Strutting: An
elevated Chest, a pinched Hat, a measurable Step, and a sly surveying
Eye, are the Marks of him. Now and then you see a Gentleman with all
these Accomplishments; but alas, any one of them is enough to undo
Thousands: When a Gentleman with such Perfections adds to it suitable
Learning, there should be publick Warning of his Residence in Town, that
we may remove our Wives and Daughters. It happens sometimes that such a
fine Man has read all the Miscellany Poems, a few of our Comedies, and
has the Translation of
Ovid's
Epistles by Heart. Oh if it were
possible that such a one could be as true as he is charming! but that is
too much, the Women will share such a dear false Man:
'A little Gallantry to hear him Talk one would indulge one's self in,
let him reckon the Sticks of one's Fan, say something of the
Cupids in it, and then call one so many soft Names which a Man
of his Learning has at his Fingers Ends. There sure is some Excuse for
Frailty, when attacked by such a Force against a weak Woman.'
Such is the Soliloquy of many a Lady one might name, at the sight of one
of these who makes it no Iniquity to go on from Day to Day in the Sin of
Woman-Slaughter.
It is certain that People are got into a Way of Affectation, with a
manner of overlooking the most solid Virtues, and admiring the most
trivial Excellencies. The Woman is so far from expecting to be contemned
for being a very injudicious silly Animal, that while she can preserve
her Features and her Mein, she knows she is still the Object of Desire;
and there is a sort of secret Ambition, from reading frivolous Books,
and keeping as frivolous Company, each side to be amiable in
Imperfection, and
at the Characters of the Dear Deceiver and the
Perjured Fair
.
T.
To this number is appended the following advertisement.
Contents
Mr.
Spectator gives his most humble Service
to
Mr. R. M. of Chippenham in
Wilts,
and hath received the Patridges.
|
Thursday, August 30, 1711 |
Steele |
... Genius natale comes qui temperat astrum
Naturæ Deus humanæ Mortalis in unum
Quodque Caput ...
Hor.

I am very much at a loss to express by any Word that occurs to me in our
Language that which is understood by
Indoles
in
Latin
. The natural
Disposition to any Particular Art, Science, Profession, or Trade, is
very much to be consulted in the Care of Youth, and studied by Men for
their own Conduct when they form to themselves any Scheme of Life. It is
wonderfully hard indeed for a Man to judge of his own Capacity
impartially; that may look great to me which may appear little to
another, and I may be carried by Fondness towards my self so far, as to
attempt Things too high for my Talents and Accomplishments: But it is
not methinks so very difficult a Matter to make a Judgment of the
Abilities of others, especially of those who are in their Infancy. My
Commonplace Book directs me on this Occasion to mention the Dawning of
Greatness in
Alexander
, who being asked in his Youth to contend for a
Prize in the Olympick Games, answered he would, if he had Kings to run
against him.
Cassius
, who was one of the Conspirators against
Cæsar
,
gave as great a Proof of his Temper, when in his Childhood he struck a
Play-fellow, the Son of
Sylla
, for saying his Father was Master of the
Roman
People.
Scipio
is reported to have answered, (when some
Flatterers at Supper were asking him what the
Romans
should do for a
General after his Death) Take
Marius
.
Marius
was then a very Boy,
and had given no Instances of his Valour; but it was visible to
Scipio
from the Manners of the Youth, that he had a Soul formed for the Attempt
and Execution of great Undertakings. I must confess I have very often
with much Sorrow bewailed the Misfortune of the Children of
Great
Britain
, when I consider the Ignorance and Undiscerning of the
Generality of Schoolmasters. The boasted Liberty we talk of is but a
mean Reward for the long Servitude, the many Heart-aches and Terrors, to
which our Childhood is exposed in going through a Grammar-School: Many
of these stupid Tyrants exercise their Cruelty without any manner of
Distinction of the Capacities of Children, or the Intention of Parents
in their Behalf. There are many excellent Tempers which are worthy to be
nourished and cultivated with all possible Diligence and Care, that were
never designed to be acquainted with
Aristotle, Tully
, or
Virgil
;
and there are as many who have Capacities for understanding every Word
those great Persons have writ, and yet were not born to have any Relish
of their Writings. For want of this common and obvious discerning in
those who have the Care of Youth, we have so many hundred unaccountable
Creatures every Age whipped up into great Scholars, that are for ever
near a right Understanding, and will never arrive at it. These are the
Scandal of Letters, and these are generally the Men who are to teach
others. The Sense of Shame and Honour is enough to keep the World itself
in Order without Corporal Punishment, much more to train the Minds of
uncorrupted and innocent Children. It happens, I doubt not, more than
once in a Year, that a Lad is chastised for a Blockhead, when it is good
Apprehension that makes him incapable of knowing what his Teacher means:
A brisk Imagination very often may suggest an Error, which a Lad could
not have fallen into, if he had been as heavy in conjecturing as his
Master in explaining: But there is no Mercy even towards a wrong
Interpretation of his Meaning, the Sufferings of the Scholar's Body are
to rectify the Mistakes of his Mind.
I am confident that no Boy who will not be allured to Letters without
Blows, will ever be brought to any thing with them. A great or good Mind
must necessarily be the worse for such Indignities; and it is a sad
Change to lose of its Virtue for the Improvement of its Knowledge. No
one who has gone through what they call a great School, but must
remember to have seen Children of excellent and ingenuous Natures, (as
has afterwards appeared in their Manhood) I say no Man has passed
through this way of Education, but must have seen an ingenuous Creature
expiring with Shame, with pale Looks, beseeching Sorrow, and silent
Tears, throw up its honest Eyes, and kneel on its tender Knees to an
inexorable Blockhead, to be forgiven the false Quantity of a Word in
making a Latin Verse; The Child is punished, and the next Day he commits
a like Crime, and so a third with the same Consequence. I would fain ask
any reasonable Man whether this Lad, in the Simplicity of his native
Innocence, full of Shame, and capable of any Impression from that Grace
of Soul, was not fitter for any Purpose in this Life, than after that
Spark of Virtue is extinguished in him, tho' he is able to write twenty
Verses in an Evening?
says, after his exalted way of Talking,
As the immortal Gods
never learnt any Virtue, tho they are endowed with all that is good; so
there are some Men who have so natural a Propensity to what they should
follow, that they learn it almost as soon as they hear it.
Plants
and Vegetables are cultivated into the Production of finer Fruit than
they would yield without that Care; and yet we cannot entertain Hopes of
producing a tender conscious Spirit into Acts of Virtue, without the
same Methods as is used to cut Timber, or give new Shape to a Piece of
Stone.
It is wholly to this dreadful Practice that we may attribute a certain
Hardiness and Ferocity which some Men, tho' liberally educated, carry
about them in all their Behaviour. To be bred like a Gentleman, and
punished like a Malefactor, must, as we see it does, produce that
illiberal Sauciness which we see sometimes in Men of Letters.
The
Spartan
Boy who suffered the Fox (which he had stolen and
hid under his Coat) to eat into his Bowels, I dare say had not half the
Wit or Petulance which we learn at great Schools among us: But the
glorious Sense of Honour, or rather Fear of Shame, which he demonstrated
in that Action, was worth all the Learning in the World without it.
It is methinks a very melancholy Consideration, that a little Negligence
can spoil us, but great Industry is necessary to improve us; the most
excellent Natures are soon depreciated, but evil Tempers are long before
they are exalted into good Habits. To help this by Punishments, is the
same thing as killing a Man to cure him of a Distemper; when he comes to
suffer Punishment in that one Circumstance, he is brought below the
Existence of a rational Creature, and is in the State of a Brute that
moves only by the Admonition of Stripes. But since this Custom of
educating by the Lash is suffered by the Gentry of
Great Britain
, I would prevail only that honest heavy Lads may be dismissed from
Slavery sooner than they are at present, and not whipped on to their
fourteenth or fifteenth Year, whether they expect any Progress from them
or not. Let the Child's Capacity be forthwith examined and
he
sent to
some Mechanick Way of Life, without respect to his Birth, if Nature
designed him for nothing higher: let him go before he has innocently
suffered, and is debased into a Dereliction of Mind for being what it is
no Guilt to be, a plain Man. I would not here be supposed to have said,
that our learned Men of either Robe who have been whipped at School, are
not still Men of noble and liberal Minds; but I am sure they had been
much more so than they are, had they never suffered that Infamy.
But tho' there is so little Care, as I have observed, taken, or
Observation made of the natural Strain of Men, it is no small Comfort to
me, as a
Spectator
, that there is any right Value set upon the
bona
Indoles
of other Animals; as appears by the following Advertisement
handed about the County of
Lincoln
, and subscribed by
Enos
Thomas
, a Person whom I have not the Honour to know, but suppose to
be profoundly learned in Horse-flesh.
A Chesnut Horse called Cæsar, bred by James Darcy,
Esq., at Sedbury, near Richmond in the County of
York; his Grandam was his old royal Mare, and got by
Blunderbuss, which was got by Hemsly Turk, and he got
Mr. Courand's Arabian, which got Mr. Minshul's
Jews-trump. Mr. Cæsar sold him to a Nobleman (coming
five Years old, when he had but one Sweat) for three hundred Guineas.
A Guinea a Leap and Trial, and a Shilling the Man .
T. Enos Thomas.
Epist. 95.
Contents
|
Friday, August 31, 1711 |
Steele |
Nos hoec novimus esse nihil.
Martial.

Out of a firm Regard to Impartiality, I print these Letters, let them
make for me or not.
Mr .
Spectator,
I have observed through the whole Course of your Rhapsodies, (as you
once very well called them) you are very industrious to overthrow all
that many your Superiors who have gone before you have made their Rule
of writing. I am now between fifty and sixty, and had the Honour to be
well with the first Men of Taste and Gallantry in the joyous Reign of
Charles the Second: We then had, I humbly presume, as good
Understandings among us as any now can pretend to. As for yourself,
Mr.
Spectator, you seem with the utmost Arrogance to undermine the
very Fundamentals upon which we conducted our selves.
It is monstrous
to set up for a Man of Wit, and yet deny that Honour in a Woman is any
thing else but Peevishness, that Inclination
is1 the best Rule of
Life, or Virtue and Vice any thing else but Health and Disease. We had
no more to do but to put a Lady into good Humour, and all we could
wish followed of Course. Then again, your
Tully, and your Discourses
of another Life, are the very Bane of Mirth and good Humour. Pr'ythee
don't value thyself on thy Reason at that exorbitant Rate, and the
Dignity of human Nature; take my Word for it, a Setting-dog has as
good Reason as any Man in
England. Had you (as by your Diurnals one
would think you do) set up for being in vogue in Town, you should have
fallen in with the Bent of Passion and Appetite; your Songs had then
been in every pretty Mouth in
England, and your little Distichs had
been the Maxims of the Fair and the Witty to walk by: But alas, Sir,
what can you hope for from entertaining People with what must needs
make them like themselves worse than they did before they read you?
Had you made it your Business to describe
Corinna charming, though
inconstant, to find something in human Nature itself to make
Zoilus
excuse himself for being fond of her; and to make every Man in good
Commerce with his own Reflections, you had done something worthy our
Applause; but indeed, Sir, we shall not commend you for disapproving
us. I have a great deal more to say to you, but I shall sum it up all
in this one Remark, In short, Sir, you do not write like a Gentleman.
'I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'The other Day we were several of us at a Tea-Table, and according to
Custom and your own Advice had the
Spectator read among us: It was
that Paper wherein you are pleased to treat with great Freedom that
Character which you call a Woman's Man. We gave up all the Kinds you
have mentioned, except those who, you say, are our constant Visitants.
I was upon the Occasion commissioned by the Company to write to you
and tell you, That we shall not part with the Men we have at present,
'till the Men of Sense think fit to relieve them, and give us their
Company in their Stead. You cannot imagine but that we love to hear
Reason and good Sense better than the Ribaldry we are at present
entertained with, but we must have Company, and among us very
inconsiderable is better than none at all. We are made for the Cements
of Society, and came into the World to create Relations among Mankind;
and Solitude is an unnatural Being to us. If the Men of good
Understanding would forget a little of their Severity, they would find
their Account in it; and their Wisdom would have a Pleasure in it, to
which they are now Strangers. It is natural among us when Men have a
true Relish of our Company and our Value, to say every thing with a
better Grace; and there is without designing it something ornamental
in what Men utter before Women, which is lost or neglected in
Conversations of Men only. Give me leave to tell you, Sir, it would do
you no great Harm if you yourself came a little more into our Company;
it would certainly cure you of a certain positive and determining
Manner in which you talk sometimes. In hopes of your Amendment,
'I am, Sir,
'Your gentle Reader.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'Your professed Regard to the Fair Sex, may perhaps make them value
your Admonitions when they will not those of other Men. I desire you,
Sir, to repeat some Lectures upon Subjects which you have now and then
in a cursory manner only just touched. I would have a
Spectator
wholly writ upon good Breeding: and after you have asserted that Time
and Place are to be very much considered in all our Actions, it will
be proper to dwell upon Behaviour at Church. On Sunday last a grave
and reverend Man preached at our Church: There was something
particular in his Accent, but without any manner of Affectation. This
Particularity a Set of Gigglers thought the most necessary Thing to be
taken notice of in his whole Discourse, and made it an Occasion of
Mirth during the whole time of Sermon: You should see one of them
ready to burst behind a Fan, another pointing to a Companion in
another Seat, and a fourth with an arch Composure, as if she would if
possible stifle her Laughter. There were many Gentlemen who looked at
them stedfastly, but this they took for ogling and admiring them:
There was one of the merry ones in particular, that found out but just
then that she had but five Fingers, for she fell a reckoning the
pretty Pieces of Ivory over and over again, to find her self
Employment and not laugh out. Would it not be expedient, Mr.
Spectator, that the Church-warden should hold up his Wand on these
Occasions, and keep the Decency of the Place as a Magistrate does the
Peace in a Tumult elsewhere?
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Woman's Man, and read with a very fine Lady your Paper, wherein
you fall upon us whom you envy: What do you think I did? you must know
she was dressing, I read the
Spectator to her, and she laughed at
the Places where she thought I was touched; I threw away your Moral,
and taking up her Girdle cried out,
Give me but what this Ribbon bound,
Take all the rest the Sun2 goes round3.
She smiled, Sir, and said you were a Pedant; so say of me what you
please, read
Seneca and quote him against me if you think fit.
I am,
Sir,
Your humble Servant.
is not
World
.
Waller,
On a Girdle
.
Contents
|
Saturday,
September 1, 1711 |
Addison |
... Omnem quæ nunc obducta tuenti
Mortales hebetat visus tibi, et humida circum
Caligat, nubem eripiam ...
Virg.

When I was at
Grand Cairo
, I picked up several Oriental
Manuscripts, which I have still by me. Among others
I met with one entitled,
The Visions of Mirzah
, which I have
read over with great Pleasure. I intend to give it to the Publick when I have no other Entertainment for them; and shall begin
with the first Vision, which I have translated Word for
Word as follows.
'On the fifth Day of the Moon, which according to the Custom of my
Forefathers I always keep holy, after having washed my self, and
offered up my Morning Devotions, I ascended the high Hills of
Bagdat, in order to pass the rest of the Day in Meditation and
Prayer. As I was here airing my self on the Tops of the Mountains, I
fell into a profound Contemplation on the Vanity of human Life; and
passing from one Thought to another, Surely, said I, Man is but a
Shadow and Life a Dream. Whilst I was thus musing, I cast my Eyes
towards the Summit of a Rock that was not far from me, where I
discovered one in the Habit of a Shepherd, with a little Musical
Instrument in his Hand. As I looked upon him he applied it to his
Lips, and began to play upon it. The Sound of it was exceeding sweet,
and wrought into a Variety of Tunes that were inexpressibly
melodious, and altogether different from any thing I had ever heard:
They put me in mind of those heavenly Airs that are played to the
departed Souls of good Men upon their first Arrival in Paradise, to
wear out the Impressions of the last Agonies, and qualify them for the
Pleasures of that happy Place. My Heart melted away in secret
Raptures.
I had been often told that the Rock before me was the Haunt of a
Genius; and that several had been entertained with Musick who had
passed by it, but never heard that the Musician had before made
himself visible. When he had raised my Thoughts by those transporting
Airs which he played, to taste the Pleasures of his Conversation, as I
looked upon him like one astonished, he beckoned to me, and by the
waving of his Hand directed me to approach the Place where he sat. I
drew near with that Reverence which is due to a superior Nature; and
as my Heart was entirely subdued by the captivating Strains I had
heard, I fell down at his Feet and wept. The Genius smiled upon me
with a Look of Compassion and Affability that familiarized him to my
Imagination, and at once dispelled all the Fears and Apprehensions
with which I approached him. He lifted me from the Ground, and taking
me by the hand,
Mirzah, said he, I have heard thee in thy
Soliloquies; follow me.
He then led me to the highest Pinnacle of the Rock, and placing me on
the Top of it, Cast thy Eyes Eastward, said he, and tell me what thou
seest. I see, said I, a huge Valley, and a prodigious Tide of Water
rolling through it. The Valley that thou seest, said he, is the Vale
of Misery, and the Tide of Water that thou seest is part of the great
Tide of Eternity. What is the Reason, said I, that the Tide I see
rises out of a thick Mist at one End, and again loses itself in a
thick Mist at the other? What thou seest, said he, is that Portion of
Eternity which is called Time, measured out by the Sun, and reaching
from the Beginning of the World to its Consummation. Examine now, said
he, this Sea that is bounded with Darkness at both Ends, and tell me
what thou discoverest in it. I see a Bridge, said I, standing in the
Midst of the Tide. The Bridge thou seest, said he, is human Life,
consider it attentively. Upon a more leisurely Survey of it, I found
that it consisted of threescore and ten entire Arches, with several
broken Arches, which added to those that were entire, made up the
Number about an hundred. As I was counting the Arches, the Genius told
me that this Bridge consisted at first of a thousand Arches; but that
a great Flood swept away the rest, and left the Bridge in the ruinous
Condition I now beheld it: But tell me further, said he, what thou
discoverest on it. I see Multitudes of People passing over it, said I,
and a black Cloud hanging on each End of it. As I looked more
attentively, I saw several of the Passengers dropping thro' the
Bridge, into the great Tide that flowed underneath it; and upon
farther Examination, perceived there were innumerable Trap-doors that
lay concealed in the Bridge, which the Passengers no sooner trod upon,
but they fell thro' them into the Tide and immediately disappeared.
These hidden Pit-falls were set very thick at the Entrance of the
Bridge, so that the Throngs of People no sooner broke through the
Cloud, but many of them fell into them. They grew thinner towards the
Middle, but multiplied and lay closer together towards the End of the
Arches that were entire.
'There were indeed some Persons, but their Number was very small, that
continued a kind of hobbling March on the broken Arches, but fell
through one after another, being quite tired and spent with so long a
Walk.
I passed some Time in the Contemplation of this wonderful Structure,
and the great Variety of Objects which it presented. My Heart was
filled with a deep Melancholy to see several dropping unexpectedly in
the midst of Mirth and Jollity, and catching at every thing that stood
by them to save themselves. Some were looking up towards the Heavens
in a thoughtful Posture, and in the midst of a Speculation stumbled
and fell out of Sight. Multitudes were very busy in the Pursuit of
Bubbles that glittered in their Eyes and danced before them; but often
when they thought themselves within the reach of them their Footing
failed and down they sunk.
In this Confusion of Objects, I observed
some with Scymetars in their Hands, and others with Urinals, who ran
to and fro upon the Bridge, thrusting several Persons on Trap-doors
which did not seem to
lie in their Way,1 and which they might have
escaped had they not been forced upon them.
The Genius seeing me indulge my self in this melancholy Prospect,
told me I had dwelt long enough upon it: Take thine Eyes off the
Bridge, said he, and tell me if thou yet seest any thing thou dost not
comprehend. Upon looking up, What mean, said I, those great Flights of
Birds that are perpetually hovering about the Bridge, and settling
upon it from time to time? I see Vultures, Harpyes, Ravens,
Cormorants, and among many other feather'd Creatures several little
winged Boys, that perch in great Numbers upon the middle Arches.
These, said the Genius, are Envy, Avarice, Superstition, Despair,
Love, with the like Cares and Passions that infest human Life.
I here fetched a deep Sigh, Alas, said I, Man was made in vain! How
is he given away to Misery and Mortality! tortured in Life, and
swallowed up in Death! The Genius being moved with Compassion towards
me, bid me quit so uncomfortable a Prospect: Look no more, said he, on
Man in the first Stage of his Existence, in his setting out for
Eternity; but cast thine Eye on that thick Mist into which the Tide
bears the several Generations of Mortals that fall into it. I directed
my Sight as I was ordered, and (whether or no the good Genius
strengthened it with any supernatural Force, or dissipated Part of the
Mist that was before too thick for the Eye to penetrate) I saw the
Valley opening at the farther End, and spreading forth into an immense
Ocean, that had a huge Rock of Adamant running through the Midst of
it, and dividing it into two equal Parts. The Clouds still rested on
one Half of it, insomuch that I could discover nothing in it: But the
other appeared to me a vast Ocean planted with innumerable Islands,
that were covered with Fruits and Flowers, and interwoven with a
thousand little shining Seas that ran among them. I could see Persons
dressed in glorious Habits with Garlands upon their Heads, passing
among the Trees, lying down by the Side of Fountains, or resting on
Beds of Flowers; and could hear a confused Harmony of singing Birds,
falling Waters, human Voices, and musical Instruments. Gladness grew
in me upon the Discovery of so delightful a Scene. I wished for the
Wings of an Eagle, that I might fly away to those happy Seats; but the
Genius told me there was no Passage to them, except through the Gates
of Death that I saw opening every Moment upon the Bridge. The Islands,
said he, that lie so fresh and green before thee, and with which the
whole Face of the Ocean appears spotted as far as thou canst see, are
more in Number than the Sands on the Sea-shore; there are Myriads of
Islands behind those which thou here discoverest, reaching further
than thine Eye, or even thine Imagination can extend it self. These
are the Mansions of good Men after Death, who according to the Degree
and Kinds of Virtue in which they excelled, are distributed among
these several Islands, which abound with Pleasures of different Kinds
and Degrees, suitable to the Relishes and Perfections of those who are
settled in them; every Island is a Paradise accommodated to its
respective Inhabitants. Are not these, O
Mirzah, Habitations
worth contending for? Does Life appear miserable, that gives thee
Opportunities of earning such a Reward? Is Death to be feared, that
will convey thee to so happy an Existence? Think not Man was made in
vain, who has such an Eternity reserved for him. I gazed with
inexpressible Pleasure on these happy Islands. At length, said I, shew
me now, I beseech thee, the Secrets that lie hid under those dark
Clouds which cover the Ocean on the other side of the Rock of Adamant.
The Genius making me no Answer, I turned about to address myself to
him a second time, but I found that he had left me; I then turned
again to the Vision which I had been so long contemplating; but
Instead of the rolling Tide, the arched Bridge, and the happy Islands,
I saw nothing but the long hollow Valley of
Bagdat, with Oxen,
Sheep, and Camels grazing upon the Sides of it.
The End of the first Vision of Mirzah.
C.
"have been laid for them", corrected by an erratum in No.
161.
Contents
|
Monday,
September 3, 1711 |
Addison |
... Cui mens divinior, atque os
Magna sonaturum, des nominis hujus honorem.
Hor.

There is no Character more frequently given to a Writer, than that of
being a Genius. I have heard many a little Sonneteer called a
fine
Genius
. There is not an Heroick Scribler in the Nation, that has not
his Admirers who think him a
great Genius
; and as for your Smatterers
in Tragedy, there is scarce a Man among them who is not cried up by one
or other for a
prodigious Genius
.
My design in this Paper is to consider what is properly a great Genius,
and to throw some Thoughts together on so uncommon a Subject.
Among great Genius's those few draw the Admiration of all the World upon
them, and stand up as the Prodigies of Mankind, who by the meer Strength
of natural Parts, and without any Assistance of Arts or Learning, have
produced Works that were the Delight of their own Times, and the Wonder
of Posterity. There appears something nobly wild and extravagant in
these great natural Genius's, that is infinitely more beautiful than all
the Turn and Polishing of what the
French
call a
Bel Esprit
, by
which they would express a Genius refined by Conversation, Reflection,
and the Reading of the most polite Authors.
greatest Genius
which
runs through the Arts and Sciences, takes a kind of Tincture from
them, and falls unavoidably into Imitation.
Many of these great natural Genius's that were never disciplined and
broken by Rules of Art, are to be found among the Ancients, and in
particular among those of the more Eastern Parts of the World.
Homer
has innumerable Flights that
Virgil
was not able to reach, and in the
Old Testament we find several Passages more elevated and sublime than
any in
Homer
. At the same time that we allow a greater and more daring
Genius to the Ancients, we must own that the greatest of them very much
failed in, or, if you will, that they were very much above the Nicety
and Correctness of the Moderns. In their Similitudes and Allusions,
provided there was a Likeness, they did not much trouble themselves
about the Decency of the Comparison: Thus
Solomon
resembles the Nose
of his Beloved to the Tower of
Libanon
which looketh toward
Damascus
; as the Coming of a Thief in the Night, is a Similitude of
the same kind in the New Testament. It would be endless to make
Collections of this Nature;
Homer
illustrates one of his Heroes
encompassed with the Enemy by an Ass in a Field of Corn that has his
Sides belaboured by all the Boys of the Village without stirring a Foot
for it: and another of them tossing to and fro in his Bed and burning
with Resentment, to a Piece of Flesh broiled on the Coals. This
particular Failure in the Ancients, opens a large Field of Raillery to
the little Wits, who can laugh at an Indecency but not relish the
Sublime in these Sorts of Writings. The present Emperor of
Persia
,
conformable to this Eastern way of Thinking, amidst a great many pompous
Titles, denominates himself The Sun of Glory and the Nutmeg of Delight.
In short, to cut off all Cavilling against the Ancients and particularly
those of the warmer Climates who had most Heat and Life in their
Imaginations, we are to consider that the Rule of observing what the
French
call the
Bienséance
in an Allusion, has been found out of
latter Years, and in the colder Regions of the World; where we would
make some Amends for our want of Force and Spirit, by a scrupulous
Nicety and Exactness in our Compositions.
Our Countryman
Shakespear
was a remarkable Instance of this first
kind of great Genius's.
I cannot quit this Head without observing that
Pindar
was a great
Genius of the first Class, who was hurried on by a natural Fire and
Impetuosity to vast Conceptions of things and noble Sallies of
Imagination. At the same time, can any thing be more ridiculous than for
Men of a sober and moderate Fancy to imitate this Poet's Way of Writing
in those monstrous Compositions which go among us under the Name of
Pindaricks? When I see People copying Works which, as
Horace
has
represented them, are singular in their Kind, and inimitable; when I see
Men following Irregularities by Rule, and by the little Tricks of Art
straining after the most unbounded Flights of Nature, I cannot but apply
to them that Passage in
Terence
:
... Incerta hæc si tu postules
Ratione certâ facere, nihilo plus agas,
Quàm si des operam, ut cum ratione insanias.
short a modern Pindarick Writer, compared with
Pindar
, is like
a Sister among the Camisars
compared with
Virgil
's Sibyl:
There is the Distortion, Grimace, and outward Figure, but nothing of
that divine Impulse which raises the Mind above its self, and makes the
Sounds more than human.
There is another kind of great Genius's which I shall place in a second
Class, not as I think them inferior to the first, but only for
Distinction's sake, as they are of a different kind. This second
Class of great Genius's are those that have formed themselves by Rules,
and submitted the Greatness of their natural Talents to the Corrections
and Restraints of Art. Such among the
Greeks
were
Plato
and
Aristotle
; among the
Romans
,
Virgil
and
Tully
; among the
English
,
Milton
and Sir
Francis
Bacon
.
The Genius
both these Classes of Authors may be equally great,
but shews itself
after
a different Manner. In the first it is like
a rich Soil in a happy Climate, that produces a whole Wilderness of
noble Plants rising in a thousand beautiful Landskips, without any
certain Order or Regularity. In the other it is the same rich Soil under
the same happy Climate, that has been laid out in Walks and Parterres,
and cut into Shape and Beauty by the Skill of the Gardener.
The great Danger in these latter kind of Genius's, is, lest they cramp
their own Abilities too much by Imitation, and form themselves
altogether upon Models, without giving the full Play to their own
natural Parts. An Imitation of the best Authors is not to compare with a
good Original; and I believe we may observe that very few Writers make
an extraordinary Figure in the World, who have not something in their
Way of thinking or expressing themselves that is peculiar to them, and
entirely their own.
It
odd to consider what great Genius's are sometimes thrown away
upon Trifles.
once saw a Shepherd, says a famous
Italian
Author,
who
used to
divert himself in his Solitudes with tossing up Eggs and catching them
again without breaking them: In which he had arrived to so great a
degree of Perfection, that he would keep up four at a time for several
Minutes together playing in the Air, and falling into his Hand by Turns.
I think, says the Author, I never saw a greater Severity than in this
Man's Face; for by his wonderful Perseverance and Application, he had
contracted the Seriousness and Gravity of a Privy-Councillor; and I
could not but reflect with my self, that the same Assiduity and
Attention, had they been rightly applied, might have made him a greater
Mathematician than
Archimedes
.
C.
that
The Camisars, or French Prophets, originally from the
Cevennes, came into England in 1707. With violent agitations and
distortions of body they prophesied and claimed also the power to work
miracles; even venturing to prophesy that Dr Ernes, a convert of theirs,
should rise from the dead five months after burial.
The
Not a new paragraph in the first issue.
in
Not a new paragraph in the first issue.
that
Contents
|
Tuesday,
September 4, 1711 |
Budgell |
Ipse dies agitat festos: Fususque per herbam,
Ignis ubi in medio et Socii cratera coronant,
Te libans, Lenæe, vocat: pecorisque magistris
Velocis Jaculi certamina ponit in ulmo,
Corporaque agresti nudat prædura Palæstra.
Hanc olim veteres vitam coluere Sabini,
Hanc Remus et Frater: Sic fortis Etruria crevit,
Scilicet et rerum facta est pulcherrima Roma.
Virg.
G. 2.

I am glad that my late going into the Country has encreased the Number
of my Correspondents, one of whom sends me the following Letter.
Sir,
'Though you are pleased to retire from us so soon into the City, I
hope you will not think the Affairs of the Country altogether unworthy
of your Inspection for the future. I had the Honour of seeing your
short Face at Sir Roger De Coverley's, and have ever since thought
your Person and Writings both extraordinary. Had you stayed there a
few Days longer you would have seen a Country Wake, which you know
in most Parts of England is the Eve-Feast of the Dedication of our
Churches. I was last Week at one of these Assemblies which was held
in a neighbouring Parish; where I found their Green covered with a
promiscuous Multitude of all Ages and both Sexes, who esteem one
another more or less the following Part of the Year according as they
distinguish themselves at this Time. The whole Company were in their
Holiday Cloaths, and divided into several Parties, all of them
endeavouring to shew themselves in those Exercises wherein they
excelled, and to gain the Approbation of the Lookers on.
I found a Ring of Cudgel-Players, who were breaking one another's
Heads in order to make some Impression on their Mistresses Hearts. I
observed a lusty young Fellow, who had the Misfortune of a broken
Pate; but what considerably added to the Anguish of the Wound, was his
over-hearing an old Man, who shook his Head and said, That he
questioned now if black Kate would marry him these three Years. I was
diverted from a farther Observation of these Combatants, by a
Foot-ball Match, which was on the other side of the Green; where
Tom Short behaved himself so well, that most People seemed to agree
it was impossible that he should remain a Batchelor till the next
Wake. Having played many a Match my self, I could have looked longer
on this Sport, had I not observed a Country Girl, who was posted on an
Eminence at some Distance from me, and was making so many odd
Grimaces, and writhing and distorting her whole Body in so strange a
Manner, as made me very desirous to know the Meaning of it. Upon my
coming up to her, I found that she was overlooking a Ring of
Wrestlers, and that her Sweetheart, a Person of small Stature, was
contending with an huge brawny Fellow, who twirled him about, and
shook the little Man so violently, that by a secret Sympathy of Hearts
it produced all those Agitations in the Person of his Mistress, who I
dare say, like Cælia in Shakespear on the same Occasion, could
have wished herself invisible to catch the strong Fellow by the Leg.
The Squire of the Parish treats the whole Company every Year with a
Hogshead of Ale; and proposes a Beaver-Hat as a Recompense to him
who gives most Falls. This has raised such a Spirit of Emulation in
the Youth of the Place, that some of them have rendered themselves
very expert at this Exercise; and I was often surmised to see a
Fellow's Heels fly up, by a Trip which was given him so smartly that I
could scarce discern it. I found that the old Wrestlers seldom entered
the Ring, till some one was grown formidable by having thrown two or
three of his Opponents; but kept themselves as it were in a reserved
Body to defend the Hat, which is always hung up by the Person who gets
it in one of the most Conspicuous Parts of the House, and looked upon
by the whole Family as something redounding much more to their Honour
than a Coat of Arms. There was a Fellow who was so busy in regulating
all the Ceremonies, and seemed to carry such an Air of Importance in
his Looks, that I could not help inquiring who he was, and was
immediately answered, That he did not value himself upon nothing,
for that he and his Ancestors had won so many Hats, that his Parlour
looked like a Haberdashers Shop: However this Thirst of Glory in
them all, was the Reason that no one Man stood Lord of the Ring
for above three Falls while I was amongst them.
The young Maids, who were not Lookers on at these Exercises, were
themselves engaged in some Diversion; and upon my asking a Farmer's
Son of my own Parish what he was gazing at with so much Attention, he
told me, That he was seeing Betty Welch, whom I knew to be his
Sweet-Heart, pitch a Bar.
In short, I found the men endeavoured to shew the Women they were no
Cowards, and that the whole Company strived to recommend themselves to
each other, by making it appear that they were all in a perfect State
of Health, and fit to undergo any Fatigues of bodily Labour.
Your Judgment upon this Method of Love and Gallantry, as
it is at present practised amongst us in the Country, will very much
oblige,
Sir, Yours, &c.'
If I would here put on the Scholar and Politician, I might inform my
Readers how these bodily Exercises or Games were formerly encouraged in
all the Commonwealths of
Greece
; from whence the
Romans
afterwards borrowed their
Pentathlum
, which was composed of
Running, Wrestling, Leaping, Throwing
, and
Boxing
, tho'
the Prizes were generally nothing but a Crown of Cypress or Parsley,
Hats not being in fashion in those Days: That there is an old Statute,
which obliges every Man in
England
, having such an Estate, to
keep and exercise the long Bow; by which Means our Ancestors excelled
all other Nations in the Use of that Weapon, and we had all the real
Advantages, without the Inconvenience of a standing Army: And that I
once met with a Book of Projects, in which the Author considering to
what noble Ends that Spirit of Emulation, which so remarkably shews it
self among our common People in these Wakes, might be directed, proposes
that for the Improvement of all our handicraft Trades there should be
annual Prizes set up for such Persons as were most excellent in their
several Arts. But laying aside all these political Considerations, which
might tempt me to pass the Limits of my Paper, I confess the greatest
Benefit and Convenience that I can observe in these Country Festivals,
is the bringing young People together, and giving them an Opportunity of
shewing themselves in the most advantageous Light. A Country Fellow that
throws his Rival upon his Back, has generally as good Success with their
common Mistress; as nothing is more usual than for a nimble-footed Wench
to get a Husband at the same time she wins a Smock. Love and Marriages
are the natural Effects of these anniversary Assemblies. I must
therefore very much approve the Method by which my Correspondent tells
me each Sex endeavours to recommend it self to the other, since nothing
seems more likely to promise a healthy Offspring or a happy
Cohabitation. And I believe I may assure my Country Friend, that there
has been many a Court Lady who would be contented to exchange her crazy
young Husband for
Tom Short
, and several Men of Quality who would have
parted with a tender Yoke-fellow for
Black Kate
.
am the more pleased with having
Love
made the principal End and
Design of these Meetings, as it seems to be most agreeable to the Intent
for which they were at first instituted, as we are informed by the
learned Dr.
Kennet
, with whose Words I shall conclude my present
Paper.
These Wakes, says he,
were in Imitation of the ancient
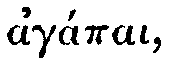 or Love-Feasts; and were first established in
or Love-Feasts; and were first established in England
by Pope Gregory
the Great, who in an Epistle to Melitus
the Abbot
gave Order that they should be kept in Sheds or Arbories made up with
Branches and Boughs of Trees round the Church.
He adds,
That this laudable Custom of Wakes prevailed for many Ages,
till the nice Puritans began to exclaim against it as a Remnant of
Popery; and by degrees the precise Humour grew so popular, that at an
Exeter
Assizes the Lord Chief Baron Walter
made an Order for the
Suppression of all Wakes; but on Bishop Laud's
complaining of this
innovating Humour, the King commanded the Order to be reversed.
X.
Parochial Antiquities
(1795), pp. 610, 614.
Contents
|
Wednesday,
September 5, 1711 |
Addison |
... Servetur ad imum,
Qualis ab incœpto processerit, et sibi constet.
Hor.

Nothing that is not a real Crime makes a Man appear so contemptible and
little in the Eyes of the World as Inconstancy, especially when it
regards Religion or Party. In either of these Cases, tho' a Man perhaps
does but his Duty in changing his Side, he not only makes himself hated
by those he left, but is seldom heartily esteemed by those he comes over
to.
In these great Articles of Life, therefore, a Man's Conviction ought to
be very strong, and if possible so well timed that worldly Advantages
may seem to have no Share in it, or Mankind will be ill natured enough
to think he does not change Sides out of Principle, but either out of
Levity of Temper or Prospects of Interest. Converts and Renegadoes of
all Kinds should take particular care to let the World see they act upon
honourable Motives; or whatever Approbations they may receive from
themselves, and Applauses from those they converse with, they may be
very well assured that they are the Scorn of all good Men, and the
publick Marks of Infamy and Derision.
on the Schemes of Life
which
offer themselves to our
Choice, and Inconstancy in pursuing them, are the greatest and most
universal Causes of all our Disquiet and Unhappiness. When
Ambition
pulls
Way, Interest another, Inclination a third, and perhaps
Reason contrary to all, a Man is likely to pass his Time but ill who has
so many different Parties to please. When the Mind hovers among such a
Variety of Allurements, one had better settle on a Way of Life that is
not the very best we might have chosen, than grow old without
determining our Choice, and go out of the World as the greatest Part of
Mankind do, before we have resolved how to live in it. There is but one
Method of setting our selves at Rest in this Particular, and that is by
adhering stedfastly to one great End as the chief and ultimate Aim of
all our Pursuits. If we are firmly resolved to live up to the Dictates
of Reason, without any Regard to Wealth, Reputation, or the like
Considerations, any more than as they fall in with our principal Design,
we may go through Life with Steadiness and Pleasure; but if we act by
several broken Views, and will not only be virtuous, but wealthy,
popular, and every thing that has a Value set upon it by the World, we
shall live and die in Misery and Repentance.
One would take more than ordinary Care to guard ones self against this
particular Imperfection, because it is that which our Nature very
strongly inclines us to; for if we examine ourselves throughly, we shall
find that we are the most changeable Beings in the Universe. In respect
of our Understanding, we often embrace and reject the very same
Opinions; whereas Beings above and beneath us have probably no Opinions
at all, or at least no Wavering and Uncertainties in those they have.
Our Superiors are guided by Intuition, and our Inferiors by Instinct. In
respect of our Wills, we fall into Crimes and recover out of them, are
amiable or odious in the Eyes of our great Judge, and pass our whole
Life in offending and asking Pardon. On the contrary, the Beings
underneath us are not capable of sinning, nor those above us of
repenting. The one is out of the Possibilities of Duty, and the other
fixed in an eternal Course of Sin, or an eternal Course of Virtue.
There is scarce a State of Life, or Stage in it which does not produce
Changes and Revolutions in the Mind of Man. Our Schemes of Thought in
Infancy are lost in those of Youth; these too take a different Turn in
Manhood, till old Age often leads us back into our former Infancy. A new
Title or an unexpected Success throws us out of ourselves, and in a
manner destroys our Identity. A cloudy Day, or a little Sunshine, have
as great an Influence on many Constitutions, as the most real Blessings
or Misfortunes. A Dream varies our Being, and changes our Condition
while it lasts; and every Passion, not to mention Health and Sickness,
and the greater Alterations in Body and Mind, makes us appear almost
different Creatures. If a Man is so distinguished among other Beings by
this Infirmity, what can we think of such as make themselves remarkable
for it even among their own Species? It is a very trifling Character to
be one of the most variable Beings of the most variable Kind, especially
if we consider that He who is the great Standard of Perfection has in
him no Shadow of Change, but is the same Yesterday, To-day, and for
ever.
As this Mutability of Temper and Inconsistency with our selves is the
greatest Weakness of human Nature, so it makes the Person who is
remarkable for it in a very particular Manner more ridiculous than any
other Infirmity whatsoever, as it sets him in a greater Variety of
foolish Lights, and distinguishes him from himself by an Opposition of
party-coloured Characters. The most humourous Character in
Horace
is
founded upon this Unevenness of Temper and Irregularity of Conduct.
... Sardus habebat
Ille Tigellius hoc: Cæsar qui cogere posset
Si peteret per amicitiam patris, atque suam, non
Quidquam proficeret: Si collibuisset, ab ovo
Usque ad mala citaret, Io Bacche, modò summâ
Voce, modò hâc, resonat quæ; chordis quatuor ima.
Nil æquale homini fuit illi: Sæpe velut qui
Currebat fugiens hostem: Persæpe velut qui
Junonis sacra ferret: Habebat sæpe ducentos,
Sæpe decem servos: Modò reges atque tetrarchas,
Omnia magna loquens: Modò sit mihi mensa tripes, et
Concha salis puri, et toga, quæ defendere frigus,
Quamvis crassa, queat. Decies centena dedisses
Huic parco paucis contento, quinque diebus
Nil erat in loculis. Noctes vigilabat ad ipsum
Manè: Diem totam stertebat. Nil fuit unquam
Sic impar sibi ...
Hor. Sat. 3, Lib. 1.
of translating this Passage in
Horace
, I shall entertain
my
English
Reader with the Description of a Parallel Character,
that is wonderfully well finished by Mr.
Dryden
, and raised
upon the same Foundation.
In the first Rank of these did Zimri stand:
A Man so various, that he seem'd to be
Not one, but all Mankind's Epitome.
Stiff in Opinions, always in the wrong;
Was ev'ry thing by Starts, and nothing long;
But, in the Course of one revolving Moon,
Was Chemist, Fidler, Statesman, and Buffoon:
Then all for Women, Painting, Rhiming, Drinking:
Besides ten thousand Freaks that dy'd in thinking.
Blest Madman, who cou'd ev'ry flour employ,
With something New to wish, or to enjoy!
C.
that
Honour
In his
Absalom and Achitophel.
The character of Villiers,
Duke of Buckingham.
Contents
|
Thursday,
September 6, 1711 |
Addison |
... Si quid ego adjuero, curamve levasso,
Quæ nunc te coquit, et versat sub pectore fixa,
Ecquid erit pretii?
Enn. ap. Tullium.

after Happiness, and Rules for attaining it, are not so
necessary and useful to Mankind as the Arts of Consolation, and
supporting
ones
self under Affliction. The utmost we can hope for
in this World is Contentment; if we aim at any thing higher, we shall
meet with nothing but Grief and Disappointments. A Man should direct all
his Studies and Endeavours at making himself easie now, and happy
hereafter.
The Truth of it is, if all the Happiness that is dispersed through the
whole Race of Mankind in this World were drawn together, and put into
the Possession of any single Man, it would not make a very happy Being.
Though on the contrary, if the Miseries of the whole Species were fixed
in a single Person, they would make a very miserable one.
I am engaged in this Subject by the following Letter, which, though
subscribed by a fictitious Name, I have reason to believe is not
Imaginary.
Mr.
Spectator2,
'I
am one of your Disciples, and endeavour to live up to your Rules,
which I hope will incline you to pity my Condition: I shall open it to
you in a very few Words. About three Years since a Gentleman, whom, I
am sure, you yourself would have approved, made his Addresses to me.
He had every thing to recommend him but an Estate, so that my Friends,
who all of them applauded his Person, would not for the sake of both
of us favour his Passion. For my own part, I resigned my self up
entirely to the Direction of those who knew the World much better than
my self, but still lived in hopes that some Juncture or other would
make me happy in the Man, whom, in my Heart, I preferred to all the
World; being determined if I could not have him, to have no Body else.
About three Months ago I received a Letter from him, acquainting me,
that by the Death of an Uncle he had a considerable Estate left him,
which he said was welcome to him upon no other Account, but as he
hoped it would remove all Difficulties that lay in the Way to our
mutual Happiness. You may well suppose, Sir, with how much Joy I
received this Letter, which was followed by several others filled with
those Expressions of Love and Joy, which I verily believe no Body felt
more sincerely, nor knew better how to describe than the Gentleman I
am speaking of. But Sir, how shall I be able to tell it you! by the
last Week's Post I received a letter from an intimate Friend of this
unhappy Gentleman, acquainting me, that as he had just settled his
Affairs, and was preparing for his Journey, he fell sick of a Fever
and died. It is impossible to express to you the Distress I am in upon
this Occasion. I can only have Recourse to my Devotions; and to the
reading of good Books for my Consolation; and as I always take a
particular Delight in those frequent Advices and Admonitions which you
give to the Publick, it would be a very great piece of Charity in you
to lend me your Assistance in this Conjuncture. If after the reading
of this Letter you find your self in a Humour, rather to Rally and
Ridicule, than to Comfort me, I desire you would throw it into the
Fire, and think no more of it; but if you are touched with my
Misfortune, which is greater than I know how to bear, your Counsels
may very much Support, and will infinitely Oblige the afflicted
Leonora.'
A Disappointment in Love is more hard to get over than any other; the
Passion itself so softens and subdues the Heart, that it disables it
from struggling or bearing up against the Woes and Distresses which
befal it. The Mind meets with other Misfortunes in her whole Strength;
she stands
within her self, and sustains the Shock with all
the Force
which
is natural to her; but a Heart in Love has its
Foundations sapped, and immediately sinks under the Weight of Accidents
that are disagreeable to its Favourite Passion.
In Afflictions Men generally draw their Consolations out of Books of
Morality, which indeed are of great use to fortifie and strengthen the
Mind against the Impressions of Sorrow.
St.
Evremont
, who
does not approve of this Method, recommends Authors
who
are apt to
stir up Mirth in the Mind of the Readers, and fancies
Don Quixote
can
give more Relief to an heavy Heart than
Plutarch
or
Seneca
, as it is
much easier to divert Grief than to conquer it. This doubtless may have
its Effects on some Tempers. I should rather have recourse to Authors of
a quite contrary kind, that give us Instances of Calamities and
Misfortunes, and shew Human Nature in its greatest Distresses.
If the Affliction we groan under be very heavy, we shall find some
Consolation in the Society of as great Sufferers as our selves,
especially when we find our Companions Men of Virtue and Merit. If our
Afflictions are light, we shall be comforted by the Comparison we make
between our selves and our Fellow Sufferers. A Loss at Sea, a Fit of
Sickness, or the Death of a Friend, are such Trifles when we consider
whole Kingdoms laid in Ashes, Families put to the Sword, Wretches shut
up in Dungeons, and the like Calamities of Mankind, that we are out of
Countenance for our own Weakness, if we sink under such little Stroaks
of Fortune.
Let the Disconsolate
Leonora
consider, that at the very time in which
she languishes for the Loss of her deceased Lover, there are Persons in
several Parts of the World just perishing in a Shipwreck; others crying
out for Mercy in the Terrors of a Death-bed Repentance; others lying
under the Tortures of an Infamous Execution, or the like dreadful
Calamities; and she will find her Sorrows vanish at the Appearance of
those which are so much greater and more astonishing.
I would further propose to the Consideration of my afflicted Disciple,
that possibly what she now looks upon as the greatest Misfortune, is not
really such in it self. For my own part, I question not but our Souls in
a separate State will look back on their Lives in quite another View,
than what they had of them in the Body; and that what they now consider
as Misfortunes and Disappointments, will very often appear to have been
Escapes and Blessings.
The Mind that hath any Cast towards Devotion, naturally flies to it in
its Afflictions.
When I was in
France
I heard a very remarkable Story of two
Lovers, which I shall relate at length in my to-Morrow's Paper, not only
because the Circumstances of it are extraordinary, but because it may
serve as an Illustration to all that can be said on this last Head, and
shew the Power of Religion in abating that particular Anguish which
seems to lie so heavy on
Leonora
. The Story was told me by a
Priest, as I travelled with him in a Stage-Coach. I shall give it my
Reader as well as I can remember, in his own Words, after having
premised, that if Consolations may be drawn from a wrong Religion and a
misguided Devotion, they cannot but flow much more naturally from those
which are founded upon Reason, and established in good Sense.
L.
one
This letter is by Miss Shepheard, the 'Parthenia' of
that
that
Contents
|
Friday,
September 7, 1711 |
Addison |
Illa; Quis et me, inquit, miseram, et te perdidit, Orpheu? Jamque vale: feror ingenti circumdata nocte, Invalidasque tibi tendens, heu! non tua, palmas.
Virg.

Constantia
was a Woman of extraordinary Wit and Beauty, but very unhappy
in a Father, who having arrived at great Riches by his own Industry,
took delight in nothing but his Money.
Theodosius
was the younger
Son of a decayed Family of great Parts and Learning, improved by a
genteel and vertuous Education. When he was in the twentieth year of his
Age he became acquainted with
Constantia
, who had not then passed
her fifteenth.
he lived but a few Miles Distance from her Father's
House, he had frequent opportunities of seeing her; and by the
Advantages of a good Person and a pleasing Conversation, made such an
Impression in her Heart as it was impossible for time to
efface
:
He was himself no less smitten with
Constantia
. A long
Acquaintance made them still discover new Beauties in each other, and by
Degrees raised in them that mutual Passion which had an Influence on
their following Lives. It unfortunately happened, that in the midst of
this intercourse of Love and Friendship between
Theodosius
and
Constantia
, there broke out an irreparable Quarrel between their
Parents, the one valuing himself too much upon his Birth, and the other
upon his Possessions. The Father of
Constantia
was so incensed at the
Father of
Theodosius
, that he contracted an unreasonable Aversion
towards his Son, insomuch that he forbad him his House, and charged his
Daughter upon her Duty never to see him more. In the mean time to break
off all Communication between the two Lovers, who he knew entertained
secret Hopes of some favourable Opportunity that should bring them
together, he found out a young Gentleman of a good Fortune and an
agreeable Person, whom he pitched upon as a Husband for his Daughter. He
soon concerted this Affair so well, that he told
Constantia
it
was his Design to marry her to such a Gentleman, and that her Wedding
should be celebrated on such a Day.
Constantia
, who was over-awed
with the Authority of her Father, and unable to object anything against
so advantageous a Match, received the Proposal with a profound Silence,
which her Father commended in her, as the most decent manner of a
Virgin's giving her Consent to an Overture of that Kind: The Noise of
this intended Marriage soon reached
Theodosius
, who, after a long
Tumult of Passions which naturally rise in a Lover's Heart on such an
Occasion, writ the following letter to
Constantia
.
'The Thought of my Constantia, which for some years has been my
only Happiness, is now become a greater Torment to me than I am able
to bear. Must I then live to see you another's? The Streams, the
Fields and Meadows, where we have so often talked together, grow
painful to me; Life it self is become a Burden. May you long be happy
in the World, but forget that there was ever such a Man in it as
Theodosius.'
This Letter was conveyed to
Constantia
that very Evening, who
fainted at the Reading of it; and the next Morning she was much more
alarmed by two or three Messengers, that came to her Father's House one
after another to inquire if they had heard any thing of
Theodosius
, who it seems had left his Chamber about Midnight, and
could nowhere be found. The deep Melancholy, which had hung upon his
Mind some Time before, made them apprehend the worst that could befall
him.
Constantia
, who knew that nothing but the Report of her
Marriage could have driven him to such Extremities, was not to be
comforted: She now accused her self for having so tamely given an Ear to
the Proposal of a Husband, and looked upon the new Lover as the Murderer
of
Theodosius:
In short, she resolved to suffer the utmost
Effects of her Father's Displeasure, rather than comply with a Marriage
which appeared to her so full of Guilt and Horror. The Father seeing
himself entirely rid of
Theodosius,
and likely to keep a
considerable Portion in his Family, was not very much concerned at the
obstinate Refusal of his Daughter; and did not find it very difficult to
excuse himself upon that Account to his intended Son-in-law, who had all
along regarded this Alliance rather as a Marriage of Convenience than of
Love.
Constantia
had now no Relief but in her Devotions and
Exercises of Religion, to which her Afflictions had so entirely
subjected her Mind, that after some Years had abated the Violence of her
Sorrows, and settled her Thoughts in a kind of Tranquillity, she
resolved to pass the Remainder of her Days in a Convent.
Father was
not displeased with
a
Resolution,
which
would save Money in
his Family, and readily complied with his Daughter's Intentions.
Accordingly in the Twenty-fifth Year of her Age, while her Beauty was
yet in all its Height and Bloom, he carried her to a neighbouring City,
in order to look out a Sisterhood of Nuns among whom to place his
Daughter. There was in this Place a Father of a Convent who was very
much renowned for his Piety and exemplary Life; and as it is usual in
the Romish Church for those who are under any great Affliction, or
Trouble of Mind, to apply themselves to the most eminent Confessors for
Pardon and Consolation, our beautiful Votary took the Opportunity of
confessing herself to this celebrated Father.
We must now return to Theodosius, who, the very Morning that the
above-mentioned Inquiries had been made after him, arrived at a
religious House in the City, where now Constantia resided; and desiring
that Secresy and Concealment of the Fathers of the Convent, which is
very usual upon any extraordinary Occasion, he made himself one of the
Order, with a private Vow never to enquire after
Constantia
; whom
he looked upon as given away to his Rival upon the Day on which,
according to common Fame, their Marriage was to have been solemnized.
in his Youth made a good Progress in Learning, that he might
dedicate
himself
more entirely to Religion, he entered into holy
Orders, and in a few Years became renowned for his Sanctity of Life, and
those pious Sentiments which he inspired into all
who
conversed
with him. It was this holy Man to whom
Constantia
had determined
to apply her self in Confession, tho' neither she nor any other besides
the Prior of the Convent, knew any thing of his Name or Family.
gay,
the amiable
Theodosius
had now taken upon him the Name of Father
Francis
, and was so far concealed in a long Beard, a
shaven
Head, and a religious Habit, that it was impossible to discover the Man
of the World in the venerable Conventual.
As he was one Morning shut up in his Confessional,
Constantia
kneeling by him opened the State of her Soul to him; and after having
given him the History of a Life full of Innocence, she burst out in
Tears, and entred upon that Part of her Story in which he himself had so
great a Share. My Behaviour, says she, has I fear been the Death of a
Man who had no other Fault but that of loving me too much. Heaven only
knows how dear he was to me whilst he liv'd, and how bitter the
Remembrance of him has been to me since his Death. She here paused, and
lifted up her Eyes that streamed with Tears towards the Father; who was
so moved with the Sense of her Sorrows, that he could only command his
Voice, which was broke with Sighs and Sobbings, so far as to bid her
proceed. She followed his Directions, and in a Flood of Tears poured out
her Heart before him. The Father could not forbear weeping aloud,
insomuch that in the Agonies of his Grief the Seat shook under him.
Constantia
, who thought the good Man was thus moved by his
Compassion towards her, and by the Horror of her Guilt, proceeded with
the utmost Contrition to acquaint him with that Vow of Virginity in
which she was going to engage herself, as the proper Atonement for her
Sins, and the only Sacrifice she could make to the Memory of
Theodosius
. The Father, who by this time had pretty well composed
himself, burst out again in Tears upon hearing that Name to which he had
been so long disused, and upon receiving this Instance of an
unparallel'd Fidelity from one who he thought had several Years since
given herself up to the Possession of another. Amidst the Interruptions
of his Sorrow, seeing his Penitent overwhelmed with Grief, he was only
able to bid her from time to time be comforted — To tell her that her
Sins were forgiven her — That her Guilt was not so great as she
apprehended — That she should not suffer her self to be afflicted above
Measure. After which he recovered himself enough to give her the
Absolution in Form; directing her at the same time to repair to him
again the next Day, that he might encourage her in the pious
Resolution
s
she had taken, and give her suitable Exhortations for her
Behaviour in it.
Constantia
retired, and the next Morning renewed
her Applications.
Theodosius
having manned his Soul with proper
Thoughts and Reflections exerted himself on this Occasion in the best
Manner he could to animate his Penitent in the Course of Life she was
entering upon, and wear out of her Mind those groundless Fears and
Apprehensions which had taken Possession of it; concluding with a
Promise to her, that he would from time to time continue his Admonitions
when she should have taken upon her the holy Veil. The Rules of our
respective Orders, says he, will not permit that I should see you, but
you may assure your self not only of having a Place in my Prayers, but
of receiving such frequent Instructions as I can convey to you by
Letters. Go on chearfully in the glorious Course you have undertaken,
and you will quickly find such a Peace and Satisfaction in your Mind,
which it is not in the Power of the World to give.
Constantia's
Heart was so elevated with the Discourse of Father
Francis
, that the very next Day she entered upon her Vow. As soon
as the Solemnities of her Reception were over, she retired, as it is
usual, with the Abbess into her own Apartment.
The Abbess had been informed the Night before of all that had passed
between her Noviciate and Father
Francis:
From whom she now
delivered to her the following Letter.
'As the First-fruits of those Joys and Consolations which you may
expect from the Life you are now engaged in, I must acquaint you that
Theodosius, whose Death sits so heavy upon your Thoughts, is
still alive; and that the Father, to whom you have confessed your
self, was once that Theodosius whom you so much lament. The
love which we have had for one another will make us more happy in its
Disappointment than it could have done in its Success. Providence has
disposed of us for our Advantage, tho' not according to our Wishes.
Consider your Theodosius still as dead, but assure your self of
one who will not cease to pray for you in Father.'
Francis.
Constantia
saw that the Hand-writing agreed with the Contents of
the Letter: and upon reflecting on the Voice of the Person, the
Behaviour, and above all the extreme Sorrow of the Father during her
Confession, she discovered
Theodosius
in every Particular. After
having wept with Tears of Joy, It is enough, says she,
Theodosius
is still in Being: I shall live with Comfort and die in Peace.
The Letters which the Father sent her afterwards are yet extant in the
Nunnery where she resided; and are often read to the young Religious, in
order to inspire them with good Resolutions and Sentiments of Virtue. It
so happened, that after
Constantia
had lived about ten Years in
the Cloyster, a violent Feaver broke out in the Place, which swept away
great Multitudes, and among others
Theodosius.
Upon his Deathbed
he sent his Benediction in a very moving Manner to
Constantia,
who at that time was herself so far gone in the same fatal Distemper,
that she lay delirious. Upon the Interval which generally precedes Death
in Sicknesses of this Nature, the Abbess, finding that the Physicians
had given her over, told her that
Theodosius
was just gone before
her, and that he had sent her his Benediction in his last Moments.
Constantia
received it with Pleasure: And now, says she, If I do
not ask anything improper, let me be buried by
Theodosius.
My Vow
reaches no farther than the Grave. What I ask is, I hope, no Violation
of it. — She died soon after, and was interred according to her Request.
Their Tombs are still to be seen, with a short Latin Inscription over
them to the following Purpose.
Here lie the Bodies of Father
Francis
and Sister
Constance.
They were lovely in their Lives, and in their Deaths they were not
divided.
C.
deface
her
that
himself up
that
shaved
Contents
|
Saturday,
September 8, 1711 |
Addison |
... Si fortè necesse est,
Fingere cinctutis non exaudita Cethegis
Continget: dabiturque licentia sumpta pudenter.1
Hor.

I have often wished, that as in our Constitution there are several
Persons whose Business it is to watch over our Laws, our Liberties and
Commerce, certain Men might be set apart as Superintendants of our
Language, to hinder any Words of a Foreign Coin from passing among us;
and in particular to prohibit any
French
Phrases from becoming Current
in this Kingdom, when those of our own Stamp are altogether as valuable.
The present War has so Adulterated our Tongue with strange Words that it
would be impossible for one of our Great Grandfathers to know what his
Posterity have been doing, were he to read their Exploits in a Modern
News Paper. Our Warriors are very industrious in propagating the
French
Language, at the same time that they are so gloriously
successful in beating down their Power. Our Soldiers are Men of strong
Heads for Action, and perform such Feats as they are not able to
express. They want Words in their own Tongue to tell us what it is they
Atchieve, and therefore send us over Accounts of their Performances in a
Jargon of Phrases, which they learn among their Conquered Enemies. They
ought however to be provided with Secretaries, and assisted by our
Foreign Ministers, to tell their Story for them in plain
English
, and
to let us know in our Mother-Tongue what it is our brave Country-Men are
about. The
French
would indeed be in the right to publish the
News of the present War in
English
Phrases, and make their
Campaigns unintelligible. Their People might flatter themselves that
Things are not so bad as they really are, were they thus palliated with
Foreign Terms, and thrown into Shades and Obscurity: but the
English
cannot be too clear in their Narrative of those Actions,
which have raised their Country to a higher Pitch of Glory than it ever
yet arrived at, and which will be still the more admired the better they
are explained.
For my part, by that time a Siege is carried on two or three Days, I am
altogether lost and bewildered in it, and meet with so many inexplicable
Difficulties, that I scarce know what Side has the better of it, till I
am informed by the Tower Guns that the Place is surrendered.
do indeed
make some Allowances for this Part of the War, Fortifications having
been foreign Inventions, and upon that Account abounding in foreign
Terms. But when we have won Battels
which
may be described in our
own Language, why are our Papers filled with so many unintelligible
Exploits, and the
French
obliged to lend us a Part of their
Tongue before we can know how they are Conquered? They must be made
accessory to their own Disgrace, as the
Britons
were formerly so
artificially wrought in the Curtain of the
Roman
Theatre, that
they seemed to draw it up in order to give the Spectators an Opportunity
of seeing their own Defeat celebrated upon the Stage: For so Mr.
Dryden
has translated that
in
Virgil
.
Purpurea intexti3 tollunt aulœa Britanni.
Georg. 3, v. 25.
Which interwoven Britains
seem to raise,
And shew the Triumph that their Shame displays.
Histories of all our former Wars are transmitted to us in our
Vernacular Idiom, to use the Phrase of a great Modern Critick
. I do
not find in any of our Chronicles, that
Edward
the Third ever
reconnoitred the Enemy, tho' he often discovered the Posture of the
French
, and as often vanquished them in Battel. The
Black
Prince
passed many a River without the help of Pontoons, and filled
a Ditch with Faggots as successfully as the Generals of our Times do it
with Fascines. Our Commanders lose half their Praise, and our People
half their Joy, by means of those hard Words and dark Expressions in
which our News Papers do so much abound. I have seen many a prudent
Citizen, after having read every Article, inquire of his next Neighbour
what News the Mail had brought.
I remember in that remarkable Year when our Country was delivered from
the greatest Fears and Apprehensions, and raised to the greatest Height
of Gladness it had ever felt since it was a Nation, I mean the Year of
Blenheim
, I had the Copy of a Letter sent me out of the Country,
which was written from a young Gentleman in the Army to his Father, a
Man of a good Estate and plain Sense: As the Letter was very modishly
chequered with this Modern Military Eloquence, I shall present my Reader
with a Copy of it.
Sir,
Upon the Junction of the
French and
Bavarian Armies they
took Post behind a great Morass which they thought impracticable.
Our
General the next Day sent a Party of Horse to reconnoitre them from a
little Hauteur, at about a
Quarter of an Hour's5 distance from
the Army, who returned again to the Camp unobserved through several
Defiles, in one of which they met with a Party of
French that
had been Marauding, and made them all Prisoners at Discretion. The Day
after a Drum arrived at our Camp, with a Message which he would
communicate to none but the General; he was followed by a Trumpet, who
they say behaved himself very saucily, with a Message from the Duke of
Bavaria. The next Morning our Army being divided into two
Corps, made a Movement towards the Enemy: You will hear in the Publick
Prints how we treated them, with the other Circumstances of that
glorious Day. I had the good Fortune to be in that Regiment that
pushed the
Gens d'Arms. Several
French Battalions, who
some say were a Corps de Reserve, made a Show of Resistance; but it
only proved a Gasconade, for upon our preparing to fill up a little
Fossé, in order to attack them, they beat the Chamade, and sent us
Charte Blanche. Their Commandant, with a great many other
General Officers, and Troops without number, are made Prisoners of
War, and will I believe give you a Visit in
England, the Cartel
not being yet settled. Not questioning but these Particulars will be
very welcome to you, I congratulate you upon them, and am your most
dutiful Son, &c.'
The Father of the young Gentleman upon the Perusal of the Letter found
it contained great News, but could not guess what it was. He immediately
communicated it to the Curate of the Parish, who upon the reading of it,
being vexed to see any thing he could not understand, fell into a kind
of a Passion, and told him that his Son had sent him a Letter that was
neither Fish, nor Flesh, nor good Red-Herring. I wish, says he, the
Captain may be
Compos Mentis
, he talks of a saucy Trumpet, and a
Drum that carries Messages; then who is this
Charte Blanche
? He
must either banter us or he is out of his Senses. The Father, who always
looked upon the Curate as a learned Man, began to fret inwardly at his
Son's Usage, and producing a Letter which he had written to him about
three Posts afore, You see here, says he, when he writes for Mony he
knows how to speak intelligibly enough; there is no Man in England can
express himself clearer, when he wants a new Furniture for his Horse. In
short, the old Man was so puzzled upon the Point, that it might have
fared ill with his Son, had he not seen all the Prints about three Days
after filled with the same Terms of Art, and that
Charles
only
writ like other Men.
L.
The motto in the original edition was
Semivirumque bovem Semibovemque virum.
Ovid.
that
Atique
Dr Richard Bentley
Mile
Contents
|
Monday,
September 10, 1711 |
Addison |
... Quod nec Jovis ira, nec ignis,
Nec poterit ferrum, nec edax abolere vetustas.
Ovid.

Aristotle tells us that the World is a Copy or Transcript of those Ideas
which are in the Mind of the first Being, and that those Ideas, which
are in the Mind of Man, are a Transcript of the World: To this we may
add, that Words are the Transcript of those Ideas which are in the Mind
of Man, and that Writing or Printing are the Transcript of words.
As the Supreme Being has expressed, and as it were printed his Ideas in
the Creation, Men express their Ideas in Books, which by this great
Invention of these latter Ages may last as long as the Sun and Moon, and
perish only in the general Wreck of Nature. Thus
Cowley
in his
Poem on the Resurrection, mentioning the Destruction of the Universe,
has those admirable Lines.
Now all the wide extended Sky,
And all th' harmonious Worlds on high,
And Virgil's sacred Work shall die.
There is no other Method of fixing those Thoughts which arise and
disappear in the Mind of Man, and transmitting them to the last Periods
of Time; no other Method of giving a Permanency to our Ideas, and
preserving the Knowledge of any particular Person, when his Body is
mixed with the common Mass of Matter, and his Soul retired into the
World of Spirits. Books are the Legacies that a great Genius leaves to
Mankind, which are delivered down from Generation to Generation, as
Presents to the Posterity of those who are yet unborn.
All other Arts of perpetuating our Ideas continue but a short Time:
Statues can last but a few Thousands of Years, Edifices fewer, and
Colours still fewer than Edifices.
Michael Angelo
,
Fontana
, and
Raphael
, will hereafter be what
Phidias
,
Vitruvius
, and
Apelles
are at present; the
Names of great Statuaries, Architects and Painters, whose Works are
lost. The several Arts are expressed in mouldring Materials: Nature
sinks under them, and is not able to support the Ideas which are imprest
upon it.
The Circumstance which gives Authors an Advantage above all these great
Masters, is this, that they can multiply their Originals; or rather can
make Copies of their Works, to what Number they please, which shall be
as valuable as the Originals themselves. This gives a great Author
something like a Prospect of Eternity, but at the same time deprives him
of those other Advantages which Artists meet with. The Artist finds
greater Returns in Profit, as the Author in Fame. What an Inestimable
Price would a
Virgil
or a
Homer
, a
Cicero
or an
Aristotle
bear, were their Works like a Statue, a Building, or a
Picture, to be confined only in one Place and made the Property of a
single Person?
If Writings are thus durable, and may pass from Age to Age throughout
the whole Course of Time, how careful should an Author be of committing
any thing to Print that may corrupt Posterity, and poison the Minds of
Men with Vice and Error? Writers of great Talents, who employ their
Parts in propagating Immorality, and seasoning vicious Sentiments with
Wit and Humour, are to be looked upon as the Pests of Society, and the
Enemies of Mankind: They leave Books behind them (as it is said of those
who die in Distempers which breed an Ill-will towards their own Species)
to scatter Infection and destroy their Posterity. They act the
Counterparts of a
Confucius
or a
Socrates
; and seem to
have been sent into the World to deprave human Nature, and sink it into
the Condition of Brutality.
I have seen some Roman-Catholick Authors, who tell us that vicious
Writers continue in Purgatory so long as the Influence of their Writings
continues upon Posterity: For Purgatory, say they, is nothing else but a
cleansing us of our Sins, which cannot be said to be done away, so long
as they continue to operate and corrupt Mankind. The vicious Author, say
they, sins after Death, and so long as he continues to sin, so long must
he expect to be punished. Tho' the Roman Catholick Notion of Purgatory
be indeed very ridiculous, one cannot but think that if the Soul after
Death has any Knowledge of what passes in this World, that of an immoral
Writer would receive much more Regret from the Sense of corrupting, than
Satisfaction from the Thought of pleasing his surviving Admirers.
To take off from the Severity of this Speculation, I shall conclude this
Paper with a Story of an Atheistical Author, who at a time when he lay
dangerously sick, and desired the Assistance of a neighbouring Curate,
confessed to him with great Contrition, that nothing sat more heavy at
his Heart than the Sense of his having seduced the Age by his Writings,
and that their evil Influence was likely to continue even after his
Death. The Curate upon further Examination finding the Penitent in the
utmost Agonies of Despair, and being himself a Man of Learning, told
him, that he hoped his Case was not so desperate as he apprehended,
since he found that he was so very sensible of his Fault, and so
sincerely repented of it. The Penitent still urged the evil Tendency of
his Book to subvert all Religion, and the little Ground of Hope there
could be for one whose Writings would continue to do Mischief when his
Body was laid in Ashes. The Curate, finding no other Way to comfort him,
told him, that he did well in being afflicted for the evil Design with
which he published his Book; but that he ought to be very thankful that
there was no danger of its doing any Hurt: That his Cause was so very
bad, and his Arguments so weak, that he did not apprehend any ill
Effects of it: In short, that he might rest satisfied his Book could do
no more Mischief after his Death, than it had done whilst he was living.
To which he added, for his farther Satisfaction, that he did not believe
any besides his particular Friends and Acquaintance had ever been at the
pains of reading it, or that any Body after his Death would ever enquire
after it. The dying Man had still so much the Frailty of an Author in
him, as to be cut to the Heart with these Consolations; and without
answering the good Man, asked his Friends about him (with a Peevishness
that is natural to a sick Person) where they had picked up such a
Blockhead? And whether they thought him a proper Person to attend one in
his Condition? The Curate finding that the Author did not expect to be
dealt with as a real and sincere Penitent, but as a Penitent of
Importance, after a short Admonition withdrew; not questioning but he
should be again sent for if the Sickness grew desperate. The Author
however recovered, and has since written two or three other Tracts with
the same Spirit, and very luckily for his poor Soul with the same
Success.
C.
Contents
|
Tuesday,
September 11, 1711 |
Steele |
Fuit haud ignobilis Argis,
Qui se credebat miros audire tragœdos,
In vacuo lætus sessor plausorque theatro;
Cætera qui vitæ servaret munia recto
More; bonus sanè vicinus, amabilis hospes,
Comis in uxorem; posset qui ignoscere servis,
Et signo læso non insanire lagenæ;
Posset qui rupem et puteum vitare patentem.
Hic ubi cognatorum opibus curisque refectus
Expulit elleboro morbum bilemque meraco,
Et redit ad sese: Pol me occidistis, amici,
Non servastis, ait; cui sic extorta valuptas,
Et demptus per vim mentis gratissimus Error.
Hor.

The unhappy Force of an Imagination, unguided by the Check of Reason and
Judgment, was the Subject of a former Speculation. My Reader may
remember that he has seen in one of my Papers a Complaint of an
Unfortunate Gentleman, who was unable to contain himself, (when any
ordinary matter was laid before him) from adding a few Circumstances to
enliven plain Narrative. That Correspondent was a Person of too warm a
Complexion to be satisfied with things merely as they stood in Nature,
and therefore formed Incidents which should have happened to have
pleased him in the Story. The same ungoverned Fancy which pushed that
Correspondent on, in spite of himself, to relate publick and notorious
Falsehoods, makes the Author of the following Letter do the same in
Private; one is a Prating, the other a Silent Liar.
There is little pursued in the Errors of either of these Worthies, but
mere present Amusement: But the Folly of him who lets his Fancy place
him in distant Scenes untroubled and uninterrupted, is very much
preferable to that of him who is ever forcing a Belief, and defending
his Untruths with new Inventions. But I shall hasten to let this Liar in
Soliloquy, who calls himself a
Castle-builder
, describe himself with the
same Unreservedness as formerly appeared in my Correspondent
above-mentioned. If a Man were to be serious on this Subject, he might
give very grave Admonitions to those who are following any thing in this
Life, on which they think to place their Hearts, and tell them that they
are really
Castle-builders
. Fame, Glory, Wealth, Honour, have in the
Prospect pleasing Illusions; but they who come to possess any of them
will find they are Ingredients towards Happiness, to be regarded only in
the second Place; and that when they are valued in the first Degree,
they are as dis-appointing as any of the Phantoms in the following
Letter.
Sept. 6, 1711.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am a Fellow of a very odd Frame of Mind, as you will find by the
Sequel; and think myself Fool enough to deserve a Place in your Paper.
I am unhappily far gone in Building, and am one of that Species of Men
who are properly denominated Castle-Builders, who scorn to be beholden
to the Earth for a Foundation, or dig in the Bowels of it for
Materials; but erect their Structures in the most unstable of
Elements, the Air, Fancy alone laying the Line, marking the Extent,
and shaping the Model. It would be difficult to enumerate what august
Palaces and stately Porticoes have grown under my forming Imagination,
or what verdant Meadows and shady Groves have started into Being, by
the powerful Feat of a warm Fancy. A Castle-builder is even just what
he pleases, and as such I have grasped imaginary Scepters, and
delivered uncontroulable Edicts, from a Throne to which conquered
Nations yielded Obeysance. I have made I know not how many Inroads
into
France, and ravaged the very Heart of that Kingdom; I have
dined in the
Louvre, and drank Champaign at
Versailles;
and I would have you take Notice, I am not only able to vanquish a
People already cowed and accustomed to Flight,
but I could,
Almanzor-like
1, drive the
British General from the
Field, were I less a Protestant, or had ever been affronted by the
Confederates. There is no Art or Profession, whose most celebrated
Masters I have not eclipsed. Where-ever I have afforded my Salutary
Preference, Fevers have ceased to burn, and Agues to shake the Human
Fabrick. When an Eloquent Fit has been upon me, an apt Gesture and
proper Cadence has animated each Sentence, and gazing Crowds have
found their Passions work'd up into Rage, or soothed into a Calm. I am
short, and not very well made; yet upon Sight of a fine Woman, I have
stretched into proper Stature, and killed with a good Air and Mein.
These are the gay Phantoms that dance before my waking Eyes and
compose my Day-Dreams. I should be the most contented happy Man alive,
were the Chimerical Happiness which springs from the Paintings of the
Fancy less fleeting and transitory. But alas! it is with Grief of Mind
I tell you, the least Breath of Wind has often demolished my
magnificent Edifices, swept away my Groves, and left no more Trace of
them than if they had never been. My Exchequer has sunk and vanished
by a Rap on my Door, the Salutation of a Friend has cost me a whole
Continent, and in the same Moment I have been pulled by the Sleeve, my
Crown has fallen from my Head. The ill Consequence of these Reveries
is inconceivably great, seeing the loss of imaginary Possessions makes
Impressions of real Woe. Besides, bad Œconomy is visible and apparent
in Builders of invisible Mansions. My Tenant's Advertisements of Ruins
and Dilapidations often cast a Damp on my Spirits, even in the Instant
when the Sun, in all his Splendor, gilds my Eastern Palaces. Add to
this the pensive Drudgery in Building, and constant grasping Aerial
Trowels, distracts and shatters the Mind, and the fond Builder of
Babells is often cursed with an incoherent Diversity and
Confusion of Thoughts. I do not know to whom I can more properly apply
my self for Relief from this Fantastical Evil, than to your self; whom
I earnestly implore to accommodate me with a Method how to settle my
Head and cool my Brain-pan. A Dissertation on Castle-Building may not
only be serviceable to my self, but all Architects, who display their
Skill in the thin Element. Such a Favour would oblige me to make my
next Soliloquy not contain the Praises of my dear Self but of the
Spectator, who shall, by complying with this, make me.'
His Obliged, Humble Servant.
Vitruvius.
"(unreadable on original page) in Dryden's
Conquest of Granada
."
Contents
|
Wednesday,
September 12, 1711 |
Steele |
... Pectus Præceptis format amicis.
Hor.

It would be Arrogance to neglect the Application of my Correspondents so
far as not sometimes to insert their Animadversions upon my Paper; that
of this Day shall be therefore wholly composed of the Hints which they
have sent me.
Mr.
Spectator,
I Send you this to congratulate your late Choice of a Subject, for
treating on which you deserve publick Thanks; I mean that on those
licensed Tyrants the Schoolmasters. If you can disarm them of their
Rods, you will certainly have your old Age reverenced by all the young
Gentlemen of
Great-Britain who are now between seven and seventeen
Years. You may boast that the incomparably wise
Quintilian and you
are of one Mind in this Particular.
'
Si cui est (says he)
mens tam illiberalis ut objurgatione non
corrigatur, is etiam ad plagas, ut pessimo quæque mancipia,
durabitur1.
If any Child be of so disingenuous a Nature, as not to stand
corrected by Reproof, he, like the very worst of Slaves, will be
hardned even against Blows themselves.'
And afterwards,
'Pudet dicere in quæ probra nefandi homines isto cædendi jure
abutantur,
i. e. I blush to say how shamefully those wicked Men abuse the
Power of Correction.'
I was bred myself, Sir, in a very great School, of which the Master
was a
Welchman, but certainly descended from a
Spanish Family, as
plainly appeared from his Temper as well as his Name
2. I leave you
to judge what sort of a Schoolmaster a
Welchman ingrafted on a
Spaniard would make. So very dreadful had he made himself to me,
that altho' it is above twenty Years since I felt his heavy Hand, yet
still once a Month at least I dream of him, so strong an Impression
did he make on my Mind. 'Tis a Sign he has fully terrified me waking,
who still continues to haunt me sleeping.
And yet I may say without Vanity, that the Business of the School was
what I did without great Difficulty; and I was not remarkably unlucky;
and yet such was the Master's Severity that once a Month, or oftner, I
suffered as much as would have satisfied the Law of the Land for a
Petty Larceny.
Many a white and tender Hand, which the fond Mother has passionately
kissed a thousand and a thousand times, have I seen whipped till it
was covered with Blood: perhaps for smiling, or for going a Yard and
half out of a Gate, or for writing an O for an A, or an A for an O:
These were our great Faults! Many a brave and noble Spirit has been
there broken; others have run from thence and were never heard of
afterwards.
It is a worthy Attempt to undertake the Cause of distrest Youth; and
it is a noble Piece of
Knight-Errantry to enter the Lists
against so many armed Pedagogues. 'Tis pity but we had a Set of Men,
polite in their Behaviour and Method of Teaching, who should be put
into a Condition of being above flattering or fearing the Parents of
those they instruct. We might then possibly see Learning become a
Pleasure, and Children delighting themselves in that which now they
abhor for coming upon such hard Terms to them: What would be a still
greater Happiness arising from the Care of such Instructors, would be,
that we should have no more Pedants, nor any bred to Learning who had
not Genius for it. I am, with the utmost Sincerity,
Sir,
Your most
affectionate humble Servant.
Richmond, Sept. 5
th, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Boy of fourteen Years of Age, and have for this last Year been
under the Tuition of a Doctor of Divinity, who has taken the School of
this Place under his Care
3. From the Gentleman's great Tenderness
to me and Friendship to my Father, I am very happy in learning my Book
with Pleasure. We never leave off our Diversions any farther than to
salute him at Hours of Play when he pleases to look on. It is
impossible for any of us to love our own Parents better than we do
him. He never gives any of us an harsh Word, and we think it the
greatest Punishment in the World when he will not speak to any of us.
My Brother and I are both together inditing this Letter: He is a Year
older than I am, but is now ready to break his Heart that the Doctor
has not taken any Notice of him these three Days. If you please to
print this he will see it, and, we hope, taking it for my Brother's
earnest Desire to be restored to his Favour, he will again smile upon
him.
Your most obedient Servant,
T. S.
Mr.
Spectator,
You have represented several sorts of
Impertinents singly, I
wish you would now proceed, and describe some of them in Sets. It
often happens in publick Assemblies, that a Party who came thither
together, or whose Impertinencies are of an equal Pitch, act in
Concert, and are so full of themselves as to give Disturbance to all
that are about them. Sometimes you have a Set of Whisperers, who lay
their Heads together in order to sacrifice every Body within their
Observation; sometimes a Set of Laughers, that keep up an insipid
Mirth in their own Corner, and by their Noise and Gestures shew they
have no Respect for the rest of the Company.
You frequently meet with
these Sets at the Opera, the Play, the Water-works
4, and other
publick Meetings, where their whole Business is to draw off the
Attention of the Spectators from the Entertainment, and to fix it upon
themselves; and it is to be observed that the Impertinence is ever
loudest, when the Set happens to be made up of three or four Females
who have got what you call a Woman's Man among them.
I am at a loss to know from whom People of Fortune should learn this
Behaviour, unless it be from the Footmen who keep their Places at a
new Play, and are often seen passing away their Time in Sets at
All-fours in the Face of a full House, and with a perfect
Disregard to People of Quality sitting on each Side of them.
For preserving therefore the Decency of publick Assemblies, methinks
it would be but reasonable that those who Disturb others should pay at
least a double Price for their Places; or rather Women of Birth and
Distinction should be informed that a Levity of Behaviour in the Eyes
of People of Understanding degrades them below their meanest
Attendants; and Gentlemen should know that a fine Coat is a Livery,
when the Person who wears it discovers no higher Sense than that of a
Footman.
I am
Sir,
Your most humble Servant.
Bedfordshire, Sept.. 1, 1711
Mr.
Spectator,
I am one of those whom every Body calls a Pocher, and sometimes go out
to course with a Brace of Greyhounds, a Mastiff, and a Spaniel or two;
and when I am weary with Coursing, and have killed Hares enough, go to
an Ale-house to refresh my self. I beg the Favour of you (as you set
up for a Reformer) to send us Word how many Dogs you will allow us to
go with, how many Full-Pots of Ale to drink, and how many Hares to
kill in a Day, and you will do a great Piece of Service to all the
Sportsmen: Be quick then, for the Time of Coursing is come on.
Yours in Haste,
T. Isaac Hedgeditch.
Instit. Orat.
Bk. I. ch. 3.
Dr. Charles Roderick, Head Master of Eton.
Dr. Nicholas Brady, Tate's colleague in versification of
the Psalms. He was Rector of Clapham and Minister of Richmond, where he
had the school. He died in 1726, aged 67.
The Water Theatre, invented by Mr. Winstanley, and
exhibited by his widow at the lower end of Piccadilly.
Contents
|
Thursday,
September 13, 1711 |
Addison |
Sic vita erat: facile omnes perferre ac pati:
Cum quibus erat cunque una, his sese dedere,
Eorum obsequi studiis: advorsus nemini;
Nunquam præponens se aliis: Ita facillime
Sine invidia invenias laudem.
Ter.
And.
Man is subject to innumerable Pains and Sorrows by the very Condition of
Humanity, and yet, as if Nature had not sown Evils enough in Life, we
are continually adding Grief to Grief, and aggravating the common
Calamity by our cruel Treatment of one another. Every Man's natural
Weight of Afflictions is still made more heavy by the Envy, Malice,
Treachery, or Injustice of his Neighbour. At the same time that the
Storm beats upon the whole Species, we are falling foul upon one
another.
Half the Misery of Human Life might be extinguished, would Men alleviate
the general Curse they lie under, by mutual Offices of Compassion,
Benevolence, and Humanity. There is nothing therefore which we ought
more to encourage in our selves and others, than that Disposition of
Mind which in our Language goes under the Title of Good-nature, and
which I shall chuse for the Subject of this Day's Speculation.
Good-nature is more agreeable in Conversation than Wit, and gives a
certain Air to the Countenance which is more amiable than Beauty. It
shows Virtue in the fairest Light, takes off in some measure from the
Deformity of Vice, and makes even Folly and Impertinence supportable.
There is no Society or Conversation to be kept up in the World without
Good-nature, or something which must bear its Appearance, and supply its
Place. For this Reason Mankind have been forced to invent a kind of
Artificial Humanity, which is what we express by the Word
Good-Breeding
. For if we examine thoroughly the Idea of what we
call so, we shall find it to be nothing else but an Imitation and
Mimickry of Good-nature, or in other Terms, Affability, Complaisance and
Easiness of Temper reduced into an Art.
These exterior Shows and Appearances of Humanity render a Man
wonderfully popular and beloved when they are founded upon a real
Good-nature; but without it are like Hypocrisy in Religion, or a bare
Form of Holiness, which, when it is discovered, makes a Man more
detestable than professed Impiety.
Good-nature is generally born with us: Health, Prosperity and kind
Treatment from the World are great Cherishers of it where they find it;
but nothing is capable of forcing it up, where it does not grow of it
self. It is one of the Blessings of a happy Constitution, which
Education may improve but not produce.
Xenophon
in
Life
of his Imaginary Prince, whom he describes as a
Pattern for Real ones, is always celebrating the
Philanthropy
or
Good-nature of his Hero, which he tells us he brought into the World
with him, and gives many remarkable Instances of it in his Childhood, as
well as in all the several Parts of his Life.
, on his Death-bed, he
describes him as being pleased, that while his Soul returned to him
who
made it, his Body should incorporate with the great Mother of all
things, and by that means become beneficial to Mankind. For which
Reason, he gives his Sons a positive Order not to enshrine it in Gold or
Silver, but to lay it in the Earth as soon as the Life was gone out of
it.
An Instance of such an Overflowing of Humanity, such an exuberant Love
to Mankind, could not have entered into the Imagination of a Writer, who
had not a Soul filled with great Ideas, and a general Benevolence to
Mankind.
that celebrated Passage of
Salust
, where
Cæsar
and
Cato
are
placed in such beautiful, but opposite Lights;
Cæsar's
Character is
chiefly made up of Good-nature, as it shewed itself in all its Forms
towards his Friends or his Enemies, his Servants or Dependants, the
Guilty or the Distressed. As for
Cato's
Character, it is rather awful
than amiable. Justice seems most agreeable to the Nature of God, and
Mercy to that of Man. A Being who has nothing to Pardon in himself, may
reward every Man according to his Works; but he whose very best Actions
must be seen with Grains of Allowance, cannot be too mild, moderate, and
forgiving. For this reason, among all the monstrous Characters in Human
Nature, there is none so odious, nor indeed so exquisitely Ridiculous,
as that of a rigid severe Temper in a Worthless Man.
This Part of Good-nature, however, which consists in the pardoning and
overlooking of Faults, is to be exercised only in doing our selves
Justice, and that too in the ordinary Commerce and Occurrences of Life;
for in the publick Administrations of Justice, Mercy to one may be
Cruelty to others.
It is grown almost into a Maxim, that Good-natured Men are not always
Men of the most Wit. This Observation, in my Opinion, has no Foundation
in Nature. The greatest Wits I have conversed with are Men eminent for
their Humanity. I take therefore this Remark to have been occasioned by
two Reasons. First, Because Ill-nature among ordinary Observers passes
for Wit. A spiteful Saying gratifies so many little Passions in those
who hear it, that it generally meets with a good Reception. The Laugh
rises upon it, and the Man who utters it is looked upon as a shrewd
Satyrist. This may be one Reason, why a great many pleasant Companions
appear so surprisingly dull, when they have endeavoured to be Merry in
Print; the Publick being more just than Private Clubs or Assemblies, in
distinguishing between what is Wit and what is Ill-nature.
Another Reason why the Good-natured Man may sometimes bring his Wit in
Question, is, perhaps, because he is apt to be moved with Compassion for
those Misfortunes or Infirmities, which another would turn into
Ridicule, and by that means gain the Reputation of a Wit. The
Ill-natured Man, though but of equal Parts, gives himself a larger Field
to expatiate in; he exposes those Failings in Human Nature which the
other would cast a Veil over, laughs at Vices which the other either
excuses or conceals, gives utterance to Reflections which the other
stifles, falls indifferently upon Friends or Enemies,
the Person
who
has obliged him, and, in short, sticks at nothing that may
establish his Character of a Wit. It is no Wonder therefore he succeeds
in it better than the Man of Humanity, as a Person who makes use of
indirect Methods, is more likely to grow Rich than the Fair Trader.
L.
Cyropædia
, Bk. viii. ch. 6.
that
Catiline
, c. 54.
that
Contents
To The Right Honourable
Henry Boyle, Esq.1
Sir,
As the profest Design of this Work is to entertain its Readers in
general, without giving Offence to any particular Person, it would be
difficult to find out so proper a Patron for it as Your Self, there
being none whose Merit is more universally acknowledged by all Parties,
and who has made himself more Friends and fewer Enemies. Your great
Abilities, and unquestioned Integrity, in those high Employments which
You have passed through, would not have been able to have raised You
this general Approbation, had they not been accompanied with that
Moderation in an high Fortune, and that Affability of Manners, which are
so conspicuous through all Parts of your Life. Your Aversion to any
Ostentatious Arts of setting to Show those great Services which you have
done the Publick, has not likewise a little contributed to that
Universal Acknowledgment which is paid You by your Country.
The Consideration of this Part of Your Character, is that which hinders
me from enlarging on those Extraordinary Talents, which have given You
so great a Figure in the
British
Senate, as well as on that Elegance
and Politeness which appear in Your more retired Conversation. I should
be unpardonable, if, after what I have said, I should longer detain You
with an Address of this Nature: I cannot, however, conclude it without
owning those great Obligations which You have laid upon,
Sir,
Your most obedient,
humble Servant,
The Spectator
.
Henry Boyle, to whom the third volume of the
Spectator
is
dedicated, was the youngest son of Charles, Lord Clifford; one of the
family founded by the Richard, Earl of Cork, who bought Raleigh's
property in Ireland.
From March, 1701, to February, 1707-8, Henry Boyle was King William's
Chancellor of the Exchequer. He was then, till September, 1710, one of
the principal Secretaries of State. He had materially helped Addison by
negotiating between him and Lord Godolphin respecting the celebration of
the Battle of Blenheim. On the accession of George I. Henry Boyle became
Lord Carleton and President of the Council. He died in 1724, and had his
Life
written by Addison's cousin Budgell.
Contents
|
Friday,
September 14, 1711 |
Addison |
In amore hæc omnia insunt vitía: injuriæ,
Suspiciones, inimicitiæ, induciæ,
Bellum, pax rursum ...
Ter.
Eun.
Upon looking over the Letters of my female Correspondents, I find
several from Women complaining of jealous Husbands, and at the same time
protesting their own Innocence; and desiring my Advice on this Occasion.
shall therefore take this Subject into my Consideration, and the more
willingly, because I find that the Marquis of
Hallifax
, who in his
Advice to a Daughter
has instructed a Wife how to behave her
self towards a false, an intemperate, a cholerick, a sullen, a covetous,
or a silly Husband, has not spoken one Word of a Jealous Husband.
Jealousy is that Pain which a Man feels from the Apprehension that he
is not equally beloved by the Person whom he entirely loves.
Now,
because our inward Passions and Inclinations can never make themselves
visible, it is impossible for a jealous Man to be thoroughly cured of
his Suspicions. His Thoughts hang at best in a State of Doubtfulness and
Uncertainty; and are never capable of receiving any Satisfaction on the
advantageous Side; so that his Enquiries are most successful when they
discover nothing: His Pleasure arises from his Disappointments, and his
Life is spent in Pursuit of a Secret that destroys his Happiness if he
chance to find it.
An ardent Love is always a strong Ingredient in this Passion; for the
same Affection which stirs up the jealous Man's Desires, and gives the
Party beloved so beautiful a Figure in his Imagination, makes him
believe she kindles the same Passion in others, and appears as amiable
to all Beholders. And as Jealousy thus arises from an extraordinary
Love, it is of so delicate a Nature, that it scorns to take up with any
thing less than an equal Return of Love. Not the warmest Expressions of
Affection, the softest and most tender Hypocrisy, are able to give any
Satisfaction, where we are not persuaded that the Affection is real and
the Satisfaction mutual. For the jealous Man wishes himself a kind of
Deity to the Person he loves: He would be the only Pleasure of her
Senses, the Employment of her Thoughts; and is angry at every thing she
admires, or takes Delight in, besides himself.
Request to his Mistress, upon his leaving her for three Days,
is inimitably beautiful and natural.
Cum milite isto præsens, absens ut sies:
Dies, noctesque me ames: me desideres:
Me somnies: me exspectes: de me cogites:
Me speres: me te oblectes: mecum tola sis:
Meus fac sis postremo animus, quando ego sum tuus.
Ter. Eun
2.
The Jealous Man's Disease is of so malignant a Nature, that it converts
all he takes into its own Nourishment. A cool Behaviour sets him on the
Rack, and is interpreted as an instance of Aversion or Indifference; a
fond one raises his Suspicions, and looks too much like Dissimulation
and Artifice. If the Person he loves be cheerful, her Thoughts must be
employed on another; and if sad, she is certainly thinking on himself.
In short, there is no Word or Gesture so insignificant, but it gives him
new Hints, feeds his Suspicions, and furnishes him with fresh Matters of
Discovery: So that if we consider the effects of this Passion, one would
rather think it proceeded from an inveterate Hatred than an excessive
Love; for certainly none can meet with more Disquietude and Uneasiness
than a suspected Wife, if we except the jealous Husband.
But the great Unhappiness of this Passion is, that it naturally tends to
alienate the Affection which it is so solicitous to engross; and that
for these two Reasons, because it lays too great a Constraint on the
Words and Actions of the suspected Person, and at the same time shews
you have no honourable Opinion of her; both of which are strong Motives
to Aversion.
Nor is this the worst Effect of Jealousy; for it often draws after it a
more fatal Train of Consequences, and makes the Person you suspect
guilty of the very Crimes you are so much afraid of. It is very natural
for such who are treated ill and upbraided falsely, to find out an
intimate Friend that will hear their Complaints, condole their
Sufferings, and endeavour to sooth and asswage their secret Resentments.
Besides, Jealousy puts a Woman often in Mind of an ill Thing that she
would not otherwise perhaps have thought of, and fills her Imagination
with such an unlucky Idea, as in Time grows familiar, excites Desire,
and loses all the Shame and Horror which might at first attend it. Nor
is it a Wonder if she who suffers wrongfully in a Man's Opinion of her,
and has therefore nothing to forfeit in his Esteem, resolves to give him
reason for his Suspicions, and to enjoy the Pleasure of the Crime, since
she must undergo the Ignominy.
probably were the Considerations
that directed the wise Man in his Advice to Husbands;
Be not jealous
over the Wife of thy Bosom, and teach her not an evil Lesson against thy
self.
Ecclus
.
here, among the other Torments which this Passion produces, we may
usually observe that none are greater Mourners than jealous Men, when
the Person
who
provoked their Jealousy is taken from them.
it
is that their Love breaks out furiously, and throws off all the Mixtures
of Suspicion
which
choaked and smothered it before.
beautiful
Parts of the Character rise uppermost in the jealous Husband's Memory,
and upbraid him with the ill Usage of so divine a Creature as was once
in his Possession; whilst all the little Imperfections, that were
before
so uneasie to him, wear off from his Remembrance, and shew
themselves no more.
We may see by what has been said, that Jealousy takes the deepest Root
in Men of amorous Dispositions; and of these we may find three Kinds who
are most over-run with it.
The First are those who are conscious to themselves of an Infirmity,
whether it be Weakness, Old Age, Deformity, Ignorance, or the like.
These Men are so well acquainted with the unamiable Part of themselves,
that they have not the Confidence to think they are really beloved; and
are so distrustful of their own Merits, that all Fondness towards them
puts them out of Countenance, and looks like a Jest upon their Persons.
They grow suspicious on their first looking in a Glass, and are stung
with Jealousy at the sight of a Wrinkle. A handsome Fellow immediately
alarms them, and every thing that looks young or gay turns their
thoughts upon their Wives.
A Second Sort of Men, who are most liable to this Passion, are those of
cunning, wary, and distrustful Tempers. It is a Fault very justly found
in Histories composed by Politicians, that they leave nothing to Chance
or Humour, but are still for deriving every Action from some Plot and
Contrivance, for drawing up a perpetual Scheme of Causes and Events, and
preserving a constant Correspondence between the Camp and the
Council-Table. And thus it happens in the Affairs of Love with Men of
too refined a Thought. They put a Construction on a Look, and find out a
Design in a Smile; they give new Senses and Significations to Words and
Actions; and are ever tormenting themselves with Fancies of their own
raising: They generally act in a Disguise themselves, and therefore
mistake all outward Shows and Appearances for Hypocrisy in others;
that I believe no Men see less of the Truth and Reality of Things, than
these great Refiners upon Incidents,
who
are so wonderfully subtle
and overwise in their Conceptions.
Now what these Men fancy they know of Women by Reflection, your lewd and
vicious Men believe they have learned by Experience. They have seen the
poor Husband so misled by Tricks and Artifices, and in the midst of his
Enquiries so lost and bewilder'd in a crooked Intreague, that they still
suspect an Under-Plot in every female Action; and especially where they
see any Resemblance in the Behaviour of two Persons, are apt to fancy it
proceeds from the same Design in both. These Men therefore bear hard
upon the suspected Party, pursue her close through all her Turnings and
Windings, and are too well acquainted with the Chace, to be slung off by
any false Steps or Doubles: Besides, their Acquaintance and Conversation
has lain wholly among the vicious Part of Womankind, and therefore it is
no Wonder they censure all alike, and look upon the whole Sex as a
Species of Impostors. But if, notwithstanding their private Experience,
they can get over these Prejudices, and entertain a favourable Opinion
of some
Women
; yet their own loose Desires will stir up new
Suspicions from another Side, and make them believe all
Men
subject to the same Inclinations with themselves.
Whether these or other Motives are most predominant, we learn from the
modern Histories of
America
, as well as from our own Experience
in this Part of the World, that Jealousy is no Northern Passion, but
rages most in those Nations that lie nearest the Influence of the Sun.
It is a Misfortune for a Woman to be born between the Tropicks; for
there lie the hottest Regions of Jealousy, which as you come Northward
cools all along with the Climate, till you scarce meet with any thing
like it in the Polar Circle. Our own Nation is very temperately situated
in this respect; and if we meet with some few disordered with the
Violence of this Passion, they are not the proper Growth of our Country,
but are many Degrees nearer the Sun in their Constitutions than in their
Climate.
this frightful Account of Jealousy, and the Persons
who
are
most subject to it, it will be but fair to shew by what means the
Passion may be best allay'd, and those who are possessed with it set at
Ease. Other Faults indeed are not under the Wife's Jurisdiction, and
should, if possible, escape her Observation; but Jealousy calls upon her
particularly for its Cure, and deserves all her Art and Application in
the Attempt: Besides, she has this for her Encouragement, that her
Endeavours will be always pleasing, and that she will still find the
Affection of her Husband rising towards her in proportion as his Doubts
and Suspicions vanish; for, as we have seen all along, there is so great
a Mixture of Love in Jealousy as is well worth separating. But this
shall be the Subject of another Paper.
L.
Miscellanies
by the late lord Marquis of Halifax
(George Saville, who died in 1695), 1704, pp. 18-31.
'When you are in company with that Soldier, behave as if you were
absent: but continue to love me by Day and by Night: want me; dream of
me; expect me; think of me; wish for me; delight in me: be wholly with
me: in short, be my very Soul, as I am yours.'
Ecclus
. ix. I.
that
that
formerly
that
that
Contents
|
Saturday,
September 15, 1711 |
Addison |
Credula res amor est ...
Ovid.
Met.
Having in my Yesterday's Paper discovered the Nature of Jealousie, and
pointed out the Persons who are most subject to it, I must here apply my
self to my fair Correspondents, who desire to live well with a Jealous
Husband, and to ease his Mind of its unjust Suspicions.
The first Rule I shall propose to be observed is, that you never seem to
dislike in another what the Jealous Man is himself guilty of, or to
admire any thing in which he himself does not excel. A Jealous Man is
very quick in his Applications, he knows how to find a double Edge in an
Invective, and to draw a Satyr on himself out of a Panegyrick on
another. He does not trouble himself to consider the Person, but to
direct the Character; and is secretly pleased or confounded as he finds
more or less of himself in it. The Commendation of any thing in another,
stirs up his Jealousy, as it shews you have a Value for others, besides
himself; but the Commendation of that which he himself wants, inflames
him more, as it shews that in some Respects you prefer others before
him.
is admirably described in this View by
Horace
in his
Ode to
Lydia
;
Quum tu, Lydia, Telephi
Cervicem roseam, et cerea Telephi
Laudas brachia, væ meum
Fervens difficili bile tumet jecur:
Tunc nec mens mihi, nec color
Certâ sede manet; humor et in genas
Furtim labitur, arguens
Quam lentis penitus macerer ignibus.
When Telephus his youthful Charms,
His rosie Neck and winding Arms,
With endless Rapture you recite,
And in the pleasing Name delight;
My Heart, inflam'd by jealous Heats,
With numberless Resentments beats;
From my pale Cheek the Colour flies,
And all the Man within me dies:
By Turns my hidden Grief appears
In rising Sighs and falling Tears,
That shew too well the warm Desires,
The silent, slow, consuming Fires,
Which on my inmost Vitals prey,
And melt my very Soul away.
The Jealous Man is not indeed angry if you dislike another, but if you
find those Faults which are to be found in his own Character, you
discover not only your Dislike of another, but of himself. In short, he
is so desirous of ingrossing all your Love, that he is grieved at the
want of any Charm, which he believes has Power to raise it; and if he
finds by your Censures on others, that he is not so agreeable in your
Opinion as he might be, he naturally concludes you could love him better
if he had other Qualifications, and that by Consequence your Affection
does not rise so high as he thinks it ought. If therefore his Temper be
grave or sullen, you must not be too much pleased with a Jest, or
transported with any thing that is gay and diverting. If his Beauty be
none of the best, you must be a professed Admirer of Prudence, or any
other Quality he is Master of, or at least vain enough to think he is.
In the next place, you must be sure to be free and open in your
Conversation with him, and to let in Light upon your Actions, to unravel
all your Designs, and discover every Secret however trifling or
indifferent. A jealous Husband has a particular Aversion to Winks and
Whispers, and if he does not see to the Bottom of every thing, will be
sure to go beyond it in his Fears and Suspicions. He will always expect
to be your chief Confident, and where he finds himself kept out of a
Secret, will believe there is more in it than there should be. And here
it is of great concern, that you preserve the Character of your
Sincerity uniform and of a piece: for if he once finds a false Gloss put
upon any single Action, he quickly suspects all the rest; his working
Imagination immediately takes a false Hint, and runs off with it into
several remote Consequences, till he has proved very ingenious in
working out his own Misery.
If both these Methods fail, the best way will be to let him see you are
much cast down and afflicted for the ill Opinion he entertains of you,
and the Disquietudes he himself suffers for your Sake.
are many
who take a kind of barbarous Pleasure in the Jealousy of those
who
love them, that insult over an aking Heart, and triumph in their Charms
which are able to excite so much Uneasiness.
Ardeat ipsa licet tormentis gaudet amantis.
Juv.
But these often carry the Humour so far, till their affected Coldness
and Indifference quite kills all the Fondness of a Lover, and are then
sure to meet in their Turn with all the Contempt and Scorn that is due
to so insolent a Behaviour. On the contrary, it is very probable a
melancholy, dejected Carriage, the usual effects of injured Innocence,
may soften the jealous Husband into Pity, make him sensible of the Wrong
he does you, and work out of his Mind all those Fears and Suspicions
that make you both unhappy. At least it will have this good Effect, that
he will keep his Jealousy to himself, and repine in private, either
because he is sensible it is a Weakness, and will therefore hide it from
your Knowledge, or because he will be apt to fear some ill Effect it may
produce, in cooling your Love towards him, or diverting it to another.
There is still another Secret that can never fail, if you can once get
it believ'd, and what is often practis'd by Women of greater Cunning
than Virtue: This is to change Sides for a while with the jealous Man,
and to turn his own Passion upon himself; to take some Occasion of
growing Jealous of him, and to follow the Example he himself hath set
you.
Counterfeited Jealousy will bring him a great deal of
Pleasure, if he thinks it real; for he knows experimentally how much
Love goes along with
this Passion,
and will
besides feel
something like the Satisfaction of a Revenge, in seeing you undergo all
his own Tortures. But this, indeed, is an Artifice so difficult, and at
the same time so dis-ingenuous, that it ought never to be put in
Practice, but by such as have Skill enough to cover the Deceit, and
Innocence to render it excusable.
shall conclude this Essay with the Story of
Herod
and
Mariamne
, as
I have collected it out of
Josephus
; which may serve almost as an
Example to whatever can be said on this Subject.
Mariamne
had all the Charms that Beauty, Birth, Wit and Youth could
give a Woman, and
Herod
all the Love that such Charms are able to
raise in a warm and amorous Disposition. In the midst of this his
Fondness for
Mariamne
, he put her Brother to Death, as he did her
Father not many Years after. The Barbarity of the Action was represented
to
Mark Antony
, who immediately summoned
Herod
into
Egypt
, to
answer for the Crime that was there laid to his Charge.
Herod
attributed the Summons to
Antony's
Desire of
Mariamne
, whom
therefore, before his Departure, he gave into the Custody of his Uncle
Joseph
, with private Orders to put her to Death, if any such Violence
was offered to himself. This
Joseph
was much delighted with
Mariamne's
Conversation, and endeavoured, with all his Art and
Rhetorick, to set out the Excess of
Herod's
Passion for her; but when
he still found her Cold and Incredulous, he inconsiderately told her, as
a certain Instance of her Lord's Affection, the private Orders he had
left behind him, which plainly shewed, according to
Joseph's
Interpretation, that he could neither Live nor Die without her. This
Barbarous Instance of a wild unreasonable Passion quite put out, for a
time, those little Remains of Affection she still had for her Lord: Her
Thoughts were so wholly taken up with the Cruelty of his Orders, that
she could not consider the Kindness that produced them, and therefore
represented him in her Imagination, rather under the frightful Idea of a
Murderer than a Lover.
Herod
was at length acquitted and
dismissed by
Mark Antony
, when his Soul was all in Flames for his
Mariamne
; but before their Meeting, he was not a little alarm'd
at the Report he had heard of his Uncle's Conversation and Familiarity
with her in his Absence. This therefore was the first Discourse he
entertained her with, in which she found it no easy matter to quiet his
Suspicions. But at last he appeared so well satisfied of her Innocence,
that from Reproaches and Wranglings he fell to Tears and Embraces. Both
of them wept very tenderly at their Reconciliation, and
Herod
poured out his whole Soul to her in the warmest Protestations of Love
and Constancy: when amidst all his Sighs and Languishings she asked him,
whether the private Orders he left with his Uncle
Joseph
were an
Instance of such an inflamed Affection. The Jealous King was immediately
roused at so unexpected a Question, and concluded his Uncle must have
been too Familiar with her, before he would have discovered such a
Secret. In short, he put his Uncle to Death, and very difficultly
prevailed upon himself to spare
Mariamne
.
After this he was forced on a second Journey into
Egypt
, when he
committed his Lady to the Care of
Sohemus
, with the same private
Orders he had before given his Uncle, if any Mischief befel himself. In
the mean while
Mariamne
so won upon
Sohemus
by her
Presents and obliging Conversation, that she drew all the Secret from
him, with which
Herod
had intrusted him; so that after his
Return, when he flew to her with all the Transports of Joy and Love, she
received him coldly with Sighs and Tears, and all the Marks of
Indifference and Aversion. This Reception so stirred up his Indignation,
that he had certainly slain her with his own Hands, had not he feared he
himself should have become the greater Sufferer by it. It was not long
after this, when he had another violent Return of Love upon him;
Mariamne
was therefore sent for to him, whom he endeavoured to
soften and reconcile with all possible conjugal Caresses and
Endearments; but she declined his Embraces, and answered all his
Fondness with bitter Invectives for the Death of her Father and her
Brother. This Behaviour so incensed
Herod
, that he very hardly
refrained from striking her; when in the Heat of their Quarrel there
came in a Witness, suborn'd by some of
Mariamne's
Enemies, who
accused her to the King of a Design to poison him.
Herod
was now
prepared to hear any thing in her Prejudice, and immediately ordered her
Servant to be stretch'd upon the Rack;
in the Extremity of his
Tortures confest, that his Mistress's Aversion to the King arose from
something
Sohemus
had told her; but as for any Design of
poisoning, he utterly disowned the least Knowledge of it. This
Confession quickly proved fatal to
Sohemus
, who now lay under the
same Suspicions and Sentence that
Joseph
had before him on the
like Occasion. Nor would
Herod
rest here; but accused her with
great Vehemence of a Design upon his Life, and by his Authority with the
Judges had her publickly Condemned and Executed.
Herod
soon after
her Death grew melancholy and dejected, retiring from the Publick
Administration of Affairs into a solitary Forest, and there abandoning
himself to all the black Considerations, which naturally arise from a
Passion made up of Love, Remorse, Pity and Despair, he used to rave for
his
Mariamne
, and to call upon her in his distracted Fits; and in
all probability would soon have followed her, had not his Thoughts been
seasonably called off from so sad an Object by Publick Storms, which at
that Time very nearly threatned him.
L.
", part of which I find Translated to my Hand."
that
it
receive
Antiquities of the Jews
, Bk. xv. ch. iii. § 5, 6, 9; ch.
vii. § 1, 2, &c.
some thing that
Contents
|
Monday,
September 17, 1711 |
Steele |
Non solum Scientia, quæ est remota a Justitia, Calliditas potius quam
Sapientia est appellanda; verum etiam Animus paratus ad periculum, si suâ
cupiditate, non utilitate communi impellitur, Audaciæ potius nomen habeat,
quam Fortitudinis.
Plato apud Tull.

There can be no greater Injury to humane Society than that good Talents
among Men should be held honourable to those who are endowed with them
without any Regard how they are applied. The Gifts of Nature and
Accomplishments of Art are valuable, but as they are exerted in the
Interest of Virtue, or governed by the Rules of Honour. We ought to
abstract our Minds from the Observation of any Excellence in those we
converse with, till we have taken some Notice, or received some good
Information of the Disposition of their Minds; otherwise the Beauty of
their Persons, or the Charms of their Wit, may make us fond of those
whom our Reason and Judgment will tell us we ought to abhor.
When we suffer our selves to be thus carried away by meer Beauty, or
meer Wit,
Omniamante
, with all her Vice, will bear away as much
of our Good-will as the most innocent Virgin or discreetest Matron; and
there cannot be a more abject Slavery in this World, than to doat upon
what we think we ought to contemn: Yet this must be our Condition in all
the Parts of Life, if we suffer our selves to approve any Thing but what
tends to the Promotion of what is good and honourable. If we would take
true Pains with our selves to consider all Things by the Light of Reason
and Justice, tho' a Man were in the Height of Youth and amorous
Inclinations, he would look upon a Coquet with the same Contempt or
Indifference as he would upon a Coxcomb: The wanton Carriage in a Woman,
would disappoint her of the Admiration which she aims at; and the vain
Dress or Discourse of a Man would destroy the Comeliness of his Shape,
or Goodness of his Understanding. I say the Goodness of his
Understanding, for it is no less common to see Men of Sense commence
Coxcombs, than beautiful Women become immodest. When this happens in
either, the Favour we are naturally inclined to give to the good
Qualities they have from Nature, should abate in Proportion. But however
just it is to measure the Value of Men by the Application of their
Talents, and not by the Eminence of those Qualities abstracted from
their Use; I say, however just such a Way of judging is, in all Ages as
well as this, the Contrary has prevailed upon the Generality of Mankind.
How many lewd Devices have been preserved from one Age to another, which
had perished as soon as they were made, if Painters and Sculptors had
been esteemed as much for the Purpose as the Execution of their Designs?
Modest and well-governed Imaginations have by this Means lost the
Representations of Ten Thousand charming Portraitures, filled with
Images of innate Truth, generous Zeal, couragious Faith, and tender
Humanity; instead of which, Satyrs, Furies, and Monsters are recommended
by those Arts to a shameful Eternity.
The unjust Application of laudable Talents, is tolerated, in the general
Opinion of Men, not only in such Cases as are here mentioned, but also
in Matters which concern ordinary Life. If a Lawyer were to be esteemed
only as he uses his Parts in contending for Justice, and were
immediately despicable when he appeared in a Cause which he could not
but know was an unjust one, how honourable would his Character be? And
how honourable is it in such among us, who follow the Profession no
otherwise than as labouring to protect the Injured, to subdue the
Oppressor, to imprison the careless Debtor, and do right to the painful
Artificer? But many of this excellent Character are overlooked by the
greater Number; who affect covering a weak Place in a Client's Title,
diverting the Course of an Enquiry, or finding a skilful Refuge to
palliate a Falsehood: Yet it is still called Eloquence in the latter,
though thus unjustly employed; but Resolution in an Assassin is
according to Reason quite as laudable, as Knowledge and Wisdom exercised
in the Defence of an ill Cause.
Were the Intention stedfastly considered, as the Measure of Approbation,
all Falsehood would soon be out of Countenance; and an Address in
imposing upon Mankind, would be as contemptible in one State of Life as
another. A Couple of Courtiers making Professions of Esteem, would make
the same Figure under Breach of Promise, as two Knights of the Post
convicted of Perjury. But Conversation is fallen so low in point of
Morality, that as they say in a Bargain,
Let the Buyer look to
it
; so in Friendship, he is the Man in Danger who is most apt to
believe: He is the more likely to suffer in the Commerce, who begins
with the Obligation of being the more ready to enter into it.
But those Men only are truly great, who place their Ambition rather in
acquiring to themselves the Conscience of worthy Enterprizes, than in
the Prospect of Glory which attends them. These exalted Spirits would
rather be secretly the Authors of Events which are serviceable to
Mankind, than, without being such, to have the publick Fame of it. Where
therefore an eminent Merit is robbed by Artifice or Detraction, it does
but encrease by such Endeavours of its Enemies: The impotent Pains which
are taken to sully it, or diffuse it among a Crowd to the Injury of a
single Person, will naturally produce the contrary Effect; the Fire will
blaze out, and burn up all that attempt to smother what they cannot
extinguish.
There is but one thing necessary to keep the Possession of true Glory,
which is, to hear the Opposers of it with Patience, and preserve the
Virtue by which it was acquired. When a Man is thoroughly perswaded that
he ought neither to admire, wish for, or pursue any thing but what is
exactly his Duty, it is not in the Power of Seasons, Persons, or
Accidents to diminish his Value: He only is a great Man who can neglect
the Applause of the Multitude, and enjoy himself independent of its
Favour. This is indeed an arduous Task; but it should comfort a glorious
Spirit that it is the highest Step to which human Nature can arrive.
Triumph, Applause, Acclamation, are dear to the Mind of Man; but it is
still a more exquisite Delight to say to your self, you have done well,
than to hear the whole human Race pronounce you glorious, except you
your self can join with them in your own Reflections. A Mind thus equal
and uniform may be deserted by little fashionable Admirers and
Followers, but will ever be had in Reverence by Souls like it self. The
Branches of the Oak endure all the Seasons of the Year, though its
Leaves fall off in Autumn; and these too will be restored with the
returning Spring.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday,
September 18, 1711 |
Addison |
... Remove fera monstra, tuægue
Saxificos vultus, quæcunque ea, tolle Medusæ.
Ovid.
Met.

In a late Paper I mention'd the Project of an Ingenious Author for the
erecting of several Handicraft Prizes to be contended for by our
British
Artizans, and the Influence they might have towards the
Improvement of our several Manufactures. I have since that been very
much surprized by the following Advertisement which I find in the
Post-Boy
of the 11th Instant, and again repeated in the
Post-Boy
of the 15th.
On the 9th of October next will be run for upon Coleshill-Heath in
Warwickshire, a Plate of 6 Guineas Value, 3 Heats, by any Horse, Mare or
Gelding that hath not won above the Value of £5, the winning Horse to be
sold for £10, to carry 10 Stone Weight, if 14 Hands high; if above or
under to carry or be allowed Weight for Inches, and to be entered Friday
the 5th at the Swan in Coleshill, before Six in the Evening. Also a
Plate of less Value to be run for by Asses. The same Day a Gold Ring to
be Grinn'd for by Men.
The first of these Diversions, that is to be exhibited by the £10
Race-Horses, may probably have its Use; but the two last, in which the
Asses and Men are concerned, seem to me altogether extraordinary and
unaccountable. Why they should keep Running Asses at
Coleshill
,
or how making Mouths turns to account in
Warwickshire
, more than
in any other Parts of
England
, I cannot comprehend. I have looked
over all the Olympic Games, and do not find any thing in them like an
Ass-Race, or a Match at Grinning. However it be, I am informed that
several Asses are now kept in Body-Cloaths, and sweated every Morning
upon the Heath, and that all the Country-Fellows within ten Miles of the
Swan
, grinn an Hour or two in their Glasses every Morning, in
order to qualify themselves for the 9th of
October
. The Prize,
which is proposed to be Grinn'd for, has raised such an Ambition among
the Common People of Out-grinning one another, that many very discerning
Persons are afraid it should spoil most of the Faces in the Country; and
that a
Warwickshire
Man will be known by his Grinn, as
Roman-Catholicks imagine a
Kentish
Man is by his Tail. The Gold
Ring which is made the Prize of Deformity, is just the Reverse of the
Golden Apple that was formerly made the Prize of Beauty, and should
carry for its Posy the old Motto inverted.
Detur tetriori.
Or to accommodate it to the Capacity of the Combatants,
The frightfull'st Grinner
Be the Winner.
In the mean while I would advise a
Dutch
Painter to be present at
this great Controversy of Faces, in order to make a Collection of the
most remarkable Grinns that shall be there exhibited.
I must not here omit an Account which I lately received of one of these
Grinning Matches from a Gentleman, who, upon reading the above-mentioned
Advertisement, entertained a Coffee-house with the following Narrative.
the taking of
Namur
, amidst other publick Rejoicings
made on that Occasion, there was a Gold Ring given by a Whig Justice of
Peace to be grinn'd for. The first Competitor that entered the Lists,
was a black swarthy
French Man
, who accidentally passed that way,
and being a Man naturally of a wither'd Look, and hard Features,
promised himself good Success. He was placed upon a Table in the great
Point of View,
looking upon the Company like
Milton's
Death,
Grinn'd horribly2
a Ghastly Smile ...
His Muscles were so drawn together on each side of his Face, that he
shew'd twenty Teeth at a Grinn, and put the County in some pain, lest a
Foreigner should carry away the Honour of the Day; but upon a farther
Tryal they found he was Master only of the merry Grinn.
The next that mounted the Table was a Malecontent in those Days, and a
great Master in the whole Art of Grinning, but particularly excelled in
the angry Grinn. He did his Part so well, that he is said to have made
half a dozen Women miscarry; but the Justice being apprised by one who
stood near him, that the Fellow who Grinned in his Face was a
Jacobite
, and being unwilling that a Disaffected Person should
win the Gold Ring, and be looked upon as the best Grinner in the
Country, he ordered the Oaths to be tendered unto him upon his quitting
the Table, which the Grinner refusing, he was set aside as an
unqualified Person. There were several other Grotesque Figures that
presented themselves, which it would be too tedious to describe. I must
not however omit a Ploughman, who lived in the farther Part of the
Country, and being very lucky in a Pair of long Lanthorn-Jaws, wrung his
face into such a hideous Grimace that every Feature of it appeared under
a different Distortion. The whole Company stood astonished at such a
complicated Grinn, and were ready to assign the Prize to him, had it not
been proved by one of his Antagonists, that he had practised with
Verjuice for some Days before, and had a Crab found upon him at the very
time of Grinning; upon which the best Judges of Grinning declared it as
their Opinion, that he was not to be looked upon as a fair Grinner, and
therefore ordered him to be set aside as a Cheat.
The Prize, it seems, fell at length upon a Cobler,
Giles Gorgon
by Name, who produced several new Grinns of his own Invention, having
been used to cut Faces for many Years together over his Last. At the
very first Grinn he cast every Human Feature out of his Countenance; at
the second he became the Face of a Spout; at the third a Baboon, at the
fourth the Head of a Base-Viol, and at the fifth a Pair of Nut-Crackers.
The whole Assembly wondered at his Accomplishments, and bestowed the
Ring on him unanimously; but, what he esteemed more than all the rest, a
Country Wench, whom he had wooed in vain for above five Years before,
was so charmed with his Grinns, and the Applauses which he received on
all Sides, that she Married him the Week following, and to this Day
wears the Prize upon her Finger, the Cobler having made use of it as his
Wedding-Ring.
Paper might perhaps seem very impertinent, if it grew serious in
the Conclusion. I would nevertheless leave it to the Consideration of
those who are the Patrons of this monstrous Tryal of Skill, whether or
no they are not guilty, in some measure, of an Affront to their Species,
in treating after this manner the
Human Face Divine
, and turning
that Part of us, which has so great an Image impressed upon it, into the
Image of a Monkey; whether the raising such silly Competitions among the
Ignorant, proposing Prizes for such useless Accomplishments, filling the
common People's Heads with such Senseless Ambitions, and inspiring them
with such absurd Ideas of Superiority and Preheminence, has not in it
something Immoral as well as Ridiculous
.
L.
Sept. 1, 1695.
horridly
. Neither is quite right.
'Death Grinn'd horrible a ghastly smile.'
P. L.
, Bk. II. 1. 864.
Two volumes of
Original Letters
sent to the Tatler and
Spectator and not inserted, were published by Charles Lillie in 1725. In
Vol. II. (pp. 72, 73), is a letter from Coleshill, informing the
Spectator that in deference to his opinion, and chiefly through the
mediation of some neighbouring ladies, the Grinning Match had been
abandoned, and requesting his advice as to the disposal of the Grinning
Prize.
Contents
|
Wednesday,
September 19, 1711 |
Steele |
Hæc memini et victum frustra contendere Thyrsin.
Virg.

There is scarce any thing more common than Animosities between Parties
that cannot subsist but by their Agreement: this was well represented in
the Sedition of the Members of the humane Body in the old
Roman
Fable. It is often the Case of lesser confederate States against a
superior Power, which are hardly held together, though their Unanimity
is necessary for their common Safety: and this is always the Case of the
landed and trading Interest of
Great Britain
: the Trader is fed
by the Product of the Land, and the landed Man cannot be clothed but by
the Skill of the Trader; and yet those Interests are ever jarring.
We had last Winter an Instance of this at our Club, in Sir
Roger De
Coverley
and Sir
Andrew Freeport
, between whom there is generally a
constant, though friendly, Opposition of Opinions.
happened that one
of the Company, in an Historical Discourse, was observing, that
Carthaginian
Faith
was a proverbial
Phrase to intimate Breach of Leagues. Sir
Roger
said it could hardly be
otherwise: That the
Carthaginians
were the greatest Traders in
the World; and as Gain is the chief End of such a People, they never
pursue any other: The Means to it are never regarded; they will, if it
comes easily, get Money honestly; but if not, they will not scruple to
attain it by Fraud or Cozenage: And indeed, what is the whole Business
of the Trader's Account, but to over-reach him who trusts to his Memory?
But were that not so, what can there great and noble be expected from
him whose Attention is for ever fixed upon ballancing his Books, and
watching over his Expences? And at best, let Frugality and Parsimony be
the Virtues of the Merchant, how much is his punctual Dealing below a
Gentleman's Charity to the Poor, or Hospitality among his Neighbours?
Captain Sentry
observed Sir
Andrew
very diligent in hearing Sir
Roger
,
and had a mind to turn the Discourse, by taking notice in general, from
the highest to the lowest Parts of human Society, there was a secret,
tho' unjust, Way among Men, of indulging the Seeds of ill Nature and
Envy, by comparing their own State of Life to that of another, and
grudging the Approach of their Neighbour to their own Happiness; and on
the other Side, he who is the less at his Ease, repines at the other
who, he thinks, has unjustly the Advantage over him. Thus the Civil and
Military Lists look upon each other with much ill Nature; the Soldier
repines at the Courtier's Power, and the Courtier rallies the Soldier's
Honour; or, to come to lower Instances, the private Men in the Horse and
Foot of an Army, the Carmen and Coachmen in the City Streets, mutually
look upon each other with ill Will, when they are in Competition for
Quarters or the Way, in their respective Motions.
It is very well, good Captain, interrupted Sir
Andrew
: You may attempt
to turn the Discourse if you think fit; but I must however have a Word
or two with Sir
Roger
, who, I see, thinks he has paid me off, and been
very severe upon the Merchant. I shall not, continued he, at this time
remind Sir
Roger
of the great and noble Monuments of Charity and Publick
Spirit, which have been erected by Merchants since the Reformation, but
at present content my self with what he allows us, Parsimony and
Frugality. If it were consistent with the Quality of so antient a
Baronet as Sir
Roger
, to keep an Account, or measure Things by the most
infallible Way, that of Numbers, he would prefer our Parsimony to his
Hospitality. If to drink so many Hogsheads is to be Hospitable, we do
not contend for the Fame of that Virtue; but it would be worth while to
consider, whether so many Artificers at work ten Days together by my
Appointment, or so many Peasants made merry on Sir
Roger's
Charge, are
the Men more obliged? I believe the Families of the Artificers will
thank me, more than the Households of the Peasants shall Sir
Roger
. Sir
Roger
gives to his Men, but I place mine above the Necessity or
Obligation of my Bounty. I am in very little Pain for the
Roman
Proverb upon the
Carthaginian
Traders; the
Romans
were
their professed Enemies: I am only sorry no
Carthaginian
Histories have come to our Hands; we might have been taught perhaps by
them some Proverbs against the
Roman
Generosity, in fighting for
and bestowing other People's Goods. But since Sir
Roger
has taken
Occasion from an old Proverb to be out of Humour with Merchants, it
should be no Offence to offer one not quite so old in their Defence.
When a Man happens to break in
Holland
, they say of him that
he has not kept true Accounts
. This Phrase, perhaps, among us,
would appear a soft or humorous way of speaking, but with that exact
Nation it bears the highest Reproach; for a Man to be Mistaken in the
Calculation of his Expence, in his Ability to answer future Demands, or
to be impertinently sanguine in putting his Credit to too great
Adventure, are all Instances of as much Infamy as with gayer Nations to
be failing in Courage or common Honesty.
Numbers are so much the Measure of every thing that is valuable, that it
is not possible to demonstrate the Success of any Action, or the
Prudence of any Undertaking, without them. I say this in Answer to what
Sir
Roger
is pleased to say, That little that is truly noble can be
expected from one who is ever poring on his Cashbook, or ballancing his
Accounts. When I have my Returns from abroad, I can tell to a Shilling,
by the Help of Numbers, the Profit or Loss by my Adventure; but I ought
also to be able to shew that I had Reason for making it, either from my
own Experience or that of other People, or from a reasonable Presumption
that my Returns will be sufficient to answer my Expence and Hazard; and
this is never to be done without the Skill of Numbers. For Instance, if
I am to trade to
Turkey
, I ought beforehand to know the Demand of
our Manufactures there, as well as of their Silks in
England
, and
the customary Prices that are given for both in each Country. I ought to
have a clear Knowledge of these Matters beforehand, that I may presume
upon sufficient Returns to answer the Charge of the Cargo I have fitted
out, the Freight and Assurance out and home, the Custom to the Queen,
and the Interest of my own Money, and besides all these Expences a
reasonable Profit to my self. Now what is there of Scandal in this
Skill? What has the Merchant done, that he should be so little in the
good Graces of Sir
Roger
? He throws down no Man's Enclosures, and
tramples upon no Man's Corn; he takes nothing from the industrious
Labourer; he pays the poor Man for his Work; he communicates his Profit
with Mankind; by the Preparation of his Cargo and the Manufacture of his
Returns, he furnishes Employment and Subsistence to greater Numbers than
the richest Nobleman; and even the Nobleman is obliged to him for
finding out foreign Markets for the Produce of his Estate, and for
making a great Addition to his Rents; and yet 'tis certain, that none of
all these Things could be done by him without the Exercise of his Skill
in Numbers.
This is the Œconomy of the Merchant; and the Conduct of the Gentleman
must be the same, unless by scorning to be the Steward, he resolves the
Steward shall be the Gentleman. The Gentleman, no more than the
Merchant, is able, without the Help of Numbers, to account for the
Success of any Action, or the Prudence of any Adventure. If, for
Instance, the Chace is his whole Adventure, his only Returns must be the
Stag's Horns in the great Hall, and the Fox's Nose upon the Stable Door.
Without Doubt Sir
Roger
knows the full Value of these Returns; and if
beforehand he had computed the Charges of the Chace, a Gentleman of his
Discretion would certainly have hanged up all his Dogs, he would never
have brought back so many fine Horses to the Kennel, he would never have
gone so often, like a Blast, over Fields of Corn. If such too had been
the Conduct of all his Ancestors, he might truly have boasted at this
Day, that the Antiquity of his Family had never been sullied by a Trade;
a Merchant had never been permitted with his whole Estate to purchase a
Room for his Picture in the Gallery of the
Coverleys
, or to claim his
Descent from the Maid of Honour. But 'tis very happy for Sir
Roger
that
the Merchant paid so dear for his Ambition. 'Tis the Misfortune of many
other Gentlemen to turn out of the Seats of their Ancestors, to make way
for such new Masters as have been more exact in their Accounts than
themselves; and certainly he deserves the Estate a great deal better,
who has got it by his Industry, than he who has lost it by his
Negligence.
T.
Punica fides.
Contents
|
Thursday,
September 20, 1711 |
Budgell |
Proximus à tectis ignis defenditur ægre:
Ov.
Rem. Am.
I shall this Day entertain my Readers with two or three Letters I have
received from my Correspondents: The first discovers to me a Species of
Females which have hitherto escaped my Notice, and is as follows.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am a young Gentleman of a competent Fortune, and a sufficient Taste
of Learning, to spend five or six Hours every Day very agreeably among
my Books. That I might have nothing to divert me from my Studies, and
to avoid the Noises of Coaches and Chair-men, I have taken Lodgings in
a very narrow Street, not far from Whitehall; but it is my
Misfortune to be so posted, that my Lodgings are directly opposite to
those of a Jezebel. You are to know, Sir, that a Jezebel
(so call'd by the Neighbourhood from displaying her pernicious Charms
at her Window) appears constantly dress'd at her Sash, and has a
thousand little Tricks and Fooleries to attract the Eyes of all the
idle young Fellows in the Neighbourhood. I have seen more than six
Persons at once from their several Windows observing the
Jezebel I am now complaining of. I at first looked on her my
self with the highest Contempt, could divert my self with her Airs for
half an Hour, and afterwards take up my Plutarch with great
Tranquillity of Mind; but was a little vexed to find that in less than
a Month she had considerably stoln upon my Time, so that I resolved to
look at her no more. But the Jezebel, who, as I suppose, might
think it a Diminution to her Honour, to have the Number of her Gazers
lessen'd, resolved not to part with me so, and began to play so many
new Tricks at her Window, that it was impossible for me to forbear
observing her. I verily believe she put her self to the Expence of a
new Wax Baby on purpose to plague me; she us'd to dandle and play with
this Figure as impertinently as if it had been a real Child: sometimes
she would let fall a Glove or a Pin Cushion in the Street, and shut or
open her Casement three or four times in a Minute. When I had almost
wean'd my self from this, she came in her Shift-Sleeves, and dress'd
at the Window. I had no Way left but to let down my Curtains, which I
submitted to, though it considerably darkned my Room, and was pleased
to think that I had at last got the better of her; but was surpriz'd
the next Morning to hear her talking out of her Window quite cross the
Street, with another Woman that lodges over me: I am since informed,
that she made her a Visit, and got acquainted with her within three
Hours after the Fall of my Window Curtains.
Sir, I am plagued every Moment in the Day one way or other in my own
Chambers; and the Jezebel has the Satisfaction to know, that,
tho' I am not looking at her, I am list'ning to her impertinent
Dialogues that pass over my Head. I would immediately change my
Lodgings, but that I think it might look like a plain Confession that
I am conquer'd; and besides this, I am told that most Quarters of the
Town are infested with these Creatures. If they are so, I am sure 'tis
such an Abuse, as a Lover of Learning and Silence ought to take notice
of.
I am, Sir,
Yours, &c.'
I am afraid, by some Lines in this Letter, that my young Student is
touched with a Distemper which he hardly seems to dream of and is too
far gone in it to receive Advice. However, I shall animadvert in due
time on the Abuse which he mentions, having my self observed a Nest of
Jezebels
near the
Temple
, who make it their Diversion to
draw up the Eyes of young Templars, that at the same time they may see
them stumble in an unlucky Gutter which runs under the Window.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I have lately read the Conclusion of your forty-seventh Speculation
upon
Butts with great Pleasure, and have ever since been
thoroughly perswaded that one of those Gentlemen is extreamly
necessary to enliven Conversation. I had an Entertainment last Week
upon the Water for a Lady to whom I make my Addresses, with several of
our Friends of both Sexes. To divert the Company in general, and to
shew my Mistress in particular my Genius for Raillery, I took one of
the most celebrated
Butts in Town along with me. It is with the
utmost Shame and Confusion that I must acquaint you with the Sequel of
my Adventure: As soon as we were got into the Boat, I played a
Sentence or two at my
Butt which I thought very smart, when my
ill Genius, who I verily believe inspir'd him purely for my
Destruction, suggested to him such a Reply, as got all the Laughter on
his Side. I was clashed at so unexpected a Turn; which the
Butt
perceiving, resolved not to let me recover my self, and pursuing his
Victory, rallied and tossed me in a most unmerciful and barbarous
manner 'till we came to
Chelsea. I had some small Success while
we were eating Cheese-Cakes; but coming Home, he renewed his Attacks
with his former good Fortune, and equal Diversion to the whole
Company. In short, Sir, I must ingenuously own that I was never so
handled in all my Life; and to compleat my Misfortune, I am since told
that the
Butt, flushed with his late Victory, has made a Visit
or two to the dear Object of my Wishes,
so that I am at once in danger
of losing all my Pretensions to Wit, and my Mistress
into1 the
Bargain. This, Sir, is a true Account of my present Troubles, which
you are the more obliged to assist me in, as you were your self in a
great measure the Cause of them, by recommending to us an Instrument,
and not instructing us at the same time how to play upon it.
I have been thinking whether it might not be highly convenient, that
all
Butts should wear an Inscription affixed to some Part of
their Bodies, shewing on which Side they are to be come at, and that
if any of them are Persons of unequal Tempers, there should be some
Method taken to inform the World at what Time it is safe to attack
them, and when you had best to let them alone. But, submitting these
Matters to your more serious Consideration,
I am, Sir,
Yours, &c.'
I have, indeed, seen and heard of several young Gentlemen under the same
Misfortune with my present Correspondent. The best Rule I can lay down
for them to avoid the like Calamities for the future, is thoroughly to
consider not only
Whether their Companions are weak
, but
Whether themselves are Wits
.
The following Letter comes to me from
Exeter
, and being credibly
informed that what it contains is Matter of Fact, I shall give it my
Reader as it was sent me.
Mr.
Spectator,
Exeter, Sept. 7.
'You were pleased in a late Speculation to take notice of the
Inconvenience we lie under in the Country, in not being able to keep
Pace with the Fashion: But there is another Misfortune which we are
subject to, and is no less grievous than the former, which has
hitherto escaped your Observation. I mean, the having Things palmed
upon us for
London Fashions, which were never once heard of
there.
A Lady of this Place had some time since a Box of the newest Ribbons
sent down by the Coach: Whether it was her own malicious Invention, or
the Wantonness of a
London Milliner, I am not able to inform
you; but, among the rest, there was one Cherry-coloured Ribbon,
consisting of about half a Dozen Yards, made up in the Figure of a
small Head-Dress. The foresaid Lady had the Assurance to affirm,
amidst a Circle of Female Inquisitors, who were present at the opening
of the Box, that this was the newest Fashion worn at Court.
Accordingly the next
Sunday we had several Females, who came to
Church with their Heads dress'd wholly in Ribbons, and looked like so
many Victims ready to be Sacrificed. This is still a reigning Mode
among us. At the same time we have a Set of Gentlemen who take the
Liberty to appear in all Publick Places without any Buttons to their
Coats, which they supply with several little Silver Hasps, tho' our
freshest Advices from
London make no mention of any such
Fashion;
and we are something shy of affording Matter to the
Button-Makers for a second Petition
2.
What I would humbly propose to the Publick is, that there may be a
Society erected in
London, to consist of the most skilful
Persons of both Sexes, for the
Inspection of Modes and
Fashions; and that hereafter no Person or Persons shall presume to
appear singularly habited in any Part of the Country, without a
Testimonial from the foresaid Society, that their Dress is answerable
to the Mode at
London. By this means, Sir, we shall know a
little whereabout we are.
If you could bring this Matter to bear, you would very much oblige
great Numbers of your Country Friends, and among the rest,
Your very Humble Servant,
Jack Modish.
X.
in
In 1609 the Button-Makers sent a petition to Parliament,
which produced the Act of the 8th year of Anne (1709), framed because
'the maintenance and subsistence of many thousands of men, women and
children depends upon the making of silk, mohair, gimp, and thread
buttons, and button-holes with the needle,' and these have been ruined
by 'a late unforeseen practice of making and binding button-holes with
cloth, serge,' &c.
Contents
|
Friday,
September 21, 1711 |
Steele |
Parvula, pumilio, 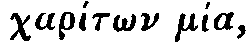 lota merum Sal.
lota merum Sal.
Luc.

There are in the following Letter Matters, which I, a Batchelor, cannot
be supposed to be acquainted with; therefore shall not pretend to
explain upon it till further Consideration, but leave the Author of the
Epistle to express his Condition his own Way.
Mr.
Spectator.
'I do not deny but you appear in many of your Papers to understand
Human Life pretty well; but there are very many Things which you
cannot possibly have a true Notion of, in a single Life; these are
such as respect the married State; otherwise I cannot account for your
having overlooked a very good Sort of People, which are commonly
called in Scorn the
Henpeckt. You are to understand that I am
one of those innocent Mortals who suffer Derision under that Word for
being governed by the best of Wives. It would be worth your
Consideration to enter into the Nature of Affection it self, and tell
us, according to your Philosophy, why it is that our Dears shall do
what they will with us, shall be froward, ill-natured, assuming,
sometimes whine, at others rail, then swoon away, then come to Life,
have the Use of Speech to the greatest Fluency imaginable, and then
sink away again, and all because they fear we do not love them enough:
that is, the poor things love us so heartily, that they cannot think
it possible we should be able to love them in so great a Degree, which
makes them take on so. I say, Sir, a true good-natured Man, whom Rakes
and Libertines call
Hen-peckt, shall fall into all these
different Moods with his dear Life, and at the same time see they are
wholly put on; and yet not be hard-hearted enough to tell the dear
good Creature that she is an Hypocrite. This sort of good Man is very
frequent in the populous and wealthy City of
London, and is the
true
Hen-peckt Man; the kind Creature cannot break through his
Kindnesses so far as to come to an Explanation with the tender Soul,
and therefore goes on to comfort her when nothing ails her, to appease
her when she is not angry, and to give her his Cash when he knows she
does not want it; rather than be uneasy for a whole Month, which is
computed by hard-hearted Men the Space of Time which a froward Woman
takes to come to her self, if you have Courage to stand out.
There are indeed several other Species of the
Hen-peckt, and in
my Opinion they are certainly the best Subjects the Queen has; and for
that Reason I take it to be your Duty to keep us above Contempt.
I do not know whether I make my self understood in the Representation
of an Hen-peckt Life, but I shall take leave to give you an Account of
my self, and my own Spouse. You are to know that I am reckoned no
Fool, have on several Occasions been tried whether I will take ill
Usage, and yet the Event has been to my Advantage; and yet there is
not such a Slave in
Turkey as I am to my Dear. She has a good
Share of Wit, and is what you call a very pretty agreeable Woman. I
perfectly doat on her, and my Affection to her gives me all the
Anxieties imaginable but that of Jealousy. My being thus confident of
her, I take, as much as I can judge of my Heart, to be the Reason,
that whatever she does, tho' it be never so much against my
Inclination, there is still left something in her Manner that is
amiable. She will sometimes look at me with an assumed Grandeur, and
pretend to resent that I have not had Respect enough for her Opinion
in such an Instance in Company. I cannot but smile at the pretty Anger
she is in, and then she pretends she is used like a Child. In a Word,
our great Debate is, which has the Superiority in point of
Understanding. She is eternally forming an Argument of Debate; to
which I very indolently answer, Thou art mighty pretty. To this she
answers, All the World but you think I have as much Sense as your
self. I repeat to her, Indeed you are pretty. Upon this there is no
Patience; she will throw down any thing about her, stamp and pull off
her Head-Cloaths. Fie, my Dear, say I; how can a Woman of your Sense
fall into such an intemperate Rage? This is an Argument which never
fails. Indeed, my Dear, says she, you make me mad sometimes, so you
do, with the silly Way you have of treating me like a pretty Idiot.
Well, what have I got by putting her into good Humour? Nothing, but
that I must convince her of my good Opinion by my Practice; and then I
am to give her Possession of my little Ready Money, and, for a Day and
half following, dislike all she dislikes, and extol every thing she
approves. I am so exquisitely fond of this Darling, that I seldom see
any of my Friends, am uneasy in all Companies till I see her again;
and when I come home she is in the Dumps, because she says she is sure
I came so soon only because I think her handsome. I dare not upon this
Occasion laugh; but tho' I am one of the warmest Churchmen in the
Kingdom, I am forced to rail at the Times, because she is a violent
Whig. Upon this we talk Politicks so long, that she is convinc'd I
kiss her for her Wisdom.
It is a common Practice with me to ask her
some Question concerning the Constitution, which she answers me in
general out of
Harington's Oceana1: Then I commend her
strange Memory, and her Arm is immediately lock'd in mine. While I
keep her in this Temper she plays before me, sometimes dancing in the
Midst of the Room, sometimes striking an Air at her Spinnet, varying
her Posture and her Charms in such a Manner that I am in continual
Pleasure: She will play the Fool if I allow her to be wise; but if she
suspects I like her for
her Trifling, she immediately grows grave.
These are the Toils in which I am taken, and I carry off my Servitude
as well as most Men; but my Application to you is in Behalf of the
Hen-peckt in general, and I desire a Dissertation from you in
Defence of us. You have, as I am informed, very good Authorities in
our Favour, and hope you will not omit the mention of the Renowned
Socrates, and his Philosophick Resignation to his Wife
Xantippe. This would be a very good Office to the World in
general, for the
Hen-peckt are powerful in their Quality and
Numbers, not only in Cities but in Courts; in the latter they are ever
the most obsequious, in the former the most wealthy of all Men. When
you have considered Wedlock throughly, you ought to enter into the
Suburbs of Matrimony, and give us an Account of the Thraldom of kind
Keepers and irresolute Lovers; the Keepers who cannot quit their Fair
Ones tho' they see their approaching Ruin; the Lovers who dare not
marry, tho' they know they never shall be happy without the Mistresses
whom they cannot purchase on other Terms.
What will be a great Embellishment to your Discourse, will be, that
you may find Instances of the Haughty, the Proud, the Frolick, the
Stubborn, who are each of them in secret downright Slaves to their
Wives or Mistresses. I must beg of you in the last Place to dwell upon
this, That the Wise and Valiant in all Ages have been
Hen-peckt: and that the sturdy Tempers who are not Slaves to
Affection, owe that Exemption to their being enthralled by Ambition,
Avarice, or some meaner Passion. I have ten thousand thousand Things
more to say, but my Wife sees me Writing, and will, according to
Custom, be consulted, if I do not seal this immediately.
Yours,
T. Nathaniel Henroost.'
The
Oceana
is an ideal of an English Commonwealth,
written by James Harrington, after the execution of Charles I. It was
published in 1656, having for a time been stopped at press by Cromwell's
government. After the Restoration, Harrington was sent to the Tower by
Charles II on a false accusation of conspiracy. Removed to Plymouth, he
there lost his health and some part of his reason, which he did not
regain before his death, in 1677, at the age of 66. His book argues that
Empire follows the balance of property, which, since Henry VII's time,
had been daily falling into the scale of the Commons from that of the
King and Lords. In the
Oceana
other theories of government are
discussed before Harrington elaborates his own, and English history
appears under disguise of names, William the Conqueror being called
Turbo; King John, Adoxus; Richard II, Dicotome; Henry VII, Panurgus;
Henry VIII, Coraunus; Queen Elizabeth, Parthenia; James I, Morpheus;
and Oliver Cromwell, Olphaus Megaletor. Scotland is Marpesia, and
Ireland, Panopæa. A careful edition of Harrington's
Oceana
and
other of his works, edited by John Toland, had been produced in 1700.
Contents
|
Saturday,
September 22, 1711 |
Addison |
... Quis enim bonus, aut face dignus
Arcanâ, qualem Cereris vult esse sacerdos,
Ulla aliena sibi credat mala?
Juv.

In one of my last Week's Papers I treated of Good-Nature, as it is the
Effect of Constitution; I shall now speak of it as it is a Moral Virtue.
The first may make a Man easy in himself and agreeable to others, but
implies no Merit in him that is possessed of it. A Man is no more to be
praised upon this Account, than because he has a regular Pulse or a good
Digestion.
Good-Nature however in the Constitution, which Mr.
Dryden
somewhere calls a
Milkiness of Blood
, is an
admirable Groundwork for the other. In order therefore to try our
Good-Nature, whether it arises from the Body or the Mind, whether it be
founded in the Animal or Rational Part of our Nature; in a word, whether
it be such as is entituled to any other Reward, besides that secret
Satisfaction and Contentment of Mind which is essential to it, and the
kind Reception it procures us in the World, we must examine it by the
following Rules.
First, whether it acts with Steadiness and Uniformity in Sickness and in
Health, in Prosperity and in Adversity; if otherwise, it is to be looked
upon as nothing else but an Irradiation of the Mind from some new Supply
of Spirits, or a more kindly Circulation of the Blood.
Sir Francis
Bacon
a cunning Solicitor,
who
would never ask a
Favour of a great Man before Dinner; but took care to prefer his
Petition at a Time when the Party petitioned had his Mind free from
Care, and his Appetites in good Humour. Such a transient temporary
Good-Nature as this, is not that
Philanthropy
, that Love of
Mankind, which deserves the Title of a Moral Virtue.
The next way of a Man's bringing his Good-Nature to the Test, is, to
consider whether it operates according to the Rules of Reason and Duty:
For if, notwithstanding its general Benevolence to Mankind, it makes no
Distinction between its Objects, if it exerts it self promiscuously
towards the Deserving and Undeserving, if it relieves alike the Idle and
the Indigent, if it gives it self up to the first Petitioner, and lights
upon any one rather by Accident than Choice, it may pass for an amiable
Instinct, but must not assume the Name of a Moral Virtue.
The third Tryal of Good-Nature will be, the examining ourselves, whether
or no we are able to exert it to our own Disadvantage, and employ it on
proper Objects, notwithstanding any little Pain, Want, or Inconvenience
which may arise to our selves from it: In a Word, whether we are willing
to risque any Part of our Fortune, our Reputation, our Health or Ease,
for the Benefit of Mankind. Among all these Expressions of Good-Nature,
I shall single out that which goes under the general Name of Charity, as
it consists in relieving the Indigent; that being a Tryal of this Kind
which offers itself to us almost at all Times and in every Place.
I should propose it as a Rule to every one who is provided with any
Competency of Fortune more than sufficient for the Necessaries of Life,
to lay aside a certain Proportion of his Income for the Use of the Poor.
This I would look upon as an Offering to him who has a Right to the
whole, for the Use of those whom, in the Passage hereafter mentioned, he
has described as his own Representatives upon Earth. At the same time we
should manage our Charity with such Prudence and Caution, that we may
not hurt our own Friends or Relations, whilst we are doing Good to those
who are Strangers to us.
This may possibly be explained better by an Example than by a Rule.
Eugenius
is a Man of an universal Good-Nature, and generous
beyond the Extent of his Fortune; but withal so prudent in the Œconomy
of his Affairs, that what goes out in Charity is made up by good
Management.
Eugenius
has what the World calls Two hundred Pounds
a Year; but never values himself above Ninescore, as not thinking he has
a Right to the Tenth Part, which he always appropriates to charitable
Uses. To this Sum he frequently makes other voluntary Additions,
insomuch that in a good Year, for such he accounts those in which he has
been able to make greater Bounties than ordinary, he has given above
twice that Sum to the Sickly and Indigent.
Eugenius
prescribes to
himself many particular Days of Fasting and Abstinence, in order to
increase his private Bank of Charity, and sets aside what would be the
current Expences of those Times for the Use of the Poor. He often goes
afoot where his Business calls him, and at the End of his Walk has given
a Shilling, which in his ordinary Methods of Expence would have gone for
Coach-Hire, to the first Necessitous Person that has fallen in his way.
I have known him, when he has been going to a Play or an Opera, divert
the Money which was designed for that Purpose, upon an Object of Charity
whom he has met with in the Street; and afterwards pass his Evening in a
Coffee-House, or at a Friend's Fire-side, with much greater Satisfaction
to himself than he could have received from the most exquisite
Entertainments of the Theatre. By these means he is generous, without
impoverishing himself, and enjoys his Estate by making it the Property
of others.
There are few Men so cramped in their private Affairs, who may not be
charitable after this manner, without any Disadvantage to themselves, or
Prejudice to their Families. It is but sometimes sacrificing a Diversion
or Convenience to the Poor, and turning the usual Course of our Expences
into a better Channel. This is, I think, not only the most prudent and
convenient, but the most meritorious Piece of Charity, which we can put
in practice.
this Method we in some measure share the Necessities of
the Poor at the same time that we relieve them, and make ourselves not
only
their Patrons
, but their Fellow Sufferers.
Thomas Brown
, in the last Part of his
Religio Medici
, in which
he describes his Charity in several Heroick Instances, and with a noble
Heat of Sentiments, mentions that Verse in the Proverbs of
Solomon, He
that giveth to the Poor, lendeth to the Lord
.
'
There is more
Rhetorick in that one Sentence, says he, than in a Library of Sermons;
and indeed if those Sentences were understood by the Reader, with the
same Emphasis as they are delivered by the Author, we needed not those
Volumes of Instructions, but might be honest by an Epitome
5.'
Passage in Scripture is indeed wonderfully persuasive; but I think
the same Thought is carried much further in the New Testament, where our
Saviour tells us in a most pathetick manner, that he shall hereafter
regard the Cloathing of the Naked, the Feeding of the Hungry, and the
Visiting of the Imprisoned, as Offices done to himself, and reward them
accordingly
. Pursuant to those Passages in Holy Scripture, I have
somewhere met with the
of a charitable Man, which has very much
pleased me. I cannot recollect the Words, but the Sense of it is to this
Purpose; What I spent I lost; what I possessed is left to others; what I
gave away remains with me
.
Since I am thus insensibly engaged in Sacred Writ, I cannot forbear
making an Extract of several Passages which I have always read with
great Delight in the Book of
Job
. It is the Account which that Holy
Man gives of his Behaviour in the Days of his Prosperity, and, if
considered only as a human Composition, is a finer Picture of a
charitable and good-natured Man than is to be met with in any other
Author.
Oh that I were as in Months past, as in the Days when God preserved me:
When his Candle shined upon my head, and when by his light I walked
through darkness: When the Almighty was yet with me: when my Children
were about me: When I washed my steps with butter, and the rock poured
out rivers of oyl.
When the Ear heard me, then it blessed me; and when the Eye saw me, it
gave witness to me. Because I delivered the poor that cried, and the
fatherless, and him that had none to help him. The blessing of him that
was ready to perish came upon me, and I caused the Widow's Heart to sing
for joy. I was eyes to the blind, and feet was I to the lame; I was a
father to the poor, and the cause which I knew not I searched out. Did
not I weep for him that was in trouble? was not my Soul grieved for the
poor? Let me be weighed in an even ballance, that God may know mine
Integrity. If I did despise the cause of my man-servant or my
maid-servant when they contended with me: What then shall I do when God
riseth up? and when he visiteth, what shall I answer him? Did not he
that made me in the womb, make him? and did not one fashion us in the
womb? If I have withheld the poor from their desire, or have caused the
eyes of the widow to fail, or have eaten my morsel myself alone, and the
fatherless hath not eaten thereof: If I have seen any perish for want of
cloathing, or any poor without covering: If his loins have not blessed
me, and if he were not warmed with the fleece of my sheep: If I have
lift up my hand against the fatherless, when I saw my help in the gate;
then let mine arm fall from my shoulder-blade, and mine arm be broken
from the bone. If I have rejoiced at the Destruction of him that hated
me, or lift up myself when evil found him: (Neither have I suffered my
mouth to sin, by wishing a curse to his soul). The stranger did not
lodge in the street; but I opened my doors to the traveller. If my land
cry against me, or that the furrows likewise thereof complain: If I have
eaten the Fruits thereof without mony, or have caused the owners thereof
to lose their Life; Let thistles grow instead of wheat, and cockle
instead of barley.
8
Cleomenes to Pantheus,
'Would I could share thy Balmy, even Temper,
And Milkiness of Blood.'
Cleomenes
, Act i. sc. I.
that
the Patrons of the Indigent
Proverbs
xix. 17.
Rel. Med.
Part II. sect. 13.
Matt
. xxi. 31, &c.
The Epitaph was in St. George's Church at Doncaster, and
ran thus:
'How now, who is heare?
I Robin of Doncastere
And Margaret my feare.
That I spent, that I had;
That I gave, that I have;
That I left, that I lost.'
Job
xxix. 2, &c.; xxx. 25, &c.; xxxi. 6, &c.
Contents
|
Monday,
September 24, 1711 |
Steele |
Comis in uxorem ...
Hor.

I cannot defer taking Notice of this Letter.
Mr. Spectator,
I am but too good a Judge of your Paper of the 15th Instant, which is
a Master-piece; I mean that of Jealousy: But I think it unworthy of
you to speak of that Torture in the Breast of a Man, and not to
mention also the Pangs of it in the Heart of a Woman. You have very
Judiciously, and with the greatest Penetration imaginable, considered
it as Woman is the Creature of whom the Diffidence is raised; but not
a Word of a Man who is so unmerciful as to move Jealousy in his Wife,
and not care whether she is so or not. It is possible you may not
believe there are such Tyrants in the World; but alas, I can tell you
of a Man who is ever out of Humour in his Wife's Company, and the
pleasantest Man in the World every where else; the greatest Sloven at
home when he appears to none but his Family, and most exactly
well-dressed in all other Places. Alas, Sir, is it of Course, that to
deliver one's self wholly into a Man's Power without Possibility of
Appeal to any other Jurisdiction but to his own Reflections, is so
little an Obligation to a Gentleman, that he can be offended and fall
into a Rage, because my Heart swells Tears into my Eyes when I see him
in a cloudy Mood? I pretend to no Succour, and hope for no Relief but
from himself; and yet he that has Sense and Justice in every thing
else, never reflects, that to come home only to sleep off an
Intemperance, and spend all the Time he is there as if it were a
Punishment, cannot but give the Anguish of a jealous Mind. He always
leaves his Home as if he were going to Court, and returns as if he
were entring a Gaol. I could add to this, that from his Company and
his usual Discourse, he does not scruple being thought an abandoned
Man, as to his Morals. Your own Imagination will say enough to you
concerning the Condition of me his Wife; and I wish you would be so
good as to represent to him, for he is not ill-natured, and reads you
much, that the Moment I hear the Door shut after him, I throw myself
upon my Bed, and drown the Child he is so fond of with my Tears, and
often frighten it with my Cries; that I curse my Being; that I run to
my Glass all over bathed in Sorrows, and help the Utterance of my
inward Anguish by beholding the Gush of my own Calamities as my Tears
fall from my Eyes. This looks like an imagined Picture to tell you,
but indeed this is one of my Pastimes. Hitherto I have only told you
the general Temper of my Mind, but how shall I give you an Account of
the Distraction of it? Could you but conceive how cruel I am one
Moment in my Resentment, and at the ensuing Minute, when I place him
in the Condition my Anger would bring him to, how compassionate; it
would give you some Notion how miserable I am, and how little I
deserve it. When I remonstrate with the greatest Gentleness that is
possible against unhandsome Appearances, and that married Persons are
under particular Rules; when he is in the best Humour to receive this,
I am answered only, That I expose my own Reputation and Sense if I
appear jealous. I wish, good Sir, you would take this into serious
Consideration, and admonish Husbands and Wives what Terms they ought
to keep towards each other. Your Thoughts on this important Subject
will have the greatest Reward, that which descends on such as feel the
Sorrows of the Afflicted. Give me leave to subscribe my self,
Your
unfortunate humble Servant,
Celinda.
I had it in my Thoughts, before I received the Letter of this Lady, to
consider this dreadful Passion in the Mind of a Woman; and the Smart she
seems to feel does not abate the Inclination I had to recommend to
Husbands a more regular Behaviour, than to give the most exquisite of
Torments to those who love them, nay whose Torment would be abated if
they did not love them.
It is wonderful to observe how little is made of this inexpressible
Injury, and how easily Men get into a Habit of being least agreeable
where they are most obliged to be so. But this Subject deserves a
distinct Speculation, and I shall observe for a Day or two the Behaviour
of two or three happy Pair I am acquainted with, before I pretend to
make a System of Conjugal Morality. I design in the first Place to go a
few Miles out of Town, and there I know where to meet one who practises
all the Parts of a fine Gentleman in the Duty of an Husband. When he was
a Batchelor much Business made him particularly negligent in his Habit;
but now there is no young Lover living so exact in the Care of his
Person. One who asked why he was so long washing his Mouth, and so
delicate in the Choice and Wearing of his Linen, was answered, Because
there is a Woman of Merit obliged to receive me kindly, and I think it
incumbent upon me to make her Inclination go along with her Duty.
If a Man would give himself leave to think, he would not be so
unreasonable as to expect Debauchery and Innocence could live in
Commerce together; or hope that Flesh and Blood is capable of so strict
an Allegiance, as that a fine Woman must go on to improve her self 'till
she is as good and impassive as an Angel, only to preserve a Fidelity to
a Brute and a Satyr. The Lady who desires me for her Sake to end one of
my Papers with the following Letter, I am persuaded, thinks such a
Perseverance very impracticable.
Husband,
Stay more at home. I know where you visited at Seven of the Clock on
Thursday Evening. The Colonel whom you charged me to see no more, is
in Town.
Martha Housewife.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday,
September 25, 1711 |
Addison |
Centuriæ seniorum agitant expertia frugis:
Celsi prætereunt austera Poemata Rhamnes.
Omne tulit punctum qui miscuit utile dulci,
Lectorem delectando, pariterque monendo ...
Hor.

I may cast my Readers under two general Divisions, the
Mercurial
and the
Saturnine
. The first are the gay Part of my Disciples,
who require Speculations of Wit and Humour; the others are those of a
more solemn and sober Turn, who find no Pleasure but in Papers of
Morality and sound Sense. The former call every thing that is Serious,
Stupid; the latter look upon every thing as Impertinent that is
Ludicrous. Were I always Grave, one half of my Readers would fall off
from me: Were I always Merry, I should lose the other. I make it
therefore my Endeavour to find out Entertainments of both Kinds, and by
that means perhaps consult the Good of both, more than I should do, did
I always write to the particular Taste of either. As they neither of
them know what I proceed upon, the sprightly Reader, who takes up my
Paper in order to be diverted, very often finds himself engaged unawares
in a serious and profitable Course of Thinking; as on the contrary, the
thoughtful Man, who perhaps may hope to find something Solid, and full
of deep Reflection, is very often insensibly betrayed into a Fit of
Mirth. In a word, the Reader sits down to my Entertainment without
knowing his Bill of Fare, and has therefore at least the Pleasure of
hoping there may be a Dish to his Palate.
I must confess, were I left to my self, I should rather aim at
Instructing than Diverting; but if we will be useful to the World, we
must take it as we find it. Authors of professed Severity discourage the
looser Part of Mankind from having any thing to do with their Writings.
A man must have Virtue in him, before he will enter upon the reading of
a
Seneca
or an
Epictetus
. The very Title of a Moral
Treatise has something in it austere and shocking to the Careless and
Inconsiderate.
For this Reason several unthinking Persons fall in my way, who would
give no Attention to Lectures delivered with a Religious Seriousness or
a Philosophick Gravity. They are insnared into Sentiments of Wisdom and
Virtue when they do not think of it; and if by that means they arrive
only at such a Degree of Consideration as may dispose them to listen to
more studied and elaborate Discourses, I shall not think my Speculations
useless. I might likewise observe, that the Gloominess in which
sometimes the Minds of the best Men are involved, very often stands in
need of such little Incitements to Mirth and Laughter, as are apt to
disperse Melancholy, and put our Faculties in good Humour. To which some
will add, that the
British
Climate, more than any other, makes
Entertainments of this Nature in a manner necessary.
If what I have here said does not recommend, it will at least excuse the
Variety of my Speculations. I would not willingly Laugh but in order to
Instruct, or if I sometimes fail in this Point, when my Mirth ceases to
be Instructive, it shall never cease to be Innocent. A scrupulous
Conduct in this Particular has, perhaps, more Merit in it than the
Generality of Readers imagine; did they know how many Thoughts occur in
a Point of Humour, which a discreet Author in Modesty suppresses; how
many Stroaks in Raillery present themselves, which could not fail to
please the ordinary Taste of Mankind, but are stifled in their Birth by
reason of some remote Tendency which they carry in them to corrupt the
Minds of those who read them; did they know how many Glances of
Ill-nature are industriously avoided for fear of doing Injury to the
Reputation of another, they would be apt to think kindly of those
Writers who endeavour to make themselves Diverting, without being
Immoral.
may apply to these Authors that Passage in
Waller
,
Poets lose half the Praise they would have got,
Were it but known what they discreetly blot.
As nothing is more easy than to be a Wit, with all the above-mentioned
Liberties, it requires some Genius and Invention to appear such without
them.
What I have here said is not only in regard to the Publick, but with an
Eye to my particular Correspondent who has sent me the following Letter,
which I have castrated in some Places upon these Considerations.
Sir,
'Having lately seen your Discourse upon a Match of Grinning, I cannot
forbear giving you an Account of a Whistling Match, which, with many
others, I was entertained with about three Years since at the
Bath. The Prize was a Guinea, to be conferred upon the ablest
Whistler, that is, on him who could whistle clearest, and go through
his Tune without Laughing,
to which
at the same time he was
provoked2 by the antick Postures of a
Merry-Andrew, who
was to stand upon the Stage and play his Tricks in the Eye of the
Performer. There were three Competitors for the Ring. The first was a
Plow-man of a very promising Aspect; his Features were steady, and his
Muscles composed in so inflexible a Stupidity, that upon his first
Appearance every one gave the Guinea for lost. The Pickled Herring
however found the way to shake him; for upon his Whistling a Country
Jigg, this unlucky Wag danced to it with such a Variety of Distortions
and Grimaces, that the Country-man could not forbear smiling upon him,
and by that means spoiled his Whistle, and lost the Prize.
The next that mounted the Stage was an Under-Citizen of the
Bath, a Person remarkable among the inferior People of that
Place for his great Wisdom and his Broad Band. He contracted his Mouth
with much Gravity, and, that he might dispose his Mind to be more
serious than ordinary, began the Tune of
The Children in the
Wood, and went through part of it with good Success; when on a
sudden the Wit at his Elbow, who had appeared wonderfully grave and
attentive for some time, gave him a Touch upon the left Shoulder, and
stared him in the Face with so bewitching a Grin, that the Whistler
relaxed his Fibres into a kind of Simper, and at length burst out into
an open Laugh. The third who entered the Lists was a Foot-man, who in
Defiance of the
Merry-Andrew, and all his Arts, whistled a
Scotch Tune and an
Italian Sonata, with so settled a
Countenance, that he bore away the Prize, to the great Admiration of
some Hundreds of Persons, who, as well as my self, were present at
this Trial of Skill. Now, Sir, I humbly conceive, whatever you have
determined of the Grinners, the Whistlers ought to be encouraged, not
only as their Art is practised without Distortion, but as it improves
Country Musick, promotes Gravity, and teaches ordinary People to keep
their Countenances, if they see any thing ridiculous in their Betters;
besides that it seems an Entertainment very particularly adapted to
the
Bath, as it is usual for a Rider to whistle to his Horse
when he would make his Waters pass.
I am, Sir, &c.
Postscript.
After having despatched these two important Points of Grinning and
Whistling, I hope you will oblige the World with some Reflections upon
Yawning, as I have seen it practised on a Twelfth-Night among other
Christmas Gambols at the House of a very worthy Gentleman, who
always entertains his Tenants at that time of the Year. They Yawn for
a
Cheshire Cheese, and begin about Midnight, when the whole
Company is disposed to be drowsie. He that Yawns widest, and at the
same time so naturally as to produce the most Yawns among his
Spectators, carries home the Cheese. If you handle this Subject as you
ought, I question not but your Paper will set half the Kingdom a
Yawning, tho' I dare promise you it will never make any Body fall
asleep.
L.
Upon Roscommon's Tr. of Horace's
Art of Poetry
.
provoked to
Contents
|
Wednesday,
September 26, 1711 |
Steele |
... Delirant Reges, plectuntur Achivi.
Hor.

following Letter
has so much Weight and good Sense, that I
cannot forbear inserting it, tho' it relates to an hardened Sinner, whom
I have very little Hopes of reforming,
viz. Lewis
XIV. of
France
.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Amidst the Variety of Subjects of which you have treated, I could
wish it had fallen in your way to expose the Vanity of Conquests. This
Thought would naturally lead one to the
French King, who has
been generally esteemed the greatest Conqueror of our Age, 'till her
Majesty's Armies had torn from him so many of his Countries, and
deprived him of the Fruit of all his former Victories.
For my own
Part, if I were to draw his Picture, I should be for taking him no
lower than to the Peace of
Reswick2, just at the End of his
Triumphs, and before his Reverse of Fortune: and even then I should
not forbear thinking his Ambition had been vain and unprofitable to
himself and his People.
As for himself, it is certain he can have gained nothing by his
Conquests, if they have not rendered him Master of more Subjects, more
Riches, or greater Power. What I shall be able to offer upon these
Heads, I resolve to submit to your Consideration.
To begin then with his Increase of Subjects. From the Time he came of
Age, and has been a Manager for himself, all the People he had
acquired were such only as he had reduced by his Wars, and were left
in his Possession by the Peace; he had conquered not above one third
Part of
Flanders, and consequently no more than one third Part
of the Inhabitants of that Province.
About 100 Years ago the Houses in that Country were all Numbered, and
by a just Computation the Inhabitants of all Sorts could not then
exceed 750 000 Souls. And if any Man will consider the Desolation by
almost perpetual Wars, the numerous Armies that have lived almost ever
since at Discretion upon the People, and how much of their Commerce
has removed for more Security to other Places, he will have little
Reason to imagine that their Numbers have since increased; and
therefore with one third Part of that Province that Prince can have
gained no more than one third Part of the Inhabitants, or 250 000 new
Subjects, even tho' it should be supposed they were all contented to
live still in their native Country. and transfer their Allegiance to a
new Master.
The Fertility of this Province, its convenient Situation for Trade and
Commerce, its Capacity for furnishing Employment and Subsistence to
great Numbers, and the vast Armies that have been maintained here,
make it credible that the remaining two Thirds of
Flanders are
equal to all his other Conquests; and consequently by all he cannot
have gained more than 750 000 new Subjects, Men, Women and Children,
especially if a Deduction shall be made of such as have retired from
the Conqueror to live under their old Masters.
It is Time now to set his Loss against his Profit, and to shew for the
new Subjects he had acquired, how many old ones he had lost in the
Acquisition: I think that in his Wars he has seldom brought less into
the Field in all Places than 200 000 fighting Men, besides what have
been left in Garrisons; and I think the common Computation is, that of
an Army, at the latter End of a Campaign, without Sieges or Battle,
scarce Four Fifths can be mustered of those that came into the Field
at the Beginning of the Year. His Wars at several Times till the last
Peace have held about 20 Years; and if 40 000 yearly lost, or a fifth
Part of his Armies, are to be multiplied by 20, he cannot have lost
less than 800 000 of his old Subjects, all able-body'd Men; a greater
Number than the new Subjects he had acquired.
But this Loss is not all: Providence seems to have equally divided the
whole Mass of Mankind into different Sexes, that every Woman may have
her Husband, and that both may equally contribute to the Continuance
of the Species. It follows then, that for all the Men that have been
lost, as many Women must have lived single, and it were but Charity to
believe they have not done all the Service they were capable of doing
in their Generation. In so long a Course of Years great part of them
must have died, and all the rest must go off at last without leaving
any Representatives behind. By this Account he must have lost not only
800000 Subjects, but double that Number, and all the Increase that was
reasonably to be expected from it.
It is said in the last War there was a Famine in his Kingdom, which
swept away two Millions of his People. This is hardly credible: If the
loss was only of one fifth Part of that Sum, it was very great. But
'tis no wonder there should be Famine, where so much of the People's
Substance is taken away for the King's Use, that they have not
sufficient left to provide against Accidents: where so many of the Men
are taken from the Plough to serve the King in his Wars, and a great
part of the Tillage is left to the weaker Hands of so many Women and
Children. Whatever was the Loss, it must undoubtedly be placed to the
Account of his Ambition.
And so must also the Destruction or Banishment of 3 or 400 000 of his
reformed Subjects; he could have no other Reasons for valuing those
Lives so very cheap, but only to recommend himself to the Bigotry of
the
Spanish Nation.
How should there be Industry in a Country where all Property is
precarious? What Subject will sow his Land that his Prince may reap
the whole Harvest? Parsimony and Frugality must be Strangers to such a
People; for will any Man save to-day what he has Reason to fear will
be taken from him to-morrow? And where is the Encouragement for
marrying? Will any Man think of raising Children, without any
Assurance of Cloathing for their Backs, or so much as Food for their
Bellies? And thus by his fatal Ambition he must have lessened the
Number of his Subjects not only by Slaughter and Destruction, but by
preventing their very Births, he has done as much as was possible
towards destroying Posterity itself.
Is this then the great, the invincible
Lewis? This the immortal
Man, the
tout-puissant, or the Almighty, as his Flatterers have
called him? Is this the Man that is so celebrated for his Conquests?
For every Subject he has acquired, has he not lost three that were his
Inheritance? Are not his Troops fewer, and those neither so well fed,
or cloathed, or paid, as they were formerly, tho' he has now so much
greater Cause to exert himself? And what can be the Reason of all
this, but that his Revenue is a great deal less, his Subjects are
either poorer, or not so many to be plundered by constant Taxes for
his Use?
It is well for him he had found out a Way to steal a Kingdom; if he
had gone on conquering as he did before, his Ruin had been long since
finished.
This brings to my Mind a saying of King
Pyrrhus,
after he had a second time beat the
Romans in a pitched Battle,
and was complimented by his Generals;
Yes, says he,
such
another Victory and I am quite undone. And since I have mentioned
Pyrrhus, I will end with a very good, though known Story of
this ambitious mad Man. When he had shewn the utmost Fondness for his
Expedition against the
Romans, Cyneas his chief Minister asked
him what he proposed to himself by this War? Why, says
Pyrrhus,
to conquer the
Romans, and reduce all
Italy to my
Obedience. What then? says
Cyneas. To pass over into
Sicily, says
Pyrrhus, and then all the
Sicilians
must be our Subjects. And what does your Majesty intend next? Why
truly, says the King, to conquer
Carthage, and make myself
Master of all
Africa. And what, Sir, says the Minister is to be
the End of all your Expeditions? Why then, says the King, for the rest
of our Lives we'll sit down to good Wine. How, Sir, replied Cyneas, to
better than we have now before us? Have we not already as much as we
can drink?
3
Riot and Excess are not the becoming Characters of Princes: but if
Pyrrhus and Lewis had debauched like Vitellius, they had been less
hurtful to their People.'
Your humble Servant,
T.
Philarithmus.
The letter is, with other contributions not now traceable
to him, by Henry Martyn, son of Edward Martyn, Esq., of Melksham, Wilts.
He was bred to the bar, but his health did not suffer him to practise.
He has been identified with the Cottilus of
of the
Spectator
. In
1713 Henry Martyn opposed the ratification of the Treaty of Commerce
made with France at the Peace of Utrecht in a Paper called
The British
Merchant, or Commerce Preserved,
which was a reply to Defoe's
Mercator, or Commerce Retrieved.
Martyn's paper is said to have been a
principal cause of the rejection of the Treaty, and to have procured him
the post of Inspector-General of Imports and Exports. He died at
Blackheath, March 25, 1721, leaving one son, who became Secretary to the
Commissioners of Excise. As an intimate friend of Steele's, it has been
thought that Henry Martyn suggested a trait or two in the Sir Andrew
Freeport of the
Spectator's
Club.
Sept. 20, 1696.
These anecdotes are from Plutarch's
Life of Pyrrhus
.
Contents
|
Thursday,
September 27, 1711 |
Addison |
His lacrymis vitam damus, et miserescimus ultrò.
Virg.

I am more pleased with a Letter that is filled with Touches of Nature
than of Wit. The following one is of this Kind.
Sir,
'Among all the Distresses which happen in Families, I do not remember
that you have touched upon the Marriage of Children without the
Consent of their Parents.
I am one of
these1 unfortunate Persons.
I was about Fifteen when I took the Liberty to choose for my self; and
have ever since languished under the Displeasure of an inexorable
Father, who, though he sees me happy in the best of Husbands, and
blessed with very fine Children, can never be prevailed upon to
forgive me. He was so kind to me before this unhappy Accident, that
indeed it makes my Breach of Duty, in some measure, inexcusable; and
at the same Time creates in me such a Tenderness towards him, that I
love him above all things, and would die to be reconciled to him. I
have thrown myself at his Feet, and besought him with Tears to pardon
me; but he always pushes me away, and spurns me from him; I have
written several Letters to him, but he will neither open nor receive
them. About two Years ago I sent my little Boy to him, dressed in a
new Apparel; but the Child returned to me crying, because he said his
Grandfather would not see him, and had ordered him to be put out of
his House. My Mother is won over to my Side, but dares not mention me
to my Father for fear of provoking him. About a Month ago he lay sick
upon his Bed, and in great Danger of his Life: I was pierced to the
Heart at the News, and could not forbear going to inquire after his
Health. My Mother took this Opportunity of speaking in my Behalf: she
told him with abundance of Tears, that I was come to see him, that I
could not speak to her for weeping, and that I should certainly break
my Heart if he refus'd at that Time to give me his Blessing, and be
reconciled to me. He was so far from relenting towards me, that he bid
her speak no more of me, unless she had a mind to disturb him in his
last Moments; for, Sir, you must know that he has the Reputation of an
honest and religious Man, which makes my Misfortune so much the
greater. God be thanked he is since recovered: But his severe Usage
has given me such a Blow, that I shall soon sink under it, unless I
may be relieved by any Impressions which the reading of this in your
Paper may make upon him.
I am, &c.
Of all Hardnesses of Heart there is none so inexcusable as that of
Parents towards their Children. An obstinate, inflexible, unforgiving
Temper is odious upon all Occasions; but here it is unnatural.
Love,
Tenderness, and Compassion, which are apt to arise in us towards those
who
depend upon us, is that by which the whole World of Life is
upheld. The Supreme Being, by the transcendent Excellency and Goodness
of his Nature, extends his Mercy towards all his Works; and because his
Creatures have not such a spontaneous Benevolence and Compassion towards
those who are under their Care and Protection, he has implanted in them
an Instinct, that supplies the Place of this inherent Goodness. I have
illustrated this kind of Instinct in former Papers, and have shewn how
it runs thro' all the Species of brute Creatures, as indeed the whole
Animal Creation subsists by it.
This Instinct in Man is more general and uncircumscribed than in Brutes,
as being enlarged by the Dictates of Reason and Duty. For if we consider
our selves attentively, we shall find that we are not only inclined to
love those who descend from us, but that we bear a kind of
or natural Affection, to every thing which relies upon us for
its Good and Preservation. Dependance is a perpetual Call upon Humanity,
and a greater Incitement to Tenderness and Pity than any other Motive
whatsoever.
The Man therefore who, notwithstanding any Passion or Resentment, can
overcome this powerful Instinct, and extinguish natural Affection,
debases his Mind even below Brutality, frustrates, as much as in him
lies, the great Design of Providence, and strikes out of his Nature one
of the most Divine Principles that is planted in it.
innumerable Arguments
which
might be brought against such an
unreasonable Proceeding, I shall only insist on one. We make it the
Condition of our Forgiveness that we forgive others. In our very Prayers
we desire no more than to be treated by this kind of Retaliation. The
Case therefore before us seems to be what they call a Case in Point; the
Relation between the Child and Father being what comes nearest to that
between a Creature and its Creator. If the Father is inexorable to the
Child who has offended, let the Offence be of never so high a Nature,
how will he address himself to the Supreme Being under the tender
Appellation of a Father, and desire of him such a Forgiveness as he
himself refuses to grant?
this I might add many other religious, as well as many prudential
Considerations; but if the last mentioned Motive does not prevail, I
despair of succeeding by any other, and shall therefore conclude my
Paper with a very remarkable Story, which is recorded in an old
Chronicle published by Freher, among the Writers of the German History
.
Eginhart, who was Secretary to Charles the Great, became exceeding
popular by his Behaviour in that Post. His great Abilities gain'd him
the Favour of his Master, and the Esteem of the whole Court. Imma, the
Daughter of the Emperor, was so pleased with his Person and
Conversation, that she fell in Love with him. As she was one of the
greatest Beauties of the Age, Eginhart answer'd her with a more than
equal Return of Passion. They stifled their Flames for some Time, under
Apprehension of the fatal Consequences that might ensue. Eginhart at
length resolving to hazard all, rather than be deprived of one whom his
Heart was so much set upon,
himself one Night into the
Princess's Apartment, and knocking gently at the Door, was admitted as a
Person
who
had something to communicate to her from the Emperor.
He was with her in private most Part of the Night; but upon his
preparing to go away about Break of Day, he observed that there had
fallen a great Snow during his Stay with the Princess. This very much
perplexed him, lest the Prints of his Feet in the Snow might make
Discoveries to the King, who often used to visit his Daughter in the
Morning. He acquainted the Princess Imma with his Fears; who, after some
Consultations upon the Matter, prevailed upon him to let her carry him
through the Snow upon her own Shoulders. It happened, that the Emperor
not being able to sleep, was at that time up and walking in his Chamber,
when upon looking through the Window he perceived his Daughter tottering
under her Burden, and carrying his first Minister across the Snow; which
she had no sooner done, but she returned again with the utmost Speed to
her own Apartment. The Emperor was extreamly troubled and astonished at
this Accident; but resolved to speak nothing of it till a proper
Opportunity. In the mean time, Eginhart knowing that what he had done
could not be long a Secret, determined to retire from Court; and in
order to it begged the Emperor that he would be pleased to dismiss him,
pretending a kind of Discontent at his not having been rewarded for his
long Services. The Emperor would not give a direct Answer to his
Petition,
told him he would think of it, and
appointed
a
certain Day when he would let him know his Pleasure. He then called
together the most faithful of his Counsellors, and acquainting them with
his Secretary's Crime, asked them their Advice in so delicate an Affair.
They most of them gave their Opinion, that the Person could not be too
severely punished who had thus dishonoured his Master. Upon the whole
Debate, the Emperor declared it was his Opinion, that Eginhart's
Punishment would rather encrease than diminish the Shame of his Family,
and that therefore he thought it the most adviseable to wear out the
Memory of the Fact, by marrying him to his Daughter. Accordingly
Eginhart was called in, and acquainted by the Emperor, that he should no
longer have any Pretence of complaining his Services were not rewarded,
for that the
Imma should be given
him
in Marriage, with a
Dower suitable to her Quality; which was soon after performed
accordingly.
L.
those
that
that
Marquard Freher, who died at Heidelberg in 1614, aged 49,
was Counsellor to the Elector Palatine, and Professor of Jurisprudence
at Heidelberg, until employed by the Elector (Frederick IV) as his
Minister in Poland, and at other courts. The chief of many works of his
were, on the Monetary System of the Ancient Romans and of the German
Empire in his day, a History of France, a collection of Writers on
Bohemian History, and another of Writers on German History,
Rerum
Germanicarum Scriptores,
in three volumes. It is from a Chronicle of the
monastery of Lorsch (or Laurisheim), in Hesse Darmstadt, under the year
805, in the first volume of the last-named collection, that the story
about Eginhart was taken by Bayle, out of whose
Dictionary
Addison got
it. Bayle, indeed, specially recommends it as good matter for a story.
Imma, the chronicle says, had been betrothed to the Grecian Emperor.
that
fixed on
to him
Contents
|
Friday,
September 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Plus aloës quàm mellis habet ...
Juv.

As all Parts of humane Life come under my Observation, my Reader must
not make uncharitable Inferences from my speaking knowingly of that Sort
of Crime which is at present treated of. He will, I hope, suppose I know
it only from the Letters of Correspondents, two of which you shall have
as follow.
Mr. Spectator,
'It is wonderful to me that among the many Enormities which you have
treated of, you have not mentioned that of Wenching, and particularly
the Insnaring Part; I mean, that it is a Thing very fit for your Pen,
to expose the Villany of the Practice of deluding Women. You are to
know, Sir, that I myself am a Woman who have been one of the Unhappy
that have fallen into this Misfortune, and that by the Insinuation of
a very worthless Fellow, who served others in the same Manner both
before my Ruin and since that Time. I had, as soon as the Rascal left
me, so much Indignation and Resolution, as not to go upon the Town, as
the Phrase is, but took to Work for my Living in an obscure Place, out
of the Knowledge of all with whom I was before acquainted.
It is the ordinary Practice and Business of Life with a Set of idle
Fellows about this Town, to write Letters, send Messages, and form
Appointments with little raw unthinking Girls, and leave them after
Possession of them, without any Mercy, to Shame, Infamy, Poverty, and
Disease. Were you to read the nauseous Impertinences which are written
on these Occasions, and to see the silly Creatures sighing over them,
it could not but be Matter of Mirth as well as Pity. A little Prentice
Girl of mine has been for some time applied to by an Irish Fellow, who
dresses very fine, and struts in a laced Coat, and is the Admiration
of Seamstresses who are under Age in Town. Ever since I have had some
Knowledge of the Matter, I have debarred my Prentice from Pen, Ink and
Paper. But the other Day he bespoke some Cravats of me: I went out of
the Shop, and left his Mistress to put them up into a Band-box in
order to be sent to him when his Man called. When I came into the Shop
again, I took occasion to send her away, and found in the Bottom of
the Box written these Words, Why would you ruin a harmless Creature
that loves you? then in the Lid, There is no resisting Strephon: I
searched a little farther, and found in the Rim of the Box, At Eleven
of clock at Night come in an Hackney-Coach at the End of our Street.
This was enough to alarm me; I sent away the things, and took my
Measures accordingly. An Hour or two before the appointed Time I
examined my young Lady, and found her Trunk stuffed with impertinent
Letters, and an old Scroll of Parchment in Latin, which her Lover had
sent her as a Settlement of Fifty Pounds a Year: Among other things,
there was also the best Lace I had in my Shop to make him a Present
for Cravats. I was very glad of this last Circumstance, because I
could very conscientiously swear against him that he had enticed my
Servant away, and was her Accomplice in robbing me: I procured a
Warrant against him accordingly. Every thing was now prepared, and the
tender Hour of Love approaching, I, who had acted for myself in my
Youth the same senseless Part, knew how to manage accordingly.
Therefore after having locked up my Maid, and not being so much unlike
her in Height and Shape, as in a huddled way not to pass for her, I
delivered the Bundle designed to be carried off to her Lover's Man,
who came with the Signal to receive them. Thus I followed after to the
Coach, where when I saw his Master take them in, I cryed out, Thieves!
Thieves! and the Constable with his Attendants seized my expecting
Lover. I kept my self unobserved till I saw the Crowd sufficiently
encreased, and then appeared to declare the Goods to be mine; and had
the Satisfaction to see my Man of Mode put into the Round-House, with
the stolen Wares by him, to be produced in Evidence against him the
next Morning. This Matter is notoriously known to be Fact; and I have
been contented to save my Prentice, and take a Year's Rent of this
mortified Lover, not to appear further in the Matter. This was some
Penance; but, Sir, is this enough for a Villany of much more
pernicious Consequence than the Trifles for which he was to have been
indicted? Should not you, and all Men of any Parts or Honour, put
things upon so right a Foot, as that such a Rascal should not laugh at
the Imputation of what he was really guilty, and dread being accused
of that for which he was arrested?
In a word, Sir, it is in the Power of you, and such as I hope you are,
to make it as infamous to rob a poor Creature of her Honour as her
Cloaths. I leave this to your Consideration, only take Leave (which I
cannot do without sighing) to remark to you, that if this had been the
Sense of Mankind thirty Years ago, I should have avoided a Life spent
in Poverty and Shame.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Alice Threadneedle.
Round-House, Sept. 9.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am a Man of Pleasure about Town, but by the Stupidity of a dull
Rogue of a Justice of Peace, and an insolent Constable, upon the Oath
of an old Harridan, am imprisoned here for Theft, when I designed only
Fornication. The Midnight Magistrate, as he conveyed me along, had you
in his Mouth, and said, this would make a pure Story for the
Spectator. I hope, Sir, you won't pretend to Wit, and take the Part of
dull Rogues of Business. The World is so altered of late Years, that
there was not a Man who would knock down a Watchman in my Behalf, but
I was carried off with as much Triumph as if I had been a Pick-pocket.
At this rate, there is an end of all the Wit and Humour in the World.
The Time was when all the honest Whore-masters in the Neighbourhood
would have rose against the Cuckolds to my Rescue. If Fornication is
to be scandalous, half the fine things that have been writ by most of
the Wits of the last Age may be burnt by the common Hangman. Harkee,
Mr. Spec, do not be queer; after having done some things pretty
well, don't begin to write at that rate that no Gentleman can read
thee. Be true to Love, and burn your Seneca. You do not expect
me to write my Name from hence, but I am
Your unknown humble,
&c.'
Contents
|
Saturday,
September 29, 1711 |
Addison |
Fables were the first Pieces of Wit that made their Appearance in the
World, and have been still highly valued, not only in Times of the
greatest Simplicity, but among the most polite Ages of Mankind.
Jotham's
of the Trees
is the oldest that is extant, and
as beautiful as any which have been made since that Time.
Nathan's
Fable of the poor Man and his Lamb
is
more
ancient than any that is extant, besides the above-mentioned, and had so
good an Effect, as to convey Instruction to the Ear of a King without
offending it, and to bring the Man after God's own Heart to a right
Sense of his Guilt and his Duty. We find
Æsop
in the most distant
Ages of
Greece
;
if we look into the very Beginnings of the
Commonwealth of
Rome
, we see a Mutiny among the Common People
appeased by a
Fable of the Belly and the Limbs
, which was indeed
very proper to gain the Attention of an incensed Rabble, at a Time when
perhaps they would have torn to Pieces any Man who had preached the same
Doctrine to them in an open and direct Manner. As Fables took their
Birth in the very Infancy of Learning, they never flourished more than
when Learning was at its greatest Height. To justify this Assertion, I
shall put my Reader in mind of
Horace
, the greatest Wit and
Critick in the
Augustan
Age; and of
Boileau
, the most
correct Poet among the Moderns: Not to mention
La Fontaine
, who
by this Way of Writing is come more into Vogue than any other Author of
our Times.
The Fables I have here mentioned are raised altogether upon Brutes and
Vegetables, with some of our own Species mixt among them, when the Moral
hath so required. But besides this kind of Fable, there is another in
which the Actors are Passions, Virtues, Vices, and other imaginary
Persons of the like Nature. Some of the ancient Criticks will have it,
that the
Iliad
and
Odyssey
of Homer are Fables of this Nature: and that
the several Names of Gods and Heroes are nothing else but the Affections
of the Mind in a visible Shape and Character. Thus they tell us, that
Achilles, in the first
Iliad
, represents Anger, or the Irascible Part of
Human Nature; That upon drawing his Sword against his Superior in a full
Assembly,
Pallas
is only another Name for Reason, which checks
and advises him upon that Occasion; and at her first Appearance touches
him upon the Head, that Part of the Man being looked upon as the Seat of
Reason. And thus of the rest of the Poem. As for the
Odyssey
, I think it
is plain that
Horace
considered it as one of these Allegorical
Fables, by the Moral which he has given us of several Parts of it. The
greatest
Italian
Wits have applied themselves to the Writing of
this latter kind of Fables: As
Spencer's Fairy-Queen
is one
continued Series of them from the Beginning to the End of that admirable
Work. If we look into the finest Prose Authors of Antiquity, such as
Cicero
,
Plato
,
Xenophon
, and many others, we shall
find that this was likewise their Favourite Kind of Fable. I shall only
further observe upon it, that the first of this Sort that made any
considerable Figure in the World,
that of
Hercules
meeting
with Pleasure and Virtue; which was invented by
Prodicus
, who
lived before
Socrates
, and in the first Dawnings of Philosophy.
He used to travel through
Greece
by vertue of this Fable, which
procured him a kind Reception in all the Market-towns, where he never
failed telling it as soon as he had gathered an Audience about him
.
After this short Preface, which I have made up of such Materials as my
Memory does at present suggest to me, before I present my Reader with a
Fable of this Kind, which I design as the Entertainment of the present
Paper, I must in a few Words open the Occasion of it.
In the Account which
Plato
gives us of the Conversation and
Behaviour of
Socrates
, the Morning he was to die, he tells the
following Circumstance.
When Socrates his Fetters were knocked off (as was usual to be done on
the Day that the condemned Person was to be executed) being seated in
the midst of his Disciples, and laying one of his Legs over the other,
in a very unconcerned Posture, he began to rub it where it had been
galled by the Iron; and whether it was to shew the Indifference with
which he entertained \the Thoughts of his approaching Death, or (after
his usual Manner) to take every Occasion of Philosophizing upon some
useful Subject, he observed the Pleasure of that Sensation which now
arose in those very Parts of his Leg, that just before had been so much
pained by the Fetter. Upon this he reflected on the Nature of Pleasure
and Pain in general, and how constantly they succeeded one another. To
this he added,
if a Man of a good Genius for a Fable were to
represent the Nature of Pleasure and Pain in that Way of Writing, he
would probably join them together after such a manner, that it would be
impossible for the one to come into any Place without being followed by
the other
.
I
t is possible, that if Plato had thought it proper at such a Time to
describe Socrates launching out into a Discourse
which
was not of
a piece with the Business of the Day, he would have enlarged upon this
Hint, and have drawn it out into some beautiful Allegory or Fable. But
since he has not done it, I shall attempt to write one myself in the
Spirit of that Divine Author.
There were two Families which from the Beginning of the World were as
opposite to each other as Light and Darkness. The one of them lived in
Heaven, and the other in Hell. The youngest Descendant of the first
Family was Pleasure, who was the Daughter of Happiness, who was the
Child of Virtue, who was the Offspring of the Gods. These, as I said
before,
had their Habitation in Heaven.
The youngest of the opposite
Family was Pain, who was the Son of Misery, who was the Child of Vice,
who was the Offspring of the Furies. The Habitation of this Race of
Beings was in Hell.
The middle Station of Nature between these two opposite Extremes was the
Earth, which was inhabited by Creatures of a middle Kind, neither so
Virtuous as the one, nor so Vicious as the other, but partaking of the
good and bad Qualities of these two opposite Families.
Jupiter
considering that this Species commonly called Man, was too virtuous
to be miserable, and too vicious to be happy; that he might make a
Distinction between the Good and the Bad, ordered the two youngest of
the above-mentioned Families, Pleasure who was the Daughter of
Happiness, and Pain who was the Son of Misery, to meet one another upon
this Part of Nature which lay in the half-Way between them, having
promised to settle it upon them both, provided they could agree upon the
Division of it, so as to share Mankind between them.
Pleasure and Pain were no sooner met in their new Habitation, but they
immediately agreed upon this Point, that Pleasure should take Possession
of the Virtuous, and Pain of the Vicious Part of that Species which was
given up to them. But upon examining to which of them any Individual
they met with belonged, they found each of them had a Right to him; for
that, contrary to what they had seen in their old Places of Residence,
there was no Person so Vicious who had not some Good in him, nor any
Person so Virtuous who had not in him some Evil. The Truth of it is,
they generally found upon Search, that in the most vicious Man Pleasure
might lay a Claim to an hundredth Part, and that in the most virtuous
Man Pain might come in for at least two Thirds. This they saw would
occasion endless Disputes between them, unless they could come to some
Accommodation. To this end there was a Marriage proposed between them,
and at length concluded: By this means it is that we find Pleasure and
Pain are such constant Yoke-fellows, and that they either make their
Visits together, or are never far asunder. If Pain comes into an Heart,
he is quickly followed by Pleasure; and if Pleasure enters, you may be
sure Pain is not far off.
But notwithstanding this Marriage was very convenient for the two
Parties, it did not seem to answer the Intention of
Jupiter
in
sending them among Mankind. To remedy therefore this Inconvenience, it
was stipulated between them by Article, and confirmed by the Consent of
each Family, that notwithstanding they here possessed the Species
indifferently; upon the Death of every single Person, if he was found to
have in him a certain Proportion of Evil, he should be dispatched into
the infernal Regions by a Passport from Pain, there to dwell with
Misery, Vice and the Furies. Or on the contrary, if he had in him a
certain Proportion of Good, he should be dispatched into Heaven by a
Passport from Pleasure, there to dwell with Happiness, Virtue and the
Gods.
L.
Judges
ix. 8 — 15.
2 Sam
. xii. 1 — 4.
Livy
, Bk. II. sec. 32.
Xenophon's
Memorabilia Socratis
, Bk. II.
Phædon
, § 10.
that
Contents
|
Monday,
October 1, 1711 |
Addison |
... Opere in longo fas est obrepere somnum ...
Hor.

When a Man has discovered a new Vein of Humour, it often carries him
much further than he expected from it. My Correspondents take the Hint I
give them, and pursue it into Speculations which I never thought of at
my first starting it. This has been the Fate of my Paper on the Match of
Grinning, which has already produced a second Paper on parallel
Subjects, and brought me the following Letter by the last Post. I shall
not premise any thing to it further than that it is built on Matter of
Fact, and is as follows.
Sir,
'You have already obliged the World with a Discourse upon Grinning,
and have since proceeded to Whistling, from
whence you
at length came1 to Yawning; from this, I think, you may make a very natural
Transition to Sleeping. I therefore recommend to you for the Subject
of a Paper the following Advertisement, which about two Months ago was
given into every Body's Hands, and may be seen with some Additions in
the
Daily Courant of August the Ninth.
'
Nicholas Hart
2, who slept last Year in St. Bartholomew's
Hospital, intends to sleep this Year at the Cock and Bottle in
Little-Britain.'
Having since inquired into the Matter of Fact, I find that the
above-mentioned Nicholas Hart is every Year seized with a periodical
Fit of Sleeping, which begins upon the Fifth of August, and ends on
the Eleventh of the same Month: That
- On the First of that Month he grew dull;
- On the Second, appeared drowsy;
- On the Third, fell a yawning;
- On the Fourth, began to nod;
- On the Fifth, dropped asleep;
- On the Sixth, was heard to snore;
- On the Seventh, turned himself in his Bed;
- On the Eighth, recovered his former Posture;
- On the Ninth fell a stretching;
- On the Tenth about Midnight, awaked;
- On the Eleventh in the Morning called for a little Small-Beer.
This Account I have extracted out of the Journal of this sleeping
Worthy, as it has been faithfully kept by a Gentleman of
Lincoln's-Inn, who has undertaken to be his Historiographer. I
have sent it to you, not only as it represents the Actions of
Nicholas Hart, but as it seems a very natural Picture of the
Life of many an honest
English Gentleman, whose whole History
very often consists of Yawning, Nodding, Stretching, Turning,
Sleeping, Drinking, and the like extraordinary Particulars. I do not
question, Sir, that, if you pleased, you could put out an
Advertisement not unlike
the3 above-mentioned, of several Men of
Figure; that Mr.
John such-a-one, Gentleman, or
Thomas
such-a-one, Esquire, who slept in the Country last Summer, intends to
sleep in Town this Winter. The worst of it is, that the drowsy Part of
our Species is chiefly made up of very honest Gentlemen, who live
quietly among their Neighbours, without ever disturbing the publick
Peace: They are Drones without Stings. I could heartily wish, that
several turbulent, restless, ambitious Spirits, would for a while
change Places with these good Men, and enter themselves into
Nicholas Hart's Fraternity. Could one but lay asleep a few busy
Heads which I could name, from the First of
November next to
the
First of
May ensuing
4, I question not but it would very
much redound to the Quiet of particular Persons, as well as to the
Benefit of the Publick.
But to return to
Nicholas Hart: I believe, Sir, you will think
it a very extraordinary Circumstance for a Man to gain his Livelihood
by Sleeping, and that Rest should procure a Man Sustenance as well as
Industry; yet so it is that Nicholas got last Year enough to support
himself for a Twelvemonth. I am likewise informed that he has this
Year had a very comfortable Nap. The Poets value themselves very much
for sleeping on Parnassus, but I never heard they got a Groat by it:
On the contrary, our Friend Nicholas gets more by Sleeping than he
could by Working, and may be more properly said, than ever Homer was,
to have had Golden Dreams. Fuvenal indeed mentions a drowsy Husband
who raised an Estate by Snoring, but then he is represented to have
slept what the common People call a Dog's Sleep; or if his Sleep was
real, his Wife was awake, and about her Business.
Your Pen,
which5 loves to moralize upon all Subjects, may raise something,
methinks, on this Circumstance also, and point out to us those Sets of
Men, who instead of growing rich by an honest Industry, recommend
themselves to the Favours of the Great, by making themselves agreeable
Companions in the Participations of Luxury and Pleasure.
I must further acquaint you, Sir, that one of the most eminent Pens in
Grub-street is now employed in Writing the Dream of this miraculous
Sleeper, which I hear will be of a more than ordinary Length, as it
must contain all the Particulars that are supposed to have passed in
his Imagination during so long a Sleep. He is said to have gone
already through three Days and
three Nights of it, and to have
comprised in them the most remarkable Passages of the four first
Empires of the World. If he can keep free from Party-Strokes, his Work
may be of Use; but this I much doubt, having been informed by one of
his Friends and Confidents, that he has spoken some things of Nimrod
with too great Freedom.
I am ever, Sir, &c.
L.
are at length come
Nicholas Hart, born at Leyden, was at this time 22 years
old, one of ten children of a learned mathematician who for two years
had been a tutor to King William. Nicholas was a sailor from the age of
twelve, and no scholar, although he spoke French, Dutch, and English. He
was a patient at St. Bartholomew's for stone and gravel some weeks
before, and on the 3rd of August, 1711, set his mark to an account of
himself, when he expected to fall asleep on the fifth of August, two
days later. His account was also signed by 'William Hill, Sen. No. I.
Lincoln's Inn,' the 'Gentleman of 'Lincoln's Inn,' presently alluded to.
that
That is, when Parliament is sitting.
that
Contents
|
Tuesday,
October 2, 1711 |
Addison |
... Tantæne Animis cœlestibus Iræ?
Virg.

There is nothing in which Men more deceive themselves than in what the
World calls Zeal. There are so many Passions which hide themselves under
it, and so many Mischiefs arising from it, that some have gone so far as
to say it would have been for the Benefit of Mankind if it had never
been reckoned in the Catalogue of Virtues. It is certain, where it is
once Laudable and Prudential, it is an hundred times Criminal and
Erroneous; nor can it be otherwise, if we consider that it operates with
equal Violence in all Religions, however opposite they may be to one
another, and in all the Subdivisions of each Religion in particular.
We are told by some of the Jewish Rabbins, that the first Murder was
occasioned by a religious Controversy; and if we had the whole History
of Zeal from the Days of Cain to our own Times, we should see it filled
with so many Scenes of Slaughter and Bloodshed, as would make a wise Man
very careful how he suffers himself to be actuated by such a Principle,
when it only regards Matters of Opinion and Speculation.
I would have every Zealous Man examine his Heart thoroughly, and, I
believe, he will often find, that what he calls a Zeal for his Religion,
is either Pride,
, or Ill-nature.
A Man who
differs from
another in Opinion, sets himself above him in his own Judgment, and in
several Particulars pretends to be the wiser Person. This is a great
Provocation to the proud Man, and gives a very keen Edge to what he
calls his Zeal. And that this is the Case very often, we may observe
from the Behaviour of some of the most zealous for Orthodoxy, who have
often great Friendships and Intimacies with vicious immoral Men,
provided they do but agree with them in the same Scheme of Belief. The
Reason is, Because the vicious Believer gives the Precedency to the
virtuous Man, and allows the good Christian to be the worthier Person,
at the same time that he cannot come up to his Perfections. This we find
exemplified in that trite Passage which we see quoted in almost every
System of Ethicks, tho' upon another Occasion.
... Video meliora proboque,
Deteriora sequor ...
(Ov.)
On the contrary, it is certain, if our Zeal were true and genuine, we
should be much more angry with a Sinner than a Heretick; since
are
several Cases
which
may excuse the latter before his great Judge,
but none
which
can excuse the former.
Interest is likewise a great Inflamer, and sets a Man on Persecution
under the colour of Zeal. For this Reason we find none are so forward to
promote the true Worship by Fire and Sword, as those who find their
present Account in it. But I shall extend the Word Interest to a larger
Meaning than what is generally given it, as it relates to our Spiritual
Safety and Welfare, as well as to our Temporal. A Man is glad to gain
Numbers on his Side, as they serve to strengthen him in his private
Opinions. Every Proselyte is like a new Argument for the Establishment
of his Faith. It makes him believe that his Principles carry Conviction
with them, and are the more likely to be true, when he finds they are
conformable to the Reason of others, as well as to his own. And that
this Temper of Mind deludes a Man very often into an Opinion of his
Zeal, may appear from the common Behaviour of the Atheist, who maintains
and spreads his Opinions with as much Heat as those who believe they do
it only out of Passion for God's Glory.
Ill-nature is another dreadful Imitator of Zeal. Many a good Man may
have a natural Rancour and Malice in
Heart,
which
has been in
some measure quelled and subdued by Religion; but if it finds any
Pretence of breaking out, which does not seem to him inconsistent with
the Duties of a Christian, it throws off all Restraint, and rages in its
full Fury. Zeal is therefore a great Ease to a malicious Man, by making
him believe he does God Service, whilst he is gratifying the Bent of a
perverse revengeful Temper. For this Reason we find, that most of the
Massacres
Devastations,
which
have been in the World, have
taken their Rise from a furious pretended Zeal.
I love to see a Man zealous in a good Matter, and especially when his
Zeal shews it self for advancing Morality, and promoting the Happiness
of Mankind: But when I find the Instruments he works with are Racks and
Gibbets, Gallies and Dungeons; when he imprisons Mens Persons,
confiscates their Estates, ruins their Families, and burns the Body to
save the Soul, I cannot stick to pronounce of such a one, that (whatever
he may think of his Faith and Religion) his Faith is vain, and his
Religion unprofitable.
After having treated of these false Zealots in Religion, I cannot
forbear mentioning a monstrous Species of Men, who one would not think
had any Existence in Nature, were they not to be met with in ordinary
Conversation, I mean the Zealots in Atheism. One would fancy that these
Men, tho' they fall short, in every other Respect, of those who make a
Profession of Religion, would at least outshine them in this Particular,
and be exempt from that single Fault which seems to grow out of the
imprudent Fervours of Religion: But so it is, that Infidelity is
propagated with as much Fierceness and Contention, Wrath and
Indignation, as if the Safety of Mankind depended upon it. There is
something so ridiculous and perverse in this kind of Zealots, that one
does not know how to set them out in their proper Colours.
are a
Sort of Gamesters
who
are eternally upon the Fret, though they
play for nothing. They are perpetually teizing their Friends to come
over to them, though at the same time they allow that neither of them
shall get any thing by the Bargain. In short, the Zeal of spreading
Atheism is, if possible, more absurd than Atheism it self.
Since I have mentioned this unaccountable Zeal which appears in Atheists
and Infidels, I must further observe that they are likewise in a most
particular manner possessed with the Spirit of Bigotry. They are wedded
to Opinions full of Contradiction and Impossibility, and at the same
time look upon the smallest Difficulty in an Article of Faith as a
sufficient Reason for rejecting it. Notions that fall in with the common
Reason of Mankind, that are conformable to the Sense of all Ages and all
Nations, not to mention their Tendency for promoting the Happiness of
Societies, or of particular Persons, are exploded as Errors and
Prejudices; and Schemes erected in their stead that are altogether
monstrous and irrational, and require the most extravagant Credulity to
embrace them. I would fain ask one of these bigotted Infidels, supposing
all the great Points of Atheism, as the casual or eternal Formation of
the World, the Materiality of a thinking Substance, the Mortality of the
Soul, the fortuitous Organization of the Body, the Motions and
Gravitation of Matter, with the like Particulars, were laid together
formed
into
a kind of Creed, according to the Opinions of the most
celebrated Atheists; I say, supposing such a Creed as this were formed,
and imposed upon any one People in the World, whether it would not
require an infinitely greater Measure of Faith, than any Set of Articles
which they so violently oppose. Let me therefore advise this Generation
of Wranglers, for their own and for the publick Good, to act at least so
consistently with themselves, as not to burn with Zeal for Irreligion,
and with Bigotry for Nonsense.
C.
The Man that
that
that
that
that
that
in
Contents
|
Wednesday,
October 3, 1711 |
Addison |
Cœlum ipsum petimus stultitiâ.
Hor.

Upon my Return to my Lodgings last Night I found a Letter from my worthy
Friend the Clergyman, whom I have given some Account of in my former
Papers. He tells me in it that he was particularly pleased with the
latter Part of my Yesterday's Speculation; and at the same time enclosed
the following Essay, which he desires me to publish as the Sequel of
that Discourse. It consists partly of uncommon Reflections, and partly
of such as have been already used, but now set in a stronger Light.
'A Believer may be excused by the most hardened Atheist for
endeavouring to make him a Convert, because he does it with an Eye to
both their Interests. The Atheist is inexcusable who tries to gain
over a Believer, because he does not propose the doing himself or the
Believer any Good by such a Conversion.
The Prospect of a future State is the secret Comfort and Refreshment
of my Soul; it is that which makes Nature look gay about me; it
doubles all my Pleasures, and supports me under all my Afflictions. I
can look at Disappointments and Misfortunes, Pain and Sickness, Death
itself, and, what is worse than Death, the Loss of those who are
dearest to me, with Indifference, so long as I keep in view the
Pleasures of Eternity, and the State of Being in which there will be
no Fears nor Apprehensions, Pains nor Sorrows, Sickness nor
Separation. Why will any Man be so impertinently Officious as to tell
me all this is only Fancy and Delusion? Is there any Merit in being
the Messenger of ill News? If it is a Dream, let me enjoy it, since it
makes me both the happier and better Man.
I must confess I do not know how to trust a Man
who1 believes
neither Heaven nor Hell, or, in other Words, a future State of Rewards
and Punishments. Not only natural Self-love, but Reason directs us to
promote our own Interest above all Things. It can never be for the
Interest of a Believer to do me a Mischief, because he is sure upon
the Balance of Accompts to find himself a Loser by it. On the
contrary, if he considers his own Welfare in his Behaviour towards me,
it will lead him to do me all the Good he can, and at the same Time
restrain him from doing me any Injury. An Unbeliever does not act like
a reasonable Creature, if he favours me contrary to his present
Interest, or does not distress me when it turns to his present
Advantage. Honour and Good-nature may indeed tie up his Hands; but as
these would be very much strengthened by Reason and Principle, so
without them they are only Instincts, or
wavering unsettled Notions,
which2 rest on no Foundation.
Infidelity has been attack'd with so good Success of late Years, that
it is driven out of all its Out-works. The Atheist has not found his
Post tenable, and is therefore retired into Deism, and a Disbelief of
revealed Religion only. But the Truth of it is, the greatest Number of
this Set of Men, are those who, for want of a virtuous Education, or
examining the Grounds of Religion, know so very little of the Matter
in Question, that their Infidelity is but another Term for their
Ignorance.
As Folly and Inconsiderateness are the Foundations of Infidelity, the
great Pillars and Supports of it are either a Vanity of appearing
wiser than the rest of Mankind, or an Ostentation of Courage in
despising the Terrors of another World, which have so great an
Influence on what they call weaker Minds; or an Aversion to a Belief
that must cut them off from many of those Pleasures they propose to
themselves, and fill them with Remorse for many of those they have
already tasted.
The great received Articles of the Christian Religion have been so
clearly proved, from the Authority of that Divine Revelation in which
they are delivered, that it is impossible for those who have Ears to
hear, and Eyes to see, not to be convinced of them. But were it
possible for any thing in the Christian Faith to be erroneous, I can
find no ill Consequences in adhering to it. The great Points of the
Incarnation and Sufferings of our Saviour produce naturally such
Habits of Virtue in the Mind of Man, that I say, supposing it were
possible for us to be mistaken in them, the Infidel himself must at
least allow that no other System of Religion could so effectually
contribute to the heightning of Morality. They give us great Ideas of
the Dignity of human Nature, and of the Love which the Supreme Being
bears to his Creatures, and consequently engage us in the highest Acts
of Duty towards our Creator, our Neighbour, and our selves. How many
noble Arguments has Saint Paul raised from the chief Articles of our
Religion, for the advancing of Morality in its three great Branches?
To give a single Example in each Kind: What can be a stronger Motive
to a firm Trust and Reliance on the Mercies of our Maker, than the
giving us his Son to suffer for us? What can make us love and esteem
even the most inconsiderable of Mankind more than the Thought that
Christ died for him? Or what dispose us to set a stricter Guard upon
the Purity of our own Hearts, than our being Members of Christ, and a
Part of the Society of which that immaculate Person is the Head? But
these are only a Specimen of those admirable Enforcements of Morality,
which the Apostle has drawn from the History of our blessed Saviour.
If our modern Infidels considered these Matters with that Candour and
Seriousness which they deserve, we should not see them act with such a
Spirit of Bitterness, Arrogance, and Malice: They would not be raising
such insignificant Cavils, Doubts, and Scruples, as may be started
against every thing that is not capable of mathematical Demonstration;
in order to unsettle the Minds of the Ignorant, disturb the publick
Peace, subvert Morality, and throw all things into Confusion and
Disorder. If none of these Reflections can have any Influence on them,
there is one that perhaps may, because it is adapted to their Vanity,
by which they seem to be guided much more than their Reason. I would
therefore have them consider, that the wisest and best of Men, in all
Ages of the World, have been those who lived up to the Religion of
their Country, when they saw nothing in it opposite to Morality, and
to the best Lights they had of the Divine Nature. Pythagoras's first
Rule directs us to worship the Gods as it is ordained by Law, for
that
is the most natural Interpretation of the Precept
3. Socrates, who
was the most renowned among the Heathens both for Wisdom and Virtue,
in his last Moments desires his Friends to offer a
Cock to
Æsculapius
4; doubtless out of a submissive Deference to the
established Worship of his Country. Xenophon tells us, that his Prince
(whom he sets forth as a Pattern of Perfection), when he found his
Death approaching, offered Sacrifices on the Mountains to the Persian
Jupiter, and the Sun, according to the Custom of the
Persians; for
those are the Words of the Historian
5. Nay, the Epicureans and
Atomical Philosophers shewed a very remarkable Modesty in this
Particular; for though the Being of a God was entirely repugnant to
their Schemes of natural Philosophy, they contented themselves with
the Denial of a Providence, asserting at the same Time the Existence
of Gods in general; because they would not shock the common Belief of
Mankind, and the Religion of their Country.'
L.
that
that
Which is motto to
.
Phædon.
Cyropædia
, Bk. viii.
Contents
|
Thursday,
October 4, 1711 |
Steele |
... Miseri quibus
Intentata nites ...
Hor.

The Intelligence given by this Correspondent is so important and useful,
in order to avoid the Persons he speaks of, that I shall insert his
Letter at length.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I do not know that you have ever touched upon a certain species of
Women, whom we ordinarily call Jilts. You cannot possibly go upon a
more useful Work, than the Consideration of these dangerous Animals.
The Coquet is indeed one Degree towards the Jilt; but the Heart of the
former is bent upon admiring her self, and giving false Hopes to her
Lovers; but the latter is not contented to be extreamly amiable, but
she must add to that Advantage a certain Delight in being a Torment to
others. Thus when her Lover is in the full Expectation of Success, the
Jilt shall meet him with a sudden Indifference, and Admiration in her
Face at his being surprised that he is received like a Stranger, and a
Cast of her Head another Way with a pleasant Scorn of the Fellow's
Insolence. It is very probable the Lover goes home utterly astonished
and dejected, sits down to his Scrutore, sends her word in the most
abject Terms, That he knows not what he has done; that all which was
desirable in this Life is so suddenly vanished from him, that the
Charmer of his Soul should withdraw the vital Heat from the Heart
which pants for her. He continues a mournful Absence for some time,
pining in Secret, and out of Humour with all things which he meets
with. At length he takes a Resolution to try his Fate, and explain
with her resolutely upon her unaccountable Carriage. He walks up to
her Apartment, with a thousand Inquietudes and Doubts in what Manner
he shall meet the first Cast of her Eye; when upon his first
Appearance she flies towards him, wonders where he has been, accuses
him of his Absence, and treats him with a Familiarity as surprising as
her former Coldness. This good Correspondence continues till the Lady
observes the Lover grows happy in it, and then she interrupts it with
some new Inconsistency of Behaviour. For (as I just now said) the
Happiness of a Jilt consists only in the Power of making others
uneasy. But such is the Folly of this Sect of Women, that they carry
on this pretty skittish Behaviour, till they have no charms left to
render it supportable. Corinna, that used to torment all who conversed
with her with false Glances, and little heedless unguarded Motions,
that were to betray some Inclination towards the Man she would
ensnare, finds at present all she attempts that way unregarded; and is
obliged to indulge the Jilt in her Constitution, by laying Artificial
Plots, writing perplexing Letters from unknown Hands, and making all
the young Fellows in Love with her, till they find out who she is.
Thus as before she gave Torment by disguising her Inclination, she is
now obliged to do it by hiding her Person.
As for my own Part, Mr,
Spectator, it has been my unhappy Fate to be
jilted from my Youth upward; and as my Taste has been very much
towards Intreague, and having Intelligence with Women of Wit, my whole
Life has passed away in a Series of Impositions. I shall, for the
Benefit of the present Race of young Men, give some Account of my
Loves. I know not whether you have ever heard of the famous Girl about
Town called Kitty: This Creature (for I must take Shame upon my self)
was my Mistress in the Days when Keeping was in Fashion. Kitty, under
the Appearance of being Wild, Thoughtless, and Irregular in all her
Words and Actions, concealed the most accomplished Jilt of her Time.
Her Negligence had to me a Charm in it like that of Chastity, and Want
of Desires seemed as great a Merit as the Conquest of them. The Air
she gave herself was that of a Romping Girl, and whenever I talked to
her with any Turn of Fondness, she would immediately snatch off my
Perriwig, try it upon herself in the Glass, clap her Arms a Kimbow,
draw my Sword, and make Passes on the Wall, take off my Cravat, and
seize it to make some other Use of the Lace, or run into some other
unaccountable Rompishness, till the Time I had appointed to pass away
with her was over. I went from her full of Pleasure at the Reflection
that I had the keeping of so much Beauty in a Woman, who, as she was
too heedless to please me, was also too inattentive to form a Design
to wrong me. Long did I divert every Hour that hung heavy upon me in
the Company of this Creature, whom I looked upon as neither Guilty or
Innocent, but could laugh at my self for my unaccountable Pleasure in
an Expence upon her, till in the End it appeared my pretty Insensible
was with Child by my Footman.
This Accident roused me into a Disdain against all Libertine Women,
under what Appearance soever they hid their Insincerity, and I
resolved after that Time to converse with none but those who lived
within the Rules of Decency and Honour. To this End I formed my self
into a more regular Turn of Behaviour, and began to make Visits,
frequent Assemblies, and lead out Ladies from the Theatres, with all
the other insignificant Duties which the professed Servants of the
Fair place themselves in constant Readiness to perform. In a very
little time, (having a plentiful Fortune) Fathers and Mothers began to
regard me as a good Match, and I found easie Admittance into the best
Families in Town to observe their daughters; but I, who was born to
follow the Fair to no Purpose, have by the Force of my ill Stars made
my Application to three Jilts successively.
Hyæna is one of those who form themselves into a melancholy and
indolent Air, and endeavour to gain Admirers from their Inattention to
all around them. Hyaena can loll in her Coach, with something so fixed
in her Countenance, that it is impossible to conceive her Meditation
is employed only on her Dress and her Charms in that Posture. If it
were not too coarse a Simile, I should say, Hyaena, in the Figure she
affects to appear in, is a Spider in the midst of a Cobweb, that is
sure to destroy every Fly that approaches it. The Net Hyaena throws is
so fine, that you are taken in it before you can observe any Part of
her Work. I attempted her for a long and weary Season, but I found her
Passion went no farther than to be admired; and she is of that
unreasonable Temper, as not to value the Inconstancy of her Lovers
provided she can boast she once had their Addresses.
Biblis was the second I aimed at, and her Vanity lay in purchasing the
Adorers of others, and not in rejoicing in their Love it self. Biblis
is no Man's Mistress, but every Woman's Rival. As soon as I found
this, I fell in Love with Chloe, who is my present Pleasure and
Torment. I have writ to her, danced with her, and fought for her, and
have been her Man in the Sight and Expectation of the
whole Town
these1 three Years, and thought my self near the End of my
Wishes; when the other Day she called me into her Closet, and told me,
with a very grave Face, that she was a Woman of Honour, and scorned to
deceive a Man who loved her with so much Sincerity as she saw I did,
and therefore she must inform me that she was by Nature the most
inconstant Creature breathing, and begg'd of me not to marry her; If I
insisted upon it, I should; but that she was lately fallen in Love
with another. What to do or say I know not, but desire you to inform
me, and you will infinitely oblige,
Sir, Your most humble Servant,
Charles Yellow.
"this", and in first reprint.
Contents
Mr. Sly, Haberdasher of Hats,
at the Corner of Devereux-Court in the Strand,
gives notice,
That he has prepared very neat Hats, Rubbers, and Brushes
for the Use of young Tradesmen in their last Year of Apprenticeship,
at reasonable Rates
1.
"Last night died of a mortification in his leg, after a long time
enduring the same, John Sly, the late famous haberdasher, so often
mentioned in the Spectator."
Evening Post
, April 15, 1729.
|
Friday,
October 5, 1711 |
Steele |
Lœtus sum Laudari à te Laudato viro.
Tull.

He is a very unhappy Man who sets his Heart upon being admired by the
Multitude, or affects a general and undistinguishing Applause among Men.
What pious Men call the Testimony of a good Conscience, should be the
Measure of our Ambition in this Kind; that is to say, a Man of Spirit
should contemn the Praise of the Ignorant, and like being applauded for
nothing but what he knows in his own Heart he deserves. Besides which
the Character of the Person who commends you is to be considered, before
you set a Value upon his Esteem. The Praise of an ignorant Man is only
Good-will, and you should receive his Kindness as he is a good Neighbour
in Society, and not as a good Judge of your Actions in Point of Fame and
Reputation. The Satyrist said very well of popular Praise and
Acclamations, Give the Tinkers and Coblers their
again, and
learn to live of your self
. It is an Argument of a loose and
ungoverned Mind to be affected with the promiscuous Approbation of the
Generality of Mankind; and a Man of Virtue should be too delicate for so
coarse an Appetite of Fame. Men of Honour should endeavour only to
please the Worthy, and the Man of Merit should desire to be tried only
by his Peers. I thought it a noble Sentiment which I heard Yesterday
uttered in Conversation; I know, said a Gentleman, a Way to be greater
than any Man: If he has Worth in him, I can rejoice in his Superiority
to me; and that Satisfaction is a greater Act of the Soul in me, than
any in him which can possibly appear to me. This Thought could not
proceed but from a candid and generous Spirit; and the Approbation of
such Minds is what may be esteemed true Praise. For with the common Rate
of Men there is nothing commendable but what they themselves may hope to
be Partakers of, or arrive at; but the Motive truly glorious is, when
the Mind is set rather to do Things laudable, than to purchase
Reputation. Where there is that Sincerity as the Foundation of a good
Name, the kind Opinion of virtuous Men will be an unsought but a
necessary Consequence.
Lacedemonians, tho' a plain People, and no
Pretenders to Politeness, had a certain Delicacy in their Sense of
Glory, and sacrificed to the Muses when they entered upon any great
Enterprise
. They would have the Commemoration of their Actions be
transmitted by the purest and most untainted Memorialists. The Din which
attends Victories and publick Triumphs is by far less eligible, than the
Recital of the Actions of great Men by honest and wise Historians. It is
a frivolous Pleasure to be the Admiration of gaping Crowds; but to have
the Approbation of a good Man in the cool Reflections of his Closet, is
a Gratification worthy an heroick Spirit. The Applause of the Crowd
makes the Head giddy, but the Attestation of a reasonable Man makes the
Heart glad.
What makes the Love of popular or general Praise still more ridiculous,
is, that it is usually given for Circumstances which are foreign to the
Persons admired. Thus they are the ordinary Attendants on Power and
Riches, which may be taken out of one Man's Hands, and put into
another's: The Application only, and not the Possession, makes those
outward things honourable. The Vulgar and Men of Sense agree in admiring
Men for having what they themselves would rather be possessed of; the
wise Man applauds him whom he thinks most virtuous; the rest of the
World, him who is most wealthy.
When a Man is in this way of Thinking, I do not know what can occur to
one more monstrous, than to see Persons of Ingenuity address their
Services and Performances to Men no way addicted to Liberal Arts: In
these Cases, the Praise on one hand, and the Patronage on the other, are
equally the Objects of Ridicule. Dedications to ignorant Men are as
absurd as any of the Speeches of Bulfinch in the Droll: Such an Address
one is apt to translate into other Words; and when the Different Parties
are thoroughly considered, the Panegyrick generally implies no more than
if the Author should say to the Patron; My very good Lord, You and I can
never understand one another, therefore I humbly desire we may be
intimate Friends for the future.
The Rich may as well ask to borrow of the Poor, as the Man of Virtue or
Merit hope for Addition to his Character from any but such as himself.
He that commends another engages so much of his own Reputation as he
gives to that Person commended; and he that has nothing laudable in
himself is not of Ability to be such a Surety.
wise Phocion was so
sensible how dangerous it was to be touched with what the Multitude
approved, that upon a general Acclamation made when he was making an
Oration, he turned to an intelligent Friend who stood near him, and
asked, in a surprized Manner, What Slip have I made
?
I shall conclude this Paper with a Billet which has fallen into my
Hands, and was written to a Lady from a Gentleman whom she had highly
commended. The Author of it had formerly been her Lover. When all
Possibility of Commerce between them on the Subject of Love was cut off,
she spoke so handsomely of him, as to give Occasion for this Letter.
Madam,
"I should be insensible to a Stupidity, if I could forbear making you
my Acknowledgments for your late mention of me with so much Applause.
It is, I think, your Fate to give me new Sentiments; as you formerly
inspired me with the true Sense of Love, so do you now with the true
Sense of Glory. As Desire had the least Part in the Passion I
heretofore professed towards you, so has Vanity no Share in the Glory
to which you have now raised me. Innocence, Knowledge, Beauty, Virtue,
Sincerity, and Discretion, are the constant Ornaments of her who has
said this of me. Fame is a Babbler, but I have arrived at the highest
Glory in this World, the Commendation of the most deserving Person in
it."
T.
Persius.
Sat
. IV. sec. 51.
Plutarch in
Life of Lycurgus
.
Plutarch in
Life of Phocion
.
Contents
|
Saturday,
October 6, 1711 |
Addison |
... Patriæ pietatis imago.
Virg.

The following Letter being written to my Bookseller, upon a Subject of
which I treated some time since, I shall publish it in this Paper,
together with the Letter that was inclosed in it.
Mr. Buckley,
"Mr. Spectator having of late descanted upon the Cruelty of Parents to
their Children, I have been induced (at the Request of several of Mr.
Spectator's Admirers) to inclose this Letter, which I assure you is
the Original from a Father to his own Son, notwithstanding the latter
gave but little or no Provocation. It would be wonderfully obliging to
the World, if Mr. Spectator would give his Opinion of it, in some of
his Speculations, and particularly to"
(Mr. Buckley)
Your Humble Servant.
Sirrah,
"You are a sawcy audacious Rascal, and both Fool and Mad, and I care
not a Farthing whether you comply or no; that does not raze out my
Impressions of your Insolence, going about Railing at me, and the next
Day to sollicit my Favour: These are Inconsistencies, such as discover
thy Reason depraved. To be brief, I never desire to see your Face;
and, Sirrah, if you go to the Work-house, it is no Disgrace to me for
you to be supported there; and if you Starve in the Streets, I'll
never give any thing underhand in your Behalf. If I have any more of
your scribling Nonsense I'll break your Head the first Time I set
Sight on you. You are a stubborn Beast; is this your Gratitude for my
giving you Mony? You Rogue, I'll better your Judgment, and give you a
greater Sense of your Duty to (I regret to say)
your Father, &c."
"P.S. It's Prudence for you to keep out of my Sight; for to reproach
me, that Might overcomes Right, on the Outside of your Letter, I shall
give you a great Knock on the Skull for it."
Was there ever such an Image of Paternal Tenderness! It was usual among
some of the Greeks to make their Slaves drink to Excess, and then expose
them to their Children, who by that means conceived an early Aversion to
a Vice which makes Men appear so monstrous and irrational. I have
exposed this Picture of an unnatural Father with the same Intention,
that its Deformity may deter others from its Resemblance.
the Reader
has a mind to see a Father of the same Stamp represented in the most
exquisite Stroaks of Humour, he may meet with it in one of the finest
Comedies that ever appeared upon the
English
Stage: I mean the
Part of Sir
Sampson
in
Love for Love
.
I must not however engage my self blindly on the Side of the Son, to
whom the fond Letter above-written was directed. His Father calls him a
sawcy and audacious Rascal
in the first Line, and I am afraid
upon Examination he will prove but an ungracious Youth.
To go about
railing
at his Father, and to find no other Place but
the Outside
of his Letter
to tell him
that Might overcomes Right
, if it
does not discover
his Reason to be depraved
, and
that he is
either Fool or Mad
, as the cholerick old Gentleman tells him, we may
at least allow that the Father will do very well in endeavouring to
better his Judgment, and give him a greater Sense of his Duty
.
But whether this may be brought about by
breaking his Head
, or
giving him a great Knock on the Skull
, ought, I think, to be well
considered. Upon the whole, I wish the Father has not met with his
Match, and that he may not be as equally paired with a Son,
the
Mother in
Virgil
.
... Crudelis tu quoque mater:
Crudelis mater magis an puer Improbus ille?
Improbus ille puer, crudelis tu quoque mater2.
Or like the Crow and her Egg, in the
Greek
Proverb,
I must here take Notice of a Letter which I have received from an
unknown Correspondent, upon the Subject of my Paper, upon which the
foregoing Letter is likewise founded. The Writer of it seems very much
concerned lest that Paper should seem to give Encouragement to the
Disobedience of Children towards their Parents; but if the Writer of it
will take the Pains to read it over again attentively, I dare say his
Apprehensions will vanish. Pardon and Reconciliation are all the
Penitent Daughter requests, and all that I contend for in her Behalf;
and in this Case I may use the Saying of an eminent Wit, who, upon some
great Men pressing him to forgive his Daughter who had married against
his Consent, told them he could refuse nothing to their Instances, but
that he would have them remember there was Difference between Giving and
Forgiving.
I must confess, in all Controversies between Parents and their Children,
I am naturally prejudiced in favour of the former. The Obligations on
that Side can never be acquitted, and I think it is one of the greatest
Reflections upon Human Nature that Parental Instinct should be a
stronger Motive to Love than Filial Gratitude; that the receiving of
Favours should be a less Inducement to Good-will, Tenderness and
Commiseration, than the conferring of them; and that the taking care of
any Person should endear the Child or Dependant more to the Parent or
Benefactor, than the Parent or Benefactor to the Child or Dependant; yet
so it happens, that for one cruel Parent we meet with a thousand
undutiful Children. This is indeed wonderfully contrived (as I have
formerly observed) for the Support of every living Species; but at the
same time that it shews the Wisdom of the Creator, it discovers the
Imperfection and Degeneracy of the Creature.
The Obedience of Children to their Parents is the Basis of all
Government, and set forth as the Measure of that Obedience which we owe
to those whom Providence hath placed over us.
is Father Le Conte
, if I am not mistaken, who tells us how Want
of Duty in this Particular is punished among the Chinese, insomuch that
if a Son should be known to kill, or so much as to strike his Father,
not only the Criminal but his whole Family would be rooted out, nay the
Inhabitants of the Place where he lived would be put to the Sword, nay
the Place itself would be razed to the Ground, and its Foundations sown
with Salt; For, say they, there must have been an utter Depravation of
Manners in that Clan or Society of People who could have bred up among
them so horrible an Offender. To this I shall add a Passage out of the
first Book of Herodotus. That Historian in his Account of the Persian
Customs and Religion tells us, It is their Opinion that no Man ever
killed his Father, or that it is possible such a Crime should be in
Nature; but that if any thing like it should ever happen, they conclude
that the reputed Son must have been Illegitimate, Supposititious, or
begotten in Adultery. Their Opinion in this Particular shews
sufficiently what a Notion they must have had of Undutifulness in
general.
L.
Sir Sampson Legend in Congreve's play, which ends with the
heroine's 'punishing an inhuman father and rewarding a faithful lover.'
Ecl
. 8.
Of bad Crow bad Egg.
Present State of China
, Part 2. Letter to the Cardinal
d'Estrees.
Contents
|
Monday,
October 8, 1711 |
Steele |
Servitus crescit nova ...
Hor.

Since I made some Reflections upon the general Negligence used in the
Case of Regard towards Women, or, in other Words, since I talked of
Wenching, I have had Epistles upon that Subject, which I shall, for the
present Entertainment, insert as they lye before me.
Mr. Spectator,
'As your Speculations are not confined to any Part of Humane Life, but
concern the Wicked as well as the Good, I must desire your favourable
Acceptance of what I, a poor stroling Girl about Town, have to say to
you. I was told by a Roman Catholic Gentleman who picked me up last
Week, and who, I hope, is absolved for what passed between us; I say I
was told by such a Person, who endeavoured to convert me to his own
Religion, that in Countries where Popery prevails, besides the
Advantage of licensed Stews, there are large Endowments given for the
Incurabili, I think he called them, such as are past all Remedy, and
are allowed such Maintenance and Support as to keep them without
further Care till they expire. This manner of treating poor Sinners
has, methinks, great Humanity in it; and as you are a Person who
pretend to carry your Reflections upon all Subjects, whatever occur to
you, with Candour, and act above the Sense of what Misinterpretation
you may meet with, I beg the Favour of you to lay before all the World
the unhappy Condition of us poor Vagrants, who are really in a Way of
Labour instead of Idleness. There are Crowds of us whose Manner of
Livelihood has long ceased to be pleasing to us; and who would
willingly lead a new Life, if the Rigour of the Virtuous did not for
ever expel us from coming into the World again. As it now happens, to
the eternal Infamy of the Male Sex, Falshood among you is not
reproachful, but Credulity in Women is infamous.
Give me Leave, Sir, to give you my History. You are to know that I am
a Daughter of a Man of a good Reputation, Tenant to a Man of Quality.
The Heir of this great House took it in his Head to cast a favourable
Eye upon me, and succeeded. I do not pretend to say he promised me
Marriage: I was not a Creature silly enough to be taken by so foolish
a Story: But he ran away with me up to this Town; and introduced me to
a grave Matron, with whom I boarded for a Day or two with great
Gravity, and was not a little pleased with the Change of my Condition,
from that of a Country Life to the finest Company, as I believed, in
the whole World. My humble Servant made me to understand that I should
be always kept in the plentiful Condition I then enjoyed; when after a
very great Fondness towards me, he one Day took his Leave of me for
four or five Days. In the Evening of the same Day my good Landlady
came to me, and observing me very pensive began to comfort me, and
with a Smile told me I must see the World. When I was deaf to all she
could say to divert me, she began to tell me with a very frank Air
that I must be treated as I ought, and not take these squeamish
Humours upon me, for my Friend had left me to the Town; and, as their
Phrase is, she expected I would see Company, or I must be treated like
what I had brought my self to. This put me into a Fit of Crying: And I
immediately, in a true Sense of my Condition, threw myself on the
Floor, deploring my Fate, calling upon all that was good and sacred to
succour me. While I was in all my Agony, I observed a decrepid old
Fellow come into the Room, and looking with a Sense of Pleasure in his
Face at all my Vehemence and Transport. In a Pause of my Distress I
heard him say to the shameless old Woman who stood by me, She is
certainly a new Face, or else she acts it rarely. With that the
Gentlewoman, who was making her Market of me, in all the Turn of my
Person, the Heaves of my Passion, and the suitable Changes of my
Posture, took Occasion to commend my Neck, my Shape, my Eyes, my
Limbs. All this was accompanied with such Speeches as you may have
heard Horse-coursers make in the Sale of Nags, when they are warranted
for their Soundness. You understand by this Time that I was left in a
Brothel, and exposed to the next Bidder that could purchase me of my
Patroness. This is so much the Work of Hell; the Pleasure in the
Possession of us Wenches, abates in proportion to the Degrees we go
beyond the Bounds of Innocence; and no Man is gratified, if there is
nothing left for him to debauch. Well, Sir, my first Man, when I came
upon the Town, was Sir Jeoffry Foible, who was extremely lavish
to me of his Money, and took such a Fancy to me that he would have
carried me off, if my Patroness would have taken any reasonable Terms
for me: But as he was old, his Covetousness was his strongest Passion,
and poor I was soon left exposed to be the common Refuse of all the
Rakes and Debauchees in Town. I cannot tell whether you will do me
Justice or no, till I see whether you print this or not; otherwise, as
I now live with Sal, I could give you a very just Account of who and
who is together in this Town. You perhaps won't believe it; but I know
of one who pretends to be a very good Protestant who lies with a
Roman-Catholick: But more of this hereafter, as you please me. There
do come to our House the greatest Politicians of the Age; and Sal is
more shrewd than any Body thinks: No Body can believe that such wise
Men could go to Bawdy-houses out of idle Purposes; I have heard them
often talk of Augustus Cæsar, who had Intrigues with the Wives of
Senators, not out of Wantonness but Stratagem.
it is a thousand Pities you should be so severely virtuous as I fear
you are; otherwise, after a Visit or two, you would soon understand
that we Women of the Town are not such useless Correspondents as you
may imagine: You have undoubtedly heard that it was a Courtesan who
discovered Cataline's Conspiracy. If you print this I'll tell you
more; and am in the mean time, Sir.
Your most humble Servant, Rebecca Nettletop.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am an idle young Woman that would work for my Livelihood, but that
I am kept in such a Manner as I cannot stir out. My Tyrant is an old
jealous Fellow, who allows me nothing to appear in. I have but one
Shooe and one Slipper; no Head-dress, and no upper Petticoat. As you
set up for a Reformer, I desire you would take me out of this wicked
Way, and keep me your self.
Eve Afterday.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am to complain to you of a Set of impertinent Coxcombs, who visit
the Apartments of us Women of the Town, only, as they call it, to see
the World. I must confess to you, this to Men of Delicacy might have
an Effect to cure them; but as they are stupid, noisy and drunken
Fellows, it tends only to make Vice in themselves, as they think,
pleasant and humourous, and at the same Time nauseous in us. I shall,
Sir, hereafter from Time to Time give you the Names of these Wretches
who pretend to enter our Houses meerly as Spectators. These Men think
it Wit to use us ill: Pray tell them, however worthy we are of such
Treatment, it is unworthy them to be guilty of it towards us. Pray,
Sir, take Notice of this, and pity the Oppressed: I wish we could add
to it, the Innocent.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday,
October 9, 1711 |
Addison |
Some ludicrous Schoolmen have put the Case, that if an Ass were placed
between two Bundles of Hay, which affected his Senses equally on each
Side, and tempted him in the very same Degree, whether it would be
possible for him to Eat of either. They generally determine this
Question to the Disadvantage of the Ass, who they say would starve in
the Midst of Plenty, as not having a single Grain of Freewill to
determine him more to the one than to the other. The Bundle of Hay on
either Side striking his Sight and Smell in the same Proportion, would
keep him in a perpetual Suspence, like the two Magnets which, Travellers
have told us, are placed one of them in the Roof, and the other in the
Floor of Mahomet's Burying-place at Mecca, and by that means, say they,
pull the Impostor's Iron Coffin with such an equal Attraction, that it
hangs in the Air between both of them. As for the Ass's Behaviour in
such nice Circumstances, whether he would Starve sooner than violate his
Neutrality to the two Bundles of Hay, I shall not presume to determine;
but only take Notice of the Conduct of our own Species in the same
Perplexity. When a Man has a mind to venture his Money in a Lottery,
every Figure of it appears equally alluring, and as likely to succeed as
any of its Fellows. They all of them have the same Pretensions to good
Luck, stand upon the same foot of Competition, and no manner of Reason
can be given why a Man should prefer one to the other before the Lottery
is drawn. In this Case therefore Caprice very often acts in the Place of
Reason, and forms to it self some Groundless Imaginary Motive, where
real and substantial ones are wanting. I know a well-meaning Man that is
very well pleased to risque his good Fortune upon the Number 1711,
because it is the Year of our Lord.
am acquainted with a Tacker that
would give a good deal for the Number 134
. On the contrary I have
been told of a certain Zealous Dissenter, who being a great Enemy to
Popery, and believing that bad Men are the most fortunate in this World,
will lay two to one
the Number
666
against any other Number,
because, says he, it is the Number of the Beast. Several would prefer
the Number 12 000 before any other, as it is the Number of the Pounds in
the great Prize. In short, some are pleased to find their own Age in
their Number; some that they have got a number which makes a pretty
Appearance in the Cyphers, and others, because it is the same Number
that succeeded in the last Lottery. Each of these, upon no other
Grounds, thinks he stands fairest for the great Lot, and that he is
possessed of what may not be improperly called the Golden Number.
These Principles of Election are the Pastimes and Extravagancies of
Human Reason, which is of so busie a Nature, that it will be exerting it
self in the meanest Trifles and working even when it wants Materials.
The wisest of Men are sometimes acted by such unaccountable Motives, as
the Life of the Fool and the Superstitious is guided by nothing else.
I am surprized that none of the Fortune-tellers, or, as the French call
them, the Diseurs de bonne Avanture, who Publish their Bills in every
Quarter of the Town, have not turned our Lotteries to their Advantage;
did any of them set up for a Caster of fortunate Figures, what might he
not get by his pretended Discoveries and Predictions?
I remember among the Advertisements in the Post-Boy of September the
27th, I was surprized to see the following one:
This is to give notice, That Ten Shillings over and above the
Market-Price, will be given for the Ticket in the £1 500 000 Lottery,
No. 132, by Nath. Cliff at the Bible and Three Crowns in Cheapside.
This Advertisement has given great Matter of Speculation to Coffee-house
Theorists. Mr. Cliff's Principles and Conversation have been canvassed
upon this Occasion, and various Conjectures made why he should thus set
his Heart upon Number 132. I have examined all the Powers in those
Numbers, broken them into Fractions, extracted the Square and Cube Root,
divided and multiplied them all Ways, but could not arrive at the Secret
till about three Days ago, when I received the following Letter from an
unknown Hand, by which I find that Mr. Nathaniel Cliff is only the
Agent, and not the Principal, in this Advertisement.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am the Person that lately advertised I would give ten Shillings
more than the current Price for the Ticket No. 132 in the Lottery now
drawing; which is a Secret I have communicated to some Friends, who
rally me incessantly upon that Account. You must know I have but one
Ticket, for which Reason, and a certain Dream I have lately had more
than once, I was resolved it should be the Number I most approved. I
am so positive I have pitched upon the great Lot, that I could almost
lay all I am worth of it. My Visions are so frequent and strong upon
this Occasion, that I have not only possessed the Lot, but disposed of
the Money which in all probability it will sell for. This Morning, in
particular, I set up an Equipage which I look upon to be the gayest in
the Town. The Liveries are very Rich, but not Gaudy. I should be very
glad to see a Speculation or two upon lottery Subjects, in which you
would oblige all People concerned, and in particular
'Your most humble Servant,
'George Gossling.
'P.S. Dear Spec, if I get the 12 000 Pound, I'll make thee a handsome
Present.'
After having wished my Correspondent good Luck, and thanked him for his
intended Kindness, I shall for this time dismiss the Subject of the
Lottery, and only observe that the greatest Part of Mankind are in some
degree guilty of my Friend Gossling's Extravagance. We are apt to rely
upon future Prospects, and become really expensive while we are only
rich in Possibility. We live up to our Expectations, not to our
Possessions, and make a Figure proportionable to what we may be, not
what we are. We out-run our present Income, as not doubting to disburse
our selves out of the Profits of some future Place, Project, or
Reversion, that we have in view. It is through this Temper of Mind,
which is so common among us, that we see Tradesmen break, who have met
with no Misfortunes in their Business; and Men of Estates reduced to
Poverty, who have never suffered from Losses or Repairs, Tenants, Taxes,
or Law-suits. In short, it is this foolish sanguine Temper, this
depending upon Contingent Futurities, that occasions Romantick
Generosity, Chymerical Grandeur, Senseless Ostentation, and generally
ends in Beggary and Ruin. The Man, who will live above his present
Circumstances, is in great Danger of living in a little time much
beneath them, or, as the Italian Proverb runs, The Man who lives by Hope
will die by Hunger.
It should be an indispensable Rule in Life, to contract our Desires to
our present Condition, and whatever may be our Expectations, to live
within the compass of what we actually possess. It will be Time enough
to enjoy an Estate when it comes into our Hands; but if we anticipate
our good Fortune, we shall lose the Pleasure of it when it arrives, and
may possibly never possess what we have so foolishly counted upon.
L.
The number of the minority who were in 1704 for Tacking a
Bill against Occasional Conformity to a Money Bill.
"1666", and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Wednesday,
October 10, 1711 |
Steele |
... Uni ore omnes omnia
Bona dicere, et Laudare fortunas meas,
Qui Gnatum haberem tali ingenio prœditum.
Ter.

I Stood the other Day, and beheld a Father sitting in the Middle of a
Room with a large Family of Children about him; and methought I could
observe in his Countenance different Motions of Delight, as he turned
his Eye towards the one and the other of them. The Man is a Person
moderate in his Designs for their Preferment and Welfare; and as he has
an easy Fortune, he is not sollicitous to make a great one. His eldest
Son is a Child of a very towardly Disposition, and as much as the Father
loves him, I dare say he will never be a Knave to improve his Fortune. I
do not know any Man who has a juster Relish of Life than the Person I am
speaking of, or keeps a better Guard against the Terrors of Want or the
Hopes of Gain. It is usual in a Crowd of Children, for the Parent to
name out of his own Flock all the great Officers of the Kingdom. There
is something so very surprizing in the Parts of a Child of a Man's own,
that there is nothing too great to be expected from his Endowments. I
know a good Woman who has but three Sons, and there is, she says,
nothing she expects with more Certainty, than that she shall see one of
them a Bishop, the other a Judge, and the third a Court Physician. The
Humour is, that any thing which can happen to any Man's Child, is
expected by every Man for his own. But my Friend whom I was going to
speak of, does not flatter himself with such vain Expectations, but has
his Eye more upon the Virtue and Disposition of his Children, than their
Advancement or Wealth. Good Habits are what will certainly improve a
Man's Fortune and Reputation; but on the other side, Affluence of
Fortune will not as probably produce good Affections of the Mind.
It is very natural for a Man of a kind Disposition to amuse himself with
the Promises his Imagination makes to him of the future Condition of his
Children, and to represent to himself the Figure they shall bear in the
World after he has left it. When his Prospects of this Kind are
agreeable, his Fondness gives as it were a longer
to his own Life;
and the Survivorship of a worthy Man
in
his Son is a Pleasure
scarce inferior to the Hopes of the Continuance of his own Life. That
Man is happy who can believe of his Son, that he will escape the Follies
and Indiscretions of which he himself was guilty, and pursue and improve
every thing that was valuable in him. The Continuance of his Virtue is
much more to be regarded than that of his Life; but it is the most
lamentable of all Reflections, to think that the Heir of a Man's Fortune
is such a one as will be a Stranger to his Friends, alienated from the
same Interests, and a Promoter of every thing which he himself
disapproved. An Estate in Possession of such a Successor to a good Man,
is worse than laid waste; and the Family of which he is the Head, is in
a more deplorable Condition than that of being extinct.
When I visit the agreeable Seat of my honoured Friend Ruricola, and walk
from Room to Room revolving many pleasing Occurrences, and the
Expressions of many just Sentiments I have heard him utter, and see the
Booby his Heir in Pain while he is doing the Honours of his House to the
Friend of his Father, the Heaviness it gives one is not to be expressed.
Want of Genius is not to be imputed to any Man, but Want of Humanity is
a Man's own Fault. The Son of Ruricola, (whose Life was one continued
Series of worthy Actions and Gentleman-like Inclinations) is the
Companion of drunken Clowns, and knows no Sense of Praise but in the
Flattery he receives from his own Servants; his Pleasures are mean and
inordinate, his
base and filthy,
his
Behaviour rough and
absurd. Is this Creature to be accounted the Successor of a Man of
Virtue, Wit and Breeding? At the same time that I have this melancholy
Prospect at the House where I miss my old Friend, I can go to a
Gentleman's not far off it, where he has a Daughter who is the Picture
both of his Body and Mind, but both improved with the Beauty and Modesty
peculiar to her Sex. It is she who supplies the Loss of her Father to
the World; she, without his Name or Fortune, is a truer Memorial of him,
than her Brother who succeeds him in both. Such an Offspring as the
eldest Son of my Friend, perpetuates his Father in the same manner as
the Appearance of his Ghost would: It is indeed Ruricola, but it is
Ruricola grown frightful.
I know not to what to attribute the brutal Turn which this young Man has
taken, except it may be to a certain Severity and Distance which his
Father used towards him, and might, perhaps, have occasioned a Dislike
to those Modes of Life which were not made amiable to him by Freedom and
Affability.
We may promise our selves that no such Excrescence will appear in the
Family of the Cornelii, where the Father lives with his Sons like their
eldest Brother, and the Sons converse with him as if they did it for no
other Reason but that he is the wisest Man of their Acquaintance. As the
Cornelii are eminent Traders, their good Correspondence with each other
is useful to all that know them, as well as to themselves: And their
Friendship, Good-will and kind Offices, are disposed of jointly as well
as their Fortune, so that no one ever obliged one of them, who had not
the Obligation multiplied in Returns from them all.
It is the most beautiful Object the Eyes of Man can behold, to see a Man
of Worth and his Son live in an entire unreserved Correspondence. The
mutual Kindness and Affection between them give an inexpressible
Satisfaction to all who know them. It is a sublime Pleasure which
encreases by the Participation. It is as sacred as Friendship, as
pleasurable as Love, and as joyful as Religion. This State of Mind does
not only dissipate Sorrow, which would be extream without it, but
enlarges Pleasures which would otherwise be contemptible. The most
indifferent thing has its Force and Beauty when it is spoke by a kind
Father, and an insignificant Trifle has it's Weight when offered by a
dutiful Child. I know not how to express it, but I think I may call it a
transplanted Self-love. All the Enjoyments and Sufferings which a Man
meets with are regarded only as they concern him in the Relation he has
to another. A Man's very Honour receives a new Value to him, when he
thinks that, when he is in his Grave, it will be had in Remembrance that
such an Action was done by such a one's Father. Such Considerations
sweeten the old Man's Evening, and his Soliloquy delights him when he
can say to himself, No Man can tell my Child his Father was either
unmerciful or unjust: My Son shall meet many a Man who shall say to him,
I was obliged to thy Father, and be my Child a Friend to his Child for
ever.
It is not in the Power of all Men to leave illustrious Names or great
Fortunes to their Posterity, but they can very much conduce to their
having Industry, Probity, Valour and Justice: It is in every Man's Power
to leave his Son the Honour of descending from a virtuous Man, and add
the Blessings of Heaven to whatever he leaves him. I shall end this
Rhapsody with a Letter to an excellent young Man of my Acquaintance, who
has lately lost a worthy Father.
Dear Sir,
'I know no Part of Life more impertinent than the Office of
administring Consolation: I will not enter into it, for I cannot but
applaud your Grief. The virtuous Principles you had from that
excellent Man whom you have lost, have wrought in you as they ought,
to make a Youth of Three and Twenty incapable of Comfort upon coming
into Possession of a great Fortune. I doubt not but that you will
honour his Memory by a modest Enjoyment of his Estate; and scorn to
triumph over his Grave, by employing in Riot, Excess, and Debauchery,
what he purchased with so much Industry, Prudence, and Wisdom. This is
the true Way to shew the Sense you have of your Loss, and to take away
the Distress of others upon the Occasion. You cannot recal your Father
by your Grief, but you may revive him to his Friends by your Conduct.'
T.
"to", and in the first reprint.
and his
Contents
|
Thursday,
October 11, 1711 |
Steele |
... Ingentem foribus domus alta superbis
Mane salutantum totis vomit œdibus undam.
Virg.

When we look round us, and behold the strange Variety of Faces and
Persons which fill the Streets with Business and Hurry, it is no
unpleasant Amusement to make Guesses at their different Pursuits, and
judge by their Countenances what it is that so anxiously engages their
present Attention. Of all this busie Crowd, there are none who would
give a Man inclined to such Enquiries better Diversion for his Thoughts,
than those whom we call good Courtiers, and such as are assiduous at the
Levées of Great Men. These Worthies are got into an Habit of being
servile with an Air, and enjoy a certain Vanity in being known for
understanding how the World passes. In the Pleasure of this they can
rise early, go abroad sleek and well-dressed, with no other Hope or
Purpose, but to make a Bow to a Man in Court-Favour, and be thought, by
some insignificant Smile of his, not a little engaged in his Interests
and Fortunes. It is wondrous, that a Man can get over the natural
Existence and Possession of his own Mind so far, as to take Delight
either in paying or receiving such cold and repeated Civilities. But
what maintains the Humour is, that outward Show is what most Men pursue,
rather than real Happiness. Thus both the Idol and Idolater equally
impose upon themselves in pleasing their Imaginations this way. But as
there are very many of her Majesty's good Subjects, who are extreamly
uneasie at their own Seats in the Country, where all from the Skies to
the Centre of the Earth is their own, and have a mighty longing to shine
in Courts, or be Partners in the Power of the World; I say, for the
Benefit of these, and others who hanker after being in the Whisper with
great Men, and vexing their Neighbours with the Changes they would be
capable of making in the Appearance at a Country Sessions, it would not
methinks be amiss to give an Account of that Market for Preferment, a
great Man's Levée.
For ought I know, this Commerce between the Mighty and their Slaves,
very justly represented, might do so much good as to incline the Great
to regard Business rather than Ostentation; and make the Little know the
Use of their Time too well, to spend it in vain Applications and
Addresses.
The famous Doctor in
Moorfields
, who gained so much Reputation
for his Horary Predictions, is said to have had in his Parlour different
Ropes to little Bells which hung in the Room above Stairs, where the
Doctor thought fit to be oraculous. If a Girl had been deceived by her
Lover, one Bell was pulled; and if a Peasant had lost a
, the
Servant
rung another. This Method was kept in respect to all other
Passions and Concerns, and
sifted the
Enquirer, and gave the Doctor Notice accordingly. The Levée of a great
Man is laid after the same manner, and twenty Whispers, false Alarms,
and private Intimations, pass backward and forward from the Porter, the
Valet, and the Patron himself, before the gaping Crew who are to pay
their Court are gathered together: When the Scene is ready, the Doors
fly open and discover his Lordship.
There are several Ways of making this first Appearance: you may be
either half dressed, and washing your self, which is indeed the most
stately; but this Way of Opening is peculiar to Military Men, in whom
there is something graceful in exposing themselves naked; but the
Politicians, or Civil Officers, have usually affected to be more
reserved, and preserve a certain Chastity of Deportment. Whether it be
Hieroglyphical or not, this Difference in the Military and
List,
I will not say;
but
have
ever understood the Fact to be, that
the close Minister is buttoned up, and the brave Officer open-breasted
on these Occasions.
However that is, I humbly conceive the Business of a Levée is to receive
the Acknowledgments of a Multitude, that a
is Wise,
Bounteous
,
Valiant and Powerful. When the first Shot of Eyes
is
made, it is
wonderful to observe how much Submission the Patron's Modesty can bear,
and how much Servitude the Client's Spirit can descend to. In the vast
Multiplicity of Business, and the Crowd about him, my Lord's Parts are
usually so great, that, to the Astonishment of the whole Assembly, he
has something to say to every Man there, and that so suitable to his
Capacity, as any Man may judge that it is not without Talents that Men
can arrive at great Employments. I have known a great Man ask a
Flag-Officer, which way was the Wind, a Commander of Horse the present
Price of Oats, and a Stock-jobber at what Discount such a Fund was, with
as much Ease as if he had been bred to each of those several Ways of
Life. Now this is extreamly obliging; for at the same time that the
Patron informs himself of Matters, he gives the Person of whom he
enquires an Opportunity to exert himself. What adds to the Pomp of those
Interviews is, that it is performed with the greatest Silence and Order
Imaginable. The Patron is usually in the midst of the Room, and some
humble Person gives him a Whisper, which his Lordship answers aloud, It
is well. Yes, I am of your Opinion. Pray inform yourself further, you
may be sure of my Part in it. This happy Man is dismissed, and my Lord
can turn himself to a Business of a quite different Nature, and offhand
give as good an Answer as any great Man is obliged to. For the chief
Point is to keep in Generals, and if there be any thing offered that's
Particular, to be in haste.
But we are now in the Height of the Affair, and my Lord's Creatures have
all had their Whispers round to keep up the Farce of the thing, and the
Dumb Show is become more general. He casts his Eye to that Corner, and
there to Mr. such-a-one; to the other, and when did you come to Town?
And perhaps just before he nods to another, and enters with him, but,
Sir, I am glad to see you, now I think of it. Each of those are happy
for the next four and twenty Hours; and those who bow in Ranks
undistinguished, and by Dozens at a Time, think they have very good
Prospects if they hope to arrive at such Notices half a Year hence.
Satyrist says
, there is seldom common Sense in high Fortune; and
one would think, to behold a Levée, that the Great were not only
infatuated with their Station, but also that they believed all below
were seized too; else how is it possible that they could think of
imposing upon themselves and others in such a degree, as to set up a
Levée for any thing but a direct Farce? But such is the Weakness of our
Nature, that when Men are a little exalted in their Condition, they
immediately conceive they have additional Senses, and their Capacities
enlarged not only above other Men, but above human Comprehension it
self. Thus it is ordinary to see a great Man attend one listning, bow to
one at a distance, and call to a third at the same instant. A Girl in
new Ribbands is not more taken with her self, nor does she betray more
apparent Coquetries, than even a wise Man in such a Circumstance of
Courtship. I do not know any thing that I ever thought so very
distasteful as the Affectation which is recorded of Cæsar, to wit, that
he would dictate to three several Writers at the same time. This was an
Ambition below the Greatness and Candour of his Mind. He indeed (if any
Man had Pretensions to greater Faculties than any other Mortal) was the
Person; but such a Way of acting is Childish, and inconsistent with the
Manner of our Being. And it appears from the very Nature of Things, that
there cannot be any thing effectually dispatched in the Distraction of a
Publick Levée: but the whole seems to be a Conspiracy of a Set of
Servile Slaves, to give up their own Liberty to take away their Patron's
Understanding.
T.
Rope
a skilful servant
I have
Beauteous, and in first reprint.
are
Juvenal, viii, 73.
Contents
|
Friday,
October 12, 1711 |
Steele |
... Difficili Bile Tumet Jecur.
Hor.

The present Paper shall consist of two Letters, which observe upon
Faults that are easily cured both in Love and Friendship. In the latter,
as far as it meerly regards Conversation, the Person who neglects
visiting an agreeable Friend is punished in the very Transgression; for
a good Companion is not found in every Room we go into. But the Case of
Love is of a more delicate Nature, and the Anxiety is inexpressible if
every little Instance of Kindness is not reciprocal. There are Things in
this Sort of Commerce which there are not Words to express, and a Man
may not possibly know how to represent, what yet may tear his Heart into
ten thousand Tortures. To be grave to a Man's Mirth, unattentive to his
Discourse, or to interrupt either with something that argues a
Disinclination to be entertained by him, has in it something so
disagreeable, that the utmost Steps which may be made in further Enmity
cannot give greater Torment. The gay
Corinna
, who sets up for an
Indifference and becoming Heedlessness, gives her Husband all the
Torment imaginable out of meer Insolence, with this peculiar Vanity,
that she is to look as gay as a Maid in the Character of a Wife. It is
no Matter what is the Reason of a Man's Grief, if it be heavy as it is.
Her unhappy Man is convinced that she means him no Dishonour, but pines
to Death because she will not have so much Deference to him as to avoid
the Appearances of it. The Author of the following Letter is perplexed
with an Injury that is in a Degree yet less criminal, and yet the Source
of the utmost Unhappiness.
Mr. Spectator,
I have read your Papers which relate to Jealousy, and desire your
Advice in my Case, which you will say is not common. I have a Wife, of
whose Virtue I am not in the least doubtful; yet I cannot be satisfied
she loves me, which gives me as great Uneasiness as being faulty the
other Way would do. I know not whether I am not yet more miserable
than in that Case, for she keeps Possession of my Heart, without the
Return of hers. I would desire your Observations upon that Temper in
some Women, who will not condescend to convince their Husbands of
their Innocence or their Love, but are wholly negligent of what
Reflections the poor Men make upon their Conduct (so they cannot call
it Criminal,) when at the same time a little Tenderness of Behaviour,
or Regard to shew an Inclination to please them, would make them
Entirely at Ease. Do not such Women deserve all the Misinterpretation
which they neglect to avoid? Or are they not in the actual Practice of
Guilt, who care not whether they are thought guilty or not? If my Wife
does the most ordinary thing, as visiting her Sister, or taking the
Air with her Mother, it is always carried with the Air of a Secret:
Then she will sometimes tell a thing of no Consequence, as if it was
only Want of Memory made her conceal it before; and this only to dally
with my Anxiety. I have complained to her of this Behaviour in the
gentlest Terms imaginable, and beseeched her not to use him, who
desired only to live with her like an indulgent Friend, as the most
morose and unsociable Husband in the World. It is no easy Matter to
describe our Circumstance, but it is miserable with this Aggravation,
That it might be easily mended, and yet no Remedy endeavoured. She
reads you, and there is a Phrase or two in this Letter which she will
know came from me. If we enter into an Explanation which may tend to
our future Quiet by your Means, you shall have our joint Thanks: In
the mean time I am (as much as I can in this ambiguous Condition be
any thing) Sir,
Your humble Servant.
Mr. Spectator,
'Give me Leave to make you a Present of a Character not yet described
in your Papers, which is that of a Man who treats his Friend with the
same odd Variety which a Fantastical Female Tyrant practises towards
her Lover. I have for some time had a Friendship with one of these
Mercurial Persons: The Rogue I know loves me, yet takes Advantage of
my Fondness for him to use me as he pleases. We are by Turns the best
Friends and the greatest Strangers imaginable; Sometimes you would
think us inseparable; at other Times he avoids me for a long Time, yet
neither he nor I know why. When we meet next by Chance, he is amazed
he has not seen me, is impatient for an Appointment the same Evening:
and when I expect he should have kept it, I have known him slip away
to another Place; where he has sat reading the News, when there is no
Post; smoaking his Pipe, which he seldom cares for; and staring about
him in Company with whom he has had nothing to do, as if he wondered
how he came there.
That I may state my Case to you the more fully, I shall transcribe
some short Minutes I have taken of him in my Almanack since last
Spring; for you must know there are certain Seasons of the Year,
according to which, I will not say our Friendship, but the Enjoyment
of it rises or falls. In March and April he was as
various as the Weather; In May and part of June I found
him the sprightliest best-humoured Fellow in the World; In the
Dog-Days he was much upon the Indolent; In September very
agreeable but very busy; and since the Glass fell last to changeable,
he has made three Appointments with me, and broke them every one.
However I have good Hopes of him this Winter, especially if you will
lend me your Assistance to reform him, which will be a great Ease and
Pleasure to,
Sir, Your most humble Servant. October 9, 1711.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday,
October 13, 1711 |
Addison |
is a Story in the
Arabian Nights Tales
of a King who
had long languished under an ill Habit of Body, and had taken abundance
of Remedies to no purpose. At length, says the Fable, a Physician cured
him by the following Method: He took an hollow Ball of Wood, and filled
it with several Drugs; after which he clos'd it up so artificially that
nothing appeared. He likewise took a Mall, and after having hollowed the
Handle, and that part which strikes the Ball, he enclosed in them
several Drugs after the same Manner as in the Ball it self. He then
ordered the Sultan, who was his Patient, to exercise himself early in
the Morning with these
rightly prepared
Instruments, till such
time as he should Sweat: When, as the Story goes, the Vertue of the
Medicaments perspiring through the Wood, had so good an Influence on the
Sultan's Constitution, that they cured him of an Indisposition which all
the Compositions he had taken inwardly had not been able to remove. This
Eastern Allegory is finely contrived to shew us how beneficial bodily
Labour is to Health, and that Exercise is the most effectual Physick. I
have described in
, from the general
Structure and Mechanism of an Human Body, how absolutely necessary
Exercise is for its Preservation. I shall in this Place recommend
another great Preservative of Health, which in many Cases produces the
same Effects as Exercise, and may, in some measure, supply its Place,
where Opportunities of Exercise are wanting. The Preservative I am
speaking of is Temperance, which has those particular Advantages above
all other Means of Health, that it may be practised by all Ranks and
Conditions, at any Season or in any Place. It is a kind of Regimen into
which every Man may put himself, without Interruption to Business,
Expence of Mony, or Loss of Time. If Exercise throws off all
Superfluities, Temperance prevents them; if Exercise clears the Vessels,
Temperance neither satiates nor overstrains them; if Exercise raises
proper Ferments in the Humours, and promotes the Circulation of the
Blood, Temperance gives Nature her full Play, and enables her to exert
her self in all her Force and Vigour; if Exercise dissipates a growing
Distemper, Temperance starves it.
Physick, for the most part, is nothing else but the Substitute of
Exercise or Temperance. Medicines are indeed absolutely necessary in
acute Distempers, that cannot wait the slow Operations of these two
great Instruments of Health; but did Men live in an habitual Course of
Exercise and Temperance, there would be but little Occasion for them.
Accordingly we find that those Parts of the World are the most healthy,
where they subsist by the Chace; and that Men lived longest when their
Lives were employed in hunting, and when they had little Food besides
what they caught. Blistering, Cupping, Bleeding, are seldom of use but
to the Idle and Intemperate; as all those inward Applications which are
so much in practice among us, are for the most part nothing else but
Expedients to make Luxury consistent with Health. The Apothecary is
perpetually employed in countermining the Cook and the Vintner.
is
said of Diogenes
, that meeting a young Man who was going to a Feast,
he took him up in the Street and carried him home to his Friends, as one
who was running into imminent Danger, had not he prevented him. What
would that Philosopher have said, had he been present at the Gluttony of
a modern Meal? Would not he have thought the Master of a Family mad, and
have begged his Servants to tie down his Hands, had he seen him devour
Fowl, Fish, and Flesh; swallow Oyl and Vinegar, Wines and Spices; throw
down Sallads of twenty different Herbs, Sauces of an hundred
Ingredients, Confections and Fruits of numberless Sweets and Flavours?
What unnatural Motions and Counterferments must such a Medley of
Intemperance produce in the Body? For my Part, when I behold a
fashionable Table set out in all its Magnificence, I fancy that I see
Gouts and Dropsies, Feavers and Lethargies, with other innumerable
Distempers lying in Ambuscade among the Dishes.
Nature delights in the most plain and simple Diet. Every Animal, but
Man, keeps to one Dish. Herbs are the Food of this Species, Fish of
that, and Flesh of a Third. Man falls upon every thing that comes in his
Way, not the smallest Fruit or Excrescence of the Earth, scarce a Berry
or a Mushroom, can escape him.
It is impossible to lay down any determinate Rule for Temperance,
because what is Luxury in one may be Temperance in another; but there
are few that have lived any time in the World, who are not Judges of
their own Constitutions, so far as to know what Kinds and what
Proportions of Food do best agree with them. Were I to consider my
Readers as my Patients, and to prescribe such a Kind of Temperance as is
accommodated to all Persons, and such as is particularly suitable to our
Climate and Way of Living, I would copy the following Rules of a very
eminent Physician. Make your whole Repast out of one Dish. If you
indulge in a second, avoid drinking any thing Strong,
you have
finished your Meal;
at
the same time abstain from all Sauces, or
at least such as are not the most plain and simple. A Man could not be
well guilty of Gluttony, if he stuck to these few obvious and easy
Rules. In the first Case there would be no Variety of Tastes to sollicit
his Palate, and occasion Excess; nor in the second any artificial
Provocatives to relieve Satiety, and create a false Appetite.
I to
prescribe a Rule for Drinking, it should be form'd upon a Saying quoted
by Sir William Temple
; The first Glass for my self, the second for
my Friends, the third for good Humour, and the fourth for mine Enemies.
But because it is impossible for one who lives in the World to diet
himself always in so Philosophical a manner, I think every Man should
have his Days of Abstinence, according as his Constitution will permit.
These are great Reliefs to Nature, as they qualifie her for struggling
with Hunger and Thirst, whenever any Distemper or Duty of Life may put
her upon such Difficulties; and at the same time give her an Opportunity
of extricating her self from her Oppressions, and recovering the several
Tones and Springs of her distended Vessels. Besides that Abstinence well
timed often kills a Sickness in Embryo, and destroys the first Seeds of
an Indisposition.
is observed by two or three Ancient Authors
,
that Socrates, notwithstanding he lived in Athens during that great
Plague, which has made so much Noise through all Ages, and has been
celebrated at different Times by such eminent Hands; I say,
notwithstanding that he lived in the time of this devouring Pestilence,
he never caught the least Infection, which those Writers unanimously
ascribe to that uninterrupted Temperance which he always observed.
And here I cannot but mention an Observation which I have often made,
upon reading the Lives of the Philosophers, and comparing them with any
Series of Kings or great Men of the same number. If we consider these
Ancient Sages, a great Part of whose Philosophy consisted in a temperate
and abstemious Course of Life, one would think the Life of a Philosopher
and the Life of a Man were of two different Dates. For we find that the
Generality of these wise Men were nearer an hundred than sixty Years of
Age at the Time of their respective Deaths. But the most remarkable
Instance of the Efficacy of Temperance towards the procuring of long
Life, is what we meet with in a little Book published by Lewis Cornare
the Venetian; which I the rather mention, because it is of undoubted
Credit, as the late Venetian Ambassador, who was of the same Family,
attested more than once in Conversation, when he resided in England.
Cornaro, who was the Author of the little Treatise I am mentioning, was
of an Infirm Constitution, till about forty, when by obstinately
persisting in an exact Course of Temperance, he recovered a perfect
State of Health;
that at fourscore he published his Book, which
has been translated into English upon the Title of
Sure and certain
Methods
of attaining a long and healthy Life. He lived to give a
3rd or 4th Edition of it, and after having passed his hundredth Year,
died without Pain or Agony, and like one who falls asleep. The Treatise
I mention has been taken notice of by several Eminent Authors, and is
written with such a Spirit of Chearfulness, Religion, and good Sense, as
are the natural Concomitants of Temperance and Sobriety. The Mixture of
the old Man in it is rather a Recommendation than a Discredit to it.
Having designed this Paper as the Sequel to that upon Exercise, I have
not here considered Temperance as it is a Moral Virtue, which I shall
make the Subject of a future Speculation, but only as it is the Means of
Health.
L.
The History of the Greek King and Douban the Physician
told by the Fisherman to the Genie in the story of
the Fisherman.
Diog. Laert.,
Lives of the Philosophers,
Bk. vi. ch. 2.
and at
Sir William Temple does not quote as a saying, but says
himself, near the end of his
Essay upon Health and Long Life of
Government of Diet and Exercise,
'In both which, all excess is to be avoided, especially in the common
use of wine: Whereof the first Glass may pass for Health, the second
for good Humour, the third for our Friends; but the fourth is for our
Enemies.'
Diogenes Laertius in
Life of Socrates
; Ælian in
Var. Hist.
Bk. xiii.
The Sure Way
Contents
|
Monday,
October 15, 1711 |
Steele |
Est Ulubris, animus si te non deficit œquus.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'There is a particular Fault which I have observed in most of the
Moralists in all Ages, and that is, that they are always professing
themselves, and teaching others to be happy. This State is not to be
arrived at in this Life, therefore I would recommend to you to talk in
an humbler Strain than your Predecessors have done, and instead of
presuming to be happy, instruct us only to be easy. The Thoughts of him
who would be discreet, and aim at practicable things, should turn upon
allaying our Pain rather than promoting our Joy. Great Inquietude is to
be avoided, but great Felicity is not to be attained. The great Lesson
is Æquanimity, a Regularity of Spirit, which is a little above
Chearfulness and below Mirth. Chearfulness is always to be supported if
a Man is out of Pain, but Mirth to a prudent Man should always be
accidental: It should naturally arise out of the Occasion, and the
Occasion seldom be laid for it; for those Tempers who want Mirth to be
pleased, are like the Constitutions which flag without the use of
Brandy. Therefore, I say, let your Precept be, Be easy. That Mind is
dissolute and ungoverned, which must be hurried out of it self by loud
Laughter or sensual Pleasure,
or else
be1 wholly unactive.
There are a Couple of old Fellows of my Acquaintance who meet every Day
and smoak a Pipe, and by their mutual Love to each other, tho' they have
been Men of Business and Bustle in the World, enjoy a greater
Tranquility than either could have worked himself into by any Chapter of
Seneca. Indolence of Body and Mind, when we aim at no more, is very
frequently enjoyed; but the very Enquiry after Happiness has something
restless in it, which a Man who lives in a Series of temperate Meals,
friendly Conversations, and easy Slumbers, gives himself no Trouble
about. While Men of Refinement are talking of Tranquility, he possesses
it.
What I would by these broken Expressions recommend to you, Mr.
Spectator, is, that you would speak of the Way of Life, which plain Men
may pursue, to fill up the Spaces of Time with Satisfaction. It is a
lamentable Circumstance, that Wisdom, or, as you call it, Philosophy,
should furnish Ideas only for the Learned; and that a Man must be a
Philosopher to know how to pass away his Time agreeably. It would
therefore be worth your Pains to place in an handsome Light the
Relations and Affinities among Men, which render their Conversation with
each other so grateful, that the highest Talents give but an impotent
Pleasure in Comparison with them. You may find Descriptions and
Discourses which will render the Fire-side of an honest Artificer as
entertaining as your own Club is to you. Good-nature has an endless
Source of Pleasure in it; and the Representation of domestick Life,
filled with its natural Gratifications, (instead of the necessary
Vexations which are generally insisted upon in the Writings of the
Witty) will be a very good Office to Society.
The Vicissitudes of Labour and Rest in the lower Part of Mankind, make
their Being pass away with that Sort of Relish which we express by the
Word Comfort; and should be treated of by you, who are a
Spectator, as
well as such Subjects which appear indeed more speculative, but are less
instructive. In a word, Sir, I would have you turn your Thoughts to the
Advantage of such as want you most; and shew that Simplicity, Innocence,
Industry and Temperance, are Arts which lead to Tranquility, as much as
Learning, Wisdom, Knowledge, and Contemplation.
I am, Sir,
Your most Humble Servant,
'T. B.'
Hackney,
October 12.2
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am the young Woman whom you did so much Justice to some time ago,
in acknowledging that I am perfect Mistress of the Fan, and use it
with the utmost Knowledge and Dexterity. Indeed the World, as
malicious as it is, will allow, that from an Hurry of Laughter I
recollect my self the most suddenly, make a Curtesie, and let fall my
Hands before me, closing my Fan at the same instant, the best of any
Woman in England. I am not a little delighted that I have had your
Notice and Approbation; and however other young Women may rally me out
of Envy, I triumph in it, and demand a Place in your Friendship. You
must therefore permit me to lay before you the present State of my
Mind. I was reading your
Spectator of the 9th Instant, and thought the
Circumstance of the Ass divided between two Bundles of Hay which
equally affected his Senses, was a lively Representation of my present
Condition: For you are to now that I am extremely enamoured with two
young Gentlemen who at this time pretend to me. One must hide nothing
when one is asking Advice, therefore I will own to you, that I am very
amorous and very covetous. My Lover
Will is very rich, and my
Lover
Tom very handsome. I can have either of them when I
please; but when I debate the Question in my own Mind, I cannot take
Tom for fear of losing
Will's Estate, nor enter upon
Will's Estate, and bid adieu to
Tom's Person. I am very
young, and yet no one in the World, dear Sir, has the main Chance more
in her Head than myself.
Tom is the gayest, the blithest
Creature! He dances well, is very civil, and diverting at all Hours
and Seasons. Oh, he is the Joy of my Eyes! But then again
Will
is so very rich and careful of the Main. How many pretty Dresses does
Tom appear in to charm me! But then it immediately occurs to
me, that a Man of his Circumstances is so much the poorer. Upon the
whole I have at last examined both these Desires of Loves and Avarice,
and upon strictly weighing the Matter I begin to think I shall be
covetous longer than fond; therefore if you have nothing to say to the
contrary, I shall take
Will. Alas, poor
Tom!
Your Humble Servant,
Biddy Loveless.
T.
is
the 12th of October.
Contents
|
Tuesday,
October 16, 1711 |
Budgell |
Alter rixatur de lanâ sæpe caprinâ,
Propugnat nugis armatus: scilicet, ut non
Sit mihi prima fides; et vere quod placet, ut non
Acriter elatrem, pretium ætas altera sordet.
Ambigitur quid enim? Castor sciat an Docilis plus,
Brundusium Numici melius via ducat an Appî.
Hor.

Every Age a Man passes through, and Way of Life he engages in, has some
particular Vice or Imperfection naturally cleaving to it, which it wil
require his nicest Care to avoid. The several Weaknesses, to which
Youth, Old Age and Manhood are exposed, have long since been set down by
many both of the Poets and Philosophers; but I do not remember to have
met with any Author who has treated of those ill Habits Men are subject
to, not so much by reason of their different Ages and Tempers, as the
particular Profession or Business in which they were educated and
brought up.
I am the more surprised to find this Subject so little touched on, since
what I am here speaking of is so apparent as not to escape the most
vulgar Observation. The Business Men are chiefly conversant in, does not
only give a certain Cast or Turn to their Minds, but is very often
apparent in their outward Behaviour, and some of the most indifferent
Actions of their Lives. It is this Air diffusing itself over the whole
Man, which helps us to find out a Person at his first Appearance; so
that the most careless Observer fancies he can scarce be mistaken in the
Carriage of a Seaman or the Gaite of a Taylor.
The liberal Arts, though they may possibly have less Effect on our
external Mein and Behaviour, make so deep an Impression on the Mind, as
is very apt to bend it wholly one Way.
The Mathematician will take little less than Demonstration in the most
common Discourse, and the Schoolman is as great a Friend to Definitions
and Syllogisms. The Physician and Divine are often heard to dictate in
private Companies with the same Authority which they exercise over their
Patients and Disciples; while the Lawyer is putting Cases and raising
Matter for Disputation out of every thing that occurs.
I may possibly some time or other animadvert more at large on the
particular Fault each Profession is most infected with; but shall at
present wholly apply my self to the Cure of what I last mentioned,
namely, That Spirit of Strife and Contention in the Conversations of
Gentlemen of the Long Robe.
This is the more ordinary, because these Gentlemen regarding Argument as
their own proper Province, and very often making ready Money of it,
think it unsafe to yield before Company. They are shewing in common Talk
how zealously they could defend a Cause in Court, and therefore
frequently forget to keep that Temper which is absolutely requisite to
render Conversation pleasant and instructive.
Captain Sentry
pushes this Matter so far, that I have heard him say,
He has known but few Pleaders that were tolerable Company
.
The Captain, who is a Man of good Sense, but dry Conversation, was last
Night giving me an Account of a Discourse, in which he had lately been
engaged with a young Wrangler in the Law. I was giving my Opinion, says
the Captain, without apprehending any Debate that might arise from it,
of a General's Behaviour in a Battle that was fought some Years before
either the Templer or my self were born. The young Lawyer immediately
took me up, and by reasoning above a Quarter of an Hour upon a Subject
which I saw he understood nothing of, endeavoured to shew me that my
Opinions were ill grounded. Upon which, says the Captain, to avoid any
farther Contests, I told him, That truly I had not consider'd those
several Arguments which he had brought against me; and that there might
be a great deal in them. Ay, but says my Antagonist, who would not let
me escape so, there are several Things to be urged in favour of your
Opinion which you have omitted, and thereupon begun to shine on the
other Side of the Question. Upon this, says the Captain, I came over to
my first Sentiments, and entirely acquiesced in his Reasons for my so
doing. Upon which the Templer again recovered his former Posture, and
confuted both himself and me a third Time. In short, says my Friend, I
found he was resolved to keep me at Sword's Length, and never let me
close with him,
that I had nothing left but to hold my tongue, and
give my Antagonist free leave to smile at his Victory, who I found, like
Hudibras, could still change Sides, and still confute
.
For my own part, I have ever regarded our Inns of Courts as Nurseries of
Statesmen and Law-givers, which makes me often frequent that Part of the
Town with great Pleasure.
Upon my calling in lately at one of the most noted
Temple
Coffee-houses, I found the whole Room, which was full of young Students,
divided into several Parties, each of which was deeply engaged in some
Controversie. The Management of the late Ministry was attacked and
defended with great Vigour; and several Preliminaries to the Peace were
proposed by some, and rejected by others; the demolishing of
Dunkirk
was so eagerly insisted on, and so warmly controverted,
as had like to have produced a Challenge. In short, I observed that the
Desire of Victory, whetted with the little Prejudices of Party and
Interest, generally carried the Argument to such an Height, as made the
Disputants insensibly conceive an Aversion towards each other, and part
with the highest Dissatisfaction on both Sides.
The managing an Argument handsomely being so nice a Point, and what I
have seen so very few excel in, I shall here set down a few Rules on
that Head, which, among other things, I gave in writing to a young
Kinsman of mine who had made so great a Proficiency in the Law, that he
began to plead in Company upon every Subject that was started.
Having the entire Manuscript by me, I may, perhaps, from time to time,
publish such Parts of it as I shall think requisite for the Instruction
of the
British
Youth. What regards my present Purpose is as
follows:
Avoid Disputes as much as possible. In order to appear easie and
well-bred in Conversation, you may assure your self that it requires
more Wit, as well as more good Humour, to improve than to contradict the
Notions of another: But if you are at any time obliged to enter on an
Argument, give your Reasons with the utmost Coolness and Modesty, two
Things which scarce ever fail of making an Impression on the Hearers.
Besides, if you are neither Dogmatical, nor shew either by your Actions
or Words, that you are full of your self, all will the more heartily
rejoice at your Victory. Nay, should you be pinched in your Argument,
you may make your Retreat with a very good Grace: You were never
positive, and are now glad to be better informed. This has made some
approve the Socratical Way of Reasoning, where while you scarce affirm
any thing, you can hardly be caught in an Absurdity; and tho' possibly
you are endeavouring to bring over another to your Opinion, which is
firmly fix'd, you seem only to desire Information from him.
In order to keep that
, which
is
so difficult, and yet so
necessary to preserve, you may please to consider, that nothing can be
more unjust or ridiculous, than to be angry with another because he is
not of your Opinion. The Interests, Education, and Means by which Men
attain their Knowledge, are so very different, that it is impossible
they should all think alike; and he has at least as much Reason to be
angry with you, as you with him. Sometimes to keep your self cool, it
may be of Service to ask your self fairly, What might have been your
Opinion, had you all the Biasses of Education and Interest your
Adversary may possibly have? but if you contend for the Honour of
Victory alone, you may lay down this as an Infallible Maxim. That you
cannot make a more false Step, or give your Antagonists a greater
Advantage over you, than by falling into a Passion.
When an Argument is over, how many weighty Reasons does a Man recollect,
which his Heat and Violence made him utterly forget?
It is yet more absurd to be angry with a Man because he does not
apprehend the Force of your Reasons, or gives weak ones of his own. If
you argue for Reputation, this makes your Victory the easier; he is
certainly in all respects an Object of your Pity, rather than Anger; and
if he cannot comprehend what you do, you ought to thank Nature for her
Favours, who has given you so much the clearer Understanding.
You may please to add this Consideration, That among your Equals no one
values your Anger, which only preys upon its Master; and perhaps you may
find it not very consistent either with Prudence or your Ease, to punish
your self whenever you meet with a Fool or a Knave.
Lastly, If you propose to your self the true End of Argument, which is
Information, it may be a seasonable Check to your Passion; for if you
search purely after Truth,'twill be almost indifferent to you where you
find it. I cannot in this Place omit an Observation which I have often
made, namely, That nothing procures a Man more Esteem and less Envy from
the whole Company, than if he chooses the Part of Moderator, without
engaging directly on either Side in a Dispute. This gives him the
Character of Impartial, furnishes him with an Opportunity of sifting
Things to the Bottom, shewing his Judgment, and of sometimes making
handsome Compliments to each of the contending Parties.
I shall close this Subject with giving you one Caution: When you have
gained a Victory, do not push it too far; 'tis sufficient to let the
Company and your Adversary see 'tis in your Power, but that you are too
generous to make use of it.
X.
Part I., canto i., v. 69, 70.
"it is", and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Wednesday,
October 17, 1711 |
Addison |
Cervæ luporum præda rapacium
Sectamur ultro, quos opimus
Fallere et effugere est triumphus.
Hor.

There is a Species of Women, whom I shall distinguish by the Name of
Salamanders. Now a Salamander is a kind of Heroine in Chastity, that
treads upon Fire, and lives in the Midst of Flames without being hurt. A
Salamander knows no Distinction of Sex in those she converses with,
grows familiar with a Stranger at first Sight, and is not so
narrow-spirited as to observe whether the Person she talks to be in
Breeches or Petticoats. She admits a Male Visitant to her Bed-side,
plays with him a whole Afternoon at Pickette, walks with him two or
three Hours by Moon-light; and is extreamly Scandalized at the
unreasonableness of an Husband, or the severity of a Parent, that would
debar the Sex from such innocent Liberties. Your Salamander is therefore
a perpetual Declaimer against Jealousie, and Admirer of the
French
Good-breeding, and a great Stickler for Freedom in
Conversation. In short, the Salamander lives in an invincible State of
Simplicity and Innocence: Her Constitution is
preserv'd
in a kind
of natural Frost; she wonders what People mean by Temptation; and defies
Mankind to do their worst. Her Chastity is engaged in a constant
Ordeal
, or fiery Tryal: (
good Queen
Emma
,) the
pretty Innocent walks blindfold among burning Ploughshares, without
being scorched or singed by them.
It is not therefore for the Use of the Salamander, whether in a married
or single State of Life, that I design the following Paper; but for such
Females only as are made of Flesh and Blood, and find themselves subject
to Human Frailties.
As for this Part of the fair Sex who are not of the Salamander Kind, I
would most earnestly advise them to observe a quite different Conduct in
their Behaviour; and to avoid as much as possible what Religion calls
Temptations
, and the World
Opportunities
. Did they but
know how many Thousands of their Sex have been gradually betrayed from
innocent Freedoms to Ruin and Infamy; and how many Millions of ours have
begun with Flatteries, Protestations and Endearments, but ended with
Reproaches, Perjury, and Perfidiousness; they would shun like Death the
very first Approaches of one that might lead them into inextricable
Labyrinths of Guilt and Misery.
must so far give up the Cause of the
Male World, as to exhort the Female Sex in the Language of
Chamont
in the
Orphan
;
Trust not a Man, we are by Nature False,
Dissembling, Subtle, Cruel, and Unconstant:
When a Man talks of Love, with Caution trust him:
But if he Swears, he'll certainly deceive thee.
might very much enlarge upon this Subject, but shall conclude it with
a Story which I lately heard from one of our
Spanish
Officers
, and which may shew the Danger a Woman incurs by too great
Familiarities with a Male Companion.
An Inhabitant of the Kingdom of
Castile
, being a Man of more than
ordinary Prudence, and of a grave composed Behaviour, determined about
the fiftieth Year of his Age to enter upon Wedlock.
order to make
himself easy in it, he cast his Eye upon a young Woman who had nothing
to recommend her but her Beauty and her Education, her Parents having
been reduced to great Poverty by the Wars,
which
for some Years
have laid that whole Country waste. The
Castilian
having made his
Addresses to her and married her, they lived together in perfect
Happiness for some time; when at length the Husband's Affairs made it
necessary for him to take a Voyage to the Kingdom of
Naples
,
where a great Part of his Estate lay. The Wife loved him too tenderly to
be left behind him. They had not been a Shipboard above a Day, when they
unluckily fell into the Hands of an
Algerine
Pirate, who carried
the whole Company on Shore, and made them Slaves. The
Castilian
and his Wife had the Comfort to be under the same Master; who seeing how
dearly they loved one another, and gasped after their Liberty, demanded
a most exorbitant Price for their Ransom. The
Castilian
, though
he would rather have died in Slavery himself, than have paid such a Sum
as he found would go near to ruin him, was so moved with Compassion
towards his Wife, that he sent repeated Orders to his Friend in
Spain
, (who happened to be his next Relation) to sell his Estate,
and transmit the Money to him. His Friend hoping that the Terms of his
Ransom might be made more reasonable, and unwilling to sell an Estate
which he himself had some Prospect of inheriting, formed so many delays,
that three whole Years passed away without any thing being done for the
setting of them at Liberty.
There happened to live a
French
Renegado in the same Place where
the
Castilian
and his Wife were kept Prisoners. As this Fellow
had in him all the Vivacity of his Nation, he often entertained the
Captives with Accounts of his own Adventures; to which he sometimes
added a Song or a Dance, or some other Piece of Mirth,
divert them
during
their Confinement. His Acquaintance with the Manners of the
Algerines
, enabled him likewise to do them several good Offices.
The
Castilian
, as he was one Day in Conversation with this
Renegado, discovered to him the Negligence and Treachery of his
Correspondent in
Castile
, and at the same time asked his Advice
how he should behave himself in that Exigency: He further told the
Renegado, that he found it would be impossible for him to raise the
Money, unless he himself might go over to dispose of his Estate. The
Renegado, after having represented to him that his
Algerine
Master
would never consent to his Release upon such a Pretence, at
length contrived a Method for the
Castlian
to make his Escape in
the Habit of a Seaman. The
Castilian
succeeded in his Attempt;
and having sold his Estate, being afraid lest the Money should miscarry
by the Way, and determining to perish with it rather than lose one who
was much dearer to him than his Life, he returned himself in a little
Vessel that was going to
Algiers
. It is impossible to describe
the Joy he felt on this Occasion, when he considered that he should soon
see the Wife whom he so much loved, and endear himself more to her by
this uncommon Piece of Generosity.
The Renegado, during the Husband's Absence, so insinuated himself into
the good Graces of his young Wife, and so turned her Head with Stories
of Gallantry, that she quickly thought him the finest Gentleman she had
ever conversed with. To be brief, her Mind was quite alienated from the
honest
Castilian
, whom she was taught to look upon as a formal
old Fellow unworthy the Possession of so charming a Creature. She had
been instructed by the Renegado how to manage herself upon his Arrival;
so that she received him with an Appearance of the utmost Love and
Gratitude, and at length perswaded him to trust their common Friend the
Renegado with the Money he had brought over for their Ransom; as not
questioning but he would beat down the Terms of it, and negotiate the
Affair more to their Advantage than they themselves could do. The good
Man admired her Prudence, and followed her Advice. I wish I could
conceal the Sequel of this Story, but since I cannot I shall dispatch it
in as few Words as possible. The
Castilian
having slept longer
than ordinary the next Morning, upon his awaking found his Wife had left
him: He immediately arose and enquired after her, but was told that she
was seen with the Renegado about Break of Day. In a Word, her Lover
having got all things ready for their Departure, they soon made their
Escape out of the Territories of
Algiers
, carried away the Money,
and left the
Castilian
in Captivity; who partly through the cruel
Treatment of the incensed
Algerine
his Master, and partly through
the unkind Usage of his unfaithful Wife, died some few Months after.
L.
The story of Queen Emma, mother of Edward the Confessor,
and her walking unhurt, blindfold and barefoot, over nine red-hot
ploughshares, is told in
Bayle's Dictionary
, a frequent suggester of
allusions in the
Spectator
. Tonson reported that he usually found
Bayle's Dictionary
open on Addison's table whenever he called on him.
Act 2.
That is, English officers who had served in Spain.
that
in
Contents
|
Thursday,
October 18, 1711 |
Steele |
Scribere jussit amor.
Ovid.

The following Letters are written with such an Air of Sincerity, that I
cannot deny the inserting of them.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Tho' you are every where in your Writings a Friend to Women, I do not
remember that you have directly considered the mercenary Practice of
Men in the Choice of Wives. If you would please to employ your
Thoughts upon that Subject, you would easily conceive the miserable
Condition many of us are in, who not only from the Laws of Custom and
Modesty are restrained from making any Advances towards our Wishes,
but are also, from the Circumstance of Fortune, out of all Hope of
being addressed to by those whom we love. Under all these
Disadvantages I am obliged to apply my self to you, and hope I shall
prevail with you to Print in your very next Paper the following
Letter, which is a Declaration of Passion to one who has made some
feint Addresses to me for some time. I believe he ardently loves me,
but the Inequality of my Fortune makes him think he cannot answer it
to the World, if he pursues his Designs by way of Marriage; and I
believe, as he does not want Discerning, he discovered me looking at
him the other Day unawares in such a Manner as has raised his Hopes of
gaining me on Terms the Men call easier. But my Heart was very full on
this Occasion, and if you know what Love and Honour are, you will
pardon me that I use no further Arguments with you,
but hasten to my
Letter to him, whom I call
Oroondates1, because if I do not
succeed it shall look like Romance; and if I am regarded, you shall
receive a pair of Gloves at my Wedding, sent you under the Name of
Statira.
To Oroondates.
Sir,
'After very much Perplexity in my self, and revolving how to acquaint
you with my own Sentiments, and expostulate with you concerning yours,
I have chosen this Way, by which means I can be at once revealed to
you, or, if you please, lie concealed. If I do not within few Days
find the Effect which I hope from this, the whole Affair shall be
buried in Oblivion. But, alas! what am I going to do, when I am about
to tell you that I love you? But after I have done so, I am to assure
you, that with all the Passion which ever entered a tender Heart, I
know I can banish you from my Sight for ever, when I am convinced that
you have no Inclinations towards me but to my Dishonour. But, alas!
Sir, why should you sacrifice the real and essential Happiness of
Life, to the Opinion of a World, that moves upon no other Foundation
but profess'd Error and Prejudice? You all can observe that Riches
alone do not make you happy, and yet give up every Thing else when it
stands in Competition with Riches. Since the World is so bad, that
Religion is left to us silly Women, and you Men act generally upon
Principles of Profit and Pleasure, I will talk to you without arguing
from any Thing but what may be most to your Advantage, as a Man of the
World. And I will lay before you the State of the Case, supposing that
you had it in your Power to make me your Mistress, or your Wife, and
hope to convince you that the latter is more for your Interest, and
will contribute more to your Pleasure.
'We will suppose then the Scene was laid, and you were now in
Expectation of the approaching Evening wherein I was to meet you, and
be carried to what convenient Corner of the Town you thought fit, to
consummate all which your wanton Imagination has promised you in the
Possession of one who is in the Bloom of Youth, and in the Reputation
of Innocence: you would soon have enough of me, as I am Sprightly,
Young, Gay, and Airy. When Fancy is sated, and finds all
the Promises
it
made2 it self false, where is now the Innocence which charmed
you? The first Hour you are alone you will find that the Pleasure of a
Debauchee is only that of a Destroyer; He blasts all the Fruit he
tastes, and where the Brute has been devouring, there is nothing left
worthy the Relish of the Man. Reason resumes her Place after
Imagination is cloyed; and I am, with the utmost Distress and
Confusion, to behold my self the Cause of uneasie Reflections to you,
to be visited by Stealth, and dwell for the future with the two
Companions (the most unfit for each other in the World) Solitude and
Guilt. I will not insist upon the shameful Obscurity we should pass
our Time in, nor run over the little short Snatches of fresh Air and
free Commerce which all People must be satisfied with, whose Actions
will not bear Examination, but leave them to your Reflections, who
have seen of that Life of which I have but a meer Idea.
On the other hand, If you can be so good and generous as to make me
your Wife, you may promise your self all the Obedience and Tenderness
with which Gratitude can inspire a virtuous Woman. Whatever
Gratifications you may promise your self from an agreeable Person,
whatever Compliances from an easie Temper, whatever Consolations from
a sincere Friendship, you may expect as the Due of your Generosity.
What at present in your ill View you promise your self from me, will
be followed by Distaste and Satiety; but the Transports of a virtuous
Love are the least Part of its Happiness. The Raptures of innocent
Passion are but like Lightning to the Day, they rather interrupt than
advance the Pleasure of it. How happy then is that Life to be, where
the highest Pleasures of Sense are but the lower Parts of its
Felicity?
Now am I to repeat to you the unnatural Request of taking me in direct
Terms. I know there stands between me and that Happiness, the haughty
Daughter of a Man who can give you suitably to your Fortune. But if
you weigh the Attendance and Behaviour of her who comes to you in
Partnership of your Fortune, and expects an Equivalent, with that of
her who enters your House as honoured and obliged by that Permission,
whom of the two will you chuse? You, perhaps, will think fit to spend
a Day abroad in the common Entertainments of Men of Sense and Fortune;
she will think herself ill-used in that Absence, and contrive at Home
an Expence proportioned to the Appearance which you make in the World.
She is in all things to have a Regard to the Fortune which she brought
you, I to the Fortune to which you introduced me. The Commerce between
you two will eternally have the Air of a Bargain, between us of a
Friendship: Joy will ever enter into the Room with you, and kind
Wishes attend my Benefactor when he leaves it. Ask your self, how
would you be pleased to enjoy for ever the Pleasure of having laid an
immediate Obligation on a grateful Mind? such will be your Case with
Me. In the other Marriage you will live in a constant Comparison of
Benefits, and never know the Happiness of conferring or receiving any.
It may be you will, after all, act rather in the prudential Way,
according to the Sense of the ordinary World. I know not what I think
or say, when that melancholy Reflection comes upon me; but shall only
add more, that it is in your Power to make me
your Grateful Wife,
but never your Abandoned Mistress.
T.
A character in Madame Scudéri's
Grand Cyrus.
made to
Contents
|
Friday,
October 19, 1711 |
Steele1 |
Vincit Amor Patriæ.
Virg.

The Ambition of Princes is many times as hurtful to themselves as to
their People. This cannot be doubted of such as prove unfortunate in
their Wars, but it is often true too of those who are celebrated for
their Successes. If a severe View were to be taken of their Conduct, if
the Profit and Loss by their Wars could be justly ballanced, it would be
rarely found that the Conquest is sufficient to repay the Cost.
I was the other Day looking over the Letters of my Correspondents, I
took this Hint from that of
Philarithmus
; which has turned my
present Thoughts upon Political Arithmetick, an Art of greater Use than
Entertainment. My Friend has offered an Essay towards proving that
Lewis
XIV with all his Acquisitions is not Master of more People
than at the Beginning of his Wars, nay that for every Subject he had
acquired, he had lost Three that were his Inheritance: If
Philarithmus
is not mistaken in his Calculations,
Lewis
must have been impoverished by his Ambition.
The Prince for the Publick Good has a Sovereign Property in every
Private Person's Estate, and consequently his Riches must encrease or
decrease in proportion to the Number and Riches of his Subjects. For
Example: If Sword or Pestilence should destroy all the People of this
Metropolis, (God forbid there should be Room for such a Supposition! but
if this should be the Case) the Queen must needs lose a great Part of
her Revenue, or, at least, what is charged upon the City must encrease
the Burden upon the rest of her Subjects. Perhaps the Inhabitants here
are not above a Tenth Part of the Whole; yet as they are better fed, and
cloth'd, and lodg'd, than her other Subjects, the Customs and Excises
upon their Consumption, the Imposts upon their Houses, and other Taxes,
do very probably make a fifth Part of the whole Revenue of the Crown.
But this is not all; the Consumption of the City takes off a great Part
of the Fruits of the whole Island; and as it pays such a Proportion of
the Rent or yearly Value of the Lands in the Country, so it is the Cause
of paying such a Proportion of Taxes upon those Lands. The Loss then of
such a People must needs be sensible to the Prince, and visible to the
whole Kingdom.
On the other hand, if it should please God to drop from Heaven a new
People equal in Number and Riches to the City, I should be ready to
think their Excises, Customs, and House-Rent would raise as great a
Revenue to the Crown as would be lost in the former Case. And as the
Consumption of this New Body would be a new Market for the Fruits of the
Country, all the Lands, especially those most adjacent, would rise in
their yearly Value, and pay greater yearly Taxes to the Publick. The
Gain in this Case would be as sensible as the former Loss.
Whatsoever is assess'd upon the General, is levied upon Individuals. It
were worth the while then to consider what is paid by, or by means of,
the meanest Subjects, in order to compute the Value of every Subject to
the Prince.
For my own part, I should believe that Seven Eighths of the People are
without Property in themselves or the Heads of their Families, and
forced to work for their daily Bread; and that of this Sort there are
Seven Millions in the whole Island of
Great Britain
: And yet one
would imagine that Seven Eighths of the whole People should consume at
least three Fourths of the whole Fruits of the Country. If this is the
Case, the Subjects without Property pay Three Fourths of the Rents, and
consequently enable the Landed Men to pay Three Fourths of their Taxes.
Now if so great a Part of the Land-Tax were to be divided by Seven
Millions, it would amount to more than three Shillings to every Head.
And thus as the Poor are the Cause, without which the Rich could not pay
this Tax, even the poorest Subject is upon this Account worth three
Shillings yearly to the Prince.
Again: One would imagine the Consumption of seven Eighths of the whole
People, should pay two Thirds of all the Customs and Excises. And if
this Sum too should be divided by seven Millions,
viz.
the Number
of poor People, it would amount to more than seven Shillings to every
Head: And therefore with this and the former Sum every poor Subject,
without Property, except of his Limbs or Labour, is worth at least ten
Shillings yearly to the Sovereign. So much then the Queen loses with
every one of her old, and gains with every one of her new Subjects.
When I was got into this Way of thinking, I presently grew conceited of
the Argument, and was just preparing to write a Letter of Advice to a
Member of Parliament, for opening the Freedom of our Towns and Trades,
for taking away all manner of Distinctions between the Natives and
Foreigners, for repealing our Laws of Parish Settlements, and removing
every other Obstacle to the Increase of the People. But as soon as I had
recollected with what inimitable Eloquence my Fellow-Labourers had
exaggerated the Mischiefs of selling the Birth-right of
Britons
for a Shilling, of spoiling the pure
British
Blood with Foreign
Mixtures, of introducing a Confusion of Languages and Religions, and of
letting in Strangers to eat the Bread out of the Mouths of our own
People, I became so humble as to let my Project fall to the Ground, and
leave my Country to encrease by the ordinary Way of Generation.
As I have always at Heart the Publick Good, so I am ever contriving
Schemes to promote it; and I think I may without Vanity pretend to have
contrived some as wise as any of the Castle-builders. I had no sooner
given up my former Project, but my Head was presently full of draining
Fens and Marshes, banking out the Sea, and joining new Lands to my
Country; for since it is thought impracticable to encrease the People to
the Land, I fell immediately to consider how much would be gained to the
Prince by encreasing the Lands to the People.
If the same omnipotent Power, which made the World, should at this time
raise out of the Ocean and join to
Great Britain
an equal Extent
of Land, with equal Buildings, Corn, Cattle and other Conveniences and
Necessaries of Life, but no Men, Women, nor Children, I should hardly
believe this would add either to the Riches of the People, or Revenue of
the Prince; for since the present Buildings are sufficient for all the
Inhabitants, if any of them should forsake the old to inhabit the new
Part of the Island, the Increase of House-Rent in this would be attended
with at least an equal Decrease of it in the other: Besides, we have
such a Sufficiency of Corn and Cattle, that we give Bounties to our
Neighbours to take what exceeds of the former off our Hands, and we will
not suffer any of the latter to be imported upon us by our
Fellow-Subjects; and for the remaining Product of the Country 'tis
already equal to all our Markets. But if all these Things should be
doubled to the same Buyers, the Owners must be glad with half their
present Prices, the Landlords with half their present Rents; and thus by
so great an Enlargement of the Country, the Rents in the whole would not
increase, nor the Taxes to the Publick.
On the contrary, I should believe they would be very much diminished;
for as the Land is only valuable for its Fruits, and these are all
perishable, and for the most part must either be used within the Year,
or perish without Use, the Owners will get rid of them at any rate,
rather than they should waste in their Possession: So that 'tis probable
the annual Production of those perishable things, even of one Tenth Part
of them, beyond all Possibility of Use, will reduce one Half of their
Value. It seems to be for this Reason that our Neighbour Merchants who
ingross all the Spices, and know how great a Quantity is equal to the
Demand, destroy all that exceeds it. It were natural then to think that
the Annual Production of twice as much as can be used, must reduce all
to an Eighth Part of their present Prices; and thus this extended Island
would not exceed one Fourth Part of its present Value, or pay more than
one Fourth Part of the present Tax.
It is generally observed, That in Countries of the greatest Plenty there
is the poorest Living; like the Schoolmen's Ass, in one of my
Speculations, the People almost starve between two Meals. The Truth is,
the Poor, which are the Bulk of the Nation, work only that they may
live; and if with two Days Labour they can get a wretched Subsistence
for a Week, they will hardly be brought to work the other four: But then
with the Wages of two Days they can neither pay such Prices for their
Provisions, nor such Excises to the Government.
paradox therefore in old
Hesiod
or Half is more than the Whole, is very applicable to the
present Case; since nothing is more true in political Arithmetick, than
that the same People with half a Country is more valuable than with the
Whole.
begin to think there was nothing absurd in Sir
W. Petty
,
when he fancied if all the Highlands of
Scotland
and the whole
Kingdom of
Ireland
were sunk in the Ocean, so that the People
were all saved and brought into the Lowlands of
Great Britain
;
nay, though they were to be reimburst the Value of their Estates by the
Body of the People, yet both the Sovereign and the Subjects in general
would be enriched by the very Loss
.
If the People only make the Riches, the Father of ten Children is a
greater Benefactor to his Country, than he who has added to it 10 000
Acres of Land and no People. It is certain
Lewis
has join'd vast
Tracts of Land to his Dominions: But if
Philarithmus
says true,
that he is not now Master of so many Subjects as before; we may then
account for his not being able to bring such mighty Armies into the
Field, and for their being neither so well fed, nor cloathed, nor paid
as formerly. The Reason is plain,
Lewis
must needs have been
impoverished not only by his Loss of Subjects, but by his Acquisition of
Lands.
T.
Or Henry Martyn.
In
.
A new edition of Sir W. Petty's
Essays in Political
Arithmetic
had just appeared.
Contents
|
Saturday,
October 20, 1711 |
Addison |
Religentem esse oportet, Religiosum nefas.
Incerti Autoris apud Aul. Gell.

It is of the last Importance to season the Passions of a Child with
Devotion, which seldom dies in a Mind that has received an early
Tincture of it. Though it may seem extinguished for a while by the Cares
of the World, the Heats of Youth, or the Allurements of Vice, it
generally breaks out and discovers it self again as soon as Discretion,
Consideration, Age, or Misfortunes have brought the Man to himself. The
Fire may be covered and overlaid, but cannot be entirely quenched and
smothered.
A State of Temperance, Sobriety, and Justice, without Devotion, is a
cold, lifeless, insipid Condition of Virtue; and is rather to be styled
Philosophy than Religion. Devotion opens the Mind to great Conceptions,
and fills it with more sublime Ideas than any that are to be met with in
the most exalted Science; and at the same time warms and agitates the
Soul more than sensual Pleasure.
It has been observed by some Writers, that Man is more distinguished
from the Animal World by Devotion than by Reason, as several Brute
Creatures discover in their Actions something like a faint Glimmering of
Reason, though they betray in no single Circumstance of their Behaviour
any Thing that bears the least Affinity to Devotion. It is certain, the
Propensity of the Mind to Religious Worship; the natural Tendency of the
Soul to fly to some Superior Being for Succour in Dangers and
Distresses, the Gratitude
an invisible Superintendent
which
rises in us upon receiving any extraordinary and unexpected good
Fortune; the Acts of Love and Admiration with which the Thoughts of Men
are so wonderfully transported in meditating upon the Divine
Perfections, and the universal Concurrence of all the Nations under
Heaven in the great Article of Adoration, plainly shew that Devotion or
Religious Worship must be the Effect of Tradition from some first
Founder of Mankind, or that it is conformable to the Natural Light of
Reason, or that it proceeds from an Instinct implanted in the Soul it
self. For my part, I look upon all these to be the concurrent Causes,
but which ever of them shall be assigned as the Principle of Divine
Worship, it manifestly points to a Supreme Being as the first Author of
it.
I may take some other Opportunity of considering those particular Forms
and Methods of Devotion which are taught us by Christianity, but shall
here observe into what Errors even this Divine Principle may sometimes
lead us, when it is not moderated by that right Reason which was given
us as the Guide of all our Actions.
The two great Errors into which a mistaken Devotion may betray us, are
Enthusiasm and Superstition.
There is not a more melancholy Object than a Man who has his Head turned
with Religious Enthusiasm. A Person that is crazed, tho' with Pride or
Malice, is a Sight very mortifying to Human Nature; but when the
Distemper arises from any indiscreet Fervours of Devotion, or too
intense an Application of the Mind to its mistaken Duties, it deserves
our Compassion in a more particular Manner. We may however learn this
Lesson from it, that since Devotion it self (which one would be apt to
think could not be too warm) may disorder the Mind, unless its Heats are
tempered with Caution and Prudence, we should be particularly careful to
keep our Reason as cool as possible, and to guard our selves in all
Parts of Life against the Influence of Passion, Imagination, and
Constitution.
Devotion, when it does not lie under the Check of Reason, is very apt to
degenerate into Enthusiasm. When the Mind finds herself very much
inflamed with her Devotions, she is too much inclined to think they are
not of her own kindling, but blown up by something Divine within her. If
she indulges this Thought too far, and humours the growing Passion, she
at last flings her self into imaginary Raptures and Extasies; and when
once she fancies her self under the Influence of a Divine Impulse, it is
no Wonder if she slights Human Ordinances, and refuses to comply with
any established Form of Religion, as thinking her self directed by a
much superior Guide.
As Enthusiasm is a kind of Excess in Devotion, Superstition is the
Excess not only of Devotion, but of Religion in general, according to an
old Heathen Saying, quoted by
Aulus Gellius
,
Religentem esse
oportet, Religiosum nefas
; A Man should be Religious, not
Superstitious:
as the Author tells us,
Nigidius
observed upon
this Passage, that the
Latin
Words which terminate in
osus
generally imply vicious Characters, and the having of any Quality to an
Excess
.
An Enthusiast in Religion is like an obstinate Clown, a Superstitious
Man like an insipid Courtier. Enthusiasm has something in it of Madness,
Superstition of Folly. Most of the Sects that fall short of the Church
of
England
have in them strong Tinctures of Enthusiasm, as the
Roman
Catholick Religion is one huge overgrown Body of childish
and idle Superstitions.
The
Roman
Catholick Church seems indeed irrecoverably lost in
this Particular. If an absurd Dress or Behaviour be introduced in the
World, it will soon be found out and discarded: On the contrary, a Habit
or Ceremony,
' never so ridiculous,
which
has taken Sanctuary
in the Church, sticks in it for ever. A
Gothic
Bishop perhaps,
thought it proper to repeat such a Form in such particular Shoes or
Slippers; another fancied it would be very decent if such a Part of
publick Devotions were performed with a Mitre on his Head, and a Crosier
in his Hand: To this a Brother
Vandal
, as wise as the others,
adds an antick Dress, which he conceived would allude very aptly to such
and such Mysteries, till by Degrees the whole Office
has
degenerated
into an empty Show.
Their Successors see the Vanity and Inconvenience of these Ceremonies;
but instead of reforming, perhaps add others, which they think more
significant, and which take Possession in the same manner, and are never
to be driven out after they have been once admitted. I have seen the
Pope officiate at St.
Peter's
where, for two Hours together, he
was busied in putting on or off his different Accoutrements, according
to the different Parts he was to act in them.
Nothing is so glorious in the Eyes of Mankind, and ornamental to Human
Nature, setting aside
infinite Advantages
which
arise from it,
as a strong, steady masculine Piety; but Enthusiasm and Superstition are
the Weaknesses of human Reason, that expose us to the Scorn and Derision
of Infidels, and sink us even below the Beasts that perish.
Idolatry may be looked upon as another Error arising from mistaken
Devotion; but because Reflections on that Subject would be of no use to
an
English
Reader, I shall not enlarge upon it.
that
Noct. Att.
, Bk. iv. ch. 9.
that
that
Contents
|
Monday,
October 22, 1711 |
Steele |
Sæpe decem vitiis instructior odit et horret.
Hor.

The other Day as I passed along the Street, I saw a sturdy Prentice-Boy
Disputing with an Hackney-Coachman; and in an Instant, upon some Word of
Provocation, throw off
Hat and
Cut-Periwig
, clench his Fist,
and strike the Fellow a Slap on the Face; at the same time calling him
Rascal, and telling him he was a Gentleman's Son. The young Gentleman
was, it seems, bound to a Blacksmith; and the Debate arose about Payment
for some Work done about a Coach, near which they Fought. His Master,
during the Combat, was full of his Boy's Praises; and as he called to
him to play with his Hand and Foot, and throw in his Head, he made all
us who stood round him of his Party, by declaring the Boy had very good
Friends, and he could trust him with untold Gold. As I am generally in
the Theory of Mankind, I could not but make my Reflections upon the
sudden Popularity which was raised about the Lad; and perhaps, with my
Friend
Tacitus
, fell into Observations upon it, which were too
great for the Occasion; or ascribed this general Favour to Causes which
had nothing to do towards it. But the young Blacksmith's being a
Gentleman was, methought, what created him good Will from his present
Equality with the Mob about him: Add to this, that he was not so much a
Gentleman, as not, at the same time that he called himself such, to use
as rough Methods for his Defence as his Antagonist. The Advantage of his
having good Friends, as his Master expressed it, was not lazily urged;
but he shewed himself superior to the Coachman in the personal Qualities
of Courage and Activity, to confirm that of his being well allied,
before his Birth was of any Service to him.
If one might Moralize from this silly Story, a Man would say, that
whatever Advantages of Fortune, Birth, or any other Good, People possess
above the rest of the World, they should shew collateral Eminences
besides those Distinctions; or those Distinctions will avail only to
keep up common Decencies and Ceremonies, and not to preserve a real
Place of Favour or Esteem in the Opinion and common Sense of their
Fellow-Creatures.
The Folly of People's Procedure, in imagining that nothing more is
necessary than Property and superior Circumstances to support them in
Distinction, appears in no way so much as in the Domestick part of Life.
It is ordinary to feed their Humours into unnatural Excrescences, if I
may so speak, and make their whole Being a wayward and uneasy Condition,
for want of the obvious Reflection that all Parts of Human Life is a
Commerce. It is not only paying Wages, and giving Commands, that
constitutes a Master of a Family; but Prudence, equal Behaviour, with
Readiness to protect and cherish them, is what entitles a Man to that
Character in their very Hearts and Sentiments. It is pleasant enough to
Observe, that Men expect from their Dependants, from their sole Motive
of Fear, all the good Effects which a liberal Education, and affluent
Fortune, and every other Advantage, cannot produce in themselves. A Man
will have his Servant just, diligent, sober and chaste, for no other
Reasons but the Terrour of losing his Master's Favour; when all the Laws
Divine and Human cannot keep him whom he serves within Bounds, with
relation to any one of those Virtues. But both in great and ordinary
Affairs, all Superiority, which is not founded on Merit and Virtue, is
supported only by Artifice and Stratagem. Thus you see Flatterers are
the Agents in Families of Humourists, and those who govern themselves by
any thing but Reason. Make-Bates, distant Relations, poor Kinsmen, and
indigent Followers, are the Fry which support the Œconomy of an
humoursome rich Man. He is eternally whispered with Intelligence of who
are true or false to him in Matters of no Consequence, and he maintains
twenty Friends to defend him against the Insinuations of one who would
perhaps cheat him of an old Coat.
I shall not enter into farther Speculation upon this Subject at present,
but think the following Letters and Petition are made up of proper
Sentiments on this Occasion.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Servant to an old Lady who is governed by one she calls her
Friend; who is so familiar an one, that she takes upon her to advise
her without being called to it, and makes her uneasie with all about
her. Pray, Sir, be pleased to give us some Remarks upon voluntary
Counsellors; and let these People know that to give any Body Advice,
is to say to that Person, I am your Betters. Pray, Sir, as near as you
can, describe that eternal Flirt and Disturber of Families, Mrs.
Taperty, who is always visiting, and putting People in a Way,
as they call it. If you can make her stay at home one Evening, you
will be a general Benefactor to all the Ladies Women in Town, and
particularly to
Your loving Friend,
Susan Civil.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a Footman, and live with one of those Men, each of whom is said
to be one of the best humoured Men in the World, but that he is
passionate. Pray be pleased to inform them, that he who is passionate,
and takes no Care to command his Hastiness, does more Injury to his
Friends and Servants in one half Hour, than whole Years can attone
for. This Master of mine, who is the best Man alive in common Fame,
disobliges Some body every Day he lives; and strikes me for the next
thing I do, because he is out of Humour at it. If
these Gentlemen
knew2 that they do all the Mischief that is ever done in
Conversation, they would reform; and I who have been a Spectator of
Gentlemen at Dinner for many Years, have seen that Indiscretion does
ten times more Mischief than Ill-nature. But you will represent this
better than
Your abused
Humble Servant,
Thomas Smoaky.
To the Spectator,
The humble Petition of
John Steward,
Robert Butler,
Harry Cook, and
Abigail Chambers, in Behalf of
themselves and their Relations, belonging to and dispersed in the
several Services of most of the great Families within the Cities of
London and Westminster;
Sheweth,
That in many of the Families in which your Petitioners live and are
employed, the several Heads of them are wholly unacquainted with what
is Business, and are very little Judges when they are well or ill used
by us your said Petitioners.
That for want of such Skill in their own Affairs, and by Indulgence
of their own Laziness and Pride, they continually keep about them
certain mischievous Animals called Spies.
That whenever a Spy is entertained, the Peace of that House is from
that Moment banished.
That Spies never give an Account of good Services, but represent our
Mirth and Freedom by the Words Wantonness and Disorder.
That in all Families where there are Spies, there is a general
Jealousy and Misunderstanding.
That the Masters and Mistresses of such Houses live in continual
Suspicion of their ingenuous and true Servants, and are given up to
the Management of those who are false and perfidious.
That such Masters and Mistresses who entertain Spies, are no longer
more than Cyphers in their own Families; and that we your Petitioners
are with great Disdain obliged to pay all our Respect, and expect all
our Maintenance from such Spies.
Your Petitioners therefore most humbly pray, that you would represent
the Premises to all Persons of Condition; and your Petitioners, as in
Duty bound, shall for ever Pray, &c.
T.
Perriwig
"know", and in first reprint.
Contents
end of Volume 1.
The Spectator
in three volumes: volume 2
A New Edition
Reproducing the Original Text
Both as First Issued
and as Corrected by its Authors
with Introduction, Notes, and Index
edited by Henry Morley
1891
Table of Contents / [Volume 3 link: Index]
- No. 203 – Tuesday, October 23, 1711 – Addison
- No. 204 – Wednesday, October 24, 1711 – Steele
- No. 205 – Thursday, October 25, 1711 – Addison
- No. 206 – Friday, October 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 207 – Saturday, October 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 208 – Monday, October 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 209 – Tuesday, October 30, 1711 – Addison
- No. 210 – Wednesday, October 31, 1711 – Hughes
- No. 211 – Thursday, November 1, 1711 – Addison
- No. 212 – Friday, November 2, 1711 – Steele
- No. 213 – Saturday, November 3, 1711 – Addison
- No. 214 – Monday, November 5, 1711 – Steele
- No. 215 – Tuesday, November 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 216 – Wednesday, November 7, 1711 – Steele
- No. 217 – Thursday, November 8, 1711 – Budgell
- No. 218 – Friday, November 9, 1711 – Steele
- No. 219 – Saturday, November 10, 1711 – Addison
- No. 220 – Monday, November 12, 1711 – Steele
- No. 221 – Tuesday, November 13, 1711 – Addison
- No. 222 – Wednesday, November 14, 1711 – Steele
- No. 223 – Thursday, November 15, 1711 – Addison
- No. 224 – Friday, November 16, 1711 – Hughes
- No. 225 – Saturday, November 17, 1711 – Addison
- No. 226 – Monday, November 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 227 – Tuesday, November 20, 1711 – Addison
- No. 228 – Wednesday, November 21, 1711 – Steele
- No. 229 – Thursday, November 22, 1711 – Addison
- No. 230 – Friday, November 23, 1711 – Steele
- No. 231 – Saturday, November 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 232 – Monday, November 26, 1711 – Hughes
- No. 233 – Tuesday, November 27, 1711 – Addison
- No. 234 – Wedneday, November 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 235 – Thursday, November 29, 1711 – Addison
- No. 236 – Friday, November 30, 1711 – Steele
- No. 237 – Saturday, December 1, 1711 – Addison
- No. 238 – Monday, December 3, 1711 – Steele
- No. 239 – Tuesday, December 4, 1711 – Addison
- No. 240 – Wednesday, December 5, 1711 – Steele
- No. 241 – Thursday, December 6, 1711 – Addison
- No. 242 – Friday, December 7, 1711 – Steele
- No. 243 – Saturday, December 8, 1711 – Addison
- No. 244 – Monday, December 10, 1711 – Steele
- No. 245 – Tuesday, December 11, 1711 – Addison
- No. 246 – Wednesday, December 12, 1711 – Steele
- No. 247 – Thursday, December 13, 1711 – Addison
- No. 248 – Friday, December 14, 1711 – Steele
- No. 249 – Saturday, December 15, 1711 – Addison
- No. 250 – Monday, December 17, 1711 –
- No. 251 – Tuesday, December 18, 1711 – Addison
- No. 252 – Wedneday, December 19, 1711 – Steele
- No. 253 – Thursday, December 20, 1711 – Addison
- No. 254 – Friday, December 21, 1711 – Steele
- No. 255 – Saturday, December 22, 1711 – Addison
- No. 256 – Monday, December 24, 1711 – Addison
- No. 257 – Tuesday, December 25, 1711 – Addison
- No. 258 – Wednesday, December 26, 1711 – Steele
- No. 259 – Thursday, December 27, 1711 – Steele
- No. 260 – Friday, December 28, 1711 – Steele
- No. 261 – Saturday, December 29, 1711 – Addison
- No. 262 – Monday, December 31, 1711 – Steele
- No. 263 – Tuesday, January 1, 1712 – Steele
- No. 264 – Wednesday, January 2, 1712 – Steele
- No. 265 – Thursday, January 3, 1712 – Addison
- No. 266 – Friday, January 4, 1712 – Steele
- No. 267 – Saturday, January 5, 1712 – Addison
- No. 268 – Monday, January 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 269 – Tuesday, January 8, 1712 – Addison
- No. 270 – Wednesday, January 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 271 – Thursday, January 10, 1712 – Addison
- No. 272 – Friday, January 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 273 – Saturday, January 12, 1712 – Addison
- No. 274 – Monday, January 14, 1712 – Steele
- No. 275 – Tuesday, January 15, 1712 – Addison
- No. 276 – Wednesday, January 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 277 – Thursday, January 17, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 278 – Friday, January 18, 1712 – Steele
- No. 279 – Saturday, January 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 280 – Monday, January 21, 1712 – Steele
- No. 281 – Tuesday, January 22, 1712 – Addison
- No. 282 – Wednesday, January 23, 1712 – Steele
- No. 283 – Thursday, January 24, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 284 – Friday, January 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 285 – Saturday, January 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 286 – Monday, January 28, 1712 – Steele
- No. 287 – Tuesday, January 29, 1712 – Addison
- No. 288 – Wednesday, January 30, 1712 – Steele
- No. 289 – Thursday, January 31, 1712 – Addison
- No. 290 – Friday, February 1, 1712 – Steele
- No. 291 – Saturday, February 2, 1712 – Addison
- No. 292 – Monday, February 4, 1712 –
- No. 293 – Tuesday, February 5, 1712 – Addison
- No. 294 – Wednesday, February 6, 1712 – Steele
- No. 295 – Thursday, February 7, 1712 – Addison
- No. 296 – Friday, February 8, 1712 – Steele
- No. 297 – Saturday, February 9, 1712 – Addison
- No. 298 – Monday, February 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 299 – Tuesday, February 12, 1712 – Addison
- No. 300 – Wednesday, February 13, 1712 – Steele
- No. 301 – Thursday, February 14, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 302 – Friday, February 15, 1712 – Steele
- No. 303 – Saturday, February 16, 1712 – Addison
- No. 304 – Monday, February 18, 1712 – Steele
- No. 305 – Tuesday, February 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 306 – Wednesday, February 20, 1712 – Steele
- No. 307 – Thursday, February 21, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 308 – Friday, February 22, 1712 – Steele
- No. 309 – Saturday, February 23, 1712 – Addison
- No. 310 – Monday, February 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 311 – Tuesday, February 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 312 – Wednesday, February 27, 1712 – Steele
- No. 313 – Thursday, February 28, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 314 – Friday, February 29, 1712 – Steele
- No. 315 – Saturday, March 1, 1712 – Addison
- No. 316 – Monday, March 3, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 317 – Tuesday, March 4, 1712 – Addison
- No. 318 – Wednesday, March 5, 1712 – Steele
- No. 319 – Thursday, March 6, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 320 – Friday, March 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 321 – Saturday, March 8, 1712 – Addison
- No. 322 – Monday, March 10, 1712 – Steele
- No. 323 – Tuesday, March 11, 1712 – Addison
- No. 324 – Wednesday, March 12, 1712 – Steele
- No. 325 – Thursday, March 13, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 326 – Friday, March 14, 1712 – Steele
- No. 327 – Saturday, March 15, 1712 – Addison
- No. 328 – Monday, March 17, 1712 – Steele
- No. 328b – Monday, March 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 329 – Tuesday, March 18, 1712 – Addison
- No. 330 – Wednesday, March 19, 1712 – Steele
- No. 331 – Thursday, March 20, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 332 – Friday, March 21, 1712 – Steele
- No. 333 – Saturday, March 22, 1712 – Addison
- No. 334 – Monday, March 24, 1712 – Steele
- No. 335 – Tuesday, March 25, 1712 – Addison
- No. 336 – Wednesday, March 26, 1712 – Steele
- No. 337 – Thursday, March 27, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 338 – Friday, March 28, 1712 –
- No. 339 – Saturday, March 29, 1712 – Addison
- No. 340 – Monday, March 31, 1712 – Steele
- No. 341 – Tuesday, April 1, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 342 – Wednesday, April 2, 1712 – Steele
- No. 343 – Thursday, April 3, 1712 – Addison
- No. 344 – Friday, April 4, 1712 – Steele
- No. 345 – Saturday, April 5, 1712 – Addison
- No. 346 – Monday, April 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 347 – Tuesday, April 8, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 348 – Wednesday, April 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 349 – Thursday, April 10, 1712 – Addison
- No. 350 – Friday, April 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 351 – Saturday, April 12, 1712 – Addison
- No. 352 – Monday, April 14, 1712 – Steele
- No. 353 – Tuesday, April 15, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 354 – Wednesday, April 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 355 – Thursday, April 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 356 – Friday, April 18, 1712 – Steele
- No. 357 – Saturday, April 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 358 – Monday, April 21, 1712 – Steele
- No. 359 – Tuesday, April 22, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 360 – Wednesday, April 23, 1712 – Steele
- No. 361 – Thursday, April 24, 1712 – Addison
- No. 362 – Friday, April 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 363 – Saturday, April 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 364 – Monday, April 28, 1712 – Steele
- No. 365 – Tuesday, April 29, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 366 – Wednesday, April 30, 1712 – Steele
- No. 367 – Thursday, May 1, 1712 – Addison
- No. 368 – Friday, May 2, 1712 – Steele
- No. 369 – Saturday, May 3, 1712 – Addison
- No. 370 – Monday, May 5, 1712 – Steele
- No. 371 – Tuesday, May 6, 1712 – Addison
- No. 372 – Wednesday, May 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 373 – Thursday, May 8, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 374 – Friday, May 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 375 – Saturday, May 10, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 376 – Monday, May 12, 1712 – Steele
- No. 377 – Tuesday, May 13, 1712 – Addison
- No. 378 – Wednesday, May 14, 1712 – Pope
- No. 379 – Thursday, May 15, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 380 – Friday, May 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 381 – Saturday, May 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 382 – Monday, May 19, 1712 – Steele
- No. 383 – Tuesday, May 20, 1712 – Addison
- No. 384 – Wednesday, May 21, 1712 – Addison
- No. 385 – Thursday, May 22, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 386 – Friday, May 23, 1712 – Steele
- No. 387 – Saturday, May 24, 1712 – Addison
- No. 388 – Monday, May 26, 1712 – Barr
- No. 389 – Tuesday, May 27, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 390 – Wednesday, May 28, 1712 – Steele
- No. 391 – Thursday, May 29, 1712 – Addison
- No. 392 – Friday, May 30, 1712 – Steele
- No. 393 – Saturday, May 31, 1712 – Addison
- No. 394 – Monday, June 2, 1712 – Steele
- No. 395 – Tuesday, June 3, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 396 – Wednesday, June 4, 1712 – Henley
- No. 397 – Thursday, June 5, 1712 – Addison
- No. 398 – Friday, June 6, 1712 – Steele
- No. 399 – Saturday, June 7, 1712 – Addison
- No. 400 – Monday, June 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 401 – Tuesday, June 10, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 402 – Wednesday, June 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 403 – Thursday, June 12, 1712 – Addison
- No. 404 – Friday, June 13, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 405 – Saturday, June 14, 1712 – Addison
- No. 406 – Monday, June 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 407 – Tuesday, June 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 408 – Wednesday, June 18, 1712 – Pope
- No. 409 – Thursday, June 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 410 – Friday, June 20, 1712 – Tickell
- No. 411 – Saturday, June 21, 1712 – Addison
- No. 412 – Monday, June 23, 1712 – Addison
- No. 413 – Tuesday, June 24, 1712 – Addison
- No. 414 – Wednesday, June 25, 1712 – Addison
- No. 415 – Thursday, June 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 416 – Friday, June 27, 1712 – Addison
List of Original Advertisements Included
|
Tuesday, October 1, 1711 |
Addison |
Phœbe pater, si das hujus mihi nominis usum,
Nec fals, Clymene culpam sub imagine celat;
Pignora da, Genitor
Ov.
Met.
There is a loose Tribe of Men whom I have not yet taken Notice of, that
ramble into all the Corners of this great City, in order to seduce such
unfortunate Females as fall into their Walks. These abandoned
Profligates raise up Issue in every Quarter of the Town, and very often,
for a valuable Consideration, father it upon the Church-warden. By this
means there are several Married Men who have a little Family in most of
the Parishes of
London
and
Westminster
, and several
Batchelors who are undone by a Charge of Children.
When a Man once gives himself this Liberty of preying at large, and
living upon the Common, he finds so much Game in a populous City, that
it is surprising to consider the Numbers which he sometimes propagates.
see many a young Fellow who is scarce of Age, that could lay his
Claim to the
Jus trium Liberorum
, or the Privileges which were
granted by the
Roman
Laws to all such as were Fathers of three
Children: Nay, I have heard a Rake
who
was not quite five and
twenty, declare himself the Father of a seventh Son, and very prudently
determine to breed him up a Physician. In short, the Town is full of
these young Patriarchs, not to mention several batter'd Beaus, who, like
heedless Spendthrifts that squander away their Estates before they are
Masters of them, have raised up their whole Stock of Children before
Marriage.
I must not here omit the particular Whim of an Impudent Libertine, that
had a little Smattering of Heraldry; and observing how the Genealogies
of great Families were often drawn up in the Shape of Trees, had taken a
Fancy to dispose of his own illegitimate Issue in a Figure of the same
kind.
—
Nec longum tempus et ingens
Exiit ad cœlum ramis felicibus arbos,
Miraturque novas frondes, et non sua poma.
Virg.
2
The Trunk of the Tree was mark'd with his own Name,
Will Maple
.
Out of the Side of it grew a large barren Branch, Inscribed
Mary
Maple
, the Name of his unhappy Wife. The Head was adorned with five
huge Boughs. On the Bottom of the first was written in Capital
Characters
Kate Cole
, who branched out into three Sprigs,
viz.
William, Richard,
and
Rebecca. Sal Twiford
gave Birth to
another Bough, that shot up into
Sarah, Tom, Will,
and
Frank
. The third Arm of the Tree had only a single Infant in it,
with a Space left for a second, the Parent from whom it sprung being
near her Time when the Author took this Ingenious Device into his Head.
The two other great Boughs were very plentifully loaden with Fruit of
the same kind; besides which there were many Ornamental Branches that
did not bear. In short, a more flourishing Tree never came out of the
Herald's Office.
What makes this Generation of Vermin so very prolifick, is the
indefatigable Diligence with which they apply themselves to their
Business. A Man does not undergo more Watchings and Fatigues in a
Campaign, than in the Course of a vicious Amour. As it is said of some
Men, that they make their Business their Pleasure, these Sons of
Darkness may be said to make their Pleasure their Business. They might
conquer their corrupt Inclinations with half the Pains they are at in
gratifying them.
Nor is the Invention of these Men less to be admired than their Industry
or Vigilance. There is a Fragment of
Apollodorus
the Comick Poet
(who was Contemporary with
Menander
) which is full of Humour as
follows:
Thou mayest shut up thy Doors, says he, with Bars and Bolts:
It will be impossible for the Blacksmith to make them so fast, but a Cat
and a Whoremaster will find a Way through them
. In a word, there is
no Head so full of Stratagems as that of a Libidinous Man.
Were I to propose a Punishment for this infamous Race of Propagators, it
should be to send them, after the second or third Offence, into our
American
Colonies, in order to people those Parts of her
Majesty's Dominions where there is a want of Inhabitants, and in the
Phrase of
Diogenes
, to
Plant Men
. Some Countries punish
this Crime with Death; but I think such a Banishment would be
sufficient, and might turn this generative Faculty to the Advantage of
the Publick.
In the mean time, till these Gentlemen may be thus disposed of, I would
earnestly exhort them to take Care of those unfortunate Creatures whom
they have brought into the World by these indirect Methods, and to give
their spurious Children such an Education as may render them more
virtuous than their Parents. This is the best Atonement they can make
for their own Crimes, and indeed the only Method that is left them to
repair their past Mis-carriages.
I
likewise desire them to consider, whether they are not bound in
common Humanity, as well as by all the Obligations of Religion and
Nature, to make some Provision for those whom they have not only given
Life to, but entail'd upon them,
tho' very unreasonably, a Degree of
Shame and
Disgrace
.
here I cannot but take notice of those
depraved Notions which prevail among us, and which must have taken rise
from our natural Inclination to favour a Vice to which we are so very
prone, namely, that
Bastardy
and
Cuckoldom
should be
look'd upon as Reproaches, and that the
Ignominy
which
only due
to Lewdness and Falsehood, should fall in so unreasonable a manner upon
the Persons who
are
innocent.
I have been insensibly drawn into this Discourse by the following
Letter, which is drawn up with such a Spirit of Sincerity, that I
question not but the Writer of it has represented his Case in a true and
genuine Light.
Sir,
'I am one of those People who by the general Opinion of the World are
counted both Infamous and Unhappy.
'My Father is a very eminent Man in this Kingdom, and one who bears
considerable Offices in it. I am his Son, but my Misfortune is, That I
dare not call him Father, nor he without Shame own me as his Issue, I
being illegitimate, and therefore deprived of that endearing
Tenderness and unparallel'd Satisfaction which a good Man finds in the
Love and Conversation of a Parent: Neither have I the Opportunities to
render him the Duties of a Son, he having always carried himself at so
vast a Distance, and with such Superiority towards me, that by long
Use I have contracted a Timorousness when before him, which hinders me
from declaring my own Necessities, and giving him to understand the
Inconveniencies I undergo.
'It is my Misfortune to have been neither bred a Scholar, a Soldier,
nor to any kind of Business, which renders me Entirely uncapable of
making Provision for my self without his Assistance; and this creates
a continual Uneasiness in my Mind, fearing I shall in Time want Bread;
my Father, if I may so call him, giving me but very faint Assurances
of doing any thing for me.
'I have hitherto lived somewhat like a Gentleman, and it would be very
hard for me to labour for my Living. I am in continual Anxiety for my
future Fortune, and under a great Unhappiness in losing the sweet
Conversation and friendly Advice of my Parents; so that I cannot look
upon my self otherwise than as a Monster, strangely sprung up in
Nature, which every one is ashamed to own.
'I am thought to be a Man of some natural Parts, and by the continual
Reading what you have offered the World, become an Admirer thereof,
which has drawn me to make this Confession; at the same time hoping,
if any thing herein shall touch you with a Sense of Pity, you would
then allow me the Favour of your Opinion thereupon; as also what Part
I, being unlawfully born, may claim of the Man's Affection who begot
me, and how far in your Opinion I am to be thought his Son, or he
acknowledged as my Father. Your Sentiments and Advice herein will be a
great Consolation and Satisfaction to,
Sir,
Your Admirer and Humble
Servant,
W. B.
C.
that
Georg. II. v. 89.
Infamy.
Shame
suffer and are
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 24, 1711 |
Steele |
Urit grata protervitas,
Et vultus nimium lubricùs aspici.
Hor.

I am not at all displeased that I am become the Courier of Love, and
that the Distressed in that Passion convey their Complaints to each
other by my Means. The following Letters have lately come to my hands,
and shall have their Place with great Willingness. As to the Reader's
Entertainment, he will, I hope, forgive the inserting such Particulars
as to him may perhaps seem frivolous, but are to the Persons who wrote
them of the highest Consequence. I shall not trouble you with the
Prefaces, Compliments, and Apologies made to me before each Epistle when
it was desired to be inserted; but in general they tell me, that the
Persons to whom they are addressed have Intimations, by Phrases and
Allusions in them, from whence they came.
To the Sothades
1.
"The Word, by which I address you, gives you, who understand
Portuguese, a lively Image of the tender Regard I have for you. The
Spectator'S late Letter from
Statira gave me the Hint to use the
same Method of explaining my self to you. I am not affronted at the
Design your late Behaviour discovered you had in your Addresses to me;
but I impute it to the Degeneracy of the Age, rather than your
particular Fault. As I aim at nothing more than being yours, I am
willing to be a Stranger to your Name, your Fortune, or any Figure
which your Wife might expect to make in the World, provided my
Commerce with you is not to be a guilty one. I resign gay Dress, the
Pleasure of Visits, Equipage, Plays, Balls, and Operas, for that one
Satisfaction of having you for ever mine. I am willing you shall
industriously conceal the only Cause of Triumph which I can know in
this Life. I wish only to have it my Duty, as well as my Inclination,
to study your Happiness. If this has not the Effect this Letter seems
to aim at, you are to understand that I had a mind to be rid of you,
and took the readiest Way to pall you with an Offer of what you would
never desist pursuing while you received ill Usage. Be a true Man; be
my Slave while you doubt me, and neglect me when you think I love you.
I defy you to find out what is your present Circumstance with me; but
I know while I can keep this Suspence.
I am your admired
Belinda.
Madam,
"It is a strange State of Mind a Man is in, when the very
Imperfections of a Woman he loves turn into Excellencies and
Advantages. I do assure you, I am very much afraid of venturing upon
you. I now like you in spite of my Reason, and think it an ill
Circumstance to owe one's Happiness to nothing but Infatuation. I can
see you ogle all the young Fellows who look at you, and observe your
Eye wander after new Conquests every Moment you are in a publick
Place; and yet there is such a Beauty in all your Looks and Gestures,
that I cannot but admire you in the very Act of endeavouring to gain
the Hearts of others.
My Condition is the same with that of the Lover
in the
Way of the World2, I have studied your Faults so long,
that they are become as familiar to me, and I like them as well as I
do my own. Look to it, Madam, and consider whether you think this gay
Behaviour will appear to me as amiable when an Husband, as it does now
to me a Lover. Things are so far advanced, that we must proceed; and I
hope you will lay it to Heart, that it will be becoming in me to
appear still your Lover, but not in you to be still my Mistress.
Gaiety in the Matrimonial Life is graceful in one Sex, but
exceptionable in the other. As you improve these little Hints, you
will ascertain the Happiness or Uneasiness of,
Madam, Your most
obedient,
Most humble Servant,
T.D.
Sir,
'When I sat at the Window, and you at the other End of the Room
by my Cousin, I saw you catch me looking at you. Since you have the
Secret at last, which I am sure you should never have known but by
Inadvertency, what my Eyes said was true. But it is too soon to
confirm it with my Hand, therefore shall not subscribe my Name.
Sir,
'There were other Gentlemen nearer, and I know no Necessity you
were under to take up that flippant Creature's Fan last Night; but you
shall never touch a Stick of mine more, that's pos.
Phillis.
To Colonel R——s
3 in Spain.
'Before this can reach the best of Husbands and the fondest Lover,
those tender Names will be no more of Concern to me. The Indisposition
in which you, to obey the Dictates of your Honour and Duty, left me,
has increased upon me; and I am acquainted by my Physicians I cannot
live a Week longer. At this time my Spirits fail me; and it is the
ardent Love I have for you that carries me beyond my Strength, and
enables me to tell you, the most painful Thing in the Prospect of
Death, is, that I must part with you. But let it be a Comfort to you,
that I have no Guilt hangs upon me, no unrepented Folly that retards
me; but I pass away my last Hours in Reflection upon the Happiness we
have lived in together, and in Sorrow that it is so soon to have an
End. This is a Frailty which I hope is so far from criminal, that
methinks there is a kind of Piety in being so unwilling to be
separated from a State which is the Institution of Heaven, and in
which we have lived according to its Laws. As we know no more of the
next Life, but that it will be an happy one to the Good, and miserable
to the Wicked, why may we not please ourselves at least, to alleviate
the Difficulty of resigning this Being, in imagining that we shall
have a Sense of what passes below, and may possibly be employed in
guiding the Steps of those with whom we walked with Innocence when
mortal? Why may not I hope to go on in my usual Work, and, tho'
unknown to you, be assistant in all the Conflicts of your Mind? Give
me leave to say to you, O best of Men, that I cannot figure to myself
a greater Happiness than in such an Employment: To be present at all
the Adventures to which human Life is exposed, to administer Slumber
to thy Eyelids in the Agonies of a Fever, to cover thy beloved Face in
the Day of Battle, to go with thee a Guardian Angel incapable of Wound
or Pain, where I have longed to attend thee when a weak, a fearful
Woman: These, my Dear, are the Thoughts with which I warm my poor
languid Heart; but indeed I am not capable under my present Weakness
of bearing the strong Agonies of Mind I fall into, when I form to
myself the Grief you will be in upon your first hearing of my
Departure. I will not dwell upon this, because your kind and generous
Heart will be but the more afflicted, the more the Person for whom you
lament offers you Consolation. My last Breath will, if I am my self,
expire in a Prayer for you. I shall never see thy Face again.
'Farewell for ever. T.
Saudades. To have
saudades
of anything is to yearn with
desire towards it.
Saudades da Patria
is home sickness. To say
Tenho
Saudades
without naming an object would be taken to mean I am all
yearning to call a certain gentleman or lady mine.
In Act I. sc. 3, of Congreve's
Way of the World
, Mirabell
says of Millamant,
'I like her with all her faults, nay, like her for her faults. Her
'follies are so natural, or so artful, that they become her; and those
affectations which in another woman would be odious, serve but to make
her more agreeable. I'll tell thee, Fainall, she once used me with
that insolence, that in revenge I took her to pieces, sifted her, and
separated her failings; I studied 'em and got 'em by rote. The
Catalogue was so large, that I was not without hopes one day or other
to hate her heartily: to which end I so used myself to think of 'em,
that at length, contrary to my design and expectation, they gave me
every hour less and less disturbance; 'till in a few days it became
habitual to me to remember 'em without being displeased. They are now
grown as familiar to me as my own frailties; and, in all probability,
in a little time longer I shall like 'em as well.'
The name was commonly believed to be Rivers, when this
Paper was published.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 25, 1711 |
Addison |
Decipimur specie recti
Hor.

When I meet with any vicious Character that is not generally known, in
order to prevent its doing Mischief, I draw it at length, and set it up
as a Scarecrow; by which means I do not only make an Example of the
Person to whom it belongs, but give Warning to all Her Majesty's
Subjects, that they may not suffer by it.
, to change the
Allusion
, I have marked out several of the Shoals and Quicksands of
Life,
am continually employed in discovering those
which
are
still concealed, in order to keep the Ignorant and Unwary from running
upon them. It is with this Intention that I publish the following
Letter, which brings to light some Secrets of this Nature.
Mr.
Spectator,
'There are none of your Speculations which I read over with greater
Delight, than those which are designed for the Improvement of our Sex.
You have endeavoured to correct our unreasonable Fears and
Superstitions, in your Seventh and Twelfth Papers; our Fancy for
Equipage, in your Fifteenth; our Love of Puppet-Shows, in your
Thirty-First; our Notions of Beauty, in your Thirty-Third; our
Inclination for Romances, in your Thirty-Seventh; our Passion for
French Fopperies, in your Forty-Fifth; our Manhood and Party-zeal,
in your Fifty-Seventh; our Abuse of Dancing, in your Sixty-Sixth and
Sixty-Seventh; our Levity, in your Hundred and Twenty-Eighth; our Love
of Coxcombs, in your Hundred and Fifty-Fourth, and Hundred and
Fifty-Seventh; our Tyranny over the Henpeckt, in your Hundred and
Seventy-Sixth. You have described the
Pict in your Forty-first; the
Idol, in your Seventy-Third; the Demurrer, in your Eighty-Ninth; the
Salamander, in your Hundred and Ninety-Eighth. You have likewise taken
to pieces our Dress, and represented to us the Extravagancies we are
often guilty of in that Particular. You have fallen upon our Patches,
in your Fiftieth and Eighty-First; our Commodes, in your
Ninety-Eighth; our Fans in your Hundred and Second; our Riding Habits
in your Hundred and Fourth; our Hoop-petticoats, in your Hundred and
Twenty-Seventh; besides a great many little Blemishes which you have
touched upon in your several other Papers, and in those many Letters
that are scattered up and down your Works. At the same Time we must
own, that the Compliments you pay our Sex are innumerable, and that
those very Faults which you represent in us, are neither black in
themselves nor, as you own, universal among us. But, Sir, it is plain
that these your Discourses are calculated for none but the fashionable
Part of Womankind, and for the Use of those who are rather indiscreet
than vicious. But, Sir, there is a Sort of Prostitutes in the lower
Part of our Sex, who are a Scandal to us, and very well deserve to
fall under your Censure. I know it would debase your Paper too much to
enter into the Behaviour of these Female Libertines; but as your
Remarks on some Part of it would be a doing of Justice to several
Women of Virtue and Honour, whose Reputations suffer by it, I hope you
will not think it improper to give the Publick some Accounts of this
Nature. You must know, Sir, I am provoked to write you this Letter by
the Behaviour of an infamous Woman, who having passed her Youth in a
most shameless State of Prostitution, is now one of those who gain
their Livelihood by seducing others, that are younger than themselves,
and by establishing a criminal Commerce between the two Sexes. Among
several of her Artifices to get Money, she frequently perswades a vain
young Fellow, that such a Woman of Quality, or such a celebrated
Toast, entertains a secret Passion for him, and wants nothing but an
Opportunity of revealing it:
Nay, she has gone so far as to write
Letters in the Name of a Woman of Figure, to borrow Money of one of
these foolish
Roderigo's3, which she has afterwards appropriated
to her own Use. In the mean time, the Person who has lent the Money,
has thought a Lady under Obligations to him, who scarce knew his Name;
and wondered at her Ingratitude when he has been with her, that she
has not owned the Favour, though at the same time he was too much a
Man of Honour to put her in mind of it.
'When this abandoned Baggage meets with a Man who has Vanity enough to
give Credit to Relations of this nature, she turns him to very good
Account, by repeating Praises that were never uttered, and delivering
Messages that were never sent. As the House of this shameless Creature
is frequented by several Foreigners, I have heard of another Artifice,
out of which she often raises Money. The Foreigner sighs after some
British Beauty, whom he only knows by Fame: Upon which she promises,
if he can be secret, to procure him a Meeting. The Stranger, ravished
at his good Fortune, gives her a Present, and in a little time is
introduced to some imaginary Title; for you must know that this
cunning Purveyor has her Representatives upon this Occasion, of some
of the finest Ladies in the Kingdom. By this Means, as I am informed,
it is usual enough to meet with a German Count in foreign Countries,
that shall make his Boasts of Favours he has received from Women of
the highest Ranks, and the most unblemished Characters. Now, Sir, what
Safety is there for a Woman's Reputation, when a Lady may be thus
prostituted as it were by Proxy, and be reputed an unchaste Woman; as
the Hero in the ninth Book of
Dryden's Virgil is looked upon as a
Coward, because the Phantom which appeared in his Likeness ran away
from
Turnus? You may depend upon what I relate to you to be Matter
of Fact, and the Practice of more than one of these female Pandars. If
you print this Letter, I may give you some further Accounts of this
vicious Race of Women.
Your humble Servant,
Belvidera.
I shall add two other Letters on different Subjects to fill up my Paper.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a Country Clergyman, and hope you will lend me your Assistance
in ridiculing some little Indecencies which cannot so properly be
exposed from the Pulpit.
'A Widow Lady, who straggled this Summer from
London into my Parish
for the Benefit of the Air, as she says, appears every
Sunday at
Church with many fashionable Extravagancies, to the great Astonishment
of my Congregation.
'But what gives us the most Offence is her theatrical Manner of
Singing the Psalms.
She introduces above fifty
Italian Airs into the
hundredth Psalm, and whilst we begin
All People in the old solemn
Tune of our Forefathers, she in a quite different Key runs Divisions
on the Vowels, and adorns them with the Graces of
Nicolini; if she
meets with Eke or Aye, which are frequent in the Metre of
Hopkins
and
Sternhold4, we are certain to hear her quavering them half a
Minute after us to some sprightly Airs of the Opera.
'I am very far from being an Enemy to Church Musick; but fear this
Abuse of it may make my
Parish ridiculous, who already look on the
Singing Psalms as an Entertainment, and no Part of their Devotion:
Besides, I am apprehensive that the Infection may spread, for Squire
Squeekum, who by his Voice seems (if I may use the Expression) to be
cut out for an
Italian Singer, was last
Sunday practising the same
Airs.
'I know the Lady's Principles, and that she will plead the Toleration,
which (as she fancies) allows her Non-Conformity in this Particular;
but I beg you to acquaint her, That Singing the Psalms in a different
Tune from the rest of the Congregation, is a Sort of Schism not
tolerated by that Act.
I am, Sir,
Your very humble Servant,
R. S.
Mr. Spectator,
'In your Paper upon Temperance, you prescribe to us a Rule of
drinking, out of Sir
William Temple, in the following Words;
The
first Glass for myself, the second for my Friends, the third for
Good-humour, and the fourth for mine Enemies. Now, Sir, you must
know, that I have read this your
Spectator, in a Club whereof I am a
Member; when our President told us, there was certainly an Error in
the Print, and that the Word
Glass should be
Bottle; and therefore
has ordered me to inform you of this Mistake, and to desire you to
publish the following
Errata: In the Paper of
Saturday, Octob.
13, Col. 3. Line 11, for
Glass read
Bottle.
L.
Yours, Robin Good-fellow.
L.
Metaphor
that
As the Roderigo whose money Iago used.
Thomas Sternhold who joined Hopkins, Norton, and others in
translation of the Psalms, was groom of the robes to Henry VIII. and
Edward VI.
Contents
|
Friday, October 26, 1711 |
Steele |
Quanto quisque sibi plura negaverit,
A Diis plura feret—
Hor.

There is a Call upon Mankind to value and esteem those who set a
moderate Price upon their own Merit; and Self-denial is frequently
attended with unexpected Blessings, which in the End abundantly
recompense such Losses as the Modest seem to suffer in the ordinary
Occurrences of Life. The Curious tell us, a Determination in our Favour
or to our Disadvantage is made upon our first Appearance, even before
they know any thing of our Characters, but from the Intimations Men
gather from our Aspect. A Man, they say, wears the Picture of his Mind
in his Countenance; and one Man's Eyes are Spectacles to his who looks
at him to read his Heart. But tho' that Way of raising an Opinion of
those we behold in Publick is very fallacious, certain it is, that
those, who by their Words and Actions take as much upon themselves, as
they can but barely demand in the strict Scrutiny of their Deserts, will
find their Account lessen every Day. A modest Man preserves his
Character, as a frugal Man does his Fortune; if either of them live to
the Height of either, one will find Losses, the other Errors, which he
has not Stock by him to make up. It were therefore a just Rule, to keep
your Desires, your Words and Actions, within the Regard you observe your
Friends have for you; and never, if it were in a Man's Power, to take as
much as he possibly might either in Preferment or Reputation. My Walks
have lately been among the mercantile Part of the World; and one gets
Phrases naturally from those with whom one converses: I say then, he
that in his Air, his Treatment of others, or an habitual Arrogance to
himself, gives himself Credit for the least Article of more Wit, Wisdom,
Goodness, or Valour than he can possibly produce if he is called upon,
will find the World break in upon him, and consider him as one who has
cheated them of all the Esteem they had before allowed him. This brings
a Commission of Bankruptcy upon him; and he that might have gone on to
his Life's End in a prosperous Way, by aiming at more than he should, is
no longer Proprietor of what he really had before, but his Pretensions
fare as all Things do which are torn instead of being divided.
There is no one living would deny
Cinna
the Applause of an agreeable
and facetious Wit; or could possibly pretend that there is not something
inimitably unforced and diverting in his Manner of delivering all his
Sentiments in Conversation, if he were able to conceal the strong Desire
of Applause which he betrays in every Syllable he utters. But they who
converse with him, see that all the Civilities they could do to him, or
the kind Things they could say to him, would fall short of what he
expects; and therefore instead of shewing him the Esteem they have for
his Merit, their Reflections turn only upon that they observe he has of
it himself.
If you go among the Women, and behold
Gloriana
trip into a Room with
that theatrical Ostentation of her Charms,
Mirtilla
with that soft
Regularity in her Motion,
Chloe
with such an indifferent Familiarity,
Corinna
with such a fond Approach, and
Roxana
with such a Demand of
Respect in the great Gravity of her Entrance; you find all the Sex, who
understand themselves and act naturally, wait only for their Absence, to
tell you that all these Ladies would impose themselves upon you; and
each of them carry in their Behaviour a Consciousness of so much more
than they should pretend to, that they lose what would otherwise be
given them.
I remember the last time I saw
Macbeth
, I was wonderfully taken with
the Skill of the Poet, in making the Murderer form Fears to himself from
the Moderation of the Prince whose Life he was going to take away. He
says of the King,
He bore his Faculties so meekly
; and justly inferred
from thence, That all divine and human Power would join to avenge his
Death, who had made such an abstinent Use of Dominion. All that is in a
Man's Power to do to advance his own Pomp and Glory, and forbears, is so
much laid up against the Day of Distress; and Pity will always be his
Portion in Adversity, who acted with Gentleness in Prosperity.
The great Officer who foregoes the Advantages he might take to himself,
and renounces all prudential Regards to his own Person in Danger, has so
far the Merit of a Volunteer; and all his Honours and Glories are
unenvied, for sharing the common Fate with the same Frankness as they do
who have no such endearing Circumstances to part with. But if there were
no such Considerations as the good Effect which Self-denial has upon the
Sense of other Men towards us, it is of all Qualities the most desirable
for the agreeable Disposition in which it places our own Minds. I cannot
tell what better to say of it, than that it is the very Contrary of
Ambition; and that Modesty allays all those Passions and Inquietudes to
which that Vice exposes us. He that is moderate in his Wishes from
Reason and Choice, and not resigned from Sourness, Distaste, or
Disappointment, doubles all the Pleasures of his Life.
Air, the
Season, a
Sun-shiny
Day, or a fair Prospect, are Instances of
Happiness, and that which he enjoys in common with all the World, (by
his Exemption from the Enchantments by which all the World are
bewitched) are to him uncommon Benefits and new Acquisitions. Health is
not eaten up with Care, nor Pleasure interrupted by Envy. It is not to
him of any Consequence what this Man is famed for, or for what the other
is preferred. He knows there is in such a Place an uninterrupted Walk;
he can meet in such a Company an agreeable Conversation: He has no
Emulation, he is no Man's Rival, but every Man's Well-wisher; can look
at a prosperous Man, with a Pleasure in reflecting that he hopes he is
as happy as himself; and has his Mind and his Fortune (as far as
Prudence will allow) open to the Unhappy and to the Stranger.
Lucceius
has Learning, Wit, Humour, Eloquence, but no ambitious
Prospects to pursue with these Advantages; therefore to the ordinary
World he is perhaps thought to want Spirit, but known among his Friends
to have a Mind of the most consummate Greatness. He wants no Man's
Admiration, is in no Need of Pomp. His Cloaths please him if they are
fashionable and warm; his Companions are agreeable if they are civil and
well-natured. There is with him no Occasion for Superfluity at Meals,
for Jollity in Company, in a word, for any thing extraordinary to
administer Delight to him. Want of Prejudice and Command of Appetite are
the Companions which make his Journey of Life so easy, that he in all
Places meets with more Wit, more good Cheer and more good Humour, than
is necessary to make him enjoy himself with Pleasure and Satisfaction.
T.
Sun-shine
, and in the first reprint.
Contents
|
Saturday, October 27, 1711 |
Addison |
Omnibus in terris, quœ sunt à Gadibus usque
Auroram et Gangem, pauci dignoscere possunt
Vera bona, atque illis multùm diversa, remotâ
Erroris nebulâ—
Juv.

In my last
Saturday's
Paper I laid down some Thoughts upon Devotion in
general, and shall here shew what were the Notions of the most refined
Heathens on this Subject, as they are represented in
Plato's
Dialogue
upon Prayer, entitled,
Alcibiades the Second
, which doubtless gave
Occasion to
Juvenal's
tenth Satire, and to the second Satire of
Persius
; as the last of these Authors has almost transcribed the
preceding Dialogue, entitled
Alcibiades the First
, in his Fourth
Satire.
The Speakers in this Dialogue upon Prayer, are
Socrates
and
Alcibiades
; and the Substance of it (when drawn together out of the
Intricacies and Digressions) as follows.
Socrates
meeting his Pupil
Alcibiades
, as he was going to his
Devotions, and observing his Eyes to be fixed upon the Earth with great
Seriousness and Attention, tells him, that he had reason to be
thoughtful on that Occasion, since it was possible for a Man to bring
down Evils upon himself by his own Prayers, and that those things, which
the Gods send him in Answer to his Petitions, might turn to his
Destruction: This, says he, may not only happen when a Man prays for
what he knows is mischievous in its own Nature, as
Œdipus
implored
the Gods to sow Dissension between his Sons; but when he prays for what
he believes would be for his Good, and against what he believes would be
to his Detriment. This the Philosopher shews must necessarily happen
among us, since most Men are blinded with Ignorance, Prejudice, or
Passion, which hinder them from seeing such things as are really
beneficial to them. For an Instance, he asks
Alcibiades
, Whether he
would not be thoroughly pleased and satisfied if that God, to whom he
was going to address himself, should promise to make him the Sovereign
of the whole Earth?
Alcibiades
answers, That he should doubtless look
upon such a Promise as the greatest Favour that he could bestow upon
.
Socrates
then asks him, If after
receiving
this great
Favour he would be content
ed
to lose his Life? or if he would receive
it though he was sure he should make an ill Use of it? To both which
Questions
Alcibiades
answers in the Negative. Socrates then shews him,
from the Examples of others, how these might very probably be the
Effects of such a Blessing. He then adds, That other reputed Pieces of
Good-fortune, as that of having a Son, or procuring the highest Post in
a Government, are subject to the like fatal Consequences; which
nevertheless, says he, Men ardently desire, and would not fail to pray
for, if they thought their Prayers might be effectual for the obtaining
of them. Having established this great Point, That all the most apparent
Blessings in this Life are obnoxious to such dreadful Consequences, and
that no Man knows what in its Events would prove to him a Blessing or a
Curse, he teaches
Alcibiades
after what manner he ought to pray.
In the first Place, he recommends to him, as the Model of his Devotions,
a short Prayer, which a
Greek
Poet composed for the Use of his
Friends, in the following Words;
O
Jupiter,
give us those Things
which are good for us, whether they are such Things as we pray for, or
such Things as we do not pray for: and remove from us those Things which
are hurtful, though they are such Things as we pray for.
In the second Place, that his Disciple may ask such Things as are
expedient for him, he shews him, that it is absolutely necessary to
apply himself to the Study of true Wisdom, and to the Knowledge of that
which is his chief Good, and the most suitable to the Excellency of his
Nature.
In the third and last Place he informs him, that the best Method he
could make use of to draw down Blessings upon himself, and to render his
Prayers acceptable, would be to live in a constant Practice of his Duty
towards the Gods, and towards Men. Under this Head he very much
recommends a Form of Prayer the
Lacedemonians
made use of, in which
they petition the Gods,
to give them all good Things so long as they
were virtuous
. Under this Head likewise he gives a very remarkable
Account of an Oracle to the following Purpose.
When the
Athenians
in the War with the
Lacedemonians
received many
Defeats both by Sea and Land, they sent a Message to the Oracle of
Jupiter Ammon
, to ask the Reason why they who erected so many Temples
to the Gods, and adorned them with such costly Offerings; why they who
had instituted so many Festivals, and accompanied them with such Pomps
and Ceremonies; in short, why they who had slain so many Hecatombs at
their Altars, should be less successful than the
Lacedemonians
, who
fell so short of them in all these Particulars. To this, says he, the
Oracle made the following Reply;
I am better pleased with the Prayer of
the
Lacedemonians,
than with all the Oblations of the
Greeks.
this
Prayer implied and encouraged Virtue in those who made it, the
Philosopher proceeds to shew how the most vicious Man might be devout,
so far as Victims could make him, but that his Offerings were regarded
by the Gods as Bribes, and his Petitions as Blasphemies. He likewise
quotes on this Occasion two Verses out of
Homer
, in which the Poet
says, That the Scent of the
Trojan
Sacrifices was carried up to Heaven
by the Winds; but that it was not acceptable to the Gods, who were
displeased with
Priam
and all his People.
The Conclusion of this Dialogue is very remarkable.
Socrates
having
deterred
Alcibiades
from the Prayers and Sacrifice which he was going
to offer, by setting forth the above-mentioned Difficulties of
performing that Duty as he ought, adds these Words,
We must therefore
wait till such Time as we may learn how we ought to behave ourselves
towards the Gods, and towards Men
. But when will that Time come, says
Alcibiades
, and who is it that will instruct us? For I would fain see
this Man, whoever he is.
is one, says
Socrates
, who takes care of
you; but as
Homer
tells us
, that
Minerva
removed the Mist from
Diomedes
his Eyes, that he might plainly discover both Gods and Men;
so the Darkness that hangs upon your Mind must be removed before you are
able to discern what is Good and what is Evil. Let him remove from my
Mind, says
Alcibiades
, the Darkness, and what else he pleases, I am
determined to refuse nothing he shall order me, whoever he is, so that I
may become the better Man by it. The remaining Part of this Dialogue is
very obscure: There is something in it that would make us think
Socrates
hinted at himself, when he spoke of this Divine Teacher who
was to come into the World, did not he own that he himself was in this
respect as much at a Loss, and in as great Distress as the rest of
Mankind.
learned Men look upon this Conclusion as a Prediction of our
Saviour, or at least that Socrates, like the High-Priest
, prophesied
unknowingly, and pointed at that Divine Teacher who was to come into the
World some Ages after him. However that may be, we find that this great
Philosopher saw, by the Light of Reason, that it was suitable to the
Goodness of the Divine Nature, to send a Person into the World who
should instruct Mankind in the Duties of Religion, and, in particular,
teach them how to Pray.
Whoever reads this Abstract of
Plato's
Discourse on Prayer, will, I
believe, naturally make this Reflection, That the great Founder of our
Religion, as well by his own Example, as in the Form of Prayer which he
taught his Disciples, did not only keep up to those Rules which the
Light of Nature had suggested to this great Philosopher, but instructed
his Disciples in the whole Extent of this Duty, as well as of all
others. He directed them to the proper Object of Adoration, and taught
them, according to the third Rule above-mentioned, to apply themselves
to him in their Closets, without Show or Ostentation, and to worship him
in Spirit and in Truth. As the
Lacedemonians
in their Form of Prayer
implored the Gods in general to give them all good things so long as
they were virtuous, we ask in particular
that our Offences may be
forgiven, as we forgive those of others
. If we look into the second
Rule which
Socrates
has prescribed, namely, That we should apply
ourselves to the Knowledge of such Things as are best for us, this too
is explain'd at large in the Doctrines of the Gospel, where we are
taught in several Instances to regard those things as Curses, which
appear as Blessings in the Eye of the World; and on the contrary, to
esteem those things as Blessings, which to the Generality of Mankind
appear as Curses. Thus in the Form which is prescribed to us we only
pray for that Happiness which is our chief Good, and the great End of
our Existence, when we petition the Supreme Being for
the coming of his
Kingdom, being solicitous for no other temporal Blessings but our daily
Sustenance
. On the other side, We pray against nothing but Sin, and
against
Evil
in general, leaving it with Omniscience to determine what
is really such. If we look into the first of
Socrates
his Rules of
Prayer, in which he recommends the above-mentioned Form of the ancient
Poet, we find that Form not only comprehended, but very much improved in
the Petition, wherein we pray to the Supreme Being that
his Will may be
done:
which is of the same Force with that Form which our Saviour used,
when he prayed against the most painful and most ignominious of Deaths,
Nevertheless not my Will, but thine be done
. This comprehensive
Petition is the most humble, as well as the most prudent, that can be
offered up from the Creature to his Creator, as it supposes the Supreme
Being wills nothing but what is for our Good, and that he knows better
than ourselves what is so.
L.
having received
, and in first reprint.
Iliad
, viii. 548, 9.
Iliad
, v. 127.
John
xi. 49.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 1, 1711 |
Addison |
—Veniunt spectentur ut ipsæ.
Ov.
1
I have several Letters of People of good Sense, who lament the Depravity
or Poverty of Taste the Town is fallen into with relation to Plays and
publick Spectacles. A Lady in particular observes, that there is such a
Levity in the Minds of her own Sex, that they seldom attend any thing
but Impertinences. It is indeed prodigious to observe how little Notice
is taken of the most exalted Parts of the best Tragedies in
Shakespear
; nay, it is not only visible that Sensuality has devoured
all Greatness of Soul, but the Under-Passion (as I may so call it) of a
noble Spirit, Pity, seems to be a Stranger to the Generality of an
Audience. The Minds of Men are indeed very differently disposed; and the
Reliefs from Care and Attention are of one Sort in a great Spirit, and
of another in an ordinary one. The Man of a great Heart and a serious
Complexion, is more pleased with Instances of Generosity and Pity, than
the light and ludicrous Spirit can possibly be with the highest Strains
of Mirth and Laughter: It is therefore a melancholy Prospect when we see
a numerous Assembly lost to all serious Entertainments, and such
Incidents, as should move one sort of Concern, excite in them a quite
contrary one.
the Tragedy of
Macbeth
, the other Night
, when the
Lady who is conscious of the Crime of murdering the King, seems utterly
astonished at the News, and makes an Exclamation at it, instead of the
Indignation which is natural to the Occasion, that Expression is
received with a loud Laugh: They were as merry when a Criminal was
stabbed. It is certainly an Occasion of rejoycing when the Wicked are
seized in their Designs; but I think it is not such a Triumph as is
exerted by Laughter.
You may generally observe, that the Appetites are sooner moved than the
Passions: A sly Expression which alludes to Bawdry, puts a whole Row
into a pleasing Smirk; when a good Sentence that describes an inward
Sentiment of the Soul, is received with the greatest Coldness and
Indifference. A Correspondent of mine, upon this Subject, has divided
the Female Part of the Audience, and accounts for their Prepossession
against this reasonable Delight in the following Manner. The Prude, says
he, as she acts always in Contradiction, so she is gravely sullen at a
Comedy, and extravagantly gay at a Tragedy. The Coquette is so much
taken up with throwing her Eyes around the Audience, and considering the
Effect of them, that she cannot be expected to observe the Actors but as
they are her Rivals, and take off the Observation of the Men from her
self. Besides these Species of Women, there are the
Examples
, or the
first of the Mode: These are to be supposed too well acquainted with
what the Actor was going to say to be moved at it. After these one might
mention a certain flippant Set of Females who are Mimicks, and are
wonderfully diverted with the Conduct of all the People around them, and
are Spectators only of the Audience. But what is of all the most to be
lamented, is the Loss of a Party whom it would be worth preserving in
their right Senses upon all Occasions, and these are those whom we may
indifferently call the Innocent or the Unaffected. You may sometimes see
one of these sensibly touched with a well-wrought Incident; but then she
is immediately so impertinently observed by the Men, and frowned at by
some insensible Superior of her own Sex, that she is ashamed, and loses
the Enjoyment of the most laudable Concern, Pity. Thus the whole
Audience is afraid of letting fall a Tear, and shun as a Weakness the
best and worthiest Part of our Sense.
| Pray settle what is to be a proper Notification of a
Person's being in Town, and how that differs according to People's
Quality. |
Sir,
'As you are one that doth not only pretend to reform, but effects it
amongst People of any Sense; makes me (who are one of the greatest of
your Admirers) give you this Trouble to desire you will settle the
Method of us Females knowing when one another is in Town: For they
have now got a Trick of never sending to their Acquaintance when they
first come; and if one does not visit them within the Week which they
stay at home, it is a mortal Quarrel. Now, dear Mr. Spec, either
command them to put it in the Advertisement of your Paper, which is
generally read by our Sex, or else order them to breathe their saucy
Footmen (who are good for nothing else) by sending them to tell all
their Acquaintance. If you think to print this, pray put it into a
better Style as to the spelling Part. The Town is now filling every
Day, and it cannot be deferred, because People take Advantage of one
another by this Means and break off Acquaintance, and are rude:
Therefore pray put this in your Paper as soon as you can possibly, to
prevent any future Miscarriages of this Nature. I am, as I ever shall
be,
Dear Spec,
Your most obedient
Humble Servant,
Mary Meanwell. |
Mr.
Spectator,
October
the 20th.
'I have been out of Town, so did not meet with your Paper dated
September the 28th, wherein you, to my Heart's Desire, expose that
cursed Vice of ensnaring poor young Girls, and drawing them from their
Friends. I assure you without Flattery it has saved a Prentice of mine
from Ruin; and in Token of Gratitude as well as for the Benefit of my
Family, I have put it in a Frame and Glass, and hung it behind my
Counter. I shall take Care to make my young ones read it every
Morning, to fortify them against such pernicious Rascals. I know not
whether what you writ was Matter of Fact, or your own Invention; but
this I will take my Oath on, the first Part is so exactly like what
happened to my Prentice, that had I read your Paper then, I should
have taken your Method to have secured a Villain. Go on and prosper.
Your most obliged Humble Servant,
Mr.
Spectator,
'Without Raillery, I desire you to insert this Word for Word in your
next, as you value a Lover's Prayers. You see it is an Hue and Cry
after a stray Heart (with the Marks and Blemishes underwritten) which
whoever shall bring to you, shall receive Satisfaction. Let me beg of
you not to fail, as you remember the Passion you had for her to whom
you lately ended a Paper.
Noble, Generous, Great, and Good,
But never to be understood;
Fickle as the Wind, still changing,
After every Female ranging,
Panting, trembling, sighing, dying,
But addicted much to Lying:
When the Siren Songs repeats,
Equal Measures still it beats;
Who-e'er shall wear it, it will smart her,
And who-e'er takes it, takes a Tartar.
T.
Spectaret Populum ludis attentius ipsis
.-Hor.
Acted Saturday, October 20.
Contents
|
Tuesday, October 30, 1711 |
Addison |
There are no Authors I am more pleased with than those who shew human
Nature in a Variety of Views, and describe the several Ages of the World
in their different Manners. A Reader cannot be more rationally
entertained, than by comparing the Virtues and Vices of his own Times
with those which prevailed in the Times of his Forefathers; and drawing
a Parallel in his Mind between his own private Character, and that of
other Persons, whether of his own Age, or of the Ages that went before
him. The Contemplation of Mankind under these changeable Colours, is apt
to shame us out of any particular Vice, or animate us to any particular
Virtue, to make us pleased or displeased with our selves in the most
proper Points, to clear our Minds of Prejudice and Prepossession, and
rectify that Narrowness of Temper which inclines us to think amiss of
those who differ from our selves.
If we look into the Manners of the most remote Ages of the World, we
discover human Nature in her Simplicity; and the more we come downwards
towards our own Times, may observe her hiding herself in Artifices and
Refinements, Polished insensibly out of her Original Plainness, and at
length entirely lost under Form and Ceremony, and (what we call) good
Breeding. Read the Accounts of Men and Women as they are given us by the
most ancient Writers, both Sacred and Prophane, and you would think you
were reading the History of another Species.
Among the Writers of Antiquity, there are none who instruct us more
openly in the Manners of their respective Times in which they lived,
than those who have employed themselves in Satyr, under what Dress
soever it may appear; as there are no other Authors whose Province it is
to enter so directly into the Ways of Men, and set their Miscarriages in
so strong a Light.
Simonides
, a Poet famous in his Generation, is, I think, Author of
the oldest Satyr that is now extant; and, as some say, of the first that
was ever written. This Poet flourished about four hundred Years after
the Siege of
Troy
; and shews, by his way of Writing, the Simplicity,
or rather Coarseness, of the Age in which he lived. I have taken notice,
in my Hundred and sixty first Speculation, that the Rule of observing
what the
French
call the
bienséance
, in an Allusion, has been found
out of later Years; and that the Ancients, provided there was a Likeness
in their Similitudes, did not much trouble themselves about the Decency
of the Comparison. The Satyr or Iambicks of
Simonides
, with which I
shall entertain my Readers in the present Paper, are a remarkable
Instance of what I formerly advanced. The Subject of this Satyr is
Woman. He describes the Sex in their several Characters, which he
derives to them from a fanciful Supposition raised upon the Doctrine of
Præexistence. He tells us, That the Gods formed the Souls of Women out
of those Seeds and Principles which compose several Kinds of Animals and
Elements; and that their Good or Bad Dispositions arise in them
according as such and such Seeds and Principles predominate in their
Constitutions. I have translated the Author very faithfully, and if not
Word for Word (which our Language would not bear) at least so as to
comprehend every one of his Sentiments, without adding any thing of my
own. I have already apologized for this Author's Want of Delicacy, and
must further premise, That the following Satyr affects only some of the
lower part of the Sex, and not those who have been refined by a Polite
Education, which was not so common in the Age of this Poet.
In the Beginning God made the Souls of Womankind out of different
Materials, and in a separate State from their Bodies.
The Souls of one Kind of Women were formed out of those Ingredients
which compose a Swine. A Woman of this Make is a Slut in her House and
a Glutton at her Table. She is uncleanly in her Person, a Slattern in
her Dress, and her Family is no better than a Dunghill.
A Second Sort of Female Soul was formed out of the same Materials
that enter into the Composition of a Fox. Such an one is what we call
a notable discerning Woman, who has an Insight into every thing,
whether it be good or bad. In this Species of Females there are some
Virtuous and some Vicious.
A Third Kind of Women were made up of Canine Particles. These are
what we commonly call Scolds, who imitate the Animals of which they
were taken, that are always busy and barking, that snarl at every one
who comes in their Way, and live in perpetual Clamour.
The Fourth Kind of Women were made out of the Earth. These are your
Sluggards, who pass away their Time in Indolence and Ignorance, hover
over the Fire a whole Winter, and apply themselves with Alacrity to no
kind of Business but Eating.
The Fifth Species of Females were made out of the Sea. These are
Women of variable uneven Tempers, sometimes all Storm and Tempest,
sometimes all Calm and Sunshine. The Stranger who sees one of these in
her Smiles and Smoothness would cry her up for a Miracle of good
Humour; but on a sudden her Looks and her Words are changed, she is
nothing but Fury and Outrage, Noise and Hurricane.
The Sixth Species were made up of the Ingredients which compose an
Ass, or a Beast of Burden. These are naturally exceeding slothful,
but, upon the Husband's exerting his Authority, will live upon hard
Fare, and do every thing to please him. They are however far from
being averse to Venereal Pleasure, and seldom refuse a Male
Companion.
The Cat furnished Materials for a Seventh Species of Women, who are
of a melancholy, froward, unamiable Nature, and so repugnant to the
Offers of Love, that they fly in the Face of their Husband when he
approaches them with conjugal Endearments. This Species of Women are
likewise subject to little Thefts, Cheats and Pilferings.
The Mare with a flowing Mane, which was never broke to any servile
Toil and Labour, composed an Eighth Species of Women. These are they
who have little Regard for their Husbands, who pass away their Time in
Dressing, Bathing, and Perfuming; who throw their Hair into the nicest
Curls, and trick it up with the fairest Flowers and Garlands. A Woman
of this Species is a very pretty Thing for a Stranger to look upon,
but very detrimental to the Owner, unless it be a King or Prince who
takes a Fancy to such a Toy.
The Ninth Species of Females were taken out of the Ape. These are
such as are both ugly and ill-natured, who have nothing beautiful in
themselves, and endeavour to detract from or ridicule every thing
which appears so in others.
The Tenth and last Species of Women were made out of the Bee; and
happy is the Man who gets such an one for his Wife. She is altogether
faultless and unblameable; her Family flourishes and improves by her
good Management. She loves her Husband, and is beloved by him. She
brings him a Race of beautiful and virtuous Children. She
distinguishes her self among her Sex. She is surrounded with Graces.
She never sits among the loose Tribe of Women, nor passes away her
Time with them in wanton Discourses. She is full of Virtue and
Prudence, and is the best Wife that Jupiter can bestow on Man.
I shall conclude these Iambicks with the Motto of this Paper, which is a
Fragment of the same Author:
A Man cannot possess any Thing that is
better than a good Woman, nor any thing that is worse than a bad one
.
As the Poet has shewn a great Penetration in this Diversity of Female
Characters, he has avoided the Fault which
Juvenal
and Monsieur
Boileau
are guilty of, the former in his sixth, and the other in his
last Satyr, where they have endeavoured to expose the Sex in general,
without doing Justice to the valuable Part of it. Such levelling Satyrs
are of no Use to the World, and for this Reason I have often wondered
how the
French
Author above-mentioned, who was a Man of exquisite
Judgment, and a Lover of Virtue, could think human Nature a proper
Subject for Satyr in another of his celebrated Pieces, which is called
The Satyr upon Man
. What Vice or Frailty can a Discourse correct,
which censures the whole Species alike, and endeavours to shew by some
Superficial Strokes of Wit, that Brutes are the more excellent Creatures
of the two? A Satyr should expose nothing but what is corrigible, and
make a due Discrimination between those who are, and those who are not
the proper Objects of it.
L.
Of the poems of Simonides, contemporary of Æschylus, only
fragments remain. He died about 467 B.C.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 31, 1711 |
John Hughes |
Nescio quomodo inhæret in mentibus quasi seculorum quoddam augurium
futurorum; idque in maximis ingeniis altissimisque animis et existit
maxime et apparet facillime.
Cic. Tusc. Quæst.

To the Spectator.
Sir,
'I am fully persuaded that one of the best Springs of generous and
worthy Actions, is the having generous and worthy Thoughts of our
selves. Whoever has a mean Opinion of the Dignity of his Nature, will
act in no higher a Rank than he has allotted himself in his own
Estimation. If he considers his Being as circumscribed by the
uncertain Term of a few Years, his Designs will be contracted into the
same narrow Span he imagines is to bound his Existence. How can he
exalt his Thoughts to any thing great and noble, who only believes
that, after a short Turn on the Stage of this World, he is to sink
into Oblivion, and to lose his Consciousness for ever?
'For this Reason I am of Opinion, that so useful and elevated a
Contemplation as that of the
Soul's Immortality cannot be resumed
too often. There is not a more improving Exercise to the human Mind,
than to be frequently reviewing its own great Privileges and
Endowments; nor a more effectual Means to awaken in us an Ambition
raised above low Objects and little Pursuits, than to value our selves
as Heirs of Eternity.
'It is a very great Satisfaction to consider the best and wisest of
Mankind in all Nations and Ages, asserting, as with one Voice, this
their Birthright, and to find it ratify'd by an express Revelation. At
the same time if we turn our Thoughts inward upon our selves, we may
meet with a kind of secret Sense concurring with the Proofs of our own
Immortality.
'You have, in my Opinion, raised a good presumptive Argument from the
increasing Appetite the Mind has to Knowledge, and to the extending
its own Faculties, which cannot be accomplished, as the more
restrained Perfection of lower Creatures may, in the Limits of a short
Life. I think another probable Conjecture may be raised from our
Appetite to Duration it self, and from a Reflection on our Progress
through the several Stages of it:
We are complaining, as you observe
in a former Speculation,
of the Shortness of Life, and yet are
perpetually hurrying over the Parts of it, to arrive at certain little
Settlements, or imaginary Points of Rest, which are dispersed up and
down in it.
'Now let us consider what happens to us when we arrive at these
imaginary Points of Rest: Do we stop our Motion, and sit down
satisfied in the Settlement we have gain'd? or are we not removing the
Boundary, and marking out new Points of Rest, to which we press
forward with the like Eagerness, and which cease to be such as fast as
we attain them?
Our Case is like that of a Traveller upon the
Alps,
who should fancy that the Top of the next Hill must end his Journey,
because it terminates his Prospect; but he no sooner arrives as it,
than he sees new Ground and other Hills beyond it, and continues to
travel on as before
1.
'This is so plainly every Man's Condition in Life, that there is no
one who has observed any thing, but may observe, that as fast as his
Time wears away, his Appetite to something future remains. The Use
therefore I would make of it is this, That since Nature (as some love
to express it) does nothing in vain, or, to speak properly, since the
Author of our Being has planted no wandering Passion in it, no Desire
which has not its Object, Futurity is the proper Object of the Passion
so constantly exercis'd about it; and this Restlessness in the
present, this assigning our selves over to further Stages of Duration,
this successive grasping at somewhat still to come, appears to me
(whatever it may to others) as a kind of Instinct or natural Symptom
which the Mind of Man has of its own Immortality.
'I take it at the same time for granted, that the Immortality of the
Soul is sufficiently established by other Arguments: And if so, this
Appetite, which otherwise would be very unaccountable and absurd,
seems very reasonable, and adds Strength to the Conclusion. But I am
amazed when I consider there are Creatures capable of Thought, who, in
spite of every Argument, can form to themselves a sullen Satisfaction
in thinking otherwise. There is something so pitifully mean in the
inverted Ambition of that Man who can hope for Annihilation, and
please himself to think that his whole Fabrick shall one Day crumble
into Dust, and mix with the Mass of inanimate Beings, that it equally
deserves our Admiration and Pity. The Mystery of such Mens Unbelief is
not hard to be penetrated; and indeed amounts to nothing more than a
sordid Hope that they shall not be immortal, because they dare not be
so.
'This brings me back to my first Observation, and gives me Occasion to
say further, That as worthy Actions spring from worthy Thoughts, so
worthy Thoughts are likewise the Consequence of worthy Actions: But
the Wretch who has degraded himself below the Character of
Immortality, is very willing to resign his Pretensions to it, and to
substitute in its Room a dark negative Happiness in the Extinction of
his Being.
'The admirable
Shakespear has given us a strong Image of the
unsupported Condition of such a Person in his last Minutes, in the
second Part of King
Henry the Sixth, where Cardinal
Beaufort, who
had been concerned in the Murder of the good Duke
Humphrey, is
represented on his Death-bed. After some short confused Speeches which
shew an Imagination disturbed with Guilt, just as he is expiring, King
Henry standing by him full of Compassion, says,
Lord Cardinal! if thou think'st on Heaven's Bliss,
Hold up thy Hand, make Signal of that Hope!
He dies, and makes no Sign!—
'The Despair which is here shewn, without a Word or Action on the Part
of the dying Person, is beyond what could be painted by the most
forcible Expressions whatever.
'I shall not pursue this Thought further, but only add, That as
Annihilation is not to be had with a Wish, so it is the most abject
Thing in the World to wish it. What are Honour, Fame, Wealth, or Power
when compared with the generous Expectation of a Being without End,
and a Happiness adequate to that Being?
'I shall trouble you no further; but with a certain Gravity which
these Thoughts have given me, I reflect upon some Things People say of
you, (as they will of Men who distinguish themselves) which I hope are
not true; and wish you as good a Man as you are an Author.
I am, Sir,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
T. D.
Z.
'Hills peep o'er Hills, and Alps on Alps arise.'
Pope's
Essay on Criticism
, then newly published.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 1, 1711 |
Addison |
Fictis meminerit nos jocari Fabulis.
Phæd.

Having lately translated the Fragment of an old Poet which describes
Womankind under several Characters, and supposes them to have drawn
their different Manners and Dispositions from those Animals and Elements
out of which he tells us they were compounded; I had some Thoughts of
giving the Sex their Revenge, by laying together in another Paper the
many vicious Characters which prevail in the Male World, and shewing the
different Ingredients that go to the making up of such different Humours
and Constitutions.
Horace
a Thought
which is something akin to
this, when, in order to excuse himself to his Mistress, for an Invective
which he had written against her, and to account for that unreasonable
Fury with which the Heart of Man is often transported, he tells us that,
when
Prometheus
made his Man of Clay, in the kneading up of his Heart,
he season'd it with some furious Particles of the Lion. But upon turning
this Plan to and fro in my Thoughts, I observed so many unaccountable
Humours in Man, that I did not know out of what Animals to fetch them.
Male Souls are diversify'd with so many Characters, that the World has
not Variety of Materials sufficient to furnish out their different
Tempers and Inclinations. The Creation, with all its Animals and
Elements, would not be large enough to supply their several
Extravagancies.
Instead therefore of pursuing the Thought of
Simonides
, I shall
observe, that as he has exposed the vicious Part of Women from the
Doctrine of Præexistence, some of the ancient Philosophers have, in a
manner, satirized the vicious Part of the human Species in general, from
a Notion of the Soul's Postexistence, if I may so call it; and that as
Simonides
describes Brutes entering into the Composition of Women,
others have represented human Souls as entering into Brutes. This is
commonly termed the Doctrine of Transmigration, which supposes that
human Souls, upon their leaving the Body, become the Souls of such Kinds
of Brutes as they most resemble in their Manners; or to give an Account
of it as Mr.
Dryden
has described it in his Translation of
Pythagoras
his Speech in the fifteenth Book of
Ovid
, where that
Philosopher dissuades his Hearers from eating Flesh:
Thus all things are but alter'd, nothing dies,
And here and there th' unbody'd Spirit flies:
By Time, or Force, or Sickness dispossess'd,
And lodges where it lights, in Bird or Beast,
Or hunts without till ready Limbs it find,
And actuates those according to their Kind:
From Tenement to Tenement is toss'd:
The Soul is still the same, the Figure only lost.
Then let not Piety be put to Flight,
To please the Taste of Glutton-Appetite;
But suffer inmate Souls secure to dwell,
Lest from their Seats your Parents you expel;
With rabid Hunger feed upon your Kind,
Or from a Beast dislodge a Brother's Mind.
Plato
the Vision of
Erus
the
Armenian
, which I may possibly
make the Subject of a future Speculation, records some beautiful
Transmigrations; as that the Soul of
Orpheus
, who was musical,
melancholy, and a Woman-hater, entered into a Swan; the Soul of
Ajax
,
which was all Wrath and Fierceness, into a Lion; the Soul of
Agamemnon
, that was rapacious and imperial, into an Eagle; and the
Soul of
Thersites
, who was a Mimick and a Buffoon, into a Monkey
.
.
Congreve
, in a Prologue to one of his Comedies
, has touch'd
upon this Doctrine with great Humour.
Thus Aristotle's Soul of old that was,
May now be damn'd to animate an Ass;
Or in this very House, for ought we know,
Is doing painful Penance in some Beau.
I shall fill up this Paper with some Letters which my last
Tuesday's
Speculation has produced. My following Correspondents will shew, what I
there observed, that the Speculation of that Day affects only the lower
Part of the Sex.
From my House in the Strand, October 30, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Upon reading your
Tuesday's Paper, I find by several Symptoms in my
Constitution that I am a Bee. My Shop, or, if you please to call it
so, my Cell, is in that great Hive of Females which goes by the Name
of
The New Exchange; where I am daily employed in gathering together
a little Stock of Gain from the finest Flowers about the Town, I mean
the Ladies and the Beaus. I have a numerous Swarm of Children, to whom
I give the best Education I am able: But, Sir, it is my Misfortune to
be married to a Drone, who lives upon what I get, without bringing any
thing into the common Stock.
Now, Sir, as on the one hand I take care
not to behave myself towards him like a Wasp, so likewise I would not
have him look upon me as an Humble-Bee; for which Reason I do all I
can to put him upon laying up Provisions for a bad Day, and frequently
represent to him the fatal Effects
his4 Sloth and Negligence may
bring upon us in our old Age. I must beg that you will join with me in
your good Advice upon this Occasion, and you will for ever oblige
Your humble Servant,
Melissa.
Picadilly, October 31, 1711.
Sir,
'I am joined in Wedlock for my Sins to one of those Fillies who are
described in the old Poet with that hard Name you gave us the other
Day. She has a flowing Mane, and a Skin as soft as Silk: But, Sir, she
passes half her Life at her Glass, and almost ruins me in Ribbons. For
my own part, I am a plain handicraft Man, and in Danger of breaking by
her Laziness and Expensiveness. Pray, Master, tell me in your next
Paper, whether I may not expect of her so much Drudgery as to take
care of her Family, and curry her Hide in case of Refusal.
Your loving Friend,
Barnaby Brittle.
Cheapside, October 30.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am mightily pleased with the Humour of the Cat, be so kind as to
enlarge upon that Subject.
Yours till Death,
Josiah Henpeck.
P. S. You must know I am married to a
Grimalkin.
Wapping, October 31, 1711.
Sir,
'Ever since your
Spectator of
Tuesday last came into our Family,
my Husband is pleased to call me his
Oceana, because the foolish old
Poet that you have translated says, That the Souls of some Women are
made of Sea-Water. This, it seems, has encouraged my Sauce-Box to be
witty upon me. When I am angry, he cries Pr'ythee my Dear
be calm;
when I chide one of my Servants, Pr'ythee Child
do not bluster. He
had the Impudence about an Hour ago to tell me, That he was a
Sea-faring Man, and must expect to divide his Life between
Storm and
Sunshine. When I bestir myself with any Spirit in my Family, it is
high Sea in his House; and when I sit still without doing any thing,
his Affairs forsooth are
Wind-bound. When I ask him whether it
rains, he makes Answer, It is no Matter, so that it be
fair Weather
within Doors. In short, Sir, I cannot speak my Mind freely to him, but
I either
swell or
rage, or do something that is not fit for a
civil Woman to hear. Pray,
Mr.
Spectator, since you are so sharp
upon other Women, let us know what Materials your Wife is made of, if
you have one. I suppose you would make us a Parcel of poor-spirited
tame insipid Creatures; but, Sir, I would have you to know, we have as
good Passions in us as your self, and that a Woman was never designed
to be a Milk-Sop.
Martha Tempest.
L.
Odes
, I. 16.
In the
Timæus
Plato derives woman and all the animals
from man, by successive degradations. Cowardly or unjust men are born
again as women. Light, airy, and superficial men, who carried their
minds aloft without the use of reason, are the materials for making
birds, the hair being transmuted into feathers and wings. From men
wholly without philosophy, who never looked heavenward, the more brutal
land animals are derived, losing the round form of the cranium by the
slackening and stopping of the rotations of the encephalic soul. Feet
are given to these according to the degree of their stupidity, to
multiply approximations to the earth; and the dullest become reptiles
who drag the whole length of their bodies on the ground. Out of the very
stupidest of men come those animals which are not judged worthy to live
at all upon earth and breathe this air, these men become fishes, and the
creatures who breathe nothing but turbid water, fixed at the lowest
depths and almost motionless, among the mud. By such transitions, he
says, the different races of animals passed originally and still pass
into each other.
In the Epilogue to
Love for Love.
that his
Contents
|
Friday, November 2, 1711 |
Steele |
—Eripe turpi
Colla jugo, liber, liber dic, sum age—
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'I Never look upon my dear Wife, but I think of the Happiness Sir
Roger De Coverley enjoys, in having such a Friend as you to expose in
proper Colours the Cruelty and Perverseness of his Mistress. I have
very often wished you visited in our Family, and were acquainted with
my Spouse; she would afford you for some Months at least Matter enough
for one
Spectator a Week. Since we are not so happy as to be of your
Acquaintance, give me leave to represent to you our present
Circumstances as well as I can in Writing. You are to know then that I
am not of a very different Constitution from
Nathaniel Henroost,
whom you have lately recorded in your Speculations; and have a Wife
who makes a more tyrannical Use of the Knowledge of my easy Temper
than that Lady ever pretended to. We had not been a Month married,
when she found in me a certain Pain to give Offence, and an Indolence
that made me bear little Inconveniences rather than dispute about
them. From this Observation it soon came to that pass, that if I
offered to go abroad, she would get between me and the Door, kiss me,
and say she could not part with me; and then down again I sat. In a
Day or two after this first pleasant Step towards confining me, she
declared to me, that I was all the World to her, and she thought she
ought to be all the World to me. If, she said, my Dear loves me as
much as I love him, he will never be tired of my Company. This
Declaration was followed by my being denied to all my Acquaintance;
and it very soon came to that pass, that to give an Answer at the Door
before my Face, the Servants would ask her whether I was within or
not; and she would answer No with great Fondness, and tell me I was a
good Dear. I will not enumerate more little Circumstances to give you
a livelier Sense of my Condition; but tell you in general, that from
such Steps as these at first, I now live the Life of a Prisoner of
State; my Letters are opened, and I have not the Use of Pen, Ink and
Paper, but in her Presence. I never go abroad, except she sometimes
takes me with her in her Coach to take the Air, if it may be called
so, when we drive, as we generally do, with the Glasses up. I have
overheard my Servants lament my Condition, but they dare not bring me
Messages without her Knowledge, because they doubt my Resolution to
stand by 'em. In the midst of this insipid Way of Life, an old
Acquaintance of mine,
Tom Meggot, who is a Favourite with her, and
allowed to visit me in her Company because he sings prettily, has
roused me to rebel, and conveyed his Intelligence to me in the
following Manner. My Wife is a great Pretender to Musick, and very
ignorant of it; but far gone in the
Italian Taste.
Tom goes to
Armstrong, the famous fine Writer of Musick, and desires him to put
this Sentence of
Tully1 in the Scale of an
Italian Air, and
write it out for my Spouse from him.
An ille mihi liber cui mulier
imperat? Cui leges imponit, præscribit, jubet, vetat quod videtur?
Qui nihil imperanti negare, nihil recusare audet? Poscit? dandum est.
Vocat? veniendum. Ejicit? abeundum. Minitatur? extimiscendum.
Does he
live like a Gentlemanwho is commanded by a Woman? He to whom she
gives Law, grants and denies what she pleases? who can neither deny
her any thing she asks, or refuse to do any thing she commands?
'To be short, my Wife was extremely pleased with it; said the
Italian was the only Language for Musick; and admired how
wonderfully tender the Sentiment was, and how pretty the Accent is of
that Language, with the rest that is said by Rote on that Occasion.
Mr.
Meggot is sent for to sing this Air, which he performs with
mighty Applause; and my Wife is in Ecstasy on the Occasion, and glad
to find, by my being so much pleased, that I was at last come into the
Notion of the
Italian; for, said she, it grows upon one when one
once comes to know a little of the Language; and pray, Mr.
Meggot,
sing again those Notes,
Nihil Imperanti negare, nihil recusare. You
may believe I was not a little delighted with my Friend
Tom's
Expedient to alarm me, and in Obedience to his Summons I give all this
Story thus at large; and I am resolved, when this appears in the
Spectator, to declare for my self. The manner of the Insurrection I
contrive by your Means, which shall be no other than that
Tom
Meggot, who is at our Tea-table every Morning, shall read it to us;
and if my Dear can take the Hint, and say not one Word, but let this
be the Beginning of a new Life without farther Explanation, it is very
well; for as soon as the
Spectator is read out, I shall, without
more ado, call for the Coach, name the Hour when I shall be at home,
if I come at all; if I do not, they may go to Dinner. If my Spouse
only swells and says nothing,
Tom and I go out together, and all is
well, as I said before; but if she begins to command or expostulate,
you shall in my next to you receive a full Account of her Resistance
and Submission, for submit the dear thing must to,
Sir,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
Anthony Freeman.
P. S. I hope I need not tell you that I desire this may be in your
very next.
T.
Paradox
V. on the Thesis that All who are wise are Free,
and the fools Slaves.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 3, 1711 |
Addison |
—Mens sibi conscia recti.
Virg.

It is the great Art and Secret of Christianity, if I may use that
Phrase, to manage our Actions to the best Advantage, and direct them in
such a manner, that every thing we do may turn to Account at that great
Day, when every thing we have done will be set before us.
In order to give this Consideration its full Weight, we may cast all our
Actions under the Division of such as are in themselves either Good,
Evil, or Indifferent. If we divide our Intentions after the same Manner,
and consider them with regard to our Actions, we may discover that great
Art and Secret of Religion which I have here mentioned.
A good Intention joined to a good Action, gives it its proper Force and
Efficacy; joined to an Evil Action, extenuates its Malignity, and in
some Cases may take it wholly away; and joined to an indifferent Action
turns it to a Virtue, and makes it meritorious as far as human Actions
can be so.
In the next Place, to consider in the same manner the Influence of an
Evil Intention upon our Actions. An Evil Intention perverts the best of
Actions, and makes them in reality, what the Fathers with a witty kind
of Zeal have termed the Virtues of the Heathen World, so many
shining
Sins
.
destroys the Innocence of an indifferent Action, and gives an
evil Action all possible Blackness and Horror, or in the emphatical
Language of Sacred Writ, makes
Sin exceeding sinful
.
If, in the last Place, we consider the Nature of an indifferent
Intention, we shall find that it destroys the Merit of a good Action;
abates, but never takes away, the Malignity of an evil Action; and
leaves an indifferent Action in its natural State of Indifference.
It is therefore of unspeakable Advantage to possess our Minds with an
habitual good Intention, and to aim all our Thoughts, Words, and Actions
at some laudable End, whether it be the Glory of our Maker, the Good of
Mankind, or the Benefit of our own Souls.
This is a sort of Thrift or Good-Husbandry in moral Life, which does not
throw away any single Action, but makes every one go as far as it can.
It multiplies the Means of Salvation, increases the Number of our
Virtues, and diminishes that of our Vices.
is something very devout, though not solid, in
Acosta's
Answer
to
Limborch
, who objects to him the Multiplicity of Ceremonies in
the
Jewish
Religion, as Washings, Dresses, Meats, Purgations, and the
like. The Reply which the
Jew
makes upon this Occasion, is, to the
best of my Remembrance, as follows: 'There are not Duties enough (says
he) in the essential Parts of the Law for a zealous and active
Obedience. Time, Place, and Person are requisite, before you have an
Opportunity of putting a Moral Virtue into Practice. We have, therefore,
says he, enlarged the Sphere of our Duty, and made many Things, which
are in themselves indifferent, a Part of our Religion, that we may have
more Occasions of shewing our Love to God, and in all the Circumstances
of Life be doing something to please him.
St. Evremond
has endeavoured to palliate the Superstitions of
the Roman Catholick Religion with the same kind of Apology, where he
pretends to consider the differing Spirit of the Papists and the
Calvinists, as to the great Points wherein they disagree. He tells us,
that the former are actuated by Love, and the other by Fear; and that in
their Expressions of Duty and Devotion towards the Supreme Being, the
former seem particularly careful to do every thing which may possibly
please him, and the other to abstain from every thing which may possibly
displease him
.
But notwithstanding this plausible Reason with which both the Jew and
the Roman Catholick would excuse their respective Superstitions, it is
certain there is something in them very pernicious to Mankind, and
destructive to Religion; because the Injunction of superfluous
Ceremonies makes such Actions Duties, as were before indifferent, and by
that means renders Religion more burdensome and difficult than it is in
its own Nature, betrays many into Sins of Omission which they could not
otherwise be guilty of, and fixes the Minds of the Vulgar to the shadowy
unessential Points, instead of the more weighty and more important
Matters of the Law.
This zealous and active Obedience however takes place in the great Point
we are recommending; for, if, instead of prescribing to our selves
indifferent Actions as Duties, we apply a good Intention to all our most
indifferent Actions, we make our very Existence one continued Act of
Obedience, we turn our Diversions and Amusements to our eternal
Advantage, and are pleasing him (whom we are made to please) in all the
Circumstances and Occurrences of Life.
is this excellent Frame of Mind, this
holy Officiousness
(if I may
be allowed to call it such) which is recommended to us by the Apostle in
that uncommon Precept, wherein he directs us to propose to ourselves the
Glory of our Creator in all our most indifferent Actions,
whether we
eat or drink, or whatsoever we do.
A Person therefore who is possessed with such an habitual good
Intention, as that which I have been here speaking of, enters upon no
single Circumstance of Life, without considering it as well-pleasing to
the great Author of his Being, conformable to the Dictates of Reason,
suitable to human Nature in general, or to that particular Station in
which Providence has placed him.
lives in a perpetual Sense of the
Divine Presence, regards himself as acting, in the whole Course of his
Existence, under the Observation and Inspection of that Being, who is
privy to all his Motions and all his Thoughts, who knows all his
Down-sitting and his Up-rising, who is about his Path, and about his
Bed, and spieth out all his Ways.
In a word, he remembers that the
Eye of his Judge is always upon him, and in every Action he reflects
that he is doing what is commanded or allowed by Him who will hereafter
either reward or punish it.
was the Character of those holy Men of
old, who in that beautiful Phrase of Scripture are said to have
walked
with God?
.
When I employ myself upon a Paper of Morality, I generally consider how
I may recommend the particular Virtue which I treat of, by the Precepts
or Examples of the ancient Heathens; by that Means, if possible, to
shame those who have greater Advantages of knowing their Duty, and
therefore greater Obligations to perform it, into a better Course of
Life; Besides that many among us are unreasonably disposed to give a
fairer hearing to a Pagan Philosopher, than to a Christian Writer.
I shall therefore produce an Instance of this excellent Frame of Mind in
a Speech of
Socrates
, which is quoted by
Erasmus
.
This great Philosopher on the Day of his Execution, a little before the
Draught of Poison was brought to him, entertaining his Friends with a
Discourse on the Immortality of the Soul, has these Words:
Whether or
no God will approve of my Actions, I know not; but this I am sure of,
that I have at all Times made it my Endeavour to please him, and I have
a good Hope that this my Endeavour will be accepted by him.
We find in
these Words of that great Man the habitual good Intention which I would
here inculcate, and with which that divine Philosopher always acted. I
shall only add, that
Erasmus
, who was an unbigotted Roman Catholick,
was so much transported with this Passage of
Socrates
, that he could
scarce forbear looking upon him as a Saint, and desiring him to pray for
him; or as that ingenious and learned Writer has expressed himself in a
much more lively manner:
When I reflect on such a Speech pronounced by
such a Person, I can scarce forbear crying out, Sancte Socrates, ora
pro nobis:
O holy Socrates, pray for us7.
L.
Rom
. vii. 16.
Arnica Collatio de Veritate Relig. Christ. cum Erudito
Judæo
, published in 1687, by Philippe de Limborch, who was eminent as
a professor of Theology at Amsterdam from 1667 until his death, in 1712,
at the age of 79. But the learned Jew was the Spanish Physician Isaac
Orobio, who was tortured for three years in the prisons of the
Inquisition on a charge of Judaism. He admitted nothing, was therefore
set free, and left Spain for Toulouse, where he practised physic and
passed as a Catholic until he settled at Amsterdam. There he made
profession of the Jewish faith, and died in the year of the publication
of Limborch's friendly discussion with him.
The Uriel Acosta, with whom Addison confounds Orobio, was a gentleman of
Oporto who had embraced Judaism, and, leaving Portugal, had also gone to
Amsterdam. There he was circumcised, but was persecuted by the Jews
themselves, and eventually whipped in the synagogue for attempting
reformation of the Jewish usages, in which, he said, tradition had
departed from the law of Moses. He took his thirty-nine lashes,
recanted, and lay across the threshold of the synagogue for all his
brethren to walk over him. Afterwards he endeavoured to shoot his
principal enemy, but his pistol missed fire. He had another about him,
and with that he shot himself. This happened about the year 1640, when
Limborch was but a child of six or seven.
Sur la Religion.
Œuvres (Ed. 1752), Vol. III. pp. 267,
268.
I
Cor
. x. 31.
Psalm
cxxxix. 2, 3.
Genesis
v.22; vi. 9
Erasm. Apophthegm. Bk. III.
Contents
|
Monday, November 5, 1711 |
Steele |
I did some time ago lay before the World the unhappy Condition of the
trading Part of Mankind, who suffer by want of Punctuality in the
Dealings of Persons above them; but there is a Set of Men who are much
more the Objects of Compassion than even those, and these are the
Dependants on great Men, whom they are pleased to take under their
Protection as such as are to share in their Friendship and Favour. These
indeed, as well from the Homage that is accepted from them, as the hopes
which are given to them, are become a Sort of Creditors; and these
Debts, being Debts of Honour, ought, according to the accustomed Maxim,
to be first discharged.
When I speak of Dependants, I would not be understood to mean those who
are worthless in themselves, or who, without any Call, will press into
the Company of their Betters. Nor, when I speak of Patrons, do I mean
those who either have it not in their Power, or have no Obligation to
assist their Friends; but I speak of such Leagues where there is Power
and Obligation on the one Part, and Merit and Expectation on the other.
The Division of Patron and Client, may, I believe, include a Third of
our Nation; the Want of Merit and real Worth in the Client, will strike
out about Ninety-nine in a Hundred of these; and the Want of Ability in
Patrons, as many of that Kind. But however, I must beg leave to say,
that he who will take up another's Time and Fortune in his Service,
though he has no Prospect of rewarding his Merit towards him, is as
unjust in his Dealings as he who takes up Goods of a Tradesman without
Intention or Ability to pay him.
the few of the Class which I think
fit to consider, there are not two in ten who succeed, insomuch that I
know a Man of good Sense who put his Son to a Blacksmith, tho' an Offer
was made him of his being received as a Page to a Man of Quality
.
There are not more Cripples come out of the Wars than there are from
those great Services; some through Discontent lose their Speech, some
their Memories, others their Senses or their Lives; and I seldom see a
Man thoroughly discontented, but I conclude he has had the Favour of
some great Man. I have known of such as have been for twenty Years
together within a Month of a good Employment, but never arrived at the
Happiness of being possessed of any thing.
There is nothing more ordinary, than that a Man who is got into a
considerable Station, shall immediately alter his manner of treating all
his Friends, and from that Moment he is to deal with you as if he were
your Fate. You are no longer to be consulted, even in Matters which
concern your self, but your Patron is of a Species above you, and a free
Communication with you is not to be expected. This perhaps may be your
Condition all the while he bears Office, and when that is at an End, you
are as intimate as ever you were, and he will take it very ill if you
keep the Distance he prescribed you towards him in his Grandeur. One
would think this should be a Behaviour a Man could fall into with the
worst Grace imaginable; but they who know the World have seen it more
than once. I have often, with secret Pity, heard the same Man who has
professed his Abhorrence against all Kind of passive Behaviour, lose
Minutes, Hours, Days, and Years in a fruitless Attendance on one who had
no Inclination to befriend him. It is very much to be regarded, that the
Great have one particular Privilege above the rest of the World, of
being slow in receiving Impressions of Kindness, and quick in taking
Offence. The Elevation above the rest of Mankind, except in very great
Minds, makes Men so giddy, that they do not see after the same Manner
they did before: Thus they despise their old Friends, and strive to
extend their Interests to new Pretenders. By this means it often
happens, that when you come to know how you lost such an Employment, you
will find the Man who got it never dreamed of it; but, forsooth, he was
to be surprized into it, or perhaps sollicited to receive it. Upon such
Occasions as these a Man may perhaps grow out of Humour; and if you are
so, all Mankind will fall in with the Patron, and you are an Humourist
and untractable if you are capable of being sour at a Disappointment:
But it is the same thing, whether you do or do not resent ill Usage, you
will be used after the same Manner; as some good Mothers will be sure to
whip their Children till they cry, and then whip them for crying.
There are but two Ways of doing any thing with great People, and those
are by making your self either considerable or agreeable: The former is
not to be attained but by finding a Way to live without them, or
concealing that you want them; the latter is only by falling into their
Taste and Pleasures: This is of all the Employments in the World the
most servile, except it happens to be of your own natural Humour. For to
be agreeable to another, especially if he be above you, is not to be
possessed of such Qualities and Accomplishments as should render you
agreeable in your self, but such as make you agreeable in respect to
him. An Imitation of his Faults, or a Compliance, if not Subservience,
to his Vices, must be the Measures of your Conduct. When it comes to
that, the unnatural State a Man lives in, when his Patron pleases, is
ended; and his Guilt and Complaisance are objected to him, tho' the Man
who rejects him for his Vices was not only his Partner but Seducer. Thus
the Client (like a young Woman who has given up the Innocence which made
her charming) has not only lost his Time, but also the Virtue which
could render him capable of resenting the Injury which is done him.
would be endless to recount the
Tricks
of turning you off from
themselves to Persons who have less Power to serve you, the Art of being
sorry for such an unaccountable Accident in your Behaviour, that such a
one (who, perhaps, has never heard of you) opposes your Advancement; and
if you have any thing more than ordinary in you, you are flattered with
a Whisper, that 'tis no Wonder People are so slow in doing for a Man of
your Talents, and the like.
After all this Treatment, I must still add the pleasantest Insolence of
all, which I have once or twice seen; to wit, That when a silly Rogue
has thrown away one Part in three of his Life in unprofitable
Attendance, it is taken wonderfully ill that he withdraws, and is
resolved to employ the rest for himself.
When we consider these things, and reflect upon so many honest Natures
(which one who makes Observation of what passes, may have seen) that
have miscarried by such sort of Applications, it is too melancholy a
Scene to dwell upon; therefore I shall take another Opportunity to
discourse of good Patrons, and distinguish such as have done their Duty
to those who have depended upon them, and were not able to act without
their Favour.
Patrons are like
Plato's
Guardian Angels, who are
always doing good to their Wards; but negligent Patrons are like
Epicurus's
Gods, that lie lolling on the Clouds, and instead of
Blessings pour down Storms and Tempests on the Heads of those that are
offering Incense to them
.
Dulcis inexperta cultura potentis amici,
Expertus metuit
Hor.
A son of one of the inferior gentry received as page by a
nobleman wore his lord's livery, but had it of more costly materials
than were used for the footmen, and was the immediate attendant of his
patron, who was expected to give him a reputable start in life when he
came of age. Percy notes that a lady who described to him the custom not
very long after it had become obsolete, remembered her own husband's
giving £500 to set up such a page in business.
Trick
The Dæmon or Angel which, in the doctrine of Immortality
according to Socrates or Plato, had the care of each man while alive,
and after death conveyed him to the general place of judgment (Phædon,
p. 130), is more properly described as a Guardian Angel than the gods of
Epicurus can be said to pour storms on the heads of their worshippers.
Epicurus only represented them as inactive and unconcerned with human
affairs.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 6, 1711 |
Addison |
—Ingenuas didicisse fideliter artes
Emollit mores, nec sinit esse feros.
Ov.

I consider an Human Soul without Education like Marble in the Quarry,
which shews none of its inherent Beauties, 'till the Skill of the
Polisher fetches out the Colours, makes the Surface shine, and discovers
every ornamental Cloud, Spot, and Vein that runs through the Body of it.
Education, after the same manner, when it works upon a noble Mind, draws
out to View every latent Virtue and Perfection, which without such Helps
are never able to make their Appearance.
If my Reader will give me leave to change the Allusion so soon upon him,
I shall make use of the same Instance to illustrate the Force of
Education, which
Aristotle
has brought to explain his Doctrine of
Substantial Forms, when he tells us that a Statue lies hid in a Block of
Marble; and that the Art of the statuary only clears away the
superfluous Matter, and removes the Rubbish. The Figure is in the Stone,
the Sculptor only finds it. What Sculpture is to a Block of Marble,
Education is to a Human Soul. The Philosopher, the Saint, or the Hero,
the Wise, the Good, or the Great Man, very often lie hid and concealed
in a Plebeian, which a proper Education might have disinterred, and have
brought to Light. I am therefore much delighted with Reading the
Accounts of Savage Nations, and with contemplating those Virtues which
are wild and uncultivated; to see Courage exerting it self in
Fierceness, Resolution in Obstinacy, Wisdom in Cunning, Patience in
Sullenness and Despair.
Mens Passions operate variously, and appear in different kinds of
Actions, according as they are more or less rectified and swayed by
Reason. When one hears of Negroes, who upon the Death of their Masters,
or upon changing their Service, hang themselves upon the next Tree, as
it frequently happens in our
American
Plantations, who can forbear
admiring their Fidelity, though it expresses it self in so dreadful a
manner? What might not that Savage Greatness of Soul which appears in
these poor Wretches on many Occasions, be raised to, were it rightly
cultivated? And what Colour of Excuse can there be for the Contempt with
which we treat this Part of our Species; That we should not put them
upon the common foot of Humanity, that we should only set an
insignificant Fine upon the Man who murders them; nay, that we should,
as much as in us lies, cut them off from the Prospects of Happiness in
another World as well as in this, and deny them that which we look upon
as the proper Means for attaining it?
Since I am engaged on this Subject, I cannot forbear mentioning a Story
which I have lately heard, and which is so well attested, that I have no
manner of Reason to suspect the Truth of it. I may call it a kind of
wild Tragedy that passed about twelve Years ago at St.
Christophers
,
one of our
British
Leeward Islands. The Negroes who were the persons
concerned in it, were all of them the Slaves of a Gentleman who is now
in
England
.
This Gentleman among his Negroes had a young Woman, who was look'd upon
as a most extraordinary Beauty by those of her own Complexion. He had at
the same time two young Fellows who were likewise Negroes and Slaves,
remarkable for the Comeliness of their Persons, and for the Friendship
which they bore to one another. It unfortunately happened that both of
them fell in love with the Female Negro above mentioned, who would have
been very glad to have taken either of them for her Husband, provided
they could agree between themselves which should be the Man. But they
were both so passionately in Love with her, that neither of them could
think of giving her up to his Rival; and at the same time were so true
to one another, that neither of them would think of gaining her without
his Friend's Consent. The Torments of these two Lovers were the
Discourse of the Family to which they belonged, who could not forbear
observing the strange Complication of Passions which perplexed the
Hearts of the poor Negroes, that often dropped Expressions of the
Uneasiness they underwent, and how impossible it was for either of them
ever to be happy.
After a long Struggle between Love and Friendship, Truth and Jealousy,
they one Day took a Walk together into a Wood, carrying their Mistress
along with them: Where, after abundance of Lamentations, they stabbed
her to the Heart, of which she immediately died. A Slave who was at his
Work not far from the Place where this astonishing Piece of Cruelty was
committed, hearing the Shrieks of the dying Person, ran to see what was
the Occasion of them. He there discovered the Woman lying dead upon the
Ground, with the two Negroes on each side of her, kissing the dead
Corps, weeping over it, and beating their Breasts in the utmost Agonies
of Grief and Despair. He immediately ran to the
English
Family with
the News of what he had seen; who upon coming to the Place saw the Woman
dead, and the two Negroes expiring by her with Wounds they had given
themselves.
We see in this amazing Instance of Barbarity, what strange Disorders are
bred in the minds of those Men whose Passions are not regulated by
Virtue, and disciplined by Reason. Though the Action which I have
recited is in it self full of Guilt and Horror, it proceeded from a
Temper of Mind which might have produced very noble Fruits, had it been
informed and guided by a suitable Education.
It is therefore an unspeakable Blessing to be born in those Parts of the
World where Wisdom and Knowledge flourish; tho' it must be confest,
there are, even in these Parts, several poor uninstructed Persons, who
are but little above the Inhabitants of those Nations of which I have
been here speaking; as those who have had the Advantages of a more
liberal Education, rise above one another by several different Degrees
of Perfection. For to return to our Statue in the Block of Marble, we
see it sometimes only begun to be chipped, sometimes rough-hewn and but
just sketched into an human Figure; sometimes we see the Man appearing
distinctly in all his Limbs and Features, sometimes we find the Figure
wrought up to a great Elegancy, but seldom meet with any to which the
Hand of a
Phidias
or
Praxiteles
could not give several nice Touches
and Finishings.
Discourses of Morality, and Reflections upon human Nature, are the best
Means we can make use of to improve our Minds, and gain a true Knowledge
of our selves, and consequently to recover our Souls out of the Vice,
Ignorance, and Prejudice, which naturally cleave to them. I have all
along profest myself in this Paper a Promoter of these great Ends; and I
flatter my self that I do from Day to Day contribute something to the
polishing of Mens Minds: at least my Design is laudable, whatever the
Execution may be. I must confess I am not a little encouraged in it by
many Letters, which I receive from unknown Hands, in Approbation of my
Endeavours; and must take this Opportunity of returning my Thanks to
those who write them, and excusing my self for not inserting several of
them in my Papers, which I am sensible would be a very great Ornament to
them. Should I publish the Praises which are so well penned, they would
do Honour to the Persons who write them; but my publishing of them would
I fear be a sufficient Instance to the World that I did not deserve them.
C.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 7, 1711 |
Steele |
Siquidem hercle possis, nil prius, neque fortius:
Verum si incipies, neque perficies naviter,
Atque ubi pati non poteris, cum nemo expetet,
Infecta pace ultrò ad eam venies indicans
Te amare, et ferre non posse: Actum est, ilicet,
Perîsti: eludet ubi te victum senserit.
Ter.

To Mr. Spectator,
Sir,
This is to inform you, that Mr. Freeman
1 had no sooner taken Coach,
but his Lady was taken with a terrible Fit of the Vapours, which,'tis
feared will make her miscarry, if not endanger her Life; therefore,
dear Sir, if you know of any Receipt that is good against this
fashionable reigning Distemper, be pleased to communicate it for the
Good of the Publick, and you will oblige
Yours,
A. Noewill.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The Uproar was so great as soon as I had read the
Spectator
concerning Mrs.
Freeman, that after many Revolutions in her Temper,
of raging, swooning, railing, fainting, pitying herself, and reviling
her Husband, upon an accidental coming in of a neighbouring Lady (who
says she has writ to you also) she had nothing left for it but to fall
in a Fit. I had the Honour to read the Paper to her, and have a pretty
good Command of my Countenance and Temper on such Occasions; and soon
found my historical Name to be
Tom Meggot in your Writings, but
concealed my self till I saw how it affected Mrs. Freeman. She looked
frequently at her Husband, as often at me; and she did not tremble as
she filled Tea, till she came to the Circumstance of
Armstrong's
writing out a Piece of
Tully for an Opera Tune: Then she burst out,
She was exposed, she was deceiv'd, she was wronged and abused. The
Tea-cup was thrown in the Fire; and without taking Vengeance on her
Spouse, she said of me, That I was a pretending Coxcomb, a Medler that
knew not what it was to interpose in so nice an Affair as between a
Man and his Wife. To which Mr.
Freeman; Madam, were I less fond of
you than I am, I should not have taken this Way of writing to the
Spectator, to inform a Woman whom God and Nature has placed under my
Direction with what I request of her; but since you are so indiscreet
as not to take the Hint which I gave you in that Paper, I must tell
you, Madam, in so many Words, that you have for a long and tedious
Space of Time acted a Part unsuitable to the Sense you ought to have
of the Subordination in which you are placed. And I must acquaint you
once for all, that the Fellow without, ha
Tom! (here the Footman
entered and answered Madam) 'Sirrah don't you know my Voice; look upon
me when I speak to you: I say, Madam, this Fellow here is to know of
me my self, whether I am at Leisure to see Company or not. I am from
this Hour Master of this House; and my Business in it, and every where
else, is to behave my self in such a Manner, as it shall be hereafter
an Honour to you to bear my Name; and your Pride, that you are the
Delight, the Darling, and Ornament of a Man of Honour, useful and
esteemed by his Friends; and I no longer one that has buried some
Merit in the World, in Compliance to a froward Humour which has grown
upon an agreeable Woman by his Indulgence. Mr.
Freeman ended this
with a Tenderness in his Aspect and a downcast Eye, which shewed he
was extremely moved at the Anguish he saw her in; for she sat swelling
with Passion, and her Eyes firmly fixed on the Fire; when I, fearing
he would lose all again, took upon me to provoke her out of that
amiable Sorrow she was in, to fall upon me; upon which I said very
seasonably for my Friend, That indeed Mr.
Freeman was become the
common Talk of the Town; and that nothing was so much a Jest, as when
it was said in Company Mr.
Freeman had promised to come to such a
Place. Upon which the good Lady turned her Softness into downright
Rage, and threw the scalding Tea-Kettle upon your humble Servant; flew
into the Middle of the Room, and cried out she was the unfortunatest
of all Women: Others kept Family Dissatisfactions for Hours of Privacy
and Retirement: No Apology was to be made to her, no Expedient to be
found, no previous Manner of breaking what was amiss in her; but all
the World was to be acquainted with her Errors, without the least
Admonition. Mr.
Freeman was going to make a soft'ning Speech, but I
interposed; Look you, Madam, I have nothing to say to this Matter, but
you ought to consider you are now past a Chicken; this Humour, which
was well enough in a Girl, is insufferable in one of your Motherly
Character. With that she lost all Patience, and flew directly at her
Husband's Periwig.
I got her in my Arms, and defended my Friend: He
making Signs at the same time that it was too much; I beckoning,
nodding, and frowning over her Shoulder, that
he2 was
lost if he did not persist.
In this manner
3 flew round and round the Room in a Moment, 'till the
Lady I spoke of above and Servants entered; upon which she fell on a
Couch as breathless. I still kept up my Friend; but he, with a very
silly Air, bid them bring the Coach to the Door, and we went off, I
forced to bid the Coachman drive on. We were no sooner come to my
Lodgings, but all his Wife's Relations came to enquire after him; and
Mrs.
Freeman's Mother writ a Note, wherein she thought never to have
seen this Day, and so forth.
In a word, Sir, I am afraid we are upon a thing we have no Talents
for; and I can observe already, my Friend looks upon me rather as a
Man that knows a Weakness of him that he is ashamed of, than one who
has rescu'd him from Slavery. Mr.
Spectator, I am but a young Fellow,
and if Mr.
Freeman submits, I shall be looked upon as an Incendiary,
and never get a Wife as long as I breathe. He has indeed sent Word
home he shall lie at
Hampstead to-night; but I believe Fear of the
first Onset after this Rupture has too great a Place in this
Resolution. Mrs.
Freeman has a very pretty Sister; suppose I
delivered him up, and articled with the Mother for her for bringing
him home. If he has not Courage to stand it, (you are a great Casuist)
is it such an ill thing to bring my self off, as well as I can? What
makes me doubt my Man, is, that I find he thinks it reasonable to
expostulate at least with her; and Capt. SENTREY will tell you, if you
let your Orders be disputed, you are no longer a Commander. I wish you
could advise me how to get clear of this Business handsomely.
Yours,
Tom Meggot.
T.
See
we
he
Contents
|
Thursday, November 1, 1711 |
Budgell |
—Tunc fœmina simplex,
Et pariter toto repetitur clamor ab antro.
Juv.
Sat. 6.
I shall entertain my Reader to-day with some Letters from my
Correspondents. The first of them is the Description of a Club, whether
real or imaginary I cannot determine; but am apt to fancy, that the
Writer of it, whoever she is, has formed a kind of Nocturnal Orgie out
of her own Fancy: Whether this be so or not, her Letter may conduce to
the Amendment of that kind of Persons who are represented in it, and
whose Characters are frequent enough in the World.
Mr. Spectator,
'In some of your first Papers you were pleased to give the Publick a
very diverting Account of several Clubs and nocturnal Assemblies; but
I am a Member of a Society which has wholly escaped your Notice, I
mean a Club of She-Romps. We take each a Hackney-Coach, and meet once
a Week in a large upper Chamber, which we hire by the Year for that
Purpose; our Landlord and his Family, who are quiet People, constantly
contriving to be abroad on our Club-Night. We are no sooner come
together than we throw off all that Modesty and Reservedness with
which our Sex are obliged to disguise themselves in publick Places. I
am not able to express the Pleasure we enjoy from Ten at Night 'till
four in the Morning, in being as rude as you Men can be, for your
Lives. As our Play runs high the Room is immediately filled with
broken Fans, torn Petticoats, Lappets of Head-dresses, Flounces,
Furbelows, Garters, and Working-Aprons. I had forgot to tell you at
first, that besides the Coaches we come in our selves, there is one
which stands always empty to carry off our dead Men, for so we call
all those Fragments and Tatters with which the Room is strewed, and
which we pack up together in Bundles and put into the aforesaid Coach.
It is no small Diversion for us to meet the next Night at some
Member's Chamber, where every one is to pick out what belonged to her
from this confused Bundle of Silks, Stuffs, Laces, and Ribbons. I have
hitherto given you an Account of our Diversion on ordinary
Club-Nights; but must acquaint you farther, that once a Month we
demolish a Prude, that is, we get some queer formal Creature in
among us, and unrig her in an Instant. Our last Month's Prude was so
armed and fortified in Whalebone and Buckram that we had much ado to
come at her; but you would have died with laughing to have seen how
the sober awkward Thing looked when she was forced out of her
Intrenchments. In short, Sir,'tis impossible to give you a true Notion
of our Sports, unless you would come one Night amongst us; and tho' it
be directly against the Rules of our Society to admit a Male Visitant,
we repose so much Confidence in your Silence and Taciturnity,
that 'twas agreed by the whole Club, at our last Meeting, to give you
Entrance for one Night as a Spectator.
I am, Your Humble Servant,
Kitty Termagant.
P. S. We shall demolish a Prude next Thursday.
Tho' I thank
Kitty
for her kind Offer, I do not at present find in my
self any Inclination, to venture my Person with her and her romping
Companions. I should regard my self as a second
Clodius
intruding on
the Mysterious Rites of the
Bona Dea
, and should apprehend being
Demolished
as much as the
Prude
.
The following Letter comes from a Gentleman, whose Taste I find is much
too delicate to endure the least Advance towards Romping. I may perhaps
hereafter improve upon the Hint he has given me, and make it the Subject
of a whole
Spectator;
in the mean time take it as it follows in his
own Words.
Mr. Spectator,
'It is my Misfortune to be in Love with a young Creature who is daily
committing Faults, which though they give me the utmost Uneasiness, I
know not how to reprove her for, or even acquaint her with. She is
pretty, dresses well, is rich, and good-humour'd; but either wholly
neglects, or has no Notion of that which Polite People have agreed to
distinguish by the Name of Delicacy. After our Return from a Walk
the other Day she threw her self into an Elbow-Chair, and professed
before a large Company, that she was all over in a Sweat. She told
me this Afternoon that her Stomach aked; and was complaining
Yesterday at Dinner of something that stuck in her Teeth. I treated
her with a Basket of Fruit last Summer, which she eat so very
greedily, as almost made me resolve never to see her more. In short,
Sir, I begin to tremble whenever I see her about to speak or move. As
she does not want Sense, if she takes these Hints I am happy; if not,
I am more than afraid, that these Things which shock me even in the
Behaviour of a Mistress, will appear insupportable in that of a Wife.
I am, Sir, Yours, &c.
My next Letter comes from a Correspondent whom I cannot but very much
value, upon the Account which she gives of her self.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am happily arrived at a State of Tranquillity, which few People
envy, I mean that of an old Maid; therefore being wholly unconcerned
in all that Medley of Follies which our Sex is apt to contract from
their silly Fondness of yours, I read your Railleries on us without
Provocation. I can say with
Hamlet,
—Man delights not me,
Nor Woman neither—
Therefore, dear Sir, as you never spare your own Sex, do not be afraid
of reproving what is ridiculous in ours, and you will oblige at least
one Woman, who is
Your humble Servant,
Susannah Frost.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am Wife to a Clergyman, and cannot help thinking that in your Tenth
or Tithe-Character of Womankind
1 you meant my self, therefore I
have no Quarrel against you for the other Nine Characters.
Your humble Servant,
A.B.
X.
See
Contents
|
Friday, November 9, 1711 |
Steele |
Quid de quoque viro et cui dicas sæpe caveto.
Hor.

I happened the other Day, as my Way is, to strole into a little
Coffee-house beyond Aldgate; and as I sat there, two or three very plain
sensible Men were talking of the
Spectator
. One said, he had that
Morning drawn the great Benefit Ticket; another wished he had; but a
third shaked his Head and said, It was pity that the Writer of that
Paper was such a sort of Man, that it was no great Matter whether he had
it or no. He is, it seems, said the good Man, the most extravagant
Creature in the World; has run through vast Sums, and yet been in
continual Want; a Man, for all he talks so well of Œconomy, unfit for
any of the Offices of Life, by reason of his Profuseness. It would be an
unhappy thing to be his Wife, his Child, or his Friend; and yet he talks
as well of those Duties of Life as any one. Much Reflection has brought
me to so easy a Contempt for every thing which is false, that this heavy
Accusation gave me no manner of Uneasiness; but at the same Time it
threw me into deep Thought upon the Subject of Fame in general; and I
could not but pity such as were so weak, as to value what the common
People say out of their own talkative Temper to the Advantage or
Diminution of those whom they mention, without being moved either by
Malice or Good-will. It will be too long to expatiate upon the Sense all
Mankind have of Fame, and the inexpressible Pleasure which there is in
the Approbation of worthy Men, to all who are capable of worthy Actions;
but methinks one may divide the general Word Fame into three different
Species, as it regards the different Orders of Mankind who have any
Thing to do with it. Fame therefore may be divided into Glory, which
respects the Hero; Reputation, which is preserved by every Gentleman;
and Credit, which must be supported by every Tradesman. These
Possessions in Fame are dearer than Life to these Characters of Men, or
rather are the Life of those Characters. Glory, while the Hero pursues
great and noble Enterprizes, is impregnable; and all the Assailants of
his Renown do but shew their Pain and Impatience of its Brightness,
without throwing the least Shade upon it. If the Foundation of an high
Name be Virtue and Service, all that is offered against it is but
Rumour, which is too short-liv'd to stand up in Competition with Glory,
which is everlasting.
Reputation, which is the Portion of every Man who would live with the
elegant and knowing Part of Mankind, is as stable as Glory, if it be as
well founded; and the common Cause of human Society is thought concerned
when we hear a Man of good Behaviour calumniated: Besides which,
according to a prevailing Custom amongst us, every Man has his Defence
in his own Arm; and Reproach is soon checked, put out of Countenance,
and overtaken by Disgrace.
The most unhappy of all Men, and the most exposed to the Malignity or
Wantonness of the common Voice, is the Trader. Credit is undone in
Whispers. The Tradesman's Wound is received from one who is more private
and more cruel than the Ruffian with the Lanthorn and Dagger. The Manner
of repeating a Man's Name, As;
Mr
. Cash,
Oh! do you leave your Money
at his Shop? Why, do you know Mr
. Searoom?
He is indeed a general
Merchant
. I say, I have seen, from the Iteration of a Man's Name,
hiding one Thought of him, and explaining what you hide by saying
something to his Advantage when you speak, a Merchant hurt in his
Credit; and him who, every Day he lived, literally added to the Value of
his Native Country, undone by one who was only a Burthen and a Blemish
to it. Since every Body who knows the World is sensible of this great
Evil, how careful ought a Man to be in his Language of a Merchant? It
may possibly be in the Power of a very shallow Creature to lay the Ruin
of the best Family in the most opulent City; and the more so, the more
highly he deserves of his Country; that is to say, the farther he places
his Wealth out of his Hands, to draw home that of another Climate.
In this Case an ill Word may change Plenty into Want, and by a rash
Sentence a free and generous Fortune may in a few Days be reduced to
Beggary. How little does a giddy Prater imagine, that an idle Phrase to
the Disfavour of a Merchant may be as pernicious in the Consequence, as
the Forgery of a Deed to bar an Inheritance would be to a Gentleman?
Land stands where it did before a Gentleman was calumniated, and the
State of a great Action is just as it was before Calumny was offered to
diminish it, and there is Time, Place and Occasion expected to unravel
all that is contrived against those Characters; but the Trader who is
ready only for probable Demands upon him, can have no Armour against the
Inquisitive, the Malicious, and the Envious, who are prepared to fill
the Cry to his Dishonour. Fire and Sword are slow Engines of
Destruction, in Comparison of the Babbler in the Case of the Merchant.
For this Reason I thought it an imitable Piece of Humanity of a
Gentleman of my Acquaintance, who had great Variety of Affairs, and used
to talk with Warmth enough against Gentlemen by whom he thought himself
ill dealt with; but he would never let any thing be urged against a
Merchant (with whom he had any Difference) except in a Court of Justice.
He used to say, that to speak ill of a Merchant, was to begin his Suit
with Judgment and Execution. One cannot, I think, say more on this
Occasion, than to repeat, That the Merit of the Merchant is above that
of all other Subjects; for while he is untouched in his Credit, his
Hand-writing is a more portable Coin for the Service of his
Fellow-Citizens, and his Word the Gold of Ophir to the Country wherein
he resides.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 10, 1711 |
Addison |
Vix ea nostra voco—
Ov.

There are but few Men, who are not ambitious of distinguishing
themselves in the Nation or Country where they live, and of growing
considerable among those with whom they converse. There is a kind of
Grandeur and Respect, which the meanest and most insignificant Part of
Mankind endeavour to procure in the little Circle of their Friends and
Acquaintance. The poorest Mechanick, nay the Man who lives upon common
Alms, gets him his Set of Admirers, and delights in that Superiority
which he enjoys over those who are in some Respects beneath him. This
Ambition, which is natural to the Soul of Man, might methinks receive a
very happy turn; and, if it were rightly directed, contribute as much to
a Person's Advantage, as it generally does to his Uneasiness and
Disquiet.
I shall therefore put together some Thoughts on this Subject, which I
have not met with in other Writers: and shall set them down as they have
occurred to me, without being at the Pains to Connect or Methodise them.
All Superiority and Preeminence that one Man can have over another, may
be reduced to the Notion of Quality, which, considered at large, is
either that of Fortune, Body, or Mind. The first is that which consists
in Birth, Title, or Riches, and is the most foreign to our Natures, and
what we can the least call our own of any of the three Kinds of Quality.
In relation to the Body, Quality arises from Health, Strength, or
Beauty, which are nearer to us, and more a Part of our selves than the
former. Quality, as it regards the Mind, has its Rise from Knowledge or
Virtue; and is that which is more essential to us, and more intimately
united with us than either of the other two.
The Quality of Fortune, tho' a Man has less Reason to value himself upon
it than on that of the Body or Mind, is however the kind of Quality
which makes the most shining Figure in the Eye of the World.
As Virtue is the most reasonable and genuine Source of Honour, we
generally find in Titles an Imitation of some particular Merit that
should recommend Men to the high Stations which they possess. Holiness
is ascribed to the Pope; Majesty to Kings; Serenity or Mildness of
Temper to Princes; Excellence or Perfection to Ambassadors; Grace to
Archbishops; Honour to Peers; Worship or Venerable Behaviour to
Magistrates; and Reverence, which is of the same Import as the former,
to the inferior Clergy.
In the Founders of great Families, such Attributes of Honour are
generally correspondent with the Virtues of the Person to whom they are
applied; but in the Descendants they are too often the Marks rather of
Grandeur than of Merit. The Stamp and Denomination still continues, but
the Intrinsick Value is frequently lost.
The Death-Bed shews the Emptiness of Titles in a true Light. A poor
dispirited Sinner lies trembling under the Apprehensions of the State he
is entring on; and is asked by a grave Attendant how his Holiness does?
Another hears himself addressed to under the Title of Highness or
Excellency, who lies under such mean Circumstances of Mortality as are
the Disgrace of Human Nature. Titles at such a time look rather like
Insults and Mockery than Respect.
The truth of it is, Honours are in this World under no Regulation; true
Quality is neglected, Virtue is oppressed, and Vice triumphant. The last
Day will rectify this Disorder, and assign to every one a Station
suitable to the Dignity of his Character; Ranks will be then adjusted,
and Precedency set right.
Methinks we should have an Ambition, if not to advance our selves in
another World, at least to preserve our Post in it, and outshine our
Inferiors in Virtue here, that they may not be put above us in a State
which is to Settle the Distinction for Eternity.
Men in Scripture are called
Strangers
and
Sojourners
upon
Earth
,
and Life a
Pilgrimage
. Several Heathen, as well as Christian Authors,
under the same kind of Metaphor, have represented the World as an Inn,
which was only designed to furnish us with Accommodations in this our
Passage. It is therefore very absurd to think of setting up our Rest
before we come to our Journey's End, and not rather to take care of the
Reception we shall there meet, than to fix our Thoughts on the little
Conveniences and Advantages which we enjoy one above another in the Way
to it.
Epictetus
makes use of another kind of Allusion, which is very
beautiful, and wonderfully proper to incline us to be satisfied with the
Post in which Providence has placed us. We are here, says he, as in a
Theatre, where every one has a Part allotted to him. The great Duty
which lies upon a Man is to act his Part in Perfection. We may indeed
say, that our Part does not suit us, and that we could act another
better. But this (says the Philosopher) is not our Business. All that we
are concerned in is to excel in the Part which is given us.
it be an
improper one, the Fault is not in us, but in him who has
cast
our
several Parts, and is the great Disposer of the Drama
.
The Part that was acted by this Philosopher himself was but a very
indifferent one, for he lived and died a Slave. His Motive to
Contentment in this Particular, receives a very great Inforcement from
the above-mentioned Consideration, if we remember that our Parts in the
other World will be new cast, and that Mankind will be there ranged in
different Stations of Superiority and Præeminence, in Proportion as
they have here excelled one another in Virtue, and performed in their
several Posts of Life the Duties which belong to them.
There are many beautiful Passages in the little Apocryphal Book,
entitled,
The Wisdom of
Solomon, to set forth the Vanity of Honour,
and the like temporal Blessings which are in so great Repute among Men,
and to comfort those who have not the Possession of them. It represents
in very warm and noble Terms this Advancement of a good Man in the other
World, and the great Surprize which it will produce among those who are
his Superiors in this.
Then shall the righteous Man stand in great
Boldness before the Face of such as have afflicted him, and made no
Account of his Labours. When they see it, they shall be troubled with
terrible Fear, and shall be amazed at the Strangeness of his Salvation,
so far beyond all that they looked for. And they repenting and groaning
for Anguish of Spirit, shall say within themselves; This was he whom we
had sometime in Derision, and a Proverb of Reproach. We Fools accounted
his Life Madness, and his End to be without Honour. How is he numbered
among the Children of God, and his Lot is among the Saints!
the Reader would see the Description of a Life that is passed away in
Vanity and among the Shadows of Pomp and Greatness, he may see it very
finely drawn in the same Place
. In the mean time, since it is
necessary in the present Constitution of things, that Order and
Distinction should be kept in the World, we should be happy, if those
who enjoy the upper Stations in it, would endeavour to surpass others in
Virtue, as much as in Rank, and by their Humanity and Condescension make
their Superiority easy and acceptable to those who are beneath them: and
if, on the contrary, those who are in meaner Posts of Life, would
consider how they may better their Condition hereafter, and by a just
Deference and Submission to their Superiors, make them happy in those
Blessings with which Providence has thought fit to distinguish them.
C.
Epict. Enchirid. ch. 23.
Wisd., ch. v. 1-5.
Ch. v. 8-14.
Contents
|
Monday, November 12, 1711 |
Steele |
Rumoresque serit varios
Virg.1
Sir,
'Why will you apply to my Father for my Love? I cannot help it if he
will give you my Person; but I assure you it is not in his Power, nor
even in my own, to give you my Heart. Dear Sir, do but consider the
ill Consequence of such a Match; you are Fifty-five, I Twenty-one. You
are a Man of Business, and mightily conversant in Arithmetick and
making Calculations; be pleased therefore to consider what Proportion
your Spirits bear to mine; and when you have made a just Estimate of
the necessary Decay on one Side, and the Redundance on the other, you
will act accordingly. This perhaps is such Language as you may not
expect from a young Lady; but my Happiness is at Stake, and I must
talk plainly. I mortally hate you; and so, as you and my Father agree,
you may take me or leave me: But if you will be so good as never to
see me more, you will for ever oblige,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Henrietta.
Mr.
Spectator2,
'There are so many Artifices and Modes of false Wit, and such a
Variety of Humour discovers it self among its Votaries, that it would
be impossible to exhaust so fertile a Subject, if you would think fit
to resume it. The following Instances may, if you think fit, be added
by Way of Appendix to your Discourses on that Subject.
'
That Feat of Poetical Activity mentioned by
Horace, of an Author
who could compose two hundred Verses while he stood upon one Leg
3,
has been imitated (as I have heard) by a modern Writer; who priding
himself on the Hurry of his Invention, thought it no small Addition to
his Fame to have each Piece minuted with the exact Number of Hours or
Days it cost him in the Composition. He could taste no Praise till he
had acquainted you in how short Space of Time he had deserved it; and
was not so much led to an Ostentation of his Art, as of his Dispatch.
—Accipe si vis,
Accipe jam tabulas; detur nobis locus, hora,
Custodes: videamus uter plus scribere possit.
Hor.
'This was the whole of his Ambition; and therefore I cannot but think
the Flights of this rapid Author very proper to be opposed to those
laborious Nothings which you have observed were the Delight of the
German Wits, and in which they so happily got rid of such a tedious
Quantity of their Time.
'I have known a Gentleman of another Turn of Humour, who, despising
the Name of an Author, never printed his Works, but contracted his
Talent, and by the help of a very fine Diamond which he wore on his
little Finger, was a considerable Poet upon Glass. He had a very good
Epigrammatick Wit; and there was not a Parlour or Tavern Window where
he visited or dined for some Years, which did not receive some
Sketches or Memorials of it. It was his Misfortune at last to lose his
Genius and his Ring to a Sharper at Play; and he has not attempted to
make a Verse since.
'
But of all Contractions or Expedients for Wit, I admire that of an
ingenious Projector whose Book I have seen
4. This Virtuoso being a
Mathematician, has, according to his Taste, thrown the Art of Poetry
into a short Problem, and contrived Tables by which any one without
knowing a Word of Grammar or Sense, may, to his great Comfort, be able
to compose or rather to erect
Latin Verses. His Tables are a kind of
Poetical Logarithms, which being divided into several Squares, and all
inscribed with so many incoherent Words, appear to the Eye somewhat
like a Fortune-telling Screen. What a Joy must it be to the unlearned
Operator to find that these Words, being carefully collected and writ
down in Order according to the Problem, start of themselves into
Hexameter and Pentameter Verses?
A Friend of mine, who is a Student in
Astrology, meeting with this Book, performed the Operation, by the
Rules there set down; he shewed his Verses to the next of his
Acquaintance, who happened to understand
Latin; and being informed
they described a Tempest of Wind, very luckily prefixed them, together
with a Translation, to an Almanack he was just then printing, and was
supposed to have foretold the last great Storm
5.
'I think the only Improvement beyond this, would be that which the
late Duke of
Buckingham mentioned to a stupid Pretender to Poetry,
as the Project of a
Dutch Mechanick,
viz. a Mill to make Verses.
This being the most compendious Method of all which have yet been
proposed, may deserve the Thoughts of our modern Virtuosi who are
employed in new Discoveries for the publick Good: and it may be worth
the while to consider, whether in an Island where few are content
without being thought Wits, it will not be a common Benefit, that Wit
as well as Labour should be made cheap.
I am, Sir, Your humble Servant, &c.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I often dine at a Gentleman's House, where there are two young
Ladies, in themselves very agreeable, but very cold in their
Behaviour, because they understand me for a Person that is to break my
Mind, as the Phrase is, very suddenly to one of them. But I take this
Way to acquaint them, that I am not in Love with either of them, in
Hopes they will use me with that agreeable Freedom and Indifference
which they do all the rest of the World, and not to drink to one
another
only, but sometimes cast a kind Look, with their Service to,
Sir, Your humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a young Gentleman, and take it for a Piece of Good-breeding to
pull off my Hat when I see any thing particularly charming in any
Woman, whether I know her or not. I take care that there is nothing
ludicrous or arch in my Manner, as if I were to betray a Woman into a
Salutation by Way of Jest or Humour; and yet except I am acquainted
with her, I find she ever takes it for a Rule, that she is to look
upon this Civility and Homage I pay to her supposed Merit, as an
Impertinence or Forwardness which she is to observe and neglect. I
wish, Sir, you would settle the Business of salutation; and please to
inform me how I shall resist the sudden Impulse I have to be civil to
what gives an Idea of Merit; or tell these Creatures how to behave
themselves in Return to the Esteem I have for them. My Affairs are
such, that your Decision will be a Favour to me, if it be only to save
the unnecessary Expence of wearing out my Hat so fast as I do at
present.
'There are some that do know me, and won't bow to me.
I am, Sir,
Yours,
T.D.
T.
—Aliena negotia centum
Per caput, et circa saliunt latus.
Hor.
This letter is by John Hughes.
—in hora saepe ducentos,
Ut magnum, versus dictabat stans pede in uno.
Sat
. I. iv. 10.
A pamphlet by John Peter,
Artificial Versifying, a New Way
to make Latin Verses.
Lond. 1678.
Of Nov. 26, 1703, which destroyed in London alone property
worth a million.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 13, 1711 |
Addison |
—Ab Ovo
Usque ad Mala—
Hor.

When I have finished any of my Speculations, it is my Method to consider
which of the ancient Authors have touched upon the Subject that I treat
of. By this means I meet with some celebrated Thought upon it, or a
Thought of my own expressed in better Words, or some Similitude for the
Illustration of my Subject. This is what gives Birth to the Motto of a
Speculation, which I rather chuse to take out of the Poets than the
Prose-writers, as the former generally give a finer Turn to a Thought
than the latter, and by couching it in few Words, and in harmonious
Numbers, make it more portable to the Memory.
My Reader is therefore sure to meet with at least one good Line in every
Paper, and very often finds his Imagination entertained by a Hint that
awakens in his Memory some beautiful Passage of a Classick Author.
was a Saying of an ancient Philosopher, which I find some of our
Writers have ascribed to Queen Elizabeth, who perhaps might have taken
occasion to repeat it, That a good Face is a Letter of Recommendation
. It naturally makes the Beholders inquisitive into the Person who is
the Owner of it, and generally prepossesses them in his Favour. A
handsome Motto has the same Effect. Besides that, it always gives a
Supernumerary Beauty to a Paper, and is sometimes in a manner necessary
when the Writer is engaged in what may appear a Paradox to vulgar Minds,
as it shews that he is supported by good Authorities, and is not
singular in his Opinion.
I must confess, the Motto is of little Use to an unlearned Reader, for
which Reason I consider it only as
a Word to the Wise
. But as for my
unlearned Friends, if they cannot relish the Motto, I take care to make
Provision for them in the Body of my Paper. If they do not understand
the Sign that is hung out, they know very well by it, that they may meet
with Entertainment in the House; and I think I was never better pleased
than with a plain Man's Compliment, who, upon his Friend's telling him
that he would like the
Spectator
much better if he understood the
Motto, replied,
That good Wine needs no Bush
.
I
heard of a Couple of Preachers in a Country Town, who endeavoured
which should outshine one another, and draw together the greatest
Congregation. One of them being well versed in the Fathers, used to
quote every now and then a
Latin
Sentence to his illiterate Hearers,
who it seems found themselves so edified by it, that they flocked in
greater Numbers to this learned Man than to his Rival. The other finding
his Congregation mouldering every
Sunday
, and hearing at length what
was the Occasion of it, resolved to give his Parish a little
Latin
in
his Turn; but being unacquainted with any of the Fathers, he digested
into his Sermons the whole Book of Quæ Genus, adding however such
Explications to it as he thought might be for the Benefit of his People.
He afterwards entered upon
As in præsenti
, which he converted in
the same manner to the Use of his Parishioners. This in a very little
time thickned his Audience, filled his Church, and routed his
Antagonist.
The natural Love to
Latin
which is so prevalent in our common People,
makes me think that my Speculations fare never the worse among them for
that little Scrap which appears at the Head of them; and what the more
encourages me in the Use of Quotations in an unknown Tongue is, that I
hear the Ladies, whose Approbation I value more than that of the whole
Learned World, declare themselves in a more particular manner pleased
with my
Greek
Mottos.
Designing this Day's Work for a Dissertation upon the two Extremities of
my Paper, and having already dispatch'd my Motto, I shall, in the next
place, discourse upon those single Capital Letters, which are placed at
the End of it, and which have afforded great Matter of Speculation to
the Curious. I have heard various Conjectures upon this Subject. Some
tell us that C is the Mark of those Papers that are written by the
Clergyman, though others ascribe them to the Club in general: That the
Papers marked with R were written by my Friend Sir
Roger
: That L
signifies the Lawyer, whom I have described in my second Speculation;
and that T stands for the Trader or Merchant: But the Letter X, which is
placed at the End of some few of my Papers, is that which has puzzled
the whole Town, as they cannot think of any Name which begins with that
Letter, except
Xenophon
and
Xerxes
, who can neither of them be
supposed to have had any Hand in these Speculations.
In
to these inquisitive Gentlemen, who have many of them made
Enquiries of me by Letter, I must tell them the Reply of an ancient
Philosopher, who carried something hidden under his Cloak. A certain
Acquaintance desiring him to let him know what it was he covered so
carefully;
I cover it,
says he,
on purpose that you should not know
.
I have made use of these obscure Marks for the same Purpose. They are,
perhaps, little Amulets or Charms to preserve the Paper against the
Fascination and Malice of evil Eyes; for which Reason I would not have
my Reader surprized, if hereafter he sees any of my Papers marked with a
Q, a Z, a Y, an &c., or with the Word
Abracadabra
.
I shall, however, so far explain my self to the Reader, as to let him
know that the Letters, C, L, and X, are Cabalistical, and carry more in
them than it is proper for the World to be acquainted with.
who
are versed in the Philosophy of Pythagoras, and swear by the
Tetrachtys
, that is, the Number Four, will know very well that the
Number
Ten
, which is signified by the Letter X, (and which has so much
perplexed the Town) has in it many particular Powers; that it is called
by Platonick Writers the Complete Number; that One, Two, Three and Four
put together make up the Number Ten; and that Ten is all. But these are
not Mysteries for ordinary Readers to be let into. A Man must have spent
many Years in hard Study before he can arrive at the Knowledge of them.
We had a Rabbinical Divine in
England
, who was Chaplain to the Earl of
Essex
in Queen
Elizabeth's
Time, that had an admirable Head for
Secrets of this Nature. Upon his taking the Doctor of Divinity's Degree,
he preached before the University of
Cambridge
, upon the
First
Verse
of the
First
Chapter of the
First
Book of
Chronicles
, in which,
says he, you have the three following Words,
Adam, Sheth, Enosh
He divided this short Text into many Parts, and by discovering several
Mysteries in each Word, made a most Learned and Elaborate Discourse.
Name of this profound Preacher was Doctor
Alabaster
, of whom the
Reader may find a more particular Account in Doctor
Fuller's
Book of
English
Worthies
. This Instance will, I hope, convince my Readers
that there may be a great deal of fine Writing in the Capital Letters
which bring up the Rear of my Paper, and give them some Satisfaction in
that Particular. But as for the full Explication of these Matters, I
must refer them to Time, which discovers all things.
C.
Diogenes Laertius, Bk. V. ch. I.
Quæ Genus
and
As in Præsenti
were the first words in
collections of rules then and until recently familiar as part of the
standard Latin Grammar, Lilly's, to which Erasmus and Colet contributed,
and of which Wolsey wrote the original Preface.
Abraxas, which in Greek letters represents 365, the number
of the deities supposed by the Basilidians to be subordinate to the All
Ruling One, was a mystical name for the supreme God, and was engraved as
a charm on stones together with the figure of a human body (Cadaver),
with cat's head and reptile's feet. From this the name Abracadabra may
have arisen, with a sense of power in it as a charm. Serenus Sammonicus,
a celebrated physician who lived about A.D. 210, who had, it is said, a
library of 62,000 volumes, and was killed at a banquet by order of
Caracalla, said in an extant Latin poem upon Medicine and Remedies, that
fevers were cured by binding to the body the word Abracadabra written in
this fashion:
Abracadabra
Abracadabr
Abracadab
Abracada
and so on, till there remained only the initial A. His word was taken,
and this use of the charm was popular even in the Spectator's time. It
is described by Defoe in his
History of the Plague.
The number Four was called Tetractys by the Pythagoreans,
who accounted it the most powerful of numbers, because it was the
foundation of them all, and as a square it signified solidity. They said
it was at the source of Nature, four elements, four seasons, &c., to
which later speculators added the four rivers of Paradise, four
evangelists, and association of the number four with God, whose name was
a mystical Tetra grammaton, Jod, He, Vau, He.
Where it is explained that Adam meaning Man; Seth, placed;
and Enosh, Misery: the mystic inference is that Man was placed in
Misery.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 14, 1711 |
Steele |
Cur alter fratrum cessare, et ludere, et ungi,
Præferat Herodis palmetis pinguibus
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'There is one thing I have often look'd for in your Papers, and have
as often wondered to find my self disappointed; the rather, because I
think it a Subject every way agreeable to your Design, and by being
left unattempted by others, seems reserved as a proper Employment for
you; I mean a Disquisition, from whence it proceeds, that Men of the
brightest Parts, and most comprehensive Genius, compleatly furnished
with Talents for any Province in humane Affairs; such as by their wise
Lessons of Œconomy to others have made it evident, that they have the
justest Notions of Life and of true Sense in the Conduct of it—: from
what unhappy contradictious Cause it proceeds, that Persons thus
finished by Nature and by Art, should so often fail in the Management
of that which they so well understand, and want the Address to make a
right Application of their own Rules. This is certainly a prodigious
Inconsistency in Behaviour, and makes much such a Figure in Morals as
a monstrous Birth in Naturals, with this Difference only, which
greatly aggravates the Wonder, that it happens much more frequently;
and what a Blemish does it cast upon Wit and Learning in the general
Account of the World? And in how disadvantageous a Light does it
expose them to the busy Class of Mankind, that there should be so many
Instances of Persons who have so conducted their Lives in spite of
these transcendent Advantages, as neither to be happy in themselves,
nor useful to their Friends; when every Body sees it was entirely in
their own Power to be eminent in both these Characters? For my part, I
think there is no Reflection more astonishing, than to consider one of
these Gentlemen spending a fair Fortune, running in every Body's Debt
without the least Apprehension of a future Reckoning, and at last
leaving not only his own Children, but possibly those of other People,
by his Means, in starving Circumstances; while a Fellow, whom one
would scarce suspect to have a humane Soul, shall perhaps raise a vast
Estate out of Nothing, and be the Founder of a Family capable of being
very considerable in their Country, and doing many illustrious
Services to it. That this Observation is just, Experience has put
beyond all Dispute. But though the Fact be so evident and glaring, yet
the Causes of it are still in the Dark; which makes me persuade my
self, that it would be no unacceptable Piece of Entertainment to the
Town, to inquire into the hidden Sources of so unaccountable an Evil.
I am,
Sir,
Your most Humble Servant.
What this Correspondent wonders at, has been Matter of Admiration ever
since there was any such thing as humane Life.
Horace
reflects upon
this Inconsistency very agreeably in the Character of
Tigellius
, whom
he makes a mighty Pretender to Œconomy, and tells you, you might one
Day hear him speak the most philosophick Things imaginable concerning
being contented with a little, and his Contempt of every thing but mere
Necessaries, and in Half a Week after spend a thousand Pound. When he
says this of him with Relation to Expence, he describes him as unequal
to himself in every other Circumstance of Life. And indeed, if we
consider lavish Men carefully, we shall find it always proceeds from a
certain Incapacity of possessing themselves, and finding Enjoyment in
their own Minds.
.
Dryden
has expressed this very excellently in the
Character of
Zimri
.
A Man so various, that he seem'd to be
Not one, but all Mankind's Epitome.
Stiff in Opinion, always in the Wrong,
Was every Thing by Starts, and Nothing long;
But in the Course of one revolving Moon,
Was Chymist, Fidler, Statesman, and Buffoon.
Then all for Women, Painting, Rhiming, Drinking,
Besides ten thousand Freaks that died in thinking;
Blest Madman, who could every Hour employ
In something new to wish or to enjoy!
In squandering Wealth was his peculiar Art,
Nothing went unrewarded but Desert.
This loose State of the Soul hurries the Extravagant from one Pursuit to
another; and the Reason that his Expences are greater than another's,
is, that his Wants are also more numerous. But what makes so many go on
in this Way to their Lives End, is, that they certainly do not know how
contemptible they are in the Eyes of the rest of Mankind, or rather,
that indeed they are not so contemptible as they deserve.
Tully
says,
it is the greatest of Wickedness to lessen your paternal Estate. And if
a Man would thoroughly consider how much worse than Banishment it must
be to his Child, to ride by the Estate which should have been his had it
not been for his Father's Injustice to him, he would be smitten with the
Reflection more deeply than can be understood by any but one who is a
Father. Sure there can be nothing more afflicting than to think it had
been happier for his Son to have been born of any other Man living than
himself.
It is not perhaps much thought of, but it is certainly a very important
Lesson, to learn how to enjoy ordinary Life, and to be able to relish
your Being without the Transport of some Passion or Gratification of
some Appetite. For want of this Capacity, the World is filled with
Whetters, Tipplers, Cutters, Sippers, and all the numerous Train of
those who, for want of Thinking, are forced to be ever exercising their
Feeling or Tasting. It would be hard on this Occasion to mention the
harmless Smoakers of Tobacco and Takers of Snuff.
The slower Part of Mankind, whom my Correspondent wonders should get
Estates, are the more immediately formed for that Pursuit: They can
expect distant things without Impatience, because they are not carried
out of their Way either by violent Passion or keen Appetite to any
thing. To Men addicted to Delight
s
, Business is an Interruption; to
such as are cold to Delights, Business is an Entertainment. For which
Reason it was said to one who commended a dull Man for his Application,
No Thanks to him; if he had no Business, he would have nothing to do.
T.
i. e.
The Duke of Buckingham, in Part I. of
Absalom and Achitophel.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 15, 1711 |
Addison |
O suavis Anima! qualem te dicam bonam
Antehac fuisse, tales cùm sint reliquiæ!
Phæd.

When I reflect upon the various Fate of those Multitudes of Ancient
Writers who flourished in
Greece
and
Italy
, I consider Time as an
Immense Ocean, in which many noble Authors are entirely swallowed up,
many very much shattered and damaged, some quite disjointed and broken
into pieces, while some have wholly escaped the Common Wreck; but the
Number of the last is very small.
Apparent rari nantes in gurgite vasto.
Among the mutilated Poets of Antiquity, there is none whose Fragments
are so beautiful as those of
Sappho
. They give us a Taste of her Way
of Writing, which is perfectly conformable with that extraordinary
Character we find of her, in the Remarks of those great Criticks who
were conversant with her Works when they were entire. One may see by
what is left of them, that she followed Nature in all her Thoughts,
without descending to those little Points, Conceits, and Turns of Wit
with which many of our modern Lyricks are so miserably infected. Her
Soul seems to have been made up of Love and Poetry; She felt the Passion
in all its Warmth, and described it in all its Symptoms. She is called
by ancient Authors the Tenth Muse; and by
Plutarch
is compared to
Cacus
the Son of
Vulcan
, who breathed out nothing but Flame. I do
not know, by the Character that is given of her Works, whether it is not
for the Benefit of Mankind that they are lost. They were filled with
such bewitching Tenderness and Rapture, that it might have been
dangerous to have given them a Reading.
An Inconstant Lover, called
Phaon
, occasioned great Calamities to this
Poetical Lady. She fell desperately in Love with him, and took a Voyage
into
Sicily
in Pursuit of him, he having withdrawn himself thither on
purpose to avoid her. It was in that Island, and on this Occasion, she
is supposed to have made the Hymn to
Venus
, with a Translation of
which I shall present my Reader. Her Hymn was ineffectual for the
procuring that Happiness which she prayed for in it.
Phaon
was still
obdurate, and
Sappho
so transported with the Violence of her Passion,
that she was resolved to get rid of it at any Price.
was a Promontory in
Acarnania
called
Leucrate
on the Top
of which was a little Temple dedicated to Apollo. In this Temple it was
usual for
despairing
Lovers to make their Vows in secret, and
afterwards to fling themselves from the Top of the Precipice into the
Sea, where they were sometimes taken up alive. This Place was therefore
called,
The Lover's Leap
; and whether or no the Fright they had been
in, or the Resolution that could push them to so dreadful a Remedy, or
the Bruises which they often received in their Fall, banished all the
tender Sentiments of Love, and gave their Spirits another Turn; those
who had taken this Leap were observed never to relapse into that
Passion.
Sappho
tried the Cure, but perished in the Experiment.
having given this short Account of
Sappho
so far as it regards
the following Ode, I shall subjoin the Translation of it as it was sent
me by a Friend, whose admirable Pastorals and
Winter-Piece
have been
already so well received
. The Reader will find in it that Pathetick
Simplicity which is so peculiar to him, and so suitable to the Ode he
has here Translated. This Ode in the Greek (besides those Beauties
observed by Madam
Dacier
) has several harmonious Turns in the Words,
which are not lost in the
English
. I must farther add, that the
Translation has preserved every Image and Sentiment of
Sappho
,
notwithstanding it has all the Ease and Spirit of an Original. In a
Word, if the Ladies have a mind to know the Manner of Writing practised by the so much celebrated
Sappho
,
they may here see it in its genuine and natural Beauty, without
any foreign or affected Ornaments.
An Hymn to Venus
| I |
O Venus, Beauty of the Skies,
To whom a Thousand Temples rise,
Gayly false in gentle Smiles,
Full of Love's perplexing Wiles;
O Goddess! from my Heart remove
The wasting Cares and Pains of Love. |
| II |
If ever thou hast kindly heard
A Song in soft Distress preferr'd,
Propitious to my tuneful Vow,
O gentle Goddess! hear me now.
Descend, thou bright, immortal Guest,
In all thy radiant Charms confest. |
| III |
Thou once didst leave Almighty Jove,
And all the Golden Roofs above:
The Carr thy wanton Sparrows drew;
Hov'ring in Air they lightly flew,
As to my Bower they wing'd their Way:
I saw their quiv'ring Pinions play. |
| IV |
The Birds dismist (while you remain)
Bore back their empty Carr again:
Then You, with Looks divinely mild,
In ev'ry heav'nly Feature smil'd,
And ask'd what new Complaints I made,
And why I call'd you to my Aid? |
| V |
What Phrenzy in my Bosom rag'd,
And by what Care to be asswag'd?
What gentle Youth I could allure,
Whom in my artful Toiles secure?
Who does thy tender Heart subdue,
Tell me, my Sappho, tell me Who? |
| VI |
Tho' now he Shuns thy longing Arms,
He soon shall court thy slighted Charms;
Tho' now thy Off'rings he despise,
He soon to thee shall Sacrifice;
Tho' now he freeze, he soon shall burn,
And be thy Victim in his turn. |
| VII |
Celestial Visitant, once more
Thy needful Presence I implore!
In Pity come and ease my Grief,
Bring my distemper'd Soul Relief;
Favour thy Suppliant's hidden Fires,
And give me All my Heart desires. |
Madam
Dacier
observes, there is something very pretty in that
Circumstance of this Ode, wherein
Venus
is described as sending away
her Chariot upon her Arrival at
Sappho's
Lodgings, to denote that it
was not a short transient Visit which she intended to make her.
Ode
was preserved by an eminent
Greek
Critick
, who inserted it intire in
his Works, as a Pattern of Perfection in the Structure of it.
Longinus
has quoted another Ode of this great Poetess, which is
likewise admirable in its Kind, and has been translated by the same Hand
with the foregoing one. I shall oblige my Reader with it in another
Paper. In the mean while, I cannot but wonder, that these two finished
Pieces have never been attempted before by any of our Countrymen. But
the Truth of it is, the Compositions of the Ancients, which have not in
them any of those unnatural Witticisms that are the Delight of ordinary
Readers, are extremely difficult to render into another Tongue, so as
the Beauties of the Original may not appear weak and faded in the
Translation.
C.
Leucas
Ambrose Philips, whose Winter Piece appeared in No. 12 of
the
Tatler
, and whose six Pastorals preceded those of Pope. Philips's
Pastorals had appeared in 1709 in a sixth volume of a Poetical
Miscellany issued by Jacob Tonson. The first four volumes of that
Miscellany had been edited by Dryden, the fifth was collected after
Dryden's death, and the sixth was notable for opening with the Pastorals
of Ambrose Philips and closing with those of young Pope which Tonson had
volunteered to print, thereby, said Wycherley, furnishing a Jacob's
ladder by which Pope mounted to immortality. In a letter to his friend
Mr. Henry Cromwell, Pope said, generously putting himself out of
account, that there were no better eclogues in our language than those
of Philips; but when afterwards Tickell in the
Guardian
, criticising
Pastoral Poets from Theocritus downwards, exalted Philips and passed
over Pope, the slighted poet took his revenge by sending to Steele an
amusing one paper more upon Pastorals. This was ironical exaltation of
the worst he could find in Philips over the best bits of his own work,
which Steele inserted (it is No. 40 of the
Guardian
). Hereupon
Philips, it is said, stuck up a rod in Button's Coffee House, which he
said was to be used on Pope when next he met him. Pope retained his
wrath, and celebrated Philips afterwards under the character of Macer,
saying of this
Spectator
time,
When simple Macer, now of high renown,
First sought a Poet's fortune in the town,
'Twas all the ambition his high soul could feel,
To wear red stockings, and to dine with Steele.
Dionysius of Halicarnassus.
Contents
|
Friday, November 16, 1711 |
Hughes |
—Fulgente trahit constrictos Gloria curru
Non minus ignotos generosis
Hor.
Sat. 6.

If we look abroad upon the great Multitudes of Mankind, and endeavour to
trace out the Principles of Action in every Individual, it will, I
think, seem highly probable that Ambition runs through the whole
Species, and that every Man in Proportion to the Vigour of his
Complection is more or less actuated by it. It is indeed no uncommon
thing to meet with Men, who by the natural Bent of their Inclinations,
and without the Discipline of Philosophy, aspire not to the Heights of
Power and Grandeur; who never set their Hearts upon a numerous Train of
Clients and Dependancies, nor other gay Appendages of Greatness; who are
contented with a Competency, and will not molest their Tranquillity to
gain an Abundance: But it is not therefore to be concluded that such a
Man is not Ambitious; his Desires may have cut out another Channel, and
determined him to other Pursuits; the Motive however may be still the
same; and in these Cases likewise the Man may be equally pushed on with
the Desire of Distinction.
Though the pure Consciousness of worthy Actions, abstracted from the
Views of popular Applause, be to a generous Mind an ample Reward, yet
the Desire of Distinction was doubtless implanted in our Natures as an
additional Incentive to exert our selves in virtuous Excellence.
Passion indeed, like all others, is frequently perverted to evil
and ignoble Purposes; so that we may account for many of the
Excellencies and Follies of Life upon the same innate Principle, to wit,
the Desire of being remarkable: For this, as it has been differently
cultivated by Education, Study and Converse, will bring forth suitable
Effects as it falls in with an
ingenuous
Disposition, or a corrupt
Mind; it does accordingly express itself in Acts of Magnanimity or
selfish Cunning, as it meets with a good or a weak Understanding. As it
has been employed in embellishing the Mind, or adorning the Outside, it
renders the Man eminently Praise-worthy or ridiculous. Ambition
therefore is not to be confined only to one Passion or Pursuit; for as
the same Humours, in Constitutions otherwise different, affect the Body
after different Manners, so the same aspiring Principle within us
sometimes breaks forth upon one Object, sometimes upon another.
It cannot be doubted, but that there is as great Desire of Glory in a
Ring of Wrestlers or Cudgel-Players, as in any other more refined
Competition for Superiority. No Man that could avoid it, would ever
suffer his Head to be broken but out of a Principle of Honour. This is
the secret Spring that pushes them forward; and the Superiority which
they gain above the undistinguish'd many, does more than repair those
Wounds they have received in the Combat. '
Mr.
Waller's
Opinion,
that
Julius Cæsar
, had he not been Master of the
Roman
Empire, would
in all Probability have made an excellent Wrestler.
Great Julius
on the Mountains bred,
A Flock perhaps or Herd had led;
He that the World subdued, had been
But the best Wrestler on the Green.2
That he subdued the World, was owing to the Accidents of Art and
Knowledge; had he not met with those Advantages, the same Sparks of
Emulation would have kindled within him, and prompted him to distinguish
himself in some Enterprize of a lower Nature. Since therefore no Man's
Lot is so unalterably fixed in this Life, but that a thousand Accidents
may either forward or disappoint his Advancement, it is, methinks, a
pleasant and inoffensive Speculation, to consider a great Man as
divested of all the adventitious Circumstances of Fortune, and to bring
him down in one's Imagination to that low Station of Life, the Nature of
which bears some distant Resemblance to that high one he is at present
possessed of. Thus one may view him exercising in Miniature those
Talents of Nature, which being drawn out by Education to their full
Length, enable him for the Discharge of some important Employment. On
the other Hand, one may raise uneducated Merit to such a Pitch of
Greatness as may seem equal to the possible Extent of his improved
Capacity.
Thus Nature furnishes a Man with a general Appetite of Glory, Education
determines it to this or that particular Object. The Desire of
Distinction is not, I think, in any Instance more observable than in the
Variety of Outsides and new Appearances, which the modish Part of the
World are obliged to provide, in order to make themselves remarkable;
for any thing glaring and particular, either in Behaviour or Apparel, is
known to have this good Effect, that it catches the Eye, and will not
suffer you to pass over the Person so adorned without due Notice and
Observation. It has likewise, upon this Account, been frequently
resented as a very great Slight, to leave any Gentleman out of a Lampoon
or Satyr, who has as much Right to be there as his Neighbour, because it
supposes the Person not eminent enough to be taken notice of. To this
passionate Fondness for Distinction are owing various frolicksome and
irregular Practices, as sallying out into Nocturnal Exploits, breaking
of Windows, singing of Catches, beating the Watch, getting Drunk twice a
Day, killing a great Number of Horses; with many other Enterprizes of
the like fiery Nature: For certainly many a Man is more Rakish and
Extravagant than he would willingly be, were there not others to look on
and give their Approbation.
One very Common, and at the same time the most absurd Ambition that ever
shewed it self in Humane Nature, is that which comes upon a Man with
Experience and old Age, the Season when it might be expected he should
be wisest; and therefore it cannot receive any of those lessening
Circumstances which do, in some measure, excuse the disorderly Ferments
of youthful Blood: I mean the Passion for getting Money, exclusive of
the Character of the Provident Father, the Affectionate Husband, or the
Generous Friend. It may be remarked, for the Comfort of honest Poverty,
that this Desire reigns most in those who have but few good Qualities to
recommend them. This is a Weed that will grow in a barren Soil.
Humanity, Good Nature, and the Advantages of a Liberal Education, are
incompatible with Avarice. 'Tis strange to see how suddenly this abject
Passion kills all the noble Sentiments and generous Ambitions that adorn
Humane Nature; it renders the Man who is over-run with it a peevish and
cruel Master, a severe Parent, an unsociable Husband, a distant and
mistrustful Friend. But it is more to the present Purpose to consider it
as an absurd Passion of the Heart, rather than as a vicious Affection of
the Mind. As there are frequent Instances to be met with of a proud
Humility, so this Passion, contrary to most others, affects Applause, by
avoiding all Show and Appearance; for this Reason it will not sometimes
endure even the common Decencies of Apparel.
A covetous Man will call
himself poor, that you may sooth his Vanity by contradicting him
. Love
and the Desire of Glory, as they are the most natural, so they are
capable of being refined into the most delicate and rational Passions.
'Tis true, the wise Man who strikes out of the secret Paths of a private
Life, for Honour and Dignity, allured by the Splendour of a Court, and
the unfelt Weight of publick Employment, whether he succeeds in his
Attempts or no, usually comes near enough to this painted Greatness to
discern the Dawbing; he is then desirous of extricating himself out of
the Hurry of Life, that he may pass away the Remainder of his Days in
Tranquillity and Retirement.
It may be thought then but common Prudence in a Man not to change a
better State for a worse, nor ever to quit that which he knows he shall
take up again with Pleasure; and yet if human Life be not a little moved
with the gentle Gales of Hopes and Fears, there may be some Danger of
its stagnating in an unmanly Indolence and Security. It is a known Story
of
Domitian
, that after he had possessed himself of the
Roman
Empire,
his Desires turn'd upon catching Flies. Active and Masculine Spirits in
the Vigour of Youth neither can nor ought to remain at Rest: If they
debar themselves from aiming at a noble Object, their Desires will move
downwards, and they will feel themselves actuated by some low and abject
Passion.
Thus if you cut off the top Branches of a Tree, and will not suffer it
to grow any higher, it will not therefore cease to grow, but will
quickly shoot out at the Bottom. The Man indeed who goes into the World
only with the narrow Views of Self-interest, who catches at the
Applause of an idle Multitude, as he can find no solid Contentment at
the End of his Journey, so he deserves to meet with Disappointments in
his Way; but he who is actuated by a noble Principle, whose Mind is so
far enlarged as to take in the Prospect of his Country's Good, who is
enamoured with that Praise which is one of the fair Attendants of
Virtue, and values not those Acclamations which are not seconded by the
impartial Testimony of his own Mind; who repines not at the low Station
which Providence has at present allotted him, but yet would willingly
advance himself by justifiable Means to a more rising and advantageous
Ground; such a Man is warmed with a generous Emulation; it is a virtuous
Movement in him to wish and to endeavour that his Power of doing Good
may be equal to his Will.
The Man who is fitted out by Nature, and sent into the World with great
Abilities, is capable of doing great Good or Mischief in it. It ought
therefore to be the Care of Education to infuse into the untainted Youth
early Notices of Justice and Honour, that so the possible Advantages of
good Parts may not take an evil Turn, nor be perverted to base and
unworthy Purposes. It is the Business of Religion and Philosophy not so
much to extinguish our Passions, as to regulate and direct them to
valuable well-chosen Objects: When these have pointed out to us which
Course we may lawfully steer, 'tis no Harm to set out all our Sail; if
the Storms and Tempests of Adversity should rise upon us, and not suffer
us to make the Haven where we would be, it will however prove no small
Consolation to us in these Circumstances, that we have neither mistaken
our Course, nor fallen into Calamities of our own procuring.
Religion therefore (were we to consider it no farther than as it
interposes in the Affairs of this Life) is highly valuable, and worthy
of great Veneration; as it settles the various Pretensions, and
otherwise interfering Interests of mortal Men, and thereby consults the
Harmony and Order of the great Community; as it gives a Man room to play
his Part, and exert his Abilities; as it animates to Actions truly
laudable in themselves, in their Effects beneficial to Society; as it
inspires rational Ambitions, correct Love, and elegant Desires.
Z.
ingenious
In the Poem
To Zelinda.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 17, 1711 |
Addison |
Nullum numen abest si sit Prudentia
Juv.

I have often thought if the Minds of Men were laid open, we should see
but little Difference between that of the Wise Man and that of the Fool.
There are infinite
Reveries
, numberless Extravagancies, and a
perpetual Train of Vanities which pass through both. The great
Difference is that the first knows how to pick and cull his Thoughts for
Conversation, by suppressing some, and communicating others; whereas the
other lets them all indifferently fly out in Words. This sort of
Discretion, however, has no Place in private Conversation between
intimate Friends. On such Occasions the wisest Men very often talk like
the weakest; for indeed the Talking with a Friend is nothing else but
thinking aloud
.
Tully
has therefore very justly exposed a Precept delivered by some
Ancient Writers, That a Man should live with his Enemy in such a manner,
as might leave him room to become his Friend; and with his Friend in
such a manner, that if he became his Enemy, it should not be in his
Power to hurt him. The first Part of this Rule, which regards our
Behaviour towards an Enemy, is indeed very reasonable, as well as very
prudential; but the latter Part of it which regards our Behaviour
towards a Friend, savours more of Cunning than of Discretion, and would
cut a Man off from the greatest Pleasures of Life, which are the
Freedoms of Conversation with a Bosom Friend. Besides, that when a
Friend is turned into an Enemy, and (as the Son of
Sirach
calls him) a
Bewrayer of Secrets, the World is just enough to accuse the
Perfidiousness of the Friend, rather than the Indiscretion of the Person
who confided in him.
Discretion does not only shew it self in Words, but in all the
Circumstances of Action; and is like an Under-Agent of Providence, to
guide and direct us in the ordinary Concerns of Life.
There are many more shining Qualities in the Mind of Man, but there is
none so useful as Discretion; it is this indeed which gives a Value to
all the rest, which sets them at work in their proper Times and Places,
and turns them to the Advantage of the Person who is possessed of them.
Without it Learning is Pedantry, and Wit Impertinence; Virtue itself
looks like Weakness; the best Parts only qualify a Man to be more
sprightly in Errors, and active to his own Prejudice.
Nor does Discretion only make a Man the Master of his own Parts, but of
other Mens. The discreet Man finds out the Talents of those he Converses
with, and knows how to apply them to proper Uses. Accordingly if we look
into particular Communities and Divisions of Men, we may observe that it
is the discreet Man, not the Witty, nor the Learned, nor the Brave, who
guides the Conversation, and gives Measures to the Society. A Man with
great Talents, but void of Discretion, is like
Polyphemus
in the
Fable, Strong and Blind, endued with an irresistible Force, which for
want of Sight is of no Use to him.
Though a Man has all other Perfections, and wants Discretion, he will be
of no great Consequence in the World; but if he has this single Talent
in Perfection, and but a common Share of others, he may do what he
pleases in his particular Station of Life.
At the same time that I think Discretion the most useful Talent a Man
can be Master of, I look upon Cunning to be the Accomplishment of
little, mean, ungenerous Minds. Discretion points out the noblest Ends
to us, and pursues the most proper and laudable Methods of attaining
them: Cunning has only private selfish Aims, and sticks at nothing which
may make them succeed. Discretion has large and extended Views, and,
like a well-formed Eye, commands a whole Horizon: Cunning is a Kind of
Short-sightedness, that discovers the minutest Objects which are near at
hand, but is not able to discern things at a distance. Discretion, the
more it is discovered, gives a greater Authority to the Person who
possesses it: Cunning, when it is once detected, loses its Force, and
makes a Man incapable of bringing about even those Events which he might
have done, had he passed only for a plain Man. Discretion is the
Perfection of Reason, and a Guide to us in all the Duties of Life;
Cunning is a kind of Instinct, that only looks out after our immediate
Interest and Welfare. Discretion is only found in Men of strong Sense
and good Understandings: Cunning is often to be met with in Brutes
themselves, and in Persons who are but the fewest Removes from them. In
short Cunning is only the Mimick of Discretion, and may pass upon weak
Men, in the same manner as Vivacity is often mistaken for Wit, and
Gravity for Wisdom.
The Cast of Mind which is natural to a discreet Man, makes him look
forward into Futurity, and consider what will be his Condition Millions
of Ages hence, as well as what it is at present. He knows that the
Misery or Happiness which are reserv'd for him in another World, lose
nothing of their Reality by being placed at so great Distance from him.
The Objects do not appear little to him because they are remote. He
considers that those Pleasures and Pains which lie hid in Eternity,
approach nearer to him every Moment, and will be present with him in
their full Weight and Measure, as much as those Pains and Pleasures
which he feels at this very Instant. For this Reason he is careful to
secure to himself that which is the proper Happiness of his Nature, and
the ultimate Design of his Being. He carries his Thoughts to the End of
every Action, and considers the most distant as well as the most
immediate Effects of it. He supersedes every little Prospect of Gain and
Advantage which offers itself here, if he does not find it consistent
with his Views of an Hereafter. In a word, his Hopes are full of
Immortality, his Schemes are large and glorious, and his Conduct
suitable to one who knows his true Interest, and how to pursue it by
proper Methods.
I have, in this Essay upon Discretion, considered it both as an
Accomplishment and as a Virtue, and have therefore described it in its
full Extent; not only as it is conversant about worldly Affairs, but as
it regards our whole Existence; not only as it is the Guide of a mortal
Creature, but as it is in general the Director of a reasonable Being. It
is in this Light that Discretion is represented by the Wise Man, who
sometimes mentions it under the Name of Discretion, and sometimes under
that of Wisdom. It is indeed (as described in the latter Part of this
Paper) the greatest Wisdom, but at the same time in the Power of every
one to attain. Its Advantages are infinite, but its Acquisition easy; or
to
of her in the Words of the Apocryphal Writer whom I quoted in
my last
Saturday's
Paper,
Wisdom is glorious, and never fadeth away,
yet she is easily seen of them that love her, and found of such as seek
her. She preventeth them that desire her, in making herself first known
unto them. He that seeketh her early, shall have no great Travel: for he
shall find her sitting at his Doors. To think therefore upon her is
Perfection of Wisdom, and whoso watcheth for her shall quickly be
without Care. For she goeth about seeking such as are worthy of her,
sheweth her self favourably unto them in the Ways, and meeteth them in
every Thought1.
C.
Wisdom
vi. 12-16.
Contents
|
Monday, November 19, 17111 |
Steele |
—Mutum est pictura poema.
Hor.
2
I have very often lamented and hinted my Sorrow in several Speculations,
that the Art of Painting is made so little Use of to the Improvement of
our Manners. When we consider that it places the Action of the Person
represented in the most agreeable Aspect imaginable, that it does not
only express the Passion or Concern as it sits upon him who is drawn,
but has under those Features the Height of the Painter's Imagination.
What strong Images of Virtue and Humanity might we not expect would be
instilled into the Mind from the Labours of the Pencil? This is a Poetry
which would be understood with much less Capacity, and less Expence of
Time, than what is taught by Writings; but the Use of it is generally
perverted, and that admirable Skill prostituted to the basest and most
unworthy Ends. Who is the better Man for beholding the most beautiful
Venus
, the best wrought
Bacchanal
, the Images of sleeping
Cupids
,
languishing Nymphs, or any of the Representations of Gods, Goddesses,
Demy-gods, Satyrs,
Polyphemes
, Sphinxes, or Fauns? But if the Virtues
and Vices, which are sometimes pretended to be represented under such
Draughts, were given us by the Painter in the Characters of real Life,
and the Persons of Men and Women whose Actions have rendered them
laudable or infamous; we should not see a good History-Piece without
receiving an instructive Lecture. There needs no other Proof of this
Truth, than the Testimony of every reasonable Creature who has seen the
Cartons in Her Majesty's Gallery at
Hampton—Court
: These are
Representations of no less Actions than those of our Blessed Saviour and
his Apostles. As I now sit and recollect the warm Images which the
admirable
Raphael
has raised, it is impossible even from the faint
Traces in one's Memory of what one has not seen these two Years, to be
unmoved at the Horror and Reverence which appear in the whole Assembly
when the mercenary Man fell down dead; at the Amazement of the Man born
blind, when he first receives Sight; or at the graceless Indignation of
the Sorcerer, when he is struck blind. The Lame, when they first find
Strength in their Feet, stand doubtful of their new Vigour. The heavenly
Apostles appear acting these great Things, with a deep Sense of the
Infirmities which they relieve, but no Value of themselves who
administer to their Weakness. They know themselves to be but
Instruments; and the generous Distress they are painted in when divine
Honours are offered to them, is a Representation in the most exquisite
Degree of the Beauty of Holiness. When St.
Paul
is preaching to the
Athenians
, with what wonderful Art are almost all the different
Tempers of Mankind represented in that elegant Audience? You see one
credulous of all that is said, another wrapt up in deep Suspence,
another saying there is some Reason in what he says, another angry that
the Apostle destroys a favourite Opinion which he is unwilling to give
up, another wholly convinced and holding out his Hands in Rapture; while
the Generality attend, and wait for the Opinion of those who are of
leading Characters in the Assembly. I will not pretend so much as to
mention that Chart on which is drawn the Appearance of our Blessed Lord
after his Resurrection.
Authority, late Suffering, Humility and
Majesty, Despotick Command, and
Divine
Love, are at once seated in
his celestial Aspect. The Figures of the Eleven Apostles are all in the
same Passion of Admiration, but discover it differently according to
their Characters.
Peter
his Master's Orders on his Knees with
an Admiration mixed with a more particular Attention: The two next with
a more open Ecstasy, though still constrained by the Awe of the Divine
Presence: The beloved Disciple, whom I take to be the Right of the
two first Figures, has in his Countenance Wonder drowned in Love; and
the last Personage, whose Back is towards the Spectator
s
, and his Side
towards the Presence, one would fancy to be St.
Thomas
, as abashed by
the Conscience of his former Diffidence; which perplexed Concern it is
possible
Raphael
thought too hard a Task to draw but by this
Acknowledgment of the Difficulty to describe it.
The whole Work is an Exercise of the highest Piety in the Painter; and
all the Touches of a religious Mind are expressed in a Manner much more
forcible than can possibly be performed by the most moving Eloquence.
invaluable Pieces are very justly in the Hands of the greatest and
most pious Sovereign in the World; and cannot be the frequent Object of
every one at their own Leisure: But as an Engraver is to the Painter
what a Printer is to an Author, it is worthy Her Majesty's Name, that
she has encouraged that Noble Artist, Monsieur
Dorigny
, to publish
these Works of
Raphael
. We have of this Gentleman a Piece of the
Transfiguration, which, I think, is held a Work second to none in the
World.
Methinks it would be ridiculous in our People of Condition, after their
large Bounties to Foreigners of no Name or Merit, should they overlook
this Occasion of having, for a trifling Subscription, a Work which it is
impossible for a Man of Sense to behold, without being warmed with the
noblest Sentiments that can be inspired by Love, Admiration, Compassion,
Contempt of this World, and Expectation of a better.
It is certainly the greatest Honour we can do our Country, to
distinguish Strangers of Merit who apply to us with Modesty and
Diffidence, which generally accompanies Merit. No Opportunity of this
Kind ought to be neglected; and a modest Behaviour should alarm us to
examine whether we do not lose something excellent under that
Disadvantage in the Possessor of that Quality. My Skill in Paintings,
where one is not directed by the Passion of the Pictures, is so
inconsiderable, that I am in very great Perplexity when I offer to speak
of any Performances of Painters of Landskips, Buildings, or single
Figures. This makes me at a loss how to mention the Pieces which Mr.
Boul
exposes to Sale by Auction on
Wednesday
next in
Shandois-street
: But having heard him commended by those who have
bought of him heretofore for great Integrity in his Dealing, and
overheard him himself (tho' a laudable Painter) say, nothing of his own
was fit to come into the Room with those he had to sell, I fear'd I
should lose an Occasion of serving a Man of Worth, in omitting to speak
of his Auction.
T.
Swift to Stella, Nov. 18, 1711.
'Do you ever read the SpectatorS? I never do; they never come in my
way; I go to no coffee-houses. They say abundance of them are very
pretty; they are going to be printed in small volumes; I'll bring them
over with me.'
Pictura Poesis erit.
Hor.
Brotherly
cœlestial
Michel Dorigny, painter and engraver, native of St.
Quentin, pupil and son-in-law of Simon Vouet, whose style he adopted,
was Professor in the Paris Academy of Painting, and died at the age of
48, in 1665. His son and Vouet's grandson, Nicolo Dorigny, in aid of
whose undertaking Steele wrote this paper in the Spectator, had been
invited from Rome by several of the nobility, to produce, with licence
from the Queen, engravings from Raphael's Cartoons, at Hampton Court. He
offered eight plates 19 inches high, and from 25 to 30 inches long, for
four guineas subscription, although, he said in his Prospectus, the five
prints of Alexander's Battles after Lebrun were often sold for twenty
guineas.
Contents
Advertisement
There is arrived from Italy
a Painter
who acknowledges himself the greatest Person of the Age in that Art,
and is willing to be as renowned in this Island
as he declares he is in Foreign Parts.
The Doctor paints the Poor for nothing.
|
Tuesday, November 20, 1711 |
Addison |
In my last
Thursday's
Paper I made mention of a Place called
The
Lover's Leap
, which I find has raised a great Curiosity among several
of my Correspondents. I there told them that this Leap was used to be
taken from a Promontory of
Leucas
.
Leucas
was formerly a Part
of
Acarnania
, being
joined to
it by a narrow Neck of Land, which
the Sea has by length of Time overflowed and washed away; so that at
present
Leucas
is divided from the Continent, and is a little Island
in the
Ionian
Sea. The Promontory of this Island, from whence the
Lover took his Leap, was formerly called
Leucate
. If the Reader has a
mind to know both the Island and the Promontory by their modern Titles,
he will find in his Map the ancient Island of
Leucas
under the Name of
St.
Mauro
, and the ancient Promontory of
Leucate
under the Name of
The Cape of St.
Mauro.
Since I am engaged thus far in Antiquity, I must observe that
Theocritus
in the Motto prefixed to my Paper, describes one of his
despairing Shepherds addressing himself to his Mistress after the
following manner,
Alas! What will become of me! Wretch that I am! Will
you not hear me? I'll throw off my Cloaths, and take a Leap into that
Part of the Sea which is so much frequented by Olphis the Fisherman.
And tho' I should escape with my Life, I know you will be pleased with
it.
I shall leave it with the Criticks to determine whether the Place,
which this Shepherd so particularly points out, was not the
above-mentioned
Leucate
, or at least some other Lover's Leap, which
was supposed to have had the same Effect. I
believe, as all the
Interpreters do, that the Shepherd means nothing farther here than that
he would drown himself, since he represents the Issue of his Leap as
doubtful, by adding, That if he should escape with
Life
, he knows
his Mistress would be pleased with it; which is, according to our
Interpretation, that she would rejoice any way to get rid of a Lover who
was so troublesome to her.
After this short Preface, I shall present my Reader with some Letters
which I have received upon this Subject. The first is sent me by a
Physician.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The Lover's Leap, which you mention in your
223d Paper, was
generally, I believe, a very effectual Cure for Love, and not only for
Love, but for all other Evils. In short, Sir, I am afraid it was such
a Leap as that which
Hero took to get rid of her Passion for
Leander. A Man is in no Danger of breaking his Heart, who breaks his
Neck to prevent it. I know very well the Wonders which ancient Authors
relate concerning this Leap; and in particular, that very many Persons
who tried it, escaped not only with their Lives but their Limbs. If by
this Means they got rid of their Love, tho' it may in part be ascribed
to the Reasons you give for it; why may not we suppose that the cold
Bath into which they plunged themselves, had also some Share in their
Cure? A Leap into the Sea or into any Creek of Salt Waters, very often
gives a new Motion to the Spirits, and a new Turn to the Blood; for
which Reason we prescribe it in Distempers which no other Medicine
will reach. I could produce a Quotation out of a very venerable
Author, in which the Frenzy produced by Love, is compared to that
which is produced by the Biting of a mad Dog. But as this Comparison
is a little too coarse for your Paper, and might look as if it were
cited to ridicule the Author who has made use of it; I shall only hint
at it, and desire you to consider whether, if the Frenzy produced by
these two different Causes be of the same Nature, it may not very
properly be cured by the same Means.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant, and Well-wisher,
Esculapius.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a young Woman crossed in Love. My Story is very long and
melancholy. To give you the heads of it: A young Gentleman, after
having made his Applications to me for three Years together, and
filled my Head with a thousand Dreams of Happiness, some few Days
since married another. Pray tell me in what Part of the World your
Promontory lies, which you call
The Lover's Leap, and whether one
may go to it by Land? But, alas, I am afraid it has lost its Virtue,
and that a Woman of our Times would find no more Relief in taking such
a Leap, than in singing an Hymn to
Venus. So that I must cry out
with
Dido in
Dryden's Virgil,
Ah! cruel Heaven, that made no Cure for Love!
Your disconsolate Servant,
Athenais.'
Mister Spictatur,
' My Heart is so full of Lofes and Passions for Mrs.
Gwinifrid, and
she is so pettish and overrun with Cholers against me, that if I had
the good Happiness to have my Dwelling (which is placed by my
Creat-Cranfather upon the Pottom of an Hill) no farther Distance but
twenty Mile from the Lofer's Leap, I would indeed indeafour to preak
my Neck upon it on Purpose. Now, good Mister
Spictatur of
Crete
Prittain, you must know it there is in
Caernaruanshire a fery pig
Mountain, the Glory of all
Wales, which is named
Penmainmaure, and
you must also know, it iss no great Journey on Foot from me; but the
Road is stony and bad for Shooes. Now, there is upon the Forehead of
this Mountain a very high Rock, (like a Parish Steeple) that cometh a
huge deal over the Sea; so when I am in my Melancholies, and I do
throw myself from it, I do desire my fery good Friend to tell me in
his
Spictatur, if I shall be cure of my grefous Lofes; for there is
the Sea clear as Glass, and as creen as the Leek: Then likewise if I
be drown, and preak my Neck, if Mrs.
Gwinifrid will not lose me
afterwards. Pray be speedy in your Answers, for I am in crete Haste,
and it is my Tesires to do my Pusiness without Loss of Time. I remain
with cordial Affections, your ever lofing Friend,
Davyth ap
Shenkyn.'
P. S. 'My Law-suits have brought me to
London, but I have lost my
Causes; and so have made my Resolutions to go down and leap before the
Frosts begin; for I am apt to take Colds.'
Ridicule, perhaps, is a better Expedient against Love than sober Advice,
and I am of Opinion, that
Hudibras
and
Don Quixote
may be as
effectual to cure the Extravagancies of this Passion, as any of the old
Philosophers. I shall therefore publish, very speedily, the Translation
of a little
Greek
Manuscript, which is sent me by a learned Friend. It
appears to have been a Piece of those Records which were kept in the
little Temple of
Apollo
, that stood upon the Promontory of
Leucate
.
The Reader will find it to be a Summary Account of several Persons who
tried the Lover's Leap, and of the Success they found in it. As there
seem to be in it some Anachronisms and Deviations from the ancient
Orthography, I am not wholly satisfied myself that it is authentick, and
not rather the Production of one of those
Grecian
Sophisters, who have
imposed upon the World several spurious Works of this Nature. I
this by way of Precaution, because I know there are several Writers, of
uncommon Erudition, who would not fail to expose my Ignorance, if they
caught me tripping in a Matter of so great Moment
.
C.
divided from
his Life.
The following Advertisement appeared in Nos.
-
,
,
and
, with the word
certainly
before
be ready
after the first insertion:
 |
There is now Printing by Subscription two Volumes of the SpectatorS on
a large Character in Octavo; the Price of the two Vols. well Bound and
Gilt two Guineas. Those who are inclined to Subscribe, are desired to
make their first Payments to Jacob Tonson, Bookseller in the Strand,
the Books being so near finished, that they will be ready for the
Subscribers at or before Christmas next.
The Third and Fourth Volumes of the Lucubrations of Isaac Bickerstaff,
Esq., are ready to be delivered at the same Place.
N .B. The Author desires that such Gentlemen who have not received
their Books for which they have Subscribed, would be pleased to
signify the same to Mr. Tonson. |
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 21, 1711 |
Steele |
Percunctatorem fugito, nam Garrulus idem est.
Hor.

There is a Creature who has all the Organs of Speech, a tolerable good
Capacity for conceiving what is said to it, together with a pretty
proper Behaviour in all the Occurrences of common Life; but naturally
very vacant of Thought in it self, and therefore forced to apply it self
to foreign Assistances. Of this Make is that Man who is very
inquisitive. You may often observe, that tho' he speaks as good Sense as
any Man upon any thing with which he is well acquainted, he cannot trust
to the Range of his own Fancy to entertain himself upon that Foundation,
but goes on to still new Enquiries. Thus, tho' you know he is fit for
the most polite Conversation, you shall see him very well contented to
sit by a Jockey, giving an Account of the many Revolutions in his
Horse's Health, what Potion he made him take, how that agreed with him,
how afterwards he came to his Stomach and his Exercise, or any the like
Impertinence; and be as well pleased as if you talked to him on the most
important Truths. This Humour is far from making a Man unhappy, tho' it
may subject him to Raillery; for he generally falls in with a Person who
seems to be born for him, which is your talkative Fellow. It is so
ordered, that there is a secret Bent, as natural as the Meeting of
different Sexes, in these two Characters, to supply each other's Wants.
I had the Honour the other Day to sit in a publick Room, and saw an
inquisitive Man look with an Air of Satisfaction upon the Approach of
one of these Talkers.
The Man of ready Utterance sat down by him, and rubbing his Head,
leaning on his Arm, and making an uneasy Countenance, he began; 'There
is no manner of News To-day. I cannot tell what is the Matter with me,
but I slept very ill last Night; whether I caught Cold or no, I know
not, but I fancy I do not wear Shoes thick enough for the Weather, and I
have coughed all this Week: It must be so, for the Custom of washing my
Head Winter and Summer with cold Water, prevents any Injury from the
Season entering that Way; so it must come in at my Feet; But I take no
notice of it: as it comes so it goes. Most of our Evils proceed from too
much Tenderness; and our Faces are naturally as little able to resist
the Cold as other Parts. The
Indian
answered very well to an
European
, who asked him how he could go naked; I am all Face.'
I observed this Discourse was as welcome to my general Enquirer as any
other of more Consequence could have been; but some Body calling our
Talker to another Part of the Room, the Enquirer told the next Man who
sat by him, that Mr. such a one, who was just gone from him, used to
wash his Head in cold Water every Morning; and so repeated almost
verbatim
all that had been said to him. The Truth is, the Inquisitive
are the Funnels of Conversation; they do not take in any thing for their
own Use, but merely to pass it to another: They are the Channels through
which all the Good and Evil that is spoken in Town are conveyed. Such as
are offended at them, or think they suffer by their Behaviour, may
themselves mend that Inconvenience; for they are not a malicious People,
and if you will supply them, you may contradict any thing they have said
before by their own Mouths. A farther Account of a thing is one of the
gratefullest Goods that can arrive to them; and it is seldom that they
are more particular than to say, The Town will have it, or I have it
from a good Hand: So that there is room for the Town to know the Matter
more particularly, and for a better Hand to contradict what was said by
a good one.
I have not known this Humour more ridiculous than in a Father, who has
been earnestly solicitous to have an Account how his Son has passed his
leisure Hours; if it be in a Way thoroughly insignificant, there cannot
be a greater Joy than an Enquirer discovers in seeing him follow so
hopefully his own Steps: But this Humour among Men is most pleasant when
they are saying something which is not wholly proper for a third Person
to hear, and yet is in itself indifferent. The other Day there came in a
well-dressed young Fellow, and two Gentlemen of this Species immediately
fell a whispering his Pedigree. I could overhear, by Breaks, She was his
Aunt; then an Answer, Ay, she was of the Mother's Side: Then again in a
little lower Voice, His Father wore generally a darker Wig; Answer, Not
much. But this Gentleman wears higher Heels to his Shoes.
As the Inquisitive, in my Opinion, are such merely from a Vacancy in
their own Imaginations, there is nothing, methinks, so dangerous as to
communicate Secrets to them; for the same Temper of Enquiry makes them
as impertinently communicative: But no Man, though he converses with
them, need put himself in their Power, for they will be contented with
Matters of less Moment as well. When there is Fuel enough, no matter
what it is—Thus the Ends of Sentences in the News Papers, as,
This
wants Confirmation, This occasions many Speculations
, and
Time will
discover the Event
, are read by them, and considered not as mere
Expletives.
One may see now and then this Humour accompanied with an insatiable
Desire of knowing what passes, without turning it to any Use in the
world but merely their own Entertainment. A Mind which is gratified this
Way is adapted to Humour and Pleasantry, and formed for an unconcerned
Character in the World; and, like my self, to be a mere Spectator. This
Curiosity, without Malice or Self-interest, lays up in the Imagination a
Magazine of Circumstances which cannot but entertain when they are
produced in Conversation. If one were to know, from the Man of the first
Quality to the meanest Servant, the different Intrigues, Sentiments,
Pleasures, and Interests of Mankind, would it not be the most pleasing
Entertainment imaginable to enjoy so constant a Farce, as the observing
Mankind much more different from themselves in their secret Thoughts and
publick Actions, than in their Night-caps and long Periwigs?
Mr. Spectator,
'Plutarch tells us, that Caius Gracchus, the Roman, was
frequently hurried by his Passion into so loud and tumultuous a way of
Speaking, and so strained his Voice as not to be able to proceed. To
remedy this Excess, he had an ingenious Servant, by Name Licinius,
always attended him with a Pitch-pipe, or Instrument to regulate the
Voice; who, whenever he heard his Master begin to be high, immediately
touched a soft Note; at which,'tis said, Caius would presently abate
and grow calm.
'Upon recollecting this Story, I have frequently wondered that this
useful Instrument should have been so long discontinued; especially
since we find that this good Office of Licinius has preserved his
Memory for many hundred Years, which, methinks, should have encouraged
some one to have revived it, if not for the publick Good, yet for his
own Credit. It may be objected, that our loud Talkers are so fond of
their own Noise, that they would not take it well to be check'd by
their Servants: But granting this to be true, surely any of their
Hearers have a very good Title to play a soft Note in their own
Defence. To be short, no Licinius appearing and the Noise
increasing, I was resolved to give this late long Vacation to the Good
of my Country; and I have at length, by the Assistance of an ingenious
Artist, (who works to the Royal Society) almost compleated my Design,
and shall be ready in a short Time to furnish the Publick with what
Number of these Instruments they please, either to lodge at
Coffee-houses, or carry for their own private Use. In the mean time I
shall pay that Respect to several Gentlemen, who I know will be in
Danger of offending against this Instrument, to give them notice of it
by private Letters, in which I shall only write, Get a Licinius.
'I should now trouble you no longer, but that I must not conclude
without desiring you to accept one of these Pipes, which shall be left
for you with Buckley; and which I hope will be serviceable to you,
since as you are silent yourself you are most open to the Insults of
the Noisy.
I am, Sir, &c.
W. B.
'I had almost forgot to inform you, that as an Improvement in this
Instrument, there will be a particular Note, which I call a Hush-Note;
and this is to be made use of against a long Story, Swearing,
Obsceneness, and the like.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 22, 1711 |
Addison |
—Spirat adhuc amor,
Vivuntque commissi calores
Æoliæ fidibus puellæ.
Hor.

the many famous Pieces of Antiquity which are still to be seen at
Rome
, there is the Trunk of a Statue
which has lost the Arms,
Legs, and Head; but discovers such an exquisite Workmanship in what
remains of it, that
Michael Angelo
declared he had learned his whole
Art from it. Indeed he studied it so attentively, that he made most of
his Statues, and even his Pictures in that
Gusto
, to make use of the
Italian
Phrase; for which Reason this maimed Statue is still called
Michael Angelo's
School.
A
of
Sappho
, which I design for the Subject of this Paper
, is in as great Reputation among the Poets and Criticks, as the
mutilated Figure above-mentioned is among the Statuaries and Painters.
Several of our Countrymen, and Mr.
Dryden
in particular, seem very
often to have copied after it in their Dramatick Writings; and in their
Poems upon Love.
Whatever might have been the Occasion of this Ode, the English Reader
will enter into the Beauties of it, if he supposes it to have been
written in the Person of a Lover sitting by his Mistress. I shall set to
View three different Copies of this beautiful Original: The first is a
Translation by
Catullus
, the second by Monsieur
Boileau
, and the
last by a Gentleman whose Translation of the
Hymn to Venus
has been so
deservedly admired.
Ad Lesbiam
Ille mî par esse deo videtur,
Ille, si fas est, superare divos,
Qui sedens adversus identidem te,
Spectat, et audit.
Dulce ridentem, misero quod omnis
Eripit sensus mihi: nam simul te,
Lesbia, adspexi, nihil est super mî
Quod loquar amens.
Lingua sed torpet, tenuis sub artus
Flamnia dimanat, sonitu suopte
Tinniunt aures, gemina teguntur
Lumina nocte.
learned Reader will know very well the Reason why one of these Verses
is printed in
Roman
Letter
; and if he compares this Translation
with the Original, will find that the three first Stanzas are rendred
almost Word for Word, and not only with the same Elegance, but with the
same short Turn of Expression which is so remarkable in the
Greek
, and
so peculiar to the
Sapphick
Ode. I cannot imagine for what Reason
Madam
Dacier
has told us, that this Ode of
Sappho
is preserved
entire in
Longinus
, since it is manifest to any one who looks into
that Author's Quotation of it, that there must at least have been
another Stanza, which is not transmitted to us.
The second Translation of this Fragment which I shall here cite, is that
of Monsieur
Boileau
.
Heureux! qui prés de toi, pour toi seule soûpire:
Qui jouït du plaisir de t'entendre parler:
Qui te voit quelquefois doucement lui soûrire.
Les Dieux, dans son bonheur, peuvent-ils l'égaler?
Je sens de veine en veine une subtile flamme
Courir par tout mon corps, si-tost que je te vois:
Et dans les doux transports, où s'egare mon ame,
Je ne sçaurois trouver de langue, ni de voix.
Un nuage confus se répand sùr ma vuë,
Je n'entens plus, je tombe en de douces langueurs;
Et pâle, sans haleine, interdite, esperduë,
Un frisson me saisit, je tremble, je me meurs.
The Reader will see that this is rather an Imitation than a Translation.
The Circumstances do not lie so thick together, and follow one another
with that Vehemence and Emotion as in the Original. In short, Monsieur
Boileau
has given us all the Poetry, but not all the Passion of this
famous Fragment. I shall, in the last Place, present my Reader with the
English
Translation.
| I |
Blest as th'immortal Gods is he,
The Youth who fondly sits by thee,
And hears and sees thee all the while
Softly speak and sweetly smile. |
| II |
'Twas this deprived my Soul of Rest,
And raised such Tumults in my Breast;
For while I gaz'd, in Transport tost,
My Breath was gone, my Voice was lost: |
| III |
My Bosom glowed; the subtle Flame
Ran quick through all my vital Frame;
O'er my dim Eyes a Darkness hung;
My Ears with hollow Murmurs rung. |
| IV |
In dewy Damps my Limbs were chil'd;
My Blood with gentle Horrors thrill'd;
My feeble Pulse forgot to play;
I fainted, sunk, and dy'd away. |
Instead of giving any Character of this last Translation, I shall desire
my learned Reader to look into the Criticisms which
Longinus
has made
upon the Original. By that means he will know to which of the
Translations he ought to give the Preference. I shall only add, that
this Translation is written in the very Spirit of
Sappho
, and as near
the
Greek
as the Genius of our Language will possibly suffer.
Longinus
has observed, that this Description of Love in
Sappho
is an
exact Copy of Nature, and that all the Circumstances which follow one
another in such an Hurry of Sentiments, notwithstanding they appear
repugnant to each other, are really such as happen in the Phrenzies of
Love.
I wonder, that not one of the Criticks or Editors, through whose Hands
this Ode has passed, has taken Occasion from it to mention a
Circumstance related by
Plutarch
.
Author in the famous Story of
Antiochus
, who fell in Love with
Stratonice
, his Mother-in-law, and
(not daring to discover his Passion) pretended to be confined to his Bed
by Sickness, tells us, that
Erasistratus
, the Physician, found out the
Nature of his Distemper by those Symptoms of Love which he had learnt
from
Sappho's
Writings
.
Stratonice
was in the Room of the Love-sick Prince, when these
Symptoms discovered themselves to his Physician; and it is probable,
that they were not very different from those which
Sappho
here
describes in a Lover sitting by his Mistress. This Story of
Antiochus
is so well known, that I need not add the Sequel of it, which has no
Relation to my present Subject.
C.
The Belvidere Torso.
The other translation by Ambrose Philips. See note to No.
.
Wanting in copies then known, it is here supplied by
conjecture.
In Plutarch's
Life of Demetrius.
'When others entered Antiochus was entirely unaffected. But when
Stratonice came in, as she often did, he shewed all the symptoms
described by Sappho, the faltering voice, the burning blush, the
languid eye, the sudden sweat, the tumultuous pulse; and at length,
the passion overcoming his spirits, a swoon and mortal paleness.'
Contents
|
Friday, November 23, 1711 |
Steele |
Homines ad Deos nullâ re propiùs accedunt, quam salutem Hominibus dando.
Tull.

Human Nature appears a very deformed, or a very beautiful Object,
according to the different Lights in which it is viewed. When we see Men
of inflamed Passions, or of wicked Designs, tearing one another to
pieces by open Violence, or undermining each other by secret Treachery;
when we observe base and narrow Ends pursued by ignominious and
dishonest Means; when we behold Men mixed in Society as if it were for
the Destruction of it; we are even ashamed of our Species, and out of
Humour with our own Being:
in another Light, when we behold them
mild, good, and benevolent, full of a generous Regard for the publick
Prosperity, compassionating
each
other's
Distresses, and relieving each other's Wants, we can hardly believe they
are Creatures of the same Kind. In this View they appear Gods to each
other, in the Exercise of the noblest Power, that of doing Good; and the
greatest Compliment we have ever been able to make to our own Being, has
been by calling this Disposition of Mind Humanity. We cannot but observe
a Pleasure arising in our own Breast upon the seeing or hearing of a
generous Action, even when we are wholly disinterested in it. I cannot
give a more proper Instance of this, than by a Letter from
Pliny
, in
which he recommends a Friend in the most handsome manner, and, methinks,
it would be a great Pleasure to know the Success of this Epistle, though
each Party concerned in it has been so many hundred Years in his Grave.
To MAXIMUS.
What I should gladly do for any Friend of yours, I think I may now
with Confidence request for a Friend of mine.
Arrianus Maturius is
the most considerable Man of his Country; when I call him so, I do not
speak with Relation to his Fortune, though that is very plentiful, but
to his Integrity, Justice, Gravity, and Prudence; his Advice is useful
to me in Business, and his Judgment in Matters of Learning: His
Fidelity, Truth, and good Understanding, are very great; besides this,
he loves me as you do, than which I cannot say any thing that
signifies a warmer Affection. He has nothing that's aspiring; and
though he might rise to the highest Order of Nobility, he keeps
himself in an inferior Rank; yet I think my self bound to use my
Endeavours to serve and promote him; and would therefore find the
Means of adding something to his Honours while he neither expects nor
knows it, nay, though he should refuse it.
Something, in short, I
would have for him that may be honourable, but not troublesome; and I
entreat that you will procure him the first thing of this kind that
offers, by which you will not only oblige me, but him also; for though
he does not covet it, I know he will be as grateful in acknowledging
your Favour as if he had asked it
2.
Mr. Spectator,
The Reflections in some of your Papers on the servile manner of
Education now in Use, have given Birth to an Ambition, which, unless
you discountenance it, will, I doubt, engage me in a very difficult,
tho not ungrateful Adventure. I am about to undertake, for the sake of
the
British Youth, to instruct them in such a manner, that the most
dangerous Page in
Virgil or
Homer may be read by them with much
Pleasure, and with perfect Safety to their Persons.
Could I prevail so far as to be honoured with the Protection of some
few of them, (for I am not Hero enough to rescue many) my Design is to
retire with them to an agreeable Solitude; though within the
Neighbourhood of a City, for the Convenience of their being instructed
in Musick, Dancing, Drawing, Designing, or any other such
Accomplishments, which it is conceived may make as proper Diversions
for them, and almost as pleasant, as the little sordid Games which
dirty School-boys are so much delighted with. It may easily be
imagined, how such a pretty Society, conversing with none beneath
themselves, and sometimes admitted as perhaps not unentertaining
Parties amongst better Company, commended and caressed for their
little Performances, and turned by such Conversations to a certain
Gallantry of Soul, might be brought early acquainted with some of the
most polite
English Writers. This having given them some tolerable
Taste of Books, they would make themselves Masters of the
Latin
Tongue by Methods far easier than those in
Lilly, with as little
Difficulty or Reluctance as young Ladies learn to speak
French, or
to sing
Italian Operas. When they had advanced thus far, it would be
time to form their Taste something more exactly: One that had any true
Relish of fine Writing, might, with great Pleasure both to himself and
them, run over together with them the best
Roman Historians, Poets,
and Orators, and point out their more remarkable Beauties; give them a
short Scheme of Chronology, a little View of Geography, Medals,
Astronomy, or what else might best feed the busy inquisitive Humour so
natural to that Age. Such of them as had the least Spark of Genius,
when it was once awakened by the shining Thoughts and great Sentiments
of those admired Writers, could not, I believe, be easily withheld
from attempting that more difficult Sister Language, whose exalted
Beauties they would have heard so often celebrated as the Pride and
Wonder of the whole Learned World. In the mean while, it would be
requisite to exercise their Style in Writing any light Pieces that ask
more of Fancy than of Judgment: and that frequently in their Native
Language, which every one methinks should be most concerned to
cultivate, especially Letters, in which a Gentleman must have so
frequent Occasions to distinguish himself. A Set of genteel
good-natured Youths fallen into such a Manner of Life, would form
almost a little Academy, and doubtless prove no such contemptible
Companions, as might not often tempt a wiser Man to mingle himself in
their Diversions, and draw them into such serious Sports as might
prove nothing less instructing than the gravest Lessons. I doubt not
but it might be made some of their Favourite Plays, to contend which
of them should recite a beautiful Part of a Poem or Oration most
gracefully, or sometimes to join in acting a Scene of
Terence,
Sophocles, or our own
Shakespear. The Cause of
Milo might again
be pleaded before more favourable Judges,
Cæsar a second time be
taught to tremble, and another Race of
Athenians be afresh enraged
at the Ambition of another
Philip. Amidst these noble Amusements, we
could hope to see the early Dawnings of their Imagination daily
brighten into Sense, their Innocence improve into Virtue, and their
unexperienced Good-nature directed to a generous Love of their
Country.
I am, &c.
T.
of each
Pliny, Jun, Epist. Bk. II. Ep. 2. Thus far the paper is by
John Hughes.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 24, 1711 |
Addison |
O Pudor! O Pietas!
Mart.

Looking over the Letters which I have lately received from from my
Correspondents, I met with the following one, which is written with such
a Spirit of Politeness, that I could not but be very much pleased with
it my self, and question not but it will be as acceptable to the Reader.
Mr. Spectator
1,
You, who are no Stranger to Publick Assemblies, cannot but have
observed the Awe they often strike on such as are obliged to exert any
Talent before them. This is a sort of elegant Distress, to which
ingenuous Minds are the most liable, and may therefore deserve some
remarks in your Paper. Many a brave Fellow, who has put his Enemy to
Flight in the Field, has been in the utmost Disorder upon making a
Speech before a Body of his Friends at home: One would think there was
some kind of Fascination in the Eyes of a large Circle of People, when
darting altogether upon one Person. I have seen a new Actor in a
Tragedy so bound up by it as to be scarce able to speak or move, and
have expected he would have died above three Acts before the Dagger or
Cup of Poison were brought in. It would not be amiss, if such an one
were at first introduced as a Ghost or a Statue, till he recovered his
Spirits, and grew fit for some living Part.
As this sudden Desertion of one's self shews a Diffidence, which is not
displeasing, it implies at the same time the greatest Respect to an
Audience that can be. It is a sort of mute Eloquence, which pleads for
their Favour much better than Words could do; and we find their
Generosity naturally moved to support those who are in so much
Perplexity to entertain them. I
was extremely pleased with a late
Instance of this Kind at the Opera of
Almahide, in the Encouragement
given to a young Singer
2, whose more than ordinary Concern on her
first Appearance, recommended her no less than her agreeable Voice,
and just Performance. Meer Bashfulness without Merit is awkward; and
Merit without Modesty, insolent. But modest Merit has a double Claim
to Acceptance, and generally meets with as many Patrons as Beholders.
I am, &c.
It is impossible that a Person should exert himself to Advantage in an
Assembly, whether it be his Part either to sing or speak, who lies under
too great Oppressions of Modesty. I remember, upon talking with a Friend
of mine concerning the Force of Pronunciation, our Discourse led us into
the Enumeration of the several Organs of Speech which an Orator ought to
have in Perfection, as the Tongue, the Teeth
the Lips
, the Nose, the
Palate, and the Wind-pipe. Upon which, says my Friend, you have omitted
the most material Organ of them all, and that is the Forehead.
But notwithstanding an Excess of Modesty obstructs the Tongue, and
renders it unfit for its Offices, a due Proportion of it is thought so
requisite to an Orator, that Rhetoricians have recommended it to their
Disciples as a Particular in their Art.
Cicero
tells us that he never
liked an Orator who did not appear in some little Confusion at the
Beginning of his Speech, and confesses that he himself never entered
upon an Oration without Trembling and Concern. It is indeed a kind of
Deference which is due to a great Assembly, and seldom fails to raise a
Benevolence in the Audience towards the Person who speaks. My
Correspondent has taken notice that the bravest Men often appear
timorous on these Occasions, as indeed we may observe, that there is
generally no Creature more impudent than a Coward.
—Linguá melior, sedfrigida bello
Dextera—
A
Tongue and a feeble Arm are the Qualifications of
Drances
in
Virgil
; as
Homer
, to express a Man both timorous and sawcy, makes
use of a kind of Point, which is very rarely to be met with in his
Writings; namely, that he had the Eyes of a Dog, but the Heart of a
Deer
.
A just and reasonable Modesty does not only recommend Eloquence, but
sets off every great Talent which a Man can be possessed of. It
heightens all the Virtues which it accompanies like the Shades in
Paintings, it raises and rounds every Figure, and makes the Colours more
beautiful, though not so glaring as they would be without it.
Modesty is not only an Ornament, but also a Guard to Virtue. It is a
kind of quick and delicate
Feeling
in the Soul, which makes her shrink
and withdraw her self from every thing that has Danger in it. It is such
an exquisite Sensibility, as warns her to shun the first Appearance of
every thing which is hurtful.
I cannot at present recollect either the Place or Time of what I am
going to mention; but I have read somewhere in the History of Ancient
Greece
, that the Women of the Country were seized with an
unaccountable Melancholy, which disposed several of them to make away
with themselves. The Senate, after having tried many Expedients to
prevent this Self-Murder, which was so frequent among them, published an
Edict, That if any Woman whatever should lay violent Hands upon her
self, her Corps should be exposed naked in the Street, and dragged about
the City in the most publick Manner. This Edict immediately put a Stop
to the Practice which was before so common. We may see in this Instance
the Strength of Female Modesty, which was able to overcome the Violence
even of Madness and Despair. The Fear of Shame in the Fair Sex, was in
those Days more prevalent than that of Death.
If Modesty has so great an Influence over our Actions, and is in many
Cases so impregnable a Fence to Virtue; what can more undermine Morality
than that Politeness which reigns among the unthinking Part of Mankind,
and treats as unfashionable the most ingenuous Part of our Behaviour;
which recommends Impudence as good Breeding, and keeps a Man always in
Countenance, not because he is Innocent, but because he is Shameless?
Seneca
thought Modesty so great a Check to Vice, that he prescribes to
us the Practice of it in Secret, and advises us to raise it in ourselves
upon imaginary Occasions, when such as are real do not offer themselves;
for this is the Meaning of his Precept, that when we are by ourselves,
and in our greatest Solitudes, we should fancy that
Cato
stands before
us, and sees every thing we do. In short, if you banish Modesty out of
the World, she carries away with her half the Virtue that is in it.
After these Reflections on Modesty, as it is a Virtue; I must observe,
that there is a vicious Modesty, which justly deserves to be ridiculed,
and which those Persons very often discover, who value themselves most
upon a well-bred Confidence. This happens when a Man is ashamed to act
up to his Reason, and would not upon any Consideration be surprized in
the Practice of those Duties, for the Performance of which he was sent
into the World. Many an impudent Libertine would blush to be caught in a
serious Discourse, and would scarce be able to show his Head, after
having disclosed a religious Thought. Decency of Behaviour, all outward
Show of Virtue, and Abhorrence of Vice, are carefully avoided by this
Set of Shame-faced People, as what would disparage their Gayety of
Temper, and infallibly bring them to Dishonour. This is such a Poorness
of Spirit, such a despicable Cowardice, such a degenerate abject State
of Mind, as one would think Human Nature incapable of, did we not meet
with frequent Instances of it in ordinary Conversation.
There is another Kind of vicious Modesty which makes a Man ashamed of
his Person, his Birth, his Profession, his Poverty, or the like
Misfortunes, which it was not in his Choice to prevent, and is not in
his Power to rectify. If a Man appears ridiculous by any of the
afore-mentioned Circumstances, he becomes much more so by being out of
Countenance for them. They should rather give him Occasion to exert a
noble Spirit, and to palliate those Imperfections which are not in his
Power, by those Perfections which are; or to use a very witty Allusion
of an eminent Author, he should imitate
Cæsar
, who, because his Head
was bald, cover'd that Defect with Laurels.
C.
This letter is by John Hughes.
Mrs. Barbier
Iliad
, i. 225.
Contents
|
Monday, November 26, 1711 |
Hughes1 |
Nihil largiundo gloriam adeptus est.
Sallust.

My wise and good Friend, Sir
Andrew Freeport
, divides himself almost
equally between the Town and the Country: His Time in Town is given up
to the Publick, and the Management of his private Fortune; and after
every three or four Days spent in this Manner, he retires for as many to
his Seat within a few Miles of the Town, to the Enjoyment of himself,
his Family, and his Friend. Thus Business and Pleasure, or rather, in
Sir
Andrew
, Labour and Rest, recommend each other. They take their
Turns with so quick a Vicissitude, that neither becomes a Habit, or
takes Possession of the whole Man; nor is it possible he should be
surfeited with either. I often see him at our Club in good Humour, and
yet sometimes too with an Air of Care in his Looks: But in his Country
Retreat he is always unbent, and such a Companion as I could desire; and
therefore I seldom fail to make one with him when he is pleased to
invite me.
The other Day, as soon as we were got into his Chariot, two or three
Beggars on each Side hung upon the Doors, and solicited our Charity with
the usual Rhetorick of a sick Wife or Husband at home, three or four
helpless little Children all starving with Cold and Hunger. We were
forced to part with some Money to get rid of their Importunity; and then
we proceeded on our Journey with the Blessings and Acclamations of these
People.
'Well then', says Sir Andrew, 'we go off with the Prayers and good
Wishes of the Beggars, and perhaps too our Healths will be drunk at
the next Ale-house: So all we shall be able to value ourselves upon,
is, that we have promoted the Trade of the Victualler and the Excises
of the Government. But how few Ounces of Wooll do we see upon the
Backs of those poor Creatures? And when they shall next fall in our
Way, they will hardly be better dressd; they must always live in Rags
to look like Objects of Compassion. If their Families too are such as
they are represented, tis certain they cannot be better clothed, and
must be a great deal worse fed: One would think Potatoes should be all
their Bread, and their Drink the pure Element; and then what goodly
Customers are the Farmers like to have for their Wooll, Corn and
Cattle? Such Customers, and such a Consumption, cannot choose but
advance the landed Interest, and hold up the Rents of the Gentlemen.
'But of all Men living, we Merchants, who live by Buying and Selling,
ought never to encourage Beggars. The Goods which we export are indeed
the Product of the lands, but much the greatest Part of their Value is
the Labour of the People: but how much of these People's Labour shall
we export whilst we hire them to sit still? The very Alms they receive
from us, are the Wages of Idleness. I have often thought that no Man
should be permitted to take Relief from the Parish, or to ask it in
the Street, till he has first purchased as much as possible of his own
Livelihood by the Labour of his own Hands; and then the Publick ought
only to be taxed to make good the Deficiency. If this Rule was
strictly observed, we should see every where such a Multitude of new
Labourers, as would in all probability reduce the Prices of all our
Manufactures. It is the very Life of Merchandise to buy cheap and sell
dear. The Merchant ought to make his Outset as cheap as possible, that
he may find the greater Profit upon his Returns; and nothing will
enable him to do this like the Reduction of the Price of Labour upon
all our Manufactures. This too would be the ready Way to increase the
Number of our Foreign Markets: The Abatement of the Price of the
Manufacture would pay for the Carriage of it to more distant
Countries; and this Consequence would be equally beneficial both to
the Landed and Trading Interests. As so great an Addition of labouring
Hands would produce this happy Consequence both to the Merchant and
the Gentle man; our Liberality to common Beggars, and every other
Obstruction to the Increase of Labourers, must be equally pernicious
to both.
Sir
Andrew
then went on to affirm, That the Reduction of the Prices of
our Manufactures by the Addition of so many new Hands, would be no
Inconvenience to any Man: But observing I was something startled at the
Assertion, he made a short Pause, and then resumed the Discourse.
'It
may seem, says he, a Paradox, that the Price of Labour should be reduced
without an Abatement of Wages, or that Wages can be abated without any
Inconvenience to the Labourer, and yet nothing is more certain than that
both those Things may happen. The Wages of the Labourers make the
greatest Part of the Price of every Thing that is useful; and if in
Proportion with the Wages the Prices of all other Things should be
abated, every Labourer with less Wages would be still able to purchase
as many Necessaries of Life; where then would be the Inconvenience? But
the Price of Labour may be reduced by the Addition of more Hands to a
Manufacture, and yet the Wages of Persons remain as high as ever.
The
admirable Sir William Petty
2 has given Examples of
this in some of his Writings: One of them, as I remember, is that of a
Watch, which I shall endeavour to explain so as shall suit my present
Purpose. It is certain that a single Watch could not be made so cheap in
Proportion by one only Man, as a hundred Watches by a hundred; for as
there is vast Variety in the Work, no one Person could equally suit
himself to all the Parts of it; the Manufacture would be tedious, and at
last but clumsily performed: But if an hundred Watches were to be made
by a hundred Men, the Cases may be assigned to one, the Dials to
another, the Wheels to another, the Springs to another, and every other
Part to a proper Artist; as there would be no need of perplexing any one
Person with too much Variety, every one would be able to perform his
single Part with greater Skill and Expedition; and the hundred Watches
would be finished in one fourth Part of the Time of the first one, and
every one of them at one fourth Part of the Cost, tho' the Wages of
every Man were equal. The Reduction of the Price of the Manufacture
would increase the Demand of it, all the same Hands would be still
employed and as well paid. The same Rule will hold in the Clothing, the
Shipping, and all the other Trades whatsoever. And thus an Addition of
Hands to our Manufactures will only reduce the Price of them; the
Labourer will still have as much Wages, and will consequently be enabled
to purchase more Conveniencies of Life; so that every Interest in the
Nation would receive a Benefit from the Increase of our Working People.
Besides, I see no Occasion for this Charity to common Beggars, since
every Beggar is an Inhabitant of a Parish, and every Parish is taxed
to the Maintenance of their own Poor
3.
For my own part, I cannot be mightily pleased with the Laws which have
done this, which have provided better to feed than employ the Poor. We
have a Tradition from our Forefathers, that after the first of those
Laws was made, they were insulted with that famous Song;
Hang Sorrow, and cast away Care,
The Parish is bound to find us, &c.
And if we will be so good-natured as to maintain them without Work,
they can do no less in Return than sing us
The Merry Beggars.
What then? Am I against all Acts of Charity? God forbid! I know of no
Virtue in the Gospel that is in more pathetical Expressions
recommended to our Practice.
I was hungry and ye4 gave me no
Meat, thirsty and ye gave me no Drink, naked and ye clothed me not, a
Stranger and ye took me not in, sick and in prison and ye visited me
not.
Our Blessed Saviour treats the Exercise or Neglect of Charity
towards a poor Man, as the Performance or Breach of this Duty towards
himself. I shall endeavour to obey the Will of my Lord and Master: And
therefore if an industrious Man shall submit to the hardest Labour and
coarsest Fare, rather than endure the Shame of taking Relief from the
Parish, or asking it in the Street, this is the Hungry, the Thirsty,
the Naked; and I ought to believe, if any Man is come hither for
Shelter against Persecution or Oppression, this is the Stranger, and I
ought to take him in. If any Countryman of our own is fallen into the
Hands of Infidels, and lives in a State of miserable Captivity, this
is the Man in Prison, and I should contribute to his Ransom. I ought
to give to an Hospital of Invalids, to recover as many useful Subjects
as I can; but I shall bestow none of my Bounties upon an Alms-house of
idle People; and for the same Reason I should not think it a Reproach
to me if I had withheld my Charity from those common Beggars. But we
prescribe better Rules than we are able to practise; we are ashamed
not to give into the mistaken Customs of our Country: But at the same
time, I cannot but think it a Reproach worse than that of common
Swearing, that the Idle and the Abandoned are suffered in the Name of
Heaven and all that is sacred, to extort from Christian and tender
Minds a Supply to a profligate Way of Life, that is always to be
supported, but never
relieved.
Z
.
Or Henry Martyn?
Surveyor-general of Ireland to Charles II. See his
Discourse of Taxes
(1689).
Our idle poor till the time of Henry VIII. lived upon alms.
After the dissolution of the monasteries experiments were made for their
care, and by a statute 43 Eliz. overseers were appointed and Parishes
charged to maintain their helpless poor and find work for the sturdy. In
Queen Anne's time the Poor Law had been made more intricate and
troublesome by the legislation on the subject that had been attempted
after the Restoration.
you
throughout, and in first reprint.
X.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 27, 1711 |
Addison |
—Tanquam hec sint nostri medicina furoris,
Aut Deus ille malis hominum mitescere discat.
Virg.

I shall, in this Paper, discharge myself of the Promise I have made to
the Publick, by obliging them with a Translation of the little
Greek
Manuscript, which is said to have been a Piece of those Records that
were preserved in the Temple of
Apollo
, upon the Promontory of
Leucate
: It is a short History of the Lover's Leap, and is inscribed,
An Account of Persons Male and Female, who offered up their Vows in the
Temple of the
Pythian Apollo,
in the Forty sixth Olympiad, and leaped
from the Promontory of
Leucate
into the
Ionian Sea,
in order to cure
themselves of the Passion of Love
.
This Account is very dry in many Parts, as only mentioning the Name of
the Lover who leaped, the Person he leaped for, and relating, in short,
that he was either cured, or killed, or maimed by the Fall. It indeed
gives the Names of so many who died by it, that it would have looked
like a Bill of Mortality, had I translated it at full length; I have
therefore made an Abridgment of it, and only extracted such particular
Passages as have something extraordinary, either in the Case, or in the
Cure, or in the Fate of the Person who is mentioned in it. After this
short Preface take the Account as follows.
Battus, the Son of
Menalcas the
Sicilian, leaped for
Bombyca
the Musician: Got rid of his Passion with the Loss of his Right Leg
and Arm, which were broken in the Fall.
Melissa, in Love with
Daphnis, very much bruised, but escaped with
Life.
Cynisca, the Wife of
Æschines, being in Love with
Lycus; and
Æschines her Husband being in Love with
Eurilla; (which had made
this married Couple very uneasy to one another for several Years) both
the Husband and the Wife took the Leap by Consent; they both of them
escaped, and have lived very happily together ever since.
Larissa, a Virgin of
Thessaly, deserted by
Plexippus, after a
Courtship of three Years; she stood upon the Brow of the Promontory
for some time, and after having thrown down a Ring, a Bracelet, and a
little Picture, with other Presents which she had received from
Plexippus, she threw her self into the Sea, and was taken up alive.
N. B. Larissa, before she leaped, made an Offering of a Silver
Cupid in the Temple of
Apollo.
Simaetha, in Love with
Daphnis the
Myndian, perished in the
Fall.
Charixus, the Brother of
Sappho, in Love with
Rhodope the
Courtesan, having spent his whole Estate upon her, was advised by his
Sister to leap in the Beginning of his Amour, but would not hearken to
her till he was reduced to his last Talent; being forsaken by
Rhodope, at length resolved to take the Leap. Perished in it.
Aridæus, a beautiful Youth of
Epirus, in Love with
Praxinoe,
the Wife of
Thespis, escaped without Damage, saving only that two of
his Fore-Teeth were struck out and his Nose a little flatted.
Cleora, a Widow of
Ephesus, being inconsolable for the Death of
her Husband, was resolved to take this Leap in order to get rid of her
Passion for his Memory; but being arrived at the Promontory, she there
met with
Dimmachus the
Miletian, and after a short Conversation
with him, laid aside the Thoughts of her Leap, and married him in the
Temple of
Apollo.
N. B. Her Widow's Weeds are still to be seen hanging up in the
Western Corner of the Temple.
Olphis, the Fisherman, having received a Box on the Ear from
Thestylis the Day before, and being determined to have no more to do
with her, leaped, and escaped with Life.
Atalanta, an old Maid, whose Cruelty had several Years before driven
two or three despairing Lovers to this Leap; being now in the fifty
fifth Year of her Age, and in Love with an Officer of
Sparta, broke
her Neck in the Fall.
Hipparchus being passionately fond of his own Wife who was enamoured
of
Bathyllus, leaped, and died of his Fall; upon which his Wife
married her Gallant.
Tettyx, the Dancing-Master, in Love with
Olympia an Athenian
Matron, threw himself from the Rock with great Agility, but was
crippled in the Fall.
Diagoras, the Usurer, in Love with his Cook-Maid; he peeped several
times over the Precipice, but his Heart misgiving him, he went back,
and married her that Evening.
Cinædus, after having entered his own Name in the Pythian Records,
being asked the Name of the Person whom he leaped for, and being
ashamed to discover it, he was set aside, and not suffered to leap.
Eunica, a Maid of
Paphos, aged Nineteen, in Love with
Eurybates.
Hurt in the Fall, but recovered.
N. B. This was her second Time of Leaping.
Hesperus, a young Man of
Tarentum, in Love with his Master's
Daughter. Drowned, the Boats not coming in soon enough to his Relief.
Sappho, the
Lesbian, in Love with
Phaon, arrived at the Temple
of
Apollo, habited like a Bride in Garments as white as Snow. She
wore a Garland of Myrtle on her Head, and carried in her Hand the
little Musical Instrument of her own Invention. After having sung an
Hymn to
Apollo, she hung up her Garland on one Side of his Altar,
and her Harp on the other.
She then tuck'd up her Vestments, like a
Spartan Virgin, and amidst thousands of Spectators, who were anxious
for her Safety, and offered up Vows for her Deliverance,
marched1
directly forwards to the utmost Summit of the Promontory, where after
having repeated a Stanza of her own Verses, which we could not hear,
she threw herself off the Rock with such an Intrepidity as was never
before observed in any who had attempted that dangerous Leap. Many who
were present related, that they saw her fall into the Sea, from whence
she never rose again; tho' there were others who affirmed, that she
never came to the Bottom of her Leap, but that she was changed into a
Swan as she fell, and that they saw her hovering in the Air under that
Shape. But whether or no the Whiteness and Fluttering of her Garments
might not deceive those who looked upon her, or whether she might not
really be metamorphosed into that musical and melancholy Bird, is
still a Doubt among the
Lesbians.
Alcæus, the famous
Lyrick Poet, who had for some time been
passionately in Love with
Sappho, arrived at the Promontory of
Leucate that very Evening, in order to take the Leap upon her
Account; but hearing that
Sappho had been there before him, and that
her Body could be no where found, he very generously lamented her
Fall, and is said to have written his hundred and twenty fifth Ode
upon that Occasion.
| Leaped in this Olympiad |
|
|
2502 |
|
Males |
124 |
|
|
Females |
126 |
|
| Cured |
|
|
1203 |
|
Males |
51 |
|
|
Females |
69 |
|
C.
she marched
350
, and in first reprint.
150
, corrected by an Erratum.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Vellum in amicitia erraremus.
Hor.
1
You very often hear People, after a Story has been told with some
entertaining Circumstances, tell it over again with Particulars that
destroy the Jest, but give Light into the Truth of the Narration. This
sort of Veracity, though it is impertinent, has something amiable in it,
because it proceeds from the Love of Truth, even in frivolous Occasions.
If such honest Amendments do not promise an agreeable Companion, they do
a sincere Friend; for which Reason one should allow them so much of our
Time, if we fall into their Company, as to set us right in Matters that
can do us no manner of Harm, whether the Facts be one Way or the other.
Lies which are told out of Arrogance and Ostentation a Man should detect
in his own Defence, because he should not be triumphed over; Lies which
are told out of Malice he should expose, both for his own sake and that
of the rest of Mankind, because every Man should rise against a common
Enemy: But the officious Liar many have argued is to be excused, because
it does some Man good, and no Man hurt. The Man who made more than
ordinary speed from a Fight in which the
Athenians
were beaten, and
told them they had obtained a complete Victory, and put the whole City
into the utmost Joy and Exultation, was check'd by the Magistrates for
his Falshood; but excused himself by saying,
O Athenians!
am I your
Enemy because I gave you two happy Days? This Fellow did to a whole
People what an Acquaintance of mine does every Day he lives in some
eminent Degree to particular Persons. He is ever lying People into good
Humour, and, as
Plato
said, it was allowable in Physicians to lie to
their Patients to keep up their Spirits, I am half doubtful whether my
Friend's Behaviour is not as excusable. His Manner is to express himself
surprised at the Chearful Countenance of a Man whom he observes
diffident of himself; and generally by that means makes his Lie a Truth.
will, as if he did not know any
thing
of the Circumstance, ask
one whom he knows at Variance with another, what is the meaning that Mr.
such a one, naming his Adversary, does not applaud him with that
Heartiness which formerly he has heard him? He said indeed, (continues
he) I would rather have that Man for my Friend than any Man in
England
; but for an Enemy—This melts the Person he talks to, who
expected nothing but downright Raillery from that Side. According as he
sees his Practices succeeded, he goes to the opposite Party, and tells
him, he cannot imagine how it happens that some People know one another
so little; you spoke with so much Coldness of a Gentleman who said more
Good of you, than, let me tell you, any Man living deserves. The Success
of one of these Incidents was, that the next time that one of the
Adversaries spied the other, he hems after him in the publick Street,
and they must crack a Bottle at the next Tavern, that used to turn out
of the other's Way to avoid one another's Eyeshot. He will tell one
Beauty she was commended by another, nay, he will say she gave the Woman
he speaks to, the Preference in a Particular for which she her self is
admired. The pleasantest Confusion imaginable is made through the whole
Town by my Friend's indirect Offices; you shall have a Visit returned
after half a Year's Absence, and mutual Railing at each other every Day
of that Time. They meet with a thousand Lamentations for so long a
Separation, each Party naming herself for the greater Delinquent, if the
other can possibly be so good as to forgive her, which she has no Reason
in the World, but from the Knowledge of her Goodness, to hope for. Very
often a whole Train of Railers of each Side tire their Horses in setting
Matters right which they have said during the War between the Parties;
and a whole Circle of Acquaintance are put into a thousand pleasing
Passions and Sentiments, instead of the Pangs of Anger, Envy,
Detraction, and Malice.
To the
Spectator.
Devonshire, Nov. 14, 1711.
Sir,
There arrived in this Neighbourhood two Days ago one of your gay
Gentlemen of the Town, who being attended at his Entry with a Servant
of his own, besides a Countryman he had taken up for a Guide, excited
the Curiosity of the Village to learn whence and what he might be. The
Countryman (to whom they applied as most easy of Access) knew little
more than that the Gentleman came from
London to travel and see
Fashions, and was, as he heard say, a Free-thinker: What Religion that
might be, he could not tell; and for his own Part, if they had not
told him the Man was a Free-thinker, he should have guessed, by his
way of talking, he was little better than a Heathen; excepting only
that he had been a good Gentleman to him, and made him drunk twice in
one Day, over and above what they had bargained for.
I do not look upon the Simplicity of this, and several odd Inquiries
with which I shall not trouble you to be wondered at, much less can I
think that our Youths of fine Wit, and enlarged Understandings, have
any Reason to laugh. There is no Necessity that every Squire in
Great
Britain should know what the Word Free-thinker stands for; but it
were much to be wished, that they who value themselves upon that
conceited Title were a little better instructed in what it ought to
stand for; and that they would not perswade themselves a Man is really
and truly a Free-thinker in any tolerable Sense, meerly by virtue of
his being an Atheist, or an Infidel of any other Distinction. It may
be doubted, with good Reason, whether there ever was in Nature a more
abject, slavish, and bigotted Generation than the Tribe of
Beaux
Esprits, at present so prevailing in this Island. Their Pretension to
be Free-thinkers, is no other than Rakes have to be Free-livers, and
Savages to be Free-men, that is, they can think whatever they have a
Mind to, and give themselves up to whatever Conceit the Extravagancy
of their Inclination, or their Fancy, shall suggest; they can think as
wildly as they talk and act, and will not endure that their Wit should
be controuled by such formal Things as Decency and common Sense:
Deduction, Coherence, Consistency, and all the Rules of Reason they
accordingly disdain, as too precise and mechanical for Men of a
liberal Education.
This, as far as I could ever learn from their Writings, or my own
Observation, is a true Account of the
British Free-thinker.
Our
Visitant here, who gave occasion to this Paper, has brought with him a
new System of common Sense, the Particulars of which I am not yet
acquainted with, but will lose no Opportunity of informing my self
whether it contain any
thing3 worth Mr.
Spectator'S Notice. In
the mean time, Sir, I cannot but think it would be for the good of
Mankind, if you would take this Subject into your own Consideration,
and convince the hopeful Youth of our Nation, that Licentiousness is
not Freedom; or, if such a Paradox will not be understood, that a
Prejudice towards Atheism is not Impartiality.
I am, Sir, Your most humble Servant,
Philonous.
Splendide mendax.
Hor.
think
think
Contents
|
Thursday, November 29, 1711 |
Addison |
Populares
Vincentum strepitus
Hor.

There is nothing which lies more within the Province of a Spectator than
publick Shows and Diversions; and as among these there are none which
can pretend to vie with those elegant Entertainments that are exhibited
in our Theatres, I think it particularly incumbent on me to take Notice
of every thing that is remarkable in such numerous and refined
Assemblies.
It is observed, that of late Years there has been a certain Person in
the upper Gallery of the Playhouse, who when he is pleased with any
Thing that is acted upon the Stage, expresses his Approbation by a loud
Knock upon the Benches or the Wainscot, which may be heard over the
whole Theatre. This Person is commonly known by the Name of the
Trunk-maker in the upper Gallery
. Whether it be, that the Blow he
gives on these Occasions resembles that which is often heard in the
Shops of such Artizans, or that he was supposed to have been a real
Trunk-maker, who after the finishing of his Day's Work used to unbend
his Mind at these publick Diversions with his Hammer in his Hand, I
cannot certainly tell. There are some, I know, who have been foolish
enough to imagine it is a Spirit which haunts the upper Gallery, and
from Time to Time makes those strange Noises; and the rather, because he
is observed to be louder than ordinary every Time the Ghost of
Hamlet
appears. Others have reported, that it is a dumb Man, who has chosen
this Way of uttering himself when he is transported with any Thing he
sees or hears. Others will have it to be the Playhouse Thunderer, that
exerts himself after this Manner in the upper Gallery, when he has
nothing to do upon the Roof.
But having made it my Business to get the best Information I could in a
Matter of this Moment, I find that the Trunk-maker, as he is commonly
called, is a large black Man, whom no body knows. He generally leans
forward on a huge Oaken Plant with great Attention to every thing that
passes upon the Stage. He is never seen to smile; but upon hearing any
thing that pleases him, he takes up his Staff with both Hands, and lays
it upon the next Piece of Timber that stands in his Way with exceeding
Vehemence: After which, he composes himself in his former Posture, till
such Time as something new sets him again at Work.
It has been observed, his Blow is so well timed, that the most judicious
Critick could never except against it. As soon as any shining Thought is
expressed in the Poet, or any uncommon Grace appears in the Actor, he
smites the Bench or Wainscot. If the Audience does not concur with him,
he smites a second Time, and if the Audience is not yet awaked, looks
round him with great Wrath, and repeats the Blow a third Time, which
never fails to produce the Clap. He sometimes lets the Audience begin
the Clap of themselves, and at the Conclusion of their Applause ratifies
it with a single Thwack.
He is of so great Use to the Play-house, that it is said a former
Director of it, upon his not being able to pay his Attendance by reason
of Sickness, kept one in Pay to officiate for him till such time as he
recovered; but the Person so employed, tho' he laid about him with
incredible Violence, did it in such wrong Places, that the Audience soon
found out that it was not their old Friend the Trunk-maker.
It has been remarked, that he has not yet exerted himself with Vigour
this Season. He sometimes plies at the Opera; and upon
Nicolini's
first Appearance, was said to have demolished three Benches in the Fury
of his Applause.
has broken half a dozen Oaken Plants upon
Dogget
and seldom goes away from a Tragedy of
Shakespear
, without leaving
the Wainscot extremely shattered.
The Players do not only connive at his obstreperous Approbation, but
very cheerfully repair at their own Cost whatever Damages he makes. They
had once a Thought of erecting a kind of Wooden Anvil for his Use that
should be made of a very sounding Plank, in order to render his Stroaks
more deep and mellow; but as this might not have been distinguished from
the Musick of a Kettle-Drum, the Project was laid aside.
In the
while, I cannot but take notice of the great Use it is to an
Audience, that a Person should thus preside over their Heads like the
Director of a Consort, in order to awaken their Attention, and beat time
to their Applauses; or, to raise my Simile, I have sometimes fancied the
Trunk-maker in the upper Gallery to be like
Virgils
Ruler of the
Wind, seated upon the Top of a Mountain, who, when he struck his Sceptre
upon the Side of it, roused an Hurricane, and set the whole Cavern in an
Uproar
.
It is certain, the Trunk-maker has saved many a good Play, and brought
many a graceful Actor into Reputation, who would not otherwise have been
taken notice of. It is very visible, as the Audience is not a little
abashed, if they find themselves betrayed into a Clap, when their Friend
in the upper Gallery does not come into it; so the Actors do not value
themselves upon the Clap, but regard it as a meer
Brutum fulmen
, or
empty Noise, when it has not the Sound of the Oaken Plant in it. I know
it has been given out by those who are Enemies to the Trunk-maker, that
he has sometimes been bribed to be in the Interest of a bad Poet, or a
vicious Player; but this is a Surmise which has no Foundation: his
Stroaks are always just, and his Admonitions seasonable; he does not
deal about his Blows at Random, but always hits the right Nail upon the
.
The
inexpressible Force wherewith he lays them on,
sufficiently shows the Evidence and Strength of his Conviction. His Zeal
for a good Author is indeed outrageous, and breaks down every Fence and
Partition, every Board and Plank, that stands within the Expression of
his Applause.
As I do not care for terminating my Thoughts in barren Speculations, or
in Reports of pure Matter of Fact, without drawing something from them
for the Advantage of my Countrymen, I shall take the Liberty to make an
humble Proposal, that whenever the Trunk-maker shall depart this Life,
or whenever he shall have lost the Spring of his Arm by Sickness, old
Age, Infirmity, or the like, some able-bodied Critick should be advanced
to this Post, and have a competent Salary settled on him for Life, to be
furnished with Bamboos for Operas, Crabtree-Cudgels for Comedies, and
Oaken Plants for Tragedy, at the publick Expence. And to the End that
this Place should be always disposed of according to Merit, I would have
none preferred to it, who has not given convincing Proofs both of a
sound Judgment and a strong Arm, and who could not, upon Occasion,
either knock down an Ox, or write a Comment upon
Horace's
Art of
Poetry. In short, I would have him a due Composition of
Hercules
and
Apollo
, and so rightly qualified for this important Office, that the
Trunk-maker may not be missed by our Posterity.
C.
Thomas Doggett, an excellent comic actor, who was for many
years joint-manager with Wilkes and Cibber, died in 1721, and bequeathed
the Coat and Badge that are rowed for by Thames Watermen every first of
August, from London Bridge to Chelsea.
Æneid
I. 85.
That.
Contents
|
Friday, November 30, 1711 |
Steele |
—Dare Jura maritis.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'You have not spoken in so direct a manner upon the Subject of
Marriage as that important Case deserves. It
would not be improper to
observe upon the Peculiarity in the Youth of
Great Britain, of
railing and laughing at that Institution; and when they fall into it,
from a profligate Habit of Mind, being insensible of the
Satisfaction1 in that Way of Life, and treating their Wives with the most
barbarous Disrespect.
'Particular Circumstances and Cast of Temper, must teach a Man the
Probability of mighty Uneasinesses in that State, (for unquestionably
some there are whose very Dispositions are strangely averse to
conjugal Friendship;) but no one, I believe, is by his own natural
Complexion prompted to teaze and torment another for no Reason but
being nearly allied to him: And can there be any thing more base, or
serve to sink a Man so much below his own distinguishing
Characteristick, (I mean Reason) than returning Evil for Good in so
open a Manner, as that of treating an helpless Creature with
Unkindness, who has had so good an Opinion of him as to believe what
he said relating to one of the greatest Concerns of Life, by
delivering her Happiness in this World to his Care and Protection?
Must not that Man be abandoned even to all manner of Humanity, who can
deceive a Woman with Appearances of Affection and Kindness, for no
other End but to torment her with more Ease and Authority? Is any
Thing more unlike a Gentleman, than when his Honour is engaged for the
performing his Promises, because nothing but that can oblige him to
it, to become afterwards false to his Word, and be alone the Occasion
of Misery to one whose Happiness he but lately pretended was dearer to
him than his own? Ought such a one to be trusted in his common
Affairs? or treated but as one whose Honesty consisted only in his
Incapacity of being otherwise?
'There is one Cause of this Usage no less absurd than common, which
takes place among the more unthinking Men: and that is the Desire to
appear to their Friends free and at Liberty,
and without those
Trammels they have so much ridiculed.
To avoid2 this they fly
into the other Extream, and grow Tyrants that they may seem Masters.
Because an uncontroulable Command of their own Actions is a certain
Sign of entire Dominion, they won't so much as recede from the
Government even in one Muscle, of their Faces. A kind Look they
believe would be fawning, and a civil Answer yielding the Superiority.
To this must we attribute an Austerity they betray in every Action:
What but this can put a Man out of Humour in his Wife's Company, tho'
he is so distinguishingly pleasant every where else? The Bitterness of
his Replies, and the Severity of his Frowns to the tenderest of Wives,
clearly demonstrate, that an ill-grounded Fear of being thought too
submissive, is at the Bottom of this, as I am willing to call it,
affected Moroseness; but if it be such only, put on to convince his
Acquaintance of his entire Dominion, let him take Care of the
Consequence, which will be certain, and worse than the present Evil;
his seeming Indifference will by Degrees grow into real Contempt, and
if it doth not wholly alienate the Affections of his Wife for ever
from him, make both him and her more miserable than if it really did
so.
However inconsistent it may appear, to be thought a well-bred Person
has no small Share in this clownish Behaviour: A Discourse therefore
relating to good Breeding towards a loving and a tender Wife, would be
of great Use to this Sort of Gentlemen. Could you but once convince
them, that to be civil at least is not beneath the Character of a
Gentleman, nor even tender Affection towards one who would make it
reciprocal, betrays any Softness or Effeminacy that the most masculine
Disposition need be ashamed of; could you satisfy them of the
Generosity of voluntary Civility, and the Greatness of Soul that is
conspicuous in Benevolence without immediate Obligations; could you
recommend to People's Practice the Saying of the Gentleman quoted in
one of your Speculations,
That he thought it incumbent upon him to
make the Inclinations of a Woman of Merit go along with her Duty:
Could you, I say, perswade these Men of the Beauty and Reasonableness
of this Sort of Behaviour, I have so much Charity for some of them at
least, to believe you would convince them of a Thing they are only
ashamed to allow: Besides, you would recommend that State in its
truest, and consequently its most agreeable Colours; and the Gentlemen
who have for any Time been such professed Enemies to it, when Occasion
should serve, would return you their Thanks for assisting their
Interest in prevailing over their Prejudices. Marriage in general
would by this Means be a more easy and comfortable Condition; the
Husband would be no where so well satisfied as in his own Parlour, nor
the Wife so pleasant as in the Company of her Husband: A Desire of
being agreeable in the Lover would be increased in the Husband, and
the Mistress be more amiable by becoming the Wife. Besides all which,
I am apt to believe we should find the Race of Men grow wiser as their
Progenitors grew kinder, and the Affection of the Parents would be
conspicuous in the Wisdom of their Children; in short, Men would in
general be much better humoured than they are, did not they so
frequently exercise the worst Turns of their Temper where they ought
to exert the best.
MR.
Spectator,
I
am a Woman who left the Admiration of this whole Town, to throw
myself (
for3 Love of Wealth) into the Arms of a Fool. When I
married him, I could have had any one of several Men of Sense who
languished for me; but my Case is just. I believed my superior
Understanding would form him into a tractable Creature. But, alas, my
Spouse has Cunning and Suspicion, the inseparable Companions of little
Minds; and every Attempt I make to divert, by putting on an agreeable
Air, a sudden Chearfulness, or kind Behaviour, he looks upon as the
first Act towards an Insurrection against his undeserved Dominion over
me. Let every one who is still to chuse, and hopes to govern a Fool,
remember
Tristissa.
St. Martins, November 25.
Mr.
Spectator,
This is to complain of an evil Practice which I think very well
deserves a Redress, though you have not as yet taken any Notice of it:
If you mention it in your Paper, it may perhaps have a very good
Effect. What I mean is the Disturbance some People give to others at
Church, by their Repetition of the Prayers after the Minister, and
that not only in the Prayers, but also the Absolution and the
Commandments fare no better, winch are in a particular Manner the
Priest's Office: This I have known done in so audible a manner, that
sometimes their Voices have been as loud as his. As little as you
would think it, this is frequently done by People seemingly devout.
This irreligious Inadvertency is a Thing extremely offensive: But I do
not recommend it as a Thing I give you Liberty to ridicule, but hope
it may be amended by the bare Mention.
Sir, Your very humble Servant,
T. S.
T.
Satisfactions
For this Reason should they appear the least like what
they were so much used to laugh at, they would become the Jest of
themselves, and the Object of that Raillery they formerly bestowed on
others. To avoid &c.
by
, and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 1, 1711 |
Addison |
Visu carentem magna pars veri latet.
Senec. in
Œdip.

It is very reasonable to believe, that Part of the Pleasure which happy
Minds shall enjoy in a future State, will arise from an enlarged
Contemplation of the Divine Wisdom in the Government of the World, and a
Discovery of the secret and amazing Steps of Providence, from the
Beginning to the End of Time. Nothing seems to be an Entertainment more
adapted to the Nature of Man, if we consider that Curiosity is one of
the strongest and most lasting Appetites implanted in us, and that
Admiration is one of our most pleasing Passions; and what a perpetual
Succession of Enjoyments will be afforded to both these, in a Scene so
large and various as shall then be laid open to our View in the Society
of superior Spirits, who perhaps will join with us in so delightful a
Prospect!
It is not impossible, on the contrary, that Part of the Punishment of
such as are excluded from Bliss, may consist not only in their being
denied this Privilege, but in having their Appetites at the same time
vastly encreased, without any Satisfaction afforded to them. In these,
the vain Pursuit of Knowledge shall, perhaps, add to their Infelicity,
and bewilder them into Labyrinths of Error, Darkness, Distraction and
Uncertainty of every thing but their own evil State.
Milton
has thus
represented the fallen Angels reasoning together in a kind of Respite
from their Torments, and creating to themselves a new Disquiet amidst
their very Amusements; he could not properly have described the Sports
of condemned Spirits, without that Cast of Horror and Melancholy he has
so judiciously mingled with them.
Others apart sate on a Hill retired,
In Thoughts more elevate, and reason'd high
Of Providence, Foreknowledge, Will, and Fate,
First Fate, Freewill, Foreknowledge absolute,
And found no End in wandring Mazes lost.1
In our present Condition, which is a middle State, our Minds are, as it
were, chequered with Truth and Falshood; and as our Faculties are
narrow, and our Views imperfect, it is impossible but our Curiosity must
meet with many Repulses. The Business of Mankind in this Life being
rather to act than to know, their Portion of Knowledge is dealt to them
accordingly.
From hence it is, that the Reason of the Inquisitive has so long been
exercised with Difficulties, in accounting for the promiscuous
Distribution of Good and Evil to the Virtuous and the Wicked in this
World.
hence come all those pathetical Complaints of so many
tragical Events, which happen to the Wise and the Good; and of such
surprising Prosperity, which is often the Lot
` of the Guilty and the
Foolish; that Reason is sometimes puzzled, and at a loss what to
pronounce upon so mysterious a Dispensation.
Plato
expresses his Abhorrence of some Fables of the Poets, which seem
to reflect on the Gods as the Authors of Injustice; and lays it down as
a Principle, That whatever is permitted to befal a just Man, whether
Poverty, Sickness, or any of those Things which seem to be Evils, shall
either in Life or Death conduce to his Good. My Reader will observe how
agreeable this Maxim is to what we find delivered by a greater
Authority.
Seneca
written a Discourse purposely on this
Subject
, in which he takes Pains, after the Doctrine of the
Stoicks
, to shew that Adversity is not in itself an Evil; and mentions
a noble Saying of
Demetrius
, That
nothing would be more unhappy than
a Man who had never known Affliction
. He compares Prosperity to the
Indulgence of a fond Mother to a Child, which often proves his Ruin; but
the Affection of the Divine Being to that of a wise Father who would
have his Sons exercised with Labour, Disappointment, and Pain, that they
may gather Strength, and improve their Fortitude. On this Occasion the
Philosopher rises into the celebrated Sentiment, That there is not on
Earth a Spectator more worthy the Regard of a Creator intent on his
Works than a brave Man superior to his Sufferings; to which he adds,
That it must be a Pleasure to
Jupiter
himself to look down from
Heaven, and see
Cato
amidst the Ruins of his Country preserving his
Integrity.
This Thought will appear yet more reasonable, if we consider human Life
as a State of Probation, and Adversity as the Post of Honour in it,
assigned often to the best and most select Spirits.
But what I would chiefly insist on here, is, that we are not at present
in a proper Situation to judge of the Counsels by which Providence acts,
since but little arrives at our Knowledge, and even that little we
discern imperfectly; or according to the elegant Figure in Holy Writ,
We see but in part, and as in a Glass darkly .
It is to be considered, that Providence
in its Œconomy regards the whole System of Time and
Things together,
so that
we cannot discover the beautiful Connection
between Incidents which lie widely separated in Time, and by losing so
many Links of the Chain, our Reasonings become broken and imperfect.
Thus those Parts in the moral World which have not an absolute, may yet
have a relative Beauty, in respect of some other Parts concealed from
us, but open to his Eye before whom
Past, Present
, and
To come
, are
set together in one Point of View: and those Events, the Permission of
which seems now to accuse his Goodness, may in the Consummation of
Things both magnify his Goodness, and exalt his Wisdom. And this is
enough to check our Presumption, since it is in vain to apply our
Measures of Regularity to Matters of which we know neither the
Antecedents nor the Consequents, the Beginning nor the End.
I
relieve my Reader from this abstracted Thought, by relating here
a
Jewish
Tradition concerning
Moses
which seems to be a kind of
Parable, illustrating what I have last mentioned. That great Prophet, it
is said, was called up by a Voice from Heaven to the top of a Mountain;
where, in a Conference with the Supreme Being, he was permitted to
propose to him some Questions concerning his Administration of the
Universe.
the midst of this Divine
Colloquy
he was commanded to
look down on the Plain below. At the Foot of the Mountain there issued
out a clear Spring of Water, at which a Soldier alighted from his Horse
to drink. He was no sooner gone than a little Boy came to the same
Place, and finding a Purse of Gold which the Soldier had dropped, took
it up and went away with it. Immediately after this came an infirm old
Man, weary with Age and Travelling, and having quenched his Thirst, sat
down to rest himself by the Side of the Spring. The Soldier missing his
Purse returns to search for it, and demands it of the old Man, who
affirms he had not seen it, and appeals to Heaven in witness of his
Innocence.
Soldier not believing his Protestations, kills him.
Moses
fell on his Face with Horror and Amazement, when the Divine
Voice thus prevented his Expostulation: 'Be not surprised,
Moses
, nor
ask why the Judge of the whole Earth has suffer'd this Thing to come to
pass: The Child is the Occasion that the Blood of the old Man is spilt;
but know, that the old Man whom thou saw'st, was the Murderer of that
Child's Father
.
Paradise Lost
, B. II. v. 557-561.
In Saturday's Spectator,
for
'reward'
read
'lot.'
Erratum in No.
.
De Constantia Sapientis
.
Since Providence, therefore
, and in 1st rep.
Henry More's
Divine Dialogues
.
Conference
No letter appended to original issue or reissue. Printed in
Addison's
Works
, 1720. The paper has been claimed for John Hughes in the
Preface to his
Poems
(1735).
Contents
|
Monday, December 3, 1711 |
Steele |
Nequicquam populo bibulas donaveris Aures;
Respue quod non es
Persius,
Sat. 4.

Among all the Diseases of the Mind, there is not one more epidemical or
more pernicious than the Love of Flattery. For as where the Juices of
the Body are prepared to receive a malignant Influence, there the
Disease rages with most Violence; so in this Distemper of the Mind,
where there is ever a Propensity and Inclination to suck in the Poison,
it cannot be but that the whole Order of reasonable Action must be
overturn'd, for, like Musick, it
So softens and disarms the Mind,
That not one Arrow can Resistance find.
First we flatter ourselves, and then the Flattery of others is sure of
Success. It awakens our Self-Love within, a Party which is ever ready to
revolt from our better Judgment, and join the Enemy without. Hence it
is, that the Profusion of Favours we so often see poured upon the
Parasite, are represented to us, by our Self-Love, as Justice done to
Man, who so agreeably reconciles us to our selves. When we are overcome
by such soft Insinuations and ensnaring Compliances, we gladly
recompense the Artifices that are made use of to blind our Reason, and
which triumph over the Weaknesses of our Temper and Inclinations.
But were every Man perswaded from how mean and low a Principle this
Passion is derived, there can be no doubt but the Person who should
attempt to gratify it, would then be as contemptible as he is now
successful. 'Tis the Desire of some Quality we are not possessed of, or
Inclination to be something we are not, which are the Causes of our
giving ourselves up to that Man, who bestows upon us the Characters and
Qualities of others; which perhaps suit us as ill and were as little
design'd for our wearing, as their Cloaths. Instead of going out of our
own complectional Nature into that of others, 'twere a better and more
laudable Industry to improve our own, and instead of a miserable Copy
become a good Original; for there is no Temper, no Disposition so rude
and untractable, but may in its own peculiar Cast and Turn be brought to
some agreeable Use in Conversation, or in the Affairs of Life.
Person
of a rougher Deportment, and less tied up to the usual Ceremonies of
Behaviour, will, like
Manly
in the Play
, please by the Grace which
Nature gives to every Action wherein she is complied with; the Brisk and
Lively will not want their Admirers, and even a more reserved and
melancholy Temper may at some times be agreeable.
When there is not Vanity enough awake in a Man to undo him, the
Flatterer stirs up that dormant Weakness, and inspires him with Merit
enough to be a Coxcomb. But if Flattery be the most sordid Act that can
be complied with, the Art of Praising justly is as commendable: For 'tis
laudable to praise well; as Poets at one and the same time give
Immortality, and receive it themselves for a Reward: Both are pleased,
the one whilst he receives the Recompence of Merit, the other whilst he
shews he knows now to discern it; but above all, that Man is happy in
this Art, who, like a skilful Painter, retains the Features and
Complection, but still softens the Picture into the most agreeable
Likeness.
There can hardly, I believe, be imagin'd a more desirable Pleasure, than
that of Praise unmix'd with any Possibility of Flattery. Such was that
which
Germanicus
enjoyed, when, the Night before a Battle, desirous of
some sincere Mark of the Esteem of his Legions for him, he is described
by
Tacitus
listening in a Disguise to the Discourse of a Soldier, and
wrapt up in the Fruition of his Glory, whilst with an undesigned
Sincerity they praised his noble and majestick Mien, his Affability, his
Valour, Conduct, and Success in War. How must a Man have his Heart
full-blown with Joy in such an Article of Glory as this? What a Spur and
Encouragement still to proceed in those Steps which had already brought
him to so pure a Taste of the greatest of mortal Enjoyments?
It sometimes happens, that even Enemies and envious Persons bestow the
sincerest Marks of Esteem when they least design it. Such afford a
greater Pleasure, as extorted by Merit, and freed from all Suspicion of
Favour or Flattery. Thus it is with
Malvolio
; he has Wit, Learning,
and Discernment, but temper'd with an Allay of Envy, Self-Love and
Detraction:
Malvolio
turns pale at the Mirth and good Humour of the
Company, if it center not in his Person; he grows jealous and displeased
when he ceases to be the only Person admired, and looks upon the
Commendations paid to another as a Detraction from his Merit, and an
Attempt to lessen the Superiority he affects; but by this very Method,
he bestows such Praise as can never be suspected of Flattery. His
Uneasiness and Distastes are so many sure and certain Signs of another's
Title to that Glory he desires, and has the Mortification to find
himself not possessed of.
A
Name is fitly compared to a precious Ointment
, and when we are
praised with Skill and Decency, 'tis indeed the most agreeable Perfume,
but if too strongly admitted into a Brain of a less vigorous and happy
Texture, 'twill, like too strong an Odour, overcome the Senses, and
prove pernicious to those Nerves 'twas intended to refresh. A generous
Mind is of all others the most sensible of Praise and Dispraise; and a
noble Spirit is as much invigorated with its due Proportion of Honour
and Applause, as 'tis depressed by Neglect and Contempt: But 'tis only
Persons far above the common Level who are thus affected with either of
these Extreams; as in a Thermometer, 'tis only the purest and most
sublimated Spirit that is either contracted or dilated by the Benignity
or Inclemency of the Season.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The Translations which you have lately given us from the
Greek, in
some of your last Papers, have been the Occasion of my looking into
some of those Authors; among whom I chanced on a Collection of Letters
which pass under the Name of
Aristænetus. Of all the Remains of
Antiquity, I believe there can be Nothing produc'd of an Air so
gallant and polite; each Letter contains a little Novel or Adventure,
which is told with all the Beauties of Language and heightened with a
Luxuriance of Wit.
There are several of them translated
3, but with
such wide Deviations from the Original, and in a Style so far
differing from the Authors, that the Translator seems rather to have
taken Hints for the expressing his own Sense and Thoughts, than to
have endeavoured to render those of
Aristænetus. In the following
Translation, I have kept as near the Meaning of the
Greek as I
could, and have only added a few Words to make the Sentences in
English fit together a little better than they would otherwise have
done. The Story seems to be taken from that of
Pygmalion and the
Statue in
Ovid: Some of the Thoughts are of the same Turn, and the
whole is written in a kind of Poetical Prose.
Philopinax to Chromation.
"Never was Man more overcome with so fantastical a Passion as mine.
I have painted a beautiful Woman, and am despairing, dying for the
Picture. My own Skill has undone me; 'tis not the Dart of Venus,
but my own Pencil has thus wounded me. Ah me! with what Anxiety am I
necessitated to adore my own Idol? How miserable am I, whilst every
one must as much pity the Painter as he praises the Picture, and own
my Torment more than equal to my Art. But why do I thus complain?
Have there not been more unhappy and unnatural Passions than mine?
Yes, I have seen the Representations of Phædra, Narcissus, and
Pasiphæ. Phædra was unhappy in her Love; that of Pasiphæ was
monstrous; and whilst the other caught at his beloved Likeness, he
destroyed the watery Image, which ever eluded his Embraces. The
Fountain represented Narcissus to himself, and the Picture both
that and him, thirsting after his adored Image. But I am yet less
unhappy, I enjoy her Presence continually, and if I touch her, I
destroy not the beauteous Form, but she looks pleased, and a sweet
Smile sits in the charming Space which divides her Lips. One would
swear that Voice and Speech were issuing out, and that one's Ears
felt the melodious Sound. How often have I, deceived by a Lover's
Credulity, hearkned if she had not something to whisper me? and when
frustrated of my Hopes, how often have I taken my Revenge in Kisses
from her Cheeks and Eyes, and softly wooed her to my Embrace, whilst
she (as to me it seem'd) only withheld her Tongue the more to
inflame me. But, Madman that I am, shall I be thus taken with the
Representation only of a beauteous Face, and flowing Hair, and thus
waste myself and melt to Tears for a Shadow? Ah, sure 'tis something
more, 'tis a Reality! for see her Beauties shine out with new
Lustre, and she seems to upbraid me with such unkind Reproaches. Oh
may I have a living Mistress of this Form, that when I shall compare
the Work of Nature with that of Art, I may be still at a loss which
to choose, and be long perplex'd with the pleasing Uncertainty.
T.
Wycherley's
Plain Dealer
.
Eccles
, vii. I.
In a volume of translated
Letters on Wit, Politicks, and
Morality,
edited by Abel Boyer, in 1701. The letters ascribed to
Aristænetus of Nicer in Bithynis, who died A.D. 358, but which were
written after the fifth century, were afterwards translated as
Letters
of Love and Gallantry, written in Greek by Aristænetus.
This volume,
12mo (1715), was dedicated to Eustace Budgell, who is named in the
Preface as the author of the
Spectator
papers signed X.
Contents
|
Tuesday, December 4, 1711 |
Addison |
Bella, horrida bella!
Virg.

I have sometimes amused myself with considering the several Methods of
managing a Debate which have obtained m the World.
The first Races of Mankind used to dispute, as our ordinary People do
now-a-days, in a kind of wild Logick, uncultivated by Rules of Art.
Socrates
introduced a catechetical Method of Arguing. He would ask his
Adversary Question upon Question, till he had convinced him out of his
own Mouth that his Opinions were wrong. This Way of Debating drives an
Enemy up into a Corner, seizes all the Passes through which he can make
an Escape, and forces him to surrender at Discretion.
Aristotle
changed this Method of Attack, and invented a great Variety
of little Weapons, call'd Syllogisms. As in the
Socratick
Way of
Dispute you agree to every thing which your Opponent advances, in the
Aristotelick
you are still denying and contradicting some Part or
other of what he says.
Socrates
conquers you by Stratagem,
Aristotle
by Force: The one takes the Town by Sap, the other Sword in Hand.
The Universities of
Europe
, for many Years, carried on their Debates
by Syllogism, insomuch that we see the Knowledge of several Centuries
laid out into Objections and Answers, and all the good Sense of the Age
cut and minced into almost an Infinitude of Distinctions.
When our Universities found that there was no End of Wrangling this Way,
they invented a kind of Argument, which is not reducible to any Mood or
Figure in
Aristotle
. It was called the
Argumentum Basilinum
(others
write it
Bacilinum
or
Baculinum
) which is pretty well express'd in
our
English
Word
Club-Law
. When they were not able to confute their
Antagonist, they knock'd him down. It was their Method in these
polemical Debates, first to discharge their Syllogisms, and afterwards
to betake themselves to their Clubs, till such Time as they had one Way
or other confounded their Gainsayers.
is in
Oxford
a narrow
Defile
, (to make use of a military Term) where the Partizans used
to encounter, for which Reason it still retains the Name of
Logic-Lane
. I
heard an old Gentleman, a Physician, make his
Boasts, that when he was a young Fellow he marched several Times at the
Head of a Troop of
Scotists,
and cudgel'd a Body of
Smiglesians
half the length of
High-street
, 'till they had dispersed
themselves for Shelter into their respective Garrisons.
Humour, I find, went very far in
Erasmus's
Time. For that Author
tells us
, That upon the Revival of
Greek
Letters, most of the
Universities in
Europe
were divided into
Greeks
and
Trojans
. The
latter were those who bore a mortal Enmity to the Language of the
Grecians
, insomuch that if they met with any who understood it, they
did not fail to treat him as a Foe.
Erasmus
himself had, it seems, the
Misfortune to fall into the Hands of a Party of
Trojans
, who laid him
on with so many Blows and Buffets that he never forgot their Hostilities
to his dying Day.
There is a way of managing an Argument not much unlike the former, which
is made use of by States and Communities, when they draw up a hundred
thousand Disputants on each Side, and convince one another by Dint of
Sword.
certain Grand Monarch
was so sensible of his Strength in
this way of Reasoning, that he writ upon his Great Guns—
Ratio ultima
Regum, The Logick of Kings
; but, God be thanked, he is now pretty well
baffled at his own Weapons. When
was to do with a Philosopher of
this kind, one should remember the old Gentleman's Saying, who had been
engaged in an Argument with one of the
Roman
Emperors
. Upon his
Friend's telling him, That he wonder'd he would give up the Question,
when he had visibly the Better of the Dispute;
I am never asham'd
,
says he,
to be confuted by one who is Master of fifty Legions
.
I
but just mention another kind of Reasoning, which may be called
arguing by Poll; and another which is of equal Force, in which Wagers
are made use of as Arguments, according to the celebrated Line in
Hudibras
.
But the most notable way of managing a Controversy, is that which we may
call
Arguing by Torture
.
is a Method of Reasoning which has been
made use of with the poor Refugees, and which was so fashionable in our
Country during the Reign of Queen
Mary
, that in a Passage of an Author
quoted by Monsieur
Bayle
it is said the Price of Wood was raised
in
England
, by reason of the Executions that were made in
Smithfield
.
Disputants convince their Adversaries with a
Sorites
, commonly called a Pile of Faggots. The Rack is also a
kind of Syllogism which has been used with good Effect, and has made
Multitudes of Converts. Men were formerly disputed out of their Doubts,
reconciled to Truth by Force of Reason, and won over to Opinions by the
Candour, Sense and Ingenuity of those who had the Right on their Side;
but this Method of Conviction operated too slowly. Pain was found to be
much more enlightning than Reason. Every Scruple was looked upon as
Obstinacy, and not to be removed but by several Engines invented for
that Purpose. In a Word, the Application of Whips, Racks, Gibbets,
Gallies, Dungeons, Fire and Faggot, in a Dispute, may be look'd upon as
Popish Refinements upon the old Heathen Logick.
There is another way of Reasoning which seldom fails, tho' it be of a
quite different Nature to that I have last mentioned. I mean, convincing
a Man by ready Money, or as it is ordinarily called, bribing a Man to an
Opinion. This Method has often proved successful, when all the others
have been made use of to no purpose. A Man who is furnished with
Arguments from the Mint, will convince his Antagonist much sooner than
one who draws them from Reason and Philosophy. Gold is a wonderful
Clearer of the Understanding; it dissipates every Doubt and Scruple in
an Instant; accommodates itself to the meanest Capacities; silences the
Loud and Clamorous, and brings over the most Obstinate and Inflexible.
Philip of Macedon
was a Man of most invincible Reason this Way. He
refuted by it all the Wisdom of
Athens
, confounded their Statesmen,
struck their Orators dumb, and at length argued them out of all their
Liberties.
Having here touched upon the several Methods of Disputing, as they have
prevailed in different Ages of the World, I shall very suddenly give my
Reader an Account of the whole Art of Cavilling; which shall be a full
and satisfactory Answer to all such Papers and Pamphlets as have yet
appeared against the
Spectator
.
C.
Defile
The followers of the famous scholastic philosopher, Duns
Scotus (who taught at Oxford and died in 1308), were Realists, and the
Scotists were as Realists opposed to the Nominalists, who, as followers
of Thomas Aquinas, were called Thomists. Abuse, in later time, of the
followers of Duns gave its present sense to the word Dunce.
The followers of Martin Simglecius a Polish Jesuit, who
taught Philosophy for four years and Theology for ten years at Vilna, in
Lithuania, and died at Kalisch in 1618. Besides theological works he
published a book of Disputations upon Logic.
Erasm.
Epist
.
Louis XIV.
Adrian, cited in Bacon's
Apophthegms
.
Hudibras, Pt. II. c. i, v. 297. See [Volume 1 links:
to
. ]
And. Ammonius in Bayle's
Life
of him, but the saying was of
the reign of Henry VIII.
A Sorites, in Logic,—from
a heap—is a
pile of syllogisms so compacted that the conclusion of one serves as a
premiss to the next.
Contents
|
Wednesday, December 5, 1711 |
Steele |
—Aliter not fit, Avite, liber.
Mart.

Mr.
Spectator,
I am of one of the most genteel Trades in the City, and understand
thus much of liberal Education, as to have an ardent Ambition of being
useful to Mankind, and to think That the chief End of Being as to this
Life. I had these good Impressions given me from the handsome
Behaviour of a learned, generous, and wealthy Man towards me when I
first began the World. Some Dissatisfaction between me and my Parents
made me enter into it with less Relish of Business than I ought; and
to turn off this Uneasiness I gave my self to criminal Pleasures, some
Excesses, and a general loose Conduct. I know not what the excellent
Man above-mentioned saw in me, but he descended from the Superiority
of his Wisdom and Merit, to throw himself frequently into my Company.
This made me soon hope that I had something in me worth cultivating,
and his Conversation made me sensible of Satisfactions in a regular
Way, which I had never before imagined. When he was grown familiar
with me, he opened himself like a good Angel, and told me, he had long
laboured to ripen me into a Preparation to receive his Friendship and
Advice, both which I should daily command, and the Use of any Part of
his Fortune, to apply the Measures he should propose to me, for the
Improvement of my own. I assure you, I cannot recollect the Goodness
and Confusion of the good Man when he spoke to this Purpose to me,
without melting into Tears; but in a word, Sir, I must hasten to tell
you, that my Heart burns with Gratitude towards him, and he is so
happy a Man, that it can never be in my Power to return him his
Favours in Kind, but I am sure I have made him the most agreeable
Satisfaction I could possibly,
in being ready to serve others to my
utmost Ability, as far as is consistent with the Prudence he
prescribes to me. Dear Mr.
Spectator, I do not owe to him only the
good Will and Esteem of my own Relations, (who are People of
Distinction) the present Ease and Plenty of my Circumstances, but also
the Government of my Passions, and Regulation of my Desires. I doubt
not, Sir, but in your Imagination such Virtues as these of my worthy
Friend, bear as great a Figure as Actions which are more glittering in
the common Estimation. What I would ask of you, is to give us a whole
Spectator upon Heroick Virtue in common Life, which may incite Men
to the same generous Inclinations, as have by this admirable Person
been shewn to, and rais'd in,
Sir, Your most humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Country Gentleman, of a good plentiful Estate, and live as the
rest of my Neighbours with great Hospitality. I have been ever
reckoned among the Ladies the best Company in the World, and have
Access as a sort of Favourite. I never came in Publick but I saluted
them, tho' in great Assemblies, all round, where it was seen how
genteelly I avoided hampering my Spurs in their Petticoats, while I
moved amongst them; and on the other side how prettily they curtsied
and received me, standing in proper Rows, and advancing as fast as
they saw their Elders, or their Betters, dispatch'd by me. But so it
is, Mr.
Spectator, that all our good Breeding is of late lost by the
unhappy Arrival of a Courtier, or Town Gentleman, who came lately
among us: This Person where-ever he came into a Room made a profound
Bow, and fell back, then recovered with a soft Air, and made a Bow to
the next, and so to one or two more, and then took the Gross of the
Room, by passing by them in a continued Bow till he arrived at the
Person he thought proper particularly to entertain. This he did with
so good a Grace and Assurance, that it is taken for the present
Fashion; and there is no young Gentlewoman within several Miles of
this Place has been kissed ever since his first Appearance among us.
We Country Gentlemen cannot begin again and learn these fine and
reserved Airs; and our Conversation is at a Stand, till we have your
Judgment for or against Kissing, by way of Civility or Salutation;
which is impatiently expected by your Friends of both Sexes, but by
none so much as
Your humble Servant,
Rustick Sprightly.
December 3, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
I
was the other Night at
Philaster1, where I expected to hear your
famous Trunk-maker, but was happily disappointed of his Company, and
saw another Person who had the like Ambition to distinguish himself in
a noisy manner, partly by Vociferation or talking loud, and partly by
his bodily Agility. This was a very lusty Fellow, but withal a sort of
Beau, who getting into one of the Side-boxes on the Stage before the
Curtain drew, was disposed to shew the whole Audience his Activity by
leaping over the Spikes; he pass'd from thence to one of the entering
Doors, where he took Snuff with a tolerable good Grace, display'd his
fine Cloaths, made two or three feint Passes at the Curtain with his
Cane, then faced about and appear'd at t'other Door: Here he affected
to survey the whole House, bow'd and smil'd at random, and then shew'd
his Teeth, which were some of them indeed very white: After this he
retired behind the Curtain, and obliged us with several Views of his
Person from every Opening.
During the Time of Acting, he appear'd frequently in the Prince's
Apartment, made one at the Hunting-match, and was very forward in the
Rebellion. If
there were no Injunctions to the contrary, yet this
Practice must be confess'd to diminish the Pleasure of the Audience,
and for that Reason presumptuous and unwarrantable: But since her
Majesty's late Command has made it criminal
2, you have Authority to
take Notice of it.
Sir,
Your humble Servant,
Charles Easy.
T.
Beaumont and Fletcher's
Philaster
had been acted on the
preceding Friday, Nov. 30. The Hunt is in the Fourth Act, the Rebellion
in the Fifth.
At this time there had been added to the playbills the line
By her Majesty's Command no Person is to be admitted behind the
Scenes.
Contents
|
Thursday, December 6, 1711 |
Addison |
—Semperque relinqui
Sola sibi, semper longam incomitata videtur
Ire viam—
Virg.

Mr.
Spectator,
Though you have considered virtuous Love inmost of its Distresses, I
do not remember that you have given us any Dissertation upon the
Absence of Lovers, or laid down any Methods how they should support
themselves under those long Separations which they are sometimes
forced to undergo. I am at present in this unhappy Circumstance,
having parted with the best of Husbands, who is abroad in the Service
of his Country, and may not possibly return for some Years. His warm
and generous Affection while we were together, with the Tenderness
which he expressed to me at parting, make his Absence almost
insupportable. I think of him every Moment of the Day, and meet him
every Night in my Dreams. Every thing I see puts me in mind of him. I
apply myself with more than ordinary Diligence to the Care of his
Family and his Estate; but this, instead of relieving me, gives me but
so many Occasions of wishing for his Return. I frequent the Rooms
where I used to converse with him, and not meeting him there, sit down
in his Chair, and fall a weeping. I love to read the Books he
delighted in, and to converse with the Persons whom he esteemed. I
visit his Picture a hundred times a Day, and place myself over-against
it whole Hours together. I pass a great part of my Time in the Walks
where I used to lean upon his Arm, and recollect in my Mind the
Discourses which have there passed between us: I look over the several
Prospects and Points of View which we used to survey together, fix my
Eye upon the Objects which he has made me take notice of, and call to
mind a thousand [agreeable] Remarks which he has made on those
Occasions. I write to him by every Conveyance, and contrary to other
People, am always in good Humour when an East-Wind blows, because it
seldom fails of bringing me a Letter from him. Let me entreat you,
Sir, to give me your Advice upon this Occasion, and to let me know how
I may relieve my self in this my Widowhood.
I am, Sir, Your most humble Servant,
Asteria.
Absence is what the Poets call Death in Love, and has given Occasion to
abundance of beautiful Complaints in those Authors who have treated of
this Passion in Verse.
Ovid's
Epistles are full of
.
Otway's
Monimia
talks very tenderly upon this Subject
.
It was not kind
To leave me like a Turtle, here alone,
To droop and mourn the Absence of my Mate.
When thou art from me, every Place is desert:
And I, methinks, am savage and forlorn.
Thy Presence only 'tis can make me blest,
Heal my unquiet Mind, and tune my Soul.
The Consolations of Lovers on these Occasions are very extraordinary.
Besides those mentioned by
Asteria
, there are many other Motives of
Comfort, which are made use of by absent Lovers.
I remember in one of
Scudery's
Romances, a Couple of honourable Lovers
agreed at their parting to set aside one half Hour in the Day to think
of each other during a tedious Absence. The Romance tells us, that they
both of them punctually observed the Time thus agreed upon; and that
whatever Company or Business they were engaged in, they left it abruptly
as soon as the Clock warned them to retire. The Romance further adds,
That the Lovers expected the Return of this stated Hour with as much
Impatience, as if it had been a real Assignation, and enjoyed an
imaginary Happiness that was almost as pleasing to them as what they
would have found from a real Meeting. It was an inexpressible
Satisfaction to these divided Lovers, to be assured that each was at the
same time employ'd in the same kind of Contemplation, and making equal
Returns of Tenderness and Affection.
If I may be allowed to mention a more serious Expedient for the
alleviating of Absence, I shall take notice of one which I have known
two Persons practise, who joined Religion to that Elegance of Sentiments
with which the Passion of Love generally inspires its Votaries. This
was, at the Return of such an Hour, to offer up a certain Prayer for
each other, which they had agreed upon before their Parting. The
Husband, who is a Man that makes a Figure in the polite World, as well
as in his own Family, has often told me, that he could not have
supported an Absence of three Years without this Expedient.
Strada, in one of his Prolusions,
gives an Account of a
chimerical Correspondence between two Friends by the Help of a certain
Loadstone,
had such Virtue in it, that if it touched two several
Needles, when one of the Needles so touched
began
, to move, the
other, tho' at never so great a Distance, moved at the same Time, and in
the same Manner. He tells us, that the two Friends, being each of them
possessed of one of these Needles, made a kind of a Dial-plate,
inscribing it with the four and twenty Letters, in the same manner as
the Hours of the Day are marked upon the ordinary Dial-plate. They then
fixed one of the Needles on each of these Plates in such a manner, that
it could move round without Impediment, so as to touch any of the four
and twenty Letters. Upon their Separating from one another into distant
Countries, they agreed to withdraw themselves punctually into their
Closets at a certain Hour of the Day, and to converse with one another
by means of this their Invention. Accordingly when they were some
hundred Miles asunder, each of them shut himself up in his Closet at the
Time appointed, and immediately cast his Eye upon his Dial-plate. If he
had a mind to write any thing to his Friend, he directed his Needle to
every Letter that formed the Words which he had occasion for, making a
little Pause at the end of every Word or Sentence, to avoid Confusion.
The Friend, in the mean while, saw his own sympathetick Needle moving of
itself to every Letter which that of his Correspondent pointed at. By
this means they talked together across a whole Continent, and conveyed
their Thoughts to one another in an Instant over Cities or Mountains,
Seas or Desarts.
If Monsieur
Scudery
, or any other Writer of Romance, had introduced a
Necromancer, who is generally in the Train of a Knight-Errant, making a
Present to two Lovers of a Couple of those above-mentioned Needles, the
Reader would not have been a little pleased to have seen them
corresponding with one another when they were guarded by Spies and
Watches, or separated by Castles and Adventures.
In the mean while, if ever this Invention should be revived or put in
practice, I would propose, that upon the Lover's Dial-plate there should
be written not only the four and twenty Letters, but several entire
Words which have always a Place in passionate Epistles, as
Flames,
Darts, Die, Language, Absence, Cupid, Heart, Eyes, Hang, Drown
, and the
like. This would very much abridge the Lover's Pains in this way of
writing a Letter, as it would enable him to express the most useful and
significant Words with a single Touch of the Needle.
C.
Orphan
, Act II.
In one of Strada's Prolusions he
; Lib. II. Prol. 6.
begun
, and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Friday, December 7, 1711 |
Steele |
Creditur, ex medio quia res arcessit, habere
Sudoris minimum—
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
Your Speculations do not so generally prevail over Men's Manners as I
could wish.
A former Paper of yours
1 concerning the Misbehaviour of
People, who are necessarily in each other's Company in travelling,
ought to have been a lasting Admonition against Transgressions of that
Kind: But I had the Fate of your Quaker, in meeting with a rude Fellow
in a Stage-Coach, who entertained two or three Women of us (for there
was no Man besides himself) with Language as indecent as was ever
heard upon the Water. The impertinent Observations which the Coxcomb
made upon our Shame and Confusion were such, that it is an unspeakable
Grief to reflect upon them. As much as you have declaimed against
Duelling, I hope you will do us the Justice to declare, that if the
Brute has Courage enough to send to the Place where he saw us all
alight together to get rid of him, there is not one of us but has a
Lover who shall avenge the Insult. It would certainly be worth your
Consideration, to look into the frequent Misfortunes of this kind, to
which the Modest and Innocent are exposed, by the licentious Behaviour
of such as are as much Strangers to good Breeding as to Virtue.
Could
we avoid hearing what we do not approve, as easily as we can seeing
what is disagreeable, there were some Consolation; but since
in a Box
at a Play,2 in an Assembly of Ladies, or even in a Pew at Church,
it is in the Power of a gross Coxcomb to utter what a Woman cannot
avoid hearing, how miserable is her Condition who comes within the
Power of such Impertinents? And how necessary is it to repeat
Invectives against such a Behaviour? If the Licentious had not utterly
forgot what it is to be modest, they would know that offended Modesty
labours under one of the greatest Sufferings to which human Life can
be exposed. If one of these Brutes could reflect thus much, tho' they
want Shame, they would be moved, by their Pity, to abhor an impudent
Behaviour in the Presence of the Chaste and Innocent. If you will
oblige us with a
Spectator on this Subject, and procure it to be
pasted against every Stage-Coach in
Great-Britain, as the Law of the
Journey, you will highly oblige the whole Sex, for which you have
professed so great an Esteem; and in particular, the two Ladies my
late Fellow-Sufferers, and,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Rebecca Ridinghood.
Mr.
Spectator,
The Matter which I am now going to send you, is an unhappy Story in
low Life, and will recommend it self, so that you must excuse the
Manner of expressing it. A poor idle drunken Weaver in
Spittle-Fields has a faithful laborious Wife, who by her Frugality
and Industry had laid by her as much Money as purchased her a Ticket
in the present Lottery. She had hid this very privately in the Bottom
of a Trunk, and had given her Number to a Friend and Confident, who
had promised to keep the Secret, and bring her News of the Success.
The poor Adventurer was one Day gone abroad, when her careless
Husband, suspecting she had saved some Money, searches every Corner,
till at length he finds this same Ticket; which he immediately carries
abroad, sells, and squanders away the Money without the Wife's
suspecting any thing of the Matter. A Day or two after this, this
Friend, who was a Woman, comes and brings the Wife word, that she had
a Benefit of Five Hundred Pounds. The poor Creature over-joyed, flies
up Stairs to her Husband, who was then at Work, and desires him to
leave his Loom for that Evening, and come and drink with a Friend of
his and hers below. The Man received this chearful Invitation as bad
Husbands sometimes do, and after a cross Word or two told her he
wou'dn't come.
His Wife with Tenderness renewed her Importunity, and
at length said to him, My Love! I have within these few Months,
unknown to you, scraped together as much Money as has bought us a
Ticket in the Lottery, and now here is Mrs. Quick
come3 to tell
me, that 'tis come up this Morning a Five hundred Pound Prize. The
Husband replies immediately, You lye, you Slut, you have no Ticket,
for I have sold it. The poor Woman upon this Faints away in a Fit,
recovers, and is now run distracted. As she had no Design to defraud
her Husband, but was willing only to participate in his good Fortune,
every one pities her, but thinks her Husband's Punishment but just.
This, Sir, is Matter of Fact, and would, if the Persons and
Circumstances were greater, in a well-wrought Play be called
Beautiful Distress. I have only sketched it out with Chalk, and know
a good Hand can make a moving Picture with worse Materials.
Sir, &c.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am what the World calls a warm Fellow, and by good Success in Trade
I have raised myself to a Capacity of making some Figure in the World;
but no matter for that. I have now under my Guardianship a couple of
Nieces, who will certainly make me run mad; which you will not wonder
at, when I tell you they are Female Virtuosos, and during the three
Years and a half that I have had them under my Care, they never in the
least inclined their Thoughts towards any one single Part of the
Character of a notable Woman.
Whilst they should have been considering
the proper Ingredients for a Sack-posset, you should hear a Dispute
concerning the
magnetick4, Virtue of the
Loadstone, or perhaps the Pressure of the Atmosphere: Their Language
is peculiar to themselves, and they scorn to express themselves on the
meanest Trifle with Words that are not of a
Latin Derivation. But
this were supportable still, would they suffer me to enjoy an
uninterrupted Ignorance; but, unless I fall in with their abstracted
Idea of Things (as they call them) I must not expect to smoak one Pipe
in Quiet. In a
late Fit of the Gout I complained of the Pain of that
Distemper when my Niece
Kitty begged Leave to assure me, that
whatever I might think, several great Philosophers, both ancient and
modern, were of Opinion, that both Pleasure and Pain were imaginary
Distinctions5, and that there was no such thing as either
in
rerum Natura. I have often heard them affirm that the Fire was not
hot; and one Day when I, with the Authority of an old Fellow, desired
one of them to put my blue Cloak on my Knees; she answered, Sir, I
will reach the Cloak; but take notice, I do not do it as allowing your
Description; for it might as well be called Yellow as Blue; for Colour
is nothing but the various Infractions of the Rays of the Sun.
Miss
Molly told me one Day; That to say Snow was white, is allowing a
vulgar Error; for as it contains a great Quantity of nitrous
Particles, it might
more reasonably be supposed to6 be black. In
short, the young Husseys would persuade me, that to believe one's Eyes
is a sure way to be deceived; and have often advised me, by no means,
to trust any thing so fallible as my Senses. What I have to beg of you
now is, to turn one Speculation to the due Regulation of Female
Literature, so far at least, as to make it consistent with the Quiet
of such whose Fate it is to be liable to its Insults; and to tell us
the Difference between a Gentleman that should make Cheesecakes and
raise Paste, and a Lady that reads
Locke, and understands the
Mathematicks. In which you will extreamly oblige
Your hearty Friend and humble Servant,
Abraham Thrifty.
T.
[Volume 1 link:
].
at a Box in a Play,
and in first reprint.
comes
, and in first reprint.
magnetical
, and in first reprint.
Distractions
, and in first reprint.
may more seasonably
, and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 8, 1711 |
Addison |
Formam quidem ipsam, Marce fili, et tanquam faciem Honesti vides: quæ si
oculis cerneretur, mirabiles amores (ut ait Plato) excitaret Sapientiæ.—
Tull.
Offic.

I do not remember to have read any Discourse written expressly upon the
Beauty and Loveliness of Virtue, without considering it as a Duty, and
as the Means of making us happy both now and hereafter. I design
therefore this Speculation as an Essay upon that Subject, in which I
shall consider Virtue no further than as it is in it self of an amiable
Nature, after having premised, that I understand by the Word Virtue such
a general Notion as is affixed to it by the Writers of Morality, and
which by devout Men generally goes under the Name of Religion, and by
Men of the World under the Name of Honour.
Hypocrisy it self does great Honour, or rather Justice, to Religion, and
tacitly acknowledges it to be an Ornament to human Nature. The Hypocrite
would not be at so much Pains to put on the Appearance of Virtue, if he
did not know it was the most proper and effectual means to gain the Love
and Esteem of Mankind.
We learn from
Hierodes
, it was a common Saying among the Heathens,
that the Wise Man hates no body, but only loves the Virtuous.
Tully
has a very beautiful Gradation of Thoughts to shew how amiable
Virtue is. We love a virtuous Man, says he, who lives in the remotest
Parts of the Earth, though we are altogether out of the Reach of his
Virtue, and can receive from it no Manner of Benefit; nay, one who died
several Ages ago, raises a secret Fondness and Benevolence for him in
our Minds, when we read his Story: Nay, what is still more, one who has
been the Enemy of our Country, provided his Wars were regulated by
Justice and Humanity, as in the Instance of
Pyrrhus
whom
Tully
mentions on this Occasion in Opposition to
Hannibal
. Such is the
natural Beauty and Loveliness of Virtue.
Stoicism, which was the Pedantry of Virtue, ascribes all good
Qualifications, of what kind soever, to the virtuous Man.
Cato
in the Character
Tully
has left of him, carried Matters so
far, that he would not allow any one but a virtuous Man to be handsome.
This indeed looks more like a Philosophical Rant than the real Opinion
of a Wise Man; yet this was what
Cato
very seriously maintained. In
short, the Stoics thought they could not sufficiently represent the
Excellence of Virtue, if they did not comprehend in the Notion of it all
possible Perfection[s]; and therefore did not only suppose, that it was
transcendently beautiful in it self, but that it made the very Body
amiable, and banished every kind of Deformity from the Person in whom it
resided.
It is a common Observation, that the most abandoned to all Sense of
Goodness, are apt to wish those who are related to them of a different
Character; and it is very observable, that none are more struck with the
Charms of Virtue in the fair Sex, than those who by their very
Admiration of it are carried to a Desire of ruining it.
A virtuous Mind in a fair Body is indeed a fine Picture in a good Light,
and therefore it is no Wonder that it makes the beautiful Sex all over
Charms.
As Virtue in general is of an amiable and lovely Nature, there are some
particular kinds of it which are more so than others, and these are such
as dispose us to do Good to Mankind. Temperance and Abstinence, Faith
and Devotion, are in themselves perhaps as laudable as any other
Virtues; but those which make a Man popular and beloved, are Justice,
Charity, Munificence, and, in short, all the good Qualities that render
us beneficial to each other. For which Reason even an extravagant Man,
who has nothing else to recommend him but a false Generosity, is often
more beloved and esteemed than a Person of a much more finished
Character, who is defective in this Particular.
The two great Ornaments of Virtue, which shew her in the most
advantageous Views, and make her altogether lovely, are Chearfulness and
Good-Nature. These generally go together, as a Man cannot be agreeable
to others who is not easy within himself. They are both very requisite
in a virtuous Mind, to keep out Melancholy from the many serious
Thoughts it is engaged in, and to hinder its natural Hatred of Vice from
souring into Severity and Censoriousness.
If Virtue is of this amiable Nature, what can we think of those who can
look upon it with an Eye of Hatred and Ill-will, or can suffer their
Aversion for a Party to blot out all the Merit of the Person who is
engaged in it. A Man must be excessively stupid, as well as
uncharitable, who believes that there is no Virtue but on his own Side,
and that there are not Men as honest as himself who may differ from him
in Political Principles. Men may oppose one another in some Particulars,
but ought not to carry their Hatred to those Qualities which are of so
amiable a Nature in themselves, and have nothing to do with the Points
in Dispute. Men of Virtue, though of different Interests, ought to
consider themselves as more nearly united with one another, than with
the vicious Part of Mankind, who embark with them in the same civil
Concerns. We should bear the same Love towards a Man of Honour, who is a
living Antagonist, which
Tully
tells us in the forementioned Passage
every one naturally does to an Enemy that is dead. In short, we should
esteem Virtue though in a Foe, and abhor Vice though in a Friend.
I speak this with an Eye to those cruel Treatments which Men of all
Sides are apt to give the Characters of those who do not agree with
them. How many Persons of undoubted Probity, and exemplary Virtue, on
either Side, are blackned and defamed? How many Men of Honour exposed to
publick Obloquy and Reproach? Those therefore who are either the
Instruments or Abettors in such Infernal Dealings, ought to be looked
upon as Persons who make use of Religion to promote their Cause, not of
their Cause to promote Religion.
C.
we find that
Cato
&c.
Contents
|
Monday, December 10, 1711 |
Steele |
—Judex et callidus audis.
Hor.

Covent-Garden, Dec. 7.
Mr.
Spectator,
I cannot, without a double Injustice, forbear expressing to you the
Satisfaction which a whole Clan of Virtuosos have received from those
Hints which you have lately given the Town on the Cartons of the
inimitable Raphael. It
1 should be methinks the Business of a
Spectator to improve the Pleasures of Sight, and there cannot be a
more immediate Way to it than recommending the Study and Observation
of excellent Drawings and Pictures. When I first went to view those of
Raphael which you have celebrated, I must confess 1 was but barely
pleased; the next time I liked them better, but at last as I grew
better acquainted with them, I fell deeply in love with them, like
wise Speeches they sunk deep into my Heart; for you know,
Mr.
Spectator, that a Man of Wit may extreamly affect one for the Present,
but if he has not Discretion, his Merit soon vanishes away, while a
Wise Man that has not so great a Stock of Wit, shall nevertheless give
you a far greater and more lasting Satisfaction: Just so it is in a
Picture that is smartly touched but not well studied; one may call it
a witty Picture, tho' the Painter in the mean time may be in Danger of
being called a Fool. On the other hand, a Picture that is thoroughly
understood in the Whole, and well performed in the Particulars, that
is begun on the Foundation of Geometry, carried on by the Rules of
Perspective, Architecture, and Anatomy, and perfected by a good
Harmony, a just and natural Colouring, and such Passions and
Expressions of the Mind as are almost peculiar to
Raphael; this is
what you may justly style a wise Picture, and which seldom fails to
strike us Dumb, till we can assemble all our Faculties to make but a
tolerable Judgment upon it. Other Pictures are made for the Eyes only,
as Rattles are made for Childrens Ears; and certainly that Picture
that only pleases the Eye, without representing some well-chosen Part
of Nature or other, does but shew what fine Colours are to be sold at
the Colour-shop, and mocks the Works of the Creator. If the best
Imitator of Nature is not to be esteemed the best Painter, but he that
makes the greatest Show and Glare of Colours; it will necessarily
follow, that he who can array himself in the most gaudy Draperies is
best drest, and he that can speak loudest the best Orator. Every Man
when he looks on a Picture should examine it according to that share
of Reason he is Master of, or he will be in Danger of making a wrong
Judgment. If Men as they walk abroad would make more frequent
Observations on those Beauties of Nature which every Moment present
themselves to their View, they would be better Judges when they saw
her well imitated at home: This would help to correct those Errors
which most Pretenders fall into, who are over hasty in their
Judgments, and will not stay to let Reason come in for a share in the
Decision. 'Tis for want of this that Men mistake in this Case, and in
common Life, a wild extravagant Pencil for one that is truly bold and
great, an impudent Fellow for a Man of true Courage and Bravery, hasty
and unreasonable Actions for Enterprizes of Spirit and Resolution,
gaudy Colouring for that which is truly beautiful, a false and
insinuating Discourse for simple Truth elegantly recommended. The
Parallel will hold through all the Parts of Life and Painting too; and
the Virtuosos above-mentioned will be glad to see you draw it with
your Terms of Art. As the Shadows in Picture represent the serious or
melancholy, so the Lights do the bright and lively Thoughts: As there
should be but one forcible Light in a Picture which should catch the
Eye and fall on the Hero, so there should be but one Object of our
Love, even the Author of Nature. These and the like Reflections well
improved, might very much contribute to open the Beauty of that Art,
and prevent young People from being poisoned by the ill Gusto of an
extravagant Workman that should be imposed upon us.
I am, Sir,
Your
most humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
Though I am a Woman, yet I am one of those who confess themselves
highly pleased with a Speculation you obliged the World with some time
ago
2, from an old
Greek Poet you call
Simonides, in relation to
the several Natures and Distinctions of our own Sex. I could not but
admire how justly the Characters of Women in this Age, fall in with
the Times of
Simonides, there being no one of those Sorts I have not
at some time or other of my Life met with a Sample of. But, Sir, the
Subject of this present Address, are a Set of Women comprehended, I
think, in the Ninth Specie of that Speculation, called the Apes; the
Description of whom I find to be, "That they are such as are both ugly
and ill-natured, who have nothing beautiful themselves, and endeavour
to detract from or ridicule every thing that appears so in others."
Now, Sir, this Sect, as I have been told, is very frequent in the
great Town where you live; but as my Circumstance of Life obliges me
to reside altogether in the Country, though not many Miles from
London, I can't have met with a great Number of 'em, nor indeed is
it a desirable Acquaintance, as I have lately found by Experience. You
must know, Sir, that at the Beginning of this Summer a Family of these
Apes came and settled for the Season not far from the Place where I
live. As they were Strangers in the Country, they were visited by the
Ladies about 'em, of whom I was, with an Humanity usual in those that
pass most of their Time in Solitude. The Apes lived with us very
agreeably our own Way till towards the End of the Summer, when they
began to bethink themselves of returning to Town; then it was,
Mr.
Spectator, that they began to set themselves about the proper and
distinguishing Business of their Character; and, as 'tis said of evil
Spirits, that they are apt to carry away a Piece of the House they are
about to leave, the Apes, without Regard to common Mercy, Civility, or
Gratitude, thought fit to mimick and fall foul on the Faces, Dress,
and Behaviour of their innocent Neighbours, bestowing abominable
Censures and disgraceful Appellations, commonly called Nicknames, on
all of them; and in short, like true fine Ladies, made their honest
Plainness and Sincerity Matter of Ridicule. I could not but acquaint
you with these Grievances, as well at the Desire of all the Parties
injur'd, as from my own Inclination. I
hope, Sir, if you can't propose
entirely to reform this Evil, you will take such Notice of it in some
of your future Speculations, as may put the deserving Part of our Sex
on their Guard against these Creatures; and at the same time the Apes
may be sensible, that this sort of Mirth is so far from an innocent
Diversion, that it is in the highest Degree that Vice which is said to
comprehend all others
3.
I am, Sir, Your humble Servant,
Constantia Field.
T.
In No. 226. Signor Dorigny's scheme was advertised in Nos.
,
,
,
, and
.
No.
.
Ingratitude.
Ingratum si dixeris, omnia dixeris.
Contents
|
Tuesday, December 11, 1711 |
Addison |
Ficta Voluptatis causâ sint proxima Veris.
Hor.

There is nothing which one regards so much with an Eye of Mirth and Pity
as Innocence, when it has in it a Dash of Folly. At the same time that
one esteems the Virtue, one is tempted to laugh at the Simplicity which
accompanies it. When a Man is made up wholly of the Dove, without the
least Grain of the Serpent in his Composition, he becomes ridiculous in
many Circumstances of Life, and very often discredits his best Actions.
The
Cordeliers
tell a Story of their Founder St.
Francis
, that as he
passed the Streets in the Dusk of the Evening, he discovered a young
Fellow with a Maid in a Corner; upon which the good Man, say they,
lifted up his Hands to Heaven with a secret Thanksgiving, that there was
still so much Christian Charity in the World. The Innocence of the Saint
made him mistake the Kiss of a Lover for a Salute of Charity. I am
heartily concerned when I see a virtuous Man without a competent
Knowledge of the World; and if there be any Use in these my Papers, it
is this, that without presenting Vice under any false alluring Notions,
they give my Reader an Insight into the Ways of Men, and represent human
Nature in all its changeable Colours. The Man who has not been engaged
in any of the Follies of the World, or, as
Shakespear
expresses it,
hackney'd in the Ways of Men
, may here find a Picture of its Follies
and Extravagancies. The Virtuous and the Innocent may know in
Speculation what they could never arrive at by Practice, and by this
Means avoid the Snares of the Crafty, the Corruptions of the Vicious,
and the Reasonings of the Prejudiced. Their Minds may be opened without
being vitiated.
It is with an Eye to my following Correspondent, Mr.
Timothy Doodle
,
who seems a very well-meaning Man, that I have written this short
Preface, to which I shall subjoin a Letter from the said Mr.
Doodle
.
Sir,
I could heartily wish that you would let us know your Opinion upon
several innocent Diversions which are in use among us, and which are
very proper to pass away a Winter Night for those who do not care to
throw away their Time at an Opera, or at the Play-house. I would
gladly know in particular, what Notion you have of Hot-Cockles; as
also whether you think that Questions and Commands, Mottoes, Similes,
and Cross-Purposes have not more Mirth and Wit in them, than those
publick Diversions which are grown so very fashionable among us. If
you would recommend to our Wives and Daughters, who read your Papers
with a great deal of Pleasure, some of those Sports and Pastimes that
may be practised within Doors, and by the Fire-side, we who are
Masters of Families should be hugely obliged to you. I need not tell
you that I would have these Sports and Pastimes not only merry but
innocent, for which Reason I have not mentioned either Whisk or
Lanterloo, nor indeed so much as One and Thirty. After having
communicated to you my Request upon this Subject, I will be so free as
to tell you how my Wife and I pass away these tedious Winter Evenings
with a great deal of Pleasure. Tho' she be young and handsome, and
good-humoured to a Miracle, she does not care for gadding abroad like
others of her Sex. There is a very friendly Man, a Colonel in the
Army, whom I am mightily obliged to for his Civilities, that comes to
see me almost every Night; for he is not one of those giddy young
Fellows that cannot live out of a Play-house. When we are together, we
very often make a Party at Blind-Man's Buff, which is a Sport that I
like the better, because there is a good deal of Exercise in it. The
Colonel and I are blinded by Turns, and you would laugh your Heart out
to see what Pains my Dear takes to hoodwink us, so that it is
impossible for us to see the least Glimpse of Light. The poor Colonel
sometimes hits his Nose against a Post, and makes us die with
laughing. I have generally the good Luck not to hurt myself, but am
very often above half an Hour before I can catch either of them; for
you must know we hide ourselves up and down in Corners, that we may
have the more Sport. I only give you this Hint as a Sample of such
Innocent Diversions as I would have you recommend; and am,
Most
esteemed Sir, your ever loving Friend,
Timothy Doodle.
The following Letter was occasioned by my last
Thursday's
Paper upon
the Absence of Lovers, and the Methods therein mentioned of making such
Absence supportable.
Sir,
Among the several Ways of Consolation which absent Lovers make use of
while their Souls are in that State of Departure, which you say is
Death in Love, there are some very material ones that have escaped
your Notice. Among these, the first and most received is a crooked
Shilling, which has administered great Comfort to our Forefathers, and
is still made use of on this Occasion with very good Effect in most
Parts of Her Majesty's Dominions. There are some, I know, who think a
Crown-Piece cut into two equal Parts, and preserved by the distant
Lovers, is of more sovereign Virtue than the former. But since
Opinions are divided in this Particular, why may not the same Persons
make use of both? The Figure of a Heart, whether cut in Stone or cast
in Metal, whether bleeding upon an Altar, stuck with Darts, or held in
the Hand of a Cupid, has always been looked upon as Talismanick in
Distresses of this Nature. I am acquainted with many a brave Fellow,
who carries his Mistress in the Lid of his Snuff-box, and by that
Expedient has supported himself under the Absence of a whole Campaign.
For my own Part, I have tried all these Remedies, but never found so
much Benefit from any as from a Ring, in which my Mistress's Hair is
platted together very artificially in a kind of True-Lover's Knot. As
I have received great Benefit from this Secret, I think myself obliged
to communicate it to the Publick, for the Good of my Fellow-Subjects.
I desire you will add this Letter as an Appendix to your Consolations
upon Absence, and am,
Your very humble Servant,
T. B.
I shall conclude this Paper with a Letter from an University Gentleman,
occasioned by my last
Tuesday's
Paper, wherein I gave some Account of
the great Feuds which happened formerly in those learned Bodies, between
the modern
Greeks
and
Trojans
.
Sir,
This will give you to understand, that there is at present in the
Society, whereof I am a Member, a very considerable Body of
Trojans,
who, upon a proper Occasion, would not fail to declare ourselves. In
the mean while we do all we can to annoy our Enemies by Stratagem, and
are resolved by the first Opportunity to attack Mr.
Joshua Barnes1, whom we look upon as the
Achilles of the opposite Party. As for
myself, I have had the Reputation ever since I came from School, of
being a trusty
Trojan, and am resolved never to give Quarter to the
smallest Particle of
Greek, where-ever I chance to meet it. It is
for this Reason I take it very ill of you, that you sometimes hang out
Greek Colours at the Head of your Paper, and sometimes give a Word
of the Enemy even in the Body of it.
When I meet with any thing of
this nature, I throw down your Speculations upon the Table, with that
Form of Words which we make use of when we declare War upon an Author.
Græcum est, non potest legi.2
I give you this Hint, that you may for the future abstain from any
such Hostilities at your Peril.
Troilus.
C.
Professor of Greek at Cambridge, who edited Homer, Euripides,
Anacreon, &c., and wrote in Greek verse a History of Esther. He died
in 1714.
It is Greek. It cannot be read.
This passed into a proverb from Franciscus Accursius, a famous
Jurisconsult and son of another Accursius, who was called the Idol of
the Jurisconsults. Franciscus Accursius was a learned man of the 13th
century, who, in expounding Justinian, whenever he came to one of
Justinian's quotations from Homer, said
Græcum est, nec potest legi
.
Afterwards, in the first days of the revival of Greek studies in Europe,
it was often said, as reported by Claude d'Espence, for example, that to
know anything of Greek made a man suspected, to know anything of Hebrew
almost made him a heretic.
Contents
|
Wednesday, December 12, 1711 |
Steele |
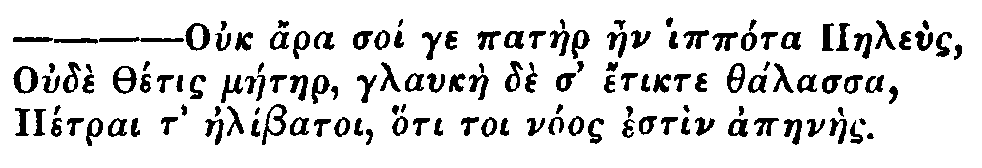

Mr. Spectator,
As your Paper is Part of the Equipage of the Tea-Table, I conjure you
to print what I now write to you; for I have no other Way to
communicate what I have to say to the fair Sex on the most important
Circumstance of Life, even the Care of Children. I do not understand
that you profess your Paper is always to consist of Matters which are
only to entertain the Learned and Polite, but that it may agree with
your Design to publish some which may tend to the Information of
Mankind in general; and when it does so, you do more than writing Wit
and Humour.
Give me leave then to tell you, that of all the Abuses
that ever you have as yet endeavoured to reform, certainly not one
wanted so much your Assistance as the Abuse in
nursing1 Children.
It is unmerciful to see, that a Woman endowed with all the Perfections
and Blessings of Nature, can, as soon as she is delivered, turn off
her innocent, tender, and helpless Infant, and give it up to a Woman
that is (ten thousand to one) neither in Health nor good Condition,
neither sound in Mind nor Body, that has neither Honour nor
Reputation, neither Love nor Pity for the poor Babe, but more Regard
for the Money than for the whole Child, and never will take further
Care of it than what by all the Encouragement of Money and Presents
she is forced to; like
Æsop's Earth, which would not nurse the Plant
of another Ground, altho' never so much improved, by reason that Plant
was not of its own Production. And since another's Child is no more
natural to a Nurse than a Plant to a strange and different Ground, how
can it be supposed that the Child should thrive? and if it thrives,
must it not imbibe the gross Humours and Qualities of the Nurse, like
a Plant in a different Ground, or like a Graft upon a different Stock?
Do not we observe, that a Lamb sucking a Goat changes very much its
Nature, nay even its Skin and Wooll into the Goat Kind? The Power of a
Nurse over a Child, by infusing into it, with her Milk, her Qualities
and Disposition, is sufficiently and daily observed: Hence came that
old Saying concerning an ill-natured and malicious Fellow, that he had
imbibed his Malice with his Nurse's Milk, or that some Brute or other
had been his Nurse. Hence
Romulus and
Remus were said to have been
nursed by a Wolf,
Telephus the Son of
Hercules by a Hind,
Pelias
the Son of
Neptune by a Mare, and
Ægisthus by a Goat; not that
they had actually suck'd such Creatures, as some Simpletons have
imagin'd, but that their Nurses had been of such a Nature and Temper,
and infused such into them.
'Many Instances may be produced from good Authorities and daily
Experience, that Children actually suck in the several Passions and
depraved Inclinations of their Nurses, as Anger, Malice, Fear,
Melancholy, Sadness, Desire, and Aversion. This
Diodorus, lib. 2,
witnesses, when he speaks, saying, That
Nero the Emperor's Nurse had
been very much addicted to Drinking; which Habit
Nero received from
his Nurse, and was so very particular in this, that the People took so
much notice of it, as instead of
Tiberius Nero, they call'd him
Biberius Mero. The same
Diodorus also relates of
Caligula,
Predecessor to
Nero, that his Nurse used to moisten the Nipples of
her Breast frequently with Blood, to make
Caligula take the better
Hold of them; which, says
Diodorus, was the Cause that made him so
blood-thirsty and cruel all his Life-time after, that he not only
committed frequent Murder by his own Hand, but likewise wished that
all human Kind wore but one Neck, that he might have the Pleasure to
cut it off.
Such like Degeneracies astonish the Parents,
who not
knowing after whom the Child can take,
see2 one to incline to
Stealing, another to Drinking, Cruelty, Stupidity; yet all these are
not minded. Nay it is easy to demonstrate, that a Child, although it
be born from the best of Parents, may be corrupted by an ill-tempered
Nurse. How many Children do we see daily brought into Fits,
Consumptions, Rickets, &c., merely by sucking their Nurses when in a
Passion or Fury? But indeed almost any Disorder of the Nurse is a
Disorder to the Child, and few Nurses can be found in this Town but
what labour under some Distemper or other.
The first Question that is
generally asked a young Woman that wants to be a Nurse,
Why3 she
should be a Nurse to other People's Children; is answered, by her
having an ill Husband, and that she must make Shift to live. I think
now this very Answer is enough to give any Body a Shock if duly
considered; for an ill Husband may, or ten to one if he does not,
bring home to his Wife an ill Distemper, or at least Vexation and
Disturbance. Besides as she takes the Child out of meer Necessity, her
Food will be accordingly, or else very coarse at best; whence proceeds
an ill-concocted and coarse Food for the Child; for as the Blood, so
is the Milk; and hence I am very well assured proceeds the Scurvy, the
Evil, and many other Distempers. I
beg of you, for the Sake of the
many poor Infants that may and will be saved, by weighing this Case
seriously, to exhort the People with the utmost Vehemence to let the
Children suck their own
Mothers4, both for the Benefit of Mother
and Child. For the general Argument, that a Mother is weakned by
giving suck to her Children, is vain and simple; I will maintain that
the Mother grows stronger by it, and will have her Health better than
she would have otherwise: She will find it the greatest Cure and
Preservative for the Vapours and future Miscarriages, much beyond any
other Remedy whatsoever: Her Children will be like Giants, whereas
otherwise they are but living Shadows and like unripe Fruit; and
certainly if a Woman is strong enough to bring forth a Child, she is
beyond all Doubt strong enough to nurse it afterwards. It grieves me
to observe and consider how many poor Children are daily ruin'd by
careless Nurses; and yet how tender ought they to be of a poor Infant,
since the least Hurt or Blow, especially upon the Head, may make it
senseless, stupid, or otherwise miserable for ever?
'But I cannot well leave this Subject as yet; for it seems to me very
unnatural, that a Woman that has fed a Child as Part of her self for
nine Months, should have no Desire to nurse it farther, when brought
to Light and before her Eyes, and when by its Cry it implores her
Assistance and the Office of a Mother. Do not the very cruellest of
Brutes tend their young ones with all the Care and Delight imaginable?
For how can she be call'd a Mother that will not nurse her young ones?
The Earth is called the Mother of all Things, not because she
produces, but because she maintains and nurses what she produces. The
Generation of the Infant is the Effect of Desire, but the Care of it
argues Virtue and Choice. I am not ignorant but that there are some
Cases of Necessity where a Mother cannot give Suck, and then out of
two Evils the least must be chosen; but there are so very few, that I
am sure in a Thousand there is hardly one real Instance; for if a
Woman does but know that her Husband can spare about three or six
Shillings a Week extraordinary, (altho' this is but seldom considered)
she certainly, with the Assistance of her Gossips, will soon perswade
the good Man to send the Child to Nurse, and easily impose upon him by
pretending In-disposition. This Cruelty is supported by Fashion, and
Nature gives Place to Custom.
Sir, Your humble Servant.
T.
nursing of
, and in first reprint.
seeing
, and in 1st r.
is, why
, and in 1st. r.
Mother
,
Contents
|
Thursday, December 13, 1711 |
Addison |
We are told by some antient Authors, that
Socrates
was instructed in
Eloquence by a Woman, whose Name, if I am not mistaken, was
Aspasia
. I
have indeed very often looked upon that Art as the most proper for the
Female Sex, and I think the Universities would do well to consider
whether they should not fill the Rhetorick Chairs with She Professors.
It has been said in the Praise of some Men, that they could Talk whole
Hours together upon any Thing; but it must be owned to the Honour of the
other Sex, that there are many among them who can Talk whole Hours
together upon Nothing. I have known a Woman branch out into a long
Extempore Dissertation upon the Edging of a Petticoat, and chide her
Servant for breaking a China Cup, in all the Figures of Rhetorick.
Were Women admitted to plead in Courts of Judicature, I am perswaded
they would carry the Eloquence of the Bar to greater Heights than it has
yet arrived at. If
one doubts this, let him but be present at those
Debates which frequently arise among the Ladies
of the
British
Fishery.
The first Kind therefore of Female Orators which I shall take notice of,
are those who are employed in stirring up the Passions, a Part of
Rhetorick in which
Socrates
his Wife had perhaps made a greater
Proficiency than his above-mentioned Teacher.
The second Kind of Female Orators are those who deal in Invectives, and
who are commonly known by the Name of the Censorious. The Imagination
and Elocution of this Set of Rhetoricians is wonderful. With what a
Fluency of Invention, and Copiousness of Expression, will they enlarge
upon every little Slip in the Behaviour of another? With how many
different Circumstances, and with what Variety of Phrases, will they
tell over the same Story? I have known an old Lady make an unhappy
Marriage the Subject of a Month's Conversation. She blamed the Bride in
one Place; pitied her in another; laughed at her in a third; wondered at
her in a fourth; was angry with her in a fifth; and in short, wore out a
Pair of Coach-Horses in expressing her Concern for her. At length, after
having quite exhausted the Subject on this Side, she made a Visit to the
new-married Pair, praised the Wife for the prudent Choice she had made,
told her the unreasonable Reflections which some malicious People had
cast upon her, and desired that they might be better acquainted. The
Censure and Approbation of this Kind of Women are therefore only to be
consider'd as Helps to Discourse.
A third Kind of Female Orators may be comprehended under the Word
Gossips
. Mrs.
Fiddle Faddle
is perfectly accomplished in this Sort
of Eloquence; she launches out into Descriptions of Christenings, runs
Divisions upon an Headdress, knows every Dish of Meat that is served up
in her Neighbourhood, and entertains her Company a whole Afternoon
together with the Wit of her little Boy, before he is able to speak.
The Coquet may be looked upon as a fourth Kind of Female Orator. To give
her self the larger Field for Discourse, she hates and loves in the same
Breath, talks to her Lap-dog or Parrot, is uneasy in all kinds of
Weather, and in every Part of the Room: She has false Quarrels and
feigned Obligations to all the Men of her Acquaintance; sighs when she
is not sad, and Laughs when she is not Merry. The Coquet is in
particular a great Mistress of that Part of Oratory which is called
Action, and indeed seems to speak for no other Purpose, but as it gives
her an Opportunity of stirring a Limb, or varying a Feature, of glancing
her Eyes, or playing with her Fan.
As for News-mongers, Politicians, Mimicks, Story-Tellers, with other
Characters of that nature, which give Birth to Loquacity, they are as
commonly found among the Men as the Women; for which Reason I shall pass
them over in Silence.
I have often been puzzled to assign a Cause why Women should have this
Talent of a ready Utterance in so much greater Perfection than Men. I
have sometimes fancied that they have not a retentive Power, or the
Faculty of suppressing their Thoughts, as Men have, but that they are
necessitated to speak every Thing they think,
if so, it would
perhaps furnish a very strong Argument to the
Cartesians
, for the
supporting of their
Doctrine
, that the Soul always thinks. But as
several are of Opinion that the Fair Sex are not altogether Strangers to
the Art of Dissembling and concealing their Thoughts, I have been forced
to relinquish that Opinion, and have therefore endeavoured to seek after
some better Reason. In
to it, a Friend of mine, who is an
excellent Anatomist, has promised me by the first Opportunity to dissect
a Woman's Tongue, and to examine whether there may not be in it certain
Juices which render it so wonderfully voluble
or
flippant, or
whether the Fibres of it may not be made up of a finer or more pliant
Thread, or whether there are not in it some particular Muscles which
dart it up and down by such sudden Glances and Vibrations; or whether in
the last Place, there may not be certain undiscovered Channels running
from the Head and the Heart, to this little Instrument of Loquacity, and
conveying into it a perpetual Affluence of animal Spirits. Nor must I
omit the Reason which
Hudibras
has given, why those who can talk on
Trifles speak with the greatest Fluency; namely, that the Tongue is like
a Race-Horse, which runs the faster the lesser Weight it carries.
Which of these Reasons soever may be looked upon as the most probable, I
think the
Irishman's
Thought was very natural, who after some Hours
Conversation with a Female Orator, told her, that he believed her Tongue
was very glad when she was asleep, for that it had not a Moment's Rest
all the while she was awake.
That excellent old Ballad of
The Wanton Wife of Bath
has the following
remarkable Lines.
I think, quoth Thomas, Womens Tongues
Of Aspen Leaves are made.
And
, though in the Description of a very barbarous Circumstance,
tells us, That when the Tongue of a beautiful Female was cut out, and
thrown upon the Ground, it could not forbear muttering even in that
Posture.
—Comprensam forcipe linguam
Abstulit ense fero. Radix micat ultima linguæ,
Ipsa jacet, terræque tremens immurmurat atræ;
Utque salire solet mutilatæ cauda colubræ
Palpitat:—4`
If a tongue would be talking without a Mouth, what could it have done
when it had all its Organs of Speech, and Accomplices of Sound about it?
I might here mention the Story of the Pippin-Woman, had not I some
Reason to look upon it as fabulous.
I must confess I am so wonderfully charmed with the Musick of this
little Instrument, that I would by no Means discourage it. All that I
aim at by this Dissertation is, to cure it of several disagreeable
Notes, and in particular of those little Jarrings and Dissonances which
arise from Anger, Censoriousness, Gossiping and Coquetry. In short, I
would always have it tuned by Good-Nature, Truth, Discretion and
Sincerity.
C.
that belong to our
Opinion
,
and
Met
. I. 6, v. 556.
Contents
|
Friday, December 14, 1711 |
Steele |
Hoc maximè Officii est, ut quisque maximè opis indigeat, ita ei
potissimùm opitulari.
Tull.

There are none who deserve Superiority over others in the Esteem of
Mankind, who do not make it their Endeavour to be beneficial to Society;
and who upon all Occasions which their Circumstances of Life can
administer, do not take a certain unfeigned Pleasure in conferring
Benefits of one kind or other. Those whose great Talents and high Birth
have placed them in conspicuous Stations of Life, are indispensably
obliged to exert some noble Inclinations for the Service of the World,
or else such Advantages become Misfortunes, and Shade and Privacy are a
more eligible Portion. Where Opportunities and Inclinations are given to
the same Person, we sometimes see sublime Instances of Virtue, which so
dazzle our Imaginations, that we look with Scorn on all which in lower
Scenes of Life we may our selves be able to practise. But this is a
vicious Way of Thinking; and it bears some Spice of romantick Madness,
for a Man to imagine that he must grow ambitious, or seek Adventures, to
be able to do great Actions. It is in every Man's Power in the World who
is above meer Poverty, not only to do Things worthy but heroick. The
great Foundation of civil Virtue is Self-Denial; and there is no one
above the Necessities of Life, but has Opportunities of exercising that
noble Quality, and doing as much as his Circumstances will bear for the
Ease and Convenience of other Men; and he who does more than ordinarily
Men practise upon such Occasions as occur in his Life, deserves the
Value of his Friends as if he had done Enterprizes which are usually
attended with the highest Glory.
of publick Spirit differ rather in
their Circumstances than their Virtue; and the Man who does all he can
in a low Station, is more
a
Hero than he who omits any worthy
Action he is able to accomplish in a great one. It is not many Years ago
since
Lapirius
, in Wrong of his elder Brother, came to a great Estate
by Gift of his Father, by reason of the dissolute Behaviour of the
First-born. Shame and Contrition reformed the Life of the disinherited
Youth, and he became as remarkable for his good Qualities as formerly
for his Errors.
Lapirius
, who observed his Brother's Amendment, sent
him on a New-Years Day in the Morning the following Letter:
Honoured Brother,
I enclose to you the Deeds whereby my Father gave me
this House and Land: Had he lived 'till now, he would not
have bestowed it in that Manner; he took it from the Man
you were, and I restore it to the Man you are. I am,
Sir,
Your affectionate Brother,
and humble Servant,
P. T.
As great and exalted Spirits undertake the Pursuit of hazardous Actions
for the Good of others, at the same Time gratifying their Passion for
Glory; so do worthy Minds in the domestick Way of Life deny themselves
many Advantages, to satisfy a generous Benevolence which they bear to
their Friends oppressed with Distresses and Calamities. Such Natures one
may call Stores of Providence, which are actuated by a secret Celestial
Influence to undervalue the ordinary Gratifications of Wealth, to give
Comfort to an Heart loaded with Affliction, to save a falling Family, to
preserve a Branch of Trade in their Neighbourhood, and give Work to the
Industrious, preserve the Portion of the helpless Infant, and raise the
Head of the mourning Father. People whose Hearts are wholly bent towards
Pleasure, or intent upon Gain, never hear of the noble Occurrences among
Men of Industry and Humanity. It would look like a City Romance, to tell
them of the generous
who the other Day sent this Billet to an
eminent Trader under Difficulties to support himself, in whose Fall many
hundreds besides himself had perished; but because I think there is more
Spirit and true Gallantry in it than in any Letter I have ever read from
Strepkon
to
Phillis
, I shall insert it even in the mercantile honest
Stile in which it was sent.
Sir,
'I Have heard of the Casualties which have involved you
in extreme Distress at this Time; and knowing you to be a
Man of great Good-Nature, Industry and Probity, have resolved
to stand by you. Be of good Chear, the Bearer brings with
him five thousand Pounds, and has my Order to answer your
drawing as much more on my Account. I did this in Haste,
for fear I should come too late for your Relief; but you may
value your self with me to the Sum of fifty thousand Pounds;
for I can very chearfully run the Hazard of being so much
less rich than I am now, to save an honest Man whom
I love.
Your Friend and Servant,
W. S.2
I think there is somewhere in
Montaigne
Mention made of a Family-book,
wherein all the Occurrences that happened from one Generation of that
House to another were recorded. Were there such a Method in the
Families, which are concerned in this Generosity, it would be an hard
Task for the greatest in
Europe
to give, in their own, an Instance of
a Benefit better placed, or conferred with a more graceful Air. It has
been heretofore urged, how barbarous and inhuman is any unjust Step made
to the Disadvantage of a Trader; and by how much such an Act towards him
is detestable, by so much an Act of Kindness towards him is laudable. I
remember to have heard a Bencher of the
Temple
tell a Story of a
Tradition in their House, where they had formerly a Custom of chusing
Kings for such a Season, and allowing him his Expences at the Charge of
the Society: One of our Kings, said my Friend, carried his Royal
Inclination a little too far, and there was a Committee ordered to look
into the Management of his Treasury. Among other Things it appeared,
that his Majesty walking
incog
, in the Cloister, had overheard a poor
Man say to another, Such a small Sum would make me the happiest Man in
the World. The King out of his Royal Compassion privately inquired into
his Character, and finding him a proper Object of Charity, sent him the
Money. When the Committee read their Report, the House passed his
Account with a Plaudite without further Examination, upon the Recital of
this Article in them.
| For making a Man happy: |
£ |
s. |
d. |
|
10 |
0 |
0 |
T.
an
W. P.
corrected by an Erratum in No.
to W.S.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 15, 1711 |
Addison |
When I make Choice of a Subject that has not been treated on by others,
I throw together my Reflections on it without any Order or Method, so
that they may appear rather in the Looseness and Freedom of an Essay,
than in the Regularity of a Set Discourse. It is after this Manner that
I shall consider Laughter and Ridicule in my present Paper.
Man is the merriest Species of the Creation, all above and below him are
Serious. He sees things in a different Light from other Beings, and
finds his Mirth
a
rising from Objects that perhaps cause something like
Pity or Displeasure in higher Natures. Laughter is indeed a very good
Counterpoise to the Spleen; and it seems but reasonable that we should
be capable of receiving Joy from what is no real Good to us, since we
can receive Grief from what is no real Evil.
I
in my [Volume 1 link:
] raised a Speculation on the Notion of a
Modern Philosopher
, who describes the first Motive of Laughter to be
a secret Comparison which we make between our selves, and the Persons we
laugh at; or, in other Words, that Satisfaction which we receive from
the Opinion of some Pre-eminence in our selves, when we see the
Absurdities of another or when we reflect on any past Absurdities of our
own. This seems to hold in most Cases, and we may observe that the
vainest Part of Mankind are the most addicted to this Passion.
I have read a Sermon of a Conventual in the Church of
Rome
, on those
Words of the Wise Man,
I said of Laughter, it is mad; and of Mirth,
what does it?
Upon which he laid it down as a Point of Doctrine, that
Laughter was the Effect of Original Sin, and that
Adam
could not laugh
before the Fall.
Laughter, while it lasts, slackens and unbraces the Mind, weakens the
Faculties, and causes a kind of Remissness and Dissolution in all the
Powers of the Soul: And thus far it may be looked upon as a Weakness in
the Composition of Human Nature. But if we consider the frequent Reliefs
we receive from it, and how often it breaks the Gloom which is apt to
depress the Mind and damp our Spirits, with transient unexpected Gleams
of Joy, one would take care not to grow too Wise for so great a Pleasure
of Life.
The Talent of turning Men into Ridicule, and exposing to Laughter those
one converses with, is the Qualification of little ungenerous Tempers. A
young Man with this Cast of Mind cuts himself off from all manner of
Improvement. Every one has his Flaws and Weaknesses; nay, the greatest
Blemishes are often found in the most shining Characters; but what an
absurd Thing is it to pass over all the valuable Parts of a Man, and fix
our Attention on his Infirmities to observe his Imperfections more than
his Virtues; and to make use of him for the Sport of others, rather than
for our own Improvement?
We therefore very often find, that Persons the most accomplished in
Ridicule are those who are very shrewd at hitting a Blot, without
exerting any thing masterly in themselves. As there are many eminent
Criticks who never writ a good Line, there are many admirable Buffoons
that animadvert upon every single Defect in another, without ever
discovering the least Beauty of their own. By this Means, these unlucky
little Wits often gain Reputation in the Esteem of Vulgar Minds, and
raise themselves above Persons of much more laudable Characters.
If the Talent of Ridicule were employed to laugh Men out of Vice and
Folly, it might be of some Use to the World; but instead of this, we
find that it is generally made use of to laugh Men out of Virtue and
good Sense, by attacking every thing that is Solemn and Serious, Decent
and Praiseworthy in Human Life.
We may observe, that in the First Ages of the World, when the great
Souls and Master-pieces of Human Nature were produced, Men shined by a
noble Simplicity of Behaviour, and were Strangers to those little
Embellishments which are so fashionable in our present Conversation. And
it is very remarkable, that notwithstanding we fall short at present of
the Ancients in Poetry, Painting, Oratory, History, Architecture, and
all the noble Arts and Sciences which depend more upon Genius than
Experience, we exceed them as much in Doggerel, Humour, Burlesque, and
all the trivial Arts of Ridicule. We meet with more Raillery among the
Moderns, but more Good Sense among the Ancients.
The two great Branches of Ridicule in Writing are Comedy and Burlesque.
The first ridicules Persons by drawing them in their proper Characters,
the other by drawing them quite unlike themselves. Burlesque is
therefore of two kinds; the first represents mean Persons in the
Accoutrements of Heroes, the other describes great Persons acting and
speaking like the basest among the People.
Don Quixote
is an Instance
of the first, and
Lucian's
Gods of the second. It is a
among
the Criticks, whether Burlesque Poetry runs best in Heroick Verse, like
that of the
Dispensary;
or in Doggerel, like that of
Hudibras
. I
think where the low Character is to be raised, the Heroick is the proper
Measure; but when an Hero is to be pulled down and degraded, it is done
best in Doggerel.
If
Hudibras
had been set out with as much Wit and Humour in Heroick
Verse as he is in Doggerel, he would have made a much more agreeable
Figure than he does; though the generality of his Readers are so
wonderfully pleased with the double Rhimes, that I do not expect many
will be of my Opinion in this Particular.
I shall conclude this Essay upon Laughter with observing that the
Metaphor of Laughing, applied to Fields and Meadows when they are in
Flower, or to Trees when they are in Blossom, runs through all
Languages; which I have not observed of any other Metaphor, excepting
that of Fire and Burning when they are applied to Love. This shews that
we naturally regard Laughter, as what is in it self both amiable and
beautiful. For this Reason likewise
Venus
has gained the Title of
the Laughter-loving Dame, as
Waller
has
Translated it, and is represented by
Horace
as the Goddess who
delights in Laughter.
Milton
,
a joyous Assembly of imaginary
Persons
, has given us a very Poetical Figure of Laughter.
whole
Band of Mirth is so finely described, that I shall
set
down
the
Passage
at length.
But come thou Goddess fair and free,
In Heaven yeleped Euphrosyne,
And by Men, heart-easing Mirth,
Whom lovely Venus at a Birth,
With two Sister Graces more,
To Ivy-crowned Bacchus bore:
Haste thee, Nymph, and bring with thee
Jest and youthful jollity,
Quips and Cranks, and wanton Wiles,
Nods, and Becks, and wreathed Smiles,
Such as hang on Hebe's Cheek,
And love to live in Dimple sleek:
Sport that wrinkled Care derides,
And Laughter holding both his Sides.
Come, and trip it, as you go,
On the light fantastick Toe:
And in thy right Hand lead with thee
The Mountain Nymph, sweet Liberty;
And if I give thee Honour due,
Mirth, admit me of thy Crew,
To live with her, and live with thee,
In unreproved Pleasures free.
C.
Hobbes.
Sir Samuel Garth, poet and physician, who was alive at this
time (died in 1719), satirized a squabble among the doctors in his poem
of
the Dispensary
.
The piercing Caustics ply their spiteful Pow'r;
Emetics ranch, and been Cathartics sour.
The deadly Drugs in double Doses fly;
And Pestles peal a martial Symphony.
L'Allegro
.
set it
Contents
|
Monday, December 17, 1711 |
|
Disce docendus adhuc, quæ censet amiculus, ut si
Cæcus iter monstrare velit; tamen aspice si quid
Et nos, quod cures proprium fecisse, loquamur.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'You see the Nature of my Request by the
Latin Motto which I address
to you. I am very sensible I ought not to use many Words to you, who
are one of but few; but the following Piece, as it relates to
Speculation in Propriety of Speech, being a Curiosity in its Kind,
begs your Patience. It was found in a Poetical Virtuoso's Closet among
his Rarities; and since the several Treatises of Thumbs, Ears, and
Noses, have obliged the World, this of Eyes is at your Service.
'The first Eye of Consequence (under the invisible Author of all) is
the visible Luminary of the Universe. This glorious Spectator is said
never to open his Eyes at his Rising in a Morning, without having a
whole Kingdom of Adorers in
Persian Silk waiting at his Levée.
Millions of Creatures derive their Sight from this Original, who,
besides his being the great Director of Opticks, is the surest Test
whether Eyes be of the same Species with that of an Eagle, or that of
an Owl: The one he emboldens with a manly Assurance to look, speak,
act or plead before the Faces of a numerous Assembly; the other he
dazzles out of Countenance into a sheepish Dejectedness. The Sun-Proof
Eye dares lead up a Dance in a full Court; and without blinking at the
Lustre of Beauty, can distribute an Eye of proper Complaisance to a
Room crowded with Company, each of which deserves particular Regard;
while the other sneaks from Conversation, like a fearful Debtor, who
never dares
to look out, but when he can see no body, and no body
him.
The next Instance of Opticks is the famous
Argus, who (to speak in
the Language of
Cambridge) was one of an Hundred; and being used as
a Spy in the Affairs of Jealousy, was obliged to have all his Eyes
about him. We have no Account of the particular Colours, Casts and
Turns of this Body of Eyes; but as he was Pimp for his Mistress
Juno, 'tis probable he used all the modern Leers, sly Glances, and
other ocular Activities to serve his Purpose. Some look upon him as
the then King at Arms to the Heathenish Deities; and make no more of
his Eyes than as so many Spangles of his Herald's Coat.
The
next upon the Optick List is old
Janus, who stood in a
double-sighted Capacity, like a Person placed betwixt two opposite
Looking-Glasses, and so took a sort of retrospective Cast at one View.
Copies of this double-faced Way are not yet out of Fashion with many
Professions, and the ingenious Artists pretend to keep up this Species
by double-headed Canes and Spoons
1; but there is no Mark of this
Faculty, except in the emblematical Way of a wise General having an
Eye to both Front and Rear, or a pious Man taking a Review and
Prospect of his past and future State at the same Time.
I must own, that the Names, Colours, Qualities, and Turns of Eyes vary
almost in every Head; for, not to mention the common Appellations of
the Black, the Blue, the White, the Gray, and the like; the most
remarkable are those that borrow their Title
s from Animals, by
Vertue of some particular Quality or Resemblance they bear to the Eyes
of the respective Creature
s; as that of a greedy rapacious Aspect
takes its Name from the Cat, that of a sharp piercing Nature from the
Hawk, those of an amorous roguish Look derive their Title even from
the Sheep, and we say such a
n one has a Sheep's Eye, not so much to
denote the Innocence as the simple Slyness of the Cast: Nor is this
metaphorical Inoculation a modern Invention, for we find
Homer
taking the Freedom to place the Eye of an Ox, Bull, or Cow in one of
his principal Goddesses, by that frequent Expression of
Now as to the peculiar Qualities of the Eye, that fine Part of our
Constitution seems as much the Receptacle and Seat of our Passions,
Appetites and Inclinations as the Mind it self; and at least it is the
outward Portal to introduce them to the House within, or rather the
common Thorough-fare to let our Affections pass in and out. Love, Anger, Pride, and Avarice, all visibly
move in those little Orbs. I know a young Lady that can't see a certain
Gentleman pass by without shewing a secret Desire of seeing him again by
a Dance in her Eye-balls; nay, she can't for the Heart of her help
looking Half a Street's Length after any Man in a gay Dress. You can't
behold a covetous Spirit walk by a Goldsmith's Shop without casting a
wistful Eye at the Heaps upon the Counter. Does not a haughty Person
shew the Temper of his Soul in the supercilious Rowl of his Eye? and how
frequently in the Height of Passion does that moving Picture in our Head
start and stare, gather a Redness and quick Flashes of Lightning, and
make all its Humours sparkle with Fire,
as Virgil finely describes it.
—Ardentis ab ore
Scintillæ absistunt: oculis micat acribus ignis.3
As for the various Turns of
the Eye-sight, such as the voluntary or
involuntary, the half or the whole Leer, I shall not enter into a very
particular Account of them; but let me observe, that oblique Vision,
when natural, was anciently the Mark of Bewitchery and magical
Fascination, and to this Day 'tis a malignant ill Look; but when 'tis
forced and affected it carries a wanton Design, and in Play-houses,
and other publick Places, this ocular Intimation is often an
Assignation for bad Practices: But this Irregularity in Vision,
together with such Enormities as Tipping the Wink, the Circumspective
Rowl, the Side-peep through a thin Hood or Fan, must be put in the
Class of Heteropticks, as all wrong Notions of Religion are ranked
under the general Name of Heterodox. All the pernicious Applications
of Sight are more immediately under the Direction of a
Spectator; and
I hope you will arm your Readers against the Mischiefs which are daily
done by killing Eyes, in which you will highly oblige your wounded
unknown Friend,
T. B.
Mr.
Spectator,
You professed in several Papers your particular Endeavours in the
Province of
Spectator, to correct the Offences committed by Starers,
who disturb whole Assemblies without any Regard to Time, Place or
Modesty. You complained also, that a Starer is not usually a Person to
be convinced by Reason of the Thing, nor so easily rebuked, as to
amend by Admonitions. I thought therefore fit to acquaint you with a
convenient Mechanical Way, which may easily prevent or correct
Staring, by an Optical Contrivance of new Perspective-Glasses, short
and commodious like Opera Glasses, fit for short-sighted People as
well as others, these Glasses making the Objects appear, either as
they are seen by the naked Eye, or more distinct, though somewhat less
than Life, or bigger and nearer. A Person may, by the Help of this
Invention, take a View of another without the Impertinence of Staring;
at the same Time it shall not be possible to know whom or what he is
looking at. One may look towards his Right or Left Hand, when he is
supposed to look forwards: This is set forth at large in the printed
Proposals for the Sale of these Glasses, to be had at Mr.
Dillon's
in
Long-Acre, next Door to the
White-Hart. Now, Sir, as your
Spectator has occasioned the Publishing of this Invention for the
Benefit of modest Spectators, the Inventor desires your Admonitions
concerning the decent Use of it; and hopes, by your Recommendation,
that for the future Beauty may be beheld without the Torture and
Confusion which it suffers from the Insolence of Starers. By this
means you will relieve the Innocent from an Insult which there is no
Law to punish, tho' it is a greater Offence than many which are within
the Cognizance of Justice.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Abraham Spy.
Q.
Apostle spoons and others with fancy heads upon their handles.
The ox-eyed, venerable Juno.
Æn. 12, v. 101.
Contents
|
Tuesday, December 18, 1711 |
Addison |
Lingua centum sunt, oraque centum.
Ferrea Vox.
Virgil.

There is nothing which more astonishes a Foreigner, and frights a
Country Squire, than the
Cries of London
. My good Friend Sir
Roger
often declares, that he cannot get them out of his Head or go to Sleep
for them, the first Week that he is in Town. On the contrary,
Will.
Honeycomb
calls them the
Ramage de la Ville
, and prefers them to the
Sounds of Larks and Nightingales, with all the Musick of the Fields and
Woods. I have lately received a Letter from some very odd Fellow upon
this Subject, which I shall leave with my Reader, without saying any
thing further of it.
Sir,
"I am a Man of all Business, and would willingly turn my Head to any
thing for an honest Livelihood. I have invented several Projects for
raising many Millions of Money without burthening the Subject, but I
cannot get the Parliament to listen to me, who look upon me, forsooth,
as a Crack, and a Projector; so that despairing to enrich either my
self or my Country by this Publick-spiritedness, I
would make some
Proposals to you relating to a Design which I have very much at Heart,
and which may procure me
a1 handsome Subsistence, if you will be
pleased to recommend it to the Cities of
Londonand
Westminster.
The Post I would aim at, is to be Comptroller-General of the
London
Cries, which are at present under no manner of Rules or Discipline. I
think I am pretty well qualified for this Place, as being a Man of
very strong Lungs, of great Insight into all the Branches of our
BritishTrades and Manufactures, and of a competent Skill in Musick.
The Cries of
Londonmay be divided into Vocal and Instrumental. As
for the latter they are at present under a very great Disorder. A
Freeman of
Londonhas the Privilege of disturbing a whole Street for
an Hour together, with the Twanking of a Brass-Kettle or a Frying-Pan.
The Watchman's Thump at Midnight startles us in our Beds, as much as
the Breaking in of a Thief. The Sowgelder's Horn has indeed something
musical in it, but this is seldom heard within the Liberties. I would
therefore propose, that no Instrument of this Nature should be made
use of, which I have not tuned and licensed, after having carefully
examined in what manner it may affect the Ears of her Majesty's liege
Subjects.
Vocal Cries are of a much larger Extent, and indeed so full of
Incongruities and Barbarisms, that we appear a distracted City to
Foreigners, who do not comprehend the Meaning of such enormous
Outcries.
Milk is generally sold in a note above
Ela, and in Sounds
so
exceeding2 shrill, that it often sets our Teeth
on3 Edge.
The Chimney-sweeper is
confined4 to no certain
Pitch; he sometimes utters himself in the deepest Base, and sometimes
in the sharpest Treble; sometimes in the highest, and sometimes in the
lowest Note of the Gamut. The same Observation might be made on the
Retailers of Small-coal, not to mention broken Glasses or Brick-dust.
In these therefore, and the like Cases, it should be my Care to
sweeten and mellow the Voices of these itinerant Tradesmen, before
they make their Appearance in our Streets; as also to accommodate
their Cries to their respective Wares; and to take care in particular,
that those may not make the most Noise who have the least to sell,
which is very observable in the Venders of Card-matches, to whom I
cannot but apply that old Proverb of
Much Cry but little Wool.
'Some of these last mentioned Musicians are so very loud in the Sale
of these trifling Manufactures, that an honest Splenetick Gentleman of
my Acquaintance bargained with one of them never to come into the
Street where he lived: But what was the Effect of this Contract? Why,
the whole Tribe of Card-match-makers which frequent that Quarter,
passed by his Door the very next Day, in hopes of being bought off
after the same manner.
'It is another great Imperfection in our
LondonCries, that there is
no just Time nor Measure observed in them. Our News should indeed be
published in a very quick Time, because it is a Commodity that will
not keep cold. It should not, however, be cried with the same
Precipitation as Fire: Yet this is generally the Case. A Bloody Battle
alarms the Town from one End to another in an Instant. Every Motion of
the
Frenchis Published in so great a Hurry, that one would think
the Enemy were at our Gates. This likewise I would take upon me to
regulate in such a manner, that there should be some Distinction made
between the spreading of a Victory, a March, or an Incampment, a
Dutch, a
Portugalor a
SpanishMail. Nor must I omit under this
Head, those excessive Alarms with which several boisterous Rusticks
infest our Streets in Turnip Season; and which are more inexcusable,
because these are Wares which are in no Danger of Cooling upon their
Hands.
'There are others who affect a very slow Time, and are, in my Opinion,
much more tuneable than the former; the Cooper in particular swells
his last Note in an hollow Voice, that is not without its Harmony; nor
can I forbear being inspired with a most agreeable Melancholy, when I
hear that sad and solemn Air with which the Public are very often
asked, if they have any Chairs to mend? Your own Memory may suggest to
you many other lamentable Ditties of the same Nature, in which the
Musick is wonderfully languishing and melodious.
'I
am always pleased with that particular Time of the Year which is
proper for the pickling of Dill and Cucumbers; but alas, this Cry,
like the Song of the
Nightingale5, is not heard above two Months.
It would therefore be worth while to consider, whether the same Air
might not in some Cases be adapted to other Words.
'It might likewise deserve our most serious Consideration, how far, in
a well-regulated City, those Humourists are to be tolerated, who, not
contented with the traditional Cries of their Forefathers, have
invented particular Songs and Tunes of their own: Such as was, not
many Years since, the Pastryman, commonly known by the Name of the
Colly-Molly-Puff; and such as is at this Day the Vender of Powder and
Wash-balls, who, if I am rightly informed, goes under the Name of
Powder-Watt.
'I must not here omit one particular Absurdity which runs through this
whole vociferous Generation, and which renders their Cries very often
not only incommodious, but altogether useless to the Publick; I mean,
that idle Accomplishment which they all of them aim at, of Crying so
as not to be understood. Whether or no they have learned this from
several of our affected Singers, I will not take upon me to say; but
most certain it is, that People know the Wares they deal in rather by
their Tunes than by their Words; insomuch that I have sometimes seen a
Country Boy run out to buy Apples of a Bellows-mender, and Gingerbread
from a Grinder of Knives and Scissars. Nay so strangely infatuated are
some very eminent Artists of this particular Grace in a Cry, that none
but then Acquaintance are able to guess at their Profession; for who
else can know, that
Work if I had it, should be the Signification of
a Corn-Cutter?
'Forasmuch therefore as Persons of this Rank are seldom Men of Genius
or Capacity, I think it would be very proper, that some Man of good
Sense and sound Judgment should preside over these Publick Cries, who
should permit none to lift up their Voices in our Streets, that have
not tuneable Throats, and are not only able to overcome the Noise of
the Croud, and the Rattling of Coaches, but also to vend their
respective Merchandizes in apt Phrases, and in the most distinct and
agreeable Sounds. I do therefore humbly recommend my self as a Person
rightly qualified for this Post; and if I meet with fitting
Encouragement, shall communicate some other Projects which I have by
me, that may no less conduce to the Emolument of the Public.'
I am
Sir, &c.,
Ralph Crotchet.
an
exceedingly
an
contained
Nightingales
Contents
Dedication of the Fourth Volume of The Spectator
To The Duke of Marlborough1.
My
LORD,
As it is natural to have a Fondness for what has cost us so much Time
and Attention to produce, I hope Your Grace will forgive an endeavour to
preserve this Work from Oblivion, by affixing to it Your memorable Name.
I shall not here presume to mention the illustrious Passages of Your
Life, which are celebrated by the whole Age, and have been the Subject
of the most sublime Pens; but if I could convey You to Posterity in your
private Character, and describe the Stature, the Behaviour and Aspect of
the Duke of
Marlborough
, I question not but it would fill the Reader
with more agreeable Images, and give him a more delightful Entertainment
than what can be found in the following, or any other Book.
One cannot indeed without Offence, to Your self, observe, that You excel
the rest of Mankind in the least, as well as the greatest Endowments.
Nor were it a Circumstance to be mentioned, if the Graces and
Attractions of Your Person were not the only Preheminence You have above
others, which is left, almost, unobserved by greater Writers.
Yet how pleasing would it be to those who shall read the surprising
Revolutions in your Story, to be made acquainted with your ordinary Life
and Deportment? How pleasing would it be to hear that the same Man who
had carried Fire and Sword into the Countries of all that had opposed
the Cause of Liberty, and struck a Terrour into the Armies of
France
,
had, in the midst of His high Station, a Behaviour as gentle as is usual
in the first Steps towards Greatness? And if it were possible to express
that easie Grandeur, which did at once perswade and command; it would
appear as clearly to those to come, as it does to his Contemporaries,
that all the great Events which were brought to pass under the Conduct
of so well-govern'd a Spirit, were the Blessings of Heaven upon Wisdom
and Valour: and all which seem adverse fell out by divine Permission,
which we are not to search into.
have pass'd that Year of Life wherein the most able and fortunate
Captain, before Your Time, declared he had lived enough both to Nature
and to Glory
; and Your Grace may make that Reflection with much more
Justice. He spoke it after he had arrived at Empire, by an Usurpation
upon those whom he had enslaved; but the Prince of
Mindleheim
may
rejoice in a Sovereignty which was the Gift of Him whose Dominions he
had preserved.
Glory established upon the uninterrupted Success of honourable Designs
and Actions is not subject to Diminution; nor can any Attempts prevail
against it, but in the Proportion which the narrow Circuit of Rumour
bears to the unlimited Extent of Fame.
We may congratulate Your Grace not only upon your high Atchievements,
but likewise upon the happy Expiration of Your Command, by which your
Glory is put out of the Power of Fortune: And when your Person shall be
so too, that the Author and Disposer of all things may place You in that
higher Mansion of Bliss and Immortality which is prepared for good
Princes, Lawgivers, and Heroes, when
He
in
His
due Time removes them
from the Envy of Mankind, is the hearty Prayer of,
My
Lord
,
Your Grace's
Most Obedient,
Most Devoted
Humble Servant
,
The
Spectator
.
John Churchill, afterwards Duke of Marlborough, was at this
time 62 years old, and past the zenith of his fame. He was born at Ashe,
in Devonshire, in 1650, the son of Sir Winston Churchill, an adherent of
Charles I. At the age of twelve John Churchill was placed as page in the
household of the Duke of York. He first distinguished himself as a
soldier in the defence of Tangier against the Moors. Between 1672 and
1677 he served in the auxiliary force sent by our King Charles II. to
his master, Louis XIV. In 1672, after the siege of Maestricht, Churchill
was praised by Louis at the head of his army, and made
Lieutenant-colonel. Continuing in the service of the Duke of York,
Churchill, about 1680, married Sarah Jennings, favourite of the Princess
Anne. In 1682 Charles II. made Churchill a Baron, and three years
afterwards he was made Brigadier-general when sent to France to announce
the accession of James II. On his return he was made Baron Churchill of
Sandridge. He helped to suppress Monmouth's insurrection, but before the
Revolution committed himself secretly to the cause of the Prince of
Orange; was made, therefore, by William III., Earl of Marlborough and
Privy Councillor. After some military service he was for a short time
imprisoned in the Tower on suspicion of treasonous correspondence with
the exiled king. In 1697 he was restored to favour, and on the breaking
out of the War of the Spanish Succession in 1701 he was chief commander
of the Forces in the United Provinces. In this war his victories made
him the most famous captain of the age. In December, 1702, he was made
Duke, with a pension of five thousand a year. In the campaign of 1704
Marlborough planned very privately, and executed on his own
responsibility, the boldest and most distant march that had ever been
attempted in our continental wars. France, allied with Bavaria, was
ready to force the way to Vienna, but Marlborough, quitting the Hague,
carried his army to the Danube, where he took by storm a strong
entrenched camp of the enemy upon the Schellenberg, and cruelly laid
waste the towns and villages of the Bavarians, who never had taken arms;
but, as he said, 'we are now going to burn and destroy the Elector's
country, to oblige him to hearken to terms.' On the 13th of August, the
army of Marlborough having been joined by the army under Prince Eugene,
battle was given to the French and Bavarians under Marshal Tallard, who
had his head-quarters at the village of Plentheim, or Blenheim. At the
cost of eleven thousand killed and wounded in the armies of Marlborough
and Eugene, and fourteen thousand killed and wounded on the other side,
a decisive victory was secured, Tallard himself being made prisoner, and
26 battalions and 12 squadrons capitulating as prisoners of war. 121 of
the enemy's standards and 179 colours were brought home and hung up in
Westminster Hall. Austria was saved, and Louis XIV. utterly humbled at
the time when he had expected confidently to make himself master of the
destinies of Europe.
For this service Marlborough was made by the Emperor a Prince of the
Empire, and his 'Most Illustrious Cousin' as the Prince of Mindelsheim.
At home he was rewarded with the manor of Woodstock, upon which was
built for him the Palace of Blenheim, and his pension of £5000 from the
Post-office was annexed to his title. There followed other victories, of
which the series was closed with that of Malplaquet, in 1709, for which
a national thanksgiving was appointed. Then came a change over the face
of home politics. England was weary of the war, which Marlborough was
accused of prolonging for the sake of the enormous wealth he drew
officially from perquisites out of the different forms of expenditure
upon the army. The Tories gathered strength, and in the beginning of
1712 a commission on a charge of taking money from contractors for
bread, and 2 1/2 per cent, from the pay of foreign troops, having
reported against him, Marlborough was dismissed from all his
employments. Sarah, his duchess, had also been ousted from the Queen's
favour, and they quitted England for a time, Marlborough writing,
'Provided that my destiny does not involve any prejudice to the public,
I shall be very content with it; and shall account myself happy in a
retreat in which I may be able wisely to reflect on the vicissitudes of
this world.' It was during this season of his unpopularity that Steele
and Addison dedicated to the Duke of Marlborough the fourth volume of
the
Spectator
.
Julius Cæsar
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, December 19, 1711 |
Steele |
Erranti, passimque oculos per cuncta ferenti.
Virgil
1
Mr. Spectator,
'I am very sorry to find by your Discourse upon the Eye, 1 that you
have not thoroughly studied the Nature and Force of that Part of a
beauteous Face. Had you ever been in Love, you would have said ten
thousand things, which it seems did not occur to you: Do but reflect
upon the Nonsense it makes Men talk, the Flames which it is said to
kindle, the Transport it raises, the Dejection it causes in the
bravest Men; and if you do believe those things are expressed to an
Extravagance, yet you will own, that the Influence of it is very great
which moves Men to that Extravagance. Certain it is, that the whole
Strength of the Mind is sometimes seated there; that a kind Look
imparts all, that a Year's Discourse could give you, in one Moment.
What matters it what she says to you, see how she looks, is the
Language of all who know what Love is. When the Mind is thus summed up
and expressed in a Glance, did you never observe a sudden Joy arise in
the Countenance of a Lover? Did you never see the Attendance of Years
paid, over-paid in an Instant? You a
Spectator, and not know that the
Intelligence of Affection is carried on by the Eye only; that
Good-breeding has made the Tongue falsify the Heart, and act a Part of
continual Constraint, while Nature has preserved the Eyes to her self,
that she may not be disguised or misrepresented. The poor Bride can
give her Hand, and say,
I do, with a languishing Air, to the Man she
is obliged by cruel Parents to take for mercenary Reasons, but at the
same Time she cannot look as if she loved; her Eye is full of Sorrow,
and Reluctance sits in a Tear, while the Offering of the Sacrifice is
performed in what we call the Marriage Ceremony. Do you never go to
Plays? Cannot you distinguish between the Eyes of those who go to see,
from those who come to be seen? I am a Woman turned of Thirty, and am
on the Observation a little; therefore if you or your Correspondent
had consulted me in your Discourse on the Eye, I could have told you
that the Eye of
Leonora is slyly watchful while it looks negligent:
she looks round her without the Help of the Glasses you speak of, and
yet seems to be employed on Objects directly before her. This Eye is
what affects Chance-medley, and on a sudden, as if it attended to
another thing, turns all its Charms against an Ogler. The Eye of
Lusitania is an Instrument of premeditated Murder; but the Design
being visible, destroys the Execution of it; and with much more Beauty
than that of
Leonora, it is not half so mischievous. There is a
brave Soldier's Daughter in Town, that by her Eye has been the Death
of more than ever her Father made fly before him. A beautiful Eye
makes Silence eloquent, a kind Eye makes Contradiction an Assent, an
enraged Eye makes Beauty deformed. This little Member gives Life to
every other Part about us, and I believe the Story of
Argus implies
no more than that the Eye is in every Part, that is to say, every
other Part would be mutilated, were not its Force represented more by
the Eye than even by it self. But this is Heathen
Greek to those who
have not conversed by Glances. This, Sir, is a Language in which there
can be no Deceit, nor can a Skilful Observer be imposed upon by Looks
even among Politicians and Courtiers. If you do me the Honour to print
this among your Speculations, I shall in my next make you a Present of
Secret History, by Translating all the Looks of the next Assembly of
Ladies and Gentlemen into Words, to adorn some future Paper.
I am,
Sir,
Your faithful Friend,
Mary Heartfree.
Dear Mr.
Spectator,
I have a Sot of a Husband that lives a very scandalous Life, and
wastes away his Body and Fortune in Debaucheries; and is immoveable to
all the Arguments I can urge to him. I would gladly know whether in
some Cases a Cudgel may not be allowed as a good Figure of Speech, and
whether it may not be lawfully used by a Female Orator.
Your humble Servant,
Barbara Crabtree.
Mr.
Spectator2,
Though I am a Practitioner in the Law of some standing, and have heard
many eminent Pleaders in my Time, as well as other eloquent Speakers
of both Universities, yet I agree with you, that Women are better
qualified to succeed in Oratory than the Men, and believe this is to
be resolved into natural Causes. You have mentioned only the
Volubility of their Tongue; but what do you think of the silent
Flattery of their pretty Faces, and the Perswasion which even an
insipid Discourse carries with it when flowing from beautiful Lips, to
which it would be cruel to deny any thing? It is certain too, that
they are possessed of some Springs of Rhetorick which Men want, such
as Tears, fainting Fits, and the like, which I have seen employed upon
Occasion with good Success. You must know I am a plain Man and love my
Money; yet I have a Spouse who is so great an Orator in this Way, that
she draws from me what Sum she pleases. Every Room in my House is
furnished with Trophies of her Eloquence, rich Cabinets, Piles of
China, Japan Screens, and costly Jars; and if you were to come into my
great Parlour, you would fancy your self in an
India Ware-house:
Besides this she keeps a Squirrel, and I am doubly taxed to pay for
the China he breaks. She is seized with periodical Fits about the Time
of the Subscriptions to a new Opera, and is drowned in Tears after
having seen any Woman there in finer Cloaths than herself: These are
Arts of Perswasion purely Feminine, and which a tender Heart cannot
resist. What I would therefore desire of you, is, to prevail with your
Friend who has promised to dissect a Female Tongue, that he would at
the same time give us the Anatomy of a Female Eye, and explain the
Springs and Sluices which feed it with such ready Supplies of
Moisture; and likewise shew by what means, if possible, they may be
stopped at a reasonable Expence: Or, indeed, since there is something
so moving in the very Image of weeping Beauty, it would be worthy his
Art to provide, that these eloquent Drops may no more be lavished on
Trifles, or employed as Servants to their wayward Wills; but reserved
for serious Occasions in Life, to adorn generous Pity, true Penitence,
or real Sorrow.
I am, &c.
T.
quis Temeros oculus mihi fascinat Agnos
Virg.
This letter is by John Hughes.
Contents
|
Thursday, December 20, 1711 |
Addison |
Indignor quicquam reprehendi, non quia crasse
Compositum, illepideve putetur, sed quia nuper.
Hor.

There is nothing which more denotes a great Mind, than the Abhorrence of
Envy and Detraction. This Passion reigns more among bad Poets, than
among any other Set of Men.
As there are none more ambitious of Fame, than those who are conversant
in Poetry, it is very natural for such as have not succeeded in it to
depreciate the Works of those who have. For since they cannot raise
themselves to the Reputation of their Fellow-Writers, they must
endeavour to sink it to their own Pitch, if they would still keep
themselves upon a Level with them.
The
Wits that ever were produced in one Age, lived together in
so good an Understanding, and celebrated one another with so much
Generosity, that each of them receives an additional Lustre from his
Contemporaries, and is more famous for having lived with Men of so
extraordinary a Genius, than if he had himself been the
sole Wonder
of the Age. I need not tell my Reader, that I here point at the
Reign of
Augustus
, and I believe he will be of my Opinion, that
neither
Virgil
nor
Horace
would have gained so great a Reputation in
the World, had they not been the Friends and Admirers of each other.
Indeed all the great Writers of that Age, for whom singly we have so
great an Esteem, stand up together as Vouchers for one another's
Reputation. But at the same time that
Virgil
was celebrated by
Gallus, Propertius, Horace, Varius, Tucca
and
Ovid
, we know that
Bavius
and
Maevius
were his declared Foes and Calumniators.
In our own Country a Man seldom sets up for a Poet, without attacking
the Reputation of all his Brothers in the Art. The Ignorance of the
Moderns, the Scribblers of the Age, the Decay of Poetry, are the Topicks
of Detraction, with which he makes his Entrance into the World: But how
much more noble is the Fame that is built on Candour and Ingenuity,
according to those beautiful Lines of Sir
John Denham
, in his Poem on
Fletcher's
Works!
But whither am I strayed? I need not raise
Trophies to thee from other Mens Dispraise:
Nor is thy Fame on lesser Ruins built,
Nor needs thy juster Title the foul Guilt
Of Eastern Kings, who, to secure their Reign,
Must have their Brothers, Sons, and Kindred slain.
I am
to find that an Author, who is very justly esteemed among the
best Judges, has admitted some Stroaks of this Nature into a very fine
Poem; I mean
The Art of Criticism
, which was publish'd some Months
since, and is a Master-piece in its kind
. The Observations follow
one another like those in
Horace's Art of Poetry
, without that
methodical Regularity which would have been requisite in a Prose Author.
They are some of them uncommon, but such as the Reader must assent to,
when he sees them explained with that Elegance and Perspicuity in which
they are delivered. As for those which are the most known, and the most
received, they are placed in so beautiful a Light, and illustrated with
such apt Allusions, that they have in them all the Graces of Novelty,
and make the Reader, who was before acquainted with them, still more
convinced of their Truth and Solidity. And here give me leave to mention
what Monsieur
Boileau
has so very well enlarged upon in the Preface to
his Works, that Wit and fine Writing doth not consist so much in
advancing Things that are new, as in giving Things that are known an
agreeable Turn. It is impossible for us, who live in the lat
t
er Ages
of the World, to make Observations in Criticism, Morality, or in any Art
or Science, which have not been touched upon by others. We have little
else left us, but to represent the common Sense of Mankind in more
strong, more beautiful, or more uncommon Lights. If a Reader examines
Horace's Art of Poetry
, he will find but very few Precepts in it,
which he may not meet with in
Aristotle
, and which were not commonly
known by all the Poets of the
Augustan
Age. His Way of expressing and
applying them, not his Invention of them, is what we are chiefly to
admire.
For this Reason I think there is nothing in the World so tiresome as the
Works of those Criticks who write in a positive Dogmatick Way, without
either Language, Genius, or Imagination. If the Reader would see how the
best of the
Latin
Criticks writ, he may find their Manner very
beautifully described in the Characters of
Horace, Petronius,
Quintilian
, and
Longinus
, as they are drawn in the Essay of which I
am now speaking.
Since I have mentioned
Longinus
, who in his Reflections has given us
the same kind of Sublime, which he observes in the several passages that
occasioned them; I cannot but take notice, that our
English
Author has
after the same manner exemplified several of his Precepts in the very
Precepts themselves. I shall produce two or three Instances of this
Kind. Speaking of the insipid Smoothness which some Readers are so much
in Love with, he has the following Verses.
These Equal Syllables alone require,
Tho' oft the Ear the open Vowels tire,
While Expletives their feeble Aid do join,
And ten low Words oft creep in one dull Line.
The gaping of the Vowels in the second Line, the Expletive
do
in the
third, and the ten Monosyllables in the fourth, give such a Beauty to
this Passage, as would have been very much admired in an Ancient Poet.
The Reader may observe the following Lines in the same View.
A needless Alexandrine ends the Song,
That like a wounded Snake, drags its slow Length along.
And afterwards,
'Tis not enough no Harshness gives Offence,
The Sound must seem an Eccho to the Sense.
Soft is the Strain when Zephyr gently blows,
And the smooth Stream in smoother Numbers flows;
But when loud Surges lash the sounding Shore,
The hoarse rough Verse shou'd like the Torrent roar.
When Ajax strives some Rock's vast Weight to throw,
The Line too labours, and the Words move slow;
Not so, when swift Camilla scours the Plain,
Flies o'er th' unbending Corn, and skims along the Main.
The
Distich upon
Ajax
in the foregoing Lines, puts me in
mind of a Description in
Homer's
Odyssey, which none of the Criticks
have taken notice of
. It is where
Sisyphus
is represented lifting
his Stone up the Hill, which is no sooner carried to the top of it, but it immediately tumbles to the Bottom. This double Motion of the Stone is admirably described in the Numbers of these Verses; As in the four first it is heaved up by several
Spondees
intermixed with proper Breathing places, and at last trundles down in a continual Line of
Dactyls
.
It would be endless to quote Verses out of
Virgil
which have this particular Kind of Beauty in the Numbers; but I may take an Occasion in a future Paper to shew several of them which have escaped the Observation of others.
I
conclude this Paper without taking notice that we have three Poems in our Tongue, which are of the same Nature, and each of them a Master-Piece in its Kind; the Essay on Translated Verse
, the Essay on the Art of Poetry
, and the Essay upon Criticism.
single Product
At the time when this paper was written Pope was in his
twenty-fourth year. He wrote to express his gratitude to Addison and
also to Steele. In his letter to Addison he said,
'Though it be the highest satisfaction to find myself commended by a
Writer whom all the world commends, yet I am not more obliged to you
for that than for your candour and frankness in acquainting me with
the error I have been guilty of in speaking too freely of my brother
moderns.'
The only moderns of whom he spoke slightingly were men of whom
after-time has ratified his opinion: John Dennis, Sir Richard Blackmore,
and Luke Milbourne. When, not long afterwards, Dennis attacked with his
criticism Addison's Cato, to which Pope had contributed the Prologue,
Pope made this the occasion of a bitter satire on Dennis, called
The
Narrative of Dr. Robert Norris
(a well-known quack who professed the
cure of lunatics)
upon the Frenzy J. D
. Addison then, through Steele,
wrote to Pope's publisher of this 'manner of treating Mr. Dennis,' that
he 'could not be privy' to it, and 'was sorry to hear of it.' In 1715,
when Pope issued to subscribers the first volume of Homer, Tickell's
translation of the first book of the Iliad appeared in the same week,
and had particular praise at Button's from Addison, Tickell's friend and
patron. Pope was now indignant, and expressed his irritation in the
famous satire first printed in 1723, and, finally, with the name of
Addison transformed to Atticus, embodied in the Epistle to Arbuthnot
published in 1735. Here, while seeing in Addison a man
Blest with each talent and each art to please,
And born to live, converse, and write with ease,
he said that should he, jealous of his own supremacy, 'damn with faint
praise,' as one
Willing to wound, and yet afraid to strike,
Just hint the fault and hesitate dislike,
Who when two wits on rival themes contest,
Approves of both, but likes the worse the best:
Like Cato, give his little Senate laws,
And sits attentive to his own applause;
While wits and templars every sentence raise:
And wonder with a foolish face of praise:
Who would not laugh if such a man there be?
Who would not weep if Addison were he?
But in this
Spectator
paper young Pope's
Essay on Criticism
certainly was not damned with faint praise by the man most able to give
it a firm standing in the world.
Odyssey
Bk. XI. In Ticknell's edition of Addison's works
the latter part of this sentence is omitted; the same observation having
been made by Dionysius of Halicarnassus.
Wentworth Dillon, Earl of Roscommon, author of the 'Essay
on Translated Verse', was nephew and godson to Wentworth, Earl of
Strafford. He was born in Ireland, in 1633, educated at the Protestant
University of Caen, and was there when his father died. He travelled in
Italy, came to England at the Restoration, held one or two court
offices, gambled, took a wife, and endeavoured to introduce into England
the principals of criticism with which he had found the polite world
occupied in France. He planned a society for refining our language and
fixing its standard. During the troubles of King James's reign he was
about to leave the kingdom, when his departure was delayed by gout, of
which he died in 1684. A foremost English representative of the chief
literary movement of his time, he translated into blank verse Horace's
Art of Poetry, and besides a few minor translations and some short
pieces of original verse, which earned from Pope the credit that
in all Charles's days
Roscommon only boasts unspotted lays,
he wrote in heroic couplets an
Essay on Translated Verse
that was
admired by Dryden, Addison, and Pope, and was in highest honour wherever
the French influence upon our literature made itself felt. Roscommon
believed in the superior energy of English wit, and wrote himself with
care and frequent vigour in the turning of his couplets. It is from this
poem that we get the often quoted lines,
Immodest words admit of no Defence:
For Want of Decency is Want of Sense.
The other piece with which Addison ranks Pope's Essay on
Criticism, was by John Sheffield, Duke of Buckingham, who was living
when the
Spectator
first appeared. He died, aged 72, in the year 1721.
John Sheffield, by the death of his father, succeeded at the age of nine
to the title of Earl of Mulgrave. In the reign of Charles II he served
by sea and land, and was, as well as Marlborough, in the French service.
In the reign of James II. he was admitted into the Privy Council, made
Lord Chamberlain, and, though still Protestant, attended the King to
mass. He acquiesced in the Revolution, but remained out of office and
disliked King William, who in 1694 made him Marquis of Normanby.
Afterwards he was received into the Cabinet Council, with a pension of
£3000. Queen Anne, to whom Walpole says he had made love before her
marriage, highly favoured him. Before her coronation she made him Lord
Privy Seal, next year he was made first Duke of Normanby, and then of
Buckinghamshire, to exclude any latent claimant to the title, which had
been extinct since the miserable death of George Villiers, Duke of
Buckingham, the author of the
Rehearsal
. When the
Spectator
appeared
John Sheffield had just built Buckingham House—now a royal palace—on
ground granted by the Crown, and taken office as Lord Chamberlain. He
wrote more verse than Roscommon and poorer verse. The
Essay on Poetry
,
in which he followed the critical fashion of the day, he was praised
into regarding as a masterpiece. He was continually polishing it, and
during his lifetime it was reissued with frequent variations. It is
polished quartz, not diamond; a short piece of about 360 lines, which
has something to say of each of the chief forms of poetry, from songs to
epics. Sheffield shows most natural force in writing upon plays, and
here in objecting to perfect characters, he struck out the often-quoted
line
A faultless monster which the world ne'er saw.
When he comes to the epics he is, of course, all for Homer and Virgil.
Read Homer once, and you can read no more;
For all books else appear so mean, so poor,
Verse will seem Prose; but still persist to read,
And Homer will be all the Books you need.
And then it is supposed that 'some Angel' had disclosed to M. Bossu, the
French author of the treatise upon Epic Poetry then fashionable, the
sacred mysteries of Homer. John Sheffield had a patronizing recognition
for the genius of Shakespeare and Milton, and was so obliging as to
revise Shakespeare's Julius Cæsar and confine the action of that play
within the limits prescribed in the French gospel according to the
Unities. Pope, however, had in the Essay on Criticism reckoned
Sheffield, Duke of Buckingham, among the sounder few
Who durst assert the juster ancient Cause
And have restored Wit's Fundamental Laws.
Such was the Muse, whose Rules and Practice tell,
Nature's chief Masterpiece is writing well.
With those last words which form the second line in the
Essay on
Poetry
Pope's citation has made many familiar. Addison paid young Pope
a valid compliment in naming him as a critic in verse with Roscommon,
and, what then passed on all hands for a valid compliment, in holding
him worthy also to be named as a poet in the same breath with the Lord
Chamberlain.
Contents
|
Friday, December 21, 1711 |
Steele |
When I consider the false Impressions which are received by the
Generality of the World, I am troubled at none more than a certain
Levity of Thought, which many young Women of Quality have entertained,
to the Hazard of their Characters, and the certain Misfortune of their
Lives. The first of the following Letters may best represent the Faults
I would now point at, and the Answer to it the Temper of Mind in a
contrary Character.
My dear Harriot,
If thou art she, but oh how fallen, how changed, what an Apostate! how
lost to all that's gay and agreeable! To be married I find is to be
buried alive; I can't conceive it more dismal to be shut up in a Vault
to converse with the Shades of my Ancestors, than to be carried down
to an old Manor-House in the Country, and confined to the Conversation
of a sober Husband and an awkward Chamber-maid. For Variety I suppose
you may entertain yourself with Madam in her Grogram Gown, the Spouse
of your Parish Vicar, who has by this time I am sure well furnished
you with Receipts for making Salves and Possets, distilling Cordial
Waters, making Syrups, and applying Poultices.
Blest Solitude! I wish thee Joy, my Dear, of thy loved Retirement,
which indeed you would perswade me is very agreeable, and different
enough from what I have here described: But, Child, I am afraid thy
Brains are a little disordered with Romances and Novels: After six
Months Marriage to hear thee talk of Love, and paint the Country
Scenes so softly, is a little extravagant; one would think you lived
the Lives of Sylvan Deities, or roved among the Walks of Paradise,
like the first happy Pair. But pr'ythee leave these Whimsies, and come
to Town in order to live and talk like other Mortals. However, as I am
extremely interested in your Reputation, I would willingly give you a
little good Advice at your first Appearance under the Character of a
married Woman: 'Tis a little Insolence in me perhaps, to advise a
Matron; but I am so afraid you'll make so silly a Figure as a fond
Wife, that I cannot help warning you not to appear in any publick
Places with your Husband, and never to saunter about St. James's
Park together: If you presume to enter the Ring at Hide-Park
together, you are ruined for ever; nor must you take the least notice
of one another at the Play-house or Opera, unless you would be laughed
at for a very loving Couple most happily paired in the Yoke of
Wedlock. I would recommend the Example of an Acquaintance of ours to
your Imitation; she is the most negligent and fashionable Wife in the
World; she is hardly ever seen in the same Place with her Husband, and
if they happen to meet, you would think them perfect Strangers: She
never was heard to name him in his Absence, and takes care he shall
never be the Subject of any Discourse that she has a Share in. I hope
you'll propose this Lady as a Pattern, tho' I am very much afraid
you'll be so silly to think Portia, &c. Sabine and Roman Wives
much brighter Examples. I wish it may never come into your Head to
imitate those antiquated Creatures so far, as to come into Publick in
the Habit as well as Air of a Roman Matron. You make already the
Entertainment at Mrs. Modish's Tea-Table; she says, she always
thought you a discreet Person, and qualified to manage a Family with
admirable Prudence: she dies to see what demure and serious Airs
Wedlock has given you, but she says she shall never forgive your
Choice of so gallant a Man as Bellamour to transform him to a meer
sober Husband; 'twas unpardonable: You see, my Dear, we all envy your
Happiness, and no Person more than
Your humble Servant,
Lydia.
Be not in pain, good Madam, for my Appearance in Town; I shall
frequent no publick Places, or make any Visits where the Character of
a modest Wife is ridiculous. As for your wild Raillery on Matrimony,
'tis all Hypocrisy; you, and all the handsome young Women of our
Acquaintance, shew yourselves to no other Purpose than to gain a
Conquest over some Man of Worth, in order to bestow your Charms and
Fortune on him. There's no Indecency in the Confession, the Design is
modest and honourable, and all your Affectation can't disguise it.
I am married, and have no other Concern but to please the Man I Love;
he's the End of every Care I have; if I dress, 'tis for him; if I read
a Poem or a Play, 'tis to qualify myself for a Conversation agreeable
to his Taste: He's almost the End of my Devotions; half my Prayers are
for his Happiness. I love to talk of him, and never hear him named but
with Pleasure and Emotion. I am your Friend, and wish your Happiness,
but am sorry to see by the Air of your Letter that there are a Set of
Women who are got into the Common-Place Raillery of every Thing that
is sober, decent, and proper: Matrimony and the Clergy are the Topicks
of People of little Wit and no Understanding. I own to you, I have
learned of the Vicar's Wife all you tax me with: She is a discreet,
ingenious, pleasant, pious Woman; I wish she had the handling of you
and Mrs. Modish; you would find, if you were too free with her, she
would soon make you as charming as ever you were, she would make you
blush as much as if you had never been fine Ladies. The Vicar, Madam,
is so kind as to visit my Husband, and his agreeable Conversation has
brought him to enjoy many sober happy Hours when even I am shut out,
and my dear Master is entertained only with his own Thoughts. These
Things, dear Madam, will be lasting Satisfactions, when the fine
Ladies, and the Coxcombs by whom they form themselves, are irreparably
ridiculous, ridiculous in old Age.
I am, Madam, your most humble
Servant,
Mary Home.
Dear Mr. Spectator,
You have no Goodness in the World, and are not in earnest in any thing
you say that is serious, if you do not send me a plain Answer to this:
I happened some Days past to be at the Play, where during the Time of
Performance, I could not keep my Eyes off from a beautiful young
Creature who sat just before me, and who I have been since informed
has no Fortune. It would utterly ruin my Reputation for Discretion to
marry such a one, and by what I can learn she has a Character of great
Modesty, so that there is nothing to be thought on any other Way. My
Mind has ever since been so wholly bent on her, that I am much in
danger of doing something very extravagant without your speedy Advice
to,
Sir, Your most humble Servant.
I am sorry I cannot answer this impatient Gentleman, but by another
Question.
Dear Correspondent, Would you marry to please other People, or your
self?
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 22, 1711 |
Addison |
Laudis amore tumes? sunt certa piacula, quæ te
Ter pure lecto poterunt recreare libello.
Hor.

The Soul, considered abstractedly from its Passions, is of a remiss and
sedentary Nature, slow in its Resolves, and languishing in its
Executions. The Use therefore of the Passions is to stir it up, and to
put it upon Action, to awaken the Understanding, to enforce the Will,
and to make the whole Man more vigorous and attentive in the
Prosecutions of his Designs. As this is the End of the Passions in
general, so it is particularly of Ambition, which pushes the Soul to
such Actions as are apt to procure Honour and Reputation to the Actor.
But if we carry our Reflections higher, we may discover further Ends of
Providence in implanting this Passion in Mankind.
It was necessary for the World, that Arts should be invented and
improved, Books written and transmitted to Posterity, Nations conquered
and civilized: Now since the proper and genuine Motives to these and the
like great Actions, would only influence virtuous Minds; there would be
but small Improvements in the World, were there not some common
Principle of Action working equally with all Men.
such a Principle
is Ambition or a Desire of Fame, by which
great
Endowments are not
suffered to lie idle and useless to the Publick, and many vicious Men
over-reached, as it were, and engaged contrary to their natural
Inclinations in a glorious and laudable Course of Action. For we may
further observe, that Men of the greatest Abilities are most fired with
Ambition: And
on the contrary, mean and narrow Minds are the least
actuated by it: whether it be that
a Man's Sense of his own
Incapacities makes
him
despair of coming at Fame, or that
he has
not enough range of Thought to look out for any Good which does not
more immediately relate to
his
Interest or Convenience, or that
Providence, in the very Frame of
his Soul
, would not subject
him
to such a Passion as would be useless to the World, and a Torment
to
himself
.
Were not this Desire of Fame very strong, the Difficulty of obtaining
it, and the Danger of losing it when obtained, would be sufficient to
deter a Man from so vain a Pursuit.
How few are there who are furnished with Abilities sufficient to
recommend their Actions to the Admiration of the World, and to
distinguish themselves from the rest of Mankind? Providence for the most
part sets us upon a Level, and observes a kind of Proportion in its
Dispensation towards us. If it renders us perfect in one Accomplishment,
it generally leaves us defective in another, and seems careful rather of
preserving every Person from being mean and deficient in his
Qualifications, than of making any single one eminent or extraordinary.
And among those who are the most richly endowed by Nature, and
accomplished by their own Industry, how few are there whose Virtues are
not obscured by the Ignorance, Prejudice or Envy of their Beholders?
Some Men cannot discern between a noble and a mean Action. Others are
apt to attribute them to some false End or Intention; and others
purposely misrepresent or put a wrong Interpretation on them. But the
more to enforce this Consideration, we may observe that those are
generally most unsuccessful in their Pursuit after Fame, who are most
desirous of obtaining it. It
Salust's
Remark upon
Cato
, that the
less he coveted Glory, the more he acquired it
.
Men take an ill-natur'd Pleasure in crossing our Inclinations, and
disappointing us in what our Hearts are most set upon. When therefore
they have discovered the passionate Desire of Fame in the Ambitious Man
(as no Temper of Mind is more apt to show it self) they become sparing
and reserved in their Commendations, they envy him the Satisfaction of
an Applause, and look on their Praises rather as a Kindness done to his
Person, than as a Tribute paid to his Merit. Others who are free from
this natural Perverseness of Temper grow wary in their Praises of one,
who sets too great a Value on them, lest they should raise him too high
in his own Imagination, and by Consequence remove him to a greater
Distance from themselves.
But further, this Desire of Fame naturally betrays the ambitious Man
into such Indecencies as are a lessening to his Reputation. He is still
afraid lest any of his Actions should be thrown away in private, lest
his Deserts should be concealed from the Notice of the World, or receive
any Disadvantage from the Reports which others make of them. This often
sets him on empty Boasts and Ostentations of himself, and betrays him
into vain fantastick Recitals of his own Performances: His Discourse
generally leans one Way, and, whatever is the Subject of it, tends
obliquely either to the detracting from others, or to the extolling of
himself. Vanity is the natural Weakness of an ambitious Man, which
exposes him to the secret Scorn and Derision of those he converses with,
and ruins the Character he is so industrious to advance by it. For tho'
his Actions are never so glorious, they lose their Lustre when they are
drawn at large, and set to show by his own Hand; and as the World is
more apt to find fault than to commend, the Boast will probably be
censured when the great Action that occasioned it is forgotten.
this very Desire of Fame is looked on as a Meanness
and
Imperfection in the greatest Character. A solid and substantial
Greatness of Soul looks down with a generous Neglect on the Censures and
Applauses of the Multitude, and places a Man beyond the little Noise and
Strife of Tongues. Accordingly we find in our selves a secret Awe and
Veneration for the Character of one who moves above us in a regular and
illustrious Course of Virtue, without any regard to our good or ill
Opinions of him, to our Reproaches or Commendations. As on the contrary
it is usual for us, when we would take off from the Fame and Reputation
of an Action, to ascribe it to Vain-Glory, and a Desire of Fame in the
Actor. Nor is this common Judgment and Opinion of Mankind ill-founded:
for certainly it denotes no great Bravery of Mind to be worked up to any
noble Action by so selfish a Motive, and to do that out of a Desire of
Fame, which we could not be prompted to by a disinterested Love to
Mankind, or by a generous Passion for the Glory of him that made us.
Thus is
a thing difficult to be obtained by all, but particularly
by those who thirst after it, since most Men have so much either of
Ill-nature, or of Wariness, as not to gratify
or
sooth the Vanity
of the Ambitious Man, and since this very Thirst after Fame naturally
betrays him into such Indecencies as are a lessening to his Reputation,
and is it self looked upon as a Weakness in the greatest Characters.
In the next Place, Fame is easily lost, and as difficult to be preserved
as it was at first to be acquired. But this I shall make the Subject of
a following Paper
C.
all great
the Sense of their own
them
they have
their
their Souls
them
themselves
Sallust.
Bell. Catil
. c. 49.
and an
and
Contents
|
Monday, December 24, 1711 |
Addison |
There are many Passions and Tempers of Mind which naturally dispose us
to depress and vilify the Merit of one rising in the Esteem of Mankind.
All those who made their Entrance into the World with the same
Advantages, and were once looked on as his Equals, are apt to think the
Fame of his Merits a Reflection on their own Indeserts; and will
therefore take care to reproach him with the Scandal of some past
Action, or derogate from the Worth of the present, that they may still
keep him on the same Level with themselves. The like Kind of
Consideration often stirs up the Envy of such as were once his
Superiors, who think it a Detraction from their Merit to see another get
ground upon them and overtake them in the Pursuits of Glory; and will
therefore endeavour to sink his Reputation, that they may the better
preserve their own. Those who were once his Equals envy and defame him,
because they now see him their Superior; and those who were once his
Superiors, because they look upon him as their Equal.
But further, a Man whose extraordinary Reputation thus lifts him up to
the Notice and Observation of Mankind draws a Multitude of Eyes upon him
that will narrowly inspect every Part of him, consider him nicely in all
Views, and not be a little pleased when they have taken him in the worst
and most disadvantageous Light. There are many who find a Pleasure in
contradicting the common Reports of Fame, and in spreading abroad the
Weaknesses of an exalted Character. They publish their ill-natur'd
Discoveries with a secret Pride, and applaud themselves for the
Singularity of their Judgment which has searched deeper than others,
detected what the rest of the World have overlooked, and found a Flaw in
what the Generality of Mankind admires. Others there are who proclaim
the Errors and Infirmities of a great Man with an inward Satisfaction
and Complacency, if they discover none of the like Errors and
Infirmities in themselves; for while they are exposing another's
Weaknesses, they are tacitly aiming at their own Commendations, who are
not subject to the like Infirmities, and are apt to be transported with
a secret kind of Vanity to see themselves superior in some respects to
one of a sublime and celebrated Reputation. Nay, it very often happens,
that none are more industrious in publishing the Blemishes of an
extraordinary Reputation, than such as lie open to the same Censures in
their own Characters, as either hoping to excuse their own Defects by
the Authority of so high an Example, or raising an imaginary Applause to
themselves for resembling a Person of an exalted Reputation, though in
the blameable Parts of his Character. If all these secret Springs of
Detraction fail, yet very often a vain Ostentation of Wit sets a Man on
attacking an established Name, and sacrificing it to the Mirth and
Laughter of those about him. A Satyr or a Libel on one of the common
Stamp, never meets with that Reception and Approbation among its
Readers, as what is aimed at a Person whose Merit places him upon an
Eminence, and gives him a more conspicuous Figure among Men. Whether it
be that we think it shews greater Art to expose and turn to ridicule a
Man whose Character seems so improper a Subject for it, or that we are
pleased by some implicit kind of Revenge to see him taken down and
humbled in his Reputation, and in some measure reduced to our own Rank,
who had so far raised himself above us in the Reports and Opinions of
Mankind.
Thus we see how many dark and intricate Motives there are to Detraction
and Defamation, and how many malicious Spies are searching into the
Actions of a great Man, who is not always the best prepared for so
narrow an Inspection. For we may generally observe, that our Admiration
of a famous Man lessens upon our nearer Acquaintance with him; and that
we seldom hear the Description of a celebrated Person, without a
Catalogue of some notorious Weaknesses and Infirmities. The Reason may
be, because any little Slip is more conspicuous and observable in his
Conduct than in another's, as it is not of a piece with the rest of his
Character, or
it is impossible for a Man at the same time to be
attentive to the more important
Part
of his Life, and to keep a
watchful Eye over all the inconsiderable Circumstances of his Behaviour
and Conversation; or because, as we have before observed, the same
Temper of Mind which inclines us to a Desire of Fame, naturally betrays
us into such Slips and Unwarinesses as are not incident to Men of a
contrary Disposition.
After all it must be confess'd, that a noble and triumphant Merit often
breaks through and dissipates these little Spots and Sullies in its
Reputation; but if by a mistaken Pursuit after Fame, or through human
Infirmity, any false Step be made in the more momentous Concerns of
Life, the whole Scheme of ambitious Designs is broken and disappointed.
The smaller Stains and Blemishes may die away and disappear amidst the
Brightness that surrounds them; but a Blot of a deeper Nature casts a
Shade on all the other Beauties, and darkens the whole Character. How
difficult therefore is it to preserve a great Name, when he that has
acquired it is so obnoxious to such little Weaknesses and Infirmities as
are no small Diminution to it when discovered, especially when they are
so industriously proclaimed, and aggravated by such as were once his
Superiors or Equals; by such as would set to show their Judgment or
their Wit, and by such as are guilty or innocent of the same Slips or
Misconducts in their own Behaviour?
But were there none of these Dispositions in others to censure a famous
Man, nor any such Miscarriages in himself, yet would he meet with no
small Trouble in keeping up his Reputation in all its Height and
Splendour. There must be always a noble Train of Actions to preserve his
Fame in Life and Motion. For when it is once at a Stand, it naturally
flags and languishes. Admiration is a very short-liv'd Passion, that
immediately decays upon growing familiar with its Object, unless it be
still fed with fresh Discoveries, and kept alive by a new perpetual
Succession of Miracles rising up to its View. And
the greatest
Actions of a celebrated
Person
labour under this Disadvantage,
that however surprising and extraordinary they may be, they are no more
than what are expected from him; but on the contrary, if they fall any
thing below the Opinion that is conceived of him, tho' they might raise
the Reputation of another, they are a Diminution to
his
.
One would think there should be something wonderfully pleasing in the
Possession of Fame, that, notwithstanding all these mortifying
Considerations, can engage a Man in so desperate a Pursuit; and yet if
we consider the little Happiness that attends a great Character, and the
Multitude of Disquietudes to which the Desire of it subjects an
ambitious Mind, one would be still the more surprised to see so many
restless Candidates for Glory.
Ambition raises a secret Tumult in the Soul, it inflames the Mind, and
puts it into a violent Hurry of Thought: It is still reaching after an
empty imaginary Good, that has not in it the Power to abate or satisfy
it. Most other Things we long for can allay the Cravings of their proper
Sense, and for a while set the Appetite at Rest: But Fame is a Good so
wholly foreign to our Natures, that we have no Faculty in the Soul
adapted to it, nor any Organ in the Body to relish it; an Object of
Desire placed out of the Possibility of Fruition. It may indeed fill the
Mind for a while with a giddy kind of Pleasure, but it is such a
Pleasure as makes a Man restless and uneasy under it; and which does not
so much satisfy the present Thirst, as it excites fresh Desires, and
sets the Soul on new Enterprises. For how few ambitious Men are there,
who have got as much Fame as they desired, and whose Thirst after it has
not been as eager in the very Height of their Reputation, as it was
before they became known and eminent among Men?
is not any
Circumstance in
Cæsar's
Character which gives me a greater Idea of
him, than a Saying which
Cicero
tells us
he frequently made use
of in private Conversation,
That he was satisfied with his Share of
Life and Fame, Se satis vel ad Naturam, vel ad Gloriam vixisse
. Many
indeed have given over their Pursuits after Fame, but that has proceeded
either from the Disappointments they have met in it, or from their
Experience of the little Pleasure which attends it, or from the better
Informations or natural Coldness of old Age; but seldom from a full
Satisfaction and Acquiescence in their present Enjoyments of it.
Nor is Fame only unsatisfying in it self, but the Desire of it lays us
open to many accidental Troubles which those are free from who have no
such a tender Regard for it. How often is the ambitious Man cast down
and disappointed, if he receives no Praise where he expected it? Nay how
often is he mortified with the very Praises he receives, if they do not
rise so high as he thinks they ought, which they seldom do unless
increased by Flattery, since few Men have so good an Opinion of us as we
have of our selves? But if the ambitious Man can be so much grieved even
with Praise it self, how will he be able to bear up under Scandal and
Defamation? For the same Temper of Mind which makes him desire Fame,
makes him hate Reproach. If he can be transported with the extraordinary
Praises of Men, he will be as much dejected by their Censures. How
little therefore is the Happiness of an ambitious Man, who gives every
one a Dominion over it, who thus subjects himself to the good or ill
Speeches of others, and puts it in the Power of every malicious Tongue
to throw him into a Fit of Melancholy, and destroy his natural Rest and
Repose of Mind? Especially when we consider that the World is more apt
to censure than applaud, and himself fuller of Imperfections than
Virtues.
We may further observe, that such a Man will be more grieved for the
Loss of Fame, than he could have been pleased with the Enjoyment of it.
For tho' the Presence of this imaginary Good cannot make us happy, the
Absence of it may make us miserable: Because in the Enjoyment of an
Object we only find that Share of Pleasure which it is capable of giving
us, but in the Loss of it we do not proportion our Grief to the real
Value it bears, but to the Value our Fancies and Imaginations set upon
it.
So inconsiderable is the Satisfaction that Fame brings along with it,
and so great the Disquietudes, to which it makes us liable. The Desire
of it stirs up very uneasy Motions in the Mind, and is rather inflamed
than satisfied by the Presence of the Thing desired. The Enjoyment of it
brings but very little Pleasure, tho' the Loss or Want of it be very
sensible and afflicting; and even this little Happiness is so very
precarious, that it wholly depends on the Will of others.
are not
only tortured by the Reproaches which are offered us, but are
disappointed by the Silence of Men when it is unexpected; and humbled
even by their Praises
.
C.
Parts
Name
Oratio pro M. Marcello
.
I shall conclude this Subject in my next Paper.
Contents
|
Tuesday, December 25, 17111 |
Addison |
That I might not lose myself upon a Subject of so great Extent as that
of Fame, I have treated it in a particular Order and Method. I have
first of all considered the Reasons why Providence may have implanted in
our Mind such a Principle of Action. I have in the next Place shewn from
many Considerations, first, that Fame is a thing difficult to be
obtained, and easily lost; Secondly, that it brings the ambitious Man
very little Happiness, but subjects him to much Uneasiness and
Dissatisfaction. I shall in the last Place shew, that it hinders us from
obtaining an End which we have Abilities to acquire, and which is
accompanied with Fulness of Satisfaction. I need not tell my Reader,
that I mean by this End that Happiness which is reserved for us in
another World, which every one has Abilities to procure, and which will
bring along with it Fulness of Joy and Pleasures for evermore.
How the Pursuit after Fame may hinder us in the Attainment of this great
End, I shall leave the Reader to collect from the three following
Considerations.
First
, Because the strong Desire of Fame breeds several vicious Habits
in the Mind.
Secondly
, Because many of those Actions, which are apt to procure
Fame, are not in their Nature conducive to this our ultimate Happiness.
Thirdly
, Because if we should allow the same Actions to be the proper
Instruments, both of acquiring Fame, and of procuring this Happiness,
they would nevertheless fail in the Attainment of this last End, if they
proceeded from a Desire of the first.
These three Propositions are self-evident to those who are versed in
Speculations of Morality. For which Reason I shall not enlarge upon
them, but proceed to a Point of the same Nature, which may open to us a
more uncommon Field of Speculation.
From what has been already observed, I think we may make a natural
Conclusion, that it is the greatest Folly to seek the Praise or
Approbation of any Being, besides the Supreme, and that for these two
Reasons, Because no other Being can make a right Judgment of us, and
esteem us according to our Merits; and because we can procure no
considerable Benefit or Advantage from the Esteem and Approbation of any
other Being.
In the first Place, No other Being can make a right Judgment of us, and
esteem us according to our Merits. Created Beings see nothing but our
Outside, and can
therefore
only frame a Judgment of us from our
exterior Actions and Behaviour; but how unfit these are to give us a
right Notion of each other's Perfections, may appear from several
Considerations. There are many Virtues, which in their own Nature are
incapable of any outward Representation: Many silent Perfections in the
Soul of a good Man, which are great Ornaments to human Nature, but not
able to discover themselves to the Knowledge of others; they are
transacted in private, without Noise or Show, and are only visible to
the great Searcher of Hearts. What Actions can express the entire Purity
of Thought which refines and sanctifies a virtuous Man? That secret Rest
and Contentedness of Mind, which gives him a Perfect Enjoyment of his
present Condition? That inward Pleasure and Complacency, which he feels
in doing Good? That Delight and Satisfaction which he takes in the
Prosperity and Happiness of another? These and the like Virtues are the
hidden Beauties of a Soul, the secret Graces which cannot be discovered
by a mortal Eye, but make the Soul lovely and precious in His Sight,
from whom no Secrets are concealed. Again, there are many Virtues which
want an Opportunity of exerting and shewing themselves in Actions. Every
Virtue requires Time and Place, a proper Object and a fit Conjuncture of
Circumstances, for the due Exercise of it. A State of Poverty obscures
all the Virtues of Liberality and Munificence. The Patience and
Fortitude of a Martyr or Confessor lie concealed in the flourishing
Times of Christianity. Some Virtues are only seen in Affliction, and
some in Prosperity; some in a private, and others in a publick Capacity.
But the great Sovereign of the World beholds every Perfection in its
Obscurity, and not only sees what we do, but what we would do. He views
our Behaviour in every Concurrence of Affairs, and sees us engaged in
all the Possibilities of Action. He discovers the Martyr and Confessor
without the Tryal of Flames and Tortures, and will hereafter entitle
many to the Reward of Actions, which they had never the Opportunity of
Performing. Another Reason why Men cannot form a right Judgment of us
is, because the same Actions may be aimed at different Ends, and arise
from quite contrary Principles. Actions are of so mixt a Nature, and so
full of Circumstances, that as Men pry into them more or less, or
observe some Parts more than others, they take different Hints, and put
contrary Interpretations on them; so that the same Actions may represent
a Man as hypocritical and designing to one, which make him appear a
Saint or Hero to another. He therefore who looks upon the Soul through
its outward Actions, often sees it through a deceitful Medium, which is
apt to discolour and pervert the Object: So that on this Account also,
He
is the only proper Judge of our Perfections, who does not guess at
the Sincerity of our Intentions from the Goodness of our Actions, but
weighs the Goodness of our Actions by the Sincerity of our Intentions.
But further; it is impossible for outward Actions to represent the
Perfections of the Soul, because they can never shew the Strength of
those Principles from whence they proceed. They are not adequate
Expressions of our Virtues, and can only shew us what Habits are in the
Soul, without discovering the Degree and Perfection of such Habits. They
are at best but weak Resemblances of our Intentions, faint and imperfect
Copies that may acquaint us with the general Design, but can never
express the Beauty and Life of the Original. But the great Judge of all
the Earth knows every different State and Degree of human Improvement,
from those weak Stirrings and Tendencies of the Will which have not yet
formed themselves into regular Purposes and Designs, to the last entire
Finishing and Consummation of a good Habit. He beholds the first
imperfect Rudiments of a Virtue in the Soul, and keeps a watchful Eye
over it in all its Progress, 'till it has received every Grace it is
capable of, and appears in its full Beauty and Perfection. Thus we see
that none but the Supreme Being can esteem us according to our proper
Merits, since all others must judge of us from our outward Actions,
which can never give them a just Estimate of us, since there are many
Perfections of a Man which are not capable of appearing in Actions; many
which, allowing no natural Incapacity of shewing themselves, want an
Opportunity of doing it; or should they all meet with an Opportunity of
appearing by Actions, yet those Actions maybe misinterpreted, and
applied to wrong Principles; or though they plainly discovered the
Principles from whence they proceeded, they could never shew the Degree,
Strength and Perfection of those Principles.
And as the Supreme Being is the only proper Judge of our Perfections, so
is He the only fit Rewarder of them. This is a Consideration that comes
home to our Interest, as the other adapts it self to our Ambition. And
what could the most aspiring, or the most selfish Man desire more, were
he to form the Notion of a Being to whom he would recommend himself,
than such a Knowledge as can discover the least Appearance of Perfection
in him, and such a Goodness as will proportion a Reward to it.
Let the ambitious Man therefore turn all his Desire of Fame this Way;
and, that he may propose to himself a Fame worthy of his Ambition, let
him consider that if he employs his Abilities to the best Advantage, the
Time will come when the supreme Governor of the World, the great Judge
of Mankind, who sees every Degree of Perfection in others, and possesses
all possible Perfection in Himself, shall proclaim His Worth before Men
and Angels, and pronounce to him in the Presence of the whole Creation
that best and most significant of Applauses,
Well done, thou good and
faithful Servant, enter thou into thy Master's Joy
.
C.
This being Christmas Day, Addison has continued to it a
religious strain of thought.
Contents
|
Wednesday, December 26, 1711 |
Steele |
Divide et Impera.
Pleasure and Recreation of one Kind or other are absolutely necessary to
relieve our Minds and Bodies from too constant Attention and Labour:
Where therefore publick Diversions are tolerated, it behoves Persons of
Distinction, with their Power and Example, to preside over them in such
a Manner as to check any thing that tends to the Corruption of Manners,
or which is too mean or trivial for the Entertainment of reasonable
Creatures. As to the Diversions of this Kind in this Town, we owe them
to the Arts of Poetry and Musick: My own private Opinion, with Relation
to such Recreations, I have heretofore given with all the Frankness
imaginable; what concerns those Arts at present the Reader shall have
from my Correspondents. The first of the Letters with which I acquit
myself for this Day, is written by one who proposes to improve our
Entertainments of Dramatick Poetry, and the other comes from three
Persons, who, as soon as named, will be thought capable of advancing the
present State of Musick.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am considerably obliged to you for your speedy Publication of my
last in yours of the 18th Instant, and am in no small Hopes of being
settled in the Post of
Comptroller of the Cries. Of all the
Objections I have hearkened after in publick Coffee-houses there is
but one that seems to carry any Weight with it,
viz. That such a
Post would come too near the Nature of a Monopoly. Now, Sir, because I
would have all Sorts of People made easy, and being willing to have
more Strings than one to my Bow; in case that of
Comptroller should
fail me, I have since formed another Project, which, being grounded on
the dividing a present Monopoly, I hope will give the Publick an
Equivalent to their full Content. You know, Sir, it is allowed that
the Business of the Stage is, as the
Latin has it,
Jucunda et
Idonea dicere Vitæ. Now there being but one Dramatick Theatre
licensed for the Delight and Profit of this extensive Metropolis, I do
humbly propose, for the Convenience of such of its Inhabitants as are
too distant from
Covent-Garden, that another
Theatre of Ease may
be erected in some spacious Part of the City; and that the Direction
thereof may be made a Franchise in Fee to me, and my Heirs for ever.
And
that the Town may have no Jealousy of my ever coming to an Union
with the Set of Actors now in being, I do further propose to
constitute for my Deputy my near Kinsman and Adventurer,
Kit
Crotchet1, whose long Experience and Improvements in those Affairs
need no Recommendation. 'Twas obvious to every Spectator what a quite
different Foot the Stage was upon during his Government; and had he
not been bolted out of his Trap-Doors, his Garrison might have held
out for ever, he having by long Pains and Perseverance arriv'd at the
Art of making his Army fight without Pay or Provisions. I must confess
it, with a melancholy Amazement, I see so wonderful a Genius laid
aside, and the late Slaves of the Stage now become its Masters, Dunces
that will be sure to suppress all Theatrical Entertainments and
Activities that they are not able themselves to shine in!
Every Man that goes to a Play is not obliged to have either Wit or
Understanding; and I insist upon it, that all who go there should see
something which may improve them in a Way of which they are capable.
In short, Sir, I would have something
done as well as
said on the
Stage. A Man may have an active Body, though he has not a quick
Conception; for the Imitation therefore of such as are, as I may so
speak, corporeal Wits or nimble Fellows, I would fain ask any of the
present Mismanagers, Why should not Rope-dancers, Vaulters, Tumblers,
Ladder-walkers, and Posture-makers appear again on our Stage? After
such a Representation, a Five-bar Gate would be leaped with a better
Grace next Time any of the Audience went a Hunting. Sir, these Things
cry loud for Reformation and fall properly under the Province of
Spectator General; but how indeed should it be otherwise, while
Fellows (that for Twenty Years together were never paid but as their
Master was in the Humour) now presume to pay others more than ever
they had in their Lives; and in Contempt of the Practice of Persons of
Condition, have the Insolence to owe no Tradesman a Farthing at the
End of the Week. Sir, all I propose is the publick Good; for no one
can imagine I shall ever get a private Shilling by it: Therefore I
hope you will recommend this Matter in one of your this Week's Papers,
and desire when my House opens you will accept the Liberty of it for
the Trouble you have receiv'd from,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Ralph Crotchet.
P. S. I have Assurances that the Trunk-maker will declare for us.
Mr.
Spectator,
"We
whose Names are subscribed
2, think you the properest Person to
signify what we have to offer the Town in Behalf of our selves, and
the Art which we profess,
Musick. We conceive Hopes of your Favour
from the Speculations on the Mistakes which the Town run into with
Regard to their Pleasure of this Kind; and believing your Method of
judging is, that you consider Musick only valuable, as it is agreeable
to, and heightens the Purpose of Poetry, we consent that That is not
only the true Way of relishing that Pleasure, but also, that without
it a Composure of Musick is the same thing as a Poem, where all the
Rules of Poetical Numbers are observed, tho' the Words have no Sense
or Meaning; to say it shorter, meer musical Sounds are in our Art no
other than nonsense Verses are in Poetry. Musick therefore is to
aggravate what is intended by Poetry; it must always have some Passion
or Sentiment to express, or else Violins, Voices, or any other Organs
of Sound, afford an Entertainment very little above the Rattles of
Children. It was from this Opinion of the Matter, that when Mr.
Clayton had finished his Studies in
Italy, and brought over the
Opera of
Arsinoe, that Mr.
Haym and Mr.
Dieupart, who had the
Honour to be well known and received among the Nobility and Gentry,
were zealously inclined to assist, by their Solicitations, in
introducing so elegant an Entertainment as the
Italian Musick
grafted upon
English Poetry. For this End Mr.
Dieupart and Mr.
Haym, according to their several Opportunities, promoted the
Introduction of
Arsinoe, and did it to the best Advantage so great a
Novelty would allow. It is not proper to trouble you with Particulars
of the just Complaints we all of us have to make; but so it is, that
without Regard to our obliging Pains, we are all equally set aside in
the present Opera. Our Application therefore to you is only to insert
this Letter, in your Papers, that the Town may know we have all Three
joined together to make Entertainments of Musick for the future at Mr.
Clayton's House in
York-buildings. What we promise ourselves, is,
to make a Subscription of two Guineas, for eight Times; and that the
Entertainment, with the Names of the Authors of the Poetry, may be
printed, to be sold in the House, with an Account of the several
Authors of the Vocal as well as the Instrumental Musick for each
Night; the Money to be paid at the Receipt of the Tickets, at Mr.
Charles Lillie's. It will, we hope, Sir, be easily allowed, that we
are capable of undertaking to exhibit by our joint Force and different
Qualifications all that can be done in Musick; but lest you should
think so dry a thing as an Account of our Proposal should be a Matter
unworthy your Paper, which generally contains something of publick
Use; give us leave to say, that favouring our Design is no less than
reviving an Art, which runs to ruin by the utmost Barbarism under an
Affectation of Knowledge. We aim at establishing some settled Notion
of what is Musick, as recovering from Neglect and Want very many
Families who depend upon it, at making all Foreigners who pretend to
succeed in
England to learn the Language of it as we our selves have
done, and not be so insolent as to expect a whole Nation, a refined
and learned Nation, should submit to learn them. In a word, Mr.
Spectator, with all Deference and Humility, we hope to behave
ourselves in this Undertaking in such a Manner, that all
English Men
who have any Skill in Musick may be furthered in it for their Profit
or Diversion by what new Things we shall produce; never pretending to
surpass others, or asserting that any Thing which is a Science is not
attainable by all Men of all Nations who have proper Genius for it: We
say, Sir, what we hope for is not expected will arrive to us by
contemning others, but through the utmost Diligence recommending
ourselves.
We are, Sir,
Your most humble Servants,
Thomas Clayton,
Nicolino Haym,
Charles Dieupart.
Christopher Rich, of whom Steele wrote in No. 12 of the
Tatler
as Divito, who
'has a perfect art in being unintelligible in discourse and
uncomeatable in business. But he, having no understanding in his
polite way, brought in upon us, to get in his money, ladder-dancers,
rope-dancers, jugglers, and mountebanks, to strut in the place of
Shakespeare's heroes and Jonson's humorists.'
Thomas Clayton (see note on p. 72) had set Dryden's
Alexander's Feast
to music at the request of Steele and John Hughes;
but its performance at his house in York Buildings was a failure.
Clayton had adapted English words to Italian airs in the drama written
for him by Motteux, of
Arsinoe, Queen of Cyprus
, and called it his own
opera. Steele and Addison were taken by his desire to nationalize the
opera, and put native music to words that were English and had
literature in them. After
Camilla
at Drury Lane, produced under the
superintendence of Nicolino Haym, Addison's
Rosamond
was produced,
with music by Clayton and Mrs. Tofts in the part of Queen Eleanor. The
music killed the piece on the third night of performance. The coming of
Handel and his opera of
Rinaldo
set Mr. Clayton aside, but the
friendship of Steele and Addison abided with him, and Steele seems to
have had a share in his enterprises at York Buildings. Of his colleagues
who join in the signing of this letter, Nicola Francesco Haym was by
birth a Roman, and resident in London as a professor of music. He
published two good operas of sonatas for two violins and a bass, and
joined Clayton and Dieupart in the service of the opera, until Handel's
success superseded them. Haym was also a man of letters, who published
two quartos upon Medals, a notice of rare Italian Books, an edition of
Tasso's Gerusalemme, and two tragedies of his own. He wrote a
History
of Music
in Italian, and issued proposals for its publication in
English, but had no success. Finally he turned picture collector, and
was employed in that quality by Dr. Mead and Sir Robert Walpole.
Charles Dieupart, a Frenchman, was a fine performer on the violin and
harpsichord. At the representation of
Arsinoe
and the other earliest
operas, he played the harpsichord and Haym the violoncello. Dieupart,
after the small success of the design set forth in this letter, taught
the harpsichord in families of distinction, but wanted self-respect
enough to save him from declining into a player at obscure ale-houses,
where he executed for the pleasure of dull ears solos of Corelli with
the nicety of taste that never left him. He died old and poor in 1740.
Contents
|
Thursday, December 27, 1711 |
Steele |
Quod decet honestum est, et quod honestum est decet.
Tull.

There are some Things which cannot come under certain Rules,
but which one would think could not need them. Of this kind are outward
Civilities and Salutations. These one would imagine might be regulated
by every Man's Common Sense without the Help of an Instructor; but that
which we call Common Sense suffers under that Word; for it sometimes
implies no more than that Faculty which is common to all Men, but
sometimes signifies right Reason, and what all Men should consent to. In
this latter Acceptation of the Phrase, it is no great Wonder People err
so much against it, since it is not every one who is possessed of it,
and there are fewer, who against common Rules and Fashions, dare obey
its Dictates. As to Salutations, which I was about to talk of, I observe
as I strole about Town, there are great Enormities committed with regard
to this Particular. You shall sometimes see a Man begin the Offer of a
Salutation, and observe a forbidding Air, or escaping Eye, in the Person
he is going to salute, and stop short in the Pole of his Neck. This in
the Person who believed he could do it with a good Grace, and was
refused the Opportunity, is justly resented with a Coldness the whole
ensuing Season. Your great Beauties, People in much Favour, or by any
Means or for any Purpose overflattered, are apt to practise this which
one may call the preventing Aspect, and throw their Attention another
Way, lest they should confer a Bow or a Curtsie upon a Person who might
not appear to deserve that Dignity. Others you shall find so obsequious,
and so very courteous, as there is no escaping their Favours of this
Kind. Of this Sort may be a Man who is in the fifth or sixth Degree of
Favour with a Minister; this good Creature is resolved to shew the
World, that great Honours cannot at all change his Manners; he is the
same civil Person he ever was; he will venture his Neck to bow out of a
Coach in full Speed, at once, to shew he is full of Business, and yet is
not so taken up as to forget his old Friend. With a Man, who is not so
well formed for Courtship and elegant Behaviour, such a Gentleman as
this seldom finds his Account in the Return of his Compliments, but he
will still go on, for he is in his own Way, and must not omit; let the
Neglect fall on your Side, or where it will, his Business is still to be
well-bred to the End. I think I have read, in one of our
English
Comedies, a Description of a Fellow that affected knowing every Body,
and for Want of Judgment in Time and Place, would bow and smile in the
Face of a Judge sitting in the Court, would sit in an opposite Gallery
and smile in the Minister's Face as he came up into the Pulpit, and nod
as if he alluded to some Familiarities between them in another Place.
But now I happen to speak of Salutation at Church, I must take notice
that several of my Correspondents have importuned me to consider that
Subject, and settle the Point of Decorum in that Particular.
I do not pretend to be the best Courtier in the World, but I have often
on publick Occasions thought it a very great Absurdity in the Company
(during the Royal Presence) to exchange Salutations from all Parts of
the Room, when certainly Common Sense should suggest, that all Regards
at that Time should be engaged, and cannot be diverted to any other
Object, without Disrespect to the Sovereign. But as to the Complaint of
my Correspondents, it is not to be imagined what Offence some of them
take at the Custom of Saluting in Places of Worship. I have a very angry
Letter from a Lady, who tells me
of
one of her Acquaintance,
who
,
out of meer Pride and a Pretence to be rude, takes upon her to return no
Civilities done to her in Time of Divine Service, and is the most
religious Woman for no other Reason but to appear a Woman of the best
Quality in the Church. This absurd Custom had better be abolished than
retained, if it were but to prevent Evils of no higher a Nature than
this is; but I am informed of Objections much more considerable: A
Dissenter of Rank and Distinction was lately prevailed upon by a Friend
of his to come to one of the greatest Congregations of the Church of
England
about Town: After the Service was over, he declared he was
very well satisfied with the little Ceremony which was used towards God
Almighty; but at the same time he feared he should not be able to go
through those required towards one another: As to this Point he was in a
State of Despair, and feared he was not well-bred enough to be a
Convert. There have been many Scandals of this Kind given to our
Protestant Dissenters from the outward Pomp and Respect we take to our
selves in our Religious Assemblies. A Quaker who came one Day into a
Church, fixed his Eyes upon an old Lady with a Carpet larger than that
from the Pulpit before her, expecting when she would hold forth. An
who designs to come over himself, and all his Family, within
few Months, is sensible they want Breeding enough for our Congregations,
and has sent his two
eldest
Daughters to learn to dance, that they
may not misbehave themselves at Church: It is worth considering whether,
in regard to awkward People with scrupulous Consciences, a good
Christian of the best Air in the World ought not rather to deny herself
the Opportunity of shewing so many Graces, than keep a bashful Proselyte
without the Pale of the Church.
elder
Contents
|
Friday, December 28, 1711 |
Steele |
Singula de nobis anni prædantur euntes.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
I am now in the Sixty fifth Year of my Age, and having been the
greater Part of my Days a Man of Pleasure, the Decay of my Faculties
is a Stagnation of my Life. But how is it, Sir, that my Appetites are
increased upon me with the Loss of Power to gratify them? I write
this, like a Criminal, to warn People to enter upon what Reformation
they may please to make in themselves in their Youth, and not expect
they shall be capable of it from a fond Opinion some have often in
their Mouths, that if we do not leave our Desires they will leave us.
It is far otherwise; I am now as vain in my Dress, and as flippant if
I see a pretty Woman, as when in my Youth I stood upon a Bench in the
Pit to survey the whole Circle of Beauties. The Folly is so
extravagant with me, and I went on with so little Check of my Desires,
or Resignation of them, that I can assure you, I very often meerly to
entertain my own Thoughts, sit with my Spectacles on, writing
Love-Letters to the Beauties that have been long since in their
Graves. This is to warm my Heart with the faint Memory of Delights
which were once agreeable to me; but how much happier would my Life
have been now, if I could have looked back on any worthy Action done
for my Country? If I had laid out that which I profused in Luxury and
Wantonness, in Acts of Generosity or Charity? I have lived a Batchelor
to this Day; and instead of a numerous Offspring, with which, in the
regular Ways of Life, I might possibly have delighted my self, I have
only to amuse my self with the Repetition of Old Stories and Intrigues
which no one will believe I ever was concerned in. I do not know
whether you have ever treated of it or not; but you cannot fall on a
better Subject, than that of the Art of growing old. In such a Lecture
you must propose, that no one set his Heart upon what is transient;
the Beauty grows wrinkled while we are yet gazing at her. The witty
Man sinks into a Humourist imperceptibly, for want of reflecting that
all Things around him are in a Flux, and continually changing: Thus he
is in the Space of ten or fifteen Years surrounded by a new Set of
People whose Manners are as natural to them as his Delights, Method of
Thinking, and Mode of Living, were formerly to him and his Friends.
But the Mischief is, he looks upon the same kind of Errors which he
himself was guilty of with an Eye of Scorn, and with that sort of
Ill-will which Men entertain against each other for different
Opinions: Thus a crasie Constitution, and an uneasie Mind is fretted
with vexatious Passions for young Mens doing foolishly what it is
Folly to do at all. Dear Sir, this is my present State of Mind; I hate
those I should laugh at, and envy those I contemn. The Time of Youth
and vigorous Manhood passed the Way in which I have disposed of it, is
attended with these Consequences; but to those who live and pass away
Life as they ought, all Parts of it are equally pleasant; only the
Memory of good and worthy Actions is a Feast which must give a quicker
Relish to the Soul than ever it could possibly taste in the highest
Enjoyments or Jollities of Youth. As for me, if I sit down in my great
Chair and begin to ponder, the Vagaries of a Child are not more
ridiculous than the Circumstances which are heaped up in my Memory.
Fine Gowns, Country Dances, Ends of Tunes, interrupted Conversations,
and midnight Quarrels, are what must necessarily compose my Soliloquy.
I beg of you to print this, that some Ladies of my Acquaintance, and
my Years, may be perswaded to wear warm Night-caps this cold Season:
and that my old Friend
Jack Tawdery may buy him a Cane, and not
creep with the Air of a Strut. I must add to all this, that if it were
not for one Pleasure, which I thought a very mean one 'till of very
late Years, I should have no one great Satisfaction left; but if I
live to the 10th of
March, 1714, and all my Securities are good, I
shall be worth Fifty thousand Pound.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Jack Afterday.
Mr.
Spectator,
You will infinitely oblige a distressed Lover, if you will insert in
your very next Paper, the following Letter to my Mistress. You must
know, I am not a Person apt to despair, but she has got an odd Humour
of stopping short unaccountably, and, as she her self told a Confident
of hers, she has cold Fits. These Fits shall last her a Month or six
Weeks together; and as she falls into them without Provocation, so it
is to be hoped she will return from them without the Merit of new
Services. But Life and Love will not admit of such Intervals,
therefore pray let her be admonished as follows.
Madam,
I Love you, and I honour you: therefore pray do not tell me of
waiting till Decencies, till Forms, till Humours are consulted and
gratified. If you have that happy Constitution as to be indolent for
ten Weeks together, you should consider that all that while I burn
in Impatiences and Fevers; but still you say it will be Time enough,
tho' I and you too grow older while we are yet talking. Which do you
think the more reasonable, that you should alter a State of
Indifference for Happiness, and that to oblige me, or I live in
Torment, and that to lay no Manner of Obligation upon you? While I
indulge your Insensibility I am doing nothing; if you favour my
Passion, you are bestowing bright Desires, gay Hopes, generous
Cares, noble Resolutions and transporting Raptures upon, Madam,
Your most devoted humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
Here's a Gentlewoman lodges in the same House with me, that I never
did any Injury to in my whole Life; and she is always railing at me to
those that she knows will tell me of it. Don't you think she is in
Love with me? or would you have me break my Mind yet or not?
Your
Servant,
T. B.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Footman in a great Family, and am in Love with the House-maid.
We were all at Hot-cockles last Night in the Hall these Holidays; when
I lay down and was blinded, she pulled off her Shoe, and hit me with
the Heel such a Rap, as almost broke my Head to Pieces. Pray, Sir, was
this Love or Spite?
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 29, 1711 |
Addison |
My Father, whom I mentioned in my first Speculation, and whom I must
always name with Honour and Gratitude, has very frequently talked to me
upon the Subject of Marriage. I was in my younger Years engaged, partly
by his Advice, and partly by my own Inclinations in the Courtship of a
Person who had a great deal of Beauty, and did not at my first
Approaches seem to have any Aversion to me; but as my natural
Taciturnity hindred me from showing my self to the best Advantage, she
by degrees began to look upon me as a very silly Fellow, and being
resolved to regard Merit more than any Thing else in the Persons who
made their Applications to her, she married a Captain of Dragoons who
happened to be beating up for Recruits in those Parts.
This unlucky Accident has given me an Aversion to pretty Fellows ever
since, and discouraged me from trying my Fortune with the Fair Sex. The
Observations which I made in this Conjuncture, and the repeated Advices
which I received at that Time from the good old Man above-mentioned,
have produced the following Essay upon Love and Marriage.
The pleasantest Part of a Man's Life is generally that which passes in
Courtship, provided his Passion be sincere, and the Party beloved kind
with Discretion. Love, Desire, Hope, all the pleasing Motions of the
Soul rise in the Pursuit.
It is easier for an artful Man who is not in Love, to persuade his
Mistress he has a Passion for her, and to succeed in his Pursuits, than
for one who loves with the greatest Violence. True Love has ten thousand
Griefs, Impatiences and Resentments, that render a Man unamiable in the
Eyes of the Person whose Affection he sollicits: besides, that it sinks
his Figure, gives him Fears, Apprehensions and Poorness of Spirit, and
often makes him appear ridiculous where he has a mind to recommend
himself.
Those Marriages generally abound most with Love and Constancy, that are
preceded by a long Courtship. The Passion should strike Root, and gather
Strength before Marriage be grafted on it. A long Course of Hopes and
Expectations fixes the Idea in our Minds, and habituates us to a
Fondness of the Person beloved.
There is Nothing of so great Importance to us, as the good Qualities of
one to whom we join ourselves for Life; they do not only make our
present State agreeable, but often determine our Happiness to all
Eternity. Where the Choice is left to Friends, the chief Point under
Consideration is an Estate: Where the Parties chuse for themselves,
their Thoughts turn most upon the Person. They have both their Reasons.
The first would procure many Conveniencies and Pleasures of Life to the
Party whose Interests they espouse; and at the same time may hope that
the Wealth of their Friend will turn to their own Credit and Advantage.
The others are preparing for themselves a perpetual Feast. A good Person
does not only raise, but continue Love, and breeds a secret Pleasure and
Complacency in the Beholder, when the first Heats of Desire are
extinguished. It puts the Wife or Husband in Countenance both among
Friends and Strangers, and generally fills the Family with a healthy and
beautiful Race of Children.
I should prefer a Woman that is agreeable in my own Eye, and not
deformed in that of the World, to a Celebrated Beauty. If
marry one
remarkably beautiful, you must have a violent Passion for her, or you
have not the proper Taste of her Charms; and if you have such a Passion
for her, it is odds but it
would
be imbittered with Fears and
Jealousies.
Good-Nature and Evenness of Temper will give you an easie Companion for
Life; Virtue and good Sense, an agreeable Friend; Love and Constancy, a
good Wife or Husband. Where we meet one Person with all these
Accomplishments, we find an hundred without any one of them. The World,
notwithstanding, is more intent on Trains and Equipages, and all the
showy Parts of Life; we love rather to dazzle the Multitude, than
consult our proper Interest
s
; and, as I have elsewhere observed, it is
one of the most unaccountable Passions of human Nature, that we are at
greater Pains to appear easie and happy to others, than really to make
our selves so. Of all Disparities, that in Humour makes the most unhappy
Marriages, yet scarce enters into our Thoughts at the contracting of
them. Several that are in this Respect unequally yoked, and uneasie for
Life, with a Person of a particular Character, might have been pleased
and happy with a Person of a contrary one, notwithstanding they are both
perhaps equally virtuous and laudable in their Kind.
Before Marriage we cannot be too inquisitive and discerning in the
Faults of the Person beloved, nor after it too dim-sighted and
superficial. However perfect and accomplished the Person appears to you
at a Distance, you will find many Blemishes and Imperfections in her
Humour, upon a more intimate Acquaintance, which you never discovered or
perhaps suspected. Here therefore Discretion and Good-nature are to shew
their Strength; the first will hinder your Thoughts from dwelling on
what is disagreeable, the other will raise in you all the Tenderness of
Compassion and Humanity, and by degrees soften those very Imperfections
into Beauties.
Marriage enlarges the Scene of our Happiness and Miseries. A Marriage of
Love is pleasant; a Marriage of Interest easie; and a Marriage, where
both meet, happy. A happy Marriage has in it all the Pleasures of
Friendship, all the Enjoyments of Sense and Reason, and indeed, all the
Sweets of Life.
is a greater Mark of a degenerate and vicious
Age, than the common Ridicule
which
passes on this State of Life.
It is, indeed, only happy in those who can look down with Scorn or
Neglect on the Impieties of the Times, and tread the Paths of Life
together in a constant uniform Course of Virtue.
will
that
Contents
|
Monday, December 31, 1711 |
Steele |
Nulla venenato Littera mista Joco est.
Ovid.

I think myself highly obliged to the Publick for their kind Acceptance
of a Paper which visits them every Morning, and has in it none of those
Seasonings
that recommend so many of the Writings which are in Vogue
among us.
As, on the one Side, my Paper has not in it a single Word of News, a
Reflection in Politics, nor a Stroak of Party; so on the other, there
are no Fashionable Touches of Infidelity, no obscene Ideas, no Satyrs
upon Priesthood, Marriage, and the like popular Topics of Ridicule; no
private Scandal, nor any Thing that may tend to the Defamation of
particular Persons, Families, or Societies.
There is not one of these above-mentioned Subjects that would not sell a
very indifferent Paper, could I think of gratifying the Publick by such
mean and base Methods. But notwithstanding I have rejected every Thing
that savours of Party, every Thing that is loose and immoral, and every
Thing that might create Uneasiness in the Minds of particular Persons, I
find that the Demand of my Papers has encreased every Month since their
first Appearance in the World. This does not perhaps reflect so much
Honour upon my self, as on my Readers, who give a much greater Attention
to Discourses of Virtue and Morality, than ever I expected, or indeed
could hope.
When I broke loose from that great Body of Writers who have employed
their Wit and Parts in propagating Vice and Irreligion, I did not
question but I should be treated as an odd kind of Fellow that had a
mind to appear singular in my Way of Writing:
the general Reception
I have found, convinces me that the World is not so corrupt as we are
apt to imagine; and that if those Men of Parts who have been employed in
vitiating the Age had endeavour'd to rectify and amend it, they needed
not
have sacrificed their good Sense and Virtue to their Fame and
Reputation.
Man is so sunk in Vice and Ignorance, but there are still
some hidden Seeds of Goodness and Knowledge in him; which give him a
Relish of such Reflections and Speculations as have an
Aptness
to
improve the Mind, and make the Heart better.
I have shewn in a former Paper, with how much Care I have avoided all
such Thoughts as are loose, obscene or immoral; and I believe my Reader
would still think the better of me, if he knew the Pains I am at in
qualifying what I write after such a manner, that nothing may be
interpreted as aimed at private Persons. For this Reason when I draw any
faulty Character, I consider all those Persons to whom the Malice of the
World may possibly apply it, and take care to dash it with such
particular Circumstances as may prevent all such ill-natured
Applications. If I write any Thing on a black Man, I run over in my Mind
all the eminent Persons in the Nation who are of that Complection: When
I place an imaginary Name at the Head of a Character, I examine every
Syllable and Letter of it, that it may not bear any Resemblance to one
that is real. I know very well the Value which every Man sets upon his
Reputation, and how painful it is to be exposed to the Mirth and
Derision of the Publick, and should therefore scorn to divert my Reader,
at the Expence of any private Man.
As I have been thus tender of every particular Person's Reputation, so I
have taken more than ordinary Care not to give Offence to those who
appear in the higher Figures of Life. I
not make myself merry even
with a Piece of Paste-board that is invested with a Publick Character;
for which Reason I have never glanced upon the late designed Procession
of his Holiness and his Attendants
, notwithstanding it might have
afforded Matter to many ludicrous Speculations. Among those Advantages,
which the Publick may reap from this Paper, it is not the least, that it
draws Mens Minds off from the Bitterness of Party, and furnishes them
with Subjects of Discourse that may be treated without Warmth or
Passion.
is said to have been the first Design of those Gentlemen
who set on Foot the Royal Society
; and had then a very good Effect,
as it turned many of the greatest Genius's of that Age to the
Disquisitions of natural Knowledge, who, if they had engaged in
Politicks with the same Parts and Application, might have set their
Country in a Flame. The Air-Pump, the Barometer, the Quadrant, and the
like Inventions were thrown out to those busie Spirits, as Tubs and
Barrels are to a Whale, that he may let the Ship sail on without
Disturbance, while he diverts himself with those innocent Amusements.
I have been so very scrupulous in this Particular of not hurting any
Man's Reputation that I have forborn mentioning even such Authors as I
could not name without Honour. This I must confess to have been a Piece
of very great Self-denial: For as the Publick relishes nothing better
than the Ridicule which turns upon a Writer of any Eminence, so there is
nothing which a Man that has but a very ordinary Talent in Ridicule may
execute with greater Ease. One might raise Laughter for a Quarter of a
Year together upon the Works of a Person who has published but a very
few Volumes.
which
Reason
I am astonished, that those who have
appeared against this Paper have made so very little of it. The
Criticisms which I have hitherto published, have been made with an
Intention rather to discover Beauties and Excellencies in the Writers of
my own Time, than to publish any of their Faults and Imperfections. In
the mean while I should take it for a very great Favour from some of my
underhand Detractors, if they would break all Measures with me so far,
as to give me a Pretence for examining their Performances with an
impartial Eye: Nor shall I look upon it as any Breach of Charity to
criticise the Author, so long as I keep clear of the Person.
In the mean while, 'till I am provoked to such Hostilities, I shall from
time to time endeavour to do Justice to those who have distinguished
themselves in the politer Parts of Learning, and to point out such
Beauties in their Works as may have escaped the Observation of others.
As the first Place among our
English
Poets is due to
Milton
; and as
I have drawn more Quotations out of him than from any other, I shall
enter into a regular Criticism upon his
Paradise Lost
, which I shall
publish every
Saturday
'till I have given my Thoughts upon that Poem.
I shall not however presume to impose upon others my own particular
Judgment on this Author, but only deliver it as my private Opinion.
Criticism is of a very large Extent, and every particular Master in this
Art has his favourite Passages in an Author, which do not equally strike
the best Judges. It will be sufficient for me if I discover many
Beauties or Imperfections which others have not attended to, and I
should be very glad to see any of our eminent Writers publish their
Discoveries on the same Subject. In short, I would always be understood
to write my Papers of Criticism in the Spirit which
Horace
has
expressed in those two famous Lines;
—Si quid novisti rectius istis,
Candidus imperti; si non, his utere mecum,
'If you have made any better Remarks of your own, communicate them
with Candour; if not, make use of these I present you with.'
C.
not to
Aptness in them
Fifteen images in waxwork, prepared for a procession on
the 17th November, Queen Elizabeth's birthday, had been seized under a
Secretary of State's warrant. Swift says, in his Journal to Stella, that
the devil which was to have waited on the Pope was saved from burning
because it was thought to resemble the Lord Treasurer.
The Royal Society was incorporated in 1663 as the Royal
Society of London 'for promoting Natural Knowledge.' In the same year
there was an abortive insurrection in the North against the infamy of
Charles II.'s government.
Reasons
Contents
|
Tuesday, January 1, 1712 |
Steele |
Gratulor quod eum quem necesse erat diligere, qualiscunque esset, talem
habemus ut libenter quoque diligamus.
Trebonius apud Tull.

Mr,
Spectator,
I am the happy Father of a very towardly Son, in whom I do not only
see my Life, but also my Manner of Life, renewed. It would be
extremely beneficial to Society, if you would frequently resume
Subjects which serve to bind these sort of Relations faster, and
endear the Ties of Blood with those of Good-will, Protection,
Observance, Indulgence, and Veneration. I would, methinks, have this
done after an uncommon Method, and do not think any one, who is not
capable of writing a good Play, fit to undertake a Work wherein there
will necessarily occur so many secret Instincts, and Biasses of human
Nature which would pass unobserved by common Eyes. I thank Heaven I
have no outrageous Offence against my own excellent Parents to answer
for; but when I am now and then alone, and look back upon my past
Life, from my earliest Infancy to this Time, there are many Faults
which I committed that did not appear to me, even till I my self
became a Father. I had not till then a Notion of the Earnings of
Heart, which a Man has when he sees his Child do a laudable Thing, or
the sudden Damp which seizes him when he fears he will act something
unworthy. It is not to be imagined, what a Remorse touched me for a
long Train of childish Negligencies of my Mother, when I saw my Wife
the other Day look out of the Window, and turn as pale as Ashes upon
seeing my younger Boy sliding upon the Ice. These slight Intimations
will give you to understand, that there are numberless little Crimes
which Children take no notice of while they are doing, which upon
Reflection, when they shall themselves become Fathers, they will look
upon with the utmost Sorrow and Contrition, that they did not regard,
before those whom they offended were to be no more seen. How many
thousand Things do I remember, which would have highly pleased my
Father, and I omitted for no other Reason, but that I thought what he
proposed the Effect of Humour and old Age, which I am now convinced
had Reason and good Sense in it. I cannot now go into the Parlour to
him, and make his Heart glad with an Account of a Matter which was of
no Consequence, but that I told it, and acted in it. The good Man and
Woman are long since in their Graves, who used to sit and plot the
Welfare of us their Children, while, perhaps, we were sometimes
laughing at the old Folks at another End of the House. The Truth of it
is, were we merely to follow Nature in these great Duties of Life,
tho' we have a strong Instinct towards the performing of them, we
should be on both Sides very deficient. Age is so unwelcome to the
Generality of Mankind, and Growth towards Manhood so desirable to all,
that Resignation to Decay is too difficult a Task in the Father; and
Deference, amidst the Impulse of gay Desires, appears unreasonable to
the Son. There are so few who can grow old with a good Grace, and yet
fewer who can come slow enough into the World, that a Father, were he
to be actuated by his Desires, and a Son, were he to consult himself
only, could neither of them behave himself as he ought to the other.
But when Reason interposes against Instinct, where it would carry
either out of the Interests of the other, there arises that happiest
Intercourse of good Offices between those dearest Relations of human
Life. The Father, according to the Opportunities which are offered to
him, is throwing down Blessings on the Son, and the Son endeavouring
to appear the worthy Offspring of such a Father. It is after this
manner that
Camillus and his firstborn dwell together.
Camillus
enjoys a pleasing and indolent old Age, in which Passion is subdued,
and Reason exalted. He waits the Day of his Dissolution with a
Resignation mixed with Delight, and the Son fears the Accession of his
Father's Fortune with Diffidence, lest he should not enjoy or become
it as well as his Predecessor. Add to this, that the Father knows he
leaves a Friend to the Children of his Friends, an easie Landlord to
his Tenants, and an agreeable Companion to his Acquaintance. He
believes his Son's Behaviour will make him frequently remembered, but
never wanted. This Commerce is so well cemented, that without the Pomp
of saying,
Son, be a Friend to such a one when I am gone; Camillus
knows, being in his Favour, is Direction enough to the grateful Youth
who is to succeed him, without the Admonition of his mentioning it.
These Gentlemen are honoured in all their Neighbourhood, and the same
Effect which the Court has on the Manner of a Kingdom, their
Characters have on all who live within the Influence of them.
My Son and I are not of Fortune to communicate our good Actions or
Intentions to so many as these Gentlemen do; but I will be bold to
say, my Son has, by the Applause and Approbation which his Behaviour
towards me has gained him, occasioned that many an old Man, besides my
self, has rejoiced. Other Men's Children follow the Example of mine,
and I have the inexpressible Happiness of overhearing our Neighbours,
as we ride by, point to their Children, and say, with a Voice of Joy,
There they go.
'You cannot,
Mr.
Spectator, pass your time better than insinuating
the Delights which these Relations well regarded bestow upon each
other. Ordinary Passions are no longer such, but mutual Love gives an
Importance to the most indifferent things, and a Merit to Actions the
most insignificant. When we look round the World, and observe the many
Misunderstandings which are created by the Malice and Insinuation of
the meanest Servants between People thus related, how necessary will
it appear that it were inculcated that Men would be upon their Guard
to support a Constancy of Affection, and that grounded upon the
Principles of Reason, not the Impulses of Instinct.
It is from the common Prejudices which Men receive from their Parents,
that Hatreds are kept alive from one Generation to another; and when
Men act by Instinct, Hatreds will descend when good Offices are
forgotten. For the Degeneracy of human Life is such, that our Anger is
more easily transferred to our Children than our Love. Love always
gives something to the Object it delights in, and Anger spoils the
Person against whom it is moved of something laudable in him. From
this Degeneracy therefore, and a sort of Self-Love, we are more prone
to take up the Ill-will of our Parents, than to follow them in their
Friendships.
One would think there should need no more to make Men keep up this
sort of Relation with the utmost Sanctity, than to examine their own
Hearts. If every Father remembered his own Thoughts and Inclinations
when he was a Son, and every Son remembered what he expected from his
Father, when he himself was in a State of Dependance, this one
Reflection would preserve Men from being dissolute or rigid in these
several Capacities. The Power and Subjection between them, when
broken, make them more emphatically Tyrants and Rebels against each
other, with greater Cruelty of Heart, than the Disruption of States
and Empires can possibly produce. I shall end this Application to you
with two Letters which passed between a Mother and Son very lately,
and are as follows.
Dear FRANK,
If the Pleasures, which I have the Grief to hear you pursue in Town,
do not take up all your Time, do not deny your Mother so much of it,
as to read seriously this Letter. You said before Mr. Letacre,
that an old Woman might live very well in the Country upon half my
Jointure, and that your Father was a fond Fool to give me a
Rent-Charge of Eight hundred a Year to the Prejudice of his Son.
What Letacre said to you upon that Occasion, you ought to have
born with more Decency, as he was your Father's well-beloved
Servant, than to have called him Country-put. In the first place,
Frank, I must tell you, I will have my Rent duly paid, for I will
make up to your Sisters for the Partiality I was guilty of, in
making your Father do so much as he has done for you. I may, it
seems, live upon half my Jointure! I lived upon much less, Frank,
when I carried you from Place to Place in these Arms, and could
neither eat, dress, or mind any thing for feeding and tending you a
weakly Child, and shedding Tears when the Convulsions you were then
troubled with returned upon you. By my Care you outgrew them, to
throw away the Vigour of your Youth in the Arms of Harlots, and deny
your Mother what is not yours to detain. Both your Sisters are
crying to see the Passion which I smother; but if you please to go
on thus like a Gentleman of the Town, and forget all Regards to your
self and Family, I shall immediately enter upon your Estate for the
Arrear due to me, and without one Tear more contemn you for
forgetting the Fondness of your Mother, as much as you have the
Example of your Father. O Frank, do I live to omit writing myself,
Your Affectionate Mother, A.T.
MADAM,
I will come down to-morrow and pay the Money on my Knees. Pray write
so no more. I will take care you never shall, for I will be for ever
hereafter,
Your most dutiful Son,
F.T.
I will bring down new Heads for my Sisters. Pray let all be
forgotten.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, January 2, 1712 |
Steele |
—Secretum iter et fallentis Semita vitæ.
Hor.

It has been from Age to Age an Affectation to love the Pleasure of
Solitude, amongst those who cannot possibly be supposed qualified for
passing Life in that Manner. This People have taken up from reading the
many agreeable things which have been writ on that Subject, for which we
are beholden to excellent Persons who delighted in being retired and
abstracted from the Pleasures that enchant the Generality of the World.
This Way of Life is recommended indeed with great Beauty, and in such a
Manner as disposes the Reader for the time to a pleasing Forgetfulness,
or Negligence of the particular Hurry of Life in which he is engaged,
together with a Longing for that State which he is charmed with in
Description. But when we consider the World it self, and how few there
are capable of a religious, learned, or philosophick Solitude, we shall
be apt to change a Regard to that sort of Solitude, for being a little
singular in enjoying Time after the Way a Man himself likes best in the
World, without going so far as wholly to withdraw from it. I have often
observed, there is not a Man breathing who does not differ from all
other Men, as much in the Sentiments of his Mind, as the Features of his
Face. The Felicity is, when anyone is so happy as to find out and follow
what is the proper Bent of this Genius, and turn all his Endeavours to
exert himself according as that prompts him. Instead of this, which is
an innocent Method of enjoying a Man's self, and turning out of the
general Tracks wherein you have Crowds of Rivals, there are those who
pursue their own Way out of a Sowrness and Spirit of Contradiction:
These Men do every thing which they are able to support, as if Guilt and
Impunity could not go together. They choose a thing only because another
dislikes it; and affect forsooth an inviolable Constancy in Matters of
no manner of Moment. Thus sometimes an old Fellow shall wear this or
that sort of Cut in his Cloaths with great Integrity, while all the rest
of the World are degenerated into Buttons, Pockets and Loops unknown to
their Ancestors. As insignificant as even this is, if it were searched
to the Bottom, you perhaps would find it not sincere, but that he is in
the Fashion in his Heart, and holds out from mere Obstinacy. But I am
running from my intended Purpose, which was to celebrate a certain
particular Manner of passing away Life, and is a Contradiction to no
Man. but a Resolution to contract none of the exorbitant Desires by
which others are enslaved. The best way of separating a Man's self from
the World, is to give up the Desire of being known to it. After a Man
has preserved his Innocence, and performed all Duties incumbent upon
him, his Time spent his own Way is what makes his Life differ from that
of a Slave. If they who affect Show and Pomp knew how many of their
Spectators derided their trivial Taste, they would be very much less
elated, and have an Inclination to examine the Merit of all they have to
do with: They would soon find out that there are many who make a Figure
below what their Fortune or Merit entities them to, out of mere Choice,
and an elegant Desire of Ease and Disincumbrance. It would look like
Romance to tell you in this Age of an old Man who is contented to pass
for an Humourist, and one who does not understand the Figure he ought to
make in the World, while he lives in a Lodging of Ten Shillings a Week
with only one Servant: While he dresses himself according to the Season
in Cloth or in Stuff, and has no one necessary Attention to any thing
but the Bell which calls to Prayers twice a Day. I say it would look
like a Fable to report that this Gentleman gives away all which is the
Overplus of a great Fortune, by secret Methods to other Men. If he has
not the Pomp of a numerous Train, and of Professors of Service to him,
he has every Day he lives the Conscience that the Widow, the Fatherless,
the Mourner, and the Stranger bless his unseen Hand in their Prayers.
This Humourist gives up all the Compliments which People of his own
Condition could make to him, for the Pleasures of helping the Afflicted,
supplying the Needy, and befriending the Neglected. This Humourist keeps
to himself much more than he wants, and gives a vast Refuse of his
Superfluities to purchase Heaven, and by freeing others from the
Temptations of Worldly Want, to carry a Retinue with him thither. Of all
Men who affect living in a particular Way, next to this admirable
Character, I am the most enamoured of
Irus
, whose Condition will not
admit of such Largesses, and perhaps would not be capable of making
them, if it were.
Irus
, tho' he is now turned of Fifty, has not
appeared in the World, in his real Character, since five and twenty, at
which Age he ran out a small Patrimony, and spent some Time after with
Rakes who had lived upon him: A Course of ten Years time, passed in all
the little Alleys, By-Paths, and sometimes open Taverns and Streets of
this Town, gave
Irus
a perfect Skill in judging of the Inclinations
of Mankind, and acting accordingly. He seriously considered he was poor,
and the general Horror which most Men have of all who are in that
Condition.
Irus
judg'd very rightly, that while he could keep his
Poverty a Secret, he should not feel the Weight of it; he improved this
Thought into an Affectation of Closeness and Covetousness. Upon this one
Principle he resolved to govern his future Life; and in the thirty sixth
Year of his Age he repaired to Long-lane, and looked upon several
Dresses which hung there deserted by their first Masters, and exposed to
the Purchase of the best Bidder. At this Place he exchanged his gay
Shabbiness of Cloaths fit for a much younger Man, to warm ones that
would be decent for a much older one.
Irus
came out thoroughly
equipped from Head to Foot, with a little oaken Cane in the Form of a
substantial Man that did not mind his Dress, turned of fifty. He had at
this time fifty Pounds in ready Money; and in this Habit, with this
Fortune, he took his present Lodging in St.
John Street
, at the
Mansion-House of a Taylor's Widow, who washes and can clear-starch his
Bands. From that Time to this, he has kept the main Stock, without
Alteration under or over to the value of five Pounds. He left off all
his old Acquaintance to a Man, and all his Arts of Life, except the Play
of Backgammon, upon which he has more than bore his Charges.
Irus
has,
ever since he came into this Neighbourhood, given all the Intimations,
he skilfully could, of being a close Hunks worth Money: No body comes to
visit him, he receives no Letters, and tells his Money Morning and
Evening. He has, from the publick Papers, a Knowledge of what generally
passes, shuns all Discourses of Money, but shrugs his Shoulder when you
talk of Securities; he denies his being rich with the Air, which all do
who are vain of being so: He is the Oracle of a Neighbouring Justice of
Peace, who meets him at the Coffeehouse; the Hopes that what he has must
come to Somebody, and that he has no Heirs, have that Effect where ever
he is known, that he every Day has three or four Invitations to dine at
different Places, which he generally takes care to choose in such a
manner, as not to seem inclined to the richer Man. All the young Men
respect him, and say he is just the same Man he was when they were Boys.
He uses no Artifice in the World, but makes use of Men's Designs upon
him to get a Maintenance out of them. This he carries on by a certain
Peevishness, (which he acts very well) that no one would believe could
possibly enter into the Head of a poor Fellow. His Mein, his Dress, his
Carriage, and his Language are such, that you would be at a loss to
guess whether in the Active Part of his Life he had been a sensible
Citizen, or Scholar that knew the World. These are the great
Circumstances in the Life of
Irus
, and thus does he pass away his Days
a Stranger to Mankind; and at his Death, the worst that will be said of
him will be, that he got by every Man who had Expectations from him,
more than he had to leave him.
I have an Inclination to print the following Letters; for that I have
heard the Author of them has some where or other seen me, and by an
excellent Faculty in Mimickry my Correspondents tell me he can assume my
Air, and give my Taciturnity a Slyness which diverts more than any Thing
I could say if I were present. Thus I am glad my Silence is attoned for
to the good Company in Town. He has carried his Skill in Imitation so
far, as to have forged a Letter from my Friend Sir
Roger
in such a
manner, that any one but I who am thoroughly acquainted with him, would
have taken it for genuine.
Mr.
Spectator,
Having observed in
Lilly's Grammar how sweetly
Bacchus and
Apollo run in a Verse: I have (to preserve the Amity between them)
call'd in
Bacchus to the Aid of my Profession of the
Theatre. So
that while some People of Quality are bespeaking Plays of me to be
acted upon such a Day, and others, Hogsheads for their Houses against
such a Time; I am wholly employ'd in the agreeable Service of Wit and
Wine: Sir, I have sent you Sir
Roger de Coverley's Letter to me,
which pray comply with in Favour of the
Bumper Tavern. Be kind, for
you know a Player's utmost Pride is the Approbation of the
Spectator.
I am your Admirer, tho' unknown,
Richard Estcourt
1
To Mr. Estcourt at his House in
Covent-Garden.
Coverley, December the 18th, 1711.
Old Comical Ones,
The Hogsheads of Neat Port came safe, and have gotten thee good
Reputation in these Parts; and I am glad to hear, that a Fellow who
has been laying out his Money ever since he was born, for the meer
Pleasure of Wine, has bethought himself of joining Profit and Pleasure
together. Our Sexton (poor Man) having received Strength from thy Wine
since his fit of the Gout, is hugely taken with it: He says it is
given by Nature for the Use of Families, that no Steward's Table can
be without it, that it strengthens Digestion, excludes Surfeits,
Fevers and Physick; which green Wines of any kind can't do. Pray get a
pure snug Room, and I hope next Term to help fill your Bumper with our
People of the Club; but you must have no Bells stirring when the
Spectator comes; I forbore ringing to Dinner while he was down with
me in the Country. Thank you for the little Hams and
Portugal
Onions; pray keep some always by you. You know my Supper is only good
Cheshire Cheese, best Mustard, a golden Pippin, attended with a Pipe
of
John Sly's Best. Sir Harry has stoln all your Songs, and tells
the Story of the 5th of
November to Perfection.
Yours to serve you,
Roger de Coverley.
We've lost old
John since you were here.'
T.
Richard Estcourt, born at Tewkesbury in 1688, and educated
in the Latin school there, stole from home at the age of 15 to join a
travelling company of comedians at Worcester, and, to avoid detection,
made his first appearance in woman's clothes as Roxana in
Alexander the
Great
. He was discovered, however, pursued, brought home, carried to
London, and bound prentice to an apothecary in Hatton Garden. He escaped
again, wandered about England, went to Ireland, and there obtained
credit as an actor; then returned to London, and appeared at Drury Lane,
where his skill as a mimic enabled him to perform each part in the
manner of the actor who had obtained chief credit by it. His power of
mimicry made him very diverting in society, and as he had natural
politeness with a sprightly wit, his company was sought and paid for at
the entertainments of the great. 'Dick Estcourt' was a great favourite
with the Duke of Marlborough, and when men of wit and rank joined in
establishing the Beefsteak Club they made Estcourt their
Providore
,
with a small gold gridiron, for badge, hung round his neck by a green
ribbon. Estcourt was a writer for the stage as well as actor, and had
shown his agreement with the
Spectator's
dramatic criticisms by
ridiculing the Italian opera with an interlude called
Prunella
. In the
Numbers of the
Spectator
for December 28 and 29 Estcourt had
advertised that he would on the 1st of January open 'the Bumper' Tavern
in James's Street, Westminster, and had laid in
'neat natural wines, fresh and in perfection; being bought by Brooke
and Hellier, by whom the said Tavern will from time to time be
supplied with the best growths that shall be imported; to be sold by
wholesale as well as retail, with the utmost fidelity by his old
servant, trusty Anthony, who has so often adorned both the theatres in
England and Ireland; and as he is a person altogether unknowing in the
wine trade, it cannot be doubted but that he will deliver the wine in
the same natural purity that he receives it from the said merchants;
and on these assurances he hopes that all his friends and acquaintance
will become his customers, desiring a continuance of their favours no
longer than they shall find themselves well served.'
This is the venture which Steele here backs for his friend with the
influence of the
Spectator
.
Contents
|
Thursday, January 3, 1712 |
Addison |
Dixerit e multis aliquis, quid virus in angues
Adjicis? et rabidæ tradis ovile lupæ?
Ov.

One of the Fathers, if I am rightly informed, has defined a Woman to be
an Animal that delights in Finery
. I have
already treated of the Sex in two or three Papers, conformably to this
Definition, and have in particular observed, that in all Ages they have
been more careful then the Men to adorn that Part of the Head, which we
generally call the Outside.
This Observation is so very notorious, that when in ordinary Discourse
we say a Man has a fine Head, a long Head, or a good Head, we express
ourselves metaphorically, and speak in relation to his Understanding;
whereas when we say of a Woman, she has a fine, a long or a good Head,
we speak only in relation to her Commode.
It is observed among Birds, that Nature has lavished all her Ornaments
upon the Male, who very often appears in a most beautiful Head-dress:
Whether it be a Crest, a Comb, a Tuft of Feathers, or a natural little
Plume, erected like a kind of
on the very Top of the Head.
As
Nature on the contrary
has poured out her Charms in the greatest
Abundance upon the Female Part of our Species, so they are very
assiduous in bestowing upon themselves the finest Garnitures of Art. The
Peacock in all his Pride, does not display half the Colours that appear
in the Garments of a
British
Lady, when she is dressed either for a
Ball or a Birth-day.
But to return to our Female Heads. The Ladies have been for some time in
a kind of
moulting Season
, with regard to that Part of their Dress,
having cast great Quantities of Ribbon, Lace, and Cambrick, and in some
measure reduced that Part of the human Figure to the beautiful globular
Form, which is natural to it. We have for a great while expected what
kind of Ornament would be substituted in the Place of those antiquated
Commodes. But our Female Projectors were all the last Summer so taken up
with the Improvement of their Petticoats, that they had not time to
attend to any thing else; but having at length sufficiently adorned
their lower Parts, they now begin to turn their Thoughts upon the other
Extremity, as well remembring the old Kitchen Proverb, that if you light
your Fire at both Ends, the middle will shift for it self.
I am engaged in this Speculation by a Sight which I lately met with at
the Opera. As I was standing in the hinder Part of the Box, I took
notice of a little Cluster of Women sitting together in the prettiest
coloured Hoods that I ever saw.
of them was Blue, another Yellow,
and another Philomot
; the fourth was of a Pink Colour, and the fifth
of a pale Green. I looked with as much Pleasure upon this little
party-coloured Assembly, as upon a Bed of Tulips, and did not know at
first whether it might not be an Embassy of
Indian
Queens; but upon my
going about into the Pit, and taking them in Front, I was immediately
undeceived, and saw so much Beauty in every Face, that I found them all
to be
English
. Such Eyes and Lips, Cheeks and Foreheads, could be the
Growth of no other Country. The Complection of their Faces hindred me
from observing any farther the Colour of their Hoods, though I could
easily perceive by that unspeakable Satisfaction which appeared in their
Looks, that their own Thoughts were wholly taken up on those pretty
Ornaments they wore upon their Heads.
I am informed that this Fashion spreads daily, insomuch that the Whig
and Tory Ladies begin already to hang out different Colours, and to shew
their Principles in their Head-dress. Nay if I may believe my Friend
Will. Honeycomb
, there is a certain old Coquet of his Acquaintance who
intends to appear very suddenly in a Rainbow Hood, like the
Iris
in
Dryden's Virgil
, not questioning but that among such a variety of
Colours she shall have a Charm for every Heart.
My Friend
Will
., who very much values himself upon his great Insights
into Gallantry, tells me, that he can already guess at the Humour a Lady
is in by her Hood, as the Courtiers of
Morocco
know the Disposition of
their present Emperor by the Colour of the Dress which he puts on. When
Melesinda
wraps her Head in Flame Colour, her Heart is set upon
Execution. When she covers it with Purple, I would not, says he, advise
her Lover to approach her; but if she appears in White, it is Peace, and
he may hand her out of her Box with Safety.
Will, informs me likewise, that these Hoods may be used as Signals. Why
else, says he, does
Cornelia
always put on a Black Hood when her
Husband is gone into the Country?
Such are my Friend
Honeycomb's
Dreams of Gallantry. For my own part, I
impute this Diversity of Colours in the Hoods to the Diversity of
Complexion in the Faces of my pretty Country Women.
Ovid
in his Art of
Love has given some Precepts as to this Particular, though I find they
are different from those which prevail among the Moderns. He recommends
a Red striped Silk to the pale Complexion; White to the Brown, and Dark
to the Fair. On the contrary my Friend
Will
., who pretends to be a
greater Master in this Art than
Ovid
, tells me, that the palest
Features look the most agreeable in white Sarsenet; that a Face which is
overflushed appears to advantage in the deepest Scarlet, and that the
darkest Complexion is not a little alleviated by a Black Hood. In short,
he is for losing the Colour of the Face in that of the Hood, as a Fire
burns dimly, and a Candle goes half out, in the Light of the Sun. This,
says he, your
Ovid
himself has hinted, where he treats of these
Matters, when he tells us that the blue Water Nymphs are dressed in Sky
coloured Garments; and that
Aurora
, who always appears in the Light of
the Rising Sun, is robed in Saffron.
Whether these his Observations are justly grounded I cannot tell: but I
have often known him, as we have stood together behind the Ladies,
praise or dispraise the Complexion of a Face which he never saw, from
observing the Colour of her Hood, and has been very seldom out in these
his Guesses.
I have Nothing more at Heart than the Honour and Improvement of the
Fair Sex
, I cannot conclude this Paper without an Exhortation to the
British
Ladies, that they would excel the Women of all other Nations
as much in Virtue and good Sense, as they do in Beauty; which they may
certainly do, if they will be as industrious to cultivate their Minds,
as they are to adorn their Bodies: In the mean while I shall recommend
to their most serious Consideration the Saying of an old
Greek
Poet,
C.
On the contrary as Nature
Feuille mort
, the russet yellow of dead leaves.
'I will not meddle with the Spectator. Let him fair-sex it to the
world's end.'
Swift's Journal to Stella.
T
. corrected by an erratum in No.
.
Contents
|
Friday, January 4, 1712 |
Steele |
Id vero est, quod ego mihi puto palmarium,
Me reperisse, quomodo adolescentulus
Meretricum ingenia et mores possit noscere:
Mature ut cum cognórit perpetuo oderit.
Ter.
Eun. Act. 5, Sc. 4.

No Vice or Wickedness which People fall into from Indulgence to
Desire
s
which are natural to all, ought to place them below the
Compassion of the virtuous Part of the World; which indeed often makes
me a little apt to suspect the Sincerity of their Virtue, who are too
warmly provoked at other Peoples personal Sins. The unlawful Commerce of
the Sexes is of all other the hardest to avoid; and yet there is no one
which you shall hear the rigider Part of Womankind speak of with so
little Mercy. It is very certain that a modest Woman cannot abhor the
Breach of Chastity too much; but pray let her hate it for her self, and
only pity it in others.
Will. Honeycomb
calls these over-offended
Ladies, the Outragiously Virtuous.
I do not design to fall upon Failures in general, with relation to the
Gift of Chastity, but at present only enter upon that large Field, and
begin with the Consideration of poor and publick Whores. The other
Evening passing along near
Covent-Garden
, I was jogged on the Elbow as
I turned into the Piazza, on the right Hand coming out of
James-street
, by a slim young Girl of about Seventeen, who with a pert
Air asked me if I was for a Pint of Wine. I do not know but I should
have indulged my Curiosity in having some Chat with her, but that I am
informed the Man of the
Bumper
knows me; and it would have made a
Story for him not very agreeable to some Part of my Writings, though I
have in others so frequently said that I am wholly unconcerned in any
Scene I am in, but meerly as a Spectator.
Impediment being in my
Way, we stood
under
one of the Arches by Twilight; and there I
could observe as exact Features as I had ever seen, the most agreeable
Shape, the finest Neck and Bosom, in a Word, the whole Person of a Woman
exquisitely Beautiful. She affected to allure me with a forced
Wantonness in her Look and Air; but I saw it checked with Hunger and
Cold: Her Eyes were wan and eager, her Dress thin and tawdry, her Mein
genteel and childish. This strange Figure gave me much Anguish of Heart,
and to avoid being seen with her I went away, but could not forbear
giving her a Crown. The poor thing sighed, curtisied, and with a
Blessing, expressed with the utmost Vehemence, turned from me. This
Creature is what they call
newly come upon the Town
, but who, I
suppose, falling into cruel Hands was left in the first Month from her
Dishonour, and exposed to pass through the Hands and Discipline of one
of those Hags of Hell whom we call Bawds. But lest I should grow too
suddenly grave on this Subject, and be my self outragiously good, I
shall turn to a Scene in one of
Fletcher's
Plays, where this Character
is drawn, and the Œconomy of Whoredom most admirably described. The
Passage I would point to is in the third Scene of the second Act of
The
Humorous Lieutenant. Leucippe
who is Agent for the King's Lust, and
bawds at the same time for the whole Court, is very pleasantly
introduced, reading her Minutes as a Person of Business, with two Maids,
her Under-Secretaries, taking Instructions at a Table before her. Her
Women, both those under her present Tutelage, and those which she is
laying wait for, are alphabetically set down in her Book; and as she is
looking over the Letter
C
, in a muttering Voice, as if between
Soliloquy and speaking out, she says,
Her Maidenhead will yield me; let me see now;
She is not Fifteen they say: For her Complexion—-
Cloe, Cloe, Cloe, here I have her,
Cloe, the Daughter of a Country Gentleman;
Here Age upon Fifteen. Now her Complexion,
A lovely brown; here 'tis; Eyes black and rolling,
The Body neatly built; she strikes a Lute well,
Sings most enticingly: These Helps consider'd,
Her Maidenhead will amount to some three hundred,
Or three hundred and fifty Crowns, 'twill bear it handsomly.
Her Father's poor, some little Share deducted,
To buy him a Hunting Nag—
These Creatures are very well instructed in the Circumstances and
Manners of all who are any Way related to the Fair One whom they have a
Design upon.
Cloe
is to be purchased with
350
Crowns, and the
Father taken off with a Pad; the Merchant's Wife next to her, who
abounds in Plenty, is not to have downright Money, but the mercenary
Part of her Mind is engaged with a Present of Plate and a little
Ambition. She is made to understand that it is a Man of Quality who dies
for her. The Examination of a young Girl for Business, and the crying
down her Value for being a slight Thing, together with every other
Circumstance in the Scene, are inimitably excellent, and have the true
Spirit of Comedy; tho' it were to be wished the Author had added a
Circumstance which should make
Leucippe's
Baseness more odious.
It must not be thought a Digression from my intended Speculation, to
talk of Bawds in a Discourse upon Wenches; for a Woman of the Town is
not thoroughly and properly such, without having gone through the
Education of one of these Houses. But the compassionate Case of very
many is, that they are taken into such Hands without any the least
Suspicion, previous Temptation, or Admonition to what Place they are
going. The last Week I went to an Inn in the City to enquire for some
Provisions which were sent by a Waggon out of the Country; and as I
waited in one of the Boxes till the Chamberlain had looked over his
Parcel, I heard an old and a young Voice repeating the Questions and
Responses of the Church-Catechism. I thought it no Breach of good
Manners to peep at a Crevice, and look in at People so well employed;
but who should I see there but the most artful Procuress in the Town,
examining a most beautiful Country-Girl, who had come up in the same
Waggon with my Things,
Whether she was well educated, could forbear
playing the Wanton with Servants, and idle fellows, of which this Town
,
says she,
is too full
: At the same time,
Whether she knew enough of
Breeding, as that if a Squire or a Gentleman, or one that was her
Betters, should give her a civil Salute, she should curtsy and be
humble, nevertheless.
Her innocent
forsooths, yes's, and't please
you's, and she would do her Endeavour
, moved the good old Lady to take
her out of the Hands of a Country Bumpkin her Brother, and hire her for
her own Maid. I staid till I saw them all marched out to take Coach; the
brother loaded with a great Cheese, he prevailed upon her to take for
her Civilities to
his
Sister. This poor Creature's Fate is not far off
that of her's whom I spoke of above,
it is not to be doubted, but
after she has been long enough a Prey to Lust she will be delivered over
to Famine; the Ironical Commendation of the Industry and Charity of
these antiquated Ladies
, these
Directors of Sin, after they can no
longer commit it, makes up the Beauty of the inimitable Dedication to
the
Plain-Dealer
, and is a Masterpiece of Raillery on this Vice.
But to understand all the Purleues of this Game the better, and to
illustrate this Subject in future Discourses, I must venture my self,
with my Friend
Will
, into the Haunts of Beauty and Gallantry; from
pampered Vice in the Habitations of the Wealthy, to distressed indigent
Wickedness expelled the Harbours of the Brothel.
T.
under in
fifty
. These
Wycherley's
Plain-Dealer
having given offence to many ladies, was
inscribed in a satirical
billet doux
dedicatory 'To My Lady B .'
Contents
|
Saturday, January 5, 1712 |
Addison |
Cedite Romani Scriptores, cedite Graii.1
Propert.

is nothing in Nature
more irksome than
general Discourses,
especially when they turn chiefly upon Words. For this Reason I shall
wave the Discussion of that Point which was started some Years since,
whether
Milton's Paradise Lost
may be called an Heroick Poem? Those
who will not give it that Title, may call it (if they please) a
Divine
Poem
. It
be sufficient to its Perfection, if it has in it all the
Beauties of the highest kind of Poetry; and as for those who
alledge
it is not an Heroick Poem, they advance no more to the Diminution
of it, than if they should say
Adam
is not
Æneas
, nor
Eve
Helen
.
I shall therefore examine it by the Rules of Epic Poetry, and see
whether it falls short of the
Iliad
or
Æneid
, in the Beauties which
are essential to that kind of Writing.
first thing to be considered
in an Epic Poem, is the Fable
, which is perfect or imperfect,
according as the Action which it relates is more or less so. This Action
should have three Qualifications in it. First, It
be but One
Action. Secondly, It should be an entire Action; and, Thirdly, It should
be a great Action
. To consider the Action of the
Iliad
,
Æneid
,
and
Paradise Lost
, in these three several Lights.
Homer
preserve
the Unity of his Action hastens into the Midst of Things, as
Horace
has observed
: Had he
up to
Leda's Egg
, or begun much later,
even at the Rape of
Helen
, or the Investing of
Troy
, it is manifest
that the Story of the Poem would have been a Series of several Actions.
He therefore opens his Poem with the Discord of his Princes, and
artfully
interweaves, in the several succeeding Parts of it, an
Account of every Thing
material
which relates to
them
and had
passed before that fatal Dissension. After the same manner,
Æneas
makes his first Appearance in the
Tyrrhene
Seas, and within Sight of
Italy
, because the Action proposed to be celebrated was that of his
settling himself in
Latium
. But because it was necessary for the
Reader to know what had happened to him in the taking of
Troy
, and in
the preceding Parts of his Voyage,
Virgil
makes his Hero relate it by
way of Episode in the second and third Books of the
Æneid
. The
Contents of both which Books come before those of the first Book in the
Thread of the Story, tho' for preserving of this Unity of Action they
follow them in the Disposition of the Poem.
Milton
, in imitation of
these two great Poets, opens his
Paradise Lost
with an Infernal
Council plotting the Fall of Man, which is the Action he proposed to
celebrate; and as for those great Actions, which preceded, in point of
Time, the Battle of the Angels, and the Creation of the World, (which
would have entirely destroyed the Unity of his principal Action, had he
related them in the same Order that they happened) he cast them into the
fifth, sixth, and seventh Books, by way of Episode to this noble Poem.
Aristotle
allows, that
Homer
has nothing to boast of as to
the Unity of his Fable
, tho' at the same time that great Critick and
Philosopher endeavours to palliate this Imperfection in the
Greek
Poet, by imputing it in some measure to the very Nature of an Epic Poem.
have been of opinion, that the
Æneid
also labours
in this
Particular, and has Episodes which may be looked upon as Excrescencies
rather than as Parts of the Action.
the contrary, the Poem, which we
have now under our Consideration, hath no other Episodes than such as
naturally arise from the Subject, and yet is filled with such a
Multitude of astonishing
Incidents
, that it gives us at the same
time a Pleasure of the greatest Variety, and of the greatest
Simplicity; uniform in its Nature, tho' diversified in the Execution.
I must observe also, that as
Virgil
, in the Poem which was designed to
celebrate the Original of the
Roman
Empire, has described the Birth of
its great Rival, the
Carthaginian
Commonwealth:
Milton
, with the
like Art, in his Poem on the
Fall of Man
, has related the Fall of
those Angels who are his professed Enemies. Besides the many other
Beauties in such an Episode, its running parallel with the great Action
of the Poem hinders it from breaking the Unity so much as another
Episode would have done, that had not so great an Affinity with the
principal Subject. In
, this is the same kind of Beauty which the
Criticks admire in
The Spanish Frier
, or
The Double Discovery
where the two different Plots look like Counter-parts and Copies of one
another.
The second Qualification required in the Action of an Epic Poem, is,
that it should be an
entire
Action: An Action is entire when it is
complete in all its Parts; or, as
Aristotle
describes it, when it
consists of a Beginning, a Middle, and an End. Nothing should go before
it, be intermixed with it, or follow after it, that is not related to
it. As on the contrary, no single Step should be omitted in that just
and regular Progress which it must be supposed to take from its Original
to its Consummation. Thus we see the Anger of
Achilles
in its Birth,
its Continuance and Effects; and
Æneas's
Settlement in
Italy
,
carried on thro' all the Oppositions in his Way to it both by Sea and
Land. The Action in
Milton
excels (I think) both the former in this
Particular; we see it contrived in Hell, executed upon Earth, and
punished by Heaven.
Parts of it are told in the most distinct
Manner, and grow out of one another in the most natural
Order
.
The third Qualification of an Epic Poem is its
Greatness
. The Anger of
Achilles
was of such Consequence, that it embroiled the Kings of
Greece
, destroyed the Heroes of
Troy
, and engaged all the Gods in
Factions.
Æneas's
Settlement in
Italy
produced the
Cæsars
, and
gave Birth to the
Roman
Empire.
Milton's
Subject was still greater
than either of the former; it does not determine the Fate of single
Persons or Nations, but of a whole Species. The united Powers of Hell
are joined together for the Destruction of Mankind, which they affected
in part, and would have completed, had not Omnipotence it self
interposed. The principal Actors are Man in his greatest Perfection, and
Woman in her highest Beauty. Their Enemies are the fallen Angels: The
Messiah their Friend, and the Almighty their Protector. In short, every
thing that is great in the whole Circle of Being, whether within the
Verge of Nature, or out of it, has a proper Part assigned it in this
noble Poem.
In Poetry, as in Architecture, not only the Whole, but the principal
Members, and every Part of them, should be Great. I
not presume to
say, that the Book of Games in the
Æneid
, or that in the
Iliad
, are
not of this Nature, nor to reprehend
Virgil's
Simile of the Top
,
and many other of the same
kind
in the
Iliad
, as liable to any
Censure in this Particular; but I think we may say, without
derogating from
those wonderful Performances, that there is an unquestionable
Magnificence in every Part of
Paradise Lost
, and indeed a much greater
than could have been formed upon any Pagan System.
But
Aristotle
, by the Greatness of the Action, does not only mean that
it should be great in its Nature, but also in its Duration, or in other
Words that it should have a due Length in it, as well as what we
properly call Greatness. The
Measure of this kind of Magnitude, he
explains by the following Similitude.
An Animal, no bigger than a
Mite, cannot appear perfect to the Eye, because the Sight takes it in at
once, and has only a confused Idea of the Whole, and not a distinct Idea
of all its Parts; if on the contrary you should suppose an Animal of ten
thousand Furlongs in length, the Eye would be so filled with a single
Part of it, that it could not give the Mind an Idea of the Whole. What
these Animals are to the Eye, a very short or a very long Action would
be to the Memory. The first would be, as it were, lost and swallowed up
by it, and the other difficult to be contained in it.
Homer
Virgil
have shewn their principal Art in this Particular; the Action
of the
Iliad
, and that of the
Æneid
, were in themselves exceeding
short, but are so beautifully extended and diversified by the
Invention
of
Episodes
, and the Machinery of Gods, with the like poetical
Ornaments, that they make up an agreeable Story, sufficient to employ
the Memory without overcharging it.
Milton's
Action is enriched with
such a Variety of Circumstances, that I have taken as much Pleasure in
reading the Contents of his Books, as in the best invented Story I ever
met with. It is possible, that the Traditions, on which the
Iliad
and
Æneid
were built, had more Circumstances in them than the History of
the
Fall of Man
, as it is related in Scripture. Besides, it was easier
for
Homer
and
Virgil
to dash the Truth with Fiction, as they were in
no danger of offending the Religion of their Country by it. But as for
Milton
, he had not only a very few Circumstances upon which to raise
his Poem, but was also obliged to proceed with the greatest Caution in
every thing that he added out of his own Invention. And, indeed,
notwithstanding all the Restraints he was under, he has filled his Story
with so many surprising Incidents, which bear so close an Analogy with
what is delivered in Holy Writ, that it is capable of pleasing the most
delicate Reader, without giving Offence to the most scrupulous.
The modern Criticks have collected from several Hints in the
Iliad
and
Æneid
the Space of Time, which is taken up by the Action of each of
those Poems; but as a great Part of
Milton's
Story was transacted in
Regions that lie out of the Reach of the Sun and the Sphere of Day, it
is impossible to gratify the Reader with such a Calculation, which
indeed would be more curious than instructive; none of the Criticks,
either Ancient or Modern, having laid down Rules to circumscribe the
Action of an Epic Poem with any determin'd Number of Years, Days or
Hours.
This Piece of Criticism on
Milton's Paradise Lost
shall be carried on
in the following
Saturdays
Papers
.
L.
'Give place to him, Writers of Rome and Greece.'
This
application to Milton of a line from the last elegy (25th) in the second
book of Propertius is not only an example of Addison's felicity in
choice of motto for a paper, but was so bold and well-timed that it must
have given a wholesome shock to the minds of many of the
Spectator's
readers. Addison was not before Steele in appreciation of Milton and
diffusion of a true sense of his genius. Milton was the subject of the
first piece of poetical criticism in the
Tatler
; where, in his sixth
number, Steele, having said that 'all Milton's 'thoughts are wonderfully
just and natural,' dwelt on the passage in which Adam tells his thoughts
upon first falling asleep, soon after his creation. This passage he
contrasts with 'the same apprehension of Annihilation' ascribed to Eve
in a much lower sense by Dryden in his operatic version of
Paradise
Lost
. In
Tatlers
and
Spectators
Steele and Addison had been equal
contributors to the diffusion of a sense of Milton's genius. In Addison
it had been strong, even when, at Oxford, in April, 1694, a young man
trained in the taste of the day, he omitted Shakespeare from a rhymed
'Account of the chief English Poets,' but of Milton said:
'Whate'er his pen describes I more than see,
Whilst ev'ry verse, array'd in majesty,
Bold and sublime, my whole attention draws,
And seems above the critics' nicer laws.'
Eighteen years older than he was when he wrote that, Addison now
prepares by a series of Saturday Essays,—the Saturday Paper which
reached many subscribers only in time for Sunday reading, being always
set apart in the
Spectator
for moral or religious topics, to show
that, judged also by Aristotle and the "critics' nicer laws," Milton was
even technically a greater epic poet than either Homer or Virgil. This
nobody had conceded. Dryden, the best critic of the outgoing generation,
had said in the Dedication of the Translations of
Juvenal
and
Persius
, published in 1692,
"As for Mr. Milton, whom we all admire with so much Justice, his
Subject, is not that of an Heroick Poem, properly so call'd: His
Design is the Losing of our Happiness; his Event is not prosperous,
like that of all other Epique Works" (Dryden's French spelling of
the word Epic is suggestive. For this new critical Mode was one of the
fashions that had been imported from Paris); "His Heavenly Machines
are many, and his Human Persons are but two. But I will not take Mr.
Rymer's work out of his Hands: He has promised the World a Critique
on that Author; wherein, tho' he will not allow his Poem for Heroick,
I hope he will grant us, that his Thoughts are elevated, his Words
sounding, and that no Man has so happily copy'd the manner of Homer;
or so copiously translated his Grecisms and the Latin Elegancies of
Virgil. 'Tis true he runs into a Flat of Thought, sometimes for a
Hundred Lines together, but 'tis when he is got into a Track of
Scripture ... Neither will I justify Milton for his Blank Verse,
tho' I may excuse him, by the Example of Hanabal Caro and other
Italians who have used it: For whatever Causes he alledges for the
abolishing of Rhime (which I have not now the leisure to examine), his
own particular Reason is plainly this, that Rhime was not his Talent;
he had neither the Ease of doing it, nor the Graces of it."
So Dryden, who appreciated Milton better than most of his critical
neighbours, wrote of him in 1692. The promise of Rymer to discuss Milton
was made in 1678, when, on the last page of his little book,
The
Tragedies of the Last Age consider'd and examined by the Practice of the
Ancients and by the Common Sense of all Ages, in a letter to Fleetwold
Shepheard, Esq
. (father of two ladies who contribute an occasional
letter to the
Spectator
), he said:
"With the remaining Tragedies I
shall also send you some reflections on that Paradise Lost of
Milton's, which some are pleased to call a Poem, and assert Rhime
against the slender Sophistry wherewith he attaques it."
But two years
after the appearance of Dryden's
Juvenal
and
Persius
Rymer prefixed
to his translation of Réné Rapin's
Reflections on Aristotle's Poesie
some Reflections of his own on Epic Poets. Herein he speaks under the
head Epic Poetry of Chaucer, 'in whose time language was not capable of
heroic character;' or Spenser, who "wanted a true Idea, and lost himself
by following an unfaithful guide, besides using a stanza which is in no
wise proper for our language;" of Sir William Davenant, who, in
Gondibert
, "has some strokes of an extraordinary judgment," but "is
for unbeaten tracks and new ways of thinking;" "his heroes are
foreigners;" of Cowley, in whose
Davideis
"David is the least part of
the Poem," and there is want of the "one illustrious and perfect action
which properly is the subject of an Epick Poem": all failing through
ignorance or negligence of the Fundamental Rules or Laws of Aristotle.
But he contemptuously passes over Milton without 'mention.' Réné Rapin,
that great French oracle of whom Dryden said, in the Preface to his own
conversion of
Paradise Lost
into an opera, that he was 'alone
sufficient, were all other critics lost, to teach anew the Art of
Writing,' Réné Rapin in the work translated and introduced by Rymer,
worshipped in Aristotle the one God of all orthodox critics. Of his Laws
he said,
'There is no arriving at Perfection but by these Rules, and they
certainly go astray that take a different course.... And if a Poem
made by these Rules fails of success, the fault lies not in the Art,
but in the Artist; all who have writ of this Art, have followed no
other Idea but that of Aristotle.'
Again as to Style,
'to say the truth, what is good on this subject is all taken from
Aristotle, who is the only source whence good sense is to be drawn,
when one goes about to write.'
This was the critical temper Addison resolved to meet on its own ground
and do battle with for the honour of that greatest of all Epic Poets to
whom he fearlessly said that all the Greeks and Latins must give place.
In so doing he might suggest here and there cautiously, and without
bringing upon himself the discredit of much heresy,—indeed, without
being much of a heretic, —that even the Divine Aristotle sometimes fell
short of perfection. The conventional critics who believed they kept the
gates of Fame would neither understand nor credit him. Nine years after
these papers appeared, Charles Gildon, who passed for a critic of
considerable mark, edited with copious annotation as '
the Laws of
Poetry
' (1721), the Duke of Buckingham's 'Essay on Poetry,' Roscommon's
'Essay on Translated Verse,' and Lord Lansdowne 'on Unnatural Flights in
Poetry,' and in the course of comment Gildon said that
'Mr. Addison in the Spectators, in his criticisms upon Milton, seems
to have mistaken the matter, in endeavouring to bring that poem to the
rules of the epopœia, which cannot be done ... It is not an Heroic
Poem, but a Divine one, and indeed of a new species. It is plain that
the proposition of all the heroic poems of the ancients mentions some
one person as the subject of their poem... But Milton begins his poem
of things, and not of men.'
The Gildons are all gone; and when, in the next generation after theirs,
national life began, in many parts of Europe, strongly to assert itself
in literature against the pedantry of the French critical lawgivers, in
Germany Milton's name was inscribed on the foremost standard of the men
who represented the new spirit of the age. Gottsched, who dealt French
critical law from Leipzig, by passing sentence against Milton in his
'Art of Poetry' in 1737, raised in Bodmer an opponent who led the revolt
of all that was most vigorous in German thought, and put an end to
French supremacy. Bodmer, in a book published in 1740
Vom Wunderbaren
in der Poesie
, justified and exalted Milton, and brought Addison to his
aid by appending to his own work a translation of these Milton papers
out of the
Spectator
. Gottsched replied; Bodmer retorted. Bodmer
translated
Paradise Lost
; and what was called the English or Milton
party (but was, in that form, really a German national party) were at
last left masters of the field. It was right that these papers of
Addison should be brought in as aids during the contest. Careful as he
was to conciliate opposing prejudices, he was yet first in the field,
and this motto to the first of his series of Milton papers, 'Yield place
to him, Writers of Greece and Rome,' is as the first trumpet note of the
one herald on a field from which only a quick ear can yet distinguish
among stir of all that is near, the distant tramp of an advancing host.
so irksom as
say
Aristotle,
Poetics
, III. § I, after a full discussion of
Tragedy, begins by saying,
'with respect to that species of Poetry which imitates by Narration
... it is obvious, that the Fable ought to be dramatically
constructed, like that of Tragedy, and that it should have for its
Subject one entire and perfect action, having a beginning, a middle,
and an end;'
forming a complete whole, like an animal, and therein differing,
Aristotle says, from History, which treats not of one Action, but of one
Time, and of all the events, casually connected, which happened to one
person or to many during that time.
Poetics
, I. § 9.
'Epic Poetry agrees so far with Tragic as it is an imitation of great
characters and actions.'
Aristotle (from whose opinion, in this matter alone, his worshippers
departed, right though he was) ranked a perfect tragedy above a perfect
epic; for, he said,
'all the parts of the Epic poem are to be found in Tragedy, not all
those of Tragedy in the Epic poem.'
Nec reditum Diomedis ab interitu Meleagri,
Nec gemino bellum Trojanum orditur ab ovo,
Semper ad eventum festinat, et in medias res,
Non secus ac notas, auditorem rapit—
De Arte Poet.
II. 146-9.
with great Art
the Story
Poetics
, V. § 3. In arguing the superiority of Tragic to
Epic Poetry, Aristotle says,
'there is less Unity in all Epic imitation; as appears from this—that
any Epic Poem will furnish matter for several Tragedies ... The
Iliad, for example, and the Odyssey, contain many such subordinate
parts, each of which has a certain Magnitude and Unity of its own; yet
is the construction of those Poems as perfect, and as nearly
approaching to the imitation of a single action, as possible.'
labours also
Circumstances
Simplicity
.
Dryden's
Spanish Friar
has been praised also by Johnson
for the happy coincidence and coalition of the tragic and comic plots,
and Sir Walter Scott said of it, in his edition of Dryden's
Works
, that
'the felicity does not consist in the ingenuity of his original
conception, but in the minutely artificial strokes by which the reader
is perpetually reminded of the dependence of the one part of the Play
on the other. These are so frequent, and appear so very natural, that
the comic plot, instead of diverting our attention from the tragic
business, recalls it to our mind by constant and unaffected allusion.
No great event happens in the higher region of the camp or court that
has not some indirect influence upon the intrigues of Lorenzo and
Elvira; and the part which the gallant is called upon to act in the
revolution that winds up the tragic interest, while it is highly in
character, serves to bring the catastrophe of both parts of the play
under the eye of the spectator, at one and the same time.'
Method
Æneid
, Bk. VII. 11. 378-384, thus translated by Dryden:
'And as young striplings whip the top for sport,
On the smooth pavement of an empty court,
The wooden engine files and whirls about,
Admir'd, with clamours, of the beardless rout;
They lash aloud, each other they provoke,
And lend their little souls at every stroke:
Thus fares the Queen, and thus her fury blows
Amidst the crowds, and trundles as she goes.'
nature
offence to
Poetics
, II. section 4, where it is said of the
magnitude of Tragedy.
Intervention
Contents
|
Monday, January 7, 1712 |
Steele |
—Minus aptus acutis
Naribus Horum Hominum.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator1,
'As you are
Spectator-General, I apply myself to you in the
following Case; viz. I d
o not wear a Sword, but I often divert my self
at the Theatre, where I frequently see a Set of Fellows pull plain
People, by way of Humour
and2 Frolick, by the Nose, upon
frivolous or no Occasions. A Friend of mine the other Night applauding
what a graceful Exit Mr.
Wilks made, one of these Nose-wringers
overhearing him, pinched him by the nose. I was in the Pit the other
Night, (when it was very much crowded) a Gentleman leaning upon me,
and very heavily, I very civilly requested him to remove his Hand; for
which he pulled me by the Nose. I would not resent it in so publick a
Place, because I was unwilling to create a Disturbance; but have since
reflected upon it as a thing that is unmanly and disingenuous, renders
the Nose-puller odious, and makes the Person pulled by the Nose look
little and contemptible. This Grievance I humbly request you would
endeavour to redress.
I am your Admirer, &c.
James Easy.
Mr.
Spectator,
Your Discourse of the 29th of
December on Love and Marriage is of so
useful a Kind, that I cannot forbear adding my Thoughts to yours on
that Subject. Methinks it is a Misfortune, that the Marriage State,
which in its own Nature is adapted to give us the compleatest
Happiness this Life is capable of, should be so uncomfortable a one to
so many as it daily proves. But the Mischief generally proceeds from
the unwise Choice People make for themselves, and Expectation of
Happiness from Things not capable of giving it. Nothing but the good
Qualities of the Person beloved can be a Foundation for a Love of
Judgment and Discretion; and whoever expects Happiness from any Thing
but Virtue, Wisdom, Good-humour, and a Similitude of Manners, will
find themselves widely mistaken. But how few are there who seek after
these things, and do not rather make Riches their chief if not their
only Aim? How rare is it for a Man, when he engages himself in the
Thoughts of Marriage, to place his Hopes of having in such a Woman a
constant, agreeable Companion? One who will divide his Cares and
double his Joys? Who will manage that Share of his Estate he intrusts
to her Conduct with Prudence and Frugality, govern his House with
Œconomy and Discretion, and be an Ornament to himself and Family?
Where shall we find the Man who looks out for one who places her chief
Happiness in the Practice of Virtue, and makes her Duty her continual
Pleasure? No: Men rather seek for Money as the Complement of all their
Desires; and regardless of what kind of Wives they take, they think
Riches will be a Minister to all kind of Pleasures, and enable them to
keep Mistresses, Horses, Hounds, to drink, feast, and game with their
Companions, pay their Debts contracted by former Extravagancies, or
some such vile and unworthy End; and indulge themselves in Pleasures
which are a Shame and Scandal to humane Nature. Now as for the Women;
how few of them are there who place the Happiness of their Marriage in
the having a wise and virtuous Friend? one who will be faithful and
just to all, and constant and loving to them? who with Care and
Diligence will look after and improve the Estate, and without grudging
allow whatever is prudent and convenient? Rather, how few are there
who do not place their Happiness in outshining others in Pomp and
Show? and that do not think within themselves when they have married
such a rich Person, that none of their Acquaintance shall appear so
fine in their Equipage, so adorned in their Persons, or so magnificent
in their Furniture as themselves? Thus their Heads are filled with
vain Ideas; and I heartily wish I could say that Equipage and Show
were not the Chief Good of so many Women as I fear it is.
After this Manner do both Sexes deceive themselves, and bring
Reflections and Disgrace upon the most happy and most honourable State
of Life; whereas if they would but correct their depraved Taste,
moderate their Ambition, and place their Happiness upon proper
Objects, we should not find Felicity in the Marriage State such a
Wonder in the World as it now is.
Sir, if you think these Thoughts worth inserting
among3 your own,
be pleased to give them a better Dress, and let them pass abroad; and
you will oblige
Your Admirer,
A. B.
Mr.
Spectator,
As I was this Day walking in the Street, there happened to pass by on
the other Side of the Way a Beauty, whose Charms were so attracting
that it drew my Eyes wholly on that Side, insomuch that I neglected my
own Way, and chanced to run my Nose directly against a Post; which the
Lady no sooner perceived, but fell out into a Fit of Laughter, though
at the same time she was sensible that her self was the Cause of my
Misfortune, which in my Opinion was the greater Aggravation of her
Crime. I being busy wiping off the Blood which trickled down my Face,
had not Time to acquaint her with her Barbarity, as also with my
Resolution,
viz. never to look out of my Way for one of her Sex
more: Therefore, that your humble Servant may be revenged, he desires
you to insert this in one of your next Papers, which he hopes will be
a Warning to all the rest of the Women Gazers, as well as to poor
Anthony Gape.
Mr.
Spectator,
I desire to know in your next, if the merry Game of
The Parson has
lost his Cloak, is not mightily in Vogue amongst the fine Ladies this
Christmas; because I see they wear Hoods of all Colours, which I
suppose is for that Purpose: If it is, and you think it proper, I will
carry some of those Hoods with me to our Ladies in
Yorkshire;
because they enjoyned me to bring them something from
London that
was very New. If you can tell any Thing in which I can obey their
Commands more agreeably, be pleased to inform me, and you will
extremely oblige
Your humble Servant
Oxford, Dec. 29.
Mr.
Spectator,
Since you appear inclined to be a Friend to the Distressed, I beg you
would assist me in an Affair under which I have suffered very much.
The reigning Toast of this Place is
Patetia; I have pursued her with
the utmost Diligence this Twelve-month, and find nothing stands in my
Way but one who flatters her more than I can. Pride is her Favourite
Passion; therefore if you would be so far my Friend as to make a
favourable Mention of her in one of your Papers, I believe I should
not fail in my Addresses. The Scholars stand in Rows, as they did to
be sure in your Time, at her Pew-door: and she has all the Devotion
paid to her by a Crowd of Youth
s who are unacquainted with the Sex,
and have Inexperience added to their Passion: However, if it succeeds
according to my Vows, you will make me the happiest Man in the World,
and the most obliged amongst all
Your humble Servants.
Mr.
Spectator,
I came
to4 my Mistress's Toilet this Morning, for I am admitted
when her Face is stark naked: She frowned, and cryed Pish when I said
a thing that I stole; and I will be judged by you whether it was not
very pretty.
Madam, said I, you
shall5 forbear that Part of your
Dress; it may be well in others, but you cannot place a Patch where it
does not hide a Beauty.
T.
This Letter was written by Mr. James Heywood, many years
wholesale linen-draper on Fish-street Hill, who died in 1776, at the age
of 90. His 'Letters and Poems' were (including this letter at p.100) in
a second edition, in 12mo, in 1726.
or
amongst
at
should
Contents
|
Tuesday, January 8, 1712 |
Addison |
—Ævo rarissima nostro
Simplicitas—
Ovid.

I was this Morning surprised with a great knocking at the Door, when my
Landlady's Daughter came up to me, and told me, that there was a Man
below desired to speak with me. Upon my asking her who it was, she told
me it was a very grave elderly Person, but that she did not know his
Name. I immediately went down to him, and found him to be the Coachman
of my worthy Friend Sir
Roger De Coverley
. He told me that his Master
came to Town last Night, and would be glad to take a Turn with me in
Gray's-Inn
Walks.
I was wondring in my self what had brought Sir
Roger
to Town, not having lately received any Letter from him, he told
me that his Master was come up to get a Sight of Prince
Eugene
and that he desired I would immediately meet him.
I was not a little pleased with the Curiosity of the old Knight, though
I did not much wonder at it, having heard him say more than once in
private Discourse, that he looked upon Prince
Eugenio
(for so the
Knight always calls him) to be a greater Man than
Scanderbeg
.
I was no sooner come into
Grays-Inn Walks
, but I heard my Friend upon
the Terrace hemming twice or thrice to himself with great Vigour, for he
loves to clear his Pipes in good Air (to make use of his own Phrase) and
is not a little pleased with any one who takes notice of the Strength
which he still exerts in his Morning Hems.
I was touched with a secret Joy at the Sight of the good old Man, who
before he saw me was engaged in Conversation with a Beggar-Man that had
asked an Alms of him. I could hear my Friend chide him for not finding
out some Work; but at the same time saw him put his Hand in his Pocket
and give him Six-pence.
Our Salutations were very hearty on both Sides, consisting of many kind
Shakes of the Hand, and several affectionate Looks which we cast upon
one another. After which the Knight told me my good Friend his Chaplain
was very well, and much at my Service, and that the
Sunday
before he
had made a most incomparable Sermon out of Dr.
Barrow
. I have left,
says he, all my Affairs in his Hands, and being willing to lay an
Obligation upon him, have deposited with him thirty Marks, to be
distributed among his poor Parishioners.
He then proceeded to acquaint me with the Welfare of
Will Wimble
.
which he put his Hand into his Fob and presented me in his Name with a
Tobacco-Stopper, telling me that
Will
had been busy all the Beginning
of the Winter in turning great Quantities of them; and that he
made
a Present of one to every Gentleman in the Country who has good
Principles, and smoaks. He added, that poor
Will
was at present under
great Tribulation, for that
Tom Touchy
had taken the Law of him for
cutting some Hazel Sticks out of one of his Hedges.
Among other Pieces of News which the Knight brought from his
Country-Seat, he informed me that
Moll White
was dead; and that about
a Month after her Death the Wind was so very high, that it blew down the
End of one of his Barns. But for my own part, says Sir
Roger
, I do not
think that the old Woman had any hand in it.
He afterwards fell into an Account of the Diversions which had passed in
his House during the Holidays; for Sir
Roger
, after the laudable Custom
of his Ancestors, always keeps open House at
Christmas
. I learned
from him that he had killed eight fat Hogs for the Season, that he had
dealt about his Chines very liberally amongst his Neighbours, and that
in particular he had sent a string of Hogs-puddings with a pack of Cards
to every poor Family in the Parish. I have often thought, says Sir
Roger
, it happens very well that
Christmas
should fall out in the
Middle of the Winter. It
the most dead uncomfortable Time of the
Year, when the poor People would suffer very much from their
Poverty and Cold
, if they had not good Cheer, warm Fires, and
Christmas
Gambols to support them. I love to rejoice their poor Hearts at this
season, and to see the whole Village merry in my great Hall. I allow a
double Quantity of Malt to my small Beer, and set it a running for
twelve Days to every one that calls for it. I have always a Piece of
cold Beef and a Mince-Pye upon the Table, and am wonderfully pleased to
see my Tenants pass away a whole Evening in playing their innocent
Tricks, and smutting one another. Our Friend
Will Wimble
is as merry
as any of them, and shews a thousand roguish Tricks upon these
Occasions.
I was very much delighted with the Reflection of my old Friend, which
carried so much Goodness in it. He
launched out into the Praise of
the late Act of Parliament
for securing the Church of
England
, and
told me, with great Satisfaction, that he believed it already began to
take Effect, for that a rigid Dissenter, who chanced to dine at his
House on
Christmas
Day, had been observed to eat very plentifully of
his Plumb-porridge.
After having dispatched all our Country Matters, Sir
Roger
made several
Inquiries concerning the Club, and particularly of his old Antagonist
Sir
Andrew Freeport
. He asked me with a kind of Smile, whether Sir
Andrew
had not taken Advantage of his Absence, to vent among them some
of his Republican Doctrines; but soon after gathering up his Countenance
into a more than ordinary Seriousness, Tell me truly, says he, don't you
think Sir
Andrew
had a Hand in the Pope's Procession—-but without
giving me time to answer him, Well, well, says he, I know you are a wary
Man, and do not care to talk of publick Matters.
The Knight then asked me, if I had seen Prince
Eugenio
, and made me
promise to get him a Stand in some convenient Place where he might have
a full Sight of that extraordinary Man, whose Presence does so much
Honour to the
British
Nation. He
very long on the Praises of
this Great General, and I found that, since I was with him in the
Country, he had drawn many Observations together out of his reading in
Baker's
Chronicle, and other Authors,
who
always lie in his Hall
Window, which very much redound to the Honour of this Prince.
Having passed away the greatest Part of the Morning in hearing the
Knight's Reflections, which were partly private, and partly political,
he asked me if I would smoak a Pipe with him over a Dish of Coffee at
Squire's
. As I love the old Man, I take Delight in complying with
every thing that is agreeable to him, and accordingly waited on him to
the Coffee-house, where his venerable Figure drew upon us the Eyes of
the whole Room. He had no sooner seated himself at the upper End of the
high Table, but he called for a clean Pipe, a Paper of Tobacco, a Dish
of Coffee, a Wax-Candle, and the
Supplement
with such an Air of
Cheerfulness and Good-humour, that all the Boys in the Coffee-room (who
seemed to take pleasure in serving him) were at once employed on his
several Errands, insomuch that no Body else could come at a Dish of Tea,
till the Knight had got all his Conveniences about him.
L.
Prince Eugene was at this in London, and caressed by
courtiers who had wished to prevent his coming, for he was careful to
mark his friendship for the Duke of Marlborough, who was the subject of
hostile party intrigues. During his visit he stood godfather to Steel's
second son, who was named, after, Eugene.
had made
Cold and Poverty
The Act against Occasional Conformity, 10 Ann. cap. 2.
that
Contents
|
Wednesday, January 9, 1712 |
Steele |
Discit enim citius, meminitque libentius illud,
Quod quis deridet, quam quod probat.
Hor.

I
not know that I have been in greater Delight for these many Years,
than in beholding the Boxes at the Play the last Time
The Scornful
Lady
was acted. So great an Assembly of Ladies placed in gradual
Rows in all the Ornaments of Jewels, Silk and Colours, gave so lively
and gay an Impression to the Heart, that methought the Season of the
Year was vanished; and I did not think it an ill Expression of a young
Fellow who stood near me, that called the Boxes Those Beds of Tulips. It
was a pretty Variation of the Prospect, when any one of these fine
Ladies rose up and did Honour to herself and Friend at a Distance, by
curtisying; and gave Opportunity to that Friend to shew her Charms to
the same Advantage in returning the Salutation. Here that Action is as
proper and graceful, as it is at Church unbecoming and impertinent. By
the way, I must take the Liberty to observe that I did not see any one
who is usually so full of Civilities at Church, offer at any such
Indecorum during any Part of the Action of the Play.
Such beautiful Prospects gladden our Minds, and when considered in
general, give innocent and pleasing Ideas. He that dwells upon any one
Object of Beauty, may fix his Imagination to his Disquiet; but the
Contemplation of a whole Assembly together, is a Defence against the
Encroachment of Desire: At least to me, who have taken pains to look at
Beauty abstracted from the Consideration of its being the Object of
Desire; at Power, only as it sits upon another, without any Hopes of
partaking any Share of it; at Wisdom and Capacity, without any
Pretensions to rival or envy its Acquisitions: I say to me, who am
really free from forming any Hopes by beholding the Persons of beautiful
Women, or warming my self into Ambition from the Successes of other Men,
this World is not only a meer Scene, but a very pleasant one. Did
Mankind but know the Freedom which there is in keeping thus aloof from
the World, I should have more Imitators, than the powerfullest Man in
the Nation has Followers. To be no Man's Rival in Love, or Competitor in
Business, is a Character which if it does not recommend you as it ought
to Benevolence among those whom you live with, yet has it certainly this
Effect, that you do not stand so much in need of their Approbation, as
you would if you aimed at it more, in setting your Heart on the same
things which the Generality doat on. By this means, and with this easy
Philosophy, I am never less at a Play than when I am at the Theatre; but
indeed I am seldom so well pleased with the Action as in that Place, for
most Men follow Nature no longer than while they are in their
Night-Gowns, and all the busy Part of the Day are in Characters which
they neither become or act in with Pleasure to themselves or their
Beholders. But to return to my Ladies: I was very well pleased to see so
great a Crowd of them assembled at a Play, wherein the Heroine, as the
Phrase is, is so just a Picture of the Vanity of the Sex in tormenting
their Admirers. The Lady who pines for the Man whom she treats with so
much Impertinence and Inconstancy, is drawn with much Art and Humour.
Her Resolutions to be extremely civil, but her Vanity arising just at
the Instant that she resolved to express her self kindly, are described
as by one who had studied the Sex. But when my Admiration is fixed upon
this excellent Character, and two or three others in the Play, I must
confess I was moved with the utmost Indignation at the trivial,
senseless, and unnatural Representation of the Chaplain. It is possible
there may be a Pedant in Holy Orders, and we have seen one or two of
them in the World; but such a Driveler as Sir
Roger
, so bereft of all
manner of Pride, which is the Characteristick of a Pedant, is what one
would not believe could come into the Head of the same Man who drew the
rest of the Play. The Meeting between
Welford
and him shews a Wretch
without any Notion of the Dignity of his Function; and it is out of all
common Sense that he should give an Account of himself
as one sent four
or five Miles in a Morning on Foot for Eggs.
It is not to be denied,
but his Part and that of the Maid whom he makes Love to, are excellently
well performed; but a Thing which is blameable in it self, grows still
more so by the Success in the Execution of it. It is so mean a Thing to
gratify a loose Age with a scandalous Representation of what is
reputable among Men, not to say what is sacred, that no Beauty, no
Excellence in an Author ought to attone for it; nay, such Excellence is
an Aggravation of his Guilt, and an Argument that he errs against the
Conviction of his own Understanding and Conscience. Wit should be tried
by this Rule, and an Audience should rise against such a Scene, as
throws down the Reputation of any thing which the Consideration of
Religion or Decency should preserve from Contempt. But all this Evil
arises from this one Corruption of Mind, that makes Men resent Offences
against their Virtue, less than those against their Understanding. An
Author shall write as if he thought there was not one Man of Honour or
Woman of Chastity in the House, and come off with Applause: For an
Insult upon all the Ten Commandments, with the little Criticks, is not
so bad as the Breach of an Unity of Time or Place. Half Wits do not
apprehend the Miseries that must necessarily flow from Degeneracy of
Manners; nor do they know that Order is the Support of Society. Sir
Roger
and his Mistress are Monsters of the Poets own forming; the
Sentiments in both of them are such as do not arise in Fools of their
Education. We all know that a silly Scholar, instead of being below
every one he meets with, is apt to be exalted above the Rank of such as
are really his Superiors: His Arrogance is always founded upon
particular Notions of Distinction in his own Head, accompanied with a
pedantick Scorn of all Fortune and Preheminence, when compared with his
Knowledge and Learning. This very one Character of Sir
Roger
, as silly
as it really is, has done more towards the Disparagement of Holy Orders,
and consequently of Virtue it self, than all the Wit that Author or any
other could make up for in the Conduct of the longest Life after it. I
do not pretend, in saying this, to give myself Airs of more Virtue than
my Neighbours, but assert it from the Principles by which Mankind must
always be governed. Sallies of Imagination are to be overlooked, when
they are committed out of Warmth in the Recommendation of what is Praise
worthy; but a deliberate advancing of Vice, with all the Wit in the
World, is as ill an Action as any that comes before the Magistrate, and
ought to be received as such by the People.
T.
Beaumont and Fletcher's. Vol. II.
Contents
|
Thursday, January 10, 1712 |
Addison |
Mille trahens varios adverso sole colores.
Virg.

I receive a double Advantage from the Letters of my Correspondents,
first as they shew me which of my Papers are most acceptable to them;
and in the next place as they furnish me with Materials for new
Speculations. Sometimes indeed I do not make use of the Letter it self,
but form the Hints of it into Plans of my own Invention; sometimes I
take the Liberty to change the Language or Thought into my own Way of
Speaking and Thinking, and always (if it can be done without Prejudice
to the Sense) omit the many Compliments and Applauses which are usually
bestowed upon me.
Besides the two Advantages above-mentioned which I receive from the
Letters that are sent me, they give me an Opportunity of lengthning out
my Paper by the skilful Management of the subscribing Part at the End of
them, which perhaps does not a little conduce to the Ease, both of my
self and Reader.
Some will have it, that I often write to my self, and am the only
punctual Correspondent I have. This Objection would indeed be material,
were the Letters I communicate to the Publick stuffed with my own
Commendations: and if, instead of endeavouring to divert or instruct my
Readers, I admired in them the Beauty of my own Performances. But I
shall leave these wise Conjecturers to their own Imaginations, and
produce the three following Letters for the Entertainment of the Day.
Sir,
'I was last Thursday in an Assembly of Ladies, where there were
Thirteen different coloured Hoods. Your Spectator of that Day lying
upon the Table, they ordered me to read it to them, which I did with a
very clear Voice, 'till I came to the Greek Verse at the End of it.
I must confess I was a little startled at its popping upon me so
unexpectedly. However, I covered my Confusion as well as I could, and
after having mutter'd two or three hard Words to my self, laugh'd
heartily, and cried, A very good Jest, Faith. The Ladies desired me
to explain it to them; but I begged their pardon for that, and told
them, that if it had been proper for them to hear, they may be sure
the Author would not have wrapp'd it up in Greek. I then let drop
several Expressions, as if there was something in it that was not fit
to be spoken before a Company of Ladies. Upon which the Matron of the
Assembly, who was dressed in a Cherry-coloured Hood, commended the
Discretion of the Writer for having thrown his filthy Thoughts into
Greek, which was likely to corrupt but few of his Readers. At the
same time she declared herself very well pleased, that he had not
given a decisive Opinion upon the new-fashioned Hoods; for to tell you
truly, says she, I was afraid he would have made us ashamed to shew
our Heads. Now, Sir, you must know, since this unlucky Accident
happened to me in a Company of Ladies, among whom I passed for a most
ingenious Man, I have consulted one who is well versed in the Greek
Language, and he assures me upon his Word, that your late Quotation
means no more, than that Manners and not Dress are the Ornaments of a
Woman. If this comes to the Knowledge of my Female Admirers, I shall
be very hard put to it to bring my self off handsomely. In the mean
while I give you this Account, that you may take care hereafter not to
betray any of your Well-wishers into the like Inconveniencies. It is
in the Number of these that I beg leave to subscribe my self,
Tom Trippit.
Mr. Spectator,
' Your Readers are so well pleased with your Character of Sir Roger De
Coverley, that there appeared a sensible Joy in every Coffee-house,
upon hearing the old Knight was come to Town. I am now with a Knot of
his Admirers, who make it their joint Request to you, that you would
give us publick Notice of the Window or Balcony where the Knight
intends to make his Appearance. He has already given great
Satisfaction to several who have seen him at Squire's Coffee-house.
If you think fit to place your short Face at Sir Roger's Left Elbow,
we shall take the Hint, and gratefully acknowledge so great a Favour.
I am, Sir,
Your most Devoted
Humble Servant,
C. D.
Sir,
' Knowing that you are very Inquisitive after every thing that is
Curious in Nature, I will wait on you if you please in the Dusk of the
Evening, with my Show upon my Back, which I carry about with me in a
Box, as only consisting of a Man, a Woman, and an Horse. The two first
are married, in which State the little Cavalier has so well acquitted
himself, that his Lady is with Child. The big-bellied Woman, and her
Husband, with their whimsical Palfry, are so very light, that when
they are put together into a Scale, an ordinary Man may weigh down the
whole Family. The little Man is a Bully in his Nature; but when he
grows cholerick I confine him to his Box till his Wrath is over, by
which Means I have hitherto prevented him from doing Mischief. His
Horse is likewise very vicious, for which Reason I am forced to tie
him close to his Manger with a Pack-thread. The Woman is a Coquet. She
struts as much as it is possible for a Lady of two Foot high, and
would ruin me in Silks, were not the Quantity that goes to a large
Pin-Cushion sufficient to make her a Gown and Petticoat. She told me
the other Day, that she heard the Ladies wore coloured Hoods, and
ordered me to get her one of the finest Blue. I am forced to comply
with her Demands while she is in her present Condition, being very
willing to have more of the same Breed. I do not know what she may
produce me, but provided it be a Show I shall be very well
satisfied. Such Novelties should not, I think, be concealed from the
British Spectator; for which Reason I hope you will excuse this
Presumption in
Your most Dutiful,
most Obedient,
and most Humble Servant,
S. T.
L.
Contents
|
Friday, January 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Longa est injuria, longæ
Ambages
Virg.
1
Mr.
Spectator,
The Occasion of this Letter is of so great Importance, and the
Circumstances of it such, that I know you will but think it just to
insert it, in Preference of all other Matters that can present
themselves to your Consideration. I need not, after I have said this,
tell you that I am in Love. The Circumstances of my Passion I shall
let you understand as well as a disordered Mind will admit. That
cursed Pickthank Mrs.
Jane! Alas, I am railing at one to you by her
Name as familiarly as if you were acquainted with her as well as my
self: But I will tell you all, as fast as the alternate Interruptions
of Love and Anger will give me Leave. There is a most agreeable young
Woman in the World whom I am passionately in Love with, and from whom
I have for some space of Time received as great Marks of Favour as
were fit for her to give, or me to desire. The successful Progress of
the Affair of all others the most essential towards a Man's Happiness,
gave a new Life and Spirit not only to my Behaviour and Discourse, but
also a certain Grace to all my Actions in the Commerce of Life in all
Things tho' never so remote from Love.
You know the predominant
Passion spreads its self thro' all a Man's Transactions, and exalts or
depresses
him2 according to the Nature of such Passion. But alas,
I have not yet begun my Story, and what is making Sentences and
Observations when a Man is pleading for his Life? To begin then: This
Lady has corresponded with me under the Names of Love, she my
Belinda, I her
Cleanthes. Tho' I am thus well got into the Account
of my Affair, I cannot keep in the Thread of it so much as to give you
the Character of Mrs.
Jane, whom I will not hide under a borrowed
Name; but let you know that this Creature has been since I knew her
very handsome, (tho' I will not allow her even she
has been for the
future) and during the Time of her Bloom and Beauty was so great a
Tyrant to her Lovers, so over-valued her self and under-rated all her
Pretenders, that they have deserted her to a Man; and she knows no
Comfort but that common one to all in her Condition, the Pleasure of
interrupting the Amours of others. It is impossible but you must have
seen several of these Volunteers in Malice, who pass their whole Time
in the most labourous Way of Life in getting Intelligence, running
from Place to Place with new Whispers, without reaping any other
Benefit but the Hopes of making others as unhappy as themselves. Mrs.
Jane happened to be at a Place where I, with many others well
acquainted with my Passion for
Belinda, passed a
Christmas
Evening. There was among the rest a young Lady so free in Mirth, so
amiable in a just Reserve that accompanied it; I wrong her to call it
a Reserve, but there appeared in her a Mirth or Chearfulness which was
not a Forbearance of more immoderate Joy, but the natural Appearance
of all which could flow from a Mind possessed of an Habit of Innocence
and Purity. I must have utterly forgot
Belinda to have taken no
Notice of one who was growing up to the same womanly Virtues which
shine to Perfection in her, had I not distinguished one who seemed to
promise to the World the same Life and Conduct with my faithful and
lovely
Belinda. When the Company broke up, the fine young Thing
permitted me to take Care of her Home. Mrs.
Jane saw my particular
Regard to her, and was informed of my attending her to her Father's
House. She came early to
Belinda the next Morning, and asked her if
Mrs.
Such-a-one had been with her? No. If Mr.
Such-a-one's Lady?
No. Nor your Cousin
Such-a-one? No. Lord, says Mrs.
Jane, what is
the Friendship of Woman?—Nay, they may laugh at it. And did no one
tell you any thing of the Behaviour of your Lover Mr.
What d'ye call
last Night? But perhaps it is nothing to you that he is to be married
to young Mrs.—on
Tuesday next?
Belinda was here ready to die with
Rage and Jealousy. Then Mrs.
Jane goes on: I have a young Kinsman
who is Clerk to a Great Conveyancer, who shall shew you the rough
Draught of the Marriage Settlement. The World says her Father gives
him Two Thousand Pounds more than he could have with you. I went
innocently to wait on
Belinda as usual, but was not admitted; I writ
to her, and my Letter was sent back unopened. Poor
Betty her Maid,
who is on my Side, has been here just now blubbering, and told me the
whole Matter. She says she did not think I could be so base; and that
she is now odious to her Mistress for having so often spoke well of
me, that she dare not mention me more. All our Hopes are placed in
having these Circumstances fairly represented in the
Spectator, which
Betty says she dare not but bring up as soon as it is brought in;
and has promised when you have broke the Ice to own this was laid
between us: And when I can come to an Hearing, the young Lady will
support what we say by her Testimony, that I never saw her but that
once in my whole Life. Dear Sir, do not omit this true Relation, nor
think it too particular; for there are Crowds of forlorn Coquets who
intermingle themselves with other Ladies, and contract Familiarities
out of Malice, and with no other Design but to blast the Hopes of
Lovers, the Expectation of Parents, and the Benevolence of Kindred. I
doubt not but I shall be,
Sir,
Your most obliged
humble Servant,
Cleanthes.
Will's Coffee-house,
Jan. 10.
Sir,
The other Day entering a Room adorned with the Fair Sex, I offered,
after the usual Manner, to each of them a Kiss; but one, more scornful
than the rest, turned her Cheek. I did not think it proper to take any
Notice of it till I had asked your Advice.
Your humble Servant,
E. S.
The Correspondent is desir'd to say which Cheek the Offender turned to
him.
T.
Ubi visus eris nostra medicabilis arte
Fac monitis fugias otia prima meis.
Ovid.
Rem. Am
.
it
Contents
Advertisement
From the Parish-Vestry,
January 9.
All Ladies who come to Church in the New-fashioned Hoods,
are desired to be there before Divine Service begins,
lest they divert the Attention of the Congregation.
Ralph.
|
Saturday, January 12, 1712 |
Addison |
Notandi sunt tibi Mores.
Hor.

Having examined the Action of
Paradise Lost
, let us in the next place
consider the Actors.
This is Aristotle's Method of considering, first the Fable, and secondly
the Manners; or, as we generally call them
in
English
, the Fable and the Characters.
Homer
has excelled all the Heroic Poets that ever wrote, in the
Multitude and Variety of his Characters. Every God that is admitted into
this Poem, acts a Part which would have been suitable to no other Deity.
His Princes are as much distinguished by their Manners, as by their
Dominions; and even those among them, whose Characters seem wholly made
up of Courage, differ from one another as to the particular kinds of
Courage in which they excel. In short, there is scarce a Speech or
Action in the
Iliad
, which the Reader may not ascribe to the Person
that speaks or acts, without seeing his Name at the Head of it.
Homer
does not only outshine all other Poets in the Variety, but also
in the Novelty of his Characters. He has introduced among his
Grecian
Princes a Person who had lived thrice the Age of Man, and conversed with
Theseus, Hercules, Polyphemus
, and the first Race of Heroes.
principal Actor is the
Son
of a Goddess, not to mention the
Offspring of other Deities, who have
likewise a Place in his Poem,
and the venerable
Trojan
Prince, who was the Father of so many Kings
and Heroes. There is in these several Characters of
Homer
, a certain
Dignity as well as Novelty, which adapts them in a more peculiar manner
to the Nature of an Heroic Poem. Tho' at the same time, to give them the
greater Variety, he has described a
Vulcan
, that is a Buffoon among
his Gods, and a
Thersites
among his Mortals.
Virgil
falls infinitely short of
Homer
in the Characters of his
Poem, both as to their Variety and Novelty.
Æneas
is indeed a perfect
Character, but as for
Achates
, tho' he is stiled the Hero's Friend, he
does nothing in the whole Poem which may deserve that Title.
Gyas
,
Mnesteus
,
Sergestus
and
Cloanthus
, are all of them Men of the same
Stamp and Character.
Fortemque Gyan, fortemque Cloanthum.
There are indeed several very Natural Incidents on the Part of
Ascanius
; as that of
Dido
cannot be sufficiently admired. I do not
see any thing new or particular in
Turnus
.
Pallas
and
Evander
are
remote
Copies of
Hector
and
Priam
, as
Lausus
and
Mezentius
are
almost Parallels to
Pallas
and
Evander
. The Characters of
Nisus
and
Eurialus
are beautiful, but common.
We must not forget the Parts
of Sinon, Camilla, and some few others, which are fine Improvements
on the Greek Poet.
In short, there is neither that Variety nor
Novelty in the Persons of the
Æneid
, which we meet with in those of
the
Iliad
.
If
look into the Characters of
Milton
, we shall find that he has
introduced all the Variety
his Fable
was capable of receiving. The
whole Species of Mankind was in two Persons at the Time to which the
Subject of his Poem is confined. We have, however, four distinct
Characters in these two Persons. We see Man and Woman in the highest
Innocence and Perfection, and in the most abject State of Guilt and
Infirmity.
two last Characters are, indeed, very common and obvious,
but the two first are not only more magnificent, but more new
than
any Characters either in
Virgil
or
Homer
, or indeed in the whole
Circle of Nature.
Milton
so sensible of this Defect in the Subject of his Poem, and
of the few Characters it would afford him, that he has brought into it
two Actors of a Shadowy and Fictitious Nature, in the Persons of
Sin
and
Death
, by which means he has
wrought into
the Body of his
Fable a very beautiful and well-invented Allegory. But notwithstanding
the Fineness of this Allegory may attone for it in some measure; I
cannot think that Persons of such a Chymerical Existence are proper
Actors in an Epic Poem; because there is not that measure of Probability
annexed to them, which is requisite in Writings of this kind,
as I
shall shew more at large hereafter
.
Virgil
has, indeed, admitted Fame as an Actress in the
Æneid
, but
the Part she acts is very short, and none of the most admired
Circumstances in that Divine Work. We
in Mock-Heroic Poems,
particularly in the
Dispensary
and the
Lutrin
several
Allegorical Persons of this Nature which are very beautiful in those
Compositions,
may, perhaps, be used as an Argument, that the Authors
of them were of Opinion,
such
Characters might have a Place in an
Epic Work. For my own part, I should be glad the Reader would think so,
for the sake of the Poem I am now examining, and must further add, that
if such empty unsubstantial Beings may be ever made use of on this
Occasion, never were any more nicely imagined, and employed in more
proper Actions, than those of which I am now speaking.
Another Principal Actor in this Poem is the great Enemy of Mankind. The
of
Ulysses
in
Homer's Odyssey
is very much admired by
Aristotle
,
as perplexing that Fable with very agreeable Plots and
Intricacies, not only by the many Adventures in his Voyage, and the
Subtility of his Behaviour, but by the various Concealments and
Discoveries of his Person in several Parts of that Poem. But the Crafty
Being I have now mentioned, makes a much longer Voyage than
Ulysses
,
puts in practice many more Wiles and Stratagems, and hides himself under
a greater Variety of Shapes and Appearances, all of which are severally
detected, to the great Delight and Surprize of the Reader.
We may likewise observe with how much Art the Poet has varied several
Characters of the Persons that speak to his infernal Assembly. On the
contrary, how has he represented the whole Godhead exerting it self
towards Man in its full Benevolence under the Three-fold Distinction of
a Creator, a Redeemer and a Comforter!
Nor must we omit the Person of
Raphael
, who amidst his Tenderness and
Friendship for Man, shews such a Dignity and Condescension in all his
Speech and Behaviour, as are suitable to a Superior Nature.
The Angels
are indeed as much diversified in Milton, and distinguished by their
proper Parts, as the Gods are in Homer or Virgil. The Reader will
find nothing ascribed to Uriel, Gabriel, Michael, or Raphael, which
is not in a particular manner suitable to their respective Characters.
There
another Circumstance in the principal Actors of the
Iliad
and
Æneid
, which gives a
peculiar
Beauty to those two Poems, and
was therefore contrived with very great Judgment. I mean the Authors
having chosen for their Heroes, Persons who were so nearly related to
the People for whom they wrote.
Achilles
was a Greek, and
Æneas
the
remote Founder of
Rome
. By this means their Countrymen (whom they
principally proposed to themselves for their Readers) were particularly
attentive to all the Parts of their Story, and sympathized with their
Heroes in all their Adventures. A
Roman
could not but rejoice in the
Escapes, Successes and Victories of
Æneas
, and be grieved at any
Defeats, Misfortunes or Disappointments that befel him; as a
Greek
must
have had the same Regard for
Achilles
. And it is plain, that each of
those Poems have lost this great Advantage, among those Readers to whom
their Heroes are as Strangers, or indifferent Persons.
Milton's
Poem is admirable in this respect, since it is impossible for
any of its Readers, whatever Nation, Country or People he may belong to,
not to be related to the Persons who are the principal Actors in it; but
what is still infinitely more to its Advantage, the principal Actors in
this Poem are not only our Progenitors, but our Representatives. We have
an actual Interest in every thing they do, and no less than our utmost
Happiness is concerned, and lies at Stake in all their Behaviour.
I shall subjoin as a Corollary to the foregoing Remark, an admirable
Observation out of
Aristotle
, which hath been very much misrepresented
in the Quotations of some Modern Criticks.
'If a Man of perfect and consummate Virtue falls into a Misfortune, it
raises our Pity, but not our Terror, because we do not fear that it
may be our own Case, who do not resemble the Suffering Person. But as
that great Philosopher adds, If we see a Man of Virtue mixt with
Infirmities, fall into any Misfortune, it does not only raise our Pity
but our Terror; because we are afraid that the like Misfortunes may
happen to our selves, who resemble the Character of the Suffering
Person.'
I shall
another Opportunity to observe, that a Person of
an absolute and consummate Virtue should never be introduced
in Tragedy, and shall only remark in this Place, that the foregoing Observation of
Aristotle
tho' it may be true in other Occasions, does not hold in this; because in the present
Case, though the Persons who fall into Misfortune are of the
most perfect and consummate Virtue, it is not to be considered
as what may possibly be, but what actually is our own Case;
since we are embarked with them on the same Bottom, and
must be Partakers of their Happiness or Misery.
In this,
some other very few Instances,
Aristotle's
Rules
for Epic Poetry (which he had drawn from his Reflections upon
Homer
) cannot be supposed to quadrate exactly with the Heroic
Poems which have been made since his Time; since it is plain
his Rules would
still have been
more perfect, could he have
perused the
Æneid
which was made some hundred Years after
his Death.
In my next, I shall go through other Parts of
Milton's
Poem;
and hope that what I shall there advance, as well as what I have
already written, will not only serve as a Comment upon
Milton,
but upon
Aristotle.
L.
These are what Aristotle means by the Fable and &c.
Offspring
Son of Aurora who has
that his Poem
It was especially for the novelty of
Paradise Lost
, that
John Dennis had in 1704 exalted Milton above the ancients. In putting
forward a prospectus of a large projected work upon 'the Grounds of
Criticism in Poetry,' he gave as a specimen of the character of his
work, the substance of what would be said in the beginning of the
Criticism upon Milton. Here he gave Milton supremacy on ground precisely
opposite to that chosen by Addison. He described him as
'one of the greatest and most daring Genius's that has appear'd in the
World, and who has made his country a glorious present of the most
lofty, but most irregular Poem, that has been produc'd by the Mind of
Man. That great Man had a desire to give the World something like an
Epick Poem; but he resolv'd at the same time to break thro' the Rules
of Aristotle. Not that he was ignorant of them, or contemned them....
Milton was the first who in the space of almost 4000 years resolv'd
for his Country's Honour and his own, to present the World with an
Original Poem; that is to say, a Poem that should have his own
thoughts, his own images, and his own spirit. In order to this he was
resolved to write a Poem, that, by virtue of its extraordinary
Subject, cannot so properly be said to be against the Rules as it may
be affirmed to be above them all ... We shall now shew for what
Reasons the choice of Milton's Subject, as it set him free from the
obligation which he lay under to the Poetical Laws, so it necessarily
threw him upon new Thoughts, new Images, and an Original Spirit. In
the next place we shall shew that his Thoughts, his Images, and by
consequence too, his Spirit are actually new, and different from those
of Homer and Virgil. Thirdly, we shall shew, that besides their
Newness, they have vastly the Advantage of Homer and Virgil.']
Paradise Lost
, Book II.
interwoven in
Sir Samuel Garth in his
Dispensary
, a mock-heroic poem
upon a dispute, in 1696, among doctors over the setting up of a
Dispensary in a room of the College of Physicians for relief of the sick
poor, houses the God of Sloth within the College, and outside, among
other allegories, personifies Disease as a Fury to whom the enemies of
the Dispensary offer libation. Boileau in his
Lutrin
a mock-heroic
poem written in 1673 on a dispute between two chief personages of the
chapter of a church in Paris, la Sainte Chapelle, as to the position of
a pulpit, had with some minor allegory, chiefly personified Discord, and
made her enter into the form of an old precentor, very much as in
Garth's poem the Fury Disease
'Shrill Colon's person took,
In morals loose, but most precise in look.'
that such
Poetics
II. § 17; III. §6.
particular
1
Poetics
II. § ii. But Addison misquotes the first clause. Aristotle
says that when a wholly virtuous man falls from prosperity into adversity,
'this is neither terrible
nor piteous, but
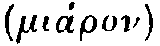
shocking. Then he adds that our pity is
excited by undeserved
misfortune, and our terror by some resemblance between the sufferer
and ourselves.'
have been still
Contents
|
Monday, January 14, 1712 |
Steele |
Audire est operæ pretium, procedere recte
Qui mœchis non vultis.
Hor.

I have upon several Occasions (that have occurred since I first took
into my Thoughts the present State of Fornication) weighed with my self,
in behalf of guilty Females, the Impulses of Flesh and Blood, together
with the Arts and Gallantries of crafty Men; and reflect with some Scorn
that most Part of what we in our Youth think gay and polite, is nothing
else but an Habit of indulging a Pruriency that Way. It will cost some
Labour to bring People to so lively a Sense of this, as to recover the
manly Modesty in the Behaviour of my Men Readers, and the bashful Grace
in the Faces of my Women; but in all Cases which come into Debate, there
are certain things previously to be done before we can have a true Light
into the Subject Matter; therefore it will, in the first Place, be
necessary to consider the impotent Wenchers and industrious Haggs, who
are supplied with, and are constantly supplying new Sacrifices to the
Devil of Lust. You are to know then, if you are so happy as not to know
it already, that the great Havock which is made in the Habitations of
Beauty and Innocence, is committed by such as can only lay waste and not
enjoy the Soil. When you observe the present State of Vice and Virtue,
the Offenders are such as one would think should have no Impulse to what
they are pursuing; as in Business, you see sometimes Fools pretend to be
Knaves, so in Pleasure, you will find old Men set up for Wenchers. This
latter sort of Men are the great Basis and Fund of Iniquity in the Kind
we are speaking of: You shall have an old rich Man often receive Scrawls
from the several Quarters of the Town, with Descriptions of the new
Wares in their Hands, if he will please to send Word when he will be
waited on. This Interview is contrived, and the Innocent is brought to
such Indecencies as from Time to Time banish Shame and raise Desire.
With these Preparatives the Haggs break their Wards by little and
little, 'till they are brought to lose all Apprehensions of what shall
befall them in the Possession of younger Men. It is a common Postscript
of an Hagg to a young Fellow whom she invites to a new Woman,
She has,
I assure you, seen none but old Mr. Such-a-one
. It pleases the old
Fellow that the Nymph is brought to him unadorned, and from his Bounty
she is accommodated with enough to dress her for other Lovers. This is
the most ordinary Method of bringing Beauty and Poverty into the
Possession of the Town: But the particular Cases of kind Keepers,
skilful Pimps, and all others who drive a separate Trade, and are not in
the general Society or Commerce of Sin, will require distinct
Consideration. At the same time that we are thus severe on the
Abandoned, we are apt to represent the Case of others with that
Mitigation as the Circumstances demand. Calling Names does no Good; to
speak worse of any thing than it deserves, does only take off from the
Credit of the Accuser, and has implicitly the Force of an Apology in the
Behalf of the Person accused. We shall therefore, according as the
Circumstances differ, vary our Appellations of these Criminals: Those
who offend only against themselves, and are not Scandals to Society, but
out of Deference to the sober Part of the World, have so much Good left
in them as to be ashamed, must not be huddled in the common Word due to
the worst of Women; but Regard is to be had to their Circumstances when
they fell, to the uneasy Perplexity under which they lived under
senseless and severe Parents, to the Importunity of Poverty, to the
Violence of a Passion in its Beginning well grounded, and all other
Alleviations which make unhappy Women resign the Characteristick of
their Sex, Modesty. To do otherwise than thus, would be to act like a
Pedantick Stoick, who thinks all Crimes alike, and not like an impartial
Spectator
, who looks upon them with all the Circumstances that diminish
or enhance the Guilt. I am in Hopes, if this Subject be well pursued,
Women will hereafter from their Infancy be treated with an Eye to their
future State in the World; and not have their Tempers made too
untractable from an improper Sourness or Pride, or too complying from
Familiarity or Forwardness contracted at their own Houses. After these
Hints on this Subject, I shall end this Paper with the following genuine
Letter; and desire all who think they may be concerned in future
Speculations on this Subject, to send in what they have to say for
themselves for some Incidents in their Lives, in order to have proper
Allowances made for their Conduct.
January 5, 1711.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The Subject of your Yesterday's Paper is of so great Importance, and
the thorough handling of it may be so very useful to the Preservation
of many an innocent young Creature, that I think every one is obliged
to furnish you with what Lights he can, to expose the pernicious Arts
and Practices of those unnatural Women called Bawds. In order to this
the enclosed is sent you, which is
verbatim the Copy of a Letter
written by a Bawd of Figure in this Town to a noble Lord. I have
concealed the Names of both, my Intention being not to expose the
Persons but the Thing.
I am,
Sir,
Your humble ServantMy Lord,
'I having a great Esteem for your Honour, and a better Opinion of
you than of any of the Quality, makes me acquaint you of an Affair
that I hope will oblige you to know. I have a Niece that came to
Town about a Fortnight ago. Her Parents being lately dead she came
to me, expecting to a found me in so good a Condition as to a set
her up in a Milliner's Shop. Her Father gave Fourscore Pounds with
her for five Years: Her Time is out, and she is not Sixteen; as
pretty a black Gentlewoman as ever you saw, a little Woman, which I
know your Lordship likes: well shaped, and as fine a Complection for
Red and White as ever I saw; I doubt not but your Lordship will be
of the same Opinion. She designs to go down about a Month hence
except I can provide for her, which I cannot at present. Her Father
was one with whom all he had died with him, so there is four
Children left destitute; so if your Lordship thinks fit to make an
Appointment where I shall wait on you with my Niece, by a Line or
two, I stay for your Answer; for I have no Place fitted up since I
left my House, fit to entertain your Honour. I told her she should
go with me to see a Gentleman a very good Friend of mine; so I
desire you to take no Notice of my Letter by reason she is ignorant
of the Ways of the Town. My Lord, I desire if you meet us to come
alone; for upon my Word and Honour you are the first that ever I
mentioned her to. So I remain,
Your Lordship's
Most humble Servant to Command.
'I beg of you to burn it when you've read it.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, January 15, 1712 |
Addison |
—tribus Anticyris caput insanabile—
Juv.

I was Yesterday engaged in an Assembly of Virtuosos, where one of them
produced many curious Observations which he had lately made in the
Anatomy of an Human Body. Another of the Company communicated to us
several wonderful Discoveries, which he had also made on the same
Subject, by the Help of very fine Glasses. This gave Birth to a great
Variety of uncommon Remarks, and furnished Discourse for the remaining
Part of the Day.
The different Opinions which were started on this Occasion, presented to
my Imagination so many new Ideas, that by mixing with those which were
already there, they employed my Fancy all the last Night, and composed a
very wild Extravagant Dream.
I was invited, methoughts, to the Dissection of a
Beau's Head
and of a
Coquet's Heart
, which were both of them laid on a Table before us. An
imaginary Operator opened the first with a great deal of Nicety, which,
upon a cursory and superficial View, appeared like the Head of another
Man; but upon applying our Glasses to it, we made a very odd Discovery,
namely, that what we looked upon as Brains, were not such in reality,
but an Heap of strange Materials wound up in that Shape and Texture, and
packed together with wonderful Art in the several Cavities of the Skull.
For, as
Homer
tells us, that the Blood of the Gods is not real Blood,
but only something like it; so we found that the Brain of a Beau is not
real Brain, but only something like it.
The
Pineal Gland
, which many of our Modern Philosophers suppose to be
the Seat of the Soul, smelt very strong of Essence and Orange-flower
Water, and was encompassed with a kind of Horny Substance, cut into a
thousand little Faces or Mirrours, which were imperceptible to the naked
Eye, insomuch that the Soul, if there had been any here, must have been
always taken up in contemplating her own Beauties.
We observed a long
Antrum
or Cavity in the
Sinciput
, that was filled
with Ribbons, Lace and Embroidery, wrought together in a most curious
Piece of Network, the Parts of which were likewise imperceptible to the
naked Eye. Another of these
Antrums
or Cavities was stuffed with
invisible Billetdoux, Love-Letters, pricked Dances, and other Trumpery
of the same Nature. In another we found a kind of Powder, which set the
whole Company a Sneezing, and by the Scent discovered it self to be
right
Spanish
. The several other Cells were stored with Commodities of
the same kind, of which it would be tedious to give the Reader an exact
Inventory.
There was a large Cavity on each side of the Head, which I must not
omit. That on the right Side was filled with Fictions, Flatteries, and
Falshoods, Vows, Promises, and Protestations; that on the left with
Oaths and Imprecations. There issued out a
Duct
from each of these
Cells, which ran into the Root of the Tongue, where both joined
together, and passed forward in one common
Duct
to the Tip of it. We
discovered several little Roads or Canals running from the Ear into the
Brain, and took particular care to trace them out through their several
Passages. One of them extended itself to a Bundle of Sonnets and little
musical Instruments. Others ended in several Bladders which were
filled either with Wind or Froth. But the latter Canal entered into a
great Cavity of the Skull, from whence there went another Canal into the
Tongue. This great Cavity was filled with a kind of Spongy Substance,
which the
French
Anatomists call
Galimatias
, and the
English
,
Nonsense.
The Skins of the Forehead were extremely tough and thick, and, what very
much surprized us, had not in them any single Blood-Vessel that we were
able to discover, either with or without our Glasses; from whence we
concluded, that the Party when alive must have been entirely deprived of
the Faculty of Blushing.
The
Os Cribriforme
was exceedingly stuffed, and in some Places damaged
with Snuff. We could not but take notice in particular of that small
Muscle which is not often discovered in Dissections, and draws the Nose
upwards, when it expresses the Contempt which the Owner of it has, upon
seeing any thing he does not like, or hearing any thing he does not
understand. I need not tell my learned Reader, this is that Muscle which
performs the Motion so often mentioned by the
Latin
Poets, when they
talk of a Man's cocking his Nose, or playing the Rhinoceros.
We did not find any thing very remarkable in the Eye, saving only, that
the
Musculi Amatorii
, or, as we may translate it into
English
, the
Ogling Muscles
, were very much worn and decayed with use; whereas on
the contrary, the
Elevator
, or the Muscle which turns the Eye towards
Heaven, did not appear to have been used at all.
I have only mentioned in this Dissection such new Discoveries as we were
able to make, and have not taken any notice of those Parts which are to
be met with in common Heads. As for the Skull, the Face, and indeed the
whole outward Shape and Figure of the Head, we could not discover any
Difference from what we observe in the Heads of other Men. We were
informed, that the Person to whom this Head belonged, had passed for
a
Man
above five and thirty Years; during which time he Eat and Drank
like other People, dressed well, talked loud, laught frequently, and on
particular Occasions had acquitted himself tolerably at a Ball or an
Assembly; to which one of the Company added, that a certain Knot of
Ladies took him for a Wit. He was cut off in the Flower of his Age by
the Blow of a Paring-Shovel, having been surprized by an eminent
Citizen, as he was tendring some Civilities to his Wife.
When we had thoroughly examined this Head with all its Apartments, and
its several kinds of Furniture, we put up the Brain, such as it was,
into its proper Place, and laid it aside under a broad Piece of Scarlet
Cloth, in order to be
prepared
, and kept in a great Repository of
Dissections; our Operator telling us that the Preparation would not be
so difficult as that of another Brain, for that he had observed several
of the little Pipes and Tubes which ran through the Brain were already
filled with a kind of Mercurial Substance, which he looked upon to be
true Quick-Silver.
He applied himself in the next Place to the
Coquet's Heart
, which he
likewise laid open with great Dexterity. There occurred to us many
Particularities in this Dissection; but being unwilling to burden my
Reader's Memory too much, I shall reserve this Subject for the
Speculation of another Day.
L.
Contents
|
Wednesday, January 16, 1712 |
Steele |
Errori nomen virtus posuisset honestum.
Hor.

Mr. Spectator,
'I hope you have Philosophy enough to be capable of bearing the
Mention of your Faults. Your Papers which regard the fallen Part of
the Fair Sex, are, I think, written with an Indelicacy, which makes
them unworthy to be inserted in the Writings of a Moralist who knows
the World. I cannot allow that you are at Liberty to observe upon the
Actions of Mankind with the Freedom which you seem to resolve upon; at
least if you do, you should take along with you the Distinction of
Manners of the World, according to the Quality and Way of Life of the
Persons concerned. A Man of Breeding speaks of even Misfortune among
Ladies without giving it the most terrible Aspect it can bear: And
this Tenderness towards them, is much more to be preserved when you
speak of Vices. All Mankind are so far related, that Care is to be
taken, in things to which all are liable, you do not mention what
concerns one in Terms which shall disgust another. Thus to tell a rich
Man of the Indigence of a Kinsman of his, or abruptly inform a
virtuous Woman of the Lapse of one who till then was in the same
degree of Esteem with her self, is in a kind involving each of them in
some Participation of those Disadvantages. It is therefore expected
from every Writer, to treat his Argument in such a Manner, as is most
proper to entertain the sort of Readers to whom his Discourse is
directed. It is not necessary when you write to the Tea-table, that
you should draw Vices which carry all the Horror of Shame and
Contempt: If you paint an impertinent Self-love, an artful Glance, an
assumed Complection, you say all which you ought to suppose they can
possibly be guilty of. When you talk with this Limitation, you behave
your self so as that you may expect others in Conversation may second
your Raillery; but when you do it in a Stile which every body else
forbears in Respect to their Quality, they have an easy Remedy in
forbearing to read you, and hearing no more of their Faults. A Man
that is now and then guilty of an Intemperance is not to be called a
Drunkard; but the Rule of polite Raillery, is to speak of a Man's
Faults as if you loved him. Of this Nature is what was said by
Cæsar: When one was railing with an uncourtly Vehemence, and broke
out, What must we call him who was taken in an Intrigue with another
Man's Wife? Cæsar answered very gravely,
A careless Fellow. This was
at once a Reprimand for speaking of a Crime which in those Days had
not the Abhorrence attending it as it ought, as well as an Intimation
that all intemperate Behaviour before Superiors loses its Aim, by
accusing in a Method unfit for the Audience. A Word to the Wise.
All I
mean here to say to you is, That the most free Person of Quality can
go no further than being
a kind Woman1; and you should never say
of a Man of Figure worse, than that he knows the World.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Francis Courtly.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a Woman of an unspotted Reputation, and know nothing I have ever
done which should encourage such Insolence; but here was one the other
Day, and he was dressed like a Gentleman too, who took the Liberty to
name the Words Lusty Fellow in my Presence. I doubt not but you will
resent it in Behalf of,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Celia.
Mr.
Spectator,
'You lately put out a dreadful Paper, wherein you promise a full
Account of the State of criminal Love; and call all the Fair who have
transgressed in that Kind by one very rude Name which I do not care to
repeat: But 1 desire to know of you whether I am or I am not of those?
My Case is as follows. I am kept by an old Batchelour, who took me so
young, that I knew not how he came by me: He is a Bencher of one of
the Inns of Court, a very gay healthy old Man; which is a lucky thing
for him, who has been, he tells me, a Scowrer, a Scamperer, a Breaker
of Windows, an Invader of Constables, in the Days of Yore when all
Dominion ended with the Day, and Males and Females met helter skelter,
and the Scowrers drove before them all who pretended to keep up Order
or Rule to the Interruption of Love and Honour. This is his way of
Talk, for he is very gay when he visits me; but as his former
Knowledge of the Town has alarmed him into an invincible Jealousy, he
keeps me in a pair of Slippers, neat Bodice, warm Petticoats, and my
own Hair woven in Ringlets, after a Manner, he says, he remembers. I
am not Mistress of one Farthing of Money, but have all Necessaries
provided for me, under the Guard of one who procured for him while he
had any Desires to gratify. I know nothing of a Wench's Life, but the
Reputation of it: I have a natural Voice, and a pretty untaught Step
in Dancing. His Manner is to bring an old Fellow who has been his
Servant from his Youth, and is gray-headed: This Man makes on the
Violin a certain Jiggish Noise to which I dance, and when that is over
I sing to him some loose Air, that has more Wantonness than Musick in
it. You must have seen a strange window'd House near
Hide-Park,
which is so built that no one can look out of any of the Apartments;
my Rooms are after that manner, and I never see Man, Woman, or Child,
but in Company with the two Persons above-mentioned. He sends me in
all the Books, Pamphlets, Plays, Operas and Songs that come out; and
his utmost Delight in me as a Woman, is to talk over old Amours in my
Presence, to play with my Neck, say
the Time was, give me a Kiss,
and bid me be sure to follow the Directions of my Guardian (the
above-mentioned Lady) and I shall never want. The Truth of my Case is,
I suppose, that I was educated for a Purpose he did not know he should
be unfit for when I came to Years. Now, Sir, what I ask of you, as a
Casuist, is to tell me how far in these Circumstances I am innocent,
though submissive; he guilty, though impotent?
I am,
Sir,
Your constant Reader,
Pucella.
To the Man called the Spectator.
Friend,
'Forasmuch as at the Birth of thy Labour, thou didst promise upon thy
Word, that letting alone the Vanities that do abound, thou wouldst
only endeavour to strengthen the crooked Morals of this our
Babylon,
I gave Credit to thy fair Speeches, and admitted one of thy Papers,
every Day save
Sunday, into my House; for the Edification of my
Daughter
Tabitha, and to the end that Susannah the Wife of my Bosom
might profit thereby. But alas, my Friend, I find that thou art a
Liar, and that the Truth is not in thee; else why didst thou in a
Paper which thou didst lately put forth, make mention of those vain
Coverings for the Heads of our Females, which thou lovest to liken
unto Tulips, and which are lately sprung up amongst us? Nay why didst
thou make mention of them in such a seeming, as if thou didst approve
the Invention, insomuch that my Daughter
Tabitha beginneth to wax
wanton, and to lust after these foolish Vanities? Surely thou dost see
with the Eyes of the Flesh. Verily therefore, unless thou dost
speedily amend and leave off following thine own Imaginations, I will
leave off thee.
Thy Friend as hereafter thou dost demean thyself,
Hezekiah Broadbrim.
T.
an unkind
Contents
|
Thursday, January 17, 1712 |
Budgell |
—fas est et ab hoste doceri.
Virg.

Mr. Spectator,
'I am so great a Lover of whatever is
French, that I lately
discarded an humble Admirer, because he neither spoke that Tongue, nor
drank Claret. I have long bewailed, in secret, the Calamities of my
Sex during the War, in all which time we have laboured under the
insupportable Inventions of
English Tire-Women, who, tho' they
sometimes copy indifferently well, can never compose with that
Goût
they do in
France.
I was almost in Despair of ever more seeing a Model from that dear
Country, when last Sunday I over-heard a Lady, in the next Pew to me,
whisper another, that at the
Seven Stars in
King-street
Covent-garden, there was a
Madamoiselle compleatly dressed just
come from
Paris.
I was in the utmost Impatience during the remaining part of the
Service, and as soon as ever it was over, having learnt the Milleners
Addresse, I went directly to her House in
King-street, but was
told that the
French Lady was at a Person of Qualitys in
Pall-mall, and would not be back again till very late that Night. I
was therefore obliged to renew my Visit very early this Morning, and
had then a full View of the dear Moppet from Head to Foot.
You cannot imagine, worthy Sir, how ridiculously I find we have all
been trussed up during the War, and how infinitely the
French Dress
excels ours.
The Mantua has no Leads in the Sleeves, and I hope we are not lighter
than the
French Ladies, so as to want that kind of Ballast; the
Petticoat has no Whale-bone; but fits with an Air altogether galant
and
degagé: the
Coiffeure is inexpressibly pretty, and in short,
the whole Dress has a thousand Beauties in it, which I would not have
as yet made too publick.
I thought fit, however, to give this Notice, that you may not be
surprized at my appearing
à la mode de Paris on the next
Birth-Night.
I am, Sir,
Your humble Servant,
Teraminta.
Within an Hour after I had read this Letter, I received another from the
Owner of the Puppet.
Sir,
'On Saturday last, being the 12th Instant, there arrived at my House
in King-street, Covent-Garden, a French Baby for the Year 1712. I
have taken the utmost Care to have her dressed by the most celebrated
Tyre-women and Mantua-makers in Paris, and do not find that I have
any Reason to be sorry for the Expence I have been at in her Cloaths
and Importation: However, as I know no Person who is so good a Judge
of Dress as your self, if you please to call at my House in your Way
to the City, and take a View of her, I promise to amend whatever you
shall disapprove in your next Paper, before I exhibit her as a Pattern
to the Publick.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Admirer,
and most obedient Servant,
Betty Cross-stitch.
As I am willing to do any thing in reason for the Service of my
Country-women, and had much rather prevent Faults than find them, I went
last Night to the House of the above-mentioned Mrs.
Cross-stitch
. As
soon as I enter'd, the Maid of the Shop, who, I suppose, was prepared
for my coming, without asking me any Questions, introduced me to the
little Damsel, and ran away to call her Mistress.
The Puppet was dressed in a Cherry-coloured Gown and Petticoat, with a
short working Apron over it, which discovered her Shape to the most
Advantage. Her Hair was cut and divided very prettily, with several
Ribbons stuck up and down in it. The Millener assured me, that her
Complexion was such as was worn by all the Ladies of the best Fashion in
Paris
. Her Head was extreamly high, on which Subject having long since
declared my Sentiments, I shall say nothing more to it at present. I was
also offended at a small Patch she wore on her Breast, which I cannot
suppose is placed there with any good Design.
Her Necklace was of an immoderate Length, being tied before in such a
manner that the two Ends hung down to her Girdle; but whether these
supply the Place of Kissing-Strings in our Enemy's Country, and whether
our
British
Ladies have any occasion for them, I shall leave to their
serious Consideration.
After having observed the Particulars of her Dress, as I was taking a
view of it altogether, the Shop-maid, who is a pert Wench, told me that
Mademoiselle
had something very Curious in the tying of her Garters;
but as I pay a due Respect even to a pair of Sticks when they are in
Petticoats, I did not examine into that Particular.
Upon the whole I was well enough pleased with the Appearance of this gay
Lady, and the more so because she was not Talkative, a Quality very
rarely to be met with in the rest of her Countrywomen.
As I was taking my leave, the Millener farther informed me, that with
the Assistance of a Watchmaker, who was her Neighbour, and the ingenious
Mr.
Powell
, she had also contrived another Puppet, which by the help
of several little Springs to be wound up within it, could move all its
Limbs, and that she had sent it over to her Correspondent in
Paris
to
be taught the various Leanings and Bendings of the Head, the Risings of
the Bosom, the Curtesy and Recovery, the genteel Trip, and the agreeable
Jet, as they are now practised in the Court of
France
.
She added that she hoped she might depend upon having my Encouragement
as soon as it arrived; but as this was a Petition of too great
Importance to be answered
extempore
, I left her without a Reply, and
made the best of my way to
Will. Honeycomb's
Lodgings, without whose
Advice I never communicate any thing to the Publick of this Nature.
X.
Contents
|
Friday, January 18, 1712 |
Steele |
Sermones ego mallem
Repentes per humum.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
Sir,
Your having done considerable Service in this great City, by
rectifying the Disorders of Families, and several Wives having
preferred your Advice and Directions to those of their Husbands,
emboldens me to apply to you at this Time. I am a Shop-keeper, and tho
but a young Man, I find by Experience that nothing but the utmost
Diligence both of Husband and Wife (among trading People) can keep
Affairs in any tolerable Order. My Wife at the Beginning of our
Establishment shewed her self very assisting to me in my Business as
much as could lie in her Way, and I have Reason to believe twas with
her Inclination; but of late she has got acquainted with a Schoolman,
who values himself for his great Knowledge in the
Greek Tongue. He
entertains her frequently in the Shop with Discourses of the Beauties
and Excellencies of that Language; and repeats to her several Passages
out of the
Greek Poets, wherein he tells her there is unspeakable
Harmony and agreeable Sounds that all other Languages are wholly
unacquainted with. He has so infatuated her with his Jargon, that
instead of using her former Diligence in the Shop, she now neglects
the Affairs of the House, and is wholly taken up with her Tutor in
learning by Heart Scraps of
Greek, which she vents upon all
Occasions. She told me some Days ago, that whereas I use some
Latin
Inscriptions in my Shop, she advised me with a great deal of Concern
to have them changed into
Greek; it being a Language less
understood, would be more conformable to the Mystery of my Profession;
that our good Friend would be assisting to us in this Work; and that a
certain Faculty of Gentlemen would find themselves so much obliged to
me, that they would infallibly make my Fortune: In short her frequent
Importunities upon this and other Impertinences of the like Nature
make me very uneasy; and if your Remonstrances have no more Effect
upon her than mine, I am afraid I shall be obliged to ruin my self to
procure her a Settlement at
Oxford with her Tutor, for she's already
too mad for
Bedlam. Now, Sir, you see the Danger my Family is
exposed to, and the Likelihood of my Wife's becoming both troublesome
and useless, unless her reading her self in your Paper may make her
reflect. She is so very learned that I cannot pretend by Word of Mouth
to argue with her. She laughed out at your ending a Paper in
Greek,
and said 'twas a Hint to Women of Literature, and very civil not to
translate it to expose them to the Vulgar. You see how it is with,
Sir,
Your humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
If you have that Humanity and Compassion in your Nature that you take
such Pains to make one think you have, you will not deny your Advice
to a distressed Damsel, who intends to be determined by your Judgment
in a Matter of great Importance to her. You must know then, There is
an agreeable young Fellow, to whose Person, Wit, and Humour no body
makes any Objection, that pretends to have been long in Love with me.
To this I must add, (whether it proceeds from the Vanity of my Nature,
or the seeming Sincerity of my Lover, I won't pretend to say) that I
verily believe he has a real Value for me; which if true, you'll allow
may justly augment his Merit for his Mistress. In short, I am so
sensible of his good Qualities, and what I owe to his Passion, that I
think I could sooner resolve to give up my Liberty to him than any
body else, were there not an Objection to be made to his Fortunes, in
regard they don't answer the utmost mine may expect, and are not
sufficient to secure me from undergoing the reproachful Phrase so
commonly used, That she has played the Fool. Now, tho' I am one of
those few who heartily despise Equipage, Diamonds, and a Coxcomb, yet
since such opposite Notions from mine prevail in the World, even
amongst the best, and such as are esteemed the most prudent People, I
can't find in my Heart to resolve upon incurring the Censure of those
wise Folks, which I am conscious I shall do, if when I enter into a
married State, I discover a Thought beyond that of equalling, if not
advancing my Fortunes. Under this Difficulty I now labour, not being
in the least determined whether I shall be governed by the vain World,
and the frequent Examples I meet with, or hearken to the Voice of my
Lover, and the Motions I find in my Heart in favour of him. Sir, Your
Opinion and Advice in this Affair, is the only thing I know can turn
the Ballance; and which I earnestly intreat I may receive soon; for
till I have your Thoughts upon it, I am engaged not to give my Swain a
final Discharge.
Besides the particular Obligation you will lay on me, by giving this
Subject Room in one of your Papers, tis possible it may be of use to
some others of my Sex, who will be as grateful for the Favour as,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Florinda.
P. S. To tell you the Truth I am Married to Him already, but pray say
something to justify me.
Mr.
Spectator,
You will forgive Us Professors of Musick if We make a second
Application to You, in order to promote our Design of exhibiting
Entertainments of Musick in
York-Buildings. It is industriously
insinuated that Our Intention is to destroy Operas in General, but we
beg of you to insert this plain Explanation of our selves in your
Paper. Our Purpose is only to improve our Circumstances, by improving
the Art which we profess. We see it utterly destroyed at present; and
as we were the Persons who introduced Operas, we think it a groundless
Imputation that we should set up against the Opera in it self. What we
pretend to assert is, That the Songs of different Authors
injudiciously put together, and a Foreign Tone and Manner which are
expected in every thing now performed among us, has put Musick it self
to a stand; insomuch that the Ears of the People cannot now be
entertained with any thing but what has an impertinent Gayety, without
any just Spirit, or a Languishment of Notes, without any Passion or
common Sense. We hope those Persons of Sense and Quality who have done
us the Honour to subscribe, will not be ashamed of their Patronage
towards us, and not receive Impressions that patronising us is being
for or against the Opera, but truly promoting their own Diversions in
a more just and elegant Manner than has been hitherto performed.
We
are, Sir,
Your most humble Servants,
Thomas Clayton.
Nicolino Haym.
Charles Dieupart
1.
There will be no Performances in
York-buildings
till after that
of the Subscription.
T.
See
Contents
|
Saturday, January 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Reddere personæ scit convenientia cuique.
Hor.

We have already taken a general Survey of the Fable and Characters in
Milton's Paradise Lost
.
Parts which remain to be considered,
according to
Aristotle's
Method, are the
Sentiments
and the
Language
.
Before I enter upon the first of these, I must advertise my Reader, that
it is my Design as soon as I have finished my general Reflections on
these four several Heads, to give particular Instances out of the Poem
which is now before us of Beauties and Imperfections which may be
observed under each of them, as also of such other Particulars as may
not properly fall under any of them. This I thought fit to premise, that
the Reader may not judge too hastily of this Piece of Criticism, or look
upon it as Imperfect, before he has seen the whole Extent of it.
The Sentiments in an Epic Poem are the Thoughts and Behaviour which the
Author ascribes to the Persons whom he introduces, and are
just
when
they are conformable to the Characters of the several Persons. The
Sentiments have likewise a relation to
Things
as well as
Persons
,
and are then perfect when they are such as are adapted to the Subject.
If
either of these Cases the Poet
endeavours to argue or explain, to magnify or diminish, to raise
Love or Hatred, Pity or Terror, or
any other Passion, we ought to consider whether the Sentiments he makes
use of are proper for
those
Ends.
Homer
is
by the
Criticks for his Defect as to this Particular in several parts of the
Iliad
and
Odyssey
, tho' at the same time those, who have treated
this great Poet with Candour, have attributed this Defect to the Times
in which he lived
. It was the Fault of the Age, and not of
Homer
,
if there wants that Delicacy in some of his Sentiments which now appears
in the Works of Men of a much inferior Genius. Besides, if there are
Blemishes in any particular Thoughts, there is an infinite Beauty in the
greatest Part of them. In short, if there are many Poets who would not
have fallen into the Meanness of some of his Sentiments, there are none
who could have risen up to the Greatness of others.
Virgil
has
excelled all others in the Propriety of his Sentiments.
Milton
shines
likewise very much in this Particular: Nor must we omit one
Consideration which adds to his Honour and Reputation.
Homer
and
Virgil
introduced Persons whose Characters are commonly known among
Men, and such as are to be met with either in History, or in ordinary
Conversation.
Milton's
Characters, most of them, lie out of Nature,
and were to be formed purely by his own Invention. It shews a greater
Genius in
Shakespear
to have drawn his
Calyban,
than his
Hotspur
or
Julius Cæsar:
The one was to be supplied out of his own
Imagination, whereas the other might have been formed upon Tradition,
History and Observation. It was much easier therefore for
Homer
to
find proper Sentiments for an Assembly of
Grecian
Generals, than for
Milton
to diversify his infernal Council with proper Characters, and
inspire them with a Variety of Sentiments. The Lovers of
Dido
and
Æneas
are only Copies of what has passed between other Persons.
Adam
and
Eve
, before the Fall, are a different Species from that of
Mankind, who are descended from them; and
but a Poet of the most
unbounded Invention, and the most exquisite Judgment, could have filled
their Conversation and Behaviour with
so many apt
Circumstances
during their State of Innocence.
Nor is it sufficient for an Epic Poem to be filled with such Thoughts as
are
Natural
, unless it abound also with such as are
Sublime
. Virgil
in this Particular falls short of
Homer
. He has not indeed so many
Thoughts that are Low and Vulgar; but at the same time has not so many
Thoughts that are Sublime and Noble. The Truth of it is,
Virgil
seldom
rises into very astonishing Sentiments, where he is not fired by the
Iliad
. He every where charms and pleases us by the Force of his own
Genius; but seldom elevates and transports us where he does not fetch
his Hints from
Homer
.
Milton's
chief Talent, and indeed his distinguishing Excellence, lies
in the Sublimity of his Thoughts. There are others of the Moderns who
rival him in every other part of Poetry; but in the Greatness of his
Sentiments he triumphs over all the Poets both Modern and Ancient,
Homer
only excepted. It is impossible for the Imagination of Man to
distend itself with greater Ideas, than those which he has laid together
in his first,
second
, and sixth Book
s
. The seventh, which describes
the Creation of the World, is likewise wonderfully Sublime, tho' not so
apt to stir up Emotion in the Mind of the Reader, nor consequently so
perfect in the Epic Way of Writing, because it is filled with less
Action.
the judicious Reader compare what
Longinus
has observed
on several Passages in
Homer
, and he will find Parallels for most
of them in the
Paradise Lost
.
From what has been said we may infer, that as there are two kinds of
Sentiments, the Natural and the Sublime, which are always to be pursued
in an Heroic Poem, there are also two kinds of Thoughts which are
carefully to be avoided. The first are such as are affected and
unnatural; the second such as are mean and vulgar. As for the first kind
of Thoughts, we meet with little or nothing that is like them in
Virgil:
has none of those
trifling
Points and Puerilities
that are so often to be met with in
Ovid
, none of the Epigrammatick
Turns of
Lucan
, none of those swelling Sentiments which are so
frequent in
Statins
and
Claudian
, none of those mixed Embellishments
of
Tasso
. Every thing is just and natural.
Sentiments shew that he
had a perfect Insight into human Nature, and that he knew every thing
which was the most proper to
affect it
.
Mr.
Dryden
has in some Places, which I may hereafter take notice of,
misrepresented
Virgil's
way of thinking as to this Particular, in the
Translation he has given us of the
Æneid
. I do not remember that
Homer
any where falls into the Faults above-mentioned, which were
indeed the false Refinements of later Ages.
Milton
, it must be
confest, has sometimes erred in this Respect, as I shall shew more at
large in another Paper; tho' considering how all the Poets of the Age in
which he writ were infected with this wrong way of thinking, he is
rather to be admired that he did not give more into it, than that he did
sometimes comply with the vicious Taste which still prevails so much
among Modern Writers.
But
several Thoughts may be natural which are low and groveling,
an Epic Poet should not only avoid such Sentiments as are unnatural or
affected, but also such as are
mean
and vulgar.
Homer
has opened
a great Field of Raillery to Men of more Delicacy than Greatness of
Genius, by the Homeliness of some of his Sentiments. But, as I have
before said, these are rather to be imputed to the Simplicity of the Age
in which he lived, to which I may also add, of that which he described,
than to any Imperfection in that Divine Poet.
Zoilus
among the
Ancients, and Monsieur
Perrault
,
among the Moderns, pushed their
Ridicule very far upon him, on account of some such Sentiments. There is
no Blemish to be observed in
Virgil
under this Head, and but
a
very
few in Milton.
I
give but one Instance of this Impropriety of
Thought
in
Homer
, and at the same time compare it with an Instance of the same
Nature, both in
Virgil
and
Milton
. Sentiments which raise Laughter,
can very seldom be admitted with any Decency into an Heroic Poem, whose
Business it is to excite Passions of a much nobler Nature.
Homer
,
however, in his Characters of
Vulcan
and
Thersites
, in his
Story of
Mars
and
Venus
,
in his Behaviour of
Irus
and in
other Passages, has been observed to have lapsed into the Burlesque
Character, and to have departed from that serious Air which seems
essential to the Magnificence of an Epic Poem. I remember but one Laugh
in the whole Æneid, which rises in the fifth Book, upon
Monætes
, where
he is represented as thrown overboard, and drying himself upon a Rock.
But this Piece. of Mirth is so well timed, that the severest Critick can
have nothing to say against it; for it is in the Book of Games and
Diversions, where the Reader's Mind may be supposed to be sufficiently
relaxed for such an Entertainment. The only Piece of Pleasantry in
Paradise Lost
, is where the Evil Spirits are described as rallying the
Angels upon the Success of their new invented Artillery. This Passage I
look upon to be the most exceptionable in the whole Poem, as being
nothing else but a String of Punns, and those too very indifferent ones.
—
Satan beheld their Plight,
And to his Mates thus in Derision call'd.
O Friends, why come not on those Victors proud?
Ere-while they fierce were coming, and when we,
To entertain them fair with open Front,
And Breast, (what could we more?) propounded terms
Of Composition, straight they chang'd their Minds,*
Flew off,
and into strange Vagaries fell
As they would dance: yet for a Dance they seem'd
Somewhat extravagant, and wild; perhaps
For Joy of offer'd Peace; but I suppose
If our Proposals once again were heard,
We should compel them to a quick Result.
To whom thus Belial
in like gamesome Mood:
Leader, the Terms we sent were Terms of Weight,
Of hard Contents,
and full of force urg'd home;
Such as we might perceive amus'd them all,
And stumbled
many: who receives them right,
Had need, from Head to Foot, will understand;
Not understood,
this Gift they have besides,
They shew us when our Foes walk not upright.
Thus they among themselves in pleasant vein
Stood scoffing17——
I.
It is in Part II. of the
Poetics
, when treating of
Tragedy, that Aristotle lays down his main principles. Here after
treating of the Fable and the Manners, he proceeds to the Diction and
the Sentiments. By Fable, he says (§ 2),
'I mean the contexture of incidents, or the Plot. By Manners, I mean,
whatever marks the Character of the Persons. By Sentiments, whatever
they say, whether proving any thing, or delivering a general
sentiment, &c.'
In dividing Sentiments from Diction, he says (§22): The Sentiments
include whatever is the Object of speech, Diction (§ 23-25) the words
themselves. Concerning Sentiment, he refers his reader to the
rhetoricians.
argues or explains, magnifies or diminishes, raises
these
René le Bossu says in his treatise on the Epic, published
in 1675, Bk, vi. ch. 3:
'What is base and ignoble at one time and in one country, is not
always so in others. We are apt to smile at Homer's comparing Ajax to
an Ass in his Iliad. Such a comparison now-a-days would be indecent
and ridiculous; because it would be indecent and ridiculous for a
person of quality to ride upon such a steed. But heretofore this
Animal was in better repute: Kings and princes did not disdain the
best so much as mere tradesman do in our time. 'Tis just the same with
many other smiles which in Homer's time were allowable. We should now
pity a Poet that should be so silly and ridiculous as to compare a
Hero to a piece of Fat. Yet Homer does it in a comparison he makes of
Ulysses... The reason is that in these Primitive Times, wherein the
Sacrifices ... were living creatures, the Blood and the Fat were the
most noble, the most august, and the most holy things.'
such Beautiful
Longimus on the Sublime, I. § 9. of Discord, Homer says
(Pope's tr.):
While scarce the skies her horrid head can bound,
She stalks on earth.
(Iliad iv.)
Of horses of the gods:
Far as a shepherd from some spot on high
O'er the wide main extends his boundless eye,
Through such a space of air, with thund'ring sound,
At one long leap th' immortal coursers bound.
(Iliad v.)
Longinus quotes also from the
Iliad
xix., the combat of the Gods, the
description of Neptune,
Iliad
xi., and the Prayer of Ajax,
Iliad
xvii.
little
affect it. I remember but one line in him which has been
objected against, by the Criticks, as a point of Wit. It is in his ninth
Book, where Juno, speaking of the Trojans, how they survived the
Ruins of their City, expresses her self in the following words;
Num copti potuere copi, num incense cremorunt Pergama?
Were the Trojans taken even after they were Captives, or did Troy burn
even when it was in Flames?
low
Zoilus, who lived about 270 B. C., in the time of Ptolemy
Philadelphus, made himself famous for attacks upon Homer and on Plato
and Isocrates, taking pride in the title of Homeromastix. Circe's men
turned into swine Zoilus ridiculed as weeping porkers. When he asked
sustenance of Ptolemy he was told that Homer sustained many thousands,
and as he claimed to be a better man than Homer, he ought to be able to
sustain himself. The tradition is that he was at last crucified, stoned,
or burnt for his heresy.
Charles Perrault, brother of Claude Perrault the architect and ex-physician,
was himself Controller of Public Buildings under Colbert, and
after his retirement from that office, published in 1690 his Parallel between
the Ancients and Moderns, taking the side of the moderns in the controversy,
and dealing sometimes disrespectfully with Homer. Boileau replied to him
in
Critical Reflections on Longinus
.
Sentiments
Iliad
, Bk. i., near the close.
Iliad
, Bk. ii.
Bk. v., at close.
Odyssey
, Bk. xviii
Paradise Lost
, Bk. vi. 1. 609, &c. Milton meant that the
devils should be shown as scoffers, and their scoffs as mean.
Contents
|
Monday, January 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Principibus Placuisse viris non ultima I laus est.
Hor.

The Desire of Pleasing makes a Man agreeable or unwelcome to those with
whom he converses, according to the Motive from which that Inclination
appears to flow. If your Concern for pleasing others arises from innate
Benevolence, it never fails of Success; if from a Vanity to excel, its
Disappointment is no less certain.
we call an agreeable Man, is he
who is endowed with
the
natural Bent to do acceptable things from
a Delight he takes in them meerly as such; and the Affectation of that
Character is what constitutes a Fop. Under these Leaders one may draw up
all those who make any Manner of Figure, except in dumb Show. A rational
and select Conversation is composed of Persons, who have the Talent of
Pleasing with Delicacy of Sentiments flowing from habitual Chastity of
Thought; but mixed Company is frequently made up of Pretenders to Mirth,
and is usually pestered with constrained, obscene, and painful
Witticisms. Now and then you meet with a Man so exactly formed for
Pleasing, that it is no matter what he is doing or saying, that is to
say, that there need no Manner of Importance in it, to make him gain
upon every Body who hears or beholds him. This Felicity is not the Gift
of Nature only, but must be attended with happy Circumstances, which add
a Dignity to the familiar Behaviour which distinguishes him whom we call
an agreeable Man. It is from this that every Body loves and esteems
Polycarpus
. He is in the Vigour of his Age and the Gayety of Life, but
has passed through very conspicuous Scenes in it; though no Soldier, he
has shared the Danger, and acted with great Gallantry and Generosity on
a decisive Day of Battle. To have those Qualities which only make other
Men conspicuous in the World as it were supernumerary to him, is a
Circumstance which gives Weight to his most indifferent Actions; for as
a known Credit is ready Cash to a Trader, so is acknowledged Merit
immediate Distinction, and serves in the Place of Equipage to a
Gentleman. This renders
Polycarpus
graceful in Mirth, important in
Business, and regarded with Love in every ordinary Occurrence. But not
to dwell upon Characters which have such particular Recommendations to
our Hearts, let us turn our Thoughts rather to the Methods of Pleasing
which must carry Men through the World who cannot pretend to such
Advantages. Falling in with the particular Humour or Manner of one above
you, abstracted from the general Rules of good Behaviour, is the Life of
a Slave. A Parasite differs in nothing from the meanest Servant, but
that the Footman hires himself for bodily Labour, subjected to go and
come at the Will of his Master, but the other gives up his very Soul: He
is prostituted to speak, and professes to think after the Mode of him
whom he courts. This Servitude to a Patron, in an honest Nature, would
be more grievous than that of wearing his Livery; therefore we will
speak of those Methods only which are worthy and ingenuous.
The happy Talent of Pleasing either those above you or below you, seems
to be wholly owing to the Opinion they have of your Sincerity. This
Quality is to attend the agreeable Man in all the Actions of his Life;
and I think there need no more be said in Honour of it, than that it is
what forces the Approbation even of your Opponents. The guilty Man has
an Honour for the Judge who with Justice pronounces against him the
Sentence of Death it self. The Author of the Sentence at the Head of
this Paper, was an excellent Judge of human Life, and passed his own in
Company the most agreeable that ever was in the World.
Augustus
lived
amongst his Friends as if he had his Fortune to make in his own Court:
Candour and Affability, accompanied with as much Power as ever Mortal
was vested with, were what made him in the utmost Manner agreeable among
a Set of admirable Men, who had Thoughts too high for Ambition, and
Views too large to be gratified by what he could give them in the
Disposal of an Empire, without the Pleasures of their mutual
Conversation. A certain Unanimity of Taste and Judgment, which is
natural to all of the same Order in the Species, was the Band of this
Society; and the Emperor assumed no Figure in it but what he thought was
his Due from his private Talents and Qualifications, as they contributed
to advance the Pleasures and Sentiments of the Company.
Cunning People, Hypocrites, all who are but half virtuous, or half wise,
are incapable of tasting the refined Pleasure of such an equal Company
as could wholly exclude the Regard of Fortune in their Conversations.
Horace
, in the Discourse from whence I take the Hint of the present
Speculation, lays down excellent Rules for Conduct in Conversation with
Men of Power; but he speaks it with an Air of one who had no Need of
such an Application for any thing which related to himself. It shews he
understood what it was to be a skilful Courtier, by just Admonitions
against Importunity, and shewing how forcible it was to speak Modestly
of your own Wants. There is indeed something so shameless in taking all
Opportunities to speak of your own Affairs, that he who is guilty of it
towards him upon whom he depends, fares like the Beggar who exposes his
Sores, which instead of moving Compassion makes the Man he begs of turn
away from the Object.
I cannot tell what is become of him, but I remember about sixteen Years
ago an honest Fellow, who so justly understood how disagreeable the
Mention or Appearance of his Wants would make him, that I have often
reflected upon him as a Counterpart of
Irus
, whom I have formerly
mentioned. This Man, whom I have missed for some Years in my Walks, and
have heard was someway employed about the Army, made it a Maxim, That
good Wigs, delicate Linen, and a chearful Air, were to a poor Dependent
the same that working Tools are to a poor Artificer. It was no small
Entertainment to me, who knew his Circumstances, to see him, who had
fasted two Days, attribute the Thinness they told him of to the Violence
of some Gallantries he had lately been guilty of. The skilful Dissembler
carried this on with the utmost Address; and if any suspected his
Affairs were narrow, it was attributed to indulging himself in some
fashionable Vice rather than an irreproachable Poverty, which saved his
Credit with those on whom he depended.
The main Art is to be as little troublesome as you can, and make all you
hope for come rather as a Favour from your Patron than Claim from you.
But I am here prating of what is the Method of Pleasing so as to succeed
in the World, when there are Crowds who have, in City, Town, Court, and
Country, arrived at considerable Acquisitions, and yet seem incapable of
acting in any constant Tenour of Life, but have gone on from one
successful Error to another: Therefore I think I may shorten this
Enquiry after the Method of Pleasing; and as the old Beau said to his
Son, once for all, Pray, Jack,
be a fine Gentleman
, so may I, to my
Reader, abridge my Instructions, and finish the Art of Pleasing in a
Word, Be rich.
T.
that
Contents
|
Tuesday, January 22, 1712 |
Addison |
Pectoribus inhians spirantia consulit exta.
Virg.

Having already given an Account of the Dissection of a Beau's Head, with
the several Discoveries made on that Occasion; I shall here, according
to my Promise, enter upon the Dissection of a Coquet's Heart, and
communicate to the Public such Particularities as we observed in that
curious Piece of Anatomy.
I should perhaps have waved this Undertaking, had not I been put in mind
of my Promise by several of my unknown Correspondents, who are very
importunate with me to make an Example of the Coquet, as I have already
done of the Beau. It is therefore in Compliance with the Request of
Friends, that I have looked over the Minutes of my former Dream, in
order to give the Publick an exact Relation to it, which I shall enter
upon without further Preface.
Our Operator, before he engaged in this Visionary Dissection, told us,
that there was nothing in his Art more difficult than to lay open the
Heart of a Coquet, by reason of the many Labyrinths and Recesses which
are to be found in it, and which do not appear in the Heart of any other
Animal.
He desired us first of all to observe the
Pericardium
, or outward Case
of the Heart, which we did very attentively; and by the help of our
Glasses discern'd in it Millions of little Scars, which seem'd to have
been occasioned by the Points of innumerable Darts and Arrows, that from
time to time had glanced upon the outward Coat; though we could not
discover the smallest Orifice, by which any of them had entered and
pierced the inward Substance.
Every Smatterer in Anatomy knows that this
Pericardium
, or Case of the
Heart, contains in it a thin reddish Liquor, supposed to be bred from
the Vapours which exhale out of the Heart, and, being stopt here, are
condensed into this watry Substance. Upon examining this Liquor, we
found that it had in it all the Qualities of that Spirit which is made
use of in the Thermometer, to shew the Change of Weather.
Nor must I here omit an Experiment one of the Company assured us he
himself had made with this Liquor, which he found in great Quantity
about the Heart of a Coquet whom he had formerly dissected. He affirmed
to us, that he had actually inclosed it in a small Tube made after the
manner of a Weather Glass; but that instead of acquainting him with the
Variations of the Atmosphere, it shewed him the Qualities of those
Persons who entered the Room where it stood. He affirmed also, that it
rose at the Approach of a Plume of Feathers, an embroidered Coat, or a
Pair of fringed Gloves; and that it fell as soon as an ill-shaped
Perriwig, a clumsy Pair of Shoes, or an unfashionable Coat came into his
House: Nay, he proceeded so far as to assure us, that upon his Laughing
aloud when he stood by it, the Liquor mounted very sensibly, and
immediately sunk again upon his looking serious. In short, he told us,
that he knew very well by this Invention whenever he had a Man of Sense
or a Coxcomb in his Room.
Having cleared away the
Pericardium
, or the Case and Liquor
above-mentioned, we came to the Heart itself. The outward Surface of it
was extremely slippery, and the
Mufro
, or Point, so very cold withal,
that, upon endeavouring to take hold of it it glided through the Fingers
like a smooth Piece of Ice.
The Fibres were turned and twisted in a more intricate and perplexed
manner than they are usually found in other Hearts; insomuch that the
whole Heart was wound up together in a Gordian Knot, and must have had
very irregular and unequal Motions, whilst it was employed in its Vital
Function.
One thing we thought very observable, namely, that, upon examining all
the Vessels which came into it or issued out of it, we could not
discover any Communication that it had with the Tongue.
We could not but take Notice likewise, that several of those little
Nerves in the Heart which are affected by the Sentiments of Love,
Hatred, and other Passions, did not descend to this before us from the
Brain, but from the Muscles which lie about the Eye.
Upon weighing the Heart in my Hand, I found it to be extreamly light,
and consequently very hollow, which I did not wonder at, when upon
looking into the Inside of it, I saw Multitudes of Cells and Cavities
running one within another, as our Historians describe the Apartments of
Rosamond's
Bower. Several of these little Hollows were stuffed with
innumerable sorts of Trifles, which I shall forbear giving any
particular Account of, and shall therefore only take Notice of what lay
first and uppermost, which, upon our unfolding it and applying our
Microscopes to it, appeared to be a Flame-coloured Hood.
We were informed that the Lady of this Heart, when living, received the
Addresses of several who made Love to her, and did not only give each of
them Encouragement, but made every one she conversed with believe that
she regarded him with an Eye of Kindness; for which Reason we expected
to have seen the Impression of Multitudes of Faces among the several
Plaits and Foldings of the Heart; but to our great Surprize not a single
Print of this nature discovered it self till we came into the very Core
and Center of it. We there observed a little Figure, which, upon
applying our Glasses to it, appeared dressed in a very fantastick
manner. The more I looked upon it, the more I thought I had seen the
Face before, but could not possibly recollect either the Place or Time;
when, at length, one of the Company, who had examined this Figure more
nicely than the rest, shew'd us plainly by the Make of its Face, and the
several Turns of its Features, that the little Idol which was thus
lodged in the very Middle of the Heart was the deceased Beau, whose Head
I gave some Account of in my last
Tuesday's
Paper.
As soon as we had finished our Dissection, we resolved to make an
Experiment of the Heart, not being able to determine among our selves
the Nature of its Substance, which differ'd in so many Particulars from
that of the Heart in other Females. Accordingly we laid it into a Pan of
burning Coals, when we observed in it a certain Salamandrine Quality,
that made it capable of living in the midst of Fire and Flame, without
being consumed, or so much as singed.
As we were admiring this strange
Phœnomenon
, and standing round the
Heart in a Circle, it gave a most prodigious Sigh or rather Crack, and
dispersed all at once in Smoke and Vapour. This imaginary Noise, which
methought was louder than the burst of a Cannon, produced such a violent
Shake in my Brain, that it dissipated the Fumes of Sleep, and left me in
an Instant broad awake.
L.
Contents
|
Wednesday, January 23, 1712 |
Steele |
Spes incerta futuri.
Virg.1
It is a lamentable thing that every Man is full of Complaints, and
constantly uttering Sentences against the Fickleness of Fortune, when
People generally bring upon themselves all the Calamities they fall
into, and are constantly heaping up Matter for their own Sorrow and
Disappointment.
which produces the greatest Part of the
Delusions
of Mankind, is a false Hope which People indulge with so sanguine a
Flattery to themselves, that their Hearts are bent upon fantastical
Advantages which they had no Reason to believe should ever have arrived
to them. By this unjust Measure of calculating their Happiness, they
often mourn with real Affliction for imaginary Losses. When I am talking
of this unhappy way of accounting for our selves, I cannot but reflect
upon a particular Set of People, who, in their own Favour, resolve every
thing that is possible into what is probable, and then reckon on that
Probability as on what must certainly happen.
Will. Honeycomb
, upon my
observing his looking on a Lady with some particular Attention, gave me
an Account of the great Distresses which had laid waste that her very
fine Face, and had given an Air of Melancholy to a very agreeable
Person, That Lady, and a couple of Sisters of hers, were, said
Will.
,
fourteen Years ago, the greatest Fortunes about Town; but without having
any Loss by bad Tenants, by bad Securities, or any Damage by Sea or
Land, are reduced to very narrow Circumstances. They were at that time
the most inaccessible haughty Beauties in Town; and their Pretensions to
take upon them at that unmerciful rate, was rais'd upon the following
Scheme, according to which all their Lovers were answered.
'Our Father is a youngish Man, but then our Mother is somewhat older,
and not likely to have any Children: His Estate, being £800 per Annum,
at 20 Years Purchase, is worth £16,000. Our Uncle who is above 50, has
£400
per Annum
, which at the foresaid Rate, is £8000. There's a Widow
Aunt, who has £10,000 at her own Disposal left by her Husband, and an
old Maiden Aunt who has £6000. Then our Father's Mother has £900
per
Annum
, which is worth £18,000 and £10,000 each of us has of her own,
which can't be taken from us. These summ'd up together stand thus.
| Father's |
£800→ |
£16000 |
|
| Uncle's |
£400→ |
£8000 |
|
| Aunts' |
£10000 |
|
|
|
+£6000→ |
£16000 |
|
| Grandmother |
£900→ |
£18000 |
|
| Own each |
£1000→ |
£3000 |
|
|
Total |
£61000 |
This equally divided between us three, amounts to £20000; and, allowance being given for Enlargement upon common Fame, we may lawfully pass for £30000 Fortunes. |
In Prospect of this, and the Knowledge of her own personal Merit, every
one was contemptible in their Eyes, and they refus'd those Offers which
had been frequently made 'em. But
mark the End:
The Mother dies, the
Father is married again, and has a Son, on him was entail'd the
Father's, Uncle's, and Grand-mother's Estate. This cut off £43,000.
The Maiden Aunt married a tall Irishman, and with her went the £6000. The
Widow died, and left but enough to pay her Debts and bury her; so that
there remained for these three Girls but their own £1000. They had
by
this time passed their Prime, and got on the wrong side of Thirty; and
must pass the Remainder of their Days, upbraiding Mankind that they mind
nothing but Money, and bewailing that Virtue, Sense and Modesty are had
at present in no manner of Estimation.
I mention this Case of Ladies before any other, because it is the most
irreparable: For tho' Youth is the Time less capable of Reflection, it
is in that Sex the only Season in which they can advance their Fortunes.
But if we turn our Thoughts to the Men, we see such Crowds of Unhappy
from no other Reason, but an ill-grounded Hope, that it is hard to say
which they rather deserve, our Pity or Contempt. It is not unpleasant to
see a Fellow after grown old in Attendance, and after having passed half
a Life in Servitude, call himself the unhappiest of all Men, and pretend
to be disappointed because a Courtier broke his Word. He that promises
himself any thing but what may naturally arise from his own Property or
Labour, and goes beyond the Desire of possessing above two Parts in
three even of that, lays up for himself an encreasing Heap of
Afflictions and Disappointments. There are but two Means in the World of
gaining by other Men, and these are by being either agreeable or
considerable. The Generality of Mankind do all things for their own
sakes; and when you hope any thing from Persons above you, if you cannot
say, I can be thus agreeable or thus serviceable, it is ridiculous to
pretend to the Dignity of being unfortunate when they leave you; you
were injudicious, in hoping for any other than to be neglected, for such
as can come within these Descriptions of being capable to please or
serve your Patron, when his Humour or Interests call for their Capacity
either way.
It would not methinks be an useless Comparison between the Condition of
a Man who shuns all the Pleasures of Life, and of one who makes it his
Business to pursue them. Hope in the Recluse makes his Austerities
comfortable, while the luxurious Man gains nothing but Uneasiness from
his Enjoyments. What is the Difference in the Happiness of him who is
macerated by Abstinence, and his who is surfeited with Excess? He who
resigns the World, has no Temptation to Envy, Hatred, Malice, Anger, but
is in constant Possession of a serene Mind; he who follows the Pleasures
of it, which are in their very Nature disappointing, is in constant
Search of Care, Solicitude, Remorse, and Confusion.
January the 14th, 1712.
Mr. Spectator,
I am a young Woman and have my Fortune to make; for which Reason I
come constantly to Church to hear Divine Service, and make Conquests:
But one great Hindrance in this my Design, is, that our Clerk, who was
once a Gardener, has this Christmas so over-deckt the Church with
Greens, that he has quite spoilt my Prospect, insomuch that I have
scarce seen the young Baronet I dress at these three Weeks, though we
have both been very constant at our Devotions, and don't sit above
three Pews off. The Church, as it is now equipt, looks more like a
Green-house than a Place of Worship: The middle Isle is a very pretty
shady Walk, and the Pews look like so many Arbours of each Side of it.
The Pulpit itself has such Clusters of Ivy, Holly, and Rosemary about
it, that a light Fellow in our Pew took occasion to say, that the
Congregation heard the Word out of a Bush, like Moses. Sir Anthony
Love's Pew in particular is so well hedged, that all my Batteries have
no Effect. I am obliged to shoot at random among the Boughs, without
taking any manner of Aim. Mr. Spectator, unless youll give Orders
for removing these Greens, I shall grow a very awkward Creature at
Church, and soon have little else to do there but to say my Prayers. I
am in haste,
Dear Sir,
Your most Obedient Servant,
Jenny Simper.
T.
Et nulli rei nisi Pœnitentiæ natus.
Pollutions
Contents
|
Thursday, January 24, 1712 |
Budgell |
Magister artis et largitor ingeni
Venter
Pers.

Lucian
rallies the Philosophers in his Time, who could not agree
whether they should admit
Riches
into the number of
real Goods
; the
Professors of the Severer Sects threw them quite out, while others as
resolutely inserted them.
I am apt to believe, that as the World grew more Polite, the rigid
Doctrines of the first were wholly discarded; and I do not find any one
so hardy at present, as to deny that there are very great Advantages in
the Enjoyment of a plentiful Fortune. Indeed the best and wisest of Men,
tho' they may possibly despise a good Part of those things which the
World calls Pleasures, can, I think, hardly be insensible of that Weight
and Dignity which a moderate Share of Wealth adds to their Characters,
Councils, and Actions.
We find it is a General Complaint in Professions and Trades, that the
richest Members of them are chiefly encouraged, and this is falsly
imputed to the Ill-nature of Mankind, who are ever bestowing their
Favours on such as least want them. Whereas if we fairly consider their
Proceedings in this Case, we shall find them founded on undoubted
Reason: Since supposing both equal in their natural Integrity, I ought,
in common Prudence, to fear foul Play from an Indigent Person, rather
than from one whose Circumstances seem to have placed him above the bare
Temptation of Money.
This Reason also makes the Common-wealth regard her richest Subjects, as
those who are most concerned for her Quiet and Interest, and
consequently fittest to be intrusted with her highest Imployments. On
the contrary,
Cataline's
Saying to those Men of desperate Fortunes,
who applied themselves to him, and of whom he afterwards composed his
Army, that
they had nothing to hope for but a Civil War
, was too true
not to make the Impressions he desired.
I believe I need not fear but that what I have said in Praise of Money,
will be more than sufficient with most of my Readers to excuse the
Subject of my present Paper, which I intend as an Essay on
The Ways to
raise a Man's Fortune
, or,
The Art of growing Rich.
The first and most infallible Method towards the attaining of this End,
is
Thrift:
All Men are not equally qualified for getting Money, but it
is in the Power of every one alike to practise this Virtue, and I
believe there are very few Persons, who, if they please to reflect on
their past Lives, will not find that had they saved all those Little
Sums which they have spent unnecessarily, they might at present have
been Masters of a competent Fortune.
Diligence
justly claims the next
Place to
Thrift:
I find both these excellently well recommended to
common use in the three following
Italian
Proverbs,
Never do that by Proxy which you can do yourself.
Never defer that 'till To-morrow which you can do To-day.
Never neglect small Matters and Expences.
A third Instrument of growing Rich, is
Method in Business
, which, as
well as the two former, is also attainable by Persons of the meanest
Capacities.
The famous
De Wit
, one of the greatest Statesmen of the Age in which
he lived, being asked by a Friend, How he was able to dispatch that
Multitude of Affairs in which he was engaged? reply'd, That his whole
Art consisted in doing
one thing at once
. If, says he, I have any
necessary Dispatches to make, I think of nothing else 'till those are
finished; If any Domestick Affairs require my Attention, I give myself
up wholly to them 'till they are set in Order.
In short, we often see Men of dull and phlegmatick Tempers, arriving to
great Estates, by making a regular and orderly Disposition of their
Business, and that without it the greatest Parts and most lively
Imaginations rather puzzle their Affairs, than bring them to an happy
Issue.
From what has been said, I think I may lay it down as a Maxim, that
every Man of good common Sense may, if he pleases, in his particular
Station of Life, most certainly be Rich. The Reason why we sometimes see
that Men of the greatest Capacities are not so, is either because they
despise Wealth in Comparison of something else; or at least are not
content to be getting an Estate, unless they may do it their own way,
and at the same time enjoy all the Pleasures and Gratifications of Life.
But besides these ordinary Forms of growing Rich, it must be allowed
that there is Room for Genius, as well in this as in all other
Circumstances of Life.
Tho' the Ways of getting Money were long since very numerous; and tho'
so many new ones have been found out of late Years, there is certainly
still remaining so large a Field for Invention, that a Man of an
indifferent Head might easily sit down and draw up such a Plan for the
Conduct and support of his Life, as was never yet once thought of.
We daily see Methods put in practice by hungry and ingenious Men, which
demonstrate the Power of Invention in this Particular.
It is reported of
Scaramouch
, the first famous Italian Comedian, that
being at
Paris
and in great Want, he bethought himself of constantly
plying near the Door of a noted Perfumer in that City, and when any one
came out who had been buying Snuff, never failed to desire a Taste of
them: when he had by this Means got together a Quantity made up of
several different Sorts, he sold it again at a lower Rate to the same
Perfumer, who finding out the Trick, called it
Tabac de mille fleures
,
or
Snuff of a thousand Flowers
. The Story farther tells us, that by
this means he got a very comfortable Subsistence, 'till making too much
haste to grow Rich, he one Day took such an unreasonable Pinch out of
the Box of a
Swiss
Officer, as engaged him in a Quarrel, and obliged
him to quit this Ingenious Way of Life.
Nor can I in this Place omit doing Justice to a Youth of my own Country,
who, tho' he is scarce yet twelve Years old, has with great Industry and
Application attained to the Art of beating the Grenadiers March on his
Chin. I am credibly informed that by this means he does not only
maintain himself and his Mother, but that he is laying up Money every
Day, with a Design, if the War continues, to purchase a Drum at least,
if not a Colours.
I shall conclude these Instances with the Device of the famous
Rabelais
, when he was at a great Distance from
Paris
, and without
Money to bear his Expences thither. This ingenious Author being thus
sharp set, got together a convenient Quantity of Brick-Dust, and having
disposed of it into several Papers, writ upon one
Poyson for Monsieur
,
upon a second,
Poyson for the Dauphin
, and on a third,
Poyson for the
King
. Having made this Provision for the Royal Family of
France
, he
laid his Papers so that his Landlord, who was an Inquisitive Man, and a
good Subject, might get a Sight of them.
The Plot succeeded as he desired: The Host gave immediate Intelligence
to the Secretary of State. The Secretary presently sent down a Special
Messenger, who brought up the Traitor to Court, and provided him at the
King's Expence with proper Accommodations on the Road. As soon as he
appeared he was known to be the Celebrated
Rabelais
, and his Powder
upon Examination being found very Innocent, the Jest was only laught at;
for which a less eminent
Drole
would have been sent to the Gallies.
Trade and Commerce might doubtless be still varied a thousand Ways, out
of which would arise such Branches as have not yet been touched. The
famous
Doily
is still fresh in every one's Memory, who raised a
Fortune by finding out Materials for such Stuffs as might at once be
cheap and genteel. I
heard it affirmed, that had not he discovered
this frugal Method of gratifying our Pride, we should hardly have been
able
to carry on the last War.
I regard Trade not only as highly advantageous to the Commonwealth in
general; but as the most natural and likely Method of making a Man's
Fortune, having observed, since my being a
Spectator
in the World,
greater Estates got about
Change
, than at
Whitehall
or at St.
James's
. I believe I may also add, that the first Acquisitions are
generally attended with more Satisfaction, and as good a Conscience.
I must not however close this Essay, without observing that what has
been said is only intended for Persons in the common ways of Thriving,
and is not designed for those Men who from low Beginnings push
themselves up to the Top of States, and the most considerable Figures in
Life. My
of
Saving
is not designed for such as these, since
nothing is more usual than for
Thrift
to disappoint the Ends of
Ambition
; it being almost impossible that the Mind should
be
intent
upon Trifles, while it is at the same time forming some great Design.
I may therefore compare these Men to a great Poet, who, as
Longinus
says, while he is full of the most magnificent Ideas, is not always at
leisure to mind the little Beauties and Niceties of his Art.
I would however have all my Readers take great care how they mistake
themselves for uncommon
Genius's
, and Men above Rule, since it is very
easy for them to be deceived in this Particular.
X.
In his Auction of Philosophers.
able so well
descend to and be
Contents
|
Thursday, January 1, 1712 |
Addison |
Posthabui tamen illorum mea seria Ludo.
Virg.1
An unaffected Behaviour is without question a very great Charm; but
under the Notion of being unconstrained and disengaged, People take upon
them to be unconcerned in any Duty of Life. A general Negligence is what
they assume upon all Occasions, and set up for an Aversion to all manner
of Business and Attention.
I am the carelessest Creature in the World,
I have certainly the worst Memory of any Man living
, are frequent
Expressions in the Mouth of a Pretender of this sort. It is a professed
Maxim with these People never to
think
; there is something so solemn
in Reflexion, they, forsooth, can never give themselves Time for such a
way of employing themselves. It happens often that this sort of Man is
heavy enough in his Nature to be a good Proficient in such Matters as
are attainable by Industry; but alas! he has such an ardent Desire to be
what he is not, to be too volatile, to have the Faults of a Person of
Spirit, that he professes himself the most unfit Man living for any
manner of Application. When this Humour enters into the Head of a
Female, she gently professes Sickness upon all Occasions, and acts all
things with an indisposed Air: She is offended, but her Mind is too lazy
to raise her to Anger, therefore she lives only as actuated by a violent
Spleen and gentle Scorn. She has hardly Curiosity to listen to Scandal
of her Acquaintance, and has never Attention enough to hear them
commended. This Affectation in both Sexes makes them vain of being
useless, and take a certain Pride in their Insignificancy.
Opposite to this Folly is another no less unreasonable, and that is the
Impertinence of being always in a Hurry. There are those who visit
Ladies, and beg Pardon afore they are well seated in their Chairs, that
they just called in, but are obliged to attend Business of Importance
elsewhere the very next Moment: Thus they run from Place to Place,
professing that they are obliged to be still in another Company than
that which they are in.
Persons who are just a going somewhere
else should never be detained;
let
all the World allow that
Business is to be minded, and their Affairs will be at an end. Their
Vanity is to be importuned, and Compliance with their Multiplicity of
Affairs would effectually dispatch 'em. The Travelling Ladies, who have
half the Town to see in an Afternoon, may be pardoned for being in
constant Hurry; but it is inexcusable in Men to come where they have no
Business, to profess they absent themselves where they have. It has been
remarked by some nice Observers and Criticks, that there is nothing
discovers the true Temper of a Person so much as his Letters. I have by
me two Epistles, which are written by two People of the different
Humours above-mentioned. It is wonderful that a Man cannot observe upon
himself when he sits down to write, but that he will gravely commit
himself to Paper the same Man that he is in the Freedom of Conversation.
I have hardly seen a Line from any of these Gentlemen, but spoke them as
absent from what they were doing, as they profess they are when they
come into Company. For the Folly is, that they have perswaded themselves
they really are busy. Thus their whole Time is spent in suspense of the
present Moment to the next, and then from the next to the succeeding,
which to the End of Life is to pass away with Pretence to many things,
and Execution of nothing.
Sir,
The Post is just going out, and I have many other Letters of very
great Importance to write this Evening, but I could not omit making my
Compliments to you for your Civilities to me when I was last in Town.
It is my Misfortune to be so full of Business, that I cannot tell you
a Thousand Things which I have to say to you. I must desire you to
communicate the Contents of this to no one living; but believe me to
be, with the greatest Fidelity,
Sir,
Your most Obedient,
Humble Servant,
Stephen Courier.
Madam,
I hate Writing, of all Things in the World; however, though I have
drunk the Waters, and am told I ought not to use my Eyes so much, I
cannot forbear writing to you, to tell you I have been to the last
Degree hipped since I saw you. How could you entertain such a Thought,
as that I should hear of that silly Fellow with Patience? Take my Word
for it, there is nothing in it; and you may believe it when so lazy a
Creature as I am undergo the Pains to assure you of it by taking Pen,
Ink, and Paper in my Hand. Forgive this, you know I shall not often
offend in this Kind. I am very much
Your Servant,
Bridget Eitherdown.
The Fellow is of your Country, pr'ythee send me Word how ever whether
he has so great an Estate.
Jan. 24, 1712.
Mr. Spectator,
'I am Clerk of the Parish from whence Mrs. Simper sends her
Complaint, in your Yesterday's Spectator. I must beg of you to
publish this as a publick Admonition to the aforesaid Mrs. Simper,
otherwise all my honest Care in the Disposition of the Greens in the
Church will have no Effect: I shall therefore with your Leave lay
before you the whole Matter. I was formerly, as she charges me, for
several Years a Gardener in the County of Kent: But I must
absolutely deny, that 'tis out of any Affection I retain for my old
Employment that I have placed my Greens so liberally about the Church,
but out of a particular Spleen I conceived against Mrs. Simper (and
others of the same Sisterhood) some time ago. As to herself, I had one
Day set the Hundredth Psalm, and was singing the first Line in order
to put the Congregation into the Tune, she was all the while curtsying
to Sir Anthony in so affected and indecent a manner, that the
Indignation I conceived at it made me forget my self so far, as from
the Tune of that Psalm to wander into Southwell Tune, and from
thence into Windsor Tune, still unable to recover my self till I had
with the utmost Confusion set a new one. Nay, I have often seen her
rise up and smile and curtsy to one at the lower End of the Church in
the midst of a Gloria Patri; and when I have spoke the Assent to a
Prayer with a long Amen uttered with decent Gravity, she has been
rolling her Eyes around about in such a Manner, as plainly shewed,
however she was moved, it was not towards an Heavenly Object. In fine,
she extended her Conquests so far over the Males, and raised such Envy
in the Females, that what between Love of those and the Jealousy of
these, I was almost the only Person that looked in the Prayer-Book all
Church-time. I had several Projects in my Head to put a Stop to this
growing Mischief; but as I have long lived in Kent, and there often
heard how the Kentish Men evaded the Conqueror, by carrying green
Boughs over their Heads, it put me in mind of practising this Device
against Mrs. Simper. I find I have preserved many a young Man from
her Eye-shot by this Means; therefore humbly pray the Boughs may be
fixed, till she shall give Security for her peaceable Intentions.
Your Humble Servant,
Francis Sternhold.
T.
Strenua nos exercet inertia.
Hor.
but
Contents
|
Saturday, January 26, 1712 |
Addison |
Ne, quicunque Deus, quicunque adhibebitur heros,
Regali conspectus in auro nuper et ostro,
Migret in Obscuras humili sermone tabernas:
Aut, dum vitat humum, nubes et inania captet.
Hor.

Having already treated of the Fable, the Characters, and Sentiments in
the
Paradise Lost
, we are in the last Place to consider the Language;
and as the Learned World is very much divided upon Milton as to this
Point, I hope they will excuse me if I appear particular in any of my
Opinions, and encline to those who judge the most advantageously of the
Author.
It
requisite that the Language of an Heroic Poem should be both
Perspicuous and Sublime
. In proportion as either of these two
Qualities are wanting, the Language is imperfect. Perspicuity is the
first and most necessary Qualification; insomuch that a good-natur'd
Reader sometimes overlooks a little Slip even in the Grammar or Syntax,
where it is impossible for him to mistake the Poet's Sense. Of this Kind
is that Passage in Milton, wherein he speaks of Satan.
—God and his Son except,
Created thing nought valu'd he nor shunn'd.
And that in which he describes Adam and Eve.
Adam the goodliest Man of Men since born
His Sons, the fairest of her Daughters Eve.
It is plain, that in the former of these Passages according to the
natural Syntax, the Divine Persons mentioned in the first Line are
represented as created Beings; and that, in the other, Adam and Eve are
confounded with their Sons and Daughters.
little Blemishes as
these, when the Thought is great and natural, we should, with Horace
impute to a pardonable Inadvertency, or to the Weakness of human Nature,
which cannot attend to each minute Particular, and give the last
Finishing to every Circumstance in so long a Work. The Ancient Criticks
therefore, who were acted by a Spirit of Candour, rather than that of
Cavilling, invented certain Figures of Speech, on purpose to palliate
little Errors of this nature in the Writings of those Authors who had so
many greater Beauties to attone for them.
If Clearness and Perspicuity were only to be consulted, the Poet would
have nothing else to do but to cloath his Thoughts in the most plain and
natural Expressions. But since it often happens that the most obvious
Phrases, and those which are used in ordinary Conversation, become too
familiar to the Ear, and contract a kind of Meanness by passing through
the Mouths of the Vulgar, a Poet should take particular Care to guard
himself against Idiomatick Ways of Speaking. Ovid and Lucan have many
Poornesses of Expression upon this Account, as taking up with the first
Phrases that offered, without putting themselves to the Trouble of
looking after such as would not only have been natural, but also
elevated and sublime.
has but few Failings in this Kind, of
which, however, you may meet with some Instances, as
in the
following Passages.
Embrios and Idiots, Eremites and Fryars,
White, Black, and Grey,—with all their Trumpery,
Here Pilgrims roam—
—A while discourse they hold,
No fear lest Dinner cool;—when thus began
Our Author—
Who of all Ages to succeed, but feeling
The Evil on him brought by me, will curse
My Head, ill fare our Ancestor impure,
For this we may thank Adam—
The Great Masters in Composition, knew very well that many an elegant
Phrase becomes improper for a Poet or an Orator, when it has been
debased by common Use. For this Reason the Works of Ancient Authors,
which are written in dead Languages, have a great Advantage over those
which are written in Languages that are now spoken. Were there any mean
Phrases or Idioms in Virgil and Homer, they would not shock the Ear of
the most delicate Modern Reader, so much as they would have done that of
an old Greek or Roman, because we never hear them pronounced in our
Streets, or in ordinary Conversation.
It is not therefore sufficient, that the Language of an Epic Poem be
Perspicuous, unless it be also Sublime. To this end it ought to deviate
from the common Forms and ordinary Phrases of Speech. The Judgment of a
Poet very much discovers it self in shunning the common Roads of
Expression, without falling into such ways of Speech as may seem stiff
and unnatural; he must not swell into a false Sublime, by endeavouring
to avoid the other Extream. Among the Greeks, Æschylus, and sometimes
Sophocles, were guilty of this Fault; among the Latins, Claudian and
Statius; and among our own Countrymen, Shakespear and Lee. In these
Authors the Affectation of Greatness often hurts the Perspicuity of the
Stile, as in many others the Endeavour after Perspicuity prejudices its
Greatness.
has observed, that the Idiomatick Stile may be avoided, and
the Sublime formed, by the following Methods
.
First
,
the Use of Metaphors
: Such are those of Milton.
Imparadised in one another's Arms.
—And in his Hand a Reed
Stood waving tipt with Fire.—
The grassie Clods now calv'd,—
Spangled with Eyes—
In these and innumerable other Instances, the Metaphors are very bold
but just; I must however observe that the Metaphors are not
so
thick
sown in Milton which always savours too much of Wit; that they never
clash with one another,
, as Aristotle observes, turns a Sentence
into a kind of an Enigma or Riddle
; and that he seldom has recourse
to them where the proper and natural Words will do as well.
Another way of raising the Language, and giving it a Poetical Turn, is
to make use of the Idioms of other Tongues. Virgil is full of the Greek
Forms of Speech, which the Criticks call Hellenisms, as Horace in his
Odes abounds with them much more than Virgil. I need not mention the
several Dialects which Homer has made use of for this end. Milton, in
conformity with the Practice of the Ancient Poets, and with Aristotle's
Rule, has infused a great many Latinisms, as well as Græcisms, and
sometimes Hebraisms, into the Language of his Poem; as towards the
Beginning of it.
Nor did they not perceive the evil Plight
In which they were, or the fierce Pains not feel,
Yet to their Gen'ral's Voice they soon obey'd.—
—Who shall tempt with wand'ring Feet
The dark unbottom'd Infinite Abyss,
And through the palpable Obscure find out
His uncouth way, or spread his airy Flight
Upborn with indefatigable Wings
Over the vast Abrupt!
—So both ascend
In the Visions of God— Book 2.
Under this Head may be reckon'd the placing the Adjective after the
Substantive, the Transposition of Words, the turning the Adjective into
a Substantive, with several other Foreign Modes of Speech which this
Poet has naturalized to give his Verse the greater Sound, and throw it
out of Prose.
The third Method mentioned by Aristotle is what agrees with the Genius
of the Greek Language more than with that of any other Tongue, and is
therefore more used by Homer than by any other Poet. I mean the
lengthning of a Phrase by the Addition of Words, which may either be
inserted or omitted, as also by the extending or contracting of
particular Words by the Insertion or Omission of certain Syllables.
Milton has put in practice this Method of raising his Language, as far
as the Nature of our Tongue will permit, as in the Passage
above-mentioned, Eremite,
for
what is Hermit, in common Discourse. If
you observe the Measure of his Verse, he has with great Judgment
suppressed a Syllable in several Words, and shortned those of two
Syllables into one, by which Method, besides the above-mentioned
Advantage, he has given a greater Variety to his Numbers. But this
Practice is more particularly remarkable in the Names of Persons and of
Countries, as Beëlzebub, Hessebon, and in many other Particulars,
wherein he has either changed the Name, or made use of that which is not
the most commonly known, that he might the better depart from the
Language of the Vulgar.
The same Reason recommended to him several old Words, which also makes
his Poem appear the more venerable, and gives it a greater Air of
Antiquity.
I must likewise take notice, that there are in Milton several Words of
his own coining, as Cerberean, miscreated, Hell-doom'd, Embryon Atoms,
and many others. If
Reader is offended at this Liberty in our
English Poet, I would recommend him to a Discourse in Plutarch
,
which shews us how frequently Homer has made use of the same Liberty.
Milton, by the above-mentioned Helps, and by the Choice of the noblest
Words and Phrases which our Tongue would afford him, has carried our
Language to a greater Height than any of the English Poets have ever
done before or after him, and made the Sublimity of his Stile equal to
that of his Sentiments.
I have been the more particular in these Observations on Milton's Stile,
because it is that Part of him in which he appears the most singular.
The Remarks I have here made upon the Practice of other Poets, with my
Observations out of Aristotle, will perhaps alleviate the Prejudice
which some have taken to his Poem upon this Account; tho' after all, I
must confess that I think his Stile, tho' admirable in general, is in
some places too much stiffened and obscured by the frequent Use of those
Methods, which Aristotle has prescribed for the raising of it.
This Redundancy of those several Ways of Speech, which Aristotle calls
foreign Language, and with which Milton has so very much enriched, and
in some Places darkned the Language of his Poem, was the more proper for
his use, because his Poem is written in Blank Verse. Rhyme, without any
other Assistance, throws the Language off from Prose, and very often
makes an indifferent Phrase pass unregarded; but where the Verse is not
built upon Rhymes, there Pomp of Sound, and Energy of Expression, are
indispensably necessary to support the Stile, and keep it from falling
into the Flatness of Prose.
Those
have not a Taste for this Elevation of Stile, and are apt to
ridicule a Poet when he departs from the common Forms of Expression,
would do well to see how Aristotle has treated an Ancient Author called
Euclid
, for his insipid Mirth upon this Occasion. Mr. Dryden used to
call
these
sort of Men his Prose-Criticks.
I
, under this Head of the Language, consider Milton's Numbers, in
which he has made use of several Elisions, which are not customary among
other English Poets, as may be particularly observed in his cutting off
the Letter Y, when it precedes a Vowel.
This, and some other
Innovation in the Measure of his Verse, has varied his Numbers in such a
manner, as makes them incapable of satiating the Ear, and cloying the
Reader, which the same uniform Measure would certainly have done, and
which the perpetual Returns of Rhime never fail to do in long Narrative
Poems. I shall close these Reflections upon the Language of Paradise
Lost, with observing that Milton has copied after Homer rather than
Virgil in the length of his Periods, the Copiousness of his Phrases, and
the running of his Verses into one another.
L.
Aristotle,
Poetics
, ii. §26.
'The excellence of Diction consists in being perspicuous without being
mean.'
Verum ubi plura nitent in carmine, non ego paucis
Offendar maculis, quas aut incuria fudit,
Aut humana parum cavit natura.
De Ar. Poet.
, II. 351-3.
see an Instance or two
Poetics
, ii. § 26
,like those in Milton
'That language is elevated and remote from the vulgar idiom which
employs unusual words: by unusual, I mean foreign,
metaphorical, extended—all, in short, that are not common words. Yet,
should a poet compose his Diction entirely of such words, the result
would be either an enigma or a barbarous jargon: an enigma if composed
of metaphors, a barbarous jargon if composed of foreign words. For the
essence of an enigma consists in putting together things apparently
inconsistent and impossible, and at the same time saying nothing but
what is true. Now this cannot be effected by the mere arrangement of
words; by the metaphorical use of them it may.'
On Life and Poetry of Homer
, wrongly ascribed to Plutarch,
Bk. I. § 16.
Poetics
, II. § 26.
'A judicious intermixture is requisite ... It is without reason,
therefore, that some critics have censured these modes of speech, and
ridiculed the poet for the use of them; as old Euclid did, objecting
that versification would be an easy business, if it were permitted to
lengthen words at pleasure, and then giving a burlesque example of
that sort of diction... In the employment of all the species of
unusual words, moderation is necessary: for metaphors, foreign words,
or any of the others improperly used, and with a design to be
ridiculous, would produce the same effect. But how great a difference
is made by a proper and temperate use of such words may be seen in
heroic verse. Let any one put common words in the place of the
metaphorical, the foreign, and others of the same kind, and he will be
convinced of the truth of what I say.'
He then gives two or three examples of the effect of changing poetical
for common words. As, that (in plays now lost)
'the same Iambic verse occurs in Æschylus and Euripides; but by means
of a single alteration—the substitution of a foreign for a common and
usual word—one of these verses appears beautiful, the other ordinary.
For Æschylus in his Philoctetes says, "The poisonous wound that eats
my flesh." But Euripides for
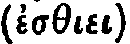
"eats" says
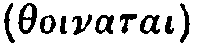
"banquets on."'
this
This is not particularly observed. On the very first page
of
P. L.
we have a line with the final y twice sounded before a vowel,
Invoke thy aid to my adventurous song.
Again a few lines later,
That to the height of this great argument
I may assert Eternal Providence.
Ten lines farther we read of the Serpent
Stirr'd up with envy and revenge.
We have only an apparent elision of y a few lines later in his aspiring
To set himself in glory above his peers,
for the line would be ruined were the y to be omitted by a reader. The
extreme shortness of the two unaccented syllables, y and a, gives them
the quantity of one in the metre, and allows by the turn of voice a
suggestion of exuberance, heightening the force of the word glory. Three
lines lower Milton has no elision of the y before a vowel in the line,
Against the throne and monarchy of God.
Nor eight lines after that in the words 'day and night.' There is elision
of y in the line,
That were an ignominy and shame beneath
This downfall.
But none a few lines lower down in
Sole reigning holds the tyranny of heaven.
When the y stands by itself, unaccented, immediately after an accented
syllable, and precedes a vowel that is part of another unaccented
syllable standing immediately before an accented one, Milton accepts the
consequence, and does not attempt to give it the force of a distinct
syllable. But Addison's vague notion that it was Milton's custom to cut
off the final y when it precedes a vowel, and that for the sake of being
uncommon, came of inaccurate observation. For the reasons just given,
the y of the word glory runs into the succeeding syllable, and most
assuredly is not cut off, when we read of
the excess
Of Glory obscured: as when the sun, new ris'n,
Looks through the horizontal misty air,
but the y in ' misty ' stands as a full syllable because the word air is
accented. So again in
Death as oft accused
Of tardy execution, since denounc'd
The day of his offence.
The y of ' tardy' is a syllable because the vowel following it is
accented; the y also of ' day' remains, because, although an unaccented
vowel follows, it is itself part of an accented syllable.
Contents
|
Monday, January 28, 1712 |
Steele |
Nomina Honesta prætenduntur vitiis.
Tacit.

York, Jan. 18, 1712.
Mr. Spectator,
I pretend not to inform a Gentleman of so just a Taste, whenever he
pleases to use it; but it may not be amiss to inform your Readers,
that there is a false Delicacy as well as a true one. True Delicacy,
as I take it, consists in Exactness of Judgment and Dignity of
Sentiment, or if you will, Purity of Affection, as this is opposed to
Corruption and Grossness. There are Pedants in Breeding as well as in
Learning. The Eye that cannot bear the Light is not delicate but sore.
A good Constitution appears in the Soundness and Vigour of the Parts,
not in the Squeamishness of the Stomach; And a false Delicacy is
Affectation, not Politeness. What then can be the Standard of Delicacy
but Truth and Virtue? Virtue, which, as the Satyrist long since
observed, is real Honour; whereas the other Distinctions among Mankind
are meerly titular. Judging by that Rule, in my Opinion, and in that
of many of your virtuous Female Readers, you are so far from deserving
Mr. Courtly's Accusation, that you seem too gentle, and to allow too
many Excuses for an enormous Crime, which is the Reproach of the Age,
and is in all its Branches and Degrees expresly forbidden by that
Religion we pretend to profess; and whose Laws, in a Nation that calls
it self Christian, one would think should take Place of those Rules
which Men of corrupt Minds, and those of weak Understandings follow. I
know not any thing more pernicious to good Manners, than the giving
fair Names to foul Actions; for this confounds Vice and Virtue, and
takes off that natural Horrour we have to Evil. An innocent Creature,
who would start at the Name of Strumpet, may think it pretty to be
called a Mistress, especially if her Seducer has taken care to inform
her, that a Union of Hearts is the principal Matter in the Sight of
Heaven, and that the Business at Church is a meer idle Ceremony. Who
knows not that the Difference between obscene and modest Words
expressing the same Action, consists only in the accessary Idea, for
there is nothing immodest in Letters and Syllables. Fornication and
Adultery are modest Words: because they express an Evil Action as
criminal, and so as to excite Horrour and Aversion: Whereas Words
representing the Pleasure rather than the Sin, are for this Reason
indecent and dishonest. Your Papers would be chargeable with something
worse than Indelicacy, they would be Immoral, did you treat the
detestable Sins of Uncleanness in the same manner as you rally an
impertinent Self-love and an artful Glance; as those Laws would be
very unjust, that should chastise Murder and Petty Larceny with the
same Punishment. Even Delicacy requires that the Pity shewn to
distressed indigent Wickedness, first betrayed into, and then expelled
the Harbours of the Brothel, should be changed to Detestation, when we
consider pampered Vice in the Habitations of the Wealthy. The most
free Person of Quality, in Mr. Courtly's Phrase, that is, to speak
properly, a Woman of Figure who has forgot her Birth and Breeding,
dishonoured her Relations and her self, abandoned her Virtue and
Reputation, together with the natural Modesty of her Sex, and risqued
her very Soul, is so far from deserving to be treated with no worse
Character than that of a kind Woman, (which is doubtless Mr. Courtly's
Meaning, if he has any,) that one can scarce be too severe on her, in
as much as she sins against greater Restraints, is less exposed, and
liable to fewer Temptations, than Beauty in Poverty and Distress. It
is hoped therefore, Sir, that you will not lay aside your generous
Design of exposing that monstrous Wickedness of the Town, whereby a
Multitude of Innocents are sacrificed in a more barbarous Manner than
those who were offered to Moloch. The Unchaste are provoked to see
their Vice exposed, and the Chaste cannot rake into such Filth without
Danger of Defilement; but a meer
Spectator may look into the Bottom,
and come off without partaking in the Guilt. The doing so will
convince us you pursue publick Good, and not meerly your own
Advantage: But if your Zeal slackens, how can one help thinking that
Mr. Courtly's Letter is but a Feint to get off from a Subject, in
which either your own, or the private and base Ends of others to whom
you are partial, or those
of whom you are afraid, would not endure a
Reformation?
I am, Sir, your humble Servant and Admirer, so long as you tread in
the Paths of Truth, Virtue, and Honour.
Mr.
Spectator,
Trin. Coll. Cantab. Jan. 12, 1711-12.
It is my Fortune to have a Chamber-Fellow, with whom, tho' I agree
very well in many Sentiments, yet there is one in which we are as
contrary as Light and Darkness. We are both in Love: his Mistress is a
lovely Fair, and mine a lovely Brown. Now as the Praise of our
Mistresses Beauty employs much of our Time, we have frequent Quarrels
in entering upon that Subject, while each says all he can to defend
his Choice. For my own part, I have racked my Fancy to the utmost; and
sometimes, with the greatest Warmth of Imagination, have told him,
That Night was made before Day, and many more fine Things, tho'
without any effect: Nay, last Night I could not forbear saying with
more Heat than Judgment, that the Devil ought to be painted white. Now
my Desire is, Sir, that you would be pleased to give us in Black and
White your Opinion in the Matter of Dispute between us; which will
either furnish me with fresh and prevailing Arguments to maintain my
own Taste, or make me with less Repining allow that of my
Chamber-Fellow. I
know very well that I have Jack Cleveland
1 and
Bond's Horace on my Side; but then he has such a Band of Rhymers and
Romance-Writers, with which he opposes me, and is so continually
chiming to the Tune of Golden Tresses, yellow Locks, Milk, Marble,
Ivory, Silver, Swan, Snow, Daisies, Doves, and the Lord knows what;
which he is always sounding with so much Vehemence in my Ears, that he
often puts me into a brown Study how to answer him; and I find that I
am in a fair Way to be quite confounded, without your timely
Assistance afforded to,
Sir,
Your humble Servant,
Philobrune.
T.
Cleveland celebrates brown beauties in his poem of 'the
Senses Festival.' John Bond, who published Commentaries on Horace and
Persius, Antony à Wood calls 'a polite and rare critic whose labours
have advanced the Commonwealth of Learning very much.'
Z.
Contents
|
Tuesday, January 29, 1712 |
Addison |
I look upon it as a peculiar Happiness, that were I to choose of what
Religion I would be, and under what Government I would live, I should
most certainly give the Preference to that Form of Religion and
Government which is established in my own Country. In this Point I think
I am determined by Reason and Conviction; but if I shall be told that I
am acted by Prejudice, I am sure it is an honest Prejudice, it is a
Prejudice that arises from the Love of my Country, and therefore such an
one as I will always indulge. I have in several Papers endeavoured to
express my Duty and Esteem for the Church of England, and design this as
an Essay upon the Civil Part of our Constitution, having often
entertained my self with Reflections on this Subject, which I have not
met with in other Writers.
That Form of Government appears to me the most reasonable, which is most
conformable to the Equality that we find in human Nature, provided it be
consistent with publick Peace and Tranquillity. This is what may
properly be called Liberty, which exempts one Man from Subjection to
another so far as the Order and Œconomy of Government will permit.
Liberty should reach every Individual of a People, as they all share one
common Nature; if it only spreads among particular Branches, there had
better be none at all, since such a Liberty only aggravates the
Misfortune of those who are depriv'd of it, by setting before them a
disagreeable Subject of Comparison. This Liberty is best preserved,
where the Legislative Power is lodged in several Persons, especially if
those Persons are of different Ranks and Interests; for where they are
of the same Rank, and consequently have an Interest to manage peculiar
to that Rank, it differs but little from a Despotical Government in a
single Person. But the greatest Security a People can have for their
Liberty, is when the Legislative Power is in the Hands of Persons so
happily distinguished, that by providing for the particular Interests of
their several Ranks, they are providing for the whole Body of the
People; or in other Words, when there is no Part of the People that has
not a common Interest with at least one Part of the Legislators.
If there be but one Body of Legislators, it is no better than a Tyranny;
if there are only two, there will want a casting Voice, and one of them
must at length be swallowed up by Disputes and Contentions that will
necessarily arise between them. Four would have the same Inconvenience
as two, and a greater Number would cause too much Confusion. I could
never read a Passage in Polybius, and another in Cicero, to this
Purpose, without a secret Pleasure in applying it to the English
Constitution, which it suits much better than the Roman. Both these
great Authors give the Pre-eminence to a mixt Government, consisting of
three Branches, the Regal, the Noble, and the Popular. They had
doubtless in their Thoughts the Constitution of the Roman Commonwealth,
in which the Consul represented the King, the Senate the Nobles, and the
Tribunes the People. This Division of the three Powers in the Roman
Constitution was by no means so distinct and natural, as it is in the
English Form of Government. Among several Objections that might be made
to it, I think the Chief are those that affect the Consular Power, which
had only the Ornaments without the Force of the Regal Authority. Their
Number had not a casting Voice in it; for which Reason, if one did not
chance to be employed Abroad, while the other sat at Home, the Publick
Business was sometimes at a Stand, while the Consuls pulled two
different Ways in it. Besides, I do not find that the Consuls had ever a
Negative Voice in the passing of a Law, or Decree of Senate, so that
indeed they were rather the chief Body of the Nobility, or the first
Ministers of State, than a distinct Branch of the Sovereignty, in which
none can be looked upon as a Part, who are not a Part of the
Legislature. Had the Consuls been invested with the Regal Authority to
as great a Degree as our Monarchs, there would never have been any
Occasions for a Dictatorship, which had in it the Power of all the three
Orders, and ended in the Subversion of the whole Constitution.
Such an History as that of Suelonius, which gives us a Succession of
Absolute Princes, is to me an unanswerable Argument against Despotick
Power. Where the Prince is a Man of Wisdom and Virtue, it is indeed
happy for his People that he is absolute; but since in the common Run of
Mankind, for one that is Wise and Good you find ten of a contrary
Character, it is very dangerous for a Nation to stand to its Chance, or
to have its publick Happiness or Misery depend on the Virtues or Vices
of a single Person.
into the
History
I have mentioned, or
into any Series of Absolute Princes, how many Tyrants must you read
through, before you come to an Emperor that is supportable. But this is
not all; an honest private Man often grows cruel and abandoned, when
converted into an absolute Prince. Give a Man Power of doing what he
pleases with Impunity, you extinguish his Fear, and consequently
overturn in him one of the great Pillars of Morality. This too we find
confirmed by Matter of Fact. How many hopeful Heirs apparent to grand
Empires, when in the Possession of them, have become such Monsters of
Lust and Cruelty as are a Reproach to Human Nature.
Some tell us we ought to make our Governments on Earth like that in
Heaven, which, say they, is altogether Monarchical and Unlimited. Was
Man like his Creator in Goodness and Justice, I should be for following
this great Model; but where Goodness and Justice are not essential to
the Ruler, I would by no means put myself into his Hands to be disposed
of according to his particular Will and Pleasure.
It is odd to consider the Connection between Despotic Government and
Barbarity, and how the making of one Person more than Man, makes the
rest less. About nine Parts of the World in ten are in the lowest State
of Slavery, and consequently sunk into the most gross and brutal
Ignorance. European Slavery is indeed a State of Liberty, if compared
with that which prevails in the other three Divisions of the World; and
therefore it is no Wonder that those who grovel under it have many
Tracks of Light among them, of which the others are wholly destitute.
Riches and Plenty are the natural Fruits of Liberty, and where these
abound, Learning and all the Liberal Arts will immediately lift up their
Heads and flourish.
a Man must have no slavish Fears and
Apprehensions hanging upon his Mind,
who
will indulge the Flights
of Fancy or Speculation, and push his Researches into all the abstruse
Corners of Truth, so it is necessary for him to have about him a
Competency of all the Conveniencies of Life.
The first thing every one looks after, is to provide himself with
Necessaries. This Point will engross our Thoughts 'till it be satisfied.
If this is taken care of to our Hands, we look out for Pleasures and
Amusements; and among a great Number of idle People, there will be many
whose Pleasures will lie in Reading and Contemplation. These are the two
great Sources of Knowledge, and as Men grow wise they naturally love to
communicate their Discoveries; and others seeing the Happiness of such a
Learned Life, and improving by their Conversation, emulate, imitate, and
surpass one another, till a Nation is filled with Races of wise and
understanding Persons. Ease and Plenty are therefore the great
Cherishers of Knowledge: and as most of the Despotick Governments of the
World have neither of them, they are naturally over-run with Ignorance
and Barbarity. In Europe, indeed, notwithstanding several of its Princes
are absolute, there are Men famous for Knowledge and Learning; but the
Reason is because the Subjects are many of them rich and wealthy, the
Prince not thinking fit to exert himself in his full Tyranny like the
Princes of the Eastern Nations, lest his Subjects should be invited to
new-mould their Constitution, having so many Prospects of Liberty within
their View. But in all Despotic Governments, tho' a particular Prince
may favour Arts and Letters, there is a natural Degeneracy of Mankind,
as you may observe from Augustus's Reign, how the Romans lost themselves
by Degrees till they fell to an Equality with the most barbarous Nations
that surrounded them. Look upon Greece under its free States, and you
would think its Inhabitants lived in different Climates, and under
different Heavens, from those at present; so different are the Genius's
which are formed under Turkish Slavery and Grecian Liberty.
Besides Poverty and Want, there are other Reasons that debase the Minds
of Men, who live under Slavery, though I look on this as the Principal.
This natural Tendency of Despotic Power to Ignorance and Barbarity, tho'
not insisted upon by others, is, I think, an unanswerable Argument
against that Form of Government, as it shews how repugnant it is to the
Good of Mankind, and the Perfection of human Nature, which ought to be
the great Ends of all Civil Institutions.
L.
Historian
that
Contents
|
Wednesday, January 30, 1712 |
Steele |
—Pavor est utrique molestus.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'When you spoke of the Jilts and Coquets, you then promised to be very
impartial, and not to spare even your own Sex, should any of their
secret or open Faults come under your Cognizance; which has given me
Encouragement to describe a certain Species of Mankind under the
Denomination of Male Jilts. They are Gentlemen who do not design to
marry, yet, that they may appear to have some Sense of Gallantry,
think they must pay their Devoirs to one particular Fair; in order to
which they single out from amongst the Herd of Females her to whom
they design to make their fruitless Addresses. This done, they first
take every Opportunity of being in her Company, and then never fail
upon all Occasions to be particular to her, laying themselves at her
Feet, protesting the Reality of their Passion with a thousand Oaths,
solliciting a Return, and saying as many fine Things as their Stock of
Wit will allow; and if they are not deficient that way, generally
speak so as to admit of a double Interpretation; which the credulous
Fair is apt to turn to her own Advantage, since it frequently happens
to be a raw, innocent, young Creature, who thinks all the World as
sincere as her self, and so her unwary Heart becomes an easy Prey to
those deceitful Monsters, who no sooner perceive it, but immediately
they grow cool, and shun her whom they before seemed so much to
admire, and proceed to act the same common-place Villany towards
another. A Coxcomb flushed with many of these infamous Victories shall
say he is sorry for the poor Fools, protest and vow he never thought
of Matrimony, and wonder talking civilly can be so strangely
misinterpreted. Now, Mr.
Spectator, you that are a professed Friend to
Love, will, I hope, observe upon those who abuse that noble Passion,
and raise it in innocent Minds by a deceitful Affectation of it, after
which they desert the Enamoured. Pray bestow a little of your Counsel
to those fond believing Females who already have or are in Danger of
broken Hearts; in which you will oblige a great Part of this Town, but
in a particular Manner,
Sir Your (yet Heart-whole) Admirer,
and devoted humble Servant,
Melainia.
Melainie's Complaint is occasioned by so general a Folly, that it is
wonderful one could so long overlook it. But this false Gallantry
proceeds from an Impotence of Mind, which makes those who are guilty of
it incapable of pursuing what they themselves approve. Many a Man wishes
a Woman his Wife whom he dares not take for such. Tho' no one has Power
over his Inclinations or Fortunes, he is a Slave to common Fame. For
this Reason I think Melainia gives them too soft a Name in that of Male
Coquets. I know not why Irresolution of Mind should not be more
contemptible than Impotence of Body; and these frivolous Admirers would
be but tenderly used, in being only included in the same Term with the
Insufficient another Way. They whom my Correspondent calls Male Coquets,
shall hereafter be called Fribblers. A Fribbler is one who professes
Rapture and Admiration for the Woman to whom he addresses, and dreads
nothing so much as her Consent. His Heart can flutter by the Force of
Imagination, but cannot fix from the Force of Judgment. It is not
uncommon for the Parents of young Women of moderate Fortune to wink at
the Addresses of Fribblers, and expose their Children to the ambiguous
Behaviour which Melainia complains of, till by the Fondness to one they
are to lose, they become incapable of Love towards others, and by
Consequence in their future Marriage lead a joyless or a miserable Life.
As therefore I shall in the Speculations which regard Love be as severe
as I ought on Jilts and Libertine Women, so will I be as little merciful
to insignificant and mischievous Men. In order to this, all Visitants
who frequent Families wherein there are young Females, are forthwith
required to declare themselves, or absent from Places where their
Presence banishes such as would pass their Time more to the Advantage of
those whom they visit. It is a Matter of too great Moment to be dallied
with; and I shall expect from all my young People a satisfactory Account
of Appearances. Strephon has from the Publication hereof seven Days to
explain the Riddle he presented to Eudamia; and Chloris an Hour after
this comes to her Hand, to declare whether she will have Philotas, whom
a Woman of no less Merit than her self, and of superior Fortune,
languishes to call her own.
To the
Spectator.
Sir1,
'Since so many Dealers turn Authors, and write quaint Advertisements
in praise of their Wares, one who from an Author turn'd Dealer may be
allowed for the Advancement of Trade to turn Author again. I will not
however set up like some of 'em, for selling cheaper than the most
able honest Tradesman can; nor do I send this to be better known for
Choice and Cheapness of China and Japan Wares, Tea, Fans, Muslins,
Pictures, Arrack, and other Indian Goods. Placed as I am in
Leadenhall-street, near the India-Company, and the Centre of that
Trade, Thanks to my fair Customers, my Warehouse is graced as well as
the Benefit Days of my Plays and Operas; and the foreign Goods I sell
seem no less acceptable than the foreign Books I translated, Rabelais
and Don Quixote: This the Criticks allow me, and while they like my
Wares they may dispraise my Writing. But as 'tis not so well known yet
that I frequently cross the Seas of late, and speaking Dutch and
French, besides other Languages, I have the Conveniency of buying and
importing rich Brocades, Dutch Atlasses, with Gold and Silver, or
without, and other foreign Silks of the newest Modes and best
Fabricks, fine Flanders Lace, Linnens, and Pictures, at the best Hand:
This my new way of Trade I have fallen into I cannot better publish
than by an Application to you. My Wares are fit only for such as your
Readers; and I would beg of you to print this Address in your Paper,
that those whose Minds you adorn may take the Ornaments for their
Persons and Houses from me. This, Sir, if I may presume to beg it,
will be the greater Favour, as I have lately received rich Silks and
fine Lace to a considerable Value, which will be sold cheap for a
quick Return, and as I have also a large Stock of other Goods. Indian
Silks were formerly a great Branch of our Trade; and since we must not
sell 'em, we must seek Amends by dealing in others. This I hope will
plead for one who would lessen the Number of Teazers of the Muses, and
who, suiting his Spirit to his Circumstances, humbles the Poet to
exalt the Citizen. Like a true Tradesman, I hardly ever look into any
Books but those of Accompts. To say the Truth, I cannot, I think, give
you a better Idea of my being a downright Man of Traffick, than by
acknowledging I oftener read the Advertisements, than the Matter of
even your Paper. I am under a great Temptation to take this
Opportunity of admonishing other Writers to follow my Example, and
trouble the Town no more; but as it is my present Business to increase
the Number of Buyers rather than Sellers, I hasten to tell you that I
am,
Sir, Your most humble,
and most obedient Servant,
Peter Motteux.
T.
Peter Anthony Motteux, the writer of this letter, was born
in Normandy, and came as a refugee to England at the Revocation of the
Edict of Nantes. Here he wrote about 14 plays, translated Bayle's
Dictionary, Montaigne's Essays, and Don Quixote, and established himself
also as a trader in Leadenhall Street. He had a wife and a fine young
family when (at the age of 56, and six years after the date of this
letter) he was found dead in a house of ill fame near Temple Bar under
circumstances that caused a reward of fifty pounds to be offered for the
discovery of his murderer.
Contents
|
Thursday, January 31, 1712 |
Addison |
Vitæ summa brevis spem nos vetat inchoare longam.
Hor.

Upon taking my Seat in a Coffee-house I often draw the Eyes of the whole
Room upon me, when in the hottest Seasons of News, and at a time that
perhaps the Dutch Mail is just come in, they hear me ask the Coffee-man
for his last Week's Bill of Mortality: I find that I have been sometimes
taken on this occasion for a Parish Sexton, sometimes for an Undertaker,
and sometimes for a Doctor of Physick. In this, however, I am guided by
the Spirit of a Philosopher, as I take occasion from hence to reflect
upon the regular Encrease and Diminution of Mankind, and consider the
several various Ways through which we pass from Life to Eternity. I am
very well pleased with these Weekly Admonitions, that bring into my Mind
such Thoughts as ought to be the daily Entertainment of every reasonable
Creature; and can consider, with Pleasure to my self, by which of those
Deliverances, or, as we commonly call them, Distempers, I may possibly
make my Escape out of this World of Sorrows, into that Condition of
Existence, wherein I hope to be Happier than it is possible for me at
present to conceive.
But this is not all the Use I make of the above-mentioned Weekly Paper.
Bill of Mortality
is in my Opinion an unanswerable Argument for a
Providence. How can we, without supposing our selves under the constant
Care of a Supreme Being, give any possible Account for that nice
Proportion, which we find in every great City, between the Deaths and
Births of its Inhabitants, and between the Number of Males and that of
Females, who are brought into the World? What else could adjust in so
exact a manner the Recruits of every Nation to its Losses, and divide
these new Supplies of People into such equal Bodies of both Sexes?
Chance could never hold the Balance with so steady a Hand. Were we not
counted out by an intelligent Supervisor, we should sometimes be
over-charged with Multitudes, and at others waste away into a Desart: We
should be sometimes a
populus virorum
, as Florus elegantly expresses it,
a Generation of Males, and at others a Species of Women. We may extend
this Consideration to every Species of living Creatures, and consider
the whole animal World as an huge Army made up of innumerable Corps, if
I may use that Term, whose Quotas have been kept entire near five
thousand Years, in so wonderful a manner, that there is not probably a
single Species lost during this long Tract of Time. Could we have
general Bills of Mortality of every kind of Animal, or particular ones
of every Species in each Continent and Island, I could almost say in
every Wood, Marsh or Mountain, what astonishing Instances would they be
of that Providence which watches over all its Works?
I have heard of a great Man in the Romish Church, who upon reading those
Words in the Vth Chapter of Genesis, And all the Days that Adam lived
were nine hundred and thirty Years, and he died; and all the Days of
Seth were nine hundred and twelve Years, and he died; and all the Days
of Methuselah were nine hundred and sixty nine Years, and he died;
immediately shut himself up in a Convent, and retired from the World, as
not thinking any thing in this Life worth pursuing, which had not regard
to another.
The Truth of it is, there is nothing in History which is so improving to
the Reader, as those Accounts which we meet with of the Deaths of
eminent Persons, and of their Behaviour in that dreadful Season. I may
also add, that there are no Parts in History which affect and please the
Reader in so sensible a manner. The Reason I take to be this, because
there is no other single Circumstance in the Story of any Person, which
can possibly be the Case of every one who reads it. A Battle or a
Triumph are Conjunctures in which not one Man in a Million is likely to
be engaged; but when we see a Person at the Point of Death, we cannot
forbear being attentive to every thing he says or does, because we are
sure that some time or other we shall our selves be in the same
melancholy Circumstances. The General, the Statesman, or the
Philosopher, are perhaps Characters which we may never act in; but the
dying Man is one whom, sooner or later, we shall certainly resemble.
It is,
, for the same kind of Reason that few Books,
written
in English, have been so much perused as Dr. Sherlock's Discourse
upon Death; though at the same time I must own, that he who has not
perused this Excellent Piece, has not perhaps read one of the strongest
Persuasives to a Religious Life that ever was written in any Language.
The Consideration, with which I shall close this Essay upon Death, is
one of the most ancient and most beaten Morals that has been recommended
to Mankind. But its being so very common, and so universally received,
though it takes away from it the Grace of Novelty, adds very much to the
Weight of it, as it shews that it falls in with the general Sense of
Mankind. In short, I would have every one consider, that he is in this
Life nothing more than a Passenger, and that he is not to set up his
Rest here, but to keep an attentive Eye upon that State of Being to
which he approaches every Moment, and which will be for ever fixed and
permanent. This single Consideration would be sufficient to extinguish
the Bitterness of Hatred, the Thirst of Avarice, and the Cruelty of
Ambition.
I am very much pleased with the Passage of Antiphanes a very ancient
Poet, who lived near an hundred Years before Socrates, which represents
the Life of Man under this View, as I have here translated it Word for
Word.
not grieved, says he, above measure for thy deceased Friends
. They
are not dead, but have only finished that Journey which it is
necessary for every one of us to take: We ourselves must go to that
great Place of Reception in which they are all of them assembled, and in
this general Rendezvous of Mankind, live together in another State of
Being.
I think I have, in a former Paper, taken notice of those beautiful
Metaphors in Scripture, where Life is termed a Pilgrimage, and those who
pass through it are called Strangers and Sojourners upon Earth. I shall
conclude this with a Story,
I have somewhere read in the Travels
of Sir John Chardin
; that Gentleman after having told us, that the
Inns which receive the Caravans in Persia, and the Eastern Countries,
are called by the Name of Caravansaries, gives us a Relation to the
following Purpose.
A Dervise, travelling through Tartary, being arrived at the Town of
Balk, went into the King's Palace by Mistake, as thinking it to be a
publick Inn or Caravansary. Having looked about him for some time, he
enter'd into a long Gallery, where he laid down his Wallet, and spread
his Carpet, in order to repose himself upon it after the Manner of the
Eastern Nations. He had not been long in this Posture before he was
discovered by some of the Guards, who asked him what was his Business in
that Place? The Dervise told them he intended to take up his Night's
Lodging in that Caravansary. The Guards let him know, in a very angry
manner, that the House he was in was not a Caravansary, but the King's
Palace. It happened that the King himself passed through the Gallery
during this Debate, and smiling at the Mistake of the Dervise, asked him
how he could possibly be so dull as not to distinguish a Palace from a
Caravansary? Sir, says the Dervise, give me leave to ask your Majesty a
Question or two. Who were the Persons that lodged in this House when it
was first built? The King replied, His Ancestors. And who, says the
Dervise, was the last Person that lodged here? The King replied, His
Father. And who is it, says the Dervise, that lodges here at present?
The King told him, that it was he himself. And who, says the Dervise,
will be here after you? The King answered, The young Prince his Son. 'Ah
Sir, said the Dervise, a House that changes its Inhabitants so often,
and receives such a perpetual Succession of Guests, is not a Palace but
a Caravansary."
L.
Bills of Mortality, containing the weekly number of
Christenings and Deaths, with the cause of Death, were first compiled by
the London Company of Parish Clerks (for 109 parishes) after the Plague
in 1592. They did not give the age at death till 1728.
which have been written
; for they
Sir John Chardin was a jeweller's son, born at Paris, who
came to England and was knighted by Charles II. He travelled into Persia
and the East Indies, and his account of his voyages was translated into
English, German, and Flemish. He was living when this paper appeared,
but died in the following year, at the age of 70.
Contents
|
Friday, February 1, 1712 |
Steele |
Projicit ampullas et sesquipedalia verba.
Hor.1
The Players, who know I am very much their Friend, take all
Opportunities to express a Gratitude to me for being so. They could not
have a better Occasion of Obliging me, than one which they lately took
hold of.
desired my Friend
Will. Honeycomb
to bring me to the
Reading of a new Tragedy; it is called The distressed Mother
. I must
confess, tho' some Days are passed since I enjoyed that Entertainment,
the Passions of the several Characters dwell strongly upon my
Imagination; and I congratulate to the Age, that they are at last to see
Truth and humane Life represented in the Incidents which concern Heroes
and Heroines. The Stile of the Play is such as becomes those of the
first Education, and the Sentiments worthy those of the highest Figure.
It was a most exquisite Pleasure to me, to observe real Tears drop from
the Eyes of those who had long made it their Profession to dissemble
Affliction; and the Player, who read, frequently throw down the Book,
till he had given vent to the Humanity which rose in him at some
irresistible Touches of the imagined Sorrow. We have seldom had any
Female Distress on the Stage, which did not, upon cool Examination,
appear to flow from the Weakness rather than the Misfortune of the
Person represented: But in this Tragedy you are not entertained with the
ungoverned Passions of such as are enamoured of each other merely as
they are Men and Women, but their Regards are founded upon high
Conceptions of each other's Virtue and Merit; and the Character which
gives Name to the Play, is one who has behaved her self with heroic
Virtue in the most important Circumstances of a Female Life, those of a
Wife, a Widow, and a Mother. If there be those whose Minds have been too
attentive upon the Affairs of Life, to have any Notion of the Passion of
Love in such Extremes as are known only to particular Tempers, yet, in
the above-mentioned Considerations, the Sorrow of the Heroine will move
even the Generality of Mankind. Domestick Virtues concern all the World,
and there is no one living who is not interested that Andromache should
be an imitable Character. The generous Affection to the Memory of her
deceased Husband, that tender Care for her Son, which is ever heightned
with the Consideration of his Father, and these Regards preserved in
spite of being tempted with the Possession of the highest Greatness, are
what cannot but be venerable even to such an Audience as at present
frequents the English Theatre. My Friend
Will Honeycomb
commended
several tender things that were said, and told me they were very
genteel; but whisper'd me, that he feared the Piece was not busy enough
for the present Taste. To supply this, he recommended to the Players to
be very careful in their Scenes, and above all Things, that every Part
should be perfectly new dressed. I was very glad to find that they did
not neglect my Friend's Admonition, because there are a great many in
his Class of Criticism who may be gained by it; but indeed the Truth is,
that as to the Work it self, it is every where Nature. The Persons are
of the highest Quality in Life, even that of Princes; but their Quality
is not represented by the Poet with Direction that Guards and Waiters
should follow them in every Scene, but their Grandeur appears in
Greatness of Sentiment
s
, flowing from Minds worthy their Condition.
To make a Character truly Great, this Author understands that it should
have its Foundation in superior Thoughts and Maxims of Conduct. It is
very certain, that many an honest Woman would make no Difficulty, tho'
she had been the Wife of Hector, for the sake of a Kingdom, to marry the
Enemy of her Husband's Family and Country; and indeed who can deny but
she might be still an honest Woman, but no Heroine? That may be
defensible, nay laudable in one Character, which would be in the highest
Degree exceptionable in another. When Cato Uticensis killed himself,
Cottius a Roman of ordinary Quality and Character did the same thing;
upon which one said, smiling, 'Cottius might have lived, tho' Cæsar has
seized the Roman Liberty.' Cottius's Condition might have been the
same, let things at the upper End of the World pass as they would. What
is further very extraordinary in this Work, is, that the Persons are all
of them laudable, and their Misfortunes arise rather from unguarded
Virtue than Propensity to Vice. The Town has an Opportunity of doing
itself Justice in supporting the Representation of Passion, Sorrow,
Indignation, even Despair itself, within the Rules of Decency, Honour
and Good-breeding; and since there is no one can flatter himself his
Life will be always fortunate, they may here see Sorrow as they would
wish to bear it whenever it arrives.
Mr. Spectator,
I am appointed to act a Part in the new Tragedy called The Distressed
Mother: It is the celebrated Grief of Orestes which I am to personate;
but I shall not act it as I ought, for I shall feel it too intimately
to be able to utter it. I was last Night repeating a Paragraph to my
self, which I took to be an Expression of Rage, and in the middle of
the Sentence there was a Stroke of Self-pity which quite unmanned me.
Be pleased, Sir, to print this Letter, that when I am oppressed in
this manner at such an Interval, a certain Part of the Audience may
not think I am out; and I hope with this Allowance to do it to
Satisfaction. I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
George Powell.
Mr. Spectator,
'As I was walking t'other Day in the Park, I saw a Gentleman with a
very short Face; I desire to know whether it was you. Pray inform me
as soon as you can, lest I become the most heroick Hecatissa's Rival.
Your humble Servant to command,
Sophia.
Dear Madam,
It is not me you are in love with, for I was very ill and kept my
Chamber all that Day.
Your most humble Servant,
The
Spectator
.
T.
Spirat Tragicum satis, et fœliciter Audet.
Hor.
This is a third blast of the Trumpet on behalf of Ambrose
Philips, who had now been adapting Racine's
Andromaque
.
Contents
|
Saturday, February 2, 1712 |
Addison |
Ubi plura nitent in carmine, non ego paucis
Offendor maculis, quas aut Incuria fudit,
Aut Humana parum cavit Natura.
Hor.

I have now considered Milton's
Paradise Lost
under those four great
Heads of the Fable, the Characters, the Sentiments, and the Language;
and have shewn that he excels, in general, under each of these Heads. I
hope that I have made several Discoveries which may appear new, even to
those who are versed in Critical Learning. Were I indeed to chuse my
Readers, by whose Judgment I would stand or fall, they should not be
such as are acquainted only with the French and Italian Criticks, but
also with the Ancient and Moderns who have written in either of the
learned Languages. Above all, I would have them well versed in the Greek
and Latin Poets, without which a Man very often fancies that he
understands a Critick, when in Reality he does not comprehend his
Meaning.
It is in Criticism, as in all other Sciences and Speculations; one who
brings with him any implicit Notions and Observations which he has made
in his reading of the Poets, will find his own Reflections methodized
and explained, and perhaps several little Hints that had passed in his
Mind, perfected and improved in the Works of a good Critick; whereas one
who has not these previous Lights is very often an utter Stranger to
what he reads, and apt to put a wrong Interpretation upon it.
Nor is it sufficient, that a Man who sets up for a Judge in Criticism,
should have perused the Authors above mentioned, unless he has also a
clear and Logical Head. Without this Talent he is perpetually puzzled
and perplexed amidst his own Blunders, mistakes the Sense of those he
would confute, or if he chances to think right, does not know how to
convey his Thoughts to another with Clearness and Perspicuity.
Aristotle, who was the best Critick, was also one of the best Logicians
that ever appeared in the World.
. Lock's
Essay on Human Understanding
would be thought a very odd
Book for a Man to make himself Master of, who would get a Reputation by
Critical Writings; though at the same time it is very certain, that an
Author who has not learned the Art of distinguishing between Words and
Things, and of ranging his Thoughts, and setting them in proper Lights,
whatever Notions he may have, will lose himself in Confusion and
Obscurity. I might further observe, that there is not a Greek or Latin
Critick who has not shewn, even in the Style of his Criticisms, that he
was a Master of all the Elegance and Delicacy of his Native Tongue.
The Truth of it is, there is nothing more absurd, than for a Man to set
up for a Critick, without a good Insight into all the Parts of Learning;
whereas many of those who have endeavoured to signalize themselves by
Works of this Nature among our English Writers, are not only defective
in the above-mentioned Particulars, but plainly discover, by the Phrases
which they make use of, and by their confused way of thinking, that they
are not acquainted with the most common and ordinary Systems of Arts and
Sciences. A
general Rules extracted out of the French Authors
,
with a certain Cant of Words, has sometimes set up an Illiterate heavy
Writer for a most judicious and formidable Critick.
One great Mark, by which you may discover a Critick who has neither
Taste nor Learning, is this, that he seldom ventures to praise any
Passage in an Author which has not been before received and applauded by
the Publick, and that his Criticism turns wholly upon little Faults and
Errors. This part of a Critick is so very easie to succeed in, that we
find every ordinary Reader, upon the publishing of a new Poem, has Wit
and Ill-nature enough to turn several Passages of it into Ridicule, and
very often in the right Place.
Mr. Dryden has very agreeably
remarked in those two celebrated Lines,
Errors, like Straws, upon the Surface flow;
He who would search for Pearls must dive below
3.
A true Critick ought to dwell rather upon Excellencies than
Imperfections, to discover the concealed Beauties of a Writer, and
communicate to the World such things as are worth their Observation. The
most exquisite Words and finest Strokes of an Author are those which
very often appear the most doubtful and exceptionable to a Man who wants
a Relish for polite Learning; and they are these, which a sower
undistinguishing Critick generally attacks with the greatest Violence.
observes, that it is very easie to brand or fix a Mark upon what
he calls
Verbum ardens
, or, as it may be rendered into English, a
glowing bold Expression, and to turn it into Ridicule by a cold
ill-natured Criticism. A little Wit is equally capable of exposing a
Beauty, and of aggravating a Fault; and though such a Treatment of an
Author naturally produces Indignation in the Mind of an understanding
Reader, it has however its Effect among the Generality of those whose
Hands it falls into, the Rabble of Mankind being very apt to think that
every thing which is laughed at with any Mixture of Wit, is ridiculous
in it self.
Such a Mirth as this is always unseasonable in a Critick, as it rather
prejudices the Reader than convinces him, and is capable of making a
Beauty, as well as a Blemish, the Subject of Derision. A Man, who cannot
write with Wit on a proper Subject, is dull and stupid, but one who
shews it in an improper Place, is as impertinent and absurd. Besides, a
Man who has the Gift of Ridicule is apt to find Fault with any thing
that gives him an Opportunity of exerting his beloved Talent, and very
often censures a Passage, not because there is any Fault in it, but
because he can be merry upon it. Such kinds of Pleasantry are very
unfair and disingenuous in Works of Criticism, in which the greatest
Masters, both Ancient and Modern, have always appeared with a serious
and instructive Air.
As I intend in my next Paper to shew the Defects in Milton's
Paradise
Lost
, I thought fit to premise these few Particulars, to the End that
the Reader may know I enter upon it, as on a very ungrateful Work, and
that I shall just point at the Imperfections, without endeavouring to
enflame them with Ridicule. I
also observe with Longinus
, that
the Productions of a great Genius, with many Lapses and Inadvertencies,
are infinitely preferable to the Works of an inferior kind of Author,
which are scrupulously exact and conformable to all the Rules of correct
Writing.
I
conclude my Paper with a Story out of Boccalini
which
sufficiently shews us the Opinion that judicious Author entertained of
the sort of Criticks I have been here mentioning. A famous Critick, says
he, having gathered together all the Faults of an eminent Poet, made a
Present of them to Apollo, who received them very graciously, and
resolved to make the Author a suitable Return for the Trouble he had
been at in collecting them. In order to this, he set before him a Sack
of Wheat, as it had been just threshed out of the Sheaf. He then bid him
pick out the Chaff from among the Corn, and lay it aside by it self.
Critick applied himself to the Task with great Industry and Pleasure,
and after having made the due Separation, was presented by Apollo with
the Chaff for his Pains
.
L.
First published in 1690.
Dryden accounted among critics 'the greatest of his age' to
be Boilean and Rapin. Boileau was the great master of French criticism.
René Rapin, born at Tours in 1621, taught Belles Lettres with
extraordinary success among his own order of Jesuits, wrote famous
critical works, was one of the best Latin poets of his time, and died at
Paris in 1687. His
Whole Critical Works
were translated by Dr. Basil
Kennett in two volumes, which appeared in 1705. The preface of their
publisher said of Rapin that
'he has long dictated in this part of letters. He is acknowledged as
the great arbitrator between the merits of the best writers; and
during the course of almost thirty years there have been few appeals
from his sentence.'
(See also a note on p. 168, vol. i. [Volume 1 links:
of
]) René le
Bossu, the great French authority on Epic Poetry, born in 1631, was a
regular canon of St. Genevieve, and taught the Humanities in several
religious houses of his order. He died, subprior of the Abbey of St.
Jean de Cartres, in 1680. He wrote, besides his Treatise upon Epic
Poetry, a parallel between the philosophies of Aristotle and Descartes,
which appeared a few months earlier (in 1674) with less success. Another
authority was Father Bouhours, of whom see note on p. 236, vol. i.
[Volume 1 links:
of
. ] Another was Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle.
called by Voltaire the most universal genius of his age. He was born at
Rouen in 1657, looking so delicate that he was baptized in a hurry, and
at 16 was unequal to the exertion of a game at billiards, being caused
by any unusual exercise to spit blood, though he lived to the age of a
hundred, less one month and two days. He was taught by the Jesuits, went
to the bar to please his father, pleaded a cause, lost it, and gave up
the profession to devote his time wholly to literature and philosophy.
He went to Paris, wrote plays and the
Dialogues of the Dead
, living
then with his uncle, Thomas Corneille. A discourse on the Eclogue
prefixed to his pastoral poems made him an authority in this manner of
composition. It was translated by Motteux for addition to the English
translation of Bossu on the Epic, which had also appended to it an
Essay
on Satire
by another of these French critics, André Dacier. Dacier, born
at Castres in 1651, was educated at Saumur under Taneguy le Févre, who
was at the same time making a scholar of his own daughter Anne. Dacier
and the young lady became warmly attached to one another, married,
united in abjuring Protestantism, and were for forty years, in the
happiest concord, man and wife and fellow-scholars. Dacier and his wife,
as well as Fontenelle, were alive when the Spectator was appearing; his
wife dying, aged 69, in 1720, the husband, aged 71, in 1722. André
Dacier translated and annotated the
Poetics
of Aristotle in 1692, and
that critical work was regarded as his best performance.
Annus Mirabilis,
st. 39.
Ad Brutum
. Orator. Towards the beginning:
'Facile est enim verbum aliquod ardens (ut ita dicam) notare, idque
restinctis jam animorum incendiis, irridere.'
On the Sublime
, § 36.
Trajan Boccalini, born at Rome in 1554, was a satirical
writer famous in Italy for his fine criticism and bold satire. Cardinals
Borghese and Cajetan were his patrons. His
Ragguagli di Parnasso
and
la Secretaria di Parnasso
, in which Apollo heard the complaints of the
world, and dispensed justice in his court on Parnassus, were received
with delight. Afterwards, in his
Pietra di Parangone
, he satirized the
Court of Spain, and, fearing consequences, retired to Venice, where in
1613 he was attacked in his bed by four ruffians, who beat him to death
with sand-bags. Boccalini's
Ragguagli di Parnasso
has been translated
into English, in 1622, as
News from Parnassus
. Also, in 1656, as
Advertisements from Parnassus,
by H. Carey, Earl of Monmouth. This
translation was reprinted in 1669 and 1674, and again in 1706 by John
Hughes, one of the contributors to the
Spectator
.
To this number of the
Spectator
, and to several numbers
since that for January 8, in which it first appeared, is added an
advertisement that,
The First and Second Volumes of the Spectator in 8vo
are now ready to be delivered to the subscribers by J. Tonson, at
Shakespeare's Head, over-against Catherine Street in the Strand.
Contents
|
Monday, February 4, 1712 |
Addison |
Illam, quicquid agit, quoquo Vestigia flectit,
Componit furlim, subsequiturque decor.
Tibull. L. 4.

As no one can be said to enjoy Health, who is only not sick, without he
feel within himself a lightsome and invigorating Principle, which will
not suffer him to remain idle, but still spurs him on to Action: so in
the Practice of every Virtue, there is some additional Grace required,
to give a Claim of excelling in this or that particular Action. A
Diamond may want polishing, though the Value be still intrinsically the
same; and the same Good may be done with different Degrees of Lustre. No
man should be contented with himself that he barely does well, but he
should perform every thing in the best and most becoming Manner that he
is able.
Tully tells us he wrote his Book of Offices, because there was no Time
of Life in which some correspondent Duty might not be practised; nor is
there a Duty without a certain Decency accompanying it, by which every
Virtue 'tis join'd to will seem to be doubled. Another may do the same
thing, and yet the Action want that Air and Beauty which distinguish it
from others; like that inimitable Sun-shine Titian is said to have
diffused over his Landschapes; which denotes them his, and has been
always unequalled by any other Person.
There is no one Action in which this Quality I am speaking of will be
more sensibly perceived, than in granting a Request or doing an Office
of Kindness. Mummius, by his Way of consenting to a Benefaction, shall
make it lose its Name; while Carus doubles the Kindness and the
Obligation: From the first the desired Request drops indeed at last, but
from so doubtful a Brow, that the Obliged has almost as much Reason to
resent the Manner of bestowing it, as to be thankful for the Favour it
self. Carus invites with a pleasing Air, to give him an Opportunity of
doing an Act of Humanity, meets the Petition half Way, and consents to a
Request with a Countenance which proclaims the Satisfaction of his Mind
in assisting the Distressed.
The Decency then that is to be observed in Liberality, seems to consist
in its being performed with such Cheerfulness, as may express the
God-like Pleasure is to be met with in obliging one's Fellow-Creatures;
that may shew Good-nature and Benevolence overflowed, and do not, as in
some Men, run upon the Tilt, and taste of the Sediments of a grutching
uncommunicative Disposition.
Since I have intimated that the greatest Decorum is to be preserved in
the bestowing our good Offices, I will illustrate it a little by an
Example drawn from private Life, which carries with it such a Profusion
of Liberality, that it can be exceeded by nothing but the Humanity and
Good-nature which accompanies it.
is a Letter of Pliny's
which I
shall here translate, because the Action will best appear in its first
Dress of Thought, without any foreign or ambitious Ornaments.
Pliny to Quintilian.
Tho I am fully acquainted with the Contentment and just Moderation of
your Mind, and the Conformity the Education you have given your
Daughter bears to your own Character; yet since she is suddenly to be
married to a Person of Distinction, whose Figure in the World makes it
necessary for her to be at a more than ordinary Expence in Cloaths and
Equipage suitable to her Husbands Quality; by which, tho her
intrinsick Worth be not augmented, yet will it receive both Ornament
and Lustre: And knowing your Estate to be as moderate as the Riches of
your Mind are abundant, I must challenge to my self some part of the
Burthen; and as a Parent of your Child. I present her with Twelve
hundred and fifty Crowns towards these Expences; which Sum had been
much larger, had I not feared the Smallness of it would be the
greatest Inducement with you to accept of it. Farewell.
Thus should a Benefaction be done with a good Grace, and shine in the
strongest Point of Light; it should not only answer all the Hopes and
Exigencies of the Receiver, but even out-run his Wishes: 'Tis this happy
manner of Behaviour which adds new Charms to it, and softens those Gifts
of Art and Nature, which otherwise would be rather distasteful than
agreeable. Without it, Valour would degenerate into Brutality, Learning
into Pedantry, and the genteelest Demeanour into Affectation. Even
Religion its self, unless Decency be the Handmaid which waits upon her,
is apt to make People appear guilty of Sourness and ill Humour: But this
shews Virtue in her first original Form, adds a Comeliness to Religion,
and gives its Professors the justest Title to the Beauty of Holiness. A
Man fully instructed in this Art, may assume a thousand Shapes, and
please in all: He may do a thousand Actions shall become none other but
himself; not that the Things themselves are different, but the Manner of
doing them.
If you examine each Feature by its self, Aglaura and Callidea are
equally handsome; but take them in the Whole, and you cannot suffer the
Comparison: Tho one is full of numberless nameless Graces, the other of
as many nameless Faults.
The Comeliness of Person, and Decency of Behaviour, add infinite Weight
to what is pronounced by any one. 'Tis the want of this that often makes
the Rebukes and Advice of old rigid Persons of no Effect, and leave a
Displeasure in the Minds of those they are directed to: But Youth and
Beauty, if accompanied with a graceful and becoming Severity, is of
mighty Force to raise, even in the most Profligate, a Sense of Shame.
Milton, the Devil is never described ashamed but once, and that at the
Rebuke of a beauteous Angel.
So spake the Cherub, and his grave Rebuke,
Severe in youthful Beauty, added Grace
Invincible: Abash'd the Devil stood,
And felt how awful Goodness is, and saw
Virtue in her own Shape ho'w lovely I saw, and pin'd
His Loss
2.
The Care of doing nothing unbecoming has accompanied the greatest Minds
to their last Moments. They avoided even an indecent Posture in the very
Article of Death. Thus Cæsar gathered his Robe about him, that he might
not fall in a manner unbecoming of himself:
the greatest Concern
that appeared in the Behaviour of Lucretia, when she stabbed her self,
was, that her Body should lie in an Attitude worthy the Mind which had
inhabited it.
Ne non procumbat honeste
Extrema hæc etiam cura, cadentis erat
3.
'Twas her last Thought, How decently to fall.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a young Woman without a Fortune; but of a very high Mind: That
is, Good Sir, I am to the last degree Proud and Vain. I am ever
railing at the Rich, for doing Things, which, upon Search into my
Heart, I find I am only angry because I cannot do the same my self. I
wear the hooped Petticoat, and am all in Callicoes when the finest are
in Silks. It is a dreadful thing to be poor and proud; therefore if
you please, a Lecture on that Subject for the Satisfaction of
Your Uneasy Humble Servant,
JEZEBEL.
Z.
Bk. vi. ep. 32.
Par. L.
, Bk. iv. 11. 844-9.
Ovid.
Fast
., iii. 833.
Contents
|
Tuesday, February 5, 1712 |
Addison |
famous Gratian
in his little Book wherein he lays down Maxims
for a Man's advancing himself at Court, advises his Reader to associate
himself with the Fortunate, and to shun the Company of the Unfortunate;
which, notwithstanding the Baseness of the Precept to an honest Mind,
may have something useful in it for those who push their Interest in the
World. It is certain a great Part of what we call good or ill Fortune,
rises out of right or wrong Measures, and Schemes of Life. When I hear a
Man complain of his being unfortunate in all his Undertakings, I
shrewdly suspect him for a very weak Man in his Affairs. In Conformity
with this way of thinking, Cardinal Richelieu used to say, that
Unfortunate and Imprudent were but two Words for the same Thing. As the
Cardinal himself had a great Share both of Prudence and Good-Fortune,
his famous Antagonist, the Count d'Olivarez, was disgraced at the Court
of Madrid, because it was alledged against him that he had never any
Success in his Undertakings. This, says an Eminent Author, was
indirectly accusing him of Imprudence.
Cicero recommended Pompey to the Romans for their General upon three
Accounts, as he was a Man of Courage, Conduct, and Good-Fortune. It was
perhaps, for the Reason above-mentioned, namely, that a Series of
Good-Fortune supposes a prudent Management in the Person whom it
befalls, that not only Sylla the Dictator, but several of the Roman
Emperors, as is still to be seen upon their Medals, among their other
Titles, gave themselves that of Felix or Fortunate. The Heathens,
indeed, seem to have valued a Man more for his Good-Fortune than for any
other Quality, which I think is very natural for those who have not a
strong Belief of another World. For how can I conceive a Man crowned
with many distinguishing Blessings, that has not some extraordinary Fund
of Merit and Perfection in him, which lies open to the Supreme Eye, tho'
perhaps it is not discovered by my Observation? What is the Reason
Homer's and Virgil's Heroes do not form a Resolution, or strike a Blow,
without the Conduct and Direction of some Deity? Doubtless, because the
Poets esteemed it the greatest Honour to be favoured by the Gods, and
thought the best Way of praising a Man was to recount those Favours
which naturally implied an extraordinary Merit in the Person on whom
they descended.
Those who believe a future State of Rewards and Punishments act very
absurdly, if they form their Opinions of a Man's Merit from his
Successes. But certainly, if I thought the whole Circle of our Being was
concluded between our Births and Deaths, I should think a Man's
Good-Fortune the Measure and Standard of his real Merit, since
Providence would have no Opportunity of rewarding his Virtue and
Perfections, but in the present Life. A Virtuous Unbeliever, who lies
under the Pressure of Misfortunes, has reason to cry out, as they say
Brutus did a little before his Death, O Virtue, I have worshipped thee
as a Substantial Good, but I find thou art an empty Name.
But to return to our first Point. Tho' Prudence does undoubtedly in a
great measure produce our good or ill Fortune in the World, it is
certain there are many unforeseen Accidents and Occurrences, which very
often pervert the finest Schemes that can be laid by Human Wisdom. The
Race is not always to the Swift, nor the Battle to the Strong. Nothing
less than infinite Wisdom can have an absolute Command over Fortune; the
highest Degree of it which Man can possess, is by no means equal to
fortuitous Events, and to such Contingencies as may rise in the
Prosecution of our Affairs. Nay, it very often happens, that Prudence,
which has always in it a great Mixture of Caution, hinders a Man from
being so fortunate as he might possibly have been without it. A Person
who only aims at what is likely to succeed, and follows closely the
Dictates of Human Prudence, never meets with those great and unforeseen
Successes, which are often the effect of a Sanguine Temper, or a more
happy Rashness; and this perhaps may be the Reason, that according to
the common Observation, Fortune, like other Females, delights rather in
favouring the young than the old.
Upon the whole, since Man is so short-sighted a Creature, and the
Accidents which may happen to him so various, I cannot but be of Dr.
Tillotson's Opinion in another Case, that were there any Doubt of a
Providence, yet it certainly would be very desirable there should be
such a Being of infinite Wisdom and Goodness, on whose Direction we
might rely in the Conduct of Human Life.
It is a great Presumption to ascribe our Successes to our own
Management, and not to esteem our selves upon any Blessing, rather as it
is the Bounty of Heaven, than the Acquisition of our own Prudence. I am
very well pleased with a Medal which was struck by Queen Elizabeth, a
little after the Defeat of the Invincible Armada, to perpetuate the
Memory of that extraordinary Event. It is well known how the King of
Spain, and others, who were the Enemies of that great Princess, to
derogate from her Glory, ascribed the Ruin of their Fleet rather to the
Violence of Storms and Tempests, than to the Bravery of the English.
Elizabeth, instead of looking upon this as a Diminution of her
Honour, valued herself upon such a signal Favour of Providence, and
accordingly in
the Reverse of the Medal above mentioned,
has
represented
a Fleet beaten by a Tempest, and falling foul upon one
another, with that Religious Inscription,
Afflavit Deus et dissipantur.
He blew with his Wind, and they were scattered.
It
remarked of a famous Grecian General, whose Name I cannot at
present recollect
, and who had been a particular Favourite
of Fortune, that upon recounting his Victories among his Friends, he
added at the End of several great Actions, And in this Fortune had no
Share. After which it is observed in History, that he never prospered in
any thing he undertook.
As Arrogance, and a Conceitedness of our own Abilities, are very
shocking and offensive to Men of Sense and Virtue, we may be sure they
are highly displeasing to that Being who delights in an humble Mind, and
by several of his Dispensations seems purposely to shew us, that our own
Schemes or Prudence have no Share in our Advancement
s
.
Since on this Subject I have already admitted several Quotations which
have occurred to my Memory upon writing this Paper, I will conclude it
with a little Persian Fable. A
of Water fell out of a Cloud into
the Sea, and finding it self lost in such an Immensity of fluid Matter,
broke out into the following Reflection: 'Alas! What an
insignificant
Creature am I in this prodigious Ocean of Waters; my Existence is
of no
Concern
to the Universe, I am reduced to a Kind of
Nothing, and am less then the least of the Works of God.'
so
happened, that an Oyster, which lay in the Neighbourhood of this Drop,
chanced to gape and swallow it up in the midst of this
its
humble
Soliloquy. The Drop, says the Fable, lay a great while hardning in the
Shell, 'till by Degrees it was ripen'd into a Pearl, which falling into
the Hands of a Diver, after a long Series of Adventures, is at present
that famous Pearl which is fixed on the Top of the Persian Diadem.
L.
Balthasar Gracian, a Spanish Jesuit, who died in 1658,
rector of the Jesuits' College of Tarragona, wrote many books in Spanish
on Politics and Society, among others the one here referred to on the
Courtier; which was known to Addison, doubtless, through the French
translation by Amelot de la Houssaye.
Corrected by an
erratum
to
you see in
, but in reprint
altered by the addition of
has represented
.
Timotheus the Athenian.
Altered by an
erratum
to
inconsiderable
to avoid the
repetition 'insignificant,' and insignificancy;' but in the reprint the
second word was changed.
significancy
his
Contents
|
Wednesday, February 6, 1712 |
Steele |
Difficile est plurimum virtutem revereri qui semper secunda fortuna
sit usus.
Tull. ad Herennium.

Insolence is the Crime of all others which every Man is most apt to rail
at; and yet is there one Respect in which almost all Men living are
guilty of it, and that is in the Case of laying a greater Value upon the
Gifts of Fortune than we ought. It is here in England come into our very
Language, as a Propriety of Distinction, to say, when we would speak of
Persons to their Advantage, they are People of Condition. There is no
doubt but the proper Use of Riches implies that a Man should exert all
the good Qualities imaginable; and if we mean by a Man of Condition or
Quality, one who, according to the Wealth he is Master of, shews himself
just, beneficent, and charitable, that Term ought very deservedly to be
had in the highest Veneration; but when Wealth is used only as it is the
Support of Pomp and Luxury, to be rich is very far from being a
Recommendation to Honour and Respect. It is indeed the greatest
Insolence imaginable, in a Creature who would feel the Extreams of
Thirst and Hunger, if he did not prevent his Appetites before they call
upon him, to be so forgetful of the common Necessity of Human Nature, as
never to cast an Eye upon the Poor and Needy. The Fellow who escaped
from a Ship which struck upon a Rock in the West, and join'd with the
Country People to destroy his Brother Sailors and make her a Wreck, was
thought a most execrable Creature; but does not every Man who enjoys the
Possession of what he naturally wants, and is unmindful of the
unsupplied Distress of other Men, betray the same Temper of Mind? When a
Man looks about him, and with regard to Riches and Poverty beholds some
drawn in Pomp and Equipage, and they and their very Servants with an Air
of Scorn and Triumph overlooking the Multitude that pass by them; and,
in the same Street, a Creature of the same Make crying out in the Name
of all that is Good and Sacred to behold his Misery, and give him some
Supply against Hunger and Nakedness, who would believe these two Beings
were of the same Species? But so it is, that the Consideration of
Fortune has taken up all our Minds, and, as I have often complained,
Poverty and Riches stand in our Imaginations in the Places of Guilt and
Innocence. But in all Seasons there will be some Instances of Persons
who have Souls too large to be taken with popular Prejudices, and while
the rest of Mankind are contending for Superiority in Power and Wealth,
have their Thoughts bent upon the Necessities of those below them. The
Charity-Schools which have been erected of late Years, are the greatest
Instances of publick Spirit the Age has produced: But indeed when we
consider how long this Sort of Beneficence has been on Foot, it is
rather from the good Management of those Institutions, than from the
Number or Value of the Benefactions to them, that they make so great a
Figure. One would think it impossible, that in the Space of fourteen
Years there should not have been five thousand Pounds bestowed in Gifts
this Way, nor sixteen hundred Children, including Males and Females, put
out to Methods of Industry. It is not allowed me to speak of Luxury and
Folly with the severe Spirit they deserve; I shall only therefore say, I
shall very readily compound with any Lady in a Hoop-Petticoat, if she
gives the Price of one half Yard of the Silk towards Cloathing, Feeding
and Instructing an Innocent helpless Creature of her own Sex in one of
these Schools.
Consciousness of such an Action will give her
Features a nobler Life on this illustrious Day
, than all the Jewels
that can hang in her Hair, or can be clustered at her Bosom. It would be
uncourtly to speak in harsher Words to the Fair, but to Men one may take
a little more Freedom. It is monstrous how a Man can live with so little
Reflection, as to fancy he is not in a Condition very unjust and
disproportioned to the rest of Mankind, while he enjoys Wealth, and
exerts no Benevolence or Bounty to others. As for this particular
Occasion of these Schools, there cannot any offer more worthy a generous
Mind. Would you do an handsome thing without Return? do it for an Infant
that is not sensible of the Obligation: Would you do it for publick
Good? do it for one who will be an honest Artificer: Would you do it for
the Sake of Heaven? give it to one who shall be instructed in the
Worship of him for whose Sake you gave it. It is methinks a most
laudable Institution this, if it were of no other Expectation than that
of producing a Race of good and useful Servants, who will have more than
a liberal, a religious Education. What would not a Man do, in common
Prudence, to lay out in Purchase of one about him, who would add to all
his Orders he gave the Weight of the Commandments to inforce an
Obedience to them? for one who would consider his Master as his Father,
his Friend, and Benefactor, upon the easy Terms, and in Expectation of
no other Return but moderate Wages and gentle Usage? It is the common
Vice of Children to run too much among the Servants; from such as are
educated in these Places they would see nothing but Lowliness in the
Servant, which would not be disingenuous in the Child. All the ill
Offices and defamatory Whispers which take their Birth from Domesticks,
would be prevented, if this Charity could be made universal; and a good
Man might have a Knowledge of the whole Life of the Persons he designs
to take into his House for his own Service, or that of his Family or
Children, long before they were admitted. This would create endearing
Dependencies: and the Obligation would have a paternal Air in the
Master, who would be relieved from much Care and Anxiety from the
Gratitude and Diligence of an humble Friend attending him as his
Servant. I fall into this Discourse from a Letter sent to me, to give me
Notice that Fifty Boys would be Cloathed, and take their Seats (at the
Charge of some generous Benefactors) in St.
Bride's
Church on
Sunday
next. I wish I could promise to my self any thing which my Correspondent
seems to expect from a Publication of it in this Paper; for there can be
nothing added to what so many excellent and learned Men have said on
this Occasion: But that there may be something here which would move a
generous Mind, like that of him who writ to me, I shall transcribe an
handsome Paragraph of Dr.
Snape's
Sermon on these Charities, which my
Correspondent enclosed with this Letter.
The wise Providence has amply compensated the Disadvantages of the Poor
and Indigent, in wanting many of the Conveniencies of this Life, by a
more abundant Provision for their Happiness in the next. Had they been
higher born, or more richly endowed, they would have wanted this Manner
of Education, of which those only enjoy the Benefit, who are low enough
to submit to it; where they have such Advantages without Money, and
without Price, as the Rich cannot purchase with it. The Learning which
is given, is generally more edifying to them, than that which is sold to
others: Thus do they become more exalted in Goodness, by being depressed
in Fortune, and their Poverty is, in Reality, their Preferment2.
T.
Queen Anne's birthday. She was born Feb. 6, 1665, and died
Aug. 1, 1714, aged 49.
From January 24 there occasionally appears the
advertisement.
'Just Published.
'A very neat Pocket Edition of the Spectator, in two volumes 12mo.
Printed for S. Buckley, at the Dolphin, in Little Britain, and J.
Tonson, at Shakespear's Head, over-against Catherine-Street in the
Strand.'
Contents
|
Thursday, February 7, 1712 |
Addison |
Prodiga non sentit pereuntem fæmina censum:
At velut exhaustâ redivivus pullulet arcâ
Nummus, et è pleno semper tollatur acervo,
Non unquam reputat quanti sibi gandia constent.
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator,
I am turned of my great Climacteric, and am naturally a Man of a meek
Temper. About a dozen Years ago I was married, for my Sins, to a young
Woman of a good Family, and of an high Spirit; but could not bring her
to close with me, before I had entered into a Treaty with her longer
than that of the Grand Alliance. Among other Articles, it was therein
stipulated, that she should have £400 a Year for Pin-money, which I
obliged my self to pay Quarterly into the hands of one who had acted
as her Plenipotentiary in that Affair. I have ever since religiously
observed my part in this solemn Agreement. Now, Sir, so it is, that
the Lady has had several Children since I married her; to which, if I
should credit our malicious Neighbours, her Pin-money has not a little
contributed. The Education of these my Children, who, contrary to my
Expectation, are born to me every Year, streightens me so much, that I
have begged their Mother to free me from the Obligation of the
above-mentioned Pin-money, that it may go towards making a Provision
for her Family. This Proposal makes her noble Blood swell in her
Veins, insomuch that finding me a little tardy in her last Quarter's
Payment, she threatens me every Day to arrest me; and proceeds so far
as to tell me, that if I do not do her Justice, I shall die in a Jayl.
To this she adds, when her Passion will let her argue calmly, that she
has several Play-Debts on her Hand, which must be discharged very
suddenly, and that she cannot lose her Money as becomes a Woman of her
Fashion, if she makes me any Abatements in this Article. I hope, Sir,
you will take an Occasion from hence to give your Opinion upon a
Subject which you have not yet touched, and inform us if there are any
Precedents for this Usage among our Ancestors; or whether you find any
mention of Pin-money in Grotius, Puffendorf, or any other of the
Civilians.
I am ever
the humblest of your Admirers,
Josiah Fribble, Esq.
As there is no Man living who is a more professed Advocate for the Fair
Sex than my self, so there is none that would be more unwilling to
invade any of their ancient Rights and Privileges; but as the Doctrine
of Pin-money is of a very late Date, unknown to our Great Grandmothers,
and not yet received by many of our Modern Ladies, I think it is for the
Interest of both Sexes to keep it from spreading.
Mr. Fribble may not, perhaps, be much mistaken where he intimates, that
the supplying a Man's Wife with Pin-money, is furnishing her with Arms
against himself, and in a manner becoming accessary to his own
Dishonour. We may indeed, generally observe, that in proportion as a
Woman is more or less Beautiful, and her Husband advanced in Years, she
stands in need of a greater or less number of Pins, and upon a Treaty of
Marriage, rises or falls in her Demands accordingly. It must likewise be
owned, that high Quality in a Mistress does very much inflame this
Article in the Marriage Reckoning.
But where the Age and Circumstances of both Parties are pretty much upon
a level, I cannot but think the insisting upon Pin-money is very
extraordinary; and yet we find several Matches broken off upon this very
Head. What would a Foreigner, or one who is a Stranger to this Practice,
think of a Lover that forsakes his Mistress, because he is not willing
to keep her in Pins; but what would he think of the Mistress, should he
be informed that she asks five or six hundred Pounds a Year for this
use? Should a Man unacquainted with our Customs be told the Sums which
are allowed in Great Britain, under the Title of Pin-money, what a
prodigious Consumption of Pins would he think there was in this Island?
A Pin a Day, says our frugal Proverb, is a Groat a Year, so that
according to this Calculation, my Friend Fribble's Wife must every Year
make use of Eight Millions six hundred and forty thousand new Pins.
I am not ignorant that our British Ladies allege they comprehend under
this general Term several other Conveniencies of Life; I could therefore
wish, for the Honour of my Countrywomen, that they had rather called it
Needle-Money, which might have implied something of Good-housewifry, and
not have given the malicious World occasion to think, that Dress and
Trifles have always the uppermost Place in a Woman's Thoughts.
I know several of my fair Reasoners urge, in defence of this Practice,
that it is but a necessary Provision they make for themselves, in case
their Husband proves a Churl or a Miser; so that they consider this
Allowance as a kind of Alimony, which they may lay their Claim to,
without actually separating from their Husbands. But with Submission, I
think a Woman who will give up her self to a Man in Marriage, where
there is the least Room for such an Apprehension, and trust her Person
to one whom she will not rely on for the common Necessaries of Life, may
very properly be accused (in the Phrase of an homely Proverb) of being
Penny wise and Pound foolish.
It is observed of over-cautious Generals, that they never engage in a
Battel without securing a Retreat, in case the Event should not answer
their Expectations; on the other hand, the greatest Conquerors have
burnt their Ships, or broke down the Bridges behind them, as being
determined either to succeed or die in the Engagement. In the same
manner I should very much suspect a Woman who takes such Precautions for
her Retreat, and contrives Methods how she may live happily, without the
Affection of one to whom she joins herself for Life. Separate Purses
between Man and Wife are, in my Opinion, as unnatural as separate Beds.
A Marriage cannot be happy, where the Pleasures, Inclinations, and
Interests of both Parties are not the same. There is no greater
Incitement to Love in the Mind of Man, than the Sense of a Person's
depending upon him for her Ease and Happiness; as a Woman uses all her
Endeavours to please the Person whom she looks upon as her Honour, her
Comfort, and her Support.
For this Reason I am not very much surprized at the Behaviour of a rough
Country 'Squire, who, being not a little shocked at the Proceeding of a
young Widow that would not recede from her Demands of Pin-money, was so
enraged at her mercenary Temper, that he told her in great Wrath, 'As
much as she thought him her Slave, he would shew all the World he did
not care a Pin for her.' Upon which he flew out of the Room, and never
saw her more.
Socrates, in Plato's Altibiades, says, he was informed by one, who had
travelled through Persia, that as he passed over a great Tract of Lands,
and enquired what the Name of the Place was, they told him it was the
Queen's Girdle; to which he adds, that another wide Field which lay by
it, was called the Queen's Veil; and that in the same Manner there was a
large Portion of Ground set aside for every part of Her Majesty's'
Dress. These Lands might not be improperly called the Queen of Persia's
Pin-money.
I
my Friend Sir
Roger
, who I dare say never read this Passage
in Plato, told me some time since, that upon his courting the Perverse
Widow (of whom I have given an Account in former Papers) he had disposed
of an hundred Acres in a Diamond-Ring, which he would have presented her
with, had she thought fit to accept it; and that upon her Wedding-Day
she should have carried on her Head fifty of the tallest Oaks upon his
Estate. He further informed me that he would have given her a Cole-pit
to keep her in clean Linnen, that he would have allowed her the Profits
of a Windmill for her Fans, and have presented her once in three Years
with the Sheering of his Sheep
for her
Under-Petticoats. To which
the Knight always adds, that though he did not care for fine Cloaths
himself, there should not have been a Woman in the Country better
dressed than my Lady Coverley. Sir
Roger
perhaps, may in this, as well
as in many other of his Devices, appear something odd and singular, but
if the Humour of Pin-money prevails, I think it would be very proper for
every Gentleman of an Estate to mark out so many Acres of it under the
Title of The Pins.
L.
to keep her in
Contents
|
Friday, February 8, 1712 |
Steele |
Nugis addere pondus.
Hor.

Dear
Spec.
Having lately conversed much with the Fair Sex on the Subject of your
Speculations, (which since their Appearance in Publick, have been the
chief Exercise of the Female loquacious Faculty) I found the fair Ones
possess'd with a Dissatisfaction at your prefixing Greek Motto's to
the Frontispiece of your late Papers; and, as a Man of Gallantry, I
thought it a Duty incumbent on me to impart it to you, in Hopes of a
Reformation, which is only to be effected by a Restoration of the
Latin to the usual Dignity in your Papers, which of late, the Greek,
to the great Displeasure of your Female Readers, has usurp'd; for tho'
the Latin has the Recommendation of being as unintelligible to them as
the Greek, yet being written of the same Character with their
Mother-Tongue, by the Assistance of a Spelling-Book it's legible;
which Quality the Greek wants: And since the Introduction of Operas
into this Nation, the Ladies are so charmed with Sounds abstracted
from their Ideas, that they adore and honour the Sound of Latin as it
is old Italian. I am a Sollicitor for the Fair Sex, and therefore
think my self in that Character more likely to be prevalent in this
Request, than if I should subscribe myself by my proper Name.
J.M.
I desire you may insert this in one of your Speculations, to shew my
Zeal for removing the Dissatisfaction of the Fair Sex, and restoring
you to their Favour.
Sir,
I was some time since in Company with a young Officer, who entertained
us with the Conquest he had made over a Female Neighbour of his; when
a Gentleman who stood by, as I suppose, envying the Captain's good
Fortune, asked him what Reason he had to believe the Lady admired him?
Why, says he, my Lodgings are opposite to hers, and she is continually
at her Window either at Work, Reading, taking Snuff, or putting her
self in some toying Posture on purpose to draw my Eyes that Way. The
Confession of this vain Soldier made me reflect on some of my own
Actions; for you must know, Sir, I am often at a Window which fronts
the Apartments of several Gentlemen, who I doubt not have the same
Opinion of me. I must own I love to look at them all, one for being
well dressed, a second for his fine Eye, and one particular one,
because he is the least Man I ever saw; but there is something so
easie and pleasant in the Manner of my little Man, that I observe he
is a Favourite of all his Acquaintance. I could go on to tell you of
many others that I believe think I have encouraged them from my
Window: But pray let me have your Opinion of the Use of the Window in
a beautiful Lady: and how often she may look out at the same Man,
without being supposed to have a Mind to jump out to him. Yours,
Aurelia Careless.'
Twice.
Mr. Spectator,
'I have for some Time made Love to a Lady, who received it with all
the kind Returns I ought to expect. But without any Provocation, that
I know of, she has of late shunned me with the utmost Abhorrence,
insomuch that she went out of Church last Sunday in the midst of
Divine Service, upon my coming into the same Pew. Pray, Sir, what must
I do in this Business?
Your Servant,
Euphues.'
Let her alone Ten Days.
York, Jan. 20, 1711-12.
Mr.
Spectator,
'We have in this Town a sort of People who pretend to Wit and write
Lampoons: I have lately been the Subject of one of them. The Scribler
had not Genius enough in Verse to turn my Age, as indeed I am an old
Maid, into Raillery, for affecting a youthier Turn than is consistent
with my Time of Day; and therefore he makes the Title to his Madrigal,
The Character of Mrs. Judith Lovebane, born in the Year
16801.
What I desire of you is, That you disallow that a Coxcomb who pretends
to write Verse, should put the most malicious Thing he can say in
Prose. This I humbly conceive will disable our Country Wits, who
indeed take a great deal of Pains to say any thing in Rhyme, tho' they
say it very ill.
I am,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Susanna Lovebane.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'We are several of us, Gentlemen and Ladies, who Board in the same
House, and after Dinner one of our Company (an agreeable Man enough
otherwise) stands up and reads your Paper to us all. We are the
civillest People in the World to one another, and therefore I am
forced to this way of desiring our Reader, when he is doing this
Office, not to stand afore the Fire. This will be a general Good to
our Family this cold Weather. He will, I know, take it to be our
common Request when he comes to these Words, Pray, Sir, sit down;
which I desire you to insert, and you will particularly oblige
Your Daily Reader,
Charity Frost.'
Sir,
I am a great Lover of Dancing, but cannot perform so well as some
others; however, by my Out-of-the-Way Capers, and some original
Grimaces, I don't fail to divert the Company, particularly the Ladies,
who laugh immoderately all the Time. Some, who pretend to be my
Friends, tell me they do it in Derision, and would advise me to leave
it off, withal that I make my self ridiculous. I don't know what to do
in this Affair, but I am resolved not to give over upon any
Account, 'till I have the Opinion of the
Spectator.
Your humble Servant,
John Trott.'
If Mr. Trott is not awkward out of Time, he has a Right to
Dance let who will Laugh: But if he has no Ear he will
interrupt others; and I am of Opinion he should sit still.
Given under my Hand this Fifth of February, 1711-12.
The
Spectator
.
T.
1750
Contents
|
Saturday, February 9, 1712 |
Addison |
—velut si
Egregio inspersos reprendas corpore nævos.
Hor.

After what I have said in my last Saturday's Paper, I shall enter on the
Subject of this without further Preface, and remark the several Defects
which appear in the Fable, the Characters, the Sentiments, and the
Language of Milton's
Paradise Lost
; not doubting but the Reader will
pardon me, if I alledge at the same time whatever may be said for the
Extenuation of such Defects. The first Imperfection which I shall
observe in the Fable is that the Event of it is unhappy.
Fable of every Poem is, according to Aristotle's Division, either
Simple or Implex
. It is called Simple when there is no change of
Fortune in it: Implex, when the Fortune of the chief Actor changes from
Bad to Good, or from Good to Bad. The Implex Fable is thought the most
perfect; I suppose, because it is more proper to stir up the Passions of
the Reader, and to surprize him with a greater Variety of Accidents.
The Implex Fable is therefore of two kinds:
the first the chief Actor
makes his Way through a long Series of Dangers and Difficulties, till he
arrives at Honour and Prosperity, as we see in the
Story of Ulysses
. In the second, the chief Actor in the Poem falls from some eminent
Pitch of Honour and Prosperity, into Misery and Disgrace. Thus we see
Adam and Eve sinking from a State of Innocence and Happiness, into the
most abject Condition of Sin and Sorrow.
The most taking Tragedies among the Ancients were built on this last
sort of Implex Fable,
the Tragedy of Œdipus, which
proceeds upon a Story, if we may believe Aristotle, the most proper for
Tragedy that could be invented by the Wit of Man
. I have taken some
Pains in a former Paper to shew, that this kind of Implex Fable, wherein
the Event is unhappy, is more apt to affect an Audience than that of the
first kind; notwithstanding many excellent Pieces among the Ancients, as
well as most of those which have been written of late Years in our own
Country, are raised upon contrary Plans. I must however own, that I
think this kind of Fable, which is the most perfect in Tragedy, is not
so proper for an Heroic Poem.
Milton seems to have been sensible of this Imperfection in his Fable,
and has therefore endeavoured to cure it by several Expedients;
particularly by the Mortification which the great Adversary of Mankind
meets with upon his Return to the Assembly of Infernal Spirits,
it is
described in
a,
beautiful Passage of the Tenth Book; and likewise
by the Vision wherein Adam at the close of the Poem sees his Off-spring
triumphing over his great Enemy, and himself restored to a happier
Paradise than that from which he fell.
There is another Objection against Milton's Fable, which is indeed
almost the same with the former, tho' placed in a different Light,
namely, That the Hero in the
Paradise Lost
is unsuccessful, and by no
means a Match for his Enemies.
gave Occasion to Mr. Dryden's
Reflection, that the Devil was in reality Milton's Hero
.
I think I have obviated this Objection in my first Paper.
The
Paradise
Lost
is an Epic
or a
Narrative Poem,
and
he that looks for an Hero
in it, searches for that which Milton never intended;
but
if he
will needs fix the Name of an Hero upon any Person in it, '
certainly
the Messiah who is the Hero, both in the Principal Action, and in the
chief Episodes
. Paganism could not furnish out a real Action for a
Fable greater than that of the Iliad or Æneid, and therefore an Heathen
could not form a higher Notion of a Poem than one of that kind, which
they call an Heroic.
Milton's is not of a
sublimer
Nature I
will not presume to determine: It is sufficient that I shew there is in
the
Paradise Lost
all the Greatness of Plan, Regularity of Design, and
masterly Beauties which we discover in Homer and Virgil.
I must in the next Place observe, that Milton has interwoven in the
Texture of his Fable some Particulars which do not seem to have
Probability enough for an Epic Poem, particularly in the Actions which
he ascribes to Sin and Death, and the Picture which he draws of the
Limbo of Vanity, with other Passages in the second Book. Such Allegories
rather savour of the Spirit of Spenser and Ariosto, than of Homer and
Virgil.
In the Structure of his Poem he has likewise admitted of too many
Digressions. It is
observed by Aristotle, that the Author of an
Heroic Poem should seldom speak himself, but throw as much of his Work
as he can into the Mouths of those who are his Principal Actors
.
Aristotle has given no reason for this Precept; but I presume it is
because the Mind of the Reader is more awed and elevated when he hears
Æneas or Achilles speak, than when Virgil or Homer talk in their own
Persons. Besides that assuming the Character of an eminent Man is apt to
fire the Imagination, and raise the Ideas of the Author.
tells us
,
mentioning his Dialogue of Old Age, in which Cato is the chief Speaker,
that upon a Review of it he was agreeably imposed upon, and fancied that
it was Cato, and not he himself, who uttered his Thoughts on that
Subject.
If the Reader would be at the Pains to see how the Story of the Iliad
and the Æneid is delivered by those Persons who act in it, he will be
surprized to find how little in either of these Poems proceeds from the
Authors. Milton has, in the general disposition of his Fable, very
finely observed this great Rule; insomuch that there is scarce a third
Part of it which comes from the Poet; the rest is spoken either by Adam
and Eve, or by some Good or Evil Spirit who is engaged either in their
Destruction or Defence.
From what has been here observed it appears, that Digressions are by no
means to be allowed of in an Epic Poem. If the Poet, even in the
ordinary course of his Narration, should speak as little as possible, he
should certainly never let his Narration sleep for the sake of any
Reflections of his own. I have often observed, with a secret Admiration,
that the longest Reflection in the Æneid is in that Passage of the
Tenth Book, where Turnus is represented as dressing himself in the
Spoils of Pallas, whom he had slain. Virgil here lets his Fable stand
still for the-sake of the following Remark. How is the Mind of Man
ignorant of Futurity, and unable to bear prosperous Fortune with
Moderation? The Time will come when Turnus shall wish that he had left
the Body of Pallas untouched, and curse the Day on which he dressed
himself in these Spoils. As the great Event of the Æneid, and the Death
of Turnus, whom Æneas slew because he saw him adorned with the Spoils of
Pallas, turns upon this Incident, Virgil went out of his way to make
this Reflection upon it, without which so small a Circumstance might
possibly have slipped out of his Reader's Memory.
, who was an
Injudicious Poet, lets drop his Story very frequently for the sake of
his unnecessary Digressions, or his Diverticula, as Scaliger calls them.
If he gives us an Account of the Prodigies which preceded the Civil
War, he declaims upon the Occasion, and shews how much happier it would
be for Man, if he did not feel his Evil Fortune before it comes to pass;
and suffer not only by its real Weight, but by the Apprehension of it.
Complaint
for
his Blindness, his Panegyrick on Marriage,
his Reflections on Adam and Eve's going naked, of the Angels eating, and
several other Passages in his Poem, are liable to the same Exception,
tho' I must confess there is so great a Beauty in these very
Digressions, that I would not wish them out of his Poem.
I have, in a former Paper, spoken of the Characters of Milton's
Paradise
Lost
, and declared my Opinion, as to the Allegorical Persons who are
introduced in it.
If we look into the Sentiments, I think they are sometimes defective
under the following Heads: First, as there are several of them too much
pointed, and some that degenerate even into Punns. Of this last kind I
am afraid is that in the First Book, where speaking of the Pigmies, he
calls them,
—The small Infantry
Warrdon by Cranes—
Blemish
that
appears in some of his Thoughts, is his
frequent Allusion to Heathen Fables, which are not certainly of a Piece
with the Divine Subject, of which he treats. I do not find fault with
these Allusions, where the Poet himself represents them as fabulous, as
he does in some Places, but where he mentions them as Truths and Matters
of Fact. The Limits of my Paper will not give me leave to be particular
in Instances of this kind; the Reader will easily remark them in his
Perusal of the Poem.
A third fault in his Sentiments, is an unnecessary Ostentation of
Learning, which likewise occurs very frequently. It is certain that both
Homer and Virgil were Masters of all the Learning of their Times, but it
shews it self in their Works after an indirect and concealed manner.
Milton seems ambitious of letting us know, by his Excursions on
Free-Will and Predestination, and his many Glances upon History,
Astronomy, Geography, and the like, as well as by the Terms and Phrases
he sometimes makes use of, that he was acquainted with the whole Circle
of Arts and Sciences.
If, in the last place, we consider the Language of this great Poet, we
must allow what I have hinted in a former Paper, that it is often too
much laboured, and sometimes obscured by old Words, Transpositions, and
Foreign Idioms. Seneca's Objection to the Style of a great Author,
Riget
ejus oratio, nihil in eâ placidum nihil lene
, is what many Criticks make
to Milton: As I cannot wholly refuse it, so I have already apologized
for it in another Paper; to which I may further add, that Milton's
Sentiments and Ideas were so wonderfully Sublime, that it would have
been impossible for him to have represented them in their full Strength
and Beauty, without having recourse to these Foreign Assistances. Our
Language sunk under him, and was unequal to that Greatness of Soul,
which furnished him with such glorious Conceptions.
A second Fault in his Language is, that he often affects a kind of
Jingle in his Words, as in the following Passages, and many others:
And brought into the World a World of Woe.
—Begirt th' Almighty throne
Beseeching or besieging—
This tempted our attempt—
At one slight bound high overleapt all bound.
I
there are Figures for this kind of Speech, that some of the
greatest Ancients have been guilty of it, and that Aristotle himself has
given it a place in his Rhetorick among the Beauties of that Art.
But as it is in its self poor and trifling, it is I think at present
universally exploded by all the Masters of Polite Writing.
The last Fault which I shall take notice of in Milton's Style, is the
frequent use of what the Learned call Technical Words , or Terms of Art.
It
one of the great Beauties of Poetry, to make hard things
intelligible, and to deliver what is abstruse
of
it self in such
easy Language as may be understood by ordinary Readers: Besides, that
the Knowledge of a Poet should rather seem born with him, or inspired,
than drawn from Books and Systems. I have often wondered how Mr. Dryden
could translate a Passage out of Virgil after the following manner.
Tack to the Larboard, and stand off to Sea.
Veer Star-board Sea and Land.
Milton makes use of Larboard in the same manner. When he is upon
Building he mentions Doric Pillars, Pilasters, Cornice, Freeze,
Architrave. When he talks of Heavenly Bodies, you meet with Eccliptic
and Eccentric, the trepidation, Stars dropping from the Zenith, Rays
culminating from the Equator. To which might be added many Instances of
the like kind in several other Arts and Sciences.
I
in my next
Papers
give an Account of the many particular
Beauties in Milton, which would have been too long to insert under those
general Heads I have already treated of, and with which I intend to
conclude this Piece of Criticism.
L.
Poetics
, cap. x. Addison got his affected word 'implex' by
reading Aristotle through the translation and notes of André Dacier.
Implex was the word used by the French, but the natural English
translation of Aristotle's
and
is
into simple and complicated.
Stories of Achilles, Ulysses, and Æneas.
Poetics
, cap. xi.
that
Dediction of the Æneid; where, after speaking of small
claimants of the honours of the Epic, he says,
'Spencer has a better for his "Fairy Queen" had his action been
finished, or been one; and Milton if the Devil had not been his hero,
instead of Adam; if the giant had not foiled the knight, and driven
him out of his stronghold, to wander through the world with his
lady-errant; and if there had not been more machining persons that
human in his poem.'
or
Episode
greater
Poetics
, cap. xxv. The reason he gives is that when the
Poet speaks in his own person 'he is not then the Imitator.' Other Poets
than Homer, Aristotle adds,
'ambitious to figure throughout themselves, imitate but little and
seldom. Homer, after a few preparatory lines, immediately introduces a
man or woman or some other character, for all have their character.'
Of Lucan, as an example of the contrary practice, Hobbes said in his
'Discourse concerning the Virtues of an Heroic Poem,'
'No Heroic Poem raises such admiration of the Poet, as his hath done,
though not so great admiration of the persons he introduceth.'
Letters to Atticus
, Bk. xiii., Ep. 44.
Poetics
, Lib. iii. cap. 25.
of
which
Rhetoric
, iii. ch. II, where he cites such verbal jokes
as, You wish him
(i.e. to side with Persia—to ruin
him), and the saying of Isocrates concerning Athens, that its
sovereignty
was to the city a beginning
of evils. As this closes Addison's comparison of Milton's practice with
Aristotle's doctrine (the following papers being expressions of his
personal appreciation of the several books of
Paradise Lost
), we may
note here that Milton would have been quite ready to have his work tried
by the test Addison has been applying. In his letter to Samuel Hartlib,
sketching his ideal of a good Education, he assigns to advanced pupils
logic and then
'rhetoric taught out of the rules of Plato, Aristotle, Phalereus,
Cicero, Hermogenes, Longinus. To which poetry would be made
subsequent, or, indeed, rather precedent, as being less subtile and
fine, but more simple, sensuous, and passionate. I mean not here the
prosody of a verse, which they could not but have hit on before among
the rudiments of grammar; but that sublime art which in Aristotle's
Poetics, in Horace, and the Italian commentaries of Castelvetro,
Tasso, Mazzoni, and others, teaches what the laws are of a true epic
poem, what of a dramatic, what of a lyric, what decorum is, which is
the grand masterpiece to observe. This would make them soon perceive
what despicable creatures our common rhymers and play-writers be; and
show them what religious, what glorious and magnificent use might be
made of poetry, both in divine and human things.'
in
Saturday's Paper
Contents
|
Monday, February 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Nusquam Tuta fides.
Virg.

'I am a Virgin, and in no Case despicable; but yet such as I am I must
remain, or else become, 'tis to be feared, less happy: for I find not
the least good Effect from the just Correction you some time since
gave, that too free, that looser Part of our Sex which spoils the Men;
the same Connivance at the Vices, the same easie Admittance of
Addresses, the same vitiated Relish of the Conversation of the
greatest of Rakes (or in a more fashionable Way of expressing one's
self, of such as have seen the World most) still abounds, increases,
multiplies.
'The humble Petition therefore of many of the most strictly virtuous,
and of my self, is, That you'll once more exert your Authority, and
that according to your late Promise, your full, your impartial
Authority, on this sillier Branch of our Kind: For why should they be
the uncontroulable Mistresses of our Fate? Why should they with
Impunity indulge the Males in Licentiousness whilst single, and we
have the dismal Hazard and Plague of reforming them when married?
Strike home, Sir, then, and spare not, or all our maiden Hopes, our
gilded Hopes of nuptial Felicity are frustrated, are vanished, and you
your self, as well as Mr. Courtly, will, by smoothing over immodest
Practices with the Gloss of soft and harmless Names, for ever forfeit
our Esteem. Nor think that I'm herein more severe than need be: If I
have not reason more than enough, do you and the World judge from this
ensuing Account, which, I think, will prove the Evil to be universal.
'You must know then, that since your Reprehension of this Female
Degeneracy came out, I've had a Tender of Respects from no less than
five Persons, of tolerable Figure too as Times go: But the Misfortune
is, that four of the five are professed Followers of the Mode. They
would face me down, that all Women of good Sense ever were, and ever
will be, Latitudinarians in Wedlock; and always did, and will, give
and take what they profanely term Conjugal Liberty of Conscience.
'The two first of them, a Captain and a Merchant, to strengthen their
Argument, pretend to repeat after a Couple, a Brace of Ladies of
Quality and Wit, That Venus was always kind to Mars; and what Soul
that has the least spark of Generosity, can deny a Man of Bravery any
thing? And how pitiful a Trader that, whom no Woman but his own Wife
will have Correspondence and Dealings with? Thus these; whilst the
third, the Country Squire, confessed, That indeed he was surprized
into good Breeding, and entered into the Knowledge of the World
unawares. That dining t'other Day at a Gentleman's House, the Person
who entertained was obliged to leave him with his Wife and Nieces;
where they spoke with so much Contempt of an absent Gentleman for
being slow at a Hint, that he had resolved never to be drowsy,
unmannerly, or stupid for the future at a Friend's House; and on a
hunting Morning, not to pursue the Game either with the Husband
abroad, or with the Wife at home.
'
The next that came was a Tradesman,
no1 less full of the Age
than the former; for he had the Gallantry to tell me, that at a late
Junket which he was invited to, the Motion being made, and the
Question being put, 'twas by Maid, Wife and Widow resolved
nemine
contradicente, That a young sprightly Journeyman is absolutely
necessary in their Way of Business: To which they had the Assent and
Concurrence of the Husbands present. I dropped him a Curtsy, and gave
him to understand that was his Audience of Leave.
'I am reckoned pretty, and have had very many Advances besides these;
but have been very averse to hear any of them, from my Observation on
these above-mentioned, 'till I hoped some Good from the Character of
my present Admirer, a Clergyman. But I find even amongst them there
are indirect Practices in relation to Love, and our Treaty is at
present a little in Suspence, 'till some Circumstances are cleared.
There is a Charge against him among the Women, and the Case is this:
It is alledged, That a certain endowed Female would have appropriated
her self to and consolidated her self with a Church, which my Divine
now enjoys; (or, which is the same thing, did prostitute her self to
her Friend's doing this for her): That my Ecclesiastick, to obtain the
one, did engage himself to take off the other that lay on Hand; but
that on his Success in the Spiritual, he again renounced the Carnal.
I put this closely to him, and taxed him with Disingenuity. He to
clear himself made the subsequent Defence, and that in the most solemn
Manner possible: That he was applied to and instigated to accept of a
Benefice: That a conditional Offer thereof was indeed made him at
first, but with Disdain by him rejected: That when nothing (as they
easily perceived) of this Nature could bring him to their Purpose,
Assurance of his being entirely unengaged before-hand, and safe from
all their After-Expectations (the only Stratagem left to draw him in)
was given him: That pursuant to this the Donation it self was without
Delay, before several reputable Witnesses, tendered to him gratis,
with the open Profession of not the least Reserve, or most minute
Condition; but that yet immediately after Induction, his insidious
Introducer (or her crafty Procurer, which you will) industriously
spread the Report, which had reached my Ears, not only in the
Neighbourhood of that said Church, but in London, in the University,
in mine and his own County, and where-ever else it might probably
obviate his Application to any other Woman, and so confine him to this
alone: And, in a Word, That as he never did make any previous Offer of
his Service, or the least Step to her Affection; so on his Discovery
of these Designs thus laid to trick him, he could not but afterwards,
in Justice to himself, vindicate both his Innocence and Freedom by
keeping his proper Distance.
'This is his Apology, and I think I shall be satisfied with it. But I
cannot conclude my tedious Epistle, without recommending to you not
only to resume your former Chastisement, but to add to your Criminals
the Simoniacal Ladies, who seduce the sacred Order into the Difficulty
of either breaking a mercenary Troth made to them whom they ought not
to deceive, or by breaking or keeping it offending against him whom
they cannot deceive. Your Assistance and Labours of this sort would be
of great Benefit, and your speedy Thoughts on this Subject would be
very seasonable to,
Sir, Your most obedient Servant,
Chastity Loveworth.'
T.
nor
Contents
|
Tuesday, February 12, 1712 |
Addison |
Malo Venusinam, quam te, Cornelia, Mater
Gracchorum, si cum magnis virtutibus affers
Grande supercilium, et numeras in dote triumphos.
Tolle tuum precor Annibalem victumque Syphacem
In castris, et cum totâ Carthagine migra.
Juv.

It is observed, that a Man improves more by reading the Story of a
Person eminent for Prudence and Virtue, than by the finest Rules and
Precepts of Morality. In the same manner a Representation of those
Calamities and Misfortunes which a weak Man suffers from wrong Measures,
and ill-concerted Schemes of Life, is apt to make a deeper Impression
upon our Minds, than the wisest Maxims and Instructions that can be
given us, for avoiding the like Follies and Indiscretions on our own
private Conduct. It is for this Reason that I lay before my Reader the
following Letter, and leave it with him to make his own use of it,
without adding any Reflections of my own upon the Subject Matter.
Mr.
Spectator,
'Having carefully perused a Letter sent you by Josiah Fribble, Esq.,
with your subsequent Discourse upon Pin-Money, I do presume to trouble
you with an Account of my own Case, which I look upon to be no less
deplorable than that of Squire Fribble. I
am a Person of no
Extraction, having begun the World with a small parcel of Rusty Iron,
and was for some Years commonly known by the Name of Jack Anvil
1. I
have naturally a very happy Genius for getting Money, insomuch that by
the Age of Five and twenty I had scraped together Four thousand two
hundred Pounds Five Shillings, and a few odd Pence. I
then launched
out into considerable Business, and became a bold Trader both by Sea
and Land, which in a few Years raised me a very
great2 Fortune.
For these my Good Services I was Knighted in the thirty fifth Year of
my Age, and lived with great Dignity among my City-Neighbours by the
Name of Sir John Anvil. Being in my Temper very Ambitious, I was now
bent upon making a Family, and accordingly resolved that my
Descendants should have a Dash of Good Blood in their Veins. In order
to this, I made Love to the Lady Mary Oddly, an Indigent young Woman
of Quality. To cut short the Marriage Treaty, I threw her a Charte
Blanche, as our News Papers call it, desiring her to write upon it her
own Terms. She was very concise in her Demands, insisting only that
the Disposal of my Fortune, and the Regulation of my Family, should be
entirely in her Hands. Her Father and Brothers appeared exceedingly
averse to this Match, and would not see me for some time; but at
present are so well reconciled, that they Dine with me almost every
Day, and have borrowed considerable Sums of me; which my Lady Mary
very often twits me with, when she would shew me how kind her
Relations are to me. She had no Portion, as I told you before, but
what she wanted in Fortune, she makes up in Spirit. She at first
changed my Name to Sir John Envil, and at present writes her self Mary
Enville. I have had some Children by her, whom she has Christened with
the Sirnames of her Family, in order, as she tells me, to wear out the
Homeliness of their Parentage by the Father's Side. Our eldest Son is
the Honourable Oddly Enville, Esq., and our eldest Daughter Harriot
Enville. Upon her first coming into my Family, she turned off a parcel
of very careful Servants, who had been long with me, and introduced in
their stead a couple of Black-a-moors, and three or four very genteel
Fellows in Laced Liveries, besides her French woman, who is
perpetually making a Noise in the House in a Language which no body
understands, except my Lady Mary. She next set her self to reform
every Room of my House, having glazed all my Chimney-pieces with
Looking-glass, and planted every Corner with such heaps of China, that
I am obliged to move about my own House with the greatest Caution and
Circumspection, for fear of hurting some of our Brittle Furniture. She
makes an Illumination once a Week with Wax-Candles in one of the
largest Rooms, in order, as she phrases it, to see Company. At which
time she always desires me to be Abroad, or to confine my self to the
Cock-loft, that I may not disgrace her among her Visitants of Quality.
Her Footmen, as I told you before, are such Beaus that I do not much
care for asking them Questions; when I do, they answer me with a sawcy
Frown, and say that every thing, which I find Fault with, was done by
my Lady Mary's Order. She tells me that she intends they shall wear
Swords with their next Liveries, having lately observed the Footmen of
two or three Persons of Quality hanging behind the Coach with Swords
by their Sides. As soon as the first Honey-Moon was over, I
represented to her the Unreasonableness of those daily Innovations
which she made in my Family, but she told me I was no longer to
consider my self as Sir John Anvil, but as her Husband; and added,
with a Frown, that I did not seem to know who she was. I was surprized
to be treated thus, after such Familiarities as had passed between us.
But she has since given me to know, that whatever Freedoms she may
sometimes indulge me in, she expects in general to be treated with the
Respect that is due to her Birth and Quality. Our Children have been
trained up from their Infancy with so many Accounts of their Mother's
Family, that they know the Stories of all the great Men and Women it
has produced. Their Mother tells them, that such an one commanded in
such a Sea Engagement, that their Great Grandfather had a Horse shot
under him at Edge-hill, that their Uncle was at the Siege of Buda, and
that her Mother danced in a Ball at Court with the Duke of Monmouth;
with abundance of Fiddle-faddle of the same Nature. I was, the other
Day, a little out of Countenance at a Question of my little Daughter
Harriot, who asked me, with a great deal of Innocence, why I never
told them of the Generals and Admirals that had been in my Family. As
for my Eldest Son Oddly, he has been so spirited up by his Mother,
that if he does not mend his Manners I shall go near to disinherit
him. He drew his Sword upon me before he was nine years old, and told
me, that he expected to be used like a Gentleman; upon my offering to
correct him for his Insolence, my Lady Mary stept in between us, and
told me, that I ought to consider there was some Difference between
his Mother and mine. She is perpetually finding out the Features of
her own Relations in every one of my Children, tho', by the way, I
have a little Chubfaced Boy as like me as he can stare, if I durst say
so; but what most angers me, when she sees me playing with any of them
upon my Knee, she has begged me more than once to converse with the
Children as little as possibly, that they may not learn any of my
awkward Tricks.
'You must farther know, since I am opening my Heart to you, that she
thinks her self my Superior in Sense, as much as she is in Quality,
and therefore treats me like a plain well-meaning Man, who does not
know the World. She dictates to me in my own Business, sets me right
in Point of Trade, and if I disagree with her about any of my Ships at
Sea, wonders that I will dispute with her, when I know very well that
her Great Grandfather was a Flag Officer.
'
To compleat my Sufferings, she has teazed me for this Quarter of
a3 Year last past, to remove into one of the Squares at the other
End of the Town, promising for my Encouragement, that I shall have as
good a Cock-loft as any Gentleman in the Square; to which the
Honourable Oddly Enville, Esq., always adds, like a Jack-a-napes as he
is, that he hopes 'twill be as near the Court as possible.
'In short, Mr.
Spectator, I am so much out of my natural Element, that
to recover my old Way of Life I would be content to begin the World
again, and be plain Jack Anvil; but alas! I am in for Life, and am
bound to subscribe my self, with great Sorrow of Heart,
Your humble Servant,
John Enville, Knt.'
L.
This has been said to refer to a Sir Ambrose Crowley, who
changed his name to Crawley.
considerable
corrected by an
erratum
in
.
an
Contents
|
Wednesday, February 13, 1712 |
Steele |
Diversum vitio vitium prope majus.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'When you talk of the Subject of Love, and the Relations arising from
it, methinks you should take Care to leave no Fault unobserved which
concerns the State of Marriage. The great Vexation that I have
observed in it, is, that the wedded Couple seem to want Opportunities
of being often enough alone together, and are forced to quarrel and be
fond before Company. Mr. Hotspur and his Lady, in a Room full of their
Friends, are ever saying something so smart to each other, and that
but just within Rules, that the whole Company stand in the utmost
Anxiety and Suspence for fear of their falling into Extremities which
they could not be present at. On the other Side, Tom Faddle and his
pretty Spouse where-ever they come are billing at such a Rate, as they
think must do our Hearts good who behold 'em. Cannot you possibly
propose a Mean between being Wasps and Doves in Publick? I should
think if you advised to hate or love sincerely it would be better: For
if they would be so discreet as to hate from the very Bottom of their
Hearts, their Aversion would be too strong for little Gibes every
Moment; and if they loved with that calm and noble Value which dwells
in the Heart, with a Warmth like that of Life-Blood, they would not be
so impatient of their Passion as to fall into observable Fondness.
This Method, in each Case, would save Appearances; but as those who
offend on the fond Side are by much the fewer, I would have you begin
with them, and go on to take Notice of a most impertinent Licence
married Women take, not only to be very loving to their Spouses in
Publick, but also make nauseous Allusions to private Familiarities,
and the like. Lucina is a Lady of the greatest Discretion, you must
know, in the World; and withal very much a Physician: Upon the
Strength of these two Qualities there is nothing she will not speak of
before us Virgins; and she every Day talks with a very grave Air in
such a Manner, as is very improper so much as to be hinted at but to
obviate the greatest Extremity. Those whom they call good Bodies,
notable People, hearty Neighbours, and the purest goodest Company in
the World, are the great Offenders in this Kind. Here I think I have
laid before you an open Field for Pleasantry; and hope you will shew
these People that at least they are not witty: In which you will save
from many a Blush a daily Sufferer, who is very much
Your most humble Servant,
Susanna Loveworth.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'In yours of Wednesday the 30th past, you and your Correspondent are
very severe on a sort of Men, whom you call Male Coquets; but without
any other Reason, in my Apprehension, than that of paying a shallow
Compliment to the fair Sex, by accusing some Men of imaginary Faults,
that the Women may not seem to be the more faulty Sex; though at the
same time you suppose there are some so weak as to be imposed upon by
fine Things and false Addresses. I can't persuade my self that your
Design is to debar the Sexes the Benefit of each other's Conversation
within the Rules of Honour; nor will you, I dare say, recommend to
'em, or encourage the common Tea-Table Talk, much less that of
Politicks and Matters of State: And if these are forbidden Subjects of
Discourse, then, as long as there are any Women in the World who take
a Pleasure in hearing themselves praised, and can bear the Sight of a
Man prostrate at their Feet, so long I shall make no Wonder that there
are those of the other Sex who will pay them those impertinent
Humiliations. We should have few People such Fools as to practise
Flattery, if all were so wise as to despise it. I don't deny but you
would do a meritorious Act, if you could prevent all Impositions on
the Simplicity of young Women; but I must confess I don't apprehend
you have laid the Fault on the proper Person, and if I trouble you
with my Thoughts upon it I promise my self your Pardon. Such of the
Sex as are raw and innocent, and most exposed to these Attacks, have,
or their Parents are much to blame if they have not, one to advise and
guard 'em, and are obliged themselves to take Care of 'em: but if
these, who ought to hinder Men from all Opportunities of this sort of
Conversation, instead of that encourage and promote it, the Suspicion
is very just that there are some private Reasons for it; and I'll
leave it to you to determine on which Side a Part is then acted. Some
Women there are who are arrived at Years of Discretion, I mean are got
out of the Hands of their Parents and Governours, and are set up for
themselves, who yet are liable to these Attempts; but if these are
prevailed upon, you must excuse me if I lay the Fault upon them, that
their Wisdom is not grown with their Years. My Client, Mr. Strephon,
whom you summoned to declare himself, gives you Thanks however for
your Warning, and begs the Favour only to inlarge his Time for a Week,
or to the last Day of the Term, and then he'll appear
gratis, and pray
no Day over.
Yours,
Philanthropes.'
Mr.
Spectator,
'I was last Night to visit a Lady who I much esteem, and always took
for my Friend; but met with so very different a Reception from what I
expected, that I cannot help applying my self to you on this Occasion.
In the room of that Civility and Familiarity I used to be treated with
by her, an affected Strangeness in her Looks, and Coldness in her
Behaviour, plainly told me I was not the welcome Guest which the
Regard and Tenderness she has often expressed for me gave me Reason to
flatter my self to think I was. Sir, this is certainly a great Fault,
and I assure you a very common one; therefore I hope you will think it
a fit Subject for some Part of a Spectator. Be pleased to acquaint us
how we must behave our selves towards this valetudinary Friendship,
subject to so many Heats and Colds, and you will oblige,
Sir, Your humble Servant,
Miranda.'
Sir,
'I cannot forbear acknowledging the Delight your late Spectators on
Saturdays have given me; for it is writ in the honest Spirit of
Criticism, and
called to my Mind the following four Lines I had read
long since in a Prologue to a Play called Julius Cæsar
1 which has
deserved a better Fate. The Verses are addressed to the little
Criticks.
Shew your small Talent, and let that suffice ye;
But grow not vain upon it, I advise ye.
For every Fop can find out Faults in Plays:
You'll ne'er arrive at Knowing when to praise.
Yours, D. G.'
T.
By William Alexander, Earl of Stirling (who died in 1640);
one of his four 'Monarchicke Tragedies.' He received a grant of Nova
Scotia to colonize, and was secretary of state for Scotland.
Contents
|
Thursday, February 14, 1712 |
Budgell |
Possint ut Juvenes visere fervidi
Multo non sine risu,
Dilapsam in cineres facem.
Hor.

We are generally so much pleased with any little Accomplishments, either
of Body or Mind, which have once made us remarkable in the World, that
we endeavour to perswade our selves it is not in the Power of Time to
rob us of them. We are eternally pursuing the same Methods which first
procured us the Applauses of Mankind. It is from this Notion that an
Author writes on, tho' he is come to Dotage; without ever considering
that his Memory is impaired, and that he has lost that Life, and those
Spirits, which formerly raised his Fancy, and fired his Imagination. The
same Folly hinders a Man from submitting his Behaviour to his Age, and
makes Clodius, who was a celebrated Dancer at five and twenty, still
love to hobble in a Minuet, tho' he is past Threescore. It is this, in a
Word, which fills the Town with elderly Fops, and superannuated Coquets.
Canidia, a Lady of this latter Species, passed by me Yesterday in her
Coach. Canidia was an haughty Beauty of the last Age, and was followed
by Crowds of Adorers, whose Passions only pleased her, as they gave her
Opportunities of playing the Tyrant. She then contracted that awful Cast
of the Eye and forbidding Frown, which she has not yet laid aside, and
has still all the Insolence of Beauty without its Charms. If she now
attracts the Eyes of any Beholders, it is only by being remarkably
ridiculous; even her own Sex laugh at her Affectation; and the Men, who
always enjoy an ill-natured Pleasure in seeing an imperious Beauty
humbled and neglected, regard her with the same Satisfaction that a free
Nation sees a Tyrant in Disgrace.
Will. Honeycomb
, who is a great Admirer of the Gallantries in King
Charles the Second's Reign, lately communicated to me a Letter written
by a Wit of that Age to his Mistress, who it seems was a Lady of
Canidia's Humour; and tho' I do not always approve of my Friend
Will's
Taste, I liked this Letter so well, that I took a Copy of it, with which
I shall here present my Reader.
To
Cloe.
Madam,
'Since my waking Thoughts have never been able to influence you in my
Favour, I am resolved to try whether my Dreams can make any Impression
on you. To this end I shall give you an Account of a very odd one
which my Fancy presented to me last Night, within a few Hours after I
left you.
'Methought I was unaccountably conveyed into the most delicious Place
mine Eyes ever beheld, it was a large Valley divided by a River of the
purest Water I had ever seen. The Ground on each Side of it rose by an
easie Ascent, and was covered with Flowers of an infinite Variety,
which as they were reflected in the Water doubled the Beauties of the
Place, or rather formed an Imaginary Scene more beautiful than the
real. On each Side of the River was a Range of lofty Trees, whose
Boughs were loaden with almost as many Birds as Leaves. Every Tree was
full of Harmony.
'I had not gone far in this pleasant Valley, when I perceived that it
was terminated by a most magnificent Temple. The Structure was
ancient, and regular. On the Top of it was figured the God Saturn, in
the same Shape and Dress that the Poets usually represent Time.
'As I was advancing to satisfie my Curiosity by a nearer View, I was
stopped by an Object far more beautiful than any I had before
discovered in the whole Place. I fancy, Madam, you will easily guess
that this could hardly be any thing but your self; in reality it was
so; you lay extended on the Flowers by the side of the River, so that
your Hands which were thrown in a negligent Posture, almost touched
the Water. Your Eyes were closed; but if your Sleep deprived me of the
Satisfaction of seeing them, it left me at leisure to contemplate
several other Charms, which disappear when your Eyes are open. I could
not but admire the Tranquility you slept in, especially when I
considered the Uneasiness you produce in so many others.
'While I was wholly taken up in these Reflections, the Doors of the
Temple flew open, with a very great Noise; and lifting up my Eyes, I
saw two Figures, in human Shape, coming into the Valley. Upon a nearer
Survey, I found them to be
Youth and
Love. The first was encircled
with a kind of Purple Light, that spread a Glory over all the Place;
the other held a flaming Torch in his Hand. I could observe, that all
the way as they came towards us, the Colours of the Flowers appeared
more lively, the Trees shot out in Blossoms, the Birds threw
themselves into Pairs, and Serenaded them as they passed: The whole
Face of Nature glowed with new Beauties. They were no sooner arrived
at the Place where you lay, when they seated themselves on each Side
of you. On their Approach, methought I saw a new Bloom arise in your
Face, and new Charms diffuse themselves over your whole Person. You
appeared more than Mortal; but, to my great Surprise, continued fast
asleep, tho' the two Deities made several gentle Efforts to awaken
you.
'After a short Time,
Youth (displaying a Pair of Wings, which I had
not before taken notice of) flew off.
Love still remained, and holding
the Torch which he had in his Hand before your Face, you still
appeared as beautiful as ever. The glaring of the Light in your Eyes
at length awakened you; when, to my great Surprise, instead of
acknowledging the Favour of the Deity, you frowned upon him, and
struck the Torch out of his Hand into the River.
The God after having
regarded you with a Look that spoke at
once1 his Pity and
Displeasure, flew away. Immediately a kind of Gloom overspread the
whole Place. At the same time I saw an hideous Spectre enter at one
end of the Valley. His Eyes were sunk into his Head, his Face was pale
and withered, and his Skin puckered up in Wrinkles. As he walked on
the sides of the Bank the River froze, the Flowers faded, the Trees
shed their Blossoms, the Birds dropped from off the Boughs, and fell
dead at his Feet. By these Marks I knew him to be
Old-age. You were
seized with the utmost Horror and Amazement at his Approach. You
endeavoured to have fled, but the Phantome caught you in his Arms. You
may easily guess at the Change you suffered in this Embrace.
For my
own Part, though I am still too full of the
frightful2 Idea, I
will not shock you with a Description of it. I was so startled at the
Sight that my Sleep immediately left me, and I found my self awake, at
leisure to consider of a Dream which seems too extraordinary to be
without a Meaning. I am, Madam, with the greatest Passion,
Your most Obedient,
most Humble Servant, &c.'
X.
the same time
dreadful
Contents
|
Friday, February 15, 1712 |
Steele |
Lachrymæque decoræ,
Gratior et pulchro veniens in corpore Virtus.
Vir.
Æn. 5.

I read what I give for the Entertainment of this Day with a great deal
of Pleasure, and publish it just as it came to my Hands. I shall be very
glad to find there are many guessed at for Emilia.
Mr.
Spectator1,
If this Paper has the good Fortune to be honoured with a Place in your
Writings, I shall be the more pleased, because the Character of Emilia
is not an imaginary but a real one. I
have industriously obscured the
whole by the Addition of one or two Circumstances of no Consequence,
that the Person it is drawn from might still be concealed; and that
the Writer of it might not be in the least suspected, and for
other2 Reasons, I chuse not to give it the Form of a Letter: But if,
besides the Faults of the Composition, there be any thing in it more
proper for a Correspondent than the
Spectator himself to write, I
submit it to your better Judgment, to receive any other Model you
think fit.
I am,
Sir,
Your very humble Servant.'
There is nothing which gives one so pleasing a Prospect of human
Nature, as the Contemplation of Wisdom and Beauty: The latter is the
peculiar Portion of that Sex which is therefore called Fair; but the
happy Concurrence of both these Excellencies in the same Person, is
a Character too celestial to be frequently met with. Beauty is an
over-weaning self-sufficient thing, careless of providing it self
any more substantial Ornaments; nay so little does it consult its
own Interests, that it too often defeats it self by betraying that
Innocence which renders it lovely and desirable. As therefore Virtue
makes a beautiful Woman appear more beautiful, so Beauty makes a
virtuous Woman really more virtuous. Whilst I am considering these
two Perfections gloriously united in one Person, I cannot help
representing to my Mind the Image of Emilia.
Who ever beheld the charming Emilia, without feeling in his Breast
at once the Glow of Love and the Tenderness of virtuous Friendship?
The unstudied Graces of her Behaviour, and the pleasing Accents of
her Tongue, insensibly draw you on to wish for a nearer Enjoyment of
them; but even her Smiles carry in them a silent Reproof to the
Impulses of licentious Love. Thus, tho' the Attractives of her
Beauty play almost irresistibly upon you and create Desire, you
immediately stand corrected not by the Severity but the Decency of
her Virtue. That Sweetness and Good-humour which is so visible in
her Face, naturally diffuses it self into every Word and Action: A
Man must be a Savage, who at the Sight of Emilia, is not more
inclined to do her Good than gratifie himself. Her Person, as it is
thus studiously embellished by Nature, thus adorned with
unpremeditated Graces, is a fit Lodging for a Mind so fair and
lovely; there dwell rational Piety, modest Hope, and chearful
Resignation.
Many of the prevailing Passions of Mankind do undeservedly pass
under the Name of Religion; which is thus made to express itself in
Action, according to the Nature of the Constitution in which it
resides: So that were we to make a Judgment from Appearances, one
would imagine Religion in some is little better than Sullenness and
Reserve, in many Fear, in others the Despondings of a melancholly
Complexion, in others the Formality of insignificant unaffecting
Observances, in others Severity, in others Ostentation. In Emilia it
is a Principle founded in Reason and enlivened with Hope; it does
not break forth into irregular Fits and Sallies of Devotion, but is
an uniform and consistent Tenour of Action; It is strict without
Severity, compassionate without Weakness; it is the Perfection of
that good Humour which proceeds from the Understanding, not the
Effect of an easy Constitution.
By a generous Sympathy in Nature, we feel our selves disposed to
mourn when any of our Fellow-Creatures are afflicted; but injured
Innocence and Beauty in Distresses an Object that carries in it
something inexpressibly moving: It softens the most manly Heart with
the tenderest Sensations of Love and Compassion, till at length it
confesses its Humanity, and flows out into Tears.
Were I to relate that part of Emilia's Life which has given her an
Opportunity of exerting the Heroism of Christianity, it would make
too sad, too tender a Story: But when I consider her alone in the
midst of her Distresses, looking beyond this gloomy Vale of
Affliction and Sorrow into the Joys of Heaven and Immortality, and
when I see her in Conversation thoughtless and easie as if she were
the most happy Creature in the World, I am transported with
Admiration. Surely never did such a Philosophic Soul inhabit such a
beauteous Form! For Beauty is often made a Privilege against Thought
and Reflection; it laughs at Wisdom, and will not abide the Gravity
of its Instructions.
Were I able to represent Emilia's Virtues in their proper Colours
and their due Proportions, Love or Flattery might perhaps be thought
to have drawn the Picture larger than Life; but as this is but an
imperfect Draught of so excellent a Character, and as I cannot, will
not hope to have any Interest in her Person, all that I can say of
her is but impartial Praise extorted from me by the prevailing
Brightness of her Virtues. So rare a Pattern of Female Excellence
ought not to be concealed, but should be set out to the View and
Imitation of the World; for how amiable does Virtue appear thus as
it were made visible to us in so fair an Example!
Honoria's Disposition is of a very different Turn: Her Thoughts are
wholly bent upon Conquest and arbitrary Power. That she has some Wit
and Beauty no Body denies, and therefore has the Esteem of all her
Acquaintance as a Woman of an agreeable Person and Conversation; but
(whatever her Husband may think of it) that is not sufficient for
Honoria: She waves that Title to Respect as a mean Acquisition, and
demands Veneration in the Right of an Idol; for this Reason her
natural Desire of Life is continually checked with an inconsistent
Fear of Wrinkles and old Age.
Emilia cannot be supposed ignorant of her personal Charms, tho' she
seems to be so; but she will not hold her Happiness upon so
precarious a Tenure, whilst her Mind is adorned with Beauties of a
more exalted and lasting Nature. When in the full Bloom of Youth and
Beauty we saw her surrounded with a Crowd of Adorers, she took no
Pleasure in Slaughter and Destruction, gave no false deluding Hopes
which might encrease the Torments of her disappointed Lovers; but
having for some Time given to the Decency of a Virgin Coyness, and
examined the Merit of their several Pretensions, she at length
gratified her own, by resigning herself to the ardent Passion of
Bromius. Bromius was then Master of many good Qualities and a
moderate Fortune, which was soon after unexpectedly encreased to a
plentiful Estate. This for a good while proved his Misfortune, as it
furnished his unexperienced Age with the Opportunities of Evil
Company and a sensual Life. He might have longer wandered in the
Labyrinths of Vice and Folly, had not Emilia's prudent Conduct won
him over to the Government of his Reason. Her Ingenuity has been
constantly employed in humanizing his Passions and refining his
Pleasures. She shewed him by her own Example, that Virtue is
consistent with decent Freedoms and good Humour, or rather, that it
cannot subsist without 'em. Her good Sense readily instructed her,
that a silent Example and an easie unrepining Behaviour, will always
be more perswasive than the Severity of Lectures and Admonitions;
and that there is so much Pride interwoven into the Make of human
Nature, that an obstinate Man must only take the Hint from another,
and then be left to advise and correct himself. Thus by an artful
Train of Management and unseen Perswasions, having at first brought
him not to dislike, and at length to be pleased with that which
otherwise he would not have bore to hear of, she then knew how to
press and secure this Advantage, by approving it as his Thoughts,
and seconding it as his Proposal. By this Means she has gained an
Interest in some of his leading Passions, and made them accessary to
his Reformation.
There is another Particular of Emilia's Conduct which I can't
forbear mentioning: To some perhaps it may at first Sight appear but
a trifling inconsiderable Circumstance but for my Part, I think it
highly worthy of Observation, and to be recommended to the
Consideration of the fair Sex. I have often thought wrapping Gowns
and dirty Linnen, with all that huddled Œconomy of Dress which
passes under the general Name of a Mob, the Bane of conjugal Love,
and one of the readiest Means imaginable to alienate the Affection
of an Husband, especially a fond one. I have heard some Ladies, who
have been surprized by Company in such a Deshabille, apologize for
it after this Manner; Truly I am ashamed to be caught in this
Pickle; but my Husband and I were sitting all alone by our selves,
and I did not expect to see such good Company —This by the way is a
fine Compliment to the good Man, which 'tis ten to one but he
returns in dogged Answers and a churlish Behaviour, without knowing
what it is that puts him out of Humour.
Emilia's Observation teaches her, that as little Inadvertencies and
Neglects cast a Blemish upon a great Character; so the Neglect of
Apparel, even among the most intimate Friends, does insensibly
lessen their Regards to each other, by creating a Familiarity too
low and contemptible. She understands the Importance of those Things
which the Generality account Trifles; and considers every thing as a
Matter of Consequence, that has the least Tendency towards keeping
up or abating the Affection of her Husband; him she esteems as a fit
Object to employ her Ingenuity in pleasing, because he is to be
pleased for Life.
By the Help of these, and a thousand other nameless Arts, which 'tis
easier for her to practise than for another to express, by the
Obstinacy of her Goodness and unprovoked Submission, in spight of
all her Afflictions and ill Usage, Bromius is become a Man of Sense
and a kind Husband, and Emilia a happy Wife.
Ye guardian Angels to whose Care Heaven has entrusted its dear
Emilia, guide her still forward in the Paths of Virtue, defend her
from the Insolence and Wrongs of this undiscerning World; at length
when we must no more converse with such Purity on Earth, lead her
gently hence innocent and unreprovable to a better Place, where by
an easie Transition from what she now is, she may shine forth an
Angel of Light.
T.
The character of Emilia in this paper was by Dr. Bromer, a
clergyman. The lady is said to have been 'the mother of Mr. Ascham, of
Conington, in Cambridgeshire, and grandmother of Lady Hatton.' The
letter has been claimed also for John Hughes (
Letters of John Hughes
,
&c., vol. iii. p. 8), and Emilia identified with Anne, Countess of
Coventry.
some other
Contents
|
Saturday, February 16, 1712 |
Addison |
—volet hæc sub luce videri,
Judicis argulum quæ non formidat acumen.
Hor.

I have seen in the Works of a Modern Philosopher, a Map of the Spots in
the Sun. My last Paper of the Faults and Blemishes in Milton's
Paradise
Lost
, may be considered as a Piece of the same Nature. To pursue the
Allusion: As it is observed, that among the bright Parts of the Luminous
Body above mentioned, there are some which glow more intensely, and dart
a stronger Light than others; so, notwithstanding I have already shewn
Milton's Poem to be very beautiful in general, I shall now proceed to
take Notice of such Beauties as appear to me more exquisite than the
rest. Milton has proposed the Subject of his Poem in the following
Verses.
Of Man's first disobedience, and the fruit
Of that forbidden tree, whose mortal taste
Brought Death into the World and all our woe,
With loss of Eden, till one greater Man
Restore us, and regain the blisful Seat,
Sing Heavenly Muse—
These Lines are perhaps as plain, simple and unadorned as any of the
whole Poem, in which Particular the Author has conformed himself to the
Example of Homer and the Precept of Horace.
His Invocation to a Work which turns in a great measure upon the
Creation of the World, is very properly made to the Muse who inspired
Moses in those Books from whence our Author drew his Subject, and to the
Holy Spirit who is therein represented as operating after a particular
manner in the first Production of Nature. This whole Exordium rises very
happily into noble Language and Sentiment, as I think the Transition to
the Fable is exquisitely beautiful and natural.
The Nine Days Astonishment, in which the Angels lay entranced after
their dreadful Overthrow and Fall from Heaven, before they could recover
either the use of Thought or Speech, is a noble Circumstance, and very
finely imagined. The Division of Hell into Seas of Fire, and into firm
Ground impregnated with the same furious Element, with that particular
Circumstance of the Exclusion of Hope from those Infernal Regions, are
Instances of the same great and fruitful Invention.
The Thoughts in the first Speech and Description of Satan, who is one of
the Principal Actors in this Poem, are wonderfully proper to give us a
full Idea of him. His Pride, Envy and Revenge, Obstinacy, Despair and
Impenitence, are all of them very artfully interwoven. In short, his
first Speech is a Complication of all those Passions which discover
themselves separately in several other of his Speeches in the Poem. The
whole part of this great Enemy of Mankind is filled with such Incidents
as are very apt to raise and terrifie the Reader's Imagination. Of this
nature, in the Book now before us, is his being the first that awakens
out of the general Trance, with his Posture on the burning Lake, his
rising from it, and the Description of his Shield and Spear.
Thus Satan talking to his nearest Mate,
With head up-lift above the wave, and eyes
That sparkling blazed, his other parts beside
Prone on the Flood, extended long and large,
Lay floating many a rood—
Forthwith upright he rears from off the pool
His mighty Stature; on each hand the flames
Driv'n backward slope their pointing Spires, and roared
In Billows, leave i'th' midst a horrid vale.
Then with expanded wings he steers his flight
Aloft, incumbent on the dusky Air
That felt unusual weight—
—His pondrous Shield
Ethereal temper, massie, large and round,
Behind him cast; the broad circumference
Hung on his Shoulders like the Moon, whose orb
Thro' Optick Glass the Tuscan Artist views
At Ev'ning, from the top of Fesole,
Or in Valdarno, to descry new Lands,
Rivers, or Mountains, on her spotted Globe.
His Spear (to equal which the tallest pine
Hewn on Norwegian Hills to be the Mast
Of some great Admiral, were but a wand)
He walk'd with, to support uneasie Steps
Over the burning Marl—
To which we may add his Call to the fallen Angels that lay plunged and
stupified in the Sea of Fire.
He call'd so loud, that all the hollow deep
Of Hell resounded—
But there is no single Passage in the whole Poem worked up to a greater
Sublimity, than that wherein his Person is described in those celebrated
Lines:
—He, above the rest
In shape and gesture proudly eminent
Stood like a Tower, &c.
His Sentiments are every way answerable to his Character, and suitable
to a created Being of the most exalted and most depraved Nature. Such is
that in which he takes Possession of his Place of Torments.
—Hail Horrors! hail
Infernal World! and thou profoundest Hell
Receive thy new Possessor, one who brings
A mind not to be changed by place or time.
And Afterwards,
—Here at least
We shall be free; th'Almighty hath not built
Here for his envy, will not drive us hence:
Here we may reign secure; and in my choice
To reign is worth Ambition, tho' in Hell:
Better to reign in Hell, than serve in Heav'n.
Amidst those Impieties which this Enraged Spirit utters in other places
of the Poem, the Author has taken care to introduce none that is not big
with absurdity, and incapable of shocking a Religious Reader; his Words,
as the Poet himself describes them, bearing only a Semblance of Worth,
not Substance. He is likewise with great Art described as owning his
Adversary to be Almighty. Whatever perverse Interpretation he puts on
the Justice, Mercy, and other Attributes of the Supreme Being, he
frequently confesses his Omnipotence, that being the Perfection he was
forced to allow him, and the only Consideration which could support his
Pride under the Shame of his Defeat.
Nor must I here omit that beautiful Circumstance of his bursting out in
Tears, upon his Survey of those innumerable Spirits whom he had involved
in the same Guilt and Ruin with himself.
—He now prepared
To speak; whereat their doubled ranks they bend
From wing to wing, and half enclose him round
With all his Peers: Attention held them mute.
Thrice he assayed, and thrice in spite of Scorn
Tears such as Angels weep, burst forth—
Catalogue of Evil Spirits has abundance of Learning in it, and a
very agreeable turn of Poetry, which rises in a great measure from
its
describing the Places where they were worshipped, by those
beautiful Marks of Rivers so frequent among the Ancient Poets. The
Author had doubtless in this place Homer's Catalogue of Ships, and
Virgil's List of Warriors, in his View. The Characters of Moloch and
Belial prepare the Reader's Mind for their respective Speeches and
Behaviour in the second and sixth Book. The Account of Thammuz is finely
Romantick, and suitable to what we read among the Ancients of the
Worship which was paid to that Idol.
—Thammuz came next behind.
Whose annual Wound in Lebanon allured
The Syrian Damsels to lament his fate,
In amorous Ditties all a Summer's day,
While smooth Adonis from his native Rock
Ran purple to the Sea, supposed with Blood
Of Thammuz yearly wounded: the Love tale
Infected Zion's Daughters with like Heat,
Whose wanton Passions in the sacred Porch
Ezekiel saw, when by the Vision led
His Eye survey'd the dark Idolatries
Of alienated Judah.—
The
will pardon me if I insert as a Note on this beautiful
Passage, the Account given us by the late ingenious Mr. Maundrell
of
this Ancient Piece of Worship, and probably the first Occasion of such a
Superstition.
'We came to a fair large River—doubtless the Ancient
River Adonis, so famous for the Idolatrous Rites performed here in
Lamentation of Adonis. We had the Fortune to see what may be supposed to
be the Occasion of that Opinion which Lucian relates, concerning this
River, viz. That this Stream, at certain Seasons of the Year, especially
about the Feast of Adonis, is of a bloody Colour; which the Heathens
looked upon as proceeding from a kind of Sympathy in the River for the
Death of Adonis, who was killed by a wild Boar in the Mountains, out of
which this Stream rises. Something like this we saw actually come to
pass; for the Water was stain'd to a surprizing Redness; and, as we
observ'd in Travelling, had discolour'd the Sea a great way into a
reddish Hue, occasion'd doubtless by a sort of Minium, or red Earth,
washed into the River by the Violence of the Rain, and not by any Stain
from Adonis's Blood.'
The Passage in the Catalogue, explaining the manner how Spirits
transform themselves by Contractions or Enlargement of their Dimensions,
is introduced with great Judgment, to make way for several surprizing
Accidents in the Sequel of the Poem. There follows one, at the very End
of the first Book, which is what the French Criticks call Marvellous,
but at the same time probable by reason of the Passage last mentioned.
As soon as the Infernal Palace is finished, we are told the Multitude
and Rabble of Spirits immediately shrunk themselves into a small
Compass, that there might be Room for such a numberless Assembly in this
capacious Hall. But it is the Poet's Refinement upon this Thought which
I most admire, and which is indeed very noble in its self. For he tells
us, that notwithstanding the vulgar, among the fallen Spirits,
contracted their Forms, those of the first Rank and Dignity still
preserved their natural Dimensions.
Thus incorporeal Spirits to smallest Forms
Reduced their Shapes immense, and were at large,
Though without Number, still amidst the Hall
Of that Infernal Court. But far within,
And in their own Dimensions like themselves,
The great Seraphick Lords and Cherubim,
In close recess and secret conclave sate,
A thousand Demy-Gods on Golden Seats,
Frequent and full—
The Character of Mammon and the Description of the Pandæmonium, are full
of Beauties.
There are several other Strokes in the first Book wonderfully poetical,
and Instances of that Sublime Genius so peculiar to the Author. Such is
the Description of Azazel's Stature, and of the Infernal Standard, which
he unfurls; as also of that ghastly Light, by which the Fiends appear to
one another in their Place of Torments.
The Seat of Desolation, void of Light,
Save what the glimm'ring of those livid Flames
Casts pale and dreadful—
The Shout of the whole Host of fallen Angels when drawn up in Battel
Array:
—The universal Host up sent
A Shout that tore Hell's Concave, and beyond
Frighted the reign of Chaos and old Night.
The Review, which the Leader makes of his Infernal Army:
—He thro' the armed files
Darts his experienc'd eye, and soon traverse
The whole Battalion mews, their Order due,
Their Visages and Stature as of Gods.
Their Number last he sums; and now his Heart
Distends with Pride, and hard'ning in his strength
Glories—
The Flash of Light which appear'd upon the drawing of their Swords:
He spake: and to confirm his words outflew
Millions of flaming Swords, drawn from the thighs
Of mighty Cherubim; the sudden Blaze
Far round illumin'd Hell—
The sudden Production of the Pandæmonium;
Anon out of the Earth a Fabrick huge
Rose like an Exhalation, with the Sound
Of dulcet Symphonies and Voices sweet.
The Artificial Illuminations made in it:
—From the arched Roof
Pendent by subtle Magick, many a Row
Of Starry Lamps and blazing Crescets, fed
With Naphtha and Asphaltus, yielded Light
As from a Sky—
There are also several noble Similes and Allusions in the First Book of
Paradise Lost. And here I must observe, that when Milton alludes either
to Things or Persons, he never quits his Simile till it rises to some
very great Idea, which is often foreign to the Occasion that gave Birth
to it. The Resemblance does not, perhaps, last above a Line or two, but
the Poet runs on with the Hint till he has raised out of it some
glorious Image or Sentiment, proper to inflame the Mind of the Reader,
and to give it that sublime kind of Entertainment, which is suitable to
the Nature of an Heroick Poem. Those who are acquainted with Homer's and
Virgil's way of Writing, cannot but be pleased with this kind of
Structure in Milton's Similitudes. I am the more particular on this
Head, because ignorant Readers, who have formed their Taste upon the
quaint Similes, and little Turns of Wit, which are so much in Vogue
among Modern Poets, cannot relish these Beauties which are of a much
higher Nature, and are therefore apt to censure Milton's Comparisons in
which they do not see any surprizing Points of Likeness.
Perrault was a Man of this viciated Relish, and for that very Reason has
endeavoured to turn into Ridicule several of Homer's Similitudes, which
he calls
Comparisons a longue queue
, Long-tail'd Comparisons
. I
shall conclude this Paper on the First Book of Milton with the Answer
which Monsieur Boileau makes to Perrault on this Occasion;
'Comparisons,
says he, in Odes and Epic Poems, are not introduced only to illustrate
and embellish the Discourse, but to amuse and relax the Mind of the
Reader, by frequently disengaging him from too painful an Attention to
the Principal Subject, and by leading him into other agreeable Images.
Homer, says he, excelled in this Particular, whose Comparisons abound
with such Images of Nature as are proper to relieve and diversifie his
Subjects. He continually instructs the Reader, and makes him take
notice, even in Objects which are every Day before our Eyes, of such
Circumstances as we should not otherwise have observed.'
To this he
adds, as a Maxim universally acknowledged,
'That it is not necessary in
Poetry for the Points of the Comparison to correspond with one another
exactly, but that a general Resemblance is sufficient, and that too much
Nicety in this Particular favours of the Rhetorician and Epigrammatist.'
In short, if we look into the Conduct of Homer, Virgil and Milton, as
the great Fable is the Soul of each Poem, so to give their Works an
agreeable Variety, their Episodes are so many short Fables, and their
Similes so many short Episodes; to which you may add, if you please,
that their Metaphors are so many short Similes. If the Reader considers
the Comparisons in the first Book of Milton, of the Sun in an Eclipse,
of the Sleeping Leviathan, of the Bees swarming about their Hive, of the
Fairy Dance, in the view wherein I have here placed them, he will easily
discover the great Beauties that are in each of those Passages.
L.
his
A journey from Aleppo to Jerusalem at Easter, A.D. 1697. By
Henry Maundrell, M.A. It was published at Oxford in 1703, and was in a
new edition in 1707. It reached a seventh edition in 1749. Maundrell was
a Fellow of Exter College, which he left to take the appointment of
chaplain to the English factory at Aleppo. The brief account of his
journey is in the form of a diary, and the passage quoted is under the
date, March 15, when they were two days' journey from Tripoli. The
stream he identifies with the Adonis was called, he says, by Turks
Ibrahim Pasha. It is near Gibyle, called by the Greeks Byblus, a place
once famous for the birth and temple of Adonis. The extract from
Paradise Lost and the passage from Maundrell were interpolated in the
first reprint of the Spectator.
See
Charles Perrault made himself a
lasting name by his Fairy Tales, a charming embodiment of French nursery
traditions. The four volumes of his Paralièle des Anciens et des
Modernes 1692-6, included the good general idea of human progress, but
worked it out badly, dealing irreverently with Plato as well as Homer
and Pindar, and exalting among the moderns not only Molière and
Corneille, but also Chapelain, Scuderi, and Quinault, whom he called
'the greatest lyrical and dramatic poet that France ever had.' The
battle had begun with a debate in the Academy: Racine having ironically
complimented Perrault on the ingenuity with which he had elevated little
men above the ancients in his poem (published 1687), le Siècle de Louis
le Grand. Fontenelle touched the matter lightly, as Perrault's ally, in
his Digression sur les Anciens et les Modernes but afterwards drew back,
saying, 'I do not belong to the party which claims me for its chief.'
The leaders on the respective sides, unequally matched, were Perrault
and Boileau.
Contents
|
Monday, February 18, 1712 |
Steele |
Vulnus alit venis et cæco carpitur igni.
Virg.

The Circumstances of my Correspondent, whose Letter I now insert, are so
frequent, that I cannot want Compassion so much as to forbear laying it
before the Town. There is something so mean and inhuman in a direct
Smithfield Bargain for Children, that if this Lover carries his Point,
and observes the Rules he pretends to follow, I do not only wish him
Success, but also that it may animate others to follow his Example. I
know not one Motive relating to this Life which would produce so many
honourable and worthy Actions, as the Hopes of obtaining a Woman of
Merit: There would ten thousand Ways of Industry and honest Ambition be
pursued by young Men, who believed that the Persons admired had Value
enough for their Passion to attend the Event of their good Fortune in
all their Applications, in order to make their Circumstances fall in
with the Duties they owe to themselves, their Families, and their
Country; All these Relations a Man should think of who intends to go
into the State of Marriage, and expects to make it a State of Pleasure
and Satisfaction.
Mr. Spectator,
I have for some Years indulged a Passion for a young Lady of Age and
Quality suitable to my own, but very much superior in Fortune. It is
the Fashion with Parents (how justly I leave you to judge) to make all
Regards give way to the Article of Wealth. From this one Consideration
it is that I have concealed the ardent Love I have for her; but I am
beholden to the Force of my Love for many Advantages which I reaped
from it towards the better Conduct of my Life. A certain Complacency
to all the World, a strong Desire to oblige where-ever it lay in my
Power, and a circumspect Behaviour in all my Words and Actions, have
rendered me more particularly acceptable to all my Friends and
Acquaintance. Love has had the same good Effect upon my Fortune; and I
have encreased in Riches in proportion to my Advancement in those Arts
which make a man agreeable and amiable. There is a certain Sympathy
which will tell my Mistress from these Circumstances, that it is I who
writ this for her Reading, if you will please to insert it. There is
not a downright Enmity, but a great Coldness between our Parents; so
that if either of us declared any kind Sentiment for each other, her
Friends would be very backward to lay an Obligation upon our Family,
and mine to receive it from hers. Under these delicate Circumstances
it is no easie Matter to act with Safety. I have no Reason to fancy my
Mistress has any Regard for me, but from a very disinterested Value
which I have for her. If from any Hint in any future Paper of yours
she gives me the least Encouragement, I doubt not but I shall surmount
all other Difficulties; and inspired by so noble a Motive for the Care
of my Fortune, as the Belief she is to be concerned in it, I will not
despair of receiving her one Day from her Father's own Hand.
I am, Sir,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
Clytander.
To his Worship the Spectator,
The humble Petition of Anthony Title-Page, Stationer, in the Centre of
Lincolns-Inn-Fields,
Sheweth,
That your Petitioner and his Fore-Fathers have been Sellers of Books
for Time immemorial; That your Petitioner's Ancestor, Crouchback
Title-Page, was the first of that Vocation in Britain; who keeping his
Station (in fair Weather) at the Corner of Lothbury, was by way of
Eminency called the Stationer, a Name which from him all succeeding
Booksellers have affected to bear: That the Station of your Petitioner
and his Father has been in the Place of his present Settlement ever
since that Square has been built: That your Petitioner has formerly
had the Honour of your Worship's Custom, and hopes you never had
Reason to complain of your Penny-worths; that particularly he sold you
your first Lilly's Grammar, and at the same Time a Wit's Commonwealth
almost as good as new: Moreover, that your first rudimental Essays in
Spectatorship were made in your Petitioner's Shop, where you often
practised for Hours together, sometimes on his Books upon the Rails,
sometimes on the little Hieroglyphicks either gilt, silvered, or
plain, which the Egyptian Woman on the other Side of the Shop had
wrought in Gingerbread, and sometimes on the English Youth, who in
sundry Places there were exercising themselves in the traditional
Sports of the Field.
From these Considerations it is, that your Petitioner is encouraged to
apply himself to you, and to proceed humbly to acquaint your Worship,
That he has certain Intelligence that you receive great Numbers of
defamatory Letters designed by their Authors to be published, which
you throw aside and totally neglect: Your Petitioner therefore prays,
that you will please to bestow on him those Refuse Letters, and he
hopes by printing them to get a more plentiful Provision for his
Family; or at the worst, he may be allowed to sell them by the Pound
Weight to his good Customers the Pastry-Cooks of London and
Westminster. And your Petitioner shall ever pray, &c.
To the Spectator,
The humble Petition of Bartholomew Ladylove, of Round-Court in the
Parish of St. Martins in the Fields, in Behalf of himself and
Neighbours,
Sheweth,
That your Petitioners have with great Industry and Application arrived
at the most exact Art of Invitation or Entreaty: That by a beseeching
Air and perswasive Address, they have for many Years last past
peaceably drawn in every tenth Passenger, whether they intended or not
to call at their Shops, to come in and buy; and from that Softness of
Behaviour, have arrived among Tradesmen at the gentle Appellation of
the Fawners.
That there have of late set up amongst us certain Persons of
Monmouth-street and Long-lane, who by the Strength of their Arms, and
Loudness of their Throats, draw off the Regard of all Passengers from
your said Petitioners; from which Violence they are distinguished by
the Name of the Worriers.
That while your Petitioners stand ready to receive Passengers with a
submissive Bow, and repeat with a gentle Voice, Ladies, what do you
want? pray look in here; the Worriers reach out their Hands at
Pistol-shot, and seize the Customers at Arms Length.
That while the Fawners strain and relax the Muscles of their Faces in
making Distinction between a Spinster in a coloured Scarf and an
Handmaid in a Straw-Hat, the Worriers use the same Roughness to both,
and prevail upon the Easiness of the Passengers, to the Impoverishment
of your Petitioners.
Your Petitioners therefore most humbly pray, that the Worriers may not
be permitted to inhabit the politer Parts of the Town; and that
Round-Court may remain a Receptacle for Buyers of a more soft
Education.
And your Petitioners, &c.
The Petition of the New-Exchange, concerning the Arts of Buying and
Selling, and particularly valuing Goods by the Complexion of the Seller,
will be considered on another Occasion.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, February 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Non tali auxilio, nec defensoribus istis
Tempus eget.
Virg.

Our late News-Papers being full of the Project now on foot in the Court
of France, for Establishing a Political Academy, and I my self having
received Letters from several Virtuoso's among my Foreign
Correspondents, which give some Light into that Affair, I intend to make
it the Subject of this Day's Speculation. A general Account of this
Project may be met with in the Daily Courant of last Friday in the
following Words, translated from the Gazette of Amsterdam.
Paris, February 12.
''Tis confirmed that the King has resolved to establish a new Academy
for Politicks, of which the Marquis de Torcy, Minister and Secretary
of State, is to be Protector. Six Academicians are to be chosen,
endowed with proper Talents, for beginning to form this Academy, into
which no Person is to be admitted under Twenty-five Years of Age: They
must likewise each have an Estate of Two thousand Livres a Year,
either in Possession, or to come to 'em by Inheritance. The King will
allow to each a Pension of a Thousand Livres. They are likewise to
have able Masters to teach 'em the necessary Sciences, and to instruct
them in all the Treaties of Peace, Alliance, and others, which have
been made in several Ages past. These Members are to meet twice a Week
at the Louvre. From this Seminary are to be chosen Secretaries to
Ambassies, who by degrees may advance to higher Employments.
Cardinal Richelieu's Politicks made France the Terror of Europe. The
Statesmen who have appeared in the Nation of late Years, have on the
contrary rendered it either the Pity or Contempt of its Neighbours. The
Cardinal erected that famous Academy which has carried all the Parts of
Polite Learning to the greatest Height. His chief Design in that
Institution was to divert the Men of Genius from meddling with
Politicks, a Province in which he did not care to have any one else
interfere with him. On the contrary, the Marquis de Torcy seems resolved
to make several young Men in France as Wise as himself, and is therefore
taken up at present in establishing a Nursery of Statesmen.
Some private Letters add, that there will also be erected a Seminary of
Petticoat Politicians, who are to be brought up at the Feet of Madam de
Maintenon, and to be dispatched into Foreign Courts upon any Emergencies
of State; but as the News of this last Project has not been yet
confirmed, I shall take no farther Notice of it.
Several of my Readers may doubtless remember that upon the Conclusion of
the last War, which had been carried on so successfully by the Enemy,
their Generals were many of them transformed into Ambassadors; but the
Conduct of those who have commanded in the present War, has, it seems,
brought so little Honour and Advantage to their great Monarch, that he
is resolved to trust his Affairs no longer in the Hands of those
Military Gentlemen.
The Regulations of this new Academy very much deserve our Attention. The
Students are to have in Possession, or Reversion, an Estate of two
thousand French Livres per Annum, which, as the present Exchange runs,
will amount to at least one hundred and twenty six Pounds English. This,
with the Royal Allowance of a Thousand Livres, will enable them to find
themselves in Coffee and Snuff; not to mention News-Papers, Pen and Ink,
Wax and Wafers, with the like Necessaries for Politicians.
A Man must be at least Five and Twenty before he can be initiated into
the Mysteries of this Academy, tho' there is no Question but many grave
Persons of a much more advanced Age, who have been constant Readers of
the Paris Gazette, will be glad to begin the World a-new, and enter
themselves upon this List of Politicians.
The Society of these hopeful young Gentlemen is to be under the
Direction of six Professors, who, it seems, are to be Speculative
Statesmen, and drawn out of the Body of the Royal Academy. These six
wise Masters, according to my private Letters, are to have the following
Parts allotted them.
The first is to instruct the Students in State Legerdemain, as how to
take off the Impression of a Seal, to split a Wafer, to open a Letter,
to fold it up again, with other the like ingenious Feats of Dexterity
and Art. When the Students have accomplished themselves in this Part of
their Profession, they are to be delivered into the Hands of their
second Instructor, who is a kind of Posture-Master.
This Artist is to teach them how to nod judiciously, to shrug up their
Shoulders in a dubious Case, to connive with either Eye, and in a Word,
the whole Practice of Political Grimace.
The Third is a sort of Language-Master, who is to instruct them in the
Style proper for a Foreign Minister in his ordinary Discourse. And to
the End that this College of Statesmen may be thoroughly practised in
the Political Style, they are to make use of it in their common
Conversations, before they are employed either in Foreign or Domestick
Affairs. If one of them asks another, what a-clock it is, the other is
to answer him indirectly, and, if possible, to turn off the Question. If
he is desired to change a Louis d'or, he must beg Time to consider of
it. If it be enquired of him, whether the King is at Versailles or
Marly, he must answer in a Whisper. If he be asked the News of the late
Gazette, or the Subject of a Proclamation, he is to reply, that he has
not yet read it: Or if he does not care for explaining himself so far,
he needs only draw his Brow up in Wrinkles, or elevate the Left
Shoulder.
The Fourth Professor is to teach the whole Art of Political Characters
and Hieroglyphics; and to the End that they may be perfect also in this
Practice, they are not to send a Note to one another (tho' it be but to
borrow a Tacitus or a Machiavil) which is not written in Cypher.
Their Fifth Professor, it is thought, will be chosen out of the Society
of Jesuits, and is to be well read in the Controversies of probable
Doctrines, mental Reservation, and the Rights of Princes. This Learned
Man is to instruct them in the Grammar, Syntax, and construing Part of
Treaty-Latin; how to distinguish between the Spirit and the Letter, and
likewise demonstrate how the same Form of Words may lay an Obligation
upon any Prince in Europe, different from that which it lays upon his
Most Christian Majesty. He is likewise to teach them the Art of finding
Flaws, Loop-holes, and Evasions, in the most solemn Compacts, and
particularly a great Rabbinical Secret, revived of late Years by the
Fraternity of Jesuits, namely, that contradictory Interpretations, of
the same Article may both of them be true and valid.
When our Statesmen are sufficiently improved by these several
Instructors, they are to receive their last Polishing from one who is to
act among them as Master of the Ceremonies. This Gentleman is to give
them Lectures upon those important Points of the Elbow Chair, and the
Stair Head, to instruct them in the different Situations of the
Right-Hand, and to furnish them with Bows and Inclinations of all Sizes,
Measures and Proportions. In short, this Professor is to give the
Society their Stiffening, and infuse into their Manners that beautiful
Political Starch, which may qualifie them for Levées, Conferences,
Visits, and make them shine in what vulgar Minds are apt to look upon as
Trifles. I have not yet heard any further Particulars, which are to be
observed in this Society of unfledged Statesmen; but I must confess, had
I a Son of five and twenty, that should take it into his Head at that
Age to set up for a Politician, I think I should go near to disinherit
him for a Block-head. Besides, I should be apprehensive lest the same
Arts which are to enable him to negotiate between Potentates might a
little infect his ordinary behaviour between Man and Man. There is no
Question but these young Machiavils will, in a little time, turn their
College upside-down with Plots and Stratagems, and lay as many Schemes
to Circumvent one another in a Frog or a Sallad, as they may hereafter
put in Practice to over-reach a Neighbouring Prince or State.
We are told, that the Spartans, tho' they punished Theft in their young
Men when it was discovered, looked upon it as Honourable if it
succeeded. Provided the Conveyance was clean and unsuspected, a Youth
might afterwards boast of it. This, say the Historians, was to keep them
sharp, and to hinder them from being imposed upon, either in their
publick or private Negotiations. Whether any such Relaxations of
Morality, such little
jeux d'esprit
, ought not to be allowed in this
intended Seminary of Politicians, I shall leave to the Wisdom of their
Founder.
In the mean time we have fair Warning given us by this doughty Body of
Statesmen: and as Sylla saw many Marius's in Cæsar, so I think we may
discover many Torcy's in this College of Academicians. Whatever we think
of our selves, I am afraid neither our Smyrna or St. James's will be a
Match for it. Our Coffee-houses are, indeed, very good Institutions, but
whether or no these our British Schools of Politicks may furnish out as
able Envoys and Secretaries as an Academy that is set apart for that
Purpose, will deserve our serious Consideration, especially if we
remember that our Country is more famous for producing Men of Integrity
than Statesmen; and that on the contrary, French Truth and British
Policy make a Conspicuous Figure in
Nothing
, as the Earl of Rochester
has very well observed in his admirable Poem upon that Barren Subject.
L.
Contents
|
Wednesday, February 20, 1712 |
Steele |
Quæ forma, ut se tibi semper
Imputet?
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator1,
'I write this to communicate to you a Misfortune which frequently
happens, and therefore deserves a consolatory Discourse on the
Subject. I was within this Half-Year in the Possession of as much
Beauty and as many Lovers as any young Lady in England. But my
Admirers have left me, and I cannot complain of their Behaviour. I
have within that Time had the Small-Pox; and this Face, which
(according to many amorous Epistles which I have by me) was the Seat
of all that is beautiful in Woman, is now disfigured with Scars. It
goes to the very Soul of me to speak what I really think of my Face;
and tho' I think I did not over-rate my Beauty while I had it, it has
extremely advanc'd in its value with me now it is lost. There is one
Circumstance which makes my Case very particular; the ugliest Fellow
that ever pretended to me, was and is most in my Favour, and he treats
me at present the most unreasonably. If you could make him return an
Obligation which he owes me, in liking a Person that is not
amiable;—But there is, I fear, no Possibility of making Passion move
by the Rules of Reason and Gratitude. But say what you can to one who
has survived her self, and knows not how to act in a new Being. My
Lovers are at the Feet of my Rivals, my Rivals are every Day bewailing
me, and I cannot enjoy what I am, by reason of the distracting
Reflection upon what I was. Consider the Woman I was did not die of
old Age, but I was taken off in the Prime of my Youth, and according
to the Course of Nature may have Forty Years After-Life to come. I
have nothing of my self left which I like, but that
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Parthenissa.'
When Lewis of France had lost the Battle of Ramelies, the Addresses to
him at that time were full of his Fortitude, and they turned his
Misfortune to his Glory; in that, during his Prosperity, he could never
have manifested his heroick Constancy under Distresses, and so the World
had lost the most eminent Part of his Character. Parthenissa's Condition
gives her the same Opportunity; and to resign Conquests is a Task as
difficult in a Beauty as an Hero. In the very Entrance upon this Work
she must burn all her Love-Letters; or since she is so candid as not to
call her Lovers who follow her no longer Unfaithful, it would be a very
good beginning of a new Life from that of a Beauty, to send them back to
those who writ them, with this honest Inscription, Articles of a
Marriage Treaty broken off by the Small-Pox. I have known but one
Instance, where a Matter of this Kind went on after a like Misfortune,
where the Lady, who was a Woman of Spirit, writ this Billet to her
Lover.
Sir,
'If you flattered me before I had this terrible Malady, pray come and
see me now: But if you sincerely liked me, stay away; for I am not the
same
Corinna.'
The Lover thought there was something so sprightly in her Behaviour,
that he answered,
Madam,
'I am not obliged, since you are not the same Woman, to let you know
whether I flattered you or not; but I assure you, I do not, when I
tell you I now like you above all your Sex, and hope you will bear
what may befall me when we are both one, as well as you do what
happens to your self now you are single; therefore I am ready to take
such a Spirit for my Companion as soon as you please.
Amilcar.'
If Parthenissa can now possess her own Mind, and think as little of her
Beauty as she ought to have done when she had it, there will be no great
Diminution of her Charms; and if she was formerly affected too much with
them, an easie Behaviour will more than make up for the Loss of them.
Take the whole Sex together, and you find those who have the strongest
Possession of Men's Hearts are not eminent for their Beauty: You see it
often happen that those who engage Men to the greatest Violence, are
such as those who are Strangers to them would take to be remarkably
defective for that End. The fondest Lover I know, said to me one Day in
a Crowd of Women at an Entertainment of Musick, You have often heard me
talk of my Beloved: That Woman there, continued he, smiling when he had
fixed my Eye, is her very Picture. The Lady he shewed me was by much the
least remarkable for Beauty of any in the whole Assembly; but having my
Curiosity extremely raised, I could not keep my Eyes off of her. Her
Eyes at last met mine, and with a sudden Surprize she looked round her
to see who near her was remarkably handsome that I was gazing at. This
little Act explain'd the Secret: She did not understand herself for the
Object of Love, and therefore she was so. The Lover is a very honest
plain Man; and what charmed him was a Person that goes along with him in
the Cares and Joys of Life, not taken up with her self, but sincerely
attentive with a ready and chearful Mind, to accompany him in either.
I can tell Parthenissa for her Comfort, That the Beauties, generally
speaking, are the most impertinent and disagreeable of Women. An
apparent Desire of Admiration, a Reflection upon their own Merit, and a
precious Behaviour in their general Conduct, are almost inseparable
Accidents in Beauties. All you obtain of them is granted to Importunity
and Sollicitation for what did not deserve so much of your Time, and you
recover from the Possession of it, as out of a Dream.
You are ashamed of the Vagaries of Fancy which so strangely mis-led you,
and your Admiration of a Beauty, merely as such, is inconsistent with a
tolerable Reflection upon your self: The chearful good-humoured
Creatures, into whose Heads it never entred that they could make any Man
unhappy, are the Persons formed for making Men happy. There's Miss Liddy
can dance a Jigg, raise Paste, write a good Hand, keep an Account, give
a reasonable Answer, and do as she is bid; while her elder Sister Madam
Martha is out of Humour, has the Spleen, learns by Reports of People of
higher Quality new Ways of being uneasie and displeased. And this
happens for no Reason in the World, but that poor Liddy knows she has no
such thing as a certain Negligence that is so becoming, that there is
not I know not what in her Air: And that if she talks like a Fool, there
is no one will say, Well! I know not what it is, but every Thing pleases
when she speaks it.
Ask any of the Husbands of your great Beauties, and they'll tell you
that they hate their Wives Nine Hours of every Day they pass together.
There is such a Particularity for ever affected by them, that they are
incumbered with their Charms in all they say or do. They pray at publick
Devotions as they are Beauties. They converse on ordinary Occasions as
they are Beauties. Ask Belinda what it is a Clock, and she is at a stand
whether so great a Beauty should answer you. In a Word, I think, instead
of offering to administer Consolation to Parthenissa, I should
congratulate her Metamorphosis; and however she thinks she was not in
the least insolent in the Prosperity of her Charms, she was enough so to
find she may make her self a much more agreeable Creature in her present
Adversity. The Endeavour to please is highly promoted by a Consciousness
that the Approbation of the Person you would be agreeable to, is a
Favour you do not deserve; for in this Case Assurance of Success is the
most certain way to Disappointment. Good-Nature will always supply the
Absence of Beauty, but Beauty cannot long supply the Absence of
Good-Nature.
P. S.
Madam, February 18.
'I have yours of this Day, wherein you twice bid me not to disoblige
you, but you must explain yourself further before I know what to do.
Your most obedient Servant,
The
Spectator
.'
T.
Mr. John Duncombe ascribed this letter to his relative,
John Hughes, and said that by Parthenissa was meant a Miss Rotherham,
afterwards married to the Rev. Mr. Wyatt, master of Felsted School, in
Essex. The name of Parthenissa is from the heroine of a romance by Roger
Boyle, Earl of Orrery.
Contents
|
Thursday, February 21, 1712 |
Budgell |
—Versate diu quid ferre recusent
Quid valeant humeri—
Hor.

I am so well pleased with the following Letter, that I am in hopes it
will not be a disagreeable Present to the Publick.
Sir,
'Though I believe none of your Readers more admire your agreeable
manner of working up Trifles than my self, yet as your Speculations
are now swelling into Volumes, and will in all Probability pass down
to future Ages, methinks I would have no single Subject in them,
wherein the general Good of Mankind is concern'd, left unfinished.
'I have a long time expected with great Impatience that you would
enlarge upon the ordinary Mistakes which are committed in the
Education of our Children. I the more easily flattered my self that
you would one time or other resume this Consideration, because you
tell us that your [Volume 1 link:
168th Paper] was only composed of a few broken Hints;
but finding myself hitherto disappointed, I have ventur'd to send you
my own Thoughts on this Subject.
'I remember Pericles in his famous Oration at the Funeral of those
Athenian young Men who perished in the Samian Expedition, has a
Thought very much celebrated by several Ancient Criticks, namely, That
the Loss which the Commonwealth suffered by the Destruction of its
Youth, was like the Loss which the Year would suffer by the
Destruction of the Spring. The Prejudice which the Publick sustains
from a wrong Education of Children, is an Evil of the same Nature, as
it in a manner starves Posterity, and defrauds our Country of those
Persons who, with due Care, might make an eminent Figure in their
respective Posts of Life.
'
I have seen a Book written by Juan Huartes
1, a Spanish Physician,
entitled
Examen de Ingenios, wherein he lays it down as one of his
first Positions, that Nothing but Nature can qualifie a Man for
Learning; and that without a proper Temperament for the particular Art
or Science which he studies, his utmost Pains and Application,
assisted by the ablest Masters, will be to no purpose.
'He illustrates this by the Example of Tully's Son Marcus.
'Cicero, in order to accomplish his Son in that sort of Learning which
he designed him for, sent him to Athens, the most celebrated Academy
at that time in the World, and where a vast Concourse, out of the most
Polite Nations, could not but furnish a young Gentleman with a
Multitude of great Examples, and Accidents that might insensibly have
instructed him in his designed Studies: He placed him under the Care
of Cratippus, who was one of the greatest Philosophers of the Age,
and, as if all the Books which were at that time written had not been
sufficient for his Use, he composed others on purpose for him:
Notwithstanding all this, History informs us, that Marcus proved a
meer Blockhead, and that Nature, (who it seems was even with the Son
for her Prodigality to the Father) rendered him incapable of improving
by all the Rules of Eloquence, the Precepts of Philosophy, his own
Endeavours, and the most refined Conversation in Athens. This Author
therefore proposes, that there should be certain Tryers or Examiners
appointed by the State to inspect the Genius of every particular Boy,
and to allot him the Part that is most suitable to his natural
Talents.
'Plato in one of his Dialogues tells us, that Socrates, who was the
Son of a Midwife, used to say, that as his Mother, tho' she was very
skilful in her Profession, could not deliver a Woman, unless she was
first with Child; so neither could he himself raise Knowledge out of a
Mind, where Nature had not planted it.
'Accordingly the Method this Philosopher took, of instructing his
Scholars by several Interrogatories or Questions, was only helping the
Birth, and bringing their own Thoughts to Light.
'The Spanish Doctor above mentioned, as his Speculations grow more
refined, asserts that every kind of Wit has a particular Science
corresponding to it, and in which alone it can be truly Excellent. As
to those Genius's, which may seem to have an equal Aptitude for
several things, he regards them as so many unfinished Pieces of Nature
wrought off in haste.
'There are, indeed, but very few to whom Nature has been so unkind,
that they are not capable of shining in some Science or other. There
is a certain Byass towards Knowledge in every Mind, which may be
strengthened and improved by proper Applications.
'
The Story of Clavius
2 is very well known; he was entered in a
College of Jesuits, and after having been tryed at several Parts of
Learning, was upon the Point of being dismissed as an hopeless
Blockhead, 'till one of the Fathers took it into his Head to make an
assay of his Parts in Geometry, which it seems hit his Genius so
luckily that he afterwards became one of the greatest Mathematicians
of the Age. It is commonly thought that the Sagacity of these Fathers,
in discovering the Talent of a young Student, has not a little
contributed to the Figure which their Order has made in the World.
'How different from this manner of Education is that which prevails in
our own Country? Where nothing is more usual than to see forty or
fifty Boys of several Ages, Tempers and Inclinations, ranged together
in the same Class, employed upon the same Authors, and enjoyned the
same Tasks? Whatever their natural Genius may be, they are all to be
made Poets, Historians, and Orators alike. They are all obliged to
have the same Capacity, to bring in the same Tale of Verse, and to
furnish out the same Portion of Prose. Every Boy is bound to have as
good a Memory as the Captain of the Form. To be brief, instead of
adapting Studies to the particular Genius of a Youth, we expect from
the young Man, that he should adapt his Genius to his Studies. This, I
must confess, is not so much to be imputed to the Instructor, as to
the Parent, who will never be brought to believe, that his Son is not
capable of performing as much as his Neighbour's, and that he may not
make him whatever he has a Mind to.
'If the present Age is more laudable than those which have gone before
it in any single Particular, it is in that generous Care which several
well-disposed Persons have taken in the Education of poor Children;
and as in these Charity-Schools there is no Place left for the
over-weening Fondness of a Parent, the Directors of them would make
them beneficial to the Publick, if they considered the Precept which I
have been thus long inculcating. They might easily, by well examining
the Parts of those under their Inspection, make a just Distribution of
them into proper Classes and Divisions, and allot to them this or that
particular Study, as their Genius qualifies them for Professions,
Trades, Handicrafts, or Service by Sea or Land.
'How is this kind of Regulation wanting in the three great
Professions!
'Dr. South complaining of Persons who took upon them Holy Orders, tho'
altogether unqualified for the Sacred Function, says somewhere, that
many a Man runs his Head against a Pulpit, who might have done his
Country excellent Service at a Plough-tail.
'In like manner many a Lawyer, who makes but an indifferent Figure at
the Bar, might have made a very elegant Waterman, and have shined at
the Temple Stairs, tho' he can get no Business in the House.
'I have known a Corn-cutter, who with a right Education would have
been an excellent Physician.
'To descend lower, are not our Streets filled with sagacious Draymen,
and Politicians in Liveries? We have several Taylors of six Foot high,
and meet with many a broad pair of Shoulders that are thrown away upon
a Barber, when perhaps at the same time we see a pigmy Porter reeling
under a Burthen, who might have managed a Needle with much Dexterity,
or have snapped his Fingers with great Ease to himself, and Advantage
to the Publick.
'The Spartans, tho' they acted with the Spirit which I am here
speaking of, carried it much farther than what I propose: Among them
it was not lawful for the Father himself to bring up his Children
after his own Fancy. As soon as they were seven Years old they were
all listed in several Companies, and disciplined by the Publick. The
old Men were Spectators of their Performances, who often raised
Quarrels among them, and set them at Strife with one another, that by
those early Discoveries they might see how their several Talents lay,
and without any regard to their Quality, dispose of them accordingly
for the Service of the Commonwealth. By this Means Sparta soon became
the Mistress of Greece, and famous through the whole World for her
Civil and Military Discipline.
'If you think this Letter deserves a place among your Speculations, I
may perhaps trouble you with some other Thoughts on the same Subject.
I am, &c.
X.
Juan Huarte was born in French Navarre, and obtained much
credit in the sixteenth century for the book here cited. It was
translated into Latin and French. The best edition is of Cologne, 1610.
Christopher Clavius, a native of Bamberg, died in 1612,
aged 75, at Rome, whither he had been sent by the Jesuits, and where he
was regarded as the Euclid of his age. It was Clavius whom Pope Gregory
XIII. employed in 1581 to effect the reform in the Roman Calendar
promulgated in 1582, when the 5th of October became throughout Catholic
countries the 15th of the New Style, an improvement that was not
admitted into Protestant England until 1752. Clavius wrote an Arithmetic
and Commentaries on Euclid, and justified his reform of the Calendar
against the criticism of Scaliger.
Contents
|
Friday, February 22, 1712 |
Steele |
Jam proterva
Fronte petet Lalage maritum.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'I give you this Trouble in order to propose my self to you as an
Assistant in the weighty Cares which you have thought fit to undergo
for the publick Good. I am a very great Lover of Women, that is to say
honestly, and as it is natural to study what one likes, I have
industriously applied my self to understand them. The present
Circumstance relating to them, is, that I think there wants under you,
as
Spectator, a Person to be distinguished and vested in the Power and
Quality of a Censor on Marriages. I lodge at the Temple, and know, by
seeing Women come hither, and afterwards observing them conducted by
their Council to Judges Chambers, that there is a Custom in Case of
making Conveyance of a Wife's Estate, that she is carried to a Judge's
Apartment and left alone with him, to be examined in private whether
she has not been frightened or sweetned by her Spouse into the Act she
is going to do, or whether it is of her own free Will. Now if this be
a Method founded upon Reason and Equity, why should there not be also
a proper Officer for examining such as are entring into the State of
Matrimony, whether they are forced by Parents on one Side, or moved by
Interest only on the other, to come together, and bring forth such
awkward Heirs as are the Product of half Love and constrained
Compliances? There is no Body, though I say it my self, would be
fitter for this Office than I am: For I am an ugly Fellow of great Wit
and Sagacity. My Father was an hail Country-'Squire, my Mother a witty
Beauty of no Fortune: The Match was made by Consent of my Mother's
Parents against her own: and I am the Child of a Rape on the
Wedding-Night; so that I am as healthy and as homely as my Father, but
as sprightly and agreeable as my Mother. It would be of great Ease to
you if you would use me under you, that Matches might be better
regulated for the future, and we might have no more Children of
Squabbles. I shall not reveal all my Pretensions till I receive your
Answer; and am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Mules Palfrey.
Mr. Spectator,
I am one of those unfortunate Men within the City-Walls, who am
married to a Woman of Quality, but her Temper is something different
from that of Lady Anvil. My Lady's whole Time and Thoughts are spent
in keeping up to the Mode both in Apparel and Furniture. All the Goods
in my House have been changed three times in seven Years. I have had
seven Children by her; and by our Marriage Articles she was to have
her Apartment new furnished as often as she lay in. Nothing in our
House is useful but that which is fashionable; my Pewter holds out
generally half a Year, my Plate a full Twelvemonth; Chairs are not fit
to sit in that were made two Years since, nor Beds fit for any thing
but to sleep in that have stood up above that Time. My Dear is of
Opinion that an old-fashioned Grate consumes Coals, but gives no Heat:
If she drinks out of Glasses of last Year, she cannot distinguish Wine
from Small-Beer. Oh dear Sir you may guess all the rest. Yours.
P. S. I could bear even all this, if I were not obliged also to eat
fashionably. I have a plain Stomach, and have a constant Loathing of
whatever comes to my own Table; for which Reason I dine at the
Chop-House three Days a Week: Where the good Company wonders they
never see you of late. I am sure by your unprejudiced Discourses you
love Broth better than Soup.
Will's, Feb. 19.
Mr. Spectator,
You may believe you are a Person as much talked of as any Man in Town.
I
am one of your best Friends in this House, and have laid a Wager you
are so candid a Man and so honest a Fellow, that you will print this
Letter, tho' it is in Recommendation of a new Paper called
The
Historian1. I have read it carefully, and find it written with
Skill, good Sense, Modesty, and Fire. You must allow the Town is
kinder to you than you deserve; and I doubt not but you have so much
Sense of the World, Change of Humour, and instability of all humane
Things, as to understand, that the only Way to preserve Favour, is to
communicate it to others with Good-Nature and Judgment. You are so
generally read, that what you speak of will be read. This with Men of
Sense and Taste is all that is wanting to recommend
The Historian.
I am, Sir,
Your daily Advocate,
Reader Gentle.
I was very much surprised this Morning, that any one should find out my
Lodging, and know it so well, as to come directly to my Closet-Door, and
knock at it, to give me the following Letter. When I came out I opened
it, and saw by a very strong Pair of Shoes and a warm Coat the Bearer
had on, that he walked all the Way to bring it me, tho' dated from York.
My Misfortune is that I cannot talk, and I found the Messenger had so
much of me, that he could think better than speak. He had, I observed, a
polite Discerning hid under a shrewd Rusticity: He delivered the Paper
with a Yorkshire Tone and a Town Leer.
Mr. Spectator,
The Privilege you have indulged John Trot has proved of very bad
Consequence to our illustrious Assembly, which, besides the many
excellent Maxims it is founded upon, is remarkable for the
extraordinary Decorum always observed in it. One Instance of which is
that the Carders, (who are always of the first Quality) never begin to
play till the French-Dances are finished, and the Country-Dances
begin: But John Trot having now got your Commission in his Pocket,
(which every one here has a profound Respect for) has the Assurance to
set up for a Minuit-Dancer. Not only so, but he has brought down upon
us the whole Body of the Trots, which are very numerous, with their
Auxiliaries the Hobblers and the Skippers, by which Means the Time is
so much wasted, that unless we break all Rules of Government, it must
redound to the utter Subversion of the Brag-Table, the discreet
Members of which value Time as Fribble's Wife does her Pin-Money. We
are pretty well assured that your Indulgence to Trot was only in
relation to Country-Dances; however we have deferred the issuing an
Order of Council upon the Premisses, hoping to get you to join with
us, that Trot, nor any of his Clan, presume for the future to dance
any but Country-Dances, unless a Horn-Pipe upon a Festival-Day. If you
will do this you will oblige a great many Ladies, and particularly
Your most humble Servant,
Eliz. Sweepstakes.
York, Feb. 16.
I never meant any other than that Mr. Trott should confine himself to
Country-Dances. And I further direct, that he shall take out none but
his own Relations according to their Nearness of Blood, but any
Gentlewoman may take out him.
London, Feb. 21.
The Spectator.
T.
Steele's papers had many imitations, as the
Historian
, here
named; the
Rhapsody, Observator, Moderator, Growler, Censor, Hermit,
Surprize, Silent Monitor, Inquisitor, Pilgrim, Restorer, Instructor,
Grumbler
, &c. There was also in 1712 a
Rambler
, anticipating the name of
Dr. Johnson's
Rambler
of 1750-2.
Contents
|
Saturday, February 23, 1712 |
Addison |
Dî, quibus imperium est animarum, umbræque silentes,
Et Chaos, et Phlegethon, loca nocte silentia late;
Sit mihi fas audita loqui! sit numine vestro
Pandere res alta terra et caligine mersas.
Virg.

I have before observed in general, that the Persons whom Milton
introduces into his Poem always discover such Sentiments and Behaviour,
as are in a peculiar manner conformable to their respective Characters.
Every Circumstance in their Speeches and Actions is with great Justness
and Delicacy adapted to the Persons who speak and act. As the Poet very
much excels in this Consistency of his Characters, I shall beg Leave to
consider several Passages of the Second Book in this Light. That
superior Greatness and Mock-Majesty, which is ascribed to the Prince of
the fallen Angels, is admirably preserved in the Beginning of this Book.
His opening and closing the Debate; his taking on himself that great
Enterprize at the Thought of which the whole Infernal Assembly trembled;
his encountering the hideous Phantom who guarded the Gates of Hell, and
appeared to him in all his Terrors, are Instances of that proud and
daring Mind which could not brook Submission even to Omnipotence.
Satan was now at hand, and from his Seat
The Monster moving onward came as fast
With horrid strides, Hell trembled as he strode,
Th' undaunted Fiend what this might be admir'd,
Admired, not fear'd—
The same Boldness and Intrepidity of Behaviour discovers it self in the
several Adventures which he meets with during his Passage through the
Regions of unformed Matter, and particularly in his Address to those
tremendous Powers who are described as presiding over it.
The Part of Moloch is likewise in all its Circumstances full of that
Fire and Fury which distinguish this Spirit from the rest of the fallen
Angels. He is described in the first Book as besmeared with the Blood of
Human Sacrifices, and delighted with the Tears of Parents and the Cries
of Children. In the Second Book he is marked out as the fiercest Spirit
that fought in Heaven: and if we consider the Figure which he makes in
the Sixth Book, where the Battle of the Angels is described, we find it
every way answerable to the same furious enraged Character.
—Where the might of Gabriel fought,
And with fierce Ensigns pierc'd the deep array
Of Moloc, furious King, who him defy'd,
And at his chariot wheels to drag him bound
Threatened, nor from the Holy one of Heav'n
Refrain'd his tongue blasphemous; but anon
Down cloven to the waste, with shatter'd arms
And uncouth pain fled bellowing.—
It may be worth while to observe, that Milton has represented this
violent impetuous Spirit, who is hurried only by such precipitate
Passions, as the first that rises in that Assembly, to give his Opinion
upon their present Posture of Affairs. Accordingly he declares himself
abruptly for War, and appears incensed at his Companions, for losing so
much Time as even to deliberate upon it. All his Sentiments are Rash,
Audacious and Desperate. Such is that of arming themselves with their
Tortures, and turning their Punishments upon him who inflicted them.
—No, let us rather chuse,
Arm'd with Hell flames and fury, all at once
O'er Heavens high tow'rs to force resistless way,
Turning our tortures into horrid arms
Against the Torturer; when to meet the Noise
Of his almighty Engine he shall hear
Infernal Thunder, and for Lightning see
Black fire and horror shot with equal rage
Among his Angels; and his throne it self
Mixt with Tartarean Sulphur, and strange Fire,
His own invented Torments—
His preferring Annihilation to Shame or Misery, is also highly suitable
to his Character; as the Comfort he draws from their disturbing the
Peace of Heaven, that if it be not Victory it is Revenge, is a Sentiment
truly Diabolical, and becoming the Bitterness of this implacable Spirit.
Belial is described in the first Book, as the Idol of the Lewd and
Luxurious. He is in the Second Book, pursuant to that Description,
characterised as timorous and slothful; and if we look in the Sixth
Book, we find him celebrated in the Battel of Angels for nothing but
that scoffing Speech which he makes to Satan, on their supposed
Advantage over the Enemy. As his Appearance is uniform, and of a Piece,
in these three several Views, we find his Sentiments in the Infernal
Assembly every way conformable to his Character. Such are his
Apprehensions of a second Battel, his Horrors of Annihilation, his
preferring to be miserable rather than not to be. I need not observe,
that the Contrast of Thought in this Speech, and that which precedes it,
gives an agreeable Variety to the Debate.
Mammon's Character is so fully drawn in the First Book, that the Poet
adds nothing to it in the Second. We were before told, that he was the
first who taught Mankind to ransack the Earth for Gold and Silver, and
that he was the Architect of Pandæmonium, or the Infernal Place, where
the Evil Spirits were to meet in Council. His Speech in this Book is
every way suitable to so depraved a Character. How proper is that
Reflection, of their being unable to taste the Happiness of Heaven were
they actually there, in the Mouth of one, who while he was in Heaven, is
said to have had his Mind dazled with the outward Pomps and Glories of
the Place, and to have been more intent on the Riches of the Pavement,
than on the Beatifick Vision. I shall also leave the Reader to judge how
agreeable the following Sentiments are to the same Character.
—This deep World
Of Darkness do we dread? How oft amidst
Thick cloud and dark doth Heav'ns all-ruling Sire
Chuse to reside, his Glory unobscured,
And with the Majesty of Darkness round
Covers his Throne; from whence deep Thunders roar
Mustering their Rage, and Heav'n resembles Hell?
As he our Darkness, cannot we his Light
Imitate when we please? This desart Soil
Wants not her hidden Lustre, Gems and Gold;
Nor want we Skill or Art, from whence to raise
Magnificence; and what can Heav'n shew more?
Beelzebub, who is reckoned the second in Dignity that fell, and is, in
the First Book, the second that awakens out of the Trance, and confers
with Satan upon the Situation of their Affairs, maintains his Rank in
the Book now before us. There is a wonderful Majesty described in his
rising up to speak. He acts as a kind of Moderator between the two
opposite Parties, and proposes a third Undertaking, which the whole
Assembly gives into. The Motion he makes of detaching one of their Body
in search of a new World is grounded upon a Project devised by Satan,
and cursorily proposed by him in the following Lines of the first Book.
Space may produce new Worlds, whereof so rife
There went a Fame in Heav'n, that he erelong
Intended to create, and therein plant
A Generation, whom his choice Regard
Should favour equal to the Sons of Heaven:
Thither, if but to pry, shall be perhaps
Our first Eruption, thither or elsewhere:
For this Infernal Pit shall never hold
Celestial Spirits in Bondage, nor th' Abyss
Long under Darkness cover. But these Thoughts
Full Counsel must mature:—
It is on this Project that Beelzebub grounds his Proposal.
—What if we find
Some easier Enterprise? There is a Place
(If ancient and prophetick Fame in Heav'n
Err not) another World, the happy Seat
Of some new Race call'd Man, about this Time
To be created like to us, though less
In Power and Excellence, but favoured more
Of him who rules above; so was his Will
Pronounc'd among the Gods, and by an Oath,
That shook Heav'n's whole Circumference, confirm'd.
The Reader may observe how just it was not to omit in the First Book the
Project upon which the whole Poem turns: As also that the Prince of the
fallen Angels was the only proper Person to give it Birth, and that the
next to him in Dignity was the fittest to second and support it.
There is besides, I think, something wonderfully Beautiful, and very apt
to affect the Reader's Imagination in this ancient Prophecy or Report in
Heaven, concerning the Creation of Man. Nothing could shew more the
Dignity of the Species, than this Tradition which ran of them before
their Existence. They are represented to have been the Talk of Heaven,
before they were created. Virgil, in compliment to the Roman
Commonwealth, makes the Heroes of it appear in their State of
Pre-existence; but Milton does a far greater Honour to Man-kind in
general, as he gives us a Glimpse of them even before they are in Being.
The rising of this great Assembly is described in a very Sublime and
Poetical Manner.
Their rising all at once was as the Sound
Of Thunder heard remote—
The Diversions of the fallen Angels, with the particular Account of
their Place of Habitation, are described with great Pregnancy of
Thought, and Copiousness of Invention. The Diversions are every way
suitable to Beings who had nothing left them but Strength and Knowledge
misapplied. Such are their Contentions at the Race, and in Feats of
Arms, with their Entertainment in the following Lines.
Others with vast Typhæan rage more fell
Rend up both Rocks and Hills, and ride the Air
In Whirlwind; Hell scarce holds the wild Uproar.
Their Musick is employed in celebrating their own criminal Exploits, and
their Discourse in sounding the unfathomable Depths of Fate, Free-will
and Fore-knowledge.
The several Circumstances in the Description of Hell are finely
imagined; as the four Rivers which disgorge themselves into the Sea of
Fire, the Extreams of Cold and Heat, and the River of Oblivion. The
monstrous Animals produced in that Infernal World are represented by a
single Line, which gives us a more horrid Idea of them, than a much
longer Description would have done.
—Nature breeds,
Perverse, all monstrous, all prodigious Things,
Abominable, inutterable, and worse
Than Fables yet have feign'd, or Fear conceiv'd,
Gorgon's, and Hydra's, and Chimera's dire.
This Episode of the fallen Spirits, and their Place of Habitation, comes
in very happily to unbend the Mind of the Reader from its Attention to
the Debate. An ordinary Poet would indeed have spun out so many
Circumstances to a great Length, and by that means have weakned, instead
of illustrated, the principal Fable.
The Flight of Satan to the Gates of Hell is finely imaged. I have
already declared my Opinion of the Allegory concerning Sin and Death,
which is however a very finished Piece in its kind, when it is not
considered as a Part of an Epic Poem. The Genealogy of the several
Persons is contrived with great Delicacy. Sin is the Daughter of Satan,
and Death the Offspring of Sin. The incestuous Mixture between Sin and
Death produces those Monsters and Hell-hounds which from time to time
enter into their Mother, and tear the Bowels of her who gave them Birth.
These are the Terrors of an evil Conscience, and the proper Fruits of
Sin, which naturally rise from the Apprehensions of Death. This last
beautiful Moral is, I think, clearly intimated in the Speech of Sin,
where complaining of this her dreadful Issue, she adds,
Before mine Eyes in Opposition sits
Grim Death my Son and Foe, who sets them on,
And me his Parent would full soon devour
For want of other Prey, but that he knows
His End with mine involv'd—
I need not mention to the Reader the beautiful Circumstance in the last
Part of this Quotation. He will likewise observe how naturally the three
Persons concerned in this Allegory are tempted by one common Interest to
enter into a Confederacy together, and how properly Sin is made the
Portress of Hell, and the only Being that can open the Gates to that
World of Tortures.
The descriptive Part of this Allegory is likewise very strong, and full
of Sublime Ideas. The Figure of Death,
the Regal Crown upon his Head,
his Menace of Satan, his advancing to the Combat, the Outcry at his
Birth, are Circumstances too noble to be past over in Silence, and
extreamly suitable to this King of Terrors. I need not mention the
Justness of Thought which is observed in the Generation of these several
Symbolical Persons; that Sin was produced upon the first Revolt of
Satan, that Death appear'd soon after he was cast into Hell, and that
the Terrors of Conscience were conceived at the Gate of this Place of
Torments. The Description of the Gates is very poetical, as the opening
of them is full of Milton's Spirit.
—On a sudden open fly
With impetuous Recoil and jarring Sound
Th' infernal Doors, and on their Hinges grate
Harsh Thunder, that the lowest Bottom shook
Of Erebus. She open'd, but to shut
Excell'd her Pow'r; the Gates wide open stood,
That with extended Wings a banner'd Host
Under spread Ensigns marching might pass through
With Horse and Chariots rank'd in loose Array;
So wide they stood, and like a Furnace Mouth
Cast forth redounding Smoak and ruddy Flame.
In Satan's Voyage through the Chaos there are several Imaginary Persons
described, as residing in that immense Waste of Matter. This may perhaps
be conformable to the Taste of those Criticks who are pleased with
nothing in a Poet which has not Life and Manners ascribed to it; but for
my own Part, I am pleased most with those Passages in this Description
which carry in them a greater Measure of Probability, and are such as
might possibly have happened. Of this kind is his first mounting in the
Smoke that rises from the Infernal Pit, his falling into a Cloud of
Nitre, and the like combustible Materials, that by their Explosion still
hurried him forward in his Voyage; his springing upward like a Pyramid
of Fire, with his laborious Passage through that Confusion of Elements
which the Poet calls
The Womb of Nature, and perhaps her Grave.
The Glimmering Light which shot into the Chaos from the utmost Verge of
the Creation, with the distant discovery of the Earth that hung close by
the Moon, are wonderfully Beautiful and Poetical.
L.
Contents
|
Monday, February 25, 1712 |
Steele |
Connubio Jungam stabili—
Virg.

Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a certain young Woman that love a certain young Man very
heartily; and my Father and Mother were for it a great while, but now
they say I can do better, but I think I cannot. They bid me love him,
and I cannot unlove him. What must I do? speak quickly.
Biddy Dow-bake.
Dear
Spec,
Feb. 19, 1712.
'I have lov'd a Lady entirely for this Year and Half, tho' for a great
Part of the Time (which has contributed not a little to my Pain) I
have been debarred the Liberty of conversing with her. The Grounds of
our Difference was this; that when we had enquired into each other's
Circumstances, we found that at our first setting out into the World,
we should owe five hundred Pounds more than her Fortune would pay off.
My Estate is seven hundred Pounds a Year, besides the benefit of
Tin-Mines. Now, dear
Spec, upon this State of the Case, and the Lady's
positive Declaration that there is still no other Objection, I beg
you'll not fail to insert this, with your Opinion as soon as possible,
whether this ought to be esteemed a just Cause or Impediment why we
should not be join'd, and you will for ever oblige
Yours sincerely,
Dick Lovesick.
P. S. Sir, if I marry this Lady by the Assistance of your Opinion, you
may expect a Favour for it.
Mr.
Spectator,
I have the misfortune to be one of those unhappy Men who are
distinguished by the Name of discarded Lovers; but I am the less
mortified at my Disgrace, because the young Lady is one of those
Creatures who set up for Negligence of Men, are forsooth the most
rigidly Virtuous in the World, and yet their Nicety will permit them,
at the Command of Parents, to go to Bed to the most utter Stranger
that can be proposed to them. As to me my self, I was introduced by
the Father of my Mistress; but find I owe my being at first received
to a Comparison of my Estate with that of a former Lover, and that I
am now in like manner turned off, to give Way to an humble Servant
still richer than I am. What makes this Treatment the more extravagant
is, that the young Lady is in the Management of this way of Fraud, and
obeys her Father's Orders on these Occasions without any Manner of
Reluctance, and does it with the same Air that one of your Men of the
World would signifie the Necessity of Affairs for turning another out
of Office. When I came home last Night I found this Letter from my
Mistress.
Sir,
I hope you will not think it is any manner of Disrespect to your
Person or Merit, that the intended Nuptials between us are
interrupted. My Father says he has a much better Offer for me than
you can make, and has ordered me to break off the Treaty between us.
If it had proceeded, I should have behaved my self with all suitable
Regard to you, but as it is, I beg we may be Strangers for the
Future. Adieu.
Lydia.
This great Indifference on this Subject, and the mercenary Motives for
making Alliances, is what I think lies naturally before you, and I beg
of you to give me your Thoughts upon it. My Answer to Lydia was as
follows, which I hope you will approve; for you are to know the
Woman's Family affect a wonderful Ease on these Occasions, tho' they
expect it should be painfully received on the Man's Side.
Madam,
"I have received yours, and knew the Prudence of your House so well,
that I always took Care to be ready to obey your Commands, tho' they
should be to see you no more. Pray give my Service to all the good
Family.
Adieu,
The Opera Subscription is full.
Clitophon."
Memorandum. The Censor of Marriage to consider this Letter, and report
the common Usages on such Treaties, with how many Pounds or Acres are
generally esteemed sufficient Reason for preferring a new to an old
Pretender; with his Opinion what is proper to be determined in such
Cases for the future.
Mr. Spectator,
There is an elderly Person, lately left off Business and settled in
our Town, in order, as he thinks, to retire from the World; but he has
brought with him such an Inclination to Talebearing, that he disturbs
both himself and all our Neighbourhood. Notwithstanding this Frailty,
the honest Gentleman is so happy as to have no Enemy: At the same time
he has not one Friend who will venture to acquaint him with his
Weakness. It is not to be doubted but if this Failing were set in a
proper Light, he would quickly perceive the Indecency and evil
Consequences of it. Now, Sir, this being an Infirmity which I hope may
be corrected, and knowing that he pays much Deference to you, I beg
that when you are at Leisure to give us a Speculation on Gossiping,
you would think of my Neighbour: You will hereby oblige several who
will be glad to find a Reformation in their gray-hair'd Friend: And
how becoming will it be for him, instead of pouring forth Words at all
Adventures to set a Watch before the Door of his Mouth, to refrain his
Tongue, to check its Impetuosity, and guard against the Sallies of
that little, pert, forward, busie Person; which, under a sober
Conduct, might prove a useful Member of a Society. In Compliance with
whose Intimations, I have taken the Liberty to make this Address to
you.
I am, Sir,
Your most obscure Servant
Philanthropos.
Mr. Spectator,
Feb. 16, 1712.
'This is to Petition you in Behalf of my self and many more of your
gentle Readers, that at any time when you have private Reasons against
letting us know what you think your self, you would be pleased to
pardon us such Letters of your Correspondents as seem to be of no use
but to the Printer.
'It is further our humble Request, that you would substitute
Advertisements in the Place of such Epistles; and that in order
hereunto Mr. Buckley may be authorized to take up of your zealous
Friend Mr. Charles Lillie, any Quantity of Words he shall from time to
time have occasion for.
'The many useful parts of Knowledge which may be communicated to the
Publick this Way, will, we hope, be a Consideration in favour of your
Petitioners.'
And your Petitioners, &c.
Note
, That particular Regard be had to this Petition; and the Papers
marked Letter R may be carefully examined for the future
.
T.
R. is one of Steele's signatures, but he had not used it
since [Volume 1 link:
] for August 3, 1711, every paper of his since that date
having been marked with a T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, February 26, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec Veneris pharetris macer est; aut lampade fervet:
Inde faces ardent, veniunt a dote sagittæ.
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator,
'I am amazed that among all the Variety of Characters, with which you
have enriched your Speculations, you have never given us a Picture of
those audacious young Fellows among us, who commonly go by the Name of
Fortune-Stealers. You must know, Sir, I am one who live in a continual
Apprehension of this sort of People that lye in wait, Day and Night,
for our Children, and may be considered as a kind of Kidnappers within
the Law. I am the Father of a Young Heiress, whom I begin to look upon
as Marriageable, and who has looked upon her self as such for above
these Six Years. She is now in the Eighteenth Year of her Age. The
Fortune-hunters have already cast their Eyes upon her, and take care
to plant themselves in her View whenever she appears in any Publick
Assembly. I have my self caught a young Jackanapes with a pair of
Silver Fringed Gloves, in the very Fact. You must know, Sir, I have
kept her as a Prisoner of State ever since she was in her Teens. Her
Chamber Windows are cross-barred, she is not permitted to go out of
the House but with her Keeper, who is a stay'd Relation of my own; I
have likewise forbid her the use of Pen and Ink for this Twelve-Month
last past, and do not suffer a Ban-box to be carried into her Room
before it has been searched. Notwithstanding these Precautions, I am
at my Wits End for fear of any sudden Surprize. There were, two or
three Nights ago, some Fiddles heard in the Street, which I am afraid
portend me no Good; not to mention a tall Irish-Man, that has been
seen walking before my House more than once this Winter. My Kinswoman
likewise informs me, that the Girl has talked to her twice or thrice
of a Gentleman in a Fair Wig, and that she loves to go to Church more
than ever she did in her Life. She gave me the slip about a Week ago,
upon which my whole House was in Alarm. I immediately dispatched a Hue
and Cry after her to the Change, to her Mantua-maker, and to the young
Ladies that Visit her; but after above an Hour's search she returned
of herself, having been taking a Walk, as she told me, by Rosamond's
Pond. I have hereupon turned off her Woman, doubled her Guards, and
given new Instructions to my Relation, who, to give her her due, keeps
a watchful Eye over all her Motions. This, Sir, keeps me in a
perpetual Anxiety, and makes me very often watch when my Daughter
sleeps, as I am afraid she is even with me in her turn. Now, Sir, what
I would desire of you is, to represent to this fluttering Tribe of
young Fellows, who are for making their Fortunes by these indirect
Means, that stealing a Man's Daughter for the sake of her Portion, is
but a kind of Tolerated Robbery; and that they make but a poor Amends
to the Father, whom they plunder after this Manner, by going to bed
with his Child. Dear Sir, be speedy in your Thoughts on this Subject,
that, if possible, they may appear before the Disbanding of the Army.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Tim. Watchwell.
Themistocles, the great Athenian General, being asked whether he would
chuse to marry his Daughter to an indigent Man of Merit, or to a
worthless Man of an Estate, replied, That he should prefer a Man without
an Estate, to an Estate without a Man. The worst of it is, our Modern
Fortune-Hunters are those who turn their Heads that way, because they
are good for nothing else. If a young Fellow finds he can make nothing
of Cook and Littleton, he provides himself with a Ladder of Ropes, and
by that means very often enters upon the Premises.
The same Art of Scaling has likewise been practised with good Success by
many military Ingineers. Stratagems of this nature make Parts and
Industry superfluous, and cut short the way to Riches.
Nor is Vanity a less Motive than Idleness to this kind of Mercenary
Pursuit. A Fop who admires his Person in a Glass, soon enters into a
Resolution of making his Fortune by it, not questioning but every Woman
that falls in his way will do him as much Justice as he does himself.
When an Heiress sees a Man throwing particular Graces into his Ogle, or
talking loud within her Hearing, she ought to look to her self; but if
withal she observes a pair of Red-Heels, a Patch, or any other
Particularity in his Dress, she cannot take too much care of her Person.
These are Baits not to be trifled with, Charms that have done a world of
Execution, and made their way into Hearts which have been thought
impregnable. The Force of a Man with these Qualifications is so well
known, that I am credibly informed there are several Female Undertakers
about the Change, who upon the Arrival of a likely Man out of a
neighbouring Kingdom, will furnish him with proper Dress from Head to
Foot, to be paid for at a double Price on the Day of Marriage.
We must however distinguish between Fortune-Hunters and
Fortune-Stealers. The first are those assiduous Gentlemen who employ
their whole Lives in the Chace, without ever coming at the Quarry.
Suffenus has combed and powdered at the Ladies for thirty Years
together, and taken his Stand in a Side Box, 'till he has grown wrinkled
under their Eyes. He is now laying the same Snares for the present
Generation of Beauties, which he practised on their Mothers. Cottilus,
after having made his Applications to more than you meet with in Mr.
Cowley's Ballad of Mistresses, was at last smitten with a City Lady of
£20,000 Sterling: but died of old Age before he could bring Matters to
bear. Nor must I here omit my worthy Friend Mr.
Honeycomb
, who has often
told us in the Club, that for twenty years successively, upon the death
of a Childless rich Man, he immediately drew on his Boots, called for
his Horse, and made up to the Widow.
he is rallied upon his ill
Success,
Will
, with his usual Gaiety tells us, that he always found
her
Pre-engaged.
Widows are indeed the great Game of your Fortune-Hunters. There is
scarce a young Fellow in the Town of six Foot high, that has not passed
in Review before one or other of these wealthy Relicts. Hudibrass's
Cupid,
—took his Stand
Upon a Widow's Jointure Land
2,
is daily employed in throwing Darts, and kindling Flames. But as for
Widows, they are such a Subtle Generation of People, that they may be
left to their own Conduct; or if they make a false Step in it, they are
answerable for it to no Body but themselves. The young innocent
Creatures who have no Knowledge and Experience of the World, are those
whose Safety I would principally consult in this Speculation. The
stealing of such an one should, in my Opinion, be as punishable as a
Rape. Where there is no Judgment there is no Choice; and why the
inveigling a Woman before she is come to Years of Discretion, should not
be as Criminal as the seducing of her before she is ten Years old, I am
at a Loss to comprehend.
L.
them
Hudibras, Part I., Canto 3, II. 310-11.
Contents
|
Wednesday, February 27, 1712 |
Steele |
Quod huic Officium, quæ laus, quod Decus erit tanti, quod adipisci cum
colore Corporis velit, qui dolorem summum malum sibi persuaserit? Quam
porro quis ignominiam, quam turpitudinem non pertulerit, ut effugiat
dolorem, si id summum malum esse decrevit?
Tull.
de Dolore tolerando.
It is a very melancholy Reflection, that Men are usually so weak, that
it is absolutely necessary for them to know Sorrow and Pain to be in
their right Senses. Prosperous People (for Happy there are none) are
hurried away with a fond Sense of their present Condition, and
thoughtless of the Mutability of Fortune: Fortune is a Term which we
must use in such Discourses as these, for what is wrought by the unseen
Hand of the Disposer of all Things. But methinks the Disposition of a
Mind which is truly great, is that which makes Misfortunes and Sorrows
little when they befall our selves, great and lamentable when they
befall other Men. The most unpardonable Malefactor in the World going to
his Death and bearing it with Composure, would win the Pity of those who
should behold him; and this not because his Calamity is deplorable, but
because he seems himself not to deplore it: We suffer for him who is
less sensible of his own Misery, and are inclined to despise him who
sinks under the Weight of his Distresses. On the other hand, without any
Touch of Envy, a temperate and well-govern'd Mind looks down on such as
are exalted with Success, with a certain Shame for the Imbecility of
human Nature, that can so far forget how liable it is to Calamity, as to
grow giddy with only the Suspence of Sorrow, which is the Portion of all
Men. He therefore who turns his Face from the unhappy Man, who will not
look again when his Eye is cast upon modest Sorrow, who shuns Affliction
like a Contagion, does but pamper himself up for a Sacrifice, and
contract in himself a greater Aptitude to Misery by attempting to escape
it. A Gentleman where I happened to be last Night, fell into a Discourse
which I thought shewed a good Discerning in him: He took Notice that
whenever Men have looked into their Heart for the Idea of true
Excellency in human Nature, they have found it to consist in Suffering
after a right Manner and with a good Grace. Heroes are always drawn
bearing Sorrows, struggling with Adversities, undergoing all kinds of
Hardships, and having in the Service of Mankind a kind of Appetite to
Difficulties and Dangers. The Gentleman went on to observe, that it is
from this secret Sense of the high Merit which there is in Patience
under Calamities, that the Writers of Romances, when they attempt to
furnish out Characters of the highest Excellence, ransack Nature for
things terrible; they raise a new Creation of Monsters, Dragons, and
Giants: Where the Danger ends, the Hero ceases; when he won an Empire,
or gained his Mistress, the rest of his Story is not worth relating. My
Friend carried his Discourse so far as to say, that it was for higher
Beings than Men to join Happiness and Greatness in the same Idea; but
that in our Condition we have no Conception of superlative Excellence,
or Heroism, but as it is surrounded with a Shade of Distress.
It is certainly the proper Education we should give our selves, to be
prepared for the ill Events and Accidents we are to meet with in a Life
sentenced to be a Scene of Sorrow: But instead of this Expectation, we
soften our selves with Prospects of constant Delight, and destroy in our
Minds the Seeds of Fortitude and Virtue, which should support us in
Hours of Anguish. The constant Pursuit of Pleasure has in it something
insolent and improper for our Being. There is a pretty sober Liveliness
in the Ode of
Horace
to
Delius
, where he tells him, loud Mirth, or
immoderate Sorrow, Inequality of Behaviour either in Prosperity or
Adversity, are alike ungraceful in Man that is born to die. Moderation
in both Circumstances is peculiar to generous Minds: Men of that Sort
ever taste the Gratifications of Health, and all other Advantages of
Life, as if they were liable to part with them, and when bereft of them,
resign them with a Greatness of Mind which shews they know their Value
and Duration. The Contempt of Pleasure is a certain Preparatory for the
Contempt of Pain: Without this, the Mind is as it were taken suddenly by
any unforeseen Event; but he that has always, during Health and
Prosperity, been abstinent in his Satisfactions, enjoys, in the worst of
Difficulties, the Reflection, that his Anguish is not aggravated with
the Comparison of past Pleasures which upbraid his present Condition.
Tully
tells us a Story after
Pompey
, which gives us a good Taste of the
pleasant Manner the Men of Wit and Philosophy had in old Times of
alleviating the Distresses of Life by the Force of Reason and
Philosophy.
Pompey
, when he came to
Rhodes
, had a Curiosity to visit the
famous Philosopher
Possidonius
; but finding him in his sick Bed, he
bewailed the Misfortune that he should not hear a Discourse from him:
But you may, answered Possidonius; and immediately entered into the
Point of Stoical Philosophy, which says Pain is not an Evil. During the
Discourse, upon every Puncture he felt from his Distemper, he smiled and
cried out, Pain, Pain, be as impertinent and troublesome as you please,
I shall never own that thou art an Evil.
Mr. Spectator,
Having seen in several of your Papers, a Concern for the Honour of the
Clergy, and their doing every thing as becomes their Character, and
particularly performing the publick Service with a due Zeal and
Devotion; I am the more encouraged to lay before them, by your Means,
several Expressions used by some of them in their Prayers before
Sermon, which I am not well satisfied in: As their giving some Titles
and Epithets to great Men, which are indeed due to them in their
several Ranks and Stations, but not properly used, I think, in our
Prayers. Is it not Contradiction to say, Illustrious, Right, Reverend,
and Right Honourable poor Sinners? These Distinctions are suited only
to our State here, and have no place in Heaven:
We see they are
omitted in the Liturgy; which I think the Clergy should take for their
Pattern in their own Forms of
Devotion1. There is another
Expression which I would not mention, but that I have heard it several
times before a learned Congregation, to bring in the last Petition of
the Prayer in these Words,
O let not the Lord be angry and I will speak
but this once; as if there was no Difference between
Abraham's
interceding for
Sodom, for which he had no Warrant as we can find, and
our asking those Things which we are required to pray for; they would
therefore have much more Reason to fear his Anger if they did not make
such Petitions to him. There is another pretty Fancy: When a young Man
has a Mind to let us know who gave him his Scarf, he speaks a
Parenthesis to the Almighty, Bless,
as I am in Duty bound to pray, the
right honourable the Countess; is not that as much as to say, Bless
her, for thou knowest I am her Chaplain?
Your humble Servant,
J. O.
T.
Devotion. Another Expression which I take to be improper,
is this, the whole Race of Mankind, when they pray for all Men; for Race
signifies Lineage or Descent; and if the Race of Mankind may be used for
the present generation, (though I think not very fitly) the whole Race
takes in all from the Beginning to the End of the World. I don't
remember to have met with that Expression in their sense anywhere but in
the old Version of Psal. 14, which those Men, I suppose, have but little
Esteem for. And some, when they have prayed for all Schools and Nurserys
of good Learning and True Religion, especially the two Universities, add
these Words, Grant that from them and all other Places dedicated to thy
Worship and Service, may come forth such Persons. But what do they mean
by all other Places? It seems to me that this is either a Tautology, as
being the same with all Schools and Nurserys before expressed, or else
it runs too far; for there are general Places dedicated to the Divine
Service which cannot properly be intended here.
Contents
|
Thursday, February 28, 1712 |
Budgell |
Exigite ut mores teneros ceu pollice ducat,
Ut si quis cerâ vultum facit.
Juv.

I shall give the following Letter no other Recommendation, than by
telling my Readers that it comes from the same Hand with that of last
Thursday
.
Sir,
'I send you, according to my Promise, some farther Thoughts on the
Education of Youth, in which I intend to discuss that famous Question,
whether the Education at a Publick School, or under a private Tutor,
is to be preferred?
'As some of the greatest Men in most Ages have been of very different
Opinions in this Matter, i shall give a short Account of what i think
may be best urged on both sides, and afterwards leave every Person to
determine for himself.
'It is certain from
Suetonius, that the Romans thought the Education
of their Children a business properly belonging to the Parents
themselves; and
Plutarch, in the
Life of Marcus Cato, tells us, that
as soon as his Son was capable of Learning,
Cato would suffer no Body
to Teach him but himself, tho' he had a Servant named
Chilo, who was
an excellent Grammarian, and who taught a great many other Youths.
'On the contrary, the
Greeks seemed more inclined to Publick Schools
and Seminaries.
' A private Education promises in the first place Virtue and
Good-Breeding; a publick School Manly Assurance, and an early
Knowledge in the Ways of the World.
'
Mr.
Locke in his celebrated Treatise of
Education1, confesses
that there are Inconveniencies to be feared on both sides;
If, says
he,
I keep my Son at Home, he is in danger of becoming my young
Master; If I send him Abroad, it is scarce possible to keep him from
the reigning Contagion of Rudeness and Vice. He will perhaps be more
Innocent at Home, but more ignorant of the World, and more sheepish
when he comes Abroad. However, as this learned Author asserts, That
Virtue is much more difficult to be attained than Knowledge of the
World; and that Vice is a more stubborn, as well as a more dangerous
Fault than Sheepishness, he is altogether for a private Education; and
the more so, because he does not see why a Youth, with right
Management, might not attain the same Assurance in his Father's House,
as at a publick School. To this end he advises Parents to accustom
their Sons to whatever strange Faces come to the House; to take them
with them when they Visit their Neighbours, and to engage them in
Conversation with Men of Parts and Breeding.
'It may be objected to this Method, that Conversation is not the only
thing necessary, but that unless it be a Conversation with such as are
in some measure their Equals in Parts and Years, there can be no room
for Emulation, Contention, and several of the most lively Passions of
the Mind; which, without being sometimes moved by these means, may
possibly contract a Dulness and Insensibility.
'One of the greatest Writers our Nation ever produced observes, That a
Boy who forms Parties, and makes himself Popular in a School or a
College, would act the same Part with equal ease in a Senate or a
Privy Council; and Mr.
Osborn speaking like a Man versed in the Ways
of the World, affirms, that the well laying and carrying on of a design to rob an
Orchard, trains up a Youth insensibly to Caution, Secrecy and
Circumspection, and fits him for Matters of greater Importance.
'In short, a private Education seems the most natural Method for the
forming of a virtuous Man; a Publick Education for making a Man of
Business. The first would furnish out a good Subject for
Plato's
Republick, the latter a Member for a Community over-run with Artifice
and Corruption.
'It must however be confessed, that a Person at the head of a publick
School has sometimes so many Boys under his Direction, that it is
impossible he should extend a due proportion of his Care to each of
them. This is, however, in reality, the Fault of the Age, in which we
often see twenty Parents, who tho' each expects his Son should be made
a Scholar, are not contented altogether to make it worth while for any
Man of a liberal Education to take upon him the Care of their
Instruction.
'In our great Schools indeed this Fault has been of late Years
rectified, so that we have at present not only Ingenious Men for the
chief Masters, but such as have proper Ushers and Assistants under
them; I must nevertheless own, that for want of the same Encouragement
in the Country, we have many a promising Genius spoiled and abused in
those Seminaries.
'I am the more inclined to this Opinion, having my self experienced the
Usage of two Rural Masters, each of them very unfit for the Trust they
took upon them to discharge. The first imposed much more upon me than
my Parts, tho' none of the weakest, could endure; and used me
barbarously for not performing Impossibilities. The latter was of
quite another Temper; and a Boy, who would run upon his Errands, wash
his Coffee-pot, or ring the Bell, might have as little Conversation
with any of the Classicks as he thought fit. I have known a Lad at
this Place excused his Exercise for assisting the Cook-maid; and
remember a Neighbouring Gentleman's Son was among us five Years, most
of which time he employed in airing and watering our Master's grey
Pad. I scorned to Compound for my Faults, by doing any of these
Elegant Offices, and was accordingly the best Scholar, and the worst
used of any Boy in the School.
'I shall conclude this Discourse with an Advantage mentioned by
Quintilian, as accompanying a Publick way of Education, which I have
not yet taken notice of; namely, That we very often contract such
Friendships at School, as are a Service to us all the following Part
of our Lives.
'I shall give you, under this Head, a Story very well known to several
Persons, and which you may depend upon as a real Truth.
'Every one, who is acquainted with Westminster-School, knows that
there is a Curtain which used to be drawn a-cross the Room, to
separate the upper School from the lower. A Youth happened, by some
Mischance, to tear the above-mentioned Curtain:
The Severity of the
Master
2 was too well known for the Criminal to expect any Pardon for
such a Fault; so that the Boy, who was of a meek Temper, was terrified
to Death at the Thoughts of his Appearance, when his Friend, who sat
next to him, bad him be of good Cheer, for that he would take the
Fault on himself. He kept his word accordingly. As soon as they were
grown up to be Men the Civil War broke out, in which our two Friends
took the opposite Sides, one of them followed the Parliament, the
other the Royal Party.
'As their Tempers were different, the Youth, who had torn the Curtain,
endeavoured to raise himself on the Civil List, and the other, who had
born the Blame of it, on the Military: The first succeeded so well,
that he was in a short time made a Judge under the Protector. The
other was engaged in the unhappy Enterprize of Penruddock and Groves
in the West. I suppose, Sir, I need not acquaint you with the Event of
that Undertaking. Every one knows that the Royal Party was routed, and
all the Heads of them, among whom was the Curtain Champion, imprisoned
at Exeter. It happened to be his Friend's Lot at that time to go to
the Western Circuit: The Tryal of the Rebels, as they were then
called, was very short, and nothing now remained but to pass Sentence
on them; when the Judge hearing the Name of his old Friend, and
observing his Face more attentively, which he had not seen for many
Years, asked him, if he was not formerly a Westminster-Scholar; by the
Answer, he was soon convinced that it was his former generous Friend;
and, without saying any thing more at that time, made the best of his
Way to London, where employing all his Power and Interest with the
Protector, he saved his Friend from the Fate of his unhappy
Associates.
'
The Gentleman, whose Life was thus preserv'd by the Gratitude of his
School-Fellow, was afterwards the Father of a Son, whom he lived to
see promoted in the Church, and who still deservedly fills one of the
highest Stations in it
3.
X.
Some Thoughts concerning Education
, § 70. The references to
Suetonius and Plutarch's
Life of Cato
are from the preceding section.
Richard Busby; appointed in 1640.
The allusion is to Colonel Wake, father of Dr. William
Wake, who was Bishop of Lincoln when this paper was written, and because
in 1716 Archbishop of Canterbury. The trials of Penruddock and his
friends were in 1685.
Contents
|
Friday, February 29, 1712 |
Steele |
Tandem desine Matrem
Tempestiva sequi viro.
Hor.
Od. 23.

Feb. 7, 1711-12.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a young Man about eighteen Years of Age, and have been in Love
with a young Woman of the same Age about this half Year. I go to see
her six Days in the Week, but never could have the Happiness of being
with her alone. If any of her Friends are at home, she will see me in
their Company; but if they be not in the Way, she flies to her
Chamber. I can discover no Signs of her Aversion; but either a Fear of
falling into the Toils of Matrimony, or a childish Timidity, deprives
us of an Interview apart, and drives us upon the Difficulty of
languishing out our Lives in fruitless Expectation. Now, Mr.
Spectator, if you think us ripe for Œconomy, perswade the dear
Creature, that to pine away into Barrenness and Deformity under a
Mother's Shade, is not so honourable, nor does she appear so amiable,
as she would in full Bloom. [
There is a great deal left out before he
concludes] Mr.
Spectator,
Your humble Servant,
Bob Harmless.
If this Gentleman be really no more than Eighteen, I must do him the
Justice to say he is the most knowing Infant I have yet met with. He
does not, I fear, yet understand, that all he thinks of is another
Woman; therefore, till he has given a further Account of himself, the
young Lady is hereby directed to keep close to her Mother. The
Spectator
.
I cannot comply with the Request in Mr. Trott's Letter; but let it go
just as it came to my Hands, for being so familiar with the old
Gentleman, as rough as he is to him. Since Mr. Trott has an Ambition to
make him his Father-in-Law, he ought to treat him with more Respect;
besides, his Style to me might have been more distant than he has
thought fit to afford me: Moreover, his Mistress shall continue in her
Confinement, till he has found out which Word in his Letter is not
wrightly spelt.
Mr. Spectator,
I shall ever own my self your obliged humble Servant for the Advice
you gave me concerning my Dancing; which unluckily came too late: For,
as I said, I would not leave off Capering till I had your Opinion of
the Matter; was at our famous Assembly the Day before I received your
Papers, and there was observed by an old Gentleman, who was informed I
had a Respect for his Daughter; told me I was an insignificant little
Fellow, and said that for the future he would take Care of his Child;
so that he did not doubt but to crosse my amorous Inclinations. The
Lady is confined to her Chamber, and for my Part, am ready to hang my
self with the Thoughts that I have danced my self out of Favour with
her Father. I hope you will pardon the Trouble I give; but shall take
it for a mighty Favour, if you will give me a little more of your
Advice to put me in a write Way to cheat the old Dragon and obtain my
Mistress. I am once more,
Sir,
Your obliged humble Servant, John Trott.
York, Feb. 23, 1711-12.
Let me desire you to make what Alterations you please, and insert this
as soon as possible. Pardon Mistake by Haste.
I never do pardon Mistakes by Haste. The
Spectator
.
Feb. 27, 1711-12.
Sir,
Pray be so kind as to let me know what you esteem to be the chief
Qualification of a good Poet, especially of one who writes Plays; and
you will very much oblige,
Sir, Your very humble Servant, N. B.
To be a very well-bred Man. The
Spectator
.
Mr. Spectator,
You are to know that I am naturally Brave, and love Fighting as well
as any Man in England. This gallant Temper of mine makes me extremely
delighted with Battles on the Stage. I give you this Trouble to
complain to you, that Nicolini refused to gratifie me in that Part of
the Opera for which I have most Taste. I observe it's become a Custom,
that whenever any Gentlemen are particularly pleased with a Song, at
their crying out Encore or Altro Volto, the Performer is so obliging
as to sing it over again. I was at the Opera the last time Hydaspes
was performed. At that Part of it where the Heroe engages with the
Lion, the graceful Manner with which he put that terrible Monster to
Death gave me so great a Pleasure, and at the same time so just a
Sense of that Gentleman's Intrepidity and Conduct, that I could not
forbear desiring a Repetition of it, by crying out Altro Volto in a
very audible Voice; and my Friends flatter me, that I pronounced those
Words with a tolerable good Accent, considering that was but the third
Opera I had ever seen in my Life. Yet, notwithstanding all this, there
was so little Regard had to me, that the Lion was carried off, and
went to Bed, without being killed any more that Night. Now, Sir, pray
consider that I did not understand a Word of what Mr. Nicolini said to
this cruel Creature; besides, I have no Ear for Musick; so that during
the long Dispute between 'em, the whole Entertainment I had was from
my Eye; Why then have not I as much Right to have a graceful Action
repeated as another has a pleasing Sound, since he only hears as I
only see, and we neither of us know that there is any reasonable thing
a doing? Pray, Sir, settle the Business of this Claim in the Audience,
and let us know when we may cry Altro Volto, Anglicè, again, again,
for the Future. I am an Englishman, and expect some Reason or other to
be given me, and perhaps an ordinary one may serve; but I expect your
Answer.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Toby Rentfree.
Nov. 29.
Mr. Spectator,
You must give me Leave, amongst the rest of your Female
Correspondents, to address you about an Affair which has already given
you many a Speculation; and which, I know, I need not tell you have
had a very happy Influence over the adult Part of our Sex: But as many
of us are either too old to learn, or too obstinate in the Pursuit of
the Vanities which have been bred up with us from our Infancy, and all
of us quitting the Stage whilst you are prompting us to act our Part
well; you ought, methinks, rather to turn your Instructions for the
Benefit of that Part of our Sex, who are yet in their native
Innocence, and ignorant of the Vices and that Variety of Unhappinesses
that reign amongst us.
I must tell you, Mr. Spectator, that it is as much a Part of your
Office to oversee the Education of the female Part of the Nation, as
well as of the Male; and to convince the World you are not partial,
pray proceed to detect the Male Administration of Governesses as
successfully as you have exposed that of Pedagogues; and rescue our
Sex from the Prejudice and Tyranny of Education as well as that of
your own, who without your seasonable Interposition are like to
improve upon the Vices that are now in vogue.
I who know the Dignity of your Post, as Spectator, and the Authority a
skilful Eye ought to bear in the Female World, could not forbear
consulting you, and beg your Advice in so critical a Point, as is that
of the Education of young Gentlewomen. Having already provided myself
with a very convenient House in a good Air, I'm not without Hope but
that you will promote this generous Design. I must farther tell you,
Sir, that all who shall be committed to my Conduct, beside the usual
Accomplishments of the Needle, Dancing, and the French Tongue, shall
not fail to be your constant Readers. It is therefore my humble
Petition, that you will entertain the Town on this important Subject,
and so far oblige a Stranger, as to raise a Curiosity and Enquiry in
my Behalf, by publishing the following Advertisement.
I am, Sir,
Your constant Admirer,
M. W.
T.
Contents
The Boarding-School for young Gentlewomen, which was formerly kept on
Mile-End-Green, being laid down, there is now one set up almost opposite
to it at the two Golden-Balls, and much more convenient in every
Respect; where, beside the common Instructions given to young
Gentlewomen, they will be taught the whole Art of Paistrey and
Preserving, with whatever may render them accomplished. Those who please
to make Tryal of the Vigilance and Ability of the Persons concerned may
enquire at the two Golden-Balls on Mile-End-Green near Stepney, where
they will receive further Satisfaction.
This is to give Notice, that the Spectator has taken upon him to be
Visitant of all Boarding-Schools, where young Women are educated; and
designs to proceed in the said Office after the same Manner that the
Visitants of Colleges do in the two famous Universities of this Land.
All Lovers who write to the Spectator, are desired to forbear one
Expression which is in most of the Letters to him, either out of
Laziness, or want of Invention, and is true of not above two thousand
Women in the whole World; viz.
She has in her all that is valuable in
Woman.
|
Saturday, March 1, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec deus intersit, nisi dignus vindice nodus
Inciderit.
Hor.

advises a Poet to consider thoroughly the Nature and Force of his
Genius
.
Milton
seems to have known perfectly well, wherein his
Strength lay, and has therefore chosen a Subject entirely conformable to
those Talents, of which he was Master. As his Genius was wonderfully
turned to the Sublime, his Subject is the noblest that could have
entered into the Thoughts of Man. Every thing that is truly great and
astonishing, has a place in it. The whole System of the intellectual
World; the
Chaos
, and the Creation; Heaven, Earth and Hell; enter into
the Constitution of his Poem.
Having in the First and Second Books represented the Infernal World with
all its Horrors, the Thread of his Fable naturally leads him into the
opposite Regions of Bliss and Glory.
If
Milton's
Majesty forsakes him any where, it is in those Parts of his
Poem, where the Divine Persons are introduced as Speakers. One may, I
think, observe that the Author proceeds with a kind of Fear and
Trembling, whilst he describes the Sentiments of the Almighty. He dares
not give his Imagination its full Play, but chuses to confine himself to
such Thoughts as are drawn from the Books of the most Orthodox Divines,
and to such Expressions as may be met with in Scripture. The Beauties,
therefore, which we are to look for in these Speeches, are not of a
Poetical Nature, nor so proper to fill the Mind with Sentiments of
Grandeur, as with Thoughts of Devotion. The Passions, which they are
designed to raise, are a Divine Love and Religious Fear. The Particular
Beauty of the Speeches in the Third Book, consists in that Shortness and
Perspicuity of Style, in which the Poet has couched the greatest
Mysteries of Christianity, and drawn together, in a regular Scheme, the
whole Dispensation of Providence, with respect to Man. He has
represented all the abstruse Doctrines of Predestination, Free-Will and
Grace, as also the great Points of Incarnation and Redemption, (which
naturally grow up in a Poem that treats of the Fall of Man) with great
Energy of Expression, and in a clearer and stronger Light than I ever
met with in any other Writer. As these Points are dry in themselves to
the generality of Readers, the concise and clear manner in which he has
treated them, is very much to be admired, as is likewise that particular
Art which he has made use of in the interspersing of all those Graces of
Poetry, which the Subject was capable of receiving.
The Survey of the whole Creation, and of every thing that is transacted
in it, is a Prospect worthy of Omniscience; and as much above that, in
which
Virgil
has drawn his
Jupiter
, as the Christian Idea of the Supreme
Being is more Rational and Sublime than that of the Heathens. The
particular Objects on which he is described to have cast his Eye, are
represented in the most beautiful and lively Manner.
Now had th' Almighty Father from above,
(From the pure Empyrean where he sits
High thron'd above all height) bent down his Eye,
His own Works and their Works at once to view.
About him all the Sanctities of Heav'n
Stood thick as Stars, and from his Sight received
Beatitude past utt'rance: On his right
The radiant Image of his Glory sat,
His only Son. On earth he first beheld
Our two first Parents, yet the only two
Of Mankind, in the happy garden plac'd,
Reaping immortal fruits of Joy and Love;
Uninterrupted Joy, unrival'd Love
In blissful Solitude. He then surveyed
Hell and the Gulph between, and Satan there
Coasting the Wall of Heaven on this side Night,
In the dun air sublime; and ready now
To stoop with wearied wings, and willing feel
On the bare outside of this world, that seem'd
Firm land imbosom'd without firmament;
Uncertain which, in Ocean or in Air.
Him God beholding from his prospect high,
Wherein past, present, future he beholds,
Thus to his only Son foreseeing spake.
Satan's
Approach to the Confines of the Creation, is finely imaged in
the beginning of the Speech, which immediately follows. The Effects of
this Speech in the blessed Spirits, and in the Divine Person to whom it
was addressed, cannot but fill the Mind of the Reader with a secret
Pleasure and Complacency.
Thus while God spake, ambrosial fragrance fill'd
All Heav'n, and in the blessed Spirits elect
Sense of new Joy ineffable diffus'd.
Beyond compare the Son of God was seen
Most glorious, in him all his Father shone
Substantially expressed, and in his face
Divine Compassion visibly appeared,
Love without end, and without measure Grace.
I need not point out the Beauty of that Circumstance, wherein the whole
Host of Angels are represented as standing Mute; nor shew how proper the
Occasion was to produce such a Silence in Heaven. The Close of this
Divine Colloquy, with the Hymn of Angels that follows upon it, are so
wonderfully Beautiful and Poetical, that I should not forbear inserting
the whole Passage, if the Bounds of my Paper would give me leave.
No sooner had th' Almighty ceas'd, but all
The multitudes of Angels with a shout
(Loud as from numbers without number, sweet
As from blest Voices) utt'ring Joy, Heav'n rung
With Jubilee, and loud Hosanna's fill'd
Th' eternal regions; &c. &c.--
Satan's
Walk upon the Outside of the Universe, which, at a Distance,
appeared to him of a globular Form, but, upon his nearer Approach,
looked like an unbounded Plain, is natural and noble: As his Roaming
upon the Frontiers of the Creation between that Mass of Matter, which
was wrought into a World, and that shapeless unformed Heap of Materials,
which still lay in Chaos and Confusion, strikes the Imagination with
something astonishingly great and wild. I have before spoken of the
Limbo of Vanity,
which the Poet places upon this outermost Surface of
the Universe, and shall here explain my self more at large on that, and
other Parts of the Poem, which are of the same Shadowy Nature.
Aristotle
observes
, that the Fable of an Epic Poem should abound in
Circumstances that are both credible and astonishing; or as the
French
Criticks chuse to phrase it, the Fable should be filled with the
Probable and the Marvellous. This Rule is as fine and just as any in
Aristotle's
whole Art of Poetry.
If the Fable is only Probable, it differs nothing from a true History;
if it is only Marvellous, it is no better than a Romance. The great
Secret therefore of Heroic Poetry is to relate such Circumstances, as
may produce in the Reader at the same time both Belief and Astonishment.
This is brought to pass in a well-chosen Fable, by the Account of such
things as have really happened, or at least of such things as have
happened according to the received Opinions of Mankind. Milton's Fable
is a Masterpiece of this Nature; as the War in Heaven, the Condition of
the fallen Angels, the State of Innocence, and Temptation of the
Serpent, and the Fall of Man, though they are very astonishing in
themselves, are not only credible, but actual Points of Faith.
The next Method of reconciling Miracles with Credibility, is by a happy
Invention of the Poet; as in particular, when he introduces Agents of a
superior Nature, who are capable of effecting what is wonderful, and
what is not to be met with in the ordinary course of things.
Ulysses's
Ship being turned into a Rock, and
Æneas's
Fleet into a Shoal of Water
Nymphs; though they are very surprising Accidents, are nevertheless
probable, when we are told that they were the Gods who thus transformed
them. It is this kind of Machinery which fills the Poems both of
Homer
and
Virgil
with such Circumstances as are wonderful, but not impossible,
and so frequently produce in the Reader the most pleasing Passion that
can rise in the Mind of Man, which is Admiration. If there be any
Instance in the
Æneid
liable to Exception upon this Account, it is in
the Beginning of the Third Book, where
Æneas
is represented as tearing
up the Myrtle that dropped Blood. To qualifie this wonderful
Circumstance,
Polydorus
tells a Story from the Root of the Myrtle, that
the barbarous Inhabitants of the Country having pierced him with Spears
and Arrows, the Wood which was left in his Body took Root in his Wounds,
and gave Birth to that bleeding Tree. This Circumstance seems to have
the Marvellous without the Probable, because it is represented as
proceeding from Natural Causes, without the Interposition of any God, or
other Supernatural Power capable of producing it. The Spears and Arrows
grow of themselves, without so much as the Modern Help of an
Enchantment. If we look into the Fiction of
Milton's
Fable, though we
find it full of surprizing Incidents, they are generally suited to our
Notions of the Things and Persons described, and tempered with a due
Measure of Probability. I must only make an Exception to the
Limbo of
Vanity
, with his Episode of
Sin
and
Death
, and some of the imaginary
Persons in his
Chaos
. These Passages are astonishing, but not credible;
the Reader cannot so far impose upon himself as to see a Possibility in
them; they are the Description of Dreams and Shadows, not of Things or
Persons. I know that many Criticks look upon the Stories of
Circe
,
Polypheme
, the
Sirens
, nay the whole
Odyssey
and
Iliad
, to be
Allegories; but allowing this to be true, they are Fables, which
considering the Opinions of Mankind that prevailed in the Age of the
Poet, might possibly have been according to the Letter. The Persons are
such as might have acted what is ascribed to them, as the Circumstances
in which they are represented, might possibly have been Truths and
Realities. This Appearance of Probability is so absolutely requisite in
the greater kinds of Poetry, that
Aristotle
observes the Ancient Tragick
Writers made use of the Names of such great Men as had actually lived in
the World, tho' the Tragedy proceeded upon Adventures they were never
engaged in, on purpose to make the Subject more Credible. In a Word,
besides the hidden Meaning of an Epic Allegory, the plain litteral Sense
ought to appear Probable. The Story should be such as an ordinary Reader
may acquiesce in, whatever Natural, Moral, or Political Truth may be
discovered in it by Men of greater Penetration.
Satan
, after having long wandered upon the Surface, or outmost Wall of
the Universe, discovers at last a wide Gap in it, which led into the
Creation, and is described as the Opening through which the Angels pass
to and fro into the lower World, upon their Errands to Mankind. His
Sitting upon the Brink of this Passage, and taking a Survey of the whole
Face of Nature that appeared to him new and fresh in all its Beauties,
with the Simile illustrating this Circumstance, fills the Mind of the
Reader with as surprizing and glorious an Idea as any that arises in the
whole Poem. He looks down into that vast Hollow of the Universe with the
Eye, or (as Milton calls it in his first Book) with the Kenn of an
Angel. He surveys all the Wonders in this immense Amphitheatre that lye
between both the Poles of Heaven, and takes in at one View the whole
Round of the Creation.
His Flight between the several Worlds that shined on every side of him,
with the particular Description of the Sun, are set forth in all the
Wantonness of a luxuriant Imagination. His Shape, Speech and Behaviour
upon his transforming himself into an Angel of Light, are touched with
exquisite Beauty. The Poet's Thought of directing Satan to the Sun,
which in the vulgar Opinion of Mankind is the most conspicuous Part of
the Creation, and the placing in it an Angel, is a Circumstance very
finely contrived, and the more adjusted to a Poetical Probability, as it
was a received Doctrine among the most famous Philosophers, that every
Orb had its Intelligence; and as an Apostle in Sacred Writ is said to
have seen such an Angel in the Sun. In the Answer which this Angel
returns to the disguised evil Spirit, there is such a becoming Majesty
as is altogether suitable to a Superior Being. The Part of it in which
he represents himself as present at the Creation, is very noble in it
self, and not only proper where it is introduced, but requisite to
prepare the Reader for what follows in the Seventh Book.
I saw when at his Word the formless Mass,
This World's material Mould, came to a Heap:
Confusion heard his Voice, and wild Uproar
Stood rul'd, stood vast Infinitude confin'd.
Till at his second Bidding Darkness fled,
Light shon, &c.
In the following Part of the Speech he points out the Earth with such
Circumstances, that the Reader can scarce forbear fancying himself
employed on the same distant View of it.
Look downward on the Globe whose hither Side
With Light from hence, tho but reflected, shines;
That place is Earth, the Seat of Man, that Light
His Day, &c.
I must not conclude my Reflections upon this Third Book of
Paradise
Lost
, without taking Notice of that celebrated Complaint of
Milton
with
which it opens, and which certainly deserves all the Praises that have
been given it; tho' as I have before hinted, it may rather be looked
upon as an Excrescence, than as an essential Part of the Poem. The same
Observation might be applied to that beautiful Digression upon
Hypocrisie, in the same Book.
L.
De Arte Poetica
,. II. 38-40.
Poetics
, iii. 4.
'The surprising is necessary in tragedy; but the Epic Poem goes
farther, and admits even the improbable and incredible, from which the
highest degree of the surprising results, because there the action is
not seen.'
Contents
|
Monday, March 3, 1712 |
John Hughes |
Libertas; quæ sera tamen respexit Inertem.
Virg.
Ecl. I.

'Mr.
Spectator,
'If you ever read a Letter which is sent with the more Pleasure for
the Reality of its Complaints, this may have Reason to hope for a
favourable Acceptance; and if Time be the most irretrievable Loss, the
Regrets which follow will be thought, I hope, the most justifiable.
The regaining of my Liberty from a long State of Indolence and
Inactivity, and the Desire of resisting the further Encroachments of
Idleness, make me apply to you; and the Uneasiness with which I I
recollect the past Years, and the Apprehensions with which I expect
the Future, soon determined me to it.
'Idleness is so general a Distemper that I cannot but imagine a
Speculation on this Subject will be of universal Use. There is hardly
any one Person without some Allay of it; and thousands besides my self
spend more Time in an idle Uncertainty which to begin first of two
Affairs, that would have been sufficient to have ended them both. The
Occasion of this seems to be the Want of some necessary Employment, to
put the Spirits in Motion, and awaken them out of their Lethargy. If I
had less Leisure, I should have more; for I should then find my Time
distinguished into Portions, some for Business, and others for the
indulging of Pleasures: But now one Face of Indolence overspreads the
whole, and I have no Land-mark to direct my self by. Were one's Time a
little straitned by Business, like Water inclosed in its Banks, it
would have some determined Course; but unless it be put into some
Channel it has no Current, but becomes a Deluge without either Use or
Motion.
'When Scanderbeg Prince of Epirus was dead, the Turks, who had but too
often felt the Force of his Arm in the Battels he had won from them,
imagined that by wearing a piece of his Bones near their Heart, they
should be animated with a Vigour and Force like to that which inspired
him when living. As I am like to be but of little use whilst I live, I
am resolved to do what Good I can after my Decease; and have
accordingly ordered my Bones to be disposed of in this Manner for the
Good of my Countrymen, who are troubled with too exorbitant a Degree
of Fire. All Fox-hunters upon wearing me, would in a short Time be
brought to endure their Beds in a Morning, and perhaps even quit them
with Regret at Ten: Instead of hurrying away to teaze a poor Animal,
and run away from their own Thoughts, a Chair or a Chariot would be
thought the most desirable Means of performing a Remove from one Place
to another. I should be a Cure for the unnatural Desire of John Trott
for Dancing, and a Specifick to lessen the Inclination Mrs. Fidget has
to Motion, and cause her always to give her Approbation to the present
Place she is in. In fine, no Egyptian Mummy was ever half so useful in
Physick, as I should be to these feaverish Constitutions, to repress
the violent Sallies of Youth, and give each Action its proper Weight
and Repose.
'I can stifle any violent Inclination, and oppose a Torrent of Anger,
or the Sollicitations of Revenge, with Success. But Indolence is a
Stream which flows slowly on, but yet undermines the Foundation of
every Virtue. A Vice of a more lively Nature were a more desirable
Tyrant than this Rust of the Mind, which gives a Tincture of its
Nature to every Action of ones Life. It were as little Hazard to be
lost in a Storm, as to lye thus perpetually becalmed: And it is to no
Purpose to have within one the Seeds of a thousand good Qualities, if
we want the Vigour and Resolution necessary for the exerting them.
Death brings all Persons back to an Equality; and this Image of it,
this Slumber of the Mind, leaves no Difference between the greatest
Genius and the meanest Understanding: A Faculty of doing things
remarkably praise-worthy thus concealed, is of no more use to the
Owner, than a Heap of Gold to the Man who dares not use it.
'To-Morrow is still the fatal Time when all is to be rectified:
To-Morrow comes, it goes, and still I please my self with the Shadow,
whilst I lose the Reality; unmindful that the present Time alone is
ours, the future is yet unborn, and the past is dead, and can only
live (as Parents in their Children) in the Actions it has produced.
'The Time we live ought not to be computed by the Numbers of Years,
but by the Use has been made of it; thus 'tis not the Extent of
Ground, but the yearly Rent which gives the Value to the Estate.
Wretched and thoughtless Creatures, in the only Place where
Covetousness were a Virtue we turn Prodigals! Nothing lies upon our
Hands with such Uneasiness, nor has there been so many Devices for any
one Thing, as to make it slide away imperceptibly and to no purpose. A
Shilling shall be hoarded up with Care, whilst that which is above the
Price of an Estate, is flung away with Disregard and Contempt. There
is nothing now-a-days so much avoided, as a sollicitous Improvement of
every part of Time; 'tis a Report must be shunned as one tenders the
Name of a Wit and a fine Genius, and as one fears the Dreadful
Character of a laborious Plodder: But notwithstanding this, the
greatest Wits any Age has produced thought far otherwise; for who can
think either Socrates or Demosthenes lost any Reputation, by their
continual Pains both in overcoming the Defects and improving the Gifts
of Nature. All are acquainted with the Labour and Assiduity with which
Tully acquired his Eloquence.
'
Seneca in his Letters to Lucelius
1 assures him, there was not a Day
in which he did not either write something, or read and epitomize some
good Author; and I remember Pliny in one of his Letters, where he
gives an Account of the various Methods he used to fill up every
Vacancy of Time, after several Imployments which he enumerates;
sometimes, says he, I hunt; but even then I carry with me a
Pocket-Book, that whilst my Servants are busied in disposing of the
Nets and other Matters I may be employed in something that may be
useful to me in my Studies; and that if I miss of my Game, I may at
the least bring home some of my own Thoughts with me, and not have the
Mortification of having caught nothing all Day
2.
'Thus, Sir, you see how many Examples I recall to Mind, and what
Arguments I use with my self, to regain my Liberty: But as I am afraid
'tis no Ordinary Perswasion that will be of Service, I shall expect
your Thoughts on this Subject, with the greatest Impatience,
especially since the Good will not be confined to me alone, but will
be of Universal Use. For there is no Hopes of Amendment where Men are
pleased with their Ruin, and whilst they think Laziness is a desirable
Character: Whether it be that they like the State it self, or that
they think it gives them a new Lustre when they do exert themselves,
seemingly to be able to do that without Labour and Application, which
others attain to but with the greatest Diligence.
I am,
Sir,
Your most obliged humble Servant,
Samuel Slack.
Clytander to Cleone.
'Madam,
Permission to love you is all I desire, to conquer all the
Difficulties those about you place in my Way, to surmount and acquire
all those Qualifications you expect in him who pretends to the Honour
of being,
'Madam,
Your most humble Servant,
'Clytander.
Z.
Ep
. 2.
Ep
. I. 6.
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 4, 1712 |
Addison |
—fruges consumere nati.
Hor.

Augustus, a few Moments before his Death, asked his Friends who stood
about him, if they thought he had acted his Part well; and upon
receiving such an Answer as was due to his extraordinary Merit,
Let me
then, says he, go off the Stage with your Applause
; using the
Expression with which the Roman Actors made their
Exit
at the
Conclusion of a Dramatick Piece. I could wish that Men, while they are
in Health, would consider well the Nature of the Part they are engaged
in, and what Figure it will make in the Minds of those they leave behind
them: Whether it was worth coming into the World for; whether it be
suitable to a reasonable Being; in short, whether it appears Graceful in
this Life, or will turn to an Advantage in the next. Let the Sycophant,
or Buffoon, the Satyrist, or the Good Companion, consider with himself,
when his Body shall be laid in the Grave, and his Soul pass into another
State of Existence, how much it will redound to his Praise to have it
said of him, that no Man in England eat better, that he had an admirable
Talent at turning his Friends into Ridicule, that no Body out-did him at
an Ill-natured Jest, or that he never went to Bed before he had
dispatched his third Bottle. These are, however, very common Funeral
Orations, and Elogiums on deceased Persons who have acted among Mankind
with some Figure and Reputation.
But if we look into the Bulk of our Species, they are such as are not
likely to be remembred a Moment after their Disappearance. They leave
behind them no Traces of their Existence, but are forgotten as tho' they
had never been. They are neither wanted by the Poor, regretted by the
Rich,
n
or celebrated by the Learned. They are neither missed in the
Commonwealth, nor lamented by private Persons. Their Actions are of no
Significancy to Mankind, and might have been performed by Creatures of
much less Dignity, than those who are distinguished by the Faculty of
Reason. An eminent French Author speaks somewhere to the following
Purpose: I have often seen from my Chamber-window two noble Creatures,
both of them of an erect Countenance and endowed with Reason. These two
intellectual Beings are employed from Morning to Night, in rubbing two
smooth Stones one upon another; that is, as the Vulgar phrase it, in
polishing Marble.
My Friend, Sir
Andrew Freeport
, as we were sitting in the Club last
Night, gave us an Account of a sober Citizen, who died a few Days since.
This honest Man being of greater Consequence in his own Thoughts, than
in the Eye of the World, had for some Years past kept a Journal of his
Life. Sir
Andrew
shewed us one Week of it.
Since
the Occurrences
set down in it mark out such a Road of Action as that I have been
speaking of, I shall present my Reader with a faithful Copy of it; after
having first inform'd him, that the Deceased Person had in his Youth
been bred to Trade, but finding himself not so well turned for Business,
he had for several Years last past lived altogether upon a moderate
Annuity.
| Monday |
Eight-a-Clock |
I put on my Cloaths and walked into the Parlour. |
|
Nine a-Clock |
ditto. Tied my Knee-strings, and washed my Hands. |
|
Hours Ten, Eleven and Twelve. |
Smoaked three Pipes of Virginia. Read
the Supplement and Daily Courant. Things go ill in the North. Mr.
Nisby's Opinion thereupon. |
|
One a-Clock in the Afternoon. |
Chid Ralph for mislaying my Tobacco-Box. |
|
Two a-Clock. |
Sate down to Dinner. Mem. Too many Plumbs, and no Sewet. |
|
From Three to Four. |
Took my Afternoon's Nap. |
|
From Four to Six. |
Walked into the Fields. Wind, S. S. E. |
|
From Six to Ten. |
At the Club. Mr. Nisby's Opinion about the Peace. |
|
Ten a-Clock. |
Went to Bed, slept sound. |
| Tuesday, Being Holiday, |
Eight a-Clock. |
Rose as usual. |
|
Nine a-Clock. |
Washed Hands and Face, shaved, put on my double-soaled
Shoes. |
|
Ten, Eleven, Twelve. |
Took a Walk to Islington. |
|
One. |
Took a Pot of Mother Cob's Mild. |
|
Between Two and Three. |
Return'd, dined on a Knuckle of Veal and Bacon.
Mem. Sprouts wanting. |
|
Three. |
Nap as usual. |
|
From Four to Six. |
Coffee-house. Read the News. A Dish of Twist. Grand
Vizier strangled. |
|
From Six to Ten. |
At the Club. Mr. Nisby's Account of the Great Turk. |
|
Ten. |
Dream of the Grand Vizier. Broken Sleep. |
| Wednesday |
Eight a-Clock. |
Tongue of my Shooe-Buckle broke. Hands but
not Face. |
|
Nine. |
Paid off the Butcher's Bill. Mem. To be allowed for the last Leg
of Mutton. |
|
Ten, Eleven. |
At the Coffee-house. More Work in the North. Stranger in
a black Wigg asked me how Stocks went. |
|
From Twelve to One. |
Walked in the Fields. Wind to the South. |
|
From One to Two. |
Smoaked a Pipe and an half. |
|
Two. |
Dined as usual. Stomach good. |
|
Three. |
Nap broke by the falling of a Pewter Dish. Mem. Cook-maid in
Love, and grown careless. |
|
From Four to Six. |
At the Coffee-house. Advice from Smyrna, that the
Grand Vizier was first of all strangled, and afterwards beheaded. |
|
Six a-Clock in the Evening. |
Was half an Hour in the Club before any
Body else came. Mr. Nisby of Opinion that the Grand Vizier was not
strangled the Sixth Instant. |
|
Ten at Night. |
Went to Bed. Slept without waking till Nine next
Morning. |
| Thursday |
Nine a-Clock. |
Staid within till Two a-Clock for Sir Timothy;
who did not bring me my Annuity according to his Promise. |
|
Two in the Afternoon. |
Sate down to Dinner. Loss of Appetite. Small
Beer sour. Beef over-corned. |
|
Three. |
Gave Ralph a box on the Ear. Turned off my Cookmaid.
Sent a Message to Sir Timothy. Mem. I did not go to the Club to-night.
Went to Bed at Nine a-Clock. |
| Friday |
|
Passed the Morning in Meditation upon Sir Timothy, who was
with me a Quarter before Twelve. |
|
Twelve a-Clock. |
Bought a new Head to my Cane, and a Tongue to my
Buckle. Drank a Glass of Purl to recover Appetite. |
|
Two and Three. |
Dined, and Slept well. |
|
From Four to Six. |
Went to the Coffee-house. Met Mr. Nisby there.
Smoaked several Pipes. Mr. Nisby of opinion that laced Coffee is bad
for the Head. |
|
Six a-Clock. |
At the Club as Steward. Sate late. |
|
Twelve a-Clock. |
Went to Bed, dreamt that I drank Small Beer with the
Grand Vizier. |
| Saturday |
|
Waked at Eleven, walked in the Fields. Wind N. E. |
|
Twelve. |
Caught in a Shower. |
|
One in the Afternoon. |
Returned home, and dryed my self. |
|
Two. |
Mr. Nisby dined with me. First Course Marrow-bones, Second
Ox-Cheek, with a Bottle of Brooks and Hellier. |
|
Three a-Clock. |
Overslept my self. |
|
Six. |
Went to the Club. Like to have faln into a Gutter. Grand Vizier
certainly Dead. etc. |
I question not but the Reader will be surprized to find the
above-mentioned Journalist taking so much care of a Life that was filled
with such inconsiderable Actions, and received so very small
Improvements; and yet, if we look into the Behaviour of many whom we
daily converse with, we shall find that most of their Hours are taken up
in those three Important Articles of Eating, Drinking and Sleeping. I do
not suppose that a Man loses his Time, who is not engaged in publick
Affairs, or in an Illustrious Course of Action. On the Contrary, I
believe our Hours may very often be more profitably laid out in such
Transactions as make no Figure in the World, than in such as are apt to
draw upon them the Attention of Mankind. One may become wiser and better
by several Methods of Employing one's Self in Secrecy and Silence, and
do what is laudable without Noise, or Ostentation. I would, however,
recommend to every one of my Readers, the keeping a Journal of their
Lives for one Week, and setting down punctually their whole Series of
Employments during that Space of Time. This Kind of Self-Examination
would give them a true State of themselves, and incline them to consider
seriously what they are about. One Day would rectifie the Omissions of
another, and make a Man weigh all those indifferent Actions, which,
though they are easily forgotten, must certainly be accounted for.
L.
As
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 5, 1712 |
Steele |
—non omnia possumus omnes.
Virg.
1
Mr.
Spectator,
A certain Vice which you have lately attacked, has not yet been
considered by you as growing so deep in the Heart of Man, that the
Affectation outlives the Practice of it. You must have observed that
Men who have been bred in Arms preserve to the most extreme and feeble
old Age a certain Daring in their Aspect: In like manner, they who
have pass'd their Time in Gallantry and Adventure, keep up, as well as
they can, the Appearance of it, and carry a petulant Inclination to
their last Moments. Let this serve for a Preface to a Relation I am
going to give you of an old Beau in Town, that has not only been
amorous, and a Follower of Women in general, but also, in Spite of the
Admonition of grey Hairs, been from his sixty-third Year to his
present seventieth, in an actual Pursuit of a young Lady, the Wife of
his Friend, and a Man of Merit. The gay old Escalus has Wit, good
Health, and is perfectly well bred; but from the Fashion and Manners
of the Court when he was in his Bloom, has such a natural Tendency to
amorous Adventure, that he thought it would be an endless Reproach to
him to make no use of a Familiarity he was allowed at a Gentleman's
House, whose good Humour and Confidence exposed his Wife to the
Addresses of any who should take it in their Head to do him the good
Office. It is not impossible that Escalus might also resent that the
Husband was particularly negligent of him; and tho' he gave many
Intimations of a Passion towards the Wife, the Husband either did not
see them, or put him to the Contempt of over-looking them. In the mean
time Isabella, for so we shall call our Heroine, saw his Passion, and
rejoiced in it as a Foundation for much Diversion, and an Opportunity
of indulging her self in the dear Delight of being admired, addressed
to, and flattered, with no ill Consequence to her Reputation. This
Lady is of a free and disengaged Behaviour, ever in good Humour, such
as is the Image of Innocence with those who are innocent, and an
Encouragement to Vice with those who are abandoned. From this Kind of
Carriage, and an apparent Approbation of his Gallantry, Escalus had
frequent Opportunities of laying amorous Epistles in her Way, of
fixing his Eyes attentively upon her Action, of performing a thousand
little Offices which are neglected by the Unconcerned, but are so many
Approaches towards Happiness with the Enamoured. It was now, as is
above hinted, almost the End of the seventh Year of his Passion, when
Escalus from general Terms, and the ambiguous Respect which criminal
Lovers retain in their Addresses, began to bewail that his Passion
grew too violent for him to answer any longer for his Behaviour
towards her; and that he hoped she would have Consideration for his
long and patient Respect, to excuse the Motions of a Heart now no
longer under the Direction of the unhappy Owner of it. Such for some
Months had been the Language of Escalus both in his Talk and his
Letters to Isabella; who returned all the Profusion of kind Things
which had been the Collection of fifty Years with I must not hear you;
you will make me forget that y'ou are a Gentleman, I would not
willingly lose you as a Friend; and the like Expressions, which the
Skilful interpret to their own Advantage, as well knowing that a
feeble Denial is a modest Assent. I should have told you, that
Isabella, during the whole Progress of this Amour, communicated it to
her Husband; and that an Account of Escalus's Love was their usual
Entertainment after half a Day's Absence: Isabella therefore, upon her
Lover's late more open Assaults, with a Smile told her Husband she
could hold out no longer, but that his Fate was now come to a Crisis.
After she had explained her self a little farther, with her Husband's
Approbation she proceeded in the following Manner. The next Time that
Escalus was alone with her, and repeated his Importunity, the crafty
Isabella looked on her Fan with an Air of great Attention, as
considering of what Importance such a Secret was to her; and upon the
Repetition of a warm Expression, she looked at him with an Eye of
Fondness, and told him he was past that Time of Life which could make
her fear he would boast of a Lady's Favour; then turned away her Head
with a very well-acted Confusion, which favoured the Escape of the
aged Escalus. This Adventure was Matter of great Pleasantry to
Isabella and her Spouse; and they had enjoyed it two Days before
Escalus could recollect himself enough to form the following Letter.
Madam,
"What happened the other Day, gives me a lively Image of the
Inconsistency of human Passions and Inclinations. We pursue what we
are denied, and place our Affections on what is absent, tho' we
neglected it when present. As long as you refused my Love, your
Refusal did so strongly excite my Passion, that I had not once the
Leisure to think of recalling my Reason to aid me against the Design
upon your Virtue. But when that Virtue began to comply in my Favour,
my Reason made an Effort over my Love, and let me see the Baseness
of my Behaviour in attempting a Woman of Honour. I own to you, it
was not without the most violent Struggle that I gained this Victory
over my self; nay, I will confess my Shame, and acknowledge I could
not have prevailed but by Flight. However, Madam, I beg that you
will believe a Moment's Weakness has not destroyed the Esteem I had
for you, which was confirmed by so many Years of Obstinate Virtue.
You have Reason to rejoice that this did not happen within the
Observation of one of the young Fellows, who would have exposed your
Weakness, and gloried in his own Brutish Inclinations.
I am, Madam,
Your most devoted Humble Servant."
Isabella, with the Help of her Husband, returned the following Answer.
Sir,
"I cannot but account my self a very happy Woman, in having a Man
for a Lover that can write so well, and give so good a Turn to a
Disappointment. Another Excellence you have above all other
Pretenders I ever heard of; on Occasions where the most reasonable
Men lose all their Reason, you have yours most powerful. We are each
of us to thank our Genius, that the Passion of one abated in
Proportion as that of the other grew violent. Does it not yet come
into your Head, to imagine that I knew my Compliance was the
greatest Cruelty I could be guilty of towards you? In Return for
your long and faithful Passion, I must let you know that you are old
enough to become a little more Gravity; but if you will leave me and
coquet it any where else, may your Mistress yield.
Isabella."'
T.
'Rideat et pulset Lasciva decentius Ætas.'
Hor.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 6, 1712 |
Budgell |
Quo teneam vultus mutantem Protea nodo?
Hor.

I have endeavoured, in the Course of my Papers, to do Justice to the
Age, and have taken care as much as possible to keep my self a Neuter
between both Sexes. I have neither spared the Ladies out of
Complaisance, nor the Men out of Partiality; but notwithstanding the
great Integrity with which I have acted in this Particular, I find my
self taxed with an Inclination to favour my own half of the Species.
Whether it be that the Women afford a more fruitful Field for
Speculation, or whether they run more in my Head than the Men, I cannot
tell, but I shall set down the Charge as it is laid against me in the
following Letter.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I always make one among a Company of young Females, who peruse your
Speculations every Morning. I am at present Commissioned, by our whole
Assembly, to let you know, that we fear you are a little enclined to
be partial towards your own Sex. We must however acknowledge, with all
due Gratitude, that in some Cases you have given us our Revenge on the
Men, and done us Justice. We could not easily have forgiven you
several Strokes in the Dissection of the Coquets Heart, if you had
not, much about the same time, made a Sacrifice to us of a Beau's
Scull.
'You may, however, Sir, please to remember, that long since you
attacked our Hoods and Commodes in such manner, as, to use your own
Expression, made very many of us ashamed to shew our Heads. We must,
therefore, beg leave to represent to you, that we are in Hopes, if you
would please to make a due Enquiry, the Men in all Ages would be found
to have been little less whimsical in adorning that Part, than our
selves. The different Forms of their Wiggs, together with the various
Cocks of their Hats, all flatter us in this Opinion.
'I had an humble Servant last Summer, who the first time he declared
himself, was in a Full-Bottom'd Wigg; but the Day after, to my no
small Surprize, he accosted me in a thin Natural one. I received him,
at this our second Interview, as a perfect Stranger, but was extreamly
confounded, when his Speech discovered who he was. I resolved,
therefore, to fix his Face in my Memory for the future; but as I was
walking in the Park the same Evening, he appeared to me in one of
those Wiggs that I think you call a Night-cap, which had altered him
more effectually than before. He afterwards played a Couple of Black
Riding Wiggs upon me, with the same Success; and, in short, assumed a
new Face almost every Day in the first Month of his Courtship.
'I observed afterwards, that the Variety of Cocks into which he
moulded his Hat, had not a little contributed to his Impositions upon
me.
'Yet, as if all these ways were not sufficient to distinguish their
Heads, you must, doubtless, Sir, have observed, that great Numbers of
young Fellows have, for several Months last past, taken upon them to
wear Feathers.
'We hope, therefore, that these may, with as much Justice, be called
Indian Princes, as you have styled a Woman in a coloured Hood an
Indian Queen; and that you will, in due time, take these airy
Gentlemen into Consideration.
'We the more earnestly beg that you would put a Stop to this Practice,
since it has already lost us one of the most agreeable Members of our
Society, who after having refused several good Estates, and two
Titles, was lured from us last Week by a mixed Feather.
'I am ordered to present you the Respects of our whole Company, and
am,
Sir,
Your very humble Servant,
Dorinda.
Note, The Person wearing the Feather, tho' our Friend took him for an
Officer in the Guards, has proved to be
an arrant Linnen-Draper1.'
I am not now at leisure to give my Opinion upon the Hat and Feather;
however to wipe off the present Imputation, and gratifie my Female
Correspondent, I shall here print a Letter which I lately received from
a Man of Mode, who seems to have a very extraordinary Genius in his way.
Sir,
'I presume I need not inform you, that among Men of Dress it is a
common Phrase to say Mr. Such an one has struck a bold Stroke; by
which we understand, that he is the first Man who has had Courage
enough to lead up a Fashion. Accordingly, when our Taylors take
Measure of us, they always demand whether we will have a plain Suit,
or strike a bold Stroke. 1 think I may without Vanity say, that I have
struck some of the boldest and most successful Strokes of any Man in
Great Britain. I was the first that struck the Long Pocket about two
Years since: I was likewise the Author of the Frosted Button, which
when I saw the Town came readily into, being resolved to strike while
the Iron was hot, I produced much about the same time the Scallop
Flap, the knotted Cravat, and made a fair Push for the Silver-clocked
Stocking.
'A few Months after I brought up the modish Jacket, or the Coat with
close Sleeves. I struck this at first in a plain Doily; but that
failing, I struck it a second time in blue Camlet; and repeated the
Stroke in several kinds of Cloth, till at last it took effect. There
are two or three young Fellows at the other End of the Town, who have
always their Eye upon me, and answer me Stroke for Stroke. I was once
so unwary as to mention my Fancy in relation to the new-fashioned
Surtout before one of these Gentlemen, who was disingenuous enough to
steal my Thought, and by that means prevented my intended Stroke.
'I have a Design this Spring to make very considerable Innovations in
the Wastcoat, and have already begun with a Coup d'essai upon the
Sleeves, which has succeeded very well.
'I must further inform you, if you will promise to encourage or at
least to connive at me, that it is my Design to strike such a Stroke
the Beginning of the next Month, as shall surprise the whole Town.
'I do not think it prudent to acquaint you with all the Particulars of
my intended Dress; but will only tell you, as a Sample of it, that I
shall very speedily appear at White's in a Cherry-coloured Hat. I took
this Hint from the Ladies Hoods, which I look upon as the boldest
Stroke that Sex has struck for these hundred Years last past.
I am, Sir,
Your most Obedient, most Humble Servant,
Will. Sprightly.'
I have not Time at present to make any Reflections on this Letter, but
must not however omit that having shewn it to Will. Honeycomb, he
desires to be acquainted with the Gentleman who writ it.
X.
only an Ensign in the Train Bands.
Contents
|
Friday, March 7, 1712 |
Steele |
'—non pronuba Juno,
Non Hymenæus adest, non illi Gratia lecto,
Eumenides stravere torum.'
Ovid
1.

Mr.
Spectator,
'You have given many Hints in your Papers to the Disadvantage of
Persons of your own Sex, who lay Plots upon Women. Among other hard
Words you have published the Term Male-Coquets, and been very severe
upon such as give themselves the Liberty of a little Dalliance of
Heart, and playing fast and loose, between Love and Indifference, till
perhaps an easie young Girl is reduced to Sighs, Dreams and Tears; and
languishes away her Life for a careless Coxcomb, who looks astonished,
and wonders at such an Effect from what in him was all but common
Civility. Thus you have treated the Men who are irresolute in
Marriage; but if you design to be impartial, pray be so honest as to
print the Information I now give you, of a certain Set of Women who
never Coquet for the Matter, but with an high Hand marry whom they
please to whom they please. As for my Part, I should not have
concerned my self with them, but that I understand I am pitched upon
by them, to be married, against my Will, to one I never saw in my
Life. It has been my Misfortune, Sir, very innocently, to rejoice in a
plentiful Fortune, of which I am Master, to bespeak a fine Chariot, to
give Direction for two or three handsome Snuff-Boxes, and as many
Suits of fine Cloaths; but before any of these were ready, I heard
Reports of my being to be married to two or three different young
Women. Upon my taking Notice of it to a young Gentleman who is often
in my Company he told me smiling, I was in the Inquisition. You may
believe I was not a little startled at what he meant, and more so when
he asked me if I had bespoke any thing of late that was fine. I told
him several; upon which he produced a Description of my Person from
the Tradesmen whom I had employed, and told me that they had certainly
informed against me. Mr.
Spectator, Whatever the World may think of
me, I am more Coxcomb than Fool, and I grew very inquisitive upon this
Head, not a little pleased with the Novelty. My Friend told me there
were a certain Set of Women of Fashion whereof the Number of Six made
a Committee, who sat thrice a Week, under the Title of the Inquisition
on Maids and Batchelors. It seems, whenever there comes such an
unthinking gay Thing as my self to Town, he must want all Manner of
Necessaries, or be put into the Inquisition by the first Tradesman he
employs. They have constant Intelligence with Cane-Shops, Perfumers,
Toymen, Coach-makers, and China-houses. From these several Places,
these Undertakers for Marriages have as constant and regular
Correspondence, as the Funeral-men have with Vintners and
Apothecaries. All Batchelors are under their immediate Inspection, and
my Friend produced to me a Report given into their Board, wherein an
old Unkle of mine, who came to Town with me, and my self, were
inserted, and we stood thus; the Unkle smoaky, rotten, poor; the
Nephew raw, but no Fool, sound at present, very rich. My Information
did not end here, but my Friend's Advices are so good, that he could
shew me a Copy of the Letter sent to the young Lady who is to have me
which I enclose to you.
Madam,
'This is to let you know, that you are to be Married to a Beau that
comes out on Thursday Six in the Evening. Be at the Park. You cannot
but know a Virgin Fop; they have a Mind to look saucy, but are out
of Countenance. The Board has denied him to several good Families. I
wish you Joy.
Corinna.'
What makes my Correspondent's Case the more deplorable, is, that as I
find by the Report from my Censor of Marriages, the Friend he speaks of
is employed by the Inquisition to take him in, as the Phrase is. After
all that is told him, he has Information only of one Woman that is laid
for him, and that the wrong one; for the Lady-Commissioners have devoted
him to another than the Person against whom they have employed their
Agent his Friend to alarm him. The Plot is laid so well about this young
Gentleman, that he has no Friend to retire to, no Place to appear in, or
Part of the Kingdom to fly into, but he must fall into the Notice, and
be subject to the Power of the Inquisition. They have their Emissaries
and Substitutes in all Parts of this united Kingdom. The first Step they
usually take, is to find from a Correspondence, by their Messengers and
Whisperers with some Domestick of the Batchelor (who is to be hunted
into the Toils they have laid for him) what are his Manners, his
Familiarities, his good Qualities or Vices; not as the Good in him is a
Recommendation, or the ill a Diminution, but as they affect or
contribute to the main Enquiry, What Estate he has in him? When this
Point is well reported to the Board, they can take in a wild roaring
Fox-hunter, as easily as a soft, gentle young Fop of the Town. The Way
is to make all Places uneasie to him, but the Scenes in which they have
allotted him to act. His Brother Huntsmen, Bottle Companions, his
Fraternity of Fops, shall be brought into the Conspiracy against him.
Then this Matter is not laid in so bare-faced a Manner before him, as to
have it intimated Mrs. Such-a-one would make him a very proper Wife; but
by the Force of their Correspondence they shall make it (as Mr. Waller
said of the Marriage of the Dwarfs) as impracticable to have any Woman
besides her they design him, as it would have been in Adam to have
refused Eve. The Man named by the Commission for Mrs. Such-a-one, shall
neither be in Fashion, nor dare ever to appear in Company, should he
attempt to evade their Determination.
The Female Sex wholly govern domestick Life; and by this Means, when
they think fit, they can sow Dissentions between the dearest Friends,
nay make Father and Son irreconcilable Enemies, in spite of all the Ties
of Gratitude on one Part, and the Duty of Protection to be paid on the
other. The Ladies of the Inquisition understand this perfectly well; and
where Love is not a Motive to a Man's chusing one whom they allot, they
can, with very much Art, insinuate Stories to the Disadvantage of his
Honesty or Courage, 'till the Creature is too much dispirited to bear up
against a general ill Reception, which he every where meets with, and in
due time falls into their appointed Wedlock for Shelter. I have a long
Letter bearing Date the fourth Instant, which gives me a large Account
of the Policies of this Court; and find there is now before them a very
refractory Person who has escaped all their Machinations for two Years
last past: But they have prevented two successive Matches which were of
his own Inclination, the one, by a Report that his Mistress was to be
married, and the very Day appointed, Wedding-Clothes bought, and all
things ready for her being given to another; the second time, by
insinuating to all his Mistress's Friends and Acquaintance, that he had
been false to several other Women, and the like. The poor Man is now
reduced to profess he designs to lead a single Life; but the Inquisition
gives out to all his Acquaintance, that nothing is intended but the
Gentleman's own Welfare and Happiness. When this is urged, he talks
still more humbly, and protests he aims only at a Life without Pain or
Reproach; Pleasure, Honour or Riches, are things for which he has no
taste. But notwithstanding all this and what else he may defend himself
with, as that the Lady is too old or too young, of a suitable Humour, or
the quite contrary, and that it is impossible they can ever do other
than wrangle from June to January, Every Body tells him all this is
Spleen, and he must have a Wife; while all the Members of the
Inquisition are unanimous in a certain Woman for him, and they think
they all together are better able to judge, than he or any other private
Person whatsoever.
Temple, March 3, 1711.
Sir,
Your Speculation this Day on the Subject of Idleness, has employed me,
ever since I read it, in sorrowful Reflections on my having loitered
away the Term (or rather the Vacation) of ten Years in this Place, and
unhappily suffered a good Chamber and Study to lie idle as long. My
Books (except those I have taken to sleep upon) have been totally
neglected, and my Lord Coke and other venerable Authors were never so
slighted in their Lives. I spent most of the Day at a Neighbouring
Coffee-House, where we have what I may call a lazy Club. We generally
come in Night-Gowns, with our Stockings about our Heels, and sometimes
but one on. Our Salutation at Entrance is a Yawn and a Stretch, and
then without more Ceremony we take our Place at the Lolling Table;
where our Discourse is, what I fear you would not read out, therefore
shall not insert. But I assure you, Sir, I heartily lament this Loss
of Time, and am now resolved (if possible, with double Diligence) to
retrieve it, being effectually awakened by the Arguments of Mr. Slack
out of the Senseless Stupidity that has so long possessed me. And to
demonstrate that Penitence accompanies my Confession, and Constancy my
Resolutions, I have locked my Door for a Year, and desire you would
let my Companions know I am not within. I am with great Respect,
Sir, Your most obedient Servant,
N. B.
T.
Hæ sunt qui tenui sudant in Cyclade.
Hor.
Contents
No. 3211 |
Saturday, March 8, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec satis est pulchra esse poemata, dulcia sunto.
Hor.

Those, who know how many Volumes have been written on the Poems of
Homer
and
Virgil
, will easily pardon the Length of my Discourse upon
Milton
.
The
Paradise Lost
is looked upon, by the best Judges, as the greatest
Production, or at least the noblest Work of Genius in our Language, and
therefore deserves to be set before an English Reader in its full
Beauty. For this Reason, tho' I have endeavoured to give a general Idea
of its Graces and Imperfections in my Six First Papers, I thought my
self obliged to bestow one upon every Book in particular. The Three
first Books I have already dispatched, and am now entering upon the
Fourth. I need not acquaint my Reader that there are Multitudes of
Beauties in this great Author, especially in the Descriptive Parts of
his Poem, which I have not touched upon, it being my Intention to point
out those only, which appear to me the most exquisite, or those which
are not so obvious to ordinary Readers. Every one that has read the
Criticks who have written upon the
Odyssey
, the
Iliad
and the
Æneid
,
knows very well, that though they agree in their Opinions of the great
Beauties in those Poems, they have nevertheless each of them discovered
several Master-Strokes, which have escaped the Observation of the rest.
In the same manner, I question not, but any Writer who shall treat of
this Subject after me, may find several Beauties in
Milton
, which I have
not taken notice of. I must likewise observe, that as the greatest
Masters of Critical Learning differ among one another, as to some
particular Points in an Epic Poem, I have not bound my self scrupulously
to the Rules which any one of them has laid down upon that Art, but have
taken the Liberty sometimes to join with one, and sometimes with
another, and sometimes to differ from all of them, when I have thought
that the Reason of the thing was on my side.
We may consider the Beauties of the Fourth Book under three Heads. In
the first are those Pictures of Still-Life, which we meet with in the
Description of Eden, Paradise,
Adam's
Bower, &c. In the next are the
Machines, which comprehend the Speeches and Behaviour of the good and
bad Angels. In the last is the Conduct of
Adam
and
Eve
, who are the
Principal Actors in the Poem.
In
Description of Paradise, the Poet has observed
Aristotle's
Rule
of lavishing all the Ornaments of Diction on the weak unactive Parts of
the Fable, which are not supported by the Beauty of Sentiments and
Characters
. Accordingly the Reader may observe, that the Expressions
are more florid and elaborate in these Descriptions, than in most other
Parts of the Poem. I must further add, that tho' the Drawings of
Gardens, Rivers, Rainbows, and the like dead Pieces of Nature, are
justly censured in an Heroic Poem, when they run out into an unnecessary
length; the Description of Paradise would have been faulty, had not the
Poet been very particular in it, not only as it is the Scene of the
Principal Action, but as it is requisite to give us an Idea of that
Happiness from which our first Parents fell. The Plan of it is
wonderfully Beautiful, and formed upon the short Sketch which we have of
it in Holy Writ.
Milton's
Exuberance of Imagination has poured forth
such a Redundancy of Ornaments on this Seat of Happiness and Innocence,
that it would be endless to point out each Particular.
I must not quit this Head, without further observing, that there is
scarce a Speech of
Adam
or
Eve
in the whole Poem, wherein the Sentiments
and Allusions are not taken from this their delightful Habitation. The
Reader, during their whole Course of Action, always finds himself in the
Walks of Paradise. In short, as the Criticks have remarked, that in
those Poems, wherein Shepherds are Actors, the Thoughts ought always to
take a Tincture from the Woods, Fields and Rivers, so we may observe,
that our first Parents seldom lose Sight of their happy Station in any
thing they speak or do; and, if the Reader will give me leave to use the
Expression, that their Thoughts are always Paradisiacal.
We are in the next place to consider the Machines of the Fourth Book.
Satan
being now within Prospect of Eden, and looking round upon the
Glories of the Creation, is filled with Sentiments different from those
which he discovered whilst he was in Hell. The Place inspires him with
Thoughts more adapted to it: He reflects upon the happy Condition from
which he fell, and breaks forth into a Speech that is softned with
several transient Touches of Remorse and Self-accusation: But at length
he confirms himself in Impenitence, and in his Design of drawing Man
into his own State of Guilt and Misery. This Conflict of Passions is
raised with a great deal of Art, as the opening of his Speech to the Sun
is very bold and noble.
O thou that with surpassing Glory crown'd,
Look'st from thy sole Dominion like the God
Of this new World; at whose Sight all the Stars
Hide their diminish'd Heads; to thee I call,
But with no friendly Voice, and add thy name,
O Sun! to tell thee how I hate thy beams,
That bring to my Remembrance from what State
I fell, how glorious once above thy Sphere.
This Speech is, I think, the finest that is ascribed to Satan in the
whole Poem. The Evil Spirit afterwards proceeds to make his Discoveries
concerning our first Parents, and to learn after what manner they may be
best attacked. His bounding over the Walls of Paradise; his sitting in
the Shape of a Cormorant upon the Tree of Life, which stood in the
Center of it, and overtopped all the other Trees of the Garden, his
alighting among the Herd of Animals, which are so beautifully
represented as playing about Adam and Eve, together with his
transforming himself into different Shapes, in order to hear their
Conversation,
Circumstances that give an agreeable Surprize to the
Reader, and are devised with great Art, to connect that Series of
Adventures in which the Poet has engaged
this
Artificer of Fraud.
The Thought of
Satan's
Transformation into a Cormorant, and placing
himself on the Tree of Life, seems raised upon that Passage in the
Iliad
, where two Deities are described, as perching on the Top of an Oak
in the shape of Vulturs.
planting himself at the Ear of
Eve
under the
form
of a Toad, in
order to produce vain Dreams and Imaginations, is a Circumstance of the
same Nature; as his starting up in his own Form is wonderfully fine,
both in the Literal Description, and in the Moral which is concealed
under it.
Answer upon his being discovered, and demanded to give an
Account of himself,
is
conformable to the Pride and Intrepidity of
his Character.
Know ye not then, said Satan, fll'd with Scorn,
Know ye not Me? ye knew me once no mate
For you, there sitting where you durst not soar;
Not to know Me argues your selves unknown,
The lowest of your throng;—
Zephon's
Rebuke, with the Influence it had on
Satan
, is exquisitely
Graceful and Moral.
Satan
is afterwards led away to
Gabriel
, the chief
of the Guardian Angels, who kept watch in Paradise. His disdainful
Behaviour on this Occasion is so remarkable a Beauty, that the most
ordinary Reader cannot but take Notice of it.
Gabriel's
discovering his
Approach at a Distance, is drawn with great strength and liveliness of
Imagination.
O Friends, I hear the tread of nimble Feet
Hasting this Way, and now by glimps discern
Ithuriel and Zephon through the shade;
And with them comes a third of Regal Port,
But faded splendor wan; who by his gait
And fierce demeanor seems the Prince of Hell;
Not likely to part hence without contest:
Stand firm, for in his look defiance lours.
The Conference between
Gabriel
and
Satan
abounds with Sentiments proper
for the Occasion, and suitable to the Persons of the two Speakers.
Satan
cloathing himself with Terror when he prepares for the Combat is truly
sublime, and at least equal to
Homer's
Description of Discord celebrated
by
Longinus
, or to that of Fame in
Virgil
, who are both represented with
their Feet standing upon the Earth, and their Heads reaching above the
Clouds.
While thus he spake, th' Angelic Squadron bright
Turn'd fiery red, sharpning in mooned Horns
Their Phalanx, and began to hem him round
With ported Spears, &c.
—On the other side Satan alarm'd,
Collecting all his might dilated stood
Like Teneriff, or Atlas, unremov'd.
His Stature reached the Sky, and on his Crest
Sat horror plum'd;—
I
here take
notice
, that
Milton
is every where full of Hints
and sometimes literal Translations, taken from the greatest of the
Greek
and
Latin
Poets. But this I may reserve for a Discourse by it self,
because I would not break the Thread of these Speculations, that are
designed for English Readers, with such Reflections as would be of no
use but to the Learned.
I must however observe in this Place, that the breaking off the Combat
between
Gabriel
and
Satan
, by the hanging out of the Golden Scales in
Heaven, is a Refinement upon
Homer's
Thought, who tells us, that before
the Battle between
Hector
and
Achilles
,
Jupiter
weighed the Event of it
in a pair of Scales. The Reader may see the whole Passage in the 22nd
Iliad
.
Virgil
, before the last decisive Combat, describes
Jupiter
in the same
manner, as weighing the Fates of
Turnus
and
Æneas
.
Milton
, though he
fetched this beautiful Circumstance from the
Iliad
and
Æneid
, does not
only insert it as a Poetical Embellishment, like the Authors
above-mentioned; but makes an artful use of it for the proper carrying
on of his Fable, and for the breaking off the Combat between the two
Warriors, who were upon the point of engaging.
To this we may further
add, that Milton is the more justified in this Passage, as we find the
same noble Allegory in Holy Writ, where a wicked Prince, some few Hours
before he was assaulted and slain, is said to have been weighed in the
Scales, and to have been found wanting.
I must here take Notice under the Head of the Machines, that
Uriel's
gliding down to the Earth upon a Sunbeam, with the Poet's Device to make
him descend, as well in his return to the Sun, as in his coming from it,
is a Prettiness that might have been admired in a little fanciful Poet,
but seems below the Genius of
Milton
. The Description of the Host of
armed Angels walking their nightly Round in Paradise, is of another
Spirit.
So saying, on he led his radiant files,
Dazling the Moon;—
as that Account of the Hymns which our first Parents used to hear them
sing in these their Midnight Walks, is altogether Divine, and
inexpressibly amusing to the Imagination.
We are, in the last place, to consider the Parts which
Adam
and
Eve
act
in the Fourth Book. The Description of them as they first appeared to
Satan
, is exquisitely drawn, and sufficient to make the fallen Angel
gaze upon them with all that Astonishment, and those Emotions of Envy,
in which he is represented.
Two of far nobler Shape erect and tall,
God-like erect! with native honour clad
In naked Majesty, seem'd lords of all;
And worthy seem'd: for in their looks divine
The image of their glorious Maker shon,
Truth, Wisdom, Sanctitude severe and pure;
Severe, but in true filial freedom plac'd:
For contemplation he and valour form'd,
For softness she and sweet attractive grace;
He for God only, she for God in him.
His fair large front, and eye sublime, declar'd
Absolute rule; and Hyacinthin Locks
Round from his parted forelock manly hung
Clustring, but not beneath his Shoulders broad.
She, as a Veil, down to her slender waste
Her unadorned golden tresses wore
Dis-shevel'd, but in wanton ringlets wav'd.
So pass'd they naked on, nor shun'd the Sight
Of God or Angel, for they thought no ill:
So hand in hand they passed, the loveliest pair
That ever since in love's embraces met.
There is a fine Spirit of Poetry in the Lines which follow, wherein they
are described as sitting on a Bed of Flowers by the side of a Fountain,
amidst a mixed Assembly of Animals.
The Speeches of these two first Lovers flow equally from Passion and
Sincerity. The Professions they make to one another are full of Warmth:
but at the same time founded on Truth. In a Word, they are the
Gallantries of Paradise:
—When Adam first of Men—
Sole partner and sole part of all these joys,
Dearer thy self than all;—
But let us ever praise him, and extol
His bounty, following our delightful Task,
To prune these growing plants, and tend these flow'rs;
Which were it toilsome, yet with thee were sweet.
To whom thus Eve reply'd. O thou for whom,
And from whom I was form'd, flesh of thy flesh,
And without whom am to no end, my Guide
And Head, what thou hast said is just and right.
For we to him indeed all praises owe.
And daily thanks; I chiefly, who enjoy
So far the happier Lot, enjoying thee
Preeminent by so much odds, while thou
Like consort to thy self canst no where find, &c.
The remaining part of
Eve's
Speech, in which she gives an Account of her
self upon her first Creation, and the manner in which she was brought to
Adam
, is I think as beautiful a Passage as any in
Milton
, or perhaps in
any other Poet whatsoever. These Passages are all worked off with so
much Art, that they are capable of pleasing the most delicate Reader,
without offending the most severe.
That Day I oft remember, when from Sleep, &c.
A
of less Judgment and Invention than this great Author, would have
found it very difficult to have filled
these
tender Parts of the
Poem with Sentiments proper for a State of Innocence; to have described
the Warmth of Love, and the Professions of it, without Artifice or
Hyperbole: to have made the Man speak the most endearing things, without
descending from his natural Dignity, and the Woman receiving them
without departing from the Modesty of her Character; in a Word, to
adjust the Prerogatives of Wisdom and Beauty, and make each appear to
the other in its proper Force and Loveliness. This mutual Subordination
of the two Sexes is wonderfully kept up in the whole Poem, as
particularly in the Speech of Eve I have before mentioned, and upon the
Conclusion of it in the following Lines.
So spake our general Mother, and with eyes
Of Conjugal attraction unreproved,
And meek surrender, half embracing lean'd
On our first father; half her swelling breast
Naked met his under the flowing Gold
Of her loose tresses hid: he in delight
Both of her beauty and submissive charms
Smil'd with superior Love.—
The Poet adds, that the Devil turned away with Envy at the sight of so
much Happiness.
We have another View of our first Parents in their Evening Discourses,
which is full of pleasing Images and Sentiments suitable to their
Condition and Characters. The Speech of
Eve
, in particular, is dressed
up in such a soft and natural Turn of Words and Sentiments, as cannot be
sufficiently admired.
I shall close my Reflections upon this Book, with observing the Masterly
Transition which the Poet makes to their Evening Worship in the
following Lines.
Thus at their shady Lodge arriv'd, both stood,
Both turn'd, and under open Sky, ador'd
The God that made both Sky, Air, Earth and Heaven,
Which they beheld, the Moon's resplendent Globe,
And Starry Pole: Thou also mad'st the Night,
Maker Omnipotent, and thou the Day, &c.
Most of the Modern Heroick Poets have imitated the Ancients, in
beginning a Speech without premising, that the Person said thus or thus;
but as it is easie to imitate the Ancients in the Omission of two or
three Words, it requires Judgment to do it in such a manner as they
shall not be missed, and that the Speech may begin naturally without
them. There is a fine Instance of this Kind out of
Homer
, in the Twenty
Third Chapter of
Longinus
.
L.
From this date to the end of the series the Saturday papers
upon Milton exceed the usual length of a
Spectator
essay. That they may
not occupy more than the single leaf of the original issue, they are
printed in smaller type; the columns also, when necessary, encroach on
the bottom margin of the paper, and there are few advertisements
inserted.
At the end of the third Book of the
Poetics
.
'The diction should be most laboured in the idle parts of the poem;
those in which neither manners nor sentiments prevail; for the manners
and the sentiments are only obscured by too splendid a diction.'
this great
shape
are
notice by the way
those
Contents
Dedication of the Fifth Volume of The Spectator
To The Right Honourable Thomas Earl of Wharton1.
My
Lord
,
The Author of the
Spectator
having prefixed before each of his Volumes
the Name of some great Person to whom he has particular Obligations,
lays his Claim to your Lordship's Patronage upon the same Account. I
must confess, my Lord, had not I already received great Instances of
your Favour, I should have been afraid of submitting a Work of this
Nature to your Perusal. You are so thoroughly acquainted with the
Characters of Men, and all the Parts of human Life, that it is
impossible for the least Misrepresentation of them to escape your
Notice. It is Your Lordship's particular Distinction that you are Master
of the whole Compass of Business, and have signalized Your Self in all
the different Scenes of it. We admire some for the Dignity, others for
the Popularity of their Behaviour; some for their Clearness of Judgment,
others for their Happiness of Expression; some for the laying of
Schemes, and others for the putting of them in Execution: It is Your
Lordship only who enjoys these several Talents united, and that too in
as great Perfection as others possess them singly. Your Enemies
acknowledge this great Extent in your Lordship's Character, at the same
time that they use their utmost Industry and Invention to derogate from
it. But it is for Your Honour that those who are now Your Enemies were
always so. You have acted in so much Consistency with Your Self, and
promoted the Interests of your Country in so uniform a Manner, that even
those who would misrepresent your Generous Designs for the Publick Good,
cannot but approve the Steadiness and Intrepidity with which You pursue
them. It is a most sensible Pleasure to me that I have this Opportunity
of professing my self one of your great Admirers, and, in a very
particular Manner,
My
Lord
,
Your Lordship's
Most Obliged,
And most Obedient,
Humble Servant,
THE
Spectator
.
This is the Thomas, Earl of Wharton, who in 1708 became
Lord-lieutenant of Ireland, and took Addison for his Chief Secretary. He
was the son of Philip, Baron Wharton, a firm Presbyterian, sometimes
called the good Lord Wharton, to distinguish him from his son and
grandson. Philip Wharton had been an opponent of Stuart encroachments, a
friend of Algernon Sidney, and one of the first men to welcome William
III. to England. He died, very old, in 1694. His son Thomas did not
inherit the religious temper of his father, and even a dedication could
hardly have ventured to compliment him on his private morals. But he was
an active politician, was with his father in the secret of the landing
of the Prince of Orange, and was made by William Comptroller of the
Household. Thwarted in his desire to become a Secretary of State, he
made himself formidable as a bold, sarcastic speaker and by the strength
of his parliamentary interest. He is said to have returned at one time
thirty members, and to have spent eighty thousand pounds upon the
maintenance of his political position. He was apt, by his manners, to
make friends of the young men of influence. He spent money freely also
on the turf, and upon his seat of Winchenden, in Wilts. Queen Anne, on
her accession, struck his name with her own hand from the list of Privy
Councillors, but he won his way not only to restoration of that rank,
but also in December, 1706, at the age of 67, to his title of Viscount
Winchendon and Earl of Wharton. In November, 1708, he became
Lord-lieutenant of Ireland, with Addison for secretary. He took over
with him also Clayton the musician, and kept a gay court, easily
accessible, except to Roman Catholics, whom he would not admit to his
presence, and against whom he enforced the utmost rigour of the penal
code. He had himself conformed to the Church of England. Swift accused
him, as Lord-lieutenant, of shameless depravity of manners, of
injustice, greed, and gross venality. This Lord Wharton died in 1715,
and was succeeded by his son Philip, whom George I., in 1718, made Duke
of Wharton for his father's vigorous support of the Hanoverian
succession. His character was much worse than that of his father, the
energetic politician and the man of cultivated taste and ready wit to
whom Steele and Addison here dedicated the Fifth Volume of the
Spectator
.
Contents
|
Monday, March 10, 1712 |
Steele |
Ad humum mærore gravi deducit et angit.
Hor.

It is often said, after a Man has heard a Story with extraordinary
Circumstances, It is a very good one if it be true: But as for the
following Relation, I should be glad were I sure it were false. It is
told with such Simplicity, and there are so many artless Touches of
Distress in it, that I fear it comes too much from the Heart.
Mr. Spectator,
'Some Years ago it happened that I lived in the same House with a
young Gentleman of Merit; with whose good Qualities I was so much
taken, as to make it my Endeavour to shew as many as I was able in my
self. Familiar Converse improved general Civilities into an unfeigned
Passion on both Sides. He watched an Opportunity to declare himself to
me; and I, who could not expect a Man of so great an Estate as his,
received his Addresses in such Terms, as gave him no reason to believe
I was displeased by them, tho' I did nothing to make him think me more
easy than was decent. His Father was a very hard worldly Man, and
proud; so that there was no reason to believe he would easily be
brought to think there was any thing in any Woman's Person or
Character that could ballance the Disadvantage of an unequal Fortune.
In the mean time the Son continued his Application to me, and omitted
no Occasion of demonstrating the most disinterested Passion imaginable
to me; and in plain direct Terms offer'd to marry me privately, and
keep it so till he should be so happy as to gain his Father's
Approbation, or become possessed of his Estate. I passionately loved
him, and you will believe I did not deny such a one what was my
Interest also to grant. However I was not so young, as not to take the
Precaution of carrying with me a faithful Servant, who had been also
my Mother's Maid, to be present at the Ceremony. When that was over I
demanded a Certificate, signed by the Minister, my Husband, and the
Servant I just now spoke of. After our Nuptials, we conversed together
very familiarly in the same House; but the Restraints we were
generally under, and the Interviews we had, being stolen and
interrupted, made our Behaviour to each other have rather the
impatient Fondness which is visible in Lovers, than the regular and
gratified Affection which is to be observed in Man and Wife. This
Observation made the Father very anxious for his Son, and press him to
a Match he had in his Eye for him. To relieve my Husband from this
Importunity, and conceal the Secret of our Marriage, which I had
reason to know would not be long in my power in Town, it was resolved
that I should retire into a remote Place in the Country, and converse
under feigned Names by Letter. We long continued this Way of Commerce;
and I with my Needle, a few Books, and reading over and over my
Husband's Letters, passed my Time in a resigned Expectation of better
Days. Be pleased to take notice, that within four Months after I left
my Husband I was delivered of a Daughter, who died within few Hours
after her Birth. This Accident, and the retired Manner of Life I led,
gave criminal Hopes to a neighbouring Brute of a Country Gentle-man,
whose Folly was the Source of all my Affliction. This Rustick is one
of those rich Clowns, who supply the Want of all manner of Breeding by
the Neglect of it, and with noisy Mirth, half Understanding, and ample
Fortune, force themselves upon Persons and Things, without any Sense
of Time and Place. The poor ignorant People where I lay conceal'd, and
now passed for a Widow, wondered I could be so shy and strange, as
they called it, to the Squire; and were bribed by him to admit him
whenever he thought fit. I happened to be sitting in a little Parlour
which belonged to my own Part of the House, and musing over one of the
fondest of my Husband's Letters, in which I always kept the
Certificate of my Marriage, when this rude Fellow came in, and with
the nauseous Familiarity of such unbred Brutes, snatched the Papers
out of my Hand. I was immediately under so great a Concern, that I
threw my self at his Feet, and begged of him to return them. He with
the same odious Pretence to Freedom and Gaiety, swore he would read
them. I grew more importunate, he more curious, till at last, with an
Indignation arising from a Passion I then first discovered in him, he
threw the Papers into the Fire, swearing that since he was not to read
them, the Man who writ them should never be so happy as to have me
read them over again. It is insignificant to tell you my Tears and
Reproaches made the boisterous Calf leave the Room ashamed and out of
Countenance, when I had leisure to ruminate on this Accident with more
than ordinary Sorrow: However, such was then my Confidence in my
Husband, that I writ to him the Misfortune, and desired another Paper
of the same kind. He deferred writing two or three Posts, and at last
answered me in general, That he could not then send me what I asked
for, but when he could find a proper Conveyance, I should be sure to
have it. From this time his Letters were more cold every Day than the
other, and as he grew indifferent I grew jealous. This has at last
brought me to Town, where I find both the Witnesses of my Marriage
dead, and that my Husband, after three Months Cohabitation, has buried
a young Lady whom he married in Obedience to his Father. In a word, he
shuns and disowns me. Should I come to the House and confront him, the
Father would join in supporting him against me, though he believed my
Story; should I talk it to the World, what Reparation can I expect for
an Injury I cannot make out? I believe he means to bring me, through
Necessity, to resign my Pretentions to him for some Provision for my
Life; but I will die first. Pray bid him remember what he said, and
how he was charmed when he laughed at the heedless Discovery I often
made of my self; let him remember how awkward he was in my dissembled
Indifference towards him before Company; ask him how I, who could
never conceal my Love for him, at his own Request, can part with him
for ever? Oh, Mr. Spectator, sensible Spirits know no Indifference in
Marriage; what then do you think is my piercing Affliction?—- I
leave you to represent my Distress your own way, in which I desire you
to be speedy, if you have Compassion for Innocence exposed to Infamy.
Octavia.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 11, 1712 |
Addison |
Modo Vir, modo Fœmina.
Virg.
1
The journal with which I presented my Reader on Tuesday last, has
brought me in several Letters, with Accounts of many private Lives cast
into that Form. I have the
Rake's Journal,
the
Sot's Journal,
the
Whoremaster's Journal,
and among several others a very curious Piece,
entituled,
The Journal of a Mohock
. By these Instances I find that the
Intention of my last Tuesday's Paper has been mistaken by many of my
Readers. I did not design so much to expose Vice as Idleness, and aimed
at those Persons who pass away their Time rather in Trifle and
Impertinence, than in Crimes and Immoralities. Offences of this latter
kind are not to be dallied with, or treated in so ludicrous a manner. In
short, my Journal only holds up Folly to the Light, and shews the
Disagreeableness of such Actions as are indifferent in themselves, and
blameable only as they proceed from Creatures endow'd with Reason.
My following Correspondent, who calls her self
Clarinda
, is such a
Journalist as I require: She seems by her Letter to be placed in a
modish State of Indifference between Vice and Virtue, and to be
susceptible of either, were there proper Pains taken with her. Had her
Journal been filled with Gallantries, or such Occurrences as had shewn
her wholly divested of her natural Innocence, notwithstanding it might
have been more pleasing to the Generality of Readers, I should not have
published it; but as it is only the Picture of a Life filled with a
fashionable kind of Gaiety and Laziness, I shall set down five Days of
it, as I have received it from the Hand of my fair Correspondent.
Dear Mr. Spectator,
'You having set your Readers an Exercise in one of your last Week's
Papers, I have perform'd mine according to your Orders, and herewith
send it you enclosed. You must know, Mr. Spectator, that I am a Maiden
Lady of a good Fortune, who have had several Matches offered me for
these ten Years last past, and have at present warm Applications made
to me by a very pretty Fellow. As I am at my own Disposal, I come up
to Town every Winter, and pass my Time in it after the manner you will
find in the following Journal, which I begun to write upon the very
Day after your Spectator upon that Subject.
| Tuesday |
Night. |
Could not go to sleep till one in the Morning for
thinking of my Journal. |
| Wednesday |
From Eight 'till Ten |
Drank two Dishes of Chocolate in
Bed, and fell asleep after 'em. |
|
From Ten to Eleven. |
Eat a Slice of Bread and Butter, drank a Dish of
Bohea, read the Spectator. |
|
From Eleven to One. |
At my Toilet, try'd a new Head. Gave Orders for
Veny to be combed and washed. Mem. I look best in Blue. |
|
From One till Half an Hour after Two. |
Drove to the Change. Cheapned
a Couple of Fans. |
|
Till Four. |
At Dinner. Mem. Mr. Froth passed by in his new Liveries. |
|
From Four to Six. |
Dressed, paid a Visit to old Lady Blithe and her
Sister, having before heard they were gone out of Town that Day. |
|
From Six to Eleven. |
At Basset. Mem. Never set again upon the Ace of
Diamonds. |
| Thursday |
From Eleven at Night to Eight in the Morning. |
Dream'd that
I punted to Mr. Froth. |
|
From Eight to Ten. |
Chocolate. Read two Acts in Aurenzebe2 abed. |
|
From Ten to Eleven. |
Tea-Table. Sent to borrow Lady Faddle's Cupid
for Veny. Read the Play-Bills. Received a Letter from Mr. Froth.
Mem. locked it up in my strong Box. |
|
Rest of the Morning. |
Fontange, the Tire-woman, her Account of my
Lady Blithe's Wash. Broke a Tooth in my little Tortoise-shell Comb.
Sent Frank to know how my Lady Hectick rested after her Monky's
leaping out at Window. Looked pale. Fontange tells me my Glass is
not true. Dressed by Three. |
|
From Three to Four. |
Dinner cold before I sat down. |
|
From Four to Eleven. |
Saw Company. Mr. Froth's Opinion of Milton. His
Account of the Mohocks. His Fancy for a Pin-cushion. Picture in the
Lid of his Snuff-box. Old Lady Faddle promises me her Woman to cut
my Hair. Lost five Guineas at Crimp. |
|
Twelve a-Clock at Night. |
Went to Bed. |
| Friday |
Eight in the Morning. |
Abed. Read over all Mr. Froth's
Letters. Cupid and Veny. |
|
Ten a-Clock. |
Stay'd within all day, not at home. |
|
From Ten to Twelve. |
In Conference with my Mantua-Maker. Sorted a
Suit of Ribbands. Broke my Blue China Cup. |
|
From Twelve to One. |
Shut my self up in my Chamber, practised Lady
Betty Modely's Skuttle. |
|
One in the Afternoon. |
Called for my flowered Handkerchief. Worked
half a Violet-Leaf in it. Eyes aked and Head out of Order. Threw by
my Work, and read over the remaining Part of Aurenzebe. |
|
From Three to Four. |
Dined. |
|
From Four to Twelve. |
Changed my Mind, dressed, went abroad, and
play'd at Crimp till Midnight. Found Mrs. Spitely at home.
Conversation: Mrs. Brilliant's Necklace false Stones. Old Lady
Loveday going to be married to a young Fellow that is not worth a
Groat. Miss Prue gone into the Country. Tom Townley has red Hair.
Mem. Mrs. Spitely whispered in my Ear that she had something to tell
me about Mr. Froth, I am sure it is not true. |
|
Between Twelve and One. |
Dreamed that Mr. Froth lay at my Feet, and
called me Indamora3. |
| Saturday |
|
Rose at Eight a-Clock in the Morning. Sate down to my
Toilet. |
|
From Eight to Nine. |
Shifted a Patch for Half an Hour before I could
determine it. Fixed it above my left Eye-brow. |
|
From Nine to Twelve. |
Drank my Tea, and dressed. |
|
From Twelve to Two. |
At Chappel. A great deal of good Company. Mem.
The third Air in the new Opera. Lady Blithe dressed frightfully. |
|
From Three to Four. |
Dined. Miss Kitty called upon me to go to the
Opera before I was risen from Table. |
|
From Dinner to Six. |
Drank Tea. Turned off a Footman for being rude
to Veny. |
|
Six a-Clock. |
Went to the Opera. I did not see Mr. Froth till the
beginning of the second Act. Mr. Froth talked to a Gentleman in a
black Wig. Bowed to a Lady in the front Box. Mr. Froth and his
Friend clapp'd Nicolini in the third Act. Mr. Froth cried out
Ancora. Mr. Froth led me to my Chair. I think he squeezed my Hand. |
|
Eleven at Night. |
Went to Bed. Melancholy Dreams. Methought Nicolini
said he was Mr. Froth. |
| Sunday |
|
Indisposed. |
| Monday |
Eight a-Clock. |
Waked by Miss Kitty. Aurenzebe lay upon the
Chair by me. Kitty repeated without Book the Eight best Lines in the
Play. Went in our Mobbs to the dumb Man4, according to
Appointment. Told me that my Lover's Name began with a G. Mem. The
Conjurer was within a Letter of Mr. Froth's Name, &c. |
Upon looking back into this my Journal, I find that I am at a loss to
know whether I pass my Time well or ill; and indeed never thought of
considering how I did it before I perused your Speculation upon that
Subject. I scarce find a single Action in these five Days that I can
thoroughly approve of, except the working upon the Violet-Leaf, which
I am resolved to finish the first Day I am at leisure. As for Mr.
Froth and Veny I did not think they took up so much of my Time and
Thoughts, as I find they do upon my Journal. The latter of them I will
turn off, if you insist upon it; and if Mr. Froth does not bring
Matters to a Conclusion very suddenly, I will not let my Life run away
in a Dream.
Your humble Servant,
Clarinda.
To resume one of the Morals of my first Paper, and to confirm Clarinda
in her good Inclinations, I would have her consider what a pretty Figure
she would make among Posterity, were the History of her whole Life
published like these five Days of it. I
conclude my Paper with an
Epitaph written by an uncertain Author
on Sir Philip Sidney's Sister, a
Lady who seems to have been of a Temper very much different from that of
Clarinda. The last Thought of it is so very noble, that I dare say my
Reader will pardon me the Quotation.
On the Countess Dowager of Pembroke.
Underneath this Marble Hearse
Lies the Subject of all Verse,
Sidney's Sister, Pembroke's Mother:
Death, ere thou hast kil'd another,
Fair, and learn'd, and good as she,
Time shall throw a Dart at thee.
A quotation from memory of Virgil's 'Et juvenis quondam
nunc fœmina.'
Æn
. vi. 448.
Dryden's.
The heroine of
Aurengzebe
.
Duncan Campbell, said to be deaf and dumb, and to tell
fortunes by second sight. In 1732 there appeared 'Secret Memoirs of the
late Mr. D. Campbell.... written by himself... with an Appendix by way
of 'vindicating Mr. C. against the groundless aspersion cast upon him,
that he but pretended to be deaf and dumb.'
Ben Jonson.
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 12, 1712 |
Steele |
O curvæ in terris animæ, et cœlestium inanes.
Pers.
1
Mr.
Spectator,
The Materials you have collected together towards a general History
of Clubs, make so bright a Part of your Speculations, that I think it
is but a Justice we all owe the learned World to furnish you with such
Assistances as may promote that useful Work. For this Reason I could
not forbear communicating to you some imperfect Informations of a Set
of Men (if you will allow them a place in that Species of Being) who
have lately erected themselves into a Nocturnal Fraternity, under the
Title of the
Mohock Club, a Name borrowed it seems from a sort of
Cannibals in India, who subsist by plundering and devouring all the
Nations about them. The President is styled Emperor of the Mohocks;
and his Arms are a Turkish Crescent, which his Imperial Majesty bears
at present in a very extraordinary manner engraven upon his Forehead.
Agreeable to their Name, the avowed design of their Institution is
Mischief; and upon this Foundation all their Rules and Orders are
framed. An outrageous Ambition of doing all possible hurt to their
Fellow-Creatures, is the great Cement of their Assembly, and the only
Qualification required in the Members. In order to exert this
Principle in its full Strength and Perfection, they take care to drink
themselves to a pitch, that is, beyond the Possibility of attending to
any Motions of Reason and Humanity; then make a general Sally, and
attack all that are so unfortunate as to walk the Streets through
which they patrole. Some are knock'd down, others stabb'd, others cut
and carbonado'd. To put the Watch to a total Rout, and mortify some of
those inoffensive Militia, is reckon'd a
Coup d'éclat. The particular
Talents by which these Misanthropes are distinguished from one
another, consist in the various kinds of Barbarities which they
execute upon their Prisoners. Some are celebrated for a happy
Dexterity in tipping the Lion upon them; which is performed by
squeezing the Nose flat to the Face, and boring out the Eyes with
their Fingers: Others are called the Dancing-Masters, and teach their
Scholars to cut Capers by running Swords thro' their Legs; a new
Invention, whether originally French I cannot tell: A third sort are
the Tumblers, whose office it is to set Women on their Heads, and
commit certain Indecencies, or rather Barbarities, on the Limbs which
they expose. But these I forbear to mention, because they can't but be
very shocking to the Reader as well as the
Spectator. In
this manner
they carry on a War against Mankind; and by the standing Maxims of
their Policy, are to enter into no Alliances but one, and that is
Offensive and Defensive with all Bawdy-Houses in general, of which
they have declared themselves Protectors and Guarantees
2.
'I must own, Sir, these are only broken incoherent Memoirs of this
wonderful Society, but they are the best I have been yet able to
procure; for being but of late Establishment, it is not ripe for a
just History; And to be serious, the chief Design of this Trouble is
to hinder it from ever being so. You have been pleas'd, out of a
concern for the good of your Countrymen, to act under the Character of
Spectator, not only the Part of a Looker-on, but an Overseer of their
Actions; and whenever such Enormities as this infest the Town, we
immediately fly to you for Redress. I have reason to believe, that
some thoughtless Youngsters, out of a false Notion of Bravery, and an
immoderate Fondness to be distinguished for Fellows of Fire, are
insensibly hurry'd into this senseless scandalous Project: Such will
probably stand corrected by your Reproofs, especially if you inform
them, that it is not Courage for half a score Fellows, mad with Wine
and Lust, to set upon two or three soberer than themselves; and that
the Manners of Indian Savages are no becoming Accomplishments to an
English fine Gentleman. Such of them as have been Bullies and Scowrers
of a long standing, and are grown Veterans in this kind of Service,
are, I fear, too hardned to receive any Impressions from your
Admonitions. But I beg you would recommend to their Perusal your [Volume 1 link:
ninth]
Speculation: They may there be taught to take warning from the Club of
Duellists; and be put in mind, that the common Fate of those Men of
Honour was to be hang'd.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Philanthropos
March the 10th, 1711-12.
The following Letter is of a quite contrary nature; but I add it here,
that the Reader may observe at the same View, how amiable Ignorance may
be when it is shewn in its Simplicities, and how detestable in
Barbarities. It is written by an honest Countryman to his Mistress, and
came to the Hands of a Lady of good Sense wrapped about a Thread-Paper,
who has long kept it by her as an Image of artless Love.
To her I very much respect, Mrs. Margaret Clark.
'Lovely, and oh that I could write loving Mrs. Margaret Clark, I pray
you let Affection excuse Presumption. Having been so happy as to enjoy
the Sight of your sweet Countenance and comely Body, sometimes when I
had occasion to buy Treacle or Liquorish Powder at the Apothecary's
Shop, I am so enamoured with you, that I can no more keep close my
flaming Desire to become your Servant. And I am the more bold now to
write to your sweet self, because I am now my own Man, and may match
where I please; for my Father is taken away, and now I am come to my
Living, which is Ten Yard Land, and a House; and there is never a Yard
of Land in our Field but it is as well worth ten Pound a Year, as a
Thief is worth a Halter; and all my Brothers and Sisters are provided
for: Besides I have good Houshold-stuff, though I say it, both Brass
and Pewter, Linnens and Woollens; and though my House be thatched,
yet, if you and I match, it shall go hard but I will have one half of
it slated. If you think well of this Motion, I will wait upon you as
soon as my new Cloaths is made and Hay Harvest is in. I could, 'though
I say it, have good—'
rest is torn off
; and Posterity must be contented to know, that
Mrs. Margaret Clark was very pretty, but are left in the dark as to the
Name of her Lover.
T.
'Sævis inter se convenit Ursis.'
Juv.
Gay tells also in his Trivia that the Mohocks rolled women
in hogs-heads down Snow hill. Swift wrote of the Mohocks, at this time,
in his Journal to Stella,
'Grub-street papers about them fly like lightning, and a list printed
of near eighty put into several prisons, and all a lie, and I begin to
think there is no truth, or very little, in the whole story.'
On the 18th of March an attempt was made to put the Mohocks down by
Royal Proclamation.
This letter is said to have been really sent to one who
married Mr. Cole, a Northampton attorney, by a neighbouring freeholder
named Gabriel Bullock, and shown to Steele by his friend the antiquary,
Browne Willis. See also
.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 13, 1712 |
Budgell |
Quid frustra Simulacra fugacia captas?
Quod petis, est nusquam: quod amas avertere, perdes.
Ista repercussæ quam cernis imaginis umbra est,
Nil habet ista sui; tecum venitque, manetque,
Tecum discedet si tu discedere possis.
Ovid.

Will. Honeycomb
diverted us last Night with an Account of a young
Fellow's first discovering his Passion to his Mistress. The young Lady
was one, it seems, who had long before conceived a favourable Opinion of
him, and was still in hopes that he would some time or other make his
Advances. As he was one day talking with her in Company of her two
Sisters, the Conversation happening to turn upon Love, each of the young
Ladies was by way of Raillery, recommending a Wife to him; when, to the
no small Surprize of her who languished for him in secret, he told them
with a more than ordinary Seriousness, that his Heart had been long
engaged to one whose Name he thought himself obliged in Honour to
conceal; but that he could shew her Picture in the Lid of his Snuff-box.
The young Lady, who found herself the most sensibly touched by this
Confession, took the first Opportunity that offered of snatching his Box
out of his Hand. He seemed desirous of recovering it, but finding her
resolved to look into the Lid, begged her, that if she should happen to
know the Person, she would not reveal her Name. Upon carrying it to the
Window, she was very agreeably surprized to find there was nothing
within the Lid but a little Looking-Glass, in which, after she had
view'd her own Face with more Pleasure than she had ever done before,
she returned the Box with a Smile, telling him, she could not but admire
at his Choice.
Will
. fancying that his Story took, immediately fell into a Dissertation
on the Usefulness of Looking-Glasses, and applying himself to me, asked,
if there were any Looking Glasses in the Times of the Greeks and Romans;
for that he had often observed in the Translations of Poems out of those
Languages, that People generally talked of seeing themselves in Wells,
Fountains, Lakes, and Rivers: Nay, says he, I remember Mr.
Dryden
in his
Ovid
tells us of a swingeing Fellow, called
Polypheme
, that made use of
the Sea for his Looking-Glass, and could never dress himself to
Advantage but in a Calm.
My Friend
Will
, to shew us the whole Compass of his Learning upon this
Subject, further informed us, that there were still several Nations in
the World so very barbarous as not to have any Looking-Glasses among
them; and that he had lately read a Voyage to the South-Sea, in which it
is said, that the Ladies of Chili always dress their Heads over a Bason
of Water.
I am the more particular in my Account of
Will.'s
last Night's Lecture
on these natural Mirrors, as it seems to bear some Relation to the
following Letter, which I received the Day before.
Sir,
'I have read your last Saturday's Observations on the Fourth Book of
Milton with great Satisfaction, and am particularly pleased with the
hidden Moral, which you have taken notice of in several Parts of the
Poem. The Design of this Letter is to desire your Thoughts, whether
there may not also be some Moral couched under that Place in the same
Book where the Poet lets us know, that the first Woman immediately
after her Creation ran to a Looking-Glass, and became so enamoured of
her own Face, that she had never removed to view any of the other
Works of Nature, had not she been led off to a Man. If you think fit
to set down the whole Passage from Milton, your Readers will be able
to judge for themselves, and the Quotation will not a little
contribute to the filling up of your Paper.
Your humble Servant,
R. T.'
The last Consideration urged by my Querist is so strong, that I cannot
forbear closing with it. The Passage he alludes to, is part of
Eve's
Speech to
Adam
, and one of the most beautiful Passages in the whole Poem.
That Day I oft remember, when from sleep
I first awaked, and found my self repos d
Under a shade of flow'rs, much wondering where
And what I was, whence thither brought, and how.
Not distant far from thence a murmuring Sound
Of Waters issu'd from a Cave, and spread
Into a liquid Plain, then stood unmoved
Pure as th' Expanse of Heav'n: I thither went
With unexperienced Thought, and laid me down
On the green Bank, to look into the clear
Smooth Lake, that to me seemed another Sky.
As I bent down to look, just opposite,
A Shape within the watry Gleam appeared
Bending to look on me; I started back,
It started back; but pleas'd I soon returned,
Pleas'd it return'd as soon with answering Looks
Of Sympathy and Love; there I had fix d
Mine Eyes till now, and pined with vain Desire,
Had not a Voice thus warn'd me, What thou seest,
What there thou seest, fair Creature, is thy self,
With thee it came and goes: but follow me,
And I will bring thee where no Shadow stays
Thy coming, and thy soft Embraces, he
Whose Image thou art, him thou shalt enjoy
Inseparably thine, to him shalt bear
Multitudes like thy self, and thence be call'd
Mother of Human Race. What could I do,
But follow streight, invisibly thus led?
Till I espy'd thee, fair indeed and tall,
Under a Platan, yet methought less fair,
Less winning soft, less amiably mild,
Than that smooth watry Image: back I turn'd,
Thou following cry'dst aloud, Return fair Eve,
Whom fly'st thou? whom thou fly'st, of him thou art,
His Flesh, his Bone; to give thee Being, I lent
Out of my Side to thee, nearest my Heart,
Substantial Life, to have thee by my side
Henceforth an individual Solace dear.
Part of my Soul I seek thee, and thee claim
My other half!—-With that thy gentle hand
Seized mine, I yielded, and from that time see
How Beauty is excell'd by manly Grace,
And Wisdom, which alone is truly fair.
So spake our general Mother,—
X.
Contents
|
Friday, March 14, 1712 |
Steele |
Inclusam Danaen turris ahenea
Robustæque fores, et vigilum canum
Tristes exubiæ, munierant satis
Nocturnis ab adulteris;
Si non—
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'Your Correspondent's Letter relating to Fortune-Hunters, and your
subsequent Discourse upon it, have given me Encouragement to send you
a State of my Case, by which you will see, that the Matter complained
of is a common Grievance both to City and Country.
'I am a Country Gentleman of between five and six thousand a Year. It
is my Misfortune to have a very fine Park and an only Daughter; upon
which account I have been so plagu'd with Deer-Stealers and Fops, that
for these four Years past I have scarce enjoy'd a Moment's Rest. I
look upon my self to be in a State of War, and am forc'd to keep as
constant watch in my Seat, as a Governour would do that commanded a
Town on the Frontier of an Enemy's Country. I have indeed pretty well
secur'd my Park, having for this purpose provided my self of four
Keepers, who are Left-handed, and handle a Quarter-Staff beyond any
other Fellow in the Country. And for the Guard of my House, besides a
Band of Pensioner-Matrons and an old Maiden Relation, whom I keep on
constant Duty, I have Blunderbusses always charged, and Fox-Gins
planted in private Places about my Garden, of which I have given
frequent Notice in the Neighbourhood; yet so it is, that in spite of
all my Care, I shall every now and then have a saucy Rascal ride by
reconnoitring (as I think you call it) under my Windows, as sprucely
drest as if he were going to a Ball. I am aware of this way of
attacking a Mistress on Horseback, having heard that it is a common
Practice in Spain; and have therefore taken care to remove my Daughter
from the Road-side of the House, and to lodge her next the Garden. But
to cut short my Story; what can a Man do after all? I durst not stand
for Member of Parliament last Election, for fear of some ill
Consequence from my being off of my Post. What I would therefore
desire of you, is, to promote a Project I have set on foot; and upon
which I have writ to some of my Friends; and that is, that care may be
taken to secure our Daughters by Law, as well as our Deer; and that
some honest Gentleman of a publick Spirit, would move for Leave to
bring in a Bill For the better preserving of the Female Game.
I am,
Sir,
Your humble Servant.
Mile-End-Green,
March 6, 1711-12.
Mr.
Spectator,
Here is a young Man walks by our Door every Day about the Dusk of the
Evening. He looks up at my Window, as if to see me; and if I steal
towards it to peep at him, he turns another way, and looks frightened
at finding what he was looking for. The Air is very cold; and pray let
him know that if he knocks at the Door, he will be carry'd to the
Parlour Fire; and I will come down soon after, and give him an
Opportunity to break his Mind.
I am,
Sir,
Your humble Servant,
Mary Comfitt.
If I observe he cannot speak, I'll give him time to recover himself,
and ask him how he does.
Dear
Sir,
I beg you to print this without Delay, and by the first Opportunity
give us the natural Causes of Longing in Women; or put me out of Fear
that my Wife will one time or other be delivered of something as
monstrous as any thing that has yet appeared to the World; for they
say the Child is to bear a Resemblance of what was desird by the
Mother. I have been marryd upwards of six Years, have had four
Children, and my Wife is now big with the fifth. The Expences she has
put me to in procuring what she has longed for during her Pregnancy
with them, would not only have handsomely defrayd the Charges of the
Month, but of their Education too; her Fancy being so exorbitant for
the first Year or two, as not to confine it self to the usual Objects
of Eatables and Drinkables, but running out after Equipage and
Furniture, and the like Extravagancies. To trouble you only with a few
of them: When she was with Child of Tom, my eldest Son, she came home
one day just fainting, and told me she had been visiting a Relation,
whose Husband had made her a Present of a Chariot and a stately pair
of Horses; and that she was positive she could not breathe a Week
longer, unless she took the Air in the Fellow to it of her own within
that time: This, rather than lose an Heir, I readily complyd with.
Then the Furniture of her best Room must be instantly changed, or she
should mark the Child with some of the frightful Figures in the
old-fashion'd Tapestry. Well, the Upholsterer was called, and her
Longing sav'd that bout. When she went with Molly, she had fix'd her
Mind upon a new Set of Plate, and as much China as would have
furnished an India Shop: These also I chearfully granted, for fear of
being Father to an Indian Pagod. Hitherto I found her Demands rose
upon every Concession; and had she gone on, I had been ruined: But by
good Fortune, with her third, which was Peggy, the Height of her
Imagination came down to the Corner of a Venison Pasty, and brought
her once even upon her Knees to gnaw off the Ears of a Pig from the
Spit. The Gratifications of her Palate were easily preferred to those
of her Vanity; and sometimes a Partridge or a Quail, a Wheat-Ear or
the Pestle of a Lark, were chearfully purchased; nay, I could be
contented tho' I were to feed her with green Pease in April, or
Cherries in May. But with the Babe she now goes, she is turned Girl
again, and fallen to eating of Chalk, pretending 'twill make the
Child's Skin white; and nothing will serve her but I must bear her
Company, to prevent its having a Shade of my Brown: In this however I
have ventur'd to deny her. No longer ago than yesterday, as we were
coming to Town, she saw a parcel of Crows so heartily at Break-fast
upon a piece of Horse-flesh, that she had an invincible Desire to
partake with them, and (to my infinite Surprize) begged the Coachman
to cut her off a Slice as if 'twere for himself, which the Fellow did;
and as soon as she came home she fell to it with such an Appetite,
that she seemed rather to devour than eat it. What her next Sally will
be, I cannot guess: but in the mean time my Request to you is, that if
there be any way to come at these wild unaccountable Rovings of
Imagination by Reason and Argument, you'd speedily afford us your
Assistance. This exceeds the Grievance of Pin-Money, and I think in
every Settlement there ought to be a Clause inserted, that the Father
should be answerable for the Longings of his Daughter. But I shall
impatiently expect your Thoughts in this Matter and am
Sir,
Your most Obliged, and
most Faithful Humble Servant,
T.B.
Let me know whether you think the next Child will love Horses as much
as Molly does China-Ware.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, March 15, 1712 |
Addison |
Major rerum mihi nascitur ordo.
Virg.

We were told in the foregoing Book how the evil Spirit practised upon
Eve
as she lay asleep, in order to inspire her with Thoughts of Vanity,
Pride, and Ambition. The Author, who shews a wonderful Art throughout
his whole Poem, in preparing the Reader for the several Occurrences that
arise in it, founds upon the above-mention'd Circumstance, the first
Part of the fifth Book.
Adam
upon his awaking finds
Eve
still asleep,
with an unusual Discomposure in her Looks. The Posture in which he
regards her, is describ'd with a Tenderness not to be express'd, as the
Whisper with which he awakens her, is the softest that ever was convey'd
to a Lover's Ear.
His wonder was, to find unwaken'd Eve
With Tresses discompos'd, and glowing Cheek,
As through unquiet Rest: he on his side
Leaning half-rais'd, with Looks of cordial Love
Hung over her enamour'd, and beheld
Beauty, which whether waking or asleep,
Shot forth peculiar Graces: then, with Voice
Mild, as when Zephyrus on Flora breathes,
Her Hand soft touching, whisper'd thus: Awake
My Fairest, my Espous'd, my latest found,
Heav'n's last best Gift, my ever new Delight!
Awake: the Morning shines, and the fresh Field
Calls us, we lose the Prime, to mark how spring
Our tended Plants, how blows the Citron Grove,
What drops the Myrrh, and what the balmy Reed,
How Nature paints her Colours, how the Bee
Sits on the Bloom, extracting liquid Sweets.
Such whispering wak'd her, but with startled Eye
On Adam, whom embracing, thus she spake:
O Sole, in whom my Thoughts find all Repose,
My Glory, my Perfection! glad I see
Thy Face, and Morn return'd—
I cannot but take notice that
Milton
, in the Conferences between
Adam
and
Eve
, had his Eye very frequently upon the
Book of Canticles
, in
which there is a noble Spirit of Eastern Poetry; and very often not
unlike what we meet with in
Homer
, who is generally placed near the Age
of
Solomon
. I think there is no question but the Poet in the preceding
Speech remember'd those two Passages which are spoken on the like
occasion, and fill'd with the same pleasing Images of Nature.
My beloved spake, and said unto me, Rise up, my Love, my Fair one, and
come away; for lo the Winter is past, the Rain is over and gone, the
Flowers appear on the Earth, the Time of the singing of Birds is come,
and the Voice of the Turtle is heard in our Land. The Fig-tree putteth
forth her green Figs, and the Vines with the tender Grape give a good
Smell. Arise my Love, my Fair-one and come away.
Come, my Beloved, let us go forth into the Field; let us get up early
to the Vineyards, let us see if the Vine flourish, whether the tender
Grape appear, and the Pomegranates bud forth.
His preferring the Garden of Eden, to that
—Where the Sapient King
Held Dalliance with his fair Egyptian Spouse,
shews that the Poet had this delightful Scene in his mind.
Eve's
Dream is full of those
high Conceits engendring Pride
, which, we
are told, the Devil endeavour'd to instill into her. Of this kind is
that Part of it where she fancies herself awaken'd by
Adam
in the
following beautiful Lines.
Why sleep'st thou Eve?
now is the pleasant Time,
The cool, the silent, save where Silence yields
To the night-warbling Bird, that now awake
Tunes sweetest his love-labour'd Song; now reigns
Full orb'd the Moon, and with more pleasing1 Light
Shadowy sets off the Face of things: In vain,
If none regard. Heav'n wakes with all his Eyes,
Whom to behold but thee, Nature's Desire,
In whose sight all things joy, with Ravishment,
Attracted by thy Beauty still to gaze!
An injudicious Poet would have made
Adam
talk thro' the whole Work in
such Sentiments as these: But Flattery and Falshood are not the
Courtship of
Milton's Adam
, and could not be heard by
Eve
in her State
of Innocence, excepting only in a Dream produc'd on purpose to taint her
Imagination. Other vain Sentiments of the same kind in this Relation of
her Dream, will be obvious to every Reader. Tho' the Catastrophe of the
Poem is finely presag'd on this Occasion, the Particulars of it are so
artfully shadow'd, that they do not anticipate the Story which follows
in the ninth Book. I shall only add, that tho' the Vision it self is
founded upon Truth, the Circumstances of it are full of that Wildness
and Inconsistency which are natural to a Dream.
Adam
, conformable to his
superior Character for Wisdom, instructs and comforts
Eve
upon this
occasion.
So chear'd he his fair Spouse, and she was chear'd,
But silently a gentle Tear let fall
From either Eye, and wiped them with her hair;
Two other precious Drops, that ready stood
Each in their chrystal Sluice, he ere they fell
Kiss'd, as the gracious Sign of sweet Remorse
And pious Awe, that fear'd to have offended.
The
Morning Hymn
is written in Imitation of one of those
Psalms
, where,
in the overflowings of Gratitude and Praise, the
Psalmist
calls not only
upon the Angels, but upon the most conspicuous Parts of the inanimate
Creation, to join with him in extolling their common Maker. Invocations
of this nature fill the Mind with glorious Ideas of God's Works, and
awaken that Divine Enthusiasm, which is so natural to Devotion. But if
this calling upon the dead Parts of Nature, is at all times a proper
kind of Worship, it was in a particular manner suitable to our first
Parents, who had the Creation fresh upon their Minds, and had not seen
the various Dispensations of Providence, nor consequently could be
acquainted with those many Topicks of Praise which might afford Matter
to the Devotions of their Posterity. I need not remark the beautiful
Spirit of Poetry, which runs through this whole
Hymn
, nor the Holiness
of that Resolution with which it concludes.
Having
mentioned those Speeches which are assigned to the
Persons in this Poem, I proceed to the Description which the Poet
gives
of
Raphael
. His Departure from before the Throne, and the Flight
through the Choirs of Angels, is finely imaged. As
Milton
every where
fills his Poem with Circumstances that are marvellous and astonishing,
he describes the Gate of Heaven as framed after such a manner, that it
opened of it self upon the Approach of the Angel who was to pass through
it.
'Till at the Gate
Of Heav'n arriv'd, the Gate self-open'd wide,
On golden Hinges turning, as by Work
Divine, the Sovereign Architect had framed.
The Poet here seems to have regarded two or three Passages in the 18th
Iliad
, as that in particular, where speaking of
Vulcan
,
Homer
says, that
he had made twenty Tripodes running on Golden Wheels; which, upon
occasion, might go of themselves to the Assembly of the Gods, and, when
there was no more Use for them, return again after the same manner.
Scaliger has rallied
Homer
very severely upon this Point, as M. Dacier
has endeavoured to defend it. I will not pretend to determine, whether
in this particular of
Homer
the Marvellous does not lose sight of the
Probable. As the miraculous Workmanship of
Milton's
Gates is not so
extraordinary as this of the
Tripodes
, so I am persuaded he would not
have mentioned it, had not he been supported in it by a Passage in the
Scripture, which speaks of Wheels in Heaven that had Life in them, and
moved of themselves, or stood still, in conformity with the Cherubims,
whom they accompanied.
There is no question but
Milton
had this Circumstance in his Thoughts,
because in the following Book he describes the Chariot of the
Messiah
with
living
Wheels, according to the Plan in
Ezekiel's
Vision.
—Forth rush'd with Whirlwind sound
The Chariot of paternal Deity
Flashing thick flames?, Wheel within Wheel undrawn,
Itself instinct with Spirit—
I question not but
Bossu
, and the two
Daciers
, who are for vindicating
every thing that is censured in
Homer
, by something parallel in Holy
Writ, would have been very well pleased had they thought of confronting
Vulcan's Tripodes
with
Ezekiel's
Wheels.
Raphael's
Descent to the Earth, with the Figure of his Person, is
represented in very lively Colours. Several of the
French, Italian
and
English
Poets have given a Loose to their Imaginations in the
Description of Angels: But I do not remember to have met with any so
finely drawn, and so conformable to the Notions which are given of them
in Scripture, as this in
Milton
. After having set him forth in all his
Heavenly Plumage, and represented him as alighting upon the Earth, the
Poet concludes his Description with a Circumstance, which is altogether
new, and imagined with the greatest Strength of Fancy.
—Like Maia's Son he stood,
And shook his Plumes, that Heavnly Fragrance fill'd
The Circuit wide.—
Raphael's
Reception by the Guardian Angels; his passing through the
Wilderness of Sweets; his distant Appearance to
Adam
, have all the
Graces that Poetry is capable of bestowing. The Author afterwards gives
us a particular Description of
Eve
in her Domestick Employments
So saying, with dispatchful Looks in haste
She turns, on hospitable Thoughts intent,
What Choice to chuse for Delicacy best,
What order, so contrived, as not to mix
Tastes, not well join'd, inelegant, but bring
Taste after Taste; upheld with kindliest Change;
Bestirs her then, &c.—
Though in this, and other Parts of the same Book, the Subject is only
the Housewifry of our first Parent, it is set off with so many pleasing
Images and strong Expressions, as make it none of the least agreeable
Parts in this Divine Work.
The natural Majesty of
Adam
, and at the same time his submissive
Behaviour to the Superior Being, who had vouchsafed to be his Guest; the
solemn Hail which the Angel bestows upon the Mother of Mankind, with the
Figure of
Eve
ministring at the Table, are Circumstances which deserve
to be admired.
Raphael's
Behaviour is every way suitable to the Dignity of his Nature,
and to that Character of a sociable Spirit, with which the Author has so
judiciously introduced him. He had received Instructions to converse
with
Adam
, as one Friend converses with another, and to warn him of the
Enemy, who was contriving his Destruction: Accordingly he is represented
as sitting down at Table with
Adam
, and eating of the Fruits of
Paradise. The Occasion naturally leads him to his Discourse on the Food
of Angels. After having thus entered into Conversation with Man upon
more indifferent Subjects, he warns him of his Obedience, and makes
natural Transition to the History of that fallen Angel, who was employ'd
in the Circumvention of our first Parents.
Had I followed Monsieur
Bossu's
Method in my first Paper of
Milton
, I
should have dated the Action of
Paradise Lost
from the Beginning of
Raphael's
Speech in this Book, as he supposes the Action of the
Æneid
to
begin in the second Book of that Poem. I could allege many Reasons for
my drawing the Action of the
Æneid
rather from its immediate Beginning
in the first Book, than from its remote Beginning in the second; and
shew why I have considered the sacking of Troy as an Episode, according
to the common Acceptation of that Word. But as this would be a dry
unentertaining Piece of Criticism, and perhaps unnecessary to those who
have read my first Paper, I shall not enlarge upon it. Whichever of the
Notions be true, the Unity of
Milton's
Action is preserved according to
either of them; whether we consider the Fall of Man in its immediate
Beginning, as proceeding from the Resolutions taken in the infernal
Council, or in its more remote Beginning, as proceeding from the first
Revolt of the Angels in Heaven. The Occasion which
Milton
assigns for
this Revolt, as it is founded on Hints in Holy Writ, and on the Opinion
of some great Writers, so it was the most proper that the Poet could
have made use of.
The Revolt in Heaven is described with great Force of Imagination and a
fine Variety of Circumstances. The learned Reader cannot but be pleased
with the Poet's Imitation of
Homer
in the last of the following Lines.
At length into the Limits of the North
They came, and Satan took his Royal Seat
High on a Hill, far blazing, as a Mount
Rais'd on a Mount, with Pyramids and Tow'rs
From Diamond Quarries hewn, and Rocks of Gold,
The Palace of great Lucifer, (so call
That Structure in the Dialect of Men
Interpreted)—
Homer
mentions Persons and Things, which he tells us in the Language of
the Gods are call'd by different Names from those they go by in the
Language of Men.
Milton
has imitated him with his usual Judgment in this
particular Place, wherein he has likewise the Authority of Scripture to
justifie him. The Part of
Abdiel
, who was the only Spirit that in this
infinite Host of Angels preserved his Allegiance to his Maker, exhibits
to us a noble Moral of religious Singularity. The Zeal of the Seraphim
breaks forth in a becoming Warmth of Sentiments and Expressions, as the
Character which is given us of him denotes that generous Scorn and
Intrepidity which attends Heroic Virtue. The Author doubtless designed
it as a Pattern to those who live among Mankind in their present State
of Degeneracy and Corruption.
So spake the Seraph Abdiel, faithful found
Among the faithless, faithful only he;
Among innumerable false, unmov'd,
Unshaken, unseduc'd, unterrify'd;
His Loyalty he kept, his Love, his Zeal:
Nor Number, nor Example with him wrought
To swerve from truth, or change his constant Mind,
Though single. From amidst them forth he pass'd,
Long way through hostile Scorn, which he sustain'd
Superior, nor of Violence fear'd ought;
And, with retorted Scorn, his Back he turn'd
On those proud Tow'rs to swift Destruction doom'd.
L.
pleasant
gives us
Contents
No. 3281 |
Monday, March 17, 1712 |
Steele |
Delectata illa urbanitate tam stulta.
Petron. Arb.

That useful Part of Learning which consists in Emendation, Knowledge of
different Readings, and the like, is what in all Ages Persons extremely
wise and learned have had in great Veneration. For this reason I cannot
but rejoyce at the following Epistle, which lets us into the true Author
of the Letter to Mrs. Margaret Clark, part of which I did myself the
Honour to publish in a former Paper. I must confess I do not naturally
affect critical Learning; but finding my self not so much regarded as I
am apt to flatter my self I may deserve from some professed Patrons of
Learning, I could not but do my self the Justice to shew I am not a
Stranger to such Erudition as they smile upon, if I were duly
encouraged. However this only to let the World see what I could do; and
shall not give my Reader any more of this kind, if he will forgive the
Ostentation I shew at present.
March 13, 1712.
Sir,
'
Upon reading your Paper of yesterday
2, I took the Pains to look
out a Copy I had formerly taken, and remembered to be very like your
last Letter: Comparing them, I found they were the very same, and
have, underwritten, sent you that Part of it which you say was torn
off. I hope you will insert it, that Posterity may know 'twas Gabriel
Bullock that made Love in that natural Stile of which you seem to be
fond. But, to let you see I have other Manuscripts in the same Way, I
have sent you Enclosed three Copies, faithfully taken by my own Hand
from the Originals, which were writ by a Yorkshire gentleman of a good
estate to Madam Mary, and an Uncle of hers, a Knight very well known
by the most ancient Gentry in that and several other Counties of Great
Britain. I have exactly followed the Form and Spelling. I have been
credibly informed that Mr. William Bullock, the famous Comedian, is
the descendant of this Gabriel, who begot Mr. William Bullock's great
grandfather on the Body of the above-mentioned Mrs. Margaret Clark.
But neither Speed, nor Baker, nor Selden, taking notice of it, I will
not pretend to be positive; but desire that the letter may be
reprinted, and what is here recovered may be in Italic.
I am,
Sir,
Your daily Reader.
To her I very much respect, Mrs. Margaret Clark.
Lovely, and oh that I could write loving Mrs. Margaret Clark, I pray
you let Affection excuse Presumption. Having been so happy as to
enjoy the Sight of your sweet Countenance and comely Body, sometimes
when I had occasion to buy Treacle or Liquorish Power at the
apothecary's shop, I am so enamoured with you, that I can no more
keep close my flaming Desire to become your Servant. And I am
the
more bold now to write to your sweet self, because I am now my own
Man, and may match where I please; for my Father is taken away; and
now I am come to my Living, which is ten yard Land, and a House; and
there is never a Yard Land
3 in our Field but is as well worth ten
Pound a Year, as a Thief's worth a Halter; and all my Brothers and
Sisters are provided for: besides I have good Household Stuff,
though I say it, both Brass and Pewter, Linnens and Woollens; and
though my House be thatched, yet if you and I match, it shall go
hard but I will have one half of it slated. If you shall think well
of this Motion, I will wait upon you as soon as my new Cloaths is
made, and Hay-Harvest is in. I could, though I say it, have good
Matches in our Town; but my Mother (God's Peace be with her) charged
me upon her Death-Bed to marry a Gentlewoman, one who had been well
trained up in Sowing and Cookery. I do not think but that if you and
I can agree to marry, and lay our Means together, I shall be made
grand Jury-man e'er two or three Years come about, and that will be
a great Credit to us. If I could have got a Messenger for Sixpence,
I would have sent one on Purpose, and some Trifle or other for a
Token of my Love; but I hope there is nothing lost for that neither.
So hoping you will take this Letter in good Part, and answer it with
what Care and Speed you can, I rest and remain,
Yours, if my own,
Mr. Gabriel Bullock,
now my father is dead.
Swepston, Leicestershire.
When the Coal Carts come, I shall send oftener; and may come in one
of them my self.
For sir William to go to london at westminster, remember a
parlement.
Sir William, i hope that you are well. i write to let you know that
i am in troubel abbut a lady you nease; and I do desire that you
will be my frend; for when i did com to see her at your hall, i was
mighty Abuesed. i would fain a see you at topecliff, and thay would
not let me go to you; but i desire that you will be our frends, for
it is no dishonor neither for you nor she, for God did make us all.
i wish that i might see you, for thay say that you are a good man:
and many doth wounder at it, but madam norton is abuesed and ceated
two i beleive. i might a had many a lady, but i con have none but
her with a good consons, for there is a God that know our harts, if
you and madam norton will come to York, there i shill meet you if
God be willing and if you pleased, so be not angterie till you know
the trutes of things.
George Nelon I give my to me lady, and to Mr. Aysenby, and to
madam norton March, the 19th; 1706.
This is for madam mary norton disforth Lady she went to York.
Madam Mary. Deare loving sweet lady, i hope you are well. Do not go
to london, for they will put you in the nunnery; and heed not Mrs.
Lucy what she saith to you, for she will ly and ceat you. go from to
another Place, and we will gate wed so with speed, mind what i write
to you, for if they gate you to london they will keep you there; and
so let us gate wed, and we will both go. so if you go to london, you
rueing your self, so heed not what none of them saith to you. let us
gate wed, and we shall lie to gader any time. i will do any thing
for you to my poore. i hope the devill will faile them all, for a
hellish Company there be. from there cursed trick and mischiefus
ways good lord bless and deliver both you and me.
I think to be at york the 24 day.
This is for madam mary norton to go to london for a lady that
belongs to dishforth.
Madam Mary, i hope you are well, i am soary that you went away from
York, deare loving sweet lady, i writt to let you know that i do
remain faithful; and if can let me know where i can meet you, i will
wed you, and I will do any thing to my poor; for you are a good
woman, and will be a loving Misteris. i am in troubel for you, so if
you will come to york i will wed you. so with speed come, and i will
have none but you. so, sweet love, heed not what to say to me, and
with speed come: heed not what none of them say to you; your Maid
makes you believe ought.
So deare love think of Mr. george Nillson with speed; i sent you 2
or 3 letters before.
I gave misteris elcock some nots, and thay put me in pruson all the
night for me pains, and non new whear i was, and i did gat cold.
But it is for mrs. Lucy to go a good way from home, for in york and
round about she is known; to writ any more her deeds, the same will
tell hor soul is black within, hor corkis stinks of hell.
March 19th, 1706.
R.
This paper is No. 328 in the original issue, but Steele
omitted it from the reprint and gave in its place the paper by Addison
which here stands next to it marked with the same number, 328. The paper
of Addison's had formed no part of the original issue. Of the original
No. 328 Steele inserted a censure at the end of No. 330.
See
.
In some counties 20, in some 24, and in others 30 acres of Land.
Contents
|
Monday, March 17, 1712 |
Addison |
Nullum me a labore reclinat otium.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
As I believe this is the first Complaint that ever was made to you of
this nature, so you are the first Person I ever could prevail upon my
self to lay it before. When I tell you I have a healthy vigorous
Constitution, a plentiful Estate, no inordinate Desires, and am
married to a virtuous lovely Woman, who neither wants Wit nor
Good-Nature, and by whom I have a numerous Offspring to perpetuate my
Family, you will naturally conclude me a happy Man. But,
notwithstanding these promising Appearances, I am so far from it, that
the prospect of being ruind and undone, by a sort of Extravagance
which of late Years is in a less degree crept into every fashionable
Family, deprives me of all the Comforts of my Life, and renders me the
most anxious miserable Man on Earth. My Wife, who was the only Child
and darling Care of an indulgent Mother, employd her early Years in
learning all those Accomplishments we generally understand by good
Breeding and polite Education. She sings, dances, plays on the Lute
and Harpsicord, paints prettily, is a perfect Mistress of the French
Tongue, and has made a considerable Progress in Italian. She is
besides excellently skilld in all domestick Sciences, as Preserving,
Pickling, Pastry, making Wines of Fruits of our own Growth,
Embroydering, and Needleworks of every Kind. Hitherto you will be apt
to think there is very little Cause of Complaint; but suspend your
Opinion till I have further explain'd my self, and then I make no
question you will come over to mine. You are not to imagine I find
fault that she either possesses or takes delight in the Exercise of
those Qualifications I just now mention'd; 'tis the immoderate
Fondness she has to them that I lament, and that what is only design'd
for the innocent Amusement and Recreation of Life, is become the whole
Business and Study of her's. The six Months we are in Town (for the
Year is equally divided between that and the Country) from almost
Break of Day till Noon, the whole Morning is laid out in practising
with her several Masters; and to make up the Losses occasion'd by her
Absence in Summer, every Day in the Week their Attendance is requir'd;
and as they all are People eminent in their Professions, their Skill
and Time must be recompensed accordingly: So how far these Articles
extend, I leave you to judge. Limning, one would think, is no
expensive Diversion, but as she manages the Matter, 'tis a very
considerable Addition to her Disbursements; Which you will easily
believe, when you know she paints Fans for all her Female
Acquaintance, and draws all her Relations Pictures in Miniature; the
first must be mounted by no body but Colmar, and the other set by no
body but Charles Mather. What follows, is still much worse than the
former; for, as I told you, she is a great Artist at her Needle, 'tis
incredible what Sums she expends in Embroidery; For besides what is
appropriated to her personal Use, as Mantua's, Petticoats, Stomachers,
Handkerchiefs, Purses, Pin-cushions, and Working Aprons, she keeps
four French Protestants continually employ'd in making divers Pieces
of superfluous Furniture, as Quilts, Toilets, Hangings for Closets,
Beds, Window-Curtains, easy Chairs, and Tabourets: Nor have I any
hopes of ever reclaiming her from this Extravagance, while she
obstinately persists in thinking it a notable piece of good
Housewifry, because they are made at home, and she has had some share
in the Performance. There would be no end of relating to you the
Particulars of the annual Charge, in furnishing her Store-Room with a
Profusion of Pickles and Preserves; for she is not contented with
having every thing, unless it be done every way, in which she consults
an Hereditary Book of Receipts; for her female Ancestors have been
always fam'd for good Housewifry, one of whom is made immortal, by
giving her Name to an Eye-Water and two sorts of Puddings. I cannot
undertake to recite all her medicinal Preparations, as Salves,
Cerecloths, Powders, Confects, Cordials, Ratafia, Persico,
Orange-flower, and Cherry-Brandy, together with innumerable sorts of
Simple Waters. But there is nothing I lay so much to Heart, as that
detestable Catalogue of counterfeit Wines, which derive their Names
from the Fruits, Herbs, or Trees of whose Juices they are chiefly
compounded: They are loathsome to the Taste, and pernicious to the
Health; and as they seldom survive the Year, and then are thrown away,
under a false Pretence of Frugality, I may affirm they stand me in
more than if I entertaind all our Visiters with the best Burgundy and
Champaign. Coffee, Chocolate, Green, Imperial, Peco, and Bohea-Tea
seem to be Trifles; but when the proper Appurtenances of the Tea-Table
are added, they swell the Account higher than one would imagine. I
cannot conclude without doing her Justice in one Article; where her
Frugality is so remarkable, I must not deny her the Merit of it, and
that is in relation to her Children, who are all confind, both Boys
and Girls, to one large Room in the remotest Part of the House, with
Bolts on the Doors and Bars to the Windows, under the Care and Tuition
of an old Woman, who had been dry Nurse to her Grandmother. This is
their Residence all the Year round; and as they are never allowd to
appear, she prudently thinks it needless to be at any Expence in
Apparel or Learning. Her eldest Daughter to this day would have
neither read nor writ, if it had not been for the Butler, who being
the Son of a Country Attorney, has taught her such a Hand as is
generally used for engrossing Bills in Chancery. By this time I have
sufficiently tired your Patience with my domestick Grievances; which I
hope you will agree could not well be containd in a narrower Compass,
when you consider what a Paradox I undertook to maintain in the
Beginning of my Epistle, and which manifestly appears to be but too
melancholy a Truth. And now I heartily wish the Relation I have given
of my Misfortunes may be of Use and Benefit to the Publick. By the
Example I have set before them, the truly virtuous Wives may learn to
avoid those Errors which have so unhappily mis-led mine, and which are
visibly these three. First, in mistaking the proper Objects of her
Esteem, and fixing her Affections upon such things as are only the
Trappings and Decorations of her Sex. Secondly, In not distinguishing
what becomes the different Stages of Life. And, Lastly, The Abuse and
Corruption of some excellent Qualities, which, if circumscribd within
just Bounds, would have been the Blessing and Prosperity of her
Family, but by a vicious Extreme are like to be the Bane and
Destruction of it.
L.
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 18, 1712 |
Addison |
Ire tamen restat, Numa quo devenit et Ancus.
Hor.

My friend Sir
Roger De Coverley
told me t'other Night, that he had been
reading my Paper upon
Westminster Abby
, in which, says he, there are a
great many ingenious Fancies. He told me at the same time, that he
observed I had promised another Paper upon the
Tombs
, and that he should
be glad to go and see them with me, not having visited them since he had
read History. I could not at first imagine how this came into the
Knight's Head, till I recollected that he had been very busy all last
Summer upon
Baker's Chronicle
, which he has quoted several times in his
Disputes with Sir
Andrew Freeport
since his last coming to Town.
Accordingly I promised to call upon him the next Morning, that we might
go together to the
Abby
.
I found the Knight under his Butler's Hands, who always shaves him. He
was no sooner Dressed, than he called for a Glass of the Widow
Trueby's
Water, which he told me he always drank before he went abroad. He
recommended me to a Dram of it at the same time, with so much
Heartiness, that I could not forbear drinking it. As soon as I had got
it down, I found it very unpalatable; upon which the Knight observing
that I
had
made several wry Faces, told me that he knew I should not
like it at first, but that it was the best thing in the World against
the Stone or Gravel.
I could have wished indeed that he had acquainted me with the Virtues of
it sooner; but it was too late to complain, and I knew what he had done
was out of Good-will. Sir
Roger
told me further, that he looked upon it
to be very good for a Man whilst he staid in Town, to keep off
Infection, and that he got together a Quantity of it upon the first News
of the Sickness being at
Dautzick
:
of a sudden turning short to one
of his Servants, who stood behind him, he bid him call
a
Hackney
Coach, and take care it was an elderly Man that drove it.
He then resumed his Discourse upon Mrs.
Trueby's
Water, telling me that
the Widow
Trueby
was one who did more good than all the Doctors and
Apothecaries in the County: That she distilled every Poppy that grew
within five Miles of her; that she distributed her Water gratis among
all Sorts of People; to which the Knight added, that she had a very
great Jointure, and that the whole Country would fain have it a Match
between him and her; and truly, says Sir
Roger
, if I had not been
engaged, perhaps I could not have done better.
His Discourse was broken off by his Man's telling him he had called a
Coach. Upon our going to it, after having cast his Eye upon the Wheels,
he asked the Coachman if his Axeltree was good; upon the Fellow's
telling him he would warrant it, the Knight turned to me, told me he
looked like an honest Man, and went in without further Ceremony.
We had not gone far, when Sir
Roger
popping out his Head, called the
Coach-man down from his Box, and upon his presenting himself at the
Window, asked him if he smoaked; as I was considering what this would
end in, he bid him stop by the way at any good Tobacconist's, and take
in a Roll of their best Virginia. Nothing material happened in the
remaining part of our Journey, till we were set down at the West end of
the
Abby
.
As we went up the Body of the Church, the Knight pointed at the Trophies
upon one of the new Monuments, and cry'd out, A brave Man, I warrant
him! Passing afterwards by Sir Cloudsly Shovel, he flung his Hand that
way, and cry'd Sir Cloudsly Shovel! a very gallant Man! As we stood
before Busby's Tomb, the Knight utter'd himself again after the same
Manner, Dr. Busby, a great Man! he whipp'd my Grandfather; a very great
Man! I should have gone to him myself, if I had not been a Blockhead; a
very great Man!
We were immediately conducted into the little Chappel on the right hand.
Sir
Roger
planting himself at our Historian's Elbow, was very attentive
to every thing he said, particularly to the Account he gave us of the
Lord who had cut off the King of
Morocco's
Head. Among several other
Figures, he was very well pleased to see the Statesman Cecil upon his
Knees; and, concluding them all to be great Men, was conducted to the
Figure which represents that Martyr to good Housewifry, who died by the
prick of a Needle. Upon our Interpreter's telling us, that she was a
Maid of Honour to Queen Elizabeth, the Knight was very inquisitive into
her Name and Family; and after having regarded her Finger for some time,
I wonder, says he, that Sir Richard Baker has said nothing of her in his
Chronicle
.
We were then convey'd to the two Coronation-Chairs, where my old Friend,
after having heard that the Stone underneath the most ancient of them,
which was brought from Scotland, was called
Jacob's Pillar
, sat himself
down in the Chair; and looking like the Figure of an old
Gothick
King,
asked our Interpreter, What Authority they had to say, that
Jacob
had
ever been in Scotland? The Fellow, instead of returning him an Answer,
told him, that he hoped his Honour would pay his Forfeit. I could
observe Sir
Roger
a little ruffled upon being thus trepanned; but our
Guide not insisting upon his Demand, the Knight soon recovered his good
Humour, and whispered in my Ear, that if
Will. Wimble
were with us, and
saw those two Chairs, it would go hard but he would get a
Tobacco-Stopper out of one or t'other of them.
Sir
Roger
, in the next Place, laid his Hand upon
Edward the Third's
Sword, and leaning upon the Pummel of it, gave us the whole History of
the Black Prince; concluding, that in Sir Richard Baker's Opinion,
Edward the Third was one of the greatest Princes that ever sate upon the
English Throne.
We were then shewn
Edward the Confessor's
Tomb; upon which Sir
Roger
acquainted us, that he was the first who touched for the Evil; and
afterwards
Henry the Fourth's
, upon which he shook his Head, and told us
there was fine Reading in the Casualties in that Reign.
Our Conductor then pointed to that Monument where there is the Figure of
one of our English Kings without an Head; and upon giving us to know,
that the Head, which was of beaten Silver, had been stolen away several
Years since: Some Whig, I'll warrant you, says Sir
Roger
; you ought to
lock up your Kings better; they will carry off the Body too, if you
don't take care.
THE glorious Names of
Henry the Fifth
and
Queen Elizabeth
gave the
Knight great Opportunities of shining, and of doing Justice to Sir
Richard Baker, who, as our Knight observed with some Surprize, had a
great many Kings in him, whose Monuments he had not seen in the
Abby
.
For my own part, I could not but be pleased to see the Knight shew such
an honest Passion for the Glory of his Country, and such a respectful
Gratitude to the Memory of its Princes.
I must not omit, that the Benevolence of my good old Friend, which flows
out towards every one he converses with, made him very kind to our
Interpreter, whom he looked upon as an extraordinary Man; for which
reason he shook him by the Hand at parting, telling him, that he should
be very glad to see him at his Lodgings in Norfolk-Buildings, and talk
over these Matters with him more at leisure.
L.
an
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 19, 1712 |
Steele |
Maxima debetur pueris reverentia.
Juv.

The following Letters, written by two very considerate Correspondents,
both under twenty Years of Age, are very good Arguments of the Necessity
of taking into Consideration the many Incidents which affect the
Education of Youth.
Sir,
'I have long expected, that in the Course of your Observations upon
the several Parts of human Life, you would one time or other fall upon
a Subject, which, since you have not, I take the liberty to recommend
to you. What I mean, is the Patronage of young modest Men to such as
are able to countenance and introduce them into the World. For want of
such Assistances, a Youth of Merit languishes in Obscurity or Poverty,
when his Circumstances are low, and runs into Riot and Excess when his
Fortunes are plentiful. I cannot make my self better understood, than
by sending you an History of my self, which I shall desire you to
insert in your Paper, it being the only Way I have of expressing my
Gratitude for the highest Obligations imaginable.
I am the Son of a Merchant of the City of
London, who, by many Losses,
was reduced from a very luxuriant Trade and Credit to very narrow
Circumstances, in Comparison to that his former Abundance. This took
away the Vigour of his Mind, and all manner of Attention to a Fortune,
which he now thought desperate; insomuch that he died without a Will,
having before buried my Mother in the midst of his other Misfortunes.
I was sixteen Years of Age when I lost my Father; and an Estate of
£200 a Year came into my Possession, without Friend or Guardian to
instruct me in the Management or Enjoyment of it. The natural
Consequence of this was, (though I wanted no Director, and soon had
Fellows who found me out for a smart young Gentleman, and led me into
all the Debaucheries of which I was capable) that my Companions and I
could not well be supplied without my running in Debt, which I did
very frankly, till I was arrested, and conveyed with a Guard strong
enough for the most desperate Assassine, to a Bayliff's House, where I
lay four Days, surrounded with very merry, but not very agreeable
Company. As soon as I had extricated my self from this shameful
Confinement, I reflected upon it with so much Horror, that I deserted
all my old Acquaintance, and took Chambers in an Inn of Court, with a
Resolution to study the Law with all possible Application. But I
trifled away a whole Year in looking over a thousand Intricacies,
without Friend to apply to in any Case of Doubt; so that I only lived
there among Men, as little Children are sent to School before they are
capable of Improvement, only to be out of harm's way. In the midst of
this State of Suspence, not knowing how to dispose of my self, I was
sought for by a Relation of mine, who, upon observing a good
Inclination in me, used me with great Familiarity, and carried me to
his Seat in the Country. When I came there, he introduced me to all
the good Company in the County; and the great Obligation I have to him
for this kind Notice and Residence with him ever since, has made so
strong an Impression upon me, that he has an Authority of a Father
over me, founded upon the Love of a Brother. I have a good Study of
Books, a good Stable of Horses always at my command; and tho' I am not
now quite eighteen Years of Age, familiar Converse on his Part, and a
strong Inclination to exert my self on mine, have had an effect upon
me that makes me acceptable wherever I go. Thus, Mr.
Spectator, by
this Gentleman's Favour and Patronage, it is my own fault if I am not
wiser and richer every day I live. I speak this as well by subscribing
the initial Letters of my Name to thank him, as to incite others to an
Imitation of his Virtue. It would be a worthy Work to shew what great
Charities are to be done without Expence, and how many noble Actions
are lost, out of Inadvertency in Persons capable of performing them,
if they were put in mind of it. If a Gentleman of Figure in a County
would make his Family a Pattern of Sobriety, good Sense, and Breeding,
and would kindly endeavour to influence the Education and growing
Prospects of the younger Gentry about him, I am apt to believe it
would save him a great deal of stale Beer on a publick Occasion, and
render him the Leader of his Country from their Gratitude to him,
instead of being a Slave to their Riots and Tumults in order to be
made their Representative. The same thing might be recommended to all
who have made any Progress in any Parts of Knowledge, or arrived at
any Degree in a Profession; others may gain Preferments and Fortunes
from their Patrons, but I have, I hope, receiv'd from mine good Habits
and Virtues. I repeat to you, Sir, my Request to print this, in return
for all the Evil an helpless Orphan shall ever escape, and all the
Good he shall receive in this Life; both which are wholly owing to
this Gentleman's Favour to,
Sir,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
S. P.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am a Lad of about fourteen. I find a mighty Pleasure in Learning. I
have been at the Latin School four Years. I
don't know I ever play'd
truant1, or neglected any Task my Master set me in my Life. I
think on what I read in School as I go home at noon and night, and so
intently, that I have often gone half a mile out of my way, not
minding whither I went. Our Maid tells me, she often hears me talk
Latin in my sleep. And I dream two or three Nights in the Week I am
reading
Juvenal and
Homer. My Master seems as well pleased with my
Performances as any Boy's in the same Class. I think, if I know my own
Mind, I would chuse rather to be a Scholar, than a Prince without
Learning. I
have a very
good2 affectionate Father; but tho' very
rich, yet so mighty near, that he thinks much of the Charges of my
Education. He often tells me, he believes my Schooling will ruin him;
that I cost him God-knows what in Books. I tremble to tell him I want
one. I am forced to keep my Pocket-Mony, and lay it out for a Book,
now and then, that he don't know of. He has order'd my Master to buy
no more Books for me, but says he will buy them himself. I asked him
for
Horace t'other Day, and he told me in a Passion, he did not
believe I was fit for it, but only my Master had a Mind to make him
think I had got a great way in my Learning. I am sometimes a Month
behind other Boys in getting the Books my Master gives Orders for. All
the Boys in the School, but I, have the Classick Authors
in usum
Delphini, gilt and letter'd on the Back. My Father is often reckoning
up how long I have been at School, and tells me he fears I do little
good. My Father's Carriage so discourages me, that he makes me grow
dull and melancholy. My Master wonders what is the matter with me; I
am afraid to tell him; for he is a Man that loves to encourage
Learning, and would be apt to chide my Father, and, not knowing my
Father's Temper, may make him worse. Sir, if you have any Love for
Learning, I beg you would give me some Instructions in this case, and
persuade Parents to encourage their Children when they find them
diligent and desirous of Learning. I have heard some Parents say, they
would do any thing for their Children, if they would but mind their
Learning: I would be glad to be in their place. Dear Sir, pardon my
Boldness. If you will but consider and pity my case, I will pray for
your Prosperity as long as I live.
London, March 2,1711.
Your humble Servant,
James Discipulus.
March the 18th.
Mr.
Spectator,
The ostentation you showed yesterday would have been pardonable had
you provided better for the two Extremities of your Paper, and placed
in one the letter R., in the other
Nescio quid meditans nugarum, et
lotus in illis. A Word to the wise.
I am your most humble Servant,
T. Trash.
to the Emendation of the above Correspondent, the Reader is
desired in the Paper of the 17th to read R. for T
.
T.
at truant
loving
Steele had discontinued the signature R. since [Volume 1 link:
], for
August 3, 1711.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 20, 1712 |
Budgell |
Stolidam præbet tibi vellere barbam.
Pers.

When I was last with my Friend Sir
Roger
in
Westminster-Abby
, I
observed that he stood longer than ordinary before the Bust of a
venerable old Man. I was at a loss to guess the Reason of it, when after
some time he pointed to the Figure, and asked me if I did not think that
our Fore-fathers looked much wiser in their Beards than we do without
them? For my part, says he, when I am walking in my Gallery in the
Country, and see my Ancestors, who many of them died before they were of
my Age, I cannot forbear regarding them as so many old Patriarchs, and
at the same time looking upon myself as an idle Smock-fac'd young
Fellow. I love to see your
Abrahams
, your
Isaacs
, and your
Jacobs
, as we
have them in old Pieces of Tapestry, with Beards below their Girdles,
that cover half the Hangings. The Knight added, if I would recommend
Beards in one of my Papers, and endeavour to restore human Faces to
their Ancient Dignity, that upon a Month's warning he would undertake to
lead up the Fashion himself in a pair of Whiskers.
I smiled at my Friend's Fancy; but after we parted, could not forbear
reflecting on the Metamorphoses our Faces have undergone in this
Particular.
The Beard, conformable to the Notion of my Friend Sir
Roger
, was for
many Ages look'd upon as the Type of Wisdom.
Lucian
more than once
rallies the Philosophers of his Time, who endeavour'd to rival one
another in Beard; and represents a learned Man who stood for a
Professorship in Philosophy, as unqualify'd for it by the Shortness of
his Beard.
Ælian
, in his Account of
Zoilus
, the pretended Critick, who wrote
against
Homer
and
Plato
, and thought himself wiser than all who had gone
before him, tells us that this
Zoilus
had a very long Beard that hung
down upon his Breast, but no Hair upon his Head, which he always kept
close shaved, regarding, it seems, the Hairs of his Head as so many
Suckers, which if they had been suffer'd to grow, might have drawn away
the Nourishment from his Chin, and by that means have starved his Beard.
I have read somewhere that one of the Popes refus'd to accept an Edition
of a Saint's Works, which were presented to him, because the Saint in
his Effigies before the Book, was drawn without a Beard.
We see by these Instances what Homage the World has formerly paid to
Beards; and that a Barber was not then allow'd to make those
Depredations on the Faces of the Learned, which have been permitted him
of later Years.
Accordingly several wise Nations have been so extremely Jealous of the
least Ruffle offer'd to their Beard, that they seem to have fixed the
Point of Honour principally in that Part. The
Spaniards
were wonderfully
tender in this Particular.
Don Quevedo
, in his third
Vision on the Last Judgment
, has carry'd the
Humour very far, when he tells us that one of his vain-glorious
Countrymen, after having receiv'd Sentence, was taken into custody by a
couple of evil Spirits; but that his Guides happening to disorder his
Mustachoes, they were forced to recompose them with a Pair of
Curling-irons before they could get him to file off.
If we look into the History of our own Nation, we shall find that the
Beard flourish'd in the
Saxon
Heptarchy, but was very much discourag'd
under the
Norman
Line. It shot out, however, from time to time, in
several Reigns under different Shapes. The last Effort it made seems to
have been in
Queen Mary's
Days, as the curious Reader may find, if he
pleases to peruse the Figures of
Cardinal Poole
, and
Bishop Gardiner;
tho' at the same time, I think it may be question'd, if Zeal against
Popery has not induced our Protestant Painters to extend the Beards of
these two Persecutors beyond their natural Dimensions, in order to make
them appear the more terrible.
I find but few Beards worth taking notice of in the Reign of
King James
the First.
During the Civil Wars there appeared one, which makes too great a Figure
in Story to be passed over in Silence; I mean that of the redoubted
Hudibras
, an Account of which
Butler
has transmitted to Posterity in the
following Lines:
His tawny Beard was th' equal Grace
Both of his Wisdom, and his Face;
In Cut and Dye so like a Tyle,
A sudden View it would beguile:
The upper Part thereof was Whey,
The nether Orange mixt with Grey.
The Whisker continu'd for some time among us after the Expiration of
Beards; but this is a Subject which I shall not here enter upon, having
discussed it at large in a distinct Treatise, which I keep by me in
Manuscript, upon the Mustachoe.
If my Friend Sir
Roger's
Project, of introducing Beards, should take
effect, I fear the Luxury of the present Age would make it a very
expensive Fashion. There is no question but the Beaux would soon provide
themselves with false ones of the lightest Colours, and the most
immoderate Lengths. A fair Beard, of the Tapestry-Size Sir
Roger
seems
to approve, could not come under twenty Guineas. The famous Golden Beard
of
Æsculapius
would hardly be more valuable than one made in the
Extravagance of the Fashion.
Besides, we are not certain that the Ladies would not come into the
Mode, when they take the Air on Horse-back. They already appear in Hats
and Feathers, Coats and Perriwigs; and I see no reason why we should not
suppose that they would have their Riding-Beards on the same Occasion.
I may give the Moral of this Discourse, in another Paper,
X.
Contents
|
Friday, March 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Minus aptus acutis
Naribus horum hominum
Hor.

Dear Short-Face,
'In your Speculation of
Wednesday last, you have given us some Account
of that worthy Society of Brutes the Mohocks; wherein you have
particularly specify'd the ingenious Performance of the Lion-Tippers,
the Dancing-Masters, and the Tumblers: But as you acknowledge you had
not then a perfect History of the whole Club, you might very easily
omit one of the most notable Species of it, the Sweaters, which may be
reckon'd a sort of Dancing-Masters too. It is it seems the Custom for
half a dozen, or more, of these well-dispos'd Savages, as soon as
they have inclos'd the Person upon whom they design the Favour of a
Sweat, to whip out their Swords, and holding them parallel to the
Horizon, they describe a sort of Magick Circle round about him with
the Points. As soon as this Piece of Conjuration is perform'd, and the
Patient without doubt already beginning to wax warm, to forward the
Operation, that Member of the Circle towards whom he is so rude as to
turn his Back first, runs his Sword directly into that Part of the
Patient wherein School-boys are punished; and, as it is very natural
to imagine this will soon make him tack about to some other Point,
every Gentleman does himself the same Justice as often as he receives
the Affront. After this Jig has gone two or three times round, and the
Patient is thought to have sweat sufficiently, he is very handsomly
rubb'd down by some Attendants, who carry with them Instruments for
that purpose, and so discharged. This Relation I had from a Friend of
mine, who has lately been under this Discipline. He tells me he had
the Honour to dance before the Emperor himself, not without the
Applause and Acclamations both of his Imperial Majesty, and the whole
Ring; tho' I dare say, neither I or any of his Acquaintance ever
dreamt he would have merited any Reputation by his Activity.
'I can assure you, Mr. SPEC, I was very near being qualify'd to have
given you a faithful and painful Account of this walking Bagnio, if I
may so call it, my self: For going the other night along Fleet-street,
and having, out of curiosity, just enter'd into Discourse with a
wandring Female who was travelling the same Way, a couple of Fellows
advanced towards us, drew their Swords, and cry'd out to each other, A
Sweat! a Sweat! Whereupon suspecting they were some of the Ringleaders
of the Bagnio, I also drew my Sword, and demanded a Parly; but finding
none would be granted me, and perceiving others behind them filing off
with great diligence to take me in Flank, I began to sweat for fear of
being forced to it: but very luckily betaking my self to a Pair of
Heels, which I had good Reason to believe would do me justice, I
instantly got possession of a very snug Corner in a neighbouring Alley
that lay in my Rear; which Post I maintain'd for above half an hour
with great Firmness and Resolution, tho' not letting this Success so
far overcome me, as to make me unmindful of the Circumspection that
was necessary to be observ'd upon my advancing again towards the
Street; by which Prudence and good Management I made a handsome and
orderly Retreat, having suffer'd no other Damage in this Action than
the Loss of my Baggage, and the Dislocation of one of my Shoe-heels,
which last I am just now inform'd is in a fair way of Recovery. These
Sweaters, by what I can learn from my Friend, and by as near a View as
I was able to take of them myself, seem to me to have at present but
a rude kind of Discipline amongst them. It is probable, if you would
take a little Pains with them, they might be brought into better
order. But I'll leave this to your own Discretion; and will only add,
that if you think it worth while to insert this by way of Caution to
those who have a mind to preserve their Skins whole from this sort of
Cupping, and tell them at the same time the Hazard of treating with
Night-Walkers, you will perhaps oblige others, as well as
Your very humble Servant,
Jack Lightfoot.
'
P. S. My Friend will have me acquaint you, That though he would not
willingly detract from the Merit of that extra-ordinary Strokes-Man
Mr. Sprightly, yet it is his real Opinion, that some of those Fellows,
who are employ'd as Rubbers to this new-fashioned Bagnio, have struck
as bold Strokes as ever he did in his Life.
'I had sent this four and twenty Hours sooner, if I had not had the
Misfortune of being in a great doubt about the Orthography of the word
Bagnio. I consulted several Dictionaries, but found no relief; at last
having recourse both to the Bagnio in Newgate-street, and to that in
Chancery lane, and finding the original Manuscripts upon the
Sign-posts of each to agree literally with my own Spelling, I returned
home, full of Satisfaction, in order to dispatch this Epistle.'
Mr.
Spectator,
As you have taken most of the Circumstances of human Life into your
Consideration, we, the under-written, thought it not improper for us
also to represent to you our Condition. We are three Ladies who live
in the Country, and the greatest Improvements we make is by reading.
We have taken a small Journal of our Lives, and find it extremely
opposite to your last Tuesday's Speculation. We rise by seven, and
pass the beginning of each Day in Devotion, and looking into those
Affairs that fall within the Occurrences of a retired Life; in the
Afternoon we sometimes enjoy the Company of some Friend or Neighbour,
or else work or read; at Night we retire to our Chambers, and take
Leave of each other for the whole Night at Ten of Clock. We take
particular Care never to be sick of a Sunday. Mr.
Spectator, We are
all very good Maids, but are ambitious of Characters which we think
more laudable, that of being very good Wives. If any of your
Correspondents enquire for a Spouse for an honest Country Gentleman,
whose Estate is not dipped, and wants a Wife that can save half his
Revenue, and yet make a better Figure than any of his Neighbours of
the same Estate, with finer bred Women, you shall have further notice
from,
Sir,
Your courteous Readers,
Martha Busie.
Deborah Thrifty.
Alice Early
1.
To this number there is added after a repeated
advertisement of the
Lucubrations of Isaac Bickerstaff
in 4 vols. 8vo, a
repetition in Italic type of the advertisement of the Boarding School on
Mile-end Green (ending at the words
'render them accomplish'd
') to which
a conspicuous place was given, with original additions by Steele, in
Contents
|
Saturday, March 22, 1712 |
Addison |
—vocat in Certamina Divos.
Virg.

We are now entering upon the Sixth Book of
Paradise Lost
, in which the
Poet describes the Battel of Angels; having raised his Reader's
Expectation, and prepared him for it by several Passages in the
preceding Books. I omitted quoting these Passages in my Observations on
the former Books, having purposely reserved them for the opening of
this, the Subject of which gave occasion to them. The Author's
Imagination was so inflam'd with this great Scene of Action, that
wherever he speaks of it, he rises, if possible, above himself. Thus
where he mentions
Satan
in the Beginning of his Poem:
—Him the Almighty Power
Hurl'd headlong flaming from th' Ethereal Sky,
With hideous ruin and combustion, down
To bottomless Perdition, there to dwell
In Adamantine Chains and penal Fire,
Who durst defy th' Omnipotent to Arms.
We have likewise several noble Hints of it in the Infernal Conference.
O Prince! O Chief of many throned Powers,
That led th' imbattel'd Seraphim to War,
Too well I see and rue the dire Event,
That with sad Overthrow and foul Defeat
Hath lost us Heav'n, and all this mighty Host
In horrible Destruction laid thus low.
But see I the angry Victor has recalled
His Ministers of Vengeance and Pursuit,
Back to the Gates of Heav'n: The sulphurous Hail
Shot after us in Storm, overblown, hath laid
The fiery Surge, that from the Precipice
Of Heaven receiv'd us falling: and the Thunder,
Winged with red Lightning and impetuous Rage,
Perhaps hath spent his Shafts, and ceases now
To bellow through the vast and boundless Deep.
There are several other very sublime Images on the same Subject in the
First Book, as also in the Second.
What when we fled amain, pursued and strook
With Heav'n's afflicting Thunder, and besought
The Deep to shelter us; this Hell then seem'd
A Refuge from those Wounds—
In short, the Poet never mentions anything of this Battel but in such
Images of Greatness and Terror as are suitable to the Subject. Among
several others I cannot forbear quoting that Passage, where the Power,
who is described as presiding over the Chaos, speaks in the Third Book.
Thus Satan; and him thus the Anarch old
With faultring Speech, and Visage incompos'd,
Answer'd, I know thee, Stranger, who thou art,
That mighty leading Angel, who of late
Made Head against Heaven's King, tho' overthrown.
I saw and heard, for such a numerous Host
Fled not in silence through the frighted Deep
With Ruin upon Ruin, Rout on Rout,
Confusion worse confounded; and Heav'n's Gates
Pour'd out by Millions her victorious Bands
Pursuing—
It requir'd great Pregnancy of Invention, and Strength of Imagination,
to fill this Battel with such Circumstances as should raise and astonish
the Mind of the Reader; and at the same time an Exactness of Judgment,
to avoid every thing that might appear light or trivial. Those who look
into
Homer
, are surprized to find his Battels still rising one above
another, and improving in Horrour, to the Conclusion of the
Iliad
.
Milton's
Fight of Angels is wrought up with the same Beauty. It is
usher'd in with such Signs of Wrath as are suitable to Omnipotence
incensed. The first Engagement is carry'd on under a Cope of Fire,
occasion'd by the Flights of innumerable burning Darts and Arrows, which
are discharged from either Host. The second Onset is still more
terrible, as it is filled with those artificial Thunders, which seem to
make the Victory doubtful, and produce a kind of Consternation even in
the good Angels. This is follow'd by the tearing up of Mountains and
Promontories; till, in the last place, the
Messiah
comes forth in the
Fulness of Majesty and Terror, The Pomp of his Appearance amidst the
Roarings of his Thunders, the Flashes of his Lightnings, and the Noise
of his Chariot-Wheels, is described with the utmost Flights of Human
Imagination.
There is nothing in the first and last Day's Engagement which does not
appear natural, and agreeable enough to the Ideas most Readers would
conceive of a Fight between two Armies of Angels.
The second Day's Engagement is apt to startle an Imagination, which has
not been raised and qualify'd for such a Description, by the reading of
the ancient Poets, and of
Homer
in particular. It was certainly a very
bold Thought in our Author, to ascribe the first Use of Artillery to the
Rebel Angels. But as such a pernicious Invention may be well supposed to
have proceeded from such Authors, so it entered very properly into the
Thoughts of that Being, who is all along describ'd as aspiring to the
Majesty of his Maker. Such Engines were the only Instruments he could
have made use of to imitate those Thunders, that in all Poetry, both
sacred and profane, are represented as the Arms of the Almighty. The
tearing up the Hills, was not altogether so daring a Thought as the
former. We are, in some measure, prepared for such an Incident by the
Description of the Giants' War, which we meet with among the Ancient
Poets. What
made this Circumstance the more proper for the Poet's
Use, is the Opinion of many learned Men, that the Fable of the Giants'
War, which makes so great a noise in Antiquity,
and gave birth to the
sublimest Description in Hesiod's Works was
an Allegory founded
upon this very Tradition of a Fight between the good and bad Angels.
It may, perhaps, be worth while to consider with what Judgment Milton,
in this Narration, has avoided every thing that is mean and trivial in
the Descriptions of the
Latin
and
Greek
Poets; and at the same time
improved every great Hint which he met with in their Works upon this
Subject.
Homer
in that Passage, which
Longinus
has celebrated for its
Sublimeness, and which
Virgil
and
Ovid
have copy'd after him, tells us,
that the Giants threw
Ossa
upon
Olympus
, and
Pelion
upon
Ossa
. He adds
an Epithet to
Pelion
which very much swells the
Idea, by bringing up to the Reader's Imagination all the Woods that grew
upon it. There is further a great Beauty in his singling out by Name
these three remarkable Mountains, so well known to the
Greeks
. This last
is such a Beauty as the Scene of
Milton's
War could not possibly furnish
him with.
Claudian
, in his Fragment upon the Giants' War, has given full
scope to that Wildness of Imagination which was natural to him. He tells
us, that the Giants tore up whole Islands by the Roots, and threw them
at the Gods. He describes one of them in particular taking up
Lemnos
in
his Arms, and whirling it to the Skies, with all
Vulcan's Shop
in the
midst of it. Another tears up
Mount Ida
, with the
River Enipeus
, which
ran down the Sides of it; but the Poet, not content to describe him with
this Mountain upon his Shoulders, tells us that the River flow'd down
his Back, as he held it up in that Posture. It is visible to every
judicious Reader, that such Ideas savour more of Burlesque, than of the
Sublime. They proceed from a Wantonness of Imagination, and rather
divert the Mind than astonish it.
Milton
has taken every thing that is
sublime in these several Passages, and composes out of them the
following great Image.
From their Foundations loos'ning to and fro,
They pluck'd the seated Hills, with all their Land,
Rocks, Waters, Woods; and by the shaggy Tops
Up-lifting bore them in their Hands—
We have the full Majesty of
Homer
in this short Description, improv'd by
the Imagination of
Claudian
, without its Puerilities. I need not point
out the Description of the fallen Angels seeing the Promontories hanging
over their Heads in such a dreadful manner, with the other numberless
Beauties in this Book, which are so conspicuous, that they cannot escape
the Notice of the most ordinary Reader.
There are indeed so many wonderful Strokes of Poetry in this Book, and
such a variety of Sublime Ideas, that it would have been impossible to
have given them a place within the bounds of this Paper. Besides that, I
find it in a great measure done to my hand at the End of my
Lord
Roscommon's Essay on Translated Poetry
. I shall refer my Reader thither
for some of the Master Strokes in the Sixth Book of
Paradise Lost
, tho'
at the same time there are many others which that noble Author has not
taken notice of.
Milton
, notwithstanding the sublime Genius he was Master of, has in this
Book drawn to his Assistance all the Helps he could meet with among the
Ancient Poets.
Sword of
Michael
, which makes so great
a
havock
among the bad Angels, was given him, we are told, out of the Armory of
God.
—But the Sword
Of Michael from the Armory of God
Was given him tempered so, that neither keen
Nor solid might resist that Edge: It met
The Sword of Satan, with steep Force to smite
Descending, and in half cut sheer—
This Passage is a Copy of that in
Virgil
, wherein the Poet tells us,
that the Sword of
Æneas
, which was given him by a Deity, broke into
Pieces the Sword of
Turnus
, which came from a mortal Forge. As the Moral
in this Place is divine, so by the way we may observe, that the
bestowing on a Man who is favoured by Heaven such an allegorical Weapon,
is very conformable to the old
Eastern
way of Thinking. Not only Homer
has made use of it, but we find the
Jewish
Hero in the
Book of
Maccabees
, who had fought the Battels of the chosen People with so much
Glory and Success, receiving in his Dream a Sword from the Hand of the
Prophet Jeremiah
. The following Passage, wherein
Satan
is described as
wounded by the Sword of
Michael
, is in imitation of
Homer
.
The griding Sword with discontinuous Wound
Passed through him; butt the Ethereal Substance closed
Not long divisible; and from the Gash
A Stream of Nectarous Humour issuing flowed
Sanguine, (such as celestial Spirits may bleed)
And all his Armour stained—
Homer
tells us in the same manner, that upon
Diomedes
wounding the Gods,
there flow'd from the Wound an Ichor, or pure kind of Blood, which was
not bred from mortal Viands; and that tho' the Pain was exquisitely
great, the Wound soon closed up and healed in those Beings who are
vested with Immortality.
I question not but
Milton
in his Description of his furious
Moloch
flying from the Battel, and bellowing with the Wound he had received,
had his Eye on
Mars
in the
Iliad
; who, upon his being wounded, is
represented as retiring out of the Fight, and making an Outcry louder
than that of a whole Army when it begins the Charge.
Homer
adds, that
the
Greeks
and
Trojans
, who were engaged in a general Battel, were
terrify'd on each side with the bellowing of this wounded Deity. The
Reader will easily observe how
Milton
has kept all the Horrour of this
Image, without running into the Ridicule of it.
—Where the Might of Gabriel fought,
And with fierce Ensigns pierc'd the deep Array
Of Moloch, furious King! who him defy'd,
And at his Chariot-wheels to drag him bound
Threaten'd, nor from the Holy One of Heav'n
Refrained his Tongue blasphemous: but anon
Down cloven to the Waste, with shattered Arms
And uncouth Pain fled bellowing.—
Milton
has likewise raised his Description in this Book with many Images
taken out of the poetical Parts of Scripture. The
Messiah's
Chariot, as
I have before taken notice, is formed upon a Vision of
Ezekiel
, who, as
Grotius
observes, has very much in him of
Homer's
Spirit in the Poetical
Parts of his Prophecy.
The following Lines in that glorious Commission which is given the
Messiah
to extirpate the Host of Rebel Angels, is drawn from a Sublime
Passage in the
Psalms
.
Go then thou Mightiest in thy Father's Might!
Ascend my Chariot, guide the rapid Wheels
That shake Heav'n's Basis; bring forth all my War,
My Bow, my Thunder, my Almighty Arms,
Gird on thy Sword on thy puissant Thigh.
The Reader will easily discover many other Strokes of the same nature.
There is no question but
Milton
had heated his Imagination with the
Fight of the Gods in
Homer
, before he enter'd upon this Engagement of
the Angels.
Homer
there gives us a Scene of Men, Heroes, and Gods, mix'd
together in Battel.
Mars
animates the contending Armies, and lifts up
his Voice in such a manner, that it is heard distinctly amidst all the
Shouts and Confusion of the Fight.
Jupiter
at the same time Thunders
over their Heads; while
Neptune
raises such a Tempest, that the whole
Field of Battel and all the Tops of the Mountains shake about them. The
Poet tells us, that
Pluto
himself, whose Habitation was in the very
Center of the Earth, was so affrighted at the Shock, that he leapt from
his Throne.
Homer
afterwards describes
Vulcan
as pouring down a Storm of
Fire upon the River
Xanthus
, and
Minerva
as throwing a Rock at
Mars
;
who, he tells us, cover'd seven Acres in his Fall.
As
Homer
has introduced into his Battel of the Gods every thing that is
great and terrible in Nature,
Milton
has filled his Fight of good and
bad Angels with all the like Circumstances of Horrour. The Shout of
Armies, the Rattling of Brazen Chariots, the Hurling of Rocks and
Mountains, the Earthquake, the Fire, the Thunder, are all of them
employ'd to lift up the Reader's Imagination, and give him a suitable
Idea of so great an Action. With what Art has the Poet represented the
whole Body of the Earth trembling, even before it was created.
All Heaven resounded, and had Earth been then,
All Earth had to its Center shook—
In how sublime and just a manner does he afterwards describe the whole
Heaven shaking under the Wheels of the
Messiah's
Chariot, with that
Exception to the
Throne of God
?
—Under his burning Wheels
The stedfast Empyrean shook throughout,
All but the Throne it self of God—
Notwithstanding the
Messiah
appears clothed with so much Terrour and
Majesty, the Poet has still found means to make his Readers conceive an
Idea of him, beyond what he himself was able to describe.
Yet half his Strength he put not forth, but checkt
His Thunder in mid Volley; for he meant
Not to destroy, but root them out of Heaven.
In a Word,
Milton's
Genius, which was so great in it self, and so
strengthened by all the helps of Learning, appears in this Book every
way equal to his Subject, which was the most Sublime that could enter
into the Thoughts of a Poet.
he knew all the Arts of affecting the
Mind,
he knew it was necessary to give
it certain Resting-places
and Opportunities of recovering it self from time to time: He has
therefore
with great Address interspersed several Speeches,
Reflections, Similitudes, and the like Reliefs to diversify his
Narration, and ease the Attention of
the
Reader, that he might
come fresh to his great Action, and by such a Contrast of Ideas, have a
more lively taste of the nobler Parts of his Description.
L.
is
an
had he not given
his
Contents
|
Monday, March 24, 1712 |
Steele |
Voluisti in suo Genere, unumquemque nostrum quasi quendam esse
Roscium, dixistique non tam ea quæ recta essent probari, quam quæ
prava sunt fastidiis adhærescere.
Cicero
de Gestu.

It is very natural to take for our whole Lives a light Impression of a
thing which at first fell into Contempt with us for want of
Consideration. The real Use of a certain Qualification (which the wiser
Part of Mankind look upon as at best an indifferent thing, and generally
a frivolous Circumstance) shews the ill Consequence of such
Prepossessions. What I mean, is the Art, Skill, Accomplishment, or
whatever you will call it, of Dancing. I knew a Gentleman of great
Abilities, who bewail'd the Want of this Part of his Education to the
End of a very honourable Life. He observ'd that there was not occasion
for the common Use of great Talents; that they are but seldom in Demand;
and that these very great Talents were often render'd useless to a Man
for want of small Attainments. A good Mein (a becoming Motion, Gesture
and Aspect) is natural to some Men; but even these would be highly more
graceful in their Carriage, if what they do from the Force of Nature
were confirm'd and heightned from the Force of Reason. To one who has
not at all considered it, to mention the Force of Reason on such a
Subject, will appear fantastical; but when you have a little attended to
it, an Assembly of Men will have quite another View: and they will tell
you, it is evident from plain and infallible Rules, why this Man with
those beautiful Features, and well fashion'd Person, is not so agreeable
as he who sits by him without any of those Advantages. When we read, we
do it without any exerted Act of Memory that presents the Shape of the
Letters; but Habit makes us do it mechanically, without staying, like
Children, to recollect and join those Letters. A Man who has not had the
Regard of his Gesture in any part of his Education, will find himself
unable to act with Freedom before new Company, as a Child that is but
now learning would be to read without Hesitation. It is for the
Advancement of the Pleasure we receive in being agreeable to each other
in ordinary Life, that one would wish Dancing were generally understood
as conducive as it really is to a proper Deportment in Matters that
appear the most remote from it. A Man of Learning and Sense is
distinguished from others as he is such, tho' he never runs upon Points
too difficult for the rest of the World; in like Manner the reaching out
of the Arm, and the most ordinary Motion, discovers whether a Man ever
learnt to know what is the true Harmony and Composure of his Limbs and
Countenance. Whoever has seen
Booth
in the Character of
Pyrrhus
, march
to his Throne to receive
Orestes
, is convinced that majestick and great
Conceptions are expressed in the very Step; but perhaps, tho' no other
Man could perform that Incident as well as he does, he himself would do
it with a yet greater Elevation were he a Dancer.
is so dangerous a
Subject to treat with Gravity, that I shall not at present enter into it
any further; but the Author of the following Letter
has treated it
in the Essay he speaks of in such a Manner, that I am beholden to him
for a Resolution, that I will never hereafter think meanly of any thing,
till I have heard what they who have another Opinion of it have to say
in its Defence.
Mr. Spectator,
'Since there are scarce any of the Arts or Sciences that have not been
recommended to the World by the Pens of some of the Professors,
Masters, or Lovers of them, whereby the Usefulness, Excellence, and
Benefit arising from them, both as to the Speculative and practical
Part, have been made publick, to the great Advantage and Improvement
of such Arts and Sciences; why should Dancing, an Art celebrated by
the Ancients in so extraordinary a Manner, be totally neglected by the
Moderns, and left destitute of any Pen to recommend its various
Excellencies and substantial Merit to Mankind?
'The low Ebb to which Dancing is now fallen, is altogether owing to
this Silence. The Art is esteem'd only as an amusing Trifle; it lies
altogether uncultivated, and is unhappily fallen under the Imputation
of Illiterate and Mechanick: And as Terence in one of his Prologues,
complains of the Rope-dancers drawing all the Spectators from his
Play, so may we well say, that Capering and Tumbling is now preferred
to, and supplies the Place of just and regular Dancing on our
Theatres. It is therefore, in my opinion, high time that some one
should come in to its Assistance, and relieve it from the many gross
and growing Errors that have crept into it, and over-cast its real
Beauties; and to set Dancing in its true light, would shew the
Usefulness and Elegancy of it, with the Pleasure and Instruction
produc'd from it; and also lay down some fundamental Rules, that might
so tend to the Improvement of its Professors, and Information of the
Spectators, that the first might be the better enabled to perform, and
the latter render'd more capable of judging, what is (if there be any
thing) valuable in this Art.
'To encourage therefore some ingenious Pen capable of so generous an
Undertaking, and in some measure to relieve Dancing from the
Disadvantages it at present lies under, I, who teach to dance, have
attempted a small Treatise as an Essay towards an History of Dancing;
in which I have enquired into its Antiquity, Original, and Use, and
shewn what Esteem the Ancients had for it: I have likewise considered
the Nature and Perfection of all its several Parts, and how beneficial
and delightful it is, both as a Qualification and an Exercise; and
endeavoured to answer all Objections that have been maliciously rais'd
against it. I have proceeded to give an Account of the particular
Dances of the Greeks and Romans, whether religious, warlike, or civil;
and taken particular notice of that Part of Dancing relating to the
ancient Stage, and in which the Pantomimes had so great a share: Nor
have I been wanting in giving an historical Account of some particular
Masters excellent in that surprising Art. After which, I have advanced
some Observations on the modern Dancing, both as to the Stage, and
that Part of it so absolutely necessary for the Qualification of
Gentlemen and Ladies; and have concluded with some short Remarks on
the Origin and Progress of the Character by which Dances are writ
down, and communicated to one Master from another. If some great
Genius after this would arise, and advance this Art to that Perfection
it seems capable of receiving, what might not be expected from it? For
if we consider the Origin of Arts and Sciences, we shall find that
some of them took rise from Beginnings so mean and unpromising, that
it is very wonderful to think that ever such surprizing Structures
should have been raised upon such ordinary Foundations. But what
cannot a great Genius effect? Who would have thought that the
clangorous Noise of a Smith's Hammers should have given the first rise
to Musick? Yet Macrobius in his second Book relates, that Pythagoras,
in passing by a Smith's Shop, found that the Sounds proceeding from
the Hammers were either more grave or acute, according to the
different Weights of the Hammers. The Philosopher, to improve this
Hint, suspends different Weights by Strings of the same Bigness, and
found in like manner that the Sounds answered to the Weights. This
being discover'd, he finds out those Numbers which produc'd Sounds
that were Consonants: As, that two Strings of the same Substance and
Tension, the one being double the Length, of the other, give that
Interval which is called Diapason, or an Eighth; the same was also
effected from two Strings of the same Length and Size, the one having
four times the Tension of the other. By these Steps, from so mean a
Beginning, did this great Man reduce, what was only before Noise, to
one of the most delightful Sciences, by marrying it to the
Mathematicks; and by that means caused it to be one of the most
abstract and demonstrative of Sciences. Who knows therefore but
Motion, whether Decorous or Representative, may not (as it seems
highly probable it may) be taken into consideration by some Person
capable of reducing it into a regular Science, tho' not so
demonstrative as that proceeding from Sounds, yet sufficient to
entitle it to a Place among the magnify'd Arts.
'Now, Mr. Spectator, as you have declared your self Visitor of
Dancing-Schools, and this being an Undertaking which more immediately
respects them, I think my self indispensably obliged, before I proceed
to the Publication of this my Essay, to ask your Advice, and hold it
absolutely necessary to have your Approbation; and in order to
recommend my Treatise to the Perusal of the Parents of such as learn
to dance, as well as to the young Ladies, to whom, as Visitor, you
ought to be Guardian.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant.
Salop, March 19, 1711-12.
T.
John Weaver.
Contents
|
Tuesday, March 25, 1712 |
Addison |
Respicere exemplar vitæ morumque jubebo
Doctum imitatorem, et veras hinc ducere voces.
Hor.

Friend Sir
Roger De Coverley
, when we last met together at the Club,
told me, that he had a great mind to see the new Tragedy
with me,
assuring me at the same time, that he had not been at a Play these
twenty Years. The
I saw, said Sir
Roger
, was the
Committee
, which I
should not have gone to neither, had not I been told before-hand that it
was a good Church-of-England Comedy
. He then proceeded to enquire of
me who this
Distrest Mother
was; and upon hearing that she was
Hector's
Widow, he told me that her Husband was a brave Man, and that when he was
a Schoolboy he had read his Life at the end of the Dictionary. My Friend
asked me, in the next place, if there would not be some danger in coming
home late, in case the Mohocks should be Abroad. I assure you, says he,
I thought I had fallen into their Hands last Night; for I observed two
or three lusty black Men that follow'd me half way up Fleet-street, and
mended their pace behind me, in proportion as I put on to get away from
them. You must know, continu'd the Knight with a Smile, I fancied they
had a mind to hunt me; for I remember an honest Gentleman in my
Neighbourhood, who was served such a trick in King Charles the Second's
time; for which reason he has not ventured himself in Town ever since. I
might have shown them very good Sport, had this been their Design; for
as I am an old Fox-hunter, I should have turned and dodg'd, and have
play'd them a thousand tricks they had never seen in their Lives before.
Sir
Roger
added, that if these Gentlemen had any such Intention, they
did not succeed very well in it: for I threw them out, says he, at the
End of Norfolk street, where I doubled the Corner, and got shelter in my
Lodgings before they could imagine what was become of me. However, says
the Knight, if Captain
Sentry
will make one with us to-morrow night, and
if you will both of you call upon me about four a-Clock, that we may be
at the House before it is full, I will have my own Coach in readiness to
attend you, for John tells me he has got the Fore-Wheels mended.
The Captain, who did not fail to meet me there at the appointed Hour,
bid Sir
Roger
fear nothing, for that he had put on the same Sword which
he made use of at the Battel of
Steenkirk
. Sir
Roger's
Servants, and
among the rest my old Friend the Butler, had, I found, provided
themselves with good Oaken Plants, to attend their Master upon this
occasion. When he had placed him in his Coach, with my self at his
Left-Hand, the Captain before him, and his Butler at the Head of his
Footmen in the Rear, we convoy'd him in safety to the Play-house, where,
after having marched up the Entry in good order, the Captain and I went
in with him, and seated him betwixt us in the Pit. As soon as the House
was full, and the Candles lighted, my old Friend stood up and looked
about him with that Pleasure, which a Mind seasoned with Humanity
naturally feels in its self, at the sight of a Multitude of People who
seem pleased with one another, and partake of the same common
Entertainment. I could not but fancy to myself, as the old Man stood up
in the middle of the Pit, that he made a very proper Center to a Tragick
Audience. Upon the entring of
Pyrrhus
, the Knight told me, that he did
not believe the King of
France
himself had a better Strut. I was indeed
very attentive to my old Friend's Remarks, because I looked upon them as
a Piece of natural Criticism, and was well pleased to hear him at the
Conclusion of almost every Scene, telling me that he could not imagine
how the Play would end. One while he appeared much concerned for
Andromache
; and a little while after as much for
Hermione
: and was
extremely puzzled to think what would become of
Pyrrhus
.
When Sir
Roger
saw
Andromache's
obstinate Refusal to her Lover's
Importunities, he whisper'd me in the Ear, that he was sure she would
never have him; to which he added, with a more than ordinary Vehemence,
you can't imagine, Sir, what 'tis to have to do with a
Widow
. Upon
Pyrrhus
his threatning afterwards to leave her, the Knight shook his
Head, and muttered to himself, Ay, do if you can. This Part dwelt so
much upon my Friend's Imagination, that at the close of the Third Act,
as I was thinking of something else, he whispered in my Ear, These
Widows, Sir, are the most perverse Creatures in the World. But pray,
says he, you that are a Critick, is this Play according to your
Dramatick Rules, as you call them? Should your People in Tragedy always
talk to be understood? Why, there is not a single Sentence in this Play
that I do not know the Meaning of.
The Fourth Act very luckily begun before I had time to give the old
Gentleman an Answer: Well, says the Knight, sitting down with great
Satisfaction, I suppose we are now to see
Hector's
Ghost. He then
renewed his Attention, and, from time to time, fell a praising the
Widow. He made, indeed, a little Mistake as to one of her Pages, whom at
his first entering, he took for
Astyanax
; but he quickly set himself
right in that Particular, though, at the same time, he owned he should
have been very glad to have seen the little Boy, who, says he, must
needs be a very fine Child by the Account that is given of him. Upon
Hermione's
going off with a Menace to
Pyrrhus
, the Audience gave a loud
Clap; to which Sir
Roger
added, On my Word, a notable young Baggage!
As there was a very remarkable Silence and Stillness in the Audience
during the whole Action, it was natural for them to take the Opportunity
of these Intervals between the Acts, to express their Opinion of the
Players, and of their respective Parts. Sir
Roger
hearing a Cluster of
them praise
Orestes
, struck in with them, and told them, that he thought
his Friend
Pylades
was a very sensible Man; as they were afterwards
applauding
Pyrrhus
, Sir
Roger
put in a second time; And let me tell you,
says he, though he speaks but little, I like the old Fellow in Whiskers
as well as any of them. Captain
Sentry
seeing two or three Waggs who sat
near us, lean with an attentive Ear towards Sir
Roger
, and fearing lest
they should Smoke the Knight, pluck'd him by the Elbow, and whisper'd
something in his Ear. that lasted till the Opening of the Fifth Act. The
Knight was wonderfully attentive to the Account which
Orestes
gives of
Pyrrhus
his Death, and at the Conclusion of it, told me it was such a
bloody Piece of Work, that he was glad it was not done upon the Stage.
Seeing afterwards
Orestes
in his raving Fit, he grew more than ordinary
serious, and took occasion to moralize (in his way) upon an Evil
Conscience, adding, that
Orestes
, in his Madness, looked as if he saw
something.
As we were the first that came into the House, so we were the last that
went out of it; being resolved to have a clear Passage for our old
Friend, whom we did not care to venture among the justling of the Crowd.
Sir
Roger
went out fully satisfied with his Entertainment, and we
guarded him to his Lodgings in the same manner that we brought him to
the Playhouse; being highly pleased, for my own part, not only with the
Performance of the excellent Piece which had been presented, but with
the Satisfaction which it had given to the good old Man.
L.
This is a fourth puff (see Nos.
,
,
) of Addison's
friend Ambrose Philips. The art of '
packing a house
' to secure applause
was also practised on the first night of the acting of this version of
Andromaque
.
The
Committee
, or the
Faithful Irishman,
was written by Sir
Robert Howard soon after the Restoration, with for its heroes two
Cavalier colonels, whose estates are sequestered, and their man Teg
(Teague), an honest blundering Irishman. The Cavaliers defy the
Roundhead Committee, and 'the day may come' says one of them, 'when
those that suffer for their consciences and honour may be rewarded.'
Nobody who heard this from the stage in the days of Charles II. could
feel that the day had come. Its comic Irishman kept the
Committee
on the
stage, and in Queen Anne's time the thorough Tory still relished the
stage caricature of the maintainers of the Commonwealth in Mr. Day with
his greed, hypocrisy, and private incontinence; his wife, who had been
cookmaid to a gentleman, but takes all the State matters on herself; and
their empty son Abel, who knows Parliament-men and Sequestrators, and
whose 'profound contemplations are caused by the constervation of his
spirits for the nation's good.'
Contents
|
Wednesday, March 26, 1712 |
Steele |
—Clament periisse pudorem
Cuncti penè patres, ea cum reprehendere coner,
Quæ gravis Æsopus, quæ doctus Roscius egit:
Vel quia nil rectum, nisi quod placuit sibi, ducunt;
Vel quia turpe putant parere minoribus, et, quæ
Imberbes didicere, senes perdenda fateri.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'As you are the daily Endeavourer to promote Learning and good Sense,
I think myself obliged to suggest to your Consideration whatever may
promote or prejudice them.. There is an Evil which has prevailed from
Generation to Generation, which grey Hairs and tyrannical Custom
continue to support; I hope your Spectatorial Authority will give a
seasonable Check to the Spread of the Infection; I mean old Men's
overbearing the strongest Sense of their Juniors by the mere Force of
Seniority; so that for a young Man in the Bloom of Life and Vigour of
Age to give a reasonable Contradiction to his Elders, is esteemed an
unpardonable Insolence, and regarded as a reversing the Decrees of
Nature. I am a young Man, I confess, yet I honour the grey Head as
much as any one; however, when in Company with old Men, I hear them
speak obscurely, or reason preposterously (into which Absurdities,
Prejudice, Pride, or Interest, will sometimes throw the wisest) I
count it no Crime to rectifie their Reasoning, unless Conscience must
truckle to Ceremony, and Truth fall a Sacrifice to Complaisance. The
strongest Arguments are enervated, and the brightest Evidence
disappears, before those tremendous Reasonings and dazling Discoveries
of venerable old Age: You are young giddy-headed Fellows, you have not
yet had Experience of the World. Thus we young Folks find our Ambition
cramp'd, and our Laziness indulged, since, while young, we have little
room to display our selves; and, when old, the Weakness of Nature must
pass for Strength of Sense, and we hope that hoary Heads will raise us
above the Attacks of Contradiction. Now, Sir, as you would enliven our
Activity in the pursuit of Learning, take our Case into Consideration;
and, with a Gloss on brave
Elihu's Sentiments, assert the Rights of
Youth, and prevent the pernicious Incroachments of Age. The generous
Reasonings of that gallant Youth would adorn your Paper; and I beg you
would insert them, not doubting but that they will give good
Entertainment to the most intelligent of your Readers.
'So these three Men ceased to answer
Job, because he was righteous in
his own Eyes. Then was kindled the Wrath of
Elihu the Son of
Barachel
the
Buzite, of the Kindred of
Ram: Against
Job was his Wrath kindled,
because he justified himself rather than God. Also against his three
Friends was his Wrath kindled, because they had found no Answer, and
yet had condemned
Job. Now
Elihu had waited till
Job had spoken,
because they were elder than he. When
Elihu saw there was no Answer in
the Mouth of these three Men, then his Wrath was kindled. And
Elihu
the Son of
Barachel the
Buzite answered and said, I am young, and ye
are very old, wherefore I was afraid, and durst not shew you mine
Opinion. I said, Days should speak, and Multitude of Years should
teach Wisdom. But there is a Spirit in Man; and the Inspiration of the
Almighty giveth them Understanding. Great Men are not always wise:
Neither do the Aged understand Judgment. Therefore I said, hearken to
me, I also will shew mine Opinion. Behold, I waited for your Words; I
gave ear to your Reasons, whilst you searched out what to say. Yea, I
attended unto you: And behold there was none of you that convinced
Job, or that answered his Words; lest ye should say, we have found out
Wisdom: God thrusteth him down, not Man. Now he hath not directed his
Words against me: Neither will I answer him with your Speeches. They
were amazed, they answered no more: They left off speaking. When I had
waited (for they spake not, but stood still and answered no more) I
said, I will answer also my Part, I also will shew mine Opinion. For I
am full of Matter, the Spirit within me constraineth me. Behold my
Belly is as Wine which hath no vent, it is ready to burst like new
Bottles. I will speak that I may be refreshed: I will open my Lips,
and answer. Let me not, I pray you, accept any Man's Person, neither
let me give flattering Titles unto Man.
For I know not to give
flattering Titles; in so doing my Maker would soon take me away
1.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I have formerly read with great Satisfaction your Papers about Idols,
and the Behaviour of Gentlemen in those Coffee-houses where Women
officiate, and impatiently waited to see you take India and China
Shops into Consideration: But since you have pass'd us over in
silence, either that you have not as yet thought us worth your Notice,
or that the Grievances we lie under have escaped your discerning Eye,
I must make my Complaints to you, and am encouraged to do it because
you seem a little at leisure at this present Writing. I am, dear Sir,
one of the top China-Women about Town; and though I say it, keep as
good Things, and receive as fine Company as any o' this End of the
Town, let the other be who she will: In short, I am in a fair Way to
be easy, were it not for a Club of Female Rakes, who under pretence of
taking their innocent Rambles, forsooth, and diverting the Spleen,
seldom fail to plague me twice or thrice a-day to cheapen Tea, or buy
a Skreen; What else should they mean? as they often repeat it. These
Rakes are your idle Ladies of Fashion, who having nothing to do,
employ themselves in tumbling over my Ware. One of these No-Customers
(for by the way they seldom or never buy any thing) calls for a Set of
Tea-Dishes, another for a Bason, a third for my best Green-Tea, and
even to the Punch Bowl, there's scarce a piece in my Shop but must be
displaced, and the whole agreeable Architecture disordered; so that I
can compare 'em to nothing but to the Night-Goblins that take a
Pleasure to over-turn the Disposition of Plates and Dishes in the
Kitchens of your housewifely Maids. Well, after all this Racket and
Clutter, this is too dear, that is their Aversion; another thing is
charming, but not wanted: The Ladies are cured of the Spleen, but I am
not a Shilling the better for it. Lord! what signifies one poor Pot of
Tea, considering the Trouble they put me to? Vapours, Mr.
Spectator,
are terrible Things; for though I am not possess'd by them my self, I
suffer more from 'em than if I were. Now I must beg you to admonish
all such Day-Goblins to make fewer Visits, or to be less troublesome
when they come to one's Shop; and to convince 'em, that we honest
Shop-keepers have something better to do, than to cure Folks of the
Vapours
gratis. A young Son of mine, a School-Boy, is my Secretary, so
I hope you'll make Allowances. I am,
Sir,
Your constant Reader, and
very humble Servant,
Rebecca the Distress'd.
March the 22nd.
T.
Job
, ch. xii.
Contents
|
Thursday, March 27, 1712 |
Budgell |
Fingit equum tenerâ docilem cervice Magister,
Ire viam quam monstrat eques—
Hor.

I have lately received a third Letter from the Gentleman, who has
already given the Publick two Essays upon Education. As his Thoughts
seem to be very just and new upon this Subject, I shall communicate them
to the Reader.
Sir,
If I had not been hindered by some extraordinary Business, I should
have sent you sooner my further Thoughts upon Education. You may
please to remember, that in my last Letter I endeavoured to give the
best Reasons that could be urged in favour of a private or publick
Education. Upon the whole it may perhaps be thought that I seemed
rather enclined to the latter, though at the same time I confessed
that Virtue, which ought to be our first and principal Care, was more
usually acquired in the former.
I intend therefore, in this Letter, to offer at Methods, by which I
conceive Boys might be made to improve in Virtue, as they advance in
Letters.
I know that in most of our public Schools Vice is punished and
discouraged whenever it is found out; but this is far from being
sufficient, unless our Youth are at the same time taught to form a
right Judgment of Things, and to know what is properly Virtue.
To this end, whenever they read the Lives and Actions of such Men as
have been famous in their Generation, it should not be thought enough
to make them barely understand so many Greek or Latin Sentences, but
they should be asked their Opinion of such an Action or Saying, and
obliged to give their Reasons why they take it to be good or bad. By
this means they would insensibly arrive at proper Notions of Courage,
Temperance, Honour and Justice.
There must be great Care taken how the Example of any particular
Person is recommended to them in gross; instead of which, they ought
to be taught wherein such a Man, though great in some respects, was
weak and faulty in others. For want of this Caution, a Boy is often so
dazzled with the Lustre of a great Character, that he confounds its
Beauties with its Blemishes, and looks even upon the faulty Parts of
it with an Eye of Admiration.
I have often wondered how Alexander, who was naturally of a generous
and merciful Disposition, came to be guilty of so barbarous an Action
as that of dragging the Governour of a Town after his Chariot. I know
this is generally ascribed to his Passion for Homer; but I lately met
with a Passage in Plutarch, which, if I am not very much mistaken,
still gives us a clearer Light into the Motives of this Action.
Plutarch tells us, that Alexander in his Youth had a Master named
Lysimachus, who, tho' he was a Man destitute of all Politeness,
ingratiated himself both with Philip and his Pupil, and became the
second Man at Court, by calling the King Peleus, the Prince Achilles,
and himself Phœnix. It is no wonder if Alexander having been thus used
not only to admire, but to personate Achilles, should think it
glorious to imitate him in this piece of Cruelty and Extravagance.
To carry this Thought yet further, I shall submit it to your
Consideration, whether instead of a Theme or Copy of Verses, which are
the usual Exercises, as they are called in the School-phrase, it
would not be more proper that a Boy should be tasked once or twice a
Week to write down his Opinion of such Persons and Things as occur to
him in his Reading; that he should descant upon the Actions of Turnus
and Æneas, shew wherein they excelled or were defective, censure or
approve any particular Action, observe how it might have been carried
to a greater Degree of Perfection, and how it exceeded or fell short
of another. He might at the same time mark what was moral in any
Speech, and how far it agreed with the Character of the Person
speaking. This Exercise would soon strengthen his Judgment in what is
blameable or praiseworthy, and give him an early Seasoning of
Morality.
Next to those Examples which may be met with in Books, I very much
approve Horace's Way of setting before Youth the infamous or
honourable Characters of their Contemporaries: That Poet tells us,
this was the Method his Father made use of to incline him to any
particular Virtue, or give him an Aversion to any particular Vice. If,
says Horace, my Father advised me to live within Bounds, and be
contented with the Fortune he should leave me; Do not you see (says
he) the miserable Condition of Burrus, and the Son of Albus? Let the
Misfortunes of those two Wretches teach you to avoid Luxury and
Extravagance. If he would inspire me with an Abhorrence to Debauchery,
do not (says he) make your self like Sectanus, when you may be happy
in the Enjoyment of lawful Pleasures. How scandalous (says he) is the
Character of Trebonius, who was lately caught in Bed with another
Man's Wife? To illustrate the Force of this Method, the Poet adds,
That as a headstrong Patient, who will not at first follow his
Physician's Prescriptions, grows orderly when he hears that his
Neighbours die all about him; so Youth is often frighted from Vice, by
hearing the ill Report it brings upon others.
'Xenophon's Schools of Equity, in his Life of Cyrus the Great, are
sufficiently famous: He tells us, that the Persian Children went to
School, and employed their Time as diligently in learning the
Principles of Justice and Sobriety, as the Youth in other Countries
did to acquire the most difficult Arts and Sciences: their Governors
spent most part of the Day in hearing their mutual Accusations one
against the other, whether for Violence, Cheating, Slander, or
Ingratitude; and taught them how to give Judgment against those who
were found to be any ways guilty of these Crimes. I omit the Story of
the long and short Coat, for which Cyrus himself was punished, as a
Case equally known with any in Littleton.
'The Method, which Apuleius tells us the Indian Gymnosophists took to
educate their Disciples, is still more curious and remarkable. His
Words are as follow: When their Dinner is ready, before it is served
up, the Masters enquire of every particular Scholar how he has
employed his Time since Sun-rising; some of them answer, that having
been chosen as Arbiters between two Persons they have composed their
Differences, and made them Friends; some, that they have been
executing the Orders of their Parents; and others, that they have
either found out something new by their own Application, or learnt it
from the Instruction of their Fellows: But if there happens to be any
one among them, who cannot make it appear that he has employed the
Morning to advantage, he is immediately excluded from the Company, and
obliged to work, while the rest are at Dinner.
'It is not impossible, that from these several Ways of producing
Virtue in the Minds of Boys, some general Method might be invented.
What I would endeavour to inculcate, is, that our Youth cannot be too
soon taught the Principles of Virtue, seeing the first Impressions
which are made on the Mind are always the strongest.
'The Archbishop of Cambray makes Telemachus say, that though he was
young in Years, he was old in the Art of knowing how to keep both his
own and his Friend's Secrets. When my Father, says the Prince, went to
the Siege of Troy, he took me on his Knees, and after having embraced
and blessed me, as he was surrounded by the Nobles of Ithaca, O my
Friends, says he, into your Hands I commit the Education of my Son; if
ever you lovd his Father, shew it in your Care towards him; but above
all, do not omit to form him just, sincere, and faithful in keeping a
Secret. These Words of my Father, says Telemachus, were continually
repeated to me by his Friends in his Absence; who made no scruple of
communicating to me in their Uneasiness to see my Mother surrounded
with Lovers, and the Measures they designed to take on that Occasion.
He adds, that he was so ravished at being thus treated like a Man, and
at the Confidence reposed in him, that he never once abused it; nor
could all the Insinuations of his Fathers Rivals ever get him to
betray what was committed to him under the Seal of Secrecy.
There is hardly any Virtue which a Lad might not thus learn by
Practice and Example.
I have heard of a good Man, who used at certain times to give his
Scholars Six Pence apiece, that they might tell him the next day how
they had employd it. The third part was always to be laid out in
Charity, and every Boy was blamed or commended as he could make it
appear that he had chosen a fit Object.
In short, nothing is more wanting to our publick Schools, than that
the Masters of them should use the same care in fashioning the Manners
of their Scholars, as in forming their Tongues to the learned
Languages. Where-ever the former is omitted, I cannot help agreeing
with Mr. Locke, That a Man must have a very strange Value for Words,
when preferring the Languages of the Greeks and Romans to that which
made them such brave Men, he can think it worth while to hazard the
Innocence and Virtue of his Son for a little Greek and Latin.
As the Subject of this Essay is of the highest Importance, and what I
do not remember to have yet seen treated by any Author, I have sent
you what occurrd to me on it from my own Observation or Reading, and
which you may either suppress or publish as you think fit.
I am, Sir, Yours, &c.
X.
Contents
—Nil fuit unquam
Tam dispar sibi.
Hor.
1
I find the Tragedy of the
Distrest Mother
is publish'd today:
Author
of the Prologue, I suppose, pleads an old Excuse I have read somewhere,
of being dull with Design; and the Gentleman who writ the Epilogue
has,
to my knowledge, so much of greater moment to value himself upon, that
he will easily forgive me for publishing the Exceptions made against
Gayety at the end of serious Entertainments, in the following Letter: I
should be more unwilling to pardon him than any body, a Practice which
cannot have any ill Consequence, but from the Abilities of the Person
who is guilty of it.
Mr.
Spectator,
I had the Happiness the other Night of sitting very near you, and your
worthy Friend Sir
Roger, at the acting of the new Tragedy, which you
have in a late Paper or two so justly recommended. I was highly
pleased with the advantageous Situation Fortune had given me in
placing me so near two Gentlemen, from one of which I was sure to hear
such Reflections on the several Incidents of the Play, as pure Nature
suggested, and from the other such as flowed from the exactest Art and
Judgment: Tho I must confess that my Curiosity led me so much to
observe the Knight's Reflections, that I was not so well at leisure to
improve my self by yours. Nature, I found, play'd her Part in the
Knight pretty well, till at the last concluding Lines she entirely
forsook him. You must know, Sir, that it is always my Custom, when I
have been well entertained at a new Tragedy, to make my Retreat before
the facetious Epilogue enters; not but that those Pieces are often
very well writ, but having paid down my Half Crown, and made a fair
Purchase of as much of the pleasing Melancholy as the Poet's Art can
afford me, or my own Nature admit of, I am willing to carry some of it
home with me; and can't endure to be at once trick'd out of all, tho'
by the wittiest Dexterity in the World. However, I kept my Seat
t'other Night, in hopes of finding my own Sentiments of this Matter
favour'd by your Friend's; when, to my great Surprize, I found the
Knight entering with equal Pleasure into both Parts, and as much
satisfied with Mrs.
Oldfield's Gaiety, as he had been before with
Andromache's Greatness. Whether this were no other than an Effect of
the Knight's peculiar Humanity, pleas'd to find at last, that after
all the tragical Doings every thing was safe and well, I don't know.
But for my own part, I must confess, I was so dissatisfied, that I was
sorry the Poet had saved
Andromache, and could heartily have wished
that he had left her stone-dead upon the Stage. For you cannot
imagine, Mr.
Spectator, the Mischief she was reserv'd to do me. I
found my Soul, during the Action, gradually work'd up to the highest
Pitch; and felt the exalted Passion which all generous Minds conceive
at the Sight of Virtue in Distress. The Impression, believe me, Sir,
was so strong upon me, that I am persuaded, if I had been let alone in
it, I could at an Extremity have ventured to defend your self and Sir
ROGER against half a Score of the fiercest Mohocks: But the ludicrous
Epilogue in the Close extinguish'd all my Ardour, and made me look
upon all such noble Atchievements, as downright silly and romantick.
What the rest of the Audience felt, I can't so well tell: For my self,
I must declare, that at the end of the Play I found my Soul uniform,
and all of a Piece; but at the End of the Epilogue it was so jumbled
together, and divided between Jest and Earnest, that if you will
forgive me an extravagant Fancy, I will here set it down. I could not
but fancy, if my Soul had at that Moment quitted my Body, and
descended to the poetical Shades in the Posture it was then in, what a
strange Figure it would have made among them. They would not have
known what to have made of my motley Spectre, half Comick and half
Tragick, all over resembling a ridiculous Face, that at the same time
laughs on one side and cries o' t'other. The only Defence, I think, I
have ever heard made for this, as it seems to me, most unnatural Tack
of the Comick Tail to the Tragick Head, is this, that the Minds of the
Audience must be refreshed, and Gentlemen and Ladies not sent away to
their own Homes with too dismal and melancholy Thoughts about them:
For who knows the Consequence of this? We are much obliged indeed to
the Poets for the great Tenderness they express for the Safety of our
Persons, and heartily thank them for it. But if that be all, pray,
good Sir, assure them, that we are none of us like to come to any
great Harm; and that, let them do their best, we shall in all
probability live out the Length of our Days, and frequent the Theatres
more than ever. What makes me more desirous to have some Reformation
of this matter, is because of an ill Consequence or two attending it:
For a great many of our Church-Musicians being related to the Theatre,
they have, in Imitation of these Epilogues, introduced in their
farewell Voluntaries a sort of Musick quite foreign to the design of
Church-Services, to the great Prejudice of well-disposed People. Those
fingering Gentlemen should be informed, that they ought to suit their
Airs to the Place and Business; and that the Musician is obliged to
keep to the Text as much as the Preacher. For want of this, I have
found by Experience a great deal of Mischief: For when the Preacher
has often, with great Piety and Art enough, handled his Subject, and
the judicious Clark has with utmost Diligence culled out two Staves
proper to the Discourse, and I have found in my self and in the rest
of the Pew good Thoughts and Dispositions, they have been all in a
moment dissipated by a merry Jigg from the Organ-Loft. One knows not
what further ill Effects the Epilogues I have been speaking of may in
time produce:
But this I am credibly informed of, that
Paul Lorrain3—has resolv'd upon a very sudden Reformation in his tragical
Dramas; and that at the next monthly Performance, he designs, instead
of a Penitential Psalm, to dismiss his Audience with an excellent new
Ballad of his own composing. Pray, Sir, do what you can to put a stop
to those growing Evils, and you will very much oblige
Your Humble Servant,
Physibulus.
Servetur ad imum
Qualis ab incepto processerit, et sibi constet.
Hor.
The Prologue was by Steele. Of the Epilogue Dr. Johnson
said (in his Lives of the Poets, when telling of Ambrose Philips),
'It was known in Tonson's family and told to Garrick, that Addison was
himself the author of it, and that when it had been at first printed
with his name, he came early in the morning, before the copies were
distributed, and ordered it to be given to Budgell, that it might add
weight to the solicitation which he was then making for a place.'
Johnson calls it
'the most successful Epilogue that was ever yet spoken on the English
theatre.'
The three first nights it was recited twice, and whenever afterwards the
play was acted the Epilogue was still expected and was spoken. This is a
fifth paper for the benefit of Ambrose Philips, inserted, perhaps, to
make occasion for a sixth (
) in the form of a reply to
Physibulus.
Paul Lorrain was the Ordinary of Newgate. He died in 1719. He
always represented his convicts as dying Penitents, wherefore in No. 63 of
the
Tatler
they had been called '
Paul Lorrain's Saints
.'
Contents
|
Saturday, March 29, 1712 |
Addison |
—Ut his exordia primis
Omnia, et ipse tener Mundi concreverit orbis.
Tum durare solum et discludere Nerea ponto
Coeperit, et rerum pauliatim sumere formas.
Virg.1
Longinus
has observed
, that there may be a Loftiness in Sentiments,
where there is no Passion, and brings Instances out of ancient Authors
to support this his Opinion. The Pathetick, as that great Critick
observes, may animate and inflame the Sublime, but is not essential to
it. Accordingly, as he further remarks, we very often find that those
who excel most in stirring up the Passions, very often want the Talent
of writing in the great and sublime manner, and so on the contrary.
Milton
has shewn himself a Master in both these ways of Writing. The
Seventh Book, which we are now entring upon, is an Instance of that
Sublime which is not mixed and worked up with Passion. The Author
appears in a kind of composed and sedate Majesty; and tho' the
Sentiments do not give so great an Emotion as those in the former Book,
they abound with as magnificent Ideas. The Sixth Book, like a troubled
Ocean, represents Greatness in Confusion; the seventh Affects the
Imagination like the Ocean in a Calm, and fills the Mind of the Reader,
without producing in it any thing like Tumult or Agitation.
The
above mentioned, among the Rules which he lays down for
succeeding in the sublime way of writing, proposes to his Reader, that
he should imitate the most celebrated Authors who have gone before him,
and been engaged in Works of the same nature
; as in particular, that
if he writes on a poetical Subject, he should consider how
Homer
would
have spoken on such an Occasion. By this means one great Genius often
catches the Flame from another, and writes in his Spirit, without
copying servilely after him. There are a thousand shining Passages in
Virgil
, which have been lighted up by
Homer
.
Milton
, tho' his own natural Strength of Genius was capable of
furnishing out a perfect Work, has doubtless very much raised and
ennobled his Conceptions, by such an Imitation as that which
Longinus
has recommended.
In this Book, which gives us an Account of the six Days Works, the Poet
received but very few Assistances from Heathen Writers, who were
Strangers to the Wonders of Creation. But as there are many glorious
strokes of Poetry upon this Subject in Holy Writ, the Author has
numberless Allusions to them through the whole course of this Book. The
great Critick I
before mentioned, though an Heathen, has taken
notice of the sublime Manner in which the Lawgiver of the
Jews
has
describ'd the Creation in the first Chapter of
Genesis
; and there are
many other Passages in Scripture, which rise up to the same Majesty,
where this Subject is touched upon.
Milton
has shewn his Judgment very
remarkably, in making use of such of these as were proper for his Poem,
and in duly qualifying those high Strains of Eastern Poetry, which were
suited to Readers whose Imaginations were set to an higher pitch than
those of colder Climates.
Adam's
Speech to the Angel, wherein he desires an Account of what had
passed within the Regions of Nature before the Creation, is very great
and solemn. The following Lines, in which he tells him, that the Day is
not too far spent for him to enter upon such a subject, are exquisite in
their kind.
And the great Light of Day yet wants to run
Much of his Race, though steep, suspense in Heav'n
Held by thy Voice; thy potent Voice he hears,
And longer will delay, to hear thee tell
His Generation, &c.
The Angel's encouraging our first Parent
s
in a modest pursuit after
Knowledge, with the Causes which he assigns for the Creation of the
World, are very just and beautiful. The
Messiah
, by whom, as we are told
in Scripture, the Worlds were made,
forth in the Power of his
Father, surrounded with an Host of Angels, and cloathed with such a
Majesty as becomes his entring upon a Work, which, according to our
Conceptions,
appears
the utmost Exertion of Omnipotence. What a
beautiful Description has our Author raised upon that Hint in one of the
Prophets.
behold there came four Chariots out from between two
Mountains, and the Mountains were Mountains of Brass
.
About his Chariot numberless were pour'd
Cherub and Seraph, Potentates and Thrones,
And Virtues, winged Spirits, and Chariots wing'd,
From th' Armoury of Gold, where stand of old
Myriads between two brazen Mountains lodg'd
Against a solemn Day, harness'd at hand;
Celestial Equipage! and now came forth
Spontaneous, for within them Spirit liv'd,
Attendant on their Lord: Heav'n open'd wide
Her ever-during Gates, Harmonious Sound!
On golden Hinges moving—
I have before taken notice of these Chariots of God, and of these Gates
of Heaven; and shall here only add, that
Homer
gives us the same Idea of
the latter, as opening of themselves; tho' he afterwards takes off from
it, by telling us, that the Hours first of all removed those prodigious
Heaps of Clouds which lay as a Barrier before them.
I do not know any thing in the whole Poem more sublime than the
Description which follows, where the
Messiah
is represented at the head
of his Angels, as looking down into the Chaos, calming its Confusion,
riding into the midst of it, and drawing the first Out-Line of the
Creation.
On Heavenly Ground they stood, and from the Shore
They view'd the vast immeasurable Abyss,
Outrageous as a Sea, dark, wasteful, wild;
Up from the bottom turned by furious Winds
And surging Waves, as Mountains to assault
Heaven's height, and with the Center mix the Pole.
Silence, ye troubled Waves, and thou Deep, Peace!
Said then th' Omnific Word, your Discord end:
Nor staid; but, on the Wings of Cherubim
Up-lifted, in Paternal Glory rode
Far into Chaos, and the World unborn;
For Chaos heard his Voice. Him all His Train
Follow'd in bright Procession, to behold
Creation, and the Wonders, of his Might.
Then staid the fervid Wheels, and in his Hand
He took the Golden Compasses, prepar'd
In God's eternal Store, to circumscribe
This Universe, and all created Things:
One Foot he center'd, and the other turn'd
Round, through the vast Profundity obscure;
And said, Thus far extend, thus far thy bounds,
This be thy just Circumference, O World!
The Thought of the Golden Compasses is conceived altogether in
Homer's
Spirit, and is a very noble Incident in this wonderful Description.
Homer
, when he speaks of the Gods, ascribes to them several Arms and
Instruments with the same greatness of Imagination. Let the Reader only
peruse the Description of
Minerva's
Ægis, or Buckler, in the Fifth Book,
with her Spear, which would overturn whole Squadrons, and her Helmet,
that was sufficient to cover an Army drawn out of an hundred Cities: The
Golden Compasses in the above-mentioned Passage appear a very natural
Instrument in the Hand of him, whom
Plato
somewhere calls the Divine
Geometrician. As Poetry delights in cloathing abstracted Ideas in
Allegories and sensible Images, we find a magnificent Description of the
Creation form'd after the same manner in one of the Prophets, wherein he
describes the Almighty Architect as measuring the Waters in the Hollow
of his Hand, meting out the Heavens with his Span, comprehending the
Dust of the Earth in a Measure, weighing the Mountains in Scales, and
the Hills in a Balance. Another of them describing the Supreme Being in
this great Work of Creation, represents him as laying the Foundations of
the Earth, and stretching a Line upon it: And in another place as
garnishing the Heavens, stretching out the North over the empty Place,
and hanging the Earth upon nothing. This last noble Thought
Milton
has
express'd in the following Verse:
And Earth self-ballanc'd on her Center hung.
The Beauties of Description in this Book lie so very thick, that it is
impossible to enumerate them in this Paper. The Poet has employ'd on
them the whole Energy of our Tongue. The several great Scenes of the
Creation rise up to view one after another, in such a manner, that the
Reader seems present at this wonderful Work, and to assist among the
Choirs of Angels, who are the Spectators of it. How glorious is the
Conclusion of the first Day.
—Thus was the first Day Ev'n and Morn
Nor past uncelebrated nor unsung
By the Celestial Quires, when Orient Light
Exhaling first from Darkness they beheld;
Birth-day of Heav'n and Earth! with Joy and Shout
The hollow universal Orb they fill'd.
We have the same elevation of Thought in the third Day, when the
Mountains were brought forth, and the Deep was made.
Immediately the Mountains huge appear
Emergent, and their broad bare Backs up-heave
Into the Clouds, their Tops ascend the Sky:
So high as heav'd the tumid Hills, so low
Down sunk a hollow Bottom, broad and deep,
Capacious Bed of Waters—
We have also the rising of the whole vegetable World described in this
Day's Work, which is filled with all the Graces that other Poets have
lavish'd on their Descriptions of the Spring, and leads the Reader's
Imagination into a Theatre equally surprising and beautiful.
The several Glories of the Heav'ns make their Appearance on the Fourth
Day.
First in his East the glorious Lamp was seen,
Regent of Day; and all th' Horizon round
Invested with bright Rays, jocund to round
His Longitude through Heav'ns high Road: the gray
Dawn, and the Pleiades before him danced,
Shedding sweet Influence. Less bright the Moon,
But opposite in level'd West was set,
His Mirror, with full face borrowing her Light
From him, for other Lights she needed none
In that aspect, and still that distance keeps
Till Night; then in the East her turn she shines,
Revolv'd on Heav'n's great Axle, and her Reign
With thousand lesser Lights dividual holds,
With thousand thousand Stars! that then appear'd
Spangling the Hemisphere—
One would wonder how the Poet could be so concise in his Description of
the six Days Works, as to comprehend them within the bounds of an
Episode, and at the same time so particular, as to give us a lively Idea
of them. This is still more remarkable in his Account of the Fifth and
Sixth Days, in which he has drawn out to our View the whole Animal
Creation, from the Reptil to the Behemoth.
the Lion and the Leviathan
are two of the noblest Productions in
the
World of living
Creatures, the Reader will find a most exquisite Spirit of Poetry in the
Account which our Author gives us of them. The Sixth Day concludes with
the Formation of Man, upon which the Angel takes occasion, as he did
after the Battel in Heaven, to remind
Adam
of his Obedience, which was
the principal Design of this his Visit.
The Poet afterwards represents the
Messiah
returning into Heaven, and
taking a Survey of his great Work. There is something inexpressibly
Sublime in this part of the Poem, where the Author describes that great
Period of Time, filled with so many Glorious Circumstances; when the
Heavens and Earth were finished; when the
Messiah
ascended up in triumph
thro' the Everlasting Gates; when he looked down with pleasure upon his
new Creation; when every Part of Nature seem'd to rejoice in its
Existence; when the Morning-Stars sang together, and all the Sons of God
shouted for joy.
So Ev'n and Morn accomplished the sixth Day:
Yet not 'till the Creator from his Work
Desisting, tho' unwearied, up return'd,
Up to the Heav'n of Heav'ns, his high Abode;
Thence to behold this new created World,
Th' Addition of his Empire, how it shewed
In prospect from his Throne, how good, how fair,
Answering his great Idea: Up he rode,
Follow'd with Acclamation, and the Sound
Symphonious of ten thousand Harps, that tuned
Angelick Harmonies; the Earth, the Air
Resounding (thou remember'st, for thou heard'sf)
The Heavens and all the Constellations rung;
The Planets in their Station listning stood,
While the bright Pomp ascended jubilant.
Open, ye everlasting Gates, they sung,
Open, ye Heavens, your living Doors; let in
The great Creator from his Work return'd
Magnificent, his six Days Work, a World!
I
conclude this Book upon the Creation, without mentioning a Poem
which has lately appeared under that Title
. The Work was undertaken
with so good an Intention, and is executed with so great a Mastery, that
it deserves to be looked upon as one of the most useful and noble
Productions in our English Verse. The Reader cannot but be pleased to
find the Depths of Philosophy enlivened with all the Charms of Poetry,
and to see so great a Strength of Reason, amidst so beautiful a
Redundancy of the Imagination. The Author has shewn us that Design in
all the Works of Nature, which necessarily leads us to the Knowledge of
its first Cause. In short, he has illustrated, by numberless and
incontestable Instances, that Divine Wisdom, which the Son of
Sirach
has
so nobly ascribed to the Supreme Being in his Formation of the World,
when he tells us, that He created her, and saw her, and numbered her,
and poured her out upon all his Works.
L.
Ovid
On the Sublime
, § 8.
§14.
Longinus, § 9:
"So likewise the Jewish legislator, no ordinary person, having
conceived a just idea of the power of God, has nobly expressed it in
the beginning of his law. 'And God said,'—What? 'Let there be Light,
and there was Light. Let the Earth be, and the Earth was.'"
looks like
Zechariah
vi. i.
this
Sir Richard Blackmore's
Creation
appeared in 1712. Besides
this praise of it from Addison, its religious character caused Dr.
Johnson to say that if Blackmore
'
had written nothing else it would have transmitted him to posterity
among the first favourites of the English muse.'
But even with the help of all his epics it has failed to secure him any
such place in the estimation of posterity. This work is not an epic, but
described on its title page as 'a Philosophical Poem, Demonstrating the
Existence and Providence of a God.' It argues in blank verse, in the
first two of its seven books, the existence of a Deity from evidences of
design in the structure and qualities of earth and sea, in the celestial
bodies and the air; in the next three books it argues against objections
raised by Atheists, Atomists, and Fatalists; in the sixth book proceeds
with evidences of design, taking the structure of man's body for its
theme; and in the next, which is the last book, treats in the same way
of the Instincts of Animals and of the Faculties and Operations of the
Soul. This is the manner of the Poem:
The Sea does next demand our View; and there
No less the Marks of perfect skill appear.
When first the Atoms to the Congress came,
And by their Concourse form'd the mighty Frame,
What did the Liquid to th' Assembly call
To give their Aid to form the ponderous Ball?
First, tell us, why did any come? next, why
In such a disproportion to the Dry!
Why were the Moist in Number so outdone,
That to a Thousand Dry, they are but one,
It is hardly a 'mark of perfect skill' that there are five or six
thousand of such dry lines in Blackmore's poem, and not even one that
should lead a critic to speak in the same breath of Blackmore and
Milton.
Contents
|
Monday, March 31, 1712 |
Steele |
Quis novus hic nostris successit sedibus Hospes?
Quem sese Ore ferens! quam forti Pectore et Armis!
Virg.

I take it to be the highest Instance of a noble Mind, to bear great
Qualities without discovering in a Man's Behaviour any Consciousness
that he is superior to the rest of the World. Or, to say it otherwise,
it is the Duty of a great Person so to demean himself, as that whatever
Endowments he may have, he may appear to value himself upon no Qualities
but such as any Man may arrive at: He ought to think no Man valuable but
for his publick Spirit, Justice and Integrity; and all other Endowments
to be esteemed only as they contribute to the exerting those Virtues.
Such a Man, if he is Wise or Valiant, knows it is of no Consideration to
other Men that he is so, but as he employs those high Talents for their
Use and Service. He who affects the Applauses and Addresses of a
Multitude, or assumes to himself a Pre-eminence upon any other
Consideration, must soon turn Admiration into Contempt. It is certain,
that there can be no Merit in any Man who is not conscious of it; but
the Sense that it is valuable only according to the Application of it,
makes that Superiority amiable, which would otherwise be invidious. In
this Light it is considered as a Thing in which every Man bears a Share:
It annexes the Ideas of Dignity, Power, and Fame, in an agreeable and
familiar manner, to him who is Possessor of it; and all Men who are
Strangers to him are naturally incited to indulge a Curiosity in
beholding the Person, Behaviour, Feature, and Shape of him, in whose
Character, perhaps, each Man had formed something in common with
himself.
such, or any other, are the Causes, all Men have
a
yearning
Curiosity to behold a Man of heroick Worth; and I
had
many Letters from all Parts of this Kingdom, that request I would give
them an exact Account of the Stature, the Mein, the Aspect of the Prince
who lately visited England, and has done such Wonders for the
Liberty of Europe. It would puzzle the most Curious to form to himself
the sort of Man my several Correspondents expect to hear of, by the
Action mentioned when they desire a Description of him: There is always
something that concerns themselves, and growing out of their own
Circumstances, in all their Enquiries. A Friend of mine in Wales
beseeches me to be very exact in my Account of that wonderful Man, who
had marched an Army and all its Baggage over the Alps; and, if possible,
to learn whether the Peasant who shew'd him the Way, and is drawn in the
Map, be yet living. A Gentleman from the University, who is deeply
intent on the Study of Humanity, desires me to be as particular, if I
had Opportunity, in observing the whole Interview between his Highness
and our late General. Thus do Men's Fancies work according to their
several Educations and Circumstances; but all pay a Respect, mixed with
Admiration, to this illustrious Character. I have waited for his Arrival
in Holland, before I would let my Correspondents know, that I have not
been so uncurious a Spectator, as not to have seen Prince Eugene. It
would be very difficult, as I said just now, to answer every Expectation
of those who have writ to me on that Head; nor is it possible for me to
find Words to let one know what an artful Glance there is in his
Countenance who surprized
Cremona
; how daring he appears who forced the
Trenches of
Turin
; But in general I can say, that he who beholds him,
will easily expect from him any thing that is to be imagined or executed
by the Wit or Force of Man. The Prince is of that Stature which makes a
Man most easily become all Parts of Exercise, has Height to be graceful
on Occasions of State and Ceremony, and no less adapted for Agility and
Dispatch: his Aspect is erect and compos'd; his Eye lively and
thoughtful, yet rather vigilant than sparkling; his Action and Address
the most easy imaginable, and his Behaviour in an Assembly peculiarly
graceful in a certain Art of mixing insensibly with the rest, and
becoming one of the Company, instead of receiving the Courtship of it.
The Shape of his Person, and Composure of his Limbs, are remarkably
exact and beautiful. There is in his Look something sublime, which does
not seem to arise from his Quality or Character, but the innate
Disposition of his Mind. It is apparent that he suffers the Presence of
much Company, instead of taking Delight in it; and he appeared in
Publick while with us, rather to return Good-will, or satisfy Curiosity,
than to gratify any Taste he himself had of being popular. As his
Thoughts are never tumultuous in Danger, they are as little discomposed
on Occasions of Pomp and Magnificence: A great Soul is affected in
either Case, no further than in considering the properest Methods to
extricate it self from them. If this Hero has the strong Incentives to
uncommon Enterprizes that were remarkable in
Alexander
, he prosecutes
and enjoys the Fame of them with the Justness, Propriety, and good Sense
of
Cæsar
. It is easy to observe in him a Mind as capable of being
entertained with Contemplation as Enterprize; a Mind ready for great
Exploits, but not impatient for Occasions to exert itself. The Prince
has Wisdom and Valour in as high Perfection as Man can enjoy it; which
noble Faculties in conjunction, banish all Vain-Glory, Ostentation,
Ambition, and all other Vices which might intrude upon his Mind to make
it unequal. These Habits and Qualities of Soul and Body render this
Personage so extraordinary, that he appears to have nothing in him but
what every Man should have in him, the Exertion of his very self,
abstracted from the Circumstances in which Fortune has placed him. Thus
were you to see Prince
Eugene
, and were told he was a private Gentleman,
you would say he is a Man of Modesty and Merit: Should you be told That
was Prince
Eugene
, he would be diminished no otherwise, than that part
of your distant Admiration would turn into familiar Good-will.
I
thought fit to entertain my Reader with, concerning an Hero who never
was equalled but by one Man
; over whom also he has this Advantage,
that he has had an Opportunity to manifest an Esteem for him in his
Adversity.
T.
an earning
Prince Eugene of Savoy, grandson of a duke of Savoy, and
son of Eugene Maurice, general of the Swiss, and Olympia Mancini, a
niece of Mazarin, was born at Paris in 1663, and intended for the
church, but had so strong a bent towards a military life, that when
refused a regiment in the French army he served the Emperor as volunteer
against the Turks. He stopped the march of the French into Italy when
Louis XIV. declared war with Austria, and refused afterwards from Louis
a Marshal's staff, a pension, and the Government of Champagne.
Afterwards in Italy, by the surprise of Cremona he made Marshal Villeroi
his prisoner, and he was Marlborough's companion in arms at Blenheim and
in other victories. It was he who saved Turin, and expelled the French
from Italy. He was 49 years old in 1712, and had come in that year to
England to induce the court to continue the war, but found Marlborough
in disgrace and the war very unpopular. He had been feasted by the city,
and received from Queen Anne a sword worth £5000, which he wore at her
birthday reception. He had also stood as godfather to Steele's third
son, who was named after him.
Marlborough.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 1, 1712 |
Budgell1 |
—Revocate animos mœstumque timorem Mittite—
Virg.

Having, to oblige my Correspondent
Physibulus
, printed his Letter last
Friday, in relation to the new Epilogue, he cannot take it amiss, if I
now publish another, which I have just received from a Gentleman who
does not agree with him in his Sentiments upon that Matter.
Sir,
I am amazed to find an Epilogue attacked in your last Friday's Paper,
which has been so generally applauded by the Town, and receiv'd such
Honours as were never before given to any in an English Theatre.
The Audience would not permit Mrs.
Oldfield to go off the Stage the
first Night, till she had repeated it twice; the second Night the
Noise of
Ancoras was as loud as before, and she was again obliged to
speak it twice: the third Night it was still called for a second time;
and, in short, contrary to all other Epilogues, which are dropt after
the third Representation of the Play, this has already been repeated
nine times.
I must own I am the more surprized to find this Censure in Opposition
to the whole Town, in a Paper which has hitherto been famous for the
Candour of its Criticisms.
I can by no means allow your melancholy Correspondent, that the new
Epilogue is unnatural because it is gay. If I had a mind to be
learned, I could tell him that the Prologue and Epilogue were real
Parts of the ancient Tragedy; but every one knows that on the
British
Stage they are distinct Performances by themselves, Pieces entirely
detached from the Play, and no way essential to it.
The moment the Play ends, Mrs.
Oldfield is no more
Andromache, but
Mrs.
Oldfield; and tho' the Poet had left
Andromache stone-dead upon
the Stage, as your ingenious Correspondent phrases it, Mrs.
Oldfield
might still have spoke a merry Epilogue.
We have an Instance of this
in a Tragedy
2 where there is not only a Death but a Martyrdom. St.
Catherine was there personated by
Nell Gwin; she lies stone dead upon
the Stage, but upon those Gentlemen's offering to remove her Body,
whose Business it is to carry off the Slain in our English Tragedies,
she breaks out into that abrupt Beginning of what was a very
ludicrous, but at the same time thought a very good Epilogue.
Hold, are you mad? you damn'd confounded Dog,
I am to rise and speak the Epilogue.
This diverting Manner was always practised by Mr.
Dryden, who if he
was not the best Writer of Tragedies in his time, was allowed by every
one to have the happiest Turn for a Prologue or an Epilogue. The
Epilogues to
Cleomenes, Don Sebastian, The Duke of Guise, Aurengzebe,
and
Love Triumphant, are all Precedents of this Nature.
I might further justify this Practice by that excellent Epilogue which
was spoken a few Years since, after the Tragedy of
Phædra and
Hippolitus; with a great many others, in which the Authors have
endeavour'd to make the Audience merry. If they have not all succeeded
so well as the Writer of this, they have however shewn that it was not
for want of Good-will.
I must further observe, that the Gaiety of it may be still the more
proper, as it is at the end of a
French Play; since every one knows
that Nation, who are generally esteem'd to have as polite a Taste as
any in Europe, always close their Tragick Entertainments with what
they call a
Petite Piece, which is purposely design'd to raise Mirth,
and send away the Audience well pleased. The same Person who has
supported the chief Character in the Tragedy, very often plays the
principal Part in the
Petite Piece; so that I have my self seen at
Paris, Orestes and
Lubin acted the same Night by the same Man.
Tragi-Comedy, indeed, you have your self in a former Speculation found
fault with very justly, because it breaks the Tide of the Passions
while they are yet flowing; but this is nothing at all to the present
Case, where they have already had their full Course.
As the new Epilogue is written conformable to the Practice of our best
Poets, so it is not such an one which, as the Duke of
Buckingham says
in his Rehearsal, might serve for any other Play; but wholly rises out
of the Occurrences of the Piece it was composed for.
The only Reason your mournful Correspondent gives against this
Facetious Epilogue, as he calls it, is, that he has mind to go home
melancholy. I wish the Gentleman may not be more Grave than Wise. For
my own part, I must confess I think it very sufficient to have the
Anguish of a fictitious Piece remain upon me while it is representing,
but I love to be sent home to bed in a good humour. If
Physibulus is
however resolv'd to be inconsolable, and not to have his Tears dried
up, he need only continue his old Custom, and when he has had his half
Crown's worth of Sorrow, slink out before the Epilogue begins.
It is pleasant enough to hear this Tragical Genius complaining of the
great Mischief
Andromache had done him: What was that? Why, she made
him laugh. The poor Gentleman's Sufferings put me in mind of Harlequin's
Case, who was tickled to Death. He tells us soon after, thro' a small
Mistake of Sorrow for Rage, that during the whole Action he was so
very sorry, that he thinks he could have attack'd half a score of the
fiercest Mohocks in the Excess of his Grief. I cannot but look upon it
as an happy Accident, that a Man who is so bloody-minded in his
Affliction, was diverted from this Fit of outragious Melancholy. The
Valour of this Gentleman in his Distress, brings to one's memory the
Knight of the sorrowful Countenance, who lays about him at such an
unmerciful rate in an old Romance. I shall readily grant him that his
Soul, as he himself says, would have made a very ridiculous Figure,
had it quitted the Body, and descended to the Poetical Shades, in such
an Encounter.
As to his Conceit of tacking a Tragic Head with a Comic Tail, in order
to refresh the Audience, it is such a piece of Jargon, that I dont
know what to make of it.
The elegant Writer makes a very sudden Transition from the Play-house
to the Church, and from thence, to the Gallows.
As for what relates to the Church, he is of Opinion, that these
Epilogues have given occasion to those merry Jiggs from the Organ-Loft
which have dissipated those good Thoughts, and Dispositions he has
found in himself, and the rest of the Pew, upon the singing of two
Staves culld out by the judicious and diligent Clark.
He fetches his next Thought from
Tyburn; and seems very apprehensive
lest there should happen any Innovations in the Tragedies of his
Friend
Paul Lorrain.
In the mean time, Sir, this gloomy Writer, who is so mightily
scandaliz'd at a gay Epilogue after a serious Play, speaking of the
Fate of those unhappy Wretches who are condemned to suffer an
ignominious Death by the Justice of our Laws, endeavours to make the
Reader merry on so improper an occasion, by those poor Burlesque
Expressions of Tragical Dramas, and Monthly Performances.
I am, Sir, with great Respect,
Your most obedient, most humble Servant,
Philomeides.
X.
Budgell here defends with bad temper the Epilogue which
Addison ascribed to him. Probably it was of his writing, but transformed
by Addison's corrections.
Dryden's
Maximin
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 2, 1712 |
Steele |
Justitiæ partes sunt non violare homines: Verecundiæ non offendere.
Tull.

As Regard to Decency is a great Rule of Life in general, but more
especially to be consulted by the Female World, I cannot overlook the
following Letter which describes an egregious Offender.
'Mr. Spectator,
'I was this Day looking over your Papers, and reading in that of
December the 6th with great delight, the amiable Grief of Asteria for
the Absence of her Husband, it threw me into a great deal of
Reflection. I cannot say but this arose very much from the
Circumstances of my own Life, who am a Soldier, and expect every Day
to receive Orders; which will oblige me to leave behind me a Wife that
is very dear to me, and that very deservedly. She is, at present, I am
sure, no way below your Asteria for Conjugal Affection: But I see the
Behaviour of some Women so little suited to the Circumstances wherein
my Wife and I shall soon be, that it is with a Reluctance I never knew
before, I am going to my Duty. What puts me to present Pain, is the
Example of a young Lady, whose Story you shall have as well as I can
give it you. Hortensius, an Officer of good Rank in her Majesty's
Service, happen'd in a certain Part of England to be brought to a
Country-Gentleman's House, where he was receiv'd with that more than
ordinary Welcome, with which Men of domestick Lives entertain such few
Soldiers whom a military Life, from the variety of Adventures, has not
render'd over-bearing, but humane, easy, and agreeable: Hortensius
stay'd here some time, and had easy Access at all hours, as well as
unavoidable Conversation at some parts of the Day with the beautiful
Sylvana, the Gentleman's Daughter. People who live in Cities are
wonderfully struck with every little Country Abode they see when they
take the Air; and 'tis natural to fancy they could live in every neat
Cottage (by which they pass) much happier than in their present
Circumstances. The turbulent way of Life which Hortensius was used to,
made him reflect with much Satisfaction on all the Advantages of a
sweet Retreat one day; and among the rest, you'll think it not
improbable, it might enter into his Thought, that such a Woman as
Sylvana would consummate the Happiness. The World is so debauched with
mean Considerations, that Hortensius knew it would be receiv'd as an
Act of Generosity, if he asked for a Woman of the Highest Merit,
without further Questions, of a Parent who had nothing to add to her
personal Qualifications. The Wedding was celebrated at her Father's
House: When that was over, the generous Husband did not proportion his
Provision for her to the Circumstances of her Fortune, but considered
his Wife as his Darling, his Pride, and his Vanity, or rather that it
was in the Woman he had chosen that a Man of Sense could shew Pride or
Vanity with an Excuse, and therefore adorned her with rich Habits and
valuable Jewels. He did not however omit to admonish her that he did
his very utmost in this; that it was an Ostentation he could not but
be guilty of to a Woman he had so much Pleasure in, desiring her to
consider it as such; and begged of her also to take these Matters
rightly, and believe the Gems, the Gowns, the Laces would still become
her better, if her Air and Behaviour was such, that it might appear
she dressed thus rather in Compliance to his Humour that Way, than out
of any Value she her self had for the Trifles. To this Lesson, too
hard for Woman, Hortensius added, that she must be sure to stay with
her Friends in the Country till his Return. As soon as Hortensius
departed, Sylvana saw in her Looking-glass that the Love he conceiv'd
for her was wholly owing to the Accident of seeing her: and she is
convinced it was only her Misfortune the rest of Mankind had not
beheld her, or Men of much greater Quality and Merit had contended for
one so genteel, tho' bred in Obscurity; so very witty, tho' never
acquainted with Court or Town. She therefore resolved not to hide so
much Excellence from the World, but without any Regard to the Absence
of the most generous Man alive, she is now the gayest Lady about this
Town, and has shut out the Thoughts of her Husband by a constant
Retinue of the vainest young Fellows this Age has produced: to
entertain whom, she squanders away all Hortensius is able to supply
her with, tho' that Supply is purchased with no less Difficulty than
the Hazard of his Life.
'Now, Mr. Spectator, would it not be a Work becoming your Office to
treat this Criminal as she deserves? You should give it the severest
Reflections you can: You should tell Women, that they are more
accountable for Behaviour in Absence than after Death. The Dead are
not dishonour'd by their Levities; the Living may return, and be
laugh'd at by empty Fops, who will not fail to turn into Ridicule the
good Man who is so unseasonable as to be still alive, and come and
spoil good Company.
I am, Sir,
your most Obedient Humble Servant.
All Strictness of Behaviour is so unmercifully laugh'd at in our Age,
that the other much worse Extreme is the more common Folly. But let any
Woman consider which of the two Offences an Husband would the more
easily forgive, that of being less entertaining than she could to please
Company, or raising the Desires of the whole Room to his disadvantage;
and she will easily be able to form her Conduct. We have indeed carry'd
Womens Characters too much into publick Life, and you shall see them
now-a-days affect a sort of Fame: but I cannot help venturing to
disoblige them for their Service, by telling them, that the utmost of a
Woman's Character is contained in Domestick Life; she is blameable or
praiseworthy according as her Carriage affects the House of her Father
or her Husband. All she has to do in this World, is contain'd within the
Duties of a Daughter, a Sister, a Wife, and a Mother: All these may be
well performed, tho' a Lady should not be the very finest Woman at an
Opera or an Assembly. They are likewise consistent with a moderate share
of Wit, a plain Dress, and a modest Air. But when the very Brains of the
Sex are turned, and they place their Ambition on Circumstances, wherein
to excel is no addition to what is truly commendable, where can this
end, but, as it frequently does, in their placing all their Industry,
Pleasure and Ambition on things, which will naturally make the
Gratifications of Life last, at best, no longer than Youth and good
Fortune? And when we consider the least ill Consequence, it can be no
less than looking on their own Condition as Years advance, with a
disrelish of Life, and falling into Contempt of their own Persons, or
being the Derision of others. But when they consider themselves as they
ought, no other than an additional Part of the Species, (for their own
Happiness and Comfort, as well as that of those for whom they were born)
their Ambition to excell will be directed accordingly; and they will in
no part of their Lives want Opportunities of being shining Ornaments to
their Fathers, Husbands, Brothers, or Children.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 3, 1712 |
Addison |
—Errat et illinc
Huc venit, hinc illuc, et quoslibet occupat artus
Spiritus: éque feris humana in corpora transit,
Inque feras noster—
Pythag. ap. Ov.

Will. Honeycomb
, who loves to shew upon occasion all the little Learning
he has picked up, told us yesterday at the Club, that he thought there
might be a great deal said for the Transmigration of Souls, and that the
Eastern Parts of the World believed in that Doctrine to this day.
Paul Rycaut
, says he, gives us an Account of several well-disposed
Mahometans
that purchase the Freedom of any little Bird they see
confined to a Cage, and think they merit as much by it, as we should do
here by ransoming any of our Countrymen from their Captivity at
Algiers
.
You must know, says
Will
., the Reason is, because they consider every
Animal as a Brother or Sister in disguise, and therefore think
themselves obliged to extend their Charity to them, tho' under such mean
Circumstances. They'll tell you, says
Will
., that the Soul of a Man,
when he dies, immediately passes into the Body of another Man, or of
some Brute, which he resembled in his Humour, or his Fortune, when he
was one of us.
As I was wondring what this profusion of Learning would end in,
Will
.
us that
Jack Freelove
, who was a Fellow of Whim, made Love to one
of those Ladies who throw away all their Fondness
on
Parrots,
Monkeys, and Lap-dogs. Upon going to pay her a Visit one Morning, he
writ a very pretty Epistle upon this Hint. Jack, says he, was conducted
into the Parlour, where he diverted himself for some time with her
favourite Monkey, which was chained in one of the Windows; till at
length observing a Pen and Ink lie by him, he writ the following Letter
to his Mistress, in the Person of the Monkey; and upon her not coming
down so soon as he expected, left it in the Window, and went about his
Business.
The Lady soon after coming into the Parlour, and seeing her Monkey look
upon a Paper with great Earnestness, took it up, and to this day is in
some doubt, says
Will
., whether it was written by
Jack
or the Monkey.
Madam,
Not having the Gift of Speech, I have a long time waited in vain for
an Opportunity of making myself known to you; and having at present
the Conveniences of Pen, Ink, and Paper by me, I gladly take the
occasion of giving you my History in Writing, which I could not do by
word of Mouth. You must know, Madam, that about a thousand Years ago I
was an Indian Brachman, and versed in all those mysterious Secrets
which your European Philosopher, called Pythagoras, is said to have
learned from our Fraternity. I had so ingratiated my self by my great
Skill in the occult Sciences with a Daemon whom I used to converse
with, that he promised to grant me whatever I should ask of him. I
desired that my Soul might never pass into the Body of a brute
Creature; but this he told me was not in his Power to grant me. I then
begg'd that into whatever Creature I should chance to Transmigrate, I
might still retain my Memory, and be conscious that I was the same
Person who lived in different Animals. This he told me was within his
Power, and accordingly promised on the word of a Daemon that he would
grant me what I desired. From that time forth I lived so very
unblameably, that I was made President of a College of Brachmans, an
Office which I discharged with great Integrity till the day of my
Death. I was then shuffled into another Human Body, and acted my Part
so very well in it, that I became first Minister to a Prince who
reigned upon the Banks of the Ganges. I here lived in great Honour for
several Years, but by degrees lost all the Innocence of the Brachman,
being obliged to rifle and oppress the People to enrich my Sovereign;
till at length I became so odious that my Master, to recover his
Credit with his Subjects, shot me thro' the Heart with an Arrow, as I
was one day addressing my self to him at the Head of his Army.
Upon my next remove I found my self in the Woods, under the shape of a
Jack-call, and soon listed my self in the Service of a Lion. I used to
yelp near his Den about midnight, which was his time of rouzing and
seeking after his Prey. He always followed me in the Rear, and when I
had run down a fat Buck, a wild Goat, or an Hare, after he had feasted
very plentifully upon it himself, would now and then throw me a Bone
that was but half picked for my Encouragement; but upon my Being
unsuccessful in two or three Chaces, he gave me such a confounded
Gripe in his Anger, that I died of it.
In my next Transmigration I was again set upon two Legs, and became an
Indian Tax-gatherer; but having been guilty of great Extravagances,
and being marry'd to an expensive Jade of a Wife, I ran so cursedly in
debt, that I durst not shew my Head. I could no sooner step out of my
House, but I was arrested by some body or other that lay in wait for
me. As I ventur'd abroad one Night in the Dusk of the Evening, I was
taken up and hurry'd into a Dungeon, where I died a few Months after.
My Soul then enter'd into a Flying-Fish, and in that State led a most
melancholy Life for the space of six Years. Several Fishes of Prey
pursued me when I was in the Water, and if I betook my self to my
Wings, it was ten to one but I had a flock of Birds aiming at me. As I
was one day flying amidst a fleet of English Ships, I observed a huge
Sea-Gull whetting his Bill and hovering just over my Head: Upon my
dipping into the Water to avoid him, I fell into the Mouth of a
monstrous Shark that swallow'd me down in an instant.
I was some Years afterwards, to my great surprize, an eminent Banker
in Lombard-street; and remembring how I had formerly suffered for want
of Money, became so very sordid and avaritious, that the whole Town
cried shame of me. I was a miserable little old Fellow to look upon,
for I had in a manner starved my self, and was nothing but Skin and
Bone when I died.
I was afterwards very much troubled and amazed to find my self
dwindled into an Emmet. I was heartily concerned to make so
insignificant a Figure, and did not know but some time or other I
might be reduced to a Mite if I did not mend my Manners. I therefore
applied my self with great diligence to the Offices that were allotted
me, and was generally look'd upon as the notablest Ant in the whole
Molehill. I was at last picked up, as I was groaning under a Burden,
by an unlucky Cock-Sparrow that lived in the Neighbourhood, and had
before made great depredations upon our Commonwealth.
I then better'd my Condition a little, and lived a whole Summer in the
Shape of a Bee; but being tired with the painful and penurious Life I
had undergone in my two last Transmigrations, I fell into the other
Extream, and turned Drone. As I one day headed a Party to plunder an
Hive, we were received so warmly by the Swarm which defended it, that
we were most of us left dead upon the Spot.
I might tell you of many other Transmigrations which I went thro': how
I was a Town-Rake, and afterwards did Penance in a Bay Gelding for ten
Years; as also how I was a Taylor, a Shrimp, and a Tom-tit. In the
last of these my Shapes I was shot in the Christmas Holidays by a
young Jack-a-napes, who would needs try his new Gun upon me.
But I shall pass over these and other several Stages of Life, to
remind you of the young Beau who made love to you about Six Years
since. You may remember, Madam, how he masked, and danced, and sung,
and play'd a thousand Tricks to gain you; and how he was at last
carry'd off by a Cold that he got under your Window one Night in a
Serenade. I was that unfortunate young Fellow, whom you were then so
cruel to. Not long after my shifting that unlucky Body, I found myself
upon a Hill in Æthiopia, where I lived in my present Grotesque Shape,
till I was caught by a Servant of the English Factory, and sent over
into Great Britain: I need not inform you how I came into your Hands.
You see, Madam, this is not the first time that you have had me in a
Chain: I am, however, very happy in this my Captivity, as you often
bestow on me those Kisses and Caresses which I would have given the
World for, when I was a Man. I hope this Discovery of my Person will
not tend to my Disadvantage, but that you will still continue your
accustomed Favours to
Your most Devoted
Humble Servant,
Pugg.
P. S. I would advise your little Shock-dog to keep out of my way; for
as I look upon him to be the most formidable of my Rivals, I may
chance one time or other to give him such a Snap as he won't like.
L.
Sir Paul Rycaut, the son of a London merchant, after an
education at Trinity College, Cambridge, went in 1661 to Constantinople
as Secretary to the Embassy. He published in 1668 his
Present State of
the Ottoman Empire
, in three Books, and in 1670 the work here quoted,
A Particular Description of the Mahometan Religion, the Seraglio, the
Maritime and Land Forces of Turkey
, abridged in 1701 in Savage's
History of the Turks
, and translated into French by Bespier in 1707.
Consul afterwards at Smyrna, he wrote by command of Charles II. a book
on
The Present State of the Greek and American Churches
, published
1679. After his return from the East he was made Privy Councillor and
Judge of the High Court of Admiralty. He was knighted by James II., and
one of the first Fellows of the Royal Society. He published between 1687
and 1700, the year of his death, Knolles's
History of the Turks
, with a
continuation of his own, and also translated Platina's
Lives of the
Popes
and Garcilaso de la Vega's
History of Peru
.
upon
Contents
|
Friday, April 4, 1712 |
Steele |
In solo vivendi causa palato est.
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator,
I think it has not yet fallen into your Way to discourse on little
Ambition, or the many whimsical Ways Men fall into, to distinguish
themselves among their Acquaintance: Such Observations, well pursued,
would make a pretty History of low Life. I my self am got into a great
Reputation, which arose (as most extraordinary Occurrences in a Man's
Life seem to do) from a mere Accident. I was some Days ago
unfortunately engaged among a Set of Gentlemen, who esteem a Man
according to the Quantity of Food he throws down at a Meal. Now I, who
am ever for distinguishing my self according to the Notions of
Superiority which the rest of the Company entertain, ate so
immoderately for their Applause, as had like to have cost me my Life.
What added to my Misfortune was, that having naturally a good Stomach,
and having lived soberly for some time, my Body was as well prepared
for this Contention as if it had been by Appointment. I had quickly
vanquished every Glutton in Company but one, who was such a Prodigy in
his Way, and withal so very merry during the whole Entertainment, that
he insensibly betrayed me to continue his Competitor, which in a
little time concluded in a compleat Victory over my Rival; after
which, by Way of Insult, I ate a considerable Proportion beyond what
the Spectators thought me obliged in Honour to do. The Effect however
of this Engagement, has made me resolve never to eat more for Renown;
and I have, pursuant to this Resolution, compounded three Wagers I had
depending on the Strength of my Stomach; which happened very luckily,
because it was stipulated in our Articles either to play or pay. How a
Man of common Sense could be thus engaged, is hard to determine; but
the Occasion of this, is to desire you to inform several Gluttons of
my Acquaintance, who look on me with Envy, that they had best moderate
their Ambition in time, lest Infamy or Death attend their Success. I
forgot to tell you, Sir, with what unspeakable Pleasure I received the
Acclamations and Applause of the whole Board, when I had almost eat my
Antagonist into Convulsions: It was then that I returned his Mirth
upon him with such success as he was hardly able to swallow, though
prompted by a Desire of Fame, and a passionate Fondness for
Distinction: I had not endeavoured to excel so far, had not the
Company been so loud in their Approbation of my Victory. I don't
question but the same Thirst after Glory has often caused a Man to
drink Quarts without taking Breath, and prompted Men to many other
difficult Enterprizes; which if otherwise pursued, might turn very
much to a Man's Advantage. This Ambition of mine was indeed
extravagantly pursued; however I can't help observing, that you hardly
ever see a Man commended for a good Stomach, but he immediately falls
to eating more (tho' he had before dined) as well to confirm the
Person that commended him in his good Opinion of him, as to convince
any other at the Table, who may have been unattentive enough not to
have done Justice to his Character.
I am, Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Epicure Mammon.
Mr.
Spectator,
I
have writ to you three or four times, to desire you would take
notice of an impertinent Custom the Women, the fine Women, have lately
fallen into, of taking Snuff
1. This silly Trick is attended with
such a Coquet Air in some Ladies, and such a sedate masculine one in
others, that I cannot tell which most to complain of; but they are to
me equally disagreeable. Mrs.
Saunter is so impatient of being without
it, that she takes it as often as she does Salt at Meals; and as she
affects a wonderful Ease and Negligence in all her manner, an upper
Lip mixed with Snuff and the Sauce, is what is presented to the
Observation of all who have the honour to eat with her. The pretty
Creature her Neice does all she can to be as disagreeable as her Aunt;
and if she is not as offensive to the Eye, she is quite as much to the
Ear, and makes up all she wants in a confident Air, by a nauseous
Rattle of the Nose, when the Snuff is delivered, and the Fingers make
the Stops and Closes on the Nostrils. This, perhaps, is not a very
courtly Image in speaking of Ladies; that is very true: but where
arises the Offence? Is it in those who commit, or those who observe
it? As for my part, I have been so extremely disgusted with this
filthy Physick hanging on the Lip, that the most agreeable
Conversation, or Person, has not been able to make up for it. As to
those who take it for no other end but to give themselves Occasion for
pretty Action, or to fill up little Intervals of Discourse, I can bear
with them; but then they must not use it when another is speaking, who
ought to be heard with too much respect, to admit of offering at that
time from Hand to Hand the Snuff-Box. But
Flavilla is so far taken
with her Behaviour in this kind, that she pulls out her Box (which is
indeed full of good Brazile) in the middle of the Sermon; and to shew
she has the Audacity of a well-bred Woman, she offers it the Men as
well as the Women who sit near her: But since by this Time all the
World knows she has a fine Hand, I am in hopes she may give her self
no further Trouble in this matter. On Sunday was sennight, when they
came about for the Offering, she gave her Charity with a very good
Air, but at the same Time asked the Churchwarden if he would take a
Pinch. Pray, Sir, think of these things in time, and you will oblige,
Sir,
Your most humble servant.
T.
Charles Lillie, the perfumer, from whose shop at the corner
of Beaufort Buildings the original Spectators were distributed, left
behind him a book of receipts and observations,
The British Perfumer,
Snuff Manufacturer, and Colourman's Guide
, of which the MS. was sold
with his business, but which remained unpublished until 1822. He opens
his Part III. on
Snuffs
with an account of the Origin of Snuff-taking
in England, the practice being one that had become fashionable in his
day, and only about eight years before the appearance of the Spectator.
It dates from Sir George Rooke's expedition against Cadiz in 1702.
Before that time snuff-taking in England was confined to a few luxurious
foreigners and English who had travelled abroad. They took their snuff
with pipes of the size of quills out of small spring boxes. The pipes
let out a very small quantity upon the back of the hand, and this was
snuffed up the nostrils with the intention of producing a sneeze which,
says Lillie, 'I need not say forms now no part of the design or rather
fashion of snuff-taking;' least of all in the ladies who took part in
this method of snuffing defiance at the public enemy. When the fleet,
after the failure of its enterprize against Cadiz, proceeded to cut off
the French ships in Vigobay, on the way it plundered Port St. Mary and
adjacent places, where, among other merchandize, seizure was made of
several thousand barrels and casks, each containing four tin canisters
of snuffs of the best growth and finest Spanish manufacture. At Vigo,
among the merchandize taken from the shipping there destroyed, were
'prodigious quantities of gross snuff, from the Havannah, in bales,
bags, and scrows' (untanned buffalo hides, used with the hairy-side
inwards, for making packages), 'which were designed for manufacture in
different parts of Spain.' Altogether fifty tons of snuff were brought
home as part of the prize of the officers and sailors of the fleet. Of
the coarse snuff, called Vigo snuff, the sailors, among whom it was
shared, sold waggon-loads at Portsmouth, Plymouth, and Chatham, for not
more than three-pence or four-pence a pound. The greater part of it was
bought up by Spanish Jews, to their own very considerable profit. The
fine snuffs taken at Port St. Mary, and divided among the officers, were
sold by some of them at once for a small price, while others held their
stocks and, as the snuff so taken became popular and gave a patriotic
impulse to the introduction of a fashion which had hitherto been almost
confined to foreigners, they got very high prices for it. This accounts
for the fact that the ladies too had added the use of the perfumed
snuff-box to their other fashionable accomplishments.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 5, 1712 |
Addison |
Sanctius his animal, mentisque capacius altæ
Deerat adhuc, et quod dominari in cœtera posset,
Natus homo est.
Ov.
Met.
The Accounts which
Raphael
gives of the Battel of Angels, and the
Creation of the World, have in them those Qualifications which the
Criticks judge requisite to an Episode. They are nearly related to the
principal Action, and have a just Connexion with the Fable.
The eighth Book opens with a beautiful Description of the Impression
which this Discourse of the Archangel made on our first Parent
s
.
Adam
afterwards, by a very natural Curiosity, enquires concerning the Motions
of those Celestial Bodies which make the most glorious Appearance among
the six days Works. The Poet here, with a great deal of Art, represents
Eve
as withdrawing from this part of their Conversation, to Amusements
more suitable to her Sex. He well knew, that the Episode in this Book,
which is filled with
Adam's
Account of his Passion and Esteem for
Eve
,
would have been improper for her hearing, and has therefore devised very
just and beautiful Reasons for her Retiring.
So spake our Sire, and by his Countenance seem'd
Entring on studious Thoughts abstruse: which Eve
Perceiving, where she sat retired in sight,
With lowliness majestick, from her Seat,
And Grace, that won who saw to wish her Stay,
Rose; and went forth among her Fruits and Flowers
To visit how they prosper'd, Bud and Bloom,
Her Nursery: they at her coming sprung,
And touch'd by her fair Tendance gladlier grew.
Yet went she not, as not with such Discourse
Delighted, or not capable her Ear
Of what was high: Such Pleasure she reserved,
Adam relating, she sole Auditress;
Her Husband the Relater she preferr'd
Before the Angel, and of him to ask
Chose rather: he, she knew, would intermix
Grateful Digressions, and solve high Dispute
With conjugal Caresses; from his Lip
Not Words alone pleas'd her. O when meet now
Such Pairs, in Love and mutual Honour join'd!
The Angel's returning a doubtful Answer to
Adam's
Enquiries, was not
only proper for the Moral Reason which the Poet assigns, but because it
would have been highly absurd to have given the Sanction of an Archangel
to any particular System of Philosophy. The chief Points in the
Ptolemaick
and
Copernican
Hypothesis are described with great
Conciseness and Perspicuity, and at the same time dressed in very
pleasing and poetical Images.
Adam
, to detain the Angel, enters afterwards upon his own History, and
relates to him the Circumstances in which he found himself upon his
Creation; as also his Conversation with his Maker, and his first meeting
with
Eve
. There is no part of the Poem more apt to raise the Attention
of the Reader, than this Discourse of our great Ancestor; as nothing can
be more surprizing and delightful to us, than to hear the Sentiments
that arose in the first Man while he was yet new and fresh from the
Hands of his Creator. The Poet has interwoven every thing which is
delivered upon this Subject in Holy Writ with so many beautiful
Imaginations of his own, that nothing can be conceived more just and
natural than this whole Episode. As our Author knew this Subject could
not but be agreeable to his Reader, he would not throw it into the
Relation of the six days Works, but reserved it for a distinct Episode,
that he might have an opportunity of expatiating upon it more at large.
Before I enter on this part of the Poem, I cannot but take notice of two
shining Passages in the Dialogue between
Adam
and the Angel. The first
is that wherein our Ancestor gives an Account of the pleasure he took in
conversing with him, which contains a very noble Moral.
For while I sit with thee, I seem in Heav'n,
And sweeter thy Discourse is to my Ear
Than Fruits of Palm-tree (pleasantest to Thirst
And Hunger both from Labour) at the hour
Of sweet Repast: they satiate, and soon fill,
Tho' pleasant; but thy Words with Grace divine
Imbu'd, bring to their Sweetness no Satiety.
The other I shall mention, is that in which the Angel gives a Reason why
he should be glad to hear the Story
Adam
was about to relate.
For I that day was absent, as befel,
Bound on a Voyage uncouth and obscure;
Far on Excursion towards the Gates of Hell,
Squar'd in full Legion such Command we had
To see that none thence issued forth a Spy,
Or Enemy; while God was in his Work,
Lest he, incens'd at such Eruption bold,
Destruction with Creation might have mix'd.
There is no question but our Poet drew the Image in what follows from
that in
Virgil's
sixth Book, where
Æneas
and the
Sibyl
stand before the
Adamantine Gates, which are there described as shut upon the Place of
Torments, and listen to the Groans, the Clank of Chains, and the Noise
of Iron Whips, that were heard in those Regions of Pain and Sorrow.
—Fast we found, fast shut
The dismal Gates, and barricado'd strong;
But long ere our Approaching heard within
Noise, other than the Sound of Dance or Song,
Torment, and loud Lament, and furious Rage.
Adam
then proceeds to give an account of his Condition and Sentiments
immediately after his Creation. How agreeably does he represent the
Posture in which he found himself, the beautiful Landskip that
surrounded him, and the Gladness of Heart which grew up in him on that
occasion?
—As new waked from soundest Sleep,
Soft on the flow'ry Herb I found me laid
In balmy Sweat, which with his Beams the Sun
Soon dried, and on the reaking Moisture fed.
Streight towards Heav'n my wond'ring Eyes I turn'd,
And gazed awhile the ample Sky, till rais'd
By quick instinctive Motion, up I sprung,
As thitherward endeavouring, and upright
Stood on my Feet: About me round I saw
Hill, Dale, and shady Woods, and sunny Plains,
And liquid lapse of murmuring Streams; by these
Creatures that liv'd, and mov'd, and walked, or flew,
Birds on the Branches warbling; all things smil'd:
With Fragrance, and with Joy my Heart o'erflow'd.
Adam
is afterwards describ'd as surprized at his own Existence, and
taking a Survey of himself, and of all the Works of Nature. He likewise
is represented as discovering by the Light of Reason, that he and every
thing about him must have been the Effect of some Being infinitely good
and powerful, and that this Being had a right to his Worship and
Adoration. His first Address to the Sun, and to those Parts of the
Creation which made the most distinguished Figure, is very natural and
amusing to the Imagination.
—Thou Sun, said I, fair Light,
And thou enlighten'd Earth, so fresh and gay,
Ye Hills and Dales, ye Rivers, Woods and Plains,
And ye that live and move, fair Creatures tell,
Tell if you saw, how came I thus, how here?
His next Sentiment, when upon his first going to sleep he fancies
himself losing his Existence, and falling away into nothing, can never
be sufficiently admired. His Dream, in which he still preserves the
Consciousness of his Existence, together with his removal into the
Garden which was prepared for his Reception, are also Circumstances
finely imagined, and grounded upon what is delivered in Sacred Story.
These and the like wonderful Incidents in this Part of the Work, have in
them all the Beauties of Novelty, at the same time that they have all
the Graces of Nature. They are such as none but a great Genius could
have thought of, tho', upon the perusal of them, they seem to rise of
themselves from the Subject of which he treats. In a word, tho' they are
natural, they are not obvious, which is the true Character of all fine
Writing.
The Impression which the Interdiction of the Tree of Life left in the
Mind of our first Parent, is describ'd with great Strength and Judgment;
as the Image of the several Beasts and Birds passing in review before
him is very beautiful and lively.
—Each Bird and Beast behold
Approaching two and two, these cowring low
With Blandishment; each Bird stoop'd on his Wing:
I nam'd them as they pass'd—
Adam
, in the next place, describes a Conference which he held with his
Maker upon the Subject of Solitude. The Poet here represents the supreme
Being, as making an Essay of his own Work, and putting to the tryal that
reasoning Faculty, with which he had endued his Creature.
Adam
urges, in
this Divine Colloquy, the Impossibility of his being happy, tho' he was
the Inhabitant of Paradise, and Lord of the whole Creation, without the
Conversation and Society of some rational Creature, who should partake
those Blessings with him. This Dialogue, which is supported chiefly by
the Beauty of the Thoughts, without other poetical Ornaments, is as fine
a Part as any in the whole Poem: The more the Reader examines the
Justness and Delicacy of its Sentiments, the more he will find himself
pleased with it. The Poet has wonderfully preserved the Character of
Majesty and Condescension in the Creator, and at the same time that of
Humility and Adoration in the Creature, as particularly in the following
Lines:
Thus I presumptuous; and the Vision bright,
As with a Smile more bright-tied, thus reply'd, &c.
—I, with leave of Speech implor'd
And humble Deprecation, thus reply d:
Let not my Words offend thee, Heav'nly Power,
My Maker, be propitious while I speak, &c.
Adam
then proceeds to give an account of his second Sleep, and of the
Dream in which he beheld the Formation of
Eve
. The new Passion that was
awaken'd in him at the sight of her, is touch'd very finely.
Under his forming Hands a Creature grew,
Manlike, but different Sex: so lovely fair,
That what seem'd fair in all the World, seemed now
Mean, or in her summ'd up, in her contained,
And in her Looks; which from that time infused
Sweetness info my Heart, unfelt before:
And into all things from her Air inspired
The Spirit of Love and amorous Delight.
Adam's
Distress upon losing sight of this beautiful Phantom, with his
Exclamations of Joy and Gratitude at the discovery of a real Creature,
who resembled the Apparition which had been presented to him in his
Dream; the Approaches he makes to her, and his Manner of Courtship; are
all laid together in a most exquisite Propriety of Sentiments.
Tho' this Part of the Poem is work'd up with great Warmth and Spirit,
the Love which is described in it is every way suitable to a State of
Innocence. If the Reader compares the Description which
Adam
here gives
of his leading
Eve
to the Nuptial Bower, with that which Mr.
Dryden
has
made on the same occasion in a Scene of his Fall of Man, he will be
sensible of the great care which
Milton
took to avoid all Thoughts on so
delicate a Subject, that might be offensive to Religion or Good-Manners.
The Sentiments are chaste, but not cold; and convey to the Mind Ideas of
the most transporting Passion, and of the greatest Purity. What a noble
Mixture of Rapture and Innocence has the Author join'd together, in the
Reflection which
Adam
makes on the Pleasures of Love, compared to those
of Sense.
Thus have I told thee all my State, and brought
My Story to the sum of earthly Bliss,
Which I enjoy; and must confess to find
In all things else Delight indeed, but such
As us'd or not, works in the Mind no Change
Nor vehement Desire; these Delicacies
I mean of Taste, Sight, Smell, Herbs, Fruits, and Flowers,
Walks, and the Melody of Birds: but here
Far otherwise, transported I behold,
Transported touch; here Passion first I felt,
Commotion strange! in all Enjoyments else
Superiour and unmov'd, here only weak
Against the Charms of Beauty's powerful Glance.
Or Nature fail'd in me, and left some Part
Not Proof enough such Object to sustain;
Or from my Side subducting, took perhaps
More than enough; at least on her bestowed
Too much of Ornament in outward shew
Elaborate, of inward less exact.
—When I approach
Her Loveliness, so absolute she seems
And in herself compleat, so well to know
Her own, that what she wills to do or say
Seems wisest, vertuousest, discreetest, best:
All higher Knowledge in her Presence falls
Degraded: Wisdom in discourse with her
Loses discountenanced, and like Folly shews;
Authority and Reason on her wait,
As one intended first, not after made
Occasionally: and to consummate all,
Greatness of Mind, and Nobleness their Seat
Build in her loveliest, and create an Awe
About her, as a Guard angelick plac'd.
These Sentiments of Love, in our first Parent, gave the Angel such an
Insight into Humane Nature, that he seems apprehensive of the Evils
which might befall the Species in general, as well as
Adam
in
particular, from the Excess of this Passion. He therefore fortifies him
against it by timely Admonitions; which very artfully prepare the Mind
of the Reader for the Occurrences of the next Book, where the Weakness
of which
Adam
here gives such distant Discoveries, brings about that
fatal Event which is the Subject of the Poem. His Discourse, which
follows the gentle Rebuke he received from the Angel, shews that his
Love, however violent it might appear, was still founded in Reason, and
consequently not improper for Paradise.
Neither her outside Form so fair, nor aught
In Procreation common to all kinds,
(Tho' higher of the genial Bed by far,
And with mysterious Reverence I deem)
So much delights me, as those graceful Acts,
Those thousand Decencies that daily flow
From all her Words and Actions, mixt with Love
And sweet Compliance, which declare unfeign'd
Union of Mind, or in us both one Soul;
Harmony to behold in—wedded Pair!
Adam's
Speech, at parting with the Angel, has in it a Deference and
Gratitude agreeable to an inferior Nature, and at the same time a
certain Dignity and Greatness suitable to the Father of Mankind in his
State of Innocence.
L.
Contents
|
Monday, April 7, 1712 |
Steele |
Consuetudinem benignitatis largitioni Munerum longe antepono. Hæc est
Gravium hominum atque Magnorum; Illa quasi assentatorum populi,
multitudinis levitatem voluptate quasi titillantium.
Tull.

When we consider the Offices of humane Life, there is, methinks,
something in what we ordinarily call Generosity, which when carefully
examined, seems to flow rather from a loose and unguarded Temper, than
an honest and liberal Mind. For this reason it is absolutely necessary
that all Liberality should have for its Basis and Support Frugality. By
this means the beneficent Spirit works in a Man from the Convictions of
Reason, not from the Impulses of Passion. The generous Man, in the
ordinary acceptation, without respect to the Demands of his own Family,
will soon find, upon the Foot of his Account, that he has sacrificed to
Fools, Knaves, Flatterers, or the deservedly Unhappy, all the
Opportunities of affording any future Assistance where it ought to be.
Let him therefore reflect, that if to bestow be in it self laudable,
should not a Man take care to secure Ability to do things praiseworthy
as long as he lives? Or could there be a more cruel Piece of Raillery
upon a Man who should have reduc'd his Fortune below the Capacity of
acting according to his natural Temper, than to say of him, That
Gentleman was generous? My beloved Author therefore has, in the Sentence
on the Top of my Paper, turned his Eye with a certain Satiety from
beholding the Addresses to the People by Largesses and publick
Entertainments, which he asserts to be in general vicious, and are
always to be regulated according to the Circumstances of Time and a
Man's own Fortune. A constant Benignity in Commerce with the rest of the
World, which ought to run through all a Man's Actions, has Effects more
useful to those whom you oblige, and less ostentatious in your self. He
turns his Recommendation of this Virtue in commercial Life: and
according to him a Citizen who is frank in his Kindnesses, and abhors
Severity in his Demands; he who in buying, selling, lending, doing acts
of good Neighbourhood, is just and easy; he who appears naturally averse
to Disputes, and above the Sense of little Sufferings; bears a nobler
Character, and does much more good to Mankind, than any other Man's
Fortune without Commerce can possibly support. For the Citizen above all
other Men has Opportunities of arriving at that highest Fruit of Wealth,
to be liberal without the least Expence of a Man's own Fortune. It is
not to be denied but such a Practice is liable to hazard; but this
therefore adds to the Obligation, that, among Traders, he who obliges is
as much concerned to keep the Favour a Secret, as he who receives it.
The unhappy Distinctions among us in England are so great, that to
celebrate the Intercourse of commercial Friendship, (with which I am
daily made acquainted) would be to raise the virtuous Man so many
Enemies of the contrary Party. I am obliged to conceal all I know of
Tom
the Bounteous, who lends at the ordinary Interest, to give Men of less
Fortune Opportunities of making greater Advantages. He conceals, under a
rough Air and distant Behaviour, a bleeding Compassion and womanish
Tenderness. This is governed by the most exact Circumspection, that
there is no Industry wanting in the Person whom he is to serve, and that
he is guilty of no improper Expences. This I know of
Tom
, but who dare
say it of so known a
Tory
? The same Care I was forced to use some time
ago in the Report of another's Virtue, and said fifty instead of a
hundred, because the Man I pointed at was a
Whig
. Actions of this kind
are popular without being invidious: for every Man of ordinary
Circumstances looks upon a Man who has this known Benignity in his
Nature, as a Person ready to be his Friend upon such Terms as he ought
to expect it; and the Wealthy, who may envy such a Character, can do no
Injury to its Interests but by the Imitation of it, in which the good
Citizens will rejoice to be rivalled. I know not how to form to myself a
greater Idea of Humane Life, than in what is the Practice of some
wealthy Men whom I could name, that make no step to the Improvement of
their own Fortunes, wherein they do not also advance those of other Men,
who would languish in Poverty without that Munificence. In a Nation
where there are so many publick Funds to be supported, I know not
whether he can be called a good Subject, who does not imbark some part
of his Fortune with the State, to whose Vigilance he owes the Security
of the whole. This certainly is an immediate way of laying an Obligation
upon many, and extending his Benignity the furthest a Man can possibly,
who is not engaged in Commerce. But he who trades, besides giving the
State some part of this sort of Credit he gives his Banker, may in all
the Occurrences of his Life have his Eye upon removing Want from the
Door of the Industrious, and defending the unhappy upright Man from
Bankruptcy. Without this Benignity, Pride or Vengeance will precipitate
a Man to chuse the Receipt of half his Demands from one whom he has
undone, rather than the whole from one to whom he has shewn Mercy. This
Benignity is essential to the Character of a fair Trader, and any Man
who designs to enjoy his Wealth with Honour and Self-Satisfaction: Nay,
it would not be hard to maintain, that the Practice of supporting good
and industrious Men, would carry a Man further even to his Profit, than
indulging the Propensity of serving and obliging the Fortunate. My
Author argues on this Subject, in order to incline Men's Minds to those
who want them most, after this manner; We must always consider the
Nature of things, and govern our selves accordingly. The wealthy Man,
when he has repaid you, is upon a Ballance with you; but the Person whom
you favour'd with a Loan, if he be a good Man, will think himself in
your Debt after he has paid you. The Wealthy and the Conspicuous are not
obliged by the Benefit you do them, they think they conferred a Benefit
when they receive one. Your good Offices are always suspected, and it is
with them the same thing to expect their Favour as to receive it. But
the Man below you, who knows in the Good you have done him, you
respected himself more than his Circumstances, does not act like an
obliged Man only to him from whom he has received a Benefit, but also to
all who are capable of doing him one. And whatever little Offices he can
do for you, he is so far from magnifying it, that he will labour to
extenuate it in all his Actions and Expressions. Moreover, the Regard to
what you do to a great Man, at best is taken notice of no further than
by himself or his Family; but what you do to a Man of an humble Fortune,
(provided always that he is a good and a modest Man) raises the
Affections towards you of all Men of that Character (of which there are
many) in the whole City.
There is nothing gains a Reputation to a Preacher so much as his own
Practice; I am therefore casting about what Act of Benignity is in the
Power of a
Spectator
. Alas, that lies but in a very narrow compass, and
I think the most immediate under my Patronage, are either Players, or
such whose Circumstances bear an Affinity with theirs: All therefore I
am able to do at this time of this Kind, is to tell the Town that on
Friday the 11th of this Instant April, there will be perform'd in
York-Buildings a Consort of Vocal and Instrumental Musick, for the
Benefit of Mr.
Edward Keen
, the Father of twenty Children; and that this
Day the haughty
George Powell
hopes all the good-natur'd part of the
Town will favour him, whom they Applauded in
Alexander, Timon, Lear
, and
Orestes
, with their Company this Night, when he hazards all his heroick
Glory for their Approbation in the humbler Condition of honest
Jack
Falstaffe.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 8, 1712 |
Budgell |
Quis furor ô Cives! quæ tanta licentia ferri!
Lucan.

I do not question but my Country Readers have been very much surprized
at the several Accounts they have met with in our publick Papers of that
Species of Men among us, lately known by the Name of Mohocks. I find the
Opinions of the Learned, as to their Origin and Designs, are altogether
various, insomuch that very many begin to doubt whether indeed there
were ever any such Society of Men. The Terror which spread it self over
the whole Nation some Years since, on account of the Irish, is still
fresh in most Peoples Memories, tho' it afterwards appeared there was
not the least Ground for that general Consternation.
The late Panick Fear was, in the Opinion of many deep and penetrating
Persons, of the same nature. These will have it, that the Mohocks are
like those Spectres and Apparitions which frighten several Towns and
Villages in her Majesty's Dominions, tho' they were never seen by any of
the Inhabitants. Others are apt to think that these Mohocks are a kind
of Bull-Beggars, first invented by prudent married Men, and Masters of
Families, in order to deter their Wives and Daughters from taking the
Air at unseasonable Hours; and that when they tell them the Mohocks will
catch them, it is a Caution of the same nature with that of our
Fore-fathers, when they bid their Children have a care of Raw-head and
Bloody-bones.
For my own part, I am afraid there was too much Reason for that great
Alarm the whole City has been in upon this Occasion; tho' at the same
time I must own that I am in some doubt whether the following Pieces are
Genuine and Authentick; and the more so, because I am not fully
satisfied that the Name by which the Emperor subscribes himself, is
altogether conformable to the Indian Orthography.
I shall only further inform my Readers, that it was some time since I
receiv'd the following Letter and Manifesto, tho' for particular Reasons
I did not think fit to publish them till now.
To the
Spectator.
Sir,
"Finding that our earnest Endeavours for the Good of Mankind have been
basely and maliciously represented to the World, we send you enclosed
our Imperial Manifesto, which it is our Will and Pleasure that you
forthwith communicate to the Publick, by inserting it in your next
daily Paper. We do not doubt of your ready Compliance in this
Particular, and therefore bid you heartily Farewell."
Sign'd,
Taw Waw Eben Zan Kaladar,
Emperor of the Mohocks.
The Manifesto of Taw Waw Eben Zan Kaladar, Emperor of the Mohocks.
"Whereas we have received Information from sundry Quarters of this
great and populous City, of several Outrages committed on the Legs,
Arms, Noses, and other Parts of the good People of England, by such
as have styled themselves our Subjects; in order to vindicate our
Imperial Dignity from those false Aspersions which have been cast on
it, as if we our selves might have encouraged or abetted any such
Practices; we have, by these Presents, thought fit to signify our
utmost Abhorrence and Detestation of all such tumultuous and
irregular Proceedings: and do hereby further give notice, that if
any Person or Persons has or have suffered any Wound, Hurt, Damage
or Detriment in his or their Limb or Limbs, otherwise than shall be
hereafter specified, the said Person or Persons, upon applying
themselves to such as we shall appoint for the Inspection and
Redress of the Grievances aforesaid, shall be forthwith committed to
the Care of our principal Surgeon, and be cured at our own Expence,
in some one or other of those Hospitals which we are now erecting
for that purpose.
"And to the end that no one may, either through Ignorance or
Inadvertency, incur those Penalties which we have thought fit to
inflict on Persons of loose and dissolute Lives, we do hereby
notifie to the Publick, that if any Man be knocked down or assaulted
while he is employed in his lawful Business, at proper Hours, that
it is not done by our Order; and we do hereby permit and allow any
such person so knocked down or assaulted, to rise again, and defend
himself in the best manner that he is able.
"We do also command all and every our good Subjects, that they do
not presume, upon any Pretext whatsoever, to issue and sally forth
from their respective Quarters till between the Hours of Eleven and
Twelve. That they never Tip the Lion upon Man, Woman or Child, till
the Clock at St. Dunstan's shall have struck One.
"That the Sweat be never given but between the Hours of One and Two;
always provided, that our Hunters may begin to Hunt a little after
the Close of the Evening, any thing to the contrary herein
notwithstanding. Provided also, that if ever they are reduced to the
Necessity of Pinking, it shall always be in the most fleshy Parts,
and such as are least exposed to view.
"It is
also our Imperial Will and Pleasure, that our good Subjects
the Sweaters do establish their
Hummums1 in such close Places,
Alleys, Nooks, and Corners, that the Patient or Patients may not be
in danger of catching Cold.
"That the Tumblers, to whose Care we chiefly commit the Female Sex,
confine themselves to Drury-Lane and the Purlieus of the Temple; and
that every other Party and Division of our Subjects do each of them
keep within the respective Quarters we have allotted to them.
Provided nevertheless, that nothing herein contained shall in any
wise be construed to extend to the Hunters, who have our full
Licence and Permission to enter into any Part of the Town where-ever
their Game shall lead them.
"And whereas we have nothing more at our Imperial Heart than the
Reformation of the Cities of London and Westminster, which to our
unspeakable Satisfaction we have in some measure already effected,
we do hereby earnestly pray and exhort all Husbands, Fathers,
Housekeepers and Masters of Families, in either of the aforesaid
Cities, not only to repair themselves to their respective
Habitations at early and seasonable Hours; but also to keep their
Wives and Daughters, Sons, Servants, and Apprentices, from appearing
in the Streets at those Times and Seasons which may expose them to a
military Discipline, as it is practised by our good Subjects the
Mohocks: and we do further promise, on our Imperial Word, that as
soon as the Reformation aforesaid shall be brought about, we will
forthwith cause all Hostilities to cease.
"Given from our Court at the Devil-Tavern,
March 15, 1712."
X.
Turkish Sweating Baths. The
Hummums
"in Covent Garden was
one of the first of these baths (
bagnios
) set up in England."
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 9, 1712 |
Steele |
Invidiam placare paras virtute relicta?
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator,
'I have not seen you lately at any of the Places where I visit, so
that I am afraid you are wholly unacquainted with what passes among my
part of the World, who are, tho' I say it, without Controversy, the
most accomplished and best bred of the Town. Give me leave to tell
you, that I am extremely discomposed when I hear Scandal, and am an
utter Enemy to all manner of Detraction, and think it the greatest
Meanness that People of Distinction can be guilty of: However, it is
hardly possible to come into Company, where you do not find them
pulling one another to pieces, and that from no other Provocation but
that of hearing any one commended. Merit, both as to Wit and Beauty,
is become no other than the Possession of a few trifling People's
Favour, which you cannot possibly arrive at, if you have really any
thing in you that is deserving. What they would bring to pass, is, to
make all Good and Evil consist in Report, and with Whispers, Calumnies
and Impertinencies, to have the Conduct of those Reports. By this
means Innocents are blasted upon their first Appearance in Town; and
there is nothing more required to make a young Woman the object of
Envy and Hatred, than to deserve Love and Admiration. This abominable
Endeavour to suppress or lessen every thing that is praise-worthy, is
as frequent among the Men as the Women. If I can remember what passed
at a Visit last Night, it will serve as an Instance that the Sexes are
equally inclined to Defamation, with equal Malice, with equal
Impotence.
Jack Triplett came into my Lady
Airy's about Eight of
the
Clock. You know the manner we sit at a Visit, and I need not describe
the Circle; but Mr.
Triplett came in, introduced by two Tapers
supported by a spruce Servant, whose Hair is under a Cap till my
Lady's Candles are all lighted up, and the Hour of Ceremony begins: I
say,
Jack Triplett came in, and singing (for he is really good
Company) 'Every Feature, Charming Creature,—he went on, It is a
most unreasonable thing that People cannot go peaceably to see their
Friends, but these Murderers are let loose. Such a Shape! such an Air!
what a Glance was that as her Chariot pass'd by mine—My Lady
herself interrupted him; Pray who is this fine Thing—I warrant, says
another, 'tis the Creature I was telling your Ladyship of just now.
You were telling of? says Jack; I wish I had been so happy as to have
come in and heard you, for I have not Words to say what she is: But if
an agreeable Height, a modest Air, a Virgin Shame, and Impatience of
being beheld, amidst a Blaze of ten thousand Charms—The whole Room
flew out—Oh Mr.
Triplett!—When Mrs.
Lofty, a known Prude, said
she believed she knew whom the Gentleman meant; but she was indeed, as
he civilly represented her, impatient of being beheld —- Then turning
to the Lady next to her—The most unbred Creature you ever saw.
Another pursued the Discourse: As unbred, Madam, as you may think her,
she is extremely bely'd if she is the Novice she appears; she was last
Week at a Ball till two in the Morning; Mr.
Triplett knows whether he
was the happy Man that took Care of her home; but—This was followed
by some particular Exception that each Woman in the Room made to some
peculiar Grace or Advantage so that Mr.
Triplett was beaten from one
Limb and Feature to another, till he was forced to resign the whole
Woman. In the end I took notice
Triplett recorded all this Malice in
his Heart; and saw in his Countenance, and a certain waggish Shrug,
that he design'd to repeat the Conversation: I therefore let the
Discourse die, and soon after took an Occasion to commend a certain
Gentleman of my Acquaintance for a Person of singular Modesty,
Courage, Integrity, and withal as a Man of an entertaining
Conversation, to which Advantages he had a Shape and Manner peculiarly
graceful. Mr.
Triplett, who is a Woman's Man, seem'd to hear me with
Patience enough commend the Qualities of his Mind: He never heard
indeed but that he was a very honest Man, and no Fool; but for a fine
Gentleman, he must ask Pardon. Upon no other Foundation than this, Mr.
Triplett took occasion to give the Gentleman's Pedigree, by what
Methods some part of the Estate was acquired, how much it was beholden
to a Marriage for the present Circumstances of it: After all, he could
see nothing but a common Man in his Person, his Breeding or
Understanding.
Thus, Mr.
Spectator, this impertinent Humour of diminishing every one
who is produced in Conversation to their Advantage, runs thro the
World; and I am, I confess, so fearful of the Force of ill Tongues,
that I have begged of all those who are my Well-wishers never to
commend me, for it will but bring my Frailties into Examination, and I
had rather be unobserved, than conspicuous for disputed Perfections. I
am confident a thousand young People, who would have been Ornaments to
Society, have, from Fear of Scandal, never dared to exert themselves
in the polite Arts of Life. Their Lives have passed away in an odious
Rusticity, in spite of great Advantages of Person, Genius and Fortune.
There is a vicious Terror of being blamed in some well-inclin'd
People, and a wicked Pleasure in suppressing them in others; both
which I recommend to your Spectatorial Wisdom to animadvert upon; and
if you can be successful in it, I need not say how much you will
deserve of the Town; but new Toasts will owe to you their Beauty, and
new Wits their Fame. I am,
Sir,
Your most Obedient
Humble Servant,
Mary."
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 10, 1712 |
Addison |
Quos ille timorum
Maximus haud urget lethi metus: inde ruendi
In ferrum mens prona viris, animæque capaces
Mortis.
Lucan.

I am very much pleased with a Consolatory Letter of
Phalaris
, to one who
had lost a Son that was a young Man of great Merit. The Thought with
which he comforts the afflicted Father, is, to the best of my Memory, as
follows; That he should consider Death had set a kind of Seal upon his
Son's Character, and placed him out of the Reach of Vice and Infamy:
That while he liv'd he was still within the Possibility of falling away
from Virtue, and losing the Fame of which he was possessed. Death only
closes a Man's Reputation, and determines it as good or bad.
This, among other Motives, may be one Reason why we are naturally averse
to the launching out into a Man's Praise till his Head is laid in the
Dust. Whilst he is capable of changing, we may be forced to retract our
Opinions. He may forfeit the Esteem we have conceived of him, and some
time or other appear to us under a different Light from what he does at
present. In short, as the Life of any Man cannot be call'd happy or
unhappy, so neither can it be pronounced vicious or virtuous, before the
Conclusion of it.
It was
this consideration that
Epaminondas
, being asked whether
Chabrias
,
Iphicrates
, or he himself, deserved most to be esteemed? You
must first see us die, said he, before that Question can be answered
.
As there is not a more melancholy Consideration to a good Man than his
being obnoxious to such a Change, so there is nothing more glorious than
to keep up an Uniformity in his Actions, and preserve the Beauty of his
Character to the last.
The End of a Man's Life is often compared to the winding up of a
well-written Play, where the principal Persons still act in Character,
whatever the Fate is which they undergo. There is scarce a great Person
in the
Grecian
or
Roman
History, whose Death has not been remarked upon
by some Writer or other, and censured or applauded according to the
Genius or Principles of the Person who has descanted on it.
Monsieur de
St. Evremont
is very particular in setting forth the Constancy and
Courage of
Petronius Arbiter
during his last Moments, and thinks he
discovers in them a greater Firmness of Mind and Resolution than in the
Death of
Seneca, Cato
, or
Socrates
. There is no question but this polite
Author's Affectation of appearing singular in his Remarks, and making
Discoveries which had escaped the Observation of others, threw him into
this course of Reflection. It was
Petronius's
Merit, that he died in the
same Gaiety of Temper in which he lived; but as his Life was altogether
loose and dissolute, the Indifference which he showed at the Close of it
is to be looked upon as a piece of natural Carelessness and Levity,
rather than Fortitude. The Resolution of
Socrates
proceeded from very
different Motives, the Consciousness of a well-spent Life, and the
prospect of a happy Eternity. If the ingenious Author above mentioned
was so pleased with Gaiety of Humour in a dying Man, he might have found
a much nobler Instance of it in our Countryman
Sir Thomas More.
This great and learned Man was famous for enlivening his ordinary
Discourses with Wit and Pleasantry; and, as
Erasmus
tells him in an
Epistle Dedicatory
, acted in all parts of Life like a second
Democritus
.
He died upon a Point of Religion, and is respected as a Martyr by that
Side for which he suffer'd. The innocent Mirth which had been so
conspicuous in his Life, did not forsake him to the last: He maintain'd
the same Chearfulness of Heart upon the Scaffold, which he used to shew
at his Table; and upon laying his Head on the Block, gave Instances of
that Good-Humour with which he had always entertained his Friends in the
most ordinary Occurrences. His Death was of a piece with his Life. There
was nothing in it new, forced, or affected. He did not look upon the
severing of his Head from his Body as a Circumstance that ought to
produce any Change in the Disposition of his Mind; and as he died under
a fixed and settled Hope of Immortality, he thought any unusual degree
of Sorrow and Concern improper on such an Occasion, as had nothing in it
which could deject or terrify him.
There is no great danger of Imitation from this Example. Men's natural
Fears will be a sufficient Guard against it. I shall only observe, that
what was Philosophy in this extraordinary Man, would be Frenzy in one
who does not resemble him as well in the Chearfulness of his Temper, as
in the Sanctity of his Life and Manners.
I shall conclude this Paper with the Instance of a Person who seems to
me to have shewn more Intrepidity and Greatness of Soul in his dying
Moments, than what we meet with among any of the most celebrated
Greeks
and
Romans
. I
with this Instance in the
History of the Revolutions
in Portugal
, written by the
Abbot de Vertot
.
When
Don Sebastian
, King of Portugal, had invaded the Territories of
Muly Moluc
, Emperor of Morocco, in order to dethrone him, and set his
Crown upon the Head of his Nephew,
Moluc
was wearing away with a
Distemper which he himself knew was incurable. However, he prepared for
the Reception of so formidable an Enemy. He was indeed so far spent with
his Sickness, that he did not expect to live out the whole Day, when the
last decisive Battel was given; but knowing the fatal Consequences that
would happen to his Children and People, in case he should die before he
put an end to that War, he commanded his principal Officers that if he
died during the Engagement, they should conceal his Death from the Army,
and that they should ride up to the Litter in which his Corpse was
carried, under Pretence of receiving Orders from him as usual. Before
the Battel begun, he was carried through all the Ranks of his Army in an
open Litter, as they stood drawn up in Array, encouraging them to fight
valiantly in defence of their Religion and Country. Finding afterwards
the Battel to go against him, tho' he was very near his last Agonies, he
threw himself out of his Litter, rallied his Army, and led them on to
the Charge; which afterwards ended in a compleat Victory on the side of
the Moors. He had no sooner brought his Men to the Engagement, but
finding himself utterly spent, he was again replaced in his Litter,
where laying his Finger on his Mouth, to enjoin Secrecy to his Officers,
who stood about him, he died a few Moments after in that Posture.
L.
Plutarch's
Life of Epaminondas.
The Abbé Vertot—Renatus Aubert de Vertot d'Auboeuf—was
born in 1655, and living in the
Spectator's
time. He died in 1735, aged
80. He had exchanged out of the severe order of the Capuchins into that
of the Præmonstratenses when, at the age of 34, he produced, in 1689,
his first work, the
History of the Revolutions of Portugal,
here quoted.
Continuing to write history, in 1701 he was made a member, and in 1705 a
paid member, of the Académie des Inscriptions et Belles Lettres.
Contents
|
Friday, April 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Ea animi elatio quæ cernitur in periculis, si Justitia
vacat pugnatque pro suis commodis, in vitio est.
Tull.

Captain Sentrey
was last Night at the Club, and produced a Letter from
Ipswich
, which his Correspondent desired him to communicate to his
Friend the
Spectator
. It contained an Account of an Engagement between a
French Privateer, commanded by one
Dominick Pottiere
, and a little
Vessel of that Place laden with Corn, the Master whereof, as I remember,
was one
Goodwin
. The
Englishman
defended himself with incredible
Bravery, and beat off the
French
, after having been boarded three or
four times. The Enemy still came on with greater Fury, and hoped by his
Number of Men to carry the Prize, till at last the
Englishman
finding
himself sink apace, and ready to perish, struck: But the Effect which
this singular Gallantry had upon the Captain of the Privateer, was no
other than an unmanly Desire of Vengeance for the Loss he had sustained
in his several Attacks. He told the
Ipswich
Man in a speaking-Trumpet,
that he would not take him aboard, and that he stayed to see him sink.
The
Englishman
at the same time observed a Disorder in the Vessel, which
he rightly judged to proceed from the Disdain which the Ship's Crew had
of their Captain's Inhumanity: With this Hope he went into his Boat, and
approached the Enemy. He was taken in by the Sailors in spite of their
Commander; but though they received him against his Command, they
treated him when he was in the Ship in the manner he directed.
Pottiere
caused his Men to hold
Goodwin
, while he beat him with a Stick till he
fainted with Loss of Blood, and Rage of Heart: after which he ordered
him into Irons without allowing him any Food, but such as one or two of
the Men stole to him under peril of the like Usage: After having kept
him several Days overwhelmed with the Misery of Stench, Hunger, and
Soreness, he brought him into
Calais
. The Governour of the Place was
soon acquainted with all that had passed, dismissed
Pottiere
from his
Charge with Ignominy, and gave
Goodwin
all the Relief which a Man of
Honour would bestow upon an Enemy barbarously treated, to recover the
Imputation of Cruelty upon his Prince and Country.
When Mr.
Sentrey
had read his Letter, full of many other circumstances
which aggravate the Barbarity, he fell into a sort of Criticism upon
Magnanimity and Courage, and argued that they were inseparable; and that
Courage, without regard to Justice and Humanity, was no other than the
Fierceness of a wild Beast. A good and truly bold Spirit, continued he,
is ever actuated by Reason and a Sense of Honour and Duty: The
Affectation of such a Spirit exerts it self in an Impudent Aspect, an
over-bearing Confidence, and a certain Negligence of giving Offence.
This is visible in all the cocking Youths you see about this Town, who
are noisy in Assemblies, unawed by the Presence of wise and virtuous
Men; in a word, insensible of all the Honours and Decencies of human
Life. A shameless Fellow takes advantage of Merit clothed with Modesty
and Magnanimity, and in the Eyes of little People appears sprightly and
agreeable; while the Man of Resolution and true Gallantry is overlooked
and disregarded, if not despised. There is a Propriety in all things;
and I believe what you Scholars call just and sublime, in opposition to
turgid and bombast Expression, may give you an Idea of what I mean, when
I say Modesty is the certain Indication of a great Spirit, and Impudence
the Affectation of it. He that writes with Judgment, and never rises
into improper Warmths, manifests the true Force of Genius; in like
manner, he who is quiet and equal in all his Behaviour, is supported in
that Deportment by what we may call true Courage. Alas, it is not so
easy a thing to be a brave Man as the unthinking part of Mankind
imagine: To dare, is not all that there is in it. The Privateer we were
just now talking of, had boldness enough to attack his Enemy, but not
Greatness of Mind enough to admire the same Quality exerted by that
Enemy in defending himself. Thus his base and little Mind was wholly
taken up in the sordid regard to the Prize, of which he failed, and the
damage done to his own Vessel; and therefore he used an honest Man, who
defended his own from him, in the Manner as he would a Thief that should
rob him.
He was equally disappointed, and had not Spirit enough to consider that
one Case would be Laudable and the other Criminal. Malice, Rancour,
Hatred, Vengeance, are what tear the Breasts of mean Men in Fight; but
Fame, Glory, Conquests, Desires of Opportunities to pardon and oblige
their Opposers, are what glow in the Minds of the Gallant. The Captain
ended his Discourse with a Specimen of his Book-Learning; and gave us to
understand that he had read a French Author on the Subject of Justness
in point of Gallantry. I love, said Mr. SENTREY, a Critick who mixes the
Rules of Life with Annotations upon Writers. My Author, added he, in his
Discourse upon Epick Poem, takes occasion to speak of the same Quality
of Courage drawn in the two different Characters of
Turnus
and
Æneas
:
He makes Courage the chief and greatest Ornament of ; but in
Æneas
there are many others which out-shine it, amongst the rest that
of Piety.
Turnus
is therefore all along painted by the Poet full of
Ostentation, his Language haughty and vain glorious, as placing his
Honour in the Manifestation of his Valour;
Æneas
speaks little, is slow
to Action; and shows only a sort of defensive Courage. If Equipage and
Address make appear more couragious than
Æneas
, Conduct and
Success prove
Æneas
more valiant than
Turnus
.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 12, 1712 |
Addison |
In te omnis domus inclinata recumbit.
Virg.

If we look into the three great Heroick Poems which have appeared in the
World, we may observe that they are built upon very slight Foundations.
Homer
lived near 300 Years after the
Trojan
War; and, as the writing of
History was not then in use among the
Greeks
, we may very well suppose,
that the Tradition of
Achilles
and
Ulysses
had brought down but very few
particulars to his Knowledge; though there is no question but he has
wrought into his two Poems such of their remarkable Adventures, as were
still talked of among his Contemporaries.
The Story of
Æneas
, on which
Virgil
founded his Poem, was likewise very
bare of Circumstances, and by that means afforded him an Opportunity of
embellishing it with Fiction, and giving a full range to his own
Invention. We find, however, that he has interwoven, in the course of
his Fable, the principal Particulars, which were generally believed
among the
Romans
, of
Æneas
his Voyage and Settlement in
Italy
.
Reader may find an Abridgment of the whole Story as collected out of the
ancient Historians, and as it was received among the Romans, in
Dionysius Halicarnasseus
.
Since none of the Criticks have consider'd
Virgil's
Fable, with relation
to this History of
Æneas
, it may not, perhaps, be amiss to examine it
in this Light, so far as regards my present Purpose. Whoever looks into
the Abridgment above mentioned, will find that the Character of
Æneas
is
filled with Piety to the Gods, and a superstitious Observation of
Prodigies, Oracles, and Predictions.
Virgil
has not only preserved this
Character in the Person of
Æneas
, but has given a place in his Poem to
those particular Prophecies which he found recorded of him in History
and Tradition. The Poet took the matters of Fact as they came down to
him, and circumstanced them after his own manner, to make them appear
the more natural, agreeable, or surprizing. I believe very many Readers
have been shocked at that ludicrous Prophecy, which one of the
Harpyes
pronounces to the
Trojans
in the third Book, namely, that before they
had built their intended City, they should be reduced by Hunger to eat
their very Tables. But, when they hear that this was one of the
Circumstances that had been transmitted to the
Romans
in the History of
Æneas
, they will think the Poet did very well in taking notice of it.
The Historian above mentioned acquaints us, a Prophetess had foretold
Æneas
, that he should take his Voyage
Westward
, till his Companions
should eat their Tables; and that accordingly, upon his landing in
Italy
, as they were eating their Flesh upon Cakes of Bread, for want of
other Conveniences, they afterwards fed on the Cakes themselves; upon
which one of the Company said merrily,
We are eating our Tables
. They
immediately took the Hint, says the Historian, and concluded the
Prophecy to be fulfilled. As
Virgil
did not think it proper to omit so
material a particular in the History of
Æneas
, it may be worth while to
consider with how much Judgment he has qualified it, and taken off every
thing that might have appeared improper for a Passage in an Heroick
Poem. The
who foretells it, is an Hungry
Harpy
, as the Person
who discovers it is young
Ascanius
.
Heus etiam mensas consumimus, inquit Inlus!
Such an observation, which is beautiful in the Mouth of a Boy, would
have been ridiculous from any other of the Company. I am apt to think
that the changing of the
Trojan
Fleet into Water-Nymphs which is the
most violent Machine in the whole
Æneid
, and has given offence to
several Criticks, may be accounted for the same way.
Virgil
himself,
before he begins that Relation, premises, that what he was going to tell
appeared incredible, but that it was justified by Tradition. What
further confirms me that this Change of the Fleet was a celebrated
Circumstance in the History of
Æneas
, is, that
Ovid
has given place to
the same Metamorphosis in his Account of the heathen Mythology.
None of the Criticks I have met with having considered the Fable of the
Æneid
in this Light, and taken notice how the Tradition, on which it was
founded, authorizes those Parts in it which appear the most
exceptionable; I hope the length of this Reflection will not make it
unacceptable to the curious Part of my Readers.
The History, which was the Basis of
Milton's
Poem, is still shorter than
either that of the
Iliad
or
Æneid
. The Poet has likewise taken care to
insert every Circumstance of it in the Body of his Fable. The ninth
Book, which we are here to consider, is raised upon that brief Account
in Scripture, wherein we are told that the Serpent was more subtle than
any Beast of the Field, that he tempted the Woman to eat of the
forbidden Fruit, that she was overcome by this Temptation, and that
Adam
followed her Example. From these few Particulars,
Milton
has formed one
of the most Entertaining Fables that Invention ever produced. He has
disposed of these several Circumstances among so many beautiful and
natural Fictions of his own, that his whole Story looks only like a
Comment upon sacred Writ, or rather seems to be a full and compleat
Relation of what the other is only an Epitome. I have insisted the
longer on this Consideration, as I look upon the Disposition and
Contrivance of the Fable to be the principal Beauty of the ninth Book,
which has more Story in it, and is fuller of Incidents, than any other
in the whole Poem.
Satan's
traversing the Globe, and still keeping
within the Shadow of the Night, as fearing to be discovered by the Angel
of the Sun, who had before detected him, is one of those beautiful
Imaginations with which he introduces this his second Series of
Adventures. Having
the Nature of every Creature, and found out
one which was the most proper for his Purpose, he again returns to
Paradise; and, to avoid Discovery, sinks by Night with a River that ran
under the Garden, and rises up again through a Fountain that
issued
from it by the Tree of Life. The Poet, who, as we have before taken
notice, speaks as little as possible in his own Person, and, after the
Example of
Homer
, fills every Part of his Work with Manners and
Characters, introduces a Soliloquy of this infernal Agent, who was thus
restless in the Destruction of Man. He is then describ'd as gliding
through the Garden, under the resemblance of a Mist, in order to find
out that Creature in which he design'd to tempt our first Parents. This
Description has something in it very Poetical and Surprizing.
So saying, through each Thicket Dank or Dry,
Like a black Mist, low creeping, he held on
His Midnight Search, where soonest he might find
The Serpent: him fast sleeping soon he found
In Labyrinth of many a Round self-roll'd,
His Head the midst, well stor'd with subtle Wiles.
The Author afterwards gives us a Description of the Morning, which is
wonderfully suitable to a Divine Poem, and peculiar to that first Season
of Nature: He represents the Earth, before it was curst, as a great
Altar, breathing out its Incense from all Parts, and sending up a
pleasant Savour to the Nostrils of its Creator; to which he adds a noble
Idea of
Adam
and
Eve
, as offering their Morning Worship, and filling up
the Universal Consort of Praise and Adoration.
Now when as sacred Light began to dawn
In Eden on the humid Flowers, that breathed
Their Morning Incense, when all things that breathe
From th' Earth's great Altar send up silent Praise
To the Creator, and his Nostrils fill
With grateful Smell; forth came the human Pair,
And join'd their vocal Worship to the Choir
Of Creatures wanting Voice—
The
which follows between our two first Parents, is represented
with great Art: It
proceeds
from a Difference of Judgment, not of
Passion, and is managed with Reason, not with Heat: It is such a Dispute
as we may suppose might have happened in Paradise, had Man continued
Happy and Innocent. There is a great Delicacy in the Moralities which
are interspersed in
Adam's
Discourse, and which the most ordinary Reader
cannot but take notice of. That Force of Love which the Father of
Mankind so finely describes in the eighth Book, and which is inserted in
my last Saturday's Paper, shews it self here in many fine Instances: As
in those fond Regards he cast towards
Eve
at her parting from him.
Her long with ardent Look his Eye pursued
Delighted, but desiring more her stay:
Oft he to her his Charge of quick return
Repeated; she to him as oft engaged
To be return'd by noon amid the Bower.
In his Impatience and Amusement during her Absence
—Adam the while,
Waiting desirous her return, had wove
Of choicest Flowers a Garland, to adorn
Her Tresses, and her rural Labours crown:
As Reapers oft are wont their Harvest Queen.
Great Joy he promised to his thoughts, and new
Solace in her return, so long delay'd.
But particularly in that passionate Speech, where seeing her
irrecoverably lost, he resolves to perish with her rather than to live
without her.
—Some cursed Fraud
Or Enemy hath beguil'd thee, yet unknown,
And me with thee hath ruin'd; for with thee
Certain my Resolution is to die!
How can I live without thee; how forego
Thy sweet Converse and Love so dearly join'd,
To live again in these wild Woods forlorn?
Should God create another Eve, and I
Another Rib afford, yet loss of thee
Would never from my Heart! no, no! I feel
The Link of Nature draw me: Flesh of Flesh,
Bone of my Bone thou art, and from thy State
Mine never shall be parted, Bliss or Woe!
The Beginning of this Speech, and the Preparation to it, are animated
with the same Spirit as the Conclusion, which I have here quoted.
The several Wiles which are put in practice by the Tempter, when he
found
Eve
separated from her Husband, the many pleasing Images of Nature
which are intermix'd in this part of the Story, with its gradual and
regular Progress to the fatal Catastrophe, are so very remarkable that
it would be superfluous to point out their respective Beauties.
I have avoided mentioning any particular Similitudes in my Remarks on
this great Work, because I have given a general Account of them in my
Paper on the first Book. There is one, however, in this part of the
Poem, which I shall here quote as it is not only very beautiful, but the
closest of any in the whole Poem. I mean that where the Serpent is
describ'd as rolling forward in all his Pride, animated by the evil
Spirit, and conducting
Eve
to her Destruction, while
Adam
was at too
great a distance from her to give her his Assistance. These several
Particulars are all of them wrought into the following Similitude.
—Hope elevates, and Joy
Brightens his Crest; as when a wandering Fire,
Compact of unctuous Vapour, which the Night
Condenses, and the Cold invirons round,
Kindled through Agitation to a Flame,
(Which oft, they say, some evil Spirit attends)
Hovering and blazing with delusive Light,
Misleads th' amaz'd Night-wanderer from his Way
To Bogs and Mires, and oft through Pond or Pool,
There swallowed up and lost, from succour far.
That
Intoxication of Pleasure, with all those transient flushings
of Guilt and Joy, which the Poet represents in our first Parents upon
their eating the forbidden Fruit, to
those
flaggings of Spirits,
damps of Sorrow, and mutual Accusations which succeed it, are conceiv'd
with a wonderful Imagination, and described in very natural Sentiments.
When
Dido
in the fourth
Æneid
yielded to that fatal Temptation which
ruined her,
Virgil
tells us the Earth trembled, the Heavens were filled
with Flashes of Lightning, and the Nymphs howled upon the Mountain-Tops.
Milton
, in the same poetical Spirit, has described all Nature as
disturbed upon
Eve's
eating the forbidden Fruit.
So saying, her rash Hand in evil hour
Forth reaching to the Fruit, she pluckt, she eat:
Earth felt the wound, and Nature from her Seat
Sighing, through all her Works gave signs of Woe
That all was lost—
Upon Adam's falling into the same Guilt, the whole Creation appears a
second time in Convulsions.
—He scrupled not to eat
Against his better knowledge; not deceiv'd,
But fondly overcome with female Charm.
Earth trembled from her Entrails, as again
In Pangs, and Nature gave a second Groan,
Sky lowred, and muttering Thunder, some sad Drops
Wept at compleating of the mortal Sin—
As all Nature suffer'd by the Guilt of our first Parents, these Symptoms
of Trouble and Consternation are wonderfully imagined, not only as
Prodigies, but as Marks of her Sympathizing in the Fall of Man.
Adam's
Converse with
Eve
, after having eaten the forbidden Fruit, is an
exact Copy of that between
Jupiter
and
Juno
in the fourteenth
Iliad
.
Juno
approaches
Jupiter
with the Girdle which she had received
from
Venus
; upon which he tells her, that she appeared more charming and
desirable than she
done before, even when their Loves were at the
highest. The Poet afterwards describes them as reposing on a Summet of
Mount
Ida
, which produced under them a Bed of Flowers, the Lotos, the
Crocus, and the Hyacinth; and concludes his Description with their
falling asleep.
Let the Reader compare this with the following Passage in
Milton
, which
begins with
Adam's
Speech to
Eve
.
For never did thy Beauty, since the Day
I saw thee first and wedded thee, adorn'd
With all Perfections, so enflame my Sense
With ardor to enjoy thee, fairer now
Than ever, Bounty of this virtuous Tree.
So said he, and forbore not Glance or Toy
Of amorous Intent, well understood
Of Eve, whose Eye darted contagious Fire.
Her hand he seiz'd, and to a shady Bank
Thick over-head with verdant Roof embower'd,
He led her nothing loth: Flow'rs were the Couch,
Pansies, and Violets, and Asphodel,
And Hyacinth, Earth's freshest softest Lap.
There they their fill of Love, and Love's disport,
Took largely, of their mutual Guilt the Seal,
The Solace of their Sin, till dewy Sleep
Oppress'd them—
As no Poet seems ever to have studied
Homer
more, or to have more
resembled him in the Greatness of Genius than
Milton
, I think I should
have given but a very imperfect Account of his Beauties, if I had not
observed the most remarkable Passages which look like Parallels in these
two great Authors. I might, in the course of these criticisms, have
taken notice of many particular Lines and Expressions which are
translated from the
Greek
Poet; but as I thought this would have
appeared too minute and over-curious, I have purposely omitted them. The
greater Incidents, however, are not only set off by being shewn in the
same Light with several of the same nature in
Homer
, but by that means
may be also guarded against the Cavils of the Tasteless or Ignorant.
In the first book of his Roman Antiquities.
Dionysius says that the prophecy was either, as some write,
given at Dodous, or, as others say, by a Sybil, and the exclamation was
by one of the sons of Æneas, as it is related; or he was some other of
his comrades.
run
arises
that
ever had
Contents
|
Monday, April 14, 1712 |
Steele |
Si ad honestatem nati sumus, ea aut sola expetenda est, aut certe omni
pondere gravior est habenda quam reliqua omnia.
Tull.

Will. Honeycomb
was complaining to me yesterday, that the Conversation
of the Town is so altered of late Years, that a fine Gentleman is at a
loss for Matter to start Discourse, as well as unable to fall in with
the Talk he generally meets with.
Will
. takes notice, that there is now
an Evil under the Sun which he supposes to be entirely new, because not
mentioned by any Satyrist or Moralist in any Age: 'Men, said he, grow
Knaves sooner than they ever did since the Creation of the World before.
If you read the Tragedies of the last Age, you find the artful Men and
Persons of Intrigue, are advanced very far in Years, and beyond the
Pleasures and Sallies of Youth; but now
Will
. observes, that the Young
have taken in the Vices of the Aged, and you shall have a Man of Five
and Twenty crafty, false, and intriguing, not ashamed to over-reach,
cozen, and beguile. My Friend adds, that till about the latter end of
King
Charles's
Reign, there was not a Rascal of any Eminence under
Forty: In the Places of Resort for Conversation, you now hear nothing
but what relates to the improving Men's Fortunes, without regard to the
Methods toward it. This is so fashionable, that young Men form
themselves upon a certain Neglect of every thing that is candid, simple,
and worthy of true Esteem; and affect being yet worse than they are, by
acknowledging in their general turn of Mind and Discourse, that they
have not any remaining Value for true Honour and Honesty; preferring the
Capacity of being Artful to gain their Ends, to the Merit of despising
those Ends when they come in competition with their Honesty. All this is
due to the very silly Pride that generally prevails, of being valued for
the Ability of carrying their Point; in a word, from the Opinion that
shallow and inexperienced People entertain of the short-liv'd Force of
Cunning. But I
, before I enter upon the various Faces which Folly
cover'd with Artifice puts on to impose upon the Unthinking, produce a
great Authority
for asserting, that nothing but Truth and Ingenuity
has any lasting good Effect, even upon a Man's Fortune and Interest.
'Truth and Reality have all the Advantages of Appearance, and many more.
If the Shew of any thing be good for any thing, I am sure Sincerity is
better: For why does any Man dissemble, or seem to be that which he is
not, but because he thinks it good to have such a Quality as he pretends
to? for to counterfeit and dissemble, is to put on the Appearance of
some real Excellency. Now the best way in the World for a Man to seem to
be any thing, is really to be what he would seem to be. Besides that it
is many times as troublesome to make good the Pretence of a good
Quality, as to have it; and if a Man have it not, it is ten to one but
he is discover'd to want it, and then all his Pains and Labour to seem
to have it is lost. There is something unnatural in Painting, which a
skillful Eye will easily discern from native Beauty and Complexion.'
'It is hard to personate and act a Part long; for where Truth is not at
the bottom, Nature will always be endeavouring to return, and will peep
out and betray her self one time or other. Therefore if any Man think it
convenient to seem good, let him be so indeed, and then his Goodness
will appear to every body's Satisfaction; so that upon all accounts
Sincerity is true Wisdom. Particularly as to the Affairs of this World,
Integrity hath many Advantages over all the fine and artificial ways of
Dissimulation and Deceit; it is much the plainer and easier, much the
safer and more secure way of dealing in the World; it has less of
Trouble and Difficulty, of Entanglement and Perplexity, of Danger and
Hazard in it; it is the shortest and nearest way to our End, carrying us
thither in a straight line, and will hold out and last longest. The Arts
of Deceit and Cunning do continually grow weaker and less effectual and
serviceable to them that use them; whereas Integrity gains Strength by
use, and the more and longer any Man practiseth it, the greater Service
it does him, by confirming his Reputation and encouraging those with
whom he hath to do, to repose the greatest Trust and Confidence in him,
which is an unspeakable Advantage in the Business and Affairs of Life.'
'Truth is always consistent with it self, and needs nothing to help it
out; it is always near at hand, and sits upon our Lips, and is ready to
drop out before we are aware: whereas a Lye is troublesome, and sets a
Man's Invention upon the rack, and one Trick needs a great many more to
make it good. It is like building upon a false Foundation, which
continually stands in need of Props to shoar it up, and proves at last
more chargeable, than to have raised a substantial Building at first
upon a true and solid Foundation; for Sincerity is firm and substantial,
and there is nothing hollow and unsound in it, and because it is plain
and open, fears no Discovery; of which the Crafty Man is always in
danger, and when he thinks he walks in the dark, all his Pretences are
so transparent, that he that runs may read them; he is the last Man that
finds himself to be found out, and whilst he takes it for granted that
he makes Fools of others, he renders himself ridiculous.
'Add to all this, that Sincerity is the most compendious Wisdom, and an
excellent Instrument for the speedy dispatch of Business; it creates
Confidence in those we have to deal with, saves the Labour of many
Enquiries, and brings things to an issue in few Words: It is like
travelling in a plain beaten Road, which commonly brings a Man sooner to
his Journeys End than By-ways, in which Men often lose themselves. In a
word, whatsoever Convenience may be thought to be in Falshood and
Dissimulation, it is soon over; but the Inconvenience of it is
perpetual, because it brings a Man under an everlasting Jealousie and
Suspicion, so that he is not believed when he speaks Truth, nor trusted
when perhaps he means honestly. When a Man hath once forfeited the
Reputation of his Integrity, he is set fast, and nothing will then serve
his turn, neither Truth nor Falshood.
'And I have often thought, that God hath in his great Wisdom hid from Men
of false and dishonest Minds the wonderful Advantages of Truth and
Integrity to the Prosperity even of our worldly Affairs; these Men are
so blinded by their Covetousness and Ambition, that they cannot look
beyond a present Advantage, nor forbear to seize upon it, tho' by Ways
never so indirect; they cannot see so far as to the remote Consequences
of a steady Integrity, and the vast Benefit and Advantages which it will
bring a Man at last. Were but this sort of Men wise and clear-sighted
enough to discern this, they would be honest out of very Knavery, not
out of any Love to Honesty and Virtue, but with a crafty Design to
promote and advance more effectually their own Interests; and therefore
the Justice of the Divine Providence hath hid this truest Point of
Wisdom from their Eyes, that bad Men might not be upon equal Terms with
the Just and Upright, and serve their own wicked Designs by honest and
lawful Means.
'Indeed, if a Man were only to deal in the World for a Day, and should
never have occasion to converse more with Mankind, never more need their
good Opinion or good Word, it were then no great Matter (speaking as to
the Concernments of this World) if a Man spent his Reputation all at
once, and ventured it at one throw: But if he be to continue in the
World, and would have the Advantage of Conversation whilst he is in it,
let him make use of Truth and Sincerity in all his Words and Actions;
for nothing but this will last and hold out to the end; all other Arts
will fail, but Truth and Integrity will carry a Man through, and bear
him out to the last.'
T.
Archbishop Tilotson's
Sermons
, Vol. II., Sermon I (folio
edition). Italics in first issue.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 15, 1712 |
Budgell |
—In tenui labor—
Virg.

The Gentleman who obliges the World in general, and me in particular,
with his Thoughts upon Education, has just sent me the following Letter.
Sir,
I take the Liberty to send you a fourth Letter upon the Education of
Youth: In my last I gave you my Thoughts about some particular Tasks
which I conceivd it might not be amiss to use with their usual
Exercises, in order to give them an early Seasoning of Virtue; I shall
in this propose some others, which I fancy might contribute to give
them a right turn for the World, and enable them to make their way in
it.
The Design of Learning is, as I take it, either to render a Man an
agreeable Companion to himself, and teach him to support Solitude with
Pleasure, or if he is not born to an Estate, to supply that Defect,
and furnish him with the means of acquiring one. A Person who applies
himself to Learning with the first of these Views may be said to study
for Ornament, as he who proposes to himself the second, properly
studies for Use. The one does it to raise himself a Fortune, the other
to set off that which he is already possessed of. But as far the
greater part of Mankind are included in the latter Class, I shall only
propose some Methods at present for the Service of such who expect to
advance themselves in the World by their Learning: In order to which,
I shall premise, that many more Estates have been acquird by little
Accomplishments than by extraordinary ones; those Qualities which make
the greatest Figure in the Eye of the World, not being always the most
useful in themselves, or the most advantageous to their Owners.
The Posts which require Men of shining and uncommon Parts to discharge
them, are so very few, that many a great Genius goes out of the World
without ever having had an opportunity to exert it self; whereas
Persons of ordinary Endowments meet with Occasions fitted to their
Parts and Capacities every day in the common Occurrences of Life.'
'I
am acquainted with two Persons who were formerly School-fellows
1,
and have been good Friends ever since. One of them was not only
thought an impenetrable Block-head at School, but still maintain'd his
Reputation at the University; the other was the Pride of his Master,
and the most celebrated Person in the College of which he was a
Member. The Man of Genius is at present buried in a Country Parsonage
of eightscore Pounds a year; while the other, with the bare Abilities
of a common Scrivener, has got an Estate of above an hundred thousand
Pounds.'
'I fancy from what I have said it will almost appear a doubtful Case
to many a wealthy Citizen, whether or no he ought to wish his Son
should be a great Genius; but this I am sure of, that nothing is more
absurd than to give a Lad the Education of one, whom Nature has not
favour'd with any particular Marks of Distinction.'
'The fault therefore of our Grammar-Schools is, that every Boy is
pushed on to Works of Genius; whereas it would be far more
advantageous for the greatest part of them to be taught such little
practical Arts and Sciences as do not require any great share of Parts
to be Master of them, and yet may come often into play during the
course of a Man's Life.'
'Such are all the Parts of Practical Geometry. I have known a Man
contract a Friendship with a Minister of State, upon cutting a Dial in
his Window; and remember a Clergyman who got one of the best Benefices
in the West of England, by setting a Country Gentleman's Affairs in
some Method, and giving him an exact Survey of his Estate.'
'While I am upon this Subject, I cannot forbear mentioning a
Particular which is of use in every Station of Life, and which
methinks every Master should teach his Scholars. I mean the writing of
English Letters. To this End, instead of perplexing them with
Latin
Epistles, Themes and Verses, there might be a punctual Correspondence
established between two Boys, who might act in any imaginary Parts of
Business, or be allowd sometimes to give a range to their own Fancies,
and communicate to each other whatever Trifles they thought fit,
provided neither of them ever fail'd at the appointed time to answer
his Correspondent's Letter.
I believe I may venture to affirm, that the generality of Boys would
find themselves more advantaged by this Custom, when they come to be
Men, than by all the
Greek and
Latin their Masters can teach them in
seven or eight Years.
The want of it is very visible in many learned Persons, who, while
they are admiring the Styles of
Demosthenes or
Cicero, want Phrases to
express themselves on the most common Occasions. I have seen a Letter
from one of these
Latin Orators, which would have been deservedly
laughd at by a common Attorney.
Under this Head of Writing I cannot omit Accounts and Short-hand,
which are learned with little pains, and very properly come into the
number of such Arts as I have been here recommending.
You must doubtless, Sir, observe that I have hitherto chiefly insisted
upon these things for such Boys as do not appear to have any thing
extraordinary in their natural Talents, and consequently are not
qualified for the finer Parts of Learning; yet I believe I might carry
this Matter still further, and venture to assert that a Lad of Genius
has sometimes occasion for these little Acquirements, to be as it were
the forerunners of his Parts, and to introduce
him2 into the
World.
History is full of Examples of Persons, who tho they have had the
largest Abilities, have been obliged to insinuate themselves into the
Favour of great Men by these trivial Accomplishments; as the compleat
Gentleman, in some of our modern Comedies, makes his first Advances to
his Mistress under the disguise of a Painter or a Dancing-Master.
The Difference is, that in a Lad of Genius these are only so many
Accomplishments, which in another are Essentials; the one diverts
himself with them, the other works at them. In short, I look upon a
great Genius, with these little Additions, in the same Light as I
regard the Grand Signior, who is obliged, by an express Command in the
Alcoran, to learn and practise some Handycraft Trade. Tho' I need not
have gone for my Instance farther than Germany, where several Emperors
have voluntarily done the same
thing.
Leopold the last
3, worked in
Wood; and I have heard there are several handycraft Works of his
making to be seen at
Vienna so neatly turned, that the best Joiner in
Europe might safely own them, without any disgrace to his Profession.
I would not be thought, by any thing I have said, to be against
improving a Boy's Genius to the utmost pitch it can be carried. What I
would endeavour to shew in this Essay is, that there may be Methods
taken, to make Learning advantageous even to the meanest Capacities.
I am,
Sir,
Yours, &c.
X.
Perhaps Swift and his old schoolfellow, Mr. Stratford, the
Hamburgh merchant.
'Stratford is worth a plumb, and is now lending the Government
£40,000; yet we were educated together at the same school and
university.'
Journal
to Stella, Sept. 14, 1710.
them
Leopold the last was also Leopold the First. He died May 6,
1705, and was succeeded by his eldest son, Joseph, who died while the
Spectator
was being issued, and had now been followed by his brother,
the Archduke Charles, whose claim to the crown of Spain England had been
supporting, when his accession to the German throne had not seemed
probable. His coronation as Charles VI. was, therefore, one cause of the
peace. Leopold, born in 1640, and educated by the Jesuits, became
Emperor in 1658, and reigned 49 years. He was an adept in metaphysics
and theology, as well as in wood-turning, but a feeble and oppressive
ruler, whose empire was twice saved for him; by Sobiesld from the Turks,
and from the French by Marlborough.
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 16, 1712 |
Steele |
—Cum magnis virtutibus affers
Grande supercilium—
Juv.

Mr.
Spectator,
You have in some of your Discourses describ'd most sorts of Women in
their distinct and proper Classes, as the Ape, the Coquet, and many
others; but I think you have never yet said anything of a Devotée. A
Devotée is one of those who disparage Religion by their indiscreet and
unseasonable introduction of the Mention of Virtue on all Occasion
s:
She professes she is what nobody ought to doubt she is; and betrays
the Labour she is put to, to be what she ought to be with Chearfulness
and Alacrity. She lives in the World, and denies her self none of the
Diversions of it, with a constant Declaration how insipid all things
in it are to her. She is never her self but at Church; there she
displays her Virtue, and is so fervent in her Devotions, that I have
frequently seen her Pray her self out of Breath. While other young
Ladies in the House are dancing, or playing at Questions and Commands,
she reads aloud in her Closet. She says all Love is ridiculous, except
it be Celestial; but she speaks of the Passion of one Mortal to
another with too much Bitterness, for one that had no Jealousy mixed
with her Contempt of it. If at any time she sees a Man warm in his
Addresses to his Mistress, she will lift up her Eyes to Heaven, and
cry, What Nonsense is that Fool talking? Will the Bell never ring for
Prayers? We have an eminent Lady of this Stamp in our Country, who
pretends to Amusements very much above the rest of her Sex. She never
carries a white Shock-dog with Bells under her Arm, nor a Squirrel or
Dormouse in her Pocket, but always an abridg'd Piece of Morality to
steal out when she is sure of being observ'd. When she went to the
famous Ass-Race (which I must confess was but an odd Diversion to be
encouraged by People of Rank and Figure) it was not, like other
Ladies, to hear those poor Animals bray, nor to see Fellows run naked,
or to hear Country Squires in bob Wigs and white Girdles make love at
the side of a Coach, and cry, Madam, this is dainty Weather. Thus she
described the Diversion; for she went only to pray heartily that no
body might be hurt in the Crowd, and to see if the poor Fellow's Face,
which was distorted with grinning, might any way be brought to it self
again. She never chats over her Tea, but covers her Face, and is
supposed in an Ejaculation before she taste
s a Sup. This
ostentatious Behaviour is such an Offence to true Sanctity, that it
disparages it, and makes Virtue not only unamiable, but also
ridiculous. The Sacred Writings are full of Reflections which abhor
this kind of Conduct; and a Devotée is so far from promoting Goodness,
that she deters others by her Example. Folly and Vanity in one of
these Ladies, is like Vice in a Clergyman; it does not only debase
him, but makes the inconsiderate Part of the World think the worse of
Religion.
I am,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Hotspur.
Mr.
Spectator,
'
Xenophon, in
his short Account of the
Spartan Commonwealth
1,
speaking of the Behavior of their young Men in the Streets, says,
There was so much Modesty in their Looks, that you might as soon have
turned the eyes of a Marble Statue upon you as theirs; and that in all
their Behaviour they were more modest than a Bride when put to bed
upon her Wedding-Night: This Virtue, which is always join'd to
Magnanimity, had such an influence upon their Courage, that in Battel
an Enemy could not look them in the Face, and they durst not but Die
for their Country.
'Whenever I walk into the Streets of
London and
Westminster, the
Countenances of all the young Fellows that pass by me, make me wish my
self in
Sparta; I meet with such blustering Airs, big Looks, and bold
Fronts, that to a superficial Observer would bespeak a Courage above
those
Grecians. I am arrived to that Perfection in Speculation, that I
understand the Language of the Eyes, which would be a great misfortune
to me, had I not corrected the Testiness of old Age by Philosophy.
There is scarce a Man in a red Coat who does not tell me, with a full
Stare, he's a bold Man: I see several swear inwardly at me, without
any Offence of mine, but the Oddness of my Person: I meet Contempt in
every Street, express'd in different Manners, by the scornful Look,
the elevated Eye-brow, and the swelling Nostrils of the Proud and
Prosperous. The Prentice speaks his Disrespect by an extended Finger,
and the Porter by stealing out his Tongue. If a Country Gentleman
appears a little curious in observing the Edifices, Signs, Clocks,
Coaches, and Dials, it is not to be imagined how the Polite Rabble of
this Town, who are acquainted with these Objects, ridicule his
Rusticity. I have known a Fellow with a Burden on his Head steal a
Hand down from his Load, and slily twirle the Cock of a Squire's Hat
behind him; while the Offended Person is swearing, or out of
Countenance, all the Wagg-Wits in the High-way are grinning in
applause of the ingenious Rogue that gave him the Tip, and the Folly
of him who had not Eyes all round his Head to prevent receiving it.
These things arise from a general Affectation of Smartness, Wit, and
Courage.
Wycherly somewhere
2 rallies the Pretensions this Way, by
making a Fellow say, Red Breeches are a certain Sign of Valour; and
Otway makes
a Man, to boast his Agility, trip up a Beggar on
Crutches
3. From such Hints I beg a Speculation on this Subject; in the
mean time I shall do all in the Power of a weak old Fellow in my own
Defence: for as
Diogenes, being in quest of an honest Man, sought for
him when it was broad Day-light with a Lanthorn and Candle, so I
intend for the future to walk the Streets with a dark Lanthorn, which
has a convex Chrystal in it; and if any Man stares at me, I give fair
Warning that I'll direct the Light full into his Eyes. Thus despairing
to find Men Modest, I hope by this Means to evade their Impudence,
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Sophrosunius.
T.
The Polity of Lacedæmon
and
the Polity of Athens
were
two of Xenophon's short treatises. In
the Polity of Lacedæmon
the
Spartan code of law and social discipline is, as Mr. Mure says in his
Critical History of the Language and Literature of Ancient Greece
,
'indiscriminately held up to admiration as superior in all respects to
all others. Some of its more offensive features, such as the Cryptia,
child murder, and more glaring atrocities of the Helot system, are
suppressed; while the legalized thieving, adultery, and other
unnatural practices, are placed in the most favourable or least odious
light.'
In the
Plain Dealer
, Act II. sc. I.
Novel
(a pert railing coxcomb) |
These sea captains make nothing of
dressing. But let me tell you, sir, a man by his dress, as much
as by anything, shows his wit and judgment; nay, and his
courage too. |
| Freeman |
How, his courage, Mr. Novel? |
| Novel |
Why, for example, by red breeches, tucked-up hair, or peruke, a
greasy broad belt, and now-a-days a short sword. |
In his
Friendship in Fashion
, Act III. sc. i
| Malagene |
I tell you what I did t'other Day: Faith't is as good a Jest
as ever you heard. |
| Valentine |
Pray, sir, do. |
| Malagene |
Why, walking alone, a lame Fellow follow'd me and ask'd my
Charity (which by the way was a pretty Proposition to me).
Being in one of my witty, merry Fits, I ask'd him how long he
had been in that Condition? The poor Fellow shook his Head,
and told me he was born so. But how d'ye think I served him? |
| Valentine |
Nay, the Devil knows. |
| Malagene |
I show'd my Parts, I think; for I tripp'd up both his Wooden
Legs, and walk'd off gravely about my Business. |
| Valentine |
And this you say is your way of Wit? |
| Malagene |
Ay, altogether, this and Mimickry. I'm a very good Mimick; I
can act Punchinello, Scaramoucho, Harlequin, Prince
Prettyman, or anything. I can act the rumbling of a
Wheel-barrow. |
| Valentine |
The rumbling of a Wheelbarrow! |
| Malagene |
Ay, the rumbling of a Wheelbarrow, so I say. Nay, more than
that, I can act a Sow and Pigs, Sausages a broiling, a
Shoulder of Mutton a roasting: I can act a Fly in a
Honey-pot. |
| Valentine |
That indeed must be the effect of very curious Observation. |
| Malagene |
No, hang it, I never make it my Business to observe anything,
that is Mechanick. |
Contents
|
Thursday, April 17, 1712 |
Addison |
Non ego mordaci distrinxi carmine quenquam.
Ovid.1
I have been very often tempted to write Invectives upon those who have
detracted from my Works, or spoken in derogation of my Person; but I
look upon it as a particular Happiness, that I have always hindred my
Resentments from proceeding to this extremity. I once had gone thro'
half a Satyr, but found so many Motions of Humanity rising in me towards
the Persons whom I had severely treated, that I threw it into the Fire
without ever finishing it. I have been angry enough to make several
little Epigrams and Lampoons; and after having admired them a Day or
two, have likewise committed them to the Flames. These I look upon as so
many Sacrifices to Humanity, and have receiv'd much greater Satisfaction
from the suppressing such Performances, than I could have done from any
Reputation they might have procur'd me, or from any Mortification they
might have given my Enemies, in case I had made them publick. If a Man
has any Talent in Writing, it shews a good Mind to forbear answering
Calumnies and Reproaches in the same Spirit of Bitterness with which
they are offered: But when a Man has been at some Pains in making
suitable Returns to an Enemy, and has the Instruments of Revenge in his
Hands, to let drop his Wrath, and stifle his Resentments, seems to have
something in it Great and Heroical. There is a particular Merit in such
a way of forgiving an Enemy; and the more violent and unprovok'd the
Offence has been, the greater still is the Merit of him who thus
forgives it.
I never
with a Consideration that is more finely spun, and what has
better pleased me, than one in
Epictetus
, which places an Enemy in a
new Light, and gives us a View of him altogether different from that in
which we are used to regard him. The Sense of it is as follows: Does a
Man reproach thee for being Proud or Ill-natured, Envious or Conceited,
Ignorant or Detracting? Consider with thy self whether his Reproaches
are true; if they are not, consider that thou art not the Person whom he
reproaches, but that he reviles an Imaginary Being, and perhaps loves
what thou really art, tho' he hates what thou appearest to be. If his
Reproaches are true, if thou art the envious ill-natur'd Man he takes
thee for, give thy self another Turn, become mild, affable and obliging,
and his Reproaches of thee naturally cease: His Reproaches may indeed
continue, but thou art no longer the Person whom he reproaches.
I often apply this Rule to my self; and when I hear of a Satyrical
Speech or Writing that is aimed at me, I examine my own Heart, whether I
deserve it or not. If I bring in a Verdict against my self, I endeavour
to rectify my Conduct for the future in those particulars which have
drawn the Censure upon me; but if the whole Invective be grounded upon a
Falsehood, I trouble my self no further about it, and look upon my Name
at the Head of it to signify no more than one of those fictitious Names
made use of by an Author to introduce an imaginary Character. Why should
a Man be sensible of the Sting of a Reproach, who is a Stranger to the
Guilt that is implied in it? or subject himself to the Penalty, when he
knows he has never committed the Crime? This is a Piece of Fortitude,
which every one owes to his own Innocence, and without which it is
impossible for a Man of any Merit or Figure to live at Peace with
himself in a Country that abounds with Wit and Liberty.
famous Monsieur
Balzac
, in a Letter to the Chancellor of
France
,
who had prevented the Publication of a Book against him, has the
following Words, which are a likely Picture of the Greatness of Mind so
visible in the Works of that Author. If it was a new thing, it may be I
should not be displeased with the Suppression of the first Libel that
should abuse me; but since there are enough of 'em to make a small
Library, I am secretly pleased to see the number increased, and take
delight in raising a heap of Stones that Envy has cast at me without
doing me any harm.
The Author here alludes to those Monuments of the
Eastern
Nations, which
were Mountains of Stones raised upon the dead Body by Travellers, that
used to cast every one his Stone upon it as they passed by. It is
certain that no Monument is so glorious as one which is thus raised by
the Hands of Envy. For my Part, I admire an Author for such a Temper of
Mind as enables him to bear an undeserved Reproach without Resentment,
more than for all the Wit of any the finest Satirical Reply.
Thus far I thought necessary to explain my self in relation to those who
have animadverted on this Paper, and to shew the Reasons why I have not
thought fit to return them any formal Answer. I must further add, that
the Work would have been of very little use to the Publick, had it been
filled with personal Reflections and Debates; for which Reason I have
never once turned out of my way to observe those little Cavils which
have been made against it by Envy or Ignorance. The common Fry of
Scriblers, who have no other way of being taken Notice of but by
attacking what has gain'd some Reputation in the World, would have
furnished me with Business enough, had they found me dispos'd to enter
the Lists with them.
I shall conclude with the Fable of
Boccalini's
Traveller, who was so
pester'd with the Noise of Grasshoppers in his Ears, that he alighted
from his Horse in great Wrath to kill them all. This, says the Author,
was troubling himself to no manner of purpose: Had he pursued his
Journey without taking notice of them, the troublesome Insects would
have died of themselves in a very few Weeks, and he would have suffered
nothing from them.
L.
quenquam, Nulla venenata littera mista joco est.
Ovid.
Enchiridion
, Cap. 48 and 64.
Letters and Remains
. Trans. by Sir. R. Baker (1655-8).
Contents
|
Friday1, April 18, 1712 |
Steele |
Aptissima quæque dabunt Dii,
Charior est illis homo quam sibi.
Juv.

It is owing to Pride, and a secret Affectation of a certain
Self-Existence, that the noblest Motive for Action that ever was
proposed to Man, is not acknowledged the Glory and Happiness of their
Being. The Heart is treacherous to it self, and we do not let our
Reflections go deep enough to receive Religion as the most honourable
Incentive to good and worthy Actions. It is our natural Weakness, to
flatter our selves into a Belief, that if we search into our inmost
thoughts, we find our selves wholly disinterested, and divested of any
Views arising from Self-Love and Vain-Glory. But however Spirits of
superficial Greatness may disdain at first sight to do any thing, but
from a noble Impulse in themselves, without any future Regards in this
or another Being; upon stricter Enquiry they will find, to act worthily
and expect to be rewarded only in another World, is as heroick a Pitch
of Virtue as human Nature can arrive at. If the Tenour of our Actions
have any other Motive than the Desire to be pleasing in the Eye of the
Deity, it will necessarily follow that we must be more than Men, if we
are not too much exalted in Prosperity and depressed in Adversity: But
the Christian World has a Leader, the Contemplation of whose Life and
Sufferings must administer Comfort in Affliction, while the Sense of his
Power and Omnipotence must give them Humiliation in Prosperity.
It is owing to the forbidding and unlovely Constraint with which Men of
low Conceptions act when they think they conform themselves to Religion,
as well as to the more odious Conduct of Hypocrites, that the Word
Christian does not carry with it at first View all that is Great,
Worthy, Friendly, Generous, and Heroick. The Man who suspends his Hopes
of the Reward of worthy Actions till after Death, who can bestow unseen,
who can overlook Hatred, do Good to his Slanderer, who can never be
angry at his Friend, never revengeful to his Enemy, is certainly formed
for the Benefit of Society: Yet these are so far from Heroick Virtues,
that they are but the ordinary Duties of a Christian.
When a Man with a steddy Faith looks back on the great Catastrophe of
this Day, with what bleeding Emotions of Heart must he contemplate the
Life and Sufferings of his Deliverer? When his Agonies occur to him, how
will he weep to reflect that he has often forgot them for the Glance of
a Wanton, for the Applause of a vain World, for an Heap of fleeting past
Pleasures, which are at present asking Sorrows?
How pleasing is the Contemplation of the lowly Steps our Almighty Leader
in conducting us to his heavenly Mansions! In plain and apt
Parable
, Similitude, and Allegory, our great Master enforced the
Doctrine of our Salvation; but
of his Acquaintance, instead of
receiving what they could not oppose, were offended at the Presumption
of being wiser than they
: They could not raise their little Ideas
above the Consideration of him, in those Circumstances familiar to them,
or conceive that he who appear'd not more Terrible or Pompous, should
have any thing more Exalted than themselves; he in that Place therefore
would not longer ineffectually exert a Power which was incapable of
conquering the Prepossession of their narrow and mean Conceptions.
Multitudes follow'd him, and brought him the Dumb, the Blind, the Sick,
and Maim'd; whom when their Creator had Touch'd, with a second Life they
Saw, Spoke, Leap'd, and Ran. In Affection to him, and admiration of his
Actions, the Crowd could not leave him, but waited near him till they
were almost as faint and helpless as others they brought for Succour.
had Compassion on them, and by a Miracle supplied their Necessities
.
Oh, the Ecstatic Entertainment, when they could behold their Food
immediately increase to the Distributer's Hand, and see their God in
Person Feeding and Refreshing his Creatures! Oh Envied Happiness!
why do I say Envied? as if our
God
did not still preside over our
temperate Meals, chearful Hours, and innocent Conversations.
But tho' the sacred Story is every where full of Miracles not inferior
to this, and tho' in the midst of those Acts of Divinity he never gave
the least Hint of a Design to become a Secular Prince, yet had not
hitherto the Apostles themselves any other than Hopes of worldly Power,
Preferment, Riches and Pomp;
Peter, upon an Accident of Ambition
among the Apostles, hearing his Master explain that his Kingdom was not
of this World, was so scandaliz'd
that he whom he had so long
follow'd should suffer the Ignominy, Shame, and Death which he foretold,
that he took him aside and said, Be it far from thee, Lord, this shall
not be unto thee: For which he suffered a severe Reprehension from his
Master, as having in his View the Glory of Man rather than that of God.
The great Change of things began to draw near, when the Lord of Nature
thought fit as a Saviour and Deliverer to make his publick Entry into
Jerusalem
with more than the Power and Joy, but none of the Ostentation
and Pomp of a Triumph; he came Humble, Meek, and Lowly: with an unfelt
new Ecstasy, Multitudes strewed his Way with Garments and
Olive-Branches, Crying with loud Gladness and Acclamation,
Hosannah
to
the Son of
David
, Blessed is he that cometh in the name of the Lord! At
this great King's Accession to his Throne, Men were not Ennobled, but
Sav'd; Crimes were not Remitted, but Sins Forgiven; he did not bestow
Medals, Honours, Favours, but Health, Joy, Sight, Speech. The first
Object the Blind ever saw, was the Author of Sight; while the Lame Ran
before, and the Dumb repeated the
Hosannah
. Thus attended, he Entered
into his own House, the sacred Temple, and by his Divine Authority
expell'd Traders and Worldlings that profaned it; and thus did he, for a
time, use a great and despotic Power, to let Unbelievers understand,
that 'twas not Want of, but Superiority to all Worldly Dominion, that
made him not exert it. But is this then the Saviour? is this the
Deliverer?
this Obscure
Nazarene
command
Israel
, and sit on the
Throne of
David
?
proud and disdainful Hearts, which were
petrified
with the Love and Pride of this World, were impregnable to
the Reception of so mean a Benefactor, and were now enough exasperated
with Benefits to conspire his Death. Our Lord was sensible of their
Design, and prepared his Disciples for it, by recounting to 'em now more
distinctly what should befal him; but
Peter
with an ungrounded
Resolution, and in a Flush of Temper, made a sanguine Protestation, that
tho' all Men were offended in him, yet would not he be offended. It was
a great Article of our Saviour's Business in the World, to bring us to a
Sense of our Inability, without God's Assistance, to do any thing great
or good; he therefore told
Peter
, who thought so well of his Courage and
Fidelity, that they would both fail him, and even he should deny him
Thrice that very Night.
But what Heart can conceive, what Tongue utter the Sequel? Who is that
yonder buffeted, mock'd, and spurn'd? Whom do they drag like a Felon?
Whither do they carry my Lord, my King, my Saviour, and my God? And will
he die to Expiate those very Injuries? See where they have nailed the
Lord and Giver of Life! How his Wounds blacken, his Body writhes, and
Heart heaves with Pity and with Agony! Oh Almighty Sufferer, look down,
look down from thy triumphant Infamy: Lo he inclines his Head to his
sacred Bosom! Hark, he Groans! see, he Expires! The Earth trembles, the
Temple rends, the Rocks burst, the Dead Arise: Which are the Quick?
Which are the Dead? Sure Nature, all Nature is departing with her
Creator.
T.
Good Friday.
From the words 'In plain and apt parable' to the end, this
paper is a reprint of the close of the second chapter of Steele's
Christian Hero
, with the variations cited in the next six notes. The
C.
H.
is quoted from the text appended to the first reprint of the
Tatler
,
in 1711.
'—wiser than they: Is not this the Carpenter's Son, is not his Mother
called Mary, his Brethren, James, Joseph, Simon and Judas? They could
not—'
Christian Hero.
'He had compassion on 'em, commanded 'em to be seated, and with Seven
Loaves, and a few little Fishes, Fed four thousand Men, besides Women
and Children: Oh, the Ecstatic—'
Christian Hero.
Good God
in first Issue and in
Christian Hero
.
In the
Christian Hero
this passage was:
'become a Secular Prince, or in a Forcible or Miraculous Manner to
cast off the Roman Yoke they were under, and restore again those
Disgraced Favourites of Heav'n, to its former Indulgence, yet had not
hitherto the Apostles themselves (so deep set is our Natural Pride)
any other than hopes of worldly Power, Preferment, Riches and Pomp:
For Peter, who it seems ever since he left his Net and his Skiff,
Dreamt of nothing but being a great Man, was utterly undone to hear
our Saviour explain to 'em that his Kingdom was not of this World; and
was so scandalized—'
'Throne of David? Such were the unpleasant Forms that ran in the
Thoughts of the then Powerful in Jerusalem, upon the most Truly
Glorious Entry that ever Prince made; for there was not one that
followed him who was not in his Interest; their Proud—'
Christian Hero
.
'Putrified with the—'
Christian Hero.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Quis talia fando
Temperet à lachrymis?
Virg.
1
The Tenth Book of
Paradise Lost
has a greater variety of Persons in it
than any other in the whole Poem. The Author upon the winding up of his
Action introduces all those who had any Concern in it, and shews with
great Beauty the Influence which it had upon each of them. It is like
the last Act of a well-written Tragedy, in which all who had a part in
it are generally drawn up before the Audience, and represented under
those Circumstances in which the Determination of the Action places
them.
I shall therefore consider this Book under four Heads, in relation to
the Celestial, the Infernal, the Human, and the Imaginary Persons, who
have their respective Parts allotted in it.
To begin with the Celestial Persons: The Guardian Angels of Paradise are
described as returning to Heaven upon the Fall of Man, in order to
approve their Vigilance; their Arrival, their Manner of Reception, with
the Sorrow which appear'd in themselves, and in those Spirits who are
said to Rejoice at the Conversion of a Sinner, are very finely laid
together in the following Lines.
Up into Heaven from Paradise in haste
Th' Angelick Guards ascended, mute and sad
For Man; for of his State by this they knew:
Much wondering how the subtle Fiend had stol'n
Entrance unseen. Soon as th' unwelcome News
From Earth arriv'd at Heaven-Gate, displeased
All were who heard: dim Sadness did not spare
That time Celestial Visages; yet mixt
With Pity, violated not their Bliss.
About the new-arriv'd, in multitudes
Th' Ethereal People ran, to hear and know
How all befel: They tow'rds the Throne supreme
Accountable made haste to make appear
With righteous Plea, their utmost vigilance,
And easily approved; when the Most High
Eternal Father, from his secret cloud,
Amidst in thunder utter'd thus his voice.
The same Divine Person, who in the foregoing Parts of this Poem
interceded for our first Parents before their Fall, overthrew the Rebel
Angels, and created the World, is now represented as descending to
Paradise, and pronouncing Sentence upon the three Offenders. The Cool of
the Evening, being a Circumstance with which Holy Writ introduces this
great Scene, it is poetically described by our Author, who has also kept
religiously to the Form of Words, in which the three several Sentences
were passed upon
Adam
,
Eve
, and the Serpent. He has rather chosen to
neglect the Numerousness of his Verse, than to deviate from those
Speeches which are recorded on this great occasion. The Guilt and
Confusion of our first Parents standing naked before their Judge, is
touched with great Beauty. Upon the Arrival of
Sin
and
Death
into the
Works of the Creation, the Almighty is again introduced as speaking to
his Angels that surrounded him.
See! with what heat these Dogs of Hell advance,
To waste and havock yonder World, which I
So fair and good created; &c.
The following Passage is formed upon that glorious Image in Holy Writ,
which compares the Voice of an innumerable Host of Angels, uttering
Hallelujahs
, to the Voice of mighty Thunderings, or of many Waters.
He ended, and the Heavenly Audience loud
Sung Hallelujah, as the sound of Seas,
Through Multitude that sung: Just are thy Ways,
Righteous are thy Decrees in all thy Works,
Who can extenuate thee?—
Tho' the Author in the whole Course of his Poem, and particularly in the
Book we are now examining, has infinite Allusions to Places of
Scripture, I have only taken notice in my Remarks of such as are of a
Poetical Nature, and which are woven with great Beauty into the Body of
this Fable. Of this kind is that Passage in the present Book, where
describing
Sin
and
Death
as marching thro' the Works of Nature he adds,
—Behind her Death
Close following pace for pace, not mounted yet
On his pale Horse—
Which alludes to that Passage in Scripture, so wonderfully poetical, and
terrifying to the Imagination.
And I look'd, and behold a pale Horse,
and his Name that sat on him was Death, and Hell followed with him: and
Power was given unto them over the fourth Part of the Earth, to kill
with Sword, and with Hunger, and with Sickness, and with the Beasts of
the Earth.
Under this first Head of Celestial Persons we must
likewise take notice of the Command which the Angels receiv'd, to
produce the several Changes in Nature, and sully the Beauty of the
Creation. Accordingly they are represented as infecting the Stars and
Planets with malignant Influences, weakning the Light of the Sun,
bringing down the Winter into the milder Regions of Nature, planting
Winds and Storms in several Quarters of the Sky, storing the Clouds with
Thunder, and in short, perverting the Whole Frame of the Universe to the
Condition of its criminal Inhabitants. As this is a noble Incident in
the Poem, the following Lines, in which we see the Angels heaving up the
Earth, and placing it in a different Posture to the Sun from what it had
before the Fall of Man, is conceived with that sublime Imagination which
was so peculiar to this great Author.
Some say he bid his Angels turn ascanse
The Poles of Earth twice ten Degrees and more
From the Sun's Axle; they with Labour push'd
Oblique the Centrick Globe—
We are in the second place to consider the Infernal Agents under the
view which
Milton
has given us of them in this Book. It is observed by
those who would set forth the Greatness of
Virgil's
Plan, that he
conducts his Reader thro' all the Parts of the Earth which were
discover'd in his time.
Asia, Africk
, and
Europe
are the several Scenes
of his Fable. The Plan of
Milton's
Poem is of an infinitely greater
Extent, and fills the Mind with many more astonishing Circumstances.
Satan
, having surrounded the Earth seven times, departs at length from
Paradise. We then see him steering his Course among the Constellations,
and after having traversed the whole Creation, pursuing his Voyage thro'
the Chaos, and entring into his own Infernal Dominions.
His first appearance in the Assembly of fallen Angels, is work'd up with
Circumstances which give a delightful Surprize to the Reader; but there
is no Incident in the whole Poem which does this more than the
Transformation of the whole Audience, that follows the Account their
Leader gives them of his Expedition. The gradual Change of
Satan
himself
is describ'd after
Ovid's
manner, and may vie with any of those
celebrated Transformations which are look'd upon as the most beautiful
Parts in that Poet's Works.
Milton
never fails of improving his own
Hints, and bestowing the last finishing Touches to every Incident which
is admitted into his Poem. The unexpected Hiss which rises in this
Episode, the Dimensions and Bulk of
Satan
so much superior to those of
the Infernal Spirits who lay under the same Transformation, with the
annual Change which they are supposed to suffer, are Instances of this
kind. The Beauty of the Diction is very remarkable in this whole
Episode, as I have observed in the sixth Paper of these Remarks the
great Judgment with which it was contrived.
The Parts of
Adam
and
Eve
, or the human Persons, come next under our
Consideration.
Milton's
Art is no where more shewn than in his
conducting the Parts of these our first Parents. The Representation he
gives of them, without falsifying the Story, is wonderfully contriv'd to
influence the Reader with Pity and Compassion towards them. Tho'
Adam
involves the whole Species in Misery, his Crime proceeds from a Weakness
which every Man is inclined to pardon and commiserate, as it seems
rather the Frailty of Human Nature, than of the Person who offended.
Every one is apt to excuse a Fault which he himself might have fallen
into. It was the Excess of Love for
Eve
, that ruin'd
Adam
, and his
Posterity. I need not add, that the Author is justify'd in this
Particular by many of the Fathers, and the most orthodox Writers.
Milton
has by this means filled a great part of his Poem with that kind of
Writing which the French Criticks call the Tender, and which is in a
particular manner engaging to all sorts of Readers.
Adam
and
Eve
, in the Book we are now considering, are likewise drawn
with such Sentiments as do not only interest the Reader in their
Afflictions, but raise in him the most melting Passions of Humanity and
Commiseration. When
Adam
sees the several Changes in Nature produced
about him, he appears in a Disorder of Mind suitable to one who had
forfeited both his Innocence and his Happiness; he is filled with
Horrour, Remorse, Despair; in the Anguish of his Heart he expostulates
with his Creator for having given him an unasked Existence.
Did I request thee, Maker, from my Clay
To mould me Man? did I sollicite thee
From Darkness to promote me? or here place
In this delicious Garden? As my Will
Concurr'd not to my Being, 'twere but right
And equal to reduce me to my Dust,
Desirous to resign, and render back
All I received—
He immediately after recovers from his Presumption, owns his Doom to be
just, and begs that the Death which is threatned him may be inflicted on
him.
—Why delays
His Hand to execute, what his Decree
Fix'd on this day? Why do I overlive?
Why am I mock'd with Death, and lengthened out
To deathless Pain? how gladly would I meet
Mortality my Sentence, and be Earth
Insensible! how glad would lay me down,
As in my Mother's Lap? there should I rest
And sleep secure; his dreadful Voice no more
Would thunder in my Ears: no fear of worse
To me and to my Offspring, would torment me
With cruel Expectation—
This whole Speech is full of the like Emotion, and varied with all those
Sentiments which we may suppose natural to a Mind so broken and
disturb'd. I must not omit that generous Concern which our first Father
shews in it for his Posterity, and which is so proper to affect the
Reader.
—Hide me from the Face
Of God, whom to behold was then my heighth
Of Happiness! yet well, if here would end
The Misery, I deserved it, and would bear
My own Deservings: but this will not serve;
All that I eat, or drink, or shall beget
Is propagated Curse. O Voice once heard
Delightfully, Increase and Multiply;
Now Death to hear!—
—In me all
Posterity stands curst! Fair Patrimony,
That I must leave ye, Sons! O were I able
To waste it all my self, and leave you none!
So disinherited, how would you bless
Me, now your Curse! Ah, why should all Mankind,
For one Man's Fault, thus guiltless be condemn'd,
If guiltless? But from me what can proceed
But all corrupt—
Who can afterwards behold the Father of Mankind extended upon the Earth,
uttering his midnight Complaints, bewailing his Existence, and wishing
for Death, without sympathizing with him in his Distress?
Thus Adam to himself lamented loud,
Thro' the still Night; not now, (as ere Man fell)
Wholesome, and cool, and mild, but with black Air
Accompanied, with Damps and dreadful Gloom;
Which to his evil Conscience represented
All things with double Terror. On the Ground
Outstretched he lay; on the cold Ground! and oft
Curs'd his Creation; Death as oft accus'd
Of tardy Execution—
The Part of
Eve
in this Book is no less passionate, and apt to sway the
Reader in her Favour. She is represented with great Tenderness as
approaching
Adam
, but is spurn' d from him with a Spirit of Upbraiding
and Indignation, conformable to the Nature of Man, whose Passions had
now gained the Dominion over him. The following Passage, wherein she is
described as renewing her Addresses to him, with the whole Speech that
follows it, have something in them exquisitely moving and pathetick.
He added not, and from her turned: But Eve
Not so repulst, with Tears that ceas'd not flowing,
And Tresses all disorder'd, at his feet
Fell humble; and embracing them, besought
His Peace, and thus proceeding in her Plaint.
Forsake me not thus, Adam! Witness Heav'n
What Love sincere, and Reverence in my Heart
I bear thee, and unweeting have offended,
Unhappily deceived! Thy Suppliant
I beg, and clasp thy Knees; bereave me not
(Whereon I live!) thy gentle Looks, thy Aid,
Thy Counsel, in this uttermost Distress,
My only Strength, and Stay! Forlorn of thee,
Whither shall I betake me, where subsist?
While yet we live, (scarce one short Hour perhaps)
Between us two let there be Peace, &c.
Adam's
Reconcilement to her is work'd up in the same Spirit of
Tenderness.
Eve
afterwards proposes to her Husband, in the Blindness of
her Despair, that to prevent their Guilt from descending upon Posterity
they should resolve to live Childless; or, if that could not be done,
they should seek their own Deaths by violent Methods. As those
Sentiments naturally engage the Reader to regard the Mother of Mankind
with more than ordinary Commiseration, they likewise contain a very fine
Moral. The Resolution of dying to end our Miseries, does not shew such a
degree of Magnanimity as a Resolution to bear them, and submit to the
Dispensations of Providence. Our Author has therefore, with great
Delicacy, represented
Eve
as entertaining this Thought, and
Adam
as
disapproving it.
We are,
the last place, to consider the Imaginary Persons, or
Death and Sin
who act a large Part in this Book. Such beautiful extended
Allegories are certainly some of the finest Compositions of Genius: but,
as, I have before observed, are not agreeable to the Nature of an
Heroick Poem. This of
Sin
and
Death
is very exquisite in its Kind, if
not considered as a Part of such a Work. The Truths contained in it are
so clear and open, that I shall not lose time in explaining them; but
shall only observe, that a Reader who knows the Strength of the
English
Tongue, will be amazed to think how the Poet could find such apt Words
and Phrases to describe the Action
s
of those two imaginary Persons,
and particularly in that Part where
Death
is exhibited as forming a
Bridge over the Chaos; a Work suitable to the Genius of
Milton
.
Since the Subject I am upon, gives me an Opportunity of speaking more at
large of such Shadowy and Imaginary Persons as may be introduced into
Heroick Poems, I shall beg leave to explain my self in a Matter which is
curious in its Kind, and which none of the Criticks have treated of. It
is certain
Homer
and
Virgil
are full of imaginary Persons, who are very
beautiful in Poetry when they are just shewn, without being engaged in
any Series of Action.
Homer
represents
Sleep
as a Person, and
ascribes a short Part to him in his
Iliad
, but we must consider that
tho' we now regard such a Person as entirely shadowy and unsubstantial,
the Heathens made Statues of him, placed him in their Temples, and
looked upon him as a real Deity. When
Homer
makes use of other such
Allegorical Persons, it is only in short Expressions, which convey an
ordinary Thought to the Mind in the most pleasing manner, and may rather
be looked upon as Poetical Phrases than Allegorical Descriptions.
Instead of telling us, that Men naturally fly when they are terrified,
he introduces the Persons of
Flight
and
Fear
, who, he tells us, are
inseparable Companions. Instead of saying that the time was come when
Apollo
ought to have received his Recompence, he tells us, that the
Hours
brought him his Reward. Instead of describing the Effects which
Minerva's
Ægis produced in Battel, he tells us, that the Brims of it
were encompassed by
Terror, Rout, Discord, Fury, Pursuit, Massacre
, and
Death
. In the same Figure of speaking, he represents
Victory
as
following
Diomedes; Discord
as the Mother of
Funerals
and
Mourning
;
Venus
as dressed by the
Graces
;
Bellona
as wearing
Terror
and
Consternation
like a Garment. I might give several other Instances out
of
Homer
, as well as a great many out of
Virgil
.
Milton
has likewise
very often made use of the same way of Speaking, as where he tells us,
that
Victory
sat on the right Hand of the
Messiah
when he marched forth
against the Rebel Angels; that at the rising of the Sun the
Hours
unbarr'd the Gates of Light; that
Discord
was the Daughter of
Sin
. Of
the same nature are those Expressions, where describing the singing of
the Nightingale, he adds,
Silence
was pleased; and upon the
Messiah's
bidding
Peace
to the Chaos,
Confusion
heard his Voice. I might add
innumerable Instances of our Poet's writing in this beautiful Figure. It
is plain that these I have mentioned, in which Persons of an imaginary
Nature are introduced, are such short Allegories as are not designed to
be taken in the literal Sense, but only to convey particular
Circumstances to the Reader after an unusual and entertaining Manner.
But when such Persons are introduced as principal Actors, and engaged in
a Series of Adventures, they take too much upon them, and are by no
means proper for an Heroick Poem, which ought to appear credible in its
principal Parts. I cannot forbear therefore thinking that
Sin
and
Death
are as improper Agents in a Work of this nature, as
Strength
and
Necessity
in
of the Tragedies of
Æschylus
, who represented those two
Persons nailing down
Prometheus
to a Rock
, for which he has been
justly censured by the greatest Criticks. I do not know any imaginary
Person made use of in a more sublime manner of thinking than that in one
of the Prophets, who
God as descending from Heaven, and
visiting the Sins of Mankind, adds that dreadful Circumstance, Before
him went the
Pestilence
. It is certain this imaginary Person might
have been described in all her purple Spots. The
Fever
might have
marched before her,
Pain
might have stood at her right Hand,
Phrenzy
on
her Left, and
Death
in her Rear. She might have been introduced as
gliding down from the Tail of a Comet, or darted upon the Earth in a
Flash of Lightning: She might have tainted the Atmosphere with her
Breath; the very glaring of her Eyes might have scattered
Infection
. But
I believe every Reader will think, that in such sublime Writings the
mentioning of her as it is done in Scripture, has something in it more
just, as well as great, than all that the most fanciful Poet could have
bestowed upon her in the Richness of his Imagination.
L.
'Reddere personæ scit convenientia cuique.'
Hor.
Revelation
vi. 8.
Sin and Death
In the fourteenth Book, where Heré visits the home of
Sleep, the brother of Death, and offers him the bribe of a gold chain if
he will shut the eyes of Zeus, Sleep does not think it can be done. Heré
then doubles her bribe, and offers Sleep a wife, the youngest of the
Graces. Sleep makes her swear by Styx that she will hold to her word,
and when she has done so flies off in her company, sits in the shape of
a night-hawk in a pine tree upon the peak of Ida, whence when Zeus was
subdued by love and sleep, Sleep went down to the ships to tell Poseidon
that now was his time to help the Greeks.
In the
Prometheus Bound
of Æschylus, the binding of
Prometheus by pitiless Strength, who mocks at compassion in the god
Hephaistos, charged to serve him in this office, opens the sublimest of
the ancient dramas. Addison is wrong in saying that there is a
personification here of Strength and Necessity; Hephaistos does indeed
say that he obeys Necessity, but his personified companions are Strength
and Force, and of these Force appears only as the dumb attendant of
Strength. Addison's 'greatest critics' had something to learn when they
were blind to the significance of the contrast between Visible Strength
at the opening of this poem, and the close with sublime prophecy of an
unseen Power of the Future that disturbs Zeus on his throne, and gathers
his thunders about the undaunted Prometheus.
Now let the shrivelling flame at me be driven,
Let him, with flaky snowstorms and the crash
Of subterraneous thunders, into ruins
And wild confusion hurl and mingle all:
For nought of these will bend me that I speak
Who is foredoomed to cast him from his throne.
(Mrs. Webster's translation.)
Habakkuk
iii. 5.
Contents
|
Monday, April 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Desipere in loco.
Hor.
Charles Lillie
me the other day, and made me a Present of a
large Sheet of Paper, on which is delineated a Pavement of Mosaick Work,
lately discovered at
Stunsfield
near
Woodstock
. A Person who has so
much the Gift of Speech as Mr.
Lillie
, and can carry on a Discourse
without Reply, had great Opportunity on that Occasion to expatiate upon
so fine a Piece of Antiquity. Among other things, I remember, he gave me
his Opinion, which he drew from the Ornaments of the Work, That this was
the Floor of a Room dedicated to Mirth and Concord. Viewing this Work,
made my Fancy run over the many gay Expressions I had read in ancient
Authors, which contained Invitations to lay aside Care and Anxiety, and
give a Loose to that pleasing Forgetfulness wherein Men put off their
Characters of Business, and enjoy their very Selves. These Hours were
usually passed in Rooms adorned for that purpose, and set out in such a
manner, as the Objects all around the Company gladdened their Hearts;
which, joined to the cheerful Looks of well-chosen and agreeable
Friends, gave new Vigour to the Airy, produced the latent Fire of the
Modest, and gave Grace to the slow Humour of the Reserved. A judicious
Mixture of such Company, crowned with Chaplets of Flowers, and the whole
Apartment glittering with gay Lights, cheared with a Profusion of Roses,
artificial Falls of Water, and Intervals of soft Notes to Songs of Love
and Wine, suspended the Cares of human Life, and made a Festival of
mutual Kindness. Such Parties of Pleasure as these, and the Reports of
the agreeable Passages in their Jollities, have in all Ages awakened the
dull Part of Mankind to pretend to Mirth and Good-Humour, without
Capacity for such Entertainments; for if I may be allowed to say so,
there are an hundred Men fit for any Employment, to one who is capable
of passing a Night in the Company of the first Taste, without shocking
any Member of the Society, over-rating his own Part of the Conversation,
but equally receiving and contributing to the Pleasure of the whole
Company. When one considers such Collections of Companions in past
Times, and such as one might name in the present Age, with how much
Spleen must a Man needs reflect upon the aukward Gayety of those who
affect the Frolick with an ill Grace? I have a Letter from a
Correspondent of mine, who desires me to admonish all loud, mischievous,
airy, dull Companions, that they are mistaken in what they call a
Frolick. Irregularity in its self is not what creates Pleasure and
Mirth; but to see a Man who knows what Rule and Decency are, descend
from them agreeably in our Company, is what denominates him a pleasant
Companion. Instead of that, you find many whose Mirth consists only in
doing Things which do not become them, with a secret Consciousness that
all the World know they know better: To this is always added something
mischievous to themselves or others. I have heard of some very merry
Fellows, among whom the Frolick was started, and passed by a great
Majority, that every Man should immediately draw a Tooth; after which
they have gone in a Body and smoaked a Cobler.
same Company, at
another Night, has each Man burned his Cravat; and one perhaps, whose
Estate would bear it, has thrown a long Wigg and laced Hat into the same
Fire
. Thus they have jested themselves stark naked, and ran into the
Streets, and frighted Women very successfully. There is no Inhabitant of
any standing in
Covent-Garden
, but can tell you a hundred good Humours,
where People have come off with little Blood-shed, and yet scowered all
the witty Hours of the Night. I know a Gentleman that has several Wounds
in the Head by Watch Poles, and has been thrice run through the Body to
carry on a good Jest: He is very old for a Man of so much Good-Humour;
but to this day he is seldom merry, but he has occasion to be valiant at
the same time. But by the Favour of these Gentlemen, I am humbly of
Opinion, that a Man may be a very witty Man, and never offend one
Statute of this Kingdom, not excepting even that of Stabbing.
The Writers of Plays have what they call Unity of Time and Place to give
a Justness to their Representation; and it would not be amiss if all who
pretend to be Companions, would confine their Action to the Place of
Meeting: For a Frolick carried farther may be better performed by other
Animals than Men. It is not to rid much Ground, or do much Mischief,
that should denominate a pleasant Fellow; but that is truly Frolick
which is the Play of the Mind, and consists of various and unforced
Sallies of Imagination. Festivity of Spirit is a very uncommon Talent,
and must proceed from an Assemblage of agreeable Qualities in the same
Person: There are some few whom I think peculiarly happy in it; but it
is a Talent one cannot name in a Man, especially when one considers that
it is never very graceful but where it is regarded by him who possesses
it in the second Place. The
Man that I know of for heightening the
Revel-Gayety of a Company, is
Estcourt
,—whose Jovial Humour
diffuses itself from the highest Person at an Entertainment to the
meanest Waiter. Merry Tales, accompanied with apt Gestures and lively
Representations of Circumstances and Persons, beguile the gravest Mind
into a Consent to be as humourous as himself. Add to this, that when a
Man is in his good Grace, he has a Mimickry that does not debase the
Person he represents; but which, taking from the Gravity of the
Character, adds to the Agreeableness of it. This pleasant Fellow gives
one some Idea of the ancient Pantomime, who is said to have given the
Audience, in Dumb-show, an exact Idea of any Character or Passion, or an
intelligible Relation of any publick Occurrence, with no other
Expression than that of his Looks and Gestures. If all who have been
obliged to these Talents in
Estcourt
, will be at
Love for Love
to-morrow
Night, they will but pay him what they owe him, at so easy a Rate as
being present at a Play which no body would omit seeing, that had, or
had not ever seen it before.
In
and some following numbers of the
Spectator
appeared an advertisement of this plate, which was engraved by Vertue.
'Whereas about nine weeks since there was accidentally discovered by
an Husbandman, at Stunsfield, near Woodstock, in Oxfordshire, (a large
Pavement of rich Mosaick Work of the Ancient Romans, which is adorn'd
with several Figures alluding to Mirth and Concord, in particular that
of Bacchus seated on a Panther.) This is to give Notice the Exact
Delineation of the same is Engraven and Imprinted on a large Elephant
sheet of Paper, which are to be sold at Mr. Charles Lillie's,
Perfumer, at the corner of Beauford Buildings, in the Strand, at 1s.
N. B. There are to be had, at the same Place, at one Guinea each, on
superfine Atlas Paper, some painted with the same variety of Colours
that the said Pavement is beautified with; this piece of Antiquity is
esteemed by the Learned to be the most considerable ever found in
Britain.'
The fine pavement discovered at Stonesfield in 1711 measures 35 feet by
60, and although by this time groundworks of more than a hundred Roman
villas have been laid open in this country, the Stonesfield mosaic is
still one of the most considerable of its kind.
Said to have been one of the frolics of Sir Charles Sedley.
See note on p. 204, ante [
of
].
Congreve's
Love for Love
was to be acted at Drury Lane on Tuesday night
'At the desire of several Ladies of Quality. For the Benefit of Mr.
Estcourt.'
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 22, 1712 |
Budgell |
Torva leæna lupum sequitur, lupus ipse capellam;
Florentem cytisum sequitur lusciva capella.
Virg.

As we were at the Club last Night, I observ'd that my Friend Sir
Roger
,
contrary to his usual Custom, sat very silent, and instead of minding
what was said by the Company, was whistling to himself in a very
thoughtful Mood, and playing with a Cork. I jogg'd Sir
Andrew Freeport
who sat between us; and as we were both observing him, we saw the Knight
shake his Head, and heard him say to himself, A foolish Woman! I can't
believe it. Sir
Andrew
gave him a gentle Pat upon the Shoulder, and
offered to lay him a Bottle of Wine that he was thinking of the Widow.
My old Friend started, and recovering out of his brown Study, told Sir
Andrew
that once in his Life he had been in the right. In short, after
some little Hesitation, Sir
Roger
told us in the fulness of his Heart
that he had just received a Letter from his Steward, which acquainted
him that his old Rival and Antagonist in the County, Sir David Dundrum,
had been making a Visit to the Widow. However, says Sir
Roger
, I can
never think that she'll have a Man that's half a Year older than I am,
and a noted Republican into the Bargain.
Will. Honeycomb
, who looks upon Love as his particular Province,
interrupting our Friend with a janty Laugh; I thought, Knight, says he,
thou hadst lived long enough in the World, not to pin thy Happiness upon
one that is a Woman and a Widow. I think that without Vanity I may
pretend to know as much of the Female World as any Man in Great-Britain,
tho' the chief of my Knowledge consists in this, that they are not to be
known.
Will
, immediately, with his usual Fluency, rambled into an
Account of his own Amours. I am now, says he, upon the Verge of Fifty,
(tho' by the way we all knew he was turned of Threescore.) You may
easily guess, continued
Will
., that I have not lived so long in the
World without having had some thoughts of settling in it, as the Phrase
is. To tell you truly, I have several times tried my Fortune that way,
though I can't much boast of my Success.
I made my first Addresses to a young Lady in the Country; but when I
thought things were pretty well drawing to a Conclusion, her Father
happening to hear that I had formerly boarded with a Surgeon, the old
Put forbid me his House, and within a Fortnight after married his
Daughter to a Fox-hunter in the Neighbourhood.
I made my next Applications to a Widow, and attacked her so briskly,
that I thought myself within a Fortnight of her. As I waited upon her
one Morning, she told me that she intended to keep her Ready-Money and
Jointure in her own Hand, and desired me to call upon her Attorney in
Lyons-Inn, who would adjust with me what it was proper for me to add to
it. I was so rebuffed by this Overture, that I never enquired either for
her or her Attorney afterwards.
A few Months after I addressed my self to a young Lady, who was an only
Daughter, and of a good Family. I danced with her at several Balls,
squeez'd her by the Hand, said soft things to her, and, in short, made
no doubt of her Heart; and though my Fortune was not equal to hers, I
was in hopes that her fond Father would not deny her the Man she had
fixed her Affections upon. But as I went one day to the House in order
to break the matter to him, I found the whole Family in Confusion, and
heard to my unspeakable Surprize, that Miss Jenny was that very Morning
run away with the Butler.
I then courted a second Widow, and am at a Loss to this day how I came
to miss her, for she had often commended my Person and Behaviour. Her
Maid indeed told me one Day, that her Mistress had said she never saw a
Gentleman with such a Spindle Pair of Legs as Mr.
Honeycomb
.
After this I laid Siege to four Heiresses successively, and being a
handsome young Dog in those Days, quickly made a Breach in their Hearts;
but I don't know how it came to pass, tho' I seldom failed of getting
the Daughters Consent, I could never in my Life get the old People on my
side.
I could give you an Account of a thousand other unsuccessful Attempts,
particularly of one which I made some Years since upon an old Woman,
whom I had certainly borne away with flying Colours, if her Relations
had not come pouring in to her Assistance from all Parts of England;
nay, I believe I should have got her at last, had not she been carried
off by an hard Frost.
As
Will's
Transitions are extremely quick, he turn'd from Sir
Roger
, and
applying himself to me, told me there was a Passage in the Book I had
considered last Saturday, which deserved to be writ in Letters of Gold;
taking out a
Pocket-Milton
read the following Lines, which are Part
of one of
Adam's
Speeches to
Eve
after the Fall.
—O! why did our
Creator wise! that peopled highest Heav'n
With Spirits masculine, create at last
This Novelty on Earth, this fair Defect
Of Nature? and not fill the World at once
With Men, as Angels, without Feminine?
Or find some other way to generate
Mankind? This Mischief had not then befall'n,
And more that shall befall; innumerable
Disturbances on Earth through Female Snares,
And strait Conjunction with this Sex: for either
He never shall find out fit Mate, but such
As some misfortune brings him, or mistake;
Or, whom he wishes most, shall seldom gain
Through her perverseness; but shall see her gain'd
By a far worse; or if she love, with-held
By Parents; or his happiest Choice too late
Shall meet already link'd, and Wedlock bound
To a fell Adversary, his Hate or Shame;
Which infinite Calamity shall cause
To human Life, and Household Peace confound1.
Sir
Roger
listened to this Passage with great Attention, and desiring
Mr.
Honeycomb
to fold down a Leaf at the Place, and lend him his Book,
the Knight put it up in his Pocket, and told us that he would read over
those Verses again before he went to Bed.
X.
Paradise Lost,
Bk x., ll 898-908.
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 23, 1712 |
Steele |
—De paupertate tacentes
Plus poscente ferent.
Hor.

I have nothing to do with the Business of this Day, any further than
affixing the piece of
Latin
on the Head of my Paper; which I think a
Motto not unsuitable, since if Silence of our Poverty is a
Recommendation, still more commendable is his Modesty who conceals it by
a decent Dress.
Mr.
Spectator,
'There is an Evil under the Sun which has not yet come within your
Speculation; and is, the Censure, Disesteem, and Contempt which some
young Fellows meet with from particular Persons, for the reasonable
Methods they take to avoid them in general. This is by appearing in a
better Dress, than may seem to a Relation regularly consistent with a
small Fortune; and therefore may occasion a Judgment of a suitable
Extravagance in other Particulars:
But the Disadvantage with which the
Man of narrow Circumstances acts and speaks, is so feelingly set forth
in a little Book called the
Christian Hero1, that the appearing to
be otherwise is not only pardonable but necessary. Every one knows the
hurry of Conclusions that are made in contempt of a Person that
appears to be calamitous, which makes it very excusable to prepare
one's self for the Company of those that are of a superior Quality and
Fortune, by appearing to be in a better Condition than one is, so far
as such Appearance shall not make us really of worse.
It is a Justice due to the Character of one who suffers hard
Reflections from any particular Person upon this Account, that such
Persons would enquire into his manner of spending his Time; of which,
tho' no further Information can be had than that he remains so many
Hours in his Chamber, yet if this is cleared, to imagine that a
reasonable Creature wrung with a narrow Fortune does not make the best
use of this Retirement, would be a Conclusion extremely uncharitable.
From what has, or will be said, I hope no Consequence can be extorted,
implying, that I would have any young Fellow spend more Time than the
common Leisure which his Studies require, or more Money than his
Fortune or Allowance may admit of, in the pursuit of an Acquaintance
with his Betters: For as to his Time, the gross of that ought to be
sacred to more substantial Acquisitions; for each irrevocable Moment
of which he ought to believe he stands religiously Accountable. And as
to his Dress, I shall engage myself no further than in the modest
Defence of two plain Suits a Year: For being perfectly satisfied in
Eutrapelus's Contrivance of making a Mohock of a Man, by presenting
him with lac'd and embroider'd Suits, I would by no means be thought
to controvert that Conceit, by insinuating the Advantages of Foppery.
It is an Assertion which admits of much Proof, that a Stranger of
tolerable Sense dress'd like a Gentleman, will be better received by
those of Quality above him, than one of much better Parts, whose Dress
is regulated by the rigid Notions of Frugality. A Man's Appearance
falls within the Censure of every one that sees him; his Parts and
Learning very few are Judges of; and even upon these few, they can't
at first be well intruded; for Policy and good Breeding will counsel
him to be reserv'd among Strangers, and to support himself only by the
common Spirit of Conversation. Indeed among the Injudicious, the Words
Delicacy, Idiom, fine Images, Structure of Periods, Genius, Fire, and
the rest, made use of with a frugal and comely Gravity, will maintain
the Figure of immense Reading, and Depth of Criticism.
'All Gentlemen of Fortune, at least the young and middle-aged, are apt
to pride themselves a little too much upon their Dress, and
consequently to value others in some measure upon the same
Consideration. With what Confusion is a Man of Figure obliged to
return the Civilities of the Hat to a Person whose Air and Attire
hardly entitle him to it? For whom nevertheless the other has a
particular Esteem, tho' he is ashamed to have it challenged in so
publick a Manner. It must be allowed, that any young Fellow that
affects to dress and appear genteelly, might with artificial
Management save ten Pound a Year; as instead of fine Holland he might
mourn in Sackcloth, and in other Particulars be proportionably shabby:
But of what great Service would this Sum be to avert any Misfortune,
whilst it would leave him deserted by the little good Acquaintance he
has, and prevent his gaining any other? As the Appearance of an easy
Fortune is necessary towards making one, I don't know but it might be
of advantage sometimes to throw into ones Discourse certain
Exclamations about Bank-Stock, and to shew a marvellous Surprize upon
its Fall, as well as the most affected Triumph upon its Rise. The
Veneration and Respect which the Practice of all Ages has preserved to
Appearances, without doubt suggested to our Tradesmen that wise and
Politick Custom, to apply and recommend themselves to the publick by
all those Decorations upon their Sign-posts and Houses, which the most
eminent Hands in the Neighbourhood can furnish them with. What can be
more attractive to a Man of Letters, than that immense Erudition of
all Ages and Languages which a skilful Bookseller, in conjunction with
a Painter, shall image upon his Column and the Extremities of his
Shop? The
same Spirit of maintaining a handsome Appearance reigns
among the grave and solid Apprentices of the Law (here I could be
particularly dull in
proving2 the Word Apprentice to be
significant of a Barrister) and you may easily distinguish who has
most lately made his Pretensions to Business, by the whitest and most
ornamental Frame of his Window: If indeed the Chamber is a
Ground-Room, and has Rails before it, the Finery is of Necessity more
extended, and the Pomp of Business better maintain'd. And what can be
a greater Indication of the Dignity of Dress, than that burdensome
Finery which is the regular Habit of our Judges, Nobles, and Bishops,
with which upon certain Days we see them incumbered? And though it may
be said this is awful, and necessary for the Dignity of the State, yet
the wisest of them have been remarkable, before they arrived at their
present Stations, for being very well dressed Persons. As to my own
Part, I am near Thirty; and since I left School have not been idle,
which is a modern Phrase for having studied hard. I brought off a
clean System of Moral Philosophy, and a tolerable Jargon of
Metaphysicks from the University; since that, I have been engaged in
the clearing Part of the perplex'd Style and Matter of the Law, which
so hereditarily descends to all its Professors: To all which severe
Studies I have thrown in, at proper Interims, the pretty Learning of
the Classicks.
Notwithstanding which, I am what
Shakespear calls
A
Fellow of no Mark or Likelihood3; which makes me understand the
more fully, that since the regular Methods of making Friends and a
Fortune by the mere Force of a Profession is so very slow and
uncertain, a Man should take all reasonable Opportunities, by
enlarging a good Acquaintance, to court that Time and Chance which is
said to happen to every Man.
T.
The passage is nearly at the beginning of Steele's third
chapter,
'It is in every body's observation with what disadvantage a Poor Man
enters upon the most ordinary affairs,' &c.
clearing
Henry IV
. Pt. I. Act iii. sc. 2.
Contents
|
Thursday, April 24, 1712 |
Addison |
Tartaream intendit vocem, quâ protinus omnis
Contremuit domus—
Virg.

I have lately received the following Letter from a Country Gentleman.
Mr.
Spectator,
'The
Night before I left London I went to see a Play, called
The
Humorous Lieutenant1. Upon the Rising of the Curtain I was very
much surprized with the great Consort of Cat-calls which was exhibited
that Evening, and began to think with myself that I had made a
Mistake, and gone to a Musick-Meeting, instead of the Play-house. It
appeared indeed a little odd to me to see so many Persons of Quality
of both Sexes assembled together at a kind of Catterwawling; for I
cannot look upon that Performance to have been any thing better,
whatever the Musicians themselves might think of it. As I had no
Acquaintance in the House to ask Questions of, and was forced to go
out of Town early the next Morning, I could not learn the Secret of
this Matter. What I would therefore desire of you, is, to give some
account of this strange Instrument, which I found the Company called a
Cat-call; and particularly to let me know whether it be a piece of
Musick lately come from Italy. For my own part, to be free with you, I
would rather hear an English Fiddle; though I durst not shew my
Dislike whilst I was in the Play-House, it being my Chance to sit the
very next Man to one of the Performers. I am,
Sir,
Your most affectionate Friend
and Servant,
John Shallow, Esq.
In compliance with Esquire
Shallow's
Request, I design this Paper as a
Dissertation upon the Cat-call. In order to make myself a Master of the
Subject, I purchased one the Beginning of last Week, though not without
great difficulty, being inform'd at two or three Toyshops that the
Players had lately bought them all up. I have since consulted many
learned Antiquaries in relation to its Original, and find them very much
divided among themselves upon that Particular. A Fellow of the Royal
Society, who is my good Friend, and a great Proficient in the
Mathematical Part of Musick, concludes from the Simplicity of its Make,
and the Uniformity of its Sound, that the Cat-call is older than any of
the Inventions of
Jubal
. He observes very well, that Musical Instruments
took their first Rise from the Notes of Birds, and other melodious
Animals; and what, says he, was more natural than for the first Ages of
Mankind to imitate the Voice of a Cat that lived under the same Roof
with them? He added, that the Cat had contributed more to Harmony than
any other Animal; as we are not only beholden to her for this
Wind-Instrument, but for our String Musick in general.
Another Virtuoso of my Acquaintance will not allow the Cat-call to be
older than
Thespis
, and is apt to think it appeared in the World soon
after the antient Comedy; for which reason it has still a place in our
Dramatick Entertainments: Nor must I here omit what a very curious
Gentleman, who is lately returned from his Travels, has more than once
assured me, namely that there was lately dug up at Rome the Statue of
Momus
, who holds an Instrument in his Right-Hand very much resembling
our Modern Cat-call.
There are others who ascribe this Invention to
Orpheus
, and look upon
the Cat-call to be one of those Instruments which that famous Musician
made use of to draw the Beasts about him. It is certain, that the
Roasting of a Cat does not call together a greater Audience of that
Species than this Instrument, if dexterously played upon in proper Time
and Place.
But notwithstanding these various and learned Conjectures, I cannot
forbear thinking that the Cat-call is originally a Piece of
English
Musick. Its Resemblance to the Voice of some of our
British
Songsters,
as well as the Use of it, which is peculiar to our Nation, confirms me
in this Opinion. It has at least received great Improvements among us,
whether we consider the Instrument it self, or those several Quavers and
Graces which are thrown into the playing of it. Every one might be
sensible of this, who
that remarkable overgrown Cat-call which was
placed in the Center of the Pit, and presided over all the rest at
the
celebrated Performance lately exhibited in
Drury-Lane
.
Having said thus much concerning the Original of the Cat-call, we are in
the next place to consider the Use of it. The Cat-call exerts it self to
most advantage in the
British
Theatre: It very much Improves the Sound
of Nonsense, and often goes along with the Voice of the Actor who
pronounces it, as the Violin or Harpsichord accompanies the
Italian
Recitativo.
It has often supplied the Place of the antient Chorus, in the Works of
Mr.—— In short, a bad Poet has as great an Antipathy to a Cat-call, as
many People have to a real Cat.
Mr.
Collier
, in his ingenious
Essay upon Musick
has the following
Passage:
I believe 'tis possible to invent an Instrument that shall have a quite
contrary Effect to those Martial ones now in use: An Instrument that
shall sink the Spirits, and shake the Nerves, and curdle the Blood, and
inspire Despair, and Cowardice and Consternation, at a surprizing rate.
'Tis probable the Roaring of Lions, the Warbling of Cats and
Scritch-Owls, together with a Mixture of the Howling of Dogs,
judiciously imitated and compounded, might go a great way in this
Invention. Whether such Anti-Musick as this might not be of Service in a
Camp, I shall leave to the Military Men to consider.
What this learned Gentleman supposes in Speculation, I have known
actually verified in Practice. The Cat-call has struck a Damp into
Generals, and frighted Heroes off the Stage. At the first sound of it I
have seen a Crowned Head tremble, and a Princess fall into Fits. The
Humorous Lieutenant
himself could not stand it; nay, I am told that even
Almanzor
looked like a Mouse, and trembled at the Voice of this
terrifying Instrument.
As it is of a Dramatick Nature, and peculiarly appropriated to the
Stage, I can by no means approve the Thought of that angry Lover, who,
after an unsuccessful Pursuit of some Years, took leave of his Mistress
in a Serenade of Cat-calls.
I must conclude this Paper with the Account I have lately received of an
ingenious Artist, who has long studied this Instrument, and is very well
versed in all the Rules of the Drama. He teaches to play on it by Book,
and to express by it the whole Art of Criticism. He has his Base and his
Treble Cat-call; the former for Tragedy, the latter for Comedy; only in
Tragy-Comedies they may both play together in Consort. He has a
particular Squeak to denote the Violation of each of the Unities, and
has different Sounds to shew whether he aims at the Poet or the Player.
In short he teaches the Smut-note, the Fustian-note, the Stupid-note,
and has composed a kind of Air that may serve as an Act-tune to an
incorrigible Play, and which takes in the whole Compass of the Cat-call.
L.
By Beaumont and Fletcher.
that
Essays upon several Moral Subjects
, by Jeremy Collier, Part
II. p. 30 (ed. 1732). Jeremy Collier published the first volume of these
Essays
in 1697, after he was safe from the danger brought on himself by
attending Sir John Friend and Sir William Perkins when they were
executed for the "assassination plot." The other two volumes appeared
successively in 1705 and 1709. It was in 1698 that Collier published his
famous
Short View of the Immorality and Profaneness of the English
Stage
.
Not being yet determined with whose Name to fill up the
Gap in this Dissertation which is marked with ——, I shall defer it
till this Paper appears with others in a Volume. L.
Contents
|
Friday, April 25, 1712 |
Steele |
Laudibus arguitur Vini vinosus—
Hor.

Temple, Apr. 24.
Mr.
Spectator,
Several of my Friends were this Morning got together over a Dish of
Tea in very good Health, though we had celebrated Yesterday with more
Glasses than we could have dispensed with, had we not been beholden to
Brooke and
Hillier. In Gratitude therefore to those good Citizens, I
am, in the Name of the Company, to accuse you of great Negligence in
overlooking their Merit, who have imported true and generous Wine, and
taken care that it should not be adulterated by the Retailers before
it comes to the Tables of private Families, or the Clubs of honest
Fellows. I cannot imagine how a
Spectator can be supposed to do his
Duty, without frequent Resumption of such Subjects as concern our
Health, the first thing to be regarded, if we have a mind to relish
anything else. It would therefore very well become your Spectatorial
Vigilance, to give it in Orders to your Officer for inspecting Signs,
that in his March he would look into the Itinerants who deal in
Provisions, and enquire where they buy their several Wares.
Ever since
the Decease of
Cully1-Mully-Puff
2 of agreeable and noisy
Memory, I cannot say I have observed any thing sold in Carts, or
carried by Horse or Ass, or in fine, in any moving Market, which is
not perished or putrified; witness the Wheel-barrows of rotten
Raisins, Almonds, Figs, and Currants, which you see vended by a
Merchant dressed in a second-hand Suit of a Foot Soldier.
You should
consider that a Child may be poisoned for the Worth of a Farthing; but
except his poor Parents send to one certain Doctor in Town
3, they
can have no advice for him under a Guinea. When Poisons are thus
cheap, and Medicines thus dear, how can you be negligent in inspecting
what we eat and drink, or take no Notice of such as the
above-mentioned Citizens, who have been so serviceable to us of late
in that particular? It was a Custom among the old Romans, to do him
particular Honours who had saved the Life of a Citizen, how much more
does the World owe to those who prevent the Death of Multitudes? As
these Men deserve well of your Office, so such as act to the Detriment
of our Health, you ought to represent to themselves and their
Fellow-Subjects in the Colours which they deserve to wear. I think it
would be for the publick Good, that all who vend Wines should be under
oaths in that behalf. The Chairman at a Quarter Sessions should inform
the Country, that the Vintner who mixes Wine to his Customers, shall
(upon proof that the Drinker thereof died within a Year and a Day
after taking it) be deemed guilty of Wilful Murder: and the Jury shall
be instructed to enquire and present such Delinquents accordingly. It
is no Mitigation of the Crime, nor will it be conceived that it can be
brought in Chance-Medley or Man-Slaughter, upon Proof that it shall
appear Wine joined to Wine, or right Herefordshire poured into Port O
Port; but his selling it for one thing, knowing it to be another, must
justly bear the foresaid Guilt of wilful Murder: For that he, the said
Vintner, did an unlawful Act willingly in the false Mixture; and is
therefore with Equity liable to all the Pains to which a Man would be,
if it were proved he designed only to run a Man through the Arm, whom
he whipped through the Lungs. This is my third Year at the Temple, and
this is or should be Law. An
ill Intention well proved should meet
with no Alleviation, because it
out-ran4 it self. There cannot be
too great Severity used against the Injustice as well as Cruelty of
those who play with Mens Lives, by preparing Liquors, whose Nature,
for ought they know, may be noxious when mixed, tho innocent when
apart:
And Brooke and
Hillier5, who have ensured our Safety at our
Meals, and driven Jealousy from our Cups in Conversation, deserve the
Custom and Thanks of the whole Town; and it is your Duty to remind
them of the Obligation. I am,
Sir,
Your Humble Servant,
Tom. Pottle.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am a Person who was long immured in a College, read much, saw
little; so that I knew no more of the World than what a Lecture or a
View of the Map taught me. By this means I improved in my Study, but
became unpleasant in Conversation. By conversing generally with the
Dead, I grew almost unfit for the Society of the Living; so by a long
Confinement I contracted an ungainly Aversion to Conversation, and
ever discoursed with Pain to my self, and little Entertainment to
others. At last I was in some measure made sensible of my failing, and
the Mortification of never being spoke to, or speaking, unless the
Discourse ran upon Books, put me upon forcing my self amongst Men. I
immediately affected the politest Company, by the frequent use of
which I hoped to wear off the Rust I had contracted; but by an uncouth
Imitation of Men used to act in publick, I got no further than to
discover I had a Mind to appear a finer thing than I really was.
Such I was, and such was my Condition, when I became an ardent Lover,
and passionate Admirer of the beauteous
Belinda: Then it was that I
really began to improve. This Passion changed all my Fears and
Diffidences in my general Behaviour, to the sole Concern of pleasing
her. I had not now to study the Action of a Gentleman, but Love
possessing all my Thoughts, made me truly be the thing I had a Mind to
appear. My Thoughts grew free and generous, and the Ambition to be
agreeable to her I admired, produced in my Carriage a faint Similitude
of that disengaged Manner of my Belinda. The way we are in at present
is, that she sees my Passion, and sees I at present forbear speaking
of it through prudential Regards. This Respect to her she returns with
much Civility, and makes my Value for her as little a Misfortune to
me, as is consistent with Discretion. She sings very charmingly, and
is readier to do so at my Request, because she knows I love her: She
will dance with me rather than another, for the same Reason. My
Fortune must alter from what it is, before I can speak my Heart to
her; and her Circumstances are not considerable enough to make up for
the Narrowness of mine. But I write to you now, only to give you the
Character of
Belinda, as a Woman that has Address enough to
demonstrate a Gratitude to her Lover, without giving him Hopes of
Success in his Passion.
Belinda has from a great Wit, governed by as
great Prudence, and both adorned with Innocence, the Happiness of
always being ready to discover her real Thoughts. She has many of us,
who now are her Admirers; but her Treatment of us is so just and
proportioned to our Merit towards her, and what we are in our selves,
that I protest to you I have neither Jealousy nor Hatred toward my
Rivals. Such is her Goodness, and the Acknowledgment of every Man who
admires her, that he thinks he ought to believe she will take him who
best deserves her. I will not say that this Peace among us is not
owing to Self-love, which prompts each to think himself the best
Deserver: I think there is something uncommon and worthy of Imitation
in this Lady's Character. If you will please to Print my Letter, you
will oblige the little Fraternity of happy Rivals, and in a more
particular Manner,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Will. Cymon.
T.
Mully
See
. He was a little man just able to bear on his
head his basket of pastry, and who was named from his cry. There is a
half-sheet print of him in the set of London Cries in Granger's
Biographical History of England.
Who advertised that he attended patients at charges ranging
from a shilling to half-a-crown, according to their distance from his
house.
out-run
Estcourt, it may be remembered, connected the advertisement
of his Bumper tavern with the recommendation of himself as one ignorant
of the wine trade who relied on Brooke and Hellier, and so ensured his
Customers good wine. Among the advertisers in the Spectator Brooke and
Hellier often appeared. One of their advertisements is preceded by the
following, evidently a contrivance of their own, which shows that the
art of puffing was not then in its infancy:
'This is to give Notice, That Brooke and Hellier have not all the New
Port Wines this Year, nor above one half, the Vintners having bought
130 Pipes of Mr. Thomas Barlow and others, which are all natural, and
shall remain Genuine, on which all Gentlemen and others may depend.
Note.—Altho' Brooke and Hellier have asserted in several Papers that
they had 140 Pipes of New Oporto Wines coming from Bristol, it now
appears, since their landing, that they have only 133 Pipes, I Hhd. of
the said Wines, which shews plainly how little what they say is to be
credited.'
Then follows their long advertisement, which ends with a note that Their
New Ports, just landed, being the only New Ports in Merchants Hands, and
above One Half of all that is in London, will begin to be sold at the
old prices the I2th inst. (April) at all their Taverns and Cellars.
Contents
|
Saturday, April 26, 1712 |
Addison |
—Crudelis ubique
Luctus, ubique pavor, et plurima Mortis
Imago.
Virg.

Milton
has shewn a wonderful Art in describing that variety of Passions
which arise in our first Parents upon the Breach of the Commandment that
had been given them. We see them gradually passing from the Triumph of
their Guilt thro Remorse, Shame, Despair, Contrition, Prayer, and Hope,
to a perfect and compleat Repentance. At the end of the tenth Book they
are represented as prostrating themselves upon the Ground, and watering
the Earth with their Tears: To which the Poet joins this beautiful
Circumstance, that they offerd up their penitential Prayers, on the very
Place where their Judge appeared to them when he pronounced their
Sentence.
—They forthwith to the place
Repairing where he judg'd them, prostrate fell
Before him Reverent, and both confess'd
Humbly their Faults, and Pardon begg'd, with Tears
Watering the Ground—
There is a Beauty of the same kind in a Tragedy of Sophocles, where
Œdipus, after having put out his own Eyes, instead of breaking his Neck
from the Palace-Battlements (which furnishes so elegant an Entertainment
for our English Audience) desires that he may be conducted to Mount
Cithoeron, in order to end his Life in that very Place where he was
exposed in his Infancy, and where he should then have died, had the Will
of his Parents been executed.
As the Author never fails to give a poetical Turn to his Sentiments, he
describes in the Beginning of this Book the Acceptance which these their
Prayers met with, in a short Allegory, formd upon that beautiful Passage
in holy Writ: And another Angel came and stood at the Altar, having a
golden Censer; and there was given unto him much Incense, that he should
offer it with the Prayers of all Saints upon the Golden Altar, which was
before the Throne: And the Smoak of the Incense which came with the
Prayers of the Saints, ascended up before God.
—To Heavn their Prayers
Flew up, nor miss'd the Way, by envious Winds
Blown vagabond or frustrate: in they pass'd
Dimensionless through heavnly Doors, then clad
With Incense, where the Golden Altar fumed,
By their great Intercessor, came in sight
Before the Father's Throne—
We have the same Thought expressed a second time in the Intercession of
the
Messiah
, which is conceived in very Emphatick Sentiments and
Expressions.
Among the Poetical Parts of Scripture, which
Milton
has so finely
wrought into this Part of his Narration, I must not omit that wherein
Ezekiel
speaking of the Angels who appeared to him in a Vision, adds,
that every one had four Faces, and that their whole Bodies, and their
Backs, and their Hands, and their Wings, were full of Eyes round about.
—The Cohort bright
Of watchful Cherubims, four Faces each
Had like a double Janus, all their Shape
Spangled with Eyes—
The Assembling of all the Angels of Heaven to hear the solemn Decree
passed upon Man, is represented in very lively Ideas. The Almighty is
here describd as remembring Mercy in the midst of Judgment, and
commanding
Michael
to deliver his Message in the mildest Terms, lest the
Spirit of Man, which was already broken with the Sense of his Guilt and
Misery, should fail before him.
—Yet lest they faint
At the sad Sentence rigorously urg'd,
For I behold them softned, and with Tears
Bewailing their Excess, all Terror hide,
The Conference of
Adam
and
Eve
is full of moving Sentiments. Upon
their going abroad after the melancholy Night which they had passed
together, they discover the Lion and the Eagle pursuing each of them
their Prey towards the Eastern Gates of Paradise. There is a double
Beauty in this Incident, not only as it presents great and just Omens,
which are always agreeable in Poetry, but as it expresses that Enmity
which was now produced in the Animal Creation. The Poet to shew the like
Changes in Nature, as well as to grace his Fable with a noble Prodigy,
represents the Sun in an Eclipse. This particular Incident has
likewise a fine Effect upon the Imagination of the Reader, in regard to
what follows; for at the same time that the Sun is under an Eclipse, a
bright Cloud descends in the Western Quarter of the Heavens, filled with
an Host of Angels, and more luminous than the Sun it self. The whole
Theatre of Nature is darkned, that this glorious Machine may appear in
all its Lustre and Magnificence.
—Why in the East
Darkness ere Days mid-course, and morning Light
More orient in that Western Cloud that draws
O'er the blue Firmament a radiant White,
And slow descends, with something Heavnly fraught?
He err'd not, for by this the heavenly Bands
Down from a Sky of Jasper lighted now
In Paradise, and on a Hill made halt;
A glorious Apparition—
I need not observe how properly this Author, who always suits his Parts
to the Actors whom he introduces, has employed
Michael
in the Expulsion
of our first Parents from Paradise. The Archangel on this Occasion
neither appears in his proper Shape, nor in that familiar Manner with
which
Raphael
the sociable Spirit entertained the Father of Mankind
before the Fall. His Person, his Port, and Behaviour, are suitable to a
Spirit of the highest Rank, and exquisitely describd in the following
Passage.
—Th' Archangel soon drew nigh,
Not in his Shape Celestial; but as Man
Clad to meet Man: over his lucid Arms
A Military Vest of Purple flow'd,
Livelier than Meliboean, or the Grain
Of Sarra, worn by Kings and Heroes old,
In time of Truce: Iris had dipt the Wooff:
His starry Helm, unbuckled, shew'd him prime
In Manhood where Youth ended; by his side,
As in a glistring Zodiack, hung the Sword,
Satan's dire dread, and in his Hand the Spear.
Adam bow'd low, he Kingly from his State
Inclined not, but his coming thus declared.
Eve's
Complaint upon hearing that she was to be removed from the Garden
of Paradise, is wonderfully beautiful: The Sentiments are not only
proper to the Subject, but have something in them particularly soft and
womanish.
Must I then leave thee, Paradise? Thus leave
Thee, native Soil, these happy Walks and Shades,
Fit haunt of Gods? Where I had hope to spend
Quiet, though sad, the respite of that Day
That must be mortal to us both. O Flowrs,
That never will in other Climate grow,
My early Visitation, and my last
At Even, which I bred up with tender Hand
From the first opening Bud, and gave you Names;
Who now shall rear you to the Sun, or rank
Your Tribes, and water from th' ambrosial Fount?
Thee, lastly, nuptial Bower, by me adorn'd
With what to Sight or Smell was sweet; from thee
How shall I part, and whither wander down
Into a lower World, to this obscure
And wild? how shall we breathe in other Air
Less pure, accustomd to immortal Fruits?
Adam's
Speech abounds with Thoughts which are equally moving, but of a
more masculine and elevated Turn. Nothing can be conceived more Sublime
and Poetical than the following Passage in it.
This most afflicts me, that departing hence
As from his Face I shall be hid, deprived
His blessed Countnance: here I could frequent,
With Worship, place by place where he vouchsaf'd
Presence Divine; and to my Sons relate,
On this Mount he appear'd, under this Tree
Stood visible, among these Pines his Voice
I heard, here with him at this Fountain talk'd;
So many grateful Altars I would rear
Of grassy Turf, and pile up every Stone
Of lustre from the Brook, in memory
Or monument to Ages, and thereon
Offer sweet-smelling Gums and Fruits and Flowers.
In yonder nether World—where shall I seek
His bright Appearances, or Footsteps trace?
For though I fled him angry, yet recalled
To Life prolonged and promised Race, I now
Gladly behold though but his utmost Skirts
Of Glory, and far off his Steps adore.
The Angel afterwards leads
Adam
to the highest Mount of Paradise, and
lays before him a whole Hemisphere, as a proper Stage for those Visions
which were to be represented on it. I have before observed how the Plan
of
Milton's
Poem is in many Particulars greater than that of the
Iliad
or
Æneid
.
Virgil's
Hero, in the last of these Poems, is entertained with a
Sight of all those who are to descend from him; but though that Episode
is justly admired as one of the noblest Designs in the whole
Æneid
,
every one-must allow that this of
Milton
is of a much higher Nature.
Adam's
Vision is not confined to any particular Tribe of Mankind, but
extends to the whole Species.
In this great Review which
Adam
takes of all his Sons and Daughters, the
first Objects he is presented with exhibit to him the Story of
Cain
and
Abel
, which is drawn together with much Closeness and Propriety of
Expression. That Curiosity and natural Horror which arises in
Adam
at
the Sight of the first dying Man, is touched with great Beauty.
But have I now seen Death? is this the way
I must return to native Dust? O Sight
Of Terror foul, and ugly to behold,
Horrid to think, how horrible to feel!
The second Vision sets before him the Image of Death in a great Variety
of Appearances. The Angel, to give him a general Idea of those Effects
which his Guilt had brought upon his Posterity, places before him a
large Hospital or Lazar-House, filled with Persons lying under all kinds
of mortal Diseases. How finely has the Poet told us that the sick
Persons languished under lingering and incurable Distempers, by an apt
and judicious use of such Imaginary Beings as those I mentioned in my
last Saturday's Paper.
Dire was the tossing, deep the Groans. Despair
Tended the Sick, busy from Couch to Couch;
And over them triumphant Death his Dart
Shook, but delayed to strike, though oft invoked
With Vows, as their chief Good and final Hope.
The Passion which likewise rises in Adam on this Occasion, is very
natural.
Sight so deform, what Heart of Rock could long
Dry-eyed behold? Adam could not, but wept,
Tho' not of Woman born; Compassion quell'd
His best of Man, and gave him up to Tears.
The Discourse between the Angel and
Adam
, which follows, abounds with
noble Morals.
As there is nothing more delightful in Poetry than a Contrast and
Opposition of Incidents, the Author, after this melancholy Prospect of
Death and Sickness, raises up a Scene of Mirth, Love, and Jollity. The
secret Pleasure that steals into
Adam's
Heart as he is intent upon this
Vision, is imagined with great Delicacy. I must not omit the Description
of the loose female Troop, who seduced the Sons of God, as they are
called in Scripture.
For that fair female Troop thou sawst, that seemed
Of Goddesses, so Blithe, so Smooth, so Gay,
Yet empty of all Good wherein consists
Woman's domestick Honour and chief Praise;
Bred only and compleated to the taste
Of lustful Appetence, to sing, to dance,
To dress, and troule the Tongue, and roll the Eye:
To these that sober Race of Men, whose Lives
Religious titled them the Sons of God,
Shall yield up all their Virtue, all their Fame
Ignobly, to the Trains and to the Smiles
Of those fair Atheists—
The next Vision is of a quite contrary Nature, and filled with the
Horrors of War.
Adam
at the Sight of it melts into Tears, and breaks out
in that passionate Speech,
—O what are these!
Death's Ministers, not Men, who thus deal Death
Inhumanly to Men, and multiply
Ten Thousandfold the Sin of him who slew
His Brother: for of whom such Massacre
Make they but of their Brethren, Men of Men?
Milton
, to keep up an agreeable Variety in his Visions, after having
raised in the Mind of his Reader the several Ideas of Terror which are
conformable to the Description of War, passes on to those softer Images
of Triumphs and Festivals, in that Vision of Lewdness and Luxury which
ushers in the Flood.
As it is visible that the Poet had his Eye upon
Ovid's
Account of the
universal Deluge, the Reader may observe with how much Judgment he has
avoided every thing that is redundant or puerile in the
Latin
Poet.
do not here see the Wolf swimming among the Sheep, nor any of those
wanton Imaginations, which
Seneca
found fault with
, as unbecoming
the
great Catastrophe of Nature. If our Poet has imitated that
Verse in which
Ovid
tells us that there was nothing but Sea, and that
this Sea had no Shore to it, he has not set the Thought in such a Light
as to incur the Censure which Criticks have passed upon it. The latter
part of that Verse in
Ovid
is idle and superfluous, but just and
beautiful in
Milton
.
Jamque mare et tellus nullum discrimen habebant,
Nil nisi pontus erat, deerant quoque littora ponto.
(Ovid)
—Sea cover'd Sea,
Sea without Shore—
(Milton.)
In
Milton
the former Part of the Description does not forestall the
latter. How much more great and solemn on this Occasion is that which
follows in our
English
Poet,
—And in their Palaces
Where Luxury late reign'd, Sea-Monsters whelp'd
And stabled—
than that in
Ovid
, where we are told that the Sea-Calfs lay in those
Places where the Goats were used to browze? The Reader may find several
other parallel Passages in the
Latin
and
English
Description of the
Deluge, wherein our Poet has visibly the Advantage. The Skys being
overcharged with Clouds, the descending of the Rains, the rising of the
Seas, and the Appearance of the Rainbow, are such Descriptions as every
one must take notice of. The Circumstance relating to Paradise is so
finely imagined, and suitable to the Opinions of many learned Authors,
that I cannot forbear giving it a Place in this Paper.
—Then shall this Mount
Of Paradise by might of Waves be mov'd
Out of his Place, pushed by the horned Flood
With all his Verdure spoil'd, and Trees adrift
Down the great River to the opning Gulf,
And there take root, an Island salt and bare,
The haunt of Seals and Orcs and Sea-Mews clang.
The Transition which the Poet makes from the Vision of the Deluge, to
the Concern it occasioned in
Adam
, is exquisitely graceful, and copied
after
Virgil
, though the first Thought it introduces is rather in the
Spirit of
Ovid
.
How didst thou grieve then, Adam, to behold
The End of all thy Offspring, End so sad,
Depopulation! thee another Flood
Of Tears and Sorrow, a Flood thee also drowned,
And sunk thee as thy Sons; till gently rear'd
By th' Angel, on thy Feet thou stoodst at last,
Tho' comfortless, as when a Father mourns
His Children, all in view destroyed at once.
I have been the more particular in my Quotations out of the eleventh
Book of
Paradise Lost,
because it is not generally reckoned among the
most shining Books of this Poem; for which Reason the Reader might be
apt to overlook those many Passages in it which deserve our Admiration.
The eleventh and twelfth are indeed built upon that single Circumstance
of the Removal of our first Parents from Paradise; but tho' this is not
in itself so great a Subject as that in most of the foregoing Books, it
is extended and diversified with so many surprising Incidents and
pleasing Episodes, that these two last Books can by no means be looked
upon as unequal Parts of this Divine Poem. I must further add, that had
not
Milton
represented our first Parents as driven out of Paradise, his
Fall of Man would not have been compleat, and consequently his Action
would have been imperfect.
L.
Nat. Quaest
. Bk. III. §27.
this
Contents
|
Monday, April 28, 1712 |
Steele |
—Navibus1 atque
Quadrigis petimus bene vivere.
Hor.

Mr.
Spectator2,
A Lady of my Acquaintance, for whom I have too much Respect to be easy
while she is doing an indiscreet Action, has given occasion to this
Trouble: She is a Widow, to whom the Indulgence of a tender Husband
has entrusted the Management of a very great Fortune, and a Son about
sixteen, both which she is extremely fond of. The Boy has Parts of the
middle Size, neither shining nor despicable, and has passed the common
Exercises of his Years with tolerable Advantage; but is withal what
you would call a forward Youth: By the Help of this last
Qualification, which serves as a Varnish to all the rest, he is
enabled to make the best Use of his Learning, and display it at full
length upon all Occasions. Last Summer he distinguished himself two or
three times very remarkably, by puzzling the Vicar before an Assembly
of most of the Ladies in the Neighbourhood; and from such weighty
Considerations as these, as it too often unfortunately falls out, the
Mother is become invincibly persuaded that her Son is a great Scholar;
and that to chain him down to the ordinary Methods of Education with
others of his Age, would be to cramp his Faculties, and do an
irreparable Injury to his wonderful Capacity.
I happened to visit at the House last Week, and missing the young
Gentleman at the Tea-Table, where he seldom fails to officiate, could
not upon so extraordinary a Circumstance avoid inquiring after him. My
Lady told me, he was gone out with her Woman, in order to make some
Preparations for their Equipage; for that she intended very speedily
to carry him to travel. The Oddness of the Expression shock'd me a
little; however, I soon recovered my self enough to let her know, that
all I was willing to understand by it was, that she designed this
Summer to shew her Son his Estate in a distant County, in which he has
never yet been: But she soon took care to rob me of that agreeable
Mistake, and let me into the whole Affair. She enlarged upon young
Master's prodigious Improvements, and his comprehensive Knowledge of
all Book-Learning; concluding, that it was now high time he should be
made acquainted with Men and Things; that she had resolved he should
make the Tour of France and Italy, but could not bear to have him out
of her Sight, and therefore intended to go along with him.
I was going to rally her for so extravagant a Resolution, but found my
self not in fit Humour to meddle with a Subject that demanded the most
soft and delicate Touch imaginable. I was afraid of dropping something
that might seem to bear hard either upon the Son's Abilities, or the
Mother's Discretion; being sensible that in both these Cases, tho'
supported with all the Powers of Reason, I should, instead of gaining
her Ladyship over to my Opinion, only expose my self to her Disesteem:
I therefore immediately determined to refer the whole Matter to the
Spectator.
When I came to reflect at Night, as my Custom is, upon the Occurrences
of the Day, I could not but believe that this Humour of carrying a Boy
to travel in his Mother's Lap, and that upon pretence of learning Men
and Things, is a Case of an extraordinary Nature, and carries on it a
particular Stamp of Folly. I did not remember to have met with its
Parallel within the Compass of my Observation, tho' I could call to
mind some not extremely unlike it. From hence my Thoughts took
Occasion to ramble into the general Notion of Travelling, as it is now
made a Part of Education. Nothing is more frequent than to take a Lad
from Grammar and Taw, and under the Tuition of some poor Scholar, who
is willing to be banished for thirty Pounds a Year, and a little
Victuals, send him crying and snivelling into foreign Countries. Thus
he spends his time as Children do at Puppet-Shows, and with much the
same Advantage, in staring and gaping at an amazing Variety of strange
things: strange indeed to one who is not prepared to comprehend the
Reasons and Meaning of them; whilst he should be laying the solid
Foundations of Knowledge in his Mind, and furnishing it with just
Rules to direct his future Progress in Life under some skilful Master
of the Art of Instruction.
Can there be a more astonishing Thought in Nature, than to consider
how Men should fall into so palpable a Mistake? It is a large Field,
and may very well exercise a sprightly Genius; but I don't remember
you have yet taken a Turn in it. I wish, Sir, you would make People
understand, that Travel is really the last Step to be taken in the
Institution of Youth; and to set out with it, is to begin where they
should end.
Certainly the true End of visiting Foreign Parts, is to look into
their Customs and Policies, and observe in what Particulars they excel
or come short of our own; to unlearn some odd Peculiarities in our
Manners, and wear off such awkward Stiffnesses and Affectations in our
Behaviour, as may possibly have been contracted from constantly
associating with one Nation of Men, by a more free, general, and mixed
Conversation. But how can any of these Advantages be attained by one
who is a mere Stranger to the Custom sand Policies of his native
Country, and has not yet fixed in his Mind the first Principles of
Manners and Behaviour? To endeavour it, is to build a gawdy Structure
without any Foundation; or, if I may be allow'd the Expression, to
work a rich Embroidery upon a Cobweb.
Another End of travelling which deserves to be considerd, is the
Improving our Taste of the best Authors of Antiquity, by seeing the
Places where they lived, and of which they wrote; to compare the
natural Face of the Country with the Descriptions they have given us,
and observe how well the Picture agrees with the Original. This must
certainly be a most charming Exercise to the Mind that is rightly
turned for it; besides that it may in a good measure be made
subservient to Morality, if the Person is capable of drawing just
Conclusions concerning the Uncertainty of human things, from the
ruinous Alterations Time and Barbarity have brought upon so many
Palaces, Cities and whole Countries, which make the most illustrious
Figures in History. And this Hint may be not a little improved by
examining every Spot of Ground that we find celebrated as the Scene of
some famous Action, or retaining any Footsteps of a
Cato,
Cicero or
Brutus, or some such great virtuous Man. A nearer View of any such
Particular, tho really little and trifling in it self, may serve the
more powerfully to warm a generous Mind to an Emulation of their
Virtues, and a greater Ardency of Ambition to imitate their bright
Examples, if it comes duly temper'd and prepar'd for the Impression.
But this I
believe you'll hardly think those to be, who are so far
from ent'ring into the Sense and Spirit of the Ancients, that they
don't yet understand their Language with any
Exactness3.
But I have wander'd from my Purpose, which was only to desire you to
save, if possible, a fond
English Mother, and Mother's own Son, from
being shewn a ridiculous Spectacle thro' the most polite Part of
Europe, Pray tell them, that though to be Sea-sick, or jumbled in an
outlandish Stage-Coach, may perhaps be healthful for the Constitution
of the Body, yet it is apt to cause such a Dizziness in young empty
Heads, as too often lasts their Life-time.
I am,
Sir,
Your most Humble Servant,
Philip Homebred.
Birchan-Lane.
Sir,
I was marry'd on
Sunday last, and went peaceably to bed; but, to my
Surprize, was awakend the next Morning by the Thunder of a Set of
Drums. These warlike Sounds (methinks) are very improper in a
Marriage-Consort, and give great Offence; they seem to insinuate, that
the Joys of this State are short, and that Jars and Discord soon
ensue. I fear they have been ominous to many Matches, and sometimes
proved a Prelude to a Battel in the Honey-Moon. A Nod from you may
hush them; therefore pray, Sir, let them be silenced, that for the
future none but soft Airs may usher in the Morning of a Bridal Night,
which will be a Favour not only to those who come after, but to me,
who can still subscribe my self,
Your most humble
and most obedient Servant,
Robin Bridegroom.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am one of that sort of Women whom the gayer Part of our Sex are apt
to call a Prude. But to shew them that I have very little Regard to
their Raillery, I shall be glad to see them all at
The Amorous Widow,
or the Wanton Wife, which is to be acted, for the Benefit of Mrs.
Porter, on Monday the 28th Instant. I assure you I can laugh at an
Amorous Widow, or Wanton Wife, with as little Temptation to imitate
them, as I could at any other vicious Character. Mrs. Porter obliged
me so very much in the exquisite Sense she seemed to have of the
honourable Sentiments and noble Passions in the Character of Hermione,
that I shall appear in her behalf at a Comedy, tho I have not great
Relish for any Entertainments where the Mirth is not seasond with a
certain Severity, which ought to recommend it to People who pretend to
keep Reason and Authority over all their Actions.
I am,
Sir,
Your frequent Reader,
Altamira.
T.
Strenua nos exercet inertia: Navibus...
Dr. Thomas Birch, in a letter dated June 15, 1764, says
that this letter was by Mr. Philip Yorke, afterwards Earl of Hardwicke,
who was author also of another piece in the
Spectator
, but his son could
not remember what that was.
Exactness.
I cant quit this head without paying my Acknowledgments to one of the
most entertaining Pieces this Age has produc'd, for the Pleasure it gave
me. You will easily guess, that the Book I have in my head is Mr. A——'s
Remarks upon Italy. That Ingenious gentleman has with so much Art and
Judgment applied his exact Knowledge of all the Parts of Classical
Learning to illustrate the several occurrences of his Travels, that his
Work alone is a pregnant Proof of what I have said. No Body that has a
Taste this way, can read him going from Rome to Naples, and making
Horace and Silius Italicus his Chart, but he must feel some Uneasiness
in himself to Reflect that he was not in his Retinue. I am sure I wish'd
it Ten Times in every Page, and that not without a secret Vanity to
think in what State I should have Travelled the Appian Road with Horace
for a Guide, and in company with a Countryman of my own, who of all Men
living knows best how to follow his Steps.
Contents
|
Tuesday, April 29, 1712 |
Budgell |
Vere magis, quia vere calor redit ossibus—
Virg.

The author of the
Menagiana
acquaints us, that discoursing one Day with
several Ladies of Quality about the Effects of the Month of
May
, which
infuses a kindly Warmth into the Earth, and all its Inhabitants; the
Marchioness of S——, who was one of the Company, told him, That though
she would promise to be chaste in every Month besides, she could not
engage for her self in
May
. As the beginning therefore of this Month is
now very near, I design this Paper for a Caveat to the Fair Sex, and
publish it before
April
is quite out, that if any of them should be
caught tripping, they may not pretend they had not timely Notice.
I am induced to this, being persuaded the above-mentioned Observation is
as well calculated for our Climate as for that of
France
, and that some
of our
British
Ladies are of the same Constitution with the
French
Marchioness.
I shall leave it among Physicians to determine what may be the Cause of
such an Anniversary Inclination; whether or no it is that the Spirits
after having been as it were frozen and congealed by
Winter
, are now
turned loose, and set a rambling; or that the gay Prospects of Fields
and Meadows, with the Courtship of the Birds in every Bush, naturally
unbend the Mind, and soften it to Pleasure; or that, as some have
imagined, a Woman is prompted by a kind of Instinct to throw herself on
a Bed of Flowers, and not to let those beautiful Couches which Nature
has provided lie useless.
it be, the Effects of this Month on
the lower part of the Sex, who act without Disguise,
are
very
visible. It is at this time that we see the young Wenches in a Country
Parish dancing round a May-Pole, which one of our learned Antiquaries
supposes to be a Relique of a certain Pagan Worship that I do not think
fit to mention.
It is likewise on the first Day of this Month that we see the ruddy
Milk-Maid exerting her self in a most sprightly manner under a Pyramid
of Silver-Tankards, and, like the Virgin
Tarpeia
, oppress'd by the
costly Ornaments which her Benefactors lay upon her.
I need not mention the Ceremony of the Green Gown, which is also
peculiar to this gay Season.
The same periodical Love-Fit spreads through the whole Sex, as Mr.
Dryden
well observes in his Description of this merry
:
For thee, sweet Month, the Groves green Livries wear,
If not the first, the fairest of the Year;
For thee the Graces lead the dancing Hours,
And Nature's ready Pencil paints the Flow'rs.
The sprightly May commands our Youth to keep
The Vigils of her Night, and breaks their Sleep;
Each gentle Breast with kindly Warmth she moves,
Inspires new Flames, revives extinguish'd Loves2.
Accordingly among the Works of the great Masters in Painting, who have
drawn this genial Season of the Year, we often observe
Cupids
confused
with
Zephirs
flying up and down promiscuously in several Parts of the
Picture. I cannot but add from my own Experience, that about this Time
of the Year Love-Letters come up to me in great Numbers from all
Quarters of the Nation.
I receiv'd an Epistle in particular by the last Post from a
Yorkshire
Gentleman, who makes heavy Complaints of one
Zelinda
, whom it seems he
has courted unsuccessfully these three Years past. He tells me that he
designs to try her this
May
, and if he does not carry his Point, he will
never think of her more.
Having thus fairly admonished the female Sex, and laid before them the
Dangers they are exposed to in this critical Month, I shall in the next
place lay down some Rules and Directions for their better avoiding those
Calentures which are so very frequent in this Season.
In the first place, I would advise them never to venture abroad in the
Fields, but in the Company of a Parent, a Guardian, or some other sober
discreet Person. I have before shewn how apt they are to trip in a
flowry Meadow, and shall further observe to them, that
Proserpine
was
out
a Maying
, when she met with that fatal Adventure to which
Milton
alludes when he
—That fair Field
Of Enna, where Proserpine gathering Flowers,
Herself a fairer Flower, by gloomy Dis
Was gathered—3
Since I am got into Quotations, I shall conclude this Head with
Virgil's
Advice to young People, while they are gathering wild Strawberries and
Nosegays, that they should have a care of the
Snake in the Grass
.
In the second place, I cannot but approve those Prescriptions, which our
Astrological Physicians give in their Almanacks for this Month; such as
are a spare and simple Diet, with the moderate Use of Phlebotomy.
Under this Head of Abstinence I shall also advise my fair Readers to be
in a particular manner careful how they meddle with Romances, Chocolate,
Novels, and the like Inflamers, which I look upon as very dangerous to
be made use of during this great Carnival of Nature.
As I have often declared, that I have nothing more at heart than the
Honour of my dear Country-Women, I would beg them to consider, whenever
their Resolutions begin to fail them, that there are but one and thirty
Days of this soft Season, and that if they can but weather out this one
Month, the rest of the Year will be easy to them. As for that Part of
the Fair-Sex who stay in Town, I would advise them to be particularly
cautious how they give themselves up to their most innocent
Entertainments. If they cannot forbear the Play-house, I would recommend
Tragedy to them, rather than Comedy; and should think the Puppet-show
much safer for them than the Opera, all the while the Sun is in
Gemini
.
The Reader will observe, that this Paper is written for the use of those
Ladies who think it worth while to war against Nature in the Cause of
Honour. As for that abandon'd Crew, who do not think Virtue worth
contending for, but give up their Reputation at the first Summons, such
Warnings and Premonitions are thrown away upon them. A Prostitute is the
same easy Creature in all Months of the Year, and makes no difference
between
May
and
December
.
X.
is
and in first Reprint.
This quotation is made up of two passages in Dryden's
version of Chaucer's
Knights Tale
,
Palamon and Arcite
. The first four
lines are from Bk. ii. 11. 663-666, the other four lines are from Bk. i.
11. 176-179.
Paradise Lost
, Bk. iv. 11. 268-271.
Contents
|
Wednesday, April 30, 1712 |
Steele |
Pone me pigris ubi nulla campis
Arbor æstiva recreatur aura,
Dulce ridentem Lalagen amabo,
Dulce loquentem.
Hor.

There are such wild Inconsistencies in the Thoughts of a Man in love,
that I have often reflected there can be no reason for allowing him more
Liberty than others possessed with Frenzy, but that his Distemper has no
Malevolence in it to any Mortal. That Devotion to his Mistress kindles
in his Mind a general Tenderness, which exerts it self towards every
Object as well as his Fair-one. When this Passion is represented by
Writers, it is common with them to endeavour at certain Quaintnesses and
Turns of Imagination, which are apparently the Work of a Mind at ease;
but the Men of true Taste can easily distinguish the Exertion of a Mind
which overflows with tender Sentiments, and the Labour of one which is
only describing Distress. In Performances of this kind, the most absurd
of all things is to be witty; every Sentiment must grow out of the
Occasion, and be suitable to the Circumstances of the Character. Where
this Rule is transgressed, the humble Servant, in all the fine things he
says, is but shewing his Mistress how well he can dress, instead of
saying how well he loves. Lace and Drapery is as much a Man, as Wit and
Turn is Passion.
Mr.
Spectator,
The
following Verses are a Translation of a
Lapland Love-Song, which I
met with in
Scheffer's History of that Country
1. I was agreeably
surprized to find a Spirit of Tenderness and Poetry in a Region which
I never suspected for Delicacy. In hotter Climates, tho' altogether
uncivilized, I had not wonder'd if I had found some sweet wild Notes
among the Natives, where they live in Groves of Oranges, and hear the
Melody of Birds about them: But a
Lapland Lyric, breathing Sentiments
of Love and Poetry, not unworthy old
Greece or
Rome; a regular Ode
from a Climate pinched with Frost, and cursed with Darkness so great a
Part of the Year; where 'tis amazing that the poor Natives should get
Food, or be tempted to propagate their Species: this, I confess,
seemed a greater Miracle to me, than the famous Stories of their
Drums, their Winds and Inchantments.
I am the bolder in commending this Northern Song, because I have
faithfully kept to the Sentiments, without adding or diminishing; and
pretend to no greater Praise from my Translation, than they who smooth
and clean the Furs of that Country which have suffered by Carriage.
The Numbers in the Original are as loose and unequal, as those in
which the
British Ladies sport their Pindaricks; and perhaps the
fairest of them might not think it a disagreeable Present from a
Lover: But I have ventured to bind it in stricter Measures, as being
more proper for our Tongue, tho perhaps wilder Graces may better suit
the Genius of the
Laponian Language.
It will be necessary to imagine, that the Author of this Song, not
having the Liberty of visiting his Mistress at her Father's House, was
in hopes of spying her at a Distance in the Fields.
| I |
Thou rising Sun, whose gladsome Ray
Invites my Fair to Rural Play,
Dispel the Mist, and clear the Skies,
And bring my Orra to my Eyes. |
| II |
Oh! were I sure my Dear to view,
I'd climb that Pine-Trees topmost Bough,
Aloft in Air that quivering plays,
And round and round for ever gaze. |
| III |
My Orra Moor, where art thou laid?
What Wood conceals my sleeping Maid?
Fast by the Roots enrag'd I'll tear
The Trees that hide my promised Fair.
|
| IV |
Oh! I cou'd ride the Clouds and Skies,
Or on the Raven's Pinions rise:
Ye Storks, ye Swans, a moment stay,
And waft a Lover on his Way. |
| V |
My Bliss too long my Bride denies,
Apace the wasting Summer flies:
Nor yet the wintry Blasts I fear,
Not Storms or Night shall keep me here. |
| VI |
What may for Strength with Steel compare?
Oh! Love has Fetters stronger far:
By Bolts of Steel are Limbs confin'd,
But cruel Love enchains the Mind. |
| VII |
No longer then perplex thy Breast,
When Thoughts torment, the first are best;
'Tis mad to go, 'tis Death to stay,
Away to Orra, haste away. |
April the 10th.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am one of those despicable Creatures called a Chamber-Maid, and have
lived with a Mistress for some time, whom I love as my Life, which has
made my Duty and Pleasure inseparable. My greatest Delight has been in
being imploy'd about her Person; and indeed she is very seldom out of
Humour for a Woman of her Quality: But here lies my Complaint, Sir; To
bear with me is all the Encouragement she is pleased to bestow upon
me; for she gives her cast-off Cloaths from me to others: some she is
pleased to bestow in the House to those that neither wants nor wears
them, and some to Hangers-on, that frequents the House daily, who
comes dressed out in them. This, Sir, is a very mortifying Sight to
me, who am a little necessitous for Cloaths, and loves to appear what
I am, and causes an Uneasiness, so that I can't serve with that
Chearfulness as formerly; which my Mistress takes notice of, and calls
Envy and Ill-Temper at seeing others preferred before me. My Mistress
has a younger Sister lives in the House with her, that is some
Thousands below her in Estate, who is continually heaping her Favours
on her Maid; so that she can appear every Sunday, for the first
Quarter, in a fresh Suit of Cloaths of her Mistress's giving, with all
other things suitable: All this I see without envying, but not without
wishing my Mistress would a little consider what a Discouragement it
is to me to have my Perquisites divided between Fawners and Jobbers,
which others enjoy intire to themselves. I have spoke to my Mistress,
but to little Purpose; I have desired to be discharged (for indeed I
fret my self to nothing) but that she answers with Silence. I beg,
Sir, your Direction what to do, for I am fully resolved to follow your
Counsel; who am
Your Admirer and humble Servant,
Constantia Comb-brush.
I beg that you would put it in a better Dress, and let it come abroad;
that my Mistress, who is an Admirer of your Speculations, may see it.
T.
John Scheffer, born in 1621, at Strasburg, was at the age
of 27 so well-known for his learning, that he was invited to Sweden,
where he received a liberal pension from Queen Christina as her
librarian, and was also a Professor of Law and Rhetoric in the
University of Upsala. He died in 1679. He was the author of 27 works,
among which is his
Lapponia
, a Latin description of Lapland, published
in 1673, of which an English version appeared at Oxford in folio, in
1674. The song is there given in the original Lapp, and in a rendering
of Scheffer's Latin less conventionally polished than that published by
the
Spectator
, which is Ambrose Philips's translation of a translation.
In the Oxford translation there were six stanzas of this kind:
With brightest beams let the Sun shine
On Orra Moor.
Could I be sure
That from the top o' th' lofty Pine
I Orra Moor might see,
I to his highest Bough would climb,
And with industrious Labour try
Thence to descry
My Mistress if that there she be.
Could I but know amidst what Flowers
Or in what Shade she stays,
The gaudy Bowers,
With all their verdant Pride,
Their Blossoms and their Sprays,
Which make my Mistress disappear;
And her in envious Darkness hide,
I from the Roots and Beds of Earth would tear.
In the same chapter another song is given of which there is a version in
of the
Spectator
.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 1, 1712 |
Addison |
—Perituræ parcite chartæ.
Juv.

I have often pleased my self with considering the two kinds of Benefits
which accrue to the Publick from these my Speculations, and which, were
I to speak after the manner of Logicians, I would distinguish into the
Material and the Formal. By the latter I understand those Advantages
which my Readers receive, as their Minds are either improv'd or
delighted by these my daily Labours; but having already several times
descanted on my Endeavours in this Light, I shall at present wholly
confine my self to the Consideration of the former. By the Word Material
I mean those Benefits which arise to the Publick from these my
Speculations, as they consume a considerable quantity of our Paper
Manufacture, employ our Artisans in Printing, and find Business for
great Numbers of Indigent Persons.
Our Paper-Manufacture takes into it several mean Materials which could
be put to no other use, and affords Work for several Hands in the
collecting of them, which are incapable of any other Employment. Those
poor Retailers, whom we see so busy in every Street, deliver in their
respective Gleanings to the Merchant. The Merchant carries them in Loads
to the Paper-Mill, where they pass thro' a fresh Set of Hands, and give
life to another Trade. Those who have Mills on their Estates, by this
means considerably raise their Rents, and the whole Nation is in a great
measure supply'd with a Manufacture, for which formerly she was obliged
to her Neighbours.
The Materials are no sooner wrought into Paper, but they are distributed
among the Presses, where they again set innumerable Artists at Work, and
furnish Business to another Mystery. From hence, accordingly as they are
stain'd with News or Politicks, they fly thro' the Town in
Post-Men,
Post-Boys, Daily-Courants, Reviews, Medleys
, and
Examiners
. Men, Women,
and Children contend who shall be the first Bearers of them, and get
their daily Sustenance by spreading them. In short, when I trace in my
Mind a Bundle of Rags to a Quire of
Spectators
, I find so many Hands
employ'd in every Step they take thro their whole Progress, that while I
am writing a
Spectator
, I fancy my self providing Bread for a Multitude.
If I do not take care to obviate some of my witty Readers, they will be
apt to tell me, that my Paper, after it is thus printed and published,
is still beneficial to the Publick on several Occasions. I must confess
I have lighted my Pipe with my own Works for this Twelve-month past: My
Landlady often sends up her little Daughter to desire some of my old
Spectators
, and has frequently told me, that the Paper they are printed
on is the best in the World to wrap Spice in. They likewise make a good
Foundation for a Mutton pye, as I have more than once experienced, and
were very much sought for, last Christmas, by the whole Neighbourhood.
It is pleasant enough to consider the Changes that a Linnen Fragment
undergoes, by passing thro' the several Hands above mentioned. The
finest pieces of Holland, when worn to Tatters, assume a new Whiteness
more beautiful than their first, and often return in the shape of
Letters to their Native Country. A Lady's Shift may be metamorphosed
into Billet
s-
doux, and come into her Possession a second time. A Beau
may peruse his Cravat after it is worn out, with greater Pleasure and
Advantage than ever he did in a Glass. In a word, a Piece of Cloth,
after having officiated for some Years as a Towel or a Napkin, may by
this means be raised from a Dung-hill, and become the most valuable
Piece of Furniture in a Prince's Cabinet.
The politest Nations of Europe have endeavoured to vie with one another
for the Reputation of the finest Printing: Absolute Governments, as well
as Republicks, have encouraged an Art which seems to be the noblest and
most beneficial that was ever invented among the Sons of Men. The
present King of
France
, in his Pursuits after Glory, has particularly
distinguished himself by the promoting of this useful Art, insomuch that
several Books have been printed in the
Louvre
at his own Expence, upon
which he sets so great a value, that he considers them as the noblest
Presents he can make to foreign Princes and Ambassadors. If we look into
the Commonwealths of
Holland
and
Venice
, we shall find that in this
Particular they have made themselves the Envy of the greatest
Monarchies.
Elziver
and
Aldus
are more frequently mentioned than any
Pensioner of the one or Doge of the other.
The several Presses which are now in
England
, and the great
Encouragement which has been given to Learning for some Years last past,
has made our own Nation as glorious upon this Account, as for its late
Triumphs and Conquests. The new
which is given us of
Cæsar's
Commentaries, has already been taken notice of in foreign Gazettes, and
is a Work that does honour to the
English
Press
. It is no wonder
that an Edition should be very correct, which has passed thro' the Hands
of one of the most accurate, learned and judicious Writers this Age has
produced. The Beauty of the Paper, of the Character, and of the several
Cuts with which this noble Work is illustrated, makes it the finest Book
that I have ever seen; and is a true Instance of the English Genius,
which, tho' it does not come the first into any Art, generally carries
it to greater Heights than any other Country in the World. I am
particularly glad that this Author comes from a
British
Printing-house
in so great a Magnificence, as he is the first who has given us any
tolerable Account of our Country.
My Illiterate Readers, if any such there are, will be surprized to hear
me talk of Learning as the Glory of a Nation, and of Printing as an Art
that gains a Reputation to a People among whom it flourishes. When Men's
Thoughts are taken up with Avarice and Ambition, they cannot look upon
any thing as great or valuable, which does not bring with it an
extraordinary Power or Interest to the Person who is concerned in it.
But as I shall never sink this Paper so far as to engage with Goths and
Vandals, I shall only regard such kind of Reasoners with that Pity which
is due to so Deplorable a Degree of Stupidity and Ignorance.
L.
Just published, 1712, by Dr. Samuel Clarke, then 37 years
old. He had been for 12 years chaplain to the Bishop of Norwich, and
Boyle Lecturer in 1704-5, when he took for his subject the
Being and
Attributes of God and the Evidences of Natural and Revealed Religion
. He
had also translated Newton's
Optics
, and was become chaplain to the
Queen, Rector of St. Jamess, Westminster, and D. D. of Cambridge. The
accusations of heterodoxy that followed him through his after life date
from this year, 1712, in which, besides the edition of
Cæsar
, he
published a book on the
Scripture Doctrine of the Trinity
.
Contents
|
Friday, May 2, 1712 |
Steele |
Nos decebat
Lugere ubi esset aliquis in lucem editus
Humanæ vitæ varia reputantes mala;
At qui labores morte finisset graves
Omnes amices laude et lætitia exequi.
Eurip.
apud Tull.

As the Spectator is in a Kind a Paper of News from the natural World, as
others are from the busy and politick Part of Mankind, I shall translate
the following Letter written to an eminent French Gentleman in this Town
from Paris, which gives us the Exit of an Heroine who is a Pattern of
Patience and Generosity.
Paris, April 18, 1712.
Sir,
It is so many Years since you left your native Country, that I am to
tell you the Characters of your nearest Relations as much as if you
were an utter Stranger to them. The Occasion of this is to give you an
account of the Death of
Madam de Villacerfe, whose Departure out of
this Life I know not whether a Man of your Philosophy will call
unfortunate or not, since it was attended with some Circumstances as
much to be desired as to be lamented. She was her whole Life happy in
an uninterrupted Health, and was always honoured for an Evenness of
Temper and Greatness of Mind. On the 10th instant that Lady was taken
with an Indisposition which confined her to her Chamber, but was such
as was too slight to make her take a sick Bed, and yet too grievous to
admit of any Satisfaction in being out of it. It is notoriously known,
that some Years ago
Monsieur Festeau, one of the most considerable
Surgeons in
Paris, was desperately in love with this Lady: Her Quality
placed her above any Application to her on the account of his Passion;
but as a Woman always has some regard to the Person whom she believes
to be her real Admirer, she now took it in her head (upon Advice of
her Physicians to lose some of her Blood) to send for
Monsieur Festeau
on that occasion. I happened to be there at that time, and my near
Relation gave me the Privilege to be present. As soon as her Arm was
stripped bare, and he began to press it in order to raise the Vein,
his Colour changed, and I observed him seized with a sudden Tremor,
which made me take the liberty to speak of it to my Cousin with some
Apprehension: She smiled, and said she knew Mr.
Festeau had no
Inclination to do her Injury. He seemed to recover himself, and
smiling also proceeded in his Work. Immediately after the Operation he
cried out, that he was the most unfortunate of all Men, for that he
had open'd an Artery instead of a Vein. It is as impossible to express
the Artist's Distraction as the Patient's Composure. I will not dwell
on little Circumstances, but go on to inform you, that within three
days time it was thought necessary to take off her Arm. She was so far
from using
Festeau as it would be natural to one of a lower Spirit to
treat him, that she would not let him be absent from any Consultation
about her present Condition, and on every occasion asked whether he
was satisfy'd in the Measures
that were taken about her. Before this
last Operation she ordered her Will to be drawn, and after having been
about a quarter of an hour alone, she bid the Surgeons, of whom poor
Festeau was one, go on in their Work. I know not how to give you the
Terms of Art, but there appeared such Symptoms after the Amputation of
her Arm, that it was visible she could not live four and twenty hours.
Her Behaviour was so magnanimous throughout this whole Affair, that I
was particularly curious in taking Notice of what passed as her Fate
approached nearer and nearer, and took Notes of what she said to all
about her, particularly Word for Word what she spoke to Mr.
Festeau,
which was as follows.
"Sir, you give me inexpressible Sorrow for the Anguish with which I
see you overwhelmed. I am removed to all Intents and Purposes from
the Interests of human Life, therefore I am to begin to think like
one wholly unconcerned in it. I do not consider you as one by whose
Error I have lost my Life; no, you are my Benefactor, as you have
hasten'd my Entrance into a happy Immortality. This is my Sense of
this Accident; but the World in which you live may have Thoughts of
it to your Disadvantage, I have therefore taken Care to provide for
you in my Will, and have placed you above what you have to fear from
their Ill-Nature."
While this excellent Woman spoke these Words,
Festeau looked as if he
received a Condemnation to die, instead of a Pension for his Life.
Madam de Villacerfe lived till Eight of
the Clock the next Night;
and tho she must have laboured under the most exquisite Torments, she
possessed her Mind with so wonderful a Patience, that one may rather
say she ceased to breathe than she died at that hour. You who had not
the happiness to be personally known to this Lady, have nothing but to
rejoyce in the Honour you had of being related to so great Merit; but
we who have lost her Conversation, cannot so easily resign our own
Happiness by Reflection upon hers.
I am,
Sir,
Your affectionate Kinsman,
and most obedient humble Servant,
Paul Regnaud.
There hardly can be a greater Instance of an Heroick Mind, than the
unprejudiced Manner in which this Lady weighed this Misfortune. The
regard of Life itself could not make her overlook the Contrition of the
unhappy Man, whose more than Ordinary Concern for her was all his Guilt.
It would certainly be of singular Use to human Society to have an exact
Account of this Lady's ordinary Conduct, which was Crowned by so
uncommon Magnanimity. Such Greatness was not to be acquired in her last
Article, nor is it to be doubted but it was a constant Practice of all
that is praise-worthy, which made her capable of beholding Death, not as
the Dissolution, but Consummation of her Life.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, May 3, 1712 |
Addison |
Segnius irritant animos demissa per aures
Quam quæ sunt oculis subjecta fidelibus—
Hor.

Milton
, after having represented in Vision the History of Mankind to the
first great Period of Nature, dispatches the remaining part of it in
Narration. He has devised a very handsome Reason for the Angels
proceeding with
Adam
after this manner; though doubtless the true Reason
was the Difficulty which the Poet would have found to have shadowed out
so mixed and complicated a Story in visible Objects. I could wish,
however, that the Author had done it, whatever Pains it might have cost
him. To give my Opinion freely, I think that the exhibiting part of the
History of Mankind in Vision, and part in Narrative, is as if an
History-Painter should put in Colours one half of his Subject, and write
down the remaining part of it. If
Milton's
Poem flags any where, it is
in this Narration, where in some places the Author has been so attentive
to his Divinity, that he has neglected his Poetry. The Narration,
however, rises very happily on several Occasions, where the Subject is
capable of Poetical Ornaments, as particularly in the Confusion which he
describes among the Builders of
Babel
, and in his short Sketch of the
Plagues of
Egypt
. The Storm of Hail and Fire, with the Darkness that
overspread the Land for three Days, are described with great Strength.
The beautiful Passage which follows, is raised upon noble Hints in
Scripture:
—Thus with ten Wounds
The River-Dragon tamed at length submits
To let his Sojourners depart, and oft
Humbles his stubborn Heart; but still as Ice
More harden'd after Thaw, till in his Rage
Pursuing whom he late dismissed, the Sea
Swallows him with his Host, but them lets pass
As on dry Land between two Chrystal Walls,
Aw'd by the Rod of Moses so to stand
Divided—
The River-Dragon is an Allusion to the Crocodile, which inhabits the
Nile
, from whence
Egypt
derives her Plenty. This Allusion is taken from
that Sublime Passage in
Ezekiel
,
Thus saith the Lord God, behold I am
against thee, Pharaoh King of Egypt, the great Dragon that lieth in the
midst of his Rivers, which hath said, my River is mine own, and I have
made it for my self.
Milton
has given us another very noble and poetical
Image in the same Description, which is copied almost Word for Word out
of the History of
Moses
.
All Night he will pursue, but his Approach
Darkness defends between till morning Watch;
Then through the fiery Pillar and the Cloud
God looking forth, will trouble all his Host,
And craze their Chariot Wheels: when by command
Moses once more his potent Rod extends
Over the Sea: the Sea his Rod obeys:
On their embattell'd Ranks the Waves return
And overwhelm their War—
As the principal Design of this Episode was to give
Adam
an Idea of the
Holy Person, who was to reinstate human Nature in that Happiness and
Perfection from which it had fallen, the Poet confines himself to the
Line of
Abraham
, from whence the
Messiah
was to Descend. The Angel is
described as seeing the
Patriarch
actually travelling towards the Land
of Promise, which gives a particular Liveliness to this part of the
Narration.
I see him, but thou canst not, with what Faith
He leaves his Gods, his Friends, his Native Soil,
Ur of Chaldæa, passing now the Ford
To Haran, after him a cumbrous Train
Of Herds and Flocks, and numerous Servitude,
Not wand'ring poor, but trusting all his Wealth
With God, who call'd him, in a Land unknown.
Canaan he now attains, I see his Tents
Pitch'd about Sechem, and the neighbouring Plain
Of Moreh, there by Promise he receives
Gifts to his Progeny of all that Land,
From Hamath Northward to the Desart South.
(Things by their Names I call, though yet unnamed.)
As
Virgil's
Vision in the sixth
Æneid
probably gave
Milton
the Hint of
this whole Episode, the last Line is a Translation of that Verse, where
Anchises
mentions the Names of Places, which they were to bear
hereafter.
Hæc tum nomina erunt, nunc sunt sine nomine terræ.
The Poet has very finely represented the Joy and Gladness of Heart which
rises in
Adam
upon his discovery of the
Messiah
. As he sees his Day at a
distance through Types and Shadows, he rejoices in it: but when he finds
the Redemption of Man compleated, and Paradise again renewed, he breaks
forth in Rapture and Transport;
O Goodness infinite, Goodness immense!
That all this Good of Evil shall produce, &c.
I have hinted in my sixth Paper on
Milton
, that an Heroick Poem,
according to the Opinion of the best Criticks, ought to end happily, and
leave the Mind of the Reader, after having conducted it through many
Doubts and Fears, Sorrows and Disquietudes, in a State of Tranquility
and Satisfaction.
Milton's
Fable, which had so many other Qualifications
to recommend it, was deficient in this Particular. It is here therefore,
that the Poet has shewn a most exquisite Judgment, as well as the finest
Invention, by finding out a Method to supply this natural Defect in his
Subject. Accordingly he leaves the Adversary of Mankind, in the last
View which he gives us of him, under the lowest State of Mortification
and Disappointment. We see him chewing Ashes, grovelling in the Dust,
and loaden with supernumerary Pains and Torments. On the contrary, our
two first Parents are comforted by Dreams and Visions, cheared with
Promises of Salvation, and, in a manner, raised to a greater Happiness
than that which they had forfeited: In short,
Satan
is represented
miserable in the height of his Triumphs, and
Adam
triumphant in the
height of Misery.
Milton's
Poem ends very nobly. The last Speeches of
Adam
and the
Arch-Angel are full of Moral and Instructive Sentiments. The Sleep that
fell upon
Eve
, and the Effects it had in quieting the Disorders of her
Mind, produces the same kind of Consolation in the Reader, who cannot
peruse the last beautiful Speech which is ascribed to the Mother of
Mankind, without a secret Pleasure and Satisfaction.
Whence thou return'st, and whither went'st, I know;
For God is also in Sleep, and Dreams advise,
Which he hath sent propitious, some great Good
Presaging, since with Sorrow and Heart's Distress
Wearied I fell asleep: but now lead on;
In me is no delay: with thee to go,
Is to stay here; without thee here to stay,
Is to go hence unwilling: thou to me
Art all things under Heav'n, all Places thou,
Who for my wilful Crime art banish'd hence.
This farther Consolation yet secure
I carry hence; though all by me is lost,
Such Favour, I unworthy, am vouchsafed,
By me the promised Seed shall all restore.
The following Lines, which conclude the Poem, rise in a most glorious
Blaze of Poetical Images and Expressions.
Heliodorus
in his
Æthiopicks
acquaints us, that the Motion of the Gods
differs from that of Mortals, as the former do not stir their Feet, nor
proceed Step by Step, but slide o'er the Surface of the Earth by an
uniform Swimming of the whole Body. The Reader may observe with how
Poetical a Description
Milton
has attributed the same kind of Motion to
the Angels who were to take Possession of Paradise.
So spake our Mother Eve, and Adam heard
Well pleas'd, but answered not; for now too nigh
Th' Archangel stood, and from the other Hill
To their fix'd Station, all in bright Array
The Cherubim descended; on the Ground
Gliding meteorous, as evening Mist
Ris'n from a River, o'er the Marish glides,
And gathers ground fast at the Lab'rer's Heel
Homeward returning. High in Front advanced,
The brandishd Sword of God before them blaz'd
Fierce as a Comet—
The Author helped his Invention in the following Passage, by reflecting
on the Behaviour of the Angel, who, in Holy Writ, has the Conduct of
Lot
and his Family. The Circumstances drawn from that Relation are very
gracefully made use of on this Occasion.
In either Hand the hast'ning Angel caught
Our ling'ring Parents, and to th' Eastern Gate
Led them direct; and down the Cliff as fast
To the subjected Plain; then disappear'd.
They looking back, &c.
Scene
which our first Parents are surprized with, upon their
looking back on Paradise, wonderfully strikes the Reader's Imagination,
as nothing can be more natural than the Tears they shed on that
Occasion.
They looking back, all th' Eastern side beheld
Of Paradise, so late their happy Seat,
Wav'd over by that flaming Brand, the Gate
With dreadful Faces throng'd and fiery Arms:
Some natural Tears they dropped, but wiped them soon;
The World was all before them, where to chuse
Their Place of Rest, and Providence their Guide.
If I might presume to offer at the smallest Alteration in this divine
Work, I should think the Poem would end better with the Passage here
quoted, than with the two Verses which follow:
They hand in hand, with wandering Steps and slow,
Through Eden took their solitary Way.
These two Verses, though they have their Beauty, fall very much below
the foregoing Passage, and renew in the Mind of the Reader that Anguish
which was pretty well laid by that Consideration.
The world was all before them, where to chuse
Their Place of Rest, and Providence their Guide.
The Number of Books in
Paradise Lost
is equal to those of the
Æneid
.
Our Author in his first Edition had divided his Poem into ten Books, but
afterwards broke the seventh and the eleventh each of them into two
different Books, by the help of some small Additions. This second
Division was made with great Judgment, as any one may see who will be at
the pains of examining it. It was not done for the sake of such a
Chimerical Beauty as that of resembling
Virgil
in this particular, but
for the more just and regular Disposition of this great Work.
Those who have read
Bossu
, and many of the Criticks who have written
since his Time, will not pardon me if I do not find out the particular
Moral which is inculcated in
Paradise Lost
. Though I can by no means
think, with the last mentioned French Author, that an Epick Writer first
of all pitches upon a certain Moral, as the Ground-Work and Foundation
of his Poem, and afterwards finds out a Story to it: I am, however, of
opinion, that no just Heroick Poem ever was or can be made, from whence
one great Moral may not be deduced. That which reigns in
Milton
, is the
most universal and most useful that can be imagined; it is in short
this, That Obedience to the Will of God makes Men happy, and that
Disobedience makes them miserable. This is visibly the Moral of the
principal Fable, which turns upon
Adam
and
Eve
, who continued in
Paradise, while they kept the command that was given them, and were
driven out of it as soon as they had transgressed. This is likewise the
Moral of the principal Episode, which shews us how an innumerable
Multitude of Angels fell from their State of Bliss, and were cast into
Hell upon their Disobedience. Besides this great Moral, which may be
looked upon as the Soul of the Fable, there are an Infinity of
Under-Morals which are to be drawn from the several parts of the Poem,
and which makes this Work more useful and Instructive than any other
Poem in any Language.
Those who have criticized on the
Odyssey
, the
Iliad
, and
Æneid
, have
taken a great deal of Pains to fix the Number of Months and Days
contained in the Action of each of those Poems. If any one thinks it
worth his while to examine this Particular in
Milton
, he will find that
from
Adam's
first Appearance in the fourth Book, to his Expulsion from
Paradise in the twelfth, the Author reckons ten Days. As for that part
of the Action which is described in the three first Books, as it does
not pass within the Regions of Nature, I have before observed that it is
not subject to any Calculations of Time.
I have now finished my Observations on a Work which does an Honour to
the
English
Nation. I have taken a general View of it under these four
Heads,
the Fable, the Characters, the Sentiments, and the Language
, and
made each of them the Subject of a particular Paper. I have in the next
Place spoken of the Censures which our Author may incur under each of
these Heads, which I have confined to two Papers, though I might have
enlarged the Number, if I had been disposed to dwell on so ungrateful a
Subject. I believe, however, that the severest Reader will not find any
little Fault in Heroick Poetry, which this Author has fallen into, that
does not come under one of those Heads among which I have distributed
his several Blemishes. After having thus treated at large of
Paradise
Lost,
I could not think it sufficient to have celebrated this Poem in
the whole, without descending to Particulars. I have therefore bestowed
a
upon each Book, and endeavoured not only to
prove
that the
Poem is beautiful in general, but to point out its Particular Beauties,
and to determine wherein they consist. I have endeavoured to shew how
some Passages are beautiful by being Sublime, others by being Soft,
others by being Natural; which of them are recommended by the Passion,
which by the Moral, which by the Sentiment, and which by the Expression.
I have likewise endeavoured to shew how the Genius of the Poet shines by
a happy Invention, a distant Allusion, or a judicious Imitation; how he
has copied or improved
Homer
or
Virgil
, and raised his own Imaginations
by the Use which he has made of several Poetical Passages in Scripture.
I might have
also several Passages of
Tasso
, which our Author
has
imitated; but as I do not look upon
Tasso
to be a sufficient
Voucher, I would not perplex my Reader with such Quotations, as might do
more Honour to the
Italian
than the
English
Poet. In short, I have
endeavoured to particularize those innumerable kinds of Beauty, which it
would be tedious to recapitulate, but which are essential to Poetry, and
which may be met with in the Works of this great Author. Had I thought,
at my first engaging in this design, that it would have led me to so
great a length, I believe I should never have entered upon it; but the
kind Reception which it has met with among those whose Judgments I have
a value for, as well as the uncommon Demands which my Bookseller tells
me have been made for these particular Discourses, give me no reason to
repent of the Pains I have been at in composing them.
L.
Prospect
shew
has likewise
Contents
|
Monday, May 5, 1712 |
Steele |
Totus Mundus agit Histrionem.
Many of my fair Readers, as well as very gay and well-received Persons
of the other Sex, are extremely perplexed at the
Latin
Sentences at the
Head of my Speculations; I do not know whether I ought not to indulge
them with Translations of each of them: However, I have to-day taken
down from the Top of the Stage in
Drury-Lane
a bit of Latin which often
stands in their View, and signifies that the whole World acts the
Player. It is certain that if we look all round us, and behold the
different Employments of Mankind, you hardly see one who is not, as the
Player is, in an assumed Character. The Lawyer, who is vehement and loud
in a Cause wherein he knows he has not the Truth of the Question on his
Side, is a Player as to the personated Part, but incomparably meaner
than he as to the Prostitution of himself for Hire; because the
Pleader's Falshood introduces Injustice, the Player feigns for no other
end but to divert or instruct you. The Divine, whose Passions transport
him to say any thing with any View but promoting the Interests of true
Piety and Religion, is a Player with a still greater Imputation of
Guilt, in proportion to his depreciating a Character more sacred.
Consider all the different Pursuits and Employments of Men, and you will
find half their Actions tend to nothing else but Disguise and Imposture;
and all that is done which proceeds not from a Man's very self, is the
Action of a Player. For this Reason it is that I make so frequent
mention of the Stage: It is, with me, a Matter of the highest
Consideration what Parts are well or ill performed, what Passions or
Sentiments are indulged or cultivated, and consequently what Manners and
Customs are transfused from the Stage to the World, which reciprocally
imitate each other. As the Writers of Epick Poems introduce shadowy
Persons, and represent Vices and Virtues under the Characters of Men and
Women; so I, who am a
Spectator
in the World, may perhaps sometimes make
use of the Names of the Actors on the Stage, to represent or admonish
those who transact Affairs in the World. When I am commending Wilks for
representing the Tenderness of a Husband and a Father in
Mackbeth
, the
Contrition of a reformed Prodigal in
Harry the Fourth
, the winning
Emptiness
a young Man of Good-nature and Wealth in the
Trip to the
Jubilee,
—the Officiousness of an artful Servant in the
Fox
:
when thus I celebrate
Wilks
, I talk to all the World who are engaged in
any of those Circumstances. If I were to speak of Merit neglected,
mis-applied, or misunderstood, might not I say
Estcourt
has a great
Capacity? But it is not the Interest of others who bear a Figure on the
Stage that his Talents were understood; it is their Business to impose
upon him what cannot become him, or keep out of his hands any thing in
which he would Shine. Were
to raise a Suspicion of himself in a Man
who passes upon the World for a fine Thing, in order to alarm him, one
might say, if
Lord Foppington
were not on the Stage, (
Cibber
acts
the false Pretensions to a genteel Behaviour so very justly), he would
have in the generality of Mankind more that would admire than deride
him. When we come to Characters directly Comical, it is not to be
imagin'd what Effect a well-regulated Stage would have upon Men's
Manners. The Craft of an Usurer, the Absurdity of a rich Fool, the
awkward Roughness of a Fellow of half Courage,
ungraceful Mirth of a
Creature of half Wit, might be for ever put out of Countenance by proper
Parts for
Dogget
.
Johnson
by acting
Corbacchio
the other Night, must
have given all who saw him a thorough Detestation of aged Avarice.
Petulancy of a peevish old Fellow, who loves and hates he knows not why,
is very excellently performed by the Ingenious
Mr. William Penkethman
in
the
Fop's Fortune
; where, in the Character of
Don Cholerick Snap Shorto de Testy
, he answers no Questions but to those whom he likes, and
wants no account of any thing from those he approves. Mr.
Penkethman
is
also Master of as many Faces in the Dumb-Scene as can be expected from a
Man in the Circumstances of being ready to perish out of Fear and
Hunger: He wonders throughout the whole Scene very masterly, without
neglecting his Victuals. If it be, as I
heard it sometimes
mentioned, a great Qualification for the World to follow Business and
Pleasure too, what is it in the Ingenious Mr.
Penkethman
to represent a
Sense of Pleasure and Pain at the same time; as you may see him do this
Evening
?
As it is certain that a Stage ought to be wholly suppressed, or
judiciously encouraged, while there is one in the Nation, Men turned for
regular Pleasure cannot employ their Thoughts more usefully, for the
Diversion of Mankind, than by convincing them that it is in themselves
to raise this Entertainment to the greatest Height. It would be a great
Improvement, as well as Embellishment to the Theatre, if Dancing were
more regarded, and taught to all the Actors. One who has the Advantage
of such an agreeable girlish Person as
Mrs. Bicknell
, joined with her
Capacity of Imitation, could in proper Gesture and Motion represent all
the decent Characters of Female Life. An amiable Modesty in one Aspect
of a Dancer, an assumed Confidence in another, a sudden Joy in another,
a falling off with an Impatience of being beheld, a Return towards the
Audience with an unsteady Resolution to approach them, and a well-acted
Sollicitude to please, would revive in the Company all the fine Touches
of Mind raised in observing all the Objects of Affection or Passion they
had before beheld. Such elegant Entertainments as these, would polish
the Town into Judgment in their Gratifications; and Delicacy in Pleasure
is the first step People of Condition take in Reformation from Vice.
Mrs.
Bicknell
has the only Capacity for this sort of Dancing of any on
the Stage; and I dare say all who see her Performance tomorrow Night,
when sure the Romp will do her best for her own Benefit, will be of my
Mind.
T.
Farquhar's Constant Couple, or A Trip to the Jubilee
.
Ben Jonson's
Volpone
.
In Colley Cibber's
Careless Husband.
In Ben Jonson's
Volpone
.
Cibber's
Love makes a Man, or The Fop's Fortune
.
For the Benefit of Mr. Penkethman. At the Desire of Several
Ladies of Quality. By Her Majesty's Company of Comedians. At the Theatre
Royal in Drury Lane, this present Monday, being the 5th of May, will be
presented a Comedy called Love makes a Man, or The Fop's Fortune. The
Part of Don Lewis, alias Don Choleric Snap Shorto de Testy, by Mr.
Penkethman; Carlos, Mr. Wilks; Clodio, alias Don Dismallo Thick-Scullo
de Half Witto, Mr. Cibber; and all the other Parts to the best
Advantage. With a new Epilogue, spoken by Mr. Penkethman, riding on an
Ass. By her Majesty's Command no Persons are to be admitted behind the
Scenes. And To-Morrow, being Tuesday, will be presented, A Comedy call'd
The Constant Couple, or A Trip to the Jubilee. For the Benefit of Mrs.
Bicknell.
To do as kind a service to Mrs. Bicknell as to Mr. Penkethman
on the occasion of their benefits is the purpose of the next paragraph
of Steele's
Essay
.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 6, 1712 |
Addison |
Jamne igitur laudas quod se sapientibus unus
Ridebat?
Juv.

I shall communicate to my Reader the following Letter for the
Entertainment of this Day.
Sir,
You know very well that our Nation is more famous for that sort of Men
who are called Whims and Humourists, than any other Country in the
World; for which reason it is observed that our
English Comedy excells
that of all other Nations in the Novelty and Variety of its
Characters.
Among those innumerable Setts of Whims which our Country produces,
there are none whom I have regarded with more Curiosity than those who
have invented any particular kind of Diversion for the Entertainment
of themselves or their Friends. My Letter shall single out those who
take delight in sorting a Company that has something of Burlesque and
Ridicule in its Appearance. I shall make my self understood by the
following Example.
One of the Wits of the last Age, who was a Man of a
good Estate
1, thought he never laid out his Money better than in a
Jest. As he was one Year at the Bath, observing that in the great
Confluence of fine People, there were several among them with long
Chins, a part of the Visage by which he himself was very much
distinguished, he invited to dinner half a Score of these remarkable
Persons who had their Mouths in the Middle of their Faces. They had no
sooner placed themselves about the Table, but they began to stare upon
one another, not being able to imagine what had brought them together.
Our
English Proverb says,
Tis merry in the Hall,
When Beards wag all.
It proved so in the Assembly I am now speaking of, who seeing so many
Peaks of Faces agitated with Eating, Drinking, and Discourse, and
observing all the Chins that were present meeting together very often
over the Center of the Table, every one grew sensible of the Jest, and
came into it with so much Good-Humour, that they lived in strict
Friendship and Alliance from that Day forward.
The same Gentleman some time after packed together a Set of Oglers, as
he called them, consisting of such as had an unlucky Cast in their
Eyes. His Diversion on this Occasion was to see the cross Bows,
mistaken Signs, and wrong Connivances that passed amidst so many
broken and refracted Rays of Sight.
The third Feast which this merry Gentleman exhibited was to the
Stammerers, whom he got together in a sufficient Body to fill his
Table. He had ordered one of his Servants, who was placed behind a
Skreen, to write down their Table-Talk, which was very easie to be
done without the help of Short-hand. It appears by the Notes which
were taken, that tho' their Conversation never fell, there were not
above twenty Words spoken during the first Course;
that upon serving
up the second, one of the Company was a quarter of an Hour in telling
them, that the Ducklins and
Asparagus2 were very good; and that
another took up the same time in declaring himself of the same
Opinion. This Jest did not, however, go off so well as the former; for
one of the Guests being a brave Man, and fuller of Resentment than he
knew how to express, went out of the Room, and sent the facetious
Inviter a Challenge in Writing, which though it was afterwards dropp'd
by the Interposition of Friends, put a Stop to these ludicrous
Entertainments.
Now, Sir, I dare say you will agree with me, that as there is no Moral
in these Jests, they ought to be discouraged, and looked upon rather
as pieces of Unluckiness than Wit. However, as it is natural for one
Man to refine upon the Thought of another, and impossible for any
single Person, how great soever his Parts may be, to invent an Art,
and bring it to its utmost Perfection; I shall here give you an
account of an honest Gentleman of my Acquaintance who upon hearing the
Character of the Wit above mentioned, has himself assumed it, and
endeavoured to convert it to the Benefit of Mankind. He invited half a
dozen of his Friends one day to Dinner, who were each of them famous
for inserting several redundant Phrases in their Discourse, as
d'y
hear me, d'ye see, that is, and so Sir. Each of the Guests making
frequent use of his particular Elegance, appeared so ridiculous to his
Neighbour, that he could not but reflect upon himself as appearing
equally ridiculous to the rest of the Company: By this means, before
they had sat long together, every one talking with the greatest
Circumspection, and carefully avoiding his favourite Expletive, the
Conversation was cleared of its Redundancies, and had a greater
Quantity of Sense, tho' less of Sound in it.
The same well-meaning Gentleman took occasion, at another time, to
bring together such of his Friends as were addicted to a foolish
habitual Custom of Swearing. In order to shew the Absurdity of the
Practice, he had recourse to the Invention above mentioned, having
placed an
Amanuensis in a private part of the Room. After the second
Bottle, when Men open their Minds without Reserve, my honest Friend
began to take notice of the many sonorous but unnecessary Words that
had passed in his House since their sitting down at Table, and how
much good Conversation they had lost by giving way to such superfluous
Phrases. What a Tax, says he, would they have raised for the Poor, had
we put the Laws in Execution upon one another? Every one of them took
this gentle Reproof in good part: Upon which he told them, that
knowing their Conversation would have no Secrets in it, he had ordered
it to be taken down in Writing, and for the humour sake would read it
to them, if they pleased. There were ten Sheets of it, which might
have been reduced to two, had there not been those abominable
Interpolations I have before mentioned. Upon the reading of it in cold
Blood, it looked rather like a Conference of Fiends than of Men. In
short, every one trembled at himself upon hearing calmly what he had
pronounced amidst the Heat and Inadvertency of Discourse.
I shall only mention another Occasion wherein he made use of the same
Invention to cure a different kind of Men, who are the Pests of all
polite Conversation, and murder Time as much as either of the two
former, though they do it more innocently; I mean that dull Generation
of Story-tellers. My Friend got together about half a dozen of his
Acquaintance, who were infected with this strange Malady. The first
Day one of them sitting down, entered upon the Siege of
Namur, which
lasted till four a-clock, their time of parting. The second Day a
North-Britain took possession of the Discourse, which it was
impossible to get out of his Hands so long as the Company staid
together. The third Day was engrossed after the same manner by a Story
of the same length. They at last began to reflect upon this barbarous
way of treating one another, and by this means awakened out of that
Lethargy with which each of them had been seized for several Years.
As you have somewhere declared, that extraordinary and uncommon
Characters of Mankind are the Game which you delight in, and as I look
upon you to be the greatest Sportsman, or, if you please, the Nimrod
among this Species of Writers, I thought this Discovery would not be
unacceptable to you.
I am,
Sir, &c.
I.
George Villiers, Duke of Buckingham, Dryden's
Zimri
, and the
author of the
Rehearsal
.
Sparrow-grass
and in first Reprint.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 7, 1712 |
Steele |
Pudet hæc opprobria nobis
Et dici potuisse et non potuisse refelli.
Ovid.

May 6, 1712.
Mr.
Spectator,
I am Sexton of the Parish of
Covent-Garden, and complained to you some
time ago, that as I was tolling in to Prayers at Eleven in the
Morning, Crowds of People of Quality hastened to assemble at a
Puppet-Show on the other Side of the Garden. I had at the same time a
very great Disesteem for Mr.
Powell and his little thoughtless
Commonwealth, as if they had enticed the Gentry into those Wandrings:
But let that be as it will, I now am convinced of the honest
Intentions of the said Mr.
Powell and Company; and send this to
acquaint you, that he has given all the Profits which shall arise
to-morrow Night by his Play to the use of the poor Charity-Children of
this Parish. I have been informed, Sir, that in
Holland all Persons
who set up any Show, or act any Stage-Play, be the Actors either of
Wood and Wire, or Flesh and Blood, are obliged to pay out of their
Gain such a Proportion to the honest and industrious Poor in the
Neighbourhood: By this means they make Diversion and Pleasure pay a
Tax to Labour and Industry. I have been told also, that all the time
of Lent, in
Roman Catholick Countries, the Persons of Condition
administred to the Necessities of the Poor, and attended the Beds of
Lazars and diseased Persons. Our
Protestant Ladies and Gentlemen are
so much to seek for proper ways of passing Time, that they are obliged
to
Punchinello for knowing what to do with themselves. Since the Case
is so, I desire only you would intreat our People of Quality, who are
not to be interrupted in their Pleasure to think of the Practice of
any moral Duty, that they would at least fine for their Sins, and give
something to these poor Children; a little out of their Luxury and
Superfluity, would attone, in some measure, for the wanton Use of the
rest of their Fortunes. It would not, methinks, be amiss, if the
Ladies who haunt the Cloysters and Passages of the Play-house, were
upon every Offence obliged to pay to this excellent Institution of
Schools of Charity: This Method would make Offenders themselves do
Service to the Publick. But in the mean time I desire you would
publish this voluntary Reparation which Mr.
Powell does our Parish,
for the Noise he has made in it by the constant rattling of Coaches,
Drums, Trumpets, Triumphs, and Battels. The Destruction of
Troy
adorned with
Highland Dances, are to make up the Entertainment of all
who are so well disposed as not to forbear a light Entertainment, for
no other Reason but that it is to do a good Action.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Ralph Bellfry.
I am credibly informed, that all the Insinuations which a certain
Writer made against Mr. Powell at the
Bath, are false and groundless.
Mr.
Spectator,
My Employment, which is that of a Broker, leading me often into
Taverns about the Exchange, has given me occasion to observe a certain
Enormity, which I shall here submit to your Animadversion. In three or
four of these Taverns, I have, at different times, taken notice of a
precise Set of People with grave Countenances, short Wiggs, black
Cloaths, or dark Camlet trimmd with Black, and mourning Gloves and
Hatbands, who meet on certain Days at each Tavern successively, and
keep a sort of moving Club. Having often met with their Faces, and
observed a certain slinking Way in their dropping in one after
another, I had the Curiosity to enquire into their Characters, being
the rather moved to it by their agreeing in the Singularity of their
Dress; and I find upon due Examination they are a Knot of
Parish-Clarks, who have taken a fancy to one another, and perhaps
settle the Bills of Mortality over their Half-pints. I have so great a
Value and Veneration for any who have but even an assenting Amen in
the Service of Religion, that I am afraid lest these Persons should
incur some Scandal by this Practice; and would therefore have them,
without Raillery, advised to send the Florence and Pullets home to
their own Houses, and not pretend to live as well as the Overseers of
the Poor.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Humphry Transfer.
May 6.
Mr.
Spectator,
I was last Wednesday Night at a Tavern in the
City, among a Set of Men
who call themselves the
Lawyer's Club. You must know, Sir, this Club
consists only of Attorneys; and at this Meeting every one proposes the
Cause he has then in hand to the Board, upon which each Member gives
his Judgment according to the Experience he has met with. If it
happens that any one puts a Case of which they have had no Precedent,
it is noted down by their Clerk
Will. Goosequill, (who registers all
their Proceedings) that one of them may go the next Day with it to a
Counsel. This indeed is commendable, and ought to be the principal End
of their Meeting; but had you been there to have heard them relate
their Methods of managing a Cause, their Manner of drawing out their
Bills, and, in short, their Arguments upon the several ways of abusing
their Clients, with the Applause that is given to him who has done it
most artfully, you would before now have given your Remarks on them.
They are so conscious that their Discourses ought to be kept secret,
that they are very cautious of admitting any Person who is not of
their Profession. When any who are not of the Law are let in, the
Person who introduces him, says, he is a very honest Gentleman, and he
is taken in, as their Cant is, to pay Costs. I am admitted upon the
Recommendation of one of their Principals, as a very honest
good-natured Fellow that will never be in a Plot, and only desires to
drink his Bottle and smoke his Pipe. You have formerly remarked upon
several Sorts of Clubs; and as the Tendency of this is only to
increase Fraud and Deceit, I hope you will please to take Notice of it.
I am (with Respect)
Your humble Servant,
H. R.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 8, 1712 |
Budgell |
Fallit enim Vitium specie virtutis et umbra.
Juv.1
Mr.
Locke
, in his
Treatise of Human Understanding
, has spent two
Chapters upon the Abuse of Words
.
The first and most palpable Abuse
of Words
, he says,
is, when they are used without clear and distinct
Ideas: The second, when we are so inconstant and unsteady in the
Application of them, that we sometimes use them to signify one Idea,
sometimes another.
He adds, that the Result of our Contemplations and
Reasonings, while we have no precise Ideas fixed to our Words, must
needs be very confused and absurd. To avoid this Inconvenience, more
especially in moral Discourses, where the same Word should constantly be
used in the same Sense, he earnestly recommends the use of Definitions.
A Definition
, says he,
is the only way whereby the precise Meaning of
Moral Words can be known.
He therefore accuses those of great
Negligence, who Discourse of Moral things with the least Obscurity in
the Terms they make use of, since upon the forementioned ground he does
not scruple to say, that he thinks Morality is capable of Demonstration
as well as the Mathematicks.
I know no two Words that have been more abused by the different and
wrong Interpretations which are put upon them, than those two,
Modesty
and
Assurance
. To say such an one is a modest Man, sometimes indeed
passes for a good Character; but at present is very often used to
signify a sheepish awkard Fellow, who has neither Good-breeding,
Politeness, nor any Knowledge of the World.
Again, A Man of Assurance, tho at first it only denoted a Person of a
free and open Carriage, is now very usually applied to a profligate
Wretch, who can break through all the Rules of Decency and Morality
without a Blush.
I shall endeavour therefore in this Essay to restore these Words to
their true Meaning, to prevent the Idea of
Modesty
from being confounded
with that of
Sheepishness
, and to hinder
Impudence
from passing for
Assurance
.
If I was put to define
Modesty
, I would call it
The Reflection of an
Ingenuous Mind
, either when a Man has committed an Action for which he
censures himself, or fancies that he is exposed to the Censure of
others.
For this Reason a Man truly Modest is as much so when he is alone as in
Company, and as subject to a Blush in his Closet, as when the Eyes of
Multitudes are upon him.
I do not remember to have met with any Instance of Modesty with which I
am so well pleased, as that celebrated one of the young Prince, whose
Father being a tributary King to the
Romans
, had several Complaints laid
against him before the
Senate
, as a Tyrant and Oppressor of his
Subjects. The Prince went to
Rome
to defend his Father; but coming into
the
Senate
, and hearing a Multitude of Crimes proved upon him, was so
oppressed when it came to his turn to speak, that he was unable to utter
a Word. The Story tells us, that the Fathers were more moved at this
Instance of Modesty and Ingenuity, than they could have been by the most
Pathetick Oration; and, in short, pardoned the guilty Father for this
early Promise of Virtue in the Son.
I take
Assurance
to be the
Faculty of possessing a Man's self
, or
of
saying and doing indifferent things without any Uneasiness or Emotion in
the Mind.
That which generally gives a Man Assurance is a moderate
Knowledge of the World, but above all a Mind fixed and determined in it
self to do nothing against the Rules of Honour and Decency. An open and
assured Behaviour is the natural Consequence of such a Resolution. A Man
thus armed, if his Words or Actions are at any time misinterpreted,
retires within himself, and from the Consciousness of his own Integrity,
assumes Force enough to despise the little Censures of Ignorance or
Malice.
Every one ought to cherish and encourage in himself the
Modesty
and
Assurance
I have here mentioned.
A Man without
Assurance
is liable to be made uneasy by the Folly or
Ill-nature of every one he converses with. A Man without
Modesty
is lost
to all Sense of
Honour
and
Virtue
.
It is more than probable, that the Prince above-mentioned possessed both
these Qualifications in a very eminent degree. Without
Assurance
he
would never have undertaken to speak before the most august Assembly in
the World; without
Modesty
he would have pleaded the Cause he had taken
upon him, tho it had appeared ever so Scandalous.
From what has been said, it is plain, that
Modesty
and
Assurance
are
both amiable, and may very well meet in the same Person. When they are
thus mixed and blended together, they compose what we endeavour to
express when we say a
modest Assurance
; by which we understand the just
Mean between
Bashfulness
and
Impudence
.
I shall conclude with observing, that as the same Man may be both
Modest
and
Assured
, so it is also possible for the same Person to be both
Impudent
and
Bashful
.
We have frequent Instances of this odd kind of Mixture in People of
depraved Minds and mean Education; who tho' they are not able to meet a
Man's Eyes, or pronounce a Sentence without Confusion, can Voluntarily
commit the greatest Villanies, or most indecent Actions.
Such a Person seems to have made a Resolution to do Ill even in spite of
himself, and in defiance of all those Checks and Restraints his Temper
and Complection seem to have laid in his way.
Upon the whole, I would endeavour to establish this Maxim,
That the
Practice of Virtue is the most proper Method to give a Man a becoming
Assurance in his Words and Actions.
Guilt always seeks to shelter it
self in one of the Extreams, and is sometimes attended with both.
X.
—Strabonem
Appellat pætumm pater; et pullum, male parvus
Si cui filius est; ut abortivus fuit olim
Sisyphus: hunc varum, distortis cruribus; illum
Balbutit scaurum, pravis fullum malè talis.
Hor.
Book III., Chapters 10, 11. Words are the subject of this
book; ch. 10 is on the Abuse of Words; ch. 11 of the Remedies of the
foregoing imperfections and abuses.
Contents
|
Friday, May 9, 1712 |
Steele |
Nil actum reputans si quid superesset agendum.
Luc.

There is a Fault, which, tho' common, wants a Name. It is the very
contrary to Procrastination: As we lose the present Hour by delaying
from Day to Day to execute what we ought to do immediately; so most of
us take Occasion to sit still and throw away the Time in our Possession,
by Retrospect on what is past, imagining we have already acquitted our
selves, and established our Characters in the sight of Mankind. But when
we thus put a Value upon our selves for what we have already done, any
further than to explain our selves in order to assist our future
Conduct, that will give us an over-weening opinion of our Merit to the
prejudice of our present Industry. The great Rule, methinks, should be
to manage the Instant in which we stand, with Fortitude, Equanimity, and
Moderation, according to Men's respective Circumstances. If our past
Actions reproach us, they cannot be attoned for by our own severe
Reflections so effectually as by a contrary Behaviour. If they are
praiseworthy, the Memory of them is of no use but to act suitably to
them. Thus a good present Behaviour is an implicit Repentance for any
Miscarriage in what is past; but present Slackness will not make up for
past Activity. Time has swallowed up all that we Contemporaries did
Yesterday, as irrevocably as it has the Actions of the Antediluvians:
But we are again awake, and what shall we do to-Day, to-Day which passes
while we are yet speaking? Shall we remember the Folly of last Night, or
resolve upon the Exercise of Virtue tomorrow? Last Night is certainly
gone, and To-morrow may never arrive: This Instant make use of. Can you
oblige any Man of Honour and Virtue? Do it immediately. Can you visit a
sick Friend? Will it revive him to see you enter, and suspend your own
Ease and Pleasure to comfort his Weakness, and hear the Impertinencies
of a Wretch in Pain? Don't stay to take Coach, but be gone. Your
Mistress will bring Sorrow, and your Bottle Madness: Go to
neither.—Such Virtues and Diversions as these are mentioned because
they occur to all Men. But every Man is sufficiently convinced, that to
suspend the use of the present Moment, and resolve better for the future
only, is an unpardonable Folly: What I attempted to consider, was the
Mischief of setting such a Value upon what is past, as to think we have
done enough. Let a Man have filled all the Offices of Life with the
highest Dignity till Yesterday, and begin to live only to himself
to-Day, he must expect he will in the Effects upon his Reputation be
considered as the Man who died Yesterday. The Man who distinguishes
himself from the rest, stands in a Press of People; those before him
intercept his Progress, and those behind him, if he does not urge on,
will tread him down.
Cæsar
, of whom it was said, that he thought nothing
done while there was anything left for him to do, went on in performing
the greatest Exploits, without assuming to himself a Privilege of taking
Rest upon the Foundation of the Merit of his former Actions. It was the
manner of that glorious Captain to write down what Scenes he passed
through, but it was rather to keep his Affairs in Method, and capable of
a clear Review in case they should be examined by others, than that he
built a Renown upon any thing which was past. I shall produce two
Fragments of his to demonstrate, that it was his Rule of Life to support
himself rather by what he should perform than what he had done already.
In the Tablet which he wore about him the same Year, in which he
obtained the Battel of
Pharsalia
, there were found these loose Notes for
his own Conduct: It is supposed, by the Circumstances they alluded to,
that they might be set down the Evening of the same Night.
My Part is now but begun, and my Glory must be sustained by the Use I
make of this Victory; otherwise my Loss will be greater than that of
Pompey. Our personal Reputation will rise or fall as we bear our
respective Fortunes. All my private Enemies among the Prisoners shall
be spared. I will forget this, in order to obtain such another Day.
Trebutius is ashamed to see me: I will go to his Tent, and be
reconciled in private. Give all the Men of Honour, who take part with
me, the Terms I offered before the Battel. Let them owe this to their
Friends who have been long in my Interests. Power is weakened by the
full Use of it, but extended by Moderation. Galbinius is proud, and
will be servile in his present Fortune; let him wait. Send for
Stertinius: He is modest, and his Virtue is worth gaining. I have
cooled my Heart with Reflection; and am fit to rejoice with the Army
to-morrow. He is a popular General who can expose himself like a
private Man during a Battel; but he is more popular who can rejoice
but like a private Man after a Victory.
What is particularly proper for the Example of all who pretend to
Industry in the Pursuit of Honour and Virtue, is, That this Hero was
more than ordinarily sollicitous about his Reputation, when a common
Mind would have thought it self in Security, and given it self a Loose
to Joy and Triumph. But though this is a very great Instance of his
Temper, I must confess I am more taken with his Reflections when he
retired to his Closet in some Disturbance upon the repeated ill Omens of
Calphurnia's
Dream the Night before his Death. The literal Translation
of that Fragment shall conclude this Paper.
Be it so
then1. If I am to die to-Morrow, that is what I am to do
to-Morrow: It will not be then, because I am willing it should be
then; nor shall I escape it, because I am unwilling. It is in the Gods
when, but in my self
how I shall die. If
Calphurnia's Dreams are Fumes
of Indigestion, how shall I behold the Day after to-morrow? If they
are from the Gods, their Admonition is not to prepare me to escape
from their Decree, but to meet it. I have lived to a Fulness of Days
and of Glory; what is there that
Cæsar has not done with as much
Honour as antient Heroes?
Cæsar has not yet died; Cæsar is prepared to
die.
T.
than
Contents
|
Saturday, May 10, 1712 |
Hughes |
Non possidentem multa vocaveris
Rectè beatum: rectiùs occupat
Nomen beati, qui Deorum
Muneribus sapienter uti,
Duramque callet Pauperiem pati,
Pejusque Letho flagitium timet.
Hor.

I have more than once had occasion to mention a noble Saying of
Seneca
the Philosopher,
That a virtuous Person struggling with Misfortunes, and
rising above them, is an Object on which the Gods themselves may look
down with Delight
. I shall therefore set before my Reader a Scene of
this kind of Distress in private Life, for the Speculation of this Day.
An eminent Citizen, who had lived in good Fashion and Credit, was by a
Train of Accidents, and by an unavoidable Perplexity in his Affairs,
reduced to a low Condition. There is a Modesty usually attending
faultless Poverty, which made him rather chuse to reduce his Manner of
Living to his present Circumstances, than sollicit his Friends in order
to support the Shew of an Estate when the Substance was gone. His Wife,
who was a Woman of Sense and Virtue, behaved her self on this Occasion
with uncommon Decency, and never appear'd so amiable in his Eyes as now.
Instead of upbraiding him with the ample Fortune she had brought, or the
many great Offers she had refused for his sake, she redoubled all the
Instances of her Affection, while her Husband was continually pouring
out his Heart to her in Complaints that he had ruined the best Woman in
the World. He sometimes came home at a time when she did not expect him,
and surpriz'd her in Tears, which she endeavour'd to conceal, and always
put on an Air of Chearfulness to receive him. To lessen their Expence,
their eldest Daughter (whom I shall call
Amanda
) was sent into the
Country, to the House of an honest Farmer, who had married a Servant of
the Family. This young Woman was apprehensive of the Ruin which was
approaching, and had privately engaged a Friend in the Neighbourhood to
give her an account of what passed from time to time in her Father's
Affairs.
Amanda
was in the Bloom of her Youth and Beauty, when the Lord
of the Manor, who often called in at the Farmer's House as he followd
his Country Sports, fell passionately in love with her. He was a Man of
great Generosity, but from a loose Education had contracted a hearty
Aversion to Marriage. He therefore entertained a Design upon
Amanda's
Virtue, which at present he thought fit to keep private. The innocent
Creature, who never suspected his Intentions, was pleased with his
Person; and having observed his growing Passion for her, hoped by so
advantageous a Match she might quickly be in a capacity of supporting
her impoverish'd Relations. One day as he called to see her, he found
her in Tears over a Letter she had just receiv'd from her Friend, which
gave an Account that her Father had lately been stripped of every thing
by an Execution. The Lover, who with some Difficulty found out the Cause
of her Grief, took this occasion to make her a Proposal. It is
impossible to express
Amanda's
Confusion when she found his Pretensions
were not honourable. She was now deserted of all her Hopes, and had no
Power to speak; but rushing from him in the utmost Disturbance, locked
her self up in her Chamber. He immediately dispatched a Messenger to her
Father with the following Letter.
Sir,
I have heard of your Misfortune, and have offer'd your Daughter, if
she will live with me, to settle on her Four hundred Pounds a year,
and to lay down the Sum for which you are now distressed. I will be
so ingenuous as to tell you that I do not intend Marriage: But if you
are wise, you will use your Authority with her not to be too nice,
when she has an opportunity of saving you and your Family, and of
making her self happy.
I am, &c.
This Letter came to the Hands of Amanda's Mother; she opend and read it
with great Surprize and Concern. She did not think it proper to explain
her self to the Messenger, but desiring him to call again the next
Morning, she wrote to her Daughter as follows.
Dearest Child,
Your Father and I have just now receiv'd a Letter from a Gentleman who
pretends Love to you, with a Proposal that insults our Misfortunes,
and would throw us to a lower Degree of Misery than any thing which is
come upon us. How could this barbarous Man think, that the tenderest
of Parents would be tempted to supply their Wants by giving up the
best of Children to Infamy and Ruin? It is a mean and cruel Artifice
to make this Proposal at a time when he thinks our Necessities must
compel us to any thing; but we will not eat the Bread of Shame; and
therefore we charge thee not to think of us, but to avoid the Snare
which is laid for thy Virtue. Beware of pitying us: It is not so bad
as you have perhaps been told. All things will yet be well, and I
shall write my Child better News.
I have been interrupted. I know not how I was moved to say things
would mend. As I was going on I was startled by a Noise of one that
knocked at the Door, and hath brought us an unexpected Supply of a
Debt which had long been owing. Oh! I will now tell thee all. It is
some days I have lived almost without Support, having conveyd what
little Money I could raise to your poor Father—Thou wilt weep to
think where he is, yet be assured he will be soon at Liberty. That
cruel Letter would have broke his Heart, but I have concealed it from
him. I have no Companion at present besides little Fanny, who stands
watching my Looks as I write, and is crying for her Sister. She says
she is sure you are not well, having discover'd that my present
Trouble is about you. But do not think I would thus repeat my Sorrows,
to grieve thee: No, it is to intreat thee not to make them
insupportable, by adding what would be worse than all. Let us bear
chearfully an Affliction, which we have not brought on our selves, and
remember there is a Power who can better deliver us out of it than by
the Loss of thy Innocence. Heaven preserve my dear Child.
Your Affectionate Mother ——
The Messenger, notwithstanding he promised to deliver this Letter to
Amanda
, carry'd it first to his Master, who he imagined would be glad to
have an Opportunity of giving it into her Hands himself. His Master was
impatient to know the Success of his Proposal, and therefore broke open
the Letter privately to see the Contents. He was not a little moved at
so true a Picture of Virtue in Distress: But at the same time was
infinitely surprized to find his Offers rejected. However, he resolved
not to suppress the Letter, but carefully sealed it up again, and
carried it to
Amanda
. All his Endeavours to see her were in vain, till
she was assured he brought a Letter from her Mother. He would not part
with it, but upon Condition that she should read it without leaving the
Room. While she was perusing it, he fixed his Eyes on her Face with the
deepest Attention: Her Concern gave a new Softness to her Beauty, and
when she burst into Tears, he could no longer refrain from bearing a
Part of her Sorrow, and telling her, that he too had read the Letter and
was resolvd to make Reparation for having been the Occasion of it. My
Reader will not be displeased to see this Second Epistle which he now
wrote to
Amanda's
Mother.
Madam,
I am full of Shame, and will never forgive my self, if I have not your
Pardon for what I lately wrote. It was far from my Intention to add
Trouble to the Afflicted; nor could any thing, but my being a Stranger
to you, have betray'd me into a Fault, for which, if I live, I shall
endeavour to make you amends, as a Son. You cannot be unhappy while
Amanda is your Daughter: nor shall be, if any thing can prevent it,
which is in the power of, Madam,
Your most obedient
Humble Servant ——
This Letter he sent by his Steward, and soon after went up to Town
himself, to compleat the generous Act he had now resolved on. By his
Friendship and Assistance
Amanda's
Father was quickly in a condition of
retrieving his perplex'd Affairs. To conclude, he Marry'd
Amanda
, and
enjoyd the double Satisfaction of having restored a worthy Family to
their former Prosperity, and of making himself happy by an Alliance to
their Virtues.
See note on p. 148 [Volume 1 links:
of
], vol. i.
Contents
|
Monday, May 12, 1712 |
Steele |
—Pavone ex Pythagoreo—
Persius.

Mr.
Spectator,
I have observed that the Officer you some time ago appointed as
Inspector of Signs, has not done his Duty so well as to give you an
Account of very many strange Occurrences in the publick Streets, which
are worthy of, but have escaped your Notice. Among all the Oddnesses
which I have ever met with, that which I am now telling you of gave me
most Delight. You must have observed that all the Criers in the Street
attract the Attention of the Passengers, and of the Inhabitants in the
several Parts, by something very particular in their Tone it self, in
the dwelling upon a Note, or else making themselves wholly
unintelligible by a Scream. The Person I am so delighted with has
nothing to sell, but very gravely receives the Bounty of the People,
for no other Merit but the Homage they pay to his Manner of signifying
to them that he wants a Subsidy. You must, sure, have heard speak of
an old Man, who walks about the City, and that part of the Suburbs
which lies beyond the Tower, performing the Office of a Day-Watchman,
followed by a Goose, which bears the Bob of his Ditty, and confirms
what he says with a Quack, Quack. I gave little heed to the mention of
this known Circumstance, till, being the other day in those Quarters,
I passed by a decrepit old Fellow with a Pole in his Hand, who just
then was bawling out, Half an Hour after one a-Clock, and immediately
a dirty Goose behind him made her Response, Quack, Quack. I could not
forbear attending this grave Procession for the length of half a
Street, with no small amazement to find the whole Place so familiarly
acquainted with a melancholy Mid-night Voice at Noon-day, giving them
the Hour, and exhorting them of the Departure of Time, with a Bounce
at their Doors. While I was full of this Novelty, I went into a
Friend's House, and told him how I was diverted with their whimsical
Monitor and his Equipage. My Friend gave me the History; and
interrupted my Commendation of the Man, by telling me the Livelihood
of these two Animals is purchased rather by the good Parts of the
Goose, than of the Leader: For it seems the Peripatetick who walked
before her was a Watchman in that Neighbourhood; and the Goose of her
self by frequent hearing his Tone, out of her natural Vigilance, not
only observed, but answer'd it very regularly from Time to Time. The
Watchman was so affected with it, that he bought her, and has taken
her in Partner, only altering their Hours of Duty from Night to Day.
The Town has come into it, and they live very comfortably. This is the
Matter of Fact: Now I desire you, who are a profound Philosopher, to
consider this Alliance of Instinct and Reason; your Speculation may
turn very naturally upon the Force the superior Part of Mankind may
have upon the Spirits of such as, like this Watchman, may be very near
the Standard of Geese. And you may add to this practical Observation,
how in all Ages and Times the World has been carry'd away by odd
unaccountable things, which one would think would pass upon no
Creature which had Reason; and, under the Symbol of this Goose, you
may enter into the Manner and Method of leading Creatures, with their
Eyes open, thro' thick and thin, for they know not what, they know not
why.
All which is humbly submitted to your
Spectatorial Wisdom by,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Michael Gander.
Mr.
Spectator,
I have for several Years had under my Care the Government and
Education of young Ladies, which Trust I have endeavour'd to discharge
with due regard to their several Capacities and Fortunes: I have left
nothing undone to imprint in every one of them an humble courteous
Mind, accompanied with a graceful becoming Mein, and have made them
pretty much acquainted with the Houshold Part of Family-Affairs; but
still I find there is something very much wanting in the Air of my
Ladies, different from what I observe in those that are esteemed your
fine bred Women. Now, Sir, I must own to you, I never suffered my
Girls to learn to Dance; but since I have read your Discourse of
Dancing, where you have described the Beauty and Spirit there is in
regular Motion, I own my self your Convert, and resolve for the future
to give my young Ladies that Accomplishment. But upon imparting my
Design to their Parents, I have been made very uneasy, for some Time,
because several of them have declared, that if I did not make use of
the Master they recommended, they would take away their Children.
There was
Colonel Jumper's Lady, a Colonel of the Train-Bands, that
has a great Interest in her Parish; she recommends
Mr. Trott for the
prettiest Master in Town, that no Man teaches a Jigg like him, that
she has seen him rise six or seven Capers together with the greatest
Ease imaginable, and that his Scholars twist themselves more ways than
the Scholars of any Master in Town: besides there is
Madam Prim, an
Alderman's Lady, recommends a Master of her own Name, but she declares
he is not of their Family, yet a very extraordinary Man in his way;
for besides a very soft Air he has in Dancing, he gives them a
particular Behaviour at a Tea-Table, and in presenting their
Snuff-Box, to twirl, flip, or flirt a Fan, and how to place Patches to
the best advantage, either for Fat or Lean, Long or Oval Faces: for my
Lady says there is more in these Things than the World Imagines. But I
must confess the major Part of those I am concern'd with leave it to
me. I desire therefore, according to the inclosed Direction, you would
send your Correspondent who has writ to you on that Subject to my
House. If proper Application this way can give Innocence new Charms,
and make Virtue legible in the Countenance, I shall spare no Charge to
make my Scholars in their very Features and Limbs bear witness how
careful I have been in the other Parts of their Education.
I am,
Sir,
Your most humble Servant,
Rachael Watchful
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 13, 1712 |
Addison |
Quid quisque vitet, nunquam homini satis
Cautum est in horas—
Hor.

Love
was the Mother of
Poetry
, and still produces, among the most
ignorant and barbarous, a thousand imaginary Distresses and Poetical
Complaints. It makes a Footman talk like
Oroondates
, and converts a
brutal Rustick into a gentle Swain. The most ordinary Plebeian or
Mechanick in Love, bleeds and pines away with a certain Elegance and
Tenderness of Sentiments which this Passion naturally inspires.
These inward Languishings of a Mind infected with this Softness, have
given birth to a Phrase which is made use of by all the melting Tribe,
from the highest to the lowest, I mean that of
dying for Love
.
Romances, which owe their very Being to this Passion, are full of these
metaphorical Deaths. Heroes and Heroines, Knights, Squires, and Damsels,
are all of them in a dying Condition. There is the same kind of
Mortality in our Modern Tragedies, where every one gasps, faints, bleeds
and dies. Many of the Poets, to describe the Execution which is done by
this Passion, represent the Fair Sex as Basilisks that destroy with
their Eyes;
I think Mr.
Cowley
has with greater Justness of Thought
compared a beautiful Woman to
a Porcupine, that sends an Arrow from
every Part
.
I have often thought, that there is no way so effectual for the Cure of
this general Infirmity, as a Man's reflecting upon the Motives that
produce it. When the Passion proceeds from the Sense of any Virtue or
Perfection in the Person beloved, I would by no means discourage it; but
if a Man considers that all his heavy Complaints of Wounds and Deaths
rise from some little Affectations of Coquetry, which are improved into
Charms by his own fond Imagination, the very laying before himself the
Cause of his Distemper, may be sufficient to effect the Cure of it.
It is in this view that I have looked over the several Bundles of
Letters which I have received from Dying People, and composed out of
them the following Bill of Mortality, which I shall lay before my Reader
without any further Preface, as hoping that it may be useful to him in
discovering those several Places where there is most Danger, and those
fatal Arts which are made use of to destroy the Heedless and Unwary.
| Lysander |
slain at a Puppet-show on the third of September. |
| Thirsis |
shot from a Casement in Pickadilly. |
| T. S. |
wounded by Zehinda's Scarlet Stocking, as she was
stepping out of a Coach. |
| Will. Simple |
smitten at the Opera by the Glance of an Eye that was
aimed at one who stood by him. |
| Tho. Vainlove |
lost his Life at a Ball. |
| Tim. Tattle |
kill'd by the Tap of a Fan on his left Shoulder
by Coquetilla, as he was talking carelessly with her in a
Bow-window. |
| Sir Simon Softly |
murder'd at the Play-house in Drury-lane by a Frown. |
| Philander |
mortally wounded by Cleora, as she was adjusting her Tucker. |
| Ralph Gapely, Esq. |
hit by a random Shot at the Ring. |
| F. R. |
caught his Death upon the Water, April the 31st. |
| W. W. |
killed by an unknown Hand, that was playing with the Glove off
upon the Side of the Front-Box in Drury-Lane. |
| Sir Christopher Crazy, Bart. |
hurt by the Brush of a Whalebone
Petticoat. |
| Sylvius |
shot through the Sticks of a Fan at St. James's Church. |
| Damon |
struck thro' the Heart by a Diamond Necklace. |
Thomas Trusty
Francis Goosequill
William Meanwell
Edward Callow, Esqrs. |
standing in a Row, fell all four at the
same time, by an Ogle of the Widow Trapland. |
| Tom. Rattle |
chancing to tread upon a Lady's Tail as he came out of
the Play-house, she turned full upon him, and laid him dead upon the
Spot. |
| Dick Tastewell |
slain by a Blush from the Queen's Box in the
third Act of the Trip to the Jubilee. |
| Samuel Felt, Haberdasher |
wounded in his Walk to Islington by Mrs. Susannah
Crossstich, as she was clambering over a Stile. |
R. F.,
T. W.,
S. I.,
M. P., &c. |
put to Death in the last Birth-Day Massacre. |
| Roger Blinko |
cut off in the Twenty-first Year of his Age by a
White-wash. |
| Musidorus |
slain by an Arrow that flew out of a Dimple in Belinda's
Left Cheek. |
| Ned Courtly |
presenting Flavia with her Glove (which she had dropped
on purpose) she receivd it, and took away his Life with a Curtsie. |
| John Gosselin |
having received a slight Hurt from a Pair of blue Eyes,
as he was making his Escape was dispatch'd by a Smile. |
| Strephon |
killed by Clarinda as she looked down into the Pit. |
| Charles Careless |
shot flying by a Girl of Fifteen, who unexpectedly popped
her Head upon him out of a Coach. |
| Josiah Wither |
aged threescore and three, sent to his long home by
Elizabeth Jet-well, Spinster. |
| Jack Freelove |
murderd by Melissa in her Hair. |
| William Wiseaker, Gent. |
drown'd in a Flood of Tears by Moll Common. |
| John Pleadwell, Esq. |
of the Middle Temple, Barrister at Law,
assassinated in his Chambers the sixth Instant by Kitty Sly, who
pretended to come to him for his Advice. |
I.
They are all weapon, and they dart
Like Porcupines from every Part.
Anacreontics
, iii.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 14, 1712 |
Pope |
Aggredere, O magnos, aderit jam tempus, honores.
Virg.

I will
no Apology for entertaining the Reader with the following
Poem, which is written by a great Genius, a Friend of mine, in the
Country, who is not ashamd to employ his Wit in the Praise of his Maker
.
Messiah
.
A sacred Eclogue, compos'd of several Passages of
Isaiah the Prophet.
Written in Imitation of
Virgil's
Pollio
.
|
Ye Nymphs of Solyma! begin the Song:
To heav'nly Themes sublimer Strains belong.
The Mossy Fountains, and the Sylvan Shades,
The Dreams of Pindus and th' Aonian Maids,
Delight no more—O Thou my Voice inspire,
Who touch'd Isaiah's hallow'd2 Lips with Fire!
Rapt into future Times, the Bard begun;
A Virgin shall conceive, a Virgin bear a Son! |
| Isaiah,
Cap. II.
v. 1. |
From Jesse's Root behold a Branch arise,
Whose sacred Flow'r with Fragrance fills the Skies.
Th' Æthereal Spirit o'er its Leaves shall move,
And on its Top descends the Mystick Dove. |
| Cap. 45. v. 8. |
Ye Heav'ns! from high the dewy Nectar pour,
And in soft Silence shed the kindly Show'r! |
| Cap. 25. v. 4. |
The Sick and Weak, the healing Plant shall aid,
From Storms a Shelter, and from Heat a Shade.
All Crimes shall cease, and ancient Fraud shall fail; |
| Cap. 9. v. 7. |
Returning Justice lift aloft her Scale;
Peace o'er the World her Olive Wand extend,
And white-rob'd Innocence from Heav'n descend.
Swift fly the Years, and rise th' expected Morn!
Oh spring to Light, Auspicious Babe, be born!
See Nature hastes her earliest Wreaths to bring,
With all the Incense of the breathing Spring: |
| Cap. 35. v. 2. |
See lofty Lebanon his Head advance,
See nodding Forests on the Mountains dance,
See spicy Clouds from lowly Sharon rise,
And Carmels flow'ry Top perfumes the Skies! |
| Cap. 40. v. 3, 4. |
Hark! a glad Voice the lonely Desart chears;
Prepare the Way! a God, a God appears:
A God! a God! the vocal Hills reply,
The Rocks proclaim th' approaching Deity.
Lo Earth receives him from the bending Skies!
Sink down ye Mountains, and ye Vallies rise!
With Heads declin'd, ye Cedars, Homage pay!
Be smooth ye Rocks, ye rapid Floods give way!
The Saviour comes! by ancient Bards foretold; |
| Cap. 42. v. 18. |
Hear him, ye Deaf, and all ye Blind behold! |
| Cap. 35. v. 5, 6. |
He from thick Films shall purge the visual Ray,
And on the sightless Eye-ball pour the Day.
'Tis he th' obstructed Paths of Sound shall clear,
And bid new Musick charm th' unfolding Ear,
The Dumb shall sing, the Lame his Crutch forego,
And leap exulting like the bounding Roe;
No Sigh, no Murmur the wide World shall hear,
From ev'ry Face he wipes off ev'ry Tear. |
| Cap. 25. v. 8. |
In Adamantine Chains shall Death be bound,
And Hell's grim Tyrant feel th' eternal Wound. 3 |
| Cap. 30. v. xx. |
As the good Shepherd tends his fleecy Care,
Seeks freshest Pastures and the purest Air,
Explores the lost, the wand'ring Sheep directs,
By day o'ersees them, and by night protects;
The tender Lambs he raises in his Arms,
Feeds from his Hand, and in his Bosom warms:
Mankind shall thus his Guardian Care engage,
The promis'd Father of the future Age4.
No more shall Nation against Nation rise5,
No ardent Warriors meet with hateful Eyes,
Nor Fields with gleaming Steel be coverd o'er,
The Brazen Trumpets kindle Rage no more;
But useless Lances into Scythes shall bend,
And the broad Falchion in a Plow-share end.
Then Palaces shall rise; the joyful Son6
Shall finish what his short-liv'd Sire begun;
Their Vines a Shadow to their Race shall yield,
And the same Hand that sow'd shall reap the Field.
The Swain in barren Desarts with Surprize7
Sees Lillies spring, and sudden Verdure rise;
And Starts, amidst the thirsty Wilds, to hear,
New Falls of Water murmuring in his Ear:
On rifted Rocks, the Dragon's late Abodes,
The green Reed trembles, and the Bulrush nods.
Waste sandy Vallies, once perplexd with Thorn8,
The spiry Fir and shapely Box adorn:
To leafless Shrubs the flow'ring Palms succeed,
And od'rous Myrtle to the noisome Weed.
The Lambs with Wolves shall graze the verdant Mead9
And Boys in flow'ry Bands the Tyger lead;
The Steer and Lion at one Crib shall meet,
And harmless Serpents Lick the Pilgrim's Feet.
The smiling Infant in his Hand shall take
The crested Basilisk and speckled Snake;
Pleas'd, the green Lustre of the Scales survey,
And with their forky Tongue and pointless Sting shall play.
Rise, crown'd with Light, imperial Salem rise!10
Exalt thy tow'ry Head, and lift thy Eyes!
See, a long Race thy spacious Courts adorn;11
See future Sons and Daughters yet unborn
In crowding Ranks on ev'ry side arise,
Demanding Life, impatient for the Skies!
See barb'rous Nations at thy Gates attend,12
Walk in thy Light, and in thy Temple bend.
See thy bright Altars throng'd with prostrate Kings,
And heap'd with Products of Sabæan Springs!13
For thee Idume's spicy Forests blow;
And seeds of Gold in Ophir's Mountains glow.
See Heav'n its sparkling Portals wide display,
And break upon thee in a Flood of Day!
No more the rising Sun shall gild the Morn,14
Nor Evening Cynthia fill her silver Horn,
But lost, dissolv'd in thy superior Rays;
One Tide of Glory, one unclouded Blaze
O'erflow thy Courts: The Light Himself shall shine
Reveal'd; and God's eternal Day be thine!
The Seas shall waste, the Skies in Smoke decay;15
Rocks fall to Dust, and Mountains melt away;
But fix'd His Word, His saving Pow'r remains:
Thy Realm for ever lasts! thy own Messiah reigns. |
T.
Thus far Steele.
hollow'd
Before him Death, the grisly Tyrant, flies;
He wipes the Tears for ever from our Eyes.
This was an alteration which Steele had suggested, and in which young
Pope had acquiesced. Steele wrote:
I have turned to every verse and chapter, and think you have preserved
the sublime, heavenly spirit throughout the whole, especially at "Hark
a glad voice," and "The lamb with wolves shall graze." There is but
one line which I think is below the original:
He wipes the tears for ever from our eyes.
You have expressed it with a good and pious but not so exalted and
poetical a spirit as the prophet:
The Lord God shall wipe away tears
from off all faces. If you agree with me in this, alter it by way of
paraphrase or otherwise, that when it comes into a volume it may be
amended.
Cap. 9. v. 6.
Cap. 2. v. 4.
Cap. 65. v. 21, 22.
Cap 35. v. 1, 7.
Cap. 41. v. 19. and Cap. 55. v. 13.
Cap. 11. v. 6, 7, 8.
Cap. 60. v. 1.
Cap. 60. v. 4.
Cap. 60. v. 3.
Cap. 60. v. 6.
Cap. 60. v. 19, 20.
Cap. 51. v. 6. and Cap. 64. v. 10.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 15, 1712 |
Budgell |
Scire tuum nihil est nisi te scire hoc sciat alter.
Pers.

I have often wondered at that ill-natur'd Position which has been
sometimes maintained in the Schools,
is comprizd in an old
Latin
Verse, namely, that
A Man's Knowledge is worth nothing, if he
communicates what he knows to any one besides.
There is certainly no
more sensible Pleasure to a good-natur'd Man, than if he can by any
means gratify or inform the Mind of another. I might add, that this
Virtue naturally carries its own reward along with it, since it is
almost impossible it should be exercised without the Improvement of the
Person who practices it. The reading of Books, and the daily Occurrences
of Life, are continually furnishing us with Matter for Thought and
Reflection. It is extremely natural for us to desire to see such our
Thoughts put into the Dress of Words, without which indeed we can scarce
have a clear and distinct Idea of them our selves: When they are thus
clothed in Expressions, nothing so truly shews us whether they are just
or false, as those Effects which they produce in the Minds of others.
I am apt to flatter my self, that in the Course of these my
Speculations, I have treated of several Subjects, and laid down many
such Rules for the Conduct of a Man's Life, which my Readers were either
wholly ignorant of before, or which at least those few who were
acquainted with them, looked upon as so many Secrets they have found out
for the Conduct of themselves, but were resolved never to have made
publick.
I am the more confirmed in this Opinion from my having received several
Letters, wherein I am censur'd for having prostituted Learning to the
Embraces of the Vulgar, and made her, as one of my Correspondents
phrases it, a common Strumpet: I am charged by another with laying open
the Arcana, or Secrets of Prudence, to the Eyes of every Reader.
The narrow Spirit which appears in the Letters of these my
Correspondents is the less surprizing, as it has shewn itself in all
Ages: There is
extant an Epistle written by
Alexander the Great
to
his Tutor
Aristotle
, upon that Philosopher's publishing some part of his
Writings; in which the Prince complains of his having made known to all
the World, those Secrets in Learning which he had before communicated to
him in private Lectures; concluding, That he had rather excel the rest
of Mankind in Knowledge than in Power
.
Luisa de Padilla
, a
of great Learning, and Countess of
Aranda
, was
in like manner angry with the famous
Gratian
, upon his publishing
his
Treatise of the Discrete
; wherein she fancied that he had laid open
those Maxims to common Readers, which ought only to have been reserved
for the Knowledge of the Great.
These Objections are thought by many of so much weight, that they often
defend the above-mentiond Authors, by affirming they have affected such
an Obscurity in their Style and Manner of Writing, that tho every one
may read their Works, there will be but very few who can comprehend
their Meaning.
Persius
, the
Latin
Satirist, affected Obscurity for another Reason; with
which however Mr.
Cowley
is so offended, that writing to one of his
Friends,
You
, says he,
tell me, that you do not know whether
Persius
be
a good Poet or no, because you cannot understand him; for which very
Reason I affirm that he is not so.
However, this Art of writing unintelligibly has been very much improved,
and follow'd by several of the Moderns, who observing the general
Inclination of Mankind to dive into a Secret, and the Reputation many
have acquired by concealing their Meaning under obscure Terms and
Phrases, resolve, that they may be still more abstruse, to write without
any Meaning at all. This Art, as it is at present practised by many
eminent Authors, consists in throwing so many Words at a venture into
different Periods, and leaving the curious Reader to find out the
Meaning of them.
The
Egyptians
, who made use of
Hieroglyphicks
to signify several things,
expressed a Man who confined his Knowledge and Discoveries altogether
within himself, by the Figure of a Dark-Lanthorn closed on all sides,
which, tho' it was illuminated within, afforded no manner of Light or
Advantage to such as stood by it. For my own part, as I shall from time
to time communicate to the Publick whatever Discoveries I happen to
make, I should much rather be compared to an ordinary Lamp, which
consumes and wastes it self for the benefit of every Passenger.
I shall conclude this Paper with the Story of
Rosicrucius's Sepulchre.
I
suppose I
not inform my Readers that this Man was the Founder of
the
Rosicrusian
Sect, and that his Disciples still pretend to new
Discoveries, which they are never to communicate to the rest of Mankind
.
A certain Person having occasion to dig somewhat deep in the Ground
where this Philosopher lay inter'd, met with a small Door having a Wall
on each side of it. His Curiosity, and the Hopes of finding some hidden
Treasure, soon prompted him to force open the Door. He was immediately
surpriz'd by a sudden Blaze of Light, and discover'd a very fair Vault:
At the upper end of it was a Statue of a Man in Armour sitting by a
Table, and leaning on his Left Arm. He held a Truncheon in his right
Hand, and had a Lamp burning before him. The Man had no sooner set one
Foot within the Vault, than the Statue erecting it self from its leaning
Posture, stood bolt upright; and upon the Fellow's advancing another
Step, lifted up the Truncheon in his Right Hand. The Man still ventur'd
a third Step, when the Statue with a furious Blow broke the Lamp into a
thousand Pieces, and left his Guest in a sudden Darkness.
Upon the Report of this Adventure, the Country People soon came with
Lights to the Sepulchre, and discovered that the Statue, which was made
of Brass, was nothing more than a Piece of Clock-work; that the Floor of
the Vault was all loose, and underlaid with several Springs, which, upon
any Man's entering, naturally produced that which had happend.
Rosicrucius
, says his Disciples, made use of this Method, to shew the
World that he had re-invented the ever-burning Lamps of the Ancients,
tho' he was resolvd no one should reap any Advantage from the Discovery.
X.
Nil proprium ducas quod mutarier potest.
Aulus Gellius.
Noct. Att.
, Bk xx., ch. 5.
Baltazar Grecian's
Discreto
has been mentioned before in
the
Spectator
, being well-known in England through a French translation.
See note on p. 303, ante [
of
]. Gracian, in Spain,
became especially popular as a foremost representative of his time in
transferring the humour for conceits—
cultismo
, as it was called—from
verse to prose. He began in 1630 with a prose tract, the Hero, laboured
in short ingenious sentences, which went through six editions. He wrote
also an
Art of Poetry
after the new style. His chief work was the
Criticon
, an allegory of the Spring, Autumn, and Winter of life. The
Discreto
was one of his minor works. All that he wrote was published,
not by himself, but by a friend, and in the name of his brother Lorenzo,
who was not an ecclesiastic.
Rosicrucius had been made fashionable by the Abbé de
Villars who was assassinated in 1675. His
Comte de Gabalis
was a popular
little book in the
Spectators
time. I suppose I need not inform my
readers that there never was a Rosicrucius or a Rosicrucian sect. The
Rosicrucian pamphlets which appeared in Germany at the beginning of the
17th century, dating from the Discovery of the
Brotherhood of the
Honourable Order of the Rosy Cross
, a pamphlet published in 1610, by a
Lutheran clergyman, Valentine Andreä, were part of a hoax designed
perhaps originally as means of establishing a sort of charitable masonic
society of social reformers. Missing that aim, the Rosicrucian story
lived to be adorned by superstitious fancy, with ideas of mystery and
magic, which in the
Comte de Gabalis
were methodized into a consistent
romance. It was from this romance that Pope got what he called the
Rosicrucian machinery of his
Rape of the Lock
. The Abbé de Villars,
professing to give very full particulars, had told how the Rosicrucians
assigned sylphs to the air, gnomes to the earth, nymphs to the water,
salamanders to the fire.
Contents
|
Friday, May 16, 1712 |
Steele |
Rivalem patienter habe—
Ovid.

Thursday, May 8, 1712.
Sir,
The Character you have in the World of being the Lady's Philosopher,
and the pretty Advice I have seen you give to others in your Papers,
make me address my self to you in this abrupt Manner, and to desire
your Opinion what in this Age a Woman may call a Lover. I have lately
had a Gentleman that I thought made Pretensions to me, insomuch that
most of my Friends took Notice of it and thought we were really
married; which I did not take much Pains to undeceive them, and
especially a young Gentlewoman of my particular Acquaintance which was
then in the Country. She coming to Town, and seeing our Intimacy so
great, she gave her self the Liberty of taking me to task concerning
it: I ingenuously told her we were not married, but I did not know
what might the Event. She soon got acquainted with the Gentleman, and
was pleased to take upon her to examine him about it. Now whether a
new Face had made a greater Conquest than the old, I'll leave you to
judge: But I am informd that he utterly deny'd all Pretensions to
Courtship, but withal profess'd a sincere Friendship for me; but
whether Marriages are propos'd by way of Friendship or not, is what I
desire to know, and what I may really call a Lover. There are so many
who talk in a Language fit only for that Character, and yet guard
themselves against speaking in direct Terms to the Point, that it is
impossible to distinguish between Courtship and Conversation. I hope
you will do me Justice both upon my Lover and my Friend, if they
provoke me further: In the mean time I carry it with so equal a
Behaviour, that the Nymph and the Swain too are mighty at a loss; each
believes I, who know them both well, think my self revenged in their
Love to one another, which creates an irreconcileable Jealousy. If all
comes right again, you shall hear further from,
Sir,
Your most obedient Servant,
Mirtilla.
April 28, 1712.
Mr.
Spectator,
Your Observations on Persons that have behaved themselves irreverently
at Church, I doubt not have had a good Effect on some that have read
them: But there is another Fault which has hitherto escaped your
Notice, I mean of such Persons as are very zealous and punctual to
perform an Ejaculation that is only preparatory to the Service of the
Church, and yet neglect to join in the Service it self. There is an
Instance of this in a Friend of
Will. Honeycomb's, who sits opposite to
me: He seldom comes in till the Prayers are about half over, and when
he has enter'd his Seat (instead of joining with the Congregation) he
devoutly holds his Hat before his Face for three or four Moments, then
bows to all his Acquaintance, sits down, takes a Pinch of Snuff, (if
it be Evening Service perhaps a Nap) and spends the remaining Time in
surveying the Congregation. Now, Sir, what I would desire, is, that
you will animadvert a little on this Gentleman's Practice. In my
Opinion, this Gentleman's Devotion, Cap-in-Hand, is only a Compliance
to the Custom of the Place, and goes no further than a little
ecclesiastical Good-Breeding. If you will not pretend to tell us the
Motives that bring such Triflers to solemn Assemblies, yet let me
desire that you will give this Letter a Place in your Paper, and I
shall remain,
Sir,
Your obliged humble Servant,
J. S.
May the 5th.
Mr.
Spectator,
The Conversation at a Club, of which I am a Member, last Night falling
upon Vanity and the Desire of being admired, put me in mind of
relating how agreeably I was entertained at my own Door last Thursday
by a clean fresh-colour'd Girl, under the most elegant and the best
furnished Milk-Pail I had ever observed. I was glad of such an
Opportunity of seeing the Behaviour of a Coquet in low Life, and how
she received the extraordinary Notice that was taken of her; which I
found had affected every Muscle of her Face in the same manner as it
does the Feature of a first-rate Toast at a Play, or in an Assembly.
This Hint of mine made the Discourse turn upon the Sense of Pleasure;
which ended in a general Resolution, that the Milk-Maid enjoys her
Vanity as exquisitely as the Woman of Quality. I think it would not be
an improper Subject for you to examine this Frailty, and trace it to
all Conditions of Life; which is recommended to you as an Occasion of
obliging many of your Readers, among the rest,
Your most humble Servant,
T. B.
Sir,
Coming last Week into a Coffee-house not far from the Exchange with my
Basket under my Arm, a
Jew of considerable Note, as I am informed,
takes half a Dozen Oranges of me, and at the same time slides a Guinea
into my Hand; I made him a Curtsy, and went my Way: He follow'd me,
and finding I was going about my Business, he came up with me, and
told me plainly, that he gave me the Guinea with no other Intent but
to purchase my Person for an Hour. Did you so, Sir? says I: You gave
it me then to make me be wicked, I'll keep it to make me honest.
However, not to be in the least ungrateful, I promise you Ill lay it
out in a couple of Rings, and wear them for your Sake. I am so just,
Sir, besides, as to give every Body that asks how I came by my Rings
this Account of my Benefactor; but to save me the Trouble of telling
my Tale over and over again, I humbly beg the favour of you so to tell
it once for all, and you will extremely oblige,
Your humble Servant,
Betty Lemon.
May 12, 1712.
St. Bride's, May 15, 1712.
Sir,
'Tis a great deal of Pleasure to me, and I dare say will be no less
Satisfaction to you, that I have an Opportunity of informing you, that
the Gentlemen and others of the Parish of
St. Bride's, have raised a
Charity-School of fifty Girls, as before of fifty Boys. You were so
kind to recommend the Boys to the charitable World, and the other Sex
hope you will do them the same Favour in Friday's Spectator for Sunday
next, when they are to appear with their humble Airs at the Parish
Church of
St. Bride's. Sir, the Mention of this may possibly be
serviceable to the Children; and sure no one will omit a good Action
attended with no Expence.
I am,
Sir, Your very humble Servant,
The Sexton.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, May 17, 1712 |
Addison |
Æquam memento rebus in arduis,
Servare mentem, non secùs in bonis
Ab insolenti temperatam
Lætitiâ, moriture Deli.
Hor.

I have always preferred
Chearfulness
to
Mirth
. The latter, I consider as
an Act, the former as an Habit of the Mind. Mirth is short and
transient. Chearfulness fixed and permanent. Those are often raised into
the greatest Transports of Mirth, who are subject to the greatest
Depressions of Melancholy: On the contrary, Chearfulness, tho' it does
not give the Mind such an exquisite Gladness, prevents us from falling
into any Depths of Sorrow. Mirth is like a Flash of Lightning, that
breaks thro a Gloom of Clouds, and glitters for a Moment; Chearfulness
keeps up a kind of Day-light in the Mind, and fills it with a steady and
perpetual Serenity.
Men of austere Principles look upon Mirth as too wanton and dissolute
for a State of Probation, and as filled with a certain Triumph and
Insolence of Heart, that is inconsistent with a Life which is every
Moment obnoxious to the greatest Dangers. Writers of this Complexion
have observed, that the sacred Person who was the great Pattern of
Perfection was never seen to Laugh.
Chearfulness of Mind is not liable to any of these Exceptions; it is of
a serious and composed Nature, it does not throw the Mind into a
Condition improper for the present State of Humanity, and is very
conspicuous in the Characters of those who are looked upon as the
greatest Philosophers among the Heathens, as well as among those who
have been deservedly esteemed as Saints and Holy Men among
Christians
.
If we consider Chearfulness in three Lights, with regard to our selves,
to those we converse with, and to the great Author of our Being, it will
not a little recommend it self on each of these Accounts. The Man who is
possessed of this excellent Frame of Mind, is not only easy in his
Thoughts, but a perfect Master of all the Powers and Faculties of his
Soul: His Imagination is always clear, and his Judgment undisturbed: His
Temper is even and unruffled, whether in Action or in Solitude. He comes
with a Relish to all those Goods which Nature has provided for him,
tastes all the Pleasures of the Creation which are poured about him, and
does not feel the full Weight of those accidental Evils which may befal
him.
If we consider him in relation to the Persons whom he converses with, it
naturally produces Love and Good-will towards him. A chearful Mind is
not only disposed to be affable and obliging, but raises the same good
Humour in those who come within its Influence. A Man finds himself
pleased, he does not know why, with the Chearfulness of his Companion:
It is like a sudden Sun-shine that awakens a secret Delight in the Mind,
without her attending to it. The Heart rejoices of its own accord, and
naturally flows out into Friendship and Benevolence towards the Person
who has so kindly an Effect upon it.
When I consider this chearful State of Mind in its third Relation, I
cannot but look upon it as a constant habitual Gratitude to the great
Author of Nature. An inward Chearfulness is an implicit Praise and
Thanksgiving to Providence under all its Dispensations. It is a kind of
Acquiescence in the State wherein we are placed, and a secret
Approbation of the Divine Will in his Conduct towards Man.
There are but two things which, in my Opinion, can reasonably deprive us
of this Chearfulness of Heart. The first of these is the Sense of Guilt.
A Man who lives in a State of Vice and Impenitence, can have no Title to
that Evenness and Tranquillity of Mind which is the Health of the Soul,
and the natural Effect of Virtue and Innocence. Chearfulness in an ill
Man deserves a harder Name than Language can furnish us with, and is
many degrees beyond what we commonly call Folly or Madness.
Atheism, by which I mean a Disbelief of a Supreme Being, and
consequently of a future State, under whatsoever Titles it shelters it
self, may likewise very reasonably deprive a Man of this Chearfulness of
Temper. There is something so particularly gloomy and offensive to human
Nature in the Prospect of Non-Existence, that I cannot but wonder, with
many excellent Writers, how it is possible for a Man to out-live the
Expectation of it. For my own Part, I think the Being of a God is so
little to be doubted, that it is almost the only Truth we are sure of,
and such a Truth as we meet with in every Object, in every Occurrence,
and in every Thought. If we look into the Characters of this Tribe of
Infidels, we generally find they are made up of Pride, Spleen, and
Cavil: It is indeed no wonder, that Men, who are uneasy to themselves,
should be so to the rest of the World; and how is it possible for a Man
to be otherwise than uneasy in himself, who is in danger every Moment of
losing his entire Existence, and dropping into Nothing?
The vicious Man and Atheist have therefore no Pretence to Chearfulness,
and would act very unreasonably, should they endeavour after it. It is
impossible for any one to live in Good-Humour, and enjoy his present
Existence, who is apprehensive either of Torment or of Annihilation; of
being miserable, or of not being at all.
After having mention'd these two great Principles, which are destructive
of Chearfulness in their own Nature, as well as in right Reason, I
cannot think of any other that ought to banish this happy Temper from a
Virtuous Mind. Pain and Sickness, Shame and Reproach, Poverty and old
Age, nay Death it self, considering the Shortness of their Duration, and
the Advantage we may reap from them, do not deserve the Name of Evils. A
good Mind may bear up under them with Fortitude, with Indolence and with
Chearfulness of Heart. The tossing of a Tempest does not discompose him,
which he is sure will bring him to a Joyful Harbour.
A Man, who uses his best endeavours to live according to the Dictates of
Virtue and right Reason, has two perpetual Sources of Chearfulness; in
the Consideration of his own Nature, and of that Being on whom he has a
Dependance. If he looks into himself, he cannot but rejoice in that
Existence, which is so lately bestowed upon him, and which, after
Millions of Ages, will be still new, and still in its Beginning. How
many Self-Congratulations naturally arise in the Mind, when it reflects
on this its Entrance into Eternity, when it takes a View of those
improveable Faculties, which in a few Years, and even at its first
setting out, have made so considerable a Progress, and which will be
still receiving an Increase of Perfection, and consequently an Increase
of Happiness? The Consciousness of such a Being spreads a perpetual
Diffusion of Joy through the Soul of a virtuous Man, and makes him look
upon himself every Moment as more happy than he knows how to conceive.
The second Source of Chearfulness to a good Mind, is its Consideration
of that Being on whom we have our Dependance, and in whom, though we
behold him as yet but in the first faint Discoveries of his Perfections,
we see every thing that we can imagine as great, glorious, or amiable.
We find our selves every where upheld by his Goodness, and surrounded
with an Immensity of Love and Mercy. In short, we depend upon a Being,
whose Power qualifies him to make us happy by an Infinity of Means,
whose Goodness and Truth engage him to make those happy who desire it of
him, and whose Unchangeableness will secure us in this Happiness to all
Eternity.
Such Considerations, which every one should perpetually cherish in his
Thoughts, will banish, from us all that secret Heaviness of Heart which
unthinking Men are subject to when they lie under no real Affliction,
all that Anguish which we may feel from any Evil that actually oppresses
us, to which I may likewise add those little Cracklings of Mirth and
Folly that are apter to betray Virtue than support it; and establish in
us such an even and chearful Temper, as makes us pleasing to our selves,
to those with whom we converse, and to him whom we were made to please.
I.
Contents
|
Monday, May 19, 1712 |
Steele |
Habes confitentem reum.
Tull.

I ought not to have neglected a Request of one of my Correspondents so
long as I have; but I dare say I have given him time to add Practice to
Profession. He sent me some time ago a Bottle or two of excellent Wine
to drink the Health of a Gentleman, who had by the Penny-Post advertised
him of an egregious Error in his Conduct. My Correspondent received the
Obligation from an unknown Hand with the Candour which is natural to an
ingenuous Mind; and promises a contrary Behaviour in that Point for the
future: He will offend his Monitor with no more Errors of that kind, but
thanks him for his Benevolence. This frank Carriage makes me reflect
upon the amiable Atonement a Man makes in an ingenuous Acknowledgment of
a Fault: All such Miscarriages as flow from Inadvertency are more than
repaid by it; for Reason, though not concerned in the Injury, employs
all its Force in the Atonement. He that says, he did not design to
disoblige you in such an Action, does as much as if he should tell you,
that tho' the Circumstance which displeased was never in his Thoughts,
he has that Respect for you, that he is unsatisfied till it is wholly
out of yours. It must be confessed, that when an Acknowledgment of
Offence is made out of Poorness of Spirit, and not Conviction of Heart,
the Circumstance is quite different: But in the Case of my
Correspondent, where both the Notice is taken and the Return made in
private, the Affair begins and ends with the highest Grace on each Side.
To make the Acknowledgment of a Fault in the highest manner graceful, it
is lucky when the Circumstances of the Offender place him above any ill
Consequences from the Resentment of the Person offended. A
Dauphin
of
France
, upon a Review of the Army, and a Command of the
King
to alter
the Posture of it by a March of one of the Wings, gave an improper Order
to an Officer at the Head of a Brigade, who told his Highness, he
presumed he had not received the last Orders, which were to move a
contrary Way. The Prince, instead of taking the Admonition which was
delivered in a manner that accounted for his Error with Safety to his
Understanding, shaked a Cane at the Officer; and with the return of
opprobrious Language, persisted in his own Orders. The whole Matter came
necessarily before the King, who commanded his Son, on foot, to lay his
right Hand on the Gentleman's Stirrup as he sat on Horseback in sight of
the whole Army, and ask his Pardon. When the Prince touched his Stirrup,
and was going to speak, the Officer with an incredible Agility, threw
himself on the Earth, and kissed his Feet.
The Body is very little concerned in the Pleasures or Sufferings of
Souls truly great; and the Reparation, when an Honour was designed this
Soldier, appeared as much too great to be borne by his Gratitude, as the
Injury was intolerable to his Resentment.
When we turn our Thoughts from these extraordinary Occurrences in common
Life, we see an ingenuous kind of Behaviour not only make up for Faults
committed, but in a manner expiate them in the very Commission. Thus
many things wherein a Man has pressed too far, he implicitly excuses, by
owning, This is a Trespass; youll pardon my Confidence; I am sensible I
have no Pretension to this Favour, and the like. But commend me to those
gay Fellows about Town who are directly impudent, and make up for it no
otherwise than by calling themselves such, and exulting in it. But this
sort of Carriage, which prompts a Man against Rules to urge what he has
a Mind to, is pardonable only when you sue for another. When you are
confident in preference of your self to others of equal Merit, every Man
that loves Virtue and Modesty ought, in Defence of those Qualities, to
oppose you: But, without considering the Morality of the thing, let us
at this time behold only the natural Consequence of Candour when we
speak of ourselves.
The
Spectator
writes often in an Elegant, often in an Argumentative, and
often in a Sublime Style, with equal Success; but how would it hurt the
reputed Author of that Paper to own, that of the most beautiful Pieces
under his Title, he is barely the Publisher? There is nothing but what a
Man really performs, can be an Honour to him; what he takes more than he
ought in the Eye of the World, he loses in the Conviction of his own
Heart; and a Man must lose his Consciousness, that is, his very Self,
before he can rejoice in any Falshood without inward Mortification.
Who has not seen a very Criminal at the Bar, when his Counsel and
Friends have done all that they could for him in vain, prevail upon the
whole Assembly to pity him, and his Judge to recommend his Case to the
Mercy of the Throne, without offering any thing new in his Defence, but
that he, whom before we wished convicted, became so out of his own
Mouth, and took upon himself all the Shame and Sorrow we were just
before preparing for him? The great Opposition to this kind of Candour,
arises from the unjust Idea People ordinarily have of what we call an
high Spirit. It is far from Greatness of Spirit to persist in the Wrong
in any thing, nor is it a Diminution of Greatness of Spirit to have been
in the Wrong: Perfection is not the Attribute of Man, therefore he is
not degraded by the Acknowledgment of an Imperfection: But it is the
Work of little Minds to imitate the Fortitude of great Spirits on worthy
Occasions, by Obstinacy in the Wrong. This Obstinacy prevails so far
upon them, that they make it extend to the Defence of Faults in their
very Servants. It would swell this Paper to too great a length, should I
insert all the Quarrels and Debates which are now on foot in this Town;
where one Party, and in some Cases both, is sensible of being on the
faulty Side, and have not Spirit enough to Acknowledge it. Among the
Ladies the Case is very common, for there are very few of them who know
that it is to maintain a true and high Spirit, to throw away from it all
which it self disapproves, and to scorn so pitiful a Shame, as that
which disables the Heart from acquiring a Liberality of Affections and
Sentiments. The candid Mind, by acknowledging and discarding its Faults,
has Reason and Truth for the Foundation of all its Passions and Desires,
and consequently is happy and simple; the disingenuous Spirit, by
Indulgence of one unacknowledged Error, is intangled with an After-Life
of Guilt, Sorrow, and Perplexity.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 20, 1712 |
Addison |
Criminibus debent Hortos—
Hor.

As I was sitting in my Chamber, and thinking on a Subject for my next
Spectator, I heard two or three irregular Bounces at my Landlady's Door,
and upon the opening of it, a loud chearful Voice enquiring whether the
Philosopher was at Home. The Child who went to the Door answered very
Innocently, that he did not Lodge there. I immediately recollected that
it was my good Friend Sir
Roger's
Voice; and that I had promised to go
with him on the Water to Spring-Garden, in case it proved a good
Evening. The Knight put me in mind of my Promise from the Bottom of the
Stair-Case, but told me that if I was Speculating he would stay below
till I had done. Upon my coming down, I found all the Children of the
Family got about my old Friend, and my Landlady herself, who is a
notable prating Gossip, engaged in a Conference with him; being mightily
pleased with his stroaking her little Boy upon the Head, and bidding him
be a good Child and mind his Book
.
We were no sooner come to the Temple Stairs, but we were surrounded with
a Crowd of Watermen, offering us their respective Services. Sir
Roger
,
after having looked about him very attentively, spied one with a
Wooden-Leg, and immediately gave him Orders to get his Boat ready. As we
were walking towards it,
You must know
, says Sir
Roger
,
I never make use
of any body to row me, that has not either lost a Leg or an Arm. I would
rather bate him a few Strokes of his Oar, than not employ an honest Man
that has been wounded in the Queen's Service. If I was a Lord or a
Bishop, and kept a Barge, I would not put a Fellow in my Livery that had
not a Wooden-Leg.
My old Friend, after having seated himself, and trimmed the Boat with
his Coachman, who, being a very sober Man, always serves for Ballast on
these Occasions, we made the best of our way for Fox-Hall. Sir
Roger
the Waterman to give us the History of his Right Leg, and
hearing that he had left it
at La Hogue
with many Particulars
which passed in that glorious Action, the Knight in the Triumph of his
Heart made several Reflections on the Greatness of the
British
Nation;
as, that one
Englishman
could beat three
Frenchmen
; that we could never
be in danger of Popery so long as we took care of our Fleet; that the
Thames
was the noblest River in
Europe
; that
London Bridge
was a greater
piece of Work, than any of the seven Wonders of the World; with many
other honest Prejudices which naturally cleave to the Heart of a true
Englishman
.
After some short Pause, the old Knight turning about his Head twice or
thrice, to take a Survey of this great Metropolis, bid me observe how
thick the City was set with Churches, and that there was scarce a single
Steeple on this side Temple-Bar.
A most Heathenish Sight!
says Sir
Roger
:
There is no Religion at this End of the Town. The fifty new
Churches will very much mend the Prospect; but Church-work is slow,
Church-work is slow!
I do not remember I have any where mentioned, in Sir
Roger's
Character,
his Custom of saluting every Body that passes by him with a Good-morrow
or a Good-night. This the old Man does out of the overflowings of his
Humanity, though at the same time it renders him so popular among all
his Country Neighbours, that it is thought to have gone a good way in
making him once or twice
Knight of the Shire
. He cannot forbear this
Exercise of Benevolence even in Town, when he meets with any one in his
Morning or Evening Walk. It broke from him to several Boats that passed
by us upon the Water; but to the Knight's great Surprize, as he gave the
Good-night to two or three young Fellows a little before our Landing,
one of them, instead of returning the Civility, asked us
what queer old
Put we had in the Boat, and whether he was not ashamed to go a Wenching
at his Years?
with a great deal of the like
Thames-Ribaldry
. Sir ROGER
seemd a little shocked at first, but at length assuming a Face of
Magistracy, told us,
That if he were a Middlesex Justice, he would make
such Vagrants know that Her Majesty's Subjects were no more to be abused
by Water than by Land.
We were now arrived at
Spring-Garden
, which is exquisitely pleasant at
this time of Year. When I considered the Fragrancy of the Walks and
Bowers, with the Choirs of Birds that sung upon the Trees, and the loose
Tribe of People that walked under their Shades, I could not but look
upon the Place as a kind of
Mahometan
Paradise. Sir
Roger
told me it put
him in mind of a little Coppice by his House in the Country, which his
Chaplain used to call
an Aviary of Nightingales
.
You must understand,
says the Knight,
there is nothing in the World that pleases a Man in
Love so much as your Nightingale. Ah, Mr. Spectator! the many Moon-light
Nights that I have walked by my self, and thought on the Widow by the
Musek of the Nightingales!
He here fetched a deep Sigh, and was falling
into a Fit of musing, when a
Masque
, who came behind him, gave him a
gentle Tap upon the Shoulder, and asked him
if he would drink a Bottle
of Mead with her?
But the Knight, being startled at so unexpected a
Familiarity, and displeased to be interrupted in his Thoughts of the
Widow, told her,
She was a wanton Baggage, and bid her go about her
Business.
We concluded our Walk with a Glass of
Burton-Ale
, and a Slice of
Hung-Beef
. When we had done eating our selves, the Knight called a
Waiter to him, and bid him
carry the remainder to the Waterman that had
but one Leg.
I perceived the Fellow stared upon him at the oddness of
the Message, and was going to be saucy; upon which I ratified the
Knight's Commands with a Peremptory Look.
As we were going out of the Garden, my old Friend, thinking himself
obliged, as a Member of the Quorum, to animadvert upon the Morals of the
Place, told the Mistress of the House, who sat at the Bar,
That he
should be a better Customer to her Garden, if there were more
Nightingales, and fewer Strumpets.
in Bantry Bay
. In Bantry Bay, on May-day, 1689, a French
Fleet, bringing succour to the adherents of James II., attacked the
English, under Admiral Herbert, and obliged them to retire. The change
of name in the text was for one with a more flattering association. In
the Battle of La Hogue, May 19, 1692, the English burnt 13 of the
enemy's ships, destroyed 8, dispersed the rest, and prevented a
threatened descent of the French upon England.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Hague, May 24. N. S.
The same Republican Hands, who have so often since the Chevalier de
St. George's Recovery killed him in our publick Prints, have now
reduced the young Dauphin of France to that desperate Condition of
Weakness, and Death it self, that it is hard to conjecture what Method
they will take to bring him to Life again. Mean time we are assured by
a very good Hand from Paris, That on the 20th Instant, this young
Prince was as well as ever he was known to be since the Day of his
Birth. As for the other, they are now sending his Ghost, we suppose,
(for they never had the Modesty to contradict their Assertions of his
Death) to Commerci in Lorrain, attended only by four Gentlemen, and a
few Domesticks of little Consideration. The Baron de Bothmar having
delivered in his Credentials to qualify him as an Ambassador to this
State, (an Office to which his greatest Enemies will acknowledge him
to be equal) is gone to Utrecht, whence he will proceed to Hanover,
but not stay long at that Court, for fear the Peace should be made
during his lamented Absence.
Post-Boy, May 20.
I should be thought not able to read, should I overlook some
excellent Pieces lately come out.
My Lord Bishop of St.
Asaph
has just now published some
Sermons
, the
Preface
to which
seems to me to determine a great Point
.—He has, like a good
Man and a good
Christian
, in opposition to all the Flattery and
base Submission of false Friends to Princes, asserted, That
Christianity
left us where it found us as to our Civil Rights.
The present Entertainment shall consist only of a Sentence out of
the
Post-Boy
, and the said
Preface
of the
Lord of St. Asaph
. I
should think it a little odd if the Author of the
Post-Boy
should
with Impunity call Men
Republicans
for a Gladness on Report of
the Death of the Pretender; and treat Baron
Bothmar
, the
Minister of
Hanover
, in such a manner as you see in my Motto.
I must own, I think every Man in
England
concerned to support
the Succession of that Family.
The publishing a few Sermons, whilst I live, the latest of which was
preached about eight Years since, and the first above seventeen, will
make it very natural for People to enquire into the Occasion of doing
so; And to such I do very willingly assign these following Reasons.
First, From the Observations I have been able to make, for these many
Years last past, upon our publick Affairs, and from the natural
Tendency of several Principles and Practices, that have of late been
studiously revived, and from what has followed thereupon, I could not
help both fearing and presaging, that these Nations would some time or
other, if ever we should have an enterprising Prince upon the Throne,
of more Ambition than Virtue, Justice, and true Honour, fall into the
way of all other Nations, and lose their Liberty.
Nor could I help foreseeing to whose Charge a great deal of this
dreadful Mischief, whenever it should happen, would be laid, whether
justly or unjustly, was not my Business to determine; but I resolved
for my own particular part, to deliver my self, as well as I could,
from the Reproaches and the Curses of Posterity, by publickly
declaring to all the World, That although in the constant Course of my
Ministry, I have never failed, on proper Occasions, to recommend,
urge, and insist upon the loving, honouring, and the reverencing the
Prince's Person, and holding it, according to the Laws, inviolable and
sacred; and paying all Obedience and Submission to the Laws, though
never so hard and inconvenient to private People: Yet did I never
think my self at liberty, or authorized to tell the People, that
either Christ, St. Peter, or St. Paul, or any other Holy Writer, had
by any Doctrine delivered by them, subverted the Laws and
Constitutions of the Country in which they lived, or put them in a
worse Condition, with respect to their Civil Liberties, than they
would have been had they not been Christians. I ever thought it a most
impious Blasphemy against that holy Religion, to father any thing upon
it that might encourage Tyranny, Oppression, or Injustice in a Prince,
or that easily tended to make a free and happy People Slaves and
Miserable. No: People may make themselves as wretched as they will,
but let not God be called into that wicked Party. When Force and
Violence, and hard Necessity have brought the Yoak of Servitude upon a
People's Neck, Religion will supply them with a patient and submissive
Spirit under it till they can innocently shake it off; but certainly
Religion never puts it on. This always was, and this at present is, my
Judgment of these Matters: And I would be transmitted to Posterity
(for the little Share of Time such Names as mine can live) under the
Character of one who lov'd his Country, and would be thought a good
Englishman, as well as a good Clergyman.
This Character I thought would be transmitted by the following
Sermons, which were made for, and preached in a private Audience, when
I could think of nothing else but doing my Duty on the Occasions that
were then offered by God's Providence, without any manner of design of
making them publick: And for that reason I give them now as they were
then delivered; by which I hope to satisfie those People who have
objected a Change of Principles to me, as if I were not now the same
Man I formerly was. I never had but one Opinion of these Matters; and
that I think is so reasonable and well-grounded, that I believe I
never can have any other. Another Reason of my publishing these
Sermons at this time, is, that I have a mind to do my self some
Honour, by doing what Honour I could to the Memory of two most
excellent Princes, and who have very highly deserved at the hands of
all the People of these Dominions, who have any true Value for the
Protestant Religion, and the Constitution of the English Government,
of which they were the great Deliverers and Defenders. I have lived to
see their illustrious Names very rudely handled, and the great
Benefits they did this Nation treated slightly and contemptuously. I
have lived to see our Deliverance from Arbitrary Power and Popery,
traduced and vilified by some who formerly thought it was their
greatest Merit, and made it part of their Boast and Glory, to have had
a little hand and share in bringing it about; and others who, without
it, must have liv'd in Exile, Poverty, and Misery, meanly disclaiming
it, and using ill the glorious Instruments thereof. Who could expect
such a Requital of such Merit? I have, I own it, an Ambition of
exempting my self from the Number of unthankful People: And as I loved
and honoured those great Princes living, and lamented over them when
dead, so I would gladly raise them up a Monument of Praise as lasting
as any thing of mine can be; and I chuse to do it at this time, when
it is so unfashionable a thing to speak honourably of them.
The Sermon that was preached upon the Duke of Gloucester's Death was
printed quickly after, and is now, because the Subject was so
suitable, join'd to the others. The Loss of that most promising and
hopeful Prince was, at that time, I saw, unspeakably great; and many
Accidents since have convinced us, that it could not have been
over-valued. That precious Life, had it pleased God to have prolonged
it the usual Space, had saved us many Fears and Jealousies, and dark
Distrusts, and prevented many Alarms, that have long kept us, and will
keep us still, waking and uneasy. Nothing remained to comfort and
support us under this heavy Stroke, but the Necessity it brought the
King and Nation under, of settling the Succession in the House of
Hannover, and giving it an Hereditary Right, by Act of Parliament, as
long as it continues Protestant. So much good did God, in his merciful
Providence, produce from a Misfortune, which we could never otherwise
have sufficiently deplored.
The fourth Sermon was preached upon the Queen's Accession to the
Throne, and the first Year in which that Day was solemnly observed,
(for, by some Accident or other, it had been overlook'd the Year
before;) and every one will see, without the date of it, that it was
preached very early in this Reign, since I was able only to promise
and presage its future Glories and Successes, from the good
Appearances of things, and the happy Turn our Affairs began to take;
and could not then count up the Victories and Triumphs that, for seven
Years after, made it, in the Prophet's Language, a Name and a Praise
among all the People of the Earth. Never did seven such Years together
pass over the head of any English Monarch, nor cover it with so much
Honour: The Crown and Sceptre seemed to be the Queen's least
Ornaments; those, other Princes wore in common with her, and her great
personal Virtues were the same before and since; but such was the Fame
of her Administration of Affairs at home, such was the Reputation of
her Wisdom and Felicity in chusing Ministers, and such was then
esteemed their Faithfulness and Zeal, their Diligence and great
Abilities in executing her Commands; to such a height of military
Glory did her great General and her Armies carry the British Name
abroad; such was the Harmony and Concord betwixt her and her Allies,
and such was the Blessing of God upon all her Counsels and
Undertakings, that I am as sure as History can make me, no Prince of
ours was ever yet so prosperous and successful, so beloved, esteemed,
and honoured by their Subjects and their Friends, nor near so
formidable to their Enemies. We were, as all the World imagined then,
just ent'ring on the ways that promised to lead to such a Peace, as
would have answered all the Prayers of our religious Queen, the Care
and Vigilance of a most able Ministry, the Payments of a willing and
obedient People, as well as all the glorious Toils and Hazards of the
Soldiery; when God, for our Sins, permitted the Spirit of Discord to
go forth, and, by troubling sore the Camp, the City, and the Country,
(and oh that it had altogether spared the Places sacred to his
Worship!) to spoil, for a time, this beautiful and pleasing Prospect,
and give us, in its stead, I know not what — Our Enemies will tell
the rest with Pleasure. It will become me better to pray to God to
restore us to the Power of obtaining such a Peace, as will be to his
Glory, the Safety, Honour, and the Welfare of the Queen and her
Dominions, and the general Satisfaction of all her High and Mighty
Allies.
May 2, 1712.
T.
Dr. William Fleetwood, Bishop of St. Asaph, had published
Four Sermons.
- On the death of Queen Mary, 1694.
- On the death of the Duke of Gloucester, 1700.
- On the death of King William, 1701.
- On the Queen's Accession to the Throne, in 1702,
with a Preface.
8vo. London, 1712.
The Preface which, says Dr. Johnson, overflowed with Whiggish
principles, was ordered to be burnt by the House of Commons. This moved
Steele to diffuse it by inserting it in the
Spectator
, which, as its
author said in a letter to Burnet, conveyed about fourteen thousand
copies of the condemned preface into people's hands that would otherwise
have never seen or heard of it. Moreover, to ensure its delivery into
the Queen's hands the publication of this number is said to have been
deferred till twelve oclock, her Majesty's breakfast hour, that no time
might be allowed for a decision that it should not be laid, as usual,
upon her breakfast table.
Fleetwood was born in 1656; had been chaplain to King William, and in
1706 had been appointed to the Bishopric of St. Asaph without any
solicitation. He was translated to Ely in 1714, and died in 1723.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 22, 1712 |
Budgell |
Theseâ pectora juncta fide.
Ovid.

I intend the Paper for this Day as a loose Essay upon Friendship, in
which I shall throw my Observations together without any set Form, that
I may avoid repeating what has been often said on this Subject.
Friendship is a strong and habitual Inclination in two Persons to
promote the Good and Happiness of one another.
Tho' the Pleasures and
Advantages of Friendship have been largely celebrated by the best moral
Writers, and are considered by all as great Ingredients of human
Happiness, we very rarely meet with the Practice of this Virtue in the
World.
Every Man is ready to give in a long Catalogue of those Virtues and good
Qualities he expects to find in the Person of a Friend, but very few of
us are careful to cultivate them in our selves.
Love
and
Esteem
are the first Principles of Friendship, which always is
imperfect where either of these two is wanting.
As, on the one hand, we are soon ashamed of loving a Man whom we cannot
esteem: so, on the other, tho we are truly sensible of a Man's
Abilities, we can never raise ourselves to the Warmths of Friendship,
without an affectionate Good-will towards his Person.
Friendship immediately banishes
Envy
under all its Disguises. A Man who
can once doubt whether he should rejoice in his Friends being happier
than himself, may depend upon it that he is an utter Stranger to this
Virtue.
There is something in Friendship so very great and noble, that in those
fictitious Stories which are invented to the Honour of any particular
Person, the Authors have thought it as necessary to make their Hero a
Friend as a Lover.
Achilles
has his
Patroclus
, and
Æneas
his
Achates
. In
the first of these Instances we may observe, for the Reputation of the
Subject I am treating of, that
Greece
was almost ruin'd by the Hero's
Love, but was preserved by his Friendship.
The Character of
Achates
suggests to us an Observation we may often make
on the Intimacies of great Men, who frequently chuse their Companions
rather for the Qualities of the Heart than those of the Head, and prefer
Fidelity in an easy inoffensive complying Temper to those Endowments
which make a much greater Figure among Mankind. I do not remember that
Achates
, who is represented as the first Favourite, either gives his
Advice, or strikes a Blow, thro' the whole
Æneid
.
A Friendship which makes the least noise, is very often most useful: for
which reason I should prefer a prudent Friend to a zealous one.
Atticus
, one of the best Men of ancient
Rome
, was a very remarkable
Instance of what I am here speaking. This extraordinary Person, amidst
the Civil Wars of his Country, when he saw the Designs of all Parties
equally tended to the Subversion of Liberty, by constantly preserving
the Esteem and Affection of both the Competitors, found means to serve
his Friends on either side: and while he sent Money to young
Marius
,
whose Father was declared an Enemy of the Commonwealth, he was himself
one of
Sylla's
chief Favourites, and always near that General.
During the War between
Cæsar
and
Pompey
, he still maintained the same
Conduct. After the Death of
Cæsar
he sent Money to
Brutus
in his
Troubles, and did a thousand good Offices to
Antony's
Wife and Friends
when that Party seemed ruined. Lastly, even in that bloody War between
Antony
and
Augustus
,
Atticus
still kept his place in both their
Friendships; insomuch that the first, says
Cornelius Nepos
, whenever he
was absent from
Rome
in any part of the Empire, writ punctually to him
what he was doing, what he read, and whither he intended to go; and the
latter gave him constantly an exact Account of all his Affairs.
A Likeness of Inclinations in every Particular is so far from being
requisite to form a Benevolence in two Minds towards each other, as it
is generally imagined, that I believe we shall find some of the firmest
Friendships to have been contracted between Persons of different
Humours; the Mind being often pleased with those Perfections which are
new to it, and which it does not find among its own Accomplishments.
Besides that a Man in some measure supplies his own Defects, and fancies
himself at second hand possessed of those good Qualities and Endowments,
which are in the possession of him who in the Eye of the World is looked
on as his other self.
The most difficult Province in Friendship is the letting a Man see his
Faults and Errors, which should, if possible, be so contrived, that he
may perceive our Advice is given him not so much to please ourselves as
for his own Advantage. The Reproaches therefore of a Friend should
always be strictly just, and not too frequent.
The violent Desire of pleasing in the Person reproved, may otherwise
change into a Despair of doing it, while he finds himself censur'd for
Faults he is not Conscious of. A Mind that is softened and humanized by
Friendship, cannot bear frequent Reproaches; either it must quite sink
under the Oppression, or abate considerably of the Value and Esteem it
had for him who bestows them.
The proper Business of Friendship is to inspire Life and Courage; and a
Soul thus supported, outdoes itself: whereas if it be unexpectedly
deprived of these Succours, it droops and languishes.
We are in some measure more inexcusable if we violate our Duties to a
Friend, than to a Relation: since the former arise from a voluntary
Choice, the latter from a Necessity to which we could not give our own
Consent.
As it has been said on one side, that a Man ought not to break with a
faulty Friend, that he may not expose the Weakness of his Choice; it
will doubtless hold much stronger with respect to a worthy one, that he
may never be upbraided for having lost so valuable a Treasure which was
once in his Possession.
X.
Contents
|
Friday, May 23, 1712 |
Steele |
Cum Tristibus severe, cum Remissis jucunde, cum Senibus graviter, cum
Juventute comiter vivere.
Tull.

The piece of
Latin
on the Head of this Paper is part of a Character
extremely vicious, but I have set down no more than may fall in with the
Rules of Justice and Honour.
Cicero
spoke it of
Catiline
, who, he said,
lived with the Sad severely, with the Chearful agreeably, with the Old
gravely, with the Young pleasantly; he added, with the Wicked boldly,
with the Wanton lasciviously.
The two last Instances of his Complaisance
I forbear to consider, having it in my thoughts at present only to speak
of obsequious Behaviour as it sits upon a Companion in Pleasure, not a
Man of Design and Intrigue. To vary with every Humour in this Manner,
cannot be agreeable, except it comes from a Man's own Temper and natural
Complection; to do it out of an Ambition to excel that Way, is the most
fruitless and unbecoming Prostitution imaginable. To put on an artful
Part to obtain no other End but an unjust Praise from the Undiscerning,
is of all Endeavours the most despicable. A Man must be sincerely
pleased to become Pleasure, or not to interrupt that of others: For this
Reason it is a most calamitous Circumstance, that many People who want
to be alone or should be so, will come into Conversation. It is certain,
that all Men who are the least given to Reflection, are seized with an
Inclination that Way; when, perhaps, they had rather be inclined to
Company: but indeed they had better go home, and be tired with
themselves, than force themselves upon others to recover their good
Humour. In
this the Cases of communicating to a Friend a sad Thought
or Difficulty, in order to relieve
a
heavy Heart, stands excepted;
but what is here meant, is, that a Man should always go with Inclination
to the Turn of the Company he is going into, or not pretend to be of the
Party. It is certainly a very happy Temper to be able to live with all
kinds of Dispositions, because it argues a Mind that lies open to
receive what is pleasing to others, and not obstinately bent on any
Particularity of its own.
This is that which makes me pleased with the Character of my good
Acquaintance
Acasto
. You meet him at the Tables and Conversations of the
Wise, the Impertinent, the Grave, the Frolick, and the Witty; and yet
his own Character has nothing in it that can make him particularly
agreeable to any one Sect of Men; but
Acasto
has natural good Sense,
good Nature and Discretion, so that every Man enjoys himself in his
company; and tho'
Acasto
contributes nothing to the Entertainment, he
never was at a Place where he was not welcome a second time. Without
these subordinate good Qualities of
Acasto
, a Man of Wit and Learning
would be painful to the Generality of Mankind, instead of being
pleasing. Witty Men are apt to imagine they are agreeable as such, and
by that means grow the worst Companions imaginable; they deride the
Absent or rally the Present in a wrong manner, not knowing that if you
pinch or tickle a Man till he is uneasy in his Seat, or ungracefully
distinguished from the rest of the Company, you equally hurt him.
I was going to say, the true Art of being agreeable in Company, (but
there can be no such thing as Art in it) is to appear well pleased with
those you are engaged with, and rather to seem well entertained, than to
bring Entertainment to others. A Man thus disposed is not indeed what we
ordinarily call a good Companion, but essentially is such, and in all
the Parts of his Conversation has something friendly in his Behaviour,
which conciliates Men's Minds more than the highest Sallies of Wit or
Starts of Humour can possibly do. The Feebleness of Age in a Man of this
Turn, has something which should be treated with respect even in a Man
no otherwise venerable. The Forwardness of Youth, when it proceeds from
Alacrity and not Insolence, has also its Allowances. The Companion who
is formed for such by Nature, gives to every Character of Life its due
Regards, and is ready to account for their Imperfections, and receive
their Accomplishments as if they were his own. It must appear that you
receive Law from, and not give it to your Company, to make you
agreeable.
I remember
Tully
, speaking, I think, of
Anthony
, says, That
in eo
facetiæ erant, quæ nulla arte tradi possunt: He had a witty Mirth, which
could be acquired by no Art.
This Quality must be of the Kind of which I
am now speaking; for all sorts of Behaviour which depend upon
Observation and Knowledge of Life, is to be acquired: but that which no
one can describe, and is apparently the Act of Nature, must be every
where prevalent, because every thing it meets is a fit Occasion to exert
it; for he who follows Nature, can never be improper or unseasonable.
How unaccountable then must their Behaviour be, who, without any manner
of Consideration of what the Company they have just now entered are
upon, give themselves the Air of a Messenger, and make as distinct
Relations of the Occurrences they last met with, as if they had been
dispatched from those they talk to, to be punctually exact in a Report
of those Circumstances: It is unpardonable to those who are met to enjoy
one another, that a fresh Man shall pop in, and give us only the last
part of his own Life, and put a stop to ours during the History. If such
a Man comes from Change, whether you will or not, you must hear how the
Stocks go; and tho' you are ever so intently employed on a graver
Subject, a young Fellow of the other end of the Town will take his
place, and tell you, Mrs. Such-a-one is charmingly handsome, because he
just now saw her. But I think I need not dwell on this Subject, since I
have acknowledged there can be no Rules made for excelling this Way; and
Precepts of this kind fare like Rules for writing Poetry, which, 'tis
said, may have prevented ill Poets, but never made good ones.
T.
an
Contents
No. 3871 |
Saturday, May 24, 1712 |
Addison |
Quid purè tranquillet—
Hor.

In my last
Saturday's
Paper I spoke of
Chearfulness
as it is
a Moral
Habit of the Mind
, and accordingly mentioned such moral Motives as are
apt to cherish and keep alive this happy Temper in the Soul of Man: I
shall now consider Chearfulness in its natural State, and reflect on
those Motives to it, which are indifferent either as to Virtue or Vice.
Chearfulness is, in the first place, the best Promoter of Health.
Repinings and secret Murmurs of Heart, give imperceptible Strokes to
those delicate Fibres of which the vital parts are composed, and wear
out the Machine insensibly; not to mention those violent Ferments which
they stir up in the Blood, and those irregular disturbed Motions, which
they raise in the animal Spirits. I scarce remember, in my own
Observation, to have met with many old Men, or with such, who (to use
our
English
Phrase) wear well, that had not at least a certain Indolence
in their Humour, if not a more than ordinary Gaiety and Chearfulness of
Heart. The truth of it is, Health and Chearfulness mutually beget each
other; with this difference, that we seldom meet with a great degree of
Health which is not attended with a certain Chearfulness, but very often
see Chearfulness where there is no great degree of Health.
Chearfulness bears the same friendly regard to the Mind as to the Body:
It banishes all anxious Care and Discontent, sooths and composes the
Passions, and keeps the Soul in a Perpetual Calm. But having already
touched on this last Consideration, I shall here take notice, that the
World, in which we are placed, is filled with innumerable Objects that
are proper to raise and keep alive this happy Temper of Mind.
If we consider the World in its Subserviency to Man, one would think it
was made for our Use; but if we consider it in its natural Beauty and
Harmony, one would be apt to conclude it was made for our Pleasure. The
Sun, which is as the great Soul of the Universe, and produces all the
Necessaries of Life, has a particular Influence in chearing the Mind of
Man, and making the Heart glad.
Those several living Creatures which are made for our Service or
Sustenance, at the same time either fill the Woods with their Musick,
furnish us with Game, or raise pleasing Ideas in us by the
delightfulness of their Appearance, Fountains, Lakes, and Rivers, are as
refreshing to the Imagination, as to the Soil through which they pass.
There are Writers of great Distinction, who have made it an Argument for
Providence, that the whole Earth is covered with Green, rather than with
any other Colour, as being such a right Mixture of Light and Shade, that
it comforts and strengthens the Eye instead of weakning or grieving it.
For this reason several Painters have a green Cloth hanging near them,
to ease the Eye upon, after too great an Application to their Colouring.
A
modern Philosopher
accounts for it in the following manner:
All Colours that are more luminous, overpower and dissipate the animal
Spirits which are employd in Sight; on the contrary, those that are more
obscure do not give the animal Spirits a sufficient Exercise; whereas
the Rays that produce in us the Idea of Green, fall upon the Eye in such
a due proportion, that they give the animal Spirits their proper Play,
and by keeping up the struggle in a just Ballance, excite a very
pleasing and agreeable Sensation
. Let the Cause be what it will, the
Effect is certain, for which reason the Poets ascribe to this particular
Colour the Epithet of Chearful.
To consider further this double End in the Works of Nature, and how they
are at the same time both useful and entertaining, we find that the most
important Parts in the vegetable World are those which are the most
beautiful. These are the Seeds by which the several Races of Plants are
propagated and continued, and which are always lodged in Flowers or
Blossoms. Nature seems to hide her principal Design, and to be
industrious in making the Earth gay and delightful, while she is
carrying on her great Work, and intent upon her own Preservation. The
Husbandman after the same manner is employed in laying out the whole
Country into a kind of Garden or Landskip, and making every thing smile
about him, whilst in reality he thinks of nothing but of the Harvest,
and Encrease which is to arise from it.
We may further observe how Providence has taken care to keep up this
Chearfulness in the Mind of Man, by having formed it after such a
manner, as to make it capable of conceiving Delight from several Objects
which seem to have very little use in them; as from the Wildness of
Rocks and Desarts, and the like grotesque Parts of Nature. Those who are
versed in Philosophy may still carry this Consideration higher, by
observing that if Matter had appeared to us endowed only with those real
Qualities which it actually possesses, it would have made but a very
joyless and uncomfortable Figure; and why has Providence given it a
Power of producing in us such imaginary Qualities, as Tastes and
Colours, Sounds and Smells, Heat and Cold, but that Man, while he is
conversant in the lower Stations of Nature, might have his Mind cheared
and delighted with agreeable Sensations? In short, the whole Universe is
a kind of Theatre filled with Objects that either raise in us Pleasure,
Amusement, or Admiration.
The Reader's own Thoughts will suggest to him the Vicissitude of Day and
Night, the Change of Seasons, with all that Variety of Scenes which
diversify the Face of Nature, and fill the Mind with a perpetual
Succession of beautiful and pleasing Images.
I shall not here mention the several Entertainments of Art, with the
Pleasures of Friendship, Books, Conversation, and other accidental
Diversions of Life, because I would only take notice of such Incitements
to a Chearful Temper, as offer themselves to Persons of all Ranks and
Conditions, and which may sufficiently shew us that Providence did not
design this World should be filled with Murmurs and Repinings, or that
the Heart of Man should be involved in Gloom and Melancholy.
I the more inculcate this Chearfulness of Temper, as it is a Virtue in
which our Countrymen are observed to be more deficient than any other
Nation. Melancholy is a kind of Demon that haunts our Island, and often
conveys her self to us in an Easterly Wind. A celebrated
French
Novelist, in opposition to those who begin their Romances with the
flow'ry Season of the Year, enters on his Story thus:
In the gloomy
Month of November, when the People of England hang and drown themselves,
a disconsolate Lover walked out into the Fields, &c.
Every one ought to fence against the Temper of his Climate or
Constitution, and frequently to indulge in himself those Considerations
which may give him a Serenity of Mind, and enable him to bear up
chearfully against those little Evils and Misfortunes which are common
to humane Nature, and which by a right Improvement of them will produce
a Satiety of Joy, and an uninterrupted Happiness.
At the same time that I would engage my Reader to consider the World in
its most agreeable Lights, I must own there are many Evils which
naturally spring up amidst the Entertainments that are provided for us;
but these, if rightly consider'd, should be far from overcasting the
Mind with Sorrow, or destroying that Chearfulness of Temper which I have
been recommending. This Interspersion of Evil with Good, and Pain with
Pleasure, in the Works of Nature, is very truly ascribed by Mr.
Locke
,
in his
Essay on Human Understanding
, to a moral Reason, in the following
Words:
Beyond all this, we may find another Reason why God hath scattered up
and down several Degrees of Pleasure and Pain, in all the things that
environ and affect us, and blended them together, in almost all that
our Thoughts and Senses have to do with; that we finding Imperfection,
Dissatisfaction, and Want of compleat Happiness in all the Enjoyments
which the Creatures can afford us, might be led to seek it in the
Enjoyment of him, with whom there is Fulness of Joy, and at whose
Right Hand are Pleasures for evermore.
L.
Numbered by mistake, in the daily issue 388, No. 388 is
then numbered 390; 389 is right, 390 is called 392, the next 391, which
is right, another 392 follows, and thus the error is corrected.
Sir Isaac Newton.
Contents
|
Monday, May 26, 1712 |
Barr?1 |
—Tibi res antiquæ Laudis et Artis
Ingredior; sanctos ausus recludere Fontes.
Virg.

Mr.
Spectator,
It is my Custom, when I read your Papers, to read over the Quotations
in the Authors from whence you take them: As you mentiond a Passage
lately out of the second Chapter of
Solomon's Song, it occasion'd my
looking into it; and upon reading it I thought the Ideas so
exquisitely soft and tender, that I could not help making this
Paraphrase of it; which, now it is done, I can as little forbear
sending to you. Some Marks of your Approbation, which I have already
receiv'd, have given me so sensible a Taste of them, that I cannot
forbear endeavouring after them as often as I can with any Appearance
of Success.
I am,
Sir,
Your most
obedient2 humble Servant.
| I |
As when in Sharon's Field the blushing Rose
Does its chaste Bosom to the Morn disclose,
Whilst all around the Zephyrs bear
The fragrant Odours thro' the Air:
Or as the Lilly in the shady Vale,
Does o'er each Flower with beauteous Pride prevail,
And stands with Dews and kindest Sun-shine blest,
In fair Pre-eminence, superior to the rest:
So if my Love, with happy Influence, shed
His Eyes bright Sun-shine on his Lover's Head,
Then shall the Rose of Sharon's Field,
And whitest Lillies to my Beauties yield.
Then fairest Flowers with studious Art combine,
The Roses with the Lillies join,
And their united Charms are3 less than mine. |
| II |
As much as fairest Lillies can surpass
A Thorn in Beauty, or in Height the Grass;
So does my Love among the Virgins shine,
Adorn'd with Graces more than half Divine;
Or as a Tree, that, glorious to behold,
Is hung with Apples all of ruddy Gold,
Hesperian Fruit! and beautifully high,
Extends its Branches to the Sky;
So does my Love the Virgin's Eyes invite:
'Tis he alone can fix their wand'ring Sight,
Among4 ten thousand eminently bright. |
| III |
Beneath this pleasing Shade
My weaned Limbs at Ease I laid,
And on his fragrant Boughs reclined my Head.
I pull'd the Golden Fruit with eager haste;
Sweet was the Fruit, and pleasing to the Taste:
With sparkling Wine he crown'd the Bowl,
With gentle Ecstacies he fill'd my Soul;
Joyous we sate beneath the shady Grove,
And o'er my Head he hung the Banners of his Love. |
| IV |
I faint; I die! my labouring Breast
Is with the mighty Weight of Love opprest:
I feel the Fire possess my Heart,
And pain conveyed to every Part.
Thro' all my Veins the Passion flies,
My feeble Soul forsakes its Place,
A trembling Faintness seals my Eyes,
And Paleness dwells upon my Face;
Oh! let my Love with pow'rful Odours stay
My fainting lovesick Soul that dies away;
One Hand beneath me let him place,
With t'other press me in a chaste Embrace. |
| V |
I charge you, Nymphs of Sion, as you go
Arm'd with the sounding Quiver and the Bow,
Whilst thro' the lonesome Woods you rove,
You ne'er disturb my sleeping Love,
Be only gentle Zephyrs there,
With downy Wings to fan the Air;
Let sacred Silence dwell around,
To keep off each intruding Sound:
And when the balmy Slumber leaves his Eyes,
May he to Joys, unknown till then, arise. |
| VI |
But see! he comes! with what majestick Gate
He onward bears his lovely State!
Now thro' the Lattice he appears,
With softest Words dispels my Fears,
Arise, my Fair-One, and receive
All the Pleasures Love can give.
For now the sullen Winters past,
No more we fear the Northern Blast:
No Storms nor threatning Clouds appear,
No falling Rains deform the Year.
My Love admits of no delay,
Arise, my Fair, and come away. |
| VII |
Already, see! the teeming Earth
Brings forth the Flow'rs, her beauteous Birth.
The Dews, and soft-descending Showers,
Nurse the new-born tender Flow'rs.
Hark! the Birds melodious sing,
And sweetly usher in the Spring.
Close by his Fellow sits the Dove,
And billing whispers her his Love.
The spreading Vines with Blossoms swell,
Diffusing round a grateful Smell,
Arise, my Fair-One, and receive
All the Blessings Love can give:
For Love admits of no delay,
Arise, my Fair, and come away. |
| VIII |
As to its Mate the constant Dove
Flies thro' the Covert of the spicy Grove,
So let us hasten to some lonely Shade,
There let me safe in thy lov'd Arms be laid,
Where no intruding hateful Noise
Shall damp the Sound of thy melodious Voice;
Where I may gaze, and mark each beauteous Grace;
For sweet thy Voice, and lovely is thy Face. |
| IX |
As all of me, my Love, is thine,
Let all of thee be ever mine.
Among the Lillies we will play,
Fairer, my Love, thou art than they,
Till the purple Morn arise,
And balmy Sleep forsake thine Eyes;
Till the gladsome Beams of Day
Remove the Shades of Night away;
Then when soft Sleep shall from thy Eyes depart,
Rise like the bounding Roe, or lusty Hart,
Glad to behold the Light again
From Bether's Mountains darting o'er the Plain. |
T.
Percy had heard that a poetical translation of a chapter in
the Proverbs, and another poetical translation from the Old Testament,
were by Mr. Barr, a dissenting minister at Morton Hampstead in
Devonshire.
obliged
Beauties shall be
And stands among
Contents
|
Tuesday, May 27, 1712 |
Budgell |
Meliora pii docuere parentes.
Hor.

has more surprized the Learned in
England
, than the Price which
a small Book, intitled
Spaccio della Bestia triom fante
, bore in a
late Auction.
Book was sold for
thirty
Pound. As it was
written by one
Jordanus Brunus
, a professed Atheist, with a design to
depreciate Religion, every one was apt to fancy, from the extravagant
Price it bore, that there must be something in it very formidable.
I must confess that happening to get a sight of one of them my self, I
could not forbear perusing it with this Apprehension; but found there
was so very little Danger in it, that I shall venture to give my Readers
a fair Account of the whole Plan upon which this wonderful Treatise is
built.
The Author pretends that
Jupiter
once upon a Time resolved on a
Reformation of the Constellations: for which purpose having summoned the
Stars together, he complains to them of the great Decay of the Worship
of the Gods, which he thought so much the harder, having called several
of those Celestial Bodies by the Names of the Heathen Deities, and by
that means made the Heavens as it were a Book of the Pagan Theology.
Momus
tells him, that this is not to be wondered at, since there were so
many scandalous Stories of the Deities; upon which the Author takes
occasion to cast Reflections upon all other Religions, concluding, that
Jupiter
, after a full Hearing, discarded the Deities out of Heaven, and
called the Stars by the Names of the Moral Virtues.
This short Fable, which has no Pretence in it to Reason or Argument, and
but a very small Share of Wit, has however recommended it self wholly by
its Impiety to those weak Men, who would distinguish themselves by the
Singularity of their Opinions.
There are two Considerations which have been often urged against
Atheists, and which they never yet could get over. The first is, that
the greatest and most eminent Persons of all Ages have been against
them, and always complied with the publick Forms of Worship established
in their respective Countries, when there was nothing in them either
derogatory to the Honour of the Supreme Being, or prejudicial to the
Good of Mankind.
The
Platos
and
Ciceros
among the Ancients; the
Bacons
, the
Boyles
, and
the
Lockes
, among our own Countrymen, are all Instances of what I have
been saying; not to mention any of the Divines, however celebrated,
since our Adversaries challenge all those, as Men who have too much
Interest in this Case to be impartial Evidences.
But what has been often urged as a Consideration of much more Weight,
is, not only the Opinion of the Better Sort, but the general Consent of
Mankind to this great Truth; which I think could not possibly have come
to pass, but from one of the three following Reasons; either that the
Idea of a God is innate and co-existent with the Mind it self; or that
this Truth is so very obvious, that it is discoverd by the first
Exertion of Reason in Persons of the most ordinary Capacities; or,
lastly, that it has been delivered down to us thro' all Ages by a
Tradition from the first Man.
The Atheists are equally confounded, to which ever of these three Causes
we assign it; they have been so pressed by this last Argument from the
general Consent of Mankind, that after great search and pains they
pretend to have found out a Nation of Atheists, I mean that Polite
People the
Hottentots
.
I dare not shock my Readers with a Description of the Customs and
Manners of these Barbarians, who are in every respect scarce one degree
above Brutes,
no Language among them but a confused
Gabble
which is neither well understood by themselves or others.
It is not however to be imagin'd how much the Atheists have gloried in
these their good Friends and Allies.
If we boast of a
Socrates
, or a
Seneca
, they may now confront them with
these great Philosophers the
Hottentots
.
Tho even this Point has, not without Reason, been several times
controverted, I see no manner of harm it could do Religion, if we should
entirely give them up this elegant Part of Mankind.
Methinks nothing more shews the Weakness of their Cause, than that no
Division of their Fellow-Creatures join with them, but those among whom
they themselves own Reason is almost defaced, and who have little else
but their Shape, which can entitle them to any Place in the Species.
Besides these poor Creatures, there have now and then been Instances of
a few crazed People in several Nations, who have denied the Existence of
a Deity.
Catalogue of these is however very short; even Vanini
the most
celebrated Champion for the Cause, professed before his Judges that he
believed the Existence of a God, and taking up a Straw which lay before
him on the Ground, assured them, that alone was sufficient to convince
him of it; alledging several Arguments to prove that 'twas impossible
Nature alone could create anything.
I
the other day reading an Account of
Casimir Liszynski
, a Gentleman
of
Poland
, who was convicted and executed for this Crime
. The manner
of his Punishment was very particular. As soon as his Body was burnt his
Ashes were put into a Cannon, and shot into the Air towards
Tartary
.
I am apt to believe, that if something like this Method of Punishment
should prevail in
England
, such is the natural good Sense of the
British
Nation, that whether we rammed an Atheist [whole] into a great Gun, or
pulverized our Infidels, as they do in
Poland
, we should not have many
Charges.
I should, however, propose, while our Ammunition lasted, that instead of
Tartary
, we should always keep two or three Cannons ready pointed
towards the
Cape of Good Hope
, in order to shoot our Unbelievers into
the Country of the
Hottentots
.
In my Opinion, a solemn judicial Death is too great an Honour for an
Atheist, tho' I must allow the Method of exploding him, as it is
practised in this ludicrous kind of Martyrdom, has something in it
proper
enough
to the Nature of his Offence.
There is indeed a great Objection against this Manner of treating them.
Zeal for Religion is of so active a Nature, that it seldom knows where
to rest; for which reason I am afraid, after having discharged our
Atheists, we might possibly think of shooting off our Sectaries; and, as
one does not foresee the Vicissitude of human Affairs, it might one time
or other come to a Man's own turn to fly out of the Mouth of a
Demi-culverin
.
If any of my Readers imagine that I have treated these Gentlemen in too
Ludicrous a Manner, I must confess, for my own part, I think reasoning
against such Unbelievers upon a Point that shocks the Common Sense of
Mankind, is doing them too great an Honour, giving them a Figure in the
Eye of the World, and making People fancy that they have more in them
than they really have.
As for those Persons who have any Scheme of Religious Worship, I am for
treating such with the utmost Tenderness, and should endeavour to shew
them their Errors with the greatest Temper and Humanity: but as these
Miscreants are for throwing down Religion in general, for stripping
Mankind of what themselves own is of excellent use in all great
Societies, without once offering to establish any thing in the Room of
it; I think the best way of dealing with them, is to retort their own
Weapons upon them, which are those of Scorn and Mockery.
X.
The book was bought in 1711 for £28 by Mr. Walter Clavel at
the sale of the library of Mr. Charles Barnard. It had been bought in
1706 at the sale of Mr. Bigot's library with five others for two
shillings and a penny. Although Giordano Bruno was burnt as a heretic,
he was a noble thinker, no professed atheist, but a man of the reformed
faith, who was in advance of Calvin, a friend of Sir Philip Sydney, and
as good a man as Mr. Budgell.
Fifty
Gabling
Vanini, like Giordano Bruno, has his memory dishonoured
through the carelessness with which men take for granted the assertions
of his enemies. Whether burnt or not, every religious thinker of the
sixteenth century who opposed himself to the narrowest views of those
who claimed to be the guardians of orthodoxy was remorselessly maligned.
If he was the leader of a party, there were hundreds to maintain his
honour against calumny. If he was a solitary searcher after truth, there
was nothing but his single life and work to set against the host of his
defamers. Of Vanini's two books, one was written to prove the existence
of a God, yet here is Mr. Budgell calling him the most celebrated
champion for the cause of atheism.
Casimir Lyszynski was a Polish Knight, executed at Warsaw in 1689,
in the barbarous manner which appears to tickle Mr. Budgell's fancy. It
does not appear that he had written anything.
Contents
|
Wednesday, May 28, 1712 |
Steele |
Non pudendo sed non faciendo id quod non decet impudentiæ nomen
effugere debemus.
Tull.

Many are the Epistles I receive from Ladies extremely afflicted that
they lie under the Observation of scandalous People, who love to defame
their Neighbours, and make the unjustest Interpretation of innocent and
indifferent Actions. They describe their own Behaviour so unhappily,
that there indeed lies some Cause of Suspicion upon them. It is certain,
that there is no Authority for Persons who have nothing else to do, to
pass away Hours of Conversation upon the Miscarriages of other People;
but since they will do so, they who value their Reputation should be
cautious of Appearances to their Disadvantage. But very often our young
Women, as well as the middle-aged and the gay Part of those growing old,
without entering into a formal League for that purpose, to a Woman agree
upon a short Way to preserve their Characters, and go on in a Way that
at best is only not vicious. The Method is, when an ill-naturd or
talkative Girl has said any thing that bears hard upon some part of
another's Carriage, this Creature, if not in any of their little Cabals,
is run down for the most censorious dangerous Body in the World. Thus
they guard their Reputation rather than their Modesty; as if Guilt lay
in being under the Imputation of a Fault, and not in a Commission of it.
Orbicilla
is the kindest poor thing in the Town, but the most blushing
Creature living: It is true she has not lost the Sense of Shame, but she
has lost the Sense of Innocence. If she had more Confidence, and never
did anything which ought to stain her Cheeks, would she not be much more
modest without that ambiguous Suffusion, which is the Livery both of
Guilt and Innocence? Modesty consists in being conscious of no Ill, and
not in being ashamed of having done it. When People go upon any other
Foundation than the Truth of their own Hearts for the Conduct of their
Actions, it lies in the power of scandalous Tongues to carry the World
before them, and make the rest of Mankind fall in with the Ill, for fear
of Reproach. On the other hand, to do what you ought, is the ready way
to make Calumny either silent or ineffectually malicious.
Spencer
, in
Fairy Queen
, says admirably to young Ladies under the Distress of
being defamed;
'The best, said he, that I can you advise,
Is to avoid th' Occasion of the Ill;
For when the Cause, whence Evil doth arise,
Removed is, th' Effect surceaseth still.
Abstain from Pleasure, and restrain your Will,
Subdue Desire, and bridle loose Delight:
Use scanted Diet, and forbear your Fill;
Shun Secrecy, and talk in open sight:
So shall you soon repair your present evil Plight1.'
Instead of this Care over their Words and Actions, recommended by a Poet
in old
Queen Bess's
Days, the modern Way is to do and say what you
please, and yet be the prettiest sort of Woman in the World. If Fathers
and Brothers will defend a Lady's Honour, she is quite as safe as in her
own Innocence. Many of the Distressed, who suffer under the Malice of
evil Tongues, are so harmless that they are every Day they live asleep
till twelve at Noon; concern themselves with nothing but their own
Persons till two; take their necessary Food between that time and four;
visit, go to the Play, and sit up at Cards till towards the ensuing
Morn; and the malicious World shall draw Conclusions from innocent
Glances, short Whispers, or pretty familiar Railleries with fashionable
Men, that these Fair ones are not as rigid as Vestals. It is certain,
say these goodest Creatures very well, that Virtue does not consist in
constrain'd Behaviour and wry Faces, that must be allow'd; but there is
a Decency in the Aspect and Manner of Ladies contracted from an Habit of
Virtue, and from general Reflections that regard a modest Conduct, all
which may be understood, tho' they cannot be described. A young Woman of
this sort claims an Esteem mixed with Affection and Honour, and meets
with no Defamation; or if she does, the wild Malice is overcome with an
undisturbed Perseverance in her Innocence. To speak freely, there are
such Coveys of Coquets about this Town, that if the Peace were not kept
by some impertinent Tongues of their own Sex, which keep them under some
Restraint, we should have no manner of Engagement upon them to keep them
in any tolerable Order.
As I am a
Spectator
, and behold how plainly one Part of Womankind
ballance the Behaviour of the other, whatever I may think of Talebearers
or Slanderers, I cannot wholly suppress them, no more than a General
would discourage Spies. The Enemy would easily surprize him whom they
knew had no Intelligence of their Motions. It is so far otherwise with
me, that I acknowledge I permit a She-Slanderer or two in every Quarter
of the Town, to live in the Characters of Coquets, and take all the
innocent Freedoms of the rest, in order to send me Information of the
Behaviour of their respective Sisterhoods.
But as the Matter of Respect to the World, which looks on, is carried
on, methinks it is so very easie to be what is in the general called
Virtuous, that it need not cost one Hour's Reflection in a Month to
preserve that Appellation. It is pleasant to hear the pretty Rogues talk
of Virtue and Vice among each other:
She is the laziest Creature in the
World, but I must confess strictly Virtuous: The peevishest Hussy
breathing, but as to her Virtue she is without Blemish: She has not the
least Charity for any of her Acquaintance, but I must allow rigidly
Virtuous.
As the unthinking Part of the Male World call every Man a Man
of Honour, who is not a Coward; so the Crowd of the other Sex terms
every Woman who will not be a Wench,
Virtuous
.
T.
F. Q.
Bk VI. canto vi. st. 14.
Contents
|
Thursday, May 29, 1712 |
Addison |
—Non tu prece poscis emaci,
Qua nisi seductis nequeas committere Divis:
At bona pars procerum tacitâ libabit acerrâ.
Haud cuivis promptum est, murmurque humilesque susurros
Tollere de Templis; et aperto vivere voto.
Mens bona, fama, fides, hæc clarè, et ut audiat hospes.
Illa sibi introrsum, et sub lingua immurmurat: O si
Ebullit patrui præclarum funus! Et O si
Sub rastro crepet argenti mihi seria dextro
Hercule! pupillumve utinam, quem proximus hæres
Impello, expungam!—
Pers.

Homer
represents
Phœnix
, the Tutor of
Achilles
, as persuading
his Pupil to lay aside his Resentments, and give himself up to the
Entreaties of his Countrymen, the Poet, in order to make him speak in
Character, ascribes to him a Speech full of those Fables and Allegories
which old Men take Delight in relating, and which are very proper for
Instruction.
The Gods
, says he,
suffer themselves to be prevailed upon
by Entreaties. When Mortals have offended them by their Transgressions,
they appease them by Vows and Sacrifices. You must know, Achilles, that
Prayers
are the Daughters of
Jupiter.
They are crippled by frequent
Kneeling, have their Faces full of Cares and Wrinkles, and their Eyes
always cast towards Heaven. They are constant Attendants on the Goddess
Ate
,
and march behind her. This Goddess walks forward with a bold and
haughty Air, and being very light of foot, runs thro' the whole Earth,
grieving and afflicting the Sons of Men. She gets the start of
Prayers
,
who always follow her, in, order to heal those Persons whom she wounds.
He who honours these Daughters of
Jupiter,
when they draw near to him,
receives great Benefit from them; but as for him who rejects them, they
intreat their Father to give his Orders to the Goddess
Ate
to punish him
for his Hardness of Heart.
This noble Allegory needs but little
Explanation; for whether the Goddess
Ate
signifies
Injury
, as some have
explained it; or
Guilt
in general, as others; or
divine Justice,
as I am
the more apt to think; the Interpretation is obvious enough.
I shall produce another Heathen Fable relating to Prayers, which is of a
more diverting kind. One would think by some Passages in it, that it was
composed by
Lucian
, or at least by some Author who has endeavourd to
imitate his Way of Writing; but as Dissertations of this Nature are more
curious than useful, I shall give my Reader the Fable, without any
further Enquiries after the Author.
Menippus
the Philosopher was a second time taken up into Heaven by
Jupiter
, when for his Entertainment he lifted up a Trap-Door that was
placed by his Foot-stool. At its rising, there issued through it such a
Din of Cries as astonished the Philosopher. Upon his asking what they
meant,
Jupiter
told him they were the Prayers that were sent up to him
from the Earth.
Menippus
, amidst the Confusion of Voices, which was so
great, that nothing less than the Ear of
Jove
could distinguish them,
heard the Words, Riches, Honour, and Long Life repeated in several
different Tones and Languages. When the first Hubbub of Sounds was over,
the Trap-Door being left open, the Voices came up more separate and
distinct. The first Prayer was a very odd one, it came from
Athens
, and
desired
Jupiter
to increase the Wisdom and the Beard of his humble
Supplicant.
Menippus
knew it by the Voice to be the Prayer of his Friend
Licander
the Philosopher. This was succeeded by the Petition of one who
had just laden a Ship, and promised
Jupiter
, if he took care of it, and
returned it home again full of Riches, he would make him an Offering of
a Silver Cup.
Jupiter
thanked him for nothing; and bending down his Ear
more attentively than ordinary, heard a Voice complaining to him of the
Cruelty of an
Ephesian
Widow, and begging him to breed Compassion in her
Heart: This, says
Jupiter
, is a very honest Fellow. I have received a
great deal of Incense from him; I will not be so cruel to him as to hear
his Prayers. He was
then
interrupted with a whole Volly of Vows, which
were made for the Health of a tyrannical Prince by his Subjects who
pray'd for him in his Presence.
Menippus
was surprized, after having
listned to Prayers offered up with so much Ardour and Devotion, to hear
low Whispers from the same Assembly, expostulating with
Jove
for
suffering such a Tyrant to live, and asking him how his Thunder could
lie idle?
Jupiter
was so offended at these prevaricating Rascals, that
he took down the first Vows, and puffed away the last. The Philosopher
seeing a great Cloud mounting upwards, and making its way directly to
the Trap-Door, enquired of
Jupiter
what it meant. This, says
Jupiter
, is
the Smoke of a whole Hecatomb that is offered me by the General of an
Army, who is very importunate with me to let him cut off an hundred
thousand Men that are drawn up in Array against him: What does the
impudent Wretch think I see in him, to believe that I will make a
Sacrifice of so many Mortals as good as himself, and all this to his
Glory, forsooth? But hark, says
Jupiter
, there is a Voice I never heard
but in time of danger; tis a Rogue that is shipwreck'd in the
Ionian
Sea: I sav'd him on a Plank but three Days ago, upon his Promise to mend
his Manners, the Scoundrel is not worth a Groat, and yet has the
Impudence to offer me a Temple if I will keep him from sinking—But
yonder, says he, is a special Youth for you, he desires me to take his
Father, who keeps a great Estate from him, out of the Miseries of human
Life. The old Fellow shall live till he makes his Heart ake, I can tell
him that for his pains. This was followed by the soft Voice of a Pious
Lady, desiring
Jupiter
that she might appear amiable and charming in the
Sight of her Emperor. As the Philosopher was reflecting on this
extraordinary Petition, there blew a gentle Wind thro the Trap-Door,
which he at first mistook for a Gale of
Zephirs
, but afterwards found it
to be a Breeze of Sighs: They smelt strong of Flowers and Incense, and
were succeeded by most passionate Complaints of Wounds and Torments,
Fires and Arrows, Cruelty, Despair and Death.
Menippus
fancied that such
lamentable Cries arose from some general Execution, or from Wretches
lying under the Torture; but
Jupiter
told him that they came up to him
from the Isle of
Paphos
, and that he every day received Complaints of
the same nature from that whimsical Tribe of Mortals who are called
Lovers. I am so trifled with, says he, by this Generation of both Sexes,
and find it so impossible to please them, whether I grant or refuse
their Petitions, that I shall order a
Western
Wind for the future to
intercept them in their Passage, and blow them at random upon the Earth.
The last Petition I heard was from a very aged Man of near an hundred
Years old, begging but for one Year more of Life, and then promising to
die contented. This is the rarest old Fellow! says
Jupiter
. He has made
this Prayer to me for above twenty Years together. When he was but fifty
Years old, he desired only that he might live to see his Son settled in
the World; I granted it. He then begged the same Favour for his
Daughter, and afterwards that he might see the Education of a Grandson:
When all this was brought about, he puts up a Petition that he might
live to finish a House he was building. In short, he is an unreasonable
old Cur, and never wants an Excuse; I will hear no more of him. Upon
which, he flung down the Trap-Door in a Passion, and was resolved to
give no more Audiences that day.
Notwithstanding the Levity of this Fable, the Moral of it very well
deserves our Attention, and is the same with that which has been
inculcated by
Socrates
and
Plato
, not to mention
Juvenal
and
Persius
,
who have each of them made the finest Satire in their whole Works upon
this Subject. The Vanity of Mens Wishes, which are the natural Prayers
of the Mind, as well as many of those secret Devotions which they offer
to the Supreme Being, are sufficiently exposed by it. Among other
Reasons for set Forms of Prayer, I have often thought it a very good
one, that by this means the Folly and Extravagance of Mens Desires may
be kept within due Bounds, and not break out in absurd and ridiculous
Petitions on so great and solemn an Occasion.
I.
Iliad
, Bk ix.
Menippus was a Cynic philosopher of Gadara, who made money
in Thebes by usury, lost it, and hanged himself. He wrote satirical
pieces, which are lost; some said that they were the joint work of two
friends, Dionysius and Zopyrus of Colophon, in whom it was one jest the
more to ascribe their jesting to Menippus. These pieces were imitated by
Terentius Varro in
Satiræ Menippeæ.
Contents
|
Friday, May 30, 1712 |
Steele |
Per Ambages et Ministeria Deorum
Præcipitandus est liber Spiritus.
Pet.

To the
Spectator.
The
Transformation of
Fidelio into a Looking-Glass.
I was lately at a Tea-Table, where some young Ladies entertained the
Company with a Relation of a Coquet in the Neighbourhood, who had been
discovered practising before her Glass. To turn the Discourse, which
from being witty grew to be malicious, the Matron of the Family took
occasion, from the Subject, to wish that there were to be found
amongst Men such faithful Monitors to dress the Mind by, as we consult
to adorn the Body. She added, that if a sincere Friend were
miraculously changed into a Looking-Glass, she should not be ashamed
to ask its Advice very often.
This whimsical Thought worked so much
upon my Fancy the whole Evening, that it produced
a very odd Dream1.
Methought, that as I stood before my Glass, the Image of a Youth, of
an open ingenuous Aspect, appeared in it; who with a small shrill
Voice spoke in the following manner.
The Looking-Glass, you see, was heretofore a Man, even I, the
unfortunate Fidelio. I had two Brothers, whose Deformity in Shape
was made out by the Clearness of their Understanding: It must be
owned however, that (as it generally happens) they had each a
Perverseness of Humour suitable to their Distortion of Body. The
eldest, whose Belly sunk in monstrously, was a great Coward; and
tho' his splenetick contracted Temper made him take fire
immediately, he made Objects that beset him appear greater than they
were. The second, whose Breast swelled into a bold Relievo, on the
contrary, took great pleasure in lessening every thing, and was
perfectly the Reverse of his Brother. These Oddnesses pleased
Company once or twice, but disgusted when often seen; for which
reason the young Gentlemen were sent from Court to study
Mathematicks at the University.
I need not acquaint you, that I was very well made, and reckoned a
bright polite Gentleman. I was the Confident and Darling of all the
Fair; and if the Old and Ugly spoke ill of me, all the World knew it
was because I scorned to flatter them. No Ball, no Assembly was
attended till I had been consulted. Flavia colour'd her Hair before
me, Celia shew'd me her Teeth, Panthea heaved her Bosom, Cleora
brandished her Diamonds; I have seen Cloe's Foot, and tied
artificially the Garters of Rhodope.
'Tis a general Maxim, that those who doat upon themselves, can have
no violent Affection for another: But on the contrary, I found that
the Women's Passion for me rose in proportion to the Love they bare
to themselves. This was verify'd in my Amour with Narcissa, who was
so constant to me, that it was pleasantly said, had I been little
enough, she would have hung me at her Girdle. The most dangerous
Rival I had, was a gay empty Fellow, who by the Strength of a long
Intercourse with Narcissa, joined to his natural Endowments, had
formed himself into a perfect Resemblance with her. I had been
discarded, had she not observed that he frequently asked my Opinion
about Matters of the last Consequence: This made me still more
considerable in her Eye.
Tho' I was eternally caressed by the Ladies, such was their Opinion
of my Honour, that I was never envy'd by the Men. A jealous Lover of
Narcissa one day thought he had caught her in an Amorous
Conversation; for tho' he was at such a Distance that he could hear
nothing, he imagined strange things from her Airs and Gestures.
Sometimes with a serene Look she stepped back in a listning Posture,
and brightened into an innocent Smile. Quickly after she swelled
into an Air of Majesty and Disdain, then kept her Eyes half shut
after a languishing Manner, then covered her Blushes with her Hand,
breathed a Sigh, and seemd ready to sink down. In rushed the furious
Lover; but how great was his Surprize to see no one there but the
innocent Fidelio, with his Back against the Wall betwixt two
Windows?
It were endless to recount all my Adventures. Let me hasten to that
which cost me my Life, and Narcissa her Happiness.
She had the misfortune to have the Small-Pox, upon which I was
expressly forbid her Sight, it being apprehended that it would
increase her Distemper, and that I should infallibly catch it at the
first Look. As soon as she was suffered to leave her Bed, she stole
out of her Chamber, and found me all alone in an adjoining
Apartment. She ran with Transport to her Darling, and without
Mixture of Fear, lest I should dislike her. But, oh me! what was her
Fury when she heard me say, I was afraid and shock'd at so loathsome
a Spectacle. She stepped back, swollen with Rage, to see if I had
the Insolence to repeat it. I did, with this Addition, that her
ill-timed Passion had increased her Ugliness. Enraged, inflamed,
distracted, she snatched a Bodkin, and with all her Force stabbed me
to the Heart. Dying, I preserv'd my Sincerity, and expressed the
Truth, tho' in broken Words; and by reproachful Grimaces to the last
I mimick'd the Deformity of my Murderess.
Cupid, who always attends the Fair, and pity'd the Fate of so useful
a Servant as I was, obtained of the Destinies, that my Body should
be made incorruptible, and retain the Qualities my Mind had
possessed. I immediately lost the Figure of a Man, and became
smooth, polished, and bright, and to this day am the first Favourite
of the Ladies.
T.
so odd a Dream, that no one but the Spectator could
believe that the Brain, clogged in Sleep, could furnish out such a
regular Wildness of Imagination.
Contents
|
Saturday, May 31, 1712 |
Addison |
Nescio quâ præter solitum dulcedine læti.
Virg.

Looking over the Letters that have been sent me, I chanced to find the
following one, which I received about two years ago from an ingenious
Friend, who was then in
Denmark
.
Copenhagen, May 1, 1710.
Dear Sir,
The Spring with you has already taken Possession of the Fields and
Woods: Now is the Season of Solitude, and of moving Complaints upon
trivial Sufferings: Now the Griefs of Lovers begin to flow, and their
Wounds to bleed afresh. I too, at this Distance from the softer
Climates, am not without my Discontents at present. You perhaps may
laugh at me for a most Romantick Wretch, when I have disclosed to you
the Occasion of my Uneasiness; and yet I cannot help thinking my
Unhappiness real, in being confined to a Region, which is the very
Reverse of Paradise. The Seasons here are all of them unpleasant, and
the Country quite Destitute of Rural Charms. I have not heard a Bird
sing, nor a Brook murmur, nor a Breeze whisper, neither have I been
blest with the Sight of a flow'ry Meadow these two years. Every Wind
here is a Tempest, and every Water a turbulent Ocean. I hope, when you
reflect a little, you will not think the Grounds of my Complaint in
the least frivolous and unbecoming a Man of serious Thought; since the
Love of Woods, of Fields and Flowers, of Rivers and Fountains, seems
to be a Passion implanted in our Natures the most early of any, even
before the Fair Sex had a Being.
I am, Sir, &c.
Could I transport my self with a Wish from one Country to another, I
should chuse to pass my Winter in
Spain
, my Spring in
Italy
, my Summer
in
England
, and my Autumn in
France
. Of all these Seasons there is none
that can vie with the Spring for Beauty and Delightfulness. It bears the
same Figure among the Seasons of the Year, that the Morning does among
the Divisions of the Day, or Youth among the Stages of Life. The
English
Summer is pleasanter than that of any other Country in
Europe
on no
other account but because it has a greater Mixture of Spring in it. The
Mildness of our Climate, with those frequent Refreshments of Dews and
Rains that fall among us, keep up a perpetual Chearfulness in our
Fields, and fill the hottest Months of the Year with a lively Verdure.
In the opening of the Spring, when all Nature begins to recover her
self, the same animal Pleasure which makes the Birds sing, and the whole
brute Creation rejoice, rises very sensibly in the Heart of Man. I know
none of the Poets who have observed so well as
Milton
those secret
Overflowings of Gladness which diffuse themselves thro' the Mind of the
Beholder, upon
the gay Scenes of Nature: he has touched upon
it twice or thrice in his
Paradise Lost,
and describes it very
beautifully under the Name of Vernal Delight, in that Passage where he
represents the Devil himself as almost sensible of it.
Blossoms and Fruits at once of golden hue
Appear'd, with gay enamel'd Colours mixt:
On which the Sun more glad impress'd his Beams
Than in fair evening Cloud, or humid Bow,
When God hath shower'd the Earth; so lovely seem'd
That Landskip: And of pure now purer Air
Meets his approach, and to the Heart inspires
Vernal Delight, and Joy able to drive
All Sadness but Despair, &c.1
Many Authors have written on the Vanity of the Creature, and represented
the Barrenness of every thing in this World, and its Incapacity of
producing any solid or substantial Happiness. As Discourses of this
Nature are very useful to the Sensual and Voluptuous; those Speculations
which shew the bright Side of Things, and lay forth those innocent
Entertainments which are to be met with among the several Objects that
encompass us, are no less beneficial to Men of dark and melancholy
Tempers. It was for this reason that I endeavoured to recommend a
Chearfulness of Mind in my two last
Saturday's
Papers, and which I would
still inculcate, not only from the Consideration of our selves, and of
that Being on whom we depend, nor from the general Survey of that
Universe in which we are placed at present, but from Reflections on the
particular Season in which this Paper is written. The Creation is a
perpetual Feast to the Mind of a good Man, every thing he sees chears
and delights him; Providence has imprinted so many Smiles on Nature,
that it is impossible for a Mind, which is not sunk in more gross and
sensual Delights, to take a Survey of them without several secret
Sensations of Pleasure. The
Psalmist
has in several of his Divine Poems
celebrated those beautiful and agreeable Scenes which make the Heart
glad, and produce in it that vernal Delight which I have before taken
Notice of.
Natural Philosophy quickens this Taste of the Creation, and renders it
not only pleasing to the Imagination, but to the Understanding. It does
not rest in the Murmur of Brooks, and the Melody of Birds, in the Shade
of Groves and Woods, or in the Embroidery of Fields and Meadows, but
considers the several Ends of Providence which are served by them, and
the Wonders of Divine Wisdom which appear in them. It heightens the
Pleasures of the Eye, and raises such a rational Admiration in the Soul
as is little inferior to Devotion.
It is not in the Power of every one to offer up this kind of Worship to
the great Author of Nature, and to indulge these more refined
Meditations of Heart, which are doubtless highly acceptable in his
Sight: I shall therefore conclude this short Essay on that Pleasure
which the Mind naturally conceives from the present Season of the Year,
by the recommending of a Practice for which every one has sufficient
Abilities.
I would have my Readers endeavour to moralize this natural Pleasure of
the Soul, and to improve this vernal Delight, as
Milton
calls it, into a
Christian
Virtue. When we find our selves inspired with this pleasing
Instinct, this secret Satisfaction and Complacency arising from the
Beauties of the Creation, let us consider to whom we stand indebted for
all these Entertainments of Sense, and who it is that thus opens his
Hand and fills the World with Good. The
Apostle
instructs us to take
advantage of our present Temper of Mind, to graft upon it such a
religious Exercise as is particularly conformable to it, by that Precept
which advises
those who are sad to pray, and those who are merry to sing
Psalms
. The Chearfulness of Heart which springs up in us from the Survey
of Nature's Works, is an admirable Preparation for Gratitude. The Mind
has gone a great way towards Praise and Thanksgiving, that is filled
with such a secret Gladness: A grateful Reflection on the supreme Cause
who produces it, sanctifies it in the Soul, and gives it its proper
Value. Such an habitual Disposition of Mind consecrates every Field and
Wood, turns an ordinary Walk into a morning or evening Sacrifice, and
will improve those transient Gleams of Joy, which naturally brighten up
and refresh the Soul on such Occasions, into an inviolable and perpetual
State of Bliss and Happiness.
I.
Paradise Lost,
Bk iv. ll. 148-156.
Contents
|
Monday, June 2, 1712 |
Steele |
Bene colligitur hæc Pueris et Mulierculis et Servis et Servorum
simillimis Liberis esse grata. Gravi vero homini et ea quæ fiunt
Judicio certo ponderanti probari posse nullo modo.
Tull.

I have been considering the little and frivolous things which give Men
Accesses to one another, and Power with each other, not only in the
common and indifferent Accidents of Life, but also in Matters of greater
importance. You see in Elections for Members to sit in Parliament, how
far saluting Rows of old Women, drinking with Clowns, and being upon a
level with the lowest Part of Mankind in that wherein they themselves
are lowest, their Diversions, will carry a Candidate. A Capacity for
prostituting a Man's Self in his Behaviour, and descending to the
present Humour of the Vulgar, is perhaps as good an Ingredient as any
other for making a considerable Figure in the World; and if a Man has
nothing else, or better, to think of, he could not make his way to
Wealth and Distinction by properer Methods, than studying the particular
Bent or Inclination of People with whom he converses, and working from
the Observation of such their Biass in all Matters wherein he has any
Intercourse with them: For his Ease and Comfort he may assure himself,
he need not be at the Expence of any great Talent or Virtue to please
even those who are possessd of the highest Qualifications. Pride in some
particular Disguise or other, (often a Secret to the proud Man himself)
is the most ordinary Spring of Action among Men. You need no more than
to discover what a Man values himself for; then of all things admire
that Quality, but be sure to be failing in it your self in comparison of
the Man whom you court. I have heard, or read, of a Secretary of State
in
Spain
, who served a Prince who was happy in an elegant use of the
Latin
Tongue, and often writ Dispatches in it with his own Hand. The
King shewed his Secretary a Letter he had written to a foreign Prince,
and under the Colour of asking his Advice, laid a Trap for his Applause.
The honest Man read it as a faithful Counsellor, and not only excepted
against his tying himself down too much by some Expressions, but mended
the Phrase in others. You may guess the Dispatches that Evening did not
take much longer Time. Mr. Secretary, as soon as he came to his own
House, sent for his eldest Son, and communicated to him that the Family
must retire out of
Spain
as soon as possible; for, said he,
the King
knows I understand Latin better than he does.
This egregious Fault in a Man of the World, should be a Lesson to all
who would make their Fortunes: But a Regard must be carefully had to the
Person with whom you have to do; for it is not to be doubted but a great
Man of common Sense must look with secret Indignation or bridled
Laughter, on all the Slaves who stand round him with ready Faces to
approve and smile at all he says in the gross. It is good Comedy enough
to observe a Superior talking half Sentences, and playing an humble
Admirer's Countenance from one thing to another, with such Perplexity
that he knows not what to sneer in Approbation of. But this kind of
Complaisance is peculiarly the Manner of Courts; in all other Places you
must constantly go farther in Compliance with the Persons you have to do
with, than a mere Conformity of Looks and Gestures. If you are in a
Country Life, and would be a leading Man, a good Stomach, a loud Voice,
and a rustick Chearfulness will go a great way, provided you are able to
drink, and drink any thing. But I was just now going to draw the Manner
of Behaviour I would advise People to practise under some Maxim, and
intimated, that every one almost was governed by his Pride. There was an
old Fellow about forty Years ago so peevish and fretful, though a Man of
Business, that no one could come at him: But he frequented a particular
little Coffee-house, where he triumphed over every body at
Trick-track
and
Baggammon
. The way to pass his Office well, was first to be insulted
by him at one of those Games in his leisure Hours; for his Vanity was to
shew, that he was a Man of Pleasure as well as Business. Next to this
sort of Insinuation, which is called in all Places (from its taking its
Birth in the Housholds of Princes)
making one's Court
, the most
prevailing way is, by what better-bred People call a
Present
, the Vulgar
a
Bribe
. I humbly conceive that such a thing is conveyed with more
Gallantry in a
Billet-doux
that should be understood at the Bank, than
in gross Money; But as to stubborn People, who are so surly as to accept
of neither Note or Cash, having formerly dabbled in Chymistry, I can
only say
that one part of Matter asks one thing, and another another, to
make it fluent; but there is nothing but may be dissolved by a proper
Mean
: Thus the Virtue which is too obdurate for Gold or Paper, shall
melt away very kindly in a Liquid. The Island of
Barbadoes
(a shrewd
People) manage all their Appeals to
Great-Britain
, by a skilful
Distribution of Citron-Water among the Whisperers about Men in Power.
Generous Wines do every Day prevail, and that in great Points, where ten
thousand times their Value would have been rejected with Indignation.
But to wave the Enumeration of the sundry Ways of applying by Presents,
Bribes, Management of People, Passions and Affections, in such a Manner
as it shall appear that the Virtue of the best Man is by one Method or
other corruptible; let us look out for some Expedient to turn those
Passions and Affections on the side of Truth and Honour. When a Man has
laid it down for a Position, that parting with his Integrity, in the
minutest Circumstance, is losing so much of his very Self, Self-love
will become a Virtue. By this means Good and Evil will be the only
Objects of Dislike and Approbation; and he that injures any Man, has
effectually wounded the Man of this Turn as much as if the Harm had been
to himself. This seems to be the only Expedient to arrive at an
Impartiality; and a Man who follows the Dictates of Truth and right
Reason, may by Artifice be led into Error, but never can into Guilt.
T.
Contents
Dedication of the Sixth Volume of The Spectator
To The Right Honorable Charles, Earl of Sunderland1.
My
Lord
,
Very many Favours and Civilities (received from You in a private
Capacity) which I have no other Way to acknowledge, will, I hope, excuse
this Presumption; but the Justice I, as a
Spectator
, owe your Character,
places me above the want of an Excuse. Candor and Openness of Heart,
which shine in all your Words and Actions, exacts the highest Esteem
from all who have the Honour to know You, and a winning Condescention to
all subordinate to You, made Business a Pleasure to those who executed
it under You, at the same time that it heightened Her Majesty's Favour
to all who had the Happiness of having it convey'd through Your Hands: A
Secretary of State, in the Interests of Mankind, joined with that of his
Fellow-Subjects, accomplished with a great Facility and Elegance in all
the Modern as well as Ancient Languages, was a happy and proper Member
of a Ministry, by whose Services Your Sovereign and Country are in so
high and flourishing a Condition, as makes all other Princes and
Potentates powerful or inconsiderable in
Europe
, as they are Friends or
Enemies to
Great-Britain
. The Importance of those great Events which
happened during that Administration, in which Your Lordship bore so
important a Charge, will be acknowledgd as long as Time shall endure; I
shall not therefore attempt to rehearse those illustrious Passages, but
give this Application a more private and particular Turn, in desiring
Your Lordship would continue your Favour and Patronage to me, as You are
a Gentleman of the most polite Literature, and perfectly accomplished in
the Knowledge of Books and Men, which makes it necessary to beseech Your
Indulgence to the following Leaves, and the Author of them: Who is, with
the greatest Truth and Respect,
My Lord,
Your Lordships Obliged,
Obedient, and Humble Servant,
The
Spectator
.
Charles Spencer, to whom the Sixth Volume of the Spectator
is here inscribed, represented Tiverton, in 1700, when he took the Lady
Anne Churchill, Marlborough's second daughter, for his second wife. On
the death of his father Robert, in 1702, he became Earl of Sunderland.
He was an accomplished man and founder of the library at Althorpe. In
1705 he was employed diplomatically at the courts of Prussia, Austria,
and Hanover. Early in 1706 he was one of the Commissioners for arranging
the Union with Scotland, and in September of that year he was forced by
the Whigs on Queen Anne, as successor to Sir Charles Hedges in the
office of Secretary of State. Steele held under him the office of
Gazetteer, to which he was appointed in the following May. In 1710
Sunderland shared in the political reverse suffered by Marlborough. In
the summer of that year Sunderland was dismissed from office, but with
an offer from the Queen of a pension of £3000 a year. He replied that he
was glad her Majesty was satisfied that he had done his duty; but if he
could not have the honour to serve his country, he would not plunder it.
The accession of George I. restored him to favour and influence. He
became Lord-lieutenant of Ireland; had, in 1715, a pension of £12,000 a
year settled on him; in April, 1717, was again Secretary of State; and
in the following March, Lord President of the Council. His political
influence was broken in 1721, the year before his death.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 3, 1712 |
Budgell |
Quod nunc ratio est, Impetus ante fuit.
Ovid.

Beware of the Ides of March
, said the
Roman
Augur to
Julius Cæsar
:
Beware of the Month of May
, says the
British Spectator
to his fair
Country-women. The Caution of the first was unhappily neglected, and
Cæsar's
Confidence cost him his Life. I am apt to flatter my self that
my pretty Readers had much more regard to the Advice I gave them, since
I have yet received very few Accounts of any notorious Trips made in the
last Month.
But tho' I hope for the best, I shall not pronounce too positively on
this point, till I have seen forty Weeks well over, at which Period of
Time, as my good Friend Sir
Roger
has often told me, he has more
Business as a Justice of Peace, among the dissolute young People in the
Country, than at any other Season of the Year.
Neither must I forget a Letter which I received near a Fortnight since
from a Lady, who, it seems, could hold out no longer, telling me she
looked upon the Month as then out, for that she had all along reckoned
by the New Style.
On the other hand, I have great reason to believe, from several angry
Letters which have been sent to me by disappointed Lovers, that my
Advice has been of very signal Service to the fair Sex, who, according
to the old Proverb, were
Forewarned forearm'd
.
One of these Gentlemen tells me, that he would have given me an hundred
Pounds, rather than I should have publishd that Paper; for that his
Mistress, who had promised to explain herself to him about the Beginning
of
May
, upon reading that Discourse told him that she would give him her
Answer in
June
.
Thyrsis
acquaints me, that when he desired
Sylvia
to take a Walk in the
Fields, she told him the
Spectator
had forbidden her.
Another of my Correspondents, who writes himself
Mat Meager,
complains,
that whereas he constantly used to Breakfast with his Mistress upon
Chocolate, going to wait upon her the first of
May
he found his usual
Treat very much changed for the worse, and has been forced to feed ever
since upon Green Tea.
As I begun this Critical Season with a
Caveat
to the Ladies, I shall
conclude it with a
Congratulation
, and do most heartily wish them Joy of
their happy Deliverance.
They may now reflect with Pleasure on the Dangers they have escaped, and
look back with as much Satisfaction on their Perils that threat'ned
them, as their Great-Grandmothers did formerly on the Burning
Plough-shares, after having passed through the
Ordeal Tryal.
The
Instigations of the Spring are now abated. The Nightingale gives over
her Love-labourd Song, as
Milton
phrases it, the Blossoms are fallen,
and the Beds of Flowers swept away by the Scythe of the Mower.
I shall now allow my Fair Readers to return to their Romances and
Chocolate, provided they make use of them with Moderation, till about
the middle of the Month, when the Sun shall have made some Progress in
the Crab. Nothing is more dangerous, than too much Confidence and
Security. The
Trojans
, who stood upon their Guard all the while the
Grecians
lay before their City, when they fancied the Siege was raised,
and the Danger past, were the very next Night burnt in their Beds: I
must also observe, that as in some Climates there is a perpetual Spring,
so in some Female Constitutions there is a perpetual May: These are a
kind of Valetudinarians in Chastity, whom I would continue in a constant
Diet. I cannot think these wholly out of Danger, till they have looked
upon the other Sex at least Five Years through a Pair of Spectacles.
Will. Honeycomb
has often assured me, that its much easier to steal one
of this Species, when she has passed her grand Climacterick, than to
carry off an icy Girl on this side Five and Twenty; and that a Rake of
his Acquaintance, who had in vain endeavoured to gain the Affections of
a young Lady of Fifteen, had at last made his Fortune by running away
with her Grandmother.
But as I do not design this Speculation for the Evergreens of the Sex, I
shall again apply my self to those who would willingly listen to the
Dictates of Reason and Virtue, and can now hear me in cold Blood. If
there are any who have forfeited their Innocence, they must now consider
themselves under that Melancholy View, in which
Chamont
regards his
, in those beautiful Lines.
—Long she flourish'd,
Grew sweet to Sense, and lovely to the Eye;
Till at the last a cruel Spoiler came,
Cropt this fair Rose, and rifled all its Sweetness;
Then cast it like a loathsome Weed away.1
On the contrary, she who has observed the timely Cautions I gave her,
and lived up to the Rules of Modesty, will now Flourish like a Rose in
June
, with all her Virgin Blushes and Sweetness about her: I must,
however, desire these last to consider, how shameful it would be for a
General, who has made a Successful Campaign, to be surprized in his
Winter Quarters: It would be no less dishonourable for a Lady to lose in
any other Month of the Year, what she has been at the pains to preserve
in
May
.
There is no Charm in the Female Sex, that can supply the place of
Virtue
. Without Innocence, Beauty is unlovely, and Quality contemptible,
Good-breeding degenerates into Wantonness, and Wit into Impudence. It is
observed, that all the Virtues are represented by both Painters and
Statuaries under Female Shapes, but if any one of them has a more
particular Title to that Sex, it is
Modesty
. I shall leave it to the
Divines to guard them against the opposite Vice, as they may be
overpowerd by Temptations; It is sufficient for me to have warned them
against it, as they may be led astray by Instinct.
I desire this Paper may be read with more than ordinary Attention, at
all Tea-Tables within the Cities of
London
and
Westminster
.
X.
Otway's
Orphan
, Act IV.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 4, 1712 |
Henley |
Barbara, Celarent, Darii, Ferio, Baralipton.
Having a great deal of Business upon my Hands at present, I shall beg
the Reader's Leave to present him with a Letter that I received about
half a Year ago from a Gentleman of
Cambridge
, who styles himself
Peter
de Quir
. I have kept it by me some Months, and though I did not know at
first what to make of it, upon my reading it over very frequently I have
at last discovered several Conceits in it: I would not therefore have my
Reader discouraged if he does not take them at the first Perusal.
To Mr.
Spectator1.
From St. John's College Cambridge, Feb. 3, 1712.
Sir,
The Monopoly of Punns in this University has been an immemorial
Privilege of the
Johnians; and we can't help resenting the late Invasion
of our ancient Right as to that Particular, by a little Pretender to
Clenching in a neighbouring College, who in an Application to you by way
of Letter, a while ago, styled himself
Philobrune. Dear Sir, as you are
by Character a profest Well-wisher to Speculation, you will excuse a
Remark which this Gentleman's Passion for the Brunette has suggested to
a Brother Theorist; 'tis an Offer towards a mechanical Account of his
Lapse to Punning, for he belongs to a Set of Mortals who value
themselves upon an uncommon Mastery in the more humane and polite Part
of Letters. A Conquest by one of this Species of Females gives a very
odd Turn to the Intellectuals of the captivated Person, and very
different from that way of thinking which a Triumph from the Eyes of
another more emphatically of the fair Sex, does generally occasion. It
fills the Imagination with an Assemblage of such Ideas and Pictures as
are hardly any thing but Shade, such as Night, the Devil, &c. These
Portraitures very near over-power the Light of the Understanding, almost
benight the Faculties, and give that melancholy Tincture to the most
sanguine Complexion, which this Gentleman calls an Inclination to be in
a
Brown-study, and is usually attended with worse Consequences in case
of a Repulse. During this Twilight of Intellects, the Patient is
extremely apt, as Love is the most witty Passion in Nature, to offer at
some pert Sallies now and then, by way of Flourish, upon the amiable
Enchantress, and unfortunately stumbles upon
that Mongrel miscreated (to
speak in
Miltonic) kind of Wit, vulgarly termed, the Punn.
It would not
be much amiss to consult
Dr. T—W—2 (who is certainly a very able
Projector, and whose system of Divinity and spiritual Mechanicks obtains
very much among the better Part of our Under-Graduates) whether a
general Intermarriage, enjoyned by Parliament, between this Sisterhood
of the Olive Beauties, and the Fraternity of the People call'd
Quakers,
would not be a very serviceable Expedient, and abate that Overflow of
Light which shines within them so powerfully, that it dazzles their
Eyes, and dances them into a thousand Vagaries of Error and Enthusiasm.
These Reflections may impart some Light towards a Discovery of the
Origin of Punning among us, and the Foundation of its prevailing so long
in this famous Body. Tis notorious from the Instance under
Consideration, that it must be owing chiefly to the use of brown Juggs,
muddy Belch, and the Fumes of a certain memorable Place of
Rendezvous
with us at Meals, known by the Name of
Staincoat Hole: For the
Atmosphere of the Kitchen, like the Tail of a Comet, predominates least
about the Fire, but resides behind and fills the fragrant Receptacle
above-mentioned. Besides, 'tis farther observable that the delicate
Spirits among us, who declare against these nauseous proceedings, sip
Tea, and put up for Critic and Amour, profess likewise an equal
Abhorrency for Punning, the ancient innocent Diversion of this Society.
After all, Sir, tho' it may appear something absurd, that I seem to
approach you with the Air of an Advocate for Punning, (you who have
justified your Censures of the Practice in a set Dissertation upon that
Subject;) yet, I'm confident, you'll think it abundantly atoned for by
observing, that this humbler Exercise may be as instrumental in
diverting us from any innovating Schemes and Hypothesis in Wit. as
dwelling upon honest Orthodox Logic would be in securing us from Heresie
in Religion.
Had
Mr. W—n's3 Researches been confined within the
Bounds of
Ramus or
Crackanthorp, that learned News-monger might have
acquiesced in what the holy Oracles pronounce upon the Deluge, like
other
Christians;
and had the surprising
Mr. L—y4 been content with
the Employment of refining upon
Shakespear's Points and Quibbles, (for
which he must be allowed to have a superlative Genius) and now and then
penning a Catch or a Ditty, instead of inditing Odes, and Sonnets, the
Gentlemen of the
Bon Goust in the Pit would never have been put to all
that Grimace in damning the Frippery of State, the Poverty and Languor
of Thought, the unnatural Wit, and inartificial Structure of his Dramas.
I am,
Sir,
Your very humble Servant,
Peter de Quir.
This letter was by John Henley, commonly called Orator
Henley. The paper is without signature in first issue or reprint, but
the few introductory lines, doubtless, are by Steele. John Henley was at
this time but 20 years old. He was born at Melton Mowbray in 1692, and
entered St. John's College, Cambridge, in 1709. After obtaining his
degree he was invited to take charge of the Grammar School in his native
place, and raised it from decay. He published
Esther
, a poem; went to
London; introduced action into pulpit oratory; missing preferment, gave
lectures and orations, religious on Sundays, and political on
Wednesdays; was described by Pope in the
Dunciad
as the Zany of his age,
and represented by Hogarth upon a scaffold with a monkey by his side
saying Amen. He edited a paper of nonsense called the
Hip Doctor,
and
once attracted to his oratory an audience of shoemakers by announcing
that he would teach a new and short way of making shoes; his way being
to cut off the tops of boots. He died in 1756.
Percy suggests very doubtfully that this may mean Thomas
Woolston, who was born in 1669, educated at Sidney College, Cambridge,
published, in 1705,
The Old Apology for the Truth against the Jews and
Gentiles Revived
, and afterwards was imprisoned and fined for levity in
discussing sacred subjects. The text points to a medical theory of
intermarriage. There was a Thomas Winston, of Clare Hall, Cambridge, who
travelled over the continent, took degrees at Basle and Padua, returned
to take his M.D. at Cambridge, and settled in London in 1607.
William Whiston, born 1667, educated at Tamworth School and
Clare Hall, Cambridge, became a Fellow in 1693, and then Chaplain to
Bishop Moore. In 1696 he published his
New Theory of the Earth,
which
divided attention with Burnet's
Sacred Theory of the Earth
already
mentioned. In 1700 Whiston was invited to Cambridge, to act as deputy to
Sir Isaac Newton, whom he succeeded in 1703 as Lucasian Professor. For
holding some unorthodox opinions as to the doctrines of the early
Christians, he was, in 1710, deprived of his Professorship, and banished
from the University. He was a pious and learned man, who, although he
was denied the Sacrament, did not suffer himself to be driven out of the
Church of England till 1747. At last he established a small congregation
in his own house in accordance with his own notion of primitive
Christianity. He lived till 1752.
No L—y of that time has written plays that are remembered.
The John Lacy whom Charles II. admired so much that he had his picture
painted in three of his characters, died in 1681, leaving four comedies
and an alteration of Shakespeare's
Taming of the Shrew
. He was a
handsome man: first dancing-master, then quarter-master, then an admired
comedian. Henley would hardly have used a blank in referring to a
well-known writer who died thirty years before. There was another John
Lacy advertising in the Post Boy, Aug. 3, 1714, The Steeleids, or the
Trial of Wits, a Poem in three cantos, with a motto:
Then will I say, swelled with poetic rage,
That I, John Lacy, have reformed the age.
Contents
|
Thursday, June 5, 1712 |
Addison |
—Dolor ipse disertum
Fecerat—
Ovid.

the Stoick Philosophers discard all Passions in general, they will
not allow a Wise Man so much as to pity the Afflictions of another.
If
thou seest thy Friend in Trouble
, says
Epictetus
,
thou mayst put on a
Look of Sorrow, and condole with him, but take care that thy Sorrow be
not real
. The more rigid of this Sect would not comply so far as to
shew even such an outward Appearance of Grief, but when one told them of
any Calamity that had befallen even the nearest of their Acquaintance,
would immediately reply,
What is that to me?
If you aggravated the
Circumstances of the Affliction, and shewed how one Misfortune was
followed by another, the Answer was still,
All this may be true, but
what is it to me?
For my own part, I am of Opinion, Compassion does not only refine and
civilize Humane Nature, but has something in it more pleasing and
agreeable than what can be met with in such an indolent Happiness, such
an Indifference to Mankind as that in which the Stoicks placed their
Wisdom. As Love is the most delightful Passion, Pity is nothing else but
Love softned by a degree of Sorrow: In short, it is a kind of pleasing
Anguish, as well as generous Sympathy, that knits Mankind together, and
blends them in the same common Lot.
Those who have laid down Rules for Rhetorick or Poetry, advise the
Writer to work himself up, if possible, to the Pitch of Sorrow which he
endeavours to produce in others. There are none therefore who stir up
Pity so much as those who indite their own Sufferings. Grief has a
natural Eloquence belonging to it, and breaks out in more moving
Sentiments than be supplied by the finest Imagination. Nature on this
Occasion dictates a thousand passionate things which cannot be supplied
by Art.
It is for this Reason that the short Speeches, or Sentences which we
often meet with in Histories, make a deeper Impression on the Mind of
the Reader, than the most laboured Strokes in a well-written Tragedy.
Truth and Matter of Fact sets the Person actually before us in the one,
whom Fiction places at a greater Distance from us in the other. I do not
remember to have seen any Ancient or Modern Story more affecting than a
Letter of
Ann of Bologne
, Wife to
King Henry the Eighth
, and Mother to
Queen Elizabeth
, which is still extant in the
Cotton Library,
as written
by her own Hand.
Shakespear
himself could not have made her talk in a Strain so suitable
to her Condition and Character. One sees in it the Expostulations of a
slighted Lover, the Resentments of an injured Woman, and the Sorrows of
an imprisoned Queen. I need not acquaint my Reader that this Princess
was then under Prosecution for Disloyalty to the King's Bed, and that
she was afterwards publickly beheaded upon the same Account, though this
Prosecution was believed by many to proceed, as she her self intimates,
rather from the King's Love to
Jane Seymour
than from any actual Crime
in
Ann of Bologne.
Queen Ann Boleyn's last Letter to King Henry.
[Cotton Libr. Otho C. 10.]
Sir,
Your Grace's Displeasure, and my Imprisonment, are Things so strange
unto me, as what to write, or what to excuse, I am altogether
ignorant. Whereas you send unto me (willing me to confess a Truth, and
so obtain your Favour) by such an one, whom you know to be mine
ancient professed Enemy, I no sooner received this Message by him,
than I rightly conceived your Meaning; and if, as you say, confessing
a Truth indeed may procure my Safety, I shall with all Willingness and
Duty perform your Command.
But let not your Grace ever imagine, that your poor Wife will ever be
brought to acknowledge a Fault, where not so much as a Thought thereof
preceded. And to speak a Truth, never Prince had Wife more Loyal in
all Duty, and in all true Affection, than you have ever found in Ann
Boleyn: with which Name and Place I could willingly have contented my
self, if God and your Grace's Pleasure had been so pleased. Neither
did I at any time so far forget my self in my Exaltation, or received
Queenship, but that I always looked for such an Alteration as now I
find; for the Ground of my Preferment being on no surer Foundation
than
your Grace's Fancy, the least Alteration I knew was fit and
sufficient to draw that Fancy to some other
Object2. You have
chosen me, from a low Estate, to be your Queen and Companion, far
beyond my Desert or Desire. If then you found me worthy of such
Honour, good your Grace let not any light Fancy, or bad Counsel of
mine Enemies, withdraw your Princely Favour from me; neither let that
Stain, that unworthy Stain, of a Disloyal Heart towards your good
Grace, ever cast so foul a Blot on your most Dutiful Wife, and the
Infant-Princess your Daughter. Try me, good King, but let me have a
lawful Tryal, and let not my sworn Enemies sit as my Accusers and
Judges; Yea let me receive an open Tryal, for my Truth shall fear no
open Shame; then shall you see either mine Innocence cleared, your
Suspicion and Conscience satisfied, the Ignominy and Slander of the
World stopped, or my Guilt openly declared. So that whatsoever God or
you may determine of me, your Grace may be freed from an open Censure,
and mine Offence being so lawfully proved, your Grace is at liberty,
both before God and Man, not only to Execute worthy Punishment on me
as an unlawful Wife, but to follow your Affection, already settled on
that Party, for whose sake I am now as I am, whose Name I could some
good while since have pointed unto, your Grace being not ignorant of
my Suspicion therein.
But if you have already determined of me, and that not only my Death,
but an Infamous Slander must bring you the enjoying of your desired
Happiness; then I desire of God, that he will pardon your great Sin
therein, and likewise mine Enemies, the Instruments thereof; and that
he will not call you to a strict Account for your unprincely and cruel
Usage of me, at his general Judgment Seat, where both you and my self
must shortly appear, and in whose Judgment I doubt not (whatsoever the
World may think of me) mine Innocence shall be openly known, and
sufficiently cleared.
My last and only Request shall be, that my self may only bear the
Burthen of your Grace's Displeasure, and that it may not touch the
innocent Souls of those poor Gentlemen, who (as I understand) are
likewise in strait Imprisonment for my sake. If ever I have found
Favour in your Sight, if ever the Name of
Ann Boleyn hath been
pleasing in your Ears, then let me obtain this Request, and I will so
leave to trouble your Grace any further, with mine earnest Prayers to
the Trinity to have your Grace in his good Keeping, and to direct you
in all your Actions. From my doleful Prison in the Tower, this sixth
of
May;
Your most Loyal,
And ever Faithful Wife,
Ann Boleyn.
When you see a Neighbour in Tears, and hear him lament the Absence of
his Son, the Hazards of his Voyage into some remote Part of the World,
or the Loss of his Estate; keep upon your Guard, for fear lest some
false Ideas that may rise upon these Occasions, surprise you into a
Mistake, as if this Man were really miserable, upon the Account of
these outward Accidents. But be sure to distinguish wisely, and tell
your self immediately, that the Thing which really afflicts this
Person is not really the Accident it self, (for other People, under
his Circumstances, are not equally afflicted with it) but merely the
Opinion which he hath formed to himself concerning this Accident.
Notwithstanding all which, you may be allowed, as far as Expressions
and outward Behaviour go, to comply with him; and if Occasion require,
to bear a part in his Sighs, and Tears too; but then you must be sure
to take care, that this Compliance does not infect your Mind, nor
betray you to an inward and real Sorrow, upon any such
Account.
Epictetus his Morals, with Simplicius his Comment.
Made English from the Greek by George Stanhope (1694) chapter xxii.
Subject
Contents
|
Friday, June 6, 1712 |
Steele |
Insanire pares certa ratione modoque.
Hor.

Cynthio
and
Flavia
are Persons of Distinction in this Town, who have
been Lovers these ten Months last past, and writ to each other for
Gallantry Sake, under those feigned Names; Mr. Such a one and Mrs. Such
a one not being capable of raising the Soul out of the ordinary Tracts
and Passages of Life, up to that Elevation which makes the Life of the
Enamoured so much superior to that of the rest of the World. But ever
since the beauteous
Cecilia
has made such a Figure as she now does in
the Circle of Charming Women,
Cynthio
has been secretly one of her
Adorers.
Lætitia
has been the finest Woman in Town these three Months,
and so long
Cynthio
has acted the Part of a Lover very awkwardly in the
Presence of
Flavia
.
Flavia
has been too blind towards him, and has too
sincere an Heart of her own to observe a thousand things which would
have discovered this Change of Mind to any one less engaged than she
was.
Cynthio
was musing Yesterday in the
Piazza
in
Covent-Garden
, and
was saying to himself that he was a very ill Man to go on in visiting
and professing Love to
Flavia
, when his Heart was enthralled to another.
It is an Infirmity that I am not constant to
Flavia;
but it would be
still a greater Crime, since I cannot continue to love her, to profess
that I do. To marry a Woman with the Coldness that usually indeed comes
on after Marriage, is ruining one's self with one's Eyes open; besides
it is really doing her an Injury.
This last Consideration, forsooth, of
injuring her in persisting, made him resolve to break off upon the first
favourable Opportunity of making her angry. When he was in this Thought,
he saw
Robin the Porter
who waits at
Will's Coffee-House
, passing by.
Robin
, you must know, is the best Man in Town for carrying a Billet; the
Fellow has a thin Body, swift Step, demure Looks, sufficient Sense, and
knows the Town. This Man carried
Cynthio's
first Letter to
Flavia
, and
by frequent Errands ever since, is well known to her. The Fellow covers
his Knowledge of the Nature of his Messages with the most exquisite low
Humour imaginable: The first he obliged
Flavia
to take, was, by
complaining to her that he had a Wife and three Children, and if she did
not take that Letter, which, he was sure, there was no Harm in, but
rather Love, his Family must go supperless to Bed, for the Gentleman
would pay him according as he did his Business.
Robin
therefore
Cynthio
now thought fit to make use of, and gave him Orders to wait before
Flavia's
Door, and if she called him to her, and asked whether it was
Cynthio
who passed by, he should at first be loth to own it was, but
upon Importunity confess it. There needed not much Search into that Part
of the Town to find a well-dressed Hussey fit for the Purpose
Cynthio
designed her. As soon as he believed
Robin
was posted, he drove by
Flavia's
Lodgings in an Hackney-Coach and a Woman in it.
Robin
was at
the Door talking with
Flavia's
Maid, and
Cynthio
pulled up the Glass as
surprized, and hid his Associate. The Report of this Circumstance soon
flew up Stairs, and
Robin
could not deny but the Gentleman favoured his
Master; yet if it was he, he was sure the Lady was but his Cousin whom
he had seen ask for him; adding that he believed she was a poor
Relation, because they made her wait one Morning till he was awake.
Flavia
immediately writ the following Epistle, which
Robin
brought to
Wills'
June 4, 1712.
Sir,
It is in vain to deny it, basest, falsest of Mankind; my Maid, as well
as the Bearer, saw you.
The injur'd Flavia.
After
Cynthio
had read the Letter, he asked
Robin
how she looked, and
what she said at the Delivery of it.
Robin
said she spoke short to him,
and called him back again, and had nothing to say to him, and bid him
and all the Men in the World go out of her Sight; but the Maid followed,
and bid him bring an Answer.
Cynthio
returned as follows.
June 4, Three Afternoon, 1712.
Madam,
That your Maid and the Bearer has seen me very often is very certain;
but I desire to know, being engaged at Picket, what your Letter means
by 'tis in vain to deny it. I shall stay here all the Evening.
Your amazed Cynthio.
As soon as
Robin
arrived with this,
Flavia
answered:
Dear Cynthio,
I have walked a Turn or two in my Anti-Chamber since I writ to you,
and have recovered my self from an impertinent Fit which you ought to
forgive me, and desire you would come to me immediately to laugh off a
Jealousy that you and a Creature of the Town went by in an
Hackney-Coach an Hour ago. I am Your most humble Servant,
Flavia
I will not open the Letter which my Cynthio writ, upon the
Misapprehension you must have been under when you writ, for want of
hearing the whole Circumstance.
Robin
came back in an Instant, and
Cynthio
answered:
Half Hour, six Minutes after Three,
June 4. Will's Coffee-house.
Madam, It is certain I went by your Lodgings with a Gentlewoman to
whom I have the Honour to be known, she is indeed my Relation, and a
pretty sort of Woman. But your starting Manner of Writing, and owning
you have not done me the Honour so much as to open my Letter, has in
it something very unaccountable, and alarms one that has had Thoughts
of passing his Days with you. But I am born to admire you with all
your little Imperfections.
Cynthio.
Robin
run back, and brought for Answer;
Exact Sir, that are at Will's Coffee-house six Minutes after Three,
June 4; one that has had Thoughts and all my little Imperfections.
Sir, come to me immediately, or I shall determine what may perhaps not
be very pleasing to you.
Flavia
Robin
gave an Account that she looked excessive angry when she gave him
the Letter; and that he told her, for she asked, that
Cynthio
only
looked at the Clock, taking Snuff, and writ two or three Words on the
Top of the Letter when he gave him his.
Now the Plot thickened so well, as that
Cynthio
saw he had not much more
to do to accomplish being irreconciliably banished, he writ,
Madam,
I have that Prejudice in Favour of all you do, that it is not possible
for you to determine upon what will not be very pleasing to Your
Obedient Servant,
Cynthio.
This was delivered, and the Answer returned, in a little more than two
Seconds.
Sir,
Is it come to this? You never loved me; and the Creature you were with
is the properest Person for your Associate. I despise you, and hope I
shall soon hate you as a Villain to
The Credulous Flavia.
Robin ran back, with
Madam,
Your Credulity when you are to gain your Point, and Suspicion when you
fear to lose it make it a very hard Part to behave as becomes Your
humble Slave,
Cynthio.
Robin whipt away, and returned with,
Mr. Wellford,
Flavia and Cynthio are no more. I relieve you from the hard Part of
which you complain, and banish you from my Sight for ever.
Ann Heart.
Robin
had a Crown for his Afternoon's Work; and this is published to
admonish
Cecilia
to avenge the Injury done to
Flavia
.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 7, 1712 |
Addison |
Ut nemo in sese tentat descendere!
Pers.

Hypocrisie
, at the fashionable End of the Town, is very different from
Hypocrisie in the City. The modish Hypocrite endeavours to appear more
vicious than he really is, the other kind of Hypocrite more virtuous.
The former is afraid of every thing that has the Shew of Religion in it,
and would be thought engaged in many Criminal Gallantries and Amours,
which he is not guilty of. The latter assumes a Face of Sanctity, and
covers a Multitude of Vices under a seeming Religious Deportment.
But there is another kind of Hypocrisie, which differs from both these,
and which I intend to make the Subject of this Paper: I mean that
Hypocrisie, by which a Man does not only deceive the World, but very
often imposes on himself; That Hypocrisie, which conceals his own Heart
from him, and makes him believe he is more virtuous than he really is,
and either not attend to his Vices, or mistake even his Vices for
Virtues. It
this fatal Hypocrisie and Self-deceit, which is taken
notice of in those Words,
Who can understand his Errors? cleanse thou me
from secret Faults
.
If the open Professors of Impiety deserve the utmost Application and
Endeavours of Moral Writers to recover them from Vice and Folly, how
much more may those lay a Claim to their Care and Compassion, who are
walking in the Paths of Death, while they fancy themselves engaged in a
Course of Virtue! I shall endeavour, therefore, to lay down some Rules
for the Discovery of those Vices that lurk in the secret Corners of the
Soul, and to show my Reader those Methods by which he may arrive at a
true and impartial Knowledge of himself. The usual Means prescribed for
this Purpose, are to examine our selves by the Rules which are laid down
for our Direction in Sacred Writ, and to compare our Lives with the Life
of that Person who acted up to the Perfection of Human Nature, and is
the standing Example, as well as the great Guide and Instructor, of
those who receive his Doctrines. Though these two Heads cannot be too
much insisted upon, I shall but just mention them, since they have been
handled by many Great and Eminent Writers.
I would therefore propose the following Methods to the Consideration of
such as would find out their secret Faults, and make a true Estimate of
themselves.
In the first Place, let them consider well what are the Characters which
they bear among their Enemies. Our Friends very often flatter us, as
much as our own Hearts. They either do not see our Faults, or conceal
them from us, or soften them by their Representations, after such a
manner, that we think them too trivial to be taken notice of. An
Adversary, on the contrary, makes a stricter Search into us, discovers
every Flaw and Imperfection in our Tempers, and though his Malice may
set them in too strong a Light, it has generally some Ground for what it
advances. A Friend exaggerates a Man's Virtues, an Enemy inflames his
Crimes. A Wise Man should give a just Attention to both of them, so far
as they may tend to the Improvement of the one, and Diminution of the
other.
Plutarch
has written an Essay on the Benefits which a Man may
receive from his Enemies
, and, among the good Fruits of Enmity,
mentions this in particular, that by the Reproaches which it casts upon
us we see the worst side of our selves, and open our Eyes to several
Blemishes and Defects in our Lives and Conversations, which we should
not have observed, without the Help of such ill-natured Monitors.
In order likewise to come at a true Knowledge of our selves, we should
consider on the other hand how far we may deserve the Praises and
Approbations which the World bestow upon us: whether the Actions they
celebrate proceed from laudable and worthy Motives; and how far we are
really possessed of the Virtues which gain us Applause among those with
whom we converse. Such a Reflection is absolutely necessary, if we
consider how apt we are either to value or condemn ourselves by the
Opinions of others, and to sacrifice the Report of our own Hearts to the
Judgment of the World.
In the next Place, that we may not deceive our selves in a Point of so
much Importance, we should not lay too great a Stress on any supposed
Virtues we possess that are of a doubtful Nature: And such we may esteem
all those in which Multitudes of Men dissent from us, who are as good
and wise as our selves. We should always act with great Cautiousness and
Circumspection in Points, where it is not impossible that we may be
deceived. Intemperate Zeal, Bigotry and Persecution for any Party or
Opinion, how praiseworthy soever they may appear to weak Men of our own
Principles, produce infinite Calamities among Mankind, and are highly
Criminal in their own Nature; and yet how many Persons eminent for Piety
suffer such monstrous and absurd Principles of Action to take Root in
their Minds under the Colour of Virtues? For my own Part, I must own I
never yet knew any Party so just and reasonable, that a Man could follow
it in its Height and Violence, and at the same time be innocent.
We should likewise be very apprehensive of those Actions which proceed
from natural Constitution, favourite Passions, particular Education, or
whatever promotes our worldly Interest or Advantage. In these and the
like Cases, a Man's Judgment is easily perverted, and a wrong Bias hung
upon his Mind. These are the Inlets of Prejudice, the unguarded Avenues
of the Mind, by which a thousand Errors and secret Faults find
Admission,
being observed or taken Notice of. A wise Man will
suspect those Actions to which he is directed by something
besides
Reason, and always apprehend some concealed Evil in every Resolution
that is of a disputable Nature, when it is conformable to his particular
Temper, his Age, or Way of Life, or when it favours his Pleasure or his
Profit.
There is nothing of greater Importance to us than thus diligently to
sift our Thoughts, and examine all these dark Recesses of the Mind, if
we would establish our Souls in such a solid and substantial Virtue as
will turn to Account in that great Day, when it must stand the Test of
infinite Wisdom and Justice.
I shall conclude this Essay with observing that the two kinds of
Hypocrisie I have here spoken of, namely that of deceiving the World,
and that of imposing on our selves, are touched with wonderful Beauty in
the hundred and thirty ninth Psalm
. The Folly of the first kind of
Hypocrisie is there set forth by Reflections on God's Omniscience and
Omnipresence, which are celebrated in as noble Strains of Poetry as any
other I ever met with, either Sacred or Profane. The other kind of
Hypocrisie, whereby a Man deceives himself, is intimated in the two last
Verses, where the Psalmist addresses himself to the great Searcher of
Hearts in that emphatical Petition;
Try me, O God, and seek the ground
of my heart; prove me, and examine my Thoughts. Look well if there be
any way of wickedness in me, and lead me in the way everlasting.
L.
Psalm
xix. 12.
See note on p. 441 [Volume 1 links:
of
], vol. i.
more than
Contents
|
Monday, June 9, 1712 |
Steele |
—Latet Anguis in Herba.
Virg.

It should, methinks, preserve Modesty and its Interests in the World,
that the Transgression of it always creates Offence; and the very
Purposes of Wantonness are defeated by a Carriage which has in it so
much Boldness, as to intimate that Fear and Reluctance are quite
extinguishd in an Object which would be otherwise desirable. It was said
a Wit of the last Age,
{
Sedley has that prevailing gentle Art,
{Which, can with a resistless Charm impart
{The loosest Wishes to the chastest Heart;
Raise such a Conflict, kindle such a Fire,
Between declining Virtue and Desire,
That the poor vanquished Maid dissolves away
In Dreams all Night, in Sighs and Tears all Day1.
This prevailing gentle Art was made up of Complaisance, Courtship, and
artful Conformity to the Modesty of a Woman's Manners. Rusticity, broad
Expression, and forward Obtrusion, offend those of Education, and make
the Transgressors odious to all who have Merit enough to attract Regard.
It is in
Taste that the Scenery is so beautifully ordered in the
Description which
Antony
makes, in the Dialogue between him and
Dolabella
, of
Cleopatra
in her Barge.
Her Galley down the Silver Cydnos row'd;
The Tackling Silk, the Streamers wav'd with Gold;
The gentle Winds were lodg'd in purple Sails:
Her Nymphs, like Nereids, round her Couch were placed,
Where she, another Sea-born Venus, lay;
She lay, and lean'd her Cheek upon her Hand,
And cast a Look so languishingly sweet,
As if, secure of all Beholders Hearts,
Neglecting she could take 'em. Boys like Cupids
Stood fanning with their painted Wings the Winds
That play'd about her Face; but if she smil'd,
A darting Glory seemed to blaze abroad,
That Men's desiring Eyes were never weary'd,
But hung upon the Object. To soft Flutes
The Silver Oars kept Time; and while they play'd,
The Hearing gave new Pleasure to the Sight,
And both to Thought2—
Here the Imagination is warmed with all the Objects presented, and yet
there is nothing that is luscious, or what raises any Idea more loose
than that of a beautiful Woman set off to Advantage. The
, or a more
delicate and careful Spirit of Modesty, appears in the following Passage
in one of Mr.
Philip's
Pastorals
.
Breathe soft ye Winds, ye Waters gently flow,
Shield her ye Trees, ye Flowers around her grow,
Ye Swains, I beg you, pass in Silence by,
My Love in yonder Vale asleep does lie.
Desire is corrected when there is a Tenderness or Admiration expressed
which partakes the Passion. Licentious Language has something brutal in
it, which disgraces Humanity, and leaves us in the Condition of the
Savages in the Field. But it may be askd to what good Use can tend a
Discourse of this Kind at all? It is to alarm chaste Ears against such
as have what is above called the prevailing gentle Art. Masters of that
Talent are capable of cloathing their Thoughts in so soft a Dress, and
something so distant from the secret Purpose of their Heart, that the
Imagination of the Unguarded is touched with a Fondness which grows too
insensibly to be resisted. Much Care and Concern for the Lady's Welfare,
to seem afraid lest she should be annoyed by the very Air which
surrounds her, and this uttered rather with kind Looks, and expressed by
an Interjection, an Ah, or an Oh, at some little Hazard in moving or
making a Step, than in my direct Profession of Love, are the Methods of
skilful Admirers: They are honest Arts when their Purpose is such, but
infamous when misapplied. It is certain that many a young Woman in this
Town has had her Heart irrecoverably won, by Men who have not made one
Advance which ties their Admirers, tho' the Females languish with the
utmost Anxiety. I have often, by way of Admonition to my female Readers,
give them Warning against agreeable Company of the other Sex, except
they are well acquainted with their Characters. Women may disguise it if
they think fit, and the more to do it, they may be angry at me for
saying it; but I say it is natural to them, that they have no Manner of
Approbation of Men, without some Degree of Love: For this Reason he is
dangerous to be entertaind as a Friend or Visitant who is capable of
gaining any eminent Esteem or Observation, though it be never so remote
from Pretensions as a Lover. If a Man's Heart has not the Abhorrence of
any treacherous Design, he may easily improve Approbation into Kindness,
and Kindness into Passion. There may possibly be no manner of Love
between them in the Eyes of all their Acquaintance, no it is all
Friendship; and yet they may be as fond as Shepherd and Shepherdess in a
Pastoral, but still the Nymph and the Swain may be to each other no
other I warrant
, than
Pylades
and
Orestes
.
When Lucy decks with Flowers her swelling Breast,
And on her Elbow leans, dissembling Rest,
Unable to refrain my madding Mind,
Nor Sleep nor Pasture worth my Care I find.
Once Delia slept, on easie Moss reclin'd,
Her lovely Limbs half bare, and rude the Wind;
I smoothed her Coats, and stole a silent Kiss:
Condemn me Shepherds if I did amiss4.
Such good Offices as these, and such friendly Thoughts and Concerns for
one another, are what make up the Amity, as they call it, between Man
and Woman.
It is the Permission of such Intercourse, that makes a young Woman come
to the Arms of her Husband, after the Disappointment of four or five
Passions which she has successively had for different Men, before she is
prudentially given to him for whom she has neither Love nor Friendship.
For what should a poor Creature do that has lost all her Friends?
There's Marinet the Agreeable, has, to my Knowledge, had a Friendship
for Lord
Welford
, which had like to break her Heart; then she had so
great a Friendship for Colonel
Hardy
, that she could not endure any
Woman else should do any thing but rail at him. Many and fatal have been
Disasters between Friends who have fallen out, and their Resentments are
more keen than ever those of other Men can possibly be:
in this it
happens unfortunately, that as there ought to be nothing concealed from
one Friend to another, the Friends of different Sexes
very often
find fatal Effects from their Unanimity.
For my Part, who study to pass Life in as much Innocence and Tranquility
as I can, I shun the Company of agreeable Women as much as possible; and
must confess that I have, though a tolerable good Philosopher, but a low
Opinion of
Platonick
Love: for which Reason I thought it necessary to
give my fair Readers a Caution against it, having, to my great Concern,
observed the Waste of a
Platonist
lately swell to a Roundness which is
inconsistent with that Philosophy.
T.
Rochester's
Allusion to the 10th Satire of the 1st Book of Horace.
Dryden's
All for Love
, Act III. sc. i.
The Sixth.
Two stanzas from different parts of Ambrose Philips's sixth
Pastoral
. The first in the original follows the second, with three
stanzas intervening.
(, for want of other Amusement, often study Anatomy
together; and what is worse than happens in any other Friendship, they)
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 10, 1712 |
Budgell |
In amore hæc omnia insunt vitia: Injuriæ,
Suspiciones, Inimicitiæ, Induciæ,
Bellum, pax rursum:
Ter..

I shall publish for the Entertainment of this Day, an odd sort of a
Packet, which I have just received from one of my Female Correspondents.
Mr.
Spectator,
Since you have often confess'd that you are not displeased your Paper
should sometimes convey the Complaints of distressed Lovers to each
other, I am in Hopes you will favour one who gives you an undoubted
Instance of her Reformation, and at the same time a convincing Proof
of the happy Influence your Labours have had over the most
Incorrigible Part of the most Incorrigible Sex. You must know, Sir, I
am one of that Species of Women, whom you have often Characteriz'd
under the Name of
Jilts, and that I send you these Lines, as well to
do Publick Penance for having so long continued in a known Error, as
to beg Pardon of the Party offended. I the rather chuse this way,
because it in some measure answers the Terms on which he intimated the
Breach between us might possibly be made up, as you will see by the
Letter he sent me the next Day after I had discarded him; which I
thought fit to send you a Copy of, that you might the better know the
whole Case.
I must further acquaint you, that before I Jilted him, there had been
the greatest Intimacy between us for an Year and half together, during
all which time I cherished his Hopes, and indulged his Flame. I leave
you to guess after this what must be his Surprize, when upon his
pressing for my full Consent one Day, I told him
I wondered what could
make him fancy he had ever any Place in my Affections. His own Sex
allow him Sense, and all ours Good-Breeding. His Person is such as
might, without Vanity, make him believe himself not incapable to be
beloved. Our Fortunes indeed, weighed in the nice Scale of Interest,
are not exactly equal, which by the way was the true Case of my
Jilting him, and I had the Assurance to acquaint him with the
following Maxim,
That I should always believe that Man's Passion to be
the most Violent, who could offer me the largest Settlement. I have
since changed my Opinion, and have endeavoured to let him know so much
by several Letters, but the barbarous Man has refused them all; so
that I have no way left of writing to him, but by your Assistance. If
we can bring him about once more, I promise to send you all Gloves and
Favours, and shall desire the Favour of Sir
Roger and your self to
stand as God-Fathers to my first Boy.
I am,
Sir,
Your most Obedient
most Humble Servant,
Amoret.
Philander to Amoret.
Madam,
I am so surprised at the Question you were pleased to ask me
Yesterday, that I am still at a loss what to say to it. At least my
Answer would be too long to trouble you with, as it would come from
a Person, who, it seems, is so very indifferent to you. Instead of
it, I shall only recommend to your Consideration the Opinion of one
whose Sentiments on these matters I have often heard you say are
extremely just. A generous and Constant Passion, says your favourite
Author, in an agreeable Lover, where there is not too great a
Disparity in their Circumstances, is the greatest Blessing that can
befal a Person beloved; and if overlook'd in one, may perhaps never
be found in another.
I do not, however, at all despair of being very shortly much better
beloved by you than Antenor is at present; since whenever my Fortune
shall exceed his, you were pleased to intimate your Passion would
encrease accordingly.
The World has seen me shamefully lose that Time to please a fickle
Woman, which might have been employed much more to my Credit and
Advantage in other Pursuits. I shall therefore take the Liberty to
acquaint you, however harsh it may sound in a Lady's Ears, that tho
your Love-Fit should happen to return, unless you could contrive a
way to make your Recantation as well known to the Publick, as they
are already apprised of the manner with which you have treated me,
you shall never more see Philander.
Amoret to Philander.
Sir,
Upon Reflection, I find the Injury I have done both to you and my
self to be so great, that though the Part I now act may appear
contrary to that Decorum usually observed by our Sex, yet I
purposely break through all Rules, that my Repentance may in some
measure equal my Crime. I assure you that in my present Hopes of
recovering you, I look upon Antenor's Estate with Contempt. The Fop
was here Yesterday in a gilt Chariot and new Liveries, but I refused
to see him. Tho' I dread to meet your Eyes after what has pass'd, I
flatter my self, that amidst all their Confusion you will discover
such a Tenderness in mine, as none can imitate but those who Love. I
shall be all this Month at Lady D—'s in the Country; but the Woods,
the Fields and Gardens, without Philander, afford no Pleasures to
the unhappy Amoret.
I must desire you, dear Mr. Spectator, to publish this my Letter to
Philander as soon as possible, and to assure him that I know nothing
at all of the Death of his rich Uncle in Gloucestershire.
X.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 11, 1712 |
Steele |
—quæ
Spectator tradit sibi—
Hor.
1.

Were I to publish all the Advertisements I receive from different Hands,
and Persons of different Circumstances and Quality, the very Mention of
them, without Reflections on the several Subjects, would raise all the
Passions which can be felt by human Mind
s
, As Instances of this, I
shall give you two or three Letters; the Writers of which can have no
Recourse to any legal Power for Redress, and seem to have written rather
to vent their Sorrow than to receive Consolation.
Mr. Spectator,
I am a young Woman of Beauty and Quality, and suitably married to a
Gentleman who doats on me. But this Person of mine is the Object of an
unjust Passion in a Nobleman who is very intimate with my Husband.
This Friendship gives him very easie Access, and frequent
Opportunities of entertaining me apart. My Heart is in the utmost
Anguish, and my Face is covered over with Confusion, when I impart to
you another Circumstance, which is, that my Mother, the most mercenary
of all Women, is gained by this false Friend of my Husband to sollicit
me for him. I am frequently chid by the poor believing Man my Husband,
for shewing an Impatience of his Friend's Company; and I am never
alone with my Mother, but she tells me Stories of the discretionary
Part of the World, and such a one, and such a one who are guilty of as
much as she advises me to. She laughs at my Astonishment; and seems to
hint to me, that as virtuous as she has always appeared, I am not the
Daughter of her Husband. It is possible that printing this Letter may
relieve me from the unnatural Importunity of my Mother, and the
perfidious Courtship of my Husband's Friend. I have an unfeigned Love
of Virtue, and am resolved to preserve my Innocence. The only Way I
can think of to avoid the fatal Consequences of the Discovery of this
Matter, is to fly away for ever; which I must do to avoid my Husband's
fatal Resentment against the Man who attempts to abuse him, and the
Shame of exposing the Parent to Infamy. The Persons concerned will
know these Circumstances relate to 'em; and though the Regard to
Virtue is dead in them, I have some Hopes from their Fear of Shame
upon reading this in your Paper; which I conjure you to do, if you
have any Compassion for Injured Virtue.
Sylvia.
Mr. Spectator,
I am the Husband of a Woman of Merit, but am fallen in Love, as they
call it, with a Lady of her Acquaintance, who is going to be married
to a Gentleman who deserves her. I am in a Trust relating to this
Lady's Fortune, which makes my Concurrence in this Matter necessary;
but I have so irresistible a Rage and Envy rise in me when I consider
his future Happiness, that against all Reason, Equity, and common
Justice, I am ever playing mean Tricks to suspend the Nuptials. I have
no manner of Hopes for my self; Emilia, for so I'll call her, is a
Woman of the most strict Virtue; her Lover is a Gentleman who of all
others I could wish my Friend; but Envy and Jealousie, though placed
so unjustly, waste my very Being, and with the Torment and Sense of a
Daemon, I am ever cursing what I cannot but approve. I wish it were
the Beginning of Repentance, that I sit down and describe my present
Disposition with so hellish an Aspect; but at present the Destruction
of these two excellent Persons would be more welcome to me than their
Happiness. Mr. Spectator, pray let me have a Paper on these terrible
groundless Sufferings, and do all you can to exorcise Crowds who are
in some Degree possessed as I am.
Canniball.
Mr. Spectator,
I have no other Means but this to express my Thanks to one Man, and my
Resentment against another. My Circumstances are as follows. I have
been for five Years last past courted by a Gentleman of greater
Fortune than I ought to expect, as the Market for Women goes. You must
to be sure have observed People who live in that sort of Way, as all
their Friends reckon it will be a Match, and are marked out by all the
World for each other. In this View we have been regarded for some
Time, and I have above these three Years loved him tenderly. As he is
very careful of his Fortune, I always thought he lived in a near
Manner to lay up what he thought was wanting in my Fortune to make up
what he might expect in another. Within few Months I have observed his
Carriage very much altered, and he has affected a certain Air of
getting me alone, and talking with a mighty Profusion of passionate
Words, How I am not to be resisted longer, how irresistible his Wishes
are, and the like. As long as I have been acquainted with him, I could
not on such Occasions say down-right to him, You know you may make me
yours when you please. But the other Night he with great Frankness and
Impudence explained to me, that he thought of me only as a Mistress. I
answered this Declaration as it deserv'd; upon which he only doubled
the Terms on which he proposed my yielding. When my Anger heightned
upon him, he told me he was sorry he had made so little Use of the
unguarded Hours we had been together so remote from Company, as
indeed, continued he, so we are at present. I flew from him to a
neighbouring Gentlewoman's House, and tho' her Husband was in the
Room, threw my self on a Couch, and burst into a Passion of Tears. My
Friend desired her Husband to leave the Room. But, said he, there is
something so extraordinary in this, that I will partake in the
Affliction; and be it what it will, she is so much your Friend, that
she knows she may command what Services I can do her. The Man sate
down by me, and spoke so like a Brother, that I told him my whole
Affliction. He spoke of the Injury done me with so much Indignation,
and animated me against the Love he said he saw I had for the Wretch
who would have betrayed me, with so much Reason and Humanity to my
Weakness, that I doubt not of my Perseverance. His Wife and he are my
Comforters, and I am under no more Restraint in their Company than if
I were alone; and I doubt not but in a small time Contempt and Hatred
will take Place of the Remains of Affection to a Rascal.
I am
Sir,
Your affectionate Reader,
Dorinda.
Mr. Spectator,
I had the Misfortune to be an Uncle before I knew my Nephews from my
Nieces, and now we are grown up to better Acquaintance they deny me
the Respect they owe. One upbraids me with being their Familiar,
another will hardly be perswaded that I am an Uncle, a third calls me
Little Uncle, and a fourth tells me there is no Duty at all due to an
Uncle. I have a Brother-in-law whose Son will win all my Affection,
unless you shall think this worthy of your Cognizance, and will be
pleased to prescribe some Rules for our future reciprocal Behaviour.
It will be worthy the Particularity of your Genius to lay down Rules
for his Conduct who was as it were born an old Man, in which you will
much oblige,
Sir,
Your most obedient Servant,
Cornelius Nepos.
T.
No motto in the first issue.
Contents
|
Thursday, June 12, 1712 |
Addison |
Qui mores hominun multorum vidit?
Hor..

When I consider this great City in its several Quarters and Divisions, I
look upon it as an Aggregate of various Nations distinguished from each
other by their respective Customs, Manners and Interests. The Courts of
two Countries do not so much differ from one another, as the Court and
City in their peculiar Ways of Life and Conversation. In short, the
Inhabitants of
St. James's
, notwithstanding they live under the same
Laws, and speak the same Language, are a distinct People from those of
Cheapside
, who are likewise removed from those of the
Temple
on the one
side, and those of
Smithfield
on the other, by several Climates and
Degrees in their way of Thinking and Conversing together.
For this Reason, when any publick Affair is upon the Anvil, I love to
hear the Reflections that arise upon it in the several Districts and
Parishes of
London
and
Westminster
, and to ramble up and down a whole
Day together, in order to make my self acquainted with the Opinions of
my Ingenious Countrymen. By this means I know the Faces of all the
principal Politicians within the Bills of Mortality; and as every
Coffee-house has some particular Statesman belonging to it, who is the
Mouth of the Street where he lives, I always take care to place my self
near him, in order to know his Judgment on the present Posture of
Affairs. The last Progress that I made with this Intention, was about
three Months ago, when we had a current Report of the King of
France's
Death. As I foresaw this would produce a new Face of things in
Europe
,
and many curious Speculations in our
British
Coffee-houses, I was very
desirous to learn the Thoughts of our most eminent Politicians on that
Occasion.
That I might begin as near the Fountain Head as possible, I first of all
called in at
St James's,
where I found the whole outward Room in a Buzz
of Politics. The Speculations were but very indifferent towards the
Door, but grew finer as you advanced to the upper end of the Room, and
were so very much improved by a Knot of Theorists, who sat in the inner
Room, within the Steams of the Coffee-Pot, that I there heard the whole
Spanish
Monarchy disposed of, and all the Line of
Bourbon
provided for
in less than a Quarter of an Hour.
I afterwards called in at
Giles's
, where I saw a Board of
French
Gentlemen sitting upon the Life and Death of their
Grand Monarque
. Those
among them who had espoused the
Whig
Interest, very positively affirmed,
that he departed this Life about a Week since, and therefore proceeded
without any further Delay to the Release of their Friends on the
Gallies
, and to their own Re-establishment; but finding they could not
agree among themselves, I proceeded on my intended Progress.
Upon my Arrival at
Jenny Man's
, I saw an alerte young Fellow that cocked
his Hat upon a Friend of his who entered just at the same time with my
self, and accosted him after the following Manner.
Well, Jack, the old
Prig is dead at last. Sharp's the Word. Now or never, Boy. Up to the
Walls of Paris directly.
With several other deep Reflections of the same
Nature.
I met with very little Variation in the Politics between
Charing-Cross
and
Covent-Garden
. And upon my going into
Wills
I found their Discourse
was gone off from the Death of the French King to that of
Monsieur
Boileau, Racine, Corneile,
and several other Poets, whom they regretted
on this Occasion, as Persons who would have obliged the World with very
noble Elegies on the Death of so great a Prince, and so eminent a Patron
of Learning.
At a Coffee-house near the
Temple
, I found a couple of young Gentlemen
engaged very smartly in a Dispute on the Succession to the
Spanish
Monarchy. One of them seemed to have been retained as Advocate for the
Duke of Anjou
, the other for his
Imperial Majesty
. They were both for
regulating the Title to that Kingdom by the Statute Laws of England; but
finding them going out of my Depth, I passed forward to
Paul's
Church-Yard,
where I listen'd with great Attention to a learned Man, who
gave the Company an Account of the deplorable State of
France
during the
Minority of the deceased King. I then turned on my right Hand into
Fish-street
, where the chief Politician of that Quarter, upon hearing
the News, (after having taken a Pipe of Tobacco, and ruminated for some
time) If, says he, the King of
France
is certainly dead, we shall have
Plenty of Mackerell this Season; our Fishery will not be disturbed by
Privateers, as it has been for these ten Years past. He afterwards
considered how the Death of this great Man would affect our Pilchards,
and by several other Remarks infused a general Joy into his whole
Audience.
I afterwards entered a By Coffee-house that stood at the upper end of a
narrow Lane, where I met with a Nonjuror, engaged very warmly with a
Laceman who was the great Support of a neighbouring Conventicle. The
Matter in Debate was, whether the late
French
King was most like
Augustus Cæsar,
or
Nero
. The Controversie was carried on with great Heat
on both Sides, and as each of them looked upon me very frequently during
the Course of their Debate, I was under some Apprehension that they
would appeal to me, and therefore laid down my Penny at the Bar, and
made the best of my way to
Cheapside
.
I here gazed upon the Signs for some time before I found one to my
Purpose. The first Object I met in the Coffeeroom was a Person who
expressed a great Grief for the Death of the
French
King; but upon his
explaining himself, I found his Sorrow did not arise from the Loss of
the Monarch, but for his having sold out of the Bank about three Days
before he heard the News of it: Upon which a Haberdasher, who was the
Oracle of the Coffee-house, and had his Circle of Admirers about him,
called several to witness that he had declared his Opinion above a Week
before, that the
French
King was certainly dead; to which he added, that
considering the late Advices we had received from France, it was
impossible that it could be otherwise. As he was laying these together,
and dictating to his Hearers with great Authority, there came in a
Gentleman from
Garraway's
, who told us that there were several Letters
from
France
just come in, with Advice that the King was in good Health,
and was gone out a Hunting the very Morning the Post came away: Upon
which the Haberdasher stole off his Hat that hung upon a wooden Pegg by
him, and retired to his Shop with great Confusion.
Intelligence put
a Stop to my Travels, which I had prosecuted with
much
Satisfaction; not being a little pleased to hear so many different
Opinions upon so great an Event, and to observe how naturally upon such
a Piece of News every one is apt to consider it with a Regard to his own
particular Interest and Advantage.
L.
great
Contents
|
Friday, June 13, 1712 |
Budgell |
—Non omnia possumus omnes.
Virg.
1.

Nature does nothing in vain:
the Creator of the Universe
has appointed
every thing to a certain Use and Purpose, and determin'd it to a settled
Course and Sphere of Action, from which, if it in the least deviates, it
becomes unfit to answer those Ends for which it was designed. In like
manner it is in the Dispositions of Society, the civil Œconomy is
formed in a Chain as well as the natural; and in either Case the Breach
but of one Link puts the Whole into some Disorder. It is, I think,
pretty plain, that most of the Absurdity and Ridicule we meet with in
the World, is generally owing to the impertinent Affectation of
excelling in Characters Men are not fit for, and for which Nature never
designed them.
Every Man has one or more Qualities which may make him useful both to
himself and others: Nature never fails of pointing them out, and while
the Infant continues under her Guardianship, she brings him on in this
Way; and then offers her self for a Guide in what remains of the
Journey; if he proceeds in that Course, he can hardly miscarry: Nature
makes good her Engagements; for as she never promises what she is not
able to perform, so she never fails of performing what she promises. But
the Misfortune is, Men despise what they may be Masters of, and affect
what they are not fit for; they reckon themselves already possessed of
what their Genius inclined them to, and so bend all their Ambition to
excel in what is out of their Reach: Thus they destroy the Use of their
natural Talents, in the same manner as covetous Men do their Quiet and
Repose; they can enjoy no Satisfaction in what they have, because of the
absurd Inclination they are possessed with for what they have not.
Cleanthes
had good Sense, a great Memory, and a Constitution capable of
the closest Application: In a Word, there was no Profession in which
Cleanthes
might not have made a very good Figure; but this won't
satisfie him, he takes up an unaccountable Fondness for the Character of
a fine Gentleman; all his Thoughts are bent upon this: instead of
attending a Dissection, frequenting the Courts of Justice, or studying
the Fathers,
Cleanthes
reads Plays, dances, dresses, and spends his Time
in drawing-rooms; instead of being a good Lawyer, Divine, or Physician,
Cleanthes
is a downright Coxcomb, and will remain to all that knew him a
contemptible Example of Talents misapplied. It is to this Affectation
the World owes its whole Race of Coxcombs: Nature in her whole Drama
never drew such a Part: she has sometimes made a Fool, but a Coxcomb is
always of a Man's own making, by applying his Talents otherwise than
Nature designed, who ever bears an high Resentment for being put out of
her Course, and never fails of taking her Revenge on those that do so.
Opposing her Tendency in the Application of a Man's Parts, has the same
Success as declining from her Course in the Production of Vegetables; by
the Assistance of Art and an hot Bed, we may possibly extort an
unwilling Plant, or an untimely Sallad; but how weak, how tasteless and
insipid? Just as insipid as the Poetry of
Valerio
:
Valerio
had an
universal Character, was genteel, had Learning, thought justly, spoke
correctly; 'twas believed there was nothing in which
Valerio
did not
excel; and 'twas so far true, that there was but one;
Valerio
had no
Genius for Poetry, yet he's resolved to be a Poet; he writes Verses, and
takes great Pains to convince the Town, that
Valerio
is not that
extraordinary Person he was taken for.
If Men would be content to graft upon Nature, and assist her Operations,
what mighty Effects might we expect?
Tully
would not stand so much alone
in Oratory,
Virgil
in Poetry, or
Cæsar
in War. To build upon Nature, is
laying the Foundation upon a Rock; every thing disposes its self into
Order as it were of Course, and the whole Work is half done as soon as
undertaken.
Cicero's
Genius inclined him to Oratory,
Virgil's
to follow
the Train of the Muses; they piously obeyed the Admonition, and were
rewarded. Had
Virgil
attended the Bar, his modest and ingenious Virtue
would surely have made but a very indifferent Figure; and
Tully's
declamatory Inclination would have been as useless in Poetry. Nature, if
left to her self, leads us on in the best Course, but will do nothing by
Compulsion and Constraint; and if we are not satisfied to go her Way, we
are always the greatest Sufferers by it.
Wherever Nature designs a Production, she always disposes Seeds proper
for it, which are as absolutely necessary to the Formation of any moral
or intellectual Excellence, as they are to the Being and Growth of
Plants; and I know not by what Fate and Folly it is, that Men are taught
not to reckon him equally absurd that will write Verses in Spite of
Nature, with that Gardener that should undertake to raise a Jonquil or
Tulip without the Help of their respective Seeds.
As there is no Good or bad Quality that does not affect both Sexes, so
it is not to be imagined but the fair Sex must have suffered by an
Affectation of this Nature, at least as much as the other: The ill
Effect of it is in none so conspicuous as in the two opposite Characters
of
Cælia
and
Iras
;
Cælia
has all the Charms of Person, together with an
abundant Sweetness of Nature, but wants Wit, and has a very ill Voice;
Iras
is ugly and ungenteel, but has Wit and good Sense: If
Cælia
would
be silent, her Beholders would adore her; if
Iras
would talk, her
Hearers would admire her; but
Cælia's
Tongue runs incessantly, while
Iras
gives her self silent Airs and soft Languors; so that 'tis
difficult to persuade one's self that
Cælia
has Beauty and
Iras
Wit:
Each neglects her own Excellence, and is ambitious of the other's
Character;
Iras
would be thought to have as much Beauty as
Cælia
, and
Cælia
as much Wit as
Iras
.
The great Misfortune of this Affectation is, that Men not only lose a
good Quality, but also contract a bad one: They not only are unfit for
what they were designed, but they assign themselves to what they are not
fit for; and instead of making a very good Figure one Way, make a very
ridiculous one another. If
Semanthe
would have been satisfied with her
natural Complexion, she might still have been celebrated by the Name of
the Olive Beauty
; but
Semanthe
has taken up an Affectation to White and
Red, and is now distinguished by the Character of
the Lady that paints
so well.
In a word, could the World be reformed to the Obedience of that
famed Dictate,
Follow Nature
, which the Oracle of Delphos pronounced to
Cicero when he consulted what Course of Studies he should pursue, we
should see almost every Man as eminent in his proper Sphere as
Tully
was
in his, and should in a very short time find Impertinence and
Affectation banished from among the Women, and Coxcombs and false
Characters from among the Men. For my Part, I could never consider this
preposterous Repugnancy to Nature any otherwise, than not only as the
greatest Folly, but also one of the most heinous Crimes, since it is
a
direct Opposition to the Disposition of Providence
, and (as
Tully
expresses it) like the Sin of the Giants,
an actual Rebellion against
Heaven.
Z.
Continuo has leges æternaque fœdera certis
Imposuit natura locis.
Virg.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 14, 1712 |
Addison |
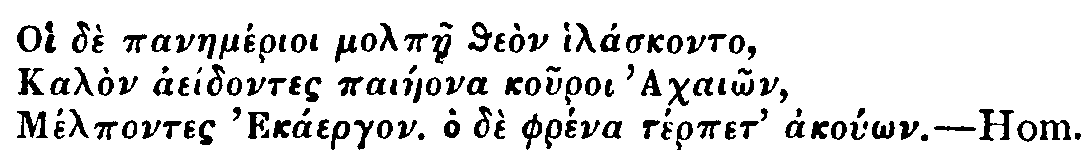
.

I am very sorry to find, by the Opera Bills for this Day, that we are
likely to lose the greatest Performer in Dramatick Musick that is now
living, or that perhaps ever appeared upon a Stage. I
not acquaint
my Reader, that I am speaking of
Signior Nicolini.
The Town is
highly obliged to that Excellent Artist, for having shewn us the
Italian
Musick in its Perfection, as well as for that generous Approbation he
lately gave to an Opera of our own Country, in which the Composer
endeavoured to do Justice to the Beauty of the Words, by following that
Noble Example, which has been set him by the greatest Foreign Masters in
that Art.
I could heartily wish there was the same Application and Endeavours to
cultivate and improve our Church-Musick, as have been lately bestowed on
that of the Stage. Our Composers have one very great Incitement to it:
They are sure to meet with Excellent Words, and, at the same time, a
wonderful Variety of them. There is no Passion that is not finely
expressed in those parts of the inspired Writings, which are proper for
Divine Songs and Anthems.
There is a certain Coldness and Indifference in the Phrases of our
European
Languages, when they are compared with the
Oriental
Forms of
Speech: and it happens very luckily, that the
Hebrew
Idioms run into the
English
Tongue with a particular Grace and Beauty. Our Language has
received innumerable Elegancies and Improvements, from that Infusion of
Hebraisms
, which are derived to it out of the Poetical Passages in
Holy
Writ
. They give a Force and Energy to our Expressions, warm and animate
our Language, and convey our Thoughts in more ardent and intense
Phrases, than any that are to be met with in our own Tongue. There is
something so pathetick in this kind of Diction, that it often sets the
Mind in a Flame, and makes our Hearts burn within us. How cold and dead
does a Prayer appear, that is composed in the most Elegant and Polite
Forms of Speech, which are natural to our Tongue, when it is not
heightened by that Solemnity of Phrase, which may be drawn from the
Sacred Writings. It has been said by some of the Ancients, that if the
Gods were to talk with Men, they would certainly speak in
Plato's
Style;
but I think we may say, with Justice, that when Mortals converse with
their Creator, they cannot do it in so proper a Style as in that of the
Holy Scriptures.
If any one would judge of the Beauties of Poetry that are to be met with
in the Divine Writings, and examine how kindly the
Hebrew
Manners of
Speech mix and incorporate with the
English
Language; after having
perused the
Book of Psalms,
let him read a literal Translation of
Horace
or
Pindar
. He will find in these two last such an Absurdity and
Confusion of Style, with such a Comparative Poverty of Imagination, as
will make him very sensible of what I have been here advancing.
Since we have therefore such a Treasury of Words, so beautiful in
themselves, and so proper for the Airs of Musick, I cannot but wonder
that Persons of Distinction should give so little Attention and
Encouragement to that Kind of Musick, which would have its Foundation in
Reason, and which would improve our Virtue in proportion as it raised
our Delight. The Passions that are excited by ordinary Compositions
generally flow from such silly and absurd Occasions, that a Man is
ashamed to reflect upon them seriously; but the Fear, the Love, the
Sorrow, the Indignation that are awakened in the Mind by Hymns and
Anthems, make the Heart better, and proceed from such Causes as are
altogether reasonable and praise-worthy. Pleasure and Duty go hand in
hand, and the greater our Satisfaction is, the greater is our Religion.
Musick among those who were styled the chosen People was a Religious
Art. The
Songs of Sion
, which we have reason to believe were in high
Repute among the Courts of the
Eastern
Monarchs, were nothing else but
Psalms
and Pieces of
Poetry
that adored or celebrated the Supreme Being.
The greatest Conqueror in this Holy Nation, after the manner of the old
Grecian
Lyricks, did not only compose the Words of his Divine Odes, but
generally set them to Musick himself: After which, his Works, tho' they
were consecrated to the
Tabernacle
, became the National Entertainment,
as well as the Devotion of his People.
The first Original of the Drama was a Religious Worship consisting only
of a Chorus, which was nothing else but an Hymn to a Deity. As Luxury
and Voluptuousness prevailed over Innocence and Religion, this Form of
Worship degenerated into Tragedies; in which however the Chorus so far
remembered its first Office, as to brand every thing that was vicious,
and recommend every thing that was laudable, to intercede with Heaven
for the Innocent, and to implore its Vengeance on the Criminal.
Homer
and
Hesiod
intimate to us how this Art should be applied, when
they represent the Muses as surrounding
Jupiter
, and warbling their
Hymns about his Throne. I might shew from innumerable Passages in
Ancient Writers, not only that Vocal and Instrumental Musick were made
use of in their Religious Worship, but that their most favourite
Diversions were filled with Songs and Hymns to their respective Deities.
Had we frequent Entertainments of this Nature among us, they would not a
little purifie and exalt our Passions, give our Thoughts a proper Turn,
and cherish those Divine Impulses in the Soul, which every one feels
that has not stifled them by sensual and immoderate Pleasures.
Musick, when thus applied, raises noble Hints in the Mind of the Hearer,
and fills it with great Conceptions. It strengthens Devotion, and
advances Praise into Rapture. It lengthens out every Act of Worship, and
produces more lasting and permanent Impressions in the Mind, than those
which accompany any transient Form of Words that are uttered in the
ordinary Method of Religious Worship.
O.
See note on p. 51, vol. i [Volume 1 links:
of
]. He
took leave, June 14, in the Opera of
Antiochus
.]
Contents
|
Monday, June 16, 1712 |
Steele |
Hæc studia Adolescentiam alunt, Senectutem oblectant, secundas res
ornant, adversis solatium et perfugium præbet delectant domi, non
impediunt foris; Pernoctant nobiscum, peregrinantur, rusticantur.
Tull..

The following Letters bear a pleasing Image of the Joys and
Satisfactions of private Life. The first is from a Gentleman to a
Friend, for whom he has a very great Respect, and to whom he
communicates the Satisfaction he takes in Retirement;
other is a
Letter to me, occasioned by an Ode written by my
Lapland
Lover; this
Correspondent is so kind as to translate another of
Scheffer's
Songs
in a very agreeable Manner. I publish them together, that the Young and
Old may find something in the same Paper which may be suitable to their
respective Taste in Solitude; for I know no Fault in the Description of
ardent Desires, provided they are honourable.
Dear Sir,
You have obliged me with a very kind Letter; by which I find you shift
the Scene of your Life from the Town to the Country, and enjoy that
mixt State which wise Men both delight in, and are qualified for.
Methinks most of the Philosophers and Moralists have run too much into
Extreams, in praising entirely either Solitude or publick Life; in the
former Men generally grow useless by too much Rest, and in the latter
are destroyed by too much Precipitation: As Waters lying still,
putrifie and are good for nothing; and running violently on, do but
the more Mischief in their Passage to others, and are swallowed up and
lost the sooner themselves. Those who, like you, can make themselves
useful to all States, should be like gentle Streams, that not only
glide through lonely Vales and Forests amidst the Flocks and
Shepherds, but visit populous Towns in their Course, and are at once
of Ornament and Service to them. But there is another sort of People
who seem designed for Solitude, those I mean who have more to hide
than to shew: As for my own Part, I am one of those of whom
Seneca
says,
Tum Umbratiles sunt, ut putent in turbido esse quicquid in luce
est. Some Men, like Pictures, are fitter for a Corner than a full
Light; and I believe such as have a natural Bent to Solitude, are like
Waters which may be forced into Fountains, and exalted to a great
Height, may make a much nobler Figure, and a much louder Noise, but
after all run more smoothly, equally and plentifully, in their own
natural Course upon the Ground. The Consideration of this would make
me very well contented with the Possession only of that Quiet which
Cowley calls the Companion of Obscurity; but whoever has the Muses too
for his Companions, can never be idle enough to be uneasie. Thus, Sir,
you see I would flatter my self into a good Opinion of my own Way of
Living;
Plutarch just now told me, that 'tis in human Life as in a
Game at Tables, one may wish he had the highest Cast, but if his
Chance be otherwise, he is even to play it as well as he can, and make
the best of it.
I am,
Sir,
Your most obliged,
and most humble Servant.
Mr.
Spectator,
The Town being so well pleased with the fine Picture of artless Love,
which Nature inspired the
Laplander to paint in the Ode you lately
printed; we were in Hopes that the ingenious Translator would have
obliged it with the other also which
Scheffer has given us; but since
he has not, a much inferior Hand has ventured to send you this.
It is a Custom with the Northern Lovers to divert themselves with a
Song, whilst they Journey through the fenny Moors to pay a visit to
their Mistresses. This is addressed by the Lover to his Rain-Deer,
which is the Creature that in that Country supplies the Want of
Horses. The Circumstances which successively present themselves to him
in his Way, are, I believe you will think, naturally interwoven. The
Anxiety of Absence, the Gloominess of the Roads, and his Resolution of
frequenting only those, since those only can carry him to the Object
of his Desires; the Dissatisfaction he expresses even at the greatest
Swiftness with which he is carried, and his joyful Surprize at an
unexpected Sight of his Mistress as she is bathing, seems beautifully
described in the Original.
If all those pretty Images of Rural Nature are lost in the Imitation,
yet possibly you may think fit to let this supply the Place of a long
Letter, when Want of Leisure or Indisposition for Writing will not
permit our being entertained by your own Hand. I propose such a Time,
because tho' it is natural to have a Fondness for what one does ones
self, yet I assure you I would not have any thing of mine displace a
single Line of yours.
| I |
Haste, my Rain-Deer, and let us nimbly go
Our am'rous Journey through this dreery Waste;
Haste, my Rain-Deer! still still thou art too slow;
Impetuous Love demands the Lightning's Haste. |
| II |
Around us far the Rushy Moors are spread:
Soon will the Sun withdraw her chearful Ray:
Darkling and tir'd we shall the Marshes tread,
No Lay unsung to cheat the tedious Way. |
| III |
The wat'ry Length of these unjoyous Moors
Does all the flow'ry Meadow's Pride excel,
Through these I fly to her my Soul adores;
Ye flowery Meadows, empty Pride, Farewel. |
| IV |
Each Moment from the Charmer I'm confin'd,
My Breast is tortur'd with impatient Fires;
Fly, my Rain-Deer, fly swifter than the Wind,
Thy tardy Feet wing with my fierce Desires. |
| V |
Our pleasing Toil will then be soon o'erpaid,
And thou, in Wonder lost, shalt view my Fair,
Admire each Feature of the lovely Maid,
Her artless Charms, her Bloom, her sprightly Air, |
| VI |
But lo! with graceful Motion there she swims,
Gently moving each ambitious Wave;
The crowding Waves transported clasp her Limbs:
When, when, oh when, shall I such Freedoms have! |
| VII |
In vain, you envious Streams, so fast you flow,
To hide her from a Lover's ardent Gaze:
From ev'ry Touch you more transparent grow,
And all reveal'd the beauteous Wanton plays. |
T.
See
and
.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 17, 1712 |
Addison |
—abest facundis Gratia dictis.
Ovid..

Most Foreign Writers who have given any Character of the
English
Nation,
whatever Vices they ascribe to it, allow in general, that the People are
naturally
Modest
. It proceeds perhaps from this our National Virtue,
that our Orators are observed to make use of less Gesture or Action than
those of other Countries. Our Preachers stand stock-still in the Pulpit,
and will not so much as move a Finger to set off the best Sermons in the
World. We meet with the same speaking Statues at our Bars, and in all
publick Places of Debate. Our Words flow from us in a smooth continued
Stream, without those Strainings of the Voice, Motions of the Body, and
Majesty of the Hand, which are so much celebrated in the Orators of
Greece
and
Rome
. We can talk of Life and Death in cold Blood, and keep
our Temper in a Discourse which turns upon every thing that is dear to
us. Though our Zeal breaks out in the finest Tropes and Figures, it is
not able to stir a Limb about us. I have heard it observed more than
once by those who have seen
Italy
, that an untravelled
Englishman
cannot
relish all the Beauties of
Italian
Pictures, because the Postures which
are expressed in them are often such as are peculiar to that Country.
One who has not seen an
Italian
in the Pulpit, will not know what to
make of that noble Gesture in
Raphael's
Picture of
St. Paul
preaching at
Athens
, where the
Apostle
is represented as lifting up both his Arms,
and pouring out the Thunder of his Rhetorick amidst an Audience of Pagan
Philosophers.
It is certain that proper Gestures and vehement Exertions of the Voice
cannot be too much studied by a publick Orator. They are a kind of
Comment to what he utters, and enforce every thing he says, with weak
Hearers, better than the strongest Argument he can make use of. They
keep the Audience awake, and fix their Attention to what is delivered to
them, at the same time that they shew the Speaker is in earnest, and
affected himself with what he so passionately recommends to others.
Violent Gesture and Vociferation naturally shake the Hearts of the
Ignorant, and fill them with a kind of Religious Horror. Nothing is more
frequent than to see Women weep and tremble at the Sight of a moving
Preacher, though he is placed quite out of their Hearing; as in
England
we very frequently see People lulled asleep with solid and elaborate
Discourses of Piety, who would be warmed and transported out of
themselves by the Bellowings and Distortions of Enthusiasm.
If Nonsense, when accompanied with such an Emotion of Voice and Body,
has such an Influence on Men's Minds, what might we not expect from many
of those Admirable Discourses which are printed in our Tongue, were they
delivered with a becoming Fervour, and with the most agreeable Graces of
Voice and Gesture?
We are told that the great
Latin
Orator very much impaired his Health by
this
laterum contentio,
this Vehemence of Action, with which he used to
deliver himself. The
Greek
Orator was likewise so very Famous for this
Particular in Rhetorick, that one of his Antagonists, whom he had
banished from
Athens
, reading over the Oration which had procured his
Banishment, and seeing his Friends admire it, could not forbear asking
them,
if they were so much affected by the bare reading of it, how much
more they would have been alarmed, had they heard him actually throwing
out such a Storm of Eloquence?
How cold and dead a Figure in Comparison of these two great Men, does an
Orator often make at the
British
Bar, holding up his Head with the most
insipid Serenity, and streaking the sides of a long Wigg that reaches
down to his Middle? The truth of it is, there is often nothing more
ridiculous than the Gestures of an
English
Speaker; you see some of them
running their Hands into their Pockets as far as ever they can thrust
them, and others looking with great Attention on a piece of Paper that
has nothing written in it; you may see many a smart Rhetorician turning
his Hat in his Hands, moulding it into several different Cocks,
examining sometimes the Lining of it, and sometimes the Button, during
the whole course of his Harangue. A deaf Man would think he was
Cheap'ning a Beaver, when perhaps he is talking of the Fate of the
British
Nation. I remember, when I was a young Man, and used to frequent
Westminster-Hall
, there was a Counsellor who never pleaded without a
Piece of Pack-thread in his Hand, which he used to twist about a Thumb,
or a Finger, all the while he was speaking: The Waggs of those Days used
to call it
the Thread of his Discourse
, for he was not able to utter a
Word without it. One of his Clients, who was more merry than wise, stole
it from him one Day in the midst of his Pleading; but he had better have
let it alone, for he lost his Cause by his Jest.
I have all along acknowledged my self to be a Dumb Man, and therefore
may be thought a very improper Person to give Rules for Oratory; but I
believe every one will agree with me in this, that we ought either to
lay aside all kinds of Gesture, (which seems to be very suitable to the
Genius of our Nation) or at least to make use of such only as are
graceful and expressive.
O.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 18, 1712 |
Pope |
Decet affectus animi neque se nimium erigere, nec subjacere
serviliter.
Tull..

Mr.
Spectator,
I have always been a very great Lover of your Speculations, as well in
Regard to the Subject, as to your Manner of Treating it. Human Nature
I always thought the most useful Object of human Reason, and to make
the Consideration of it pleasant and entertaining, I always thought
the best Employment of human Wit: Other Parts of Philosophy may
perhaps make us wiser, but this not only answers that End, but makes
us better too. Hence it was that the Oracle pronounced
Socrates the
wisest of all Men living, because he judiciously made Choice of human
Nature for the Object of his Thoughts; an Enquiry into which as much
exceeds all other Learning, as it is of more Consequence to adjust the
true Nature and Measures of Right and Wrong, than to settle the
Distance of the Planets, and compute the Times of their
Circumvolutions.
One good Effect that will immediately arise from a near Observation of
human Nature, is, that we shall cease to wonder at those Actions which
Men are used to reckon wholly unaccountable; for as nothing is
produced without a Cause, so by observing the Nature and Course of the
Passions, we shall be able to trace every Action from its first
Conception to its Death; We shall no more admire at the Proceedings of
Catiline or
Tiberius, when we know the one was actuated by a cruel
Jealousie, the other by a furious Ambition; for the Actions of Men
follow their Passions as naturally as Light does Heat, or as any other
Effect flows from its Cause; Reason must be employed in adjusting the
Passions, but they must ever remain the Principles of Action.
The strange and absurd Variety that is so apparent in Men's Actions,
shews plainly they can never proceed immediately from Reason; so pure
a Fountain emits no such troubled Waters: They must necessarily arise
from the Passions, which are to the Mind as the Winds to a Ship, they
only can move it, and they too often destroy it; if fair and gentle,
they guide it into the Harbour; if contrary and furious, they overset
it in the Waves: In the same manner is the Mind assisted or endangered
by the Passions; Reason must then take the Place of Pilot, and can
never fail of securing her Charge if she be not wanting to her self:
The Strength of the Passions will never be accepted as an Excuse for
complying with them, they were designed for Subjection, and if a Man
suffers them to get the upper Hand, he then betrays the Liberty of his
own Soul.
As Nature has framed the several Species of Beings as it were in a
Chain, so Man seems to be placed as the middle Link between Angels and
Brutes: Hence he participates both of Flesh and Spirit by an admirable
Tie, which in him occasions perpetual War of Passions; and as a Man
inclines to the angelick or brute Part of his Constitution, he is then
denominated good or bad, virtuous or wicked; if Love, Mercy, and
Good-nature prevail, they speak him of the Angel; if Hatred, Cruelty,
and Envy predominate, they declare his Kindred to the Brute. Hence it
was that some of the Ancients imagined, that as Men in this Life
inclined more to the Angel or Brute, so after their Death they should
transmigrate into the one or the other: and it would be no unpleasant
Notion, to consider the several Species of Brutes, into which we may
imagine that Tyrants, Misers, the Proud, Malicious, and Ill-natured
might be changed.
As a Consequence of this Original, all Passions are in all Men, but
all appear not in all; Constitution, Education, Custom of the Country,
Reason, and the like Causes, may improve or abate the Strength of
them, but still the Seeds remain, which are ever ready to sprout forth
upon the least Encouragement. I have heard a Story of a good religious
Man, who, having been bred with the Milk of a Goat, was very modest in
Publick by a careful Reflection he made on his Actions, but he
frequently had an Hour in Secret, wherein he had his Frisks and
Capers; and if we had an Opportunity of examining the Retirement of
the strictest Philosophers, no doubt but we should find perpetual
Returns of those Passions they so artfully conceal from the Publick. I
remember Matchiavel observes, that every State should entertain a
perpetual jealousie of its Neighbours, that so it should never be
unprovided when an Emergency happens
1; in like manner should the
Reason be perpetually on its Guard against the Passions, and never
suffer them to carry on any Design that may be destructive of its
Security; yet at the same Time it must be careful, that it don't so
far break their Strength as to render them contemptible, and
consequently it self unguarded.
The Understanding being of its self too slow and lazy to exert it self
into Action, its necessary it should be put in Motion by the gentle
Gales of the Passions, which may preserve it from stagnating and
Corruption; for they are as necessary to the Health of the Mind, as
the Circulation of the animal Spirits is to the Health of the Body;
they keep it in Life, and Strength, and Vigour; nor is it possible for
the Mind to perform its Offices without their Assistance: These
Motions are given us with our Being, they are little Spirits that are
born and dye with us; to some they are mild, easie, and gentle, to
others wayward and unruly, yet never too strong for the Reins of
Reason and the Guidance of Judgment.
We may generally observe a pretty nice Proportion between the Strength
of Reason and Passion; the greatest Genius's have commonly the
strongest Affections, as on the other hand, the weaker Understandings
have generally the weaker Passions; and 'tis fit the Fury of the
Coursers should not be too great for the Strength of the Charioteer.
Young Men whose Passions are not a little unruly, give small Hopes of
their ever being considerable; the Fire of Youth will of course abate,
and is a Fault, if it be a Fault, that mends every Day; but surely
unless a Man has Fire in Youth, he can hardly have Warmth in Old Age.
We must therefore be very cautious, lest while we think to regulate
the Passions, we should quite extinguish them, which is putting out
the Light of the Soul: for to be without Passion, or to be hurried
away with it, makes a Man equally blind. The extraordinary Severity
used in most of our Schools has this fatal Effect, it breaks the
Spring of the Mind, and most certainly destroys more good Genius's
than it can possibly improve. And surely 'tis a mighty Mistake that
the Passions should be so intirely subdued; for little Irregularities
are sometimes not only to be borne with, but to be cultivated too,
since they are frequently attended with the greatest Perfections. All
great Geniuss have Faults mixed with their Virtues, and resemble the
flaming Bush which has Thorns amongst Lights.
Since, therefore the Passions are the Principles of human Actions, we
must endeavour to manage them so as to retain their Vigour, yet keep
them under strict Command; we must govern them rather like free
Subjects than Slaves, lest while we intend to make them obedient, they
become abject, and unfit for those great Purposes to which they were
designed. For my Part I must confess, I could never have any Regard to
that Sect of Philosophers, who so much insisted upon an absolute
Indifference and Vacancy from all Passion; for it seems to me a Thing
very inconsistent for a Man to divest himself of Humanity, in order to
acquire Tranquility of Mind, and to eradicate the very Principles of
Action, because its possible they may produce ill Effects.
I am,
Sir,
Your Affectionate Admirer,
T. B.
Z.
The Prince
, ch. xlv, at close.
Contents
|
Thursday, June 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Musæo contingere cuncta lepore.
Lucr..

Gratian
very often recommends the
Fine Taste,
as the utmost
Perfection of an accomplished Man. As this Word arises very often in
Conversation, I shall endeavour to give some Account of it, and to lay
down Rules how we may know whether we are possessed of it, and how we
may acquire that fine Taste of Writing, which is so much talked of among
the Polite World.
Most Languages make use of this Metaphor, to express that Faculty of the
Mind, which distinguishes all the most concealed Faults and nicest
Perfections in Writing. We may be sure this Metaphor would not have been
so general in all Tongues, had there not been a very great Conformity
between that Mental Taste, which is the Subject of this Paper, and that
Sensitive Taste which gives us a Relish of every different Flavour that
affects the Palate. Accordingly we find, there are as many Degrees of
Refinement in the intellectual Faculty, as in the Sense, which is marked
out by this common Denomination.
I knew a Person who possessed the one in so great a Perfection, that
after having tasted ten different Kinds of Tea, he would distinguish,
without seeing the Colour of it, the particular Sort which was offered
him; and not only so, but any two Sorts of them that were mixt together
in an equal Proportion; nay he has carried the Experiment so far, as
upon tasting the Composition of three different Sorts, to name the
Parcels from whence the three several Ingredients were taken. A Man of a
fine Taste in Writing will discern, after the same manner, not only the
general Beauties and Imperfections of an Author, but discover the
several Ways of thinking and expressing himself, which diversify him
from all other Authors, with the several Foreign Infusions of Thought
and Language, and the particular Authors from whom they were borrowed.
After having thus far explained what is generally meant by a fine Taste
in Writing, and shewn the Propriety of the Metaphor which is used on
this Occasion, I think I may define it to be that Faculty of the Soul,
which discerns the Beauties of an Author with Pleasure, and the
Imperfections with Dislike. If a Man would know whether he is possessed
of this Faculty, I would have him read over the celebrated Works of
Antiquity, which have stood the Test of so many different Ages and
Countries, or those Works among the Moderns which have the Sanction of
the Politer Part of our Contemporaries. If upon the Perusal of such
Writings he does not find himself delighted in an extraordinary Manner,
or if, upon reading the admired Passages in such Authors, he finds a
Coldness and Indifference in his Thoughts, he ought to conclude, not (as
is too usual among tasteless Readers) that the Author wants those
Perfections which have been admired in him, but that he himself wants
the Faculty of discovering them.
He should, in the second Place, be very careful to observe, whether he
tastes the distinguishing Perfections, or, if I may be allowed to call
them so, the Specifick Qualities of the Author whom he peruses; whether
he is particularly pleased with
Livy
for his Manner of telling a Story,
with
Sallust
for his entering into those internal Principles of Action
which arise from the Characters and Manners of the Persons he describes,
or with
Tacitus
for his displaying those outward Motives of Safety and
Interest, which give Birth to the whole Series of Transactions which he
relates.
He may likewise consider, how differently he is affected by the same
Thought, which presents it self in a great Writer, from what he is when
he finds it delivered by a Person of an ordinary Genius. For there is as
much Difference in apprehending a Thought cloathed in
Cicero's
Language,
and that of a common Author, as in seeing an Object by the Light of a
Taper, or by the Light of the Sun.
It is very difficult to lay down Rules for the Acquirement of such a
Taste as that I am here speaking of. The Faculty must in some degree be
born with us, and it very often happens, that those who have other
Qualities in Perfection are wholly void of this. One of the most eminent
Mathematicians of the Age has assured me, that the greatest Pleasure he
took in reading
Virgil
, was in examining
Æneas
his Voyage by the Map; as
I question not but many a Modern Compiler of History, would be delighted
with little more in that Divine Author, than in the bare Matters of
Fact.
But notwithstanding this Faculty must in some measure be born with us,
there are several Methods for Cultivating and Improving it, and without
which it will be very uncertain, and of little use to the Person that
possesses it. The most natural Method for this Purpose is to be
conversant among the Writings of the most Polite Authors. A Man who has
any Relish for fine Writing, either discovers new Beauties, or receives
stronger Impressions from the Masterly Strokes of a great Author every
time he peruses him; Besides that he naturally wears himself into the
same manner of Speaking and Thinking.
Conversation with Men of a Polite Genius is another Method for improving
our Natural Taste. It is impossible for a Man of the greatest Parts to
consider anything in its whole Extent, and in all its Variety of Lights.
Every Man, besides those General Observations which are to be made upon
an Author, forms several Reflections that are peculiar to his own Manner
of Thinking; so that Conversation will naturally furnish us with Hints
which we did not attend to, and make us enjoy other Men's Parts and
Reflections as well as our own. This is the best Reason I can give for
the Observation which several have made, that Men of great Genius in the
same way of Writing seldom rise up singly, but at certain Periods of
Time appear together, and in a Body; as they did at
Rome
in the Reign of
Augustus
, and in
Greece
about the Age of
Socrates
. I cannot think that
Corneille, Racine, Moliere, Boileau, la Fontaine, Bruyere, Bossu
, or the
Daciers
, would have written so well as they have done, had they not been
Friends and Contemporaries.
It is likewise necessary for a Man who would form to himself a finished
Taste of good Writing, to be well versed in the Works of the best
Criticks both Ancient and Modern. I must confess that I could wish there
were Authors of this kind, who beside the Mechanical Rules which a Man
of very little Taste may discourse upon, would enter into the very
Spirit and Soul of fine Writing, and shew us the several Sources of that
Pleasure which rises in the Mind upon the Perusal of a noble Work. Thus
although in Poetry it be absolutely necessary that the Unities of Time,
Place and Action, with other Points of the same Nature, should be
thoroughly explained and understood; there is still something more
essential to the Art, something that elevates and astonishes the Fancy,
and gives a Greatness of Mind to the Reader, which few of the Criticks
besides
Longinus
have considered.
Our general Taste in
England
is for Epigram, Turns of Wit, and forced
Conceits, which have no manner of Influence, either for the bettering or
enlarging the Mind of him who reads them, and have been carefully
avoided by the greatest Writers, both among the Ancients and Moderns. I
have endeavoured in several of my Speculations to banish this
Gothic
Taste, which has taken Possession among us. I entertained the Town, for
a Week together, with an
Essay upon Wit,
in which I endeavoured to
detect several of those false Kinds which have been admired in the
different Ages of the World; and at the same time to shew wherein the
Nature of true Wit consists. I afterwards gave an Instance of the great
Force which lyes in a natural Simplicity of Thought to affect the Mind
of the Reader, from such vulgar Pieces as have little else besides this
single Qualification to recommend them. I have likewise examined the
Works of the greatest Poet which our Nation or perhaps any other has
produced, and particularized most of those rational and manly Beauties
which give a Value to that Divine Work. I shall next Saturday enter upon
an Essay on the Pleasures of the Imagination, which, though it shall
consider that Subject at large, will perhaps suggest to the Reader what
it is that gives a Beauty to many Passages of the finest Writers both in
Prose and Verse. As an Undertaking of this Nature is entirely new, I
question not but it will be received with Candour.
O.
See note on p. 620, ante [
of
]. This fine taste was the
cultismo
the taste for false concepts, which Addison condemns.
Contents
|
Friday, June 20, 1712 |
Tickell |
Dum foris sunt, nihil videtur Mundius,
Nec magis compositum quidquam, nec magis elegans:
Quæ, cum amatore suo cum coenant, Liguriunt,
Harum videre ingluviem, sordes, inopiam:
Quam inhonestæ solæ sint domi, atque avidæ cibi,
Quo pacto ex Jure Hesterno panem atrum varent.
Nosse omnia hæc, salus est adolescentulis.
Tert.

Will. Honeycomb
, who disguises his present Decay by visiting the Wenches
of the Town only by Way of Humour, told us, that the last rainy Night he
with Sir
Roger De Coverly
was driven into the Temple Cloister, whither
had escaped also a Lady most exactly dressed from Head to Foot.
Will
,
made no Scruple to acquaint us, that she saluted him very familiarly by
his Name, and turning immediately to the Knight, she said, she supposed
that was his good Friend, Sir
Roger De Coverly
: Upon which nothing less
could follow than Sir
Roger's
Approach to Salutation, with,
Madam the
same at your Service
. She was dressed in a black Tabby Mantua and
Petticoat, without Ribbons; her Linnen striped Muslin, and in the whole
in an agreeable Second-Mourning; decent Dresses being often affected by
the Creatures of the Town, at once consulting Cheapness and the
Pretensions to Modesty. She went on with a familiar easie Air.
Your
Friend, Mr. Honeycomb, is a little surprized to see a Woman here alone
and unattended; but I dismissed my Coach at the Gate, and tripped it
down to my Council's Chambers, for Lawyer's Fees take up too much of a
small disputed Joynture to admit any other Expence but meer Necessaries.
Mr.
Honeycomb
begged they might have the Honour of setting her down, for
Sir
Roger's
Servant was gone to call a Coach. In the Interim the Footman
returned, with no Coach to be had; and there appeared nothing to be done
but trusting herself with Mr.
Honeycomb
and his Friend to wait at the
Tavern at the Gate for a Coach, or to be subjected to all the
Impertinence she must meet with in that publick Place. Mr.
Honeycomb
being a Man of Honour determined the Choice of the first, and Sir
Roger
,
as the better Man, took the Lady by the Hand, leading through all the
Shower, covering her with his Hat, and gallanting a familiar
Acquaintance through Rows of young Fellows, who winked at Sukey in the
State she marched off,
Will. Honeycomb
bringing up the Rear.
Much Importunity prevailed upon the Fair one to admit of a Collation,
where, after declaring she had no Stomach, and eaten a Couple of
Chickens, devoured a Trusse of Sallet, and drunk a full Bottle to her
Share, she sung
the Old Man's Wish
to Sir
Roger
. The Knight left the
Room for some Time after Supper, and writ the following Billet, which he
conveyed to Sukey, and Sukey to her Friend
Will. Honeycomb. Will
. has
given it to Sir
Andrew Freeport
, who read it last Night to the Club.
Madam,
I am not so meer a Country-Gentleman, but I can guess at the
Law-Business you had at the Temple. If you would go down to the
Country and leave off all your Vanities but your Singing, let me know
at my Lodgings in Bow-street Covent-Garden, and you shall be
encouraged by
Your humble Servant,
Roger De Coverly.
My good Friend could not well stand the Raillery which was rising upon
him; but to put a Stop to it I deliverd
Will. Honeycomb
the following
Letter, and desired him to read it to the Board.
Mr. Spectator,
Having seen a Translation of one of the Chapters in the Canticles into
English Verse inserted among your late Papers, I have ventured to send
you the 7th Chapter of the Proverbs in a poetical Dress. If you think
it worthy appearing among your Speculations, it will be a sufficient
Reward for the Trouble of
Your constant Reader,
A. B.
My Son, th' Instruction that my Words impart,
Grave on the Living Tablet of thy Heart;
And all the wholesome Precepts that I give,
Observe with strictest Reverence, and live.
Let all thy Homage be to Wisdom paid,
Seek her Protection and implore her Aid;
That she may keep thy Soul from Harm secure,
And turn thy Footsteps from the Harlot's Door,
Who with curs'd Charms lures the Unwary in,
And sooths with Flattery their Souls to Sin.
Once from my Window as I cast mine Eye
On those that pass'd in giddy Numbers by,
A Youth among the foolish Youths I spy'd,
Who took not sacred Wisdom for his Guide.
Just as the Sun withdrew his cooler Light,
And Evening soft led on the Shades of Night,
He stole in covert Twilight to his Fate,
And pass'd the Corner near the Harlot's Gate
When, lo, a Woman comes!—
Loose her Attire, and such her glaring Dress,
As aptly did the Harlot's Mind express:
Subtle she is, and practisd in the Arts,
By which the Wanton conquer heedless Hearts:
Stubborn and loud she is; she hates her Home,
Varying her Place and Form; she loves to roam;
Now she's within, now in the Street does stray;
Now at each Corner stands, and waits her Prey.
The Youth she seiz'd; and laying now aside
All Modesty, the Female's justest Pride,
She said, with an Embrace, Here at my House
Peace-offerings are, this Day I paid my Vows.
I therefore came abroad to meet my Dear,
And, Lo, in Happy Hour I find thee here.
My Chamber I've adornd, and o'er my Bed
Are cov'rings of the richest Tapstry spread,
With Linnen it is deck'd from Egypt brought,
And Carvings by the Curious Artist wrought,
It wants no Glad Perfume Arabia yields
In all her Citron Groves, and spicy Fields;
Here all her store of richest Odours meets,
Ill lay thee in a Wilderness of Sweets.
Whatever to the Sense can grateful be
I have collected there—I want but Thee.
My Husband's gone a Journey far away, }
Much Gold he took abroad, and long will stay, }
He nam'd for his return a distant Day. }
Upon her Tongue did such smooth Mischief dwell,
And from her Lips such welcome Flatt'ry fell,
Th' unguarded Youth, in Silken Fetters ty'd,
Resign'd his Reason, and with Ease comply'd.
Thus does the Ox to his own Slaughter go,
And thus is senseless of th' impending Blow.
Thus flies the simple Bird into the Snare,
That skilful Fowlers for his Life prepare.
But let my Sons attend, Attend may they
Whom Youthful Vigour may to Sin betray;
Let them false Charmers fly, and guard their Hearts
Against the wily Wanton's pleasing Arts,
With Care direct their Steps, nor turn astray,
To tread the Paths of her deceitful Way;
Lest they too late of Her fell Power complain,
And fall, where many mightier have been Slain.
T.
Contents
|
Saturday, June 21, 1712 |
Addison |
Avia Pieridum peragro loca, nullius ante
Trita solo; juvat integros accedere fonteis;
Atque haurire:—
Lucr.

Our Sight is the most perfect and most delightful of all our Senses. It
fills the Mind with the largest Variety of Ideas, converses with its
Objects at the greatest Distance, and continues the longest in Action
without being tired or satiated with its proper Enjoyments. The Sense of
Feeling can indeed give us a Notion of Extension, Shape, and all other
Ideas that enter at the Eye, except Colours; but at the same time it is
very much streightned and confined in its Operations, to the number,
bulk, and distance of its particular Objects. Our Sight seems designed
to supply all these Defects, and may be considered as a more delicate
and diffusive kind of Touch, that spreads it self over an infinite
Multitude of Bodies, comprehends the largest Figures, and brings into
our reach some of the most remote Parts of the Universe.
It is this Sense which furnishes the Imagination with its Ideas; so that
by the Pleasures of the Imagination or Fancy (which I shall use
promiscuously) I here mean such as arise from visible Objects, either
when we have them actually in our View, or when we call up their Ideas
in our Minds by Paintings, Statues, Descriptions, or any the like
Occasion. We cannot indeed have a single Image in the Fancy that did not
make its first Entrance through the Sight; but we have the Power of
retaining, altering and compounding those Images, which we have once
received, into all the varieties of Picture and Vision that are most
agreeable to the Imagination; for by this Faculty a Man in a Dungeon is
capable of entertaining himself with Scenes and Landskips more beautiful
than any that can be found in the whole Compass of Nature.
There are few Words in the English Language which are employed in a more
loose and uncircumscribed Sense than those of the Fancy and the
Imagination. I therefore thought it necessary to fix and determine the
Notion of these two Words, as I intend to make use of them in the Thread
of my following Speculations, that the Reader may conceive rightly what
is the Subject which I proceed upon. I must therefore desire him to
remember, that by the Pleasures of the Imagination, I mean only such
Pleasures as arise originally from Sight, and that I divide these
Pleasures into two Kinds: My Design being first of all to Discourse of
those Primary Pleasures of the Imagination,
entirely proceed from
such Objects as are
before our
Eye
s
; and in the next place to
speak of those Secondary Pleasures of the Imagination which flow from
the Ideas of visible Objects, when the Objects are not actually before
the Eye, but are called up into our Memories, or formed into agreeable
Visions of Things that are either Absent or Fictitious.
The Pleasures of the Imagination, taken in the full Extent, are not so
gross as those of Sense, nor so refined as those of the Understanding.
The last are, indeed, more preferable, because they are founded on some
new Knowledge or Improvement in the Mind of Man; yet it must be confest,
that those of the Imagination are as great and as transporting as the
other. A beautiful Prospect delights the Soul, as much as a
Demonstration; and a Description in
Homer
has charmed more Readers than
a Chapter in
Aristotle
. Besides, the Pleasures of the Imagination have
this Advantage, above those of the Understanding, that they are more
obvious, and more easie to be acquired. It is but opening the Eye, and
the Scene enters. The Colours paint themselves on the Fancy, with very
little Attention of Thought or Application of Mind in the Beholder. We
are struck, we know not how, with the Symmetry of any thing we see, and
immediately assent to the Beauty of an Object, without enquiring into
the particular Causes and Occasions of it.
A Man of a Polite Imagination is let into a great many Pleasures, that
the Vulgar are not capable of receiving. He can converse with a Picture,
and find an agreeable Companion in a Statue. He meets with a secret
Refreshment in a Description, and often feels a greater Satisfaction in
the Prospect of Fields and Meadows, than another does in the Possession.
It gives him, indeed, a kind of Property in every thing he sees, and
makes the most rude uncultivated Parts of Nature administer to his
Pleasures: So that he looks upon the World, as it were in another Light,
and discovers in it a Multitude of Charms, that conceal themselves from
the generality of Mankind.
There are, indeed, but very few who know how to be idle and innocent, or
have a Relish of any Pleasures that are not Criminal; every Diversion
they take is at the Expence of some one Virtue or another, and their
very first Step out of Business is into Vice or Folly. A Man should
endeavour, therefore, to make the Sphere of his innocent Pleasures as
wide as possible, that he may retire into them with Safety, and find in
them such a Satisfaction as a wise Man would not blush to take. Of this
Nature are those of the Imagination, which do not require such a Bent of
Thought as is necessary to our more serious Employments, nor, at the
same time, suffer the Mind to sink into that Negligence and Remissness,
which are apt to accompany our more sensual Delights, but, like a gentle
Exercise to the Faculties, awaken them from Sloth and Idleness, without
putting them upon any Labour or Difficulty.
We might here add, that the Pleasures of the Fancy are more conducive to
Health, than those of the Understanding, which are worked out by Dint of
Thinking, and attended with too violent a Labour of the Brain.
Delightful Scenes, whether in Nature, Painting, or Poetry, have a kindly
Influence on the Body, as well as the Mind, and not only serve to clear
and brighten the Imagination, but are able to disperse Grief and
Melancholy, and to set the Animal Spirits in pleasing and agreeable
Motions. For this Reason
Sir Francis Bacon
, in his
Essay upon Health
,
has not thought it improper to prescribe to his Reader a Poem or a
Prospect, where he particularly dissuades him from knotty and subtile
Disquisitions, and advises him to pursue Studies that fill the Mind with
splendid and illustrious Objects, as Histories, Fables, and
Contemplations of Nature.
I have in this Paper, by way of Introduction, settled the Notion of
those Pleasures of the Imagination which are the Subject of my present
Undertaking, and endeavoured, by several Considerations, to recommend to
my Reader the Pursuit of those Pleasures. I
, in my next Paper,
examine the several Sources from whence these Pleasures are derived
.
O.
present to the
From a MS. Note-book of Addison's, met with in 1858, Mr. J.
Dykes Campbell printed at Glasgow, in 1864, 250 copies of some portions
of the first draught of these papers on Imagination with the
Essay on
Jealousy
([Volume 1 link:
]) and that on Fame (
). The MS. was an old calf
bound 8vo volume obtained from a dealer. There were about 31 pages
written on one side of each leaf in a beautiful print-like hand, which
contained the Essays in their first state. Passages were added by
Addison in his ordinary handwriting upon the blank pages opposite to
this carefully-written text, and there are pieces in a third
hand-writing which neither the keeper of the MSS. Department of the
British Museum nor the Librarian of the Bodleian could identify. The
insertions in this third hand form part of the paper as finally
published. Thus in the paper on Jealousy ([Volume 1 link:
]) it wrote the English
verse translation added to the quotation from Horace's
Ode
I. xiii. The
MS. shows with how much care Addison revised and corrected the first
draught of his papers, especially where, as in the series of eleven upon
Imagination
here commenced, he meant to put out all his strength. In
Blair's
Rhetoric
four Lectures (20-23) are given to a critical
Examination of the Style of Mr. Addison
in Nos.
,
,
, and
of the
Spectator
. Akenside's poem on the
Pleasures of the Imagination
,
published in 1744, when he was 23 years old, was suggested by these
papers. Many disquisitions upon Taste were written towards the close of
the last century. They formed a new province in literature, of which
Addison here appears as the founder and first lawgiver.
Contents
|
Monday, June 23, 1712 |
Addison |
—Divisum sic breve fiet Opus.
Mart.

I shall first consider those Pleasures of the Imagination, which arise
from the actual View and Survey of outward Objects: And these, I think,
all proceed from the Sight of what is Great, Uncommon, or Beautiful.
There may, indeed, be something so terrible or offensive, that the
Horror or Loathsomeness of an Object may over-bear the Pleasure which
results from its Greatness, Novelty, or Beauty; but still there will be
such a Mixture of Delight in the very Disgust it gives us, as any of
these three Qualifications are most conspicuous and prevailing.
By Greatness, I do not only mean the Bulk of any single Object, but the
Largeness of a whole View, considered as one entire Piece. Such are the
Prospects of an open Champain Country, a vast uncultivated Desart, of
huge Heaps of Mountains, high Rocks and Precipices, or a wide Expanse of
Waters, where we are not struck with the Novelty or Beauty of the Sight,
but with that rude kind of Magnificence which appears in many of these
stupendous Works of Nature. Our Imagination loves to be filled with an
Object, or to grasp at any thing that is too big for its Capacity. We
are flung into a pleasing Astonishment at such unbounded Views, and feel
a delightful Stillness and Amazement in the Soul at the Apprehension[s]
of them. The Mind of Man naturally hates every thing that looks like a
Restraint upon it, and is apt to fancy it self under a sort of
Confinement, when the Sight is pent up in a narrow Compass, and shortned
on every side by the Neighbourhood of Walls or Mountains. On the
contrary, a spacious Horizon is an Image of Liberty, where the Eye has
Room to range abroad, to expatiate at large on the Immensity of its
Views, and to lose it self amidst the Variety of Objects that offer
themselves to its Observation. Such wide and undetermined Prospects are
as pleasing to the Fancy, as the Speculations of Eternity or Infinitude
are to the Understanding. But if there be a Beauty or Uncommonness
joined with this Grandeur, as in a troubled Ocean, a Heaven adorned with
Stars and Meteors, or a spacious Landskip cut out into Rivers, Woods,
Rocks, and Meadows, the Pleasure still grows upon us, as it rises from
more than a single Principle.
Every thing that is new or uncommon raises a Pleasure in the
Imagination, because it fills the Soul with an agreeable Surprize,
gratifies its Curiosity, and gives it an Idea of which it was not before
possest. We are indeed so often conversant with one Set of Objects, and
tired out with so many repeated Shows of the same Things, that whatever
is new or uncommon contributes a little to vary human Life, and to
divert our Minds, for a while, with the Strangeness of its Appearance:
It serves us for a kind of Refreshment, and takes off from that Satiety
we are apt to complain of in our usual and ordinary Entertainments. It
is this that bestows Charms on a Monster,
makes even the
Imperfections of Nature
please
us. It is this that recommends
Variety, where the Mind is every Instant called off to something new,
and the Attention not suffered to dwell too long, and waste it self on
any particular Object. It is this, likewise, that improves what is great
or beautiful, and make it afford the Mind a double Entertainment.
Groves, Fields, and Meadows, are at any Season of the Year pleasant to
look upon, but never so much as in the Opening of the Spring, when they
are all new and fresh, with their first Gloss upon them, and not yet too
much accustomed and familiar to the Eye. For this Reason there is
nothing that more enlivens a Prospect than Rivers, Jetteaus, or Falls of
Water, where the Scene is perpetually shifting, and entertaining the
Sight every Moment with something that is new. We are quickly tired with
looking upon Hills and Vallies, where every thing continues fixed and
settled in the same Place and Posture, but find our Thoughts a little
agitated and relieved at the Sight of such Objects as are ever in
Motion, and sliding away from beneath the Eye of the Beholder.
But there is nothing that makes its Way more directly to the Soul than
Beauty, which immediately diffuses a secret Satisfaction and Complacency
through the Imagination, and gives a Finishing to any thing that is
Great or Uncommon. The very first Discovery of it strikes the Mind with
an inward Joy, and spreads a Chearfulness and Delight through all its
Faculties. There is not perhaps any real Beauty or Deformity more in one
Piece of Matter than another, because we might have been so made, that
whatsoever now appears loathsome to us, might have shewn it self
agreeable; but we find by Experience, that there are several
Modifications of Matter which the Mind, without any previous
Consideration, pronounces at first sight Beautiful or Deformed. Thus we
see that every different Species of sensible Creatures has its different
Notions of Beauty, and that each of them is most affected with the
Beauties of its own Kind. This is no where more remarkable than in Birds
of the same Shape and Proportion, where we often see the Male determined
in his Courtship by the single Grain or Tincture of a Feather, and never
discovering any Charms but in the Colour of its Species.
Scit thalamo servare fidem, sanctasque veretur
Connubii leges, non illum in pectore candor
Sollicitat niveus; neque pravum accendit amorem
Splendida Lanugo, vel honesta in vertice crista,
Purpureusve nitor pennarum; ast agmina latè
Fœminea explorat cautus, maculasque requirit
Cognatas, paribusque interlita corpora guttis:
Ni faceret, pictis sylvam circum undique monstris
Confusam aspiceres vulgò, partusque biformes,
Et genus ambiguum, et Veneris monumenta nefandæ.
Hinc merula in nigro se oblectat nigra marito,
Hinc socium lasciva petit Philomela canorum,
Agnoscitque pares sonitus, hinc Noctua tetram
Canitiem alarum, et glaucos miratur ocellos.
Nempe sibi semper constat, crescitque quotannis
Lucida progenies, castos confessa parentes;
Dum virides inter saltus lucosque sonoros
Vere novo exultat, plumasque decora Juventus
Explicat ad solem, patriisque coloribus ardet2
There is a second Kind of Beauty that we find in the several Products of
Art and Nature, which does not work in the Imagination with that Warmth
and Violence as the Beauty that appears in our proper Species, but is
apt however to raise in us a secret Delight, and a kind of Fondness for
the Places or Objects in which we discover it. This consists either in
the Gaiety or Variety of Colours, in the Symmetry and Proportion of
Parts, in the Arrangement and Disposition of Bodies, or in a just
Mixture and Concurrence of all together. Among these several Kinds of
Beauty the Eye takes most Delight in Colours. We no where meet with a
more glorious or pleasing Show in Nature than what appears in the
Heavens at the rising and setting of the Sun, which is wholly made up of
those different Stains of Light that shew themselves in Clouds of a
different Situation. For this Reason we find the Poets, who are always
addressing themselves to the Imagination, borrowing more of their
Epithets from Colours than from any other Topic. As the Fancy delights
in every thing that is Great, Strange, or Beautiful, and is still more
pleased the more it finds of these Perfections in the same Object, so is
it capable of receiving a new Satisfaction by the Assistance of another
Sense. Thus any continued Sound, as the Musick of Birds, or a Fall of
Water, awakens every moment the Mind of the Beholder, and makes him more
attentive to the several Beauties of the Place that lye before him. Thus
if there arises a Fragrancy of Smells or Perfumes, they heighten the
Pleasures of the Imagination, and make even the Colours and Verdure of
the Landskip appear more agreeable; for the Ideas of both Senses
recommend each other, and are pleasanter together than when they enter
the Mind separately: As the different Colours of a Picture, when they
are well disposed, set off one another, and receive an additional Beauty
from the Advantage of their Situation.
O.
to please
Addison's MS. described in the
to
shows, by
corrections in his handwriting of four or five lines in this piece of
Latin verse, that he was himself its author. Thus in the last line he
had begun with
Scintillat solitis
, altered that to
Ostentat solitas
,
struck out that also, and written, as above,
Explicat ad solem.
Contents
|
Tuesday, June 24, 1712 |
Addison |
—Causa latet, vis est notissima—
Ovid.

Though in Yesterday's Paper we considered how every thing that is Great,
New, or Beautiful, is apt to affect the Imagination with Pleasure, we
must own that it is impossible for us to assign the necessary Cause of
this Pleasure, because we know neither the Nature of an Idea, nor the
Substance of a Human Soul, which might help us to discover the
Conformity or Disagreeableness of the one to the other; and therefore,
for want of such a Light, all that we can do in Speculations of this
kind is to reflect on those Operations of the Soul that are most
agreeable, and to range under their proper Heads, what is pleasing or
displeasing to the Mind, without being able to trace out the several
necessary and efficient Causes from whence the Pleasure or Displeasure
arises.
Final Causes lye more bare and open to our Observation, as there are
often a great Variety that belong to the same Effect; and these, tho'
they are not altogether so satisfactory, are generally more useful than
the other, as they give us greater Occasion of admiring the Goodness and
Wisdom of the first Contriver.
One of the Final Causes of our Delight, in any thing that is great, may
be this. The Supreme Author of our Being has so formed the Soul of Man,
that nothing but himself can be its last, adequate, and proper
Happiness. Because, therefore, a great Part of our Happiness must arise
from the Contemplation of his Being, that he might give our Souls a just
Relish of such a Contemplation, he has made them naturally delight in
the Apprehension of what is Great or Unlimited. Our Admiration, which is
a very pleasing Motion of the Mind, immediately rises at the
Consideration of any Object that takes up a great deal of Room in the
Fancy, and by Consequence, will improve into the highest Pitch of
Astonishment and Devotion when we contemplate his Nature, that is
neither circumscribed by Time nor Place, nor to be comprehended by the
largest Capacity of a Created Being.
He has annexed a secret Pleasure to the Idea of any thing that is new or
uncommon, that he might encourage us in the Pursuit after Knowledge, and
engage us to search into the Wonders of his Creation; for every new Idea
brings such a Pleasure along with it, as rewards any Pains we have taken
in its Acquisition, and consequently serves as a Motive to put us upon
fresh Discoveries.
He has made every thing that is beautiful in our own Species pleasant,
that all Creatures might be tempted to multiply their Kind, and fill the
World with Inhabitants; for 'tis very remarkable that where-ever Nature
is crost in the Production of a Monster (the Result of any unnatural
Mixture) the Breed is incapable of propagating its Likeness, and of
founding a new Order of Creatures; so that unless all Animals were
allured by the Beauty of their own Species, Generation would be at an
End, and the Earth unpeopled.
In the last Place, he has made every thing that is beautiful in all
other Objects pleasant, or rather has made so many Objects appear
beautiful, that he might render the whole Creation more gay and
delightful. He has given almost every thing about us the Power of
raising an agreeable Idea in the Imagination: So that it is impossible
for us to behold his Works with Coldness or Indifference, and to survey
so many Beauties without a secret Satisfaction and Complacency. Things
would make but a poor Appearance to the Eye, if we saw them only in
their proper Figures and Motions: And what Reason can we assign for
their exciting in us many of those Ideas which are different from any
thing that exists in the Objects themselves, (for such are Light and
Colours) were it not to add Supernumerary Ornaments to the Universe, and
make it more agreeable to the Imagination? We are every where
entertained with pleasing Shows and Apparitions, we discover Imaginary
Glories in the Heavens, and in the Earth, and see some of this Visionary
Beauty poured out upon the whole Creation; but what a rough unsightly
Sketch of Nature should we be entertained with, did all her Colouring
disappear, and the several Distinctions of Light and Shade vanish? In
short, our Souls are at present delightfully lost and bewildered in a
pleasing Delusion, and we walk about like the enchanted Hero of a
Romance, who sees beautiful Castles, Woods and Meadows; and at the same
time hears the warbling of Birds, and the purling of Streams; but upon
the finishing of some secret Spell, the fantastick Scene breaks up, and
the disconsolate Knight finds himself on a barren Heath, or in a
solitary Desart. It is not improbable that something like this may be
the State of the Soul after its first Separation, in respect of the
Images it will receive from Matter; tho indeed the Ideas of Colours are
so pleasing and beautiful in the Imagination, that it is possible the
Soul will not be deprived of them, but perhaps find them excited by some
other Occasional Cause, as they are at present by the different
Impressions of the subtle Matter on the Organ of Sight.
I have here supposed that my Reader is acquainted with that great Modern
Discovery, which is at present universally acknowledged by all the
Enquirers into Natural Philosophy: Namely, that Light and Colours, as
apprehended by the Imagination, are only Ideas in the Mind, and not
Qualities that have any Existence in Matter. As this is a Truth which
has been proved incontestably by many Modern Philosophers, and is indeed
one of the finest Speculations in that Science, if the English Reader
would see the Notion explained at large, he may find it in the Eighth
Chapter of the second Book of Mr.
Lock's Essay on Human Understanding
.
O.
[To Addison's short paper there was added in number 413 of the Spectator
the following letter, which was not included in the reprint into volumes:
June 24, 1712.
Mr. Spectator,
I would not divert the Course of your Discourses, when you seem bent
upon obliging the World with a train of Thinking, which, rightly
attended to, may render the Life of every Man who reads it, more easy
and happy for the future. The Pleasures of the Imagination are what
bewilder Life, when Reason and Judgment do not interpose; It is
therefore a worthy Action in you to look carefully into the Powers of
Fancy, that other Men, from the Knowledge of them, may improve their
Joys and allay their Griefs, by a just use of that Faculty: I say,
Sir, I would not interrupt you in the progress of this Discourse; but
if you will do me the Favour of inserting this Letter in your next
Paper, you will do some Service to the Public, though not in so noble
a way of Obliging, as that of improving their Minds. Allow me, Sir, to
acquaint you with a Design (of which I am partly Author), though it
tends to no greater a Good than that of getting Money. I should not
hope for the Favour of a Philosopher in this Matter, if it were not
attempted under all the Restrictions which you Sages put upon private
Acquisitions.
The first Purpose which every good Man is to propose to himself, is
the Service of his Prince and Country; after that is done, he cannot
add to himself, but he must also be beneficial to them. This Scheme of
Gain is not only consistent with that End, but has its very Being in
Subordination to it; for no Man can be a Gainer here but at the same
time he himself, or some other, must succeed in their Dealings with
the Government. It is called the Multiplication Table, and is so far
calculated for the immediate Service of Her Majesty, that the same
Person who is fortunate in the Lottery of the State, may receive yet
further Advantage in this Table. And I am sure nothing can be more
pleasing to Her gracious Temper than to find out additional Methods of
increasing their good Fortune who adventure anything in Her Service,
or laying Occasions for others to become capable of serving their
Country who are at present in too low Circumstances to exert
themselves. The manner of executing the Design is, by giving out
Receipts for half Guineas received, which shall entitle the fortunate
Bearer to certain Sums in the Table, as is set forth at large in the
Proposals Printed the 23rd instant. There is another Circumstance in
this Design, which gives me hopes of your Favour to it, and that is
what Tully advises, to wit, that the Benefit is made as diffusive as
possible. Every one that has half a Guinea is put into a possibility,
from that small Sum, to raise himself an easy Fortune; when these
little parcels of Wealth are, as it were, thus thrown back again into
the Redonation of Providence, we are to expect that some who live
under Hardship or Obscurity, may be produced to the World in the
Figure they deserve by this means. I doubt not but this last Argument
will have Force with you, and I cannot add another to it, but what
your Severity will, I fear, very little regard; which is, that
I am, Sir, Your greatest Admirer,
Richard Steele.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 25, 1712 |
Addison |
—Alterius sic
Altera poscit opem res et conjurat amicè.
Hor.

If we consider the Works of Nature and Art, as they are qualified to
entertain the Imagination, we shall find the last very defective, in
Comparison of the former; for though they may sometimes appear as
Beautiful or Strange, they can have nothing in them of that Vastness and
Immensity, which afford so great an Entertainment to the Mind of the
Beholder. The one may be as Polite and Delicate as the other, but can
never shew her self so August and Magnificent in the Design. There is
something more bold and masterly in the rough careless Strokes of
Nature, than in the nice Touches and Embellishments of Art. The Beauties
of the most stately Garden or Palace lie in a narrow Compass, the
Imagination immediately runs them over, and requires something else to
gratifie her; but, in the wide Fields of Nature, the Sight wanders up
and down without Confinement, and is fed with an infinite variety of
Images, without any certain Stint or Number. For this Reason we always
find the Poet in Love with a Country-Life, where Nature appears in the
greatest Perfection, and furnishes out all those Scenes that are most
apt to delight the Imagination.
Scriptorum chorus omnis amat nemus et fugit Urbes.
Hor.
Hic Secura quies, et nescia fallere vita,
Dives opum variarum; hic latis otia fundis,
Speluncæ, vivique lacus, hic frigida Tempe,
Mugitusque boum, mollesque sub arbore somni.
Virg.
But tho' there are several of these wild Scenes, that are more
delightful than any artificial Shows; yet we find the Works of Nature
still more pleasant, the more they resemble those of Art: For in this
case our Pleasure rises from a double Principle; from the Agreeableness
of the Objects to the Eye, and from their Similitude to other Objects:
We are pleased as well with comparing their Beauties, as with surveying
them, and can represent them to our Minds, either as Copies or
Originals. Hence it is that we take Delight in a Prospect which is well
laid out, and diversified with Fields and Meadows, Woods and Rivers; in
those accidental Landskips of Trees, Clouds and Cities, that are
sometimes found in the Veins of Marble; in the curious Fret-work of
Rocks and Grottos; and, in a Word, in any thing that hath such a Variety
or Regularity as may seem the Effect of Design, in what we call the
Works of Chance.
If the Products of Nature rise in Value, according as they more or less
resemble those of Art, we may be sure that artificial Works receive a
greater Advantage from their Resemblance of such as are natural; because
here the Similitude is not only pleasant, but the Pattern more perfect.
The prettiest Landskip I ever saw, was one drawn on the Walls of a dark
Room, which stood opposite on one side to a navigable River, and on the
other to a Park. The Experiment is very common in Opticks. Here you
might discover the Waves and Fluctuations of the Water in strong and
proper Colours, with the Picture of a Ship entering at one end, and
sailing by Degrees through the whole Piece. On another there appeared
the Green Shadows of Trees, waving to and fro with the Wind, and Herds
of Deer among them in Miniature, leaping about upon the Wall. I must
confess, the Novelty of such a Sight may be one occasion of its
Pleasantness to the Imagination, but certainly the chief Reason is its
near Resemblance to Nature, as it does not only, like other Pictures,
give the Colour and Figure, but the Motion of the Things it represents.
We have before observed, that there is generally in Nature something
more Grand and August, than what we meet with in the Curiosities of Art.
When therefore, we see this imitated in any measure, it gives us a
nobler and more exalted kind of Pleasure than what we receive from the
nicer and more accurate Productions of Art. On this Account our
English
Gardens are not so entertaining to the Fancy as those in
France
and
Italy
, where we see a large Extent of Ground covered over with an
agreeable mixture of Garden and Forest, which represent every where an
artificial Rudeness, much more charming than that Neatness and Elegancy
which we meet with in those of our own Country. It might, indeed, be of
ill Consequence to the Publick, as well as unprofitable to private
Persons, to alienate so much Ground from Pasturage, and the Plow, in
many Parts of a Country that is so well peopled, and cultivated to a far
greater Advantage. But why may not a whole Estate be thrown into a kind
of Garden by frequent Plantations, that may turn as much to the Profit,
as the Pleasure of the Owner? A Marsh overgrown with Willows, or a
Mountain shaded with Oaks, are not only more beautiful, but more
beneficial, than when they lie bare and unadorned. Fields of Corn make a
pleasant Prospect, and if the Walks were a little taken care of that lie
between them, if the natural Embroidery of the Meadows were helpt and
improved by some small Additions of Art, and the several Rows of Hedges
set off by Trees and Flowers, that the Soil was capable of receiving, a
Man might make a pretty Landskip of his own Possessions.
Writers who have given us an Account of
China
, tell us the Inhabitants
of that Country laugh at the Plantations of our
Europeans
, which are
laid out by the Rule and Line; because, they say, any one may place
Trees in equal Rows and uniform Figures. They chuse rather to shew a
Genius in Works of this Nature, and therefore always conceal the Art by
which they direct themselves. They have a Word, it seems, in their
Language, by which they express the particular Beauty of a Plantation
that thus strikes the Imagination at first Sight, without discovering
what it is that has so agreeable an Effect. Our
British
Gardeners, on
the contrary, instead of humouring Nature, love to deviate from it as
much as possible. Our Trees rise in Cones, Globes, and Pyramids. We see
the Marks of the Scissars upon every Plant and Bush. I do not know
whether I am singular in my Opinion, but, for my own part, I would
rather look upon a Tree in all its Luxuriancy and Diffusion of Boughs
and Branches, than when it is thus cut and trimmed into a Mathematical
Figure; and
but fancy that an Orchard in Flower looks infinitely
more delightful, than all the little Labyrinths of the
more
finished Parterre. But as our great Modellers of Gardens have their
Magazines of Plants to dispose of, it is very natural for them to tear
up all the beautiful Plantations of Fruit Trees, and contrive a Plan
that may most turn to their own Profit, in taking off their Evergreens,
and the like Moveable Plants, with which their Shops are plentifully
stocked.
O.
most
Contents
|
Thursday, June 26, 1712 |
Addison |
Adde tot egregias urbes, operumque laborem.
Virg.

Having already shewn how the Fancy is affected by the Works of Nature,
and afterwards considered in general both the Works of Nature and of
Art, how they mutually assist and compleat each other, in forming such
Scenes and Prospects as are most apt to delight the Mind of the
Beholder, I shall in this Paper throw together some Reflections on that
Particular Art, which has a more immediate Tendency, than any other, to
produce those Primary Pleasures of the Imagination, which have hitherto
been the Subject of this Discourse. The Art I mean is that of
Architecture, which I shall consider only with regard to the Light in
which the foregoing Speculations have placed it, without entring into
those Rules and Maxims which the great Masters of Architecture have laid
down, and explained at large in numberless Treatises upon that Subject.
Greatness, in the Works of Architecture, may be considered as relating
to the Bulk and Body of the Structure, or to the Manner in which it is
built. As for the first, we find the Ancients, especially among the
Eastern
Nations of the World, infinitely superior to the Moderns.
Not to mention the
Tower of Babel,
of which an old Author says, there
were the Foundations to be seen in his time, which looked like a
spacious Mountain; what could be more noble than the
Walls of Babylon
,
its
hanging Gardens,
and its
Temple to Jupiter Belus
, that rose a Mile
high by Eight several Stories, each Story a Furlong in Height, and on
the Top of which was the
Babylonian Observatory;
I might here, likewise,
take Notice of the huge Rock that was cut into the Figure of
Semiramis
,
with the smaller Rocks that lay by it in the Shape of Tributary Kings;
the prodigious Basin, or artificial Lake, which took in the whole
Euphrates
, till such time as a new Canal was formed for its Reception,
with the several Trenches through which that River was conveyed. I know
there
persons who look upon some of these Wonders of Art as
Fabulous, but I cannot find any
Grand
for such a Suspicion, unless
it be that we have no such Works among us at present. There were indeed
many greater Advantages for Building in those Times, and in that Part of
the World, than have been met with ever since. The Earth was extremely
fruitful, Men lived generally on Pasturage, which requires a much
smaller number of Hands than Agriculture: There were few Trades to
employ the busie Part of Mankind, and fewer Arts and Sciences to give
Work to Men of Speculative Tempers; and what is more than all the rest,
the Prince was absolute; so that when he went to War, he put himself at
the Head of a whole People:
we find
Semiramis
leading her
three
Millions to the Field, and yet over-powered by the Number of her
Enemies. 'Tis no wonder, therefore, when she was at Peace, and turned
her Thoughts on Building, that she could accomplish so great Works, with
such a prodigious Multitude of Labourers: Besides that, in her Climate,
there was small Interruption of Frosts and Winters, which make the
Northern
Workmen lie half the Year Idle. I might mention too, among the
Benefits of the Climate, what Historians say of the Earth, that it
sweated out a
Bitumen
or natural kind of Mortar, which is doubtless the
same with that mentioned in
Holy Writ
, as contributing to the Structure
of
Babel
. Slime they used instead of Mortar.
In
Egypt
we still see their
Pyramids
, which answer to the Descriptions
that have been made of them; and I question not but a traveller might
find out some Remains of the
Labyrinth
that covered a whole Province,
and had a hundred Temples disposed among its several Quarters and
Divisions.
The
Wall of China
is one of these
Eastern
Pieces of Magnificence, which
makes a Figure even in the Map of the World, altho an Account of it
would have been thought Fabulous, were not the Wall it self still
extant.
We are obliged to Devotion for the noblest Buildings that have adornd
the several Countries of the World. It is this which has set Men at work
on Temples and Publick Places of Worship, not only that they might, by
the Magnificence of the Building, invite the Deity to reside within it,
but that such stupendous Works might, at the same time, open the Mind to
vast Conceptions, and fit it to converse with the Divinity of the Place.
For every thing that is Majestick imprints an Awfulness and Reverence on
the Mind of the Beholder, and strikes in with the Natural Greatness of
the Soul.
In the Second place we are to consider Greatness of Manner in
Architecture, which has such Force upon the Imagination, that a small
Building, where it appears, shall give the Mind nobler Ideas than one of
twenty times the Bulk, where the Manner is ordinary or little. Thus,
perhaps, a Man
have been more astonished with the Majestick Air
that appeared in one of
Lysippus's
Statues of
Alexander
, tho' no
bigger than the Life,
he might have been with
Mount Athos
, had it
been cut into the Figure of the Hero, according to the Proposal of
Phidias
, with a River in one Hand, and a City in the other.
Let any one reflect on the Disposition of Mind he finds in himself, at
his first Entrance into the
Pantheon
at
Rome
, and how his Imagination is
filled with something Great and Amazing; and, at the same time, consider
how little, in proportion, he is affected with the Inside of a
Gothick
Cathedral, tho' it be five times larger than the other; which can arise
from nothing else, but the Greatness of the Manner in the one, and the
Meanness in the other.
I have seen an Observation upon this Subject in a
French
Author, which
very much pleased me. It is in
Monsieur Freart's Parallel of the Ancient
and Modern Architecture.
I shall give it the Reader with the same Terms
of Art which he has made use of.
I am observing
(says he)
a thing which,
in my Opinion, is very curious, whence it proceeds, that in the same
Quantity of Superficies, the one Manner seems great and magnificent, and
the other poor and trifling; the Reason is fine and uncommon. I say
then, that to introduce into Architecture this Grandeur of Manner, we
ought so to proceed, that the Division of the Principal Members of the
Order may consist but of few Parts, that they be all great and of a bold
and ample Relievo, and Swelling; and that the Eye, beholding nothing
little and mean, the Imagination may be more vigorously touched and
affected with the Work that stands before it. For example; In a Cornice,
if the Gola or Cynatium of the Corona, the Coping, the Modillions or
Dentelli, make a noble Show by their graceful Projections, if we see
none of that ordinary Confusion which is the Result of those little
Cavities, Quarter Rounds of the Astragal and I know not how many other
intermingled Particulars, which produce no Effect in great and massy
Works, and which very unprofitably take up place to the Prejudice of the
Principal Member, it is most certain that this Manner will appear Solemn
and Great; as on the contrary, that it will have but a poor and mean
Effect, where there is a Redundancy of those smaller Ornaments, which
divide and scatter the Angles of the Sight into such a Multitude of
Rays, so pressed together that the whole will appear but a Confusion.
Among all the Figures in Architecture, there are none that have a
greater Air than the
Concave
and the
Convex
, and we find in all the
Ancient and Modern Architecture, as well in the remote Parts of
China
,
as in Countries nearer home, that round Pillars and Vaulted Roofs make a
great Part of those Buildings which are designed for Pomp and
Magnificence. The Reason I take to be, because in these Figures we
generally see more of the Body, than in those of other Kinds. There are,
indeed, Figures of Bodies, where the Eye may take in two Thirds of the
Surface; but as in such Bodies the Sight must split upon several Angles,
it does not take in one uniform Idea, but several Ideas of the same
kind. Look upon the Outside of a Dome, your Eye half surrounds it; look
up into the Inside, and at one Glance you have all the Prospect of it;
the entire Concavity falls into your Eye at once, the Sight being as the
Center that collects and gathers into it the Lines of the whole
Circumference: In a Square Pillar, the Sight often takes in but a fourth
Part of the Surface: and in a Square Concave, must move up and down to
the different Sides, before it is Master of all the inward Surface. For
this Reason, the Fancy is infinitely more struck with the View of the
open Air, and Skies, that passes through an Arch, than what comes
through a Square, or any other Figure. The Figure of the Rainbow does
not contribute less to its Magnificence, than the Colours to its Beauty,
as it is very poetically described
the Son of
Sirach
:
Look upon the
Rainbow and praise him that made it; very beautiful it is in its
Brightness; it encompasses the Heavens with a glorious Circle, and the
Hands of the most High5 have bended it.
Having thus spoken of that Greatness which affects the Mind in
Architecture, I might next shew the Pleasure that arises in the
Imagination from what appears new and beautiful in this Art; but as
every Beholder has naturally a greater Taste of these two Perfections in
every Building which offers it self to his View, than of that which I
have hitherto considered, I shall not trouble my Reader with any
Reflections upon it. It is sufficient for my present Purpose, to
observe, that there is nothing in this whole Art which pleases the
Imagination, but as it is Great, Uncommon, or Beautiful.
O.
Grounds
two
Protogenes's
Dinocrates.
Almighty
Contents
|
Friday, June 27, 1712 |
Addison |
Quatenûs hoc simile est oculis, quod mente videmus.
Lucr.

I at first divided the Pleasures of the Imagination, into such as arise
from Objects that are actually before our Eyes, or that once entered in
at our Eyes, and are afterwards called up into the Mind either barely by
its own Operations, or on occasion of something without us, as Statues,
or Descriptions. We have already considered the first Division, and
shall therefore enter on the other, which for Distinction sake, I have
called the Secondary Pleasures of the Imagination. When I say the Ideas
we receive from Statues, Descriptions, or such like Occasions, are the
same that were once actually in our View, it must not be understood that
we had once see the very Place, Action, or Person which are carved or
described. It is sufficient, that we have seen Places, Persons, or
Actions, in general, which bear a Resemblance, or at least some remote
Analogy with what we find represented. Since it is in the Power of the
Imagination, when it is once Stocked with particular Ideas, to enlarge,
compound, and vary them at her own Pleasure.
Among the different Kinds of Representation, Statuary is the most
natural, and shews us something likest the Object that is represented.
To make use of a common Instance, let one who is born Blind take an
Image in his Hands, and trace out with his Fingers the different Furrows
and Impressions of the Chissel, and he will easily conceive how the
Shape of a Man, or Beast, may be represented by it; but should he draw
his Hand over a Picture, where all is smooth and uniform, he would never
be able to imagine how the several Prominencies and Depressions of a
human Body could be shewn on a plain Piece of Canvas, that has in it no
Unevenness or Irregularity. Description runs yet further from the Things
it represents than Painting; for a Picture bears a real Resemblance to
its Original, which Letters and Syllables are wholly void of. Colours
speak of Languages, but Words are understood only by such a People or
Nation. For this Reason, tho' Men's Necessities quickly put them on
finding out Speech, Writing is probably of a later invention than
Painting; particularly we are told, that in
America
when the
Spaniards
first arrived there Expresses were sent to the
Emperor of Mexico
in
Paint, and the News of his Country delineated by the Strokes of a
Pencil, which was a more natural Way than that of Writing, tho' at the
same time much more imperfect, because it is impossible to draw the
little Connexions of Speech, or to give the Picture of a Conjunction or
an Adverb. It would be yet more strange, to represent visible Objects by
Sounds that have no Ideas annexed to them, and to make something like
Description in Musick. Yet it is certain, there may be confused,
imperfect Notions of this Nature raised in the Imagination by an
Artificial Composition of Notes; and we find that great Masters in the
Art are able, sometimes, to set their Hearers in the Heat and Hurry of a
Battel, to overcast their Minds with melancholy Scenes and Apprehensions
of Deaths and Funerals, or to lull them into pleasing Dreams of Groves
and Elisiums.
In all these Instances, this Secondary Pleasure of the Imagination
proceeds from that Action of the Mind, which compares the Ideas arising
from the Original Objects, with the Ideas we receive from the Statue,
Picture, Description, or Sound that represents them. It is impossible
for us to give the necessary Reason, why this Operation of the Mind is
attended with so much Pleasure, as I have before observed on the same
Occasion; but we find a great Variety of Entertainments derived from
this single Principle: For it is this that not only gives us a Relish of
Statuary, Painting and Description, but makes us delight in all the
Actions and Arts of Mimickry. It is this that makes the several kinds of
Wit Pleasant, which consists, as I have formerly shewn, in the Affinity
of Ideas: And we may add, it is this also that raises the little
Satisfaction we sometimes find in the different Sorts of false Wit;
whether it consists in the Affinity of Letters, as in Anagram,
Acrostick; or of Syllables, as in Doggerel Rhimes, Ecchos; or of Words,
as in Punns, Quibbles; or of a whole Sentence or Poem, to Wings, and
Altars. The final Cause, probably, of annexing Pleasure to this
Operation of the Mind, was to quicken and encourage us in our Searches
after Truth, since the distinguishing one thing from another, and the
right discerning betwixt our Ideas, depends wholly upon our comparing
them together, and observing the Congruity or Disagreement that appears
among the several Works of Nature.
I shall here confine my self to those Pleasures of the Imagination,
which
proceed from Ideas raised by Words, because most of the
Observations that agree with Descriptions, are equally Applicable to
Painting and Statuary.
Words, when well chosen, have so great a Force in them, that a
Description often gives us more lively Ideas than the Sight of Things
themselves. The Reader finds a Scene drawn in stronger Colours, and
painted more to the Life in his Imagination, by the help of Words, than
by an actual Survey of the Scene which they describe. In this case the
Poet seems to get the better of Nature; he takes, indeed, the Landskip
after her, but gives it more vigorous Touches, heightens its Beauty, and
so enlivens the whole Piece, that the Images which flow from the Objects
themselves appear weak and faint, in Comparison of those that come from
the Expressions. The Reason, probably, may be, because in the Survey of
any Object we have only so much of it painted on the Imagination, as
comes in at the Eye; but in its Description, the Poet gives us as free a
View of it as he pleases, and discovers to us several Parts, that either
we did not attend to, or that lay out of our Sight when we first beheld
it. As we look on any Object, our Idea of it is, perhaps, made up of two
or three simple Ideas; but when the Poet represents it, he may either
give us a more complex Idea of it, or only raise in us such Ideas as are
most apt to affect the Imagination.
It may be here worth our while to Examine how it comes to pass that
several Readers, who are all acquainted with the same Language, and know
the Meaning of the Words they read, should nevertheless have a different
Relish of the same Descriptions. We find one transported with a Passage,
which another runs over with Coldness and Indifference, or finding the
Representation extreamly natural, where another can perceive nothing of
Likeness and Conformity. This different Taste must proceed, either from
the Perfection of Imagination in one more than in another, or from the
different Ideas that several Readers affix to the same Words. For, to
have a true Relish, and form a right Judgment of a Description, a Man
should be born with a good Imagination, and must have well weighed the
Force and Energy that lye in the several Words of a Language, so as to
be able to distinguish which are most significant and expressive of
their proper Ideas, and what additional Strength and Beauty they are
capable of receiving from Conjunction with others. The Fancy must be
warm to retain the Print of those Images it hath received from outward
Objects and the Judgment discerning, to know what Expressions are most
proper to cloath and adorn them to the best Advantage. A Man who is
deficient in either of these Respects, tho' he may receive the general
Notion of a Description, can never see distinctly all its particular
Beauties: As a Person, with a weak Sight, may have the confused Prospect
of a Place that lies before him, without entering into its several
Parts, or discerning the variety of its Colours in their full Glory and
Perfection.
O.
that
end of Volume 2.
The Spectator
in three volumes: volume 3
A New Edition
Reproducing the Original Text
Both as First Issued
and as Corrected by its Authors
with Introduction, Notes, and Index
edited by Henry Morley
1891
Table of Contents / Index
- No. 417 – Saturday, June 28, 1712 – Addison
- No. 418 – Monday, June 30, 1712 – Addison
- No. 419 – Tuesday, July 1, 1712 – Addison
- No. 420 – Wednesday, July 2, 1712 – Addison
- No. 421 – Thursday, July 3, 1712 – Addison
- No. 422 – Friday, July 4, 1712 – Steele
- No. 423 – Saturday, July 5, 1712 – Steele
- No. 424 – Monday, July 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 425 – Tuesday, July 8, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 426 – Wednesday, July 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 427 – Thursday, July 10, 1712 – Steele
- No. 428 – Friday, July 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 429 – Saturday, July 12, 1712 – Steele
- No. 430 – Monday, July 14, 1712 – Steele
- No. 431 – Tuesday, July 15, 1712 – Steele
- No. 432 – Wednesday, July 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 433 – Thursday, July 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 434 – Friday, July 18, 1712 – Addison
- No. 435 – Saturday, July 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 436 – Monday, July 21, 1712 – Steele
- No. 437 – Tuesday, July 22, 1712 –
- No. 438 – Wednesday, July 23, 1712 – Steele
- No. 439 – Thursday, July 24, 1712 – Addison
- No. 440 – Friday, July 25, 1712 – Addison
- No. 441 – Saturday, July 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 442 – Monday, July 28, 1712 – Steele
- No. 443 – Tuesday, July 29, 1712 – Steele
- No. 444 – Wednesday, July 30, 1712 – Steele
- No. 445 – Thursday, July 31, 1712 – Addison
- No. 446 – Friday, August 1, 1712 – Addison
- No. 447 – Saturday, August 2, 1712 – Addison
- No. 448 – Monday, August 4, 1712 – Steele
- No. 449 – Tuesday, August 5, 1712 – Steele
- No. 450 – Wednesday, August 6, 1712 – Steele
- No. 451 – Thursday, August 7, 1712 – Addison
- No. 452 – Friday, August 8, 1712 – Addison
- No. 453 – Saturday, August 9, 1712 – Addison
- No. 454 – Monday, August 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 455 – Tuesday, August 12, 1712 – Steele
- No. 456 – Wednesday, August 13, 1712 – Steele
- No. 457 – Thursday, August 14, 1712 – Addison
- No. 458 – Friday, August 15, 1712 – Addison
- No. 459 – Saturday, August 16, 1712 – Addison
- No. 460 – Monday, August 18, 1712 – Parnell
- No. 461 – Tuesday, August 19, 1712 – Steele
- No. 462 – Wednesday, August 20, 1712 – Steele
- No. 463 – Thursday, August 21, 1712 – Addison
- No. 464 – Friday, August 22, 1712 – Addison
- No. 465 – Saturday, August 23, 1712 – Addison
- No. 466 – Monday, August 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 467 – Tuesday, August 26, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 468 – Wednesday, August 27, 1712 – Steele
- No. 469 – Thursday, August 28, 1712 – Addison
- No. 470 – Friday, August 29, 1712 – Addison
- No. 471 – Saturday, August 30, 1712 – Addison
- No. 472 – Monday, September 1, 1712 – Steele
- No. 473 – Tuesday, September 2, 1712 – Steele
- No. 474 – Wednesday, September 3, 1712 – Steele
- No. 475 – Thursday, September 4, 1712 – Addison
- No. 476 – Friday, September 5, 1712 – Addison
- No. 477 – Saturday, September 6, 1712 – Addison
- No. 478 – Monday, September 8, 1712 – Steele
- No. 479 – Tuesday, September 9, 1712 – Steele
- No. 480 – Wednesday, September 10, 1712 – Steele
- No. 481 – Thursday, September 11, 1712 – Addison
- No. 482 – Friday, September 12, 1712 – Addison
- No. 483 – Saturday, September 13, 1712 – Addison
- No. 484 – Monday, September 15, 1712 – Steele
- No. 485 – Tuesday, September 16, 1712 – Steele
- No. 486 – Wednesday, September 17, 1712 – Steele
- No. 487 – Thursday, September 18, 1712 – Addison
- No. 488 – Friday, September 19, 1712 – Addison
- No. 489 – Saturday, September 20, 1712 – Addison
- No. 490 – Monday, September 22, 1712 – Steele
- No. 491 – Tuesday, September 22, 1712 – Steele
- No. 492 – Wednesday, September 24, 1712 – Steele
- No. 493 – Thursday, September 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 494 – Friday, September 26, 1712 – Addison
- No. 495 – Saturday, September 27, 1712 – Addison
- No. 496 – Monday, September 29, 1712 – Steele
- No. 497 – Tuesday, September 30, 1712 – Steele
- No. 498 – Wednesday, October 1, 1712 – Steele
- No. 499 – Thursday, October 2, 1712 – Addison
- No. 500 – Friday, October 3, 1712 – Addison
- No. 501 – Saturday, October 4, 1712 – Parnell
- No. 502 – Monday, October 6, 1712 – Steele
- No. 503 – Tuesday, October 7, 1712 – Steele
- No. 504 – Wednesday, October 8, 1712 – Steele
- No. 505 – Thursday, October 9, 1712 – Addison
- No. 506 – Friday, October 10, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 507 – Saturday, October 11, 1712 – Addison
- No. 508 – Monday, October 13, 1712 – Steele
- No. 509 – Tuesday, October 14, 1712 – Steele
- No. 510 – Wednesday, October 15, 1712 – Steele
- No. 511 – Thursday, October 16, 1712 – Addison
- No. 512 – Friday, October 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 513 – Saturday, October 18, 1712 – Addison
- No. 514 – Monday, October 20, 1712 – Steele
- No. 515 – Tuesday, October 21, 1712 – Steele
- No. 516 – Wednesday, October 22, 1712 – Steele
- No. 517 – Thursday, October 23, 1712 – Addison
- No. 518 – Friday, October 24, 1712 – Steele
- No. 519 – Saturday, October 25, 1712 – Addison
- No. 520 – Monday, October 27, 1712 – Francham
- No. 521 – Tuesday, October 28, 1712 – Steele
- No. 522 – Wednesday, October 29, 1712 – Steele
- No. 523 – Thursday, October 30, 1712 – Addison
- No. 524 – Friday, October 31, 1712 –
- No. 525 – Saturday, November 1, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 526 – Monday, November 3, 1712 – Steele
- No. 527 – Tuesday, November 4, 1712 –
- No. 528 – Wednesday, November 5, 1712 – Steele
- No. 529 – Thursday, November 6, 1712 – Addison
- No. 530 – Friday, November 7, 1712 – Addison
- No. 531 – Saturday, November 8, 1712 – Addison
- No. 532 – Monday, November 10, 1712 – Steele
- No. 533 – Tuesday, November 11, 1712 – Steele
- No. 534 – Wednesday, November 12, 1712 – Steele
- No. 535 – Thursday, November 13, 1712 – Addison
- No. 536 – Friday, November 14, 1712 – Addison
- No. 537 – Saturday, November 15, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 538 – Monday, November 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 539 – Tuesday, November 18, 1712 – Budgell
- No. 540 – Wednesday, November 19, 1712 – Steele
- No. 541 – Thursday, November 20, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 542 – Friday, November 21, 1712 – Addison
- No. 543 – Saturday, November 22, 1712 – Addison
- No. 544 – Monday, November 24, 1712 – Steele
- No. 545 – Tuesday, November 25, 1712 – Steele
- No. 546 – Wednesday, November 26, 1712 – Steele
- No. 547 – Thursday, November 27, 1712 – Addison
- No. 548 – Friday, November 28, 1712 –
- No. 549 – Saturday, November 29, 1712 – Addison
- No. 550 – Monday, December 1, 1712 – Addison
- No. 551 – Tuesday, December 2, 1712 –
- No. 552 – Wednesday, December 3, 1712 – Steele
- No. 553 – Thursday, December 4, 1712 – Addison
- No. 554 – Friday, December 5, 1712 – Hughes
- No. 555 – Thursday, December 17, 1712 – Addison
- No. 556 – Friday, June 18, 1714 – Addison
- No. 557 – Monday, June 21, 1714 – Addison
- No. 558 – Wednesday, June 23, 1714 – Addison
- No. 559 – Friday, June 25, 1714 – Addison
- No. 560 – Monday, June 28, 1714 – Addison
- No. 561 – Wednesday, June 30, 1714 – Addison
- No. 562 – Friday, July 2, 1714 – Addison
- No. 563 – Monday, July 5, 1714 –
- No. 564 – Wednesday, July 7, 1714 –
- No. 565 – Friday, July 9, 1714 – Addison
- No. 566 – Monday, July 12, 1714 –
- No. 567 – Wednesday, July 14, 1714 – Addison
- No. 568 – Friday, July 16, 1714 – Addison
- No. 569 – Monday, July 19, 1714 – Addison
- No. 570 – Wednesday, July 21, 1714 –
- No. 571 – Friday, July 23, 1714 – Addison
- No. 572 – Monday, July 26, 1714 – Pearce
- No. 573 – Wednesday, July 28, 1714 –
- No. 574 – Friday, July 30, 1714 – Addison
- No. 575 – Monday, August 2, 1714 – Addison
- No. 576 – Wednesday, August 4, 1714 – Addison
- No. 577 – Friday, August 6, 1714 –
- No. 578 – Monday, August 9, 1714 –
- No. 579 – Wednesday, August 11, 1714 – Addison
- No. 580 – Friday, August 13, 1714 – Addison
- No. 581 – Monday, August 16, 1714 – Addison
- No. 582 – Wednesday, August 18, 1714 –
- No. 583 – Friday, August 20, 1714 – Addison
- No. 584 – Monday, August 23, 1714 – Addison
- No. 585 – Wdnesday, August 25, 1714 – Addison
- No. 586 – Friday, August 27, 1714 – Byrom
- No. 587 – Monday, August 30, 1714 – Byrom
- No. 588 – Wednesday, September 1, 1714 – Grove
- No. 589 – Friday, September 3, 1714 –
- No. 590 – Monday, September 6, 1714 – Addison
- No. 591 – Wednesday, September 8, 1714 – Budgell
- No. 592 – Friday, September 10, 1714 – Addison
- No. 593 – Monday, September 13, 1714 – Byrom
- No. 594 – Wednesday, September 15, 1714 –
- No. 595 – Friday, September 17, 1714 –
- No. 596 – Monday, September 20, 1714 –
- No. 597 – Wednesday, September 22, 1714 – Byrom
- No. 598 – Friday, September 24, 1714 – Addison
- No. 599 – Monday, September 27, 1714 –
- No. 600 – Wednesday, September 29, 1714 – Addison
- No. 601 – Friday, October 1, 1714 – Grove
- No. 602 – Monday, October 4, 1714 – Budgell
- No. 603 – Wednesday, October 6, 1714 – Byrom
- No. 604 – Friday, October 8, 1714 –
- No. 605 – Monday, October 11, 1714 – Budgell
- No. 606 – Wednesday, October 13, 1714 –
- No. 607 – Friday, October 15, 1714 –
- No. 608 – Monday, October 18, 1714 – Addison
- No. 609 – Wdnesday, October 20, 1714 –
- No. 610 – Friday, October 22, 1714 –
- No. 611 – Monday, October 25, 1714 –
- No. 612 – Wednesday, October 27, 1714 –
- No. 613 – Friday, October 29, 1714 –
- No. 614 – Monday, November 1, 1714 –
- No. 615 – Wednesday, November 3, 1714 –
- No. 616 – Friday, November 5, 1714 –
- No. 617 – Monday, November 8, 1714 –
- No. 618 – Wednesday, November 10, 1714 –
- No. 619 – Friday, November 12, 1714 –
- No. 620 – Monday, November 15, 1714 – Tickell
- No. 621 – Wednesday, November 17, 1714 –
- No. 622 – Friday, November 19, 1714 –
- No. 623 – Monday, November 22, 1714 – Addison
- No. 624 – Wednesday, November 24, 1714 –
- No. 625 – Friday, November 26, 1714 –
- No. 626 – Monday, November 29, 1714 – Grove
- No. 627 – Wednesday, December 1, 1714 –
- No. 628 – Friday, December 3, 1714 –
- No. 629 – Monday, December 6, 1714 –
- No. 630 – Wednesday, December 8, 1714 –
- No. 631 – Friday, December 10, 1714 –
- No. 632 – Monday, December 13, 1714 –
- No. 633 – Wednesday, December 15, 1714 –
- No. 634 – Friday, December 17, 1714 –
- No. 635 – Monday, December 20, 1714 – Grove
List of Original Advertisements Included
Contents
|
Saturday, June 28, 1712 |
Addison |
Quem tu Melpomene semel
Nascentem placido lumine videris,
Non illum labor Isthmius
Clarabit pugilem, non equus impiger, &c.
Sed quæ Tibur aquæ fertile perfluunt,
Et Spissæ nemorum comæ
Fingent Æolio carmine nobilem.
Hor.
We
observe, that any single Circumstance of what we have formerly
seen often raises up a whole Scene of Imagery, and awakens
numberless
Ideas that before slept in the Imagination; such a particular Smell
or Colour is able to fill the Mind, on a sudden, with the Picture of the
Fields or Gardens, where we first met with it, and to bring up into View
all the Variety of Images that once attended it. Our Imagination takes
the Hint, and leads us unexpectedly into Cities or Theatres, Plains or
Meadows. We may further observe, when the Fancy thus reflects on the
Scenes that have past in it formerly, those which were at first pleasant
to behold, appear more so upon Reflection, and that the Memory heightens
the Delightfulness of the Original. A
Cartesian
would account for
both these Instances in the following Manner.
The Sett of Ideas, which we received from such a Prospect or Garden,
having entered the Mind at the same time, have a Sett of Traces
belonging to them in the Brain, bordering very near upon one another;
when, therefore, any one of these Ideas arises in the Imagination, and
consequently dispatches a flow of Animal Spirits to its proper Trace,
these Spirits, in the Violence of their Motion, run not only into the
Trace, to which they were more particularly directed, but into several
of those that lie about it: By this means they awaken other Ideas of the
same Sett, which immediately determine a new Dispatch of Spirits, that
in the same manner open other Neighbouring Traces, till at last the
whole Sett of them is blown up, and the whole Prospect or Garden
flourishes in the Imagination. But because the Pleasure we received from
these Places far surmounted, and overcame the little Disagreeableness we
found in them; for this Reason there was at first a wider Passage worn
in the Pleasure Traces, and, on the contrary, so narrow a one in those
which belonged to the disagreeable Ideas, that they were quickly stopt
up, and rendered incapable of receiving any Animal Spirits, and
consequently of exciting any unpleasant Ideas in the Memory.
It would be in vain to enquire, whether the Power of Imagining Things
strongly proceeds from any greater Perfection in the Soul, or from any
nicer Texture in the Brain of one Man than of another. But this is
certain, that a noble Writer should be born with this Faculty in its
full Strength and Vigour, so as to be able to receive lively Ideas from
outward Objects, to retain them long, and to range them together, upon
Occasion, in such Figures and Representations as are most likely to hit
the Fancy of the Reader. A Poet should take as much Pains in forming his
Imagination, as a Philosopher in cultivating his Understanding. He must
gain a due Relish of the Works of Nature, and be thoroughly conversant
in the various Scenary of a Country Life.
When he is stored with Country Images, if he would go beyond Pastoral,
and the lower kinds of Poetry, he ought to acquaint himself with the
Pomp and Magnificence of Courts. He should be very
versed in every
thing that is noble and stately in the Productions of Art, whether it
appear in Painting or Statuary, in the great Works of Architecture which
are in their present Glory, or in the Ruins of those
which
flourished in former Ages.
Such Advantages as these help to open a Man's Thoughts, and to enlarge
his Imagination, and will therefore have their Influence on all kinds of
Writing, if the Author knows how to make right use of them. And among
those of the learned Languages who excel in this Talent, the most
perfect in their several kinds, are perhaps
Homer
,
Virgil
,
and
Ovid
. The first strikes the Imagination wonderfully with what
is Great, the second with what is Beautiful, and the last with what is
Strange. Reading the
Iliad
is like travelling through a Country
uninhabited, where the Fancy is entertained with a thousand Savage
Prospects of vast Desarts, wide uncultivated Marshes, huge Forests,
mis-shapen Rocks and Precipices. On the contrary, the
Æneid
is
like a well ordered Garden, where it is impossible to find out any Part
unadorned, or to cast our Eyes upon a single Spot, that does not produce
some beautiful Plant or Flower. But when we are in the
Metamorphoses
, we are walking on enchanted Ground, and see
nothing but Scenes of Magick lying round us.
Homer
is in his Province, when he is describing a Battel or a
Multitude, a Heroe or a God.
Virgil
is never better pleased, than
when he is in his
Elysium
, or copying out an entertaining
Picture.
Homer's
Epithets generally mark out what is Great,
Virgil's
what is Agreeable. Nothing can be more Magnificent than
the Figure
Jupiter
makes in the first
Iliad
, no more
Charming than that of Venus in the first
Æneid
.
Dixit et avertens roseâ cervice refulsit:
Ambrosiæque comæ; divinum vertice odorem
Spiravere: Pedes vestis defluxit ad imos:
Et vera incessu patuit Dea—
Homer's
Persons are most of them God-like and Terrible;
Virgil
has scarce admitted any into his Poem, who are not
Beautiful, and has taken particular Care to make his Heroe so.
—lumenque juventæ
Purpureum, et lætos oculis afflavit honores.
In a Word,
Homer
fills his Readers with Sublime Ideas, and, I
believe, has raised the Imagination of all the good Poets that have come
after him. I shall only instance
Horace
, who immediately takes
Fire at the first Hint of any Passage in the
Iliad
or
Odyssey
, and always rises above himself, when he has
Homer
in his View.
Virgil
has drawn together, into his
Æneid
,
all the pleasing Scenes his Subject is capable of admitting, and in his
Georgics
has given us a Collection of the most delightful
Landskips that can be made out of Fields and Woods, Herds of Cattle, and
Swarms of Bees.
Ovid
, in his
Metamorphoses
, has shewn us how the
Imagination may be affected by what is Strange. He describes a Miracle
in every Story, and always gives us the Sight of some new Creature at
the end of it. His Art consists chiefly in well-timing his Description,
before the first Shape is quite worn off, and the new one perfectly
finished; so that he every where entertains us with something we never
saw before, and shews Monster after Monster, to the end of the
Metamorphoses
.
If I were to name a Poet that is a perfect Master in all these Arts of
working on the Imagination, I think
Milton
may pass for one: And
if his
Paradise Lost
falls short of the
Æneid
or
Iliad
in this respect, it proceeds rather from the Fault of the
Language in which it is written, than from any Defect of Genius in the
Author. So Divine a Poem in
English
, is like a stately Palace
built of Brick, where one may see Architecture in as great a Perfection
as in one of Marble, tho' the Materials are of a coarser Nature. But to
consider it only as it regards our present Subject: What can be
conceived greater than the Battel of Angels, the Majesty of Messiah, the
Stature and Behaviour of Satan and his Peers? What more beautiful than
Pandæmonium
, Paradise, Heaven, Angels,
Adam
and
Eve
? What more strange, than the Creation of the World, the
several Metamorphoses of the fallen Angels, and the surprising
Adventures their Leader meets with in his Search after Paradise? No
other Subject could have furnished a Poet with Scenes so proper to
strike the Imagination, as no other Poet could have painted those Scenes
in more strong and lively Colours.
O.
a Thousand
that
Contents
Advertisement
Whereas the Proposal called the Multiplication Table
is under an Information from the Attorney General,
in Humble Submission and Duty to her Majesty
the said Undertaking is laid down, and Attendance is this Day given ...
in order to repay such Sums
as have been paid into the said Table without Deduction.
Contents
|
Monday, June 30, 1712 |
Addison |
—ferat et rubus asper amomum.
Virg.
The Pleasures of these Secondary Views of the Imagination, are of a
wider and more Universal Nature than those it has when joined with
Sight; for not only what is Great, Strange or Beautiful, but any Thing
that is Disagreeable when looked upon, pleases us in an apt Description.
Here, therefore, we must enquire after a new Principle of Pleasure,
which is nothing else but the Action of the Mind, which
compares
the Ideas that arise from Words, with the Ideas that arise from the
Objects themselves; and why this Operation of the Mind is attended with
so much Pleasure, we have before considered. For this Reason therefore,
the Description of a Dunghill is pleasing to the Imagination, if the
Image be represented to our Minds by suitable Expressions; tho' perhaps,
this may be more properly called the Pleasure of the Understanding than
of the Fancy, because we are not so much delighted with the Image that
is contained in the Description, as with the Aptness of the Description
to excite the Image.
But if the Description of what is Little, Common, or Deformed, be
acceptable to the Imagination, the Description of what is Great,
Surprising or Beautiful, is much more so; because here we are not only
delighted with
comparing
the Representation with the Original,
but are highly pleased with the Original itself. Most Readers, I
believe, are more charmed with
Milton's
Description of Paradise,
than of Hell; they are both, perhaps, equally perfect in their Kind, but
in the one the Brimstone and Sulphur are not so refreshing to the
Imagination, as the Beds of Flowers and the Wilderness of Sweets in the
other.
There is yet another Circumstance which recommends a Description more
than all the rest, and that is if it represents to us such Objects as
are apt to raise a secret Ferment in the Mind of the Reader, and to
work, with Violence, upon his Passions. For, in this Case, we are at
once warmed and enlightened, so that the Pleasure becomes more
Universal, and is several ways qualified to entertain us. Thus in
Painting, it is pleasant to look on the Picture of any Face, where the
Resemblance is hit, but the Pleasure increases, if it be the Picture of
a Face that is Beautiful, and is still greater, if the Beauty be
softened with an Air of Melancholy or Sorrow. The two leading Passions
which the more serious Parts of Poetry endeavour to stir up in us, are
Terror and Pity. And here, by the way, one would wonder how it comes to
pass, that such Passions as are very unpleasant at all other times, are
very agreeable when excited by proper Descriptions. It is not strange,
that we should take Delight in such Passions as are apt to produce Hope,
Joy, Admiration, Love, or the like Emotions in us, because they never
rise in the Mind without an inward Pleasure which attends them. But how
comes it to pass,
we should take delight in being terrified or
dejected by a Description, when we find so much Uneasiness in the Fear
or Grief
which
we receive from any other Occasion?
If we consider, therefore, the Nature of this Pleasure, we shall find
that it does not arise so properly from the Description of what is
terrible, as from the Reflection we make on our selves at the time of
reading it. When we look on such hideous Objects, we are not a little
pleased to think we are in no Danger of them. We consider them at the
same time, as Dreadful and Harmless; so that the more frightful
Appearance they make, the greater is the Pleasure we receive from the
Sense of our own Safety. In short, we look upon the Terrors of a
Description, with the same Curiosity and Satisfaction that we survey a
dead Monster.
—Informe cadaver
Protrahitur, nequeunt expleri corda tuendo
Terribiles oculos: vultum, villosaque satis
Pectora semiferi, atque extinctos faucibus ignes.
Virg.
It is for the same Reason that we are delighted with the reflecting upon
Dangers that are past, or in looking on a Precipice at a distance, which
would fill us with a different kind of Horror, if we saw it hanging over
our Heads.
In the like manner, when we read of Torments, Wounds, Deaths, and the
like dismal Accidents, our Pleasure does not flow so properly from the
Grief which
melancholy Descriptions give us, as from the secret
Comparison which we make between our selves and the Person
who
suffers. Such Representations teach us to set a just Value upon our own
Condition, and make us prize our good Fortune, which exempts us from the
like Calamities. This is, however, such a kind of Pleasure as we are not
capable of receiving, when we see a Person actually lying under the
Tortures that we meet with in a Description; because in this case, the
Object presses too close upon our Senses, and bears so hard upon us,
that it does not give us Time or Leisure to reflect on our selves. Our
Thoughts are so intent upon the Miseries of the Sufferer, that we cannot
turn them upon our own Happiness. Whereas, on the contrary, we consider
the Misfortunes we read in History or Poetry, either as past, or as
fictitious, so that the Reflection upon our selves rises in us
insensibly, and over-bears the Sorrow we conceive for the Sufferings of
the Afflicted.
But because the Mind of Man requires something more perfect in Matter,
than what it finds there, and can never meet with any Sight in Nature
which sufficiently answers its highest Ideas of Pleasantness; or, in
other Words, because the Imagination can fancy to it self Things more
Great, Strange, or Beautiful, than the Eye ever saw, and is still
sensible of some Defect in what it has seen; on this account it is the
part of a Poet to humour the Imagination in its own Notions, by mending
and perfecting Nature where he describes a Reality, and by adding
greater Beauties than are put together in Nature, where he describes a
Fiction.
He is not obliged to attend her in the slow Advances which she makes
from one Season to another, or to observe her Conduct, in the successive
Production of Plants and Flowers. He may draw into his Description all
the Beauties of the Spring and Autumn, and make the whole Year
contribute something to render it the more agreeable. His Rose-trees,
Wood-bines, and Jessamines may flower together, and his Beds be cover'd
at the same time with Lillies, Violets, and Amaranths. His Soil is not
restrained to any particular Sett of Plants, but is proper either for
Oaks or Mirtles, and adapts itself to the Products of every Climate.
Oranges may grow wild in it; Myrrh may be met with in every Hedge, and
if he thinks it proper to have a Grove of Spices, he can quickly command
Sun enough to raise it. If all this will not furnish out an agreeable
Scene, he can make several new Species of Flowers, with richer Scents
and higher Colours than any that grow in the Gardens of Nature. His
Consorts of Birds may be as full and harmonious, and his Woods as thick
and gloomy as he pleases. He is at no more Expence in a long Vista, than
a short one, and can as easily throw his Cascades from a Precipice of
half a Mile high, as from one of twenty Yards. He has his Choice of the
Winds, and can turn the Course of his Rivers in all the Variety of
Meanders
, that are most delightful to the Reader's Imagination.
In a word, he has the modelling of Nature in his own Hands, and may give
her what Charms he pleases, provided he does not reform her too much,
and run into Absurdities, by endeavouring to excel.
O.
that
that
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 1, 1712 |
Addison |
—mentis gratissimus Error.
Hor.
There is a kind of Writing, wherein the Poet quite loses Sight of
Nature, and entertains his Reader's Imagination with the Characters and
Actions of such Persons as have many of them no Existence, but what he
bestows on them. Such are Fairies, Witches, Magicians, Demons, and
departed Spirits. This Mr.
Dryden
calls
the Fairy Way of
Writing
, which is, indeed, more difficult than any other that
depends on the Poet's Fancy, because he has no Pattern to follow in it,
and must work altogether out of his own Invention.
There is a very odd Turn of Thought required for this sort of Writing,
and it is impossible for a Poet to succeed in it, who has not a
particular Cast of Fancy, and an Imagination naturally fruitful and
superstitious. Besides this, he ought to be very well versed in Legends
and Fables, antiquated Romances, and the Traditions of Nurses and old
Women, that he may fall in with our natural Prejudices, and humour those
Notions which we have imbibed in our Infancy. For otherwise he will be
apt to make his Fairies talk like People of his own Species, and not
like other Setts of Beings, who converse with different Objects, and
think in a different Manner from that of Mankind;
Sylvis deducti caveant, me Judice, Fauni
Ne velut innati triviis ac pœne forenses
Aut nimium teneris juvenentur versibus
Hor.
I do not say with Mr.
Bays
in the
Rehearsal
, that Spirits must not
be confined to speak Sense, but it is certain their Sense ought to be a
little discoloured, that it may seem particular, and proper to the
Person and the Condition of the Speaker.
These Descriptions raise a pleasing kind of Horrour in the Mind of the
Reader, and amuse his Imagination with the Strangeness and Novelty of
the Persons who are represented in them. They bring up into our Memory
the Stories we have heard in our Childhood, and favour those secret
Terrors and Apprehensions to which the Mind of Man is naturally subject.
We are pleased with surveying the different Habits and Behaviours of
Foreign Countries, how much more must we be delighted and surprised when
we are led, as it were, into a new Creation, and see the Persons and
Manners of another Species? Men of cold Fancies, and Philosophical
Dispositions, object to this kind of Poetry, that it has not Probability
enough to affect the Imagination. But to this it may be answered, that
we are sure, in general, there are many Intellectual Beings in the World
besides our selves, and several Species of Spirits, who are subject to
different Laws and œconomies from those of Mankind; when we see,
therefore, any of these represented naturally, we cannot look upon the
Representation as altogether impossible; nay, many are prepossest with
such false Opinions, as dispose them to believe these particular
Delusions; at least, we have all heard so many pleasing Relations in
favour of them, that we do not care for seeing through the Falshood, and
willingly give our selves up to so agreeable an Imposture.
The Ancients have not much of this Poetry among them, for, indeed,
almost the whole Substance of it owes its Original to the Darkness and
Superstition of later Ages, when pious Frauds were made use of to amuse
Mankind, and frighten them into a Sense of their Duty. Our Forefathers
look'd upon Nature with more Reverence and Horrour, before the World was
enlightened by Learning and Philosophy, and lov'd to astonish themselves
with the Apprehensions of Witchcraft, Prodigies, Charms and
Enchantments. There was not a Village in
England
, that had not a Ghost
in it, the Church-yards were all haunted, every large Common had a
Circle of Fairies belonging to it, and there was scarce a Shepherd to be
met with who had not seen a Spirit.
Among all the Poets of this Kind our
English
are much the best, by
what I have yet seen; whether it be that we abound with more Stories of
this Nature, or that the Genius of our Country is fitter for this sort
of Poetry. For the
English
are naturally fanciful, and very often
disposed by that Gloominess and Melancholy of Temper, which is so
frequent in our Nation, to many wild Notions and Visions, to which
others are not so liable.
Among the
English
,
Shakespear
has incomparably excelled all others.
That noble Extravagance of Fancy which he had in so great Perfection,
thoroughly qualified him to touch this weak superstitious Part of his
Reader's Imagination; and made him capable of succeeding, where he had
nothing to support him besides the Strength of his own Genius. There is
something so wild and yet so solemn in the Speeches of his Ghosts,
Fairies, Witches and the like Imaginary Persons, that we cannot forbear
thinking them natural, tho' we have no rule by which to judge of them,
and must confess, if there are such Beings in the World, it looks highly
probable that they should talk and act as he has represented them.
There is another sort of imaginary Beings, that we sometimes meet with
among the Poets, when the Author represents any Passion, Appetite,
Virtue or Vice, under a visible Shape, and makes it a Person or an Actor
in his Poem. Of this Nature are the Descriptions of Hunger and Envy in
Ovid
, of Fame in
Virgil
, and of Sin and Death in
Milton
. We find a
whole Creation of the like Shadowy Persons in
Spencer
, who had an
admirable Talent in Representations of this kind. I have discoursed of
these Emblematical Persons in former Papers, and shall therefore only
mention them in this Place. Thus we see how many Ways Poetry addresses
it self to the Imagination, as it has not only the whole Circle of
Nature for its Province, but makes new Worlds of its own, shews us
Persons who are not to be found in Being, and represents even the
Faculties of the Soul, with her several Virtues and Vices, in a sensible
Shape and Character.
I shall, in my two following Papers, consider in general, how other
kinds of Writing are qualified to please the Imagination, with which I
intend to conclude this Essay.
O.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 2, 1712 |
Addison |
Quocunque volunt mentem Auditoris agunto.
Hor.
As the Writers in Poetry and Fiction borrow their several Materials from
outward Objects, and join them together at their own Pleasure, there are
others who are obliged to follow Nature more closely, and to take entire
Scenes out of her. Such are Historians, natural Philosophers,
Travellers, Geographers, and in a Word, all who describe visible Objects
of a real Existence.
It is the most agreeable Talent of an Historian, to be able to draw up
his Armies and fight his Battels in proper Expressions, to set before
our Eyes the Divisions, Cabals, and Jealousies of great Men, and to lead
us Step by Step into the several Actions and Events of his History. We
love to see the Subject unfolding it self by just Degrees, and breaking
upon us insensibly, that so we may be kept in a pleasing Suspense, and
have time given us to raise our Expectations, and to side with one of
the Parties concerned in the Relation. I confess this shews more the Art
than the Veracity of the Historian, but I am only to speak of him as he
is qualified to please the Imagination. And in this respect
Livy
has,
perhaps, excelled all who went before him, or have written since his
Time. He describes every thing in so lively a Manner, that his whole
History is an admirable Picture, and touches on such proper
Circumstances in every Story, that his Reader becomes a kind of
Spectator, and feels in himself all the Variety of Passions which are
correspondent to the several Parts of the Relation.
But among this Sett of Writers there are none who more gratifie and
enlarge the Imagination, than the Authors of the new Philosophy, whether
we consider their Theories of the Earth or Heavens, the Discoveries they
have made by Glasses, or any other of their Contemplations on Nature. We
are not a little pleased to find every green Leaf swarm with Millions of
Animals, that at their largest Growth are not visible to the naked Eye.
There is something very engaging to the Fancy, as well as to our Reason,
in the Treatises of Metals, Minerals, Plants, and Meteors. But when we
survey the whole Earth at once, and the several Planets that lie within
its Neighbourhood, we are filled with a pleasing Astonishment, to see so
many Worlds hanging one above another, and sliding round their Axles in
such an amazing Pomp and Solemnity. If, after this, we contemplate those
wild Fields of
Æther
, that reach in Height as far as from
Saturn
to
the fixt Stars, and run abroad almost to an Infinitude, our Imagination
finds its Capacity filled with so immense a Prospect, and puts it self
upon the Stretch to comprehend it. But if we yet rise higher, and
consider the fixt Stars as so many vast Oceans of Flame, that are each
of them attended with a different Sett of Planets, and still discover
new Firmaments and new Lights that are sunk farther in those
unfathomable Depths of
Æther
, so as not to be seen by the strongest of
our Telescopes, we are lost in such a Labyrinth of Suns and Worlds, and
confounded with the Immensity and Magnificence of Nature.
Nothing is
pleasant to the Fancy, than to enlarge it self by
Degrees, in its Contemplation of the various Proportions
which
its
several Objects bear to each other, when it compares the Body of Man to
the Bulk of the whole Earth, the Earth to the Circle it describes round
the Sun, that Circle to the Sphere of the fixt Stars, the sphere of the
fixt Stars to the Circuit of the whole Creation, the whole Creation it
self to the infinite Space that is every where diffused about it; or
when the Imagination works downward, and considers the Bulk of a human
Body in respect of an Animal, a
times less than a Mite, the
particular Limbs of such an Animal, the different Springs
which
actuate the Limbs, the Spirits which set these Springs a going, and the
proportionable Minuteness of these several Parts, before they have
arrived at their full Growth and Perfection. But if, after all this, we
take the least Particle of these Animal Spirits, and consider its
Capacity of being Wrought into a World, that shall contain within those
narrow Dimensions a Heaven and Earth, Stars and Planets, and every
different Species of living Creatures, in the same Analogy and
Proportion they bear to each other in our own Universe; such a
Speculation, by reason of its Nicety, appears ridiculous to those who
have not turned their Thoughts that way, though at the same time it is
founded on no less than the Evidence of a Demonstration. Nay, we might
yet carry it farther, and discover in the smallest Particle of this
little World a new and inexhausted Fund of Matter, capable of being spun
out into another Universe.
I have dwelt the longer on this Subject, because I think it may shew us
the proper Limits, as well as the Defectiveness of our Imagination; how
it is confined to a very small Quantity of Space, and immediately stopt
in its Operations, when it endeavours to take in any thing that is very
great, or very little. Let a Man try to conceive the different Bulk of
an Animal, which is twenty, from another which is a hundred times less
than a Mite, or to compare, in his Thoughts, a length of a thousand
Diameters of the Earth, with that of a Million, and he will quickly find
that he has no different Measures in his Mind, adjusted to such
extraordinary Degrees of Grandeur or Minuteness. The Understanding,
indeed, opens an infinite Space on every side of us, but the
Imagination, after a few faint Efforts, is immediately at a stand, and
finds her self swallowed up in the Immensity of the Void that surrounds
it: Our Reason can pursue a Particle of Matter through an infinite
Variety of Divisions, but the Fancy soon loses sight of it, and feels in
it self a kind of Chasm, that wants to be filled with Matter of a more
sensible Bulk. We can neither widen, nor contract the Faculty to the
Dimensions of either Extreme. The Object is too big for our Capacity,
when we would comprehend the Circumference of a World, and dwindles into
nothing, when we endeavour after the Idea of an Atome.
It is possible this defect of Imagination may not be in the Soul it
self, but as it acts in Conjunction with the Body. Perhaps there may not
be room in the Brain for such a variety of Impressions, or the Animal
Spirits may be incapable of figuring them in such a manner, as is
necessary to excite so very large or very minute Ideas. However it be,
we may well suppose that Beings of a higher Nature very much excel us in
this respect, as it is probable the Soul of Man will be infinitely more
perfect hereafter in this Faculty, as well as in all the rest; insomuch
that, perhaps, the Imagination will be able to keep Pace with the
Understanding, and to form in it self distinct Ideas of all the
different Modes and Quantities of Space.
O.
that
that
Contents
|
Thursday, July 3, 1712 |
Addison |
Ignotis errare locis, ignota videre
Flumina gaudebat; studio minuente laborem.
Ovid.
The Pleasures of the Imagination are not wholly confined to such
particular Authors as are conversant in material Objects, but are often
to be met with among the Polite Masters of Morality, Criticism, and
other Speculations abstracted from Matter, who, tho' they do not
directly treat of the visible Parts of Nature, often draw from them
their Similitudes, Metaphors, and Allegories. By these Allusions a Truth
in the Understanding is as it were reflected by the Imagination; we are
able to see something like Colour and Shape in a Notion, and to discover
a Scheme of Thoughts traced out upon Matter. And here the Mind receives
a great deal of Satisfaction, and has two of its Faculties gratified at
the same time, while the Fancy is busie in copying after the
Understanding, and transcribing Ideas out of the Intellectual World into
the Material.
The Great Art of a Writer shews it self in the Choice of pleasing
Allusions, which are generally to be taken from the
great
or
beautiful
Works of Art or Nature; for though whatever is New or
Uncommon is apt to delight the Imagination, the chief Design of an
Allusion being to illustrate and explain the Passages of an Author, it
should be always borrowed from what is more known and common, than the
Passages which are to be explained.
Allegories, when well chosen, are like so many Tracks of Light in a
Discourse, that make every thing about them clear and beautiful. A noble
Metaphor, when it is placed to an Advantage, casts a kind of Glory round
it, and darts a Lustre through a whole Sentence: These different Kinds
of Allusion are but so many different Manners of Similitude, and, that
they may please the Imagination, the Likeness ought to be very exact, or
very agreeable, as we love to see a Picture where the Resemblance is
just, or the Posture and Air graceful. But we often find eminent Writers
very faulty in this respect; great Scholars are apt to fetch their
Comparisons and Allusions from the Sciences in which they are most
conversant, so that a Man may see the Compass of their Learning in a
Treatise on the most indifferent Subject. I have read a Discourse upon
Love, which none but a profound Chymist could understand, and have heard
many a Sermon that should only have been preached before a Congregation
of
Cartesians
. On the contrary, your Men of Business usually have
recourse to such Instances as are too mean and familiar. They are for
drawing the Reader into a Game of Chess or Tennis, or for leading him
from Shop to Shop, in the Cant of particular Trades and Employments. It
is certain, there may be found an infinite Variety of very agreeable
Allusions in both these kinds, but for the generality, the most
entertaining ones lie in the Works of Nature, which are obvious to all
Capacities, and more delightful than what is to be found in Arts and
Sciences.
It is this Talent of affecting the Imagination, that gives an
Embellishment to good Sense, and makes one Man's Compositions more
agreeable than another's. It sets off all Writings in general, but is
the very Life and highest Perfection of Poetry: Where it shines in an
Eminent Degree, it has preserved several Poems for many Ages, that have
nothing else to recommend them; and where all the other Beauties are
present, the Work appears dry and insipid, if this single one be
wanting. It has something in it like Creation; It bestows a kind of
Existence, and draws up to the Reader's View several Objects which are
not to be found in Being. It makes Additions to Nature, and gives a
greater Variety to God's Works. In a Word, it is able to beautifie and
adorn the most illustrious Scenes in the Universe, or to fill the Mind
with more glorious Shows and Apparitions, than can be found in any Part
of it.
We have now discovered the several Originals of those Pleasures that
gratify the Fancy; and here, perhaps, it would not be very difficult to
cast under their proper Heads those contrary Objects, which are apt to
fill it with Distaste and Terrour; for the Imagination is as liable to
Pain as Pleasure. When the Brain is hurt by any Accident, or the Mind
disordered by Dreams or Sickness, the Fancy is over-run with wild dismal
Ideas, and terrified with a thousand hideous Monsters of its own framing.
Eumenidum veluti demens videt Agmina Pentheus,
Et solem geminum, et duplices se ostendere Thebas.
Aut Agamemnonius scenis agitatus Orestes,
Armatam facibus matrem et serpentibus atris
Cum videt, ultricesque sedent in limine Diræ.
Vir.
There is not a Sight in Nature so mortifying as that of a Distracted
Person, when his Imagination is troubled, and his whole Soul disordered
and confused.
Babylon
in Ruins is not so melancholy a Spectacle. But
to quit so disagreeable a Subject, I shall only consider, by way of
Conclusion, what an infinite Advantage this Faculty gives an Almighty
Being over the Soul of Man, and how great a measure of Happiness or
Misery we are capable of receiving from the Imagination only.
We have already seen the Influence that one Man has over the Fancy of
another, and with what Ease he conveys into it a Variety of Imagery; how
great a Power then may we suppose lodged in him, who knows all the ways
of affecting the Imagination, who can infuse what Ideas he pleases, and
fill those Ideas with Terrour and Delight to what Degree he thinks fit?
He can excite Images in the Mind, without the help of Words, and make
Scenes rise up before us and seem present to the Eye without the
Assistance of Bodies or Exterior Objects. He can transport the
Imagination with such beautiful and glorious Visions, as cannot possibly
enter into our present Conceptions, or haunt it with such ghastly
Spectres and Apparitions, as would make us hope for Annihilation, and
think Existence no better than a Curse. In short, he can so exquisitely
ravish or torture the Soul through this single Faculty, as might suffice
to make up the whole Heaven or Hell of any finite Being.
This Essay on the Pleasures of the Imagination having been published in
separate Papers, I shall conclude it with a Table of the principal
Contents in each Paper.
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper I |
The Perfection of our Sight above our other Senses. The Pleasures of
the Imagination arise originally from Sight. The Pleasures of the
Imagination divided under two Heads. The Pleasures of the Imagination
in some Respects equal to those of the Understanding. The Extent of
the Pleasures of the Imagination. The Advantages a Man receives from a
Relish of these Pleasures. In what Respect they are preferable to
those of the Understanding. |
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper II |
Three Sources of all the Pleasures of the Imagination, in our Survey
of outward Objects. How what is Great pleases the Imagination. How
what is New pleases the Imagination. How what is Beautiful in our
own Species, pleases the Imagination. How what is Beautiful in
general pleases the Imagination. What other Accidental Causes may
contribute to the heightening of these Pleasures.
|
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper III |
Why the Necessary Cause of our being pleased with what is Great,
New, or Beautiful, unknown. Why the Final Cause more known and more
useful. The Final Cause of our being pleased with what is Great. The
Final Cause of our being pleased with what is New. The Final Cause
of our being pleased with what is Beautiful in our own Species. The
Final Cause of our being pleased with what is Beautiful in general.
|
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper IV |
The Works of Nature more pleasant to the Imagination than those of
Art. The Works of Nature still more pleasant, the more they resemble
those of Art. The Works of Art more pleasant, the more they resemble
those of Nature. Our English Plantations and Gardens considered
in the foregoing Light.
|
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper V |
Of Architecture as it affects the Imagination. Greatness in
Architecture relates either to the Bulk or to the Manner.
Greatness of Bulk in the Ancient Oriental Buildings. The ancient
Accounts of these Buildings confirm'd,
- From the Advantages, for
raising such Works, in the first Ages of the World and in the Eastern
Climates:
-
From several of them which are still extant.
Instances how Greatness of Manner affects the Imagination. A French
Author's Observation on this Subject. Why Concave and Convex Figures
give a Greatness of Manner to Works of Architecture. Every thing that
pleases the Imagination in Architecture is either Great, Beautiful, or
New. |
[Vol. 2 link]
Paper VI |
The Secondary Pleasures of the Imagination. The several Sources of
these Pleasures (Statuary, Painting, Description and Musick)
compared together. The Final Cause of our receiving Pleasure from
these several Sources. Of Descriptions in particular. The Power of
Words over the Imagination. Why one Reader more pleased with
Descriptions than another.
|
| Paper VII |
How a whole Set of Ideas Hang together, &c. A Natural Cause
assigned for it. How to perfect the Imagination of a Writer. Who
among the Ancient Poets had this Faculty in its greatest
Perfection. Homer excelled in Imagining what is Great; Virgil in
Imagining what is Beautiful; Ovid in imagining what is New. Our own
Country-man Milton very perfect in all three respects.
|
| Paper VIII |
Why any thing that is unpleasant to behold, pleases the Imagination
when well described. Why the Imagination receives a more Exquisite
Pleasure from the Description of what is Great, New, or Beautiful.
The Pleasure still heightned, if—what is described raises Passion
in the Mind. Disagreeable Passions pleasing when raised by apt
Descriptions. Why Terror and Grief are pleasing to the Mind when
excited by Descriptions. A particular Advantage the Writers in Poetry
and Fiction have to please the Imagination. What Liberties are allowed
them.
|
| Paper IX |
Of that kind of Poetry which Mr. Dryden calls the Fairy Way of
Writing. How a Poet should be Qualified for it. The Pleasures of
the Imagination that arise from it. In this respect why the Moderns
excell the Ancients. Why the English excell the Moderns. Who the
Best among the English. Of Emblematical Persons.
|
| Paper X |
What Authors please the Imagination who have nothing to do with
Fiction. How History pleases the Imagination. How the Authors of
the new Philosophy please the Imagination. The Bounds and Defects
of the Imagination. Whether these Defects are Essential to the
Imagination.
|
| Paper XI |
How those please the Imagination who treat of Subjects abstracted
from Matter, by Allusions taken from it. What Allusions most
pleasing to the Imagination. Great Writers how Faulty in this
Respect. Of the Art of Imagining in General. The Imagination capable
of Pain as well as Pleasure. In what Degree the Imagination is
capable either of Pain or Pleasure.
|
O.
Contents
|
Friday, July 4, 1712 |
Steele |
Hæc scripsi non otii abundantia sed amoris erga te.
Tull.
Epis.
I do not know any thing which gives greater Disturbance to Conversation,
than the false Notion some People have of Raillery. It ought certainly
to be the first Point to be aimed at in Society, to gain the good Will
of those with whom you converse. The Way to that, is to shew you are
well inclined towards them: What then can be more absurd, than to set up
for being extremely sharp and biting, as the Term is, in your
Expressions to your Familiars? A Man who has no good Quality but
Courage, is in a very ill way towards making an agreeable Figure in the
World, because that which he has superior to other People cannot be
exerted, without raising himself an
Enemy
. Your Gentleman of a
Satyrical Vein is in the like Condition. To say a Thing which perplexes
the Heart of him you speak to, or brings Blushes into his Face, is a
degree of Murder; and it is, I think, an unpardonable Offence to shew a
Man you do not care, whether he is pleased or displeased. But won't you
then take a Jest? Yes: but pray let it be a Jest. It is no Jest to put
me, who am so unhappy as to have an utter Aversion to speaking to more
than one Man at a time, under a Necessity to explain my self in much
Company, and reducing me to Shame and Derision, except I perform what my
Infirmity of Silence disables me to do.
Callisthenes
has great Wit accompanied with that Quality (without
which a Man can have no Wit at all) a Sound Judgment. This Gentleman
rallies the best of any Man I know, for he forms his Ridicule upon a
Circumstance which you are in your Heart not unwilling to grant him, to
wit, that you are Guilty of an Excess in something which is in it self
laudable. He very well understands what you would be, and needs not fear
your Anger for declaring you are a little too much that Thing. The
Generous will bear being reproached as Lavish, and the Valiant, Rash,
without being provoked to Resentment against their Monitor. What has
been said to be a Mark of a good Writer, will fall in with the Character
of a good Companion. The good Writer makes his Reader better pleased
with himself, and the agreeable Man makes his Friends enjoy themselves,
rather than him, while he is in their Company.
Callisthenes
does this
with inimitable Pleasantry. He whispered a Friend the other Day, so as
to be overheard by a young Officer, who gave Symptoms of Cocking upon
the Company, That Gentleman has very much of the Air of a General
Officer. The Youth immediately put on a Composed Behaviour, and behaved
himself suitably to the Conceptions he believed the Company had of him.
It is to be allowed that
Callisthenes
will make a Man run into
impertinent Relations, to his own Advantage, and express the
Satisfaction he has in his own dear self till he is very ridiculous, but
in this case the Man is made a Fool by his own Consent, and not exposed
as such whether he will or no. I take it therefore that to make Raillery
agreeable, a Man must either not know he is rallied, or think never the
worse of himself if he sees he is.
Acetus
is of a quite contrary Genius, and is more generally admired
than
Callisthenes
, but not with Justice.
Acetus
has no regard to the
Modesty or Weakness of the Person he rallies; but if his Quality or
Humility gives him any Superiority to the Man he would fall upon, he has
no Mercy in making the Onset. He can be pleased to see his best Friend
out of Countenance, while the Laugh is loud in his own Applause. His
Raillery always puts the Company into little Divisions and separate
Interests, while that of
Callisthenes
cements it, and makes every Man
not only better pleased with himself, but also with all the rest in the
Conversation.
To rally well, it is absolutely necessary that Kindness must run thro'
all you say, and you must ever preserve the Character of a Friend to
support your Pretensions to be free with a Man.
Acetus
ought to be
banished human Society, because he raises his Mirth upon giving Pain to
the Person upon whom he is pleasant. Nothing but the Malevolence, which
is too general towards those who excell, could make his Company
tolerated; but they with whom he converses, are sure to see some Man
sacrificed where-ever he is admitted, and all the Credit he has for Wit
is owing to the Gratification it gives to other Men's Ill-nature.
Minutius
has a Wit that conciliates a Man's Love at the same time that
it is exerted against his Faults. He has an Art of keeping the Person he
rallies in Countenance, by insinuating that he himself is guilty of the
same Imperfection. This he does with so much Address, that he seems
rather to bewail himself, than fall upon his Friend.
It is really monstrous to see how unaccountably it prevails among Men,
to take the Liberty of displeasing each other. One would think sometimes
that the Contention is, who shall be most disagreeable, Allusions to
past Follies, Hints which revive what a Man has a Mind to forget for
ever, and deserves that all the rest of the World should, are commonly
brought forth even in Company of Men of Distinction. They do not thrust
with the Skill of Fencers, but cut up with the Barbarity of Butchers. It
is, methinks, below the Character of Men of Humanity and Good-manners,
to be capable of Mirth while there is any one of the Company in Pain and
Disorder. They who have the true Taste of Conversation, enjoy themselves
in a Communication of each other's Excellencies, and not in a Triumph
over their Imperfections.
Fortius
would have been reckoned a Wit, if
there had never been a Fool in the World: He wants not Foils to be a
Beauty, but has that natural Pleasure in observing Perfection in others,
that his own Faults are overlooked out of Gratitude by all his
Acquaintance.
After these several Characters of Men who succeed or fail in Raillery,
it may not be amiss to reflect a little further what one takes to be the
most agreeable Kind of it; and that to me appears when the Satyr is
directed against Vice, with an Air of Contempt of the Fault, but no
Ill-will to the Criminal. Mr.
Congreve's Doris
is a Master-piece in
this Kind. It is the Character of a Woman utterly abandoned, but her
Impudence by the finest Piece of Raillery is made only Generosity.
Peculiar therefore is her Way,
Whether by Nature taught,
I shall not undertake to say,
Or by experience bought;
For who o'er Night obtain'd her Grace,
She can next Day disown,
And stare upon the strange Man's Face,
As one she ne'er had known,
So well she can the Truth disguise,
Such artful Wonder frame,
The Lover or distrusts his Eyes,
Or thinks 'twas all a Dream.
Some censure this as lewd or low,
Who are to Bounty blind;
For to forget what we bestow,
Bespeaks a noble Mind.
T.
Contents
|
Satday, July 5, 1712 |
Steele |
—Nuper Idoneus.
Hor.
I look upon my self as a Kind of Guardian to the Fair, and am always
watchful to observe any thing which concerns their Interest. The present
Paper shall be employed in the Service of a very fine young Woman; and
the Admonitions I give her, may not be unuseful to the rest of the Sex.
Gloriana
shall be the Name of the Heroine in To-day's Entertainment;
and when I have told you that she is rich, witty, young and beautiful,
you will believe she does not want Admirers. She has had since she came
to Town about twenty five of those Lovers, who make their Addresses by
way of Jointure and Settlement. These come and go, with great
Indifference on both Sides; and as beauteous as she is, a Line in a Deed
has had Exception enough against it, to outweigh the Lustre of her Eyes,
the Readiness of her Understanding, and the Merit of her general
Character. But among the Crowd of such cool Adorers, she has two who are
very assiduous in their Attendance. There is something so extraordinary
and artful in their Manner of Application, that I think it but common
Justice to alarm her in it. I have done it in the following Letter.
Madam,
'I have for some time taken Notice of two Gentlemen who attend you in
all publick Places, both of whom have also easie Access to you at your
own House: But the Matter is adjusted between them, and
Damon
, who
so passionately addresses you, has no Design upon you; but
Strephon
,
who seems to be indifferent to you, is the Man, who is, as they have
settled it, to have you. The Plot was laid over a Bottle of Wine; and
Strephon
, when he first thought of you, proposed to
Damon
to be
his Rival. The manner of his breaking of it to him, I was so placed at
a Tavern, that I could not avoid hearing.
Damon
, said he with a deep
Sigh, I have long languished for that Miracle of Beauty
Gloriana
,
and if you will be very stedfastly my Rival, I shall certainly obtain
her. Do not, continued he, be offended at this Overture; for I go upon
the Knowledge of the Temper of the Woman, rather than any Vanity that
I should profit by an Opposition of your Pretensions to those of your
humble Servant.
Gloriana
has very good Sense, a quick Relish of the
Satisfactions of Life, and will not give her self, as the Crowd of
Women do, to the Arms of a Man to whom she is indifferent. As she is a
sensible Woman, Expressions of Rapture and Adoration will not move her
neither; but he that has her must be the Object of her De
Sir
e, not her
Pity. The Way to this End I take to be, that a Man's general Conduct
should be agreeable, without addressing in particular to the Woman he
loves. Now,
Sir
, if you will be so kind as to sigh and die for
Gloriana
, I will carry it with great Respect towards her, but seem
void of any Thoughts as a Lover. By this Means I shall be in the most
amiable Light of which I am capable; I shall be received with Freedom,
you with Reserve.
Damon
, who has himself no Designs of Marriage at
all, easily fell into the Scheme; and you may observe, that where-ever
you are
Damon
appears also. You see he carries on an unaffecting
Exactness in his Dress and Manner, and strives always to be the very
Contrary of
Strephon
. They have already succeeded so far, that your
Eyes are ever in Search of
Strephon
, and turn themselves of Course
from
Damon
. They meet and compare Notes upon your Carriage; and the
Letter which, was brought to you the other Day, was a Contrivance to
remark your Resentment. When you saw the Billet subscribed
Damon
,
and turned away with a scornful Air, and cried Impertinence! you gave
Hopes to him that shuns you, without mortifying him that languishes
for you. What I am concerned for, Madam, is, that in the disposal of
your Heart, you should know what you are doing, and examine it before
it is lost.
Strephon
contradicts you in Discourse with the Civility
of one who has a Value for you, but gives up nothing like one that
loves you. This seeming Unconcern gives this Behaviour the advantage
of Sincerity, and insensibly obtains your good Opinion, by appearing
disinterested in the purchase of it. If you watch these Correspondents
hereafter, you will find that
Strephon
makes his Visit of Civility
immediately after
Damon
has tired you with one of Love. Tho' you are
very discreet, you will find it no easie matter to escape the Toils so
well laid, as when one studies to be disagreeable in Passion, the
other to be pleasing without it. All the Turns of your Temper are
carefully watched, and their quick and faithful Intelligence gives
your Lovers irresistible Advantage. You will please, Madam, to be upon
your guard, and take all the necessary Precautions against one who is
amiable to you before you know he is enamoured.
I am, Madam,
Your most Obedient Servant.
Strephon
makes great Progress in this Lady's good Graces, for most
Women being actuated by some little Spirit of Pride and Contradiction,
he has the good effects of both those Motives by this Covert-Way of
Courtship. He received a Message Yesterday from
Damon
in the following
Words, superscribed
With Speed
.
'All goes well; she is very angry at me, and I dare say hates me in
earnest. It is a good time to Visit.
Yours.'
The Comparison of
Strephon's
Gayety to
Damon's
Languishment, strikes
her Imagination with a Prospect of very agreeable Hours with such a Man
as the former, and Abhorrence of the insipid Prospect with one like the
latter. To know when a Lady is displeased with another, is to know the
best time of advancing your self. This method of two Persons playing
into each other's Hand is so dangerous, that I cannot tell how a Woman
could be able to withstand such a Siege. The Condition of
Gloriana
, I
am afraid, is irretrievable, for
Strephon
has had so many
Opportunities of pleasing without suspicion, that all which is left for
her to do is to bring him, now she is advised, to an Explanation of his
Passion, and beginning again, if she can conquer the kind Sentiments she
has already conceived for him. When one shews himself a Creature to be
avoided, the other proper to be fled to for Succour, they have the whole
Woman between them, and can occasionally rebound her Love and Hatred
from one to the other, in such a manner as to keep her at a distance
from all the rest of the World, and cast Lots for the Conquest.
N. B.
I have many other Secrets which concern the Empire of Love, but I
consider that while I alarm my Women, I instruct my Men
.
T.
Contents
|
Monday, July 7, 1712 |
Steele |
Est Ulubris, animus si te non deficit—
Hor.
London, June 24.
Mr.
Spectator,
'A man who has it in his Power to chuse his own Company, would
certainly be much to blame should he not, to the best of his Judgment,
take such as are of a Temper most suitable to his own; and where that
Choice is wanting, or where a Man is mistaken in his Choice, and yet
under a Necessity of continuing in the same Company, it will certainly
be to his Interest to carry himself as easily as possible.
'In this I am sensible I do but repeat what has been said a thousand
times, at which however I think no Body has any Title to take
Exception, but they who never failed to put this in Practice—Not to
use any longer Preface, this being the Season of the Year in which
great Numbers of all sorts of People retire from this Place of
Business and Pleasure to Country Solitude, I think it not improper to
advise them to take with them as great a Stock of Good-humour as they
can; for tho' a Country-Life is described as the most pleasant of all
others, and though it may in Truth be so, yet it is so only to those
who know how to enjoy Leisure and Retirement.
'As for those who can't live without the constant helps of Business or
Company, let them consider, that in the Country there is no
Exchange, there are no Play-houses, no Variety of Coffee-houses, nor
many of those other Amusements which serve here as so many Reliefs
from the repeated Occurrences in their own Families; but that there
the greatest Part of their Time must be spent within themselves, and
consequently it behoves them to consider how agreeable it will be to
them before they leave this dear Town.
'I remember, Mr. SPECTATOR, we were very well entertained last Year,
with the Advices you gave us from
Sir Roger's Country Seat; which I
the rather mention, because 'tis almost impossible not to live
pleasantly, where the Master of a Family is such a one as you there
describe your Friend, who cannot therefore (I mean as to his domestick
Character) be too often recommended to the Imitation of others. How
amiable is that Affability and Benevolence with which he treats his
Neighbours, and every one, even the meanest of his own Family! And yet
how seldom imitated? instead of which we commonly meet with
ill-natured Expostulations, Noise, and Chidings—And this I hinted,
because the Humour and Disposition of the Head, is what chiefly
influences all the other Parts of a Family.
'An Agreement and kind Correspondence between Friends and
Acquaintance, is the greatest Pleasure of Life. This is an undoubted
Truth, and yet any Man who judges from the Practice of the World, will
be almost persuaded to believe the contrary; for how can we suppose
People should be so industrious to make themselves uneasie? What can
engage them to entertain and foment Jealousies of one another upon
every the least Occasion? Yet so it is, there are People who (as it
should seem) delight in being troublesome and vexatious, who (as
Tully speaks)
Mira sunt alacritate ad litigandum, Have a certain
Chearfulness in wrangling. And thus it happens, that there are very
few Families in which there are not Feuds and Animosities, tho' 'tis
every one's Interest, there more particularly, to avoid 'em, because
there (as I would willingly hope) no one gives another Uneasiness,
without feeling some share of it—But I am gone beyond what I
designed, and had almost forgot what I chiefly proposed; which was,
barely to tell you, how hardly we who pass most of our Time in Town
dispense with a long Vacation in the Country, how uneasie we grow to
our selves and to one another when our Conversation is confined,
insomuch that by
Michaelmas 'tis odds but we come to downright
squabbling, and make as free with one another to our Faces, as we do
with the rest of the World behind their Backs. After I have told you
this, I am to de
Sir e that you would now and then give us a Lesson of
Good-humour, a Family-Piece; which, since we are all very fond of you,
I hope may have some Influence upon us—
'After these plain Observations give me leave to give you an Hint of
what a Set of Company of my Acquaintance, who are now gone into the
Country, and have the Use of an absent Nobleman's Seat, have settled
among themselves, to avoid the Inconveniencies above mentioned. They
are a Collection of ten or twelve, of the same good Inclination
towards each other, but of very different Talents and Inclinations:
From hence they hope, that the Variety of their Tempers will only
create Variety of Pleasures. But as there always will arise, among the
same People, either for want of Diversity of Objects, or the like
Causes, a certain Satiety, which may grow into ill Humour or
Discontent, there is a large Wing of the House which they design to
employ in the Nature of an Infirmary. Whoever says a peevish thing, or
acts any thing which betrays a Sowerness or Indisposition to Company,
is immediately to be conveyed to his Chambers in the Infirmary; from
whence he is not to be relieved, till by his Manner of Submission, and
the Sentiments expressed in his Petition for that Purpose, he appears
to the Majority of the Company to be again fit for Society. You are to
understand, that all ill-natured Words or uneasie Gestures are
sufficient Cause for Banishment; speaking impatiently to Servants,
making a Man repeat what he says, or any thing that betrays
Inattention or Dishumour, are also criminal without Reprieve: But it
is provided, that whoever observes the ill-natured Fit coming upon
himself, and voluntarily retires, shall be received at his return from
the Infirmary with the highest Marks of Esteem. By these and other
wholesome Methods it is expected that if they cannot cure one another,
yet at least they have taken Care that the ill Humour of one shall not
be troublesome to the rest of the Company. There are many other Rules
which the Society have established for the Preservation of their Ease
and Tranquility, the Effects of which, with the Incidents that arise
among them, shall be communicated to you from Time to Time for the
publick Good, by,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
R. O.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 8, 1712 |
Budgell |
Frigora mitescunt Zephyris, Ver proterit Æstas
Interitura, simul
Pomifer Autumnus fruges effuderit, et mox
Bruma recurrit iners
Hor.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'There is hardly any thing gives me a more sensible Delight, than the
Enjoyment of a cool still Evening after the Uneasiness of a hot sultry
Day. Such a one I passed not long ago, which made me rejoice when the
Hour as come for the Sun to set, that I might enjoy the Freshness of
the Evening in my Garden, which then affords me the pleasantest Hours
I pass in the whole Four and twenty. I immediately rose from my Couch,
and went down into it. You descend at first by twelve Stone Steps into
a large Square divided into four Grass-plots, in each of which is a
Statue of white Marble. This is separated from a large Parterre by a
low Wall, and from thence, thro' a Pair of Iron Gates, you are led
into a long broad Walk of the finest Turf, set on each Side with tall
Yews, and on either Hand bordered by a Canal, which on the Right
divides the Walk from a Wilderness parted into Variety of Allies and
Arbours, and on the Left from a kind of Amphitheatre, which is the
Receptacle of a great Number of Oranges and Myrtles. The Moon shone
bright, and seemed then most agreeably to supply the Place of the Sun,
obliging me with as much Light as was necessary to discover a thousand
pleasing Objects, and at the same time divested of all Power of Heat.
The Reflection of it in the Water, the Fanning of the Wind rustling on
the Leaves, the Singing of the Thrush and Nightingale, and the
Coolness of the Walks, all conspired to make me lay aside all
displeasing Thoughts, and brought me into such a Tranquility of Mind,
as is I believe the next Happiness to that of hereafter. In this sweet
Retirement I naturally fell into the Repetition of some Lines out of a
Poem of
Milton's, which he entitles
Il Penseroso, the Ideas of
which were exquisitely suited to my present Wandrings of Thought.
Sweet Bird! that shun'st the Noise of Folly,
Most musical! most melancholy!
Thee Chauntress, oft the Woods among,
I wooe to hear thy Evening Song:
And missing thee, I walk unseen
On the dry smooth-shaven Green,
To behold the wandring Moon,
Riding near her highest Noon,
Like one that hath been led astray,
Thro' the Heavn's wide pathless Way,
And oft, as if her Head she bow'd,
Stooping thro' a fleecy Cloud.
Then let some strange mysterious Dream
Wave with his Wings in airy Stream,
Of lively Portraiture displaid,
Softly on my Eyelids laid;
And as I wake, sweet Musick breathe
Above, about, or underneath,
Sent by Spirits to Mortals Good,
Or th' unseen Genius of the Wood.
I reflected then upon the sweet Vicissitudes of Night and Day, on the
charming Disposition of the Seasons, and their Return again in a
perpetual Circle; and oh! said I, that I could from these my declining
Years return again to my first Spring of Youth and Vigour; but that,
alas! is impossible: All that remains within my Power, is to soften
the Inconveniences I feel, with an easie contented Mind, and the
Enjoyment of such Delights as this Solitude affords me. In this
Thought I sate me down on a Bank of Flowers and dropt into a Slumber,
which whether it were the Effect of Fumes and Vapours, or my present
Thoughts, I know not; but methought the Genius of the Garden stood
before me, and introduced into the Walk where I lay this Drama and
different Scenes of the Revolution of the Year, which whilst I then
saw, even in my Dream, I resolved to write down, and send to the
SPECTATOR.
The first Person whom I saw advancing towards me was a Youth of a most
beautiful Air and Shape, tho' he seemed not yet arrived at that exact
Proportion and Symmetry of Parts which a little more time would have
given him; but however, there was such a Bloom in his Countenance,
such Satisfaction and Joy, that I thought it the most de
Sir able Form
that I had ever seen. He was cloathed in a flowing Mantle of green
Silk, interwoven with Flowers: He had a Chaplet of Roses on his Head,
and a
Narcissus in his Hand; Primroses and Violets sprang up under
his Feet, and all Nature was cheer'd at his Approach.
Flora was on
one Hand and
Vertumnus on the other in a Robe of changeable Silk.
After this I was surprized to see the Moon-beams reflected with a
sudden Glare from Armour, and to see a Man compleatly armed advancing
with his Sword drawn. I was soon informed by the Genius it was
Mars,
who had long usurp'd a Place among the Attendants of the
Spring. He
made Way for a softer Appearance, it was
Venus, without any Ornament
but her own Beauties, not so much as her own Cestus, with which she
had incompass'd a Globe, which she held in her right Hand, and in her
left she had a Sceptre of Gold. After her followed the Graces with
their Arms intwined within one another, their Girdles were loosed, and
they moved to the Sound of soft Musick, striking the Ground
alternately with their Feet: Then came up the three Months which
belong to this Season. As
March advanced towards me, there was
methought in his Look a louring Roughness, which ill befitted a Month
which was ranked in so soft a Season; but as he came forwards his
Features became insensibly more mild and gentle: He smooth'd his Brow,
and looked with so sweet a Countenance that I could not but lament his
Departure, though he made way for
April. He appeared in the greatest
Gaiety imaginable, and had a thousand Pleasures to attend him: His
Look was frequently clouded, but immediately return'd to its first
Composure, and remained fixed in a Smile. Then came
May attended by
Cupid, with his Bow strung, and in a Posture to let fly an Arrow: As
he passed by methought I heard a confused Noise of soft Complaints,
gentle Ecstacies, and tender Sighs of Lovers; Vows of Constancy, and
as many Complainings of Perfidiousness; all which the Winds wafted
away as soon as they had reached my Hearing. After these I saw a Man
advance in the full Prime and Vigour of his Age, his Complexion was
sanguine and ruddy, his Hair black, and fell down in beautiful
Ringlets not beneath his Shoulders, a Mantle of Hair-colour'd Silk
hung loosely upon him: He advanced with a hasty Step after the
Spring, and sought out the Shade and cool Fountains which plaid in
the Garden. He was particularly well pleased when a Troop of
Zephyrs
fanned him with their Wings: He had two Companions who walked on each
Side that made him appear the most agreeable, the one was
Aurora
with Fingers of Roses, and her Feet dewy, attired in grey: The other
was
Vesper in a Robe of Azure beset with Drops of Gold, whose Breath
he caught whilst it passed over a Bundle of Honey-Suckles and
Tuberoses which he held in his Hand.
Pan and
Ceres followed them
with four Reapers, who danced a Morrice to the Sound of Oaten Pipes
and Cymbals. Then came the Attendant Months.
June retained still
some small Likeness of the
Spring; but the other two seemed to step
with a less vigorous Tread, especially
August, who seem'd almost to
faint whilst for half the Steps he took the Dog-Star levelled his Rays
full at his Head: They passed on and made Way for a Person that seemed
to bend a little under the Weight of Years; his Beard and Hair, which
were full grown, were composed of an equal Number of black and grey;
he wore a Robe which he had girt round him of a yellowish Cast, not
unlike the Colour of fallen Leaves, which he walked upon. I thought he
hardly made Amends for expelling the foregoing Scene by the large
Quantity of Fruits which he bore in his Hands.
Plenty walked by his
Side with an healthy fresh Countenance, pouring out from an Horn all
the various Product of the Year.
Pomona followed with a Glass of
Cyder in her Hand, with
Bacchus in a Chariot drawn by Tygers,
accompanied by a whole Troop of Satyrs, Fauns, and Sylvans.
September, who came next, seem'd in his Looks to promise a new
Spring, and wore the Livery of those Months. The succeeding Month
was all soiled with the Juice of Grapes, as if he had just come from
the Wine-Press.
November, though he was in this Division, yet, by
the many Stops he made seemed rather inclined to the
Winter, which
followed close at his Heels. He advanced in the Shape of an old Man in
the Extremity of Age: The Hair he had was so very white it seem'd a
real Snow; his Eyes were red and piercing, and his Beard hung with a
great Quantity of Icicles: He was wrapt up in Furrs, but yet so
pinched with Excess of Cold that his Limbs were all contracted and his
Body bent to the Ground, so that he could not have supported himself
had it not been for
Comus the God of Revels, and
Necessity the
Mother of Fate, who sustained him on each side. The Shape and Mantle
of
Comus was one of the things that most surprized me; as he
advanced towards me, his Countenance seemed the most de
Sir able I had
ever seen: On the fore Part of his Mantle was pictured Joy, Delight,
and Satisfaction, with a thousand Emblems of Merriment, and Jests with
Faces looking two Ways at once; but as he passed from me I was amazed
at a Shape so little correspondent to his Face: His Head was bald, and
all the rest of his Limbs appeared old and deformed. On the hinder
Part of his Mantle was represented Murder with dishevelled Hair and a
Dagger all bloody, Anger in a Robe of Scarlet, and Suspicion squinting
with both Eyes; but above all the most conspicuous was the Battel of
the
Lapithæ and the
Centaurs. I detested so hideous a Shape, and
turned my Eyes upon
Saturn, who was stealing away behind him with a
Scythe in one Hand, and an Hour-glass in t'other unobserved. Behind
Necessity was
Vesta the Goddess of Fire with a Lamp which was
perpetually supply'd with Oyl; and whose Flame was eternal. She
cheered the rugged Brow of
Necessity, and warmed her so far as
almost to make her assume the Features and Likeness of
Choice.
December, January, and
February, passed on after the rest all in
Furrs; there was little Distinction to be made amongst them, and they
were only more or less displeasing as they discovered more or less
Haste towards the grateful Return of
Spring.
Z.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 9, 1712 |
Steele |
—Quid non mortalia Pectora cogis
Auri sacra fames—
Virg.
A very agreeable Friend of mine, the other Day, carrying me in his Coach
into the Country to Dinner, fell into Discourse concerning the Care of
Parents due to their Children, and the Piety of Children towards their
Parents. He was reflecting upon the Succession of particular Virtues and
Qualities there might be preserved from one Generation to another, if
these Regards were reciprocally held in Veneration: But as he never
fails to mix an Air of Mirth and good Humour with his good Sense and
Reasoning, he entered into the following Relation.
I will not be confident in what Century, or under what Reign it
happened, that this Want of mutual Confidence and right Understanding
between Father and Son was fatal to the Family of the
Valentines
in
Germany
.
Basilius Valentinus
was a Person who had arrived at the
utmost Perfection in the Hermetick Art, and initiated his Son
Alexandrinus
in the same Mysteries: But as you know they are not to be
attained but by the Painful, the Pious, the Chaste, and Pure of Heart,
Basilius
did not open to him, because of his Youth, and the Deviations
too natural to it, the greatest Secrets of which he was Master, as well
knowing that the Operation would fail in the Hands of a Man so liable to
Errors in Life as
Alexandrinus
. But believing, from a certain
Indisposition of Mind as well as Body, his Dissolution was drawing nigh,
he called
Alexandrinus
to him, and as he lay on a Couch, over-against
which his Son was seated, and prepared by sending out Servants one after
another, and Admonition to examine that no one over-heard them, he
revealed the most important of his Secrets with the Solemnity and
Language of an Adept. My Son, said he, many have been the Watchings,
long the Lucubrations, constant the Labours of thy Father, not only to
gain a great and plentiful Estate to his Posterity, but also to take
Care that he should have no Posterity. Be not amazed, my Child; I do not
mean that thou shalt be taken from me, but that I will never leave thee,
and consequently cannot be said to have Posterity. Behold, my dearest
Alexandrinus
, the Effect of what was propagated in nine Months: We are
not to contradict Nature but to follow and to help her; just as long as
an Infant is in the Womb of its Parent, so long are these Medicines of
Revification in preparing. Observe this small Phial and this little
Gallipot, in this an Unguent, in the other a Liquor. In these, my child,
are collected such Powers, as shall revive the Springs of Life when they
are yet but just ceased, and give new Strength, new Spirits, and, in a
Word, wholly restore all the Organs and Senses of the human Body to as
great a Duration, as it had before enjoyed from its Birth to the Day of
the Application of these my Medicines. But, my beloved Son, Care must be
taken to apply them within ten Hours after the Breath is out of the
Body, while yet the Clay is warm with its late Life, and yet capable of
Resuscitation. I find my Frame grown crasie with perpetual Toil and
Meditation; and I conjure you, as soon as I am dead, to anoint me with
this Unguent; and when you see me begin to move, pour into my Lips this
inestimable Liquor, else the Force of the Ointment will be ineffectual.
By this Means you will give me Life as I have you, and we will from that
Hour mutually lay aside the Authority of having bestowed Life on each
other, but live as Brethren, and prepare new Medicines against such
another Period of Time as will demand another Application of the same
Restoratives. In a few Days after these wonderful Ingredients were
delivered to
Alexandrinus
,
Basilius
departed this Life. But such was
the pious Sorrow of the Son at the Loss of so excellent a Father, and
the first Transports of Grief had so wholly disabled him from all manner
of Business, that he never thought of the Medicines till the Time to
which his Father had limited their Efficacy was expired. To tell the
Truth,
Alexandrinus
was a Man of Wit and Pleasure, and considered his
Father had lived out his natural Time, his Life was long and uniform,
suitable to the Regularity of it; but that he himself, poor Sinner,
wanted a new Life, to repent of a very bad one hitherto; and in the
Examination of his Heart, resolved to go on as he did with this natural
Being of his, but repent very faithfully and spend very piously the Life
to which he should be restored by Application of these Rarities, when
Time should come, to his own Person.
It has been observed, that Providence frequently punishes the Self-love
of Men who would do immoderately for their own Off-spring, with Children
very much below their Characters and Qualifications, insomuch that they
only transmit their Names to be born by those who give daily Proofs of
the Vanity of the Labour and Ambition of their Progenitors.
It happened thus in the Family of
Basilius
; for
Alexandrinus
began
to enjoy his ample Fortune in all the Extremities of Houshold Expence,
Furniture, and insolent Equipage; and this he pursued till the Day of
his own Departure began, as he grew sensible, to approach. As
Basilius
was punished with a Son very unlike him,
Alexandrinus
was visited with
one of his own Disposition. It is natural that ill Men should be
suspicious, and
Alexandrinus
, besides that Jealousie, had Proofs of
the vitious Disposition of his Son
Renatus
, for that was his Name.
Alexandrinus
, as I observed, having very good Reasons for thinking it
unsafe to trust the real Secret of his Phial and Gallypot to any Man
living, projected to make sure Work, and hope for his Success depending
from the Avarice, not the Bounty of his Benefactor.
With this Thought he called
Renatus
to his Bed-side, and bespoke him
in the most pathetick Gesture and Accent. As much, my Son, as you have
been addicted to Vanity and Pleasure, as I also have been before you,
you nor I could escape the Fame, or the good Effects of the profound
Knowledge of our Progenitor, the Renowned
Basilius
. His Symbol is very
well known in the Philosophick World, and I shall never forget the
venerable Air of his Countenance, when he let me into the profound
Mysteries of
the Smaragdine Table of
Hermes.
It is true
, said he,
and far removed from all Colour of Deceit, That which is Inferior is
like that which is Superior, by which are acquired and perfected all the
Miracles of a certain Work. The Father is the Sun, the Mother the Moon:
the Wind is the Womb, the Earth is the Nurse of it, and Mother of all
Perfection. All this must be received with Modesty and Wisdom.
The
Chymical People carry in all their Jargon a whimsical sort of Piety,
which is ordinary with great Lovers of Money, and is no more but
deceiving themselves, that their Regularity and Strictness of Manners
for the Ends of this World, has some Affinity to the Innocence of Heart
which must recommend them to the next.
Renatus
wondered to hear his
Father talk so like an Adept, and with such a Mixture of Piety, while
Alexandrinus
observing his Attention fixed, proceeded: This Phial,
Child, and this little Earthen-Pot will add to thy Estate so much, as to
make thee the richest Man in the
German
Empire. I am going to my Long
Home, but shall not return to common Dust. Then he resumed a Countenance
of Alacrity, and told him, That if within an Hour after his Death he
anointed his whole Body, and poured down his Throat that Liquor which he
had from old
Basilius
, the Corps would be converted into pure Gold. I
will not pretend to express to you the unfeigned Tendernesses that
passed between these two extraordinary Persons; but if the Father
recommended the Care of his Remains with Vehemence and Affection, the
Son was not behind-hand in professing that he would not cut the least
Bit off him, but upon the utmost Extremity, or to provide for his
younger Brothers and Sisters.
Well,
Alexandrinus
died, and the Heir of his Body (as our Term is)
could not forbear in the Wantonness of his Heart, to measure the Length
and Breadth of his beloved Father, and cast up the ensuing Value of him
before he proceeded to Operation. When he knew the immense Reward of his
Pains, he began the Work:
lo! when he had anointed the Corps all
over, and began to apply the Liquor, the Body stirred, and
Renatus
, in
a Fright, broke the Phial
.
This tale is from the Description of the memorable
Sea and
Land Travels through Persia to the East Indies,
by Johann Albrecht von
Mandelslo, translated from the German of Olearius, by J. B. B. Bk v. p.
189. Basil Valentine, whom it makes the hero of a story after the manner
of the romances of Virgil the Enchanter, was an able chemist (in those
days an alchemist) of the sixteenth century, who is believed to have
been a Benedictine monk of Erfurth, and is not known to have had any
children. He was the author of the
Currus Triumphalis Antimonii
,
mentioned in a former note. His name was familiar through several books
in French, especially
L'Azoth des Philosophes, avec les 12 Clefs de
Philosophie
(Paris, 1660), and a
Testament de Basile Valentine
(London, 1671).
Contents
|
Thursday, July 10, 1712 |
Steele |
Quartum a rerum turpitudine abes, tantum Te a verborum libertate
sejungas.
Tull.
It is a certain Sign of an ill Heart to be inclined to Defamation. They
who are harmless and innocent, can have no Gratification that way; but
it ever arises from a Neglect of what is laudable in a Man's self, and
an Impatience of seeing it in another. Else why should Virtue provoke?
Why should Beauty displease in such a Degree, that a Man given to
Scandal never lets the Mention of either pass by him without offering
something to the Diminution of it? A Lady the other Day at a Visit being
attacked somewhat rudely by one, whose own Character has been very
roughly treated, answered a great deal of Heat and Intemperance very
calmly,
Good Madam spare me, who am none of your Match; I speak Ill of
no Body, and it is a new Thing to me to be spoken ill of.
Little Minds
think Fame consists in the Number of Votes they have on their Side among
the Multitude, whereas it is really the inseparable Follower of good and
worthy Actions. Fame is as natural a Follower of Merit, as a Shadow is
of a Body. It is true, when Crowds press upon you, this Shadow cannot be
seen, but when they separate from around you, it will again appear. The
Lazy, the Idle, and the Froward, are the Persons who are most pleas'd
with the little Tales which pass about the Town to the Disadvantage of
the rest of the World. Were it not for the Pleasure of speaking Ill,
there are Numbers of People who are too lazy to go out of their own
Houses, and too ill-natur'd to open their Lips in Conversation. It was
not a little diverting the other Day to observe a Lady reading a
Post-Letter, and at these Words,
After all her Airs, he has heard some
Story or other, and the Match is broke off
, give Orders in the midst of
her Reading,
Put to the Horses.
That a young Woman of Merit has missed
an advantagious Settlement, was News not to be delayed, lest some Body
else should have given her malicious Acquaintance that Satisfaction
before her. The Unwillingness to receive good Tidings is a Quality as
inseparable from a Scandal-Bearer, as the Readiness to divulge bad. But,
alas, how wretchedly low and contemptible is that State of Mind, that
cannot be pleased but by what is the Subject of Lamentation. This Temper
has ever been in the highest Degree odious to gallant Spirits. The
Persian
Soldier, who was heard reviling
Alexander
the Great, was
well admonished by his Officer;
Sir , you are paid to fight against
Alexander,
and not to rail at him
.
Cicero
in
of his Pleadings
, defending his Client from general
Scandal, says very handsomely, and with much Reason,
There are many who
have particular Engagements to the Prosecutor: There are many who are
known to have ill-will to him for whom I appear; there are many who are
naturally addicted to Defamation, and envious of any Good to any Man,
who may have contributed to spread Reports of this kind: For nothing is
so swift as Scandal, nothing is more easily sent abroad, nothing
received with more Welcome, nothing diffuses it self so universally. I
shall not deSir e, that if any Report to our Disadvantage has any Ground
for it, you would overlook or extenuate it: But if there be any thing
advanced without a Person who can say whence he had it, or which is
attested by one who forgot who told him it, or who had it from one of so
little Consideration that he did not then think it worth his Notice, all
such Testimonies as these, I know, you will think too slight to have any
Credit against the Innocence and Honour of your Fellow-Citizen
. When an
ill Report is traced, it very often vanishes among such as the Orator
has here recited. And how despicable a Creature must that be, who is in
Pain for what passes among so frivolous a People? There is a Town in
Warwickshire
of good Note, and formerly pretty famous for much
Animosity and Dissension, the chief Families of which have now turned
all their Whispers, Backbitings, Envies, and private Malices, into Mirth
and Entertainment, by means of a peevish old Gentlewoman, known by the
Title of the Lady
Bluemantle
. This Heroine had for many Years together
out-done the whole Sisterhood of Gossips in Invention, quick Utterance,
and unprovoked Malice. This good Body is of a lasting Constitution,
though extremely decayed in her Eyes, and decrepid in her Feet. The two
Circumstances of being always at Home from her Lameness, and very
attentive from her Blindness, make her Lodgings the Receptacle of all
that passes in Town, Good or Bad; but for the latter, she seems to have
the better Memory. There is another Thing to be noted of her, which is,
That as it is usual with old People, she has a livelier Memory of Things
which passed when she was very young, than of late Years. Add to all
this, that she does not only not love any Body, but she hates every
Body. The Statue in Rome does not serve to vent Malice half so well, as
this old Lady does to disappoint it. She does not know the Author of any
thing that is told her, but can readily repeat the Matter it self;
therefore, though she exposes all the whole Town, she offends no one
Body in it. She is so exquisitely restless and peevish, that she
quarrels with all about her, and sometimes in a Freak will instantly
change her Habitation. To indulge this Humour, she is led about the
Grounds belonging to the same House she is in, and the Persons to whom
she is to remove, being in the Plot, are ready to receive her at her own
Chamber again. At stated Times, the Gentlewoman at whose House she
supposes she is at the Time, is sent for to quarrel with, according to
her common Custom: When they have a Mind to drive the Jest, she is
immediately urged to that Degree, that she will board in a Family with
which she has never yet been; and away she will go this Instant, and
tell them all that the rest have been saying of them. By this means she
has been an Inhabitant of every House in the Place without stirring from
the same Habitation; and the many Stories which every body furnishes her
with to favour that Deceit, make her the general Intelligencer of the
Town of all that can be said by one Woman against another. Thus
groundless Stories die away, and sometimes Truths are smothered under
the general Word: When they have a Mind to discountenance a thing, Oh!
that is in my Lady
Bluemantle's
Memoirs.
Whoever receives Impressions to the Disadvantage of others without
Examination, is to be had in no other Credit for Intelligence than this
good Lady
Bluemantle
, who is subjected to have her Ears imposed upon
for want of other Helps to better Information. Add to this, that other
Scandal-Bearers suspend the Use of these Faculties which she has lost,
rather than apply them to do Justice to their Neighbours; and I think,
for the Service of my fair Readers, to acquaint them, that there is a
voluntary Lady
Bluemantle
at every Visit in Town.
T.
Orat. pro Cu. Plancio.
A little beyond the middle.
Contents
|
Friday, July 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Occupet extremum Scabies—
Hor.
It is an impertinent and unreasonable Fault in Conversation, for one Man
to take up all the Discourse. It may possibly be objected to me my self,
that I am guilty in this kind, in entertaining the Town every Day, and
not giving so many able Persons who have it more in their Power, and as
much in their Inclination, an Opportunity to oblige Mankind with their
Thoughts. Besides, said one whom I overheard the other Day, why must
this Paper turn altogether upon Topicks of Learning and Morality? Why
should it pretend only to Wit, Humour, or the like? Things which are
useful only to amuse Men of Literature and superior Education. I would
have it consist also of all Things which may be necessary or useful to
any Part of Society, and the mechanick Arts should have their Place as
well as the Liberal. The Ways of Gain, Husbandry, and Thrift, will serve
a greater Number of People, than Discourses upon what was well said or
done by such a Philosopher, Heroe, General, or Poet. I no sooner heard
this Critick talk of my Works, but I minuted what he had said; and from
that Instant resolved to enlarge the Plan of my Speculations, by giving
Notice to all Persons of all Orders, and each Sex, that if they are
pleased to send me Discourses, with their Names and Places of Abode to
them, so that I can be satisfied the Writings are authentick, such their
Labours shall be faithfully inserted in this Paper. It will be of much
more Consequence to a Youth in his Apprenticeship, to know by what Rules
and Arts such a one became Sheriff of the City of
London
, than to see
the Sign of one of his own Quality with a Lion's Heart in each Hand. The
World indeed is enchanted with romantick and improbable Atchievements,
when the plain Path to respective Greatness and Success in the Way of
Life a Man is in, is wholly overlooked. Is it possible that a young Man
at present could pass his Time better, than in reading the History of
Stocks, and knowing by what secret Springs they have had such sudden
Ascents and Falls in the same Day? Could he be better conducted in his
Way to Wealth, which is the great Article of Life, than in a Treatise
dated from
Change-Alley
by an able Proficient there? Nothing certainly
could be more useful, than to be well instructed in his Hopes and Fears;
to be diffident when others exult, and with a secret Joy buy when others
think it their Interest to sell. I invite all Persons who have any thing
to say for the Profitable Information of the Publick, to take their
Turns in my Paper: They
welcome, from the late noble Inventor of the
Longitude
, to the humble Author of Strops for Razors. If to carry
Ships in Safety, to give Help to People tost in a troubled Sea, without
knowing to what Shoar they bear, what Rocks to avoid, or what Coast to
pray for in their Extremity, be a worthy Labour, and an Invention that
deserves a Statue; at the same Time, he who has found a Means to let the
Instrument
is to make your Visage less
horrible
, and your
Person more smug, easie in the Operation, is worthy of some kind of good
Reception: If Things of high Moment meet with Renown, those of little
Consideration, since of any Consideration, are not to be despised. In
order that no Merit may lye hid and no Art unimproved, I repeat it, that
I call Artificers, as well as Philosophers, to my Assistance in the
Publick Service. It would be of great Use if we had an exact History of
the Successes of every great Shop within the City-Walls, what Tracts of
Land have been purchased by a constant Attendance within a Walk of
thirty Foot. If it could also be noted in the Equipage of those who are
ascended from the Successful Trade of their Ancestors into Figure and
Equipage, such Accounts would quicken Industry in the Pursuit of such
Acquisitions, and discountenance Luxury in the Enjoyment of them.
To diversifie these kinds of Informations, the Industry of the Female
World is not to be unobserved: She to whose Houshold Virtues it is
owing, that Men do Honour to her Husband, should be recorded with
Veneration; she who had wasted his Labours, with Infamy. When we are
come into Domestick Life in this manner, to awaken Caution and
Attendance to the main Point, it
not be amiss to give now and then
a Touch of Tragedy, and describe
the
most dreadful of all human
Conditions, the Case of Bankruptcy; how Plenty, Credit, Chearfulness,
full Hopes, and easy Possessions, are in an Instant turned into Penury,
faint Aspects, Diffidence, Sorrow, and Misery; how the Man, who with an
open Hand the Day before could administer to the Extremities of others,
is shunned today by the Friend of his Bosom. It would be useful to shew
how just this is on the Negligent, how lamentable on the Industrious. A
Paper written by a Merchant, might give this Island a true Sense of the
Worth and Importance of his Character: It might be visible from what he
could say, That no Soldier entring a Breach adventures more for Honour,
than the Trader does for Wealth to his Country. In both Cases the
Adventurers have their own Advantage, but I know no Cases wherein every
Body else is a Sharer in the Success.
It is objected by Readers of History, That the Battels in those
Narrations are scarce ever to be understood. This Misfortune is to be
ascribed to the Ignorance of Historians in the Methods of drawing up,
changing the Forms of a Battalia, and the Enemy retreating from, as well
as approaching to, the Charge. But in the Discourses from the
Correspondents, whom I now invite, the Danger will be of another kind;
and it is necessary to caution them only against using Terms of Art, and
describing Things that are familiar to them in Words unknown to their
Readers. I promise my self a great Harvest of new Circumstances,
Persons, and Things from this Proposal; and a World, which many think
they are well acquainted with, discovered as wholly new. This Sort of
Intelligence will give a lively Image of the Chain and mutual Dependance
of humane Society, take off impertinent Prejudices, enlarge the Minds of
those, whose Views are confined to their own Circumstances; and, in
short, if the Knowing in several Arts, Professions, and Trades will
exert themselves, it cannot but produce a new Field of Diversion, an
Instruction more agreeable than has yet appeared.
T.
If this means the Marquis of Worcester, the exact
ascertainment of the longitude was not one of his century of Inventions.
The sextant had its origin in the mind of
Sir
Isaac Newton, who was
knighted in 1705, and living at this time, but its practical inventor
was Thomas Godfrey, a glazier at Philadelphia. Godfrey's instrument is
said to have been seen by John Hadley, or that English philosopher,
after whom the instrument is named, invented it at the same time, about
1730. Honours of invention were assigned to both Godfrey and Hadley.
Means of exact observation of the heavenly bodies would not suffice for
exact determining of longitude until the sailor was provided with a
timepiece that could be relied upon in all climates for a true uniform
standard of time. The invention of such a time-piece, for which
Parliament offered a reward of £20,000, was the real solution of the
difficulty, and this we owe to the Yorkshireman John Harrison, a
carpenter and son of a carpenter, who had a genius for clockmaking, and
was stimulated to work at the construction of marine chronometers by
living in sight of the sea. He came to London in 1728, and after fifty
years of labour finished in 1759 a chronometer which, having stood the
test of two voyages, obtained for him the offered reward of £20,000.
Harrison died in 1776 at the age of 83.
horrid
that
Contents
|
Saturday, July 12, 1712 |
Steele |
—Populumque falsis dedocet uti
Vocibus—
Mr. SPECTATOR,
Since I gave an Account of an agreeable Set of Company which were gone
down into the Country, I have received Advices from thence, that the
Institution of an Infirmary for those who should be out of Humour, has
had very good Effects. My Letters mention particular Circumstances of
two or three Persons, who had the good Sense to retire of their own
Accord, and notified that they were withdrawn, with the Reasons of it,
to the Company, in their respective Memorials.
The Memorial of Mrs. Mary Dainty, Spinster,
Humbly Sheweth,
That conscious of her own want of Merit, accompanied with a Vanity
of being admired, she had gone into Exile of her own accord.
She is sensible, that a vain Person is the most insufferable
Creature living in a well-bred Assembly.
That she deSir ed, before she appeared in publick again, she might
have Assurances, that tho' she might be thought handsome, there
might not more Address or Compliment be paid to her, than to the
rest of the Company.
That she conceived it a kind of Superiority, that one Person should
take upon him to commend another.
Lastly, That she went into the Infirmary, to avoid a particular
Person who took upon him to profess an Admiration of her.
She therefore prayed, that to applaud out of due place, might be
declar'd an Offence, and punished in the same Manner with
Detraction, in that the latter did but report Persons defective, and
the former made them so.
All which is submitted, &c.
There appeared a Delicacy and Sincerity in this Memorial very
uncommon, but my Friend informs me, that the Allegations of it were
groundless, insomuch that this Declaration of an Aversion to being
praised, was understood to be no other than a secret Trap to purchase
it, for which Reason it lies still on the Table unanswered.
The humble Memorial of the Lady Lydia Loller, Sheweth,
That the Lady Lydia is a Woman of Quality; married to a private
Gentleman.
That she finds her self neither well nor ill.
That her Husband is a Clown.
That Lady Lydia cannot see Company. That she deSir es the Infirmary
may be her Apartment during her stay in the Country.
That they would please to make merry with their Equals.
That Mr. Loller might stay with them if he thought fit.
It was immediately resolved, that Lady
Lydia was still at
London.
The humble Memorial of Thomas Sudden, Esq., of the Inner-Temple,
Sheweth,
That Mr. Sudden is conscious that he is too much given to
Argumentation.
That he talks loud.
That he is apt to think all things matter of Debate.
That he stayed behind in Westminster-Hall, when the late Shake of
the Roof happened, only because a Council of the other Side asserted
it was coming down.
That he cannot for his Life consent to any thing.
That he stays in the Infirmary to forget himself.
That as soon as he has forgot himself, he will wait on the Company.
His Indisposition was allowed to be sufficient to require a Cessation
from Company.
The Memorial of Frank Jolly, Sheweth,
That he hath put himself into the Infirmary, in regard he is
sensible of a certain rustick Mirth which renders him unfit for
polite Conversation.
That he intends to prepare himself by Abstinence and thin Diet to be
one of the Company.
That at present he comes into a Room as if he were an Express from
Abroad.
That he has chosen an Apartment with a matted Anti-Chamber, to
practise Motion without being heard.
That he bows, talks, drinks, eats, and helps himself before a Glass,
to learn to act with Moderation.
That by reason of his luxuriant Health he is oppressive to Persons
of composed Behaviour.
That he is endeavouring to forget the Word Pshaw, Pshaw.
That he is also weaning himself from his Cane.
That when he has learnt to live without his said Cane, he will wait
on the Company, &c.
...
The Memorial of John Rhubarb, Esq.,
Sheweth,
That your Petitioner has retired to the Infirmary, but that he is
in perfect good Health, except that he has by long Use. and for want
of Discourse, contracted an Habit of Complaint that he is sick.
That he wants for nothing under the Sun, but what to say, and
therefore has fallen into this unhappy Malady of complaining that he
is sick.
That this Custom of his makes him, by his own Confession, fit only
for the Infirmary, and therefore he has not waited for being
sentenced to it.
That he is conscious there is nothing more improper than such a
Complaint in good Company, in that they must pity, whether they
think the Lamenter ill or not; and that the Complainant must make a
silly Figure, whether he is pitied or not.
Your Petitioner humbly prays, that he may have Time to know how he
does, and he will make his Appearance.
The Valetudinarian was likewise easily excused; and this Society being
resolved not only to make it their Business to pass their Time
agreeably for the present Season, but also to commence such Habits in
themselves as may be of Use in their future Conduct in general, are
very ready to give into a fancied or real Incapacity to join with
their Measures, in order to have no Humourist, proud Man, impertinent
or sufficient ellow, break in upon their Happiness. Great Evils seldom
happen to disturb Company; but Indulgence in Particularities of
Humour, is the Seed of making half our Time hang in Suspence, or waste
away under real Discomposures.
Among other Things it is carefully provided that there may not be
disagreeable Familiarities. No one is to appear in the publick Rooms
undressed, or enter abruptly into each other's Apartment without
intimation. Every one has hitherto been so careful in his Behaviour,
that there has but one Offender in ten Days Time been sent into the
Infirmary, and that was for throwing away his Cards at Whist.
He has offered his Submission in the following Terms.
The humble Petition of Jeoffry Hotspur, Esq.,
Sheweth,
Though the Petitioner swore, stamped, and threw down his Cards, he
has all imaginable Respect for the Ladies, and the whole Company.
That he humbly deSir es it may be considered in the Case of Gaming,
there are many Motives which provoke to Disorder.
That the DeSir e of Gain, and the DeSir e of Victory, are both
thwarted in Losing.
That all Conversations in the World have indulged Human Infirmity in
this Case.
Your Petitioner therefore most humbly prays, that he may be restored
to the Company, and he hopes to bear ill Fortune with a good Grace
for the future, and to demean himself so as to be no more than
chearful when he wins, than grave when he loses.
T.
Contents
|
Monday, July 14, 1712 |
Steele |
Quære peregrinum vicinia rauca reclamat.
Hor.
Sir ,
As you are Spectator-General, you may with Authority censure
whatsoever looks ill, and is offensive to the Sight; the worst Nusance
of which kind, methinks, is the scandalous Appearance of Poor in all
Parts of this wealthy City. Such miserable Objects affect the
compassionate Beholder with dismal Ideas, discompose the Chearfulness
of his Mind, and deprive him of the Pleasure that he might otherwise
take in surveying the Grandeur of our Metropolis. Who can without
Remorse see a disabled Sailor, the Purveyor of our Luxury, destitute
of Necessaries? Who can behold an honest Soldier, that bravely
withstood the Enemy, prostrate and in Want amongst his Friends? It
were endless to mention all the Variety of Wretchedness, and the
numberless Poor, that not only singly, but in Companies, implore your
Charity. Spectacles of this Nature every where occur; and it is
unaccountable, that amongst the many lamentable Cries that infest this
Town, your Comptroller-General should not take notice of the most
shocking,
viz. those of the Needy and Afflicted. I can't but think
he wav'd it meerly out of good Breeding, chusing rather to stifle his
Resentment, than upbraid his Countrymen with Inhumanity; however, let
not Charity be sacrificed to Popularity, and if his Ears were deaf to
their Complaints, let not your Eyes overlook their Persons. There are,
I know, many Impostors among them. Lameness and Blindness are
certainly very often acted; but can those that have their Sight and
Limbs, employ them better than in knowing whether they are
counterfeited or not? I know not which of the two misapplies his
Senses most, he who pretends himself blind to move Compassion, or he
who beholds a miserable Object without pitying it. But in order to
remove such Impediments, I wish, Mr. SPECTATOR, you would give us a
Discourse upon Beggars, that we may not pass by true Objects of
Charity, or give to Impostors. I looked out of my Window the other
Morning earlier than ordinary, and saw a blind Beggar, an Hour before
the Passage he stands in is frequented, with a Needle and Thread,
thriftily mending his Stockings: My Astonishment was still greater,
when I beheld a lame Fellow, whose Legs were too big to walk within an
Hour after, bring him a Pot of Ale. I will not mention the Shakings,
Distortions, and Convulsions which many of them practise to gain an
Alms; but sure I am, they ought to be taken Care of in this Condition,
either by the Beadle or the Magistrate. They, it seems, relieve their
Posts according to their Talents. There is the Voice of an old Woman
never begins to beg 'till nine in the Evening, and then she is
destitute of Lodging, turned out for want of Rent, and has the same
ill Fortune every Night in the Year. You should employ an Officer to
hear the Distress of each Beggar that is constant at a particular
Place, who is ever in the same Tone, and succeeds because his Audience
is continually changing, tho' he does not alter his Lamentation. If we
have nothing else for our Money, let us have more Invention to be
cheated with. All which is submitted to your Spectatorial Vigilance:
and I am,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant.
Sir ,
I was last
Sunday highly transported at our Parish-Church; the
Gentleman in the Pulpit pleaded movingly in Behalf of the poor
Children, and they for themselves much more forcibly by singing an
Hymn; And I had the Happiness to be a Contributor to this little
religious Institution of Innocents, and am sure I never disposed of
Money more to my Satisfaction and Advantage. The inward Joy I find in
my self, and the Good-will I bear to Mankind, make me heartily wish
those pious Works may be encouraged, that the present Promoters may
reap the Delight, and Posterity the Benefit of them. But whilst we are
building this beautiful Edifice, let not the old Ruins remain in View
to sully the Prospect: Whilst we are cultivating and improving this
young hopeful Offspring, let not the ancient and helpless Creatures be
shamefully neglected. The Crowds of Poor, or pretended Poor, in every
Place, are a great Reproach to us, and eclipse the Glory of all other
Charity. It is the utmost Reproach to Society, that there should be a
poor Man unrelieved, or a poor Rogue unpunished. I hope you will think
no Part of Human Life out of your Consideration, but will, at your
Leisure, give us the History of Plenty and Want, and the natural
Gradations towards them, calculated for the Cities of
London and
Westminster.
I am, Sir ,
Your most Humble Servant,
T. D.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I beg you would be pleased to take Notice of a very great Indecency,
which is extreamly common, though, I think, never yet under your
Censure. It is,
Sir , the strange Freedoms some ill-bred married People
take in Company: The unseasonable Fondness of some Husbands, and the
ill-timed Tenderness of some Wives. They talk and act, as if Modesty
was only fit for Maids and Batchelors, and that too before both. I was
once, Mr. SPECTATOR, where the Fault I speak of was so very flagrant,
that (being, you must know, a very bashful Fellow, and several young
Ladies in the Room) I protest I was quite out of Countenance.
Lucina, it seems, was breeding, and she did nothing but entertain
the Company with a Discourse upon the Difficulty of Reckoning to a
Day, and said she knew those who were certain to an Hour; then fell a
laughing at a silly unexperienced Creature, who was a Month above her
Time. Upon her Husband's coming in, she put several Questions to him;
which he not caring to resolve, Well, cries
Lucina, I shall have 'em
all at Night—But lest I should seem guilty of the very Fault I write
against, I shall only intreat
Mr.
Spectator to correct such
Misdemeanors;
For higher of the Genial Bed by far,
And with mysterious Reverence, I deem.1
I am, Sir ,
Your humble Servant,
T. Meanwell.
T.
Paradise Lost
, Bk VIII. 11. 598-9.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 15, 1712 |
Steele |
Quid Dulcius hominum generi a Natura datum est quam sui cuique
liberi?
Tull.
I have lately been casting in my Thoughts the several Unhappinesses of
Life, and comparing the Infelicities of old Age to those of Infancy. The
Calamities of Children are due to the Negligence and Misconduct of
Parents, those of Age to the past Life which led to it. I have here the
History of a Boy and Girl to their Wedding-Day, and I think I cannot
give the Reader a livelier Image of the insipid way which Time
uncultivated passes, than by entertaining him with their authentick
Epistles, expressing all that was remarkable in their Lives, 'till the
Period of their Life above mentioned. The Sentence at the Head of this
Paper, which is only a warm Interrogation,
What is there in Nature so
dear as a Man's own Children to him?
is all the Reflection I shall at
present make on those who are negligent or cruel in the Education of
them.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I am now entring into my One and Twentieth Year, and do not know that
I had one Day's thorough Satisfaction since I came to Years of any
Reflection, till the Time they say others lose their Liberty, the Day
of my Marriage. I am Son to a Gentleman of a very great Estate, who
resolv'd to keep me out of the Vices of the Age; and in order to it
never let me see any Thing that he thought could give me the least
Pleasure. At ten Years old I was put to a Grammar-School, where my
Master received Orders every Post to use me very severely, and have no
regard to my having a great Estate. At Fifteen I was removed to the
University, where I liv'd, out of my Father's great Discretion, in
scandalous Poverty and Want, till I was big enough to be married, and
I was sent for to see the Lady who sends you the Underwritten. When we
were put together, we both considered that we could not be worse than
we were in taking one another, out of a DeSir e of Liberty entered into
Wedlock. My Father says I am now a Man, and may speak to him like
another Gentleman.
I am, Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
Richard Rentfree.
Mr. SPEC.
I grew tall and wild at my Mother's, who is a gay Widow, and did not
care for shewing me 'till about two Years and a half ago; at which
time my Guardian Uncle sent me to a Boarding-School, with Orders to
contradict me in nothing, for I had been misused enough already. I had
not been there above a Month, when being in the Kitchin, I saw some
Oatmeal on the Dresser; I put two or three Corns in my Mouth, liked
it, stole a Handful, went into my Chamber, chewed it, and for two
Months after never failed taking Toll of every Pennyworth of Oatmeal
that came into the House: But one Day playing with a Tobacco-pipe
between my Teeth, it happened to break in my Mouth, and the spitting
out the Pieces left such a delicious Roughness on my Tongue, that I
could not be satisfied 'till I had champed up the remaining Part of
the Pipe. I forsook the Oatmeal, and stuck to the Pipes three Months,
in which Time I had dispensed with thirty seven foul Pipes, all to the
Boles; They belonged to an old Gentleman, Father to my Governess—He
lock'd up the clean ones. I left off eating of Pipes, and fell to
licking of Chalk. I was soon tired of this; I then nibbled all the red
Wax of our last Ball-Tickets, and three Weeks after the black Wax from
the Burying-Tickets of the old Gentleman. Two Months after this I
liv'd upon Thunder-bolts, a certain long, round bluish Stone, which I
found among the Gravel in our Garden. I was wonderfully delighted with
this; but Thunder-bolts growing scarce, I fasten'd Tooth and Nail upon
our Garden-Wall, which I stuck to almost a Twelvemonth, and had in
that time peeled and devoured half a Foot towards our Neighbour's
Yard. I now thought my self the happiest Creature in the World, and I
believe in my Conscience, I had eaten quite through, had I had it in
my Chamber; but now I became lazy, and unwilling to stir, and was
obliged to seek Food nearer Home. I then took a strange Hankering to
Coals; I fell to scranching 'em, and had already consumed, I am
certain, as much as would have dressed my Wedding Dinner, when my
Uncle came for me Home. He was in the Parlour with my Governess when I
was called down. I went in, fell on my Knees, for he made me call him
Father; and when I expected the Blessing I asked, the good Gentleman,
in a Surprize, turns himself to my Governess, and asks, Whether this
(pointing to me) was his Daughter? This (added he) is the very Picture
of Death. My Child was a plump-fac'd, hale, fresh-coloured Girl; but
this looks as if she was half-starved, a mere Skeleton. My Governess,
who is really a good Woman, assured my Father I had wanted for
nothing; and withal told him I was continually eating some Trash or
other, and that I was almost eaten up with the Green-sickness, her
Orders being never to cross me. But this magnified but little with my
Father, who presently, in a kind of Pett, paying for my Board, took me
home with him. I had not been long at home, but one Sunday at Church
(I shall never forget it) I saw a young neighbouring Gentleman that
pleased me hugely; I liked him of all Men I ever saw in my Life, and
began to wish I could be as pleasing to him. The very next Day he
came, with his Father, a visiting to our House: We were left alone
together, with Directions on both Sides to be in Love with one
another, and in three Weeks time we were married. I regained my former
Health and Complexion, and am now as happy as the Day is long. Now,
Mr. SPEC., I deSir e you would find out some Name for these craving
Damsels, whether dignified or distinguished under some or all of the
following Denominations, (to wit) Trash-eaters, Oatmeal-chewers,
Pipe-champers, Chalk-lickers, Wax-nibbles, Coal-Scranchers,
Wall-peelers, or Gravel-diggers: And, good Sir , do your utmost
endeavour to prevent (by exposing) this unaccountable Folly, so
prevailing among the young ones of our Sex, who may not meet with such
sudden good Luck as,
Sir ,
Your constant Reader,
and very humble Servant,
Sabina Green,
Now Sabina Rentfree.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 16, 1712 |
Steele |
Inter-strepit anser olores.
Virg.
Oxford,
July 14.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
According to a late Invitation in one of your Papers to every Man who
pleases to write, I have sent you the following short Dissertation
against the Vice of being prejudiced.
Your most humble Servant.
Man is a sociable Creature, and a Lover of Glory; whence it is that
when several Persons are united in the same Society, they are studious
to lessen the Reputation of others, in order to raise their own. The
Wise are content to guide the Springs in Silence, and rejoice in
Secret at their regular Progress: To prate and triumph is the Part
allotted to the Trifling and Superficial: The Geese were
providentially ordained to save the
Capitol. Hence it is, that the
Invention of Marks and Devices to distinguish Parties, is owing to the
Beaux and
Belles of this Island. Hats moulded into different Cocks
and Pinches, have long bid mutual Defiance; Patches have been set
against Patches in Battel-aray; Stocks have risen or fallen in
Proportion to Head-Dresses; and Peace or War been expected, as the
White or the
Red Hood hath prevailed. These are the
Standard-Bearers in our contending Armies, the Dwarfs and Squires who
carry the Impresses of the Giants or Knights, not born to fight
themselves, but to prepare the Way for the ensuing Combat.
It is Matter of Wonder to reflect how far Men of weak Understanding
and strong Fancy are hurried by their Prejudices, even to the
believing that the whole Body of the adverse Party are a Band of
Villains and Dæmons. Foreigners complain, that the
English are the
proudest Nation under Heaven. Perhaps they too have their Share; but
be that as it will, general Charges against Bodies of Men is the Fault
I am writing against. It must be own'd, to our Shame, that our common
People, and most who have not travelled, have an irrational Contempt
for the Language, Dress, Customs, and even the Shape and Minds of
other Nations. Some Men otherwise of Sense, have wondered that a great
Genius should spring out of
Ireland; and think you mad in affirming,
that fine Odes have been written in
Lapland.
This Spirit of Rivalship, which heretofore reigned in the Two
Universities, is extinct, and almost over betwixt College and College:
In Parishes and Schools the Thirst of Glory still obtains. At the
Seasons of Football and Cock-fighting, these little Republicks
reassume their national Hatred to each other. My Tenant in the Country
is verily perswaded, that the Parish of the Enemy hath not one honest
Man in it.
I always hated Satyrs against Woman, and Satyrs against Man; I am apt
to suspect a Stranger who laughs at the Religion of
The Faculty; My
Spleen rises at a dull Rogue, who is severe upon Mayors and Aldermen;
and was never better pleased than with a Piece of Justice executed
upon the Body of a Templer, who was very arch upon Parsons.
The Necessities of Mankind require various Employments; and whoever
excels in his Province is worthy of Praise. All Men are not educated
after the same Manner, nor have all the same Talents. Those who are
deficient deserve our Compassion, and have a Title to our Assistance.
All cannot be bred in the same Place; but in all Places there arise,
at different Times, such Persons as do Honour to their Society, which
may raise Envy in little Souls, but are admired and cherished by
generous Spirits.
It is certainly a great Happiness to be educated in Societies of great
and eminent Men. Their Instructions and Examples are of extraordinary
Advantage. It is highly proper to instill such a Reverence of the
governing Persons, and Concern for the Honour of the Place, as may
spur the growing Members to worthy Pursuits and honest Emulation: But
to swell young Minds with vain Thoughts of the Dignity of their own
Brotherhood, by debasing and villifying all others, doth them a real
Injury. By this means I have found that their Efforts have become
languid, and their Prattle irksome, as thinking it sufficient Praise
that they are Children of so illustrious and ample a Family. I should
think it a surer as well as more generous Method, to set before the
Eyes of Youth such Persons as have made a noble Progress in
Fraternities less talk'd of; which seems tacitly to reproach their
Sloth, who loll so heavily in the Seats of mighty Improvement: Active
Spirits hereby would enlarge their Notions, whereas by a servile
Imitation of one, or perhaps two, admired Men in their own Body, they
can only gain a secondary and derivative kind of Fame. These Copiers
of Men, like those of Authors or Painters, run into Affectations of
some Oddness, which perhaps was not disagreeable in the Original, but
sits ungracefully on the narrow-soul'd Transcriber.
By such early Corrections of Vanity, while Boys are growing into Men,
they will gradually learn not to censure superficially; but imbibe
those Principles of general Kindness and Humanity, which alone can
make them easie to themselves, and beloved by others.
Reflections of this nature have expunged all Prejudices out of my
Heart, insomuch that, tho' I am a firm Protestant, I hope to see the
Pope and Cardinals without violent Emotions; and tho' I am naturally
grave, I expect to meet good Company at
Paris.
I am, Sir ,
Your obedient Servant.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I find you are a general Undertaker, and have by your Correspondents
or self an Insight into most things: which makes me apply my self to
you at present in the sorest Calamity that ever befel Man. My Wife has
taken something ill of me, and has not spoke one Word, good or bad, to
me, or any Body in the Family, since
Friday was Seven-night. What
must a Man do in that Case? Your Advice would be a great Obligation
to,
Sir , Your most humble Servant,
Ralph Thimbleton.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
When you want a Trifle to fill up a Paper, in inserting this you will
lay an Obligation on
Your humble Servant,
Olivio.
July 15th, 1712.
Dear Olivia,
It is but this Moment I have had the Happiness of knowing to whom I
am obliged for the Present I received the second of April. I am
heartily sorry it did not come to Hand the Day before; for I can't
but think it very hard upon People to lose their Jest, that offer at
one but once a Year. I congratulate my self however upon the Earnest
given me of something further intended in my Favour, for I am told,
that the Man who is thought worthy by a Lady to make a Fool of,
stands fair enough in her Opinion to become one Day her Husband.
Till such time as I have the Honour of being sworn, I take Leave to
subscribe my self,
Dear Olivia, Your Fool Elect,
Nicodemuncio.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, July 17, 1712 |
Addison |
Perlege Mæonio cantatas carmine Ranas,
Et frontem nugis solvere disce meis.
Mart.

The Moral World, as consisting of Males and Females, is of a mixt
Nature, and filled with several Customs, Fashions and Ceremonies, which
would have no place in it, were there but
One
Sex. Had our Species no
Females in it, Men would be quite different Creatures from what they are
at present; their Endeavours to please the opposite Sex, polishes and
refines them out of those Manners which are most Natural to them, and
often sets them upon modelling themselves, not according to the Plans
which they approve in their own Opinions, but according to those Plans
which they think are most agreeable to the Female World. In a Word, Man
would not only be unhappy, but a rude unfinished Creature, were he
conversant with none but those of his own Make.
Women, on the other side, are apt to form themselves in every thing with
regard to that other half of reasonable Creatures, with whom they are
here blended and confused; their Thoughts are ever turned upon appearing
amiable to the other Sex; they talk, and move, and smile, with a Design
upon us; every Feature of their Faces, every part of their Dress is
filled with Snares and Allurements. There would be no such Animals as
Prudes or Coquets in the World, were there not such an Animal as Man. In
short, it is the Male that gives Charms to Womankind, that produces an
Air in their Faces, a Grace in their Motions, a Softness in their
Voices, and a Delicacy in their Complections.
As this mutual Regard between the two Sexes tends to the Improvement of
each of them, we may observe that Men are apt to degenerate into rough
and brutal Natures, who live as if there were no such things as Women in
the World; as on the contrary, Women, who have an Indifference or
Aversion for their Counter-parts in human Nature, are generally Sower
and Unamiable, Sluttish and Censorious.
I am led into this Train of Thoughts by a little Manuscript which is
lately fallen into my Hands, and which I shall communicate to the
Reader, as I have done some other curious Pieces of the same Nature,
without troubling him with any Enquiries about the Author of it. It
contains a summary Account of two different States which bordered upon
one another. The one was a Commonwealth of
Amazons
, or Women without
Men; the other was a Republick of Males that had not a Woman in their
whole Community. As these two States bordered upon one another, it was
their way, it seems, to meet upon their Frontiers at a certain Season of
the Year, where those among the Men who had not made their Choice in any
former Meeting, associated themselves with particular Women, whom they
were afterwards obliged to look upon as their Wives in every one of
these yearly Rencounters. The Children that sprung from this Alliance,
if Males, were sent to their respective Fathers, if Females, continued
with their Mothers. By means of this Anniversary Carnival, which lasted
about a Week, the Commonwealths were recruited from time to time, and
supplied with their respective Subjects.
These two States were engaged together in a perpetual League, Offensive
and Defensive, so that if any Foreign Potentate offered to attack either
of them, both the Sexes fell upon him at once, and quickly brought him
to Reason. It was remarkable that for many Ages this Agreement continued
inviolable between the two States, notwithstanding, as was said before,
they were Husbands and Wives; but this will not appear so wonderful, if
we consider that they did not live together above a Week in a Year.
In the Account which my Author gives of the Male Republick, there were
several Customs very remarkable. The Men never shaved their Beards, or
pared their Nails above once in a Twelvemonth, which was probably about
the time of the great annual Meeting upon their Frontiers. I find the
Name of a Minister of State in one Part of their History, who was fined
for appearing too frequently in clean Linnen; and of a certain great
General who was turned out of his Post for Effeminacy, it having been
proved upon him by several credible Witnesses that he washed his Face
every Morning. If any Member of the Commonwealth had a soft Voice, a
smooth Face, or a supple Behaviour, he was banished into the
Commonwealth of Females, where he was treated as a Slave, dressed in
Petticoats, and set a Spinning. They had no Titles of Honour among them,
but such as denoted some Bodily Strength or Perfection, as such an one
the Tall
, such an one
the Stocky
, such an one
the Gruff
. Their
publick Debates were generally managed with Kicks and Cuffs, insomuch
that they often came from the Council Table with broken Shins, black
Eyes, and bloody Noses. When they would reproach a Man in the most
bitter Terms, they would tell him his Teeth were white, or that he had a
fair Skin, and a soft Hand. The greatest Man I meet with in their
History, was one who could lift Five hundred Weight, and wore such a
prodigious Pair of Whiskers as had never been seen in the Commonwealth
before his Time. These Accomplishments it seems had rendred him so
popular, that if he had not died very seasonably, it is thought he might
have enslaved the Republick. Having made this short Extract out of the
History of the Male Commonwealth, I shall look into the History of the
neighbouring State which consisted of Females, and if I find any thing
in it, will not fail to Communicate it to the Publick.
C.
Contents
|
Friday, July 18, 1712 |
Addison |
Quales Threiciæ cùm flumina Thermodoontis
Pulsant, et pictis bellantur Amazones armis:
Seu circum Hippolyten, seu cùm se Martia curru
Penthesilea refert, magnoque ululante tumultu
Fæminea exultant lunatis agmina peltis.
Virg.

Having carefully perused the Manuscript I mentioned in my Yesterday's
Paper, so far as it relates to the Republick of Women, I find in it
several Particulars which may very well deserve the Reader's Attention.
The Girls of Quality, from six to twelve Years old, were put to publick
Schools, where they learned to Box and play at Cudgels, with several
other Accomplishments of the same Nature; so that nothing was more usual
than to see a little Miss returning Home at Night with a broken Pate, or
two or three Teeth knocked out of her Head. They were afterwards taught
to ride the great Horse, to Shoot, Dart, or Sling, and listed into
several Companies, in order to perfect themselves in Military Exercises.
No Woman was to be married till she had killed her Man. The Ladies of
Fashion used to play with young Lions instead of Lap-dogs, and when they
made any Parties of Diversion, instead of entertaining themselves at
Ombre or Piquet, they would wrestle and pitch the Bar for a whole
Afternoon together. There was never any such thing as a Blush seen, or a
Sigh heard, in the Commonwealth. The Women never dressed but to look
terrible, to which end they would sometimes after a Battel paint their
Cheeks with the Blood of their Enemies. For this Reason likewise the
Face which had the most Scars was looked upon as the most beautiful. If
they found Lace, Jewels, Ribbons, or any Ornaments in Silver or Gold
among the Booty which they had taken, they used to dress their Horses
with it, but never entertained a Thought of wearing it themselves. There
were particular Rights and Privileges allowed to any Member of the
Commonwealth, who was a Mother of three Daughters. The Senate was made
up of old Women; for by the Laws of the Country none was to be a
Councellor of State that was not past Child-bearing. They used to boast
their Republick had continued Four thousand Years, which is altogether
improbable, unless we may suppose, what I am very apt to think, that
they measured their Time by
Lunar
Years.
There was a great Revolution brought about in this Female Republick, by
means of a neighbouring King, who had made War upon them several Years
with various Success, and at length overthrew them in a very great
Battel. This Defeat they ascribe to several Causes; some say that the
Secretary of State having been troubled with the Vapours, had committed
some fatal Mistakes in several Dispatches about that Time. Others
pretend, that the first Minister being big with Child, could not attend
the Publick Affairs, as so great an Exigency of State required; but this
I can give no manner of Credit to, since it seems to contradict a
Fundamental Maxim in their Government which I have before mentioned. My
Author gives the most probable Reason of this great Disaster; for he
affirms, that the General was brought to Bed, or (as others say)
Miscarried the very Night before the Battel: However it was, this signal
Overthrow obliged them to call in the Male Republick to their
Assistance; but notwithstanding their Common Efforts to repulse the
Victorious Enemy, the War continued for many Years before they could
entirely bring it to a happy Conclusion.
The Campaigns which both Sexes passed together made them so well
acquainted with one another, that at the End of the War they did not
care for parting. In the Beginning of it they lodged in separate Camps,
but afterwards as they grew more familiar, they pitched their Tents
promiscuously.
From this time the Armies being Chequered with both Sexes, they polished
apace. The Men used to invite their Fellow-Soldiers into their Quarters,
and would dress their Tents with Flowers and Boughs, for their
Reception. If they chanced to like one more than another, they would be
cutting her Name in the Table, or Chalking out her Figure upon a Wall,
or talking of her in a kind of rapturous Language, which by degrees
improved into Verse and Sonnet. These were as the first Rudiments of
Architecture, Painting, and Poetry among this Savage People. After any
Advantage over the Enemy, both Sexes used to Jump together and make a
Clattering with their Swords and Shields, for Joy, which in a few Years
produced several Regular Tunes and Sett Dances.
As the two Armies romped on these Occasions, the Women complained of the
thick bushy Beards and long Nails of their Confederates, who thereupon
took care to prune themselves into such Figures as were most pleasing to
their Female Friends and Allies.
When they had taken any Spoils from the Enemy, the Men would make a
Present of every thing that was Rich and Showy to the Women whom they
most admired, and would frequently dress the Necks, or Heads, or Arms of
their Mistresses, with any thing which they thought appeared Gay or
Pretty. The Women observing that the Men took delight in looking upon
them, when they were adorned with such Trappings and Gugaws, set their
Heads at Work to find out new Inventions, and to outshine one another in
all Councils of War or the like solemn Meetings. On the other hand, the
Men observing how the Women's Hearts were set upon Finery, begun to
Embellish themselves and look as agreeably as they could in the Eyes of
their Associates. In short, after a few Years conversing together, the
Women had learnt to Smile, and the Men to Ogle, the Women grew Soft, and
the Men Lively.
When they had thus insensibly formed one another, upon the finishing of
the War, which concluded with an entire Conquest of their common Enemy,
the Colonels in one Army Married the Colonels in the other; the Captains
in the same Manner took the Captains to their Wives: The whole Body of
common Soldiers were matched, after the Example of their Leaders. By
this means the two Republicks incorporated with one another, and became
the most Flourishing and Polite Government in the Part of the World
which they Inhabited.
C.
Contents
|
Saturday, July 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec duo sunt at forma duplex, nec fæmina dici
Nec puer ut possint, neutrumque et utrumque videntur.
Ovid.

Most of the Papers I give the Publick are written on Subjects that never
vary, but are for ever fixt and immutable. Of this kind are all my more
serious Essays and Discourses; but there is another sort of
Speculations, which I consider as Occasional Papers, that take their
Rise from the Folly, Extravagance, and Caprice of the present Age. For I
look upon my self as one set to watch the Manners and Behaviour of my
Countrymen and Contemporaries, and to mark down every absurd Fashion,
ridiculous Custom, or affected Form of Speech that makes its Appearance
in the World, during the Course of these my Speculations. The Petticoat
no sooner begun to swell, but I observed its Motions. The Party-patches
had not time to muster themselves before I detected them. I had
Intelligence of the Coloured Hood the very first time it appeared in a
Publick Assembly. I might here mention several other the like Contingent
Subjects, upon which I have bestowed distinct Papers. By this Means I
have so effectually quashed those Irregularities which gave Occasion to
'em, that I am afraid Posterity will scarce have a sufficient Idea of
them, to relish those Discourses which were in no little Vogue at the
time when they were written. They will be apt to think that the Fashions
and Customs I attacked were some Fantastick Conceits of my own, and that
their Great-Grand-mothers could not be so whimsical as I have
represented them. For this Reason, when I think on the Figure my several
Volumes of Speculations will make about a Hundred Years hence, I
consider them as so many Pieces of old Plate, where the Weight will be
regarded, but the Fashion lost.
Among the several Female Extravagancies I have already taken Notice of,
there is one which still keeps its Ground. I mean that of the Ladies who
dress themselves in a Hat and Feather, a Riding-coat and a Perriwig, or
at least tie up their Hair in a Bag or Ribbond, in imitation of the
smart Part of the opposite Sex. As in my Yesterday's Paper I gave an
Account of the Mixture of two Sexes in one Commonwealth, I shall here
take notice of this Mixture of two Sexes in one Person. I have already
shewn my Dislike of this Immodest Custom more than once; but in Contempt
of every thing I have hitherto said, I am informed that the Highways
about this great City are still very much infested with these Female
Cavaliers.
I remember when I was at my Friend
Sir
Roger De Coverly's
about this
time Twelve-month, an Equestrian Lady of this Order appeared upon the
Plains which lay at a distance from his House. I was at that time
walking in the Fields with my old Friend; and as his Tenants ran out on
every side to see so strange a Sight,
Sir
ROGER asked one of them who
came by us what it was? To which the Country Fellow reply'd, 'Tis a
Gentlewoman, saving your Worship's Presence, in a Coat and Hat. This
produced a great deal of Mirth at the Knight's House, where we had a
Story at the same time of another of his Tenants, who meeting this
Gentleman-like Lady on the High-way, was asked by her
whether that was
Coverly-Hall, the Honest Man seeing only the Male Part of the Querist,
replied,
Yes, Sir
; but upon the second Question,
whether
Sir
Roger
De Coverly
was a married Man
, having dropped his Eye upon the
Petticoat, he changed his Note into
No, Madam
.
Had one of these Hermaphrodites appeared in
Juvenal's
Days, with what
an Indignation should we have seen her described by that excellent
Satyrist. He would have represented her in a Riding Habit, as a greater
Monster than the Centaur. He would have called for Sacrifices or
Purifying Waters, to expiate the Appearance of such a Prodigy. He would
have invoked the Shades of
Portia
or
Lucretia
, to see into what the
Roman
Ladies had transformed themselves.
For my own part, I am for treating the Sex with greater Tenderness, and
have all along made use of the most gentle Methods to bring them off
from any little Extravagance into which they are sometimes unwarily
fallen: I think it however absolutely necessary to keep up the Partition
between the two Sexes, and to take Notice of the smallest Encroachments
which the one makes upon the other. I hope therefore that I shall not
hear any more Complaints on this Subject. I am sure my She-Disciples who
peruse these my daily Lectures, have profited but little by them, if
they are capable of giving into such an Amphibious Dress. This I should
not have mentioned, had not I lately met one of these my Female Readers
in
Hyde Park
, who looked upon me with a masculine Assurance, and
cocked her Hat full in my Face.
For my part, I have one general Key to the Behaviour of the Fair Sex.
When I see them singular in any Part of their Dress, I conclude it is
not without some Evil Intention; and therefore question not but the
Design of this strange Fashion is to smite more effectually their Male
Beholders. Now to set them right in this Particular, I would fain have
them consider with themselves whether we are not more likely to be
struck by a Figure entirely Female, than with such an one as we may see
every Day in our Glasses: Or, if they please, let them reflect upon
their own Hearts, and think how they would be affected should they meet
a Man on Horseback, in his Breeches and Jack-Boots, and at the same time
dressed up in a Commode and a Night-raile.
I must observe that this Fashion was first of all brought to us from
France
, a Country which has Infected all the Nations of
Europe
with
its Levity. I speak not this in derogation of a whole People, having
more than once found fault with those general Reflections which strike
at Kingdoms or Commonwealths in the Gross: A piece of Cruelty, which an
ingenious Writer of our own compares to that of
Caligula
, who wished
the
Roman
People had all but one Neck, that he might behead them at a
Blow. I shall therefore only Remark, that as Liveliness and Assurance
are in a peculiar manner the Qualifications of the
French
Nation, the
same Habits and Customs will not give the same Offence to that People,
which they produce among those of our own Country. Modesty is our
distinguishing Character, as Vivacity is theirs: And when this our
National Virtue appears in that Female Beauty, for which our
British
Ladies are celebrated above all others in the Universe, it makes up the
most amiable Object that the Eye of Man can possibly behold.
C.
Contents
|
Monday, July 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Verso pollice vulgi
Quemlibet occidunt Populariter.
Juv.

Being a Person of insatiable Curiosity, I could not forbear going on
Wednesday
last to a Place of no small Renown for the Gallantry of the
lower Order of
Britons
,
, to the Bear-Garden at
Hockley in the
Hole
; where (as a whitish brown Paper, put into my Hands in the
Street, informed me) there was to be a Tryal of Skill to be exhibited
between two Masters of the Noble Science of Defence, at two of the Clock
precisely. I was not a little charm'd with the Solemnity of the
Challenge, which ran thus:
I James Miller,
Serjeant, (lately come from the Frontiers of
Portugal)
Master of the noble Science of Defence, hearing in most
Places where I have been of the great Fame of Timothy Buck
of
London,
Master of the said Science, do invite him to meet me, and
exercise at the several Weapons following, viz.
| Back-Sword |
Single Falchon |
| Sword and Dagger |
Case of Falchons |
| Sword and Buckler |
Quarter Staff |
If the generous Ardour in
James Miller
to dispute the Reputation of
Timothy Buck
, had something resembling the old Heroes of Romance,
Timothy Buck
return'd Answer in the same Paper with the like Spirit,
adding a little Indignation at being challenged, and seeming to
condescend to fight
James Miller
,
in regard to
Miller
himself,
but in that, as the Fame went out, he had fought
Parkes
of
Coventry
. The Acceptance of the Combat ran in these Words:
I Timothy Buck of Clare-Market, Master of the Noble Science of
Defence, hearing he did fight Mr. Parkes of Coventry, will not
fail (God Willing) to meet this fair Inviter at the Time and Place
appointed, deSir ing a clear Stage and no Favour.
Vivat Regina.
I shall not here look back on the Spectacles of the
Greeks
and
Romans
of this kind, but must believe this Custom took its rise from
the Ages of Knight-Errantry; from those who lov'd one Woman so well,
that they hated all Men and Women else; from those who would fight you,
whether you were or were not of their Mind; from those who demanded the
Combat of their Contemporaries, both for admiring their Mistress or
discommending her. I cannot therefore but lament, that the terrible Part
of the ancient Fight is preserved, when the amorous Side of it is
forgotten. We have retained the Barbarity, but lost the Gallantry of the
old Combatants. I could wish, methinks, these Gentlemen had consulted me
in the Promulgation of the Conflict. I was obliged by a fair young Maid
whom I understood to be called
Elizabeth Preston
, Daughter of the
Keeper of the Garden, with a Glass of Water; whom I imagined might have
been, for Form's sake, the general Representative of the Lady sought
for, and from her Beauty the proper
Amarillis
on these Occasions. It
would have ran better in the Challenge,
I
James Miller,
Serjeant, who
have travelled Parts abroad, and came last from the Frontiers of
Portugal,
for the Love of
Elizabeth Preston,
do assert, That the
said
Elizabeth is the Fairest of Women. Then the Answer;
I
Timothy
Buck,
who have stay'd in
Great Britain
during all the War in Foreign
Parts, for the Sake of
Susanna Page,
do deny that
Elizabeth Preston
is so fair as the said
Susanna Page. Let
Susanna Page
look on, and I
de
Sir
e of
James Miller
no Favour.
This would give the Battel quite another Turn; and a proper Station for
the Ladies, whose Complexion was disputed by the Sword, would animate
the Disputants with a more gallant Incentive than the Expectation of
Money from the
Spectators
; tho' I would not have that neglected, but
thrown to that Fair One, whose Lover was approved by the Donor.
Yet, considering the Thing wants such Amendments, it was carried with
great Order.
James Miller
came on first, preceded by two disabled
Drummers, to shew, I suppose, that the Prospect of maimed Bodies did not
in the least deter him. There ascended with the daring
Miller
a
Gentleman, whose Name I could not learn, with a dogged Air, as
unsatisfied that he was not Principal. This Son of Anger lowred at the
whole Assembly, and weighing himself as he march'd around from Side to
Side, with a stiff Knee and Shoulder, he gave Intimations of the Purpose
he smothered till he saw the Issue of this Encounter.
Miller
had a
blue Ribband tied round the Sword Arm; which Ornament I conceive to be
the Remain of that Custom of wearing a Mistress's Favour on such
Occasions of old.
Miller
is a Man of six Foot eight Inches Height, of a kind but bold
Aspect, well-fashioned, and ready of his Limbs: and such Readiness as
spoke his Ease in them, was obtained from a Habit of Motion in Military
Exercise.
The Expectation of the
Spectators
was now almost at its Height, and the
Crowd pressing in, several active Persons thought they were placed
rather according to their Fortune than their Merit, and took it in their
Heads to prefer themselves from the open Area, or Pitt, to the
Galleries. This Dispute between Desert and Property brought many to the
Ground, and raised others in proportion to the highest Seats by Turns
for the Space of ten Minutes, till
Timothy Buck
came on, and the whole
Assembly giving up their Disputes, turned their Eyes upon the Champions.
Then it was that every Man's Affection turned to one or the other
irresistibly. A judicious Gentleman near me said,
I could methinks be
Miller's
Second, but I had rather have
Buck
for mine
.
Miller
had
an Audacious Look, that took the Eye;
Buck
a perfect Composure, that
engaged the Judgment.
Buck
came on in a plain Coat, and kept all his
Air till the Instant of Engaging; at which time he undress'd to his
Shirt, his Arm adorned with a Bandage of red Ribband. No one can
describe the sudden Concern in the whole Assembly; the most tumultuous
Crowd in Nature was as still and as much engaged, as if all their Lives
depended on the first Blow. The Combatants met in the Middle of the
Stage, and shaking Hands as removing all Malice, they retired with much
Grace to the Extremities of it; from whence they immediately faced
about, and approached each other,
Miller
with an Heart full of
Resolution,
Buck
with a watchful untroubled Countenance;
Buck
regarding principally his own Defence,
Miller
chiefly thoughtful of
annoying his Opponent. It is not easie to describe the many Escapes and
imperceptible Defences between two Men of quick Eyes and ready Limbs,
but
Miller's
Heat laid him open to the Rebuke of the calm
Buck
, by a
large Cut on the Forehead. Much Effusion of Blood covered his Eyes in a
Moment, and the Huzzas of the Crowd undoubtedly quickened the Anguish.
The Assembly was divided into Parties upon their different ways of
Fighting; while a poor Nymph in one of the Galleries apparently suffered
for
Miller
, and burst into a Flood of Tears. As soon as his Wound was
wrapped up, he came on again with a little Rage, which still disabled
him further. But what brave Man can be wounded into more Patience and
Caution? The next was a warm eager Onset, which ended in a decisive
Stroke on the Left Leg of
Miller
. The Lady in the Gallery, during this
second Strife, covered her Face; and for my Part, I could not keep my
Thoughts from being mostly employed on the Consideration of her unhappy
Circumstance that Moment, hearing the Clash of Swords, and apprehending
Life or Victory concerned her Lover in every Blow, but not daring to
satisfie her self on whom they fell. The Wound was exposed to the View
of all who could delight in it, and sowed up on the Stage. The surly
Second of
Miller
declared at this Time, that he would that Day
Fortnight fight Mr.
Buck
at the same Weapons, declaring himself the
Master of the renowned
Gorman
; but
Buck
denied him the Honour of
that couragious Disciple, and asserting that he himself had taught that
Champion, accepted the Challenge.
There is something in Nature very unaccountable on such Occasions, when
we see the People take a certain painful Gratification in beholding
these Encounters. Is it Cruelty that administers this Sort of Delight?
Or is it a Pleasure which is taken in the Exercise of Pity? It was
methought pretty remarkable, that the Business of the Day being a Tryal
of Skill, the Popularity did not run so high as one would have expected
on the Side of
Buck
. Is it that People's Passions have their Rise in
Self-Love, and thought themselves (in spite of all the Courage they had)
liable to the Fate of
Miller
, but could not so easily think themselves
qualified like
Buck
?
Tully
of this Custom with less Horrour than one would expect,
though he confesses it was much abused in his Time, and seems directly
to approve of it under its first Regulations, when Criminals only fought
before the People.
Crudele Gladiatorum spectaculum et inhumanum
nonnullis videri solet; et haud scio annon ita sit ut nunc fit; cum vero
sontes ferro depugnabant, auribus fortasse multa, oculis quidem nulla,
poterat esse fortior contra dolorem et mortem disciplina. The Shows of
Gladiators may be thought barbarous and inhumane, and I know not but it
is so as it is now practised; but in those Times when only Criminals
were Combatants, the Ear perhaps might receive many better Instructions,
but it is impossible that any thing which affects our Eyes, should
fortifie us so well against Pain and Death.
T.
See note on p. 118, vol. i. [Volume 1 links:
of
.]
John Sparkes of Coventry has this piece of biography upon
his tombstone:
'To the memory of Mr. John Sparkes, a native of this city; he was a
man of a mild disposition, a gladiator by profession, who, after
having fought 350 battles in the principal parts of Europe with honour
and applause, at length quitted the stage, sheathed his sword, and,
with Christian resignation, submitted to the grand victor in the 52nd
year of his age.
Anno salutis humanæ, 1733.'
Serjeant James Miller afterwards became a captain, and fought in
Scotland, under the Duke of Cumberland in 1745.
Tuscul. Quaest. lib. II.,
De Tolerando Dolore
.
Contents
Tune impune hæc facias? Tune hic homines adolescentulos
Imperitos rerum, eductos libere, in fraudem illicis?
Sollicitando, et pollicitando eorum animos lactas?
Ac meritricios amores nuptiis conglutinas?
Ter. And.

The other Day passed by me in her Chariot a Lady with that pale and wan
Complexion, which we sometimes see in young People, who are fallen into
Sorrow and private Anxiety of Mind, which antedate Age and Sickness. It
is not three Years ago since she was gay, airy, and a little towards
Libertine in her Carriage; but, methought, I easily forgave her that
little Insolence, which she so severely pays for in her present
Condition.
Favilla
, of whom I am speaking, is married to a sullen Fool
with Wealth: Her Beauty and Merit are lost upon the Dolt, who is
insensible of Perfection in any thing. Their Hours together are either
painful or insipid: The Minutes she has to herself in his Absence, are
not sufficient to give Vent at her Eyes to the Grief and Torment of his
last Conversation. This poor Creature was sacrificed with a Temper
(which, under the Cultivation of a Man of Sense, would have made the
most agreeable Companion) into the Arms of this loathsome Yoak-fellow by
Sempronia
.
Sempronia
is a good Lady, who supports herself in an
affluent Condition, by contracting Friendship with rich young Widows and
Maids of plentiful Fortunes at their own Disposal, and bestowing her
Friends upon worthless indigent Fellows; on the other Side, she ensnares
inconsiderate and rash Youths of great Estates into the Arms of vitious
Women. For this Purpose, she is accomplished in all the Arts which can
make her acceptable at impertinent Visits; she knows all that passes in
every Quarter, and is well acquainted with all the favourite Servants,
Busiebodies, Dependants, and poor Relations of all Persons of Condition
in the whole Town. At the Price of a good Sum of Money,
Sempronia
, by
the Instigation of
Favilla's
Mother, brought about the Match for the
Daughter, and the Reputation of this, which is apparently, in point of
Fortune, more than
Favilla
could expect, has gained her the Visits and
frequent Attendance of the Crowd of Mothers, who had rather see their
Children miserable in great Wealth, than the happiest of the Race of
Mankind in a less conspicuous State of Life. When
Sempronia
is so well
acquainted with a Woman's Temper and Circumstance, that she believes
Marriage would be acceptable to her, and advantageous to the Man who
shall get her; her next Step is to look out for some one, whose
Condition has some secret Wound in it, and wants a Sum, yet, in the Eye
of the World, not unsuitable to her. If such is not easily had, she
immediately adorns a worthless Fellow with what Estate she thinks
convenient, and adds as great a Share of good Humour and Sobriety as is
requisite: After this is settled, no Importunities, Arts, and Devices
are omitted to hasten the Lady to her Happiness. In the general indeed
she is a Person of so strict Justice, that she marries a poor Gallant to
a rich Wench, and a Moneyless Girl to a Man of Fortune. But then she has
no manner of Conscience in the Disparity, when she has a Mind to impose
a poor Rogue for one of an Estate, she has no Remorse in adding to it,
that he is illiterate, ignorant, and unfashioned; but makes those
Imperfections Arguments of the Truth of his Wealth, and will, on such an
Occasion, with a very grave Face, charge the People of Condition with
Negligence in the Education of their Children. Exception being made
t'other Day against an ignorant Booby of her own Cloathing, whom she was
putting off for a rich Heir,
Madam
, said she,
you know there is no
making Children who know they have Estates attend their Books.
Sempronia,
by these Arts, is loaded with Presents, importuned for her
Acquaintance, and admired by those who do not know the first Taste of
Life, as a Woman of exemplary good Breeding. But sure, to murder and to
rob are less Iniquities, than to raise Profit by Abuses, as irreparable
as taking away Life; but more grievous, as making it lastingly unhappy.
To rob a Lady at Play of Half her Fortune, is not so ill, as giving the
whole and her self to an unworthy Husband. But
Sempronia
can
administer Consolation to an unhappy Fair at Home, by leading her to an
agreeable Gallant elsewhere. She can then preach the general Condition
of all the Married World, and tell an unexperienced young Woman the
Methods of softning her Affliction, and laugh at her Simplicity and Want
of Knowledge, with an
Oh! my Dear, you will know better.
The Wickedness of
Sempronia,
one would think, should be superlative;
but I cannot but esteem that of some Parents equal to it; I mean such as
sacrifice the greatest Endowments and Qualifications to base Bargains. A
Parent who forces a Child of a liberal and ingenious Spirit into the
Arms of a Clown or a Blockhead, obliges her to a Crime too odious for a
Name. It is in a Degree the unnatural Conjunction of rational and brutal
Beings. Yet what is there so common, as the bestowing an accomplished
Woman with such a Disparity. And I could name Crowds who lead miserable
Lives, or want of Knowledge in their Parents, of this Maxim, that good
Sense and good Nature always go together. That which is attributed to
Fools, and called good Nature, is only an Inability of observing what is
faulty, which turns in Marriage, into a Suspicion of every thing as
such, from a Consciousness of that Inability.
Mr.
Spectator,
'I am entirely of your Opinion with Relation to the Equestrian
Females, who affect both the Masculine and Feminine Air at the same
time; and cannot forbear making a Presentment against another Order of
them who grow very numerous and powerful; and since our Language is
not very capable of good compound Words, I must be contented to call
them only the
Naked Shouldered. These Beauties are not contented to
make Lovers where-ever they appear, but they must make Rivals at the
same time. Were you to see
Gatty walk the
Park at high Mall, you
would expect those who followed her and those who met her could
immediately draw their Swords for her. I hope,
Sir , you will provide
for the future, that Women may stick to their Faces for doing any
future Mischief and not allow any but direct Traders in Beauty to
expose more than the fore Part of the Neck, unless you please to allow
this After-Game to those who are very defective in the Charms of the
Countenance. I can say, to my Sorrow, the present Practice is very
unfair, when to look back is Death; and it may be said of our
Beauties, as a great Poet did of Bullets,
They kill and wound like Parthians as they fly.
I submit this to your Animadversion; and am, for the little while I
have left,
Your humble Servant, the languishing Philanthus.
P. S. Suppose you mended my Letter, and made a Simile about the
Porcupine, but I submit that also.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 23, 1712 |
Steele |
—Animum rege qui nisi paret
Imperat—
Hor.

It is a very common Expression, That such a one is very good-natur'd,
but very passionate. The Expression indeed is very good-natur'd, to
allow passionate People so much Quarter: But I think a passionate Man
deserves the least Indulgence Imaginable. It is said, it is soon over;
that is, all the Mischief he does is quickly dispatch'd, which, I think,
is no great Recommendation to Favour. I have known one of these
good-natur'd passionate Men say in a mix'd Company even to his own Wife
or Child, such Things as the most inveterate Enemy of his Family would
not have spoke, even in Imagination. It is certain that quick
Sensibility is inseparable from a ready Understanding; but why should
not that good Understanding call to it self all its Force on such
Occasions, to master that sudden Inclination to Anger.
of the
greatest Souls now in the World
is the most subject by Nature to
Anger, and yet so famous from a Conquest of himself this Way, that he is
the known Example when you talk of Temper and Command of a Man's Self.
To contain the Spirit of Anger, is the worthiest Discipline we can put
our selves to. When a Man has made any Progress this way, a frivolous
Fellow in a Passion, is to him as contemptible as a froward Child. It
ought to be the Study of every Man, for his own Quiet and Peace. When he
stands combustible and ready to flame upon every thing that touches him,
Life is as uneasie to himself as it is to all about him.
Syncropius
leads, of all Men living, the most ridiculous Life; he is ever
offending, and begging Pardon. If his Man enters the Room without what
he sent for,
That Blockhead
, begins he—
Gentlemen, I ask your
Pardon, but Servants now a-days
—The wrong Plates are laid, they are
thrown into the Middle of the Room; his Wife stands by in Pain for him,
which he sees in her Face, and answers as if he had heard all she was
thinking;
Why, what the Devil! Why don't you take Care to give Orders
in these things?
His Friends sit down to a tasteless Plenty of every
thing, every Minute expecting new Insults from his impertinent Passions.
In a Word, to eat with, or visit
Syncropius
, is no other than going to
see him exercise his Family, exercise their Patience, and his own Anger.
It is monstrous that the Shame and Confusion in which this good-natured
angry Man must needs behold his Friends while he thus lays about him,
does not give him so much Reflection as to create an Amendment. This is
the most scandalous Disuse of Reason imaginable; all the harmless Part
of him is no more than that of a Bull-Dog, they are tame no longer than
they are not offended. One of these good-natured angry Men shall, in an
Instant, assemble together so many Allusions to secret Circumstances, as
are enough to dissolve the Peace of all the Families and Friends he is
acquainted with, in a Quarter of an Hour, and yet the next Moment be the
best-natured Man in the whole World. If you would see Passion in its
Purity, without Mixture of Reason, behold it represented in a mad Hero,
drawn by a mad Poet.
Nat Lee
makes his
Alexander
say thus:
Away, begon, and give a Whirlwind Room,
Or I will blow you up like Dust! Avaunt;
Madness but meanly represents my Toil.
Eternal Discord!
Fury! Revenge! Disdain and Indignation!
Tear my swoln Breast, make way for Fire and Tempest.
My Brain is burst, Debate and Reason quench'd;
The Storm is up, and my hot bleeding Heart
Splits with the Rack, while Passions, like the Wind,
Rise up to Heav'n, and put out all the Stars.
Every passionate Fellow in Town talks half the Day with as little
Consistency, and threatens Things as much out of his Power.
The next disagreeable Person to the outrageous Gentleman, is one of a
much lower Order of Anger, and he is what we commonly call a peevish
Fellow. A peevish Fellow is one who has some Reason in himself for being
out of Humour, or has a natural Incapacity for Delight, and therefore
disturbs all who are happier than himself with Pishes and Pshaws, or
other well-bred Interjections, at every thing that is said or done in
his Presence. There should be Physick mixed in the Food of all which
these Fellows eat in good Company. This Degree of Anger passes,
forsooth, for a Delicacy of Judgment, that won't admit of being easily
pleas'd: but none above the Character of wearing a peevish Man's Livery,
ought to bear with his ill Manners. All Things among Men of Sense and
Condition should pass the Censure, and have the Protection, of the Eye
of Reason.
No Man ought to be tolerated in an habitual Humour, Whim, or
Particularity of Behaviour, by any who do not wait upon him for Bread.
Next to the peevish Fellow is the Snarler. This Gentleman deals mightily
in what we call the Irony, and as those sort of People exert themselves
most against these below them, you see their Humour best, in their Talk
to their Servants.
That is so like you, You are a fine Fellow, Thou art
the quickest Head-piece
, and the like. One would think the Hectoring,
the Storming, the Sullen, and all the different Species and
Subordinations of the Angry should be cured, by knowing they live only
as pardoned Men; and how pityful is the Condition of being only
suffered? But I am interrupted by the pleasantest Scene of Anger and the
Disappointment of it that I have ever known, which happened while I was
yet Writing, and I overheard as I sat in the Backroom at a
French
Bookseller's. There came into the Shop a very learned Man with an erect
Solemn Air, and tho' a Person of great Parts otherwise, slow in
understanding anything which makes against himself. The Composure of the
faulty Man, and the whimsical Perplexity of him that was justly angry,
is perfectly New: After turning over many Volumes, said the Seller to
the Buyer,
Sir , you know I have long asked you to send me back the
first Volume of French Sermons I formerly lent you;
Sir
, said the
Chapman, I have often looked for it but cannot find it; It is certainly
lost, and I know not to whom I lent it, it is so many Years ago;
then,
Sir , here is the other Volume, I'll send you home that, and please to
pay for both
. My Friend, reply'd he, canst thou be so Senseless as not
to know that one Volume is as imperfect in my Library as in your Shop?
Yes, Sir , but it is you have lost the first Volume, and to be short I
will be Paid.
Sir
, answered the Chapman, you are a young Man, your Book
is lost, and learn by this little Loss to bear much greater Adversities,
which you must expect to meet with.
Yes, Sir , I'll bear when I must,
but I have not lost now, for I say you have it and shall pay me.
Friend, you grow Warm, I tell you the Book is lost, and I foresee in the
Course even of a prosperous Life, that you will meet Afflictions to make
you Mad, if you cannot bear this Trifle.
Sir , there is in this Case no
need of bearing, for you have the Book.
I say,
Sir
, I have not the
Book. But your Passion will not let you hear enough to be informed that
I have it not. Learn Resignation of your self to the Distresses of this
Life: Nay do not fret and fume, it is my Duty to tell you that you are
of an impatient Spirit, and an impatient Spirit is never without Woe.
Was ever any thing like this?
Yes,
Sir
, there have been many things
like this. The Loss is but a Trifle, but your Temper is Wanton, and
incapable of the least Pain; therefore let me advise you, be patient,
the Book is lost, but do not you for that Reason lose your self.
T.
Lord Somers.
Contents
|
Thursday, July 24, 1712 |
Addison |
Hi narrata ferunt alio: mensuraque ficti
Crescit; et auditis aliquid novus adjicit auctor.
Ovid.

Ovid
the Palace of Fame
as situated in the very Center of
the Universe, and perforated with so many Windows and Avenues as gave
her the Sight of every thing that was done in the Heavens, in the Earth,
and in the Sea. The Structure of it was contrived in so admirable a
manner, that it Eccho'd every Word which was spoken in the whole Compass
of Nature; so that the Palace, says the Poet, was always filled with a
confused Hubbub of low dying Sounds, the Voices being almost spent and
worn out before they arrived at this General Rendezvous of Speeches and
Whispers.
I consider Courts with the same Regard to the Governments which they
superintend, as
Ovid's
Palace of Fame with regard to the Universe. The
Eyes of a watchful Minister run through the whole People. There is
scarce a Murmur or Complaint that does not reach his Ears. They have
News-gatherers and Intelligencers distributed into their several Walks
and Quarters, who bring in their respective Quotas, and make them
acquainted with the Discourse and Conversation of the whole Kingdom or
Common-wealth where they are employed. The wisest of Kings, alluding to
these invisible and unsuspected Spies, who are planted by Kings and
Rulers over their Fellow-Citizens, as well as to those Voluntary
Informers that are buzzing about the Ears of a great Man, and making
their Court by such secret Methods of Intelligence, has given us a very
prudent
:
Curse not the King, no not in thy Thought, and Curse
not the Rich in thy Bedchamber: For a Bird of the Air shall carry the
Voice, and that which hath Wings shall tell the matter.
As it is absolutely necessary for Rulers to make use of other People's
Eyes and Ears, they should take particular Care to do it in such a
manner, that it may not bear too hard on the Person whose Life and
Conversation are enquired into. A Man who is capable of so infamous a
Calling as that of a Spy, is not very much to be relied upon. He can
have no great Ties of Honour, or Checks of Conscience, to restrain him
in those covert Evidences, where the Person accused has no Opportunity
of vindicating himself. He will be more industrious to carry that which
is grateful, than that which is true.
There will be no Occasion for him, if he does not hear and see things
worth Discovery; so that he naturally inflames every Word and
Circumstance, aggravates what is faulty, perverts what is good, and
misrepresents what is indifferent. Nor is it to be doubted but that such
ignominious Wretches let their private Passions into these their
clandestine Informations, and often wreck their particular Spite or
Malice against the Person whom they are set to watch. It is a pleasant
Scene enough, which an
Italian
Author describes between a Spy, and a
Cardinal who employed him. The Cardinal is represented as minuting down
every thing that is told him. The Spy begins with a low Voice, Such an
one, the Advocate, whispered to one of his Friends, within my Hearing,
that your Eminence was a very great Poultron; and after having given his
Patron time to take it down, adds that another called him a Mercenary
Rascal in a publick Conversation. The Cardinal replies, Very well, and
bids him go on. The Spy proceeds, and loads him with Reports of the same
Nature, till the Cardinal rises in great Wrath, calls him an impudent
Scoundrel, and kicks him out of the Room.
It is observed of great and heroick Minds, that they have not only shewn
a particular Disregard to those unmerited Reproaches which have been
cast upon 'em, but have been altogether free from that Impertinent
Curiosity of enquiring after them, or the poor Revenge of resenting
them. The Histories of
Alexander
and
Cæsar
are full of this kind of
Instances. Vulgar Souls are of a quite contrary Character.
Dionysius
,
the Tyrant of
Sicily
, had a Dungeon which was a very curious Piece of
Architecture; and of which, as I am informed, there are still to be seen
some Remains in that Island. It was called
Dionysius's
Ear, and built
with several little Windings and Labyrinths in the form of a real Ear.
The Structure of it made it a kind of whispering Place, but such a one
as gathered the Voice of him who spoke into a Funnel, which was placed
at the very Top of it. The Tyrant used to lodge all his State-Criminals,
or those whom he supposed to be engaged together in any Evil Designs
upon him, in this Dungeon. He had at the
time an Apartment over it,
where he used to apply himself to the Funnel, and by that Means
over-hear every thing that was whispered in
the
Dungeon. I believe
one may venture to affirm, that a
Cæsar
or an
Alexander
would rather
have died by the Treason, than have used such disingenuous Means for the
detecting of it. A Man, who in ordinary Life is very Inquisitive after
every thing which is spoken ill of him, passes his Time but very
indifferently. He is wounded by every Arrow that is shot at him, and
puts it in the Power of every insignificant Enemy to disquiet him. Nay,
he will suffer from what has been said of him, when it is forgotten by
those who said or heard it. For this Reason I could never bear one of
those officious Friends,
would be telling every malicious Report,
every idle Censure that
passed
upon me. The Tongue of Man is so
petulant, and his Thoughts so variable, that one should not lay too
great a Stress upon any present Speeches and Opinions. Praise and
Obloquy proceed very frequently out of the same Mouth upon the same
Person, and upon the same Occasion. A generous Enemy will sometimes
bestow Commendations, as the dearest Friend cannot sometimes refrain
from speaking Ill. The Man who is indifferent in either of these
Respects, gives his Opinion at random, and praises or disapproves as he
finds himself in Humour.
I shall conclude this Essay with Part of a Character, which
is finely
by the Earl of
Clarendon
, in the first Book of
his History, and which gives us the lively Picture of a great
Man teizing himself with an absurd Curiosity.
'He had not that Application and Submission, and Reverence for the
Queen, as might have been expected from his Wisdom and Breeding; and
often crossed her Pretences and De
Sir es with more Rudeness than was
natural to him. Yet he was impertinently sollicitous to know what her
Majesty said of him in private, and what Resentments she had towards
him. And when by some Confidents, who had their Ends upon him from
those Offices, he was informed of some bitter Expressions fallen from
her Majesty, he was so exceedingly afflicted and tormented with the
Sense of it, that sometimes by passionate Complaints and
Representations to the King; sometimes by more dutiful Addresses and
Expostulations with the Queen, in bewailing his Misfortune; he
frequently exposed himself, and left his Condition worse than it was
before, and the Eclaircisment commonly ended in the Discovery of the
Persons from whom he had received his most secret Intelligence.'
5
C.
Metamorphoses
, Bk xii.
Eccl
. x. 20.
this
passes
Written of Lord Treasurer Western, Earl of Portland.
Contents
|
Friday, July 25, 1712 |
Addison |
Vivere si rectè nescis, discede peritis.
Hor.

I have already given my Reader an Account of a Sett of merry Fellows,
who are passing their Summer together in the Country, being provided of
a great House, where there is not only a convenient Apartment for every
particular Person, but a large Infirmary for the Reception of such of
them as are any way indisposed, or out of Humour. Having lately received
a Letter from the Secretary of this Society, by Order of the whole
Fraternity, which acquaints me with their Behaviour during the last
Week, I shall here make a Present of it to the Publick.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'We are glad to find that you approve the Establishment which we have
here made for the retrieving of good Manners and agreeable
Conversation, and shall use our best Endeavours so to improve our
selves in this our Summer Retirement, that we may next Winter serve as
Patterns to the Town. But to the end that this our Institution may be
no less Advantageous to the Publick than to our selves, we shall
communicate to you one Week of our Proceedings, deSir ing you at the
same time, if you see any thing faulty in them, to favour us with your
Admonitions. For you must know, Sir , that it has been proposed among
us to chuse you for our Visitor, to which I must further add, that one
of the College having declared last Week, he did not like the
Spectator of the Day, and not being able to assign any just Reasons
for such his Dislike, he was sent to the Infirmary Nemine
Contradicente.
'On Monday the Assembly was in very good Humour, having received
some Recruits of French Claret that Morning: when unluckily, towards
the middle of the Dinner, one of the Company swore at his Servant in a
very rough manner, for having put too much Water in his Wine. Upon
which the President of the Day, who is always the Mouth of the
Company, after having convinced him of the Impertinence of his
Passion, and the Insult it had made upon the Company, ordered his Man
to take him from the Table and convey him to the Infirmary. There was
but one more sent away that Day; this was a Gentleman who is reckoned
by some Persons one of the greatest Wits, and by others one of the
greatest Boobies about Town. This you will say is a strange Character,
but what makes it stranger yet, it is a very true one, for he is
perpetually the Reverse of himself, being always merry or dull to
Excess. We brought him hither to divert us, which he did very well
upon the Road, having lavished away as much Wit and Laughter upon the
Hackney Coachman as might have served him during his whole Stay here,
had it been duly managed. He had been lumpish for two or three Days,
but was so far connived at, in hopes of Recovery, that we dispatched
one of the briskest Fellows among the Brotherhood into the Infirmary,
for having told him at Table he was not merry. But our President
observing that he indulged himself in this long Fit of Stupidity, and
construing it as a Contempt of the College, ordered him to retire into
the Place prepared for such Companions. He was no sooner got into it,
but his Wit and Mirth returned upon him in so violent a manner, that
he shook the whole Infirmary with the Noise of it, and had so good an
Effect upon the rest of the Patients, that he brought them all out to
Dinner with him the next Day.
'On Tuesday we were no sooner sat down, but one of the Company
complained that his Head aked; upon which another asked him, in an
insolent manner, what he did there then; this insensibly grew into
some warm Words; so that the President, in order to keep the Peace,
gave directions to take them both from the Table, and lodge them in
the Infirmary. Not long after, another of the Company telling us, he
knew by a Pain in his Shoulder that we should have some Rain, the
President ordered him to be removed, and placed as a Weather-glass in
the Apartment above mentioned.
'On Wednesday a Gentleman having received a Letter written in a
Woman's Hand, and changing Colour twice or thrice as he read it,
deSir ed leave to retire into the Infirmary. The President consented,
but denied him the Use of Pen, Ink and Paper, till such time as he had
slept upon it. One of the Company being seated at the lower end of the
Table, and discovering his secret Discontent by finding fault with
every Dish that was served up, and refusing to Laugh at any thing that
was said, the President told him, that he found he was in an uneasie
Seat, and deSir ed him to accommodate himself better in the Infirmary.
After Dinner a very honest Fellow chancing to let a Punn fall from
him, his Neighbour cryed out, to the Infirmary; at the same time
pretending to be Sick at it, as having the same Natural Antipathy to a
Punn, which some have to a Cat. This produced a long Debate. Upon the
whole, the Punnster was Acquitted and his Neighbour sent off.
'On Thursday there was but one Delinquent. This was a Gentleman of
strong Voice, but weak Understanding. He had unluckily engaged himself
in a Dispute with a Man of excellent Sense, but of a modest Elocution.
The Man of Heat replied to every Answer of his Antagonist with a
louder Note than ordinary, and only raised his Voice when he should
have enforced his Argument. Finding himself at length driven to an
Absurdity, he still reasoned in a more clamorous and confused manner,
and to make the greater Impression upon his Hearers, concluded with a
loud Thump upon the Table. The President immediately ordered him to be
carried off, and dieted with Water-gruel, till such time as he should
be sufficiently weakened for Conversation.
'On Friday there passed very little remarkable, saving only, that
several Petitions were read of the Persons in Custody, deSir ing to be
released from their Confinement, and vouching for one another's good
Behaviour for the future.
'On Saturday we received many Excuses from Persons who had found
themselves in an unsociable Temper, and had voluntarily shut
themselves up. The Infirmary was indeed never so full as on this Day,
which I was at some loss to account for, till upon my going Abroad I
observed that it was an Easterly Wind. The Retirement of most of my
Friends has given me Opportunity and Leisure of writing you this
Letter, which I must not conclude without assuring you, that all the
Members of our College, as well those who are under Confinement, as
those who are at Liberty, are your very humble Servants, tho' none
more than, &c.'
C.
Contents
|
Saturday, July 26, 1712 |
Addison |
Si fractus illabatur orbis
Impavidum ferient ruinæ.
Hor.

Man, considered in himself, is a very helpless and a very wretched
Being. He is subject every Moment to the greatest Calamities and
Misfortunes. He is beset with Dangers on all sides, and may become
unhappy by numberless Casualties, which he could not foresee, nor have
prevented, had he foreseen them.
It is our Comfort, while we are obnoxious to so many Accidents, that we
are under the Care of one who directs Contingencies, and has in his
Hands the Management of every Thing that is capable of annoying or
offending us; who knows the Assistance we stand in need of, and is
always ready to bestow it on those who ask it of him.
The natural Homage, which such a Creature bears to so infinitely Wise
and Good a Being, is a firm Reliance on him for the Blessings and
Conveniences of Life, and an habitual Trust in him for Deliverance out
of all such Dangers and Difficulties as may befall us.
The Man, who always lives in this Disposition of Mind, has not the same
dark and melancholy Views of Human Nature, as he who considers himself
abstractedly from this Relation to the Supreme Being. At the same time
that he reflects upon his own Weakness and Imperfection, he comforts
himself with the Contemplation of those Divine Attributes, which are
employed for his Safety and his Welfare. He finds his Want of Foresight
made up by the Omniscience of him who is his Support. He is not sensible
of his own want of Strength, when he knows that his Helper is Almighty.
In short, the Person who has a firm trust on the Supreme Being is
Powerful in
his
Power, Wise by
his
Wisdom, Happy by
his
Happiness.
He reaps the Benefit of every Divine Attribute, and loses his own
Insufficiency in the Fullness of Infinite Perfection.
To make our Lives more easie to us, we are commanded to put our Trust in
him, who is thus able to relieve and succour us; the Divine Goodness
having made such a Reliance a Duty, notwithstanding we should have been
miserable had it been forbidden us.
Among several Motives, which might be made use of to recommend this Duty
to us, I shall only take notice of those that follow.
The first and strongest is, that we are promised,
He will not fail those
who put their Trust in him.
But without considering the Supernatural Blessing which accompanies this
Duty, we may observe that it has a natural Tendency to its own Reward,
or in other Words, that this firm Trust and Confidence in the great
Disposer of all Things, contributes very much to the getting clear of
any Affliction, or to the bearing it manfully. A Person who believes he
has his Succour at hand, and that he acts in the sight of his Friend,
often excites himself beyond his Abilities, and does Wonders that are
not to be matched by one who is not animated with such a Confidence of
Success. I could produce Instances from History, of Generals, who out of
a Belief that they were under the Protection of some invisible
Assistant, did not only encourage their Soldiers to do their utmost, but
have acted themselves beyond what they would have done, had they not
been inspired by such a Belief. I might in the same manner show how such
a Trust in the Assistance of an Almighty Being, naturally produces
Patience, Hope, Cheerfulness, and all other Dispositions of Mind that
alleviate those Calamities which we are not able to remove.
The Practice of this Virtue administers great Comfort to the Mind of Man
in Times of Poverty and Affliction, but most of all in the Hour of
Death.
the Soul is hovering in the last Moments of its
Separation
, when it is just entring on another State of Existence, to converse
with Scenes, and Objects, and Companions that are altogether new, what
can support her under such Tremblings of Thought, such Fear, such
Anxiety, such Apprehensions, but
casting of all her Cares upon him
who first gave her Being, who has conducted her through one Stage of it,
and will be always with her to Guide and Comfort her in her
Progress
through Eternity?
David
has very beautifully represented this steady Reliance on God
Almighty in his
twenty third Psalm
, which is a kind of
Pastoral
Hymn,
and filled with those Allusions which are usual in that kind of Writing.
As
Poetry is very exquisite, I shall present my Reader with the
following Translation of it
.
| I |
The Lord my Pasture shall prepare,
And feed me with a Shepherd's Care;
His Presence shall my Wants supply,
And guard me with a watchful Eye;
My Noon-day Walks he shall attend,
And all my Mid-night Hours defend. |
| II |
When in the sultry Glebe I faint,
Or on the thirsty Mountain pant;
To fertile Vales, and dewy Meads
My weary wand'ring Steps he leads;
Where peaceful Rivers, soft and slow,
Amid the verdant Landskip flow. |
| III |
Tho' in the Paths of Death I tread,
With gloomy Horrors overspread,
My steadfast Heart shall fear no Ill,
For thou, O Lord, art with me still;
Thy friendly Crook shall give me Aid,
And guide me through the dreadful Shade. |
| IV |
Tho' in a bare and rugged Way,
Through devious lonely Wilds I stray,
Thy Bounty shall my Pains beguile;
The barren Wilderness shall smile,
With sudden Greens and Herbage crown'd,
And Streams shall murmur all around. |
C.
Dissolution
text
By Addison
Contents
|
Monday, July 28, 1712 |
Steele |
—Scribimus Indocti Doctique—
Hor.

I do not know whether I enough explained my self to the World, when I
invited all Men to be assistant to me in this my Work of Speculation;
for I have not yet acquainted my Readers, that besides the Letters and
valuable Hints I have from Time to Time received from my Correspondents,
I have by me several curious and extraordinary Papers sent with a Design
(as no one will doubt when they are published) that they might be
printed entire, and without any Alteration, by way of
Spectator
. I
must acknowledge also, that I my self being the first Projector of the
Paper, thought I had a Right to make them my own, by dressing them in my
own Style, by leaving out what would not appear like mine, and by adding
whatever might be proper to adapt them to the Character and Genius of my
Paper, with which it was almost impossible these could exactly
correspond, it being certain that hardly two Men think alike, and
therefore so many Men so many
Spectators
. Besides, I must own my
Weakness for Glory is such, that if I consulted that only, I might be so
far sway'd by it, as almost to wish that no one could write a
Spectator
besides myself; nor can I deny, but upon the first Perusal
of those Papers, I felt some secret Inclinations of Ill-will towards the
Persons who wrote them. This was the Impression I had upon the first
reading them; but upon a late Review (more for the Sake of Entertainment
than Use) regarding them with another Eye than I had done at first, (for
by converting them as well as I could to my own Use, I thought I had
utterly disabled them from ever offending me again as
Spectators
) I
found my self moved by a Passion very different from that of Envy;
sensibly touched with Pity, the softest and most generous of all
Passions, when I reflected what a cruel Disapointment the Neglect of
those Papers must needs have been to the Writers who impatiently longed
to see them appear in Print, and who, no doubt, triumphed to themselves
in the Hopes of having a Share with me in the Applause of the Publick; a
Pleasure so great, that none but those who have experienced it can have
a Sense of it. In this Manner of viewing these Papers, I really found I
had not done them Justice, there being something so extremely natural
and peculiarly good in some of them, that I will appeal to the World
whether it was possible to alter a Word in them without doing them a
manifest Hurt and Violence; and whether they can ever appear rightly,
and, as they ought, but in their own native Dress and Colours: And
therefore I think I should not only wrong them, but deprive the World of
a considerable Satisfaction, should I any longer delay the making them
publick.
After I have published a few of these
Spectators
, I doubt not but I
shall find the Success of them to equal, if not surpass, that of the
best of my own. An Author should take all Methods to humble himself in
the Opinion he has of his own Performances. When these Papers appear to
the World, I doubt not but they will be followed by many others; and I
shall not repine, though I my self shall have left me but very few Days
to appear in Publick: But preferring the general Weal and Advantage to
any Consideration of my self, I am resolved for the Future to publish
any
Spectator
that deserves it, entire, and without any Alteration;
assuring the World (if there can be Need of it) that it is none of mine
and if the Authors think fit to subscribe their Names, I will add them.
I think the best way of promoting this generous and useful Design, will
be by giving out Subjects or Themes of all Kinds whatsoever, on which
(with a Preamble of the extraordinary Benefit and Advantage that may
accrue thereby to the Publick) I will invite all manner of Persons,
whether Scholars, Citizens, Courtiers, Gentlemen of the Town or Country,
and all Beaux, Rakes, Smarts, Prudes, Coquets, Housewives, and all Sorts
of Wits, whether Male or Female, and however distinguished, whether they
be True-Wits, Whole, or Half-Wits, or whether Arch, Dry, Natural,
Acquired, Genuine, or Deprav'd Wits; and Persons of all sorts of Tempers
and Complexions, whether the Severe, the Delightful, the Impertinent,
the Agreeable, the Thoughtful, Busie, or Careless; the Serene or Cloudy,
Jovial or Melancholy, Untowardly or Easie; the Cold, Temperate, or
Sanguine; and of what Manners or Dispositions soever, whether the
Ambitious or Humble-minded, the Proud or Pitiful, Ingenious or
Base-minded, Good or Ill-natur'd, Publick-spirited or Selfish; and under
what Fortune or Circumstance soever, whether the Contented or Miserable,
Happy or Unfortunate, High or Low, Rich or Poor (whether so through Want
of Money, or De
Sir
e of more) Healthy or Sickly, Married or Single; nay,
whether Tall or Short, Fat or Lean; and of what Trade, Occupation,
Profession, Station, Country, Faction, Party, Persuasion, Quality, Age
or Condition soever, who have ever made Thinking a Part of their
Business or Diversion, and have any thing worthy to impart on these
Subjects to the World, according to their several and respective Talents
or Genius's, and as the Subject given out hits their Tempers, Humours,
or Circumstances, or may be made profitable to the Publick by their
particular Knowledge or Experience in the Matter proposed, to do their
utmost on them by such a Time; to the End they may receive the
inexpressible and irresistible Pleasure of seeing their Essay allowed of
and relished by the rest of Mankind.
I will not prepossess the Reader with too great Expectation of the
extraordinary Advantages which must redound to the Publick by these
Essays, when the different Thoughts and Observations of all Sorts of
Persons, according to their Quality, Age, Sex, Education, Professions,
Humours, Manners and Conditions, &c. shall be set out by themselves in
the clearest and most genuine Light, and as they themselves would wish
to have them appear to the World.
The
Thesis
propos'd for the present Exercise of the Adventurers to
write
Spectators
,
is
Money
,
on which Subject all Persons are deSir ed
to send their Thoughts within Ten Days after the Date hereof.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, July 29, 1712 |
Steele |
Sublatam ex oculis Quærimus invidi.
Hor.

Camillia
to the Spectator.
Venice, July 10, N. S.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I Take it extreamly ill, that you do not reckon conspicuous Persons
of your Nation are within your Cognizance, tho' out of the Dominions
of Great Britain. I little thought in the green Years of my Life, that
I should ever call it an Happiness to be out of dear
England; but as
I grew to Woman, I found my self less acceptable in Proportion to the
Encrease of my Merit. Their Ears in
Italy are so differently formed
from the Make of yours in
England, that I never come upon the Stage,
but a general Satisfaction appears in every Countenance of the whole
People. When I dwell upon a Note, I behold all the Men accompanying me
with Heads enclining and falling of their Persons on one Side, as
dying away with me. The Women too do Justice to my Merit, and no
ill-natur'd worthless Creature cries,
The vain Thing, when I am rapt
up in the Performance of my Part, and sensibly touched with the Effect
my Voice has upon all who hear me. I live here distinguished as one
whom Nature has been liberal to in a graceful Person, an exalted Mein,
and Heavenly Voice. These Particularities in this strange Country, are
Arguments for Respect and Generosity to her who is possessed of them.
The
Italians see a thousand Beauties I am sensible I have no
Pretence to, and abundantly make up to me the Injustice I received in
my own Country, of disallowing me what I really had. The Humour of
Hissing, which you have among you, I do not know any thing of; and
their Applauses are uttered in Sighs, and bearing a Part at the
Cadences of Voice with the Persons who are performing. I
am often put
in Mind of those complaisant Lines of my own Countryman
1, when he
is calling all his Faculties together to hear
Arabella;
Let all be hush'd, each softest Motion cease,
Be ev'ry loud tumultuous Thought at Peace;
And ev'ry ruder Gasp of Breath
Be calm, as in the Arms of Death:
And thou, most fickle, most uneasie Part,
Thou restless Wanderer, my Heart,
Be still; gently, ah! gently leave,
Thou busie, idle Thing, to heave.
Stir not a Pulse: and let my Blood,
That turbulent, unruly Flood,
Be softly staid;
Let me be all but my Attention dead.
'The whole City of
Venice is as still when I am singing, as this
Polite Hearer was to Mrs.
Hunt. But when they break that Silence,
did you know the Pleasure I am in, when every Man utters his Applause,
by calling me aloud the
Dear Creature, the
Angel, the
Venus; What
Attitude she moves with!—Hush, she sings again! We have no boistrous
Wits who dare disturb an Audience, and break the publick Peace meerly
to shew they dare. Mr. SPECTATOR, I write this to you thus in Haste,
to tell you I am so very much at ease here, that I know nothing but
Joy; and I will not return, but leave you in
England to hiss all
Merit of your own Growth off the Stage. I
know,
Sir , you were always
my Admirer, and therefore I am yours,
Camilla2.
P. S. I am ten times better dressed than ever I was in
England.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The Project in yours of the 11th Instant, of furthering the
Correspondence and Knowledge of that considerable Part of Mankind, the
Trading World, cannot but be highly commendable. Good Lectures to
young Traders may have very good Effects on their Conduct: but beware
you propagate no false Notions of Trade; let none of your
Correspondents impose on the World, by putting forth base Methods in a
good Light, and glazing them over with improper Terms. I would have no
Means of Profit set for Copies to others, but such as are laudable in
themselves. Let not Noise be called Industry, nor Impudence Courage.
Let not good Fortune be imposed on the World for good Management, nor
Poverty be called Folly; impute not always Bankruptcy to Extravagance,
nor an Estate to Foresight; Niggardliness is not good Husbandry, nor
Generosity Profusion.
'
Honestus is a well-meaning and judicious Trader, hath substantial
Goods, and trades with his own Stock; husbands his Money to the best
Advantage, without taking all Advantages of the Necessities of his
Workmen, or grinding the Face of the Poor.
Fortunatus is stocked
with Ignorance, and consequently with Self-Opinion; the Quality of his
Goods cannot but be suitable to that of his Judgment.
Honestus
pleases discerning People, and keeps their Custom by good Usage; makes
modest Profit by modest Means, to the decent Support of his Family:
Whilst
Fortunatus blustering always, pushes on, promising much, and
performing little, with Obsequiousness offensive to People of Sense;
strikes at all, catches much the greater Part; raises a considerable
Fortune by Imposition on others, to the Disencouragement and Ruin of
those who trade in the same Way.
'I give here but loose Hints, and beg you to be very circumspect in
the Province you have now undertaken: If you perform it successfully,
it will be a very great Good; for nothing is more wanting, than that
Mechanick Industry were set forth with the Freedom and Greatness of
Mind which ought always to accompany a Man of a liberal Education.
Your humble Servant,
R. C.
From my Shop under the Royal-Exchange, July 14.
July 24, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Notwithstanding the repeated Censures that your Spectatorial Wisdom
has passed upon People more remarkable for Impudence than Wit, there
are yet some remaining, who pass with the giddy Part of Mankind for
sufficient Sharers of the latter, who have nothing but the former
Qualification to recommend them. Another timely Animadversion is
absolutely necessary; be pleased therefore once for all to let these
Gentlemen know, that there is neither Mirth nor Good Humour in hooting
a young Fellow out of Countenance; nor that it will ever constitute a
Wit, to conclude a tart Piece of Buffoonry with a
what makes you
blush? Pray please to inform them again, That to speak what they know
is shocking, proceeds from ill Nature, and a Sterility of Brain;
especially when the Subject will not admit of Raillery, and their
Discourse has no Pretension to Satyr but what is in their Design to
disoblige. I should be very glad too if you would take Notice, that a
daily Repetition of the same over-bearing Insolence is yet more
insupportable, and a Confirmation of very extraordinary Dulness. The
sudden Publication of this, may have an Effect upon a notorious
Offender of this Kind, whose Reformation would redound very much to the
Satisfaction and Quiet of
Your most humble Servant,
F. B.
3
William Congreve upon Arabella Hunt.
Mrs. Tofts, see note on p. 85, vol, i. [Volume 1 links:
of
.]
Said to be the initials of Francis Beasniffe.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 30, 1712 |
Steele |
Parturiunt montes.
Hor.1
It gives me much Despair in the Design of reforming the World by my
Speculations, when I find there always arise, from one Generation to
another, successive Cheats and Bubbles, as naturally as Beasts of Prey,
and those which are to be their Food. There is hardly a Man in the
World, one would think, so ignorant, as not to know that the ordinary
Quack Doctors, who publish their great Abilities in little brown
Billets, distributed to all who pass by, are to a Man Impostors and
Murderers; yet such is the Credulity of the Vulgar, and the Impudence of
these Professors, that the Affair still goes on, and new Promises of
what was never done before are made every Day. What aggravates the Just
is, that even this Promise has been made as long as the Memory of Man
can trace it, and yet nothing performed, and yet still prevails. As I
was passing along to-day, a Paper given into my Hand by a Fellow without
a Nose tells us as follows what good News is come to Town, to wit, that
there is now a certain Cure for the
French
Disease, by a Gentleman
just
from his Travels.
In Russel-Court,
over-against the Cannon-Ball,
at the Surgeon's
Arms
in Drury-Lane,
is lately come from his Travels a Surgeon who
has practised Surgery and Physick both by Sea and Land these twenty
four Years. He (by the Blessing) cures the Yellow Jaundice, Green
Sickness, Scurvy, Dropsy, Surfeits, long Sea Voyages, Campains, and
Womens Miscarriages, Lying-Inn,
&c. as some People that has been lame
these thirty Years can testifie; in short, he cureth all Diseases
incident to Men, Women, or Children2.
If a Man could be so indolent as to look upon this Havock of the human
Species which is made by Vice and Ignorance, it would be a good
ridiculous Work to comment upon the Declaration of this accomplished
Traveller. There is something unaccountably taking among the Vulgar in
those who come from a great Way off. Ignorant People of Quality, as many
there are of such, doat excessively this Way; many Instances of which
every Man will suggest to himself without my Enumeration of them. The
Ignorants of lower Order, who cannot, like the upper Ones, be profuse of
their Money to those recommended by coming from a Distance, are no less
complaisant than the others, for they venture their Lives from the same
Admiration.
The Doctor is lately come from his Travels
, and has
practised
both
by Sea and Land, and therefore Cures the
Green Sickness, long Sea
Voyages, Campains, and Lying-Inn
. Both by Sea and Land!—I will not
answer for the Distempers called
Sea Voyages and Campains
; But I dare
say, those of Green Sickness and Lying-Inn might be as well taken Care
of if the Doctor staid a-shoar. But the Art of managing Mankind, is only
to make them stare a little, to keep up their Astonishment, to let
nothing be familiar to them, but ever to have something in your Sleeve,
in which they must think you are deeper than they are. There is an
ingenious Fellow, a Barber, of my Acquaintance, who, besides his broken
Fiddle and a dryed Sea-Monster, has a Twine-Cord, strained with two
Nails at each End, over his Window, and the Words
Rainy, Dry, Wet
, and
so forth, written, to denote the Weather according to the Rising or
Falling of the Cord. We very great Scholars are not apt to wonder at
this: But I observed a very honest Fellow, a chance Customer, who sate
in the Chair before me to be shaved, fix his Eye upon this Miraculous
Performance during the Operation upon his Chin and Face. When those and
his Head also were cleared of all Incumbrances and Excrescences, he
looked at the Fish, then at the Fiddle, still grubling in his Pockets,
and casting his Eye again at the Twine, and the Words writ on each Side;
then altered his mind as to Farthings, and gave my Friend a Silver
Six-pence. The Business, as I said, is to keep up the Amazement; and if
my Friend had had only the Skeleton and Kitt, he must have been
contented with a less Payment. But the Doctor we were talking of, adds
to his long Voyages the Testimony of some People
that has been thirty
Years lame.
When I received my Paper, a sagacious Fellow took one at
the same time, and read till he came to the Thirty Years Confinement of
his Friends, and went off very well convinced of the Doctor's
Sufficiency. You have many of these prodigious Persons, who have had
some extraordinary Accident at their Birth, or a great Disaster in some
Part of their Lives. Any thing, however foreign from the Business the
People want of you, will convince them of your Ability in that you
profess. There is a Doctor in
Mouse-Alley
near
Wapping,
who sets up
for curing Cataracts upon the Credit of having, as his Bill sets forth,
lost an Eye in the Emperor's Service. His Patients come in upon this,
and he shews the Muster-Roll, which confirms that he was in his Imperial
Majesty's Troops; and he puts out their Eyes with great Success. Who
believe that a Man should be a Doctor for the Cure of bursten
Children, by declaring that his Father and Grandfather were
born
bursten? But
Charles Ingoltson,
next Door to the
Harp
in
Barbican,
has made a pretty Penny by that Asseveration. The Generality go upon
their first Conception, and think no further; all the rest is granted.
They take it, that there is something uncommon in you, and give you
Credit for the rest. You may be sure it is upon that I go, when
sometimes, let it be to the Purpose or not, I keep a
Latin
Sentence in
my Front; and I was not a little pleased when I observed one of my
Readers say, casting his Eye on my twentieth Paper,
More
Latin
still?
What a prodigious Scholar is this Man!
But as I have here taken much
Liberty with this learned Doctor, I must make up all I have said by
repeating what he seems to be in Earnest in, and honestly promise to
those who will not receive him as a great Man; to wit, That from
Eight
to Twelve, and from Two till Six, he attends for the good of the Publick
to bleed for Three Pence.
T.
Dignum tanto feret hic promissor hiatu
Hor.
In the first issue the whole bill was published.
Two-thirds of it, including its more infamous part, was omitted from the
reprint, and the reader will, I hope, excuse me the citation of it in
this place.
both
Contents
|
Thursday, July 31, 1712 |
Addison |
Tanti non es ais. Sapis, Luperce.
Mart.

This is the Day on which many eminent Authors will probably Publish
their Last Words. I am afraid that few of our Weekly Historians, who are
Men that above all others delight in War, will be able to subsist under
the Weight of a Stamp, and an approaching Peace. A Sheet of Blank Paper
that must have this new Imprimatur clapt upon it, before it is qualified
to Communicate any thing to the Publick, will make its way in the World
very heavily. In short, the Necessity of carrying a Stamp
, and
the Improbability of notifying a Bloody Battel, will, I am afraid, both
concur to the sinking of those thin Folios, which have every other Day
retailed to us the History of
Europe
for several Years last past. A
Facetious Friend of mine, who loves a Punn, calls this present Mortality
among Authors,
The Fall of the Leaf.
I remember, upon Mr.
Baxter's
Death, there was Published a Sheet of
very good Sayings, inscribed,
The last Words of Mr.
Baxter. The Title
sold so great a Number of these Papers, that about a Week after there
came out a second Sheet, inscrib'd,
More last Words of Mr.
Baxter. In
the same manner, I have Reason to think, that several Ingenious Writers,
who have taken their Leave of the Publick, in farewell Papers, will not
give over so, but intend to appear again, tho' perhaps under another
Form, and with a different Title. Be that as it will, it is my Business,
in this place, to give an Account of my own Intentions, and to acquaint
my Reader with the Motives by which I Act, in this great Crisis of the
Republick of Letters.
I have been long debating in my own Heart, whether I should throw up my
Pen, as an Author that is cashiered by the Act of Parliament, which is
to Operate within these Four and Twenty Hours, or whether I should still
persist in laying my Speculations, from Day to Day, before the Publick.
The Argument which prevails with me most on the first side of the
Question is, that I am informed by my Bookseller he must raise the Price
of every single Paper to Two-Pence, or that he shall not be able to pay
the Duty of it. Now as I am very de
Sir
ous my Readers should have their
Learning as cheap as possible, it is with great Difficulty that I comply
with him in this Particular.
However, upon laying my Reasons together in the Balance, I find that
those which plead for the Continuance of this Work, have much the
greater Weight. For, in the first Place, in Recompence for the Expence
to which this will put my Readers, it is to be hoped they may receive
from every Paper so much Instruction, as will be a very good Equivalent.
And, in order to this, I would not advise any one to take it in, who
after the Perusal of it, does not find himself Two-pence the wiser, or
the better Man for it; or who upon Examination, does not believe that he
has had Two-pennyworth of Mirth or Instruction for his Money.
But I must confess there is another Motive which prevails with me more
than the former. I consider that the Tax on Paper was given for the
Support of the Government; and as I have Enemies, who are apt to pervert
every thing I do or say, I fear they would ascribe the laying down my
Paper, on such an Occasion, to a Spirit of Malecontentedness, which I am
resolved none shall ever justly upbraid me with. No, I shall glory in
contributing my utmost to the Weal Publick; and if my Country receives
Five or Six Pounds a-day by my Labours, I shall be very well pleased to
find my self so useful a Member. It is a received Maxim, that no honest
Man should enrich himself by Methods that are prejudicial to the
Community in which he lives; and by the same Rule I think we may
pronounce the Person to deserve very well of his Countrymen, whose
Labours bring more into the publick Coffers, than into his own Pocket.
Since I have mentioned the Word Enemies, I must explain my self so far
as to acquaint my Reader, that I mean only the insignificant Party
Zealots on both sides; Men of such poor narrow Souls, that they are not
capable of thinking on any thing but with an Eye to Whig or Tory. During
the Course of this Paper, I have been accused by these despicable
Wretches of Trimming, Time-serving, Personal Reflection, secret Satire,
and the like. Now, tho' in these my Compositions, it is visible to any
Reader of Common Sense, that I consider nothing but my Subject, which is
always of an indifferent Nature; how is it possible for me to write so
clear of Party, as not to lie open to the Censures of those who will be
applying every Sentence, and finding out Persons and Things in it, which
it has no regard to?
Several Paltry Scriblers and Declaimers have done me the Honour to be
dull upon me in Reflections of this Nature; but notwithstanding my Name
has been sometimes traduced by this contemptible Tribe of Men, I have
hitherto avoided all Animadversions upon 'em. The Truth of it is, I am
afraid of making them appear considerable by taking Notice of them, for
they are like those imperceptible Insects which are discover'd by the
Microscope, and cannot be made the Subject of Observation without being
magnified.
Having mentioned those few who have shewn themselves the Enemies of this
Paper, I should be very ungrateful to the Publick, did not I at the same
time testifie my Gratitude to those who are its Friends, in which Number
I may reckon many of the most distinguished Persons of all Conditions,
Parties and Professions in the Isle of
Great-Britain
. I am not so vain
as to think this Approbation is so much due to the Performance as to the
Design. There is, and ever will be, Justice enough in the World, to
afford Patronage and Protection for those who endeavour to advance Truth
and Virtue, without regard to the Passions and Prejudices of any
particular Cause or Faction. If I have any other Merit in me, it is that
I have new-pointed all the Batteries of Ridicule. They have been
generally planted against Persons who have appeared Serious rather than
Absurd; or at best, have aimed rather at what is Unfashionable than what
is Vicious. For my own part, I have endeavoured to make nothing
Ridiculous that is not in some measure Criminal. I have set up the
Immoral Man as the Object of Derision: In short, if I have not formed a
new Weapon against Vice and Irreligion, I have at least shewn how that
Weapon may be put to a right Use, which has so often fought the Battels
of Impiety and Profaneness.
C.
The Stamp Act was to take effect from the first of August.
Censorship of the press began in the Church soon after the invention of
printing. The ecclesiastical superintendence introduced in 1479 and 1496
was more completely established by a bull of Leo X. in 1515, which
required Bishops and Inquisitors to examine all books before printing,
and suppress heretical opinions. The Church of Rome still adheres to the
Index Librorum Prohibitorum
begun by the Council of Trent in 1546; and
there is an Index Expurgatorius for works partly prohibited, or to be
read after expurgation. In accordance with this principle, the licensing
of English books had been in the power of the Archbishop of Canterbury
and his delegates before the decree of the Star Chamber in 1637, which
ordered that all books of Divinity, Physic, Philosophy, and Poetry
should be licensed either by the Archbishop of Canterbury or by the
Bishop of London personally or through their appointed substitutes. The
object of this decree was to limit the reprint of old books of divinity,
&c. Thus Foxe's
Book of Martyrs
was denied a license. In 1640
Sir
Edward
Dering complained to Parliament that
'the most learned labours of our
ancient and best divines must now be corrected and defaced with a
deleatur by the supercilious pen of my Lord's young chaplain, fit,
perhaps, for the technical arts, but unfit to hold the chair of
Divinity.'
(Rushworth's Hist. Coll. iv. 55.) Historical works seem to
have been submitted to the Secretary of State for his sanction. To May's
poem of the
Victorious Reign of King Edward the Third
is prefixed,
'I
have perused this Book, and conceive it very worthy to be published. Io.
Coke, Knight, Principal Secretary of State, Whitehall, 17 of November,
1634.'
But Aleyn's metrical
History of Henry VII.
(1638) is licensed
by the Bishop of London's domestic chaplain, who writes:
'Perlegi
historicum hoc poema, dignumque judico quod Typis mandetur. Tho. Wykes
R. P. Episc. Lond. Chapell. Domest.'
The first newspaper had been
the
Weekly Newes
, first published May 23, 1622, at a time when, says
Sir
Erskine May (in his
Constitutional History of England
, 1760-1860),
'political discussion was silenced by the licenser, the Star Chamber,
the dungeon, the pillory, mutilation, and branding.'
The contest between
King and Commons afterwards developed the free controversial use of
tracts and newspapers, but the Parliament was not more tolerant than the
king, and against the narrow spirit of his time Milton rose to his
utmost height, fashioning after the masterpiece of an old Greek orator
who sought to stir the blood of the Athenians, his
Areopagitica
, or
Defence of the Liberty of Unlicensed Printing
. In the reign of Charles
II. the Licensing Act (13 and 14 Charles II. cap. 33) placed the control
of printing in the Government, confined exercise of the printer's art to
London, York, and the Universities, and limited the number of the master
printers to twenty. Government established a monopoly of news in the
London Gazette.
'Authors and printers of obnoxious works,' says Sir E.
May, citing cases in notes, were hung, 'quartered, and mutilated,
exposed in the pillory and flogged, or fined and imprisoned, according
to the temper of their judges: their productions were burned by the
common hangman. Freedom of opinion was under interdict: even news could
not be published without license... James II. and his infamous judges
carried the Licensing Act into effect with barbarous severity. But the
Revolution brought indulgence even to the Jacobite Press; and when the
Commons, in 1695, refused to renew the Licensing Act, a censorship of
the press was for ever renounced by the law of England.'
There remained,
however, a rigorous interpretation of the libel laws; Westminster Hall
accepting the traditions of the Star Chamber. Still there was enough
removal of restriction to ensure the multiplication of newspapers and
the blending of intelligence with free political discussion. In Queen
Anne's reign the virulence of party spirit produced bitter personal
attacks and willingness on either side to bring an antagonist under the
libel laws. At the date of this
Spectator
paper Henry St. John, who
had been made Secretary of State at the age of 32, was 34 years old, and
the greatest commoner in England, as Swift said, turning the whole
Parliament, who can do nothing without him. This great position and the
future it might bring him he was throwing away for a title, and becoming
Viscount Bolingbroke. His last political act as a commoner was to impose
the halfpenny stamp upon newspapers and sheets like those of the
Spectator.
Intolerant of criticism, he had in the preceding session
brought to the bar of the House of Commons, under his warrant as
Secretary of State, fourteen printers and publishers. In the beginning
of 1712, the Queen's message had complained that by seditious papers and
factious rumours designing men had been able to sink credit, and the
innocent had suffered. On the 12th of February a committee of the whole
house was appointed to consider how to stop the abuse of the liberty of
the press. Some were for a renewal of the Licensing Act, some for
requiring writers' names after their articles. The Government carried
its own design of a half-penny stamp by an Act (10 Anne, cap. 19) passed
on the 10th of June, which was to come in force on the 1st of August,
1712, and be in force for 32 years.
'Do you know,' wrote Swift to Stella five days after the date of this
Spectator paper, 'Do you know that all Grub street is dead and gone
last week? No more ghosts or murders now for love or money... Every
single half sheet pays a halfpenny to the Queen. The Observator is
fallen; the Medleys are jumbled together with the Flying Post; the
Examiner is deadly sick; the Spectator keeps up and doubles its
price; I know not how long it will last.'
It so happened that the mortality was greatest among Government papers.
The Act presently fell into abeyance, was revived in 1725, and
thenceforth maintained the taxation of newspapers until the abolition of
the Stamp in 1859. One of its immediate effects was a fall in the
circulation of the
Spectator.
The paper remained unchanged, and some
of its subscribers seem to have resented the doubling of the tax upon
them, by charging readers an extra penny for each halfpenny with which
it had been taxed. (See
.)
Contents
|
Friday, August 1, 1712 |
Addison |
Quid deceat, quid non; quò Virtus, quò ferat Error.
Hor.

Since two or three Writers of Comedy who are now living have taken their
Farewell of the Stage, those who succeed them finding themselves
incapable of rising up to their Wit, Humour and good Sense, have only
imitated them in some of those loose unguarded Strokes, in which they
complied with the corrupt Taste of the more Vicious Part of their
Audience. When Persons of a low Genius attempt this kind of Writing,
they know no difference between being Merry and being Lewd. It is with
an Eye to some of these degenerate Compositions that I have written the
following Discourse.
Were our
English
Stage but half so virtuous as that of the
Greeks
or
Romans
, we should quickly see the Influence of it in the Behaviour of
all the Politer Part of Mankind. It would not be fashionable to ridicule
Religion, or its Professors; the Man of Pleasure would not be the
compleat Gentleman; Vanity would be out of Countenance, and every
Quality which is Ornamental to Human Nature, would meet with that Esteem
which is due to it.
If the
English
Stage were under the same Regulations the
Athenian
was formerly, it would have the same Effect that had, in recommending
the Religion, the Government, and Publick Worship of its Country. Were
our Plays subject to proper Inspections and Limitations, we might not
only pass away several of our vacant Hours in the highest
Entertainments; but should always rise from them wiser and better than
we sat down to them.
It is one of the most unaccountable things in our Age, that the Lewdness
of our Theatre should be so much complained of, so well exposed, and so
little redressed. It is to be hoped, that some time or other we may be
at leisure to restrain the Licentiousness of the Theatre, and make it
contribute its Assistance to the Advancement of Morality, and to the
Reformation of the Age. As Matters stand at present, Multitudes are shut
out from this noble Diversion, by reason of those Abuses and Corruptions
that accompany it. A Father is often afraid that his Daughter should be
ruin'd by those Entertainments, which were invented for the
Accomplishment and Refining of Human Nature. The
Athenian
and
Roman
Plays were written with such a Regard to Morality, that
Socrates
used
to frequent the one, and
Cicero
the other.
It happened once indeed, that Cato dropped into the
Roman
Theatre,
when the
Floralia
were to be represented; and as in that Performance,
which was a kind of Religious Ceremony, there were several indecent
Parts to be acted, the People refused to see them whilst
Cato
was
present.
Martial
on this Hint made the following Epigram, which we
must suppose was applied to some grave Friend of his, that had been
accidentally present at some such Entertainment.
Nosces jocosæ dulce cum sacrum Floræ,
Festosque lusus, et licentiam vulgi,
Cur in Theatrum Cato severe venisti?
An ideo tantum veneras, ut exires?
Why dost thou come, great Censor of the Age,
To see the loose Diversions of the Stage?
With awful Countenance and Brow severe,
What in the Name of Goodness dost thou here?
See the mixt Crowd! how Giddy, Lewd and Vain!
Didst thou come in but to go out again?
An Accident of this Nature might happen once in an Age among the
Greeks
or
Romans
; but they were too wise and good to let the
constant Nightly Entertainment be of such a Nature, that People of the
most Sense and Virtue could not be at it. Whatever Vices are represented
upon the Stage, they ought to be so marked and branded by the Poet, as
not to appear either laudable or amiable in the Person who is tainted
with them. But if we look into the
English
Comedies above mentioned,
we would think they were formed upon a quite contrary Maxim, and that
this Rule, tho' it held good upon the Heathen Stage, was not be regarded
in Christian Theatres. There is another Rule likewise, which was
observed by Authors of Antiquity, and which these modern Genius's have
no regard to, and that was never to chuse an improper Subject for
Ridicule. Now a Subject is improper for Ridicule, if it is apt to stir
up Horrour and Commiseration rather than Laughter. For this Reason, we
do not find any Comedy in so polite an Author as
Terence
, raised upon
the Violations of the Marriage-Bed. The Falshood of the Wife or Husband
has given Occasion to noble Tragedies, but a
Scipio
or a
Lelius
would have look'd upon Incest or Murder to have been as proper Subjects
for Comedy. On the contrary, Cuckoldom is the Basis of most of our
Modern Plays. If an Alderman appears upon the Stage, you may be sure it
is in order to be Cuckolded. An Husband that is a little grave or
elderly, generally meets with the same Fate. Knights and Baronets,
Country Squires, and Justices of the
Quorum
, come up to Town for no
other Purpose. I have seen poor
Dogget
Cuckolded in all these
Capacities. In short, our
English
Writers are as frequently severe
upon this innocent unhappy Creature, commonly known by the Name of a
Cuckold, as the Ancient Comick Writers were upon an eating Parasite or a
vain-glorious Soldier.
At the same time the Poet so contrives Matters, that the two Criminals
are the Favourites of the Audience. We sit still, and wish well to them
through the whole Play, are pleased when they meet with proper
Opportunities, and out of humour when they are disappointed. The Truth
of it is, the accomplished Gentleman upon the
English Stage
, is the
Person that is familiar with other Men's Wives, and indifferent to his
own; as the fine Woman is generally a Composition of Sprightliness and
Falshood. I do not know whether it proceeds from Barrenness of
Invention, Depravation of Manners, or Ignorance of Mankind, but I have
often wondered that our ordinary Poets cannot frame to themselves the
Idea of a Fine Man who is not a Whore-master, or of a Fine Woman that is
not a Jilt.
I have sometimes thought of compiling a System of Ethics out of the
Writings of these corrupt Poets, under the Title of
Stage Morality
.
But I have been diverted from this Thought, by a Project which has been
executed by an ingenious Gentleman of my Acquaintance. He has compos'd,
it seems, the History of a young Fellow, who has taken all his Notions
of the World from the Stage, and who has directed himself in every
Circumstance of his Life and Conversation, by the Maxims and Examples of
the Fine Gentlemen in
English
Comedies. If I can prevail upon him to
give me a Copy of this new-fashioned Novel, I will bestow on it a Place
in my Works, and question not but it may have as good an Effect upon the
Drama, as
Don Quixote
had upon Romance.
C.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 2, 1712 |
Addison |
There is not a Common Saying which has a better turn of Sense in it,
than what we often hear in the Mouths of the Vulgar, that Custom is a
second Nature. It is indeed able to form the Man anew, and to give him
Inclinations and Capacities altogether different from those he was born
with.
Dr.
Plot
, in his History of
Staffordshire
, tells us of an
Ideot that chancing to live within the Sound of a Clock, and always
amusing himself with counting the Hour of the Day whenever the Clock
struck, the Clock being spoiled by some Accident, the Ideot continued to
strike and count the Hour without the help of it, in the same manner as
he had done when it was entire. Though I dare not vouch for the Truth of
this Story, it is very certain that Custom has a Mechanical Effect upon
the Body, at the same time that it has a very extraordinary Influence
upon the Mind.
I shall in this Paper consider one very remarkable Effect which Custom
has upon Human Nature; and which, if rightly observed, may lead us into
very useful Rules of Life. What I shall here take notice of in Custom,
is its wonderful Efficacy in making every thing pleasant to us. A Person
who is addicted to Play or Gaming, though he took but little delight in
it at first, by degrees contracts so strong an Inclination towards it,
and gives himself up so entirely to it, that it seems the only End of
his Being. The Love of a retired or busie Life will grow upon a Man
insensibly, as he is conversant in the one or the other, till he is
utterly unqualified for relishing that to which he has been for some
time disused. Nay, a Man may Smoak, or Drink, or take Snuff, till he is
unable to pass away his Time without it; not to mention our Delight in
any particular Study, Art, or Science, rises and improves in Proportion
to the Application which we bestow upon it. Thus what was at first an
Exercise, becomes at length an Entertainment. Our Employments are
changed into our Diversions. The Mind grows fond of those Actions she is
accustomed to, and is drawn with Reluctancy from those Paths in which
she has been used to walk.
Not only such Actions as were at first Indifferent to us, but even such
as were Painful, will by Custom and Practice become pleasant.
Sir
Francis Bacon
observes in his Natural Philosophy, that our Taste is
never pleased better, than with those things which at first created a
Disgust in it. He gives particular Instances of Claret, Coffee, and
other Liquors, which the palate seldom approves upon the first Taste;
but when it has once got a Relish of them, generally retains it for
Life. The Mind is constituted after the same manner, and after having
habituated her self to any particular Exercise or Employment, not only
loses her first Aversion towards it, but conceives a certain Fondness
and Affection for it. I
heard one of the greatest Genius's this Age
has produced
, who had been trained up in all the Polite Studies of
Antiquity assure me, upon his being obliged to search into several Rolls
and Records, that notwithstanding such an Employment was at first very
dry and irksome to him, he at last took an incredible Pleasure in it,
and preferred it even to the reading of
Virgil
or
Cicero
. The Reader
will observe, that I have not here considered Custom as it makes things
easie, but as it renders them delightful; and though others have often
made the same Reflections, it is possible they may not have drawn those
Uses from it, with which I intend to fill the remaining Part of this
Paper.
If we consider attentively this Property of Human Nature, it may
instruct us in very fine Moralities. In the first place, I would have no
Man discouraged with that kind of Life or Series of Action, in which the
Choice of others, or his own Necessities, may have engaged him. It may
perhaps be very disagreeable to him at first; but Use and Application
will certainly render it not only less painful, but pleasing and
satisfactory.
In
second place I would recommend to every one that admirable
Precept which
Pythagoras
is said to have given to his Disciples,
and which that Philosopher must have drawn from the Observation I have
enlarged upon.
Optimum vitæ genus eligito, nam consuetudo faciet
jucundissimum
, Pitch upon that Course of Life which is the most
Excellent, and Custom will render it the most Delightful. Men, whose
Circumstances will permit them to chuse their own Way of Life, are
inexcusable if they do not pursue that which their Judgment tells them
is the most laudable. The Voice of Reason is more to be regarded than
the Bent of any present Inclination, since by the Rule above mentioned,
Inclination will at length come over to Reason, though we can never
force Reason to comply with Inclination.
In the third place, this Observation may teach the most sensual and
irreligious Man, to overlook those Hardships and Difficulties which are
apt to discourage him from the Prosecution of a Virtuous Life.
The
Gods
, said
Hesiod
,
have placed Labour before Virtue, the Way to
her is at first rough and difficult, but grows more smooth and easier
the further you advance in it
. The Man who proceeds in it, with
Steadiness and Resolution, will in a little time find that
her Ways are
Ways of Pleasantness, and that all her Paths are Peace
.
To enforce this Consideration, we may further observe that the Practice
of Religion will not only be attended with that Pleasure, which
naturally accompanies those Actions to which we are habituated, but with
those Supernumerary Joys of Heart, that rise from the Consciousness of
such a Pleasure, from the Satisfaction of acting up to the Dictates of
Reason, and from the Prospect of an happy Immortality.
In the fourth place, we may learn from this Observation which we have
made on the Mind of Man, to take particular Care, when we are once
settled in a regular Course of Life, how we too frequently indulge our
selves in any of the most innocent Diversions and Entertainments, since
the Mind may insensibly fall off from the Relish of virtuous Actions,
and, by degrees, exchange that Pleasure which it takes in the
Performance of its Duty, for Delights of a much more inferior and
unprofitable Nature.
The last Use which I shall make of this remarkable Property in Human
Nature, of being delighted with those Actions to which it is accustomed,
is to shew how absolutely necessary it is for us to gain Habits of
Virtue in this Life, if we would enjoy the Pleasures of the next. The
State of Bliss we call Heaven will not be capable of affecting those
Minds, which are not thus qualified for it; we must, in this World, gain
a Relish of Truth and Virtue, if we would be able to taste that
Knowledge and Perfection, which are to make us happy in the next. The
Seeds of those spiritual Joys and Raptures, which are to rise up and
Flourish in the Soul to all Eternity, must be planted in her, during
this her present State of Probation. In short, Heaven is not to be
looked upon only as the Reward, but as the natural Effect of a religious
Life.
On the other hand, those evil Spirits, who, by long Custom, have
contracted in the Body Habits of Lust and Sensuality, Malice and
Revenge, an Aversion to every thing that is good, just or laudable, are
naturally seasoned and prepared for Pain and Misery. Their Torments have
already taken root in them, they cannot be happy when divested of the
Body, unless we may suppose, that Providence will, in a manner, create
them anew, and work a Miracle in the Rectification of their Faculties.
They may, indeed, taste a kind of malignant Pleasure in those Actions to
which they are accustomed, whilst in this Life; but when they are
removed from all those Objects which are here apt to gratifie them, they
will
become their own Tormentors, and cherish in themselves
those painful Habits of Mind, which are called,
in
Scripture
Phrase, the Worm which never dies. This Notion of Heaven and Hell is so
very conformable to the Light of Nature, that it was discovered by
several of the most exalted Heathens. It has been finely improved by
many Eminent Divines of the last Age, as in
by Arch-Bishop
Tillotson
and Dr.
Sherlock
, but there is none who has raised such
noble Speculations upon it as Dr.
Scott
in the First Book of his
Christian Life, which is one of the finest and most rational Schemes of
Divinity, that is written in our Tongue, or in any other. That Excellent
Author has shewn how every particular Custom and Habit of Virtue will,
in its own Nature, produce the Heaven, or a State of Happiness, in him
who shall hereafter practise it: As on the contrary, how every Custom or
Habit of Vice will be the natural Hell of him in whom it subsists.
C.
Natural History of Staffordshire, by Robert Plot, L.L.D.,
fol. 1686. Dr. Plot wrote also a Natural History of Oxfordshire, and was
a naturalist of mark, one of the Secretaries of the Royal Society, First
Keeper of the Ashmolean Museum, Historiographer Royal, and Archivist of
the Herald's Office. He died in 1696, aged 55.
Dr. Atterbury
Diogenes Laertius, Bk. viii.
The paths of Virtue must be reached by toil,
Arduous and long, and on a rugged soil,
Thorny the gate, but when the top you gain,
Fair is the future and the prospect plain.
Works and Days
, Bk. i. (
Cooke's Translation
).
in the
John Scott, a young tradesman of Chippenham, Wilts.,
prevailed on his friends to send him to Oxford, and became D. D. in
1685. He was minister of St. Thomas's, Southwark, Rector of St. Giles in
the Fields, Prebendary of St. Paul's, Canon of Windsor, and refused a
Bishopric. He was a strong opponent of the Catholics, and his
Christian
Life,
in folio, and 5 vols. 8vo, became very popular. He died in 1694.
Contents
|
Monday, August 4, 1712 |
Steele |
Fœdius hoc aliquid quandoque audebis.
Juv.

The first Steps towards Ill are very carefully to be avoided, for Men
insensibly go on when they are once entered, and do not keep up a lively
Abhorrence of the least Unworthiness. There is a certain frivolous
Falshood that People indulge themselves in, which ought to be had in
greater Detestation than it commonly meets with: What I mean is a
Neglect of Promises made on small and indifferent Occasions, such as
Parties of Pleasure, Entertainments, and sometimes Meetings out of
Curiosity in Men of like Faculties to be in each other's Company. There
are many Causes to which one may assign this light Infidelity.
Jack
Sippet
never keeps the Hour he has appointed to come to a Friend's to
Dinner; but he is an insignificant Fellow who does it out of Vanity. He
could never, he knows, make any Figure in Company, but by giving a
little Disturbance at his Entry, and therefore takes Care to drop in
when he thinks you are just seated. He takes his Place after having
discomposed every Body, and de
Sir
es there may be no Ceremony; then does
he begin to call himself the saddest Fellow, in disappointing so many
Places as he was invited to elsewhere. It is the Fop's Vanity to name
Houses of better Chear, and to acquaint you that he chose yours out of
ten Dinners which he was obliged to be at that Day. The last Time I had
the Fortune to eat with him, he was imagining how very fat he should
have been had he eaten all he had ever been invited to. But it is
impertinent to dwell upon the Manners of such a Wretch as obliges all
whom he disappoints, though his Circumstances constrain them to be civil
to him. But there are those that every one would be glad to see, who
fall into the same detestable Habit. It is a merciless thing that any
one can be at Ease, and suppose a Set of People who have a Kindness for
him, at that Moment waiting out of Respect to him, and refusing to taste
their Food or Conversation with the utmost Impatience. One of these
Promisers sometimes shall make his Excuses for not coming at all, so
late that half the Company have only to lament, that they have neglected
Matters of Moment to meet him whom they find a Trifler. They immediately
repent of the Value they had for him; and such Treatment repeated, makes
Company never depend upon his Promise any more; so that he often comes
at the Middle of a Meal, where he is secretly slighted by the Persons
with whom he eats, and cursed by the Servants, whose Dinner is delayed
by his prolonging their Master's Entertainment. It is wonderful, that
Men guilty this Way, could never have observed, that the whiling Time,
the gathering together, and waiting a little before Dinner, is the most
awkwardly passed away of any Part in the four and twenty Hours. If they
did think at all, they would reflect upon their Guilt, in lengthning
such a Suspension of agreeable Life. The constant offending this Way,
has, in a Degree, an Effect upon the Honesty of his Mind who is guilty
of it, as common Swearing is a kind of habitual Perjury: It makes the
Soul unattentive to what an Oath is, even while it utters it at the
Lips.
Phocion
beholding a wordy Orator while he was making a
magnificent Speech to the People full of vain Promises,
Methinks
, said
he,
I am now fixing my Eyes upon a Cypress Tree, it has all the Pomp
and Beauty imaginable in its Branches, Leaves, and Height, but alas it
bears no Fruit.
Though the Expectation which is raised by impertinent Promisers is thus
barren, their Confidence, even after Failures, is so great, that they
subsist by still promising on. I have heretofore discoursed of the
insignificant Liar, the Boaster, and the Castle-Builder, and treated
them as no ill-designing Men, (tho' they are to be placed among the
frivolously false ones) but Persons who fall into that Way purely to
recommend themselves by their Vivacities; but indeed I cannot let
heedless Promisers, though in the most minute Circumstances, pass with
so slight a Censure. If a Man should take a Resolution to pay only Sums
above an hundred Pounds, and yet contract with different People Debts of
five and ten, how long can we suppose he will keep his Credit? This Man
will as long support his good Name in Business, as he will in
Conversation, who without Difficulty makes Assignations which he is
indifferent whether he keeps or not.
I am the more severe upon this Vice, because I have been so unfortunate
as to be a very great Criminal my self.
Sir
Andrew Freeport
, and all
other my Friends who are scrupulous to Promises of the meanest
Consideration imaginable from an Habit of Virtue that way, have often
upbraided me with it. I take Shame upon my self for this Crime, and more
particularly for the greatest I ever committed of the Sort, that when as
agreeable a Company of Gentlemen and Ladies as ever were got together,
and I forsooth, Mr. SPECTATOR, to be of the Party with Women of Merit,
like a Booby as I was, mistook the time of Meeting, and came the Night
following. I wish every Fool who is negligent in this Kind, may have as
great a Loss as I had in this; for the same Company will never meet
more, but are dispersed into various Parts of the World, and I am left
under the Compunction that I deserve, in so many different Places to be
called a Trifler.
This Fault is sometimes to be accounted for, when de
Sir
able People are
fearful of appearing precious and reserved by Denials; but they will
find the Apprehension of that Imputation will betray them into a
childish Impotence of Mind, and make them promise all who are so kind to
ask it of them. This leads such soft Creatures into the Misfortune of
seeming to return Overtures of Good-will with Ingratitude. The first
Steps in the Breach of a Man's Integrity are much more important than
Men are aware of. The Man who scruples breaking his Word in little
Things would not suffer in his own Conscience so great Pain for Failures
of Consequence, as he who thinks every little Offence against Truth and
Justice a Disparagement. We should not make any thing we our selves
disapprove habitual to us, if we would be sure of our Integrity.
I remember a Falshood of the trivial Sort, tho' not in relation to
Assignations, that exposed a Man to a very uneasie Adventure.
Will.
Trap
and
Jack Stint
were Chamber-fellows in the
Inner-Temple
about
25 Years ago. They one Night sate in the Pit together at a Comedy, where
they both observed and liked the same young Woman in the Boxes. Their
Kindness for her entered both Hearts deeper than they imagined.
Stint
had a good Faculty at writing Letters of Love, and made his Address
privately that way; while
Trap
proceeded in the ordinary Course, by
Money and her Waiting-Maid. The Lady gave them both Encouragement,
receiving
Trap
into the utmost Favour, and answering at the same time
Stint's
Letters, and giving him appointments at third Places.
Trap
began to suspect the Epistolary Correspondence of his Friend, and
discovered also that
Stint
opened all his Letters which came to their
common Lodgings, in order to form his own Assignations. After much
Anxiety and Restlessness,
Trap
came to a Resolution, which he thought
would break off their Commerce with one another without any hazardous
Explanation. He therefore writ a Letter in a feigned Hand to Mr.
Trap
at his Chambers in the
Temple
.
Stint
, according to Custom, seized
and opened it, and was not a little surpriz'd to find the Inside
directed to himself, when, with great Perturbation of Spirit, he read as
follows.
Mr. Stint,
You have gained a slight Satisfaction at the Expence of doing a very
heinous Crime. At the Price of a faithful Friend you have obtained an
inconstant Mistress. I rejoice in this Expedient I have thought of to
break my Mind to you, and tell you, You are a base Fellow, by a Means
which does not expose you to the Affront except you deserve it. I
know, Sir , as criminal as you are, you have still Shame enough to
avenge yourself against the Hardiness of any one that should publickly
tell you of it. I therefore, who have received so many secret Hurts
from you, shall take Satisfaction with Safety to my self. I call you
Base, and you must bear it, or acknowledge it; I triumph over you that
you cannot come at me; nor do I think it dishonourable to come in
Armour to assault him, who was in Ambuscade when he wounded me.
What need more be said to convince you of being guilty of the basest
Practice imaginable, than that it is such as has made you liable to be
treated after this Manner, while you your self cannot in your own
Conscience but allow the Justice of the Upbraidings of Your Injured
Friend,
Ralph Trap.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 5, 1712 |
Addison |
—Tibi scriptus, Matrona, libellus—
Mart.

When I reflect upon my Labours for the Publick, I cannot but observe,
that Part of the Species, of which I profess my self a Friend and
Guardian, is sometimes treated with Severity; that is, there are in my
Writings many Descriptions given of ill Persons, and not yet any direct
Encomium made of those who are good. When I was convinced of this Error,
I could not but immediately call to Mind several of the Fair Sex of my
Acquaintance, whose Characters deserve to be transmitted to Posterity in
Writings which will long outlive mine. But I do not think that a Reason
why I should not give them their Place in my Diurnal as long as it will
last. For the Service therefore of my Female Readers, I shall single out
some Characters of Maids, Wives and Widows, which deserve the Imitation
of the Sex. She who shall lead this small illustrious Number of Heroines
shall be the amiable
Fidelia
.
Before I enter upon the particular Parts of her Character, it is
necessary to Preface, that she is the only Child of a decrepid Father,
whose Life is bound up in hers. This Gentleman has used
Fidelia
from
her Cradle with all the Tenderness imaginable, and has view'd her
growing Perfections with the Partiality of a Parent, that soon thought
her accomplished above the Children of all other Men, but never thought
she was come to the utmost Improvement of which she her self was
capable. This Fondness has had very happy Effects upon his own
Happiness, for she reads, she dances, she sings, uses her Spinet and
Lute to the utmost Perfection: And the Lady's Use of all these
Excellencies, is to divert the old Man in his easie Chair, when he is
out of the Pangs of a Chronical Distemper.
Fidelia
is now in the
twenty third Year of her Age; but the Application of many Lovers, her
vigorous time of Life, her quick Sense of all that is truly gallant and
elegant in the Enjoyment of a plentiful Fortune, are not able to draw
her from the Side of her good old Father. Certain it is, that there is
no kind of Affection so pure and angelick as that of a Father to a
Daughter. He beholds her both with, and without Regard to her Sex. In
Love to our Wives there is De
Sir
e, to our Sons there is Ambition; but in
that to our Daughters, there is something which there are no Words to
express. Her Life is designed wholly Domestick, and she is so ready a
Friend and Companion, that every thing that passes about a Man, is
accompanied with the Idea of her Presence. Her Sex also is naturally so
much exposed to Hazard, both as to Fortune and Innocence, that there is,
perhaps, a new Cause of Fondness arising from that Consideration also.
None but Fathers can have a true Sense of these sort of Pleasures and
Sensations; but my Familiarity with the Father of
Fidelia
, makes me
let drop the Words which I have heard him speak, and observe upon his
Tenderness towards her.
Fidelia
on her Part, as I was going to say, as accomplished as she is,
with all her Beauty, Wit, Air, and Mien, employs her whole Time in Care
and Attendance upon her Father. How have I been charmed to see one of
the most beauteous Women the Age has produced on her Knees helping on an
old Man's Slipper! Her filial Regard to him is what she makes her
Diversion, her Business, and her Glory. When she was asked by a Friend
of her deceased Mother to admit of the Courtship of her Son, she
answer'd, That she had a great Respect and Gratitude to her for the
Overture in Behalf of one so near to her, but that during her Father's
Life, she would admit into her Heart no Value for any thing that should
interfere with her Endeavour to make his Remains of Life as happy and
easie as could be expected in his Circumstances. The Lady admonished her
of the Prime of Life with a Smile; which
Fidelia
answered with a
Frankness that always attends unfeigned Virtue.
It is true, Madam,
there is to be sure very great Satisfactions to be expected in the
Commerce of a Man of Honour, whom one tenderly loves; but I find so much
Satisfaction in the Reflection, how much I mitigate a good Man's Pains,
whose Welfare depends upon my Assiduity about him, that I wittingly
exclude the loose Gratifications of Passion for the solid Reflections of
Duty. I know not whether any Man's Wife would be allow'd, and (what I
still more fear) I know not whether I, a Wife, should be willing to be
as officious as I am at present about my Parent
. The happy Father has
her Declaration that she will not marry during his Life, and the
Pleasure of seeing that Resolution not uneasie to her. Were one to paint
filial Affection in its utmost Beauty, he could not have a more lively
Idea of it than in beholding
Fidelia
serving her Father at his Hours
of Rising, Meals, and Rest.
When the general Crowd of Female Youth are consulting their Glasses,
preparing for Balls, Assemblies, or Plays; for a young Lady, who could
be regarded among the foremost in those Places, either for her Person,
Wit, Fortune, or Conversation, and yet contemn all these Entertainments,
to sweeten the heavy Hours of a decrepid Parent, is a Resignation truly
heroick.
Fidelia
performs the Duty of a Nurse with all the Beauty of a
Bride; nor does she neglect her Person, because of her Attendance on
him, when he is too ill to receive Company, to whom she may make an
Appearance.
Fidelia
, who gives him up her Youth, does not think it any great
Sacrifice to add to it the Spoiling of her Dress. Her Care and Exactness
in her Habit, convince her Father of the Alacrity of her Mind; and she
has of all Women the best Foundation for affecting the Praise of a
seeming Negligence. What adds to the Entertainment of the good old Man
is, that
Fidelia
, where Merit and Fortune cannot be overlook'd by
Epistolary Lovers, reads over the Accounts of her Conquests, plays on
her Spinet the gayest Airs, (and while she is doing so, you would think
her formed only for Gallantry) to intimate to him the Pleasures she
despises for his Sake.
Those who think themselves the Patterns of good Breeding and Gallantry,
would be astonished to hear that in those Intervals when the old
Gentleman is at Ease, and can bear Company, there are at his House in
the most regular Order, Assemblies of People of the highest Merit; where
there is Conversation without Mention of the Faults of the Absent,
Benevolence between Men and Women without Passion, and the highest
Subjects of Morality treated of as natural and accidental Discourse; All
which is owing to the Genius of
Fidelia
, who at once makes her
Father's Way to another World easie, and her self capable of being an
Honour to his Name in this.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I was the other Day at the Bear-Garden, in hopes to have seen your
short Face; but not being so fortunate, I must tell you by way of
Letter, That there is a Mystery among the Gladiators which has escaped
your Spectatorial Penetration. For being in a Box at an Ale-house,
near that renowned Seat of Honour above-mentioned, I over-heard two
Masters of the Science agreeing to quarrel on the next Opportunity.
This was to happen in the Company of a Set of the Fraternity of
Basket-Hilts, who were to meet that Evening. When this was settled,
one asked the other, Will you give Cuts or receive? the other
answered, Receive. It was replied, Are you a passionate Man? No,
provided you cut no more nor no deeper than we agree. I thought it my
Duty to acquaint you with this, that the People may not pay their
Money for Fighting, and be cheated.
Your Humble Servant,
Scabbard Rusty.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 6, 1712 |
Steele |
—Quærenda pecunia primum
Virtus post nummos.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
All Men, through different Paths, make at the same common thing,
Money; and it is to her we owe the Politician, the Merchant, and the
Lawyer; nay, to be free with you, I believe to that also we are
beholden for our
Spectator. I am apt to think, that could we look
into our own Hearts, we should see Money ingraved in them in more
lively and moving Characters than Self-Preservation; for who can
reflect upon the Merchant hoisting Sail in a doubtful Pursuit of her,
and all Mankind sacrificing their Quiet to her, but must perceive that
the Characters of Self-Preservation (which were doubtless originally
the brightest) are sullied, if not wholly defaced; and that those of
Money (which at first was only valuable as a Mean to Security) are of
late so brightened, that the Characters of Self-Preservation, like a
less Light set by a greater, are become almost imperceptible? Thus has
Money got the upper Hand of what all Mankind formerly thought most
dear,
viz. Security; and I wish I could say she had here put a Stop
to her Victories; but, alas! common Honesty fell a Sacrifice to her.
This is the Way Scholastick Men talk of the greatest Good in the
World; but I, a Tradesman, shall give you another Account of this
Matter in the plain Narrative of my own Life. I think it proper, in
the first Place, to acquaint my Readers, that since my setting out in
the World, which was in the Year 1660, I never wanted Money; having
begun with an indifferent good Stock in the Tobacco-Trade, to which I
was bred; and by the continual Successes, it
has pleased Providence to
bless my Endeavours with, am at last arrived at what they call a
Plumb1. To uphold my Discourse in the Manner of your Wits or
Philosophers, by speaking fine things, or drawing Inferences, as they
pretend, from the Nature of the Subject, I account it vain; having
never found any thing in the Writings of such Men, that did not favour
more of the Invention of the Brain, or what is styled Speculation,
than of sound Judgment or profitable Observation. I will readily grant
indeed, that there is what the Wits call Natural in their Talk; which
is the utmost those curious Authors can assume to themselves, and is
indeed all they endeavour at, for they are but lamentable Teachers.
And, what, I pray, is Natural? That which is pleasing and easie: And
what are Pleasing and Easie? Forsooth, a new Thought or Conceit
dressed up in smooth quaint Language, to make you smile and wag your
Head, as being what you never imagined before, and yet wonder why you
had not; meer frothy Amusements! fit only for Boys or silly Women to
be caught with.
'It is not my present Intention to instruct my Readers in the Methods
of acquiring Riches; that may be the Work of another Essay; but to
exhibit the real and solid Advantages I have found by them in my long
and manifold Experience; nor yet all the Advantages of so worthy and
valuable a Blessing, (for who does not know or imagine the Comforts of
being warm or living at Ease? And that Power and Preheminence are
their inseperable Attendants?) But only to instance the great Supports
they afford us under the severest Calamities and Misfortunes; to shew
that the Love of them is a special Antidote against Immorality and
Vice, and that the same does likewise naturally dispose Men to Actions
of Piety and Devotion: All which I can make out by my own Experience,
who think my self no ways particular from the rest of Mankind, nor
better nor worse by Nature than generally other Men are.
'In the Year 1665, when the Sickness was, I lost by it my Wife and two
Children, which were all my Stock. Probably I might have had more,
considering I was married between 4 and 5 Years; but finding her to be
a teeming Woman, I was careful, as having then little above a Brace of
thousand Pounds, to carry on my Trade and maintain a Family with. I
loved them as usually Men do their Wives and Children, and therefore
could not resist the first Impulses of Nature on so wounding a Loss;
but I quickly roused my self, and found Means to alleviate, and at
last conquer my Affliction, by reflecting how that she and her
Children having been no great Expence to me, the best Part of her
Fortune was still left; that my Charge being reduced to my self, a
Journeyman, and a Maid, I might live far cheaper than before; and that
being now a childless Widower, I might perhaps marry a no less
deserving Woman, and with a much better Fortune than she brought,
which was but £800. And to convince my Readers that such
Considerations as these were proper and apt to produce such an Effect,
I remember it was the constant Observation at that deplorable Time,
when so many Hundreds were swept away daily, that the Rich ever bore
the Loss of their Families and Relations far better than the Poor; the
latter having little or nothing before-hand, and living from Hand to
Mouth, placed the whole Comfort and Satisfaction of their Lives in
their Wives and Children, and were therefore inconsolable.
'The following Year happened the Fire; at which Time, by good
Providence, it was my Fortune to have converted the greatest Part of
my Effects into ready Money, on the Prospect of an extraordinary
Advantage which I was preparing to lay Hold on. This Calamity was very
terrible and astonishing, the Fury of the Flames being such, that
whole Streets, at several distant Places, were destroyed at one and
the same Time, so that (as it is well known) almost all our Citizens
were burnt out of what they had. But what did I then do? I did not
stand gazing on the Ruins of our noble Metropolis; I did not shake my
Head, wring my Hands, sigh, and shed Tears; I consider'd with my self
what could this avail; I fell a plodding what Advantages might be made
of the ready Cash I had, and immediately bethought my self what
wonderful Pennyworths might be bought of the Goods, that were saved
out of the Fire. In short, with about £2000 and a little Credit, I
bought as much Tobacco as rais'd my Estate to the Value of £10000 I
then
looked on the Ashes of our City, and, the Misery of its late
Inhabitants, as an Effect of the just Wrath and Indignation of Heaven
towards a sinful and perverse People.
'After this I married again, and that Wife dying, I took another; but
both proved to be idle Baggages: the first gave me a great deal of
Plague and Vexation by her Extravagancies, and I became one of the
Bywords of the City. I knew it would be to no manner of Purpose to go
about to curb the Fancies and Inclinations of Women, which fly out the
more for being restrained; but what I could I did. I watched her
narrowly, and by good Luck found her in the Embraces (for which I had
two Witnesses with me) of a wealthy Spark of the Court-end of the
Town; of whom I recovered 15000 Pounds, which made me Amends for what
she had idly squanderd, and put a Silence to all my Neighbours, taking
off my Reproach by the Gain they saw I had by it. The last died about
two Years after I married her, in Labour of three Children. I
conjecture they were begotten by a Country Kinsman of hers, whom, at
her Recommendation, I took into my Family, and gave Wages to as a
Journeyman. What this Creature expended in Delicacies and high Diet
with her Kinsman (as well as I could compute by the Poulterers,
Fishmongers, and Grocers Bills) amounted in the said two Years to one
hundred eighty six Pounds, four Shillings, and five Pence Half-penny.
The fine Apparel, Bracelets, Lockets, and Treats, &c. of the other,
according to the best Calculation, came in three Years and about three
Quarters to Seven hundred forty four Pounds, seven Shillings and nine
Pence. After this I resolv'd never to marry more, and found I had been
a Gainer by my Marriages, and the Damages granted me for the Abuses of
my Bed, (all Charges deducted) eight thousand three hundred Pounds
within a Trifle.
'I come now to shew the good Effects of the Love of Money on the Lives
of Men towards rendring them honest, sober, and religious. When I was
a young Man, I had a Mind to make the best of my Wits, and
over-reached a Country Chap in a Parcel of unsound Goods; to whom,
upon his upbraiding, and threatning to expose me for it, I returned
the Equivalent of his Loss; and upon his good Advice, wherein he
clearly demonstrated the Folly of such Artifices, which can never end
but in Shame, and the Ruin of all Correspondence, I never after
transgressed. Can your Courtiers, who take Bribes, or your Lawyers or
Physicians in their Practice, or even the Divines who intermeddle in
worldly Affairs, boast of making but one Slip in their Lives, and of
such a thorough and lasting Reformation? Since my coming into the
World I do not remember I was ever overtaken in Drink, save nine
times, one at the Christening of my first Child, thrice at our City
Feasts, and five times at driving of Bargains. My Reformation I can
attribute to nothing so much as the Love and Esteem of Money, for I
found my self to be extravagant in my Drink, and apt to turn
Projector, and make rash Bargains. As for Women, I never knew any,
except my Wives: For my Reader must know, and it is what he may
confide in as an excellent Recipe, That the Love of Business and Money
is the greatest Mortifier of inordinate De
Sir es imaginable, as
employing the Mind continually in the careful Oversight of what one
has, in the eager Quest after more, in looking after the Negligences
and Deceits of Servants, in the due Entring and Stating of Accounts,
in hunting after Chaps, and in the exact Knowledge of the State of
Markets; which Things whoever thoroughly attends, will find enough and
enough to employ his Thoughts on every Moment of the Day; So that I
cannot call to Mind, that in all the Time I was a Husband, which, off
and on, was about twelve Years, I ever once thought of my Wives but in
Bed. And, lastly, for Religion, I have ever been a constant Churchman,
both Forenoons and Afternoons on Sundays, never forgetting to be
thankful for any Gain or Advantage I had had that Day; and on
Saturday Nights, upon casting up my Accounts, I always was grateful
for the Sum of my Week's Profits, and at
Christmas for that of the
whole Year. It is true, perhaps, that my Devotion has not been the
most fervent; which, I think, ought to be imputed to the Evenness and
Sedateness of my Temper, which never would admit of any Impetuosities
of any Sort: And I can remember that in my Youth and Prime of Manhood,
when my Blood ran brisker, I took greater Pleasure in Religious
Exercises than at present, or many Years past, and that my Devotion
sensibly declined as Age, which is dull and unwieldly, came upon me.
'I have, I hope, here proved, that the Love of Money prevents all
Immorality and Vice; which if you will not allow, you must, that the
Pursuit of it obliges Men to the same Kind of Life as they would
follow if they were really virtuous: Which is all I have to say at
present, only recommending to you, that you would think of it, and
turn ready Wit into ready Money as fast as you can. I conclude,
Your Servant,
Ephraim Weed.'
T.
£100,000.
Contents
|
Thursday, August 7, 1712 |
Addison |
—Jam sævus apertam
In rabiem cæpit verti jocus, et per honestas
Ire minax impunè domos—
There is nothing so scandalous to a Government, and detestable in the
Eyes of all good Men, as defamatory Papers and Pamphlets; but at the
same time there is nothing so difficult to tame, as a Satyrical Author.
An angry Writer, who cannot appear in Print, naturally vents his Spleen
in Libels and Lampoons. A gay old Woman, says the Fable, seeing all her
Wrinkles represented in a large Looking-glass, threw it upon the Ground
in a Passion, and broke it into a thousand Pieces, but as she was
afterwards surveying the Fragments with a spiteful kind of Pleasure, she
could not forbear uttering her self in the following Soliloquy. What
have I got by this revengeful Blow of mine, I have only multiplied my
Deformity, and see an hundred ugly Faces, where before I saw but one.
It has been proposed,
to oblige every Person that writes a Book, or a
Paper, to swear himself the Author of it, and enter down in a publick
Register his Name and Place of Abode
.
This, indeed, would have effectually suppressed all printed Scandal,
which generally appears under borrowed Names, or under none at all. But
it is to be feared, that such an Expedient would not only destroy
Scandal, but Learning. It would operate promiscuously, and root up the
Corn and Tares together. Not to mention some of the most celebrated
Works of Piety, which have proceeded from Anonymous Authors, who have
made it their Merit to convey to us so great a Charity in secret: There
are few Works of Genius that come out at first with the Author's Name.
The Writer generally makes a Tryal of them in the World before he owns
them; and, I believe, very few, who are capable of Writing, would set
Pen to Paper, if they knew, before-hand, that they must not publish
their Productions but on such Conditions. For my own part, I must
declare, the Papers I present the Publick are like Fairy Favours, which
shall last no longer than while the Author is concealed.
That which makes it particularly difficult to restrain these Sons of
Calumny and Defamation is, that all Sides are equally guilty of it, and
that every dirty Scribler is countenanced by great Names, whose
Interests he propagates by such vile and infamous Methods. I have never
yet heard of a Ministry, who have inflicted an exemplary Punishment on
an Author that has supported their Cause with Falsehood and Scandal, and
treated, in a most cruel manner, the names of those who have been looked
upon as their Rivals and Antagonists. Would a Government set an
everlasting Mark of their Displeasure upon one of those infamous
Writers, who makes his Court to them by tearing to Pieces the Reputation
of a Competitor, we should quickly see an End put to this Race of
Vermin, that are a Scandal to Government, and a Reproach to Human
Nature. Such a Proceeding would make a Minister of State shine in
History, and would fill all Mankind with a just Abhorrence of Persons
who should treat him unworthily, and employ against him those Arms which
he scorned to make use of against his Enemies.
I cannot think that any one will be so unjust as to imagine, what I have
here said is spoken with a Respect to any Party or Faction. Every one
who has in him the Sentiments either of a Christian or a Gentleman,
cannot but be highly offended at this wicked and ungenerous Practice,
which is so much in use among us at present, that it is become a kind of
National Crime, and distinguishes us from all the Governments that lie
about us. I cannot but look upon the finest Strokes of Satyr which are
aimed at particular Persons, and which are supported even with the
Appearances of Truth, to be the Marks of an evil Mind, and highly
Criminal in themselves. Infamy, like other Punishments, is under the
Direction and Distribution of the Magistrate, and not of any private
Person. Accordingly we learn from a Fragment of
Cicero
, that tho'
there were very few Capital Punishments in the twelve Tables, a Libel or
Lampoon which took away the good Name of another, was to be punished by
Death. But this is far from being our Case. Our Satyr is nothing but
Ribaldry, and
Billingsgate
. Scurrility passes for Wit; and he who can
call Names in the greatest Variety of Phrases, is looked upon to have
the shrewdest Pen. By this Means the Honour of Families is ruined, the
highest Posts and greatest Titles are render'd cheap and vile in the
Sight of the People; the noblest Virtues, and most exalted Parts,
exposed to the Contempt of the Vicious and the Ignorant. Should a
Foreigner, who knows nothing of our private Factions, or one who is to
act his Part in the World when our present Heats and Animosities are
forgot, should, I say, such an one form to himself a Notion of the
greatest Men of all Sides in the
British
Nation, who are now living,
from the Characters which are given them in some or other of those
abominable Writings which are daily Published among us, what a Nation of
Monsters must we appear!
As this cruel Practice tends to the utter Subversion of all Truth and
Humanity among us, it deserves the utmost Detestation and Discouragement
of all who have either the Love of their Country, or the Honour of their
Religion at Heart. I would therefore earnestly recommend it to the
Consideration of those who deal in these pernicious Arts of Writing; and
of those who take Pleasure in the Reading of them. As for the first, I
have spoken of them in former Papers, and have not stuck to rank them
with the Murderer and Assassin. Every honest Man sets as high a Value
upon a good Name, as upon Life it self; and I cannot but think that
those who privily assault the one, would destroy the other, might they
do it with the same Secrecy and Impunity.
As for Persons who take Pleasure in the reading and dispersing of such
detestable Libels, I am afraid they fall very little short of the Guilt
of the first Composers. By a Law of the Emperors
Valentinian
and
Valens
, it was made Death for any Person not only to write a Libel,
but if he met with one by chance, not to tear or burn it. But because I
would not be thought singular in my Opinion of this Matter, I shall
conclude my Paper with the Words of Monsieur
Bayle
, who was a Man of
great Freedom of Thought, as well as of exquisite Learning and Judgment.
I
cannot imagine, that a Man who disperses a Libel is less de
Sir ous of
doing Mischief than the Author himself. But what shall we say of the
Pleasure which a Man takes in the reading of a Defamatory Libel? Is it
not an heinous Sin in the Sight of God? We must distinguish in this
Point. This Pleasure is either an agreeable Sensation we are afflicted
with, when we meet with a witty Thought which is well expressed, or it
is a Joy which we conceive from the Dishonour of the Person who is
defamed. I will say nothing to the first of these Cases; for perhaps
some would think that my Morality is not severe enough, if I should
affirm that a Man is not Master of those agreeable Sensations, any
more than of those occasioned by Sugar or Honey, when they touch his
Tongue; but as to the second, every one will own that Pleasure to be a
heinous Sin. The Pleasure in the first Case is of no Continuance; it
prevents our Reason and Reflection, and may be immediately followed by
a secret Grief, to see our Neighbour's Honour blasted. If it does not
cease immediately, it is a Sign that we are not displeased with the
Ill-nature of the Satyrist, but are glad to see him defame his Enemy
by all kinds of Stories; and then we deserve the Punishment to which
the Writer of the Libel is subject. I shall here add the Words of a
Modern Author.
St. Gregory
upon excommunicating those Writers who
had dishonoured Castorius, does not except those who read their Works;
because, says he,
if Calumnies have always been the delight of the
Hearers, and a gratification of those Persons who have no other
Advantage over honest Men, is not he who takes Pleasure in reading
them as guilty as he who composed them? It is an uncontested Maxim,
that they who approve an Action would certainly do it if they could;
that is, if some Reason of Self-love did not hinder them. There is no
difference, says
Cicero, between advising a Crime, and approving it
when committed. The
Roman Law confirmed this Maxim, having subjected
the Approvers and Authors of this Evil to the same Penalty. We may
therefore conclude, that those who are pleased with reading Defamatory
Libels, so far as to approve the Authors and Dispersers of them, are
as guilty as if they had composed them: for if they do not write such
Libels themselves, it is because they have not the Talent of Writing,
or because they will run no hazard
1.
The Author produces other Authorities to confirm his Judgment in this
particular.
C.
Dissertation upon Defamatory Libels.
§17.
Contents
|
Friday, August 8, 1712 |
Addison |
Est natura Hominum Novitatis avida.
Plin. apud Lill.

There is no Humour in my Countrymen, which I am more enclined to wonder
at, than their general Thirst after News. There are about half a Dozen
Ingenious Men, who live very plentifully upon this Curiosity of their
Fellow-Subjects. They all of them receive the same Advices from abroad,
and very often in the same Words; but their Way of Cooking it is so
different, that there is no Citizen, who has an Eye to the publick Good,
that can leave the Coffee-house with Peace of Mind before he has given
every one of them a Reading. These several Dishes of News are so very
agreeable to the Palate of my Countrymen, that they are not only pleased
with them when they are served up hot, but when they are again set cold
before them, by those penetrating Politicians, who oblige the Publick
with their Reflections and Observations upon every piece of Intelligence
that is sent us from abroad. The Text is given us by one set of Writers,
and the Comment by another.
But notwithstanding we have the same Tale told us in so many different
papers, and if occasion requires in so many Articles of the same Paper;
notwithstanding a Scarcity of Foreign Posts we hear the same Story
repeated, by different Advices from
Paris
,
Brussels
, the
Hague
,
and from every great Town in
Europe;
notwithstanding the Multitude of
Annotations, Explanations, Reflections, and various Readings which it
passes through, our Time lies heavy on our Hands till the Arrival of a
fresh Mail: We long to receive further particulars, to hear what will be
the next Step, or what will be the Consequences of that which has been
already taken. A Westerly Wind keeps the whole Town in Suspence, and
puts a Stop to Conversation.
This general Curiosity has been raised and inflamed by our late Wars,
and, if rightly directed, might be of good Use to a Person who has such
a Thirst awakened in him. Why should not a Man, who takes Delight in
reading every thing that is new, apply himself to History, Travels, and
other Writings of the same kind, where he will find perpetual Fuel for
his Curiosity, and meet with much more Pleasure and Improvement, than in
these Papers of the Week? An honest Tradesman, who languishes a whole
Summer in Expectation of a Battel, and perhaps is balked at last, may
here meet with half a dozen in a Day. He may read the News of a whole
Campaign, in less time than he now bestows upon the Products of any
single Post. Fights, Conquests and Revolutions lye thick together. The
Reader's Curiosity is raised and satisfied every Moment, and his
Passions
or gratified, without being detained in a State of
uncertainty from Day to Day, or lying at the Mercy of Sea
and
Wind. In short, the Mind is not here kept in a perpetual Gape after
Knowledge, nor punished with that Eternal Thirst, which is the Portion
of all our modern News-mongers and Coffee-house Politicians.
All Matters of Fact, which a Man did not know before, are News to him;
and I do not see how any Haberdasher in
Cheapside
is more concerned in
the present Quarrel of the Cantons, than he was in that of the League.
At least, I believe every one will allow me, it is of more Importance to
an
Englishman
to know the History of his Ancestors, than that of his
Contemporaries who live upon the Banks of the
Danube
or the
Borysthenes
. As for those who are of another Mind, I shall recommend
to them the following Letter, from a Projector, who is willing to turn a
Penny by this remarkable Curiosity of his Countrymen.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You must have observed, that Men who frequent Coffee-houses, and
delight in News, are pleased with every thing that is Matter of Fact,
so it be what they have not heard before. A Victory, or a Defeat, are
equally agreeable to them. The shutting of a Cardinal's Mouth pleases
them one Post, and the opening of it another. They are glad to hear
the
French Court is removed to
Marli, and are afterwards as much
delighted with its Return to
Versailles. They read the
Advertisements with the same Curiosity as the Articles of publick
News; and are as pleased to hear of a Pye-bald Horse that is stray'd
out of a Field near
Islington, as of a whole Troop that has been
engaged in any Foreign Adventure. In short, they have a Relish for
every thing that is News, let the matter of it be what it will; or to
speak more properly, they are Men of a Voracious Appetite, but no
Taste. Now,
Sir , since the great Fountain of News, I mean the War, is
very near being dried up; and since these Gentlemen have contracted
such an inextinguishable Thirst after it; I have taken their Case and
my own into Consideration, and have thought of a Project which may
turn to the Advantage of us both. I have Thoughts of publishing a
daily Paper, which shall comprehend in it all the most remarkable
Occurences in every little Town, Village and Hamlet, that lye within
ten Miles of
London, or in other Words, within the Verge of the
Penny-Post. I have pitched upon this Scene of Intelligence for two
Reasons; first, because the Carriage of Letters will be very cheap;
and secondly, because I may receive them every Day. By this means my
Readers will have their News fresh and fresh, and many worthy Citizens
who cannot Sleep with any Satisfaction at present, for want of being
informed how the World goes, may go to Bed contentedly, it being my
Design to put out my Paper every Night at nine-a-Clock precisely. I
have already established Correspondences in these several Places, and
received very good Intelligence.
By my last Advices from
Knights-bridge I hear that a Horse was
clapped into the Pound on the third Instant, and that he was not
released when the Letters came away.
We are informed from
Pankridge2 that a dozen Weddings were lately
celebrated in the Mother Church of that Place, but are referred to
their next Letters for the Names of the Parties concerned.
Letters from
Brompton advise. That the Widow
Bligh had received
several Visits from
John Milldew, which affords great matter of
Speculation in those Parts.
By a Fisherman which lately touched at
Hammersmith, there is Advice
from
Putney, that a certain Person well known in that Place, is like
to lose his Election for Church-warden; but this being Boat-news, we
cannot give entire Credit to it.
Letters from
Paddington bring little more, than that
William
Squeak, the Sow-gelder, passed through that Place the 5th Instant.
They advise from
Fulham, that things remained there in the same
State they were. They had Intelligence, just as the Letters came away,
of a Tub of excellent Ale just set abroach at
Parson's Green; but
this wanted Confirmation.
I have here,
Sir , given you a Specimen of the News with which I intend
to entertain the Town, and which, when drawn up regularly in the Form
of a News Paper, will, I doubt not, be very acceptable to many of
those Publick-spirited Readers, who take more delight in acquainting
themselves with other People's Business than their own. I hope a Paper
of this kind, which lets us know what is done near home, may be more
useful to us, than those which are filled with Advices from
Zug and
Bender, and make some amends for that Dearth of Intelligence, which
we may justly apprehend from times of Peace. If I find that you
receive this Project favourably, I will shortly trouble you with one
or two more; and in the mean time am, most worthy
Sir , with all due
Respect,
Your most Obedient,
and most Humble Servant.
or
Pancras
.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 9, 1712 |
Addison |
Non usitatâ nec tenui ferar
Pennâ—
Hor.

There is not a more pleasing Exercise of the Mind than Gratitude. It is
accompanied with such an inward Satisfaction, that the Duty is
sufficiently rewarded by the Performance. It is not like the Practice of
many other Virtues, difficult and painful, but attended with so much
Pleasure, that were there no positive Command which enjoin'd it, nor any
Recompence laid up for it hereafter, a generous Mind would indulge in
it, for the natural Gratification that accompanies it.
If Gratitude is due from Man to Man, how much more from Man to his
Maker? The Supream Being does not only confer upon us those Bounties
which proceed more immediately from his Hand, but even those Benefits
which are conveyed to us by others. Every Blessing we enjoy, by what
Means soever it may be derived upon us, is the Gift of him who is the
great Author of Good, and Father of Mercies.
If Gratitude, when exerted towards one another, naturally produces a
very pleasing Sensation in the Mind of a Grateful Man; it exalts the
Soul into Rapture, when it is employed on this great Object of
Gratitude; on this Beneficent Being who has given us every thing we
already possess, and from whom we expect every thing we yet hope for.
Most of the Works of the Pagan Poets were either direct Hymns to their
Deities, or tended indirectly to the Celebration of their respective
Attributes and Perfections. Those who are acquainted with the Works of
the Greek and Latin Poets which are still extant, will upon Reflection
find this Observation so true, that I shall not enlarge upon it. One
would wonder that more of our Christian Poets have not turned their
Thoughts this way, especially if we consider, that our Idea of the
Supream Being is not only infinitely more Great and Noble than what
could possibly enter into the Heart of an Heathen, but filled with every
thing that can raise the Imagination, and give an Opportunity for the
sublimest Thoughts and Conceptions.
Plutarch
tells of a Heathen who was singing an Hymn to
Diana
, in
which he celebrated her for her Delight in Human Sacrifices, and other
Instances of Cruelty and Revenge; upon which a Poet who was present at
this piece of Devotion, and seems to have had a truer Idea of the Divine
Nature, told the Votary, by way of Reproof, that in recompence for his
Hymn, he heartily wished he might have a Daughter of the same Temper
with the Goddess he celebrated. It was indeed impossible to write the
Praises of one of those false Deities, according to the Pagan Creed,
without a mixture of Impertinence and Absurdity.
The
Jews
, who before the Times of Christianity were the only People
that had the Knowledge of the True God, have set the Christian World an
Example how they ought to employ this Divine Talent of which I am
speaking. As that Nation produced Men of great Genius, without
considering them as inspired Writers, they have transmitted to us many
Hymns and Divine Odes, which excel those that are delivered down to us
by the Ancient
Greeks
and
Romans
, in the Poetry, as much as in the
Subject to which it was consecrated. This I think might easily be shewn,
if there were occasion for it.
I have already communicated to the Publick some Pieces of Divine Poetry,
and as they have met with a very favourable Reception, I
from time
to time publish any Work of the same nature which has not yet appeared
in Print
, and may be acceptable to my Readers.
| I |
When all thy Mercies, O my God,
My rising Soul surveys;
Transported with the View, I'm lost
In Wonder, Love, and Praise: |
| II |
O how shall Words with equal Warmth
The Gratitude declare
That glows within my ravish'd Heart?
But thou canst read it there. |
| III |
Thy Providence my Life sustain'd,
And all my Wants redrest,
When in the silent Womb I lay,
And hung upon the Breast. |
| IV |
To all my weak Complaints and Cries,
Thy Mercy lent an Ear,
Ere yet my feeble Thoughts had learnt
To form themselves in Pray'r.
|
| V |
Unnumbered Comforts to my Soul
Thy tender Care bestow'd,
Before my infant Heart conceiv'd
From whom those Comforts flow'd. |
| VI |
When in the slippery Paths of Youth
With heedless Steps I ran,
Thine Arm unseen convey'd me safe
And led me up to Man. |
| VII |
Through hidden Dangers, Toils, and Deaths,
It gently clear'd my Way,
And through the pleasing Snares of Vice,
More to be fear'd than they. |
| VIII |
When worn with Sickness oft hast thou
With Health renew'd my Face,
And when in Sins and Sorrows sunk
Revived my Soul with Grace. |
| IX |
Thy bounteous Hand with worldly Bliss
Has made my Cup run o'er,
And in a kind and faithful Friend
Has doubled all my Store. |
| X |
Ten thousand thousand precious Gifts
My Daily Thanks employ,
Nor is the least a chearful Heart,
That tastes those Gifts with Joy. |
| XI |
Through every Period of my Life
Thy Goodness I'll pursue;
And after Death in distant Worlds
The Glorious Theme renew. |
| XII |
When Nature fails, and Day and Night
Divide thy Works no more,
My Ever-grateful Heart, O Lord,
Thy Mercy shall adore. |
| XIII |
Through all Eternity to Thee
A joyful Song I'll raise,
For oh! Eternity's too short
To utter all thy Praise. |
C.
By himself.
Contents
|
Monday, August 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Sine me, Vacivum tempus ne quod dem mihi Laboris.
Ter.
Heau.
It is an inexpressible Pleasure to know a little of the World, and be of
no Character or Significancy in it. To be ever unconcerned, and ever
looking on new Objects with an endless Curiosity, is a Delight known
only to those who are turned for Speculation: Nay, they who enjoy it,
must value Things only as they are the Objects of Speculation, without
drawing any worldly Advantage to themselves from them, but just as they
are what contribute to their Amusement, or the Improvement of the Mind.
I lay one Night last Week at
Richmond
; and being restless, not out of
Dissatisfaction, but a certain busie Inclination one sometimes has, I
rose at Four in the Morning, and took Boat for
London
, with a
Resolution to rove by Boat and Coach for the next Four and twenty Hours,
till the many different Objects I must needs meet with should tire my
Imagination, and give me an Inclination to a Repose more profound than I
was at that Time capable of. I beg People's Pardon for an odd Humour I
am guilty of, and was often that Day, which is saluting any Person whom
I like, whether I know him or not. This is a Particularity would be
tolerated in me, if they considered that the greatest Pleasure I know I
receive at my Eyes, and that I am obliged to an agreeable Person for
coming abroad into my View, as another is for a Visit of Conversation at
their own Houses.
The Hours of the Day and Night are taken up in the Cities of
London
and
Westminster
by People as different from each other as those who
are born in different Centuries. Men of Six a Clock give way to those of
Nine, they of Nine to the Generation of Twelve, and they of Twelve
disappear, and make Room for the fashionable World, who have made Two a
Clock the Noon of the Day.
When we first put off from Shore, we soon fell in with a Fleet of
Gardeners bound for the several Market-Ports of
London
; and it was the
most pleasing Scene imaginable to see the Chearfulness with which those
industrious People ply'd their Way to a certain Sale of their Goods. The
Banks on each Side are as well peopled, and beautified with as agreeable
Plantations, as any Spot on the Earth; but the
Thames
it self, loaded
with the Product of each Shore, added very much to the Landskip. It was
very easie to observe by their Sailing, and the Countenances of the
ruddy Virgins, who were Super-Cargoes, the Parts of the Town to which
they were bound. There was an Air in the Purveyors for
Covent-Garden
,
who frequently converse with Morning Rakes, very unlike the seemly
Sobriety of those bound for
Stocks Market
.
Nothing remarkable happened in our Voyage; but I landed
with Ten Sail of Apricock Boats at
Strand-Bridge
, after having
put in at
Nine-Elms
, and taken in Melons, consigned by
Mr.
Cuffe
of that Place, to
Sarah Sewell
and Company, at
their Stall in
Covent-Garden
. We arrived at
Strand-Bridge
at
Six of the Clock, and were unloading: when the Hackney Coachmen
of the foregoing Night took their leave of each other
at the
Dark-House
, to go to Bed before the Day was too far
spent, Chimney-Sweepers pass'd by us as we made up to the
Market, and some Raillery happened between one of the Fruit
Wenches and those black Men, about the Devil and
Eve
, with
Allusion to their several Professions. I could not believe any
Place more entertaining than
Covent-Garden
; where I strolled
from one Fruit-Shop to another, with Crowds of agreeable
young Women around me, who were purchasing Fruit for their
respective Families. It was almost eight of the Clock before
I could leave that Variety of Objects. I took Coach and
followed a Young Lady, who tripped into another just before
me, attended by her Maid. I saw immediately she was of the
Family of the
Vainloves
. There are a set of these who of all
Things affect the Play of
Blindman's-Buff
, and leading Men
into Love for they know not whom, who are fled they know
not where. This sort of Woman is usually a janty Slattern;
she hangs on her Cloaths, plays her Head, varies her Posture,
and changes Place incessantly, and all with an Appearance of
striving at the same time to hide her self, and yet give you to
understand she is in Humour to laugh at you. You must have
often seen the Coachmen make Signs with their Fingers as
they drive by each other, to intimate how much they have got
that Day. They can carry on that Language to give Intelligence
where they are driving. In an Instant my Coachman
took the Wink to pursue, and the Lady's Driver gave the Hint
that he was going through
Long-Acre
towards St.
James's
:
While he whipped up
James-Street
, we drove for
King-Street
,
to save the Pass at St.
Martin's-Lane
. The Coachmen took
care to meet, jostle, and threaten each other for Way, and be
entangled at the End of
Newport-Street
and
Long-Acre
. The
Fright, you must believe, brought down the Lady's Coach
Door, and obliged her, with her Mask off, to enquire into the
Bustle, when she sees the Man she would avoid. The Tackle
of the Coach-Window is so bad she cannot draw it up again,
and she drives on sometimes wholly discovered, and sometimes
half escaped, according to the Accident of Carriages in
her Way. One of these Ladies keeps her Seat in a Hackney-Coach,
as well as the best Rider does on a managed Horse.
The laced Shooe of her left Foot, with a careless Gesture, just
appearing on the opposite Cushion, held her both firm, and in
a proper Attitude to receive the next Jolt.
As she was an excellent Coach Woman, many were the Glances at each other
which we had for an Hour and an Half in all Parts of the Town by the
Skill of our Drivers; till at last my Lady was conveniently lost with
Notice from her Coachman to ours to make off, and he should hear where
she went. This Chase was now at an End, and the Fellow who drove her
came to us, and discovered that he was ordered to come again in an Hour,
for that she was a Silk-Worm. I was surprized with this Phrase, but
found it was a Cant among the Hackney Fraternity for their best
Customers, Women who ramble twice or thrice a Week from Shop to Shop, to
turn over all the Goods in Town without buying any thing. The Silk-worms
are, it seems, indulged by the Tradesmen; for tho' they never buy, they
are ever talking of new Silks, Laces and Ribbands, and serve the Owners
in getting them Customers as their common Dunners do in making them pay.
The Day of People of Fashion began now to Break, and Carts and Hacks
were mingled with Equipages of Show and Vanity; when I resolved to walk
it out of Cheapness; but my unhappy Curiosity is such, that I find it
always my Interest to take Coach, for some odd Adventure among Beggars,
Ballad-Singers, or the like, detains and throws me into Expence. It
happened so immediately; for at the Corner of
Warwick Street
, as I was
listening to a new Ballad, a ragged Rascal, a Beggar who knew me, came
up to me, and began to turn the Eyes of the good Company upon me, by
telling me he was extream Poor, and should die in the Street for want of
Drink, except I immediately would have the Charity to give him Six-pence
to go into the next Ale-house and save his Life. He urged, with a
melancholy Face, that all his Family had died of Thirst. All the Mob
have Humour, and two or three began to take the Jest; by which Mr.
Sturdy
carried his Point, and let me sneak off to a Coach. As I drove
along, it was a pleasing Reflection to see the World so prettily
chequered since I left
Richmond
, and the Scene still filling with
Children of a new Hour. This Satisfaction encreased as I moved towards
the City; and gay Signs, well disposed Streets, magnificent publick
Structures, and wealthy Shops, adorned with contented Faces, made the
Joy still rising till we came into the Centre of the City, and Centre of
the World of Trade, the
Exchange
of
London
. As other men in the
Crowds about me were pleased with their Hopes and Bargains, I found my
Account in observing them, in Attention to their several Interests. I,
indeed, looked upon my self as the richest Man that walked the
Exchange
that Day; for my Benevolence made me share the Gains of every
Bargain that was made. It was not the least of my Satisfactions in my
Survey, to go up Stairs, and pass the Shops of agreeable Females; to
observe so many pretty Hands busie in the Foldings of Ribbands, and the
utmost Eagerness of agreeable Faces in the sale of Patches, Pins, and
Wires, on each Side the Counters, was an Amusement, in which I should
longer have indulged my self, had not the dear Creatures called to me to
ask what I wanted, when I could not answer, only
To look at you
. I
went to one of the Windows which opened to the Area below, where all the
several Voices lost their Distinction, and rose up in a confused
Humming; which created in me a Reflection that could not come into the
Mind of any but of one a little too studious; for I said to my self,
with a kind of Pun in Thought,
What Nonsense is all the Hurry of this
World to those who are above it?
In these, or not much wiser Thoughts,
I had like to have lost my Place at the Chop-House, where every Man
according to the natural Bashfulness or Sullenness of our Nation, eats
in a publick Room a Mess of Broth, or Chop of Meat, in dumb Silence, as
if they had no pretence to speak to each other on the Foot of being Men,
except they were of each other's Acquaintance.
I went afterwards to
Robin's
, and saw People who had dined with me at
the Five-penny Ordinary just before, give Bills for the Value of large
Estates; and could not but behold with great Pleasure, Property lodged
in, and transferred in a Moment from such as would never be Masters of
half as much as is seemingly in them, and given from them every Day they
live. But before Five in the Afternoon I left the City, came to my
common Scene of
Covent-Garden
, and passed the Evening at
Will's
in
attending the Discourses of several Sets of People, who relieved each
other within my Hearing on the Subjects of Cards, Dice, Love, Learning,
and Politicks. The last Subject kept me till I heard the Streets in the
Possession of the Bellman, who had now the World to himself, and cry'd,
Past Two of Clock
. This rous'd me from my Seat, and I went to my
Lodging, led by a Light, whom I put into the Discourse of his private
œconomy, and made him give me an Account of the Charge, Hazard, Profit
and Loss of a Family that depended upon a Link, with a Design to end my
trivial Day with the Generosity of Six-pence, instead of a third Part of
that Sum. When I came to my Chambers I writ down these Minutes; but was
at a Loss what Instruction I should propose to my Reader from the
Enumeration of so many Insignificant Matters and Occurrences; and I
thought it of great Use, if they could learn with me to keep their Minds
open to Gratification, and ready to receive it from any thing it meets
with. This one Circumstance will make every Face you see give you the
Satisfaction you now take in beholding that of a Friend; will make every
Object a pleasing one; will make all the Good which arrives to any Man,
an Encrease of Happiness to your self.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 12, 1712 |
Steele |
—Ergo Apis Matinæ
More modoque
Grata Carpentis thyma per laborem
Plurimum—
The following Letters have in them Reflections which will seem of
Importance both to the Learned World and to Domestick Life. There is in
the first an Allegory so well carry'd on, that it cannot but be very
pleasing to those who have a Taste of good Writing; and the other
Billets may have their Use in common Life.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
As I walked t'other Day in a fine Garden, and observed the great
Variety of Improvements in Plants and Flowers beyond what they
otherwise would have been, I was naturally led into a Reflection upon
the Advantages of Education, or Moral Culture; how many good Qualities
in the Mind are lost, for want of the like due Care in nursing and
skilfully managing them, how many Virtues are choaked, by the
Multitude of Weeds which are suffered to grow among them; how
excellent Parts are often starved and useless, by being planted in a
wrong Soil; and how very seldom do these Moral Seeds produce the noble
Fruits which might be expected from them, by a Neglect of proper
Manuring, necessary Pruning, and an artful Management of our tender
Inclinations and first Spring of Life: These obvious Speculations made
me at length conclude, that there is a sort of vegetable Principle in
the Mind of every Man when he comes into the World. In Infants the
Seeds lie buried and undiscovered, till after a while they sprout
forth in a kind of rational Leaves, which are Words; and in due
Season the Flowers begin to appear in Variety of beautiful Colours,
and all the gay Pictures of youthful Fancy and Imagination; at last
the Fruit knits and is formed, which is green, perhaps, first, and
soure, unpleasant to the Taste, and not fit to be gathered; till
ripened by due Care and Application, it discovers itself in all the
noble Productions of Philosophy, Mathematicks, close Reasoning, and
handsome Argumentation: And these Fruits, when they arrive at a just
Maturity, and are of a good Kind, afford the most vigorous Nourishment
to the Minds of Men. I reflected further on the intellectual Leaves
beforementioned, and found almost as great a Variety among them as in
the vegetable World. I could easily observe the smooth shining
Italian Leaves; the nimble French Aspen always in Motion; the
Greek and Latin Evergreens, the Spanish Myrtle, the English
Oak, the Scotch Thistle, the Irish Shambrogue, the prickly
German and Dutch Holly, the Polish and Russian Nettle, besides
a vast Number of Exoticks imported from Asia, Africk, and
America. I saw several barren Plants, which bore only Leaves,
without any Hopes of Flower or Fruit: The Leaves of some were fragrant
and well-shaped, of others ill-scented and irregular. I wonder'd at a
Set of old whimsical Botanists, who spent their whole Lives in the
Contemplation of some withered Ægyptian, Coptick, Armenian, or
Chinese Leaves, while others made it their Business to collect in
voluminous Herbals all the several Leaves of some one Tree. The
Flowers afforded a most diverting Entertainment, in a wonderful
Variety of Figures, Colours and Scents; however, most of them withered
soon, or at best are but Annuals. Some professed Florists make them
their constant Study and Employment, and despise all Fruit; and now
and then a few fanciful People spend all their Time in the Cultivation
of a single Tulip, or a Carnation: But the most agreeable Amusement
seems to be the well chusing, mixing, and binding together these
Flowers, in pleasing Nosegays to present to Ladies. The Scent of
Italian Flowers is observed, like their other Perfume, to be too
strong, and to hurt the Brain; that of the French with glaring,
gaudy Colours, yet faint and languid; German and Northern Flowers
have little or no Smell, or sometimes an unpleasant one. The Antients
had a Secret to give a lasting Beauty, Colour, and Sweetness to some
of their choice Flowers, which flourish to this Day, and which few of
the Moderns can effect. These are becoming enough and agreeable in
their Season, and do often handsomely adorn an Entertainment, but an
Over-fondness of them seems to be a Disease. It rarely happens to find
a Plant vigorous enough, to have (like an Orange-Tree) at once
beautiful shining Leaves, fragrant Flowers, and delicious nourishing
Fruit.
Sir , Yours, &c.
August 6, 1712.
Dear SPEC,
You have given us in your Spectator of Saturday last, a very
excellent Discourse upon the Force of Custom, and its wonderful
Efficacy in making every thing pleasant to us. I cannot deny but that
I received above Two penny-worth of Instruction from your Paper, and
in the general was very well pleased with it; but I am, without a
Compliment, sincerely troubled that I cannot exactly be of your
Opinion, That it makes every thing pleasing to us. In short, I have
the Honour to be yoked to a young Lady, who is, in plain English, for
her Standing, a very eminent Scold. She began to break her Mind very
freely both to me and to her Servants about two Months after our
Nuptials; and tho' I have been accustomed to this Humour of hers this
three Years, yet, I do not know what's the Matter with me, but I am no
more delighted with it than I was at the very first. I have advised
with her Relations about her, and they all tell me that her Mother and
her Grandmother before her were both taken much after the same Manner;
so that since it runs in the Blood, I have but small Hopes of her
Recovery. I should be glad to have a little of your Advice in this
Matter: I would not willingly trouble you to contrive how it may be a
Pleasure to me; if you will but put me in a Way that I may bear it
with Indifference, I shall rest satisfied.
Dear SPEC,
Your very humble Servant.
P. S. I must do the poor Girl the Justice to let you know, that this
Match was none of her own chusing, (or indeed of mine either;) in
Consideration of which I avoid giving her the least Provocation; and
indeed we live better together than usually Folks do who hated one
another when they were first joined: To evade the Sin against Parents,
or at least to extenuate it, my Dear rails at my Father and Mother,
and I curse hers for making the Match.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I like the Theme you lately gave out extremely, and should be as glad
to handle it as any Man living: But I find myself no better qualified
to write about Money, than about my Wife; for, to tell you a Secret
which I deSir e may go no further, I am Master of neither of those
Subjects.
Yours,
Pill Garlick.
Aug. 8, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I deSir e you would print this in Italick, so as it may be generally
taken Notice of. It is designed only to admonish all Persons, who
speak either at the Bar, Pulpit, or any publick Assembly whatsoever,
how they discover their Ignorance in the Use of Similes. There are in
the Pulpit it self, as well as other Places, such gross Abuses in this
Kind, that I give this Warning to all I know, I shall bring them for
the Future before your Spectatorial Authority. On Sunday last, one,
who shall be nameless, reproving several of his Congregation for
standing at Prayers, was pleased to say, One would think, like the
Elephant, you had no Knees. Now I my self saw an Elephant in
Bartholomew-Fair kneel down to take on his Back the ingenious Mr.
William Penkethman.
Your most humble Servant.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 13, 1712 |
Steele |
De quo libelli in celeberrimis locis proponuntur
Huic ne perire quidem tacite conceditur.
Tull.

Otway
, in his Tragedy of
Venice Preserv'd
, has described the Misery of
a Man, whose Effects are in the Hands of the Law, with great Spirit. The
Bitterness of being the Scorn and Laughter of base Minds, the Anguish of
being insulted by Men hardened beyond the Sense of Shame or Pity, and
the Injury of a Man's Fortune being wasted, under Pretence of Justice,
excellently aggravated in the following Speech of
Pierre
to
Faffeir
:
I pass'd this very Moment by thy Doors,
And found them guarded by a Troop of Villains:
The Sons of publick Rapine were destroying.
They told me, by the Sentence of the Law,
They had Commission to seize all thy Fortune:
Nay more, Priuli's cruel Hand had sign'd it.
Here stood a Ruffian with a horrid Face,
Lording it o'er a Pile of massy Plate,
Tumbled into a Heap for publick Sale.
There was another making villanous Jests
At thy Undoing: He had ta'en Possession
Of all thy ancient most domestick Ornaments:
Rich Hangings intermix'd and wrought with Gold;
The very Bed, which on thy Wedding Night
Received thee to the Arms of Belvedira,
The Scene of all thy Joys, was violated
By the coarse Hands of filthy Dungeon Villains,
And thrown amongst the common Lumber.
Nothing indeed can be more unhappy than the Condition of Bankrupcy. The
Calamity which happens to us by ill Fortune, or by the Injury of others,
has in it some Consolation; but what arises from our own Misbehaviour or
Error, is the State of the most exquisite Sorrow. When a Man considers
not only an ample Fortune, but even the very Necessaries of Life, his
Pretence to Food it self at the Mercy of his Creditors, he cannot but
look upon himself in the State of the Dead, with his Case thus much
worse, that the last Office is performed by his Adversaries, instead of
his Friends. From this Hour the cruel World does not only take
Possession of his whole Fortune, but even of every thing else, which had
no Relation to it. All his indifferent Actions have new Interpretations
put upon them; and those whom he has favoured in his former Life,
discharge themselves of their Obligations to him, by joining in the
Reproaches of his Enemies. It is almost incredible that it should be so;
but it is too often seen that there is a Pride mixed with the Impatience
of the Creditor, and there are who would rather recover their own by the
Downfal of a prosperous Man, than be discharged to the common
Satisfaction of themselves and their Creditors. The wretched Man, who
was lately Master of Abundance, is now under the Direction of others;
and the Wisdom, œconomy, good Sense and Skill in human Life before, by
reason of his present Misfortune, are of no Use to him in the
Disposition of any thing. The Incapacity of an Infant or a Lunatick, is
designed for his Provision and Accommodation; but that of a Bankrupt,
without any Mitigation in respect of the Accidents by which it arrived,
is calculated for his utter Ruin, except there be a Remainder ample
enough after the Discharge of his Creditors to bear also the Expence of
rewarding those by whose Means the Effect of all his Labours was
transferred from him. This Man is to look on and see others giving
Directions upon what Terms and Conditions his Goods are to be purchased,
and all this usually done not with an Air of Trustees to dispose of his
Effects, but Destroyers to divide and tear them to Pieces.
There is something sacred in Misery to great and good Minds; for this
Reason all wise Lawgivers have been extremely tender how they let loose
even the Man who has Right on his Side, to act with any Mixture of
Resentment against the Defendant. Virtuous and modest Men, though they
be used with some Artifice, and have it in their Power to avenge
themselves, are slow in the Application of that Power, and are ever
constrained to go into rigorous Measures. They are careful to
demonstrate themselves not only Persons injured, but also that to bear
it longer, would be a Means to make the Offender injure others, before
they proceed. Such Men clap their Hands upon their Hearts, and consider
what it is to have at their Mercy the Life of a Citizen. Such would have
it to say to their own Souls, if possible, That they were merciful when
they could have destroyed, rather than when it was in their Power to
have spared a Man, they destroyed. This is a Due to the common Calamity
of Human Life, due in some measure to our very Enemies. They who scruple
doing the least Injury, are cautious of exacting the utmost Justice.
Let any one who is conversant in the Variety of Human Life reflect upon
it, and he will find the Man who wants Mercy has a Taste of no Enjoyment
of any Kind. There is a natural Disrelish of every thing which is good
in his very Nature, and he is born an Enemy to the World. He is ever
extremely partial to himself in all his Actions, and has no Sense of
Iniquity but from the Punishment which shall attend it. The Law of the
Land is his Gospel, and all his Cases of Conscience are determined by
his Attorney. Such Men know not what it is to gladden the Heart of a
miserable Man, that Riches are the Instruments of serving the Purposes
of Heaven or Hell, according to the Disposition of the Possessor. The
wealthy can torment or gratifie all who are in their Power, and chuse to
do one or other as they are affected with Love or Hatred to Mankind. As
for such who are insensible of the Concerns of others, but merely as
they affect themselves, these Men are to be valued only for their
Mortality, and as we hope better Things from their Heirs. I could not
but read with great Delight a Letter from an eminent Citizen, who has
failed, to one who was intimate with him in his better Fortune, and able
by his Countenance to retrieve his lost Condition.
Sir ,
It is in vain to multiply Words and make Apologies for what is never
to be defended by the best Advocate in the World, the Guilt of being
Unfortunate. All that a Man in my Condition can do or say, will be
received with Prejudice by the Generality of Mankind, but I hope not
with you: You have been a great Instrument in helping me to get what I
have lost, and I know (for that Reason, as well as Kindness to me) you
cannot but be in pain to see me undone. To shew you I am not a Man
incapable of bearing Calamity, I will, though a poor Man, lay aside
the Distinction between us, and talk with the Frankness we did when we
were nearer to an Equality: As all I do will be received with
Prejudice, all you do will be looked upon with Partiality. What I
deSir e of you, is, that you, who are courted by all, would smile upon
me who am shunned by all. Let that Grace and Favour which your Fortune
throws upon you, be turned to make up the Coldness and Indifference
that is used towards me. All good and generous Men will have an Eye of
Kindness for me for my own Sake, and the rest of the World will regard
me for yours. There is an happy Contagion in Riches, as well as a
destructive one in Poverty; the Rich can make rich without parting
with any of their Store, and the Conversation of the Poor makes Men
poor, though they borrow nothing of them. How this is to be accounted
for I know not? but Men's Estimation follows us according to the
Company we keep. If you are what you were to me, you can go a great
Way towards my Recovery; if you are not, my good Fortune, if ever it
returns, will return by slower Approaches.
I am Sir ,
Your Affectionate Friend,
and Humble Servant.
This was answered with a Condescension that did not, by long impertinent
Professions of Kindness, insult his Distress, but was as follows.
Dear Tom,
I am very glad to hear that you have Heart enough to begin the World a
second Time. I assure you, I do not think your numerous Family at all
diminished (in the Gifts of Nature for which I have ever so much
admired them) by what has so lately happened to you. I shall not only
countenance your Affairs with my Appearance for you, but shall
accommodate you with a considerable Sum at common Interest for three
Years. You know I could make more of it; but I have so great a Love
for you that I can wave Opportunities of Gain to help you: For I do
not care whether they say of me after I am dead, that I had an hundred
or fifty thousand Pounds more than I wanted when I was living.
Your obliged humble Servant.
T.
Act I., sc. 2.
Contents
|
Thursday, August 14, 1712 |
Addison |
—Multa et præclara minantis.
Hor.

I shall this Day lay before my Reader a Letter, written by the same Hand
with that of last Friday, which contained Proposals for a Printed
News-paper, that should take in the whole Circle of the Penny-Post.
Sir ,
The kind Reception you gave my last Friday's Letter, in which I
broached my Project of a News-Paper, encourages me to lay before you
two or three more; for, you must know,
Sir , that we look upon you to
be the
Lowndes of the learned World, and cannot think any Scheme
practicable or rational before you have approved of it, tho' all the
Money we raise by it is on our own Funds, and for our private Use.
I have often thought that a
News-Letter of Whispers, written every
Post, and sent about the Kingdom, after the same Manner as that of Mr.
Dyer, Mr.
Dawkes, or any other Epistolary Historian, might be
highly gratifying to the Publick, as well as beneficial to the Author.
By Whispers I mean those Pieces of News which are communicated as
Secrets, and which bring a double Pleasure to the Hearer; first, as
they are private History, and in the next place as they have always in
them a Dash of Scandal.
These are the two chief Qualifications in an
Article of News,
which1 recommend it, in a more than ordinary
Manner, to the Ears of the Curious. Sickness of Persons in high Posts,
Twilight Visits paid and received by Ministers of State, Clandestine
Courtships and Marriages, Secret Amours, Losses at Play, Applications
for Places, with their respective Successes or Repulses, are the
Materials in which I chiefly intend to deal. I have two Persons, that
are each of them the Representative of a Species, who are to furnish
me with those Whispers which I intend to convey to my Correspondents.
The first of these is
Peter Hush, descended from the ancient Family
of the
Hushes. The other is the old Lady
Blast, who has a very
numerous Tribe of Daughters in the two great Cities of
London and
Westminster.
Peter Hush has a whispering Hole in most of the great
Coffee-houses about Town. If you are alone with him in a wide Room, he
carries you up into a Corner of it, and speaks in your Ear. I have
seen
Peter seat himself in a Company of seven or eight Persons, whom
he never saw before in his Life; and after having looked about to see
there was no one that overheard him, has communicated to them in a low
Voice, and under the Seal of Secrecy, the Death of a great Man in the
Country, who was
perhaps a Fox-hunting the very Moment this Account
was
given2 of him. If upon your entring into a Coffee-house you
see a Circle of Heads bending over the Table, and lying close by one
another, it is ten to one but my Friend
Peter is among them. I have
known
Peter publishing the Whisper of the Day by eight a-Clock in
the Morning at
Garraway's, by twelve at
Will's, and before two at
the
Smyrna. When
Peter has thus effectually launched a Secret, I
have been very well pleased to hear People whispering it to one
another at second Hand, and spreading it about as their own; for you
must know,
Sir , the great Incentive to Whispering is the Ambition
which every one has of being thought in the Secret, and being look'd
upon as a Man who has Access to greater People than one would imagine.
After having given you this Account of
Peter Hush, I proceed to that
virtuous Lady, the old Lady
Blast, who is to communicate to me the
private Transactions of the Crimp Table, with all the
Arcana of the
Fair Sex. The Lady
Blast, you must understand, has such a particular
Malignity in her Whisper, that it blights like an Easterly Wind, and
withers every Reputation that it breathes upon. She has a particular
Knack at making private Weddings, and last Winter married above five
Women of Quality to their Footmen. Her Whisper can make an innocent
young Woman big with Child, or fill an healthful young Fellow with
Distempers that are not to be named. She can turn a Visit into an
Intrigue, and a distant Salute into an Assignation. She can beggar the
Wealthy, and degrade the Noble. In short, she can whisper Men Base or
Foolish, Jealous or Ill-natured, or, if Occasion requires, can tell
you the Slips of their Great Grandmothers, and traduce the Memory of
honest Coachmen that have been in their Graves above these hundred
Years. By these and the like Helps, I question not but I shall furnish
out a very handsome News-Letter. If you approve my Project, I shall
begin to whisper by the very next Post, and question not but every one
of my Customers will be very well pleased with me, when he considers
that every Piece of News I send him is a Word in his Ear, and lets him
into a Secret.
Having given you a Sketch of this Project, I shall, in the next Place,
suggest to you another for a Monthly Pamphlet, which I shall likewise
submit to your Spectatorial Wisdom. I need not tell you,
Sir , that
there are several Authors in
France,
Germany, and
Holland, as
well as in our own Country, who publish every Month, what they call
An Account of the Works of the Learned, in which they give us an
Abstract of all such Books as are printed in any Part of
Europe.
Now,
Sir , it is my Design to publish every Month,
An Account of the
Works of the Unlearned. Several late Productions of my own
Countrymen, who many of them make a very eminent Figure in the
Illiterate World, Encourage me in this Undertaking. I may, in this
Work, possibly make a Review of several Pieces which have appeared in
the Foreign
Accounts above-mentioned, tho' they ought not to have
been taken Notice of in Works which bear such a Title. I may,
likewise, take into Consideration, such Pieces as appear, from time to
time, under the Names of those Gentlemen who Compliment one another,
in Publick Assemblies, by the Title of the
Learned Gentlemen. Our
Party-Authors will also afford me a great Variety of Subjects, not to
mention Editors, Commentators, and others, who are often Men of no
Learning, or, what is as bad, of no Knowledge. I shall not enlarge
upon this Hint; but if you think any thing can be made of it, I shall
set about it with all the Pains and Application that so useful a Work
deserves.
I am ever,
Most Worthy Sir , &c.
C.
that
giving
Contents
|
Friday, August 15, 1712 |
Addison |
 —Pudor malus—
—Pudor malus—
Hor.

I could not Smile at the Account that was Yesterday given me of a modest
young Gentleman, who being invited to an Entertainment, though he was
not used to drink, had not the Confidence to refuse his Glass in his
Turn, when on a sudden he grew so flustered that he took all the Talk of
the Table into his own Hands, abused every one of the Company, and flung
a Bottle at the Gentleman's Head who treated him. This has given me
Occasion to reflect upon the ill Effects of a vicious Modesty, and to
remember the Saying of
Brutus
, as it is quoted by
Plutarch
, that
the Person has had but an ill Education, who has not been taught to
deny any thing
. This false kind of Modesty has, perhaps, betrayed both
Sexes into as many Vices as the most abandoned Impudence, and is the
more inexcusable to Reason, because it acts to gratify others rather
than it self, and is punished with a kind of Remorse, not only like
other vicious Habits when the Crime is over, but even at the very time
that it is committed.
Nothing is more amiable than true Modesty, and nothing is more
contemptible than the false. The one guards Virtue, the other betrays
it. True Modesty is ashamed to do any thing that is repugnant to the
Rules of right Reason: False Modesty is ashamed to do any thing that is
opposite to the Humour of the Company. True Modesty avoids every thing
that is criminal, false Modesty every thing that is unfashionable. The
latter is only a general undetermined Instinct; the former is that
Instinct, limited and circumscribed by the Rules of Prudence and
Religion.
We may conclude that Modesty to be false and vicious, which engages a
Man to do any thing that is ill or indiscreet, or which restrains him
from doing any thing that is of a contrary Nature. How many Men, in the
common Concerns of Life, lend Sums of Money which they are not able to
spare, are bound for Persons whom they have but little Friendship for,
give Recommendatory Characters of Men whom they are not acquainted with,
bestow Places on those whom they do not esteem, live in such a Manner as
they themselves do not approve, and all this meerly because they have
not the Confidence to resist Solicitation, Importunity or Example?
Nor does this false Modesty expose us only to such Actions as are
indiscreet,
very often to such as are highly criminal. When
Xenophanes
was called timorous, because he would not venture his
Money in a Game at Dice:
I confess
, said he,
that I am exceeding
timorous, for I dare not do any ill thing
. On the contrary, a Man of
vicious Modesty complies with every thing, and is only fearful of doing
what may look singular in the Company where he is engaged. He falls in
with the Torrent, and lets himself go to every Action or Discourse,
however unjustifiable in it self, so it be in Vogue among the present
Party. This, tho' one of the most common, is one of the most ridiculous
Dispositions in Human Nature, that Men should not be ashamed of speaking
or acting in a dissolute or irrational Manner, but that one who is in
their Company should be ashamed of governing himself by the Principles
of Reason and Virtue.
In the second place we are to consider false Modesty, as it restrains a
Man from doing what is good and laudable. My Reader's own Thoughts will
suggest to him many Instances and Examples under this Head. I shall only
dwell upon one Reflection, which I cannot make without a Secret Concern.
We have in
England
a particular Bashfulness in every thing that
regards Religion. A well-bred Man is obliged to conceal any Serious
Sentiment of this Nature, and very often to appear a greater Libertine
than he is, that he may keep himself in Countenance among the Men of
Mode. Our Excess of Modesty makes us shamefaced in all the Exercises of
Piety and Devotion. This Humour prevails upon us daily; insomuch, that
at many well-bred Tables, the Master of the House is so very Modest a
Man, that he has not the Confidence to say Grace at his own Table: A
Custom which is not only practised by all the Nations about us, but was
never omitted by the Heathens themselves.
English
Gentlemen who travel
into Roman-Catholick Countries, are not a little surprized to meet with
People of the best Quality kneeling in their Churches, and engaged in
their private Devotions, tho' it be not at the Hours of Publick Worship.
An Officer of the Army, or a Man of Wit and Pleasure in those Countries,
would be afraid of passing not only for an irreligious, but an ill-bred
Man, should he be seen to go to Bed, or sit down at Table, without
offering up his Devotions on such Occasions. The same Show of Religion
appears in all the Foreign Reformed Churches, and enters so much into
their Ordinary Conversation, that an
Englishman
is apt to term them
Hypocritical and Precise.
This little Appearance of a Religious Deportment in our Nation, may
proceed in some measure from that Modesty which is natural to us, but
the great occasion of it is certainly this. Those Swarms of Sectaries
that overran the Nation in the time of the great Rebellion, carried
their Hypocrisie so high, that they had converted our whole Language
into a Jargon of Enthusiasm; insomuch that upon the Restoration Men
thought they could not recede too far from the Behaviour and Practice of
those Persons, who had made Religion a Cloak to so many Villanies. This
led them into the other Extream, every Appearance of Devotion was looked
upon as Puritannical, and falling into the Hands of the Ridiculers who
flourished in that Reign, and attacked every thing that was Serious, it
has ever since been out of Countenance among us. By this means we are
gradually fallen into that Vicious Modesty which has in some measure
worn out
among us the Appearance of Christianity in Ordinary Life
and Conversation, and which distinguishes us from all
our Neighbours
.
Hypocrisie cannot indeed be too much detested, but at the same time is
to be preferred to open Impiety. They are both equally destructive to
the Person who is possessed with them; but in regard to others,
Hypocrisie is not so pernicious as bare-faced Irreligion. The due Mean
to be observed is to be sincerely Virtuous, and at the same time to let
the World see we are so. I do not know a more dreadful Menace in the
Holy Writings, than that which is pronounced against those who have this
perverted Modesty, to be ashamed before Men in a Particular of such
unspeakable Importance.
C.
Xenophon
the Nations that lie about us.
No letter affixed in the first issue.
Contents
|
Saturday, August 16, 1712 |
Addison |
—quicquid dignum sapiente bonoque est.
Hor.

Religion may be considered under two General Heads. The first
comprehends what we are to believe, the other what we are to practise.
By those things which we are to believe, I mean whatever is revealed to
us in the Holy Writings, and which we could not have obtained the
Knowledge of by the Light of Nature; by the things which we are to
practise, I mean all those Duties to which we are directed by Reason or
Natural Religion. The first of these I shall distinguish by the Name of
Faith
, the Second by that of
Morality
.
If we look into the more Serious Part of Mankind, we find many who lay
so great a Stress upon Faith, that they neglect Morality; and many who
build so much upon Morality, that they do not pay a due Regard to Faith.
The perfect Man should be defective in neither of these Particulars, as
will be very evident to those who consider the Benefits which arise from
each of them, and which I shall make the Subject of this Day's Paper.
Notwithstanding this general Division of Christian Duty into Morality
and Faith, and that they have both their peculiar Excellencies, the
first has the Pre-eminence in several Respects.
- First: Because the greatest Part of Morality (as I have stated the
Notion of it,) is of a fixt Eternal Nature, and will endure when Faith
shall fail, and be lost in Conviction.
- Secondly: Because a Person may be qualified to do greater
Good to Mankind, and become more beneficial to the World,
by Morality, without Faith, than by Faith without Morality.
- Thirdly: Because Morality gives a greater Perfection to human
Nature, by quieting the Mind, moderating the Passions, and advancing
the Happiness of every Man in his private Capacity.
- Fourthly: Because the Rule of Morality is much more certain than
that of Faith, all the Civilized Nations of the World agreeing in the
great Points of Morality, as much as they differ in those of Faith.
- Fifthly: Because Infidelity is not of so malignant a Nature as
Immorality; or to put the same Reason in another Light, because it is
generally owned, there may be Salvation for a virtuous Infidel,
(particularly in the Case of Invincible Ignorance) but none for a
vicious Believer.
- Sixthly: Because Faith seems to draw its principal, if not all its
Excellency, from the Influence it has upon Morality; as we shall see
more at large, if we consider wherein consists the Excellency of
Faith, or the Belief of Revealed Religion; and this I think is,
- First: In explaining and carrying to greater Heights, several
Points of Morality.
- Secondly: In furnishing new and stronger Motives to enforce the
Practice of Morality.
- Thirdly: In giving us more amiable Ideas of the Supreme Being,
more endearing Notions of one another, and a truer State of our
selves, both in regard to the Grandeur and Vileness of our Natures.
- Fourthly: By shewing us the Blackness and Deformity of Vice, which
in the Christian System is so very great, that he who is possessed
of all Perfection and the Sovereign Judge of it, is represented by
several of our Divines as hating Sin to the same Degree that he
loves the Sacred Person who was made the Propitiation of it.
- Fifthly: In being the ordinary and prescribed Method of making
Morality effectual to Salvation.
I have only touched on these several Heads, which every one who is
conversant in Discourses of this Nature will easily enlarge upon in his
own Thoughts, and draw Conclusions from them which may be useful to him
in the Conduct of his Life. One I am sure is so obvious, that he cannot
miss it, namely that a Man cannot be perfect in his Scheme of Morality,
who does not strengthen and support it with that of the Christian Faith.
Besides this, I shall lay down two or three other Maxims which I think
we may deduce from what has been said.
- First: That we should be particularly cautious of making any
thing an Article of Faith, which does not contribute to the
Confirmation or Improvement of Morality.
- Secondly: That no Article of Faith can be true and authentick, which
weakens or subverts the practical part of Religion, or what I have
hitherto called Morality.
- Thirdly: That the greatest Friend of Morality, or Natural Religion,
cannot possibly apprehend any Danger from embracing Christianity, as
it is preserved pure and uncorrupt in the Doctrines of our National
Church.
There is likewise another Maxim which I think may be drawn from the
foregoing Considerations, which is this, that we should, in all dubious
Points, consider any ill Consequences that may arise from them,
supposing they should be Erroneous, before we give up our Assent to
them.
For example, In that disputable Point of Prosecuting Men for Conscience
Sake, besides the imbittering their Minds with Hatred, Indignation, and
all the Vehemence of Resentment, and ensnaring them to profess what they
do not believe; we cut them off from the Pleasures and Advantages of
Society, afflict their Bodies, distress their Fortunes, hurt their
Reputations, ruin their Families, make their Lives painful, or put an
End to them. Sure when I see such dreadful Consequences rising from a
Principle, I would be as fully convinced of the Truth of it, as of a
Mathematical Demonstration, before I would venture to act upon it, or
make it a part of my Religion.
In this Case the Injury done our Neighbour is plain and evident, the
Principle that puts us upon doing it, of a dubious and disputable
Nature. Morality seems highly violated by the one, and whether or no a
Zeal for what a Man thinks the true System of Faith may justifie it, is
very uncertain. I cannot but think, if our Religion produce Charity as
well as Zeal, it will not be for shewing it self by such cruel
Instances.
, to conclude with the Words of an excellent Author
,
We have just enough Religion to make us hate, but not enough to make us
love, one another.
C.
Probably Tillotson. The thought is expanded in part of his
sermon on the Example of Jesus in doing good. It appears in another form
in his sermon for the 5th of November, 1678, where he applies to our
religious hatreds the saying that
the richest and noblest wines make
the sharpest vinegar;
again in another form in his sermon at the
Yorkshire Feast.
Contents
|
Monday, August 18, 1712 |
Parnell1 |
—Decipimur Specie Recti—
Hor.

Our defects and Follies are too often unknown to us; nay, they are so
far from being known to us, that they pass for Demonstrations of our
Worth. This makes us easy in the midst of them, fond to shew them, fond
to improve in them, and to be esteemed for them. Then it is that a
thousand unaccountable Conceits, gay Inventions, and extravagant Actions
must afford us Pleasures, and display us to others in the Colours which
we ourselves take a Fancy to glory in: And indeed there is something so
amusing for the time in this State of Vanity and ill-grounded
Satisfaction, that even the wiser World has chosen an exalted Word to
describe its Enchantments, and called it the
Paradise of Fools
.
Perhaps the latter part of this Reflection may seem a false Thought to
some, and bear another Turn than what I have given: but it is at present
none of my Business to look after it, who am going to confess that I
have been lately amongst them in a Vision.
Methought I was transported to a Hill, green, flowery, and of an easie
Ascent. Upon the broad Top of it resided squinteyed
Error
, and popular
Opinion
with many Heads; two that dealt in Sorcery, and were famous
for bewitching People with the Love of themselves. To these repaired a
Multitude from every Side, by two different Paths which lead towards
each of them. Some who had the most assuming Air, went directly of
themselves to
Errour
, without expecting a Conductor; others of a
softer Nature went first to popular
Opinion
, from whence as she
influenced and engaged them with their own Praises, she delivered them
over to his Government.
When we had ascended to an open Part of the Summit where
Opinion
abode, we found her entertaining several who had arrived before us. Her
Voice was pleasing; she breathed Odours as she spoke: She seemed to have
a Tongue for every one; every one thought he heard of something that was
valuable in himself, and expected a Paradise, which she promised as the
Reward of his Merit. Thus were we drawn to follow her, till she should
bring us where it was to be bestowed: And it was observable, that all
the Way we went, the Company was either praising themselves for their
Qualifications, or one another for those Qualifications which they took
to be conspicuous in their own Characters, or dispraising others for
wanting theirs, or vying in the Degrees of them.
At last we approached a Bower, at the Entrance of which
Errour
was
seated. The Trees were thick-woven, and the Place where he sat artfully
contrived to darken him a little. He was disguised in a whitish Robe,
which he had put on, that he might appear to us with a nearer
Resemblance to
Truth:
And as she has a Light whereby she manifests the
Beauties of Nature to the Eyes of her Adorers, so he had provided
himself with a magical Wand, that he might do something in Imitation of
it, and please with Delusions. This he lifted solemnly, and muttering to
himself, bid the Glories which he kept under Enchantment to appear
before us. Immediately we cast our Eyes on that part of the Sky to which
he pointed, and observed a thin blue Prospect, which cleared as
Mountains in a Summer Morning when the Mists go off, and the Palace of
Vanity
appeared to Sight.
The Foundation hardly seemed a Foundation, but a Set of curling Clouds,
which it stood upon by magical Contrivance. The Way by which we ascended
was painted like a Rainbow; and as we went the Breeze that played about
us bewitched the Senses. The Walls were gilded all for Show; the lowest
Set of Pillars were of the slight fine
Corinthian
Order, and the Top
of the Building being rounded, bore so far the Resemblance of a Bubble.
At the Gate the Travellers neither met with a Porter, nor waited till
one should appear; every one thought his Merits a sufficient Passport,
and pressed forward. In the Hall we met with several Phantoms, that
rov'd amongst us, and rang'd the Company according to their Sentiments.
There was decreasing
Honour
, that had nothing to shew in but an old
Coat of his Ancestors Atchievements: There was
Ostentation
, that made
himself his own constant Subject, and
Gallantry
strutting upon his
Tiptoes. At the upper End of the Hall stood a Throne, whose Canopy
glitter'd with all the Riches that Gayety could contrive to lavish on
it; and between the gilded Arms sat
Vanity
, deck'd in the Peacock's
Feathers, and acknowledged for another
Venus
by her Votaries. The Boy
who stood beside her for a
Cupid
, and who made the World to bow before
her, was called
Self-Conceit
. His Eyes had every now and then a Cast
inwards to the Neglect of all Objects about him; and the Arms which he
made use of for Conquest, were borrowed from those against whom he had a
Design. The Arrow which he shot at the Soldier, was fledged from his own
Plume of Feathers; the Dart he directed against the Man of Wit, was
winged from the Quills he writ with; and that which he sent against
those who presumed upon their Riches, was headed with Gold out of their
Treasuries: He made Nets for Statesmen from their own Contrivances; he
took Fire from the Eyes of Ladies, with which he melted their Hearts;
and Lightning from the Tongues of the Eloquent, to enflame them with
their own Glories. At the Foot of the Throne sat three false Graces.
Flattery
with a Shell of Paint,
Affectation
with a Mirrour to
practise at, and
Fashion
ever changing the Posture of her Cloaths.
These applied themselves to secure the Conquests which
Self-Conceit
had gotten, and had each of them their particular Polities.
Flattery
gave new Colours and Complections to all Things.
Affectation
new Airs
and Appearances, which, as she said, were not vulgar, and
Fashion
both
concealed some home Defects, and added some foreign external Beauties
As I was reflecting upon what I saw, I heard a Voice in the Crowd,
bemoaning the Condition of Mankind, which is thus managed by the Breath
of
Opinion
, deluded by
Errour
, fired by
Self-Conceit
, and given up
to be trained in all the Courses of
Vanity
, till
Scorn
or
Poverty
come upon us. These Expressions were no sooner handed about, but I
immediately saw a general Disorder, till at last there was a Parting in
one Place, and a grave old Man, decent and resolute, was led forward to
be punished for the Words he had uttered. He appeared inclined to have
spoken in his own Defence, but I could not observe that any one was
willing to hear him.
Vanity
cast a scornful Smile at him;
Self-Conceit
was angry;
Flattery
, who knew him for
Plain-dealing
,
put on a Vizard, and turned away;
Affectation
tossed her Fan, made
Mouths, and called him
Envy
or
Slander
; and
Fashion
would have it,
that at least he must be
Ill-Manners
. Thus slighted and despised by
all, he was driven out for abusing People of Merit and Figure; and I
heard it firmly resolved, that he should be used no better wherever they
met with him hereafter.
I had already seen the Meaning of most part of that Warning which he had
given, and was considering how the latter Words should be fulfilled,
when a mighty Noise was heard without, and the Door was blackned by a
numerous Train of Harpies crowding in upon us.
Folly
and
Broken
Credit
were seen in the House before they entered.
Trouble, Shame,
Infamy, Scorn
and
Poverty
brought up the Rear.
Vanity
, with her
Cupid
and
Graces
, disappeared; her Subjects ran into Holes and
Corners; but many of them were found and carried off (as I was told by
one who stood near me) either to Prisons or Cellars, Solitude, or little
Company, the meaner Arts or the viler Crafts of Life. But these, added
he with a disdainful Air, are such who would fondly live here, when
their Merits neither matched the Lustre of the Place, nor their Riches
its Expences. We have seen such Scenes as these before now; the Glory
you saw will all return when the Hurry is over. I thanked him for his
Information, and believing him so incorrigible as that he would stay
till it was his Turn to be taken, I made off to the Door, and overtook
some few, who, though they would not hearken to
Plain-dealing
, were
now terrified to good purpose by the Example of others: But when they
had touched the Threshold, it was a strange Shock to them to find that
the Delusion of
Errour
was gone, and they plainly discerned the
Building to hang a little up in the Air without any real Foundation. At
first we saw nothing but a desperate Leap remained for us, and I a
thousand times blamed my unmeaning Curiosity that had brought me into so
much Danger. But as they began to sink lower in their own Minds,
methought the Palace sunk along with us, till they were arrived at the
due Point of
Esteem
which they ought to have for themselves; then the
Part of the Building in which they stood touched the Earth, and we
departing out, it retired from our Eyes. Now, whether they who stayed in
the Palace were sensible of this Descent, I cannot tell; it was then my
Opinion that they were not. However it be, my Dream broke up at it, and
has given me Occasion all my Life to reflect upon the fatal Consequences
of following the Suggestions of
Vanity
.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I write to you to de
Sir e, that you would again touch upon a certain
Enormity, which is chiefly in Use among the Politer and better-bred
Part of Mankind; I mean the Ceremonies, Bows, Courtsies, Whisperings,
Smiles, Winks, Nods, with other familiar Arts of Salutation, which
take up in our Churches so much Time, that might be better employed,
and which seem so utterly inconsistent with the Duty and true Intent
of our entering into those Religious Assemblies. The Resemblance which
this bears to our indeed proper Behaviour in Theatres, may be some
Instance of its Incongruity in the above-mentioned Places. In
Roman
Catholick Churches and Chappels abroad, I my self have observed, more
than once, Persons of the first Quality, of the nearest Relation, and
intimatest Acquaintance passing by one another unknowing as it were
and unknown, and with so little Notices of each other, that it looked
like having their Minds more suitably and more solemnly engaged; at
least it was an Acknowledgment that they ought to have been so. I have
been told the same even of the
Mahometans, with relation to the
Propriety of their Demeanour in the Conventions of their erroneous
Worship: And I cannot but think either of them sufficient and laudable
Patterns for our Imitation in this Particular.
'I cannot help upon this Occasion remarking on the excellent Memories
of those Devotionists, who upon returning from Church shall give a
particular Account how two or three hundred People were dressed; a
Thing, by reason of its Variety, so difficult to be digested and fixed
in the Head, that 'tis a Miracle to me how two poor Hours of
Divine Service can be Time sufficient for so elaborate an undertaking,
the Duty of the Place too being jointly and, no doubt, oft
pathetically performed along with it. Where it is
said in Sacred Wit,
that
the Woman ought to have a Covering on her Head, because of the
Angels2 that last Word is by some thought to be metaphorically
used, and to signify young Men. Allowing this Interpretation to be
right, the Text may not appear to be wholly foreign to our present
Purpose.
'When you are in a Disposition proper for writing on such a Subject, I
earnestly recommend this to you, and am,
Sir ,
Your very humble Servant.
T.
Thomas Parnell, the writer of this allegory, was the son of
a commonwealthsman, who at the Restoration ceased to live on his
hereditary lands at Congleton, in Cheshire, and bought an estate in
Ireland. Born in 1679, at Dublin, where he became M.A. of Trinity
College, in 1700 he was ordained after taking his degree, and in 1705
became Archdeacon of Clogher. At the same time he took a wife, who died
in 1711. Parnell had been an associate of the chief Whig writers, had
taste as a poet, and found pleasure in writing for the papers of the
time. When the Whigs went out of power in Queen Anne's reign, Parnell
connected himself with the Tories. On the warm recommendation of Swift,
he obtained a prebend in 1713, and in May, 1716, a vicarage in the
diocese of Dublin, worth £400 a year. He died in July, 1717, aged 38.
Inheriting his father's estates in Cheshire and Ireland, Pamell was not
in need. Wanting vigour and passion, he was neither formidable nor
bitter as a political opponent, and in 1712 his old friends, Steele and
Addison, were glad of a paper from him; though, with Swift, he had gone
over to the other side in politics.
I
Corinthians
xi. 10.
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 19, 1712 |
Steele |
—Non Ego credulus illis—
Virg.

For want of Time to substitute something else in the Room of them, I am
at present obliged to publish Compliments above my Desert in the
following Letters. It is no small Satisfaction, to have given Occasion
to ingenious Men to employ their Thoughts upon sacred Subjects, from the
Approbation of such Pieces of Poetry as they have seen in my
Saturday's
Papers. I shall never publish Verse on that Day but what is
written by the same Hand; yet shall I not accompany those Writings with
Eulogiums
, but leave them to speak for themselves.
For the SPECTATOR.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You very much promote the Interests of Virtue, while you reform the
Taste of a Prophane Age, and persuade us to be entertained with Divine
Poems, while we are distinguished by so many thousand Humours, and
split into so many different Sects and Parties; yet Persons of every
Party, Sect, and Humour are fond of conforming their Taste to yours.
You can transfuse your own Relish of a Poem into all your Readers,
according to their Capacity to receive; and when you recommend the
pious Passion that reigns in the Verse, we seem to feel the Devotion,
and grow proud and pleas'd inwardly, that we have Souls capable of
relishing what the
Spectator approves.
'Upon reading the Hymns that you have published in some late Papers, I
had a Mind to try Yesterday whether I could write one. The 114th
Psalm appears to me an admirable Ode, and I began to turn it into
our Language. As I was describing the Journey of
Israel from
Egypt, and added the Divine Presence amongst them, I perceived a
Beauty in the
Psalm which was entirely new to me, and which I was
going to lose; and that is, that the Poet utterly conceals the
Presence of God in the Beginning of it, and rather lets a Possessive
Pronoun go without a Substantive, than he will so much as mention any
thing of Divinity there.
Judah was his Sanctuary, and Israel
his
Dominion or Kingdom. The Reason now seems evident, and this Conduct
necessary: For if God had appeared before, there could be no wonder
why the Mountains should leap and the Sea retire; therefore that this
Convulsion of Nature may be brought in with due Surprise, his Name is
not mentioned till afterward, and then with a very agreeable Turn of
Thought God is introduced at once in all his Majesty. This is what I
have attempted to imitate in a Translation without Paraphrase, and to
preserve what I could of the Spirit of the sacred Author.
'If the following Essay be not too incorrigible, bestow upon it a few
Brightnings from your Genius, that I may learn how to write better, or
to write no more.
Your daily Admirer, and humble Servant1, &c.
| I |
When Israel, freed from Pharaoh's Hand,
Left the proud Tyrant and his Land,
The Tribes with chearful Homage own
Their King, and Judah was his Throne. |
| II |
Across the Deep their Journey lay,
The Deep divides to make them Way;
The Streams of Jordan saw, and fed
With backward Current to their Head. |
| III |
The Mountains shook like frighted Sheep,
Like Lambs the little Hillocks leap;
Not Sinai on her Base could stand,
Conscious of Sovereign Power at hand. |
| IV |
What Power could make the Deep divide?
Make Jordan backward roll his Tide?
Why did ye leap, ye little Hills?
And whence the Fright that Sinai feels? |
| V |
Let every Mountain, every Flood
Retire, and know th' approaching God,
The King of Israel: See him here;
Tremble thou Earth, adore and fear. |
| VI |
He thunders, and all Nature mourns:
The Rock to standing Pools he turns;
Flints spring with Fountains at his Word,
And Fires and Seas confess their Lord. |
Mr. SPECTATOR,
There are those who take the Advantage of your putting an Half-penny
Value upon your self above the rest of our daily Writers, to defame
you in publick Conversation, and strive to make you unpopular upon the
Account of this said Half-penny. But if I were you, I would insist
upon that small Acknowledgment for the superior Merit of yours, as
being a Work of Invention. Give me Leave therefore to do you Justice,
and say in your Behalf what you cannot your self, which is, That your
Writings have made Learning a more necessary Part of good Breeding
than it was before you appeared: That Modesty is become fashionable,
and Impudence stands in need of some Wit, since you have put them both
in their proper Lights. Prophaneness, Lewdness, and Debauchery are not
now Qualifications, and a Man may be a very fine Gentleman, tho' he is
neither a Keeper nor an Infidel.
I would have you tell the Town the Story of the
Sybills, if they
deny giving you Two-Pence. Let them know, that those sacred Papers
were valued at the same Rate after two Thirds of them were destroyed,
as when there was the whole Set. There are so many of us who will give
you your own Price, that you may acquaint your Non-Conformist Readers,
That they shall not have it, except they come in within such a Day,
under Three-pence. I don't know, but you might bring in the
Date
Obolum Belisario with a good Grace. The Witlings come in Clusters to
two or three Coffee-houses which have left you off, and I hope you
will make us, who fine to your Wit, merry with their Characters who
stand out against it.
I am your most humble Servant.
P. S. I
have lately got the ingenious Authors of Blacking for Shoes,
Powder for colouring the Hair, Pomatum for the Hands, Cosmetick for
the Face, to be your constant Customers; so that your Advertisements
will as much adorn the outward Man, as your Paper does the inward
2.
T.
This letter and the version of the
114th Psalm
are by Dr
Isaac Watts, who was at this time 38 years old, broken down by an attack
of illness, and taking rest and change with his friend
Sir
Thomas Abney,
at Theobalds. Isaac Watts, the son of a Nonconformist schoolmaster at
Southampton, had injured his health by excessive study. After acting for
a time as tutor to the son of
Sir
John Hartupp, he preached his first
sermon in 1698, and three years later became pastor of the Nonconformist
congregation in Mark Lane. By this office he abided, and with
Sir
Thomas
Abney also he abided; his visit to Theobalds, in 1712, being, on all
sides, so agreeable that he stayed there for the remaining 36 years of
his life. There he wrote his
Divine and Moral Songs
for children, his
Hymns
, and his metrical version of the
Psalms
. But his
Horæ Lyricæ
,
published in 1709, had already attracted much attention when he
contributed this Psalm to the
Spectator
. In the Preface to that
collection of
Poems chiefly of the Lyric kind, in Three Books, sacred,
I. to Devotion and Piety. II. To Virtue, Honour, and Friendship. III. To
the Memory of the Dead,
he had argued that Poesy, whose original is
divine, had been desecrated to the vilest purpose, enticed unthinking
youth to sin, and fallen into discredit among some weaker Christians.
'They submit indeed to use it in divine psalmody, but they love the
driest translation of the Psalms best.' Watts bade them look into their
Bibles and observe the boldness of its poetic imagery, rejected the
dictum of Boileau, that
De la foy d'un Chrétien les mystères terribles
D'ornemens egayéz ne sont point susceptibles;
and pointed to the way he had chosen for himself as a Biblical rhymer.
Poesy, he reminds his readers, is, as his title indicates, not the business of
his life.
'And if I seized those hours of leisure, wherein my soul was in a more
sprightly frame, to entertain them or myself with a divine or moral
song, I hope I shall find an easy pardon.'
Watts died in 1748, aged 74.
Written in jest, but 'The Famous Spanish Blacking for
Gentlemen's Shoes,' and 'The famous Bavarian Red Liquor which gives such
a delightful blushing colour to the cheeks,' had long been advertised in
the
Spectator
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 20, 1712 |
Steele |
Nil ego prætulerem Jucundo sanus amico.
Hor.

People are not aware of the very great Force which Pleasantry in Company
has upon all those with whom a Man of that Talent converses. His Faults
are generally overlooked by all his Acquaintance, and a certain
Carelessness that constantly attends all his Actions, carries him on
with greater Success, than Diligence and Assiduity does others who have
no Share of this Endowment.
Dacinthus
breaks his Word upon all
Occasions both trivial and important; and when he is sufficiently railed
at for that abominable Quality, they who talk of him end with,
After
all he is a very pleasant Fellow. Dacinthus
is an ill-natured Husband,
and yet the very Women end their Freedom of Discourse upon this Subject,
But after all he is very pleasant Company.
Dacinthus
is neither in
point of Honour, Civility, good Breeding, or good Nature
unexceptionable, and yet all is answered,
For he is a very pleasant
Fellow.
When this Quality is conspicuous in a Man who has, to accompany
it, manly and virtuous Sentiments, there cannot certainly be any thing
which can give so pleasing Gratification as the Gaiety of such a Person;
but when it is alone, and serves only to gild a Crowd of ill Qualities,
there is no Man so much to be avoided as your pleasant Fellow. A very
pleasant Fellow shall turn your good Name to a Jest, make your Character
contemptible, debauch your Wife or Daughter, and yet be received by the
rest of the World with Welcome where-ever he appears. It is very
ordinary with those of this Character to be attentive only to their own
Satisfactions, and have very little Bowels for the Concerns or Sorrows
of other Men; nay, they are capable of purchasing their own Pleasures at
the Expence of giving Pain to others. But they who do not consider this
sort of Men thus carefully, are irresistibly exposed to his
Insinuations. The Author of the following Letter carries the Matter so
high, as to intimate that the Liberties of
England
have been at the
Mercy of a Prince merely as he was of this pleasant Character.
Mr. Spectator,
'There is no one Passion which all Mankind so naturally give into as
Pride, nor any other Passion which appears in such different
Disguises: It is to be found in all Habits and all Complexions. Is it
not a Question, whether it does more Harm or Good in the World? And if
there be not such a Thing as what we may call a virtuous and laudable
Pride?
'It is this Passion alone, when misapplyed, that lays us so open to
Flatterers; and he who can agreeably condescend to sooth our Humour or
Temper, finds always an open Avenue to our Soul; especially if the
Flatterer happen to be our Superior.
'One might give many Instances of this in a late
English Monarch,
under the Title of,
The Gayeties of King Charles II. This Prince was
by Nature extreamly familiar, of very easie Access, and much delighted
to see and be seen; and this happy Temper, which in the highest Degree
gratified his Peoples Vanity, did him more Service with his loving
Subjects than all his other Virtues, tho' it must be confessed he had
many. He delighted, tho' a mighty King, to give and take a Jest, as
they say; and a Prince of this fortunate Disposition, who were
inclined to make an ill Use of his Power, may have any thing of his
People, be it never so much to their Prejudice. But this good King
made generally a very innocent Use, as to the Publick, of this
ensnaring Temper; for, 'tis well known, he pursued Pleasure more than
Ambition: He seemed to glory in being the first Man at Cock-matches,
Horse-races, Balls, and Plays; he appeared highly delighted on those
Occasions, and never failed to warm and gladden the Heart of every
Spectator. He more than once dined with his good Citizens of
London
on their Lord-Mayor's Day, and did so the Year that
Sir Robert Viner
was Mayor.
Sir Robert was a very loyal Man, and, if you will allow
the Expression, very fond of his Sovereign; but what with the Joy he
felt at Heart for the Honour done him by his Prince, and thro' the
Warmth he was in with continual toasting Healths to the Royal Family,
his Lordship grew a little fond of his Majesty, and entered into a
Familiarity not altogether so graceful in so publick a Place. The King
understood very well how to extricate himself on all kinds of
Difficulties, and with an Hint to the Company to avoid Ceremony, stole
off and made towards his Coach, which stood ready for him in
Guild-Hall Yard: But the Mayor liked his Company so well, and was
grown so intimate, that he pursued him hastily, and catching him fast
by the Hand, cryed out with a vehement Oath and Accent,
Sir , You
shall stay and take t'other Bottle. The airy Monarch looked kindly at
him over his Shoulder, and with a Smile and graceful Air, (for I saw
him at the Time, and do now)
repeated this Line of the old Song;
He that's drunk is as great as a King.
and immediately
turned1 back and complied with his Landlord.
I give you this Story, Mr. SPECTATOR, because, as I said, I saw the
Passage; and I assure you it's very true, and yet no common one; and
when I tell you the Sequel, you will say I have yet a better Reason
for't.
This very Mayor afterwards erected a Statue of his merry
Monarch in
Stocks-Market2, and did the Crown many and great
Services; and it was owing to this Humour of the King, that his Family
had so great a Fortune shut up in the Exchequer of their pleasant
Sovereign. The many good-natured Condescensions of this Prince are
vulgarly known: and
it is excellently said of him by a great Hand
which writ his Character,
That he was not a King a Quarter of an Hour
together in his whole Reign3. He would receive Visits even from
Fools and half Mad-men, and at Times I have met with People who have
Boxed, fought at Back-sword, and taken Poison before King
Charles
II. In a Word, he was so pleasant a Man, that no one could be
sorrowful under his Government. This made him capable of baffling,
with the greatest Ease imaginable, all Suggestions of Jealousie, and
the People could not entertain Notions of any thing terrible in him,
whom they saw every way agreeable. This Scrap of the familiar Part of
that Prince's History I thought fit to send you, in compliance to the
Request you lately made to your Correspondents.
I am, Sir ,
Your most humble Servant.
T.
return'd
Stocks-market, upon the site of which the Mansion House was
built in 1738, received its name from a pair of stocks erected near it
as early as the year 1281.
Sir
Robert Viner here erected, in 1675, his
white marble statue of Charles II., that he bought a bargain at Leghorn.
It was a statue of John Sobieski trampling on a Turk, which had been
left on the sculptor's hands, but his worship the Mayor caused a few
alterations to be made for the conversion of Sobieski into Charles, and
the Turk (still with a turban on his head) into Oliver Cromwell. After
the building of the Mansion House this statue lay as lumber in an inn
yard till, in 1779, the Corporation gave it to a descendant of the
Mayor, who had the reason above given for reverencing Charles II.
Sheffield, Duke of Buckingham.
Contents
|
Thursday, August 21, 1712 |
Addison |
Omnia quæ sensu volvuntur vota diurno
Pectore sopito reddit amica quies.
Venator defessa toro cùm membra reponit
Mens tamen ad sylvas et sua lustra redit.
Judicibus lites, aurigis somnia currus,
Vanaque nocturnis meta cavetur equis.
Me quoque Musarum studium sub nocte silenti
Artibus assuetis sollicitare solet.
Claud.

I was lately entertaining my self with comparing
Homer's
Ballance, in
which
Jupiter
is represented as weighing the Fates of
Hector
and
Achilles
, with a Passage of
Virgil
, wherein that Deity is introduced
as weighing the Fates of
Turnus
and
Æneas
. I then considered how the
same way of thinking prevailed in the Eastern Parts of the World, as in
those noble Passages of Scripture, wherein we are told, that the great
King of
Babylon
the Day before his Death, had been weighed in the
Ballance, and been found wanting. In other Places of the Holy Writings,
the Almighty is described as weighing the Mountains in Scales, making
the Weight for the Winds, knowing the Ballancings of the Clouds, and in
others, as weighing the Actions of Men, and laying their Calamities
together in a Ballance.
Milton
, as I
observed in a former Paper,
had an Eye to several of these foregoing Instances, in that beautiful
Description
wherein he represents the Arch-Angel and the Evil Spirit
as addressing themselves for the Combat, but parted by the Ballance
which appeared in the Heavens and weighed the Consequences of such a
Battel.
Th' Eternal to prevent such horrid fray
Hung forth in Heav'n his golden Scales, yet seen
Betwixt Astrea and the Scorpion Sign,
Wherein all things created first he weigh'd,
The pendulous round Earth with ballanc'd Air
In counterpoise, now ponders all events,
Battels and Realms; in these he puts two weights
The sequel each of parting and of fight,
The latter quick up flew, and kickt the Beam:
Which Gabriel spying, thus bespake the Fiend.
Satan, I know thy Strength, and thou know'st mine,
Neither our own, but giv'n; what folly then
To boast what Arms can do, since thine no more
Than Heav'n permits; nor mine, though doubled now
To trample thee as mire: For proof look up,
And read thy Lot in yon celestial Sign
Where thou art weigh'd, and shewn how light, how weak,
If thou resist. The Fiend look'd up, and knew
His mounted Scale aloft; nor more, but fled
Murm'ring, and with him fled the Shades of Night.
These several amusing Thoughts having taken Possession of my Mind some
time before I went to sleep, and mingling themselves with my ordinary
Ideas, raised in my Imagination a very odd kind of Vision. I was,
methought, replaced in my Study, and seated in my Elbow Chair, where I
had indulged the foregoing Speculations, with my Lamp burning by me, as
usual. Whilst I was here meditating on several Subjects of Morality, and
considering the Nature of many Virtues and Vices, as Materials for those
Discourses with which I daily entertain the Publick; I saw, methought, a
Pair of Golden Scales hanging by a Chain of the same Metal over the
Table that stood before me; when on a sudden, there were great Heaps of
Weights thrown down on each side of them. I found upon examining these
Weights, they shewed the Value of every thing that is in Esteem among
Men. I made an Essay of them, by putting the Weight of Wisdom in one
Scale, and that of Riches in another, upon which the latter, to shew its
comparative Lightness, immediately
flew up and kickt the Beam
.
But, before I proceed, I must inform my Reader, that these Weights did
not exert their Natural Gravity, 'till they were laid in the Golden
Ballance, insomuch that I could not guess which was light or heavy,
whilst I held them in my Hand. This I found by several Instances; for
upon my laying a Weight in one of the Scales, which was inscribed by the
Word
Eternity
; tho' I threw in that of Time, Prosperity, Affliction,
Wealth, Poverty, Interest, Success, with many other Weights, which in my
Hand seemed very ponderous, they were not able to stir the opposite
Ballance, nor could they have prevailed, though assisted with the Weight
of the Sun, the Stars, and the Earth.
Upon emptying the Scales, I laid several Titles and Honours, with Pomps,
Triumphs, and many Weights of the like Nature, in one of them, and
seeing a little glittering Weight lie by me, I threw it accidentally
into the other Scale, when, to my great Surprize, it proved so exact a
Counterpoise, that it kept the Ballance in an Equilibrium. This little
glittering Weight was inscribed upon the Edges of it with the Word
Vanity
. I found there were several other Weights which were equally
Heavy, and exact Counterpoises to one another; a few of them I tried, as
Avarice and Poverty, Riches and Content, with some others.
There were likewise several Weights that were of the same Figure, and
seemed to Correspond with each other, but were entirely different when
thrown into the Scales; as Religion and Hypocrisie, Pedantry and
Learning, Wit and Vivacity, Superstition and Devotion, Gravity and
Wisdom, with many others.
I observed one particular Weight lettered on both sides, and upon
applying my self to the Reading of it, I found on one side written,
In
the Dialect of Men
, and underneath it,
Calamities
; on the other side
was written,
In the Language of the Gods
, and underneath,
Blessings
.
I found the Intrinsick value of this Weight to be much greater than I
imagined, for it overpowered Health, Wealth, Good Fortune, and many
other Weights, which were much more ponderous in my Hand than the other.
There is a Saying among the
Scotch
, that an Ounce of Mother is worth a
Pound of Clergy; I was sensible of the Truth of this Saying, when I saw
the Difference between the Weight of Natural Parts, and that of
Learning. The Observation which I made upon these two Weights opened to
me a new Field of Discoveries, for notwithstanding the Weight of Natural
Parts was much heavier than that of Learning; I observed that it weighed
an hundred times heavier than it did before, when I put Learning into
the same Scale with it. I made the same Observation upon Faith and
Morality, for notwithstanding the latter out-weighed the former
separately, it received a thousand times more additional Weight from its
Conjunction with the former, than what it had by it self. This odd
Phænomenon shewed it self, in other Particulars, as in Wit and Judgment,
Philosophy and Religion, Justice and Humanity, Zeal and Charity, Depth
of Sense and Perspicuity of Style, with innumerable other Particulars
too long to be mentioned in this Paper.
As a Dream seldom fails of dashing Seriousness with Impertinence, Mirth
with Gravity, methought I made several other Experiments of a more
ludicrous Nature, by one of which I found that an
English
Octavo was
very often heavier than a
French
Folio; and by another, that an old
Greek
or
Latin
Author weighed down a whole Library of Moderns.
Seeing one of my
Spectators
lying by me, I laid it into one of the
Scales, and flung a two-penny Piece into the other. The Reader will not
enquire into the Event, if he remembers the first Tryal which I have
recorded in this Paper. I afterwards threw both the Sexes into the
Ballance; but as it is not for my Interest to disoblige either of them,
I shall de
Sir
e to be excused from telling the Result of this Experiment.
Having an Opportunity of this Nature in my Hands, I could not forbear
throwing into one Scale the Principles of a Tory, and into the other
those of a Whig; but as I have all along declared this to be a Neutral
Paper, I shall likewise de
Sir
e to be silent under this Head also, though
upon examining one of the Weights, I saw the Word
TEKEL
Engraven on it
in Capital Letters.
I made many other Experiments, and though I have not Room for them all
in this Day's Speculation, I may perhaps reserve them for another. I
shall only add, that upon my awaking I was sorry to find my Golden
Scales vanished, but resolved for the future to learn this Lesson from
them, not to despise or value any Things for their Appearances, but to
regulate my Esteem and Passions towards them according to their real and
intrinsick Value.
C.
Paradise Lost
, end of Book IV.
Contents
|
Friday, August 22, 1712 |
Addison |
Auream quisquis mediocritatem
Diligit, tutus caret obsoleti
Sordibus tecti, caret invidendâ
Sobrius aulâ.
Hor.

I am wonderfully pleased when I meet with any Passage in an old
Greek
or
Latin
Author, that is not blown upon, and which I have never met
with in a Quotation. Of this kind is a beautiful Saying in
Theognis
;
Vice is covered by Wealth, and Virtue by Poverty
; or to give it in the
Verbal Translation,
Among Men there are some who have their Vices
concealed by Wealth, and others who have their Virtues concealed by
Poverty.
Every Man's Observation will supply him with Instances of Rich
Men, who have several Faults and Defects that are overlooked, if not
entirely hidden, by means of their Riches; and, I think, we cannot find
a more Natural Description of a Poor Man, whose Merits are lost in his
Poverty, than that in the Words of the Wise Man.
There was a little
City, and a few Men within it; and there came a great King against it,
and besieged it, and built great Bulwarks against it: Now there was
found in it a poor Wise Man, and he, by his Wisdom, delivered the City;
yet no Man remembered that same poor Man. Then said I, Wisdom is better
than Strength; nevertheless, the poor Man's Wisdom is despised, and his
Words are not heard.
The middle Condition seems to be the most advantageously situated for
the gaining of Wisdom. Poverty turns our Thoughts too much upon the
supplying of our Wants, and Riches upon enjoying our Superfluities; and,
as
Cowley
has said in another Case,
It is hard for a Man to keep a
steady Eye upon Truth, who is always in a Battel or a Triumph.
If we regard Poverty and Wealth, as they are apt to produce Virtues or
Vices in the Mind of Man, one may observe, that there is a Set of each
of these growing out of Poverty, quite different from that which rises
out of Wealth. Humility and Patience, Industry and Temperance, are very
often the good Qualities of a poor Man. Humanity and Good-nature,
Magnanimity, and a Sense of Honour, are as often the Qualifications of
the Rich. On the contrary, Poverty is apt to betray a Man into Envy,
Riches into Arrogance. Poverty is too often attended with Fraud, vicious
Compliance, Repining, Murmur and Discontent; Riches expose a Man to
Pride and Luxury, a foolish Elation of Heart, and too great a Fondness
for the present World. In short, the middle Condition is most eligible
to the Man who would improve himself in Virtue; as I have before shewn,
it is the most advantageous for the gaining of Knowledge. It was upon
this Consideration that
Agur
founded his Prayer, which for the Wisdom
of it is recorded in
Writ.
Two things have I required of thee,
deny me them not before I die. Remove far from me Vanity and Lies; give
me neither Poverty, nor Riches; feed me with Food convenient for me.
Lest I be full and deny thee, and say, who is the Lord? or lest I be
poor and steal, and take the name of my God in vain.
I shall
the remaining Part of my Paper with a very pretty Allegory,
which is wrought into a Play
by
Aristophanes
the
Greek
Comedian.
It seems originally designed as a Satyr upon the Rich, though, in some
Parts of it, 'tis like the foregoing Discourse, a kind of Comparison
between Wealth and Poverty.
Chremylus
, who was an old and a good Man, and withal exceeding Poor,
being de
Sir
ous to leave some Riches to his Son, consults the Oracle of
Apollo
upon the Subject. The Oracle bids him follow the first Man he
should see upon his going out of the Temple. The Person he chanced to
see was to Appearance an old sordid blind Man, but upon his following
him from Place to Place, he at last found by his own Confession, that he
was
Plutus
the God of Riches, and that he was just come out of the
House of a Miser.
Plutus
further told him, that when he was a Boy, he
used to declare, that as soon as he came to Age he would distribute
Wealth to none but virtuous and just Men; upon which
Jupiter
,
considering the pernicious Consequences of such a Resolution, took his
Sight away from him, and left him to strole about the World in the Blind
Condition wherein
Chremylus
beheld him. With much ado
Chremylus
prevailed upon him to go to his House, where he met an old Woman in a
tattered Raiment, who had been his Guest for many Years, and whose Name
was
Poverty
. The old Woman refusing to turn out so easily as he would
have her, he threatned to banish her not only from his own House, but
out of all
Greece
, if she made any more Words upon the Matter.
Poverty
on this Occasion pleads her Cause very notably, and represents
to her old Landlord, that should she be driven out of the Country, all
their Trades, Arts and Sciences would be driven out with her; and that
if every one was Rich, they would never be supplied with those Pomps,
Ornaments and Conveniences of Life which made Riches de
Sir
able. She
likewise represented to him the several Advantages which she bestowed
upon her Votaries, in regard to their Shape, their Health, and their
Activity, by preserving them from Gouts, Dropsies, Unweildiness, and
Intemperance. But whatever she had to say for her self, she was at last
forced to troop off.
Chremylus
immediately considered how he might
restore
Plutus
to his Sight; and in order to it conveyed him to the
Temple of
Æsculapius
, who was famous for Cures and Miracles of this
Nature. By this means the Deity
his Eyes, and begun to make a
right use of them, by enriching every one that
was
distinguished
by Piety
the Gods, and Justice towards
Men
and at the same
time by taking away his Gifts from the Impious and Undeserving. This
produces several merry Incidents, till in the last Act
Mercury
descends with great Complaints from the Gods, that since the Good Men
were grown Rich they had received no Sacrifices, which is confirmed by a
Priest of
Jupiter
, who enters with a Remonstrance, that since this
late Innovation he was reduced to a starving Condition, and could not
live upon his Office.
Chremylus
, who in the beginning of the Play was
Religious in his Poverty, concludes it with a Proposal which was
relished by all the Good Men who were now grown rich as well as himself,
that they should carry
Plutus
in a Solemn Procession to the Temple,
and Install him in the Place of
Jupiter
. This Allegory instructed the
Athenians
in two Points, first, as it vindicated the Conduct of
Providence in its ordinary Distributions of Wealth; and in the next
Place, as it shewed the great Tendency of Riches to corrupt the Morals
of those who possessed them.
C.
Eccl
. ix. 14-16.
Proverbs
xxx. 7-9.
The Plutus.
were
Man
Contents
|
Saturday, August 23, 1712 |
Addison |
Quâ ratione queas traducere leniter ævum:
Ne te semper inops agitet vexetque cupido;
Ne pavor et rerum mediocriter utilium Spes.
Hor.

Having endeavoured in my last
Saturday's
Paper to shew the great
Excellency of Faith, I here consider what are proper Means of
strengthning and confirming it in the Mind of Man. Those who delight in
reading Books of Controversie, which are written on both sides of the
Question in Points of Faith, do very seldom arrive at a fixed and
settled Habit of it. They are one Day entirely convinced of its
important Truths, and
next meet with something that shakes and
disturbs them. The Doubt
which
was laid revives again, and shews
it self in new Difficulties, and that generally for this Reason, because
the Mind which is perpetually tost in Controversies and Disputes, is apt
to forget the Reasons which had once set it at rest, and to be
disquieted with any former Perplexity, when it appears in a new Shape,
or is started by a different Hand. As nothing is more laudable than an
Enquiry after Truth, so nothing is more irrational than to pass away our
whole Lives, without determining our selves one way or other in those
Points which are of the last Importance to us. There are indeed many
things from which we may with-hold our Assent; but in Cases by which we
are to regulate our Lives, it is the greatest Absurdity to be wavering
and unsettled, without closing with that Side which appears the most
safe and [the] most probable. The first Rule therefore which I shall lay
down is this, that when by Reading or Discourse we find our selves
thoroughly convinced of the Truth of any Article, and of the
Reasonableness of our Belief in it, we should never after suffer our
selves to call it into question. We may perhaps forget the Arguments
which occasioned our Conviction, but we ought to remember the Strength
they had with us, and therefore still to retain the Conviction which
they once produced. This is no more than what we do in every common Art
or Science, nor is it possible to act otherwise, considering the
Weakness and Limitation of our Intellectual Faculties. It was thus, that
Latimer
, one of the glorious Army of Martyrs who introduced the
Reformation in
England
, behaved himself in that great Conference which
was managed between the most learned among the Protestants and Papists
in the Reign of Queen
Mary
. This venerable old Man knowing how his
Abilities were impaired by Age, and that it was impossible for him to
recollect all those Reasons which had directed him in the Choice of his
Religion, left his Companions who were in the full Possession of their
Parts and Learning, to baffle and confound their Antagonists by the
Force of Reason. As for himself he only repeated to his Adversaries the
Articles in which he firmly believed, and in the Profession of which he
was determined to die. It is in this manner that the Mathematician
proceeds upon the Propositions which he has once demonstrated; and
though the Demonstration may have slipt out of his Memory, he builds
upon the Truth, because he knows it was demonstrated. This Rule is
absolutely necessary for weaker Minds, and in some measure for Men of
the greatest Abilities; but to these last I would propose, in the second
place, that they should lay up in their Memories, and always keep by
them in a readiness, those Arguments which appear to them of the
greatest Strength, and which cannot be got over by all the Doubts and
Cavils of Infidelity.
But, in the third place, there is nothing which strengthens Faith more
than Morality. Faith and Morality naturally produce each other. A Man is
quickly convinced of the Truth of Religion, who finds it is not against
his Interest that it should be true. The Pleasure he receives at
Present, and the Happiness which he promises himself from it hereafter,
will both dispose him very powerfully to give Credit to it, according to
the ordinary Observation that
we are easie to believe what we wish
. It
is very certain, that a Man of sound Reason cannot forbear closing with
Religion upon an impartial Examination of it; but at the same time it is
as certain, that Faith is kept alive in us, and gathers Strength from
Practice more than from Speculation.
There is still another Method which is more Persuasive than any of the
former, and that is an habitual Adoration of the Supreme Being, as well
in constant Acts of mental Worship, as in outward Forms. The devout Man
does not only believe but feels there is a Deity. He has actual
Sensations of Him; his Experience concurs with his Reason; he sees him
more and more in all his Intercourses with him, and even in this Life
almost loses his Faith in Conviction.
The last Method which I shall mention for the giving Life to a Man's
Faith, is frequent Retirement from the World, accompanied with religious
Meditation. When a Man thinks of any thing in the Darkness of the Night,
whatever deep Impressions it may make in his Mind, they are apt to
vanish as soon as the Day breaks about him. The Light and Noise of the
Day, which are perpetually soliciting his Senses, and calling off his
Attention, wear out of his Mind the Thoughts that imprinted themselves
in it, with so much Strength, during the Silence and Darkness of the
Night. A Man finds the same Difference as to himself in a Crowd and in a
Solitude: the Mind is stunned and dazzled amidst that Variety of Objects
which press upon her in a great City: She cannot apply herself to the
Consideration of these Things which are of the utmost Concern to her.
The Cares or Pleasures of the World strike in with
Thought, and a
Multitude of vicious Examples
give
a kind of Justification
to
our Folly. In our Retirements every thing disposes us to be
serious. In Courts and Cities we are entertained with the Works of Men;
in the Country with those of God. One is the Province of Art, the other
of Nature. Faith and Devotion naturally grow in the Mind of every
reasonable Man, who sees the Impressions of Divine Power and Wisdom in
every Object on which he casts his Eye. The Supream Being has made the
best Arguments for his own Existence, in the Formation of the Heavens
and the Earth, and these are Arguments which a Man of Sense cannot
forbear attending to, who is out of the Noise and Hurry of Human
Affairs.
Aristotle
says, that should a Man live under Ground, and
there converse with Works of Art and Mechanism, and should afterwards be
brought up into the open Day, and see the several Glories of the Heaven
and Earth, he would immediately pronounce them the Works of such a Being
as we define God to be. The
has very beautiful Strokes of
Poetry to this Purpose, in that exalted Strain,
The Heavens declare the
Glory of God: And the Firmament showeth his handy-work. One Day telleth
another: And one Night certifieth another. There is neither Speech nor
Language: But their Voices are heard among them. Their Sound is gone out
into all Lands: And their Words into the Ends of the World.
As such
a bold and sublime manner of Thinking furnishes very noble Matter for an
Ode, the Reader may see it wrought into the following one
.
| I |
The Spacious Firmament on high
With all the blue Etherial Sky,
And spangled Heav'ns, a Shining Frame,
Their great Original proclaim:
Th' unwearied Sun, from Day to Day,
Does his Creator's Pow'r display,
And publishes to every Land
The Work of an Almighty Hand. |
| II |
Soon as the Evening Shades prevail,
The Moon takes up the wondrous Tale,
And nightly to the listning Earth
Repeats the Story of her Birth:
Whilst all the Stars that round her burn,
And all the Planets in their turn,
Confirm the Tidings as they rowl,
And spread the Truth from Pole to Pole. |
| III |
What though, in solemn Silence, all
Move round the dark terrestrial Ball?
What tho' nor real Voice nor Sound
Amid their radiant Orbs be found?
In Reason's Ear they all rejoice,
And utter forth a glorious Voice,
For ever singing, as they shine,
'The Hand that made us is Divine?' |
C.
that
give us
in
Psalm xix. 1-3.
By Addison.
Contents
|
Monday, August 25, 1712 |
Steele |
—Vera incessu patuit Dea.
Virg.

When
Æneas
, the Hero of
Virgil
, is lost in the Wood, and a perfect
Stranger in the Place on which he is landed, he is accosted by a Lady in
an Habit for the Chase. She enquires of him, Whether he has seen pass by
that Way any young Woman dressed as she was? Whether she were following
the Sport in the Wood, or any other Way employed, according to the
Custom of Huntresses? The Hero answers with the Respect due to the
beautiful Appearance she made, tells her, He saw no such Person as she
enquired for: but intimates, that he knows her to be of the Deities, and
de
Sir
es she would conduct a Stranger. Her Form from her first Appearance
manifested she was more than mortal; but tho' she was certainly a
Goddess, the Poet does not make her known to be the Goddess of
Beauty
till she moved: All the Charms of an agreeable Person are then in their
highest Exertion, every Limb and Feature appears with its respective
Grace. It is from this Observation,
I cannot help being so
passionate an Admirer as I am of good Dancing
. As all Art is an
Imitation of Nature, this is an Imitation of Nature in its highest
Excellence, and at a Time when she is most agreeable. The Business of
Dancing is to display Beauty, and for that Reason all Distortions and
Mimickries, as such, are what raise Aversion instead of Pleasure: But
Things that are in themselves excellent, are ever attended with
Imposture and false Imitation. Thus, as in Poetry there are laborious
Fools who write Anagrams and Acrosticks, there are Pretenders in
Dancing, who think meerly to do what others cannot, is to excel. Such
Creatures should be rewarded like him who had acquired a Knack of
throwing a Grain of Corn through the Eye of
Needle, with a Bushel to
keep his Hand in Use. The
Dancers
on our Stages are very faulty in
this Kind; and what they mean by writhing themselves into such Postures,
as it would be a Pain for any of the
Spectators
to stand in, and yet
hope to please those
Spectators
, is unintelligible. Mr.
Prince
has a
Genius, if he were encouraged, would prompt them to better things. In
all the Dances he invents, you see he keeps close to the Characters he
represents. He does not hope to please by making his Performers move in
a manner in which no one else ever did, but by Motions proper to the
Characters he represents. He gives to Clowns and Lubbards clumsie
Graces, that is, he makes them Practise what they would think Graces:
And I have seen Dances of his, which might give Hints that would be
useful to a Comick Writer. These Performances have pleas'd the Taste of
such as have not Reflection enough to know their Excellence, because
they are in Nature; and the distorted Motions of others have offended
those who could not form Reasons to themselves for their Displeasure,
from their being a Contradiction to Nature.
When one considers the inexpressible Advantage there is in arriving at
some Excellence in this Art, it is monstrous to behold it so much
neglected. The following Letter has in it something very natural on this
Subject.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I am a Widower with but one Daughter; she was by Nature much inclined
to be a Romp, and I had no way of educating her, but commanding a
young Woman, whom I entertained to take Care of her, to be very
watchful in her Care and Attendance about her. I am a Man of Business,
and obliged to be much abroad. The Neighbours have told me, that in my
Absence our Maid has let in the Spruce Servants in the Neighbourhood
to Junketings, while my Girl play'd and romped even in the Street. To
tell you the plain Truth, I catched her once, at eleven Years old, at
Chuck-Farthing among the Boys. This put me upon new Thoughts about my
Child, and I determined to place her at a Boarding-School, and at the
same Time gave a very discreet young Gentlewoman her Maintenance at
the same Place and Rate, to be her Companion. I took little Notice of
my Girl from Time to Time, but saw her now and then in good Health,
out of Harm's way, and was satisfied. But by much Importunity I was
lately prevailed with to go to one of their Balls. I cannot express to
you the anxiety my silly Heart was in, when I saw my Romp, now
fifteen, taken out: I never felt the pangs of a Father upon me so
strongly in my whole Life before; and I could not have suffered more,
had my whole Fortune been at Stake. My Girl came on with the most
becoming Modesty I had ever seen, and casting a respectful Eye, as if
she feared me more than all the Audience, I gave a Nod, which, I
think, gave her all the Spirit she assumed upon it, but she rose
properly to that Dignity of Aspect. My Romp, now the most graceful
Person of her Sex, assumed a Majesty which commanded the highest
Respect; and when she turned to me, and saw my Face in Rapture, she
fell into the prettiest Smile, and I saw in all her Motion that she
exulted in her Father's Satisfaction. You, Mr. SPECTATOR, will, better
than I can tell you, imagine to yourself all the different Beauties
and Changes of Aspect in an accomplished young Woman, setting forth
all her Beauties with a Design to please no one so much as her Father.
My Girl's Lover can never know half the Satisfaction that I did in her
that Day. I could not possibly have imagined, that so great
Improvement could have been wrought by an Art that I always held in it
self ridiculous and contemptible. There is, I am convinced, no Method
like this, to give young Women a Sense of their own Value and Dignity;
and I am sure there can be none so expeditious to communicate that
Value to others. As for the flippant insipidly Gay and wantonly
Forward, whom you behold among Dancers, that Carriage is more to be
attributed to the perverse Genius of the Performers, than imputed to
the Art it self. For my Part, my Child has danced her self into my
Esteem, and I have as great an Honour for her as ever I had for her
Mother, from whom she derived those latent good Qualities which
appeared in her Countenance when she was dancing; for my Girl, tho' I
say it my self, shewed in one Quarter of an Hour the innate Principles
of a modest Virgin, a tender Wife, a generous Friend, a kind Mother,
and an indulgent Mistress. I'll strain hard but I will purchase for
her an Husband suitable to her Merit. I am your Convert in the
Admiration of what I thought you jested when you recommended; and if
you please to be at my House on Thursday next, I make a Ball for my
Daughter, and you shall see her Dance, or, if you will do her that
Honour, dance with her. I am, Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
Philipater.
I have some time ago spoken of a Treatise written by Mr.
Weaver
on
this Subject, which is now, I understand, ready to be published. This
Work sets this Matter in a very plain and advantageous Light; and I am
convinced from it, that if the Art was under proper Regulations, it
would be a mechanick way of implanting insensibly in Minds, not capable
of receiving it so well by any other Rules, a Sense of good Breeding and
Virtue.
Were any one to see
Mariamne
Dance, let him be never so sensual a
Brute, I defie him to entertain any Thoughts but of the highest Respect
and Esteem towards her. I was shewed last Week a Picture in a Lady's
Closet, for which she had an hundred different Dresses, that she could
clap on round the Face, on purpose to demonstrate the force of Habits in
the diversity of the same Countenance. Motion, and change of Posture and
Aspect, has an Effect no less surprising on the Person of
Mariamne
when she Dances.
Chloe
is extremely pretty, and as silly as she is pretty. This Ideot
has a very good Ear, and a most agreeable Shape; but the Folly of the
Thing is such, that it Smiles so impertinently, and affects to please so
sillily, that while she Dances you see the Simpleton from Head to Foot.
For you must know (as Trivial as this Art is thought to be) no one ever
was a good Dancer, that had not a good Understanding. If this be a
Truth, I shall leave the Reader to judge from that Maxim, what Esteem
they ought to have for such Impertinents as fly, hop, caper, tumble,
twirl, turn round, and jump over their Heads, and, in a Word, play a
thousand Pranks which many Animals can do better than a Man, instead of
performing to Perfection what the human Figure only is capable of
Performing.
It may perhaps appear odd, that I, who set up for a mighty Lover, at
least, of Virtue, should take so much Pains to recommend what the
soberer Part of Mankind look upon to be a Trifle; but under Favour of
the soberer Part of Mankind, I think they have not enough considered
this Matter, and for that Reason only disesteem it. I must also, in my
own Justification, say that I attempt to bring into the Service of
Honour and Virtue every Thing in Nature that can pretend to give elegant
Delight. It may possibly be proved, that Vice is in it self destructive
of Pleasure, and Virtue in it self conducive to it. If the Delights of a
free Fortune were under proper Regulations, this Truth would not want
much Argument to support it; but it would be obvious to every Man, that
there is a strict Affinity between all Things that are truly laudable
and beautiful, from the highest Sentiment of the Soul, to the most
indifferent Gesture of the Body.
T.
See Nos. [Volume 1 links:
,
], [Volume 2 links:
,
,
].
Dancing
Contents
|
Tuesday, August 26, 1712 |
John Hughes? |
Quodcunque meæ poterunt Audere Camænæ
Seu Tibi par poterunt, seu, quod spes abnuit ultra;
Sive minus; certeque canent minus; omne vovemus
Hoc tibi; ne tanto careat mihi nomine Charta.
Tibull. ad Messalam.

The Love of Praise is a Passion deeply fixed in the Mind of every
extraordinary Person, and those who are most affected with it, seem most
to partake of that Particle of the Divinity which distinguishes Mankind
from the Inferior Creation. The Supreme Being it self is most pleased
with Praise and Thanksgiving; the other Part of our Duty is but an
Acknowledgment of our Faults, whilst this is the immediate Adoration of
his Perfections. 'Twas an excellent Observation, That we then only
despise Commendation when we cease to deserve it:
we have still
extant two Orations of
Tully
and
Pliny
, spoken to the greatest and
best Princes of all the
Roman
Emperors
, who, no doubt, heard with
the greatest Satisfaction, what even the most disinterested Persons, and
at so large a Distance of Time, cannot read without Admiration.
Cæsar
thought his Life consisted in the Breath of Praise, when he professed he
had lived long enough for himself when he had for his Glory; others have
sacrificed themselves for a Name which was not to begin till they were
dead, giving away themselves to purchase a Sound which was not to
commence till they were out of hearing: But by Merit and superior
Excellencies not only to gain, but, whilst living, to enjoy a great and
universal Reputation, is the last Degree of Happiness which we can hope
for here. Bad Characters are dispersed abroad with Profusion, I hope for
example Sake, and (as Punishments are designed by the Civil Power) more
for the deterring the Innocent, than the chastising the Guilty. The Good
are less frequent, whether it be that there are indeed fewer Originals
of this Kind to copy after, or that, thro' the Malignity of our Nature,
we rather delight in the Ridicule than the Virtues we find in others.
However, it is but just, as well as pleasing, even for Variety,
sometimes to give the World a Representation of the bright Side of
humane Nature, as well as the dark and gloomy: The De
Sir
e of Imitation
may, perhaps, be a greater Incentive to the Practice of what is good,
than the Aversion we may conceive at what is blameable; the one
immediately directs you what you should do, whilst the other only shews
you what you should avoid:
I cannot at present do this with more
Satisfaction, than by endeavouring to do some Justice to the Character
of
Manilius
.
It would far exceed my present Design, to give a particular Description
of
Manilius
thro' all the Parts of his excellent Life: I shall now
only draw him in his Retirement, and pass over in Silence the various
Arts, the courtly Manners, and the undesigning Honesty by which he
attained the Honours he has enjoyed, and which now give a Dignity and
Veneration to the Ease he does enjoy. Tis here that he looks back with
Pleasure on the Waves and Billows thro' which he has steered to so fair
an Haven; he is now intent upon the Practice of every Virtue, which a
great Knowledge and Use of Mankind has discovered to be the most useful
to them. Thus in his private domestick Employments he is no less
glorious than in his publick; for 'tis in Reality a more difficult Task
to be conspicuous in a sedentary inactive Life, than in one that is
spent in Hurry and Business; Persons engaged in the latter, like Bodies
violently agitated, from the Swiftness of their Motion have a Brightness
added to them, which often vanishes when they are at Rest; but if it
then still remain, it must be the Seeds of intrinsick Worth that thus
shine out without any foreign Aid or Assistance.
His Liberality in another might almost bear the Name of Profusion; he
seems to think it laudable even in the Excess, like that River which
most enriches when it overflows: But
Manilius
has too perfect a Taste
of the Pleasure of doing good, ever to let it be out of his Power; and
for that Reason he will have a just œconomy, and a splendid Frugality
at home, the Fountain from whence those Streams should flow which he
disperses abroad. He looks with Disdain on those who propose their Death
as the Time when they are to begin their Munificence; he will both see
and enjoy (which he then does in the highest Degree) what he bestows
himself; he will be the living Executor of his own Bounty, whilst they
who have the Happiness to be within his Care and Patronage at once, pray
for the Continuation of his Life, and their own good Fortune. No one is
out of the reach of his Obligations; he knows how, by proper and
becoming Methods, to raise himself to a Level with those of the highest
Rank; and his good Nature is a sufficient Warrant against the Want of
those who are so unhappy as to be in the very lowest.
may say of
him, as
Pindar
bids his Muse say of
Theron
:
Swear, that Theron sure has sworn,
No one near him should be Poor.
Swear, that none e'er had such a graceful Art,
Fortune's Free-Gifts as freely to impart,
With an unenvious Hand, and an unbounded Heart.
Never did
Atticus
succeed better in gaining the universal Love and
Esteem of all Men; nor steer with more Success betwixt the Extreams of
two contending Parties. 'Tis his peculiar Happiness, that while he
espouses neither with an intemperate Zeal, he is not only admired, but,
what is a more rare and unusual Felicity, he is beloved and caressed by
both and I never yet saw any Person of whatsoever Age or Sex, but was
immediately struck with the Merit of
Manilius
. There are many who are
acceptable to some particular Persons, whilst the rest of Mankind look
upon them with Coldness and Indifference but he is the first whose
entire good Fortune it is ever to please and to be pleased, where-ever
he comes to be admired, and where-ever he is absent to be lamented. His
Merit fares like the Pictures of
Raphael
, which are either seen with
Admiration by all, or at least no one dare own he has no Taste for a
Composition which has received so universal an Applause. Envy and Malice
find it against their Interest to indulge Slander and Obloquy. 'Tis as
hard for an Enemy to detract from as for a Friend to add to his Praise.
An Attempt upon his Reputation is a sure lessening of one's own; and
there is but one Way to injure him, which is to refuse him his just
Commendations, and be obstinately silent.
It is below him to catch the Sight with any Care of Dress; his outward
Garb is but the Emblem of his Mind, it is genteel, plain, and
unaffected; he knows that Gold and Embroidery can add nothing to the
Opinion which all have of his Merit, and that he gives a Lustre to the
plainest Dress, whilst 'tis impossible the richest should communicate
any to him. He is still the principal Figure in the Room: He first
engages your Eye, as if there were some Point of Light which shone
stronger upon him than on any other Person.
puts me in mind of a Story of the famous
Bussy d'Amboise
, who
at an Assembly at Court, where every one appeared with the utmost
Magnificence, relying upon his own superior Behaviour, instead of
adorning himself like the rest, put on that Day a plain Suit of Cloaths,
and dressed all his Servants in the most costly gay Habits he could
procure: The Event was, that the Eyes of the whole Court were fixed upon
him, all the rest looked like his Attendants, whilst he alone had the
Air of a Person of Quality and Distinction.
Like
Aristippus
, whatever Shape or Condition he appears in, it still
sits free and easie upon him; but in some Part of his Character, 'tis
true, he differs from him; for as he is altogether equal to the
Largeness of his present Circumstances, the Rectitude of his Judgment
has so far corrected the Inclinations of his Ambition, that he will not
trouble himself with either the De
Sir
es or Pursuits of any thing beyond
his present Enjoyments.
A thousand obliging Things flow from him upon every Occasion, and they
are always so just and natural, that it is impossible to think he was at
the least Pains to look for them. One would think it were the Dæmon of
good Thoughts that discovered to him those Treasures, which he must have
blinded others from seeing, they lay so directly in their Way. Nothing
can equal the Pleasure is taken in hearing him speak, but the
Satisfaction one receives in the Civility and Attention he pays to the
Discourse of others. His Looks are a silent Commendation of what is good
and praise-worthy, and a secret Reproof to what is licentious and
extravagant. He knows how to appear free and open without Danger of
Intrusion, and to be cautious without seeming reserved. The Gravity of
his Conversation is always enlivened with his Wit and Humour, and the
Gaiety of it is tempered with something that is instructive, as well as
barely agreeable. Thus with him you are sure not to be merry at the
Expence of your Reason, nor serious with the Loss of your good Humour;
but, by a happy mixture in his Temper, they either go together, or
perpetually succeed each other. In fine, his whole Behaviour is equally
distant from Constraint and Negligence, and he commands your Respect,
whilst he gains your Heart.
There is in his whole Carriage such an engaging Softness, that one
cannot persuade one's self he is ever actuated by those rougher
Passions, which, where-ever they find Place, seldom fail of shewing
themselves in the outward Demeanour of the Persons they belong to: But
his Constitution is a just Temperature between Indolence on one hand and
Violence on the other. He is mild and gentle, where-ever his Affairs
will give him Leave to follow his own Inclinations; but yet never
failing to exert himself with Vigour and Resolution in the Service of
his Prince, his Country, or his Friend.
Z.
Julius Cæsar and Trajan. Cicero most flattered Cæsar in the
speech
pro Marcello
, but the memorable speech of his before Cæsar was
that for Ligarius, who had borne arms against the new master of Rome in
the African campaign. Cæsar had said,
'Why might we not as well once more hear a speech from Cicero? There
is no doubt that Ligarius is a bad man and an enemy.'
Yet the effect of the speech was that Cæsar was stirred with emotion,
changed colour, and at reference to the battle of Pharsalia,
'he was,' says Plutarch, 'so affected that his body trembled, and some
of the papers he held dropped from his hands, and thus he was
overpowered, and acquitted Ligarius.'
Of Pliny the younger there remains a fulsome Panegyric upon Trajan.
Lord Cowper?
Second Olympic Ode.
Bussy d'Amboise had become famous in England through a
tragedy by George Chapman, often presented in the time of James I., and
revived after the Restoration. In 1691 Chapman's play was produced with
some changes by Thomas D'Urfey. The man himself killed a relation in the
massacre of St. Bartholomew, to get a title, and was trapped and killed
by the Comte de Montsoreau, whose wife he went to seduce.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 27, 1712 |
Steele |
Erat Homo ingeniosus, acutus, acer, et qui plurimum et salis haberet
et fellis, nec candoris minus.
Plin.
Epist.
My Paper is in a kind a Letter of News, but it regards rather what
passes in the World of Conversation than that of Business. I am very
sorry that I have at present a Circumstance before me, which is of very
great
to all who have a Relish for Gayety, Wit, Mirth, or
Humour; I mean the Death of poor
Dick Eastcourt
. I have been
oblig'd to him for so many Hours of Jollity, that it is but a small
Recompence, tho' all I can give him, to pass a Moment or two in Sadness
for the Loss of so agreeable a Man. Poor
Eastcourt
! the last Time I
saw him we were plotting to shew the Town his great Capacity for acting
in its full Light, by introducing him as dictating to a Set of young
Players, in what manner to speak this Sentence, and utter t'other
Passion—He had so exquisite a Discerning of what was defective in any
Object before him, that in an Instant he could shew you the ridiculous
Side of what would pass for beautiful and just, even to Men of no ill
Judgment, before he had pointed at the Failure. He was no less skilful
in the Knowledge of Beauty; and, I dare say, there is no one who knew
him well, but can repeat more well-turned Compliments, as well as smart
Repartees, of Mr.
Eastcourt's
, than of any other Man in
England
.
This was easily to be observed in his inimitable Faculty of telling a
Story, in which he would throw in natural and unexpected Incidents to
make his Court to one Part, and rally the other Part of the Company:
Then he would vary the Usage he gave them, according as he saw them bear
kind or sharp Language. He had the Knack to raise up a pensive Temper,
and mortifie an impertinently gay one, with the most agreeable Skill
imaginable. There are a thousand things which crowd into my Memory,
which make me too much concerned to tell on about him.
Hamlet
holding
up the Skull which the Grave-digger threw to him, with an Account that
it was the Head of the King's Jester, falls into very pleasing
Reflections, and cries out to his Companion,
Alas, poor Yorick! I knew him, Horatio, a Fellow of infinite Jest,
of most excellent Fancy; he hath born me on his Back a thousand times:
And how abhorred my Imagination is now, my Gorge rises at it. Here
hung those Lips that I have kiss'd I know not how oft. Where be your
Gibes now, your Gambols, your Songs, your Flashes of Merriment, that
were wont to set the Table on a Roar: No one now to mock your own
Jeerings: quite Chop-fallen. Now get you to my Lady's Chamber, and
tell her, Let her paint an Inch thick, to this Favour she must come.
Make her laugh at that.
It is an Insolence natural to the Wealthy, to affix, as much as in them
lies, the Character of a Man to his Circumstances. Thus it is ordinary
with them to praise faintly the good Qualities of those below them, and
say, It is very extraordinary in such a Man as he is, or the like, when
they are forced to acknowledge the Value of him whose Lowness upbraids
their Exaltation. It is to this Humour only, that it is to be ascribed,
that a quick Wit in Conversation, a nice Judgment upon any Emergency,
that could arise, and a most blameless inoffensive Behaviour, could not
raise this Man above being received only upon the Foot of contributing
to Mirth and Diversion. But he was as easy under that Condition, as a
Man of so excellent Talents was capable; and since they would have it,
that to divert was his Business, he did it with all the seeming Alacrity
imaginable, tho' it stung him to the Heart that it was his Business. Men
of Sense, who could taste his Excellencies, were well satisfied to let
him lead the Way in Conversation, and play after his own Manner; but
Fools who provoked him to Mimickry, found he had the Indignation to let
it be at their Expence who called for it, and he would shew the Form of
conceited heavy Fellows as Jests to the Company at their own Request, in
Revenge for interrupting him from being a Companion to put on the
Character of a Jester.
What was peculiarly excellent in this memorable Companion, was, that in
the Accounts he gave of Persons and Sentiments, he did not only hit the
Figure of their Faces, and Manner of their Gestures, but he would in his
Narration fall into their very Way of thinking, and this when he
recounted Passages, wherein Men of the best Wit were concerned, as well
as such wherein were represented Men of the lowest Rank of
Understanding. It is certainly as great an Instance of Self-love to a
Weakness, to be impatient of being mimick'd, as any can be imagined.
There were none but the Vain, the Formal, the Proud, or those who were
incapable of amending their Faults, that dreaded him; to others he was
in the highest Degree pleasing; and I do not know any Satisfaction of
any indifferent kind I ever tasted so much, as having got over an
Impatience of seeing my self in the Air he could put me when I have
displeased him. It is indeed to his exquisite Talent this way, more than
any Philosophy I could read on the Subject, that my Person is very
little of my Care; and it is indifferent to me what is said of my Shape,
my Air, my Manner, my Speech, or my Address. It is to poor
Eastcourt
I
chiefly owe that I am arrived at the Happiness of thinking nothing a
Diminution to me, but what argues a Depravity of my Will.
It has as much surprized me as any thing in Nature, to have it
frequently said, That he was not a good Player: But that must be owing
to a Partiality for former Actors in the Parts in which he succeeded
them, and judging by Comparison of what was liked before, rather than by
the Nature of the Thing. When
Man of his Wit and Smartness could put
on an utter Absence of common Sense in his Face as he did in the
Character of
Bulfinch
in the
Northern Lass
and an
of insipid
Cunning and Vivacity in the Character of
Pounce
in the
Tender
Husband
, it is Folly to dispute his Capacity and Success, as he was
an Actor.
Poor
Eastcourt
! let the Vain and Proud be at Rest; thou wilt no more
disturb their Admiration of their dear selves, and thou art no longer to
drudge in raising the Mirth of Stupids, who know nothing of thy Merit,
for thy Maintenance.
It is natural for the Generality of Mankind to run into Reflections upon
our Mortality, when Disturbers of the World are laid at Rest, but to
take no Notice when they who can please and divert are pulled from us:
But for my Part, I cannot but think the Loss of such Talents as the Man
of whom I am speaking was Master of, a more melancholy Instance of
Mortality, than the Dissolution of Persons of never so high Characters
in the World, whose Pretensions were that they were noisy and
mischievous.
But I must grow more succinct, and as a SPECTATOR, give an Account of
this extraordinary Man, who, in his Way, never had an Equal in any Age
before him, or in that wherein he lived. I speak of him as a Companion,
and a Man qualified for Conversation. His Fortune exposed him to an
Obsequiousness towards the worst Sort of Company, but his excellent
Qualities rendered him capable of making the best Figure in the most
refined. I have been present with him among Men of the most delicate
Taste a whole Night, and have known him (for he saw it was de
Sir
ed) keep
the Discourse to himself the most Part of it, and maintain his good
Humour with a Countenance in a Language so delightful, without Offence
to any Person or Thing upon Earth, still preserving the Distance his
Circumstances obliged him to; I say, I have seen him do all this in such
a charming manner, that I am sure none of those I hint at will read
this, without giving him some Sorrow for their abundant Mirth, and one
Gush of Tears for so many Bursts of Laughter. I
it were any Honour
to the pleasant Creature's Memory, that my Eyes are too much suffused to
let me
go on—.
T.
See p. 204, vol. ii. [Volume 2 links:
of
]
By Richard Brome, first acted in 1632.
By Steele.
go on—
It is a felicity his Friends may rejoice in, that he had his Senses,
and used them as he ought to do, in his last Moments. It is remarkable
that his Judgment was in its calm Perfection to the utmost Article,
for when his Wife out of her fondness, deSir ed she might send for a
certain illiterate Humourist (whom he had accompanied in a thousand
mirthful Moments, and whose Insolence makes Fools think he assumes
from conscious Merit) he answered, 'Do what you please, but he won't
come near me.' Let poor Eastcourt's Negligence about this Message
convince the unwary of a triumphant Empiric's Ignorance and
Inhumanity.
This passage, omitted from the reprint, expresses Steele's anger at the
neglect of Estcourt in his last hours by Dr. John Radcliffe, one of the
chief physicians of the time, who as a rough-spoken humourist made many
enemies, and was condemned as an empiric by many of his professional
brethren. When called, in 1699, to attend King William, who asked his
opinion on his swollen ankles, he said, 'I would not have your Majesty's
two legs for your three kingdoms.' His maxim for making a fortune was to
use all men ill, but Mead, it has been observed, made more money by the
opposite method. Not very long after this bitter censure of Radcliffe
for neglect of Estcourt, attempts were made to censure him formally in
the House of Commons for refusal to attend in the last illness of Queen
Anne, although requested to do so by the Privy Council. He denied that
he had been asked to attend. He died himself three months after the
Queen (in 1714, aged 64), his last days embittered by the public odium
following the charge of disrespect to his dying sovereign. He died
unmarried, and left the greater part of his money to beneficent uses,
among them the erection of an infirmary and of the Radcliffe Library in
Oxford.
Contents
|
Thursday, August 28, 1712 |
Addison |
Detrahere aliquid altieri, et hominem hominis incommodo suum augere
commodum, magis est contra naturam, quam mors, quam paupertas, quam
dolor, quam cætera quæ possunt aut corpori accidere, aut rebus
externis.
Tull.

I am perswaded there are few Men of generous Principles, who would seek
after great Places, were it not rather to have an Opportunity in their
Hands of obliging their particular Friends, or those whom they look upon
as Men of Worth, than to procure Wealth and Honour for themselves. To an
honest Mind the best Perquisites of a Place are the Advantages it gives
a Man of doing Good.
Those who are under the great Officers of State, and are the Instruments
by which they act, have more frequent Opportunities for the Exercise of
Compassion, and Benevolence, than their Superiors themselves. These Men
know every little Case that is to come before the Great Man, and if they
are possessed with honest Minds, will consider Poverty as a
Recommendation in the Person who applies himself to them, and make the
Justice of his Cause the most powerful Solicitor in his Behalf. A Man of
this Temper, when he is in a Post of Business, becomes a Blessing to the
Publick: He patronizes the Orphan and the Widow, assists the Friendless,
and guides the Ignorant: He does not reject the Person's Pretensions,
who does not know how to explain them, or refuse doing a good Office for
a Man because he cannot pay the Fee of it. In
, tho' he regulates
himself in all his Proceedings by Justice and Equity, he finds a
thousand
Occasions for all the Good-natured Offices of
Generosity
and Compassion.
A Man is unfit for such a Place of Trust, who is of a sower untractable
Nature, or has any other Passion that makes him uneasie to those who
approach him. Roughness of Temper is apt to discountenance the Timorous
or Modest. The proud Man discourages those from approaching him, who are
of a mean Condition, and who most want his Assistance. The impatient Man
will not give himself time to be informed of the Matter that lies before
him. An Officer with one or more of these unbecoming Qualities, is
sometimes looked upon as a proper Person to keep off Impertinence and
Solicitation from his Superior; but this is a kind of Merit, that can
never attone for the Injustice which may very often arise from it.
There are two other vicious Qualities which render a Man very unfit for
such a Place of Trust. The first of these is a Dilatory Temper, which
commits innumerable Cruelties without Design. The Maxim which several
have laid down for a Man's Conduct in ordinary Life should be inviolable
with a Man in Office, never to think of doing that To-morrow which may
be done To-day. A Man who defers doing what ought to be done, is guilty
of Injustice so long as he defers it. The Dispatch of a good Office is
very often as beneficial to the Solicitor as the good Office it self. In
short, if a Man compared the Inconveniences which another suffers by his
Delays, with the trifling Motives and Advantages which he himself may
reap by such a Delay, he would never be guilty of a Fault which very
often does an irreparable Prejudice to the Person who depends upon him,
and which might be remedied with little Trouble to himself.
But in the last Place, there is no Man so improper to be employed in
Business, as he who is in any degree capable of Corruption; and such an
one is the Man, who, upon any Pretence whatsoever, receives more than
what is the stated and unquestioned Fee of his Office. Gratifications,
Tokens of Thankfulness, Dispatch Money, and the like specious Terms, are
the Pretences under which Corruption very frequently shelters it self.
An honest Man will however look on all these Methods as unjustifiable,
and will enjoy himself better in a moderate Fortune that is gained with
honour and Reputation, than in an overgrown Estate that is cankered with
the Acquisitions of Rapine and Exaction. Were all our Offices discharged
with such an inflexible Integrity, we should not see Men in all Ages,
who grow up to exorbitant Wealth with the Abilities which are to be met
with in an ordinary Mechanick. I cannot but think that such a Corruption
proceeds chiefly from Mens employing the first that offer themselves, or
those who have the Character of shrewd worldly Men, instead of searching
out such as have had a liberal Education, and have been trained up in
the Studies of Knowledge and Virtue.
It has been observed, that Men of Learning who take to Business,
discharge it generally with greater Honesty than Men of the World. The
chief Reason for it I take to be as follows. A Man that has spent his
Youth in Reading, has been used to find Virtue extolled, and Vice
stigmatized. A Man that has past his Time in the World, has often seen
Vice triumphant, and Virtue discountenanced. Extortion, Rapine and
Injustice, which are branded with Infamy in Books, often give a Man a
Figure in the World; while several Qualities which are celebrated in
Authors, as Generosity, Ingenuity and Good-Nature, impoverish and ruin
him. This cannot but have a proportionable Effect on Men, whose Tempers
and Principles are equally Good and Vicious.
There would be at least this Advantage in employing Men of Learning and
Parts in Business, that their Prosperity would set more gracefully on
them, and that we should not see many worthless Persons shot up into the
greatest Figures of Life.
C.
Opportunities of exercising his
Contents
|
Friday, August 29, 1712 |
Addison |
Turpe est difficiles babere nugas,
Et stultus est labor ineptiarum.
Mart.

I have been very often disappointed of late Years, when upon examining
the new Edition of a Classick Author, I have found above half the Volume
taken up with various Readings. When I have expected to meet with a
learned Note upon a doubtful Passage in a
Latin
Poet, I have only been
informed, that such or such Ancient Manuscripts for an
et
write an
ac
, or of some other notable Discovery of the like Importance. Indeed,
when a different Reading gives us a different Sense, or a new Elegance
in an Author, the Editor does very well in taking Notice of it; but when
he only entertains us with the several ways of spelling the same Word,
and gathers together the various Blunders and Mistakes of twenty or
thirty different Transcribers, they only take up the Time of the learned
Reader, and puzzle the Minds of the Ignorant. I have often fancied with
my self how enraged an old
Latin
Author would be, should he see the
several Absurdities in Sense and Grammar, which are imputed to him by
some or other of these various Readings. In one he speaks Nonsense; in
another, makes use of a Word that was never heard of: And indeed there
is scarce a Solecism in Writing which the best Author is not guilty of,
if we may be at Liberty to read him in the Words of some Manuscript,
which the laborious Editor has thought fit to examine in the Prosecution
of his Work.
I question not but the Ladies and pretty Fellows will be very curious to
understand what it is that I have been hitherto talking of. I shall
therefore give them a Notion of this Practice, by endeavouring to write
after the manner of several Persons who make an eminent Figure in the
Republick of Letters. To
end we will suppose that the following
Song
is an old Ode which I present to the Publick in a new
Edition, with the several various Readings which I find of it in former
Editions, and in Ancient Manuscripts. Those who cannot relish the
various Readings, will perhaps find their Account in the Song, which
never before appeared in Print.
My Love was fickle once and changing,
Nor e'er would settle in my Heart;
From Beauty still to Beauty ranging,
In ev'ry Face I found a Dart.
'Twas first a charming Shape enslav'd me,
An Eye then gave the fatal Stroke;
'Till by her Wit Corinna sav'd me,
And all my former Fetters broke.
But now a long and lasting Anguish
For Belvidera I endure;
Hourly I Sigh and hourly Languish,
Nor hope to find the wonted Cure.
For here the false unconstant Lover,
After a thousand Beauties shown,
Does new surprizing Charms discover,
And finds Variety in One.
Various Readings.
Stanza the First, Verse the First.
And changing
.] The
and
in some
Manuscripts is written thus,
&
, but that in the
Cotton
Library
writes it in three distinct Letters.
Verse the Second,
Nor e'er would
.]
Aldus
reads it
ever would
; but
as this would hurt the Metre, we have restored it to its genuine
Reading, by observing that
Synæresis
which had been neglected by
ignorant Transcribers.
Ibid
.
In my Heart
.]
Scaliger
, and others,
on my Heart
.
Verse the Fourth,
I found a Dart
.] The
Vatican
Manuscript for
I
reads
it
, but this must have been the Hallucination of the
Transcriber, who probably mistook the Dash of the
I
for a
T
.
Stanza the Second, Verse the Second.
The fatal Stroke
.]
Scioppius,
Salmasius
and many others, for
the
read
a
, but I have stuck to the
usual Reading.
Verse the Third,
Till by her Wit
.] Some Manuscripts have it
his Wit
,
others
your
, others
their Wit
. But as I find
Corinna
to be the
Name of a Woman in other Authors, I cannot doubt but it should be
her
.
Stanza the third, Verse the First.
A long and lasting Anguish
.] The
German
Manuscript reads
a lasting Passion
, but the Rhyme will not
admit it.
Verse the Second.
For
Belvidera
I endure
.] Did not all the
Manuscripts reclaim, I should change
Belvidera
into
Pelvidera;
Pelvis
being used by several of the Ancient Comick Writers for a
Looking-glass, by which means the Etymology of the Word is very visible,
and
Pelvidera
will signifie a Lady who often looks in her Glass; as
indeed she had very good reason, if she had all those Beauties which our
Poet here ascribes to her.
Verse the Third.
Hourly I sigh and hourly languish
.] Some for the Word
hourly
read
daily
, and others
nightly
; the last has great
Authorities of its side.
Verse the Fourth.
The wonted Cure
.] The Elder
Stevens
reads
wanted
Cure
.
Stanza the Fourth, Verse the Second.
After a thousand Beauties
] In
several Copies we meet with a
Hundred Beauties
by the usual Errour of
the Transcribers, who probably omitted a Cypher, and had not Taste
enough to know that the Word
Thousand
was ten Times a greater
Compliment to the Poet's Mistress than an
Hundred
.
Verse the Fourth.
And finds Variety in one
] Most of the Ancient
Manuscripts have it
in two
. Indeed so many of them concur in this last
reading, that I am very much in doubt whether it ought not to take
place. There are but two Reasons which incline me to the Reading as I
have published it; First, because the Rhime, and, Secondly, because the
Sense is preserved by it. It might likewise proceed from the Oscitancy
of Transcribers, who, to dispatch their Work the sooner, use to write
all Numbers in Cypher, and seeing the Figure 1 following by a little
Dash of the Pen, as is customary in old Manuscripts, they perhaps
mistook the Dash for a second Figure, and by casting up both together
composed out of them the Figure 2. But this I shall leave to the
Learned, without determining any thing in a Matter of so great
Uncertainty.
C.
Song, which by the way is a beautiful Descant upon a
single Thought, like the Compositions of the best Ancient Lyrick Poets,
I say we will suppose this Song
Contents
|
Saturday, August 30, 1712 |
Addison |
The
Time present
seldom affords sufficient Employment to the Mind of
Man. Objects of Pain or Pleasure, Love or Admiration, do not lie thick
enough together in Life to keep the Soul in constant Action, and supply
an immediate Exercise to its Faculties. In order, therefore, to remedy
this Defect, that the Mind may not want Business, but always have
Materials for thinking, she is endowed with certain Powers, that can
recall what is passed, and anticipate what is to come.
That wonderful Faculty, which we call the Memory, is perpetually looking
back, when we have nothing present to entertain us. It is like those
Repositories in several Animals, that are filled with Stores of their
former Food, on which they may ruminate when their present Pasture
fails.
As the Memory relieves the Mind in her vacant Moments, and prevents any
Chasms of Thought by Ideas of what is
past
, we have other Faculties
that agitate and employ her upon what
is to come
. These are the
Passions of Hope and Fear.
By these two Passions we reach forward into Futurity, and bring up to
our present Thoughts Objects that lie hid in the remotest Depths of
Time. We suffer Misery, and enjoy Happiness, before they are in Being;
we can set the Sun and Stars forward, or lose sight of them by wandring
into those retired Parts of Eternity, when the Heavens and Earth shall
be no more.
By the way, who can imagine that the Existence of a Creature is to be
circumscribed by Time, whose Thoughts are not? But I shall, in this
Paper, confine my self to that particular Passion which goes by the Name
of Hope.
Our Actual Enjoyments are so few and transient, that Man would be a very
miserable Being, were he not endowed with this Passion, which gives him
a Taste of those good Things that may possibly come into his Possession.
We should hope for every thing that is good , says the old Poet
Linus, because there is nothing which may not be hoped for, and
nothing but what the Gods are able to give us
. Hope quickens all
the still Parts of Life, and keeps the Mind awake in her most Remiss and
Indolent Hours. It gives habitual Serenity and good Humour. It is a kind
of Vital Heat in the Soul, that cheers and gladdens her, when she does
not attend to it. It makes Pain easie, and Labour pleasant.
Beside these several Advantages which rise from
Hope
, there is another
which is none of the least, and that is, its great Efficacy in
preserving us from setting too high a value on present Enjoyments. The
saying of
Cæsar
is very well known. When he had given away all his
Estate in Gratuities among his Friends, one of them asked what he had
left for himself; to which that great Man replied,
Hope
. His Natural
Magnanimity hindered him from prizing what he was certainly possessed
of, and turned all his Thoughts upon something more valuable that be had
in View. I question not but every Reader will draw a Moral from this
Story, and apply it to himself without my Direction.
The old Story of
Pandora's
Box (which many of the Learned believe was
formed among the Heathens upon the Tradition of the Fall of Man) shews
us how deplorable a State they thought the present Life, without Hope:
To set forth the utmost Condition of Misery they tell us, that our
Forefather, according to the Pagan Theology, had a great Vessel
presented him by
Pandora:
Upon his lifting up the Lid of it, says the
Fable, there flew out all the Calamities and Distempers incident to Men,
from which, till that time, they had been altogether exempt.
Hope
, who
had been enclosed in the Cup with so much bad Company, instead of flying
off with the rest, stuck so close to the Lid of it, that it was shut
down upon her.
I shall make but two Reflections upon what I have hitherto said. First,
that no kind of Life is so happy as that which is full of Hope,
especially when the Hope is well grounded, and when the Object of it is
of an exalted kind, and in its Nature proper to make the Person happy
who enjoys it. This Proposition must be very evident to those who
consider how few are the present Enjoyments of the most happy Man, and
how insufficient to give him an entire Satisfaction and Acquiescence in
them.
My next Observation is this, that a Religious Life is that which most
abounds in a well-grounded Hope, and such an one as is fixed on Objects
that are capable of making us entirely happy. This Hope in a Religious
Man, is much more sure and certain than the Hope of any Temporal
Blessing, as it is strengthened not only by Reason, but by Faith. It has
at the same time its Eye perpetually fixed on that State, which implies
in the very Notion of it the most full and the most compleat Happiness.
I have before shewn how the Influence of Hope in general sweetens Life,
and makes our present Condition supportable, if not pleasing; but a
Religious Hope has still greater Advantages. It does not only bear up
the Mind under her Sufferings, but makes her rejoice in them, as they
may be the Instruments of procuring her the great and ultimate End of
all her Hope.
Religious Hope has likewise this Advantage above any other kind of Hope,
that it is able to revive the
dying
Man, and to fill his Mind not only
with secret Comfort and Refreshment, but sometimes with Rapture and
Transport. He triumphs in his Agonies, whilst the Soul springs forward
with Delight to the great Object which she has always had in view, and
leaves the Body with an Expectation of being re-united to her in a
glorious and joyful Resurrection.
I shall conclude
Essay with those emphatical Expressions of a
lively Hope, which the Psalmist made use of in the midst of those
Dangers and Adversities which surrounded him; for the following Passage
had its present and personal, as well as its future and prophetick
Sense.
I have set the Lord always before me: Because he is at my right Hand,
I shall not be moved. Therefore my Heart is glad, and my Glory
rejoiceth: my Flesh also shall rest in hope. For thou wilt not leave
my Soul in Hell, neither wilt thou suffer thine Holy One to see
Corruption. Thou wilt shew me the Path of Life: in thy Presence is
Fullness of Joy, at thy right Hand there are Pleasures for evermore2.
C.
Translation of the fragment on Hope.
Psal
. xvi. 8—ii.
Contents
|
Monday, September 1, 1712 |
Steele |
—Voluptas
Solamenque mali—
Virg.

I received some time ago a Proposal, which had a Preface to it, wherein
the Author discoursed at large of the innumerable Objects of Charity in
a Nation, and admonished the Rich, who were afflicted with any Distemper
of Body, particularly to regard the Poor in the same Species of
Affliction, and confine their Tenderness to them, since it is impossible
to assist all who are presented to them. The Proposer had been relieved
from a Malady in his Eyes by an Operation performed by
Sir
William
Read
, and being a Man of Condition, had taken a Resolution to maintain
three poor blind Men during their Lives, in Gratitude for that great
Blessing. This Misfortune is so very great and unfrequent, that one
would think, an Establishment for all the Poor under it might be easily
accomplished, with the Addition of a very few others to those Wealthy
who are in the same Calamity. However, the Thought of the Proposer arose
from a very good Motive, and the parcelling of our selves out, as called
to particular Acts of Beneficence, would be a pretty Cement of Society
and Virtue. It is the ordinary Foundation for Mens holding a Commerce
with each other, and becoming familiar, that they agree in the same sort
of Pleasure; and sure it may also be some Reason for Amity, that they
are under one common Distress. If all the Rich who are lame in the Gout,
from a Life of Ease, Pleasure, and Luxury, would help those few who have
it without a previous Life of Pleasure, and add a few of such laborious
Men, who are become lame from unhappy Blows, Falls, or other Accidents
of Age or Sickness; I say, would such gouty Persons administer to the
Necessities of Men disabled like themselves, the Consciousness of such a
Behaviour would be the best Julep, Cordial, and Anodine in the feverish,
faint and tormenting Vicissitudes of that miserable Distemper. The same
may be said of all other, both bodily and intellectual Evils. These
Classes of Charity would certainly bring down Blessings upon an Age and
People; and if Men were not petrifyed with the Love of this World,
against all Sense of the Commerce which ought to be among them, it would
not be an unreasonable Bill for a poor Man in the Agony of Pain,
aggravated by Want and Poverty, to draw upon a sick Alderman after this
Form;
Mr. Basil Plenty,
Sir ,
You have the Gout and Stone, with Sixty thousand Pound Sterling; I
have the Gout and Stone, not worth one Farthing; I shall pray for you,
and deSir e you would pay the Bearer Twenty Shillings for Value
received from,
Sir ,
Your humble Servant,
Lazarus Hopeful.
Cripple-Gate,
Aug. 29, 1712.
The Reader's own Imagination will suggest to him the Reasonableness of
such Correspondence; and diversify them into a thousand Forms; but I
shall close this as I began upon the Subject of Blindness. The following
Letter seems to be written by a Man of Learning, who is returned to his
Study after a Suspence of an Ability to do so. The Benefit he reports
himself to have received, may well claim the handsomest Encomium he can
give the Operator.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Ruminating lately on your admirable Discourses on the
Pleasures of
the Imagination, I began to consider to which of our Senses we are
obliged for the greatest and most important Share of those Pleasures;
and I soon concluded that it was to the
Sight: That is the Sovereign
of the Senses, and Mother of all the Arts and Sciences, that have
refined the Rudeness of the uncultivated Mind to a Politeness that
distinguishes the fine Spirits from the barbarous
Goût of the
great Vulgar and the
small. The Sight is the obliging
Benefactress, that bestows on us the most transporting Sensations that
we have from the various and wonderful Products of Nature. To the
Sight we owe the amazing Discoveries of the Height, Magnitude, and
Motion of the Planets; their several Revolutions about their common
Centre of Light, Heat, and Motion, the
Sun. The
Sight travels yet
farther to the fixed Stars, and furnishes the Understanding with solid
Reasons to prove, that each of them is a
Sun moving on its own Axis
in the Centre of its own Vortex or Turbillion, and performing the same
Offices to its dependant Planets, that our glorious Sun does to this.
But the Enquiries of the
Sight will not be stopped here, but make
their Progress through the immense Expanse to the
Milky Way, and
there divide the blended Fires of the
Galaxy into infinite and
different Worlds, made up of distinct Suns, and their peculiar
Equipages of Planets, till unable to pursue this Track any farther, it
deputes the Imagination to go on to new Discoveries, till it fill the
unbounded Space with endless Worlds.
The
Sight informs the Statuary's Chizel with Power to give Breath to
lifeless Brass and Marble, and the Painter's Pencil to swell the flat
Canvas with moving Figures actuated by imaginary Souls. Musick indeed
may plead another Original, since
Jubal, by the different Falls of
his Hammer on the Anvil, discovered by the Ear the first rude Musick
that pleasd the Antediluvian Fathers; but then the
Sight has not
only reduced those wilder Sounds into artful Order and Harmony, but
conveys that Harmony to the most distant Parts of the World without
the Help of Sound. To the
Sight we owe not only all the Discoveries
of Philosophy, but all the Divine Imagery of Poetry that transports
the intelligent Reader of
Homer,
Milton, and
Virgil.
As the Sight has polished the World, so does it supply us with the
most grateful and lasting Pleasure. Let Love, let Friendship, paternal
Affection, filial Piety, and conjugal Duty, declare the Joys the
Sight bestows on a Meeting after Absence. But it would be endless to
enumerate all the Pleasures and Advantages of
Sight; every one that
has it, every Hour he makes use of it, finds them, feels them, enjoys
them.
Thus as our greatest Pleasures and Knowledge are derived from the
Sight, so has Providence been more curious in the Formation of its
Seat, the Eye, than of the Organs of the other Senses. That stupendous
Machine is compos'd in a wonderful Manner of Muscles, Membranes, and
Humours. Its Motions are admirably directed by the Muscles; the
Perspicuity of the Humours transmit the Rays of Light; the Rays are
regularly refracted by their Figure, the black Lining of the Sclerotes
effectually prevents their being confounded by Reflection. It is
wonderful indeed to consider how many Objects the Eye is fitted to
take in at once, and successively in an Instant, and at the same time
to make a Judgment of their Position, Figure, or Colour. It watches
against our Dangers, guides our Steps, and lets in all the visible
Objects, whose Beauty and Variety instruct and delight.
The Pleasures and Advantages of Sight being so great, the Loss must be
very grievous; of which
Milton, from Experience, gives the most
sensible Idea, both in the third Book of his
Paradise Lost, and in
his
Sampson Agonistes.
To Light in the former.
—Thee I revisit safe,
And feel thy sovereign vital Lamp; but thou
Revisit'st not these Eyes, that roul in vain
To find thy piercing Ray, but find no Dawn.
And a little after,
Seasons return, but not to me returns
Day, or the sweet Approach of Ev'n and Morn,
Or Sight of vernal Bloom, or Summer's Rose,
Or Flocks or Herds, or human Face divine;
But Cloud instead, and ever-during Dark
Surround me: From the chearful Ways of Men
Cut off, and for the Book of Knowledge fair,
Presented—with an universal Blank
Of Nature's Works, to me expung'd and raz'd,
And Wisdom at one Entrance quite shut out.
Again, in
Sampson Agonistes.
—But Chief of all,
O Loss of Sight! of thee I most complain;
Blind among Enemies! O worse than Chains,
Dungeon, or Beggary, or decrepid Age!
Light, the prime Work of God, to me extinct,
And all her various Objects of Delight
Annull'd—
—Still as a Fool,
In Power of others, never in my own,
Scarce half I seem to live, dead more than Half:
O dark! dark! dark! amid the Blaze of Noon:
Irrecoverably dark, total Eclipse,
Without all Hopes of Day!
The Enjoyment of Sight then being so great a Blessing, and the Loss of
it so terrible an Evil, how excellent and valuable is the Skill of
that Artist which can restore the former, and redress the latter? My
frequent Perusal of the Advertisements in the publick News-Papers
(generally the most agreeable Entertainment they afford) has presented
me with many and various Benefits of this kind done to my Countrymen
by that skilful Artist Dr.
Grant, Her Majesty's Oculist
Extraordinary, whose happy Hand has brought and restored to Sight
several Hundreds in less than Four Years. Many
have received Sight by
his Means, who came blind from their Mother's Womb, as in the famous
Instance of
Jones of
Newington1. I my self have been cured by
him of a Weakness in my Eyes next to Blindness, and am ready to
believe any thing that is reported of his Ability this way; and know
that many, who could not purchase his Assistance with Money, have
enjoy'd it from his Charity. But a List of Particulars would swell my
Letter beyond its Bounds, what I have said being sufficient to comfort
those who are in the like Distress, since they may conceive Hopes of
being no longer miserable in this Kind, while there is yet alive so
able an Oculist as Dr. Grant.
I am the
Spectator's humble Servant,
Philanthropus
T.
A Full and True Account of a Miraculous Cure of a young Man
in Newington, &c,
was a pamphlet of 15 pages, published in 1709. William
Jones was not born blind, and little benefited by the operation of the
Doctor Grant, who in this pamphlet puffed himself.
Contents
|
Tuesday, September 2, 1712 |
Steele |
Quid? si quis vultu torvo ferus et pede nudo
Exiguæque togæ simulet textore Catonem;
Virtutemne repræsentet moresque Catonis?
Hor.

To the SPECTATOR.
Sir ,
I am now in the Country, and employ most of my Time in reading, or
thinking upon what I have read. Your paper comes constantly down to
me, and it affects me so much, that I find my Thoughts run into your
Way; and I recommend to you a Subject upon which you have not yet
touched, and that is the Satisfaction some Men seem to take in their
Imperfections, I think one may call it glorying in their
Insufficiency; a certain great Author is of Opinion it is the contrary
to Envy, tho perhaps it may proceed from it. Nothing is so common, as
to hear Men of this Sort, speaking of themselves, add to their own
Merit (as they think) by impairing it, in praising themselves for
their Defects, freely allowing they commit some few frivolous Errors,
in order to be esteemed persons of uncommon Talents and great
Qualifications. They are generally professing an injudicious Neglect
of Dancing, Fencing and Riding, as also an unjust Contempt for
Travelling and the Modern Languages; as for their Part (say they) they
never valued or troubled their Head about them. This panegyrical Satyr
on themselves certainly is worthy of your Animadversion. I have known
one of these Gentlemen think himself obliged to forget the Day of an
Appointment, and sometimes even that you spoke to him; and when you
see em, they hope youll pardon 'em, for they have the worst Memory in
the World. One of em started up tother Day in some Confusion, and
said, Now I think on't, I'm to meet Mr.
Mortmain the Attorney about
some Business, but whether it is to Day or to Morrow, faith, I can't
tell. Now to my certain Knowledge he knew his Time to a Moment, and
was there accordingly. These forgetful Persons have, to heighten their
Crime, generally the best Memories of any People, as I have found out
by their remembring sometimes through Inadvertency. Two or three of em
that I know can say most of our modern Tragedies by Heart. I asked a
Gentleman the other Day that is famous for a Good Carver, (at which
Acquisition he is out of Countenance, imagining it may detract from
some of his more essential Qualifications) to help me to something
that was near him; but he excused himself, and blushing told me, Of
all things he could never carve in his Life; though it can be proved
upon him, that he cuts up, disjoints, and uncases with incomparable
Dexterity. I would not be understood as if I thought it laudable for a
Man of Quality and Fortune to rival the Aquisitions of Artificers, and
endeavour to excel in little handy Qualities; No, I argue only against
being ashamed at what is really Praiseworthy. As these Pretences to
Ingenuity shew themselves several Ways, you'll often see a Man of this
Temper ashamed to be clean, and setting up for Wit only from
Negligence in his Habit. Now I am upon this Head, I can't help
observing also upon a very different Folly proceeding from the same
Cause. As these above-mentioned arise from affecting an Equality with
Men of greater Talents from having the same Faults, there are others
who would come at a Parallel with those above them, by possessing
little Advantages which they want. I heard a young Man not long ago,
who has sense, comfort himself in his Ignorance of
Greek,
Hebrew, and
the
Orientals: At the same Time that he published his Aversion to
those Languages, he said that the Knowledge of 'em was rather a
Diminution than an Advancement of a Man's Character: tho' at the same
Time I know he languishes and repines he is not Master of them
himself. Whenever I take any of these fine Persons, thus detracting
from what they don't understand, I tell them I will complain to you,
and say I am sure you will not allow it an Exception against a thing,
that he who contemns it is an Ignorant in it.
I am, Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
S. P.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I am a Man of a very good Estate, and am honourably in Love. I hope
you will allow, when the ultimate Purpose is honest, there may be,
without Trespass against Innocence, some Toying by the Way. People of
Condition are perhaps too distant and formal on those Occasions; but,
however that is, I am to confess to you, that I have writ some Verses
to atone for my Offence. You profess'd Authors are a little severe
upon us, who write like Gentlemen: But if you are a Friend to Love,
you will insert my Poem. You cannot imagine how much Service it will
do me with my Fair one, as well as Reputation with all my Friends, to
have something of mine in the
Spectator. My Crime was, that I
snatch'd a Kiss, and my Poetical Excuse as follows:
| I |
Belinda, see from yonder Flowers
The Bee flies loaded to its Cell;
Can you perceive what it devours?
Are they impar'd in Show or Smell? |
| II |
So, tho' I robb'd you of a Kiss,
Sweeter than their Ambrosial Dew;
Why are you angry at my Bliss?
Has it at all impoverish'd you? |
| III |
'Tis by this Cunning I contrive,
In spight of your unkind Reserve,
To keep my famish'd Love alive,
Which you inhumanly would starve. |
I am,
Sir ,
Your humble Servant,
Timothy Stanza.
Aug. 23, 1712.
Sir ,
Having a little Time upon my Hands, I could not think of bestowing it
better, than in writing an Epistle to the SPECTATOR, which I now do,
and am,
Sir , Your humble Servant,
BOB SHORT.
P. S. If you approve of my Style, I am likely enough to become your
Correspondent. I de
Sir e your Opinion of it. I design it for that Way
of Writing called by the Judicious the
Familiar.
Contents
Dedication of the Seventh Volume of The Spectator
Sir
It is with very great Pleasure I take an Opportunity of publishing the
Gratitude I owe You, for the Place You allow me in your Friendship and
Familiarity. I will not acknowledge to You that I have often had You in
my Thoughts, when I have endeavoured to Draw, in some Parts of these
Discourses, the Character of a Good-natured, Honest, and Accomplished
Gentleman. But such Representations give my Reader an Idea of a Person
blameless only, or only laudable for such Perfections as extend no
farther than to his own private Advantage and Reputation.
But when I speak of You, I Celebrate One who has had the Happiness of
Possessing also those Qualities which make a Man useful to Society, and
of having had Opportunities of Exerting them in the most Conspicuous
Manner.
The Great Part You had, as
British
Embassador, in Procuring and
Cultivating the Advantageous Commerce between the Courts of
England
and
Portugal
, has purchased you the lasting Esteem of all who
understand the Interest of either Nation.
Those Personal Excellencies which are overrated by the ordinary World,
and too much neglected by Wise Men, You have applied with the justest
Skill and Judgment. The most graceful Address in Horsemanship, in the
Use of the Sword, and in Dancing, has been employed by You as lower
Arts, and as they have occasionally served to recover, or introduce the
Talents of a skilful Minister.
But your Abilities have not appear'd only in one Nation. When it was
your Province to Act as Her Majesty's Minister at the Court of
Savoy
,
at that time encamped, You accompanied that Gallant Prince thro' all the
Vicissitudes of his Fortune, and shared, by His Side, the Dangers of
that Glorious Day in which He recovered His Capital. As far as it
regards Personal Qualities, You attained, in that one Hour, the highest
Military Reputation. The Behaviour of our Minister in the Action, and
the good Offices done the Vanquished in the Name of the Queen of
England
, gave both the Conqueror and the Captive the most lively
Examples of the Courage and Generosity of the Nation He represented.
Your Friends and Companions in your Absence frequently talk these things
of You, and You cannot hide from us, (by the most discreet Silence in
any Thing which regards Your self) that the frank Entertainment we have
at your Table, your easie Condescension in little Incidents of Mirth and
Diversion, and general Complacency of Manners, are far from being the
greatest Obligations we have to You. I do assure You there is not one of
your Friends has a Greater Sense of your Merit in general, and of the
Favours You every Day do us, than,
Sir
,
Your most Obedient, and
most Humble Servant,
Richard
Steele.
Paul Methuen, at the date of this Dedication M.P. for
Brackley, and forty-two years old, was a lawyer who had distinguished
himself as a diplomatist at the Court of Lisbon in 1703, and arranged
the very short commercial treaty between Great Britain and Portugal which
bears his name. Methuen then represented England at the Court of the
Duke of Savory, who deserted the French cause at the end of 1602, and
the ambassador proved his courage also as a combatant when he took part
in the defence and rescue of Turin from the French in 1706. After his
return to England Paul Methuen was made (in 1709) a Commissioner of the
Admirality. In the year 1713 he first sat in Parliament as member of
Brackley. He held afterwards various offices in the States, as those of
Commissioner of the Treasury, Comptroller of the Household, Treasurer of
the Household, Commissioner for inspecting the Law, was made
Sir
Paul
Methuen, Knight of the Bath, and attained his highest dignity as Lord
Chancellor of Ireland before his death in 1757, at the age of 86. The
seventh volume, to which this Dedication is prefixed, is the last of the
original
Spectator
. With the eighth volume, representing an unsuccessful
attempt made to revive it, some time after its demise, Steele had
nothing to do, and that volume is not inscribed to any living person.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 3, 1712 |
Steele |
Asperitas agrestis et inconcinna.
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
Being of the Number of those that have lately retired from the Center
of Business and Pleasure, my Uneasiness in the Country where I am,
arises rather from the Society than the Solitude of it. To be obliged
to receive and return Visits from and to a Circle of Neighbours, who
through Diversity of Age or Inclinations, can neither be entertaining
or serviceable to us, is a vile Loss of Time, and a Slavery from which
a Man should deliver himself, if possible: For why must I lose the
remaining part of my Life, because they have thrown away the former
Part of theirs? It is to me an insupportable Affliction, to be
tormented with the Narrations of a Set of People, who are warm in
their Expressions of the quick Relish of that Pleasure which their
Dogs and Horses have a more delicate Taste of. I do also in my Heart
detest and abhor that damnable Doctrine and Position of the Necessity
of a Bumper, though to one's own Toast; for though 'tis pretended that
these deep Politicians are used only to inspire Gaiety, they certainly
drown that Chearfulness which would survive a moderate Circulation. If
at these Meetings it were left to every Stranger either to fill his
Glass according to his own Inclination, or to make his Retreat when he
finds he has been sufficiently obedient to that of others, these
Entertainments would be governed with more good Sense, and
consequently with more good Breeding, than at present they are. Indeed
where any of the Guests are known to measure their Fame or Pleasure by
their Glass, proper Exhortations might be used to these to push their
Fortunes in this sort of Reputation; but where 'tis unseasonably
insisted on to a modest Stranger, this Drench may be said to be
swallowed with
the same Necessity, as if it had been tendered in the
Horn
1 for that purpose, with this aggravating Circumstance, that it
distresses the Entertainer's Guest in the same degree as it relieves
his Horses.
To attend without Impatience an Account of five-barr'd Gates, double
Ditches, and Precipices, and to survey the Orator with de
Sir ing Eyes,
is to me extremely difficult, but absolutely necessary, to be upon
tolerable Terms with him: but then the occasional Burstings out into
Laughter, is of all other Accomplishments the most requisite. I
confess at present I have not that command of these Convulsions, as is
necessary to be good Company; therefore I beg you would publish this
Letter, and let me be known all at once for a queer Fellow, and
avoided. It is monstrous to me, that we, who are given to Reading and
calm Conversation, should ever be visited by these Roarers: But they
think they themselves, as Neighbours, may come into our Rooms with the
same Right, that they and their Dogs hunt in our Grounds.
Your Institution of Clubs I have always admir'd, in which you
constantly endeavoured the Union of the metaphorically Defunct, that
is such as are neither serviceable to the Busy and Enterprizing part
of Mankind, nor entertaining to the Retir'd and Speculative. There
should certainly therefore in each County be established a Club of the
Persons whose Conversations I have described, who for their own
private, as also the publick Emolument, should exclude, and be
excluded all other Society. Their Attire should be the same with their
Huntsmen's, and none should be admitted into this green
Conversation-Piece, except he had broke his Collar-bone thrice. A
broken Rib or two might also admit a Man without the least Opposition.
The President must necessarily have broken his Neck, and have been
taken up dead once or twice: For the more Maims this Brotherhood shall
have met with, the easier will their Conversation flow and keep up;
and when any one of these vigorous Invalids had finished his Narration
of the Collar-bone, this naturally would introduce the History of the
Ribs. Besides, the different Circumstances of their Falls and
Fractures would help to prolong and diversify their Relations. There
should also be another Club of such Men, who have not succeeded so
well in maiming themselves, but are however in the constant Pursuit of
these Accomplishments. I would by no means be suspected by what I have
said to traduce in general the Body of Fox-hunters; for whilst I look
upon a reasonable Creature full-speed after a Pack of Dogs, by way of
Pleasure, and not of Business, I shall always make honourable mention
of it.
But the most irksome Conversation of all others I have met with in the
Neighbourhood, has been among two or three of your Travellers, who
have overlooked Men and Manners, and have passed through
Franceand
Italywith the same Observation that the Carriers and Stage-Coachmen
do through
Great-Britain;that is, their Stops and Stages have been
regulated according to the Liquor they have met with in their Passage.
They indeed remember the Names of abundance of Places, with the
particular Fineries of certain Churches: But their distinguishing Mark
is certain Prettinesses of Foreign Languages, the Meaning of which
they could have better express'd in their own. The Entertainment of
these fine Observers,
Shakespearhas described to consist
In talking of the Alps and Appennines,
The Pyrenean, and the River Po.2
and then concludes with a Sigh,
Now this is worshipful Society!
I would not be thought in all this to hate such honest Creatures as
Dogs; I am only unhappy that I cannot partake in their Diversions. But
I love them so well, as Dogs, that I often go with my Pockets stuffed
with Bread to dispense my Favours, or make my way through them at
Neighbours' Houses. There is in particular a young Hound of great
Expectation, Vivacity, and Enterprize, that attends my Flights
where-ever he spies me. This Creature observes my Countenance, and
behaves himself accordingly. His Mirth, his Frolick, and Joy upon the
Sight of me has been observed, and I have been gravely de
Sir ed not to
encourage him so much, for it spoils his Parts; but I think he shews
them sufficiently in the several Boundings, Friskings, and Scourings,
when he makes his Court to me: But I foresee in a little time he and I
must keep Company with one another only, for we are fit for no other
in these Parts. Having informd you how I do pass my time in the
Country where I am, I must proceed to tell you how I would pass it,
had I such a Fortune as would put me above the Observance of Ceremony
and Custom.
My Scheme of a Country Life then should be as follows. As I am happy
in three or four very agreeable Friends, these I would constantly have
with me; and the Freedom we took with one another at School and the
University, we would maintain and exert upon all Occasions with great
Courage. There should be certain Hours of the Day to be employ'd in
Reading, during which time it should be impossible for any one of us
to enter the other's Chamber, unless by Storm. After this we would
communicate the Trash or Treasure we had met with, with our own
Reflections upon the Matter; the Justness of which we would controvert
with good-humour'd Warmth, and never spare one another out of the
complaisant Spirit of Conversation, which makes others affirm and deny
the same matter in a quarter of an Hour. If any of the Neighbouring
Gentlemen, not of our Turn, should take it in their heads to visit me,
I should look upon these Persons in the same degree Enemies to my
particular state of Happiness, as ever the French were to that of the
Publick, and I would be at an annual Expence in Spies to observe their
Motions. Whenever I should be surprized with a Visit, as I hate
Drinking. I would be brisk in swilling Bumpers, upon this Maxim, That
it is better to trouble others with my Impertinence, than to be
troubled my self with theirs. The Necessity of an Infirmary makes me
resolve to fall into that Project; and as we should be but Five, the
Terrors of an involuntary Separation, which our Number cannot so well
admit of, would make us exert our selves, in opposition to all the
particulars mentioned in your Institution of that equitable
Confinement. This my way of Life I know would subject me to the
Imputation of a morose, covetous and singular Fellow. These and all
other hard words, with all manner of insipid Jests, and all other
Reproach, would be matter of Mirth to me and my Friends: Besides, I
would destroy the Application of the Epithets Morose and Covetous, by
a yearly Relief of my undeservedly necessitous Neighbours, and by
treating my Friends and Domesticks with an Humanity that should
express the Obligation to lie rather on my side; and for the word
Singular, I was always of opinion every Man must be so, to be what one
would de
Sir e him.
Your very humble Servant,
J. R.
3
Mr. SPECTATOR,
About two Years ago I was called upon by the younger part of a Country
Family,
by my Mother's side related to me, to visit Mr.
Campbell,
the dumb Man
4; for they told me that that was chiefly what brought
them to Town, having heard Wonders of him in
Essex. I, who always
wanted Faith in Matters of that kind, was not easily prevailed on to
go; but lest they should take it ill, I went with them; when to my
surprize, Mr.
Campbell related all their past Life, (in short, had
he not been prevented, such a Discovery would have come out, as would
have ruined the next design of their coming to Town,
viz. buying
Wedding-Cloaths.) Our Names—though he never heard of us before—and
we endeavoured to conceal—were as familiar to him as to our selves.
To be sure,
Mr. SPECTATOR, he is a very learned and wise Man. Being
impatient to know my Fortune, having paid my respects in a
Family-
Jacobus, he told me (after his manner) among several other
things, that in a Year and nine Months I should fall ill of a new
Fever, be given over by my Physicians, but should with much difficulty
recover: That the first time I took the Air afterwards, I should be
address'd to by a young Gentleman of a plentiful Fortune, good Sense,
and a generous Spirit.
Mr. SPECTATOR, he is the purest Man in the
World, for all he said is come to pass, and I am the happiest She in
Kent. I have been in quest of Mr.
Campbell these three Months, and
cannot find him out. Now hearing you are a dumb Man too, I thought you
might correspond, and be able to tell me something; for I think my
self highly oblig'd to make his Fortune, as he has mine. 'Tis very
possible your Worship, who has Spies all over this Town, can inform me
how to send to him: If you can, I Beseech you be as speedy as
possible, and you will highly oblige
Your constant Reader and Admirer,
Dulcibella Thankley.
Ordered
, That the Inspector I employ about Wonders, enquire at the
Golden-Lion
, opposite to the
Half-Moon
Tavern in
Drury-Lane
, into
the Merit of this Silent Sage, and report accordingly.
T.
Used for giving a drench to horses.
Falconbridge in
King John
Act. I sc. i.
This letter was by Steele's old college friend, Richard
Parker, who took his degree of M.A. in 1697, became fellow of Merton,
and died Vicar of Embleton, in Northumberland. This is the friend whose
condemnation of the comedy written by him in student days Steele had
accepted without question.
See note p. 421, vol. ii. [Volume 2 links:
of
.]
Contents
|
Thursday, September 4, 1712 |
Addison |
—Quæ res in se neque Consilium neque modum
Habet ullum, eam consilio regere non potes.
Tert.

It is an old Observation, which has been made of Politicians who would
rather ingratiate themselves with their Sovereign, than promote his real
Service, that they accommodate their Counsels to his Inclinations, and
advise him to such Actions only as his Heart is naturally set upon. The
Privy-Counsellor of one in Love must observe the same Conduct, unless he
would forfeit the Friendship of the Person who de
Sir
es his Advice. I
have known several odd Cases of this Nature.
Hipparchus
was going to
marry a common Woman, but being resolved to do nothing without the
Advice of his Friend
Philander
, he consulted him upon the Occasion.
Philander
told him his Mind freely, and represented his Mistress to
him in such strong Colours, that the next Morning he received a
Challenge for his Pains, and before Twelve a Clock was run through the
Body by the Man who had asked his Advice.
Celia
was more prudent on
the like occasion; she de
Sir
ed
Leonilla
to give her Opinion freely
upon a young Fellow who made his Addresses to her.
Leonilla
, to oblige
her, told her with great Frankness, that, she looked upon him as one of
the most worthless—
Celia
, foreseeing what a Character she was to
expect, begged her not to go on, for that she had been privately married
to him above a Fortnight. The truth of it is, a Woman seldom asks Advice
before she has bought her Wedding-Cloaths. When she has made her own
Choice, for Form's sake she sends a
Congé d'elire
to her Friends.
If we look into the secret Springs and Motives that set People at work
in these Occasions, and put them upon asking Advice, which they never
intend to take; I look upon it to be none of the least, that they are
incapable of keeping a Secret which is so very pleasing to them. A Girl
longs to tell her Confident, that she hopes to be married in a little
time, and, in order to talk of the pretty Fellow that dwells so much in
her Thoughts, asks her very gravely, what she would advise her to do in
a case of so much Difficulty. Why else should
Melissa
, who had not a
Thousand Pound in the World, go into every Quarter of the Town to ask
her Acquaintance whether they would advise her to take
Tom Townly
,
that made his Addresses to her with an Estate of Five Thousand a Year?
'Tis very pleasant on this occasion, to hear the Lady propose her
Doubts, and to see the Pains she is at to get over them.
I must not here omit a Practice that is in use among the vainer Part of
our own Sex, who will often ask a Friend's Advice, in relation to a
Fortune whom they are never likely to come at.
Will. Honeycomb
, who is
now on the Verge of Threescore, took me aside not long since, and asked
me in his most serious Look, whether I would advise him to marry my Lady
Betty Single
, who, by the way, is one of the greatest Fortunes about
Town. I star'd him full in the Face upon so strange a Question; upon
which he immediately gave me an Inventory of her Jewels and Estate,
adding, that he was resolved to do nothing in a matter of such
Consequence without my Approbation. Finding he would have an Answer, I
told him, if he could get the Lady's Consent, he had mine. This is about
the Tenth Match which, to my knowledge,
Will
, has consulted his Friends
upon, without ever opening his Mind to the Party herself.
I have been engaged in this Subject by the following Letter, which comes
to me from some notable young Female Scribe, who, by the Contents of it,
seems to have carried Matters so far, that she is ripe for asking
Advice; but as I would not lose her Good-Will, nor forfeit the
Reputation which I have with her for Wisdom, I shall only communicate
the Letter to the Publick, without returning any Answer to it.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
Now, Sir , the thing is this: Mr. Shapely is the prettiest Gentleman
about Town. He is very tall, but not too tall neither. He dances like
a Angel. His Mouth is made I don't know how, but 'tis the prettiest
that I ever saw in my Life. He is always laughing, for he has an
infinite deal of Wit. If you did but see how he rolls his Stockins! He
has a thousand pretty Fancies, and I am sure, if you saw him, you
would like him. He is a very good Scholar, and can talk Latin as
fast as English. I wish you could but see him dance. Now you must
understand poor Mr. Shapely has no Estate; but how can he help that,
you know? And yet my Friends are so unreasonable as to be always
teazing me about him, because he has no Estate: but I am sure he has
that that is better than an Estate; for he is a Good-natured,
Ingenious, Modest, Civil, Tall, Well-bred, Handsome Man, and I am
obliged to him for his Civilities ever since I saw him. I forgot to
tell you that he has black Eyes, and looks upon me now and then as if
he had tears in them. And yet my Friends are so unreasonable, that
they would have me be uncivil to him. I have a good Portion which they
cannot hinder me of, and I shall be fourteen on the 29th Day of
August next, and am therefore willing to settle in the World as soon
as I can, and so is Mr. Shapely. But every body I advise with here
is poor Mr. Shapely's Enemy. I deSir e therefore you will give me
your Advice, for I know you are a wise Man; and if you advise me well,
I am resolved to follow it. I heartily wish you could see him dance,
and am,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
B. D.
He loves your Spectators mightily.
C.
Contents
|
Friday, September 5, 1712 |
Addison |
—lucidus Ordo—
Hor.

Among my Daily-Papers which I bestow on the Publick, there are some
which are written with Regularity and Method, and others that run out
into the Wildness of those Compositions which go by the Names of
Essays
. As for the first, I have the whole Scheme of the Discourse in
my Mind before I set Pen to Paper. In the other kind of Writing, it is
sufficient that I have several Thoughts on a Subject, without troubling
my self to range them in such order, that they may seem to grow out of
one another, and be disposed under the proper Heads.
Seneca
and
Montaigne
are Patterns for Writing in this last kind, as
Tully
and
Aristotle
excel in the other. When I read an Author of Genius who
writes without Method, I fancy myself in a Wood that abounds with a
great many noble Objects, rising among one another in the greatest
Confusion and Disorder. When I read a methodical Discourse, I am in a
regular Plantation, and can place my self in its several Centres, so as
to take a view of all the Lines and Walks that are struck from them. You
may ramble in the one a whole Day together, and every Moment discover
something or other that is new to you; but when you have done, you will
have but a confused imperfect Notion of the Place: In the other, your
Eye commands the whole Prospect, and gives you such an Idea of it, as is
not easily worn out of the Memory.
Irregularity and want of Method are only supportable in Men of great
Learning or Genius, who are often too full to be exact, and therefore
chuse to throw down their Pearls in Heaps before the Reader, rather than
be at the Pains of stringing them.
Method is of advantage to a Work, both in respect to the Writer and the
Reader. In regard to the first, it is a great help to his Invention.
When a Man has plann'd his Discourse, he finds a great many Thoughts
rising out of every Head, that do not offer themselves upon the general
Survey of a Subject. His Thoughts are at the same time more
intelligible, and better discover their Drift and Meaning, when they are
placed in their proper Lights, and follow one another in a regular
Series, than when they are thrown together without Order and Connexion.
There is always an Obscurity in Confusion, and the same Sentence that
would have enlightened the Reader in one part of a Discourse, perplexes
him in another. For the same reason likewise
Thought in a
methodical Discourse shews
it
` self in its greatest Beauty, as the
several Figures in a piece of Painting receive new Grace from their
Disposition in the Picture. The Advantages of a Reader from a methodical
Discourse, are correspondent with those of the Writer. He comprehends
every thing easily, takes it in with Pleasure, and retains it long.
Method is not less requisite in ordinary Conversation than in Writing,
provided a Man would talk to make himself understood. I, who hear a
thousand Coffee-house Debates every Day, am very sensible of this want
of Method in the Thoughts of my honest Countrymen. There is not one
Dispute in ten which is managed in those Schools of Politicks, where,
after the three first Sentences, the Question is not entirely lost. Our
Disputants put me in mind of the Cuttle-Fish, that when he is unable to
extricate himself, blackens all the Water about him till he becomes
invisible. The Man who does not know how to methodize his Thoughts, has
always,
borrow a Phrase from the Dispensary,
a barren Superfluity of
Words;
the Fruit is lost amidst the Exuberance of Leaves.
Tom Puzzle
is one of the most Eminent Immethodical Disputants of any
that has fallen under my Observation.
Tom
has read enough to make him
very Impertinent; his Knowledge is sufficient to raise Doubts, but not
to clear them. It is pity that he has so much Learning, or that he has
not a great deal more. With these Qualifications
Tom
sets up for a
Free-thinker, finds a great many things to blame in the Constitution of
his Country, and gives shrewd Intimations that he does not believe
another World. In short,
Puzzle
is an Atheist as much as his Parts
will give him leave. He has got about half a dozen common-place Topicks,
into which he never fails to turn the Conversation, whatever was the
Occasion of it: Tho' the matter in debate be about
Doway
or
Denain
,
it is ten to one but half his Discourse runs upon the Unreasonableness
of Bigottry and Priest-craft. This makes Mr.
Puzzle
the Admiration of
all those who have less Sense than himself, and the Contempt of those
who have more. There is none in Town whom
Tom
dreads so much as my
Friend
Will Dry
.
Will
, who is acquainted with
Tom's
Logick, when
he finds him running off the Question, cuts him short with a
What then?
We allow all this to be true, but what is it to our present Purpose?
I
have known
Tom
eloquent half an hour together, and triumphing, as he
thought, in the Superiority of the Argument, when he has been non-plus'd
on a sudden by Mr.
Dry's
de
Sir
ing him to tell the Company what it was
that he endeavoured to prove. In short,
Dry
is a Man of a clear
methodical Head, but few Words, and gains the same Advantage over
Puzzle
, that a small Body of regular Troops would gain over a
numberless undisciplined Militia.
C.
its
It is said of Colon in the second Canto,
Hourly his learn'd Impertinence affords
A barren Superfinity of Words.
Contents
|
Saturday, September 6, 1712 |
Addison |
—An me ludit amabilis
Insania? audire et videor pios
Errare per lucos, amœnæ
Quos et aquæ subeunt et auræ.
Hor.

Sir ,
Having lately read your Essay on the Pleasures of the Imagination, I
was so taken with your Thoughts upon some of our
English Gardens,
that I cannot forbear troubling you with a Letter upon that Subject. I
am one, you must know, who am looked upon as an Humorist in Gardening.
I have several Acres about my House, which I call my Garden, and which
a skilful Gardener would not know what to call. It is a Confusion of
Kitchin and Parterre, Orchard and Flower-Garden, which lie so mixt and
interwoven with one another, that if a Foreigner who had seen nothing
of our Country should be convey'd into my Garden at his first landing,
he would look upon it as a natural Wilderness, and one of the
uncultivated Parts of our Country. My Flowers grow up in several Parts
of the Garden in the greatest Luxuriancy and Profusion. I am so far
from being fond of any particular one, by reason of its Rarity, that
if I meet with any one in a Field which pleases me, I give it a place
in my Garden. By this means, when a Stranger walks with me, he is
surprized to see several large Spots of Ground cover'd with ten
thousand different Colours, and has often singled out Flowers that he
might have met with under a common Hedge, in a Field, or in a Meadow,
as some of the greatest Beauties of the Place. The only Method I
observe in this Particular, is to range in the same Quarter the
Products of the same Season, that they may make their Appearance
together, and compose a Picture of the greatest Variety. There is the
same Irregularity in my Plantations, which run into as great a
Wildness as their Natures will permit. I take in none that do not
naturally rejoice in the Soil, and am pleased when I am walking in a
Labyrinth of my own raising, not to know whether the next Tree I shall
meet with is an Apple or an Oak, an Elm or a Pear-Tree. My Kitchin has
likewise its particular Quarters assigned it; for besides the
wholesome Luxury which that Place abounds with, I have always thought
a Kitchin-Garden a more pleasant Sight than the finest Orangery, or
artificial Greenhouse. I love to see everything in its Perfection, and
am more pleased to survey my Rows of Coleworts and Cabbages, with a
thousand nameless Pot-herbs, springing up in their full Fragrancy and
Verdure, than to see the tender Plants of Foreign Countries kept alive
by artificial Heats, or withering in an Air and Soil that are not
adapted to them. I must not omit, that there is a Fountain rising in
the upper part of my Garden, which forms a little wandring Rill, and
administers to the Pleasure as well as the Plenty of the Place. I have
so conducted it, that it visits most of my Plantations; and have taken
particular Care to let it run in the same manner as it would do in an
open Field, so that it generally passes through Banks of Violets and
Primroses, Plats of Willow, or other Plants, that seem to be of its
own producing. There is another Circumstance in which I am very
particular, or, as my Neighbours call me, very whimsical: As my Garden
invites into it all the Birds of the Country, by offering them the
Conveniency of Springs and Shades, Solitude and Shelter, I do not
suffer any one to destroy their Nests in the Spring, or drive them
from their usual Haunts in Fruit-time. I value my Garden more for
being full of Blackbirds than Cherries, and very frankly give them
Fruit for their Songs. By this means I have always the Musick of the
Season in its Perfection, and am highly delighted to see the Jay or
the Thrush hopping about my Walks, and shooting before my Eye across
the several little Glades and Alleys that I pass thro'. I think there
are as many kinds of Gardening as of Poetry: Your Makers of Parterres
and Flower-Gardens, are Epigrammatists and Sonneteers in this Art:
Contrivers of Bowers and Grotto's, Treillages and Cascades, are
Romance Writers.
Wise and
London are our heroick Poets; and if, as
a Critick, I may single out any Passage of their Works to commend, I
shall take notice of that Part in the upper Garden at
Kensington,
which was at first nothing but a Gravel-Pit. It must have been a fine
Genius for Gardening, that could have thought of forming such an
unsightly Hollow into so beautiful an Area, and to have hit the Eye
with so uncommon and agreeable a Scene as that which it is now wrought
into. To give this particular Spot of Ground the greater Effect, they
have made a very pleasing Contrast; for as on one side of the Walk you
see this hollow Basin, with its several little Plantations lying so
conveniently under the Eye of the Beholder; on the other side of it
there appears a seeming Mount, made up of Trees rising one higher than
another in proportion as they approach the Center. A Spectator, who
has not heard this Account of it, would think this Circular Mount was
not only a real one, but that it had been actually scooped out of that
hollow Space which I have before mention'd. I never yet met with any
one who had walked in this Garden, who was not struck with that Part
of it which I have here mention'd. As for my self, you will find, by
the Account which I have already given you, that my Compositions in
Gardening are altogether after the
Pindarick Manner, and run into
the beautiful Wildness of Nature, without affecting the nicer
Elegancies of Art. What I am now going to mention, will, perhaps,
deserve your Attention more than any thing I have yet said. I find
that in the Discourse which I spoke of at the Beginning of my Letter,
you are against filling an
English Garden with Ever-Greens; and
indeed I am so far of your Opinion, that I can by no means think the
Verdure of an Ever-Green comparable to that which shoots out annually,
and clothes our Trees in the Summer-Season. But I have often wonder'd
that those who are like my self, and love to live in Gardens, have
never thought of contriving a
Winter Garden, which would consist of
such Trees only as never cast their Leaves. We have very often little
Snatches of Sunshine and fair Weather in the most uncomfortable Parts
of the Year; and have frequently several Days in
November and
January that are as agreeable as any in the finest Months. At such
times, therefore, I think there could not be a greater Pleasure, than
to walk in such a
Winter-Garden as I have proposed. In the
Summer-Season the whole Country blooms, and is a kind of Garden, for
which reason we are not so sensible of those Beauties that at this
time may be every where met with; but when Nature is in her
Desolation, and presents us with nothing but bleak and barren
Prospects, there is something unspeakably chearful in a Spot of Ground
which is covered with Trees that smile amidst all the Rigours of
Winter, and give us a View of the most gay Season in the midst of that
which is the most dead and melancholy. I have so far indulged my self
in this Thought, that I have set apart a whole Acre of Ground for the
executing of it. The Walls are covered with Ivy instead of Vines. The
Laurel, the Hornbeam, and the Holly, with many other Trees and Plants
of the same nature, grow so thick in it, that you cannot imagine a
more lively Scene. The glowing Redness of the Berries, with which they
are hung at this time, vies with the Verdure of their Leaves, and are
apt to inspire the Heart of the Beholder with that vernal Delight
which you have somewhere taken notice of in your former papers
1. It
is very pleasant, at the same time, to see the several kinds of Birds
retiring into this little Green Spot, and enjoying themselves among
the Branches and Foliage, when my great Garden, which I have before
mention'd to you, does not afford a single Leaf for their Shelter.
You must know,
Sir , that I look upon the Pleasure which we take in a
Garden, as one of the most innocent Delights in Human Life. A Garden
was the Habitation of our first Parents before the Fall. It is
naturally apt to fill the Mind with Calmness and Tranquillity, and to
lay all its turbulent Passions at rest. It gives us a great insight
into the Contrivance and Wisdom of Providence, and suggests
innumerable Subjects for Meditation. I cannot but think the very
Complacency and Satisfaction which a Man takes in these Works of
Nature, to be a laudable, if not a virtuous Habit of Mind. For all
which Reasons I hope you will pardon the Length of my present Letter.
I am,
C.
In [Volume 2 link:
]
Contents
|
Monday, September 8, 1712 |
Steele |
—Usus
Quem penes Arbitrium est, et Jus et Norma—
Mr. SPECTATOR,
It happened lately, that a Friend of mine, who had many things to buy
for his Family, would oblige me to walk with him to the Shops. He was
very nice in his way, and fond of having every thing shewn, which at
first made me very uneasy; but as his Humour still continu'd, the
things which I had been staring at along with him, began to fill my
Head, and led me into a Set of amusing Thoughts concerning them.
I fancied it must be very surprizing to any one who enters into a
detail of Fashions, to consider how far the Vanity of Mankind has laid
it self out in Dress, what a prodigious number of People it maintains,
and what a Circulation of Money it occasions. Providence in this Case
makes use of the Folly which we will not give up, and it becomes
instrumental to the Support of those who are willing to labour. Hence
it is that Fringe-Makers, Lace-Men, Tire-Women, and a number of other
Trades, which would be useless in a simple State of Nature, draw their
Subsistence; tho' it is seldom seen that such as these are extremely
rich, because their original Fault of being founded upon Vanity, keeps
them poor by the light Inconstancy of its Nature. The Variableness of
Fashion turns the Stream of Business which flows from it now into one
Channel, and anon into another; so that different Sets of People sink
or flourish in their turns by it.
From the Shops we retir'd to the Tavern, where I found my Friend
express so much satisfaction for the Bargains he had made, that my
moral Reflections, (if I had told them) might have pass'd for a
Reproof; so I chose rather to fall in with him, and let the Discourse
run upon the use of Fashions.
Here we remembred how much Man is govern'd by his Senses, how lively
he is struck by the Objects which appear to him in an agreeable
manner, how much Clothes contribute to make us agreeable Objects, and
how much we owe it to our selves that we should appear so.
We considered Man as belonging to Societies; Societies as form'd of
different Ranks; and different Ranks distinguished by Habits, that all
proper Duty or Respect might attend their Appearance.
We took notice of several Advantages which are met with in the
Occurrences of Conversation. How the bashful Man has been sometimes so
rais'd, as to express himself with an Air of Freedom, when he imagines
that his Habit introduces him to Company with a becoming Manner: And
again, how a Fool in fine Clothes shall be suddenly heard with
Attention, till he has betray'd himself; whereas a Man of Sense
appearing with a Dress of Negligence, shall be but coldly received,
till he be proved by Time, and established in a Character. Such things
as these we cou'd recollect to have happen'd to our knowledge so very
often, that we concluded the Author had his Reasons, who advises his
Son to go in Dress rather above his Fortune than under it.
At last the Subject seem'd so considerable, that it was proposed to
have a Repository built for Fashions, as there are Chambers for Medals
and other Rarities. The Building may be shap'd as that which stands
among the Pyramids, in the Form of a Woman's Head. This may be rais'd
upon Pillars, whose Ornaments shall bear a just relation to the
Design. Thus there may be an Imitation of Fringe carv'd in the Base, a
sort of Appearance of Lace in the Frieze, and a Representation of
curling Locks, with Bows of Ribband sloping over them, may fill up the
Work of the Cornish. The Inside may be divided into two Apartments
appropriated to each Sex. The Apartments may be fill'd with Shelves,
on which Boxes are to stand as regularly as Books in a Library. These
are to have Folding-Doors, which being open'd, you are to behold a
Baby dressed out in some Fashion which has flourish'd, and standing
upon a Pedestal, where the time of its Reign is mark'd down. For its
further Regulation, let it be order'd, that every one who invents a
Fashion shall bring in his Box, whose Front he may at pleasure have
either work'd or painted with some amorous or gay Device, that, like
Books with gilded Leaves and Covers, it may the sooner draw the Eyes
of the Beholders. And to the end that these may be preserv'd with all
due Care, let there be a Keeper appointed, who shall be a Gentleman
qualify'd with a competent Knowledge in Clothes; so that by this means
the Place, will be a comfortable Support for some Beau who has spent
his Estate in dressing.
The Reasons offer'd by which we expected to gain the Approbation of
the Publick, were as follows.
First, That every one who is considerable enough to be a Mode, and has
any Imperfection of Nature or Chance, which it is possible to hide by
the Advantage of Clothes, may, by coming to this Repository, be
furnish'd her self, and furnish all who are under the same Misfortune,
with the most agreeable Manner of concealing it; and that on the other
side, every one who has any Beauty in Face or Shape, may also be
furnished with the most agreeable Manner of shewing it.
Secondly, That whereas some of our young Gentlemen who travel, give us
great reason to suspect that they only go abroad to make or improve a
Fancy for Dress, a Project of this nature may be a means to keep them
at home, which is in effect the keeping of so much Money in the
Kingdom. And perhaps the Balance of Fashion in
Europe, which now
leans upon the side of
France, may be so alter'd for the future,
that it may become as common with
Frenchmen to come to
England for
their finishing Stroke of Breeding, as it has been for
Englishmen to
go to
France for it.
Thirdly, Whereas several great Scholars, who might have been otherwise
useful to the World, have spent their time in studying to describe the
Dresses of the Ancients from dark Hints, which they are fain to
interpret and support with much Learning, it will from henceforth
happen, that they shall be freed from the Trouble, and the World from
useless Volumes. This Project will be a Registry, to which Posterity
may have recourse, for the clearing such obscure Passages as tend that
way in Authors; and therefore we shall not for the future submit our
selves to the Learning of Etymology, which might persuade the Age to
come, that the Farthingal was worn for Cheapness, or the Furbeloe for
Warmth.
Fourthly, Whereas they who are old themselves, have often a way of
railing at the Extravagance of Youth, and the whole Age in which their
Children live; it is hoped that this ill Humour will be much
suppress'd, when we can have recourse to the Fashions of their Times,
produce them in our Vindication, and be able to shew that it might
have been as expensive in Queen
Elizabeth's time only to wash and
quill a Ruff, as it is now to buy Cravats or Neck-Handkerchiefs.
We de
Sir e also to have it taken Notice of, That because we would shew
a particular respect to Foreigners, which may induce them to perfect
their Breeding here in a Knowledge which is very proper for pretty
Gentlemen, we have conceived the Motto for the House in the Learned
Language. There is to be a Picture over the Door, with a Looking-Glass
and a Dressing-Chair in the Middle of it: Then on one side are to be
seen, above one another, Patch-Boxes, Pin-Cushions, and little
Bottles; on the other, Powder Baggs, Puffs, Combs and Brushes; beyond
these, Swords with fine Knots, whose Points are hidden, and Fans
almost closed, with the Handles downward, are to stand out
interchangeably from the Sides till they meet at the Top, and form a
Semicircle over the rest of the Figures: Beneath all, the Writing is
to run in
this pretty sounding Manner:
Adeste, O quotquot sunt, Veneres, Gratiæ, Cupidines1,
En vobis adsunt in promptu
Faces, Vincula, Spicula,
Hinc eligite, sumite, regite.
I am,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
A. B.
The Proposal of my Correspondent I cannot but look upon as an ingenious
Method of placing Persons (whose Parts make them ambitious to exert
themselves in frivolous things) in a Rank by themselves. In order to
this, I would propose, That there be a Board of Directors of the
fashionable Society; and because it is a Matter of too much Weight for a
private Man to determine alone, I should be highly obliged to my
Correspondents if they would give in Lists of Persons qualify'd for this
Trust. If the chief Coffee-houses, the Conversations of which Places are
carry'd on by Persons, each of whom has his little number of Followers
and Admirers, would name from among themselves two or three to be
inserted, they should be put up with great Faithfulness. Old Beaus are
to be presented in the first place; but as that Sect, with relation to
Dress, is almost extinct, it will, I fear, be absolutely necessary to
take in all Time-Servers, properly so deem'd; that is, such as, without
any Conviction of Conscience or View of Interest, change with the World,
and that merely from a Terror of being out of Fashion. Such also, who
from Facility of Temper, and too much Obsequiousness, are vicious
against their Will, and follow Leaders whom they do not approve, for
Want of Courage to go their own Way, are capable Persons for this
Superintendency. Those who are both to grow old, or would do any thing
contrary to the Course and Order of things, out of Fondness to be in
Fashion, are proper Candidates. To conclude, those who are in Fashion
without apparent Merit, must be supposed to have latent Qualities, which
would appear in a Post of Direction; and therefore are to be regarded in
forming these Lists. Any who shall be pleased, according to these, or
what further Qualifications may occur to himself, to send a List, is
de
Sir
ed to do it within fourteen days after this Date.
N. B. The Place of the Physician to this Society, according to the last
mentioned Qualification, is already engag'd.
T.
All ye Venuses, Graces, and Cupids, attend:
See prepared to your hands
Darts, torches, and bands:
Your weapons here choose, and your empire extend.
Contents
|
Tuesday, September 9, 1712 |
Steele |
—Dare Jure maritis.
Hor.

Many are the Epistles I every day receive from Husbands, who complain of
Vanity, Pride, but above all Ill-nature, in their Wives. I cannot tell
how it is, but I think I see in all their Letters that the Cause of
their Uneasiness is in themselves; and indeed I have hardly ever
observed the married Condition unhappy, but from want of Judgment or
Temper in the Man. The truth is, we generally make Love in a Style, and
with Sentiments very unfit for ordinary Life: They are half Theatrical,
half Romantick. By this Means we raise our Imaginations to what is not
to be expected in human Life; and because we did not beforehand think of
the Creature we were enamoured of as subject to Dishumour, Age,
Sickness, Impatience or Sullenness, but altogether considered her as the
Object of Joy, human Nature it self is often imputed to her as her
particular Imperfection or Defect.
I take it to be a Rule proper to be observed in all Occurrences of Life,
but more especially in the domestick or matrimonial Part of it, to
preserve always a Disposition to be pleased. This cannot be supported
but by considering things in their right light, and as Nature has form'd
them, and not as our own Fancies or Appetites would have them. He then
who took a young Lady to his Bed, with no other Consideration than the
Expectation of Scenes of Dalliance, and thought of her (as I said
before) only as she was to administer to the Gratification of De
Sir
e; as
that De
Sir
e flags, will, without her Fault, think her Charms and her
Merit abated: From hence must follow Indifference, Dislike, Peevishness,
and Rage. But the Man who brings his Reason to support his Passion, and
beholds what he loves as liable to all the Calamities of human Life both
in Body and Mind, and even at the best what must bring upon him new
Cares and new Relations; such a Lover, I say, will form himself
accordingly, and adapt his Mind to the Nature of his Circumstances. This
latter Person will be prepared to be a Father, a Friend, an Advocate, a
Steward for People yet unborn, and has proper Affections ready for every
Incident in the Marriage State. Such a Man can hear the Cries of
Children with Pity instead of Anger; and when they run over his Head, he
is not disturb'd at their Noise, but is glad of their Mirth and Health.
Tom Trusty
has told me, that he thinks it doubles his Attention to the
most intricate Affair he is about, to hear his Children, for whom all
his Cares are applied, make a Noise in the next Room:
the other side
Will Sparkish
cannot put on his Perriwig, or adjust his Cravat at the
Glass, for the Noise of those damned Nurses and
squaling
Brats; and
then ends with a gallant Reflection upon the Comforts of Matrimony, runs
out of the Hearing, and drives to the Chocolate-house.
According as the Husband is dispos'd in himself, every Circumstance of
his Life is to give him Torment or Pleasure. When the Affection is
well-placed, and supported by the Considerations of Duty, Honour, and
Friendship, which are in the highest Degree engaged in this Alliance,
there can nothing rise in the common Course of Life, or from the Blows
or Favours of Fortune, in which a Man will not find Matters of some
Delight unknown to a single Condition.
He who sincerely loves his Wife and Family, and studies to improve that
Affection in himself, conceives Pleasure from the most indifferent
things; while the married Man, who has not bid adieu to the Fashions and
false Gallantries of the Town, is perplexed with every thing around him.
In both these Cases Men cannot, indeed, make a sillier Figure, than in
repeating such Pleasures and Pains to the rest of the World; but I speak
of them only, as they sit upon those who are involved in them. As I
visit all sorts of People, I cannot indeed but smile, when the good Lady
tells her Husband what extraordinary things the Child spoke since he
went out. No longer than yesterday I was prevail'd with to go home with
a fond Husband: and his Wife told him, that his Son, of his own head,
when the Clock in the Parlour struck two, said, Pappa would come home to
Dinner presently. While the Father has him in a rapture in his Arms, and
is drowning him with Kisses, the Wife tells me he is but just four Years
old. Then they both struggle for him, and bring him up to me, and repeat
his Observation of two a-Clock. I was called upon, by Looks upon the
Child, and then at me, to say something; and I told the Father, that
this Remark of the Infant of his coming home, and joining the Time with
it, was a certain Indication that he would be a great Historian and
Chronologer. They are neither of them Fools, yet received my Compliment
with great Acknowledgment of my Prescience. I fared very well at Dinner,
and heard many other notable Sayings of their Heir, which would have
given very little Entertainment to one less turned to Reflection than I
was; but it was a pleasing Speculation to remark on the Happiness of a
Life, in which things of no Moment give Occasion of Hope,
Self-Satisfaction, and Triumph. On the other Hand, I have known an
ill-natur'd Coxcomb, who was hardly improved in any thing but Bulk, for
want of this Disposition, silence the whole Family, as a Set of silly
Women and Children, for recounting things which were really above his
own Capacity.
When I say all this, I cannot deny but there are perverse Jades that
fall to Mens Lots, with whom it requires more than common Proficiency in
Philosophy to be able to live. When these are joined to Men of warm
Spirits, without Temper or Learning, they are frequently corrected with
Stripes; but one of our famous Lawyers is of Opinion, That this ought to
be used sparingly.
I remember, those are his very Words
; but as
it is proper to draw some spiritual Use out of all Afflictions, I should
rather recommend to those who are visited with Women of Spirit, to form
themselves for the World by Patience at home.
Socrates
, who is by all
Accounts the undoubted Head of the Sect of the Hen-peck'd, own'd and
acknowledged that he ow'd great part of his Virtue to the Exercise which
his useful Wife constantly gave it. There are several good Instructions
may be drawn from his wise Answers to People of less Fortitude than
himself on her Subject. A Friend, with Indignation, asked how so good a
Man could live with so violent a Creature?
observ'd to him,
That
they who learn to keep a good Seat on horseback, mount the least
managable they can get, and when they have master'd them, they are sure
never to be discomposed on the Backs of Steeds less restive.
At
several times, to different Persons, on the same Subject, he has said,
My dear Friend, you are beholden to
Xantippe,
that I bear so well
your flying out in a Dispute.
To another,
My Hen clacks very much, but
she brings me Chickens. They that live in a trading Street, are not
disturbed at the Passage of Carts.
I would have, if possible, a wise
Man be contented with his Lot, even with a Shrew; for tho' he cannot
make her better, he may, you see, make himself better by her means.
But instead of pursuing my Design of Displaying Conjugal Love in its
natural Beauties and Attractions, I am got into Tales to the
disadvantage of that State of Life. I must say, therefore, that I am
verily persuaded that whatever is delightful in human Life, is to be
enjoy'd in greater Perfection in the marry'd, than in the single
Condition. He that has this Passion in Perfection, in Occasions of Joy
can say to himself, besides his own Satisfaction,
How happy will this
make my Wife and Children?
Upon Occurrences of Distress or Danger can
comfort himself,
But, all this while my Wife and Children are safe
.
There is something in it that doubles Satisfactions, because others
participate them; and dispels Afflictions, because others are exempt
from them. All who are marry'd without this Relish of their
Circumstance, are in either a tasteless Indolence and Negligence, which
is hardly to be attain'd, or else live in the hourly Repetition of sharp
Answers, eager Upbraidings, and distracting Reproaches. In a word the
married State, with and without the Affection suitable to it, is the
compleatest Image of Heaven and Hell we are capable of receiving in this
Life.
T.
squalwing
Henry de Bracton in his treatise of live books
de Legibus
et Dounsuetudinibus Anglia
, written about the middle of the thirteen
centry, says (Bk. I. ch. x.)
quædam sunt sub virga, ut uxores, &c.
but qualifies private right with the secondary claim of the community.
Xenophon's
Symposium
, Bk. II.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 10, 1712 |
Steele |
Responsare cupidinibus, contemnere honores,
Fortis, et in seipso totus teres, atque rotundus.
Hor.

The other Day looking over those old Manuscripts, of which I have
formerly given some Account, and which relate to the Character of the
Pharamond
of
France
, and the close Friendship between him and
his Friend
Eucrate
; I found, among the Letters which had been in
the custody of the latter, an Epistle from a Country Gentleman to
Pharamond
, wherein he excuses himself from coming to Court. The
Gentleman, it seems, was contented with his Condition, had formerly been
in the King's Service, but at the writing the following Letter, had,
from Leisure and Reflection, quite another Sense of things than that
which he had in the more active Part of his Life.
Monsieur Chezluy
to Pharamond.
Dread Sir ,
I have from your own Hand (enclosed under the Cover of Mr.
Eucrate
of your Majesty's Bed-Chamber) a Letter which invites me to Court. I
understand this great Honour to be done me out of Respect and
Inclination to me, rather than Regard to your own Service: For which
Reason I beg leave to lay before your Majesty my Reasons for declining
to depart from Home; and will not doubt but, as your Motive in
de
Sir ing my Attendance was to make me an happier Man, when you think
that will not be effected by my Remove, you will permit me to stay
where I am. Those who have an Ambition to appear in Courts, have ever
an Opinion that their Persons or their Talents are particularly formed
for the Service or Ornament of that Place; or else are hurried by
downright De
Sir e of Gain, or what they call Honour, or take upon
themselves whatever the Generosity of their Master can give them
Opportunities to grasp at. But your Goodness shall not be thus imposed
upon by me: I will therefore confess to you, that frequent Solitude,
and long Conversation with such who know no Arts which polish Life,
have made me the plainest Creature in your Dominions. Those less
Capacities of moving with a good Grace, bearing a ready Affability to
all around me, and acting with ease before many, have quite left me. I
am come to that, with regard to my Person, that I consider it only as
a Machine I am obliged to take Care of, in order to enjoy my Soul in
its Faculties with Alacrity; well remembering, that this Habitation of
Clay will in a few years be a meaner Piece of Earth than any Utensil
about my House. When this is, as it really is, the most frequent
Reflection I have, you will easily imagine how well I should become a
Drawing-Room: Add to this, What shall a Man without De
Sir es do about
the generous
Pharamond? Monsieur
Eucrate has hinted to me, that
you have thoughts of distinguishing me with Titles. As for my self, in
the Temper of my present Mind, Appellations of Honour would but
embarrass Discourse, and new Behaviour towards me perplex me in every
Habitude of Life. I am also to acknowledge to you, that my Children,
of whom your Majesty condescended to enquire, are all of them mean,
both in their Persons and Genius. The Estate my eldest Son is Heir to,
is more than he can enjoy with a good Grace. My Self-love will not
carry me so far, as to impose upon Mankind the Advancement of Persons
(merely for their being related to me) into high Distinctions, who
ought for their own Sakes, as well as that of the Publick, to affect
Obscurity. I wish, my generous Prince, as it is in your power to give
Honours and Offices, it were also to give Talents suitable to them:
Were it so, the noble
Pharamond would reward the Zeal of my Youth
with Abilities to do him Service in my Age.
'Those who accept of Favour without Merit, support themselves in it at
the Expence of your Majesty. Give me Leave to tell you,
Sir , this is
the Reason that we in the Country hear so often repeated the Word
Prerogative. That Part of your Law which is reserved in your self
for the readier Service and Good of the Publick, slight Men are
eternally buzzing in our Ears to cover their own Follies and
Miscarriages. It would be an Addition to the high Favour you have done
me, if you would let
Eucrate send me word how often, and in what
Cases you allow a Constable to insist upon the Prerogative. From the
highest to the lowest Officer in your Dominions, something of their
own Carriage they would exempt from Examination under the Shelter of
the Word
Prerogative. I would fain, most noble
Pharamond, see one
of your Officers assert your Prerogative by good and gracious Actions.
When is it used to help the Afflicted, to rescue the Innocent, to
comfort the Stranger? Uncommon Methods, apparently undertaken to
attain worthy Ends, would never make Power invidious. You see,
Sir , I
talk to you with the Freedom your noble Nature approves, in all whom
you admit to your Conversation.
'But, to return to your Majesty's Letter, I humbly conceive, that all
Distinctions are useful to Men, only as they are to act in Publick;
and it would be a romantick Madness, for a Man to be a Lord in his
Closet. Nothing can be honourable to a Man apart from the World, but
the Reflection upon worthy Actions; and he that places Honour in a
Consciousness of Well-doing, will have but little Relish for any
outward Homage that is paid him, since what gives him distinction to
himself, cannot come within the Observation of his Beholders. Thus all
the Words of Lordship, Honour, and Grace, are only Repetitions to a
Man that the King has order'd him to be called so; but no Evidences
that there is any thing in himself that would give the Man who applies
to him those Ideas, without the Creation of his Master.
'I have, most noble
Pharamond, all Honours and all Titles in your
own Approbation; I triumph in them as they are your Gift, I refuse
them as they are to give me the Observation of others. Indulge me, my
Noble Master, in this Chastity of Renown; let me know my self in the
Favour of
Pharamond; and look down upon the Applause of the People.
I am,
in all Duty and Loyally,
Your Majesty's most obedient
Subject and Servant,
Jean Chezluy.
Sir ,
'I need not tell you with what Disadvantages Men of low Fortunes and
great Modesty come into the World; what wrong Measures their
Diffidence of themselves, and Fear of offending, often obliges them to
take; and what a Pity it is that their greatest Virtues and Qualities,
that should soonest recommend them, are the main Obstacle in the way
of their Preferment.
'This,
Sir , is my Case; I was bred at a Country-School, where I
learned
Latin and
Greek. The Misfortunes of my Family forced me up
to Town, where a Profession of the politer sort has protected me
against Infamy and Want. I am now Clerk to a Lawyer, and, in times of
Vacancy and Recess from Business, have made my self Master of
Italian and
French; and tho' the Progress I have made in my
Business has gain'd me Reputation enough for one of my standing, yet
my Mind suggests to me every day, that it is not upon that Foundation
I am to build my Fortune.
'The Person I have my present Dependance upon, has it in his Nature,
as well as in his Power, to advance me, by recommending me to a
Gentleman that is going beyond Sea in a publick Employment. I know the
printing this Letter would point me out to those I want Confidence to
speak to, and I hope it is not in your Power to refuse making any Body
happy.
September 9, 1712.
Yours, &c.
M. D.
2
T.
See [Volume 1 links: Nos.
,
,
.]
Mr. Robert Harper, who died an eminent conveyancer of
Lincoln's Inn. He sent his letter on the 9th of August, and it appeared
September the 10th with omissions and alterations by Steele.
Contents
|
Thursday, September 11, 1712 |
Addison |
—Uti non
Compositus melius cum Bitho Bacchius, in jus
Acres procurrunt—
Hor.

is
something
pleasant enough to consider the different Notions,
which different Persons have of the same thing. If Men of low Condition
very often set a Value on Things, which are not prized by those who are
in an higher Station of Life, there are many things these esteem which
are in no Value among Persons of an inferior Rank. Common People are, in
particular, very much astonished, when they hear of those solemn
Contests and Debates, which are made among the Great upon the
Punctilio's of a publick Ceremony, and wonder to hear that any Business
of Consequence should be retarded by those little Circumstances, which
they represent to themselves as trifling and insignificant. I
mightily pleased with a Porter's Decision in one of Mr.
Southern's
Plays
, which is founded upon that fine Distress of a Virtuous
Woman's marrying a second Husband, while her first was yet living. The
first Husband, who was suppos'd to have been dead, returning to his
House after a long Absence, raises a noble Perplexity for the Tragick
Part of the Play. In the mean while, the Nurse and the Porter conferring
upon the Difficulties that would ensue in such a Case, honest
Sampson
thinks the matter may be easily decided, and solves it very judiciously,
by the old Proverb, that if his first Master be still living,
The Man
must have his Mare again
. There is
in my time which has so much
surprized and confounded the greatest part of my honest Countrymen, as
the present Controversy between Count
Rechteren
and Monsieur
Mesnager
, which employs the wise Heads of so many Nations, and holds
all the Affairs of
Europe
in suspence
.
Upon my going into a Coffee-house yesterday, and lending an ear to the
next Table, which was encompassed with a Circle of inferior Politicians,
one of them, after having read over the News very attentively, broke out
into the following Remarks. I am afraid, says he, this unhappy Rupture
between the Footmen at
Utrecht
will retard the Peace of Christendom. I
wish the Pope may not be at the Bottom of it. His Holiness has a very
good hand at fomenting a Division, as the poor
Suisse Cantons
have
lately experienced to their Cost.
Mo
u
nsieur
What-d'ye-call-him's
Domesticks will not come to an Accommodation, I
do not know how the Quarrel can be ended, but by a Religious War.
Why truly, says a
Wiseacre
that sat by him, were I as the King of
France
, I would scorn to take part with the Footmen of either side:
Here's all the Business of
Europe
stands still, because Mo
u
nsieur
Mesnager's
Man has had his Head broke. If Count
Rectrum
had given
them a Pot of Ale after it, all would have been well, without any of
this Bustle; but they say he's a warm Man, and does not care to be made
Mouths at.
Upon
, one, that had held his Tongue hitherto,
began
to exert
himself; declaring, that he was very well pleased the Plenipotentiaries
of our Christian Princes took this matter into their serious
Consideration; for that Lacqueys were never so saucy and pragmatical, as
they are now-a-days, and that he should be glad to see them taken down
in the Treaty of Peace, if it might be done without prejudice to
the
Publick Affairs.
One who sat at the other End of the Table, and seemed to be in the
Interests of the
French
King, told them, that they did not take the
matter right, for that his most Christian Majesty did not resent this
matter because it was an Injury done to Monsieur
Mesnager's
Footmen;
for, says he, what are Monsieur
Mesnager's
Footmen to him? but because
it was done to his Subjects. Now, says he, let me tell you, it would
look very odd for a Subject of
France
to have a bloody Nose, and his
Sovereign not to take Notice of it. He is obliged in Honour to defend
his People against Hostilities; and if the
Dutch
will be so insolent
to a Crowned Head, as, in any wise, to cuff or kick those who are under
His
Protection, I think he is in the right to call them to an Account
for it.
This Distinction set the Controversy upon a new Foot, and seemed to be
very well approved by most that heard it, till a little warm Fellow, who
declared himself a Friend to the House of
Austria
, fell most
unmercifully upon his
Gallick
Majesty, as encouraging his Subjects to
make Mouths at their Betters, and afterwards screening them from the
Punishment that was due to their Insolence. To which he added that the
French
Nation was so addicted to Grimace, that if there was not a Stop
put to it at the General Congress, there would be no walking the Streets
for them in a time of Peace, especially if they continued Masters of the
West-Indies
. The little Man proceeded with a great deal of warmth,
declaring that if the Allies were of his Mind, he would oblige the
French
King to burn his Gallies, and tolerate the Protestant Religion
in his Dominions, before he would Sheath his Sword. He concluded with
calling Mo
u
nsieur
Mesnager
an Insignificant Prig.
The Dispute was now growing very Warm, and one does not know where it
would have ended, had not a young Man of about One and Twenty, who seems
to have been brought up with an Eye to the Law, taken the Debate into
his Hand, and given it as his Opinion, that neither Count
Rechteren
nor Mo[u]nsieur
Mesnager
had behaved themselves right in this Affair.
Count
Rechteren
, says he, should have made Affidavit that his Servants
had been affronted, and then Mo
u
nsieur
Mesnager
would have done him
Justice, by taking away their Liveries from 'em, or some other way that
he might have thought the most proper; for let me tell you, if a Man
makes a Mouth at me, I am not to knock the Teeth out of it for his
Pains. Then again, as for Mo[u]nsieur
Mesnager
, upon his Servants
being beaten, why! he might have had his Action of Assault and Battery.
But as the case now stands, if you will have my Opinion, I think they
ought to bring it to Referees.
I heard a great deal more of this Conference, but I must confess with
little Edification; for all I could learn at last from these honest
Gentlemen, was, that the matter in Debate was of too high a Nature for
such Heads as theirs, or mine, to Comprehend.
O.
sometimes
The Fatal Marriage, or the Innocent Adultery
.
The negotiations for Peace which were going on at Utrecht
had been checked by the complaint of Count Rechteren, deputy for the
Province of Overyssel. On the 24th of July the French, under Marshal
Villars, had obtained a great victory at Denain, capturing the Earl of
Albemarle, the Princes of Anhalt, of Holstein, Nassau Seeken, and 2500
men, under the eyes of Prince Eugene, who was stopped at the bridge of
Prouy on his way to rescue and entreated by the deputies of the
States-general to retire. The allies lost a thousand killed and fifteen
hundred drowned; the French only five hundred, and sixty flags were sent
as trophies to Versailles. The insecure position taken by the Earl of
Albemarle had been forced on Prince Eugene by the Dutch deputies, who
found the arrangement cheapest.
'Tell me,' he said, 'of the conquests of Alexander. He had no Dutch deputies in his army.'
Count Rechteren,
deputy for Overyssel, complained that, a few days after this battle,
when he was riding in his carriage by the gate of M. Ménager, the French
Plenipotentiary, that gentleman's lackeys insulted his lackeys with
grimaces and indecent gestures. He sent his secretary to complain to M.
Ménager, demand satisfaction, and say that if it were not given, he
should take it. Ménager replied, in writing, that although this was but
an affair between lackeys, he was far from approving ill behaviour in
his servants towards other servants, particularly towards servants of
Count Rechteren, and he was ready to send to the Count those lackeys
whom he had seen misbehaving, or even those whom his other servants
should point out as guilty of the offensive conduct. Rechteren, when the
answer arrived, was gone to the Hague, and it was forwarded to his
colleague, M. Moîrman. Upon his return to Utrecht, Rechteren sent his
secretary again to Ménager, with the complaint as before, and received
the answer as before. He admitted that he had not himself seen the
grimaces and insulting gestures, but he ought, he said, to be at liberty
to send his servants into Ménager's house for the detection of the
offenders. A few days afterwards Ménager and Rechteren were on the chief
promenade of Utrecht, with others who were Plenipotentiaries of the
United Provinces, and after exchange of civilities, Rechteren said that
he was still awaiting satisfaction. Ménager replied as before, and said
that his lackeys all denied the charge against them. Ménager refused
also to allow the accusers of his servants to come into his house and be
their judges. Rechteren said he would have justice yet upon master and
men. He was invested with a sovereign power as well as Ménager. He was
not a man to take insults. He spoke some words in Dutch to his
attendants, and presently Ménager's lackeys came with complaint that the
lackeys of Rechteren tripped them up behind, threw them upon their
faces, and threatened them with knives. Rechteren told the French
Plenipotentiary that he would pay them for doing that, and discharge
them if they did not do it. Rechteren's colleagues did what they could
to cover or excuse his folly, and begged that the matter might not
appear in a despatch to France or be represented to the States-general,
but be left to the arbitration of the English Plenipotentiaries. This
the French assented to, but they now demanded satisfaction against
Rechteren, and refused to accept the excuse made for him, that he was
drunk. He might, under other circumstances, says M. Torcy, the French
minister of the time, in his account of the Peace Negociations, have
dismissed the petty quarrel of servants by accepting such an excuse but,
says M. de Torcy,
'it was deSir able to retard the Conferences, and this
dispute gave a plausible reason.'
Therefore until the King of France and
Bolingbroke had come to a complete understanding, the King of France
ordered his three Plenipotentiaries to keep the States-general busy,
with the task of making it clear to his French Majesty whether
Rechteren's violence was sanctioned by them, or whether he had acted
under private passion, excited by the Ministers of the House of Austria.
Then they must further assent to a prescribed form of disavowal, and
deprive Rechteren of his place as a deputy. This was the high policy of
the affair of the lackeys, which, as Addison says, held all the affairs
of Europe in suspense, a policy avowed with all complacency by the high
politician who was puller of the strings. (
Memoires de Torcy
, Vol. iii.
pp. 411-13.)
It is
Monsieur
in the first issue and also in the first reprint.
begun
Contents
|
Friday, September 12, 1712 |
Addison |
Floriferis ut apes in saltibus omnia libant.
Lucr.

When I have published any single Paper that falls in with the Popular
Taste, and pleases more than ordinary, it always brings me in a great
return of Letters. My
Tuesday's
Discourse, wherein I gave several
Admonitions to the Fraternity of the
Henpeck'd
, has already produced
me very many Correspondents; the Reason I cannot guess at, unless it be
that such a Discourse is of general Use, and every married Man's Money.
An honest Tradesman, who dates his Letter from
Cheapside
, sends me
Thanks in the name of a Club, who, he tells me, meet as often as their
Wives will give them leave, and stay together till they are sent for
home. He informs me, that my Paper has administered great Consolation to
their whole Club, and de
Sir
es me to give some further Account of
Socrates
, and to acquaint them in whose Reign he lived, whether he was
a Citizen or a Courtier, whether he buried
Xantippe
, with many other
particulars: For that by his Sayings he appears to have been a very Wise
Man and a good Christian. Another, who writes himself
Benjamin Bamboo
,
tells me, that being coupled with a Shrew, he had endeavoured to tame
her by such lawful means as those which I mentioned in my last
Tuesday's
Paper, and that in his Wrath he had often gone further than
Bracton
allows in those cases; but that for the future he was resolved
to bear it like a Man of Temper and Learning, and consider her only as
one who lives in his House to teach him Philosophy.
Tom Dapperwit
says, that he agrees with me in that whole Discourse, excepting only the
last Sentence, where I affirm the married State to be either an Heaven
or an Hell.
Tom
has been at the charge of a Penny upon this occasion,
to tell me, that by his Experience it is neither one nor the other, but
rather that middle kind of State, commonly known by the Name of
Purgatory
.
The Fair Sex have likewise obliged me with their Reflections upon the
same Discourse. A Lady, who calls herself
Euterpe
, and seems a Woman
of Letters, asks me whether I am for establishing the
Salick
Law in
every Family, and why it is not fit that a Woman who has Discretion and
Learning should sit at the Helm, when the Husband is weak and
illiterate? Another, of a quite contrary Character, subscribes herself
Xantippe
, and tells me, that she follows the Example of her Name-sake;
for being married to a Bookish Man, who has no Knowledge of the World,
she is forced to take their Affairs into her own Hands, and to spirit
him up now and then, that he may not grow musty, and unfit for
Conversation.
After this Abridgment of some Letters which are come to my hands upon
this Occasion, I shall publish one of them at large.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
You have given us a lively Picture of that kind of Husband who comes
under the Denomination of the Hen-peck'd; but I do not remember that
you have ever touched upon one that is of the quite different
Character, and who, in several Places of
England, goes by the Name
of a Cot-Quean. I
have the Misfortune to be joined for Life with one
of this Character, who in reality is more a Woman than
I am1. He
was bred up under the Tuition of a tender Mother, till she had made
him as good a House-wife as her self. He could preserve Apricots, and
make Gellies, before he had been two Years out of the Nursery. He was
never suffered to go abroad, for fear of catching Cold: when he should
have been hunting down a Buck, he was by his Mother's Side learning
how to Season it, or put it in Crust; and was making Paper-Boats with
his Sisters, at an Age when other young Gentlemen are crossing the
Seas, or travelling into Foreign Countries. He has the whitest Hand
that you ever saw in your Life, and raises Paste better than any Woman
in
England. These Qualifications make him a sad Husband: He is
perpetually in the Kitchin, and has a thousand Squabbles with the
Cook-maid. He is better acquainted with the Milk-Score, than his
Steward's Accounts. I fret to Death when I hear him find fault with a
Dish that is not dressed to his liking, and instructing his Friends
that dine with him in the best Pickle for a Walnut, or Sauce for an
Haunch of Venison. With all this, he is a very good-natured Husband,
and never fell out with me in his Life but once, upon the
over-roasting of a Dish of Wild-Fowl: At the same time I must own I
would rather he was a Man of a rough Temper, that would treat me
harshly sometimes, than of such an effeminate busy Nature in a
Province that does not belong to him. Since you have given us the
Character of a Wife who wears the Breeches, pray say something of a
Husband that wears the Petticoat. Why should not a Female Character be
as ridiculous in a Man, as a Male Character in one of our Sex?
I am, &c.
O.
my self.
Contents
|
Saturday, September 13, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec Deus intersit nisi dignus vindice nodus
Inciderit—
Hor.

We cannot be guilty of a greater Act of Uncharitableness, than to
interpret the Afflictions which befal our Neighbours, as
Punishments
and
Judgments
. It aggravates the Evil to him who suffers, when he
looks upon himself as the Mark of Divine Vengeance, and abates the
Compassion of those towards him, who regard him in so dreadful a Light.
This Humour of turning every Misfortune into a Judgment, proceeds from
wrong Notions of Religion, which, in its own nature, produces Goodwill
towards Men, and puts the mildest Construction upon every Accident that
befalls them. In this case, therefore, it is not Religion that sours a
Man's Temper, but it is his Temper that sours his Religion: People of
gloomy unchearful Imaginations, or of envious malignant Tempers,
whatever kind of Life they are engaged in, will discover their natural
Tincture of Mind in all their Thoughts, Words, and Actions. As the
finest Wines have often the Taste of the Soil, so even the most
religious Thoughts often draw something that is particular from the
Constitution of the Mind in which they arise. When Folly or Superstition
strike in with this natural Depravity of Temper, it is not in the power,
even of Religion it self, to preserve the Character of the Person who is
possessed with it, from appearing highly absurd and ridiculous.
An old Maiden Gentlewoman, whom I shall conceal under the Name of
Nemesis
, is the greatest Discoverer of Judgments that I have met with.
She can tell you what Sin it was that set such a Man's House on fire, or
blew down his Barns. Talk to her of an unfortunate young Lady that lost
her Beauty by the Small-Pox, she fetches a deep Sigh, and tells you,
that when she had a fine Face she was always looking on it in her Glass.
Tell her of a Piece of good Fortune that has befallen one of her
Acquaintance; and she wishes it may prosper with her, but her Mother
used one of her Nieces very barbarously. Her usual Remarks turn upon
People who had great Estates, but never enjoyed them, by reason of some
Flaw in their own, or their Father's Behaviour. She can give you the
Reason why such a one died Childless: Why such an one was cut off in the
Flower of his Youth: Why such an one was Unhappy in her Marriage: Why
one broke his Leg on such a particular Spot of Ground, and why another
was killed with a Back-Sword, rather than with any other kind of Weapon.
She has a Crime for every Misfortune that can befal any of her
Acquaintance, and when she hears of a Robbery that has been made, or a
Murder that has been committed, enlarges more on the Guilt of the
suffering Person, than on that of the Thief, or the Assassin. In short,
she is so good a Christian, that whatever happens to her self is a
Tryal, and whatever happens to her Neighbours is a Judgment.
The very Description of this Folly, in ordinary Life, is sufficient to
expose it; but when it appears in a Pomp and Dignity of Style, it is
very apt to amuse and terrify the Mind of the Reader.
Herodotus
and
Plutarch
very often apply their Judgments as impertinently as the old
Woman I have before mentioned, though their manner of relating them,
makes the Folly it self appear venerable.
, most Historians, as
well Christian as Pagan, have fallen into this idle Superstition, and
spoken of ill
Success
, unforeseen Disasters, and terrible Events,
as if they had been let into the Secrets of Providence, and made
acquainted with that private Conduct by which the World is governed. One
would think several of our own Historians in particular had many
Revelations of this kind made to them. Our old
English
Monks seldom
let any of their Kings depart in Peace, who had endeavoured to diminish
the Power or Wealth of which the Ecclesiasticks were in those times
possessed.
William the Conqueror's
Race generally found their
Judgments in the
New Forest
, where their Father had pulled down
Churches and Monasteries. In short, read one of the Chronicles written
by an Author of this frame of Mind, and you would think you were reading
an History of the Kings of
Israel
or
Judah
, where the Historians
were actually inspired, and where, by a particular Scheme of Providence,
the Kings were distinguished by Judgments or Blessings, according as
they promoted Idolatry or the Worship of the true God.
I cannot but look upon this manner of judging upon Misfortunes, not only
to be very uncharitable, in regard to the Person whom they befall, but
very presumptuous in regard to him who is supposed to inflict them. It
is a strong Argument for a State of Retribution hereafter, that in this
World virtuous Persons are very often unfortunate, and vicious Persons
prosperous; which is wholly repugnant to the Nature of a Being who
appears infinitely wise and good in all his Works, unless we may suppose
that such a promiscuous and undistinguishing Distribution of Good and
Evil, which was necessary for carrying on the Designs of Providence in
this Life, will be rectified and made amends for in another. We are not
therefore to expect that Fire should fall from Heaven in the ordinary
Course of Providence; nor when we see triumphant Guilt or depressed
Virtue in particular Persons, that Omnipotence will make bare its holy
Arm in the Defence of the one, or Punishment of the other. It is
sufficient that there is a Day set apart for the hearing and requiting
of both according to their respective Merits.
The Folly of ascribing Temporal Judgments to any particular Crimes, may
appear from several Considerations. I shall only mention two: First,
That, generally speaking, there is no Calamity or Affliction, which is
supposed to have happened as a Judgment to a vicious Man, which does not
sometimes happen to Men of approved Religion and
. When
Diagoras
the Atheist
was on board one of the
Athenian
Ships, there arose a
very violent Tempest; upon which the Mariners told him, that it was a
just Judgment upon them for having taken so impious a Man on board.
Diagoras
begged them to look upon the rest of the Ships that were in
the same Distress, and ask'd them whether or no
Diagoras
was on board
every Vessel in the Fleet. We are all involved in the same Calamities,
and subject to the same Accidents: and when we see any one of the
Species under any particular Oppression, we should look upon it as
arising from the common Lot of human Nature, rather than from the Guilt
of the Person who suffers.
Another Consideration, that may check our Presumption in putting such a
Construction upon a Misfortune, is this, That it is impossible for us to
know what are Calamities, and what are Blessings. How many Accidents
have pass'd for Misfortunes, which have turned to the Welfare and
Prosperity of the Persons in whose Lot they have fallen? How many
Disappointments have, in their Consequences, saved a man from Ruin? If
we could look into the Effects of every thing, we might be allowed to
pronounce boldly upon Blessings and Judgments; but for a Man to give his
Opinion of what he sees but in part, and in its Beginnings, is an
unjustifiable Piece of Rashness and Folly. The Story of
Biton
and
Clitobus
, which was in great Reputation among the Heathens, (for we
see it quoted by all the ancient Authors, both
Greek
and
Latin
, who
have written upon the Immortality of the Soul,) may teach us a Caution
in this Matter. These two Brothers, being the Sons of a Lady who was
Priestess to
Juno
, drew their Mother's Chariot to the Temple at the
time of a great Solemnity, the Persons being absent who by their Office
were to have drawn her Chariot on that Occasion. The Mother was so
transported with this Instance of filial Duty, that she petition'd her
Goddess to bestow upon them the greatest Gift that could be given to
Men; upon which they were both cast into a deep Sleep, and the next
Morning found dead in the Temple. This was such an Event, as would have
been construed into a Judgment, had it happen'd to the two Brothers
after an Act of Disobedience, and would doubtless have been represented
as such by any Ancient Historian who had given us an Account of it.
O.
Successes
Diagoras the Melian, having attacked the popular religion
and the Eleusinian mysteries, had a price set on his head, and left
Athens B.C. 411. The Athenians called him Atheist, and destroyed his
writings. The story in the text is from the third book of Cicero
de
Natura Deorum.
Contents
|
Monday, September 15, 1712 |
Steele |
Neque cuiquam tam statim clarum ingenium est, ut possit emergere;
nisi illi materia, occasio, fautor etiam, commendatorque contingat.
Plin.
Epist.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
Of all the young Fellows who are in their Progress thro' any
Profession, none seem to have so good a Title to the Protection of the
Men of Eminence in it as the modest Man; not so much because his
Modesty is a certain Indication of his Merit, as because 'tis a
certain Obstacle to the producing of it. Now, as of all Professions
this Virtue is thought to be more particularly unnecessary in that of
the Law than in any other, I shall only apply my self to the Relief of
such who follow this Profession with this Disadvantage. What
aggravates the matter is, that those Persons who, the better to
prepare themselves for this Study, have made some Progress in others,
have, by addicting themselves to Letters, encreased their natural
Modesty, and consequently heighten'd the Obstruction to this sort of
Preferment; so that every one of these may emphatically be said to be
such a one as
laboureth and taketh pains, and is still the more
behind. It may be a Matter worth discussing then, Why that which made
a Youth so amiable to the Ancients, should make him appear so
ridiculous to the Moderns? and, Why in our days there should be
Neglect, and even Oppression of young Beginners, instead of that
Protection which was the Pride of theirs? In the Profession spoken of,
'tis obvious to every one whose Attendance is required at
Westminster-Hall, with what Difficulty a Youth of any Modesty has
been permitted to make an Observation, that could in no wise detract
from the Merit of his Elders, and is absolutely necessary for the
advancing his own. I have often seen one of these not only molested in
his Utterance of something very pertinent, but even plunder'd of his
Question, and by a strong Serjeant shoulder'd out of his Rank, which
he has recover'd with much Difficulty and Confusion. Now as great part
of the Business of this Profession might be dispatched by one that
perhaps
—Abest virtute diserti
Messalæ, nec scit quantum Causellius Aulus—
Hor.
so I can't conceive the Injustice done to the Publick, if the Men of
Reputation in this Calling would introduce such of the young ones into
Business, whose Application to this Study will let them into the
Secrets of it, as much as their Modesty will hinder them from the
Practice: I say, it would be laying an everlasting Obligation upon a
young Man, to be introduc'd at first only as a Mute, till by this
Countenance, and a Resolution to support the good Opinion conceiv'd of
him in his Betters, his Complexion shall be so well settled, that the
Litigious of this Island may be secure of his obstreperous Aid. If I
might be indulged to speak in the Style of a Lawyer, I would say, That
any one about thirty years of Age, might make a common Motion to the
Court with as much Elegance and Propriety as the most aged Advocates
in the Hall.
I can't advance the Merit of Modesty by any Argument of my own so
powerfully, as by enquiring into the Sentiments the greatest among the
Ancients of different Ages entertain'd upon this Virtue. If we go back
to the Days of
Solomon, we shall find Favour a necessary Consequence
to a shame-fac'd Man.
Pliny, the greatest Lawyer and most Elegant
Writer of the Age he lived in, in several of his Epistles is very
sollicitous in recommending to the Publick some young Men of his own
Profession, and very often undertakes to become an Advocate, upon
condition that some one of these his Favourites might be joined with
him, in order to produce the Merit of such, whose Modesty otherwise
would have suppressed it. It may
seem very marvellous to a saucy
Modern, that
Multum sanguinis, multum verecundiæ, multum
sollicitudinis in ore; to have the Face first full of Blood, then the
Countenance dashed with Modesty, and then the whole Aspect as of one
dying with Fear, when a Man begins to speak; should be esteem'd by
Pliny the necessary Qualifications of a fine Speaker
1.
Shakespear has also express'd himself in the same favourable Strain
of Modesty, when he says,
—In the Modesty of fearful Duty
I read as much as from the rattling Tongue
Of saucy and audacious Eloquence—2
Now since these Authors have profess'd themselves for the Modest Man,
even in the utmost Confusions of Speech and Countenance, why should an
intrepid Utterance and a resolute Vociferation thunder so successfully
in our Courts of Justice? And why should that Confidence of Speech and
Behaviour, which seems to acknowledge no Superior, and to defy all
Contradiction, prevail over that Deference and Resignation with which
the Modest Man implores that favourable Opinion which the other seems
to command?
As the Case at present stands, the best Consolation that I can
administer to those who cannot get into that Stroke of Business (as
the Phrase is) which they deserve, is to reckon every particular
Acquisition of Knowledge in this Study as a real Increase of their
Fortune; and fully to believe, that one day this imaginary Gain will
certainly be made out by one more substantial. I wish you would talk
to us a little on this Head, you would oblige,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant.
The Author of this Letter is certainly a Man of good Sense; but I am
perhaps particular in my Opinion on this Occasion; for I have observed,
that under the Notion of Modesty, Men have indulged themselves in a
Spiritless Sheepishness, and been for ever lost to themselves, their
Families, their Friends, and their Country. When a Man has taken care to
pretend to nothing but what he may justly aim at, and can execute as
well as any other, without Injustice to any other; it is ever want of
Breeding or Courage to be brow-beaten or elbow'd out of his honest
Ambition. I have said often, Modesty must be an Act of the Will, and yet
it always implies Self-Denial: For if a Man has an ardent De
Sir
e to do
what is laudable for him to perform, and, from an unmanly Bashfulness,
shrinks away, and lets his Merit languish in Silence, he ought not to be
angry at the World that a more unskilful Actor succeeds in his Part,
because he has not Confidence to come upon the Stage himself. The
Generosity my Correspondent mentions of
Pliny
, cannot be enough
applauded. To cherish the Dawn of Merit, and hasten its Maturity, was a
Work worthy a noble
Roman
and a liberal Scholar. That Concern which is
described in the Letter, is to all the World the greatest Charm
imaginable: but then the modest Man must proceed, and shew a latent
Resolution in himself; for the Admiration of his Modesty arises from the
Manifestation of his Merit. I must confess we live in an Age wherein a
few empty Blusterers carry away the Praise of Speaking, while a Crowd of
Fellows over-stock'd with Knowledge are run down by them. I say
Over-stock'd, because they certainly are so as to their Service of
Mankind, if from their very Store they raise to themselves Ideas of
Respect, and Greatness of the Occasion, and I know not what, to disable
themselves from explaining their Thoughts. I must confess, when I have
seen
Charles Frankair
rise up with a commanding Mien, and Torrent of
handsome Words, talk a Mile off the Purpose, and drive down twenty
bashful Boobies of ten times his Sense, who at the same time were
envying his Impudence and despising his Understanding, it has been
matter of great Mirth to me; but it soon ended in a secret Lamentation,
that the Fountains of every thing praiseworthy in these Realms, the
Universities, should be so muddied with a false Sense of this Virtue, as
to produce Men capable of being so abused. I will be bold to say, that
it is a ridiculous Education which does not qualify a Man to make his
best Appearance before the greatest Man and the finest Woman to whom he
can address himself. Were this judiciously corrected in the Nurseries of
Learning, pert Coxcombs would know their Distance: But we must bear with
this false Modesty in our young Nobility and Gentry, till they cease at
Oxford
and
Cambridge
to grow dumb in the Study of Eloquence.
T.
The citation is from a charming letter in which Pliny (Bk. v. letter 17)
tells Spurinna the pleasure he had just received from a recitation by a noble
youth in the house of Calpurnius Piso, and how, when it was over, he gave
the youth many kisses and praises, congratulated his mother and his brother,
in whom, as the reciter tried his powers, first fear for him and then delight
in him was manifest. To the sentences quoted above the next is
'Etenim, nescio quo pacto, magis in studiis homines timor quam fiducia
decet.'
'I don't know how it is, but in brain-work mistrust better becomes men
than self-confidence.'
Midsummer Night's Dream
, Act v. sc. 1.
Contents
|
Tuesday, September 16, 1712 |
Steele |
Nihil tam firmum est, cui periculum non sit, etiam ab Invalido.
Quint. Curt.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'My
Lord Clarendon has observed,
That few Men have done more harm
than those who have been thought to be able to do least; and there
cannot be a greater Error, than to believe a Man whom we see qualified
with too mean Parts to do good, to be therefore incapable of doing
hurt. There is a Supply of Malice, of Pride, of Industry, and even of
Folly, in the Weakest, when he sets his heart upon it, that makes a
strange progress in Mischief1. What may seem to the Reader the
greatest Paradox in the Reflection of the Historian, is, I suppose,
that Folly, which is generally thought incapable of contriving or
executing any Design, should be so formidable to those whom it exerts
it self to molest. But this will appear very plain, if we remember
that
Solomon says,
It is as Sport to a Fool to do mischief; and
that he might the more emphatically express the calamitous
Circumstances of him who falls under the displeasure of this wanton
Person, the same Author adds further,
That a Stone is heavy, and the
Sand weighty, but a Fool's Wrath is heavier than them both. It is
impossible to suppress my own Illustration upon this Matter, which is,
That as the Man of Sagacity bestirs himself to distress his Enemy by
Methods probable and reducible to Reason, so the same Reason will
fortify his Enemy to elude these his regular Efforts; but your Fool
projects, acts, and concludes with such notable Inconsistence, that no
regular Course of Thought can evade or counterplot his prodigious
Machinations. My Frontispiece, I believe, may be extended to imply,
That several of our Misfortunes arise from Things, as well as Persons,
that seem of very little consequence. Into what tragical
Extravagancies does
Shakespear hurry
Othello upon the loss of an
Handkerchief only? and what Barbarities does
Desdemona suffer from a
slight Inadvertency in regard to this fatal Trifle? If the Schemes of
all enterprizing Spirits were to be carefully examined, some
intervening Accident, not considerable enough to occasion any Debate
upon, or give 'em any apprehension of ill Consequence from it, will be
found to be the occasion of their ill Success, rather than any Error
in Points of Moment and Difficulty, which naturally engag'd their
maturest Deliberations. If you go to the Levée of any great Man, you
will observe him exceeding gracious to several very insignificant
Fellows; and this upon this Maxim, That the Neglect of any Person must
arise from the mean Opinion you have of his Capacity to do you any
Service or Prejudice; and that this calling his Sufficiency in
question, must give him Inclination, and where this is, there never
wants Strength or Opportunity to annoy you. There is no body so weak
of Invention, that can't aggravate or make some little Stories to
vilify his Enemy; and there are very few but have good Inclinations to
hear 'em, and 'tis infinite Pleasure to the Majority of Mankind to
level a Person superior to his Neighbours. Besides, in all matter of
Controversy, that Party which has the greatest Abilities labours under
this Prejudice, that he will certainly be supposed, upon Account of
his Abilities, to have done an Injury, when perhaps he has received
one. It would be tedious to enumerate the Strokes that Nations and
particular Friends have suffer'd from Persons very contemptible.
I Think
Henry IV. of
France, so formidable to his Neighbours,
could no more be secur'd against the resolute Villany of
Ravillac,
than
Villiers, Duke of
Buckingham, could be against that of
Felton. And there is no incens'd Person so destitute, but can
provide himself with a Knife or a Pistol, if he finds stomach to apply
them. That Things and Persons of no moment should give such powerful
Revolutions to the progress of those of the greatest, seems a
providential Disposition to baffle and abate the Pride of human
Sufficiency; as also to engage the Humanity and Benevolence of
Superiors to all below 'em, by letting them into this Secret, that the
Stronger depends upon the Weaker.
I am, Sir ,
Your very humble Servant.
Temple, Paper-Buildings.
Dear Sir ,
'I received a Letter from you some time ago, which I should have
answered sooner, had you informed me in yours to what part of this
Island I might have directed my Impertinence; but having been let into
the Knowledge of that Matter, this handsome Excuse is no longer
serviceable. My Neighbour
Prettyman shall be the Subject of this
Letter; who falling in with the
Spectator's Doctrine concerning the
Month of
May, began from that Season to dedicate himself to the
Service of the Fair in the following Manner. I observed at the
Beginning of the Month he bought him a new Night-gown, either side to
be worn outwards, both equally gorgeous and attractive; but till the
End of the Month I did not enter so fully into the knowledge of his
Contrivance, as the Use of that Garment has since suggested to me. Now
you must know that all new Clothes raise and warm the Bearer's
Imagination into a Conceit of his being a much finer Gentleman than he
was before, banishing all Sobriety and Reflection, and giving him up
to Gallantry and Amour. Inflam'd therefore with this way of thinking,
and full of the Spirit of the Month of
May, did this merciless Youth
resolve upon the Business of Captivating. At first he confin'd himself
to his Room only, now and then appearing at his Window in his
Night-gown, and practising that easy Posture which expresses the very
Top and Dignity of Languishment. It was pleasant to see him diversify
his Loveliness, sometimes obliging the Passengers only with a
Side-Face, with a Book in his Hand; sometimes being so generous as to
expose the whole in the fulness of its Beauty; at the other times, by
a judicious throwing back of his Perriwig, he would throw in his Ears.
You know he is that Sort of Person which the Mob call a handsome jolly
Man; which Appearance can't miss of Captives in this part of the Town.
Being emboldened by daily Success, he leaves his Room with a
Resolution to extend his Conquests; and I have apprehended him in his
Night-gown smiting in all Parts of this Neighbourhood.
This I, being of an amorous Complection, saw with Indignation, and had
Thoughts of purchasing a Wig in these Parts; into which, being at a
greater Distance from the Earth, I might have thrown a very liberal
Mixture of white Horse-hair, which would make a fairer, and
consequently a handsomer Appearance, while my Situation would secure
me against any Discoveries. But the Passion to the handsome Gentleman
seems to be so fixed to that part of the Building, that it will be
extremely difficult to divert it to mine; so that I am resolved to
stand boldly to the Complection of my own Eye-brow, and prepare me an
immense Black Wig of the same sort of Structure with that of my Rival.
Now, tho' by this I shall not, perhaps, lessen the number of the
Admirers of his Complection, I shall have a fair Chance to divide the
Passengers by the irresistible Force of mine.
I expect sudden Dispatches from you, with Advice of the Family you are
in now, how to deport my self upon this so delicate a Conjuncture;
with some comfortable Resolutions in favour of the handsome black Man
against the handsome fair one.
I am, Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
C.
N. B. He who writ this, is a black Man two Pair of Stairs; the
Gentleman of whom he writes, is fair, and one Pair of Stairs.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I only say, that it is impossible for me to say how much I am
Yours,
Robin Shorter.
P. S. 'I shall think it a little hard, if you do not take as much
notice of this Epistle, as you have of the ingenious Mr.
Short's. I
am not afraid to let the World see which is the Deeper Man of the two.
T.
When this was quoted Clarendon had been dead only 38 years,
and his
History of the Rebellion
, first published in Queen Anne's reign,
was almost a new Book. It was published at Oxford in three folio
volumes, which appeared in the successive years 1702, 3,4, and in this
year, 1712, there had appeared a new edition of it (the sixth).
Contents
Advertisement
London, September 15.
Whereas a young Woman on horseback,
in an Equestrian Habit on the 13th Instant in the Evening,
met the Spectator within a Mile and an half of this Town,
and flying in the Face of Justice,
pull'd off her Hat, in which there was a Feather,
with the Mein and Air of a young Officer,
saying at the same time,
Your Servant Mr. SPEC. or Words to that Purpose;
This is to give Notice,
that if any Person can discover the Name,
and Place of Abode of the said Offender,
so as she can be brought to Justice,
the Informant shall have all fitting Encouragement.
|
Wednesday, September 17, 1712 |
Steele |
—Audire est operæ pretium procedere recte
Qui mechis non vultis—
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'There are very many of my Acquaintance Followers of
Socrates, with
more particular regard to that part of his Philosophy which we, among,
our selves, call his
Domesticks; under which Denomination, or Title,
we include all the Conjugal Joys and Sufferings. We have indeed, with
very great Pleasure, observed the Honour you do the whole Fraternity
of the Hen-peck'd, in placing that illustrious Man at our Head, and it
does in a very great measure baffle the Raillery of pert Rogues, who
have no advantage above us, but in that they are single. But when you
look about into the Crowd of Mankind, you will find the Fair Sex
reigns with greater Tyranny over Lovers than Husbands. You shall
hardly meet one in a thousand who is wholly exempt from their
Dominion, and those that are so, are capable of no Taste of Life, and
breathe and walk about the Earth as Insignificants. But I am going to
de
Sir e your further Favour in behalf of our harmless Brotherhood, and
hope you will shew in a true light the un-married Hen-peck'd, as well
as you have done Justice to us, who submit to the Conduct of our
Wives. I am very particularly acquainted with one who is under entire
Submission to a kind Girl, as he calls her; and tho' he knows I have
been Witness both to the ill Usage he has received from her, and his
Inability to resist her Tyranny, he still pretends to make a Jest of
me for a little more than ordinary Obsequiousness to my Spouse. No
longer than
Tuesday last he took me with him to visit his Mistress;
and he having, it seems, been a little in Disgrace before, thought by
bringing me with him she would constrain herself, and insensibly fall
into general Discourse with him; and so he might break the Ice, and
save himself all the ordinary Compunctions and Mortifications she used
to make him suffer before she would be reconciled after any Act of
Rebellion on his Part. When we came into the Room, we were received
with the utmost Coldness; and when he presented me as Mr. Such-a-one,
his very good Friend, she just had Patience to suffer my Salutation;
but when he himself, with a very gay Air, offered to follow me, she
gave him a thundering Box on the Ear, called him pitiful poor-spirited
Wretch, how durst he see her Face? His Wig and Hat fell on different
Parts of the Floor. She seized the Wig too soon for him to recover it,
and kicking it down Stairs, threw herself into an opposite Room,
pulling the Door after her with a Force, that you would have thought
the Hinges would have given Way. We went down, you must think, with no
very good Countenances; and as we sneaked off, and were driving home
together, he confessed to me, that her Anger was thus highly raised,
because he did not think fit to fight a Gentleman who had said she was
what she was; but, says he, a kind Letter or two, or fifty pieces,
will put her in Humour again. I asked him why he did not part with
her; he answered, he loved her with all the Tenderness imaginable, and
she had too many Charms to be abandoned for a little Quickness of
Spirit. Thus does this illegitimate Hen-pecked over-look the Hussy's
having no Regard to his very Life and Fame, in putting him upon an
infamous Dispute about her Reputation; yet has he the Confidence to
laugh at me, because I obey my poor Dear in keeping out of Harm's Way,
and not staying too late from my own Family, to pass through the
Hazards of a Town full of Ranters and Debauchees. You that are a
Philosopher should urge in our behalf, that when we bear with a
froward Woman, our Patience is preserved, in consideration that a
breach with her might be a Dishonour to Children who are descended
from us, and whose Concern makes us tolerate a thousand Frailties, for
fear they should redound Dishonour upon the Innocent. This and the
like Circumstances, which carry with them the most valuable Regards of
human Life, may be mentioned for our long Suffering; but in the case
of Gallants, they swallow ill Usage from one to whom they have no
Obligation, but from a base Passion, which it is mean to indulge, and
which it would be glorious to overcome.
'These Sort of Fellows are very numerous, and some have been
conspicuously such, without Shame; nay they have carried on the Jest
in the very Article of Death, and, to the Diminution of the Wealth and
Happiness of their Families, in bar of those honourably near to them,
have left immense Wealth to their Paramours. What is this but being a
Cully in the Grave! Sure this is being Hen-peck'd with a Vengeance!
But without dwelling upon these less frequent Instances of eminent
Cullyism, what is there so common as to hear a Fellow curse his Fate
that he cannot get rid of a Passion to a Jilt, and quote an Half-Line
out of a Miscellany Poem to prove his Weakness is natural? If they
will go on thus, I have nothing to say to it: But then let them not
pretend to be free all this while, and laugh at us poor married
Patients.
'I have known one Wench in this Town carry an haughty Dominion over
her Lovers so well, that she has at the same time been kept by a
Sea-Captain in the
Straits, a Merchant in the City, a Country
Gentleman in
Hampshire, and had all her Correspondences managed by
one she kept for her own Uses. This happy Man (as the Phrase is) used
to write very punctually every Post, Letters for the Mistress to
transcribe. He would sit in his Night-Gown and Slippers, and be as
grave giving an Account, only changing Names, that there was nothing
in those idle Reports they had heard of such a Scoundrel as one of the
other Lovers was; and how could he think she could condescend so low,
after such a fine Gentleman as each of them? For the same Epistle said
the same thing to and of every one of them. And so Mr. Secretary and
his Lady went to Bed with great Order.
'To be short,
Mr. SPECTATOR, we Husbands shall never make the Figure
we ought in the Imaginations of young Men growing up in the World,
except you can bring it about that a Man of the Town shall be as
infamous a Character as a Woman of the Town. But of all that I have
met in my time, commend me to
Betty Duall: She is the Wife of a
Sailor, and the kept Mistress of a Man of Quality; she dwells with the
latter during the Sea-faring of the former. The Husband asks no
Questions, sees his Apartments furnished with Riches not his, when he
comes into Port, and the Lover is as joyful as a Man arrived at his
Haven when the other puts to Sea.
Betty is the most eminently
victorious of any of her Sex, and ought to stand recorded the only
Woman of the Age in which she lives, who has possessed at the same
time two Abused, and two Contented...
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, September 18, 1712 |
Addison |
—Cum prostrata sopore
Urget membra quies, et mem sine pondere ludit—
Petr.

Tho' there are many Authors, who have written on Dreams, they have
generally considered them only as Revelations of what has already
happened in distant parts of the World, or as Presages of what is to
happen in future Periods of time.
I shall consider this Subject in another Light, as Dreams may give us
some Idea of the great Excellency of an Human Soul, and some Intimation
of its Independency on Matter. In the first Place, our Dreams are great
Instances of that Activity which is natural to the human Soul, and which
it is not in the power of Sleep to deaden or abate. When the Man appears
tired and worn out with the Labours of the Day, this active part in his
Composition is still busied and unwearied. When the Organs of Sense want
their due Repose and necessary Reparations, and the Body is no longer
able to keep pace with that spiritual Substance to which it is united,
the Soul exerts her self in her several Faculties, and continues in
Action till her Partner is again qualified to bear her Company. In this
case Dreams look like the Relaxations and Amusements of the Soul, when
she is disincumbred of her Machine, her Sports and Recreations, when she
has laid her Charge asleep.
In the Second Place, Dreams are an Instance of that Agility and
Perfection which is natural to the Faculties of the Mind, when they are
disengaged from the Body. The Soul is clogged and retarded in her
Operations, when she acts in Conjunction with a Companion that is so
heavy and unwieldy in its Motions. But in Dreams it is wonderful to
observe with what a Sprightliness and Alacrity she exerts her self. The
slow of Speech make unpremeditated Harangues, or converse readily in
Languages that they are but little acquainted with. The Grave abound in
Pleasantries, the Dull in Repartees and Points of Wit. There is not a
more painful Action of the Mind, than Invention; yet in Dreams it works
with that Ease and Activity, that we are not sensible when the Faculty
is employed. For instance, I believe every one, some time or other,
dreams that he is reading Papers, Books, or Letters; in which case the
Invention prompts so readily, that the Mind is imposed upon, and
mistakes its own Suggestions for the Compositions of another.
I
, under this Head, quote a Passage out of the
Religio Medici
, in which the ingenious Author gives an account of himself in his
dreaming and his waking Thoughts.
We are somewhat more than our selves in our Sleeps, and the Slumber
of the Body seems to be but the Waking of the Soul. It is the
Litigation of Sense, but the Liberty of Reason; and our waking
Conceptions do not match the Fancies of our Sleeps. At my Nativity my
Ascendant was the watery Sign of Scorpius: I was born in the
Planetary Hour of Saturn, and I think I have a piece of that leaden
Planet in me. I am no way facetious, nor disposed for the Mirth and
Galliardize of Company; yet in one Dream I can compose a whole Comedy,
behold the Action, apprehend the Jests, and laugh my self awake at the
Conceits thereof. Were my Memory as faithful as my Reason is then
fruitful, I would never study but in my Dreams; and this time also
would I chuse for my Devotions: but our grosser Memories have then so
little hold of our abstracted Understandings, that they forget the
Story, and can only relate to our awaked Souls a confused and broken
Tale of that that has passed—Thus it is observed that Men sometimes,
upon the Hour of their Departure, do speak and reason above
themselves; for then the Soul beginning to be freed from the Ligaments
of the Body, begins to reason like her self, and to discourse in a
strain above Mortality.
We may likewise observe in the third Place, that the Passions affect the
Mind with greater Strength when we are asleep, than when we are awake.
Joy and Sorrow give us more vigorous Sensations of Pain or Pleasure at
this time, than at any other. Devotion likewise, as the excellent Author
above-mentioned has hinted, is in a very particular manner heightned and
inflamed, when it rises in the Soul at a time that the Body is thus laid
at Rest. Every Man's Experience will inform him in this matter, though
it is very probable, that this may happen differently, in different
Constitutions. I shall conclude this Head with the two following
Problems, which I shall leave to the Solution of my Reader. Supposing a
Man always happy in his Dreams, and miserable in his waking Thoughts,
and that his Life was equally divided between them, whether would he be
more happy or miserable? Were a Man a King in his Dreams, and a Beggar
awake, and dreamt as consequentially, and in as continued unbroken
Schemes as he thinks when awake, whether he would be in reality a King
or Beggar, or rather whether he would not be both?
There is another Circumstance, which methinks gives us a very high Idea
of the Nature of the Soul, in regard to what passes in Dreams, I mean
that innumerable Multitude and Variety of Ideas which then arise in her.
Were that active watchful Being only conscious of her own Existence at
such a time, what a painful Solitude would her Hours of Sleep be? Were
the Soul sensible of her being alone in her sleeping Moments, after the
same manner that she is sensible of it while awake, the time would hang
very heavy on her, as it often actually does when she Dreams that she is
in such a Solitude?
—Semperque relinqui
Sola sili, semper longam incomitata videtur
Ire viam—
Virg.
But this Observation I only make by the way. What I would here remark,
is that wonderful Power in the Soul, of producing her own Company on
these Occasions. She converses with numberless Beings of her own
Creation, and is transported into ten thousand Scenes of her own
raising. She is herself the Theatre, the Actors, and the Beholder. This
puts me in
of a Saying which I am infinitely pleased with, and
which
Plutarch
ascribes to
Heraclitus, That all Men whilst they are
awake are in one common World; but that each of them, when he is asleep,
is in a World of his own.
The waking Man is conversant in the World
of Nature, when he sleeps he retires to a private World that is
particular to himself. There seems something in this Consideration that
intimates to us a natural Grandeur and Perfection in the Soul, which is
rather to be admired than explained.
I must not
that Argument for the Excellency of the Soul, which I
have seen quoted out of
Tertullian
, namely, its Power of divining
in Dreams. That several such Divinations have been made, none can
question, who believes the Holy Writings, or who has but the least
degree of a common Historical Faith; there being innumerable Instances
of this nature in several Authors, both Antient and Modern, Sacred and
Profane. Whether such dark Presages, such Visions of the Night proceed
from any latent Power in the Soul, during this her state of Abstraction,
or from any Communication with the Supreme Being, or from any operation
of Subordinate Spirits, has been a great Dispute among the Learned; the
matter of Fact is, I think, incontestable, and has been looked upon as
such by the greatest Writers, who have been never suspected either of
Superstition or Enthusiasm.
I do not suppose, that the Soul in these Instances is entirely loose and
unfettered from the Body: It is sufficient, if she is not so far sunk,
and immersed in Matter, nor intangled and perplexed in her Operations,
with such Motions of Blood and Spirits, as when she actuates the Machine
in its waking Hours. The Corporeal Union is slackned enough to give the
Mind more Play. The Soul seems gathered within herself, and recovers
that Spring which is broke and weakned, when she operates more in
concert with the Body.
The Speculations I have here made, if they are not Arguments, they are
at least strong Intimations, not only of the Excellency of an Human
Soul, but of its Independence on the Body; and if they do not prove, do
at least confirm these two great Points, which are established by many
other Reasons that are altogether unanswerable.
O.
Part ii. § 11.
The reference is in the little book
On Superstition
,
where Plutarch quotes Heraclitus to add this comment of his own:
But to the superstitious man there is no common world, for neither
does he use right reason when awake, nor is he freed, when sleeping,
from his perturbations.
Tertullian, in his book
On the Soul,
has seven chapters (43-49) on
Sleep and Dreams, with abundant recognition of divine communications to
the soul in sleep, and quotations of several authors, sacred and profane.
Contents
|
Friday, September 19, 1712 |
Addison |
Quanti emptæ? parvi. Quanti ergo? octo assibus. Eheu!
Hor.

I find, by several Letters which I receive daily, that many of my
Readers would be better pleased to pay Three Half-Pence for my Paper,
than Two-Pence. The ingenious
T. W.
tells me, that I have deprived him
of the best Part of his Breakfast, for that since the rise of my Paper,
he is forced every Morning to drink his Dish of Coffee by it self,
without the Addition of the
Spectator
, that used to be better than
Lace to it.
Eugenius
informs me very obligingly, that he never thought
he should have disliked any Passage in my Paper, but that of late there
have been two Words in every one of them, which he could heartily wish
left out,
viz. Price Two-Pence
. I have a Letter from a Soap-boiler,
who condoles with me very affectionately, upon the necessity we both lie
under of setting an higher Price on our Commodities, since the late Tax
has been laid upon them, and de
Sir
ing me, when I write next on that
Subject, to speak a Word or two upon the present Duties on Castile-Soap.
But there is none of these my Correspondents, who writes with a greater
Turn of good Sense and Elegance of Expression, than the generous
Philomedes
, who advises me to value every
Spectator
at Six Pence,
and promises that he himself will engage for above a Hundred of his
Acquaintance, who shall take it in at that Price.
Letters from the Female World are likewise come to me, in great
quantities, upon the same Occasion; and as I naturally bear a great
Deference to this Part of our Species, I am very glad to find that those
who approve my Conduct in this Particular, are much more numerous than
those who condemn it. A large Family of Daughters have drawn me up a
very handsome Remonstrance, in which they set forth, that their Father
having refused to take in the
Spectator
, since the additional Price
was set upon it, they offered him unanimously to bate him the Article of
Bread and Butter in the Tea-Table Account, provided the
Spectator
might be served up to them every Morning as usual. Upon this the old
Gentleman, being pleased, it seems, with their De
Sir
e of improving
themselves, has granted them the continuance both of the
Spectator
and
their Bread and Butter; having given particular Orders, that the
Tea-Table shall be set forth every Morning with its Customary Bill of
Fare, and without any manner of Defalcation. I thought my self obliged
to mention this Particular, as it does Honour to this worthy Gentleman;
and if the young Lady
Lætitia
, who sent me this Account, will acquaint
me with his Name, I will insert it at length in one of my Papers, if he
de
Sir
es it.
I should be very glad to find out any Expedient that might alleviate the
Expence which this my Paper brings to any of my Readers; and, in order
to it, must propose two Points to their Consideration. First, that if
they retrench any the smallest Particular in their ordinary Expence, it
will easily make up the Half Penny a Day, which we have now under
Consideration. Let a Lady sacrifice but a single Ribband to her Morning
Studies, and it will be sufficient: Let a Family burn but a Candle a
Night less than the usual Number, and they may take in the
Spectator
without Detriment to their private Affairs.
In the next Place, if my Readers will not go to the Price of buying my
Papers by Retail, let them have Patience, and they may buy them in the
Lump, without the Burthen of a Tax upon them. My Speculations, when they
are sold single, like Cherries upon the Stick, are Delights for the Rich
and Wealthy; after some time they come to Market in greater Quantities,
and are every ordinary Man's Money. The Truth of it is, they have a
certain Flavour at their first Appearance, from several accidental
Circumstances of Time, Place and Person, which they may lose if they are
not taken early; but in this case every Reader is to consider, whether
it is not better for him to be half a Year behind-hand with the
fashionable and polite part of the World, than to strain himself beyond
his Circumstances. My Bookseller has now about Ten Thousand of the Third
and Fourth Volumes, which he is ready to publish, having already
disposed of as large an Edition both of the First and Second Volume. As
he is a Person whose Head is very well turned to his Business, he thinks
they would be a very proper Present to be made to Persons at
Christenings, Marriages, Visiting-Days, and the like joyful Solemnities,
as several other Books are frequently given at Funerals. He has printed
them in such a little portable Volume, that many of them may be ranged
together upon a single Plate; and is of Opinion, that a Salver of
Spectators
would be as acceptable an Entertainment to the Ladies, as a
Salver of Sweetmeats.
I shall conclude this Paper with an Epigram lately sent to the Writer of
the
Spectator
, after having returned my Thanks to the ingenious Author
of it.
Sir ,
'Having heard the following Epigram very much commended, I wonder that
it has not yet had a place in any of your Papers: I think the Suffrage
of our Poet Laureat should not be overlooked, which shews the Opinion
he entertains of your Paper, whether the Notion he proceeds upon be
true or false. I make bold to convey it to you, not knowing if it has
yet come to your Hands.
Sir ,
'Having heard the following Epigram very much commended, I wonder that
it has not yet had a place in any of your Papers: I think the Suffrage
of our Poet Laureat should not be overlooked, which shews the Opinion
he entertains of your Paper, whether the Notion he proceeds upon be
true or false. I make bold to convey it to you, not knowing if it has
yet come to your Hands.
On the SPECTATOR.
By Mr.
Tate1.
--Aliusque et idem
Nasceris—
Hor.
'When first the Tatler to a Mute was turn'd,
Great Britain for her Censor's Silence mourn'd.
Robb'd of his sprightly Beams, she wept the Night,
'Till the Spectator rose, and blaz'd as bright.
So the first Man the Sun's first Setting view'd,
And sigh'd, till circling Day his Joys renew'd;
Yet doubtful how that second Sun to name,
Whether a bright Successor, or the same.
So we: but now from this Suspense are freed,
Since all agree, who both with Judgment read,
'Tis the same Sun, and does himself succeed.'
O.
Nahum Tate, born and educated at Dublin, and befriended
in his youth by Dryden and Dorset, was at this time 60 years old, and
poet-laureate, having in 1692 succeeded in that office Thomas Shadwell,
the Whig substitute for Dryden. Besides his version of the Psalms
produced in concert with his friend Dr. Nicholas Brady, Tate produced
his own notion of an improvement upon Shakespeare's King Lear and nine
dramatic pieces, with other poetry, of which the above lines are a
specimen. Tate was in his younger days the writer of the second part of
Dryden's
Absalom and Achithophel,
to which Dryden himself contributed
only the characters of Julian Johnson as Ben Jochanan, of Shadwell as
Og, and of Settle as Doeg. His salary as poet-laureate was £100 a year,
and a butt of canary. He died three years after the date of this
Spectator
a poor man who had made his home in the Mint to escape his
creditors.
Contents
|
Saturday, September 20, 1712 |
Addison |

Sir ,
Upon reading your
Essay concerning the Pleasures of the Imagination,
I find, among the three Sources of those Pleasures which you have
discovered,
that Greatness is one. This has suggested to me the
reason why, of all Objects that I have ever seen, there is none which
affects my Imagination so much as the Sea or Ocean. I cannot see the
Heavings of this prodigious Bulk of Waters, even in a Calm, without a
very pleasing Astonishment; but when it is worked up in a Tempest, so
that the Horizon on every side is nothing but foaming Billows and
floating Mountains, it is impossible to describe the agreeable Horrour
that rises from such a Prospect. A troubled Ocean, to a Man who sails
upon it, is, I think, the biggest Object that he can see in motion,
and consequently gives his Imagination one of the highest kinds of
Pleasure that can arise from Greatness. I must confess, it is
impossible for me to survey this World of fluid Matter, without
thinking on the Hand that first poured it out, and made a proper
Channel for its Reception. Such an Object naturally raises in my
Thoughts the Idea of an Almighty Being, and convinces me of his
Existence as much as a metaphysical Demonstration. The Imagination
prompts the Understanding, and by the Greatness of the sensible
Object, produces in it the Idea of a Being who is neither
circumscribed by Time nor Space.
As I have made several Voyages upon the Sea, I have often been tossed
in Storms, and on that occasion have frequently reflected on the
Descriptions of them in ancient Poets. I remember
Longinus highly
recommends
one in
Homer, because the Poet has not amused himself
with little Fancies upon the occasion, as Authors of an inferiour
Genius, whom he mentions, had done, but because he has gathered
together those Circumstances which are the most apt to terrify the
Imagination, and which really happen in the raging of a Tempest
1.
It is for the same reason, that I prefer
the following Description of
a Ship in a Storm, which the Psalmist has made, before any other I
have ever met with.
They that go down to the Sea in Ships, that do Business in great
Waters: These see the Works of the Lord, and his Wonders in the
Deep. For he commandeth and raiseth the stormy Wind, which lifteth
up the Waters thereof. They mount up to the Heaven, they go down
again to the Depths, their Soul is melted because of Trouble. They
reel to and fro, and stagger like a drunken Man, and are at their
Wits End. Then they cry unto the Lord in their Trouble, and he
bringeth them out of their Distresses. He maketh the Storm a Calm,
so that the Waves thereof are still. Then they are glad because they
be quiet, so he bringeth them unto their deSir ed Haven.2
By the way, how much more comfortable, as well as rational, is this
System of the Psalmist, than the Pagan Scheme in
Virgil, and other
Poets, where one Deity is represented as raising a Storm, and another
as laying it? Were we only to consider the Sublime in this Piece of
Poetry, what can be nobler than the Idea it gives us of the Supreme
Being thus raising the Tumult among the Elements, and recovering them
out of their Confusion; thus troubling and becalming Nature?
Great Painters do not only give us Landskips of Gardens, Groves, and
Meadows, but very often employ their Pencils upon Sea-Pieces: I could
wish you would follow their Example. If this small Sketch may deserve
a Place among your Works, I
shall accompany it with a divine Ode, made
by a Gentleman
3 upon the Conclusion of his Travels.
| I |
r1c2 |
| I |
How are thy Servants blest, O Lord!
How sure is their Defence!
Eternal Wisdom is their Guide,
Their Help Omnipotence. |
| II |
In foreign Realms, and Lands remote,
Supported by thy Care,
Thro' burning Climes I pass'd unhurt,
And breath'd in tainted Air. |
| III |
Thy Mercy sweeten'd ev'ry Soil,
Made ev'ry Region please;
The hoary Alpine Hills it warm'd,
And smooth'd the Tyrrhene Seas: |
| IV |
Think, O my Soul, devoutly think,
How with affrighted Eyes
Thou saw'st the wide extended Deep
In all its Horrors rise! |
| V |
Confusion dwelt in ev'ry Face,
And Fear in ev'ry Heart;
When Waves on Waves, and Gulphs in Gulphs,
O'ercame the Pilot's Art. |
| VI |
Yet then from all my Griefs, O Lord,
Thy Mercy set me free,
Whilst in the Confidence of Pray'r
My Soul took hold on thee; |
| VII |
For tho' in dreadful Whirles we hung
High on the broken Wave,
I knew thou wert not slow to Hear,
Nor impotent to Save. |
| VIII |
The Storm was laid, the Winds retir'd,
Obedient to thy Will;
The Sea that roar'd at thy Command,
At thy Command was still. |
| IX |
In midst of Dangers, Fears and Death,
Thy Goodness I'll adore,
And praise Thee for Thy Mercies past;
And humbly hope for more. |
| X |
My Life, if thou preserv'st my Life,
Thy Sacrifice shall be;
And Death, if Death must be my Doom,
Shall join my Soul to thee. |
O.
On the Sublime
, § 10, where he compares a description of
the terrors of the sea in a lost poem on the Arimaspians, by Aristaeus
the Procomnesian, with the passage in the 15th Book of the
Iliad
, which
Pope thus translates:
He bursts upon them all:
Bursts as a wave that from the cloud impends,
And swell'd with tempests on the ship descends;
White are the decks with foam; the winds aloud
Howl o'er the masts, and sing through every shroud:
Pale, trembling, tir'd, the sailors freeze with fears,
And instant death on every wave appears.
Psalm
cvii. 23-30.
Addison.
Appended to this number is the following
Advertisement
.
The Author of the Spectator having received the Pastoral Hymn in his
441st Paper, set to Musick by one of the most Eminent Composers of our
own Country and by a Foreigner, who has not put his name to his
ingenious Letter, thinks himself obliged to return his thanks to those
Gentlemen for the Honour they have done him.
Contents
|
Monday, September 22, 1712 |
Steele |
Domus et placens Uxor.
Hor.

I have very long entertain'd an Ambition to make the Word
Wife
the
most agreeable and delightful Name in Nature. If it be not so in it
self, all the wiser Part of Mankind from the Beginning of the World to
this Day has consented in an Error: But our Unhappiness in
England
has
been, that a few loose Men of Genius for Pleasure, have turn'd it all to
the Gratification of ungovern'd De
Sir
es, in spite of good Sense, Form
and Order; when, in truth, any Satisfaction beyond the Boundaries of
Reason, is but a Step towards Madness and Folly. But is the Sense of Joy
and Accomplishment of De
Sir
e no way to be indulged or attain'd? and have
we Appetites given us not to be at all gratify'd? Yes certainly.
Marriage is an Institution calculated for a constant Scene of as much
Delight as our Being is capable of. Two Persons who have chosen each
other out of all the Species, with design to be each other's mutual
Comfort and Entertainment, have in that Action bound themselves to be
good-humour'd, affable, discreet, forgiving, patient and joyful, with
respect to each other's Frailties and Perfections, to the End of their
Lives. The wiser of the two (and it always happens one of them is such)
will for her or his own sake, keep things from Outrage with the utmost
Sanctity. When this Union is thus preserved (as I have often said) the
most indifferent Circumstance administers Delight. Their Condition is an
endless Source of new Gratifications. The married Man can say, If I am
unacceptable to all the World beside, there is one whom I entirely love,
that will receive me with Joy and Transport, and think herself obliged
to double her Kindness and Caresses of me from the Gloom with which she
sees me overcast. I need not dissemble the Sorrow of my Heart to be
agreeable there, that very Sorrow quickens her Affection.
This Passion towards each other, when once well fixed, enters into the
very Constitution, and the Kindness flows as easily and silently as the
Blood in the Veins. When this Affection is enjoy'd in the most sublime
Degree, unskilful Eyes see nothing of it; but when it is subject to be
chang'd, and has an Allay in it that may make it end in Distaste, it is
apt to break into Rage, or overflow into Fondness, before the rest of
the World.
Uxander
and
Viramira
are amorous and young, and have been married
these two Years; yet do they so much distinguish each other in Company,
that in your Conversation with the Dear Things you are still put to a
Sort of Cross-Purposes. Whenever you address your self in ordinary
Discourse to
Viramira
, she turns her Head another way, and the Answer
is made to the dear
Uxander
: If you tell a merry Tale, the Application
is still directed to her Dear; and when she should commend you, she says
to him, as if he had spoke it, That is, my Dear, so pretty—This puts
me in mind of what I have somewhere read in the admired Memoirs of the
famous
Cervantes
, where, while honest
Sancho Pana
is putting some
necessary humble Question concerning
Rozinante
, his Supper, or his
Lodgings, the Knight of the Sorrowful Countenance is ever improving the
harmless lowly Hints of his Squire to the poetical Conceit, Rapture and
Flight, in Contemplation of the dear
Dulcinea
of his Affections.
On the other side,
Dictamnus
and
Moria
are ever squabbling, and you
may observe them all the time they are in Company in a State of
Impatience. As
Uxander
and
Viramira
wish you all gone, that they may
be at freedom for Dalliance;
Dictamnus
and
Moria
wait your Absence,
that they may speak their harsh Interpretations on each other's Words
and Actions during the time you were with them.
It is certain that the greater Part of the Evils attending this
Condition of Life, arises from Fashion. Prejudice in this Case is turn'd
the wrong way, and instead of expecting more Happiness than we shall
meet with in it, we are laugh'd into a Prepossession, that we shall be
disappointed if we hope for lasting Satisfactions.
With all Persons who have made good Sense the Rule of Action, Marriage
is describ'd as the State capable of the highest human Felicity.
Tully
has Epistles full of affectionate Pleasure, when he writes to his Wife,
or speaks of his Children. But
all the Hints of this kind I have
met with in Writers of ancient date, I am pleas'd with an Epigram of
Martial
in honour of the Beauty of his Wife
Cleopatra
.
Commentators say it was written the day after his Wedding-Night. When
his Spouse was retir'd to the Bathing-room in the Heat of the Day, he,
it seems, came in upon her when she was just going into the Water. To
her Beauty and Carriage on this occasion we owe the following Epigram,
which I shew'd my Friend
Will. Honeycomb
in
French
, who has translated
it as follows, without understanding the Original. I expect it will
please the
English
better than the
Latin
Reader.
When my bright Consort, now nor Wife nor Maid,
Asham'd and wanton, of Embrace afraid,
Fled to the Streams, the Streams my Fair betray'd;
To my fond Eyes she all transparent stood,
She blush'd, I smil'd at the slight covering Flood.
Thus thro' the Glass the Lovely Lilly glows,
Thus thro' the ambient Gem shines forth the Rose.
I saw new Charms, and plung'd to seize my Store,
Kisses I snatch'd, the Waves prevented more.
My Friend would not allow that this luscious Account could be given of a
Wife, and therefore used the Word
Consort
; which, he learnedly said,
would serve for a Mistress as well, and give a more Gentlemanly Turn to
the Epigram. But, under favour of him and all other such fine Gentlemen,
I cannot be persuaded but that the Passion a Bridegroom has for a
virtuous young Woman, will,
little and little, grow into Friendship,
and then it is ascended to
a
higher Pleasure than it was in its
first Fervour. Without this happens, he is a very unfortunate Man who
has enter'd into this State, and left the Habitudes of Life he might
have enjoy'd with a faithful Friend. But when the Wife proves capable of
filling serious as well as joyous Hours, she brings Happiness unknown to
Friendship itself.
Spencer
of each kind of Love with great
Justice, and attributes the highest Praise to Friendship; and indeed
there is no disputing that Point, but by making that Friendship take
Place
between two married Persons.
Hard is the Doubt, and difficult to deem,
When all three kinds of Love together meet,
And to dispart the Heart with Power extreme,
Whether shall weigh the Ballance down; to wit,
The dear Affection unto Kindred sweet,
Or raging Fire of Love to Womenkind,
Or Zeal of Friends combin'd by Virtues meet.
But, of them all, the Band of virtuous Mind
Methinks the gentle Heart should most assured bind.
For natural Affection soon doth cease,
And quenched is with Cupid's greater Flame;
But faithful Friendship doth them both suppress,
And them with mastering Discipline does tame,
Through Thoughts aspiring to eternal Fame.
For as the Soul doth rule the Earthly Mass,
And all the Service of the Body frame;
So Love of Soul doth Love of Body pass,
No less than perfect Gold surmounts the meanest Brass.
T.
Lib. iv. ep. 22.
an
its Place
Contents
|
Tuesday, September 23, 1712 |
Steele |
Digna satis fortuna revisit.
Virg.

It is common with me to run from Book to Book to exercise my Mind with
many Objects, and qualify my self for my daily Labours. After an Hour
spent in this loitering Way of Reading, something will remain to be Food
to the Imagination. The Writings that please me most on such Occasions
are Stories, for the Truth of which there is good Authority. The Mind of
Man is naturally a Lover of Justice, and when we read a Story wherein a
Criminal is overtaken, in whom there is no Quality which is the Object
of Pity, the Soul enjoys a certain Revenge for the Offence done to its
Nature, in the wicked Actions committed in the preceding Part of the
History.
will be better understood by the Reader from the following
Narration
it self, than from any thing which I can say to introduce
it.
When
Charles
Duke of
Burgundy
, surnamed
The Bold
, reigned over
spacious Dominions now swallowed up by the Power of
France
, he heaped
many Favours and Honours upon
Claudius Rhynsault
, a
German
, who had
serv'd him in his Wars against the Insults of his Neighbours. A great
part of
Zealand
was at that time in Subjection to that Dukedom. The
Prince himself was a Person of singular Humanity and Justice.
Rhynsault
, with no other real Quality than Courage, had Dissimulation
enough to pass upon his generous and unsuspicious Master for a Person of
blunt Honesty and Fidelity, without any Vice that could bias him from
the Execution of Justice. His Highness prepossessed to his Advantage,
upon the Decease of the Governour of his chief Town of
Zealand
, gave
Rhynsault
that Command. He was not long seated in that Government,
before he cast his Eyes upon
Sapphira
, a Woman of Exquisite Beauty,
the Wife of
Paul Danvelt
, a wealthy Merchant of the City under his
Protection and Government.
Rhynsault
was a Man of a warm Constitution,
and violent Inclination to Women, and not unskilled in the soft Arts
which win their Favour. He knew what it was to enjoy the Satisfactions
which are reaped from the Possession of Beauty, but was an utter
Stranger to the Decencies, Honours and Delicacies that attend the
Passion towards them in elegant Minds. However he had so much of the
World, that he had a great share of the Language which usually prevails
upon the weaker Part of that Sex, and he could with his Tongue utter a
Passion with which his Heart was wholly untouch'd. He was one of those
brutal Minds which can be gratified with the Violation of Innocence and
Beauty, without the least Pity, Passion or Love to that with which they
are so much delighted. Ingratitude is a Vice inseparable to a lustful
Man; and the Possession of a Woman by him who has no thought but
allaying a Passion painful to himself, is necessarily followed by
Distaste and Aversion.
Rhynsault
being resolv'd to accomplish his Will
on the Wife of
Danvelt
, left no Arts untried to get into a Familiarity
at her House; but she knew his Character and Disposition too well, not
to shun all Occasions that might ensnare her into his Conversation. The
Governor despairing of Success by ordinary Means, apprehended and
Imprisoned her Husband, under pretence of an Information that he was
guilty of a Correspondence with the Enemies of the Duke, to betray the
Town into their Possession. This Design had its de
Sir
ed Effect; and the
Wife of the unfortunate
Danvelt
, the day before that which was
appointed for his Execution, presented herself in the Hall of the
Governor's House, and as he pass'd thro' the Apartment, threw her self
at his Feet, and holding his Knees, beseeched his Mercy.
Rhynsault
beheld her with a dissembled Satisfaction, and assuming an Air of
Thought and Authority, he bid her arise, and told her she must follow
him to his Closet; and asking her whether she knew the Hand of the
Letter he pulled out of his Pocket, went from her, leaving this
Admonition aloud,
If you will save your Husband, you must give me an
account of all you know without Prevarication; for every body is
satisfied he was too fond of you to be able to hide from you the Names
of the rest of the Conspirators, or any other Particulars whatsoever
.
He went to his Closet, and soon after the Lady was sent to for an
Audience. The Servant knew his distance when Matters of State were to be
debated; and the Governor, laying aside the Air with which he had
appear'd in publick, began to be the Supplicant, to rally an Affliction,
which it was in her Power easily to remove, and relieve an innocent Man
from his Imprisonment. She easily perceiv'd his Intention, and, bathed
in Tears, began to deprecate so wicked a Design. Lust, like Ambition,
takes all the Faculties of the Mind and Body into its Service and
Subjection. Her becoming Tears, her honest Anguish, the wringing of her
Hands, and the many Changes of her Posture and Figure in the Vehemence
of speaking, were but so many Attitudes in which he beheld her Beauty,
and further Incentives of his De
Sir
e. All Humanity was lost in that one
Appetite, and he signified to her in so many plain Terms, that he was
unhappy till he had possess'd her, and nothing less shou'd be the Price
of her Husband's Life; and she must, before the following Noon,
pronounce the Death or Enlargement of
Danvelt
. After this
Notification, when he saw
Sapphira
enough again distracted to make the
Subject of their Discourse to common Eyes appear different from what it
was, he called Servants to conduct her to the Gate. Loaded with
insupportable Affliction, she immediately repairs to her Husband, and
having signified to his Gaolers, that she had a Proposal to make to her
Husband from the Governor, she was left alone with him, reveal'd to him
all that had pass'd, and represented the endless Conflict she was in
between Love to his Person, and Fidelity to his Bed. It is easie to
imagine the sharp Affliction this honest Pair was in upon such an
Incident, in Lives not us'd to any but ordinary Occurrences. The Man was
bridled by Shame from speaking what his Fear prompted, upon so near an
approach of Death; but let fall Words that signify'd to her, he should
not think her polluted, though she had not yet confess'd to him that the
Governor had violated her Person, since he knew her Will had no part in
the Action. She parted from him with this oblique Permission to save a
Life he had not Resolution enough to resign for the safety of his
Honour.
The next Morning the unhappy
Sapphira
attended the Governor, and being
led into a remote Apartment, submitted to his De
Sir
es.
Rhynsault
commended her Charms, claim'd a Familiarity after what had pass'd
between them, and with an Air of Gaiety in the Language of a Gallant,
bid her return, and take her Husband out of Prison: But, continu'd he,
my Fair one must not be offended that I have taken care he should not be
an Interruption to our future Assignations. These last Words foreboded
what she found when she came to the Gaol, her Husband executed by the
Order of
Rhynsault.
It was remarkable that the Woman, who was full of Tears and Lamentations
during the whole Course of her Affliction, uttered neither Sigh nor
Complaint, but stood fix'd with Grief at this Consummation of her
Misfortunes. She betook herself to her abode, and after having in
Solitude paid her Devotions to him who is the Avenger of Innocence, she
repair'd privately to Court. Her Person and a certain Grandeur of Sorrow
negligent of Forms gain'd her Passage into the Presence of the Duke her
Sovereign. As soon as she came into the Presence, she broke forth into
the following words,
Behold, O mighty
Charles,
a Wretch weary of
Life, though it has always been spent with Innocence and Virtue. It is
not in your power to redress my Injuries, but it is to avenge them. And
if the Protection of the Distress'd, and the Punishment of Oppressors,
is a Task worthy a Prince, I bring the Duke of
Burgundy
ample matter
for doing Honour to his own great Name, and wiping Infamy off of mine.
When she had spoke this, she deliver'd the Duke a Paper reciting her
Story. He read it with all the Emotions that Indignation and Pity could
raise in a Prince jealous of his Honour in the Behaviour of his
Officers, and Prosperity of his Subjects.
Upon an appointed Day,
Rhynsault
was sent for to Court, and in the
Presence of a few of the Council, confronted by
Sapphira
: the Prince
asking,
Do you know that Lady? Rhynsault
, as soon as he could
recover his Surprize, told the Duke he would marry her, if his Highness
would please to think that a Reparation. The Duke seem'd contented with
this Answer, and stood by during the immediate Solemnization of the
Ceremony. At the Conclusion of it he told
Rhynsault, Thus far have you
done as constrain'd by my Authority: I shall not be satisfied of your
kind Usage of her, without you sign a Gift of your whole Estate to her
after your Decease
. To the Performance of this also the Duke was a
Witness. When these two Acts were executed, the Duke turn'd to the Lady,
and told her, it now remains for me to put you in quiet Possession of
what your Husband has so bountifully bestow'd on you; and order'd the
immediate Execution of
Rhynsault
.
T.
Founded upon note N to the Memoir of Charles of Burgundy in
Bayle's Dictionary
, where the authorities cited are Pontus Heuterus and
others. It is not in Comines.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 24, 1712 |
Steele |
Quicquid est boni moris Levitate extinguiter.
Sen.

Tunbridge, Sept. 18.
Dear Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am a young Woman of Eighteen Years of Age, and, I do assure you, a
Maid of unspotted Reputation, founded upon a very careful Carriage in
all my Looks, Words and Actions. At the same time I must own to you,
that it is with much constraint to Flesh and Blood that my Behaviour
is so strictly irreproachable; for I am naturally addicted to Mirth,
to Gaiety, to a Free Air, to Motion and Gadding. Now what gives me a
great deal of Anxiety, and is some Discouragement in the Pursuit of
Virtue, is, that the young Women who run into greater Freedoms with
the Men are more taken Notice of than I am. The Men are such
unthinking Sots, that they do not prefer her who restrains all her
Passions and Affections and keeps much within the Bounds of what is
lawful, to her who goes to the utmost Verge of Innocence, and parlies
at the very Brink of Vice, whether she shall be a Wife or a Mistress.
But I must appeal to your Spectatorial Wisdom, who, I find, have
passed very much of your Time in the Study of Woman, whether this is
not a most unreasonable Proceeding. I have read somewhere, that
Hobbes of
Malmesbury asserts, that continent Persons have more of
what they contain, than those who give a loose to their De
Sir es.
According to this Rule, let there be equal Age, equal Wit, and equal
Good-Humour, in the Woman of Prudence, and her of Liberty; what Stores
has he to expect, who takes the former? What Refuse must he be
contented with, who chuses the latter? Well, but I sate down to write
to you to vent my Indignation against several pert Creatures who are
address'd to and courted in this Place, while poor I, and two or three
like me, are wholly unregarded.
Every one of these affect gaining the Hearts of your Sex: This is
generally attempted by a particular manner of carrying themselves with
Familiarity.
Glycera has a dancing Walk, and keeps Time in her
ordinary Gate.
Chloe, her Sister, who is unwilling to interrupt her
Conquests, comes into the Room before her with a familiar Run.
Dulcissa takes Advantage of the Approach of the Winter, and has
introduc'd a very pretty Shiver; closing up her Shoulders, and
shrinking as she moves. All that are in this Mode carry their Fans
between both Hands before them.
Dulcissa herself, who is Author of
this Air, adds the pretty Run to it; and has also, when she is in very
good Humour, a taking Familiarity in throwing herself into the lowest
Seat in the Room, and letting her hoop'd Petticoats fall with a lucky
Decency about her. I know she practices this way of sitting down in
her Chamber; and indeed she does it as well as you may have seen an
Actress fall down dead in a Tragedy. Not the least Indecency in her
Posture. If you have observ'd what pretty Carcasses are carry'd off at
the end of a Verse at the Theatre, it will give you a Notion how
Dulcissa plumps into a Chair. Here's a little Country Girl that's
very cunning, that makes her use of being young and unbred, and
outdoes the Insnarers, who are almost twice her Age. The Air that she
takes is to come into Company after a Walk, and is very successfully
out of Breath upon occasion. Her Mother is in the Secret, and calls
her Romp, and then looks round to see what young Men stare at her.
It would take up more than can come into one of your Papers, to
enumerate all the particular Airs of the younger Company in this
Place. But I cannot omit
Dulceorella, whose manner is the most
indolent imaginable, but still as watchful of Conquest as the busiest
Virgin among us. She has a peculiar Art of staring at a young Fellow,
till she sees she has got him, and inflam'd him by so much
Observation. When she sees she has him, and he begins to toss his Head
upon it, she is immediately short-sighted, and labours to observe what
he is at a distance with her Eyes half shut. Thus the Captive, that
thought her first struck, is to make very near Approaches, or be
wholly disregarded. This Artifice has done more Execution than all the
ogling of the rest of the Women here, with the utmost Variety of half
Glances, attentive Heedlessnesses, childish Inadvertencies, haughty
Contempts, or artificial Oversights. After I have said thus much of
Ladies among us who fight thus regularly, I am to complain to you of a
Set of Familiar Romps, who have broken thro' all common Rules, and
have thought of a very effectual way of shewing more Charms than all
of us. These, Mr. SPECTATOR, are the Swingers. You are to know these
careless pretty Creatures are very Innocents again; and it is to be no
matter what they do, for 'tis all harmless Freedom. They get on Ropes,
as you must have seen the Children, and are swung by their Men
Visitants. The Jest is, that Mr. such a one can name the Colour of
Mrs. Such-a-one's Stockings; and she tells him, he is a lying Thief,
so he is, and full of Roguery; and she'll lay a Wager, and her Sister
shall tell the Truth if he says right, and he can't tell what Colour
her Garters are of. In this Diversion there are very many pretty
Shrieks, not so much for fear of falling, as that their Petticoats
shou'd untye: For there is a great care had to avoid Improprieties;
and the Lover who swings the Lady, is to tye her Clothes very close
with his Hatband, before she admits him to throw up her Heels.
'Now,
Mr. SPECTATOR, except you can note these Wantonnesses in their
Beginnings, and bring us sober Girls into Observation, there is no
help for it, we must swim with the Tide; the Coquets are too powerful
a Party for us. To look into the Merit of a regular and well-behav'd
Woman, is a slow thing. A loose trivial Song gains the Affections,
when a wise Homily is not attended to. There is no other way but to
make war upon them, or we must go over to them. As for my Part, I will
shew all the World it is not for want of Charms that I stand so long
unasked; and if you do not take measures for the immediate Redress of
us Rigids, as the Fellows call us, I can move with a speaking Mien,
can look significantly, can lisp, can trip, can loll, can start, can
blush, can rage, can weep, if I must do it, and can be frighted as
agreeably as any She in
England. All which is humbly submitted to
your Spectatorial Consideration with all Humility, by
Your most humble Servant,
Matilda Mohair.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, September 25, 1712 |
Steele |
Qualem commendes etiam atque etiam adspice, ne mox
Incutiant aliena tibi peccata pudorem.
Hor.

It is no unpleasant matter of Speculation to consider the recommendatory
Epistles that pass round this Town from Hand to Hand, and the abuse
People put upon one another in that kind. It is indeed come to that
pass, that instead of being the Testimony of Merit in the Person
recommended, the true reading of a Letter of this sort is,
The Bearer hereof is so uneasie to me, that it will be an Act of
Charity in you to take him off my Hands; whether you prefer him or
not, it is all one, for I have no manner of Kindness for him, or
Obligation to him or his; and do what you please as to that.
As negligent as Men are in this respect, a point of Honour is concerned
in it; and there is nothing a Man should be more ashamed of, than
passing a worthless Creature into the Service or Interests of a Man who
has never injured you. The Women indeed are a little too keen in their
Resentments, to trespass often this Way: But you shall sometimes know
that the Mistress and the Maid shall quarrel, and give each other very
free Language, and at last the Lady shall be pacified to turn her out of
Doors, and give her a very good Word to any body else. Hence it is that
you see, in a Year and Half's time, the same Face a Domestick in all
parts of the Town. Good-breeding and Good-nature lead People in a great
Measure to this Injustice: When Suitors of no Consideration will have
Confidence enough to press upon their Superiors, those in Power are
tender of speaking the Exceptions they have against them, and are
mortgaged into Promises out of their Impatience of Importunity. In this
latter Case, it would be a very useful Enquiry to know the History of
Recommendations: There are, you must know, certain Abettors of this way
of Torment, who make it a Profession to manage the Affairs of
Candidates: These Gentlemen let out their Impudence to their Clients,
and supply any Defective Recommendation, by informing how such and such
a Man is to be attacked. They will tell you, get the least Scrap from
Mr. Such-a-one, and leave the rest to them. When one of these
Undertakers have your Business in hand, you may be sick, absent in Town
or Country, and the Patron shall be worried, or you prevail. I remember
to have been shewn a Gentleman some Years ago, who punish'd a whole
People for their Facility in giving their Credentials. This Person had
belonged to a Regiment which did Duty in the
West-Indies
, and by the
Mortality of the Place happened to be commanding Officer in the Colony.
He oppressed his Subjects with great frankness, till he became sensible
that he was heartily hated by every Man under his Command. When he had
carried his Point, to be thus detestable, in a pretended Fit of
Dishumour, and feigned Uneasiness of living where he found he was so
universally unacceptable, he communicated to the chief Inhabitants a
Design he had to return for
England
, provided they would give him
ample Testimonials of their Approbation. The Planters came into it to a
Man; and in proportion to his deserving the quite contrary, the Words
Justice, Generosity, and Courage, were inserted in his Commission, not
omitting the general Good-liking of People of all Conditions in the
Colony. The Gentleman returns for
England
, and within few Months after
came back to them their Governour on the Strength of their own
Testimonials.
Such a Rebuke as this cannot indeed happen to easy Recommenders, in the
ordinary course of things from one hand to another; but how would a Man
bear to have it said to him, the Person I took into Confidence on the
Credit you gave him, has proved false, unjust, and has not answered any
way the Character you gave me of him?
I cannot but conceive very good hopes of that Rake
Jack Toper
of the
Temple
, for an honest Scrupulousness in this Point. A Friend of his
meeting with a Servant that had formerly lived with
Jack
, and having a
mind to take him, sent to him to know what Faults the Fellow had, since
he could not please such a careless Fellow as he was. His Answer was as
follows:
Sir ,
'Thomas that lived with me was turned away because he was too good for
me. You know I live in Taverns; he is an orderly sober Rascal, and
thinks much to sleep in an Entry till two in a Morning. He told me one
day when he was dressing me, that he wondered I was not dead before
now, since I went to Dinner in the Evening, and went to Supper at two
in the Morning. We were coming down Essex-street one Night a little
flustrated, and I was giving him the Word to alarm the Watch; he had
the Impudence to tell me it was against the Law. You that are married,
and live one Day after another the same Way, and so on the whole Week,
I dare say will like him, and he will be glad to have his Meat in due
Season. The Fellow is certainly very Honest. My Service to your Lady.
Yours, J. T.
Now this was very fair Dealing.
Jack
knew very well, that though the
Love of Order made a Man very awkward in his Equipage, it was a valuable
Quality among the Queer People who live by Rule; and had too much good
Sense and good Nature to let the Fellow starve, because he was not fit
to attend his Vivacities.
I shall end this Discourse with a Letter of Recommendation from
Horace
to
Claudius Nero
. You will see in that Letter a Slowness to ask a
Favour, a strong Reason for being unable to deny his good Word any
longer, and that it is a Service to the Person to whom he recommends, to
comply with what is asked: All which are necessary Circumstances, both
in Justice and Good-breeding, if a Man would ask so as to have reason to
complain of a Denial; and indeed a Man should not in strictness ask
otherwise. In hopes
Authority of
Horace
, who perfectly understood
how to live with great Men, may have a good Effect towards amending this
Facility in People of Condition, and the Confidence of those who apply
to them without Merit, I have translated the Epistle
.
To Claudius Nero.
Sir ,
'Septimus, who waits upon you with this, is very well acquainted
with the place you are pleased to allow me in your Friendship. For
when he beseeches me to recommend him to your Notice, in such a manner
as to be received by you, who are delicate in the choice of your
Friends and Domesticks, he knows our Intimacy, and understands my
Ability to serve him better than I do myself. I have defended my self
against his Ambition to be yours, as long as I possibly could; but
fearing the Imputation of hiding my Power in you out of mean and
selfish Considerations, I am at last prevailed upon to give you this
Trouble. Thus, to avoid the Appearance of a greater Fault, I have put
on this Confidence. If you can forgive this Transgression of Modesty
in behalf of a Friend, receive this Gentleman into your Interests and
Friendship, and take it from me that he is an honest and brave Man.
T.
This is a translation from Horace of the verse of No. 9 in
Book I. of his
Epistles
; showing how it would read in the customary
prose form of a letter of introduction.
Contents
|
Friday, September 26, 1712 |
Addison |
Ægritudinem laudare, unam rem maximè detestabilem, quorum est tandem
Philosophorum?
Cic.

About an Age ago it was the fashion in
England
, for every one that
would be thought religious, to throw as much Sanctity as possible into
his Face, and in particular to abstain from all Appearances of Mirth and
Pleasantry, which were looked upon as the Marks of a Carnal Mind. The
Saint was of a sorrowful Countenance, and generally eaten up with Spleen
and Melancholy. A
, who was lately a great Ornament to the
Learned World
, has diverted me more than once with an Account of the
Reception
he met with from a very famous Independent Minister, who
was Head of a College in those times
. This Gentleman was then a
young Adventurer in the Republick of Letters, and just fitted out for
the University with a good Cargo of
Latin
and
Greek
. His Friends
were resolved that he should try his Fortune at an Election which was
drawing near in the College, of which the Independent Minister whom I
have before mentioned was Governor. The Youth, according to Custom,
waited on him in order to be examined. He was received at the Door by a
Servant, who was one of that gloomy Generation that were then in
fashion. He conducted him, with great Silence and Seriousness, to a long
Gallery which was darkned at Noon-day, and had only a single Candle
burning in it. After a short stay in this melancholy Apartment, he was
led into a Chamber hung with Black, where he entertained himself for
some time by the glimmering of a Taper, till at length the Head of the
College came out to him, from an inner Room, with half a Dozen Night
Caps upon his Head, and a religious Horror in his Countenance. The young
Man trembled; but his Fears encreased when, instead of being ask'd what
Progress he had made in Learning, he was examined how he abounded in
Grace. His
Latin
and
Greek
stood him in little stead; he was to give
an account only of the state of his Soul, whether he was of the Number
of the Elect; what was the Occasion of his Conversion; upon what Day of
the Month, and Hour of the Day it happened; how it was carried on, and
when compleated. The whole Examination was summed up with one short
Question, namely,
Whether he was prepared for Death?
The Boy, who had
been bred up by honest Parents, was frighted out of his Wits at the
Solemnity of the Proceeding, and by the last dreadful Interrogatory; so
that upon making his Escape out of this House of Mourning, he could
never be brought a second time to the Examination, as not being able to
go through the Terrors of it.
Notwithstanding this general Form and Outside of Religion is pretty well
worn out among us, there are many Persons, who, by a natural
Unchearfulness of Heart, mistaken Notions of Piety, or Weakness of
Understanding, love to indulge this uncomfortable way of Life, and give
up themselves a Prey to Grief and Melancholy. Superstitious Fears and
groundless Scruples cut them off from the Pleasures of Conversation, and
all those social Entertainments, which are not only innocent, but
laudable; as if Mirth was made for Reprobates, and Chearfulness of Heart
denied those who are the only Persons that have a proper Title to it.
Sombrius
is one of these Sons of Sorrow. He thinks himself obliged in
Duty to be sad and disconsolate. He looks on a sudden fit of Laughter as
a Breach of his Baptismal Vow. An innocent Jest startles him like
Blasphemy. Tell him of one who is advanced to a Title of Honour, he
lifts up his Hands and Eyes; describe a publick Ceremony, he shakes his
Head; shew him a gay Equipage, he blesses himself. All the little
Ornaments of Life are Pomps and Vanities. Mirth is wanton, and Wit
profane. He is scandalized at Youth for being lively, and at Childhood
for being playful. He sits at a Christening, or a Marriage Feast, as at
a Funeral; sighs at the Conclusion of a merry Story, and grows devout
when the rest of the Company grow pleasant. After all,
Sombrius
is a
religious Man, and would have behaved himself very properly, had he
lived when Christianity was under a general Persecution.
I would by no means presume to tax such Characters with Hypocrisy, as is
done too frequently; that being a Vice which I think none but He, who
knows the Secrets of Men's Hearts, should pretend to discover in
another, where the Proofs of it do not amount to a Demonstration. On the
contrary, as there are many excellent Persons, who are weighed down by
this habitual Sorrow of Heart, they rather deserve our Compassion than
our Reproaches. I think, however, they would do well to consider,
whether such a Behaviour does not deter Men from a Religious Life, by
representing it as an unsociable State, that extinguishes all Joy and
Gladness, darkens the Face of Nature, and destroys the Relish of Being
it self.
I have, in former Papers, shewn how great a Tendency there is to
Chearfulness in Religion, and how such a Frame of Mind is not only the
most lovely, but the most commendable in a virtuous Person. In short,
those who represent Religion in so unamiable a Light, are like the Spies
sent by
Moses
to make a Discovery of the Land of
Promise
, when by
their Reports they discouraged the People from entering upon it. Those
who shew us the Joy, the Chearfulness, the Good-humour, that naturally
spring up in this happy State, are like the Spies bringing along with
them the Clusters of Grapes, and delicious Fruits, that might invite
their Companions into the pleasant Country which produced them.
eminent Pagan Writer
has made a Discourse, to shew that the
Atheist, who denies a God, does him less Dishonour than the Man who owns
his Being, but at the same time believes him to be cruel, hard to
please, and terrible to Human Nature. For my own part, says he, I would
rather it should be said of me, that there was never any such Man as
Plutarch
, than that
Plutarch
was ill-natured, capricious, or inhuman.
If we may believe our Logicians, Man is distinguished from all other
Creatures by the Faculty of Laughter. He has an Heart capable of Mirth,
and naturally disposed to it. It is not the Business of Virtue to
extirpate the Affections of the Mind, but to regulate them. It may
moderate and restrain, but was not designed to banish Gladness from the
Heart of Man. Religion contracts the Circle of our Pleasures, but leaves
it wide enough for her Votaries to expatiate in. The Contemplation of
the Divine Being, and the Exercise of Virtue, are in their own Nature so
far from excluding all Gladness of Heart, that they are perpetual
Sources of it. In a word, the true Spirit of Religion cheers, as well as
composes the Soul; it banishes indeed all Levity of Behaviour, all
vicious and dissolute Mirth, but in exchange fills the Mind with a
perpetual Serenity, uninterrupted Chearfulness, and an habitual
Inclination to please others, as well as to be pleased in it self.
O.
Supposed to be Anthony Henley, a gentleman of property, who
corresponded with Swift, was a friend of Steele's, and contributed some
unidentified papers to the
Tatler
. He died in August, 1711.
Dr. Thomas Goodwin, who was born in 1600, and educated at
Cambridge. He was one of those who, like Milton's tutor, Dr. Thomas
Young, went to Holland to escape from persecution, and was pastor of the
English church at Arnheim, till in the Civil Wars he came to London, and
sat at Westminster as one of the Assembly of Divines. In 1649 Cromwell
made him President of Magdalen College As Oliver Cromwell's chaplain, he
prayed with and for him in his last illness. At the Restoration, Dr.
Goodwin was deprived of his post at Oxford, and he then preached in
London to an Assembly of Independents till his death, in 1679. His works
were collected in five volumes folio.
Plutarch, in his short Treatise
On Superstition
.
Contents
|
Saturday, September 27, 1712 |
Addison |
Duris ut ilex tonsa bipennibus
Nigræ feraci frondis in Algido,
Per damna, per cades, ab ipso
Ducit opes animumque ferro.
Hor.

As I am one, who, by my Profession, am obliged to look into all kinds of
Men, there are none whom I consider with so much Pleasure, as those who
have any thing new or extraordinary in their Characters, or Ways of
living. For this reason I have often amused my self with Speculations on
the Race of People called
Jews
, many of whom I have met with in most
of the considerable Towns which I have passed through in the Course of
my Travels. They are, indeed, so disseminated through all the trading
parts of the World, that they are become the Instruments by which the
most distant Nations converse with one another, and by which Mankind are
knit together in a general Correspondence: They are like the Pegs and
Nails in a great Building, which, though they are but little valued in
themselves, are absolutely necessary to keep the whole Frame together.
That I may not fall into any common beaten Tracks of Observation, I
shall consider this People in three Views: First, with regard to their
Number; Secondly, their Dispersion; and, Thirdly, their Adherence to
their Religion: and afterwards endeavour to shew, First, what Natural
Reasons, and, Secondly, what Providential Reasons may be assigned for
these three remarkable Particulars.
The
Jews
are looked upon by many to be as numerous at present, as they
were formerly in the Land of
Canaan
.
This is wonderful, considering the dreadful Slaughter made of them under
some of the
Roman
Emperors, which Historians describe by the Death of
many Hundred Thousands in a War; and the innumerable Massacres and
Persecutions they have undergone in
Turkey
, as well as in all
Christian Nations of the World. The
Rabbins
, to express the great
Havock which has been sometimes made of them, tell us, after their usual
manner of Hyperbole, that there were such Torrents of Holy Blood shed as
carried Rocks of an hundred Yards in Circumference above three Miles
into the Sea.
Their Dispersion is the second remarkable Particular in this People.
They swarm over all the
East
; and are settled in the remotest Parts of
China
: They are spread through most of the Nations of
Europe
and
Africk
, and many Families of them are established in the
West-Indies
: not to mention whole Nations bordering on
Prester-John's
Country, and some discovered in the inner Parts of
America
, if we may give any Credit to their own Writers.
Their firm Adherence to their Religion, is no less remarkable than their
Numbers and Dispersion, especially considering it as persecuted or
contemned over the Face of the whole Earth. This is likewise the more
remarkable, if we consider the frequent Apostacies of this People, when
they lived under their Kings, in the Land of
Promise
, and within sight
of their Temple.
If in the next place we examine, what may be the Natural Reasons for
these three Particulars which we find in the
Jews
, and which are not
to be found in any other Religion or People, I can, in the first place,
attribute their Numbers to nothing but their constant Employment, their
Abstinence, their Exemption from Wars, and above all, their frequent
Marriages; for they look on Celibacy as an accursed State, and generally
are married before Twenty, as hoping the
Messiah
may descend from them.
The Dispersion of the
Jews
into all the Nations of the Earth, is the
second remarkable Particular of that People, though not so hard to be
accounted for. They were always in Rebellions and Tumults while they had
the Temple and Holy City in View, for which reason they have often been
driven out of their old Habitations in the Land of
Promise
. They have
as often been banished out of most other Places where they have settled,
which must very much disperse and scatter a People, and oblige them to
seek a Livelihood where they can find it. Besides, the whole People is
now a Race of such Merchants as are Wanderers by Profession, and at the
same time, are in most if not all Places incapable of either Lands or
Offices, that might engage them to make any Part of the World their
Home.
This Dispersion would probably have lost their Religion, had it not been
secured by the Strength of its Constitution: For they are to live all in
a Body, and generally within the same Enclosure; to marry among
themselves, and to eat no Meats that are not killed or prepared their
own way. This shuts them out from all Table Conversation, and the most
agreeable Intercourses of Life; and, by consequence, excludes them from
the most probable Means of Conversion.
If, in the last place, we consider what Providential Reason may be
assigned for these three Particulars, we shall find that their Numbers,
Dispersion, and Adherence to their Religion, have furnished every Age,
and every Nation of the World, with the strongest Arguments for the
Christian Faith, not only as these very Particulars are foretold of
them, but as they themselves are the Depositaries of these and all the
other Prophecies, which tend to their own Confusion. Their Number
furnishes us with a sufficient Cloud of Witnesses that attest the Truth
of the Old Bible. Their Dispersion spreads these Witnesses thro' all
parts of the World. The Adherence to their Religion makes their
Testimony unquestionable. Had the whole Body of the
Jews
been
converted to Christianity, we should certainly have thought all the
Prophecies of the old Testament, that relate to the Coming and History
of our Blessed Saviour, forged by Christians, and have looked upon them,
with the Prophecies of the
Sybils
, as made many Years after the Events
they pretended to foretell.
O.
Contents
|
Monday, September 29, 1712 |
Steele |
Gnatum pariter uti his decuit aut etiam amplius,
Quod illa ætas magis ad hæc utenda idonea est.
Terent.
Heaut. A. 1. Sc. 1.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Those Ancients who were the most accurate in their Remarks on the
Genius and Temper of Mankind, by considering the various Bent and
Scope of our Actions throughout the Progress of Life, have with great
Exactness allotted Inclinations and Objects of De
Sir e particular to
every Stage, according to the different Circumstances of our
Conversation and Fortune, thro' the several Periods of it. Hence they
were disposed easily to excuse those Excesses which might possibly
arise from a too eager Pursuit of the Affections more immediately
proper to each State: They indulged the Levity of Childhood with
Tenderness, overlooked the Gayety of Youth with Good-nature, tempered
the forward Ambition and Impatience of ripen'd Manhood with
Discretion, and kindly imputed the tenacious Avarice of old Men to
their want of relish for any other Enjoyment. Such Allowances as these
were no less advantageous to common Society than obliging to
particular Persons; for by maintaining a Decency and Regularity in the
Course of Life, they supported the Dignity of human Nature, which then
suffers the greatest Violence when the Order of things is inverted;
and in nothing is it more remarkably vilify'd and ridiculous, than
when Feebleness preposterously attempts to adorn it self with that
outward Pomp and Lustre, which serve only to set off the Bloom of
Youth with better advantage. I was insensibly carried into Reflections
of this nature, by just now meeting
Paulino (who is in his
Climacterick) bedeck'd with the utmost Splendour of Dress and
Equipage, and giving an unbounded Loose to all manner of Pleasure,
whilst his only Son is debarr'd all innocent Diversion, and may be
seen frequently solacing himself in the
Mall with no other
Attendance than one antiquated Servant of his Father's for a Companion
and Director.
'It is a monstrous want of Reflection, that a Man cannot consider,
that when he cannot resign the Pleasures of Life in his Decay of
Appetite and Inclination to them, his Son must have a much uneasier
Task to resist the Impetuosity of growing De
Sir es. The Skill therefore
should, methinks, be to let a Son want no lawful Diversion, in
proportion to his future Fortune, and the Figure he is to make in the
World. The first Step towards Virtue that I have observed in young Men
of Condition that have run into Excesses, has been that they had a
regard to their Quality and Reputation in the Management of their
Vices. Narrowness in their Circumstances has made many Youths, to
supply themselves as Debauchees, commence Cheats and Rascals. The
Father who allows his Son to his utmost ability avoids this latter
Evil, which as to the World is much greater than the former. But the
contrary Practice has prevail'd so much among some Men, that I have
known them deny them what was merely necessary for Education suitable
to their Quality. Poor young
Antonio is a lamentable Instance of ill
Conduct in this kind. The young Man did not want natural Talents; but
the Father of him was a Coxcomb, who affected being a fine Gentleman
so unmercifully, that he could not endure in his sight, or the
frequent mention of one, who was his Son, growing into Manhood, and
thrusting him out of the gay World. I have often thought the Father
took a secret Pleasure in reflecting that when that fine House and
Seat came into the next hands, it would revive his Memory, as a Person
who knew how to enjoy them, from Observation of the Rusticity and
Ignorance of his Successor. Certain it is that a Man may, if he will,
let his Heart close to the having no regard to any thing but his dear
self, even with exclusion of his very Children. I recommend this
Subject to your Consideration, and am,
Sir , Your most humble Servant,
T. B.
London, Sept. 26, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am just come from
Tunbridge, and have since my return read Mrs.
Matilda Mohair's Letter to you: She pretends to make a mighty Story
about the Diversion of Swinging in that Place. What was done, was only
among Relations; and no Man swung any Woman who was not second Cousin
at farthest. She is pleased to say, care was taken that the Gallants
tied the Ladies Legs before they were wafted into the Air. Since she
is so spiteful, I'll tell you the plain Truth; there was no such
Nicety observed, since we were all, as I just now told you, near
Relations; but Mrs.
Mohair her self has been swung there, and she
invents all this Malice, because it was observed she has crooked Legs,
of which I was an Eye-Witness.
Your humble Servant,
Rachel Shoestring.
Tunbridge, Sept. 26, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'We have just now read your Paper, containing Mrs.
Mohair's Letter.
It is an Invention of her own from one end to the other; and I de
Sir e
you would print the enclosed Letter by it self, and shorten it so as
to come within the Compass of your Half-Sheet. She is the most
malicious Minx in the World, for all she looks so innocent. Don't
leave out that Part about her being in love with her Father's Butler,
which makes her shun Men; for that is the truest of it all.
Your humble Servant,
Sarah Trice.
P. S. 'She has crooked Legs.'
Tunbridge, Sept. 26, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'All that Mrs.
Mohair is so vexed at against the good Company of
this Place, is, that we all know she has crooked Legs. This is
certainly true. I don't care for putting my Name, because one would
not be in the Power of the Creature.
Your humble Servant unknown.
Tunbridge, Sept. 26, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'That insufferable Prude Mrs.
Mohair, who has told such Stories of
the Company here, is with Child, for all her nice Airs and her crooked
Legs. Pray be sure to put her in for both those two Things, and you'll
oblige every Body here, especially
Your humble Servant,
Alice Bluegarter.'
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, September 30, 1712 |
Steele |
A favour well bestow'd, is almost as great an Honour to him who confers
it, as to him who receives it. What indeed makes for the superior
Reputation of the Patron in this case, is, that he is always surrounded
with specious Pretences of unworthy Candidates, and is often alone in
the kind Inclination he has towards the Well-deserving. Justice is the
first Quality in the Man who is in a Post of Direction; and I remember
to have heard an old Gentleman talk of the Civil Wars, and in his
Relation give an Account of a General Officer, who with this one
Quality, without any shining Endowments, became so peculiarly beloved
and honoured, that all Decisions between Man and Man were laid before
him by the Parties concerned in a private Way; and they would lay by
their Animosities implicitly, if he bid them be Friends, or submit
themselves in the Wrong without Reluctance, if he said it, without
waiting the Judgment of Court-Martials. His Manner was to keep the Dates
of all Commissions in his Closet, and wholly dismiss from the Service
such who were deficient in their Duty; and after that, took Care to
prefer according to the Order of Battel. His Familiars were his entire
Friends, and could have no interested Views in courting his
Acquaintance; for his Affection was no Step to their Preferment, tho' it
was to their Reputation. By this means a kind Aspect, a Salutation, a
Smile, and giving out his Hand, had the weight of what is esteem'd by
vulgar Minds more substantial. His Business was very short, and he who
had nothing to do but Justice, was never affronted with a Request of a
familiar daily Visitant for what was due to a brave Man at a Distance.
Extraordinary Merit he used to recommend to the King for some
Distinction at home, till the Order of Battel made way for his rising in
the Troops. Add to this, that he had an excellent Manner of getting rid
of such whom he observed were good at
an Halt
, as his Phrase was.
Under this Description he comprehended all those who were contented to
live without Reproach, and had no Promptitude in their Minds towards
Glory. These Fellows were also recommended to the King, and taken off of
the General's hands into Posts wherein Diligence and common Honesty were
all that were necessary. This General had no weak Part in his Line; but
every Man had as much Care upon him, and as much Honour to lose as
himself. Every Officer could answer for what pass'd where he was, and
the General's Presence was never necessary any where, but where he had
placed himself at the first Disposition, except that Accident happen'd
from extraordinary Efforts of the Enemy which he could not foresee; but
it was remarkable that it never fell out from Failure in his own Troops.
It must be confess'd, the World is just so much out of order, as an
unworthy Person possesses what should be in the Direction of him who has
better Pretensions to it.
Instead of such a Conduct as this old Fellow us'd to describe in his
General, all the Evils which have ever happen'd among Mankind have arose
from the wanton Disposition of the Favours of the Powerful. It is
generally all that Men of Modesty and Virtue can do, to fall in with
some whimsical Turn in a Great Man, to make way for things of real and
absolute Service. In the time of Don
Sebastian
of
Portugal
, or some
time since, the first Minister would let nothing come near him but what
bore the most profound Face of Wisdom and Gravity. They carry'd it so
far, that, for the greater Shew of their profound Knowledge, a Pair of
Spectacles tied on their Noses, with a black Ribband round their Heads,
was what compleated the Dress of those who made their court at his
Levee, and none with naked Noses were admitted to his Presence. A blunt
honest Fellow, who had a Command in the Train of Artillery, had
attempted to make an Impression upon the Porter day after day in vain,
till at length he made his appearance in a very thoughtful dark sute of
Clothes, and two Pair of Spectacles on at once. He was conducted from
Room to Room with great deference, to the Minister; and carrying on the
Farce of the Place, he told his Excellence, That he had pretended in
this manner to be wiser than he really was, but with no ill Intention;
but he was honest Such-a-one of the Train, and he came to tell him that
they wanted Wheel-barrows and Pick-axes. The thing happened not to
displease, the Great Man was seen to smile, and the successful Officer
was reconducted with the same profound Ceremony out of the House.
Leo X.
reigned Pope of
Rome
, his Holiness, tho' a Man of Sense,
and of an excellent Taste of Letters, of all things affected Fools,
Buffoons, Humourists, and Coxcombs: Whether it were from Vanity, and
that he enjoy'd no Talents in other Men but what were inferiour to him,
or whatever it was, he carried it so far, that his whole Delight was in
finding out new Fools, and, as our Phrase is, playing them off, and
making them shew themselves to advantage. A Priest of his former
Acquaintance suffered a great many Disappointments in attempting to find
access to him in a regular Character, till at last in despair he retired
from
Rome
, and returned in an Equipage so very fantastical, both as to
the Dress of himself and Servants, that the whole Court were in an
Emulation who should first introduce him to his Holiness
. What added
to the Expectation his Holiness had of the Pleasure he should have in
his Follies, was, that this Fellow, in a Dress the most exquisitely
ridiculous, de
Sir
ed he might speak to him alone, for he had Matters of
the highest Importance, upon which he wanted a Conference. Nothing could
be denied to a Coxcomb of so great hope; but when they were apart, the
Impostor revealed himself, and spoke as follows:
Do not be surprized, most holy Father, at seeing, instead of a Coxcomb
to laugh at, your old Friend who has taken this way of Access to
admonish you of your own Folly. Can any thing shew your Holiness how
unworthily you treat Mankind, more than my being put upon this
Difficulty to speak with you? It is a degree of Folly to delight to
see it in others, and it is the greatest Insolence imaginable to
rejoice in the Disgrace of human Nature. It is a criminal Humility in
a Person of your Holiness's Understanding, to believe you cannot excel
but in the Conversation of Half-wits, Humorists, Coxcombs, and
Buffoons. If your Holiness has a mind to be diverted like a rational
Man, you have a great opportunity for it, in disrobing all the
Impertinents you have favour'd, of all their Riches and Trappings at
once, and bestowing them on the Humble, the Virtuous, and the Meek. If
your Holiness is not concerned for the sake of Virtue and Religion, be
pleased to reflect, that for the sake of your own Safety it is not
proper to be so very much in jest. When the Pope is thus merry, the
People will in time begin to think many things, which they have
hitherto beheld with great Veneration, are in themselves Objects of
Scorn and Derision. If they once get a Trick of knowing how to laugh,
your Holiness's saying this Sentence in one Night-Cap and t'other with
the other, the change of your Slippers, bringing you your Staff in the
midst of a Prayer, then stripping you of one Vest and clapping on a
second during divine Service, will be found out to have nothing in it.
Consider, Sir , that at this rate a Head will be reckoned never the
wiser for being Bald; and the ignorant will be apt to say, that going
bare-foot does not at all help on in the way to Heaven. The red Cap
and the Coul will fall under the same Contempt; and the Vulgar will
tell us to our Faces that we shall have no Authority over them, but
from the Force of our Arguments, and the Sanctity of our Lives.
T.
Founded on Note F to Bayle's account of Leo X.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 1, 1712 |
Steele |
—Frustra retinacula tendens
Fertur equis Auriga, neque audit currus habenas.
To the SPECTATOR-GENERAL of Great Britain.
From the farther end of the Widow's Coffee-house in Devereaux Court,
Monday Evening, twenty eight Minutes and a Half past Six.
Dear Dumb,
'In short, to use no further Preface, if I should tell you that I have
seen a Hackney-Coachman, when he has come to set down his Fare, which
has consisted of two or three very fine Ladies, hand them out, and
salute every one of them with an Air of Familiarity, without giving
the least Offence, you would perhaps think me guilty of a Gasconade.
But to clear my self from that Imputation, and to explain this Matter
to you, I assure you that there are many Illustrious Youths within
this City, who frequently recreate themselves by driving of a
Hackney-Coach: But those whom, above all others, I would recommend to
you, are the young Gentlemen belonging to our Inns of Court. We have,
I think, about a dozen Coachmen, who have Chambers here in the
Temple; and as it is reasonable to believe others will follow their
Example, we may perhaps in time (if it shall be thought convenient) be
drove to
Westminster by our own Fraternity, allowing every fifth
Person to apply his Meditations in this way, which is but a modest
Computation, as the Humour is now likely to take. It is to be hop'd
likewise, that there are in the other Nurseries of the Law to be found
a proportionable number of these hopeful Plants, springing up to the
everlasting Renown of their native Country. Of how long standing this
Humour has been, I know not; the first time I had any particular
Reason to take notice of it, was about this time twelvemonth, when
being upon
Hampstead-Heath with some of these studious young Men,
who went thither purely for the Sake of Contemplation, nothing would
serve them but I must go thro' a Course of this Philosophy too; and
being ever willing to embelish my self with any commendable
Qualification, it was not long e'er they persuaded me into the
Coach-box; nor indeed much longer, before I underwent the Fate of my
Brother
Phaeton, for having drove about fifty Paces with pretty good
Success, through my own natural Sagacity, together with the good
Instructions of my Tutors, who, to give them their due, were on all
Hands encouraging and assisting me in this laudable Undertaking; I
say,
Sir , having drove about fifty Paces with pretty good Success, I
must needs be exercising the Lash, which the Horses resented so ill
from my Hands, that they gave a sudden Start, and thereby pitched me
directly upon my Head, as I very well remembered about Half an Hour
afterwards, which not only deprived me of all the Knowledge I had
gain'd for fifty Yards before, but had like to have broken my Neck
into the Bargain. After such a severe Reprimand, you may imagine I was
not very easily prevail'd with to make a second Attempt; and indeed,
upon mature Deliberation, the whole Science seem'd, at least to me, to
be surrounded with so many Difficulties, that notwithstanding the
unknown Advantages which might have accrued to me thereby, I gave over
all Hopes of attaining it; and I believe had never thought of it more,
but that my Memory has been lately refreshed by seeing some of these
ingenious Gentlemen ply in the open Streets, one of which I saw
receive so suitable a Reward of his Labours, that tho' I know you are
no Friend to Story-telling, yet I must beg leave to trouble you with
this at large.
'About a fortnight since, as I was diverting my self with a pennyworth
of Walnuts at the
Temple-Gate, a lively young Fellow in a Fustian
Jacket shot by me, beckon'd a Coach, and told the Coachman he wanted
to go as far as
Chelsey: They agreed upon the Price, and this young
Gentleman mounts the Coach-box; the Fellow staring at him, de
Sir 'd to
know if he should not drive till they were out of Town? No, no,
replied he: He was then going to climb up to him, but received another
Check, and was then ordered to get into the Coach, or behind it, for
that he wanted no Instructors; but be sure you Dog you, says he, don't
you bilk me. The Fellow thereupon surrender'd his Whip, scratch'd his
Head, and crept into the Coach. Having my self occasion to go into the
Strand about the same Time, we started both together; but the Street
being very full of Coaches, and he not so able a Coachman as perhaps
he imagined himself, I had soon got a little Way before him; often,
however, having the curiosity to cast my Eye back upon him, to observe
how he behaved himself in this high Station; which he did with great
Composure till he came to the Pass, which is a Military Term the
Brothers of the Whip have given the Strait at St.
Clement's Church:
when he was arrived near this Place, where are always Coaches in
waiting, the Coachmen began to suck up the Muscles of their Cheeks,
and to tip the Wink upon each other, as if they had some Roguery in
their Heads, which I was immediately convinced of; for he no sooner
came within Reach, but the first of them with his Whip took the exact
Dimension of his Shoulders, which he very ingeniously call'd
Endorsing; and indeed I must say, that every one of them took due Care
to endorse him as he came thro' their Hands. He seem'd at first a
little uneasy under the Operation, and was going in all haste to take
the Numbers of their Coaches; but at length by the Mediation of the
worthy Gentleman in the Coach, his Wrath was asswaged, and he
prevail'd upon to pursue his Journey; tho' indeed I thought they had
clapt such a Spoke in his Wheel, as had disabled him from being a
Coachman for that Day at least: For I am only mistaken, Mr.
Spec. if
some of these Endorsements were not wrote in so strong a Hand, that
they are still legible. Upon my enquiring the Reason of this unusual
Salutation, they told me, that it was a Custom among them, whenever
they saw a Brother tottering or unstable in his Post, to lend him a
hand in order to settle him again therein: For my part I thought their
Allegations but reasonable, and so march'd off. Besides our Coachmen,
we abound in divers other Sorts of ingenious robust Youth, who, I
hope, will not take it ill if I refer giving you an account of their
several Recreations to another Opportunity. In the mean time, if you
would but bestow a little of your wholesome Advice upon our Coachmen,
it might perhaps be a Reprieve to some of their Necks. As I understand
you have several Inspectors under you, if you would but send one
amongst us here in the
Temple, I am persuaded he would not want
Employment. But I leave this to your own Consideration, and am,
'
Sir , Your very humble Servant,
'Moses Greenbag.
'
P. S. I have heard our Criticks in the Coffee-houses hereabout talk
mightily of the Unity of Time and Place: According to my Notion of the
Matter, I have endeavoured at something like it in the Beginning of my
Epistle. I de
Sir e to be inform'd a little as to that Particular. In my
next I design to give you some account of excellent Watermen, who are
bred to the Law, and far outdo the Land-Students above-mentioned.'
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 2, 1712 |
Addison |
—Nimis uncis
Naribus indulges—
Pers.

My Friend
Will. Honeycomb
has told me, for above this half Year, that he
had a great mind to try his Hand at a
Spectator
, and that he would
fain have one of his writing in my Works. This Morning I received from
him the following Letter, which, after having rectified some little
Orthographical Mistakes, I shall make a Present of to the Publick.
Dear SPEC.
'I was, about two Nights ago, in Company with very agreeable young
People of both Sexes, where talking of some of your Papers which are
written on Conjugal Love, there arose a Dispute among us, whether
there were not more bad Husbands in the World than bad Wives. A
Gentleman, who was Advocate for the Ladies, took this occasion to tell
us the story of a famous Siege in Germany, which I have since found
related in my Historical Dictionary, after the following manner. When
the Emperor Conrade the Third had besieged Guelphus, Duke of
Bavaria, in the City of Hensberg, the Women finding that the Town
could not possibly hold out long, petitioned the Emperor that they
might depart out of it, with so much as each of them could carry. The
Emperor knowing they could not convey away many of their Effects,
granted them their Petition; When the Women, to his great Surprize,
came out of the Place with every one her Husband upon her back. The
Emperor was so moved at the sight, that he burst into Tears, and after
having very much extolled the Women for their conjugal Affection, gave
the Men to their Wives, and received the Duke into his Favour.
'The Ladies did not a little triumph at this Story, asking us at the
same time, whether in our Consciences we believed that the Men of any
Town in Great Britain would, upon the same Offer, and at the same
Conjuncture, have loaden themselves with their Wives; or rather,
whether they would not have been glad of such an opportunity to get
rid of them? To this my very good Friend Tom Dapperwit, who took
upon him to be the Mouth of our Sex, replied, that they would be very
much to blame if they would not do the same good Office for the Women,
considering that their Strength would be greater, and their Burdens
lighter. As we were amusing our selves with Discourses of this nature,
in order to pass away the Evening, which now begins to grow tedious,
we fell into that laudable and primitive Diversion of Questions and
Commands. I was no sooner vested with the regal Authority, but I
enjoined all the Ladies, under pain of my Displeasure, to tell the
Company ingenuously, in case they had been in the Siege
abovementioned, and had the same Offers made them as the good Women of
that Place, what every one of them would have brought off with her,
and have thought most worth the saving? There were several merry
Answers made to my Question, which entertained us till Bed-time. This
filled my Mind with such a huddle of Ideas, that upon my going to
sleep, I fell into the following Dream.
'I saw a Town of this Island, which shall be nameless, invested on
every side, and the Inhabitants of it so straitned as to cry for
Quarter. The General refused any other Terms than those granted to the
abovementioned Town of Hensberg, namely, that the married Women
might come out with what they could bring along with them. Immediately
the City-Gates flew open, and a Female Procession appeared. Multitudes
of the Sex following one another in a row, and staggering under their
respective Burdens. I took my Stand upon an Eminence in the Enemies
Camp, which was appointed for the general Rendezvous of these Female
Carriers, being very deSir ous to look into their several Ladings. The
first of them had a huge Sack upon her Shoulders, which she set down
with great Care: Upon the opening of it, when I expected to have seen
her Husband shot out of it, I found it was filled with China-Ware. The
next appeared in a more decent Figure, carrying a handsome young
Fellow upon her Back: I could not forbear commending the young Woman
for her Conjugal Affection, when to my great Surprize, I found that
she had left the good Man at home, and brought away her Gallant. I saw
the third, at some distance, with a little withered Face peeping over
her Shoulder, whom I could not suspect for any but her Spouse, till
upon her setting him down I heard her call him dear Pugg, and found
him to be her Favourite Monkey. A fourth brought a huge Bale of Cards
along with her; and the fifth a Bolonia Lap-Dog; for her Husband, it
seems, being a very Burly Man, she thought it would be less trouble
for her to bring away little Cupid. The next was the Wife of a rich
Usurer, loaden with a Bag of Gold; she told us that her Spouse was
very old, and by the course of Nature could not expect to live long;
and that to shew her tender regards for him, she had saved that which
the poor Man loved better than his Life. The next came towards us with
her Son upon her Back, who, we were told, was the greatest Rake in the
Place, but so much the Mother's Darling, that she left her Husband
behind with a large Family of hopeful Sons and Daughters, for the sake
of this Graceless Youth.
'It would be endless to mention the several Persons, with their
several Loads that appeared to me in this strange Vision. All the
Place about me was covered with packs of Ribbands, Brocades,
Embroidery, and Ten thousand other Materials, sufficient to have
furnished a whole Street of Toy-shops. One of the Women, having an
Husband who was none of the heaviest, was bringing him off upon her
Shoulders, at the same time that she carried a great bundle of
Flanders-lace under her Arm; but finding herself so overloaden, that
she could not save both of them, she dropp'd the good Man, and brought
away the Bundle. In short, I found but one Husband among this great
Mountain of Baggage, who was a lively Cobler, that kick'd and spurr'd
all the while his Wife was carrying him on, and, as it was said, had
scarce passed a Day in his Life without giving her the Discipline of
the Strap.
'I cannot conclude my Letter, Dear Spec., without telling thee one
very odd Whim in this my Dream, I saw, methoughts, a dozen Women
employed in bringing off one Man; I could not guess who it should be,
till upon his nearer approach I discover'd thy short Phiz. The Women
all declared that it was for the sake of thy Works, and not thy
Person, that they brought thee off, and that it was on condition that
thou should'st continue the Spectator. If thou thinkest this Dream
will make a tolerable one, it is at thy Service, from,
'Dear Spec.
'Thine, Sleeping and Waking,
'Will. Honeycomb.'
The Ladies will see, by this Letter, what I have often told them, that
Will
. is one of those old-fashioned Men of Wit and Pleasure of the Town,
that shews his Parts by Raillery on Marriage, and one who has often
tried his Fortune that way without Success. I
however dismiss his
Letter, without observing, that the true Story on which it is built does
Honour to the Sex, and that in order to abuse them, the Writer is
obliged to have recourse to Dream and Fiction
.
At the end of this number and in all following numbers
there is a change in the colophon, caused by the addition of Tonson's
name to Buckley's. It runs henceforth thus:
LONDON: Printed for S. Buckley and J. Tonson: And Sold by A.
Baldwin in Warwick-Lane. But an announcement at the head of the
advertisement sets forth that Advertisements for this Paper continue
to be taken in by S. Buckley at the Dolphin in Little-Britain, J.
Tonson at Shakespear's Head in the Strand, C. Lillie at the
Corner of Beauford Buildings, and A. Baldwin in Warwick-Lane.
Contents
|
Friday, October 3, 1712 |
Addison |
—Huc natas adjice septem,
Et totidem juvenes, et mox generosque nurusque.
Quærite nunc, habeat quam nostra superbia causam.
Ov.
Met.
Sir ,
'You who are so well acquainted with the Story of
Socrates, must
have read how, upon his making a Discourse concerning Love, he pressed
his Point with so much Success, that all the Batchelors in his
Audience took a Resolution to Marry by the first Opportunity, and that
all the married Men immediately took Horse and galloped home to their
Wives. I am apt to think your Discourses, in which you have drawn so
many agreeable Pictures of Marriage, have had a very good Effect this
way in
England. We are obliged to you, at least for having taken off
that Senseless Ridicule, which for many Years the Witlings of the Town
have turned upon their Fathers and Mothers. For my own part, I was
born in Wedlock, and I don't care who knows it; For which Reason,
among many others, I should look upon my self as a most insufferable
Coxcomb, did I endeavour to maintain that Cuckoldom was inseparable
from Marriage, or to make use of
Husband and
Wife as Terms of
Reproach. Nay,
Sir , I will go one step further, and declare to you
before the whole World, that I am a married Man, and at the same time
I have so much Assurance as not to be ashamed of what I have done.
'Among the several Pleasures that accompany this state of Life, and
which you have described in your former Papers, there are two you have
not taken Notice of, and which are seldom cast into the Account, by
those who write on this Subject. You must have observed, in your
Speculations on Human Nature, that nothing is more gratifying to the
Mind of Man than Power or Dominion; and this I think my self amply
possessed of, as I am the Father of a Family. I am perpetually taken
up in giving out Orders, in prescribing Duties, in hearing Parties, in
administring Justice, and in distributing Rewards and Punishments. To
speak in the Language of the Centurion,
I say unto one, Go, and he
goeth; and to another, Come, and he cometh; and to my Servant, Do
This, and he doth it. In short,
Sir , I look upon my Family as a
Patriarchal Sovereignty, in which I am my self both King and Priest.
All great Governments are nothing else but Clusters of these little
private Royalties, and therefore I consider the Masters of Families as
small Deputy-Governors presiding over the several little Parcels and
Divisions of their Fellow Subjects.
As I take great pleasure in the
Administration of my Government in particular, so I look upon my self
not only as a more useful, but as a much greater and happier Man than
any Batchelor in
England of
my1 Rank and Condition.
'There is another accidental Advantage in Marriage, which has likewise
fallen to my share, I mean the having a Multitude of Children. These I
cannot but regard as very great Blessings. When I see my little Troop
before me, I rejoice in the Additions which I have made to my Species,
to my Country, and to my Religion, in having produced such a Number of
reasonable Creatures, Citizens, and Christians. I am pleased to see my
self thus perpetuated; and as there is no Production comparable to
that of a human Creature, I am more proud of having been the Occasion
of ten such glorious Productions, than if I had built a hundred
Pyramids at my own Expence, or published as many Volumes of the finest
Wit and Learning. In what a beautiful Light has the Holy Scripture
represented
Abdon, one of the Judges of
Israel, who had forty Sons
and thirty Grandsons, that rode on Threescore and Ten Ass-Colts,
according to the Magnificence of the Eastern Countries? How must the
Heart of the old Man rejoice, when he saw such a beautiful Procession
of his own Descendants, such a numerous Cavalcade of his own raising?
For my own part, I can sit in my Parlour with great content, when I
take a review of half a dozen of my little Boys mounting upon
Hobby-Horses, and of as many little Girls tutoring their Babies, each
of them endeavouring to excel the rest, and to do something that may
gain my Favour and Approbation. I cannot question but he who has
blessed me with so many Children, will assist my Endeavours in
providing for them. There is one thing I am able to give each of them,
which is a virtuous Education. I think it is
Sir Francis Bacon's
Observation, that in a numerous Family of Children the eldest is often
spoiled by the Prospect of an Estate, and the youngest by being the
Darling of the Parent; but that some one or other in the middle, who
has not perhaps been regarded, has made his way in the World, and
over-topped the rest. It is my Business to implant in every one of my
Children the same Seeds of Industry, and the same honest Principles.
By this Means I think I have a fair Chance, that one or other of them
may grow considerable in some or other way of Life, whether it be in
the Army, or in the Fleet, in Trade, or any of the three learned
Professions; for you must know,
Sir , that from long Experience and
Observation, I am persuaded of what seems a Paradox to most of those
with whom I converse, namely, That a Man who has many Children, and
gives them a good Education, is more likely to raise a Family, than he
who has but one, notwithstanding he leaves him his whole Estate. For
this reason I cannot forbear amusing my self with finding out a
General, an Admiral, or an Alderman of
London, a Divine, a
Physician, or a Lawyer, among my little People who are now perhaps in
Petticoats; and when I see the Motherly Airs of my little Daughters
when they are playing with their Puppets, I cannot but flatter my self
that their Husbands and Children will be happy in the Possession of
such Wives and Mothers.
'If you are a Father, you will not perhaps think this Letter
impertinent: but if you are a single Man, you will not know the
Meaning of it, and probably throw it into the Fire: Whatever you
determine of it, you may assure yourself that it comes from one who is
'
Your most humble Servant, and Well-wisher,
'Philogamus.'
O.
my own
Contents
|
Saturday, October 4, 1712 |
Parnell |
Durum: sed levius sit patientiâ
Quicquid corrigere est nefas.
Hor.

As some of the finest Compositions among the Ancients are in Allegory, I
have endeavoured, in several of my Papers, to revive that way of
Writing, and hope I have not been altogether unsuccessful in it; for I
find there is always a great Demand for those particular Papers, and
cannot but observe that several Authors have endeavoured of late to
excel in Works of this Nature. Among these, I do not know any one who
has succeeded better than a very ingenious Gentleman, to whom I am much
obliged for the following Piece, and who was the Author of the Vision in
the
.
O.
How are we tortured with the Absence of what we covet to possess, when
it appears to be lost to us! What Excursions does the Soul make in
Imagination after it! And how does it turn into it self again, more
foolishly fond and dejected, at the Disappointment? Our Grief, instead
of having recourse to Reason, which might restrain it, searches to find
a further Nourishment. It calls upon Memory to relate the several
Passages and Circumstances of Satisfactions which we formerly enjoyed:
the Pleasures we purchased by those Riches that are taken from us; or
the Power and Splendour of our departed Honours; or the Voice, the
Words, the Looks, the Temper, and Affections of our Friends that are
deceased. It needs must happen from hence that the Passion should often
swell to such a Size as to burst the Heart which contains it, if Time
did not make these Circumstances less strong and lively, so that Reason
should become a more equal Match for the Passion, or if another De
Sir
e
which becomes more present did not overpower them with a livelier
Representation. These are Thoughts which I had, when I fell into a kind
of Vision upon this Subject, and may therefore stand for a proper
Introduction to a Relation of it.
I found my self upon a naked Shore, with Company whose afflicted
Countenances witnessed their Conditions. Before us flowed a Water deep,
silent, and called the River of
Tears
, which issuing from two
Fountains on an upper Ground, encompassed an Island that lay before us.
The Boat which plied in it was old and shattered, having been sometimes
overset by the Impatience and Haste of single Passengers to arrive at
the other side. This immediately was brought to us by
Misfortune
who
steers it, and we were all preparing to take our places, when there
appeared a Woman of a mild and composed Behaviour, who began to deter us
from it, by representing the Dangers which would attend our Voyage.
Hereupon some who knew her for
Patience
, and some of those too who
till then cry'd the loudest, were persuaded by her, and returned back.
The rest of us went in, and she (whose Good-nature would not suffer her
to forsake Persons in Trouble) de
Sir
ed leave to accompany us, that she
might at least administer some small Comfort or Advice while we sailed.
We were no sooner embarked but the Boat was push'd off, the Sheet was
spread; and being filled with
Sighs
, which are the Winds of that
Country, we made a passage to the farther Bank, through several
Difficulties of which the most of us seemed utterly regardless.
When we landed, we perceived the Island to be strangely overcast with
Fogs, which no Brightness could pierce, so that a kind of gloomy Horror
sat always brooding over it. This had something in it very shocking to
easy Tempers, insomuch that some others, whom
Patience
had by this
time gained over, left us here, and privily convey'd themselves round
the Verge of the Island to find a Ford by which she told them they might
escape.
For my part, I still went along with those who were for piercing into
the Centre of the Place; and joining our selves to others whom we found
upon the same Journey, we marched solemnly as at a Funeral, through
bordering Hedges of Rosemary, and through a Grove of Yew-trees, which
love to overshadow Tombs and flourish in Church-yards. Here we heard on
every side the Wailings and Complaints of several of the Inhabitants,
who had cast themselves disconsolately at the Feet of Trees; and as we
chanced to approach any of these, we might perceive them wringing their
Hands, beating their Breasts, tearing their Hair, or after some other
manner visibly agitated with Vexation. Our Sorrows were heightened by
the Influence of what we heard and saw, and one of our Number was
wrought up to such a Pitch of Wildness, as to talk of hanging himself
upon a Bough which shot temptingly across the Path we travelled in; but
he was restrained from it by the kind Endeavours of our above-mentioned
Companion.
We had now gotten into the most dusky silent part of the Island, and by
the redoubled Sounds of Sighs, which made a doleful Whistling in the
Branches, the thickness of Air which occasioned faintish Respiration,
and the violent Throbbings of Heart which more and more affected us, we
found that we approached the
Grotto of Grief
. It was a wide, hollow,
and melancholy Cave, sunk deep in a Dale, and watered by Rivulets that
had a Colour between Red and Black. These crept slow and half congealed
amongst its Windings, and mixed their heavy Murmur with the Echo of
Groans that rolled through all the Passages. In the most retired Part of
it sat the
Doleful Being
her self; the Path to her was strowed with
Goads, Stings and Thorns; and her Throne on which she sat was broken
into a Rock, with ragged Pieces pointing upwards for her to lean upon. A
heavy Mist hung above her, her Head oppressed with it reclined upon her
Arm: Thus did she reign over her disconsolate Subjects, full of her self
to stupidity, in eternal Pensiveness, and the profoundest Silence. On
one side of her stood
Dejection
just dropping into a Swoon, and
Paleness
wasting to a Skeleton; on the other side were
Care
inwardly
tormented with Imaginations, and
Anguish
suffering outward
Troubles
to suck the Blood from her Heart in the shape of
Vultures
. The whole
Vault had a genuine Dismalness in it, which a few scattered Lamps, whose
bluish Flames arose and sunk in their Urns, discovered to our Eyes with
Encrease. Some of us fell down, overcome and spent with what they
suffered in the way, and were given over to those Tormentors that stood
on either hand of the Presence; others, galled and mortified with Pain,
recover'd the Entrance, where
Patience
, whom we had left behind, was
still waiting to receive us.
With her (whose Company was now become more grateful to us by the want
we had found of her) we winded round the Grotto, and ascended at the
back of it, out of the mournful Dale in whose Bottom it lay. On this
Eminence we halted, by her Advice, to pant for Breath; and lifting our
Eyes, which till then were fixed downwards, felt a sullen sort of
Satisfaction, in observing through the Shades what Numbers had entred
the Island. The Satisfaction, which appears to have Ill-nature in it,
was excusable, because it happened at a time when we were too much taken
up with our own concern, to have respect to that of others; and
therefore we did not consider them as suffering, but ourselves as not
suffering in the most forlorn Estate. It had also the Ground-work of
Humanity and Compassion in it, tho' the Mind was then too dark and too
deeply engaged to perceive it; but as we proceeded onwards, it began to
discover it self, and from observing that others were unhappy, we came
to question one another, when it was that we met, and what were the sad
Occasions that brought us together. Then we heard our Stories, we
compared them, we mutually gave and received
Pity
, and so by degrees
became tolerable Company.
A considerable part of the troublesome Road was thus deceived; at length
the Openings among the Trees grew larger, the Air seemed thinner, it lay
with less oppression upon us, and we could now and then discern tracks
in it of a lighter Greyness, like the Breakings of Day, short in
duration, much enlivening, and called in that Country
Gleams of
Amusement
. Within a short while these Gleams began to appear more
frequent, and then brighter and of a longer continuance; the
Sighs
that hitherto filled the Air with so much Dolefulness, altered to the
Sound of common Breezes, and in general the Horrors of the Island were
abated.
When we had arrived at last at the Ford by which we were to pass out, we
met with those fashionable Mourners who had been ferried over along with
us, and who being unwilling to go as far as we, had coasted by the Shore
to find the place, where they waited our coming; that by shewing
themselves to the World only at the time when we did, they might seem
also to have been among the Troubles of the Grotto. Here the Waters that
rolled on the other side so deep and silent, were much dried up, and it
was an easier matter for us to wade over.
The River being crossed, we were received upon the further Bank by our
Friends and Acquaintance, whom
Comfort
had brought out to congratulate
our Appearance in the World again. Some of these blamed us for staying
so long away from them, others advised us against all Temptations of
going back again; every one was cautious not to renew our Trouble, by
asking any particulars of the Journey; and all concluded, that in a case
of so much Melancholy and Affliction, we could not have made choice of a
fitter Companion than
Patience
. Here
Patience
, appearing serene at
her Praises, delivered us over to
Comfort
.
Comfort
smiled at his
receiving the Charge; immediately the Sky purpled on that side to which
he turned, and double Day at once broke in upon me.
Contents
|
Monday, October 6, 1712 |
Steele |
Melius, pejus, prosit, obsit, nil vident nisi quod lubent.
Ter.

When Men read, they taste the Matter with which they are entertained,
according as their own respective Studies and Inclinations have prepared
them, and make their Reflections accordingly. Some perusing
Roman
Writers, would find in them, whatever the Subject of the Discourses
were, parts which implied the Grandeur of that People in their Warfare
or their Politicks. As for my part, who am a meer SPECTATOR, I drew this
Morning Conclusions of their Eminence in what I think great, to wit, in
having worthy Sentiments, from the reading a Comedy of
Terence
. The
Play was the
Self-Tormentor
. It is from the Beginning to the End a
perfect Picture of human Life, but I did not observe in the whole one
Passage that could raise a Laugh. How well disposed must that People be,
who could be entertained with Satisfaction by so sober and polite Mirth?
In the first Scene of the Comedy, when one of the old Men accuses the
other of Impertinence for interposing in his Affairs, he answers,
I am
a Man, and cannot help feeling any Sorrow that can arrive at Man
. It is
said, this Sentence was received with an universal Applause. There
cannot be a greater Argument of the general good Understanding of a
People, than a sudden Consent to give their Approbation of a Sentiment
which has no Emotion in it. If it were spoken with never so great Skill
in the Actor, the Manner of uttering that Sentence could have nothing in
it which could strike any but People of the greatest Humanity, nay
People elegant and skilful in Observations upon it. It is possible he
might have laid his Hand on his Breast, and with a winning Insinuation
in his Countenance, expressed to his Neighbour that he was a Man who
made his case his own; yet I'll engage a Player in
Covent-Garden
might
hit such an Attitude a thousand times before he would have been
regarded. I have
that a Minister of State in the Reign of Queen
Elizabeth
had all manner of Books and Ballads brought to him, of what
kind soever, and took great Notice how much they took with the People;
upon which he would, and certainly might, very well judge of their
present Dispositions, and the most proper way of applying them according
to his own purposes
. What passes on the Stage, and the Reception it
meets with from the Audience, is a very useful Instruction of this Kind.
According to what you may observe there on our Stage, you see them often
moved so directly against all common Sense and Humanity, that you would
be apt to pronounce us a Nation of Savages. It cannot be called a
Mistake of what is pleasant, but the very contrary to it is what most
assuredly takes with them. The other Night an old Woman carried off with
a Pain in her Side, with all the Distortions and Anguish of Countenance
which is natural to one in that Condition, was laughed and clapped off
the Stage.
Terence's
Comedy, which I am speaking of, is indeed written
as if he hoped to please none but such as had as good a Taste as
himself. I
not but reflect upon the natural Description of the
innocent young Woman made by the Servant to his Master.
When I came to
the House, said he,
an old Woman opened the Door, and I followed her
in, because I could by entring upon them unawares better observe what
was your Mistress's ordinary manner of spending her Time, the only way
of judging any one's Inclinations and Genius. I found her at her Needle
in a sort of second Mourning, which she wore for an Aunt she had lately
lost. She had nothing on but what shewed she dressed only for herself.
Her Hair hung negligently about her Shoulders. She had none of the Arts
with which others use to set themselves off, but had that Negligence of
Person which is remarkable in those who are careful of their Minds—Then
she had a Maid who was at work near her, that was a Slattern, because
her Mistress was careless; which I take to be another Argument of your
security in her; for the Go-betweens
of Women of Intrigue are rewarded
too well to be dirty. When you were named, I told her you deSir ed to see
her, she threw down her Work for Joy, covered her Face, and decently hid
her Tears2
He must be a very good Actor, and draw Attention rather
from his own Character than the Words of the Author, that could gain it
among us for this Speech, though so full of Nature and good Sense.
The intolerable Folly and Confidence of Players putting in Words of
their own, does in a great measure feed the absurd Taste of the
Audience. But however that is, it is ordinary for a Cluster of Coxcombs
to take up the House to themselves, and equally insult both the Actors
and the Company. These Savages, who want all manner of Regard and
Deference to the rest of Mankind, come only to shew themselves to us,
without any other Purpose than to let us know they despise us.
The gross of an Audience is composed of two sorts of People, those who
know no Pleasure but of the Body, and those who improve or command
corporeal Pleasures by the addition of fine Sentiments of the Mind. At
present the intelligent part of the Company are wholly subdued, by the
Insurrections of those who know no Satisfactions but what they have in
common with all other Animals.
This is the reason that when a Scene tending to Procreation is acted,
you see the whole Pit in such a Chuckle, and old Letchers, with Mouths
open, stare at the loose Gesticulations on the Stage with shameful
Earnestness; when the justest Pictures of human Life in its calm
Dignity, and the properest Sentiments for the Conduct of it, pass by
like meer Narration, as conducing only to somewhat much better which is
to come after. I have seen the whole House at some times in so proper a
Disposition, that indeed I have trembled for the Boxes, and feared the
Entertainment would end in the Representation of the Rape of the
Sabines
.
I would not be understood in this Talk to argue, that nothing is
tolerable on the Stage but what has an immediate Tendency to the
Promotion of Virtue. On the contrary, I can allow, provided there is
nothing against the Interests of Virtue, and is not offensive to
Good-manners, that things of an indifferent nature may be represented.
For
Reason I have no Exception to the well-drawn Rusticities in the
Country-Wake
; and there is something so miraculously pleasant in
Dogget's
acting the aukward Triumph and comick Sorrow of
Hob
in
different Circumstances, that I shall not be able to stay away whenever
it is acted. All that vexes me is, that the Gallantry of taking the
Cudgels for
Gloucestershire
, with the Pride of Heart in tucking
himself up, and taking Aim at his Adversary, as well as the other's
Protestation in the Humanity of low Romance, That he could not promise
the Squire to break
Hob's
Head, but he would, if he could, do it in
Love; then flourish and begin: I say, what vexes me is, that such
excellent Touches as these, as well as the Squire's being out of all
patience at
Hob's
Success, and venturing himself into the Croud, are
Circumstances hardly taken Notice of, and the height of the Jest is only
in the very Point that Heads are broken. I am confident, were there a
Scene written, wherein
Penkethman
should break his Leg by wrestling
with
Bullock
, and
Dicky
come in to set it, without one word said but
what should be according to the exact Rules of Surgery in making this
Extention, and binding up the Leg, the whole House should be in a Roar
of Applause at the dissembled Anguish of the Patient, the help given by
him who threw him down, and the handy Address and arch Looks of the
Surgeon. To enumerate the entrance of Ghosts, the Embattling of Armies,
the Noise of Heroes in Love, with a thousand other Enormities, would be
to transgress the bounds of this Paper, for which reason it is possible
they may have hereafter distinct Discourses; not forgetting any of the
Audience who shall set up for Actors, and interrupt the Play on the
Stage; and Players who shall prefer the Applause of Fools to that of the
reasonable part of the Company.
T.
Is this another version of the very wise man whom Andrew
Fletcher of Saltoun, in a letter to Montrose, said that he knew, who
'believed, that if a Man were permitted to make all the ballads, he
need not care who should make the laws of a nation'?
Andrew Fletcher, who could not have known any of Elizabeth's statesmen,
was yet alive when this paper was written.
Heautontimoroumenos
, Act ii. sc. 2.
Dogget had been acting a few nights before in
the Country
Wake
. The part of Hob was his own in every sense, he being the author
of the farce, which afterwards was made into a very popular ballad opera
called
Flora
, or
Hob in the Well
.
Contents
|
Tuesday, October 7, 1712 |
Steele |
Deleo omnes dehinc ex animo Mulieres.
Ter.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You have often mention'd with great Vehemence and Indignation the
Misbehaviour of People at Church; but I am at present to talk to you
on that Subject, and complain to you of one, whom at the same time I
know not what to accuse of, except it be looking too well there, and
diverting the Eyes of the Congregation to that one Object. However I
have this to say, that she might have stay'd at her own Parish, and
not come to perplex those who are otherwise intent upon their Duty.
'Last
Sunday was Seven-night I went into a Church not far from
London-Bridge; but I wish I had been contented to go to my own
Parish, I am sure it had been better for me: I say, I went to Church
thither, and got into a Pew very near the Pulpit. I had hardly been
accommodated with a Seat, before there entered into the Isle a young
Lady in the very Bloom of Youth and Beauty, and dressed in the most
elegant manner imaginable. Her Form was such, that it engaged the Eyes
of the whole Congregation in an Instant, and mine among the rest. Tho'
we were all thus fixed upon her, she was not in the least out of
Countenance, or under the least Disorder, tho' unattended by any one,
and not seeming to know particularly where to place her self. However,
she had not in the least a confident Aspect, but moved on with the
most graceful Modesty, every one making Way till she came to a Seat
just over-against that in which I was placed. The Deputy of the Ward
sat in that Pew, and she stood opposite to him; and at a Glance into
the Seat, tho' she did not appear the least acquainted with the
Gentleman, was let in, with a Confusion that spoke much Admiration at
the Novelty of the Thing. The Service immediately began, and she
compos'd her self for it with an Air of so much Goodness and
Sweetness, that the Confession which she uttered so as to be heard
where I sat, appeared an Act of Humiliation more than she had Occasion
for. The Truth is, her Beauty had something so innocent, and yet so
sublime, that we all gazed upon her like a Phantom. None of the
Pictures which we behold of the best
Italian Painters, have any
thing like the Spirit which appeared in her Countenance, at the
different Sentiments expressed in the several Parts of Divine Service:
That Gratitude and Joy at a Thanksgiving, that Lowliness and Sorrow at
the Prayers for the Sick and Distressed, that Triumph at the Passages
which gave Instances of divine Mercy, which appeared respectively in
her Aspect, will be in my Memory to my last Hour. I protest to you,
Sir , she suspended the Devotion of every one around her; and the Ease
she did every thing with, soon dispersed the churlish Dislike and
Hesitation in approving what is excellent, too frequent amongst us, to
a general Attention and Entertainment in observing her Behaviour. All
the while that we were gazing at her, she took Notice of no Object
about her, but had an Art of seeming awkwardly attentive, whatever
else her Eyes were accidentally thrown upon. One Thing indeed was
particular, she stood the whole Service, and never kneeled or sat; I
do not question but that was to shew her self with the greater
Advantage, and set forth to better Grace her Hands and Arms, lifted up
with the most ardent Devotion, and her Bosom, the fairest Observation;
while she, you must think, knew nothing of the Concern she gave
others, any other than as an Example of Devotion, that threw her self
out, without regard to Dress or Garment, all Contrition, and loose of
all Worldly Regards, in Ecstasy of Devotion. Well, now the Organ was
to play a Voluntary, and she was so skilful in Musick, and so touched
with it, that she kept time not only with some Motion of her Head, but
also with a different Air in her Countenance. When the Musick was
strong and bold, she look'd exalted, but serious; when lively and
airy, she was smiling and gracious; when the Notes were more soft and
languishing, she was kind and full of Pity. When she had now made it
visible to the whole Congregation, by her Motion and Ear, that she
could dance, and she wanted now only to inform us that she could sing
too, when the Psalm was given out, her Voice was distinguished above
all the rest, or rather People did not exert their own in order to
hear her. Never was any heard so sweet and so strong. The Organist
observed it, and he thought fit to play to her only, and she swelled
every Note; when she found she had thrown us all out, and had the last
Verse to herself in such a manner as the whole Congregation was intent
upon her, in the same manner as we see in the Cathedrals, they are on
the Person who sings alone the Anthem. Well, it came at last to the
Sermon, and our young Lady would not lose her Part in that neither;
for she fixed her Eye upon the Preacher, and as he said any thing she
approved, with one of
Charles Mathers's fine Tablets she set down
the Sentence, at once shewing her fine Hand, the Gold-Pen, her
Readiness in Writing, and her Judgment in chusing what to write. To
sum up what I intend by this long and particular Account, I mean to
appeal to you, whether it is reasonable that such a Creature as this
shall come from a jaunty Part of the Town, and give herself such
violent Airs, to the disturbance of an innocent and inoffensive
Congregation, with her Sublimities. The Fact, I assure you, was as I
have related; but I had like to have forgot another very considerable
Particular. As soon as Church was done, she immediately stepp'd out of
her Pew, and fell into the finest pitty-pat Air, forsooth, wonderfully
out of Countenance, tossing her Head up and down as she swam along the
Body of the Church. I, with several others of the Inhabitants,
follow'd her out, and saw her hold up her Fan to an Hackney-Coach at a
Distance, who immediately came up to her, and she whipp'd into it with
great Nimbleness, pull'd the Door with a bowing Mein, as if she had
been used to a better Glass. She said aloud,
You know where to go,
and drove off. By this time the best of the Congregation was at the
Church-Door, and I could hear some say,
A very fine Lady; others,
I'll warrant ye, she's no better than she should be; and one very
wise old Lady said,
She ought to have been taken up. Mr. SPECTATOR,
I think this Matter lies wholly before you: for the Offence does not
come under any Law, tho' it is apparent this Creature came among us
only to give herself Airs, and enjoy her full Swing in being admir'd.
I de
Sir e you would print this, that she may be confin'd to her own
Parish; for I can assure you there is no attending any thing else in a
Place where she is a Novelty. She has been talked of among us ever
since under the Name of the
Phantom: But I would advise her to come
no more; for there is so strong a Party made by the Women against her,
that she must expect they will not be excell'd a second time in so
outrageous a manner, without doing her some Insult. Young Women, who
assume after this rate, and affect exposing themselves to view in
Congregations at t'other end of the Town, are not so mischievous,
because they are rivall'd by more of the same Ambition, who will not
let the rest of the Company be particular: But in the Name of the
whole Congregation where I was, I de
Sir e you to keep these agreeable
Disturbances out of the City, where Sobriety of Manners is still
preserv'd, and all glaring and ostentatious Behaviour, even in things
laudable, discountenanced. I wish you may never see the Phantom, and
am,'
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
Ralph Wonder.
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 8, 1712 |
Steele |
Lepus tute es, et pulpamentum quæris.
Ter.

It is a great Convenience to those who want Wit to furnish out a
Conversation, that there is something or other in all Companies where it
is wanted substituted in its stead, which according to their Taste, does
the Business as well. Of this nature is the agreeable Pastime in
Country-Halls of Cross-purposes, Questions and Commands, and the like. A
little superior to these are those who can play at Crambo, or cap
Verses. Then above them are such as can make Verses, that is, Rhime; and
among those who have the
Latin
Tongue, such as use to make what they
call golden Verses. Commend me also to those who have not Brains enough
for any of these Exercises, and yet do not give up their Pretensions to
Mirth. These can slap you on the Back unawares, laugh loud, ask you how
you do with a Twang on your Shoulders, say you are dull to-day, and
laugh a Voluntary to put you in Humour; the laborious Way among the
minor Poets, of making things come into such and such a Shape, as that
of an Egg, an Hand, an Ax, or any thing that no body had ever thought on
before for that purpose, or which would have cost a great deal of Pains
to accomplish it if they did. But all these Methods, tho' they are
mechanical, and may be arrived at with the smallest Capacity, do not
serve an honest Gentleman who wants Wit for his Ordinary Occasions;
therefore it is absolutely necessary that the Poor in Imagination should
have something which may be serviceable to them at all Hours upon all
common Occurrences. That which we call Punning is therefore greatly
affected by Men of small Intellects. These Men need not be concerned
with you for the whole Sentence; but if they can say a quaint thing, or
bring in a Word which sounds like any one Word you have spoken to them
they can turn the Discourse, or distract you so that you cannot go on,
and by consequence if they cannot be as witty as you are, they can
hinder your being any wittier than they are. Thus if you talk of a
Candle, he
can deal
with you; and if you ask him to help you to some
Bread, a Punster should think himself very ill-
bred
if he did not; and
if he is not as well-
bred
as your self, he hopes for
Grains
of
Allowance. If you do not understand that last Fancy, you must recollect
that Bread is made of Grain; and so they go on for ever, without
Possibility of being exhausted.
There are another Kind of People of small Faculties, who supply want of
Wit with want of Breeding; and because Women are both by Nature and
Education more offended at any thing which is immodest than we Men are,
these are ever harping upon things they ought not to allude to, and deal
mightily in double Meanings. Every one's own Observation will suggest
Instances enough of this kind, without my mentioning any; for your
double Meaners are dispersed up and down thro' all Parts of Town or City
where there are any to offend, in order to set off themselves. These Men
are mighty loud Laughers, and held very pretty Gentlemen with the
sillier and unbred Part of Womankind. But above all already mentioned,
or any who ever were, or ever can be in the World, the happiest and
surest to be pleasant, are a Sort of People whom we have not indeed
lately heard much of, and those are your
Biters
.
A
Biter
is one who tells you a thing you have no reason to
disbelieve in it self; and perhaps has given you, before he bit you, no
reason to disbelieve it for his saying it; and if you give him Credit,
laughs in your Face, and triumphs that he has deceiv'd you. In a Word, a
Biter
is one who thinks you a Fool, because you do not think him a
Knave. This Description of him one may insist upon to be a just one; for
what else but a Degree of Knavery is it, to depend upon Deceit for what
you gain of another, be it in point of Wit, or Interest, or any thing
else?
This way of Wit is called
Biting
, by a Metaphor taken from Beasts of
Prey, which devour harmless and unarmed Animals, and look upon them as
their Food wherever they meet them. The Sharpers about Town very
ingeniously understood themselves to be to the undesigning Part of
Mankind what Foxes are to Lambs, and therefore used the Word
Biting
to
express any Exploit wherein they had over-reach'd any innocent and
inadvertent Man of his Purse. These Rascals of late Years have been the
Gallants of the Town, and carried it with a fashionable haughty Air, to
the discouragement of Modesty and all honest Arts. Shallow Fops, who are
govern'd by the Eye, and admire every thing that struts in vogue, took
up from the Sharpers the Phrase of
Biting
, and used it upon all
Occasions, either to disown any nonsensical Stuff they should talk
themselves, or evade the Force of what was reasonably said by others.
Thus, when one of these cunning Creatures was enter'd into a Debate with
you, whether it was practicable in the present State of Affairs to
accomplish such a Proposition, and you thought he had let fall what
destroy'd his Side of the Question, as soon as you look'd with an
Earnestness ready to lay hold of it, he immediately cry'd,
Bite
, and
you were immediately to acknowledge all that Part was in Jest. They
carry this to all the Extravagance imaginable, and if one of these
Witlings knows any Particulars which may give Authority to what he says,
he is still the more ingenious if he imposes upon your Credulity. I
remember a remarkable Instance of this Kind. There came up a shrewd
young Fellow to a plain young Man, his Countryman, and taking him aside
with a grave concern'd Countenance, goes on at this rate: I see you
here, and have you heard nothing out of
Yorkshire
—You look so
surpriz'd you could not have heard of it—and yet the Particulars are
such, that it cannot be false: I am sorry I am got into it so far that I
now must tell you; but I know not but it may be for your Service to
know—on
Tuesday
last, just after Dinner—you know his Manner is to
smoke, opening his Box, your Father fell down dead in an Apoplexy. The
Youth shew'd the filial Sorrow which he ought—Upon which the witty Man
cry'd,
Bite, there was nothing in all this
—
To put an end to this silly, pernicious, frivolous Way at once, I will
give the Reader one late Instance of a
Bite
, which no
Biter
for the
future will ever be able to equal, tho' I heartily wish him the same
Occasion. It is a Superstition with some Surgeons who beg the Bodies of
condemn'd Malefactors, to go to the Gaol, and bargain for the Carcase
with the Criminal himself. A good honest Fellow did so last Sessions,
and was admitted to the condemned Men on the Morning wherein they died.
The Surgeon communicated his Business, and fell into discourse with a
little Fellow, who refused Twelve Shillings, and insisted upon Fifteen
for his Body. The Fellow, who kill'd the Officer of
Newgate
, very
forwardly, and like a Man who was willing to deal, told him, Look you,
Mr. Surgeon, that little dry Fellow, who has been half-starved all his
Life, and is now half-dead with Fear, cannot answer your Purpose. I have
ever liv'd high and freely, my Veins are full, I have not pined in
Imprisonment; you see my Crest swells to your Knife, and after
Jack-Catch
has done, upon my Honour you'll find me as sound as e'er a
Bullock in any of the Markets. Come, for Twenty Shillings I am your
Man—Says the Surgeon, Done, there's a Guinea—This witty Rogue took the
Money, and as soon as he had it in his Fist, cries,
Bite, I am to be
hang'd in Chains.
T.
See [Volume 1 link:
]. Swift writes,
'I'll teach you a way to outwit Mrs. Johnson; it is a new fashioned
way of being witty, and they call it a Bite. You must ask a
bantering question, or tell some lie in a serious manner, then she
will answer, or speak as if you were in earnest, and then cry you,
"Madam, there's a Bite." I would not have you undervalue this, for
it is the constant amusement in Court, and every where else among the
great people; and I let you know it, in order to have it among you,
and to teach you a new refinement.'
(Journal to Stella). Although 'bite' and 'biter' have not retained this
sense, it remains in an occasional use of the word 'bitten.'
Contents
|
Thursday, October 9, 1712 |
Addison |
Non habeo denique nauci Marsum Augurem,
Non vicanos Aruspices, non de circo Astrologos,
Non Isiacos Conjectores, non Interpletes somnium:
Non enim sunt ii aut scientiâ, aut arte Divini,
Sed superstitiosi vates, impudentesque harioli,
Aut inertes, aut insani, aut quibus egestas imperat:
Qui sui questus causa fictas suscitant sententias,
Qui sibi semitam non sapiunt, alteri monstrant viam,
Quibus divitias pollicentur, ab iis drachmam petunt;
De divitiis deducant drachmam, reddant cœtera.
Ennius.

Those who have maintain'd that Men would be more miserable than Beasts,
were their Hopes confin'd to this Life only; among other Considerations
take notice that the latter are only afflicted with the Anguish of the
present Evil, whereas the former are very often pained by the Reflection
on what is passed, and the Fear of what is to come. This Fear of any
Future Difficulties or Misfortunes is so natural to the Mind, that were
a Man's Sorrows and Disquietudes summ'd up at the End of his Life, it
would generally be found that he had suffer'd more from the Apprehension
of such Evils as never happen'd to him, than from those Evils which had
really befallen him. To this we may add, that among those Evils which
befal us, there are many that have been more painful to us in the
Prospect, than by their actual Pressure.
This natural Impatience to look into Futurity, and to know what
Accidents may happen to us hereafter, has given birth to many ridiculous
Arts and Inventions. Some found their Prescience on the Lines of a Man's
Hand, others on the Features of his Face; some on the Signatures which
Nature has impressed on his Body, and others on his own Hand-Writing:
Some read Men's Fortunes in the Stars, as others have searched after
them in the Entrails of Beasts, or the Flights of Birds. Men of the best
Sense have been touched, more or less, with these groundless Horrours
and Presages of Futurity, upon surveying the most indifferent Works of
Nature. Can any thing be more surprizing than to consider
Cicero
, who
made the greatest Figure at the Bar, and in the Senate of the
Roman
Commonwealth, and, at the same time, outshined all the Philosophers of
Antiquity in his Library and in his Retirements, as busying himself in
the College of Augurs, and observing, with a religious Attention, after
what manner the Chickens peck'd the several Grains of Corn which were
thrown to them?
Notwithstanding these Follies are pretty well worn out of the Minds of
the Wise and Learned in the present Age, Multitudes of weak and ignorant
Persons are still Slaves to them. There are numberless Arts of
Prediction among the Vulgar, which are too trifling to enumerate; and
infinite Observations, of Days, Numbers, Voices, and Figures, which are
regarded by them as Portents and Prodigies. In short, every thing
Prophesies to the superstitious Man, there is scarce a Straw or a rusty
Piece of Iron that lies in his way by Accident.
It is not to be conceiv'd how many Wizards, Gypsies, and Cunning-Men are
dispers'd thro' all the Countries and Market-Towns of
Great-Britain
,
not to mention the Fortune-tellers and Astrologers, who live very
comfortably upon the Curiosity of several well-dispos'd Persons in the
Cities of
London
and
Westminster
.
Among the many pretended Arts of Divination, there is none which so
universally amuses as that by Dreams. I have indeed observ'd in a late
Speculation, that there have been sometimes, upon very extraordinary
Occasions, supernatural Revelations made to certain Persons by this
means; but as it is the chief Business of this Paper to root out popular
Errors, I must endeavour to expose the Folly and Superstition of those
Persons, who, in the common and ordinary course of Life, lay any stress
upon things of so uncertain, shadowy, and chimerical a nature. This I
cannot do more effectually than by the following Letter, which is dated
from a Quarter of the Town that has always been the Habitation of some
prophetick
Philomath
; it
been usual, time out of Mind, for all
such People as have lost their Wits, to resort to that Place either for
their Cure
or for their Instruction.
Moor-Fields, Oct. 4, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Having long consider'd whether there be any Trade wanting in this
great City, after having survey'd very attentively all kinds of Ranks
and Professions, I do not find in any Quarter of the Town an
Oneirocritick, or, in plain English, an Interpreter of Dreams. For
want of so useful a Person, there are several good People who are very
much puzled in this Particular, and dream a whole Year together
without being ever the wiser for it. I hope I am pretty well qualify'd
for this Office, having studied by Candlelight all the Rules of Art
which have been laid down upon this Subject. My great Uncle by my
Wife's Side was a Scotch Highlander, and second-sighted. I have four
Fingers and two Thumbs upon one Hand, and was born on the longest
Night of the Year. My Christian and Sir -Name begin and end with the
same Letters. I am lodg'd in Moorfields, in a House that for these
fifty years has been always tenanted by a Conjurer.
'If you had been in Company, so much as my self, with ordinary Women
of the Town, you must know that there are many of them who every day
in their Lives, upon seeing or hearing of any thing that is
unexpected, cry, My Dream is out; and cannot go to sleep in quiet
the next night, till something or other has happen'd which has
expounded the Visions of the preceding one. There are others who are
in very great pain for not being able to recover the Circumstances of
a Dream, that made strong Impressions upon them while it lasted. In
short, Sir , there are many whose waking Thoughts are wholly employ'd
on their sleeping ones. For the benefit therefore of this curious and
inquisitive Part of my Fellow-Subjects, I shall in the first place
tell those Persons what they dreamt of, who fancy they never dream at
all. In the next place, I shall make out any Dream, upon hearing a
single Circumstance of it; and in the last place, shall expound to
them the good or bad Fortune which such Dreams portend. If they do not
presage good luck, I shall deSir e nothing for my Pains; not
questioning at the same time that those who consult me will be so
reasonable as to afford me a moderate Share out of any considerable
Estate, Profit or Emolument which I shall thus discover to them. I
interpret to the Poor for nothing, on condition that their Names may
be inserted in Publick Advertisements, to attest the Truth of such my
Interpretations. As for People of Quality or others, who are
indisposed, and do not care to come in Person, I can interpret their
Dreams by seeing their Water. I set aside one Day in the Week for
Lovers; and interpret by the great for any Gentlewoman who is turned
of Sixty, after the rate of half a Crown per Week, with the usual
Allowances for good Luck. I have several Rooms and Apartments fitted
up, at reasonable rates, for such as have not Conveniences for
dreaming at their own Houses.
Titus Trophonius.
N. B. I am not dumb.
O.
Bedlam was then in Moorfields.
Contents
|
Friday, October 10, 1712 |
Budgell |
Candida perpetuo reside, concordia, lecto,
Tamque pari semper sit Venus æqua jugo.
Diligat illa, senem quondam: Sed et ipsa marito,
Tunc quoque cum fuerit, non videatur anus.
Mart.

The following Essay is written by the Gentleman, to whom the World is
oblig'd for those several excellent Discourses which have been marked
with the Letter X.
I have somewhere met with a Fable that made
Wealth
the Father of
Love
. It is certain a Mind ought, at least, to be free from the
Apprehensions of Want and Poverty, before it can fully attend to all the
Softnesses and Endearments of this Passion. Notwithstanding we see
Multitudes of married People, who are utter Strangers to this delightful
Passion amidst all the Affluence of the most plentiful Fortunes.
It is not sufficient to make a Marriage happy, that the Humours of two
People should be alike; I could instance an hundred Pair, who have not
the least Sentiment of Love remaining for one another, yet are so like
in their Humours, that if they were not already married, the whole World
would design them for Man and Wife.
The Spirit of Love has something so extremely fine in it, that it is
very often disturbed and lost, by some little Accidents which the
Careless and Unpolite never attend to, till it is gone past Recovery.
Nothing has more contributed to banish it from a married State, than too
great a Familiarity, and laying aside the common Rules of Decency. Tho'
I could give Instances of this in several Particulars, I shall only
mention that of
Dress
. The Beaus and Belles about Town, who dress
purely to catch one another, think there is no further occasion for the
Bait, when their first Design has succeeded. But besides the too common
Fault in point of Neatness, there are several others which I do not
remember to have seen touched upon,
in one of our modern Comedies
, where a
French
Woman offering to undress and dress herself before
the Lover of the Play, and assuring his Mistress that it was very useful
in
France
, the Lady tells her that's a Secret in Dress she never knew
before, and that she was so unpolish'd an
English
Woman, as to resolve
never to learn even to dress before her Husband.
There is something so gross in the Carriage of some Wives, that they
lose their Husbands Hearts for Faults, which, if a Man has either
Good-Nature or Good-Breeding, he knows not how to tell them of. I am
afraid, indeed, the Ladies are generally most faulty in this Particular,
who, at their first giving into Love, find the Way so smooth and
pleasant, that they fancy 'tis scarce possible to be tired in it.
There is so much Nicety and Discretion requir'd to keep Love alive after
Marriage, and make Conversation still new and agreeable after twenty or
thirty years, that I know nothing which seems readily to promise it, but
an earnest endeavour to please on both sides, and superior good Sense on
the part of Man.
By a Man of Sense, I mean one acquainted with Business and Letters.
A Woman very much settles her Esteem for a Man, according to the Figure
he makes in the World, and the Character he bears among his own Sex. As
Learning is the chief Advantage we have over them, it is, methinks, as
scandalous and inexcusable for a Man of Fortune to be illiterate, as for
a Woman not to know how to behave her self on the most ordinary
Occasions. It is this which sets the two Sexes at the greatest Distance;
a Woman is vexed and surpriz'd, to find nothing more in the Conversation
of a Man, than in the common Tattle of her own Sex.
Some small Engagement at least in Business, not only sets a Man's
Talents in the fairest Light, and allots him a Part to act, in which a
Wife cannot well intermeddle; but gives frequent occasions for those
little Absences, which, whatever seeming Uneasiness they may give, are
some of the best Preservatives of Love and De
Sir
e.
Lætitia
is pretty, modest, tender, and has Sense enough; she married
Erastus
, who is in a Post of some Business, and has a general Taste in
most Parts of polite Learning.
Lætitia
, where ever she visits, has the
pleasure to hear of something which was handsomely said or done by
Erastus
.
Erastus
, since his Marriage, is more gay in his Dress than
ever, and in all Companies is as complaisant to
Lætitia
as to any
other Lady. I have seen him give her her Fan, when it has dropped, with
all the Gallantry of a Lover. When they take the Air together,
Erastus
is continually improving her Thoughts, and with a Turn of Wit and Spirit
which is peculiar to him, giving her an Insight into things she had no
notion of before.
Lætitia
is transported at having a new World thus
open'd to her, and hangs upon the Man that gives her such agreeable
Informations.
Erastus
has carried this Point still further, as he
makes her daily not only more fond of him, but infinitely more satisfied
with herself.
Erastus
finds a Justness or Beauty in whatever she says
or observes, that
Lætitia
herself was not aware of; and, by his
Assistance, she has discovered an hundred good Qualities and
Accomplishments in herself, which she never before once dreamed of.
Erastus
, with the most artful Complaisance in the World, by several
remote Hints, finds the means to make her say or propose almost whatever
he has a mind to, which he always receives as her own Discovery, and
gives her all the Reputation of it.
Erastus
has a perfect Taste in Painting, and carried
Lætitia
with
him the other day to see a Collection of Pictures. I sometimes visit
this happy Couple. As we were last Week walking in the long Gallery
before Dinner,
I have lately laid out some Mony in Paintings
, says
Erastus; I bought that
Venus
and
Adonis
purely upon
Lætitia's
Judgment; it cost me three-score Guineas, and I was this morning
offer'd a2 hundred for it . I turned towards
Lætitia
, and saw her
Cheeks glow with Pleasure, while at the same time she cast a look upon
Erastus
, the most tender and affectionate I ever beheld.
Flavilla
married
Tom Tawdry
; she was taken with his laced Coat and
rich Sword-knot; she has the mortification to see
Tom
despised by all
the worthy Part of his own Sex.
Tom
has nothing to do after Dinner,
but to determine whether he will pare his Nails at St.
James's,
White's
, or his own House. He has said nothing to
Flavilla
since they
were married, which she might not have heard as well from her own Woman.
He however takes great care to keep up the saucy ill-natur'd Authority
of a Husband. Whatever
Flavilla
happens to assert,
Tom
immediately
contradicts with an Oath, by way of Preface, and,
My Dear, I must tell
you, you talk most confoundedly silly. Flavilla
had a Heart naturally
as well dispos'd for all the Tenderness of Love as that of
Lætitia
;
but as Love seldom continues long after Esteem, it is difficult to
determine, at present, whether the unhappy
Flavilla
hates or despises
the Person most, whom she is obliged to lead her whole Life with.
X
.
Steele's
Funeral
, or
Grief à la Mode
, Act III.
an
and in first reprint.
Contents
|
Saturday, October 11, 1712 |
Addison |
Defendit numerus, junctæque umbone Phalanges.
Juv.

There is something very Sublime, tho' very fanciful, in
Plato's
Description of the Supreme Being, That
Truth is his Body, and Light his
Shadow
. According to this Definition, there is nothing so contradictory
to his Nature, as Error and Falshood. The Platonists have so just a
Notion of the Almighty's Aversion to every thing which is false and
erroneous, that they looked upon
Truth
as no less necessary than
Virtue
, to qualifie an human Soul for the Enjoyment of a separate
State. For this reason as they recommended Moral Duties to qualifie and
season the Will for a future Life, so they prescribed several
Contemplations and Sciences to rectifie the Understanding. Thus
Plato
has called Mathematical Demonstrations the Catharticks or Purgatives of
the Soul, as being the most proper Means to cleanse it from Error, and
to give it a Relish of Truth; which is the natural Food and Nourishment
of the Understanding, as Virtue is the Perfection and Happiness of the
Will.
There are many Authors who have shewn wherein the Malignity of a
Lie
consists, and set forth in proper Colours, the Heinousness of the
Offence. I shall here consider one Particular Kind of this Crime, which
has not been so much spoken to; I mean that abominable Practice of
Party-lying
. This Vice is so very predominant among us at present,
that a Man is thought of no Principles, who does not propagate a certain
System of Lies. The Coffee-Houses are supported by them, the Press is
choaked with them, eminent Authors live upon them. Our
Bottle-Conversation is so infected with them, that a Party-Lie is grown
as fashionable an Entertainment, as a lively Catch or a merry Story: The
Truth of it is, half the great Talkers in the Nation would be struck
dumb, were this Fountain of Discourse dried up. There is however one
Advantage resulting from this detestable Practice; the very Appearances
of Truth are so little regarded, that Lies are at present discharg'd in
the Air, and begin to hurt no Body. When we hear a Party-story from a
Stranger, we consider whether he is a Whig or a Tory that relates it,
and immediately conclude they are Words of course, in which the honest
Gentleman designs to recommend his Zeal, without any Concern for his
Veracity. A Man is looked upon as bereft of common Sense, that gives
Credit to the Relations of Party-Writers;
nay
his own Friends shake
their Heads at him, and consider him in no other Light than as an
officious Tool or a well-meaning Ideot. When it was formerly the Fashion
to husband a Lie, and trump it up in some extraordinary Emergency, it
generally did Execution, and was not a little serviceable to the Faction
that made use of it; but at present every Man is upon his Guard, the
Artifice has been too often repeated to take Effect.
I have frequently wonder'd to see Men of Probity, who would scorn to
utter a Falshood for their own particular Advantage, give so readily
into a Lie when it becomes the Voice of their Faction, notwithstanding
they are thoroughly sensible of it as such. How is it possible for those
who are Men of Honour in their Persons, thus to become notorious Liars
in their Party? If we look into the Bottom of this Matter, we may find,
I think, three Reasons for it, and at the same time discover the
Insufficiency of these Reasons to justify so Criminal a Practice.
In the first place, Men are apt to think that the Guilt of a Lie, and
consequently the Punishment, may be very much diminish'd, if not wholly
worn out, by the Multitudes of those who partake in it. Tho' the Weight
of a Falshood would be too heavy for
one
to bear, it grows light in
their Imaginations, when it is shared among
many
. But in this Case a
Man very much deceives himself; Guilt, when it spreads thro' numbers, is
not so properly divided as multiplied: Every one is criminal in
proportion to the Offence which he commits, not to the Number of those
who are his Companions in it. Both the Crime and the Penalty lie as
heavy upon every Individual of an offending Multitude, as they would
upon any single Person had none shared with him in the Offence. In a
word, the Division of Guilt is like that of Matter; tho' it may be
separated into infinite Portions, every Portion shall have the whole
Essence of Matter in it, and consist of as many Parts as the Whole did
before it was divided.
But in the second place, tho' Multitudes, who join in a Lie, cannot
exempt themselves from the Guilt, they may from the Shame of it. The
Scandal of a Lie is in a manner lost and annihilated, when diffused
among several Thousands; as a Drop of the blackest Tincture wears away
and vanishes, when mixed and confused in a considerable Body of Water;
the Blot is still in it, but is not able to discover it self. This is
certainly a very great Motive to several Party-Offenders, who avoid
Crimes, not as they are prejudicial to their Virtue, but to their
Reputation. It is enough to shew the Weakness of this Reason, which
palliates Guilt without removing it, that every Man who is influenced by
it declares himself in effect an infamous Hypocrite, prefers the
Appearance of Virtue to its Reality, and is determined in his Conduct
neither by the Dictates of his own Conscience, the Suggestions of true
Honour, nor the Principles of Religion.
The third and last great Motive for Mens joining in a popular Falshood,
or, as I have hitherto called it, a Party-Lie, notwithstanding they are
convinced of it as such, is the doing Good to a Cause which every Party
may be supposed to look upon as the most meritorious. The Unsoundness of
this Principle has been so often exposed, and is so universally
acknowledged, that a Man must be an utter Stranger to the Principles,
either of natural Religion or Christianity, who suffers himself to be
guided by it. If a Man might promote the supposed Good of his Country by
the blackest Calumnies and Falshoods, our Nation abounds more in
Patriots than any other of the Christian World.
Pompey
was
de
Sir
ed not to set Sail in a Tempest that would hazard his Life,
It is
necessary for me
, says he,
to Sail, but it is not necessary for me to
Live
: Every Man should say to himself, with the same Spirit, It is
my Duty to speak Truth, tho' it is not my Duty to be in an Office. One
of the Fathers hath carried this Point so high, as to declare,
He would
not tell a Lie, tho' he were sure to gain Heaven by it
. However
extravagant such a Protestation may appear, every one will own, that a
Man may say very reasonably,
He would not tell a Lie, if he were sure
to gain Hell by it
; or, if you have a mind to soften the Expression,
that he would not tell a Lie to gain any Temporal Reward by it, when he
should run the hazard of losing much more than it was possible for him
to gain.
O.
Quoted from Plutarch's
Life
, § 50. Terser in the
original:
Contents
|
Monday, October 13, 1712 |
Steele |
Omnes autem et habentur et dicuntur Tyranni, qui potestate sunt
perpetua, in ea Civitate quæ libertate usa est.
Corn. Nepos.

The following Letters complain of what I have frequently observed with
very much Indignation; therefore I shall give them to the Publick in the
Words with which my Correspondents, who suffer under the Hardships
mention'd in them, describe them.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'In former Ages all Pretensions to Dominion have been supported and
submitted to, either upon Account of Inheritance, Conquest or
Election; and all such Persons who have taken upon 'em any Soveraignty
over their Fellow-Creatures upon any other Account, have been always
called Tyrants, not so much because they were guilty of any particular
Barbarities, as because every Attempt to such a Superiority was in its
Nature tyrannical. But there is another sort of Potentates, who may
with greater Propriety be call'd Tyrants, than those last mention'd,
both as they assume a despotick Dominion over those as free as
themselves, and as they support it by Acts of notable Oppression and
Injustice; and these are the Rulers in all Clubs and Meetings. In
other Governments, the Punishments of some have been alleviated by the
Reward of others; but what makes the Reign of these Potentates so
particularly grievous, is, that they are exquisite in punishing their
Subjects, at the same time they have it not in their power to reward
'em. That the Reader may the better comprehend the Nature of these
Monarchs, as well as the miserable State of those that are their
Vassals, I shall give an Account of the King of the Company I am
fallen into, whom for his particular Tyranny I shall call
Dionysius; as also of the Seeds that sprung up to this odd sort of
Empire.
'Upon all Meetings at Taverns, 'tis necessary some one of the Company
should take it upon him to get all things in such order and readiness,
as may contribute as much as possible to the Felicity of the
Convention; such as hastening the Fire, getting a sufficient number of
Candles, tasting the Wine with a judicious Smack, fixing the Supper,
and being brisk for the Dispatch of it. Know then, that
Dionysius
went thro' these Offices with an Air that seem'd to express a
Satisfaction rather in serving the Publick, than in gratifying any
particular Inclination of his own. We thought him a Person of an
exquisite Palate, and therefore by consent beseeched him to be always
our Proveditor; which Post, after he had handsomely denied, he could
do no otherwise than accept. At first he made no other use of his
Power, than in recommending such and such things to the Company, ever
allowing these Points to be disputable; insomuch that I have often
carried the Debate for Partridge, when his Majesty has given
Intimation of the high Relish of Duck, but at the same time has
chearfully submitted, and devour'd his Partridge with most gracious
Resignation. This Submission on his side naturally produc'd the like
on ours; of which he in a little time made such barbarous Advantage,
as in all those Matters, which before seem'd indifferent to him, to
issue out certain Edicts as uncontroulable and unalterable as the Laws
of the
Medes and
Persians. He is by turns outragious, peevish,
froward and jovial. He thinks it our Duty for the little Offices, as
Proveditor, that in Return all Conversation is to be interrupted or
promoted by his Inclination for or against the present Humour of the
Company. We feel, at present, in the utmost Extremity, the Insolence
of Office; however, I being naturally warm, ventur'd to oppose him in
a Dispute about a Haunch of Venison. I was altogether for roasting,
but
Dionysius declar'd himself for boiling with so much Prowess and
Resolution, that the Cook thought it necessary to consult his own
Safety rather than the Luxury of my Proposition. With the same
Authority that he orders what we shall eat and drink, he also commands
us where to do it, and we change our Taverns according as he suspects
any Treasonable Practices in the settling the Bill by the Master, or
sees any bold Rebellion in point of Attendance by the Waiters. Another
Reason for changing the Seat of Empire, I conceive to be the Pride he
takes in the Promulgation of our Slavery, tho' we pay our Club for our
Entertainments even in these Palaces of our grand Monarch. When he has
a mind to take the Air, a Party of us are commanded out by way of
Life-Guard, and we march under as great Restrictions as they do. If we
meet a neighbouring King, we give or keep the Way according as we are
outnumber'd or not; and if the Train of each is equal in number,
rather than give Battle, the Superiority is soon adjusted by a
Desertion from one of 'em.
'Now, the Expulsion of these unjust Rulers out of all Societies, would
gain a Man as everlasting a Reputation, as either of the
Brutus's
got from their Endeavours to extirpate Tyranny from among the
Romans. I confess my self to be in a Conspiracy against the Usurper
of our Club; and to shew my Reading, as well as my merciful
Disposition, shall allow him till the Ides of
March to dethrone
himself. If he seems to affect Empire till that time, and does not
gradually recede from the Incursions he has made upon our Liberties,
he shall find a Dinner dress'd which he has no Hand in, and shall be
treated with an Order, Magnificence and Luxury as shall break his
proud Heart; at the same time that he shall be convinc'd in his
Stomach he was unfit for his Post, and a more mild and skilful Prince
receive the Acclamations of the People, and be set up in his Room:
but, as
Milton says,
—These Thoughts
Full Counsel must mature. Peace is despair'd,
And who can think Submission? War, then War
Open, or understood, must be resolved.1
'I am,
Sir , Your most obedient humble Servant.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am a young Woman at a Gentleman's Seat in the Country, who is a
particular Friend of my Father's, and came hither to pass away a Month
or two with his Daughters. I have been entertained with the utmost
Civility by the whole Family, and nothing has been omitted which can
make my Stay easy and agreeable on the Part of the Family; but there
is a Gentleman here, a Visitant as I am, whose Behaviour has given me
great Uneasinesses. When I first arrived here, he used me with the
utmost Complaisance; but, forsooth, that was not with regard to my
Sex, and since he has no Designs upon me, he does not know why he
should distinguish me from a Man in things indifferent. He is, you
must know, one of those familiar Coxcombs, who have observed some
well-bred Men with a good Grace converse with Women, and say no fine
things, but yet treat them with that sort of Respect which flows from
the Heart and the Understanding, but is exerted in no Professions or
Compliments. This Puppy, to imitate this Excellence, or avoid the
contrary Fault of being troublesome in Complaisance, takes upon him to
try his Talent upon me, insomuch that he contradicts me upon all
Occasions, and one day told me I lied. If I had stuck him with my
Bodkin, and behaved my self like a Man, since he won't treat me as a
Woman, I had, I think, served him right. I wish,
Sir , you would please
to give him some Maxims of Behaviour in these Points, and resolve me
if all Maids are not in point of Conversation to be treated by all
Batchelors as their Mistresses? if not so, are they not to be used as
gently as their Sisters? Is it sufferable, that the Fop of whom I
complain should say, as he would rather have such a-one without a
Groat, than me with the
Indies? What right has any Man to make
Suppositions of things not in his Power, and then declare his Will to
the dislike of one that has never offended him? I assure you these are
things worthy your Consideration, and I hope we shall have your
Thoughts upon them. I am, tho' a Woman justly offended, ready to
forgive all this, because I have no Remedy but leaving very agreeable
Company sooner than I de
Sir e. This also is an heinous Aggravation of
his Offence, that he is inflicting Banishment upon me. Your printing
this Letter may perhaps be an Admonition to reform him: As soon as it
appears I will write my Name at the End of it, and lay it in his Way;
the making which just Reprimand, I hope you will put in the Power of,
Sir ,
Your constant Reader,
and humble Servant.
T.
Paradise Lost,
i. 659-662.
Contents
|
Tuesday, October 14, 1712 |
Steele |
Hominis frugi et temperantis functus officium.
Ter.

The useful Knowledge in the following Letter shall have a Place in my
Paper, tho' there is nothing in it which immediately regards the Polite
or the Learned World; I say immediately, for upon Reflection every Man
will find there is a remote Influence upon his own Affairs, in the
Prosperity or Decay of the Trading Part of Mankind. My present
Correspondent, I believe, was never in Print before; but what he says
well deserves a general Attention, tho' delivered in his own homely
Maxims, and a Kind of Proverbial Simplicity; which Sort of Learning has
rais'd more Estates than ever were, or will be, from attention to
Virgil, Horace, Tully, Seneca, Plutarch
, or any of the rest, whom, I
dare say, this worthy Citizen would hold to be indeed ingenious, but
unprofitable Writers. But to the Letter.
Broadstreet, Oct. 10, 1712.
Mr. WILLIAM SPECTATOR,
Sir ,
'I accuse you of many Discourses on the Subject of Money, which you
have heretofore promis'd the Publick, but have not discharg'd your
self thereof. But, forasmuch as you seem to depend upon Advice from
others what to do in that Point, have sate down to write you the
Needful upon that Subject. But, before I enter thereupon, I shall take
this Opportunity to observe to you, that the thriving frugal Man shews
it in every Part of his Expence, Dress, Servants, and House; and I
must in the first place, complain to you, as SPECTATOR, that in these
Particulars there is at this Time, throughout the City of
London, a
lamentable Change from that Simplicity of Manners, which is the true
Source of Wealth and Prosperity. I just now said, the Man of Thrift
shews Regularity in every thing; but you may, perhaps, laugh that I
take Notice of such a Particular as I am going to do, for an Instance
that this City is declining, if their antient œconomy is not
restor'd. The Thing which gives me this Prospect, and so much Offence,
is the Neglect of the
Royal-Exchange, I mean the Edifice so called,
and the Walks appertaining thereunto. The
Royal-Exchange is a
Fabrick that well deserves to be so called, as well to express that
our Monarch's highest Glory and Advantage consists in being the
Patrons of Trade, as that it is commodious for Business, and an
Instance of the Grandeur both of Prince and People. But alas! at
present it hardly seems to be set apart for any such Use or Purpose.
Instead of the Assembly of honourable Merchants, substantial
Tradesmen, and knowing Masters of Ships; the Mumpers, the Halt, the
Blind, and the Lame; your Venders of Trash, Apples, Plumbs; your
Ragamuffins, Rakeshames, and Wenches, have justled the greater Number
of the former out of that Place. Thus it is, especially on the
Evening-Change; so that what with the Din of Squalings, Oaths and
Cries of Beggars, Men of the greatest Consequence in our City absent
themselves from the Place. This Particular, by the way, is of evil
Consequence; for if the Change be no Place for Men of the highest
Credit to frequent, it will not be a Disgrace to those of less
Abilities to absent. I remember the time when Rascally Company were
kept out, and the unlucky Boys with Toys and Balls were whipped away
by a Beadle. I have seen this done indeed of late, but then it has
been only to chase the Lads from Chuck, that the Beadle might seize
their Copper.
I must repeat the Abomination, that the Walnut Trade is carry'd on by
old Women within the Walks, which makes the Place impassable by reason
of Shells and Trash. The Benches around are so filthy, that no one can
sit down, yet the Beadles and Officers have the Impudence at
Christmas to ask for their Box, though they deserve the Strapado. I
do not think it impertinent to have mentioned this, because it speaks
a neglect in the Domestick Care of the City, and the Domestick is the
truest Picture of a Man every where else.
But I designed to speak on the Business of Money and Advancement of
Gain. The Man proper for this, speaking in the general, is of a
sedate, plain, good Understanding, not apt to go out of his way, but
so behaving himself at home, that Business may come to him.
Sir
William Turner, that valuable Citizen, has left behind him a most
excellent Rule, and couched it in very few Words, suited to the
meanest Capacity. He would say,
Keep your Shop and your Shop will
keep you. It must be confessed, that if a Man of a great Genius could
add Steadiness to his Vivacities, or substitute slower Men of Fidelity
to transact the methodical part of his Affairs, such a one would
outstrip the rest of the World: But Business and Trade is not to be
managed by the same Heads which write Poetry, and make Plans for the
Conduct of Life in general. So tho' we are at this day beholden to the
late witty and inventive Duke of
Buckingham for the whole Trade and
Manufacture of Glass, yet I suppose there is no one will aver, that,
were his Grace yet living, they would not rather deal with my diligent
Friend and Neighbour, Mr.
Gumley, for any Goods to be prepared and
delivered on such a Day, than he would with that illustrious Mechanick
abovementioned.
'No, no,
Mr. SPECTATOR, you Wits must not pretend to be rich; and it
is possible the Reason may be, in some Measure, because you despise,
or at least you do not value it enough to let it take up your chief
Attention; which the Trader must do, or lose his Credit, which is to
him what Honour, Reputation, Fame, or Glory is to other sort of Men.
'I shall not speak to the Point of Cash it self, till I see how you
approve of these my Maxims in general: But, I think, a Speculation
upon
Many a Little makes a Mickle, A Penny sav'd is a Penny got,
Penny wise and Pound foolish, It is Need that makes the old Wife
trot, would be very useful to the World, and if you treated them with
Knowledge would be useful to your self, for it would make Demands for
your Paper among those who have no Notion of it at present. But of
these Matters more hereafter. If you did this, as you excel many
Writers of the present Age for Politeness, so you would outgo the
Author of the true Strops of Razors for Use.
'I shall conclude this Discourse with an Explanation of a Proverb,
which by vulgar Errour is taken and used when a Man is reduced to an
Extremity, whereas the Propriety of the Maxim is to use it when you
would say, there is Plenty, but you must make such a Choice, as not to
hurt another who is to come after you.
'Mr.
Tobias Hobson, from whom we have the Expression, was a very
honourable Man, for I shall ever call the Man so who gets an Estate
honestly. Mr.
Tobias Hobson was a Carrier, and being a Man of great
Abilities and Invention, and one that saw where there might good
Profit arise, though the duller Men overlooked it; this ingenious Man
was the first in this Island who let out Hackney-Horses. He lived in
Cambridge, and observing that the Scholars rid hard, his manner was
to keep a large Stable of Horses, with Boots, Bridles, and Whips to
furnish the Gentlemen at once, without going from College to College
to borrow, as they have done since the Death of this worthy Man: I
say, Mr.
Hobson kept a Stable of forty good Cattle, always ready and
fit for travelling; but when a Man came for a Horse, he was led into
the Stable, where there was great Choice, but he obliged him to take
the Horse which stood next to the Stable-Door; so that every Customer
was alike well served according to his Chance, and every Horse ridden
with the same Justice: From whence it became a Proverb, when what
ought to be your Election was forced upon you, to say,
Hobson's
Choice. This memorable Man stands drawn in Fresco at an Inn (which he
used) in
Bishopsgate-street, with an hundred Pound Bag under his
Arm, with this Inscription upon the said Bag,
The fruitful Mother of an Hundred more.
'Whatever Tradesman will try the Experiment, and begin the day after
you publish this my Discourse to treat his Customers all alike, and
all reasonably and honestly, I will ensure him the same Success.
I am,
Sir ,
Your loving Friend,
Hezekiah Thrift
T.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 15, 1712 |
Steele |
—Si sapis
Neque præterquam quas ipse amor molestias
Habet addas; et illas, quas habet, recte feras.
Ter.

I
the other day driving in
a
Hack thro'
Gerrard-street
, when
my Eye was immediately catch'd with the prettiest Object imaginable, the
Face of a very fair Girl, between Thirteen and Fourteen, fixed at the
Chin to a painted Sash, and made part of the Landskip. It seemed
admirably done, and upon throwing my self eagerly out of the Coach to
look at it, it laugh'd and flung from the Window. This amiable Figure
dwelt upon me; and I was considering the Vanity of the Girl, and her
pleasant Coquettry in acting a Picture till she was taken Notice of, and
raised the Admiration of her Beholders. This little Circumstance made me
run into Reflections upon the Force of Beauty, and the wonderful
Influence the Female Sex has upon the other part of the Species. Our
Hearts are seized with their Enchantments, and there are few of us, but
brutal Men, who by that Hardness lose the chief Pleasure in them, can
resist their Insinuations, tho' never so much against our own Interest
and Opinion. It is common with Women to destroy the good Effects a Man's
following his own Way and Inclination might have upon his Honour and
Fortune, by interposing their Power over him in matters wherein they
cannot influence him, but to his Loss and Disparagement. I do not know
therefore a Task so difficult in human Life, as to be proof against the
Importunities of a Woman a Man loves. There is certainly no Armour
against Tears, sullen Looks, or at best constrained Familiarities, in
her whom you usually meet with Transport and Alacrity.
Sir
Walter
Rawleigh
was quoted in a Letter (of a very ingenious Correspondent of
mine) on this Subject. That Author, who had lived in Courts, Camps,
travelled through many Countries, and seen many Men under several
Climates, and of as various Complections, speaks of our Impotence to
resist the Wiles of Women, in very severe Terms.
words are as
follows
:
What Means did the Devil find out, or what Instruments did his own
Subtlety present him, as fittest and aptest to work his Mischief by?
Even the unquiet Vanity of the Woman; so as by Adam's hearkening to
the Voice of his Wife, contrary to the express Commandment of the
living God, Mankind by that her Incantation became the subject of
Labour, Sorrow, and Death; the Woman being given to Man for a
Comforter and Companion, but not for a Counsellor. It is also to be
noted by whom the Woman was tempted; even by the most ugly and
unworthy of all Beasts, into whom the Devil entered and persuaded.
Secondly, What was the Motive of her Disobedience? Even a deSir e to
know what was most unfitting her Knowledge; an Affection which has
ever since remained in all the Posterity of her Sex. Thirdly, What was
it that moved the Man to yield to her Persuasions; even the same Cause
which hath moved all Men since to the like Consent, namely, an
Unwillingness to grieve her or make her sad, lest she should pine, and
be overcome with Sorrow. But if Adam in the state of Perfection,
and Solomon the Son of David, God's chosen Servant, and himself a
Man endued with the greatest Wisdom, did both of them disobey their
Creator by the Persuasion and for the Love they bare to a Woman, it is
not so wonderful as lamentable, that other Men in succeeding Ages have
been allured to so many inconvenient and wicked Practices by the
Persuasion of their Wives, or other beloved Darlings, who cover over
and shadow many malicious Purposes with a counterfeit Passion of
dissimulate Sorrow and Unquietness.
The Motions of the Minds of Lovers are no where so well described, as in
the Works of skillful Writers for the Stage. The Scene between
Fulvia
and
Curius
, in the second Act of
Johnson's Catiline
, is an excellent
Picture of the Power of a Lady over her Gallant. The Wench plays with
his Affections; and as a Man of all Places in the World wishes to make a
good Figure with his Mistress, upon her upbraiding him with Want of
Spirit, he alludes to Enterprizes which he cannot reveal but with the
Hazard of his Life. When he is worked thus far, with a little Flattery
of her Opinion of his Gallantry, and de
Sir
e to know more of it out of
her overflowing Fondness to him, he brags to her till his Life is in her
Disposal.
When a Man is thus liable to be vanquished by the Charms of her he
loves, the safest Way is to determine what is proper to be done, but to
avoid all Expostulation with her before he executes what he has
resolved. Women are ever too hard for us upon a Treaty, and one must
consider how senseless a thing it is to argue with one whose Looks and
Gestures are more prevalent with you, than your Reason and Arguments can
be with her. It is a most miserable Slavery to submit to what you
disapprove, and give up a Truth for no other Reason, but that you had
not Fortitude to support you in asserting it. A Man has enough to do to
conquer his own unreasonable Wishes and De
Sir
es; but he does that in
vain, if he has those of another to gratify. Let his Pride be in his
Wife and Family, let him give them all the Conveniences of Life in such
a manner as if he were proud of them; but let it be his own innocent
Pride, and not their exorbitant De
Sir
es, which are indulged by him. In
this case all the little Arts imaginable are used to soften a Man's
Heart, and raise his Passion above his Understanding; but in all
Concessions of this Kind, a Man should consider whether the Present he
makes flows from his own Love, or the Importunity of his Beloved: If
from the latter, he is her Slave; if from the former, her Friend. We
laugh it off, and do not weigh this Subjection to Women with that
Seriousness which so important a Circumstance deserves. Why was Courage
given to Man, if his Wife's Fears are to frustrate it? When this is once
indulged, you are no longer her Guardian and Protector, as you were
designed by Nature; but, in Compliance to her Weaknesses, you have
disabled your self from avoiding the Misfortunes into which they will
lead you both, and you are to see the Hour in which you are to be
reproached by her self for that very Complaisance to her. It is indeed
the most difficult Mastery over our selves we can possibly attain, to
resist the Grief of her who charms us; but let the Heart ake, be the
Anguish never so quick and painful, it is what must be suffered and
passed through, if you think to live like a Gentleman, or be conscious
to your self that you are a Man of Honesty. The old Argument, that
You
do not love me if you deny me this
, which first was used to obtain a
Trifle, by habitual Success will oblige the unhappy Man who gives Way to
it, to resign the Cause even of his Country and his Honour.
T.
an
and in first reprint.
History of the World
, Bk. i. ch. 4, sect. 4.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 16, 1712 |
Addison |
Quis non invenit turbâ quod amaret in illâ?
Ovid.

Dear SPEC.
'Finding that my last Letter took, I do intend to continue my
epistolary Correspondence with thee, on those dear confounded
Creatures,
Women. Thou knowest, all the little Learning I am Master
of is upon that Subject; I never looked in a Book, but for their
sakes. I have lately met with two pure Stories for a
Spectator,
which I am sure will please mightily, if they pass through thy Hands.
The first of them I found by chance in a
English Book
called
Herodotus, that lay in my Friend
Dapperwit's Window, as I
visited him one Morning. It luckily opened in the Place where I met
with the following Account. He tells us that it was the Manner among
the
Persians to have several Fairs in the Kingdom, at which all the
young unmarried Women were annually exposed to Sale. The Men who
wanted Wives came hither to provide themselves: Every Woman was given
to the highest Bidder, and the Mony which she fetched laid aside for
the publick Use, to be employed as thou shalt hear by and by. By this
means the richest People had the Choice of the Market, and culled out
all the most extraordinary Beauties. As soon as the Fair was thus
picked, the Refuse was to be distributed among the Poor, and among
those who could not go to the Price of a
Beauty Several of these
married the
Agreeables, without paying a Farthing for them, unless
somebody chanced to think it worth his while to bid for them, in which
Case the best Bidder was always the Purchaser. But now you must know,
Spec. it happened in
Persia as it does in our own Country, that
there were as many
ugly Women, as
Beauties or
Agreeables; so
that by Consequence, after the Magistrates had put off a great many,
there were still a great many that stuck upon their Hands. In order
therefore to clear the Market, the Money which the Beauties had sold
for, was disposed of among the Ugly; so that a poor Man, who could not
afford to have a Beauty for his Wife, was forced to take up with a
Fortune; the greatest Portion being always given to the most Deformed.
To this the Author adds, that every poor Man was forced to live kindly
with his Wife, or in case he repented of his Bargain, to return her
Portion with her to the next publick Sale.
What I would recommend to thee on this Occasion is, to establish such
an imaginary Fair in
Great Britain: Thou couldst make it very
pleasant, by matching Women of Quality with Coblers and Carmen, or
describing Titles and Garters leading off in great Ceremony
Shop-keepers and Farmers Daughters. Tho' to tell thee the Truth, I am
confoundedly afraid that as the love of Mony prevails in our Island
more than it did in
Persia, we should find that some of our greatest
Men would chuse out the Portions, and rival one another for the
richest Piece of Deformity; and that on the contrary, the Toasts and
Belles would be bought up by extravagant Heirs, Gamesters and
Spendthrifts. Thou couldst make very pretty Reflections upon this
Occasion in Honour of the
Persian Politicks, who took care, by such
Marriages, to beautify the upper part of the Species, and to make the
greatest Persons in the Government the most graceful. But this I shall
leave to thy judicious Pen.
'I have another Story to tell thee, which I likewise met with in a
Book. It seems the General of the
Tartars, after having laid siege
to a strong Town in
China, and taken it by Storm, would set to Sale
all the Women that were found in it. Accordingly, he put each of them
into a Sack, and after having thoroughly considered the Value of the
Woman who was inclosed, marked the Price that was demanded for her
upon the Sack. There were a great Confluence of Chapmen, that resorted
from every Part, with a Design to purchase, which they were to do
unsight unseen. The Book mentions a Merchant in particular, who
observing one of the Sacks to be marked pretty high, bargained for it,
and carried it off with him to his House. As he was resting with it
upon a half-way Bridge, he was resolved to take a Survey of his
Purchase: Upon opening the Sack, a little old Woman popped her Head
out of it; at which the Adventurer was in so great a Rage, that he was
going to shoot her out into the River. The old Lady, however, begged
him first of all to hear her Story, by which he learned that she was
sister to a great
Mandarin, who would infallibly make the Fortune of
his Brother-in-Law as soon as he should know to whose Lot she fell.
Upon which the Merchant again tied her up in his Sack, and carried her
to his House, where she proved an excellent Wife, and procured him all
the Riches from her Brother that she had promised him.
'I fancy, if I was disposed to dream a second time, I could make a
tolerable Vision upon this Plan. I would suppose all the unmarried
Women in
London and
Westminster brought to Market in Sacks, with
their respective Prices on each Sack. The first Sack that is sold is
marked with five thousand Pound: Upon the opening of it, I find it
filled with an admirable Housewife, of an agreeable Countenance: The
Purchaser, upon hearing her good Qualities, pays down her Price very
chearfully. The second I would open, should be a five hundred Pound
Sack: The Lady in it, to our surprize, has the Face and Person of a
Toast: As we are wondering how she came to be set at so low a Price,
we hear that she would have been valued at ten thousand Pound, but
that the Publick had made those Abatements for her being a Scold. I
would afterwards find some beautiful, modest, and discreet Woman, that
should be the top of the Market; and perhaps discover half a dozen
Romps tyed up together in the same Sack, at one hundred Pound an Head.
The Prude and the Coquet should be valued at the same Price, tho' the
first should go off the better of the two. I fancy thou wouldst like
such a Vision, had I time to finish it; because, to talk in thy own
way, there is a Moral in it. Whatever thou may'st think of it,
pr'ythee do not make any of thy queer Apologies for this Letter, as
thou didst for my last. The Women love a gay lively Fellow, and are
never angry at the Railleries of one who is their known Admirer. I am
always bitter upon them, but well with them.
Thine,
Honeycomb.
O.
Contents
|
Friday, October 17, 1712 |
Addison |
Lectorem delectando pariterque monendo.
Hor.

There is nothing which we receive with so much Reluctance as Advice. We
look upon the Man who gives it us as offering an Affront to our
Understanding, and treating us like Children or Ideots. We consider the
Instruction as an implicit Censure, and the Zeal which any one shews for
our Good on such an Occasion as a Piece of Presumption or Impertinence.
The Truth of it is, the Person who pretends to advise, does, in that
particular, exercise a Superiority over us, and can have no other Reason
for it, but that in comparing us with himself, he thinks us defective
either in our Conduct or our Understanding. For these Reasons, there is
nothing so difficult as the Art of making Advice agreeable; and indeed
all the Writers, both Ancient and Modern, have distinguished themselves
among one another, according to the Perfection at which they have
arrived in this Art. How many Devices have been made use of, to render
this bitter Potion palatable? Some convey their Instructions to us in
the best chosen Words, others in the most harmonious Numbers, some in
Points of Wit, and others in short Proverbs.
But among all the different Ways of giving Counsel, I think the finest,
and that which pleases the most universally, is
Fable
, in whatsoever
shape it appears. If we consider this way of instructing or giving
Advice, it excels all others, because it is the least shocking, and the
least subject to those Exceptions which I have before mentioned.
This will appear to us, if we reflect in the first place, that upon the
reading of a Fable we are made to believe we advise ourselves. We peruse
the Author for the sake of the Story, and consider the Precepts rather
as our own Conclusions, than his Instructions. The Moral insinuates it
self imperceptibly, we are taught by Surprise, and become wiser and
better unawares. In short, by this method a Man is so far over-reached
as to think he is directing himself, whilst he is following the Dictates
of another, and consequently is not sensible of that which is the most
unpleasing Circumstance in Advice.
In the next place, if we look into human Nature, we shall find that the
Mind is never so much pleased, as when she exerts her self in any Action
that gives her an Idea of her own Perfections and Abilities. This
natural Pride and Ambition of the Soul is very much gratified in the
reading of a Fable: for in Writings of this kind, the Reader comes in
for half of the Performance; every thing appears to him like a Discovery
of his own; he is busied all the while in applying Characters and
Circumstances, and is in this respect both a Reader and a Composer. It
is no wonder therefore that on such Occasions, when the Mind is thus
pleased with it self, and amused with its own Discoveries, that it is
highly delighted with the Writing which is the occasion of it.
this
reason the
Absalom
and
Achitophel
was one of the most popular
Poems that ever appeared in
English
. The poetry is indeed very fine,
but had it been much finer, it would not have so much pleased, without a
plan which gave the Reader an Opportunity of exerting his own Talents.
This oblique manner of giving Advice is so inoffensive, that if we look
into ancient Histories, we find the wise Men of old very often chose to
give Counsel to their Kings in Fables. To omit many which will occur to
every one's Memory,
is a pretty Instance of this Nature in a
Turkish
Tale, which I do not like the worse for that little Oriental
Extravagance which is mixed with it.
We are told that the Sultan
Mahmoud
, by his perpetual Wars abroad, and
his Tyranny at home, had filled his Dominions with Ruin and Desolation,
and half unpeopled the
Persian
Empire. The Visier to this great Sultan
(whether an Humourist or an Enthusiast, we are not informed) pretended
to have learned of a certain Dervise to understand the Language of
Birds, so that there was not a Bird that could open his Mouth, but the
Visier knew what it was he said. As he was one Evening with the Emperor,
in their return from Hunting, they saw a couple of Owls upon a Tree that
grew near an old Wall out of an Heap of Rubbish.
I would fain know
,
says the Sultan,
what those two Owls are saying to one another; listen
to their Discourse, and give me an account of it
. The Visier approached
the Tree, pretending to be very attentive to the two Owls. Upon his
return to the Sultan,
Sir
, says he,
I have heard part of their
Conversation, but dare not tell you what it is
. The Sultan would not be
satisfied with such an Answer, but forced him to repeat word for word
every thing the Owls had said.
You must know then
, said the
Visier,
that one of these Owls has a Son, and the other a Daughter,
between whom they are now upon a Treaty of Marriage. The Father of the
Son said to the Father of the Daughter, in my hearing, Brother, I
consent to this Marriage, provided you will settle upon your Daughter
fifty ruined Villages for her Portion. To which the Father of the
Daughter replied, Instead of fifty I will give her five hundred, if you
please. God grant a long Life to Sultan
Mahmoud;
whilst he reigns over
us, we shall never want ruined Villages
.
The Story says, the Sultan was so touched with the Fable, that he
rebuilt the Towns and Villages which had been destroyed, and from that
time forward consulted the Good of his People
.
To fill up my Paper, I shall add a most ridiculous piece of natural
Magic, which was taught by no less a Philosopher than
Democritus
,
namely, that if the Blood of certain Birds, which he mentioned, were
mixed together, it would produce a Serpent of such a wonderful Virtue,
that whoever did eat it should be skill'd in the Language of Birds, and
understand every thing they said to one another. Whether the Dervise
abovementioned might not have eaten such a Serpent, I shall leave to the
Determinations of the Learned.
O.
Dryden's satire on the intrigues of the Duke of Monmouth
and Lord Shaftesbury to exclude the King's brother from the Throne.
Monmouth was
Absalom
, and Shaftesbury
Achitophel
.
Pilpay's Fables.
Contents
|
Saturday, October 18, 1712 |
Addison |
—Afflata est numine quando
Jam propiore Dei—
Virg.

The following Letter comes to me from that excellent Man in Holy Orders,
whom I have mentioned more than once as one of that Society who assist
me in my Speculations. It is a
Thought in Sickness
, and of a very
serious Nature, for which Reason I give it a place in the Paper of this
Day.
Sir ,
'The
Indisposition which has long hung upon me, is at last grown to
such
a1 Head, that it must quickly make an End of me, or of it
self. You may imagine, that whilst I am in this bad state of Health,
there are none of your Works which I read with greater Pleasure than
your
Saturday's Papers. I should be very glad if I could furnish you
with any Hints for that Day's Entertainment. Were I able to dress up
several Thoughts of a serious nature, which have made great
Impressions on my Mind during a long Fit of Sickness, they might not
be an improper Entertainment for that Occasion.
'Among all the Reflections which usually rise in the Mind of a sick
Man, who has Time and Inclination to consider his approaching End,
there is none more natural than that of his going to appear Naked and
Unbodied before Him who made him. When a Man considers, that as soon
as the vital Union is dissolved, he shall see that Supreme Being, whom
he now contemplates at a Distance, and only in his Works; or, to speak
more philosophically, when by some Faculty in the Soul he shall
apprehend the Divine Being, and be more sensible of his Presence, than
we are now of the Presence of any Object which the Eye beholds, a Man
must be lost in Carelessness and Stupidity, who is not alarmed at such
a Thought. Dr.
Sherlock, in his excellent Treatise upon Death, has
represented, in very strong and lively Colours, the State of the Soul
in its first Separation from the Body, with regard to that invisible
World which every where surrounds us, tho' we are not able to discover
it through this grosser World of Matter, which is accommodated to our
Senses in this Life. His Words are as follow.
That Death, which is our leaving this World, is nothing else but our
putting off these Bodies, teaches us, that it is only our Union to
these Bodies, which intercepts the sight of the other World: The other
World is not at such a distance from us, as we may imagine; the Throne
of God indeed is at a great remove from this Earth, above the third
Heavens, where he displays his Glory to those blessed Spirits which
encompass his Throne; but as soon as we step out of these Bodies, we
step into the other World, which is not so properly another World,
(for there is the same Heaven and Earth still) as a new state of Life.
To live in these Bodies is to live in this World; to live out of them
is to remove into the next: For while our Souls are confined to these
Bodies, and can look only thro' these material Casements, nothing but
what is material can affect us; nay, nothing but what is so gross,
that it can reflect Light, and convey the Shapes and Colours of Things
with it to the Eye: So that though within this visible World, there be
a more glorious Scene of Things than what appears to us, we perceive
nothing at all of it; for this Veil of Flesh parts the visible and
invisible World: But when we put off these Bodies, there are new and
surprizing Wonders present themselves to our Views; when these
material Spectacles are taken off, the Soul, with its own naked Eyes,
sees what was invisible before: And then we are in the other World,
when we can see it, and converse with it: Thus St. Paul tell us,
That when we are at home in the Body, we are absent from the Lord;
but when we are absent from the Body, we are present with the Lord, 2
Cor. 5. 6, 8. And methinks this is enough to cure us of our
Fondness for these Bodies, unless we think it more deSir able to be
confined to a Prison, and to look through a Grate all our Lives, which
gives us but a very narrow prospect, and that none of the best
neither, than to be set at liberty to view all the Glories of the
World. What would we give now for the least Glimpse of that invisible
World, which the first step we take out of these Bodies will present
us with? There are such things as Eye hath not seen, nor Ear heard,
neither hath it entered into the Heart of Man to conceive: Death
opens our Eyes, enlarges our Prospect, presents us with a new and more
glorious World, which we can never see while we are shut up in Flesh;
which should make us as willing to part with this Veil, as to take the
Film off of our Eyes, which hinders our Sight.
'As a thinking Man cannot but be very much affected with the Idea of
his appearing in the presence of that Being
whom none can see and
live; he must be much more affected when he considers that this Being
whom he appears before, will examine all the Actions of his past Life,
and reward or punish him accordingly. I must confess that I think
there is no Scheme of Religion, besides that of Christianity, which
can possibly support the most virtuous Person under this Thought. Let
a Man's Innocence be what it will, let his Virtues rise to the highest
pitch of Perfection attainable in this Life, there will be still in
him so many secret Sins, so many human Frailties, so many Offences of
Ignorance, Passion and Prejudice, so many unguarded Words and
Thoughts, and in short, so many Defects in his best Actions, that,
without the Advantages of such an Expiation and Atonement as
Christianity has revealed to us, it is impossible that he should be
cleared before his Sovereign Judge, or that he should be able
to
stand in his Sight. Our Holy Religion suggests to us the only Means
whereby our Guilt may be taken away, and our imperfect Obedience
accepted.
'It is this Series of Thought that I have endeavoured to express in
the following Hymn, which I have composed during this my Sickness.
| I |
When rising from the Bed of Death,
O'erwhelm'd with Guilt and Fear,
I see my Maker, Face to Face,
O how shall I appear! |
| II |
If yet, while Pardon may be found,
And Mercy may be sought,
My Heart with inward Horrour shrinks,
And trembles at the Thought; |
| III |
When thou, O Lord, shalt stand disclos'd
In Majesty severe,
And sit in Judgment on my Soul,
O how shall I appear! |
| IV |
But thou hast told the troubled Mind,
Who does her Sins lament,
The timely Tribute of her Tears
Shall endless Woe prevent. |
| V |
Then see the Sorrows of my Heart,
Ere yet it be too late;
And hear my Saviour's dying Groans,
To give those Sorrows Weight. |
| VI |
For never shall my Soul despair
Her Pardon to procure,
Who knows thine only Son has dy'd
To make her Pardon sure. |
'There
is a noble Hymn in
French, which Monsieur
Bayle has
celebrated for a
very fine one, and which the famous Author of the
Art of Speaking calls an
Admirable one, that turns upon a Thought of
the same Nature. If I could have done it Justice in
English, I would
have sent it you translated; it was written by Monsieur
Des
Barreaux; who had been one of the greatest Wits and Libertines in
France, but in his last Years was as remarkable a Penitent
2.
Grand Dieu, tes jugemens sont remplis d'equité;
Toûjours tu prens plaiSir à nous tre propice:
Mais j'ai tant fait de mal, que jamais ta bonté
Ne me pardonnera sans choquer ta Justice.
Ouy, mon Dieu, la grandeur de mon impieté
Ne laisse à ton pouvoir que le choix du suplice:
Ton interest s' oppose a ma felicité;
Et ta clemence meme attend que je perisse.
Contente ton deSir puis qu'il t'est glorieux;
Offense toy des pleurs qui coulent de mes yeux;
Tonne, frappe, il est temps, rens moi guerre pour guerre.
J'adore en perissant la raison qui t'aigrit:
Mais dessus quel endroit tombera ton tonnerre,
Qui ne soit tout convert du sang de Jesus Christ.
'If these Thoughts may be serviceable to you, I de
Sir e you would place
them in a proper Light, and am ever, with great Sincerity,'
Sir ,
Yours, &c.
O.
an
in first reprint.
Jacques Vallée Seigneur des Barreaux, born in Paris in
1602, was Counsellor of the Parliament of Paris, and gave up his charge
to devote himself to pleasure. He was famous for his songs and verses,
for his affability and generosity and irreligion. A few years before his
death he was converted, and wrote the pious sonnet given above, which
had been very widely praised and quoted. In his religious days he lived
secluded at Châlon sur Saône, where he died, in 1673.
Contents
|
Monday, October 20, 1712 |
Steele |
Me Parnassi deserta per ardua, dulcis
Raptat Amor; juvat ire jugis qua nulla priorum
Castaliam molle divertitur Orbita Clivo.
Virg.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I came home a little later than usual the other Night, and not
finding my self inclined to sleep, I took up
Virgil to divert me
till I should be more disposed to Rest. He is the Author whom I always
chuse on such Occasions, no one writing in so divine, so harmonious,
nor so equal a Strain, which leaves the Mind composed, and softened
into an agreeable Melancholy; the Temper in which, of all others, I
chuse to close the Day. The Passages I turned to were those beautiful
Raptures in his
Georgicks, where he professes himself entirely given
up to the Muses, and smit with the Love of Poetry, passionately
wishing to be transported to the cool Shades and Retirements of the
Mountain
Hæmus. I clos'd the Book and went to Bed. What I had just
before been reading made so strong an Impression on my Mind, that
Fancy seemed almost to fulfil to me the Wish of
Virgil, in
presenting to me the following Vision.
'Methought I was on a sudden plac'd in the Plains of
Boeotia, where
at the end of the Horizon I saw the Mountain
Parnassus rising before
me. The Prospect was of so large an Extent, that I had long wander'd
about to find a Path which should directly lead me to it, had I not
seen at some distance a Grove of Trees, which in a Plain that had
nothing else remarkable enough in it to fix my Sight, immediately
determined me to go thither. When I arrived at it, I found it parted
out into a great Number of Walks and Alleys, which often widened into
beautiful Openings, as Circles or Ovals, set round with Yews and
Cypresses, with Niches, Grotto's, and Caves placed on the Sides,
encompassed with Ivy. There was no Sound to be heard in the whole
Place, but only that of a gentle Breeze passing over the Leaves of the
Forest, every thing beside was buried in a profound Silence. I was
captivated with the Beauty and Retirement of the Place, and never so
much, before that Hour, was pleased with the Enjoyment of my self. I
indulged the Humour, and suffered my self to wander without Choice or
Design. At length, at the end of a Range of Trees, I saw three Figures
seated on a Bank of Moss, with a silent Brook creeping at their Feet.
I ador'd them as the tutelar Divinities of the Place, and stood still
to take a particular View of each of them. The Middlemost, whose Name
was
Solitude, sat with her Arms across each other, and seemed rather
pensive and wholly taken up with her own Thoughts, than any ways
grieved or displeased. The only Companions which she admitted into
that Retirement, was the Goddess
Silence, who sat on her right Hand
with her Finger on her Mouth, and on her left
Contemplation, with
her Eyes fixed upon the Heavens. Before her lay a celestial Globe,
with several Schemes of Mathematical Theorems. She prevented my Speech
with the greatest Affability in the World: Fear not, said she, I know
your Request before you speak it; you would be led to the Mountain of
the Muses; the only way to it lies thro' this Place, and no one is so
often employ'd in conducting Persons thither as my self. When she had
thus spoken, she rose from her Seat, and I immediately placed my self
under her Direction; but whilst I passed through the Grove, I could
not help enquiring of her who were the Persons admitted into that
sweet Retirement. Surely, said I, there can nothing enter here but
Virtue and virtuous Thoughts: The whole Wood seems design'd for the
Reception and Reward of such Persons as have spent their Lives
according to the Dictates of their Conscience and the Commands of the
Gods. You imagine right, said she; assure your self this Place was at
first designed for no other: Such it continued to be in the Reign of
Saturn, when none entered here but holy Priests, Deliverers of their
Country from Oppression and Tyranny, who repos'd themselves here after
their Labours, and those whom the Study and Love of Wisdom had fitted
for divine Conversation. But now it is become no less dangerous than
it was before de
Sir able: Vice has learned so to mimick Virtue, that it
often creeps in hither under its Disguise. See there! just before you,
Revenge stalking by, habited in the Robe of
Honour. Observe not
far from him
Ambition standing alone; if you ask him his Name, he
will tell you it is
Emulation or
Glory. But the most frequent
Intruder we have is
Lust, who succeeds now the Deity to whom in
better Days this Grove was entirely devoted.
Virtuous Love, with
Hymen, and the Graces attending him, once reign'd over this happy
Place; a whole Train of Virtues waited on him, and no dishonourable
Thought durst presume for Admittance: But now! how is the whole
Prospect changed? and how seldom renewed by some few who dare despise
sordid Wealth, and imagine themselves fit Companions for so charming a
Divinity?
'The Goddess had no sooner said thus, but we were arriv'd at the
utmost Boundaries of the Wood, which lay contiguous to a Plain that
ended at the Foot of the Mountain. Here I kept close to my Guide,
being sollicited by several Phantomes, who assured me they would shew
me a nearer Way to the Mountain of the Muses. Among the rest
Vanity
was extremely importunate, having deluded infinite Numbers, whom I saw
wandering at the Foot of the Hill. I turned away from this despicable
Troop with Disdain, and addressing my self to my Guide, told her, that
as I had some Hopes I should be able to reach up part of the Ascent,
so I despaired of having Strength enough to attain the Plain on the
Top. But being informed by her that it was impossible to stand upon
the Sides, and that if I did not proceed onwards, I should
irrecoverably fall down to the lowest Verge, I resolved to hazard any
Labour and Hardship in the Attempt: So great a de
Sir e had I of
enjoying the Satisfaction I hoped to meet with at the End of my
Enterprize!
'There were two Paths, which led up by different Ways to the Summit of
the Mountain; the one was guarded by the Genius which presides over
the Moment of our Births. He had it in charge to examine the several
Pretensions of those who de
Sir ed a Pass that Way, but to admit none
excepting those only on whom
Melpomene had look'd with a propitious
Eye at the Hour of their Nativity. The other Way was guarded by
Diligence, to whom many of those Persons apply'd who had met with a
Denial the other Way; but he was so tedious in granting their Request,
and indeed after Admittance the Way was so very intricate and
laborious, that many after they had made some Progress, chose rather
to return back than proceed, and very few persisted so long as to
arrive at the End they proposed. Besides these two Paths, which at
length severally led to the Top of the Mountain, there was a third
made up of these two, which a little after the Entrance joined in one.
This carried those happy Few, whose good Fortune it was to find it,
directly to the Throne of
Apollo. I don't know whether I should even
now have had the Resolution to have demanded Entrance at either of
these Doors, had I not seen a Peasant-like Man (followed by a numerous
and lovely Train of Youths of both Sexes) insist upon Entrance for all
whom he led up. He put me in mind of the Country Clown who is painted
in the Map for leading Prince
Eugene over the
Alps. He had a
Bundle of Papers in his Hand, and producing several, which he said,
were given to him by Hands which he knew
Apollo would allow as
Passes; among which, methoughts, I saw some of my own Writing; the
whole Assembly was admitted, and gave, by their Presence, a new Beauty
and Pleasure to these happy Mansions. I found the Man did not pretend
to enter himself, but served as a kind of Forester in the Lawns to
direct Passengers, who by their own Merit, or Instructions he procured
for them, had Virtue enough to travel that way. I looked very
attentively upon this kind homely Benefactor, and forgive me,
Mr.
SPECTATOR, if I own to you I took him for your self. We were no sooner
entered, but we were sprinkled three times with the Water of the
Fountain
Aganippe, which had Power to deliver us from all Harms, but
only Envy, which reached even to the End of our Journey. We had not
proceeded far in the middle Path when we arrived at the Summit of the
Hill, where there immediately appeared to us two Figures, which
extremely engaged my Attention: the one was a young Nymph in the Prime
of her Youth and Beauty; she had Wings on her Shoulders and Feet, and
was able to transport herself to the most distant Regions in the
smallest Space of Time. She was continually varying her Dress,
sometimes into the most natural and becoming Habits in the World, and
at others into the most wild and freakish Garb that can be imagined.
There stood by her a Man full-aged, and of great Gravity, who
corrected her Inconsistences, by shewing them in his Mirror, and still
flung her affected and unbecoming Ornaments down the Mountain, which
fell in the Plain below, and were gathered up and wore with great
Satisfaction by those that inhabited it. The Name of the Nymph was
Fancy, the Daughter of
Liberty, the most beautiful of all the
Mountain-Nymphs. The other was
Judgment, the Off-spring of
Time,
and the only Child he acknowledged to be his. A Youth, who sat upon a
Throne just between them, was their genuine Offspring; his Name was
Wit, and his Seat was composed of the Works of the most celebrated
Authors. I could not but see with a secret Joy, that though the
Greeks and
Romans made the Majority, yet our own Countrymen were
the next both in Number and Dignity. I was now at Liberty to take a
full Prospect of that delightful Region. I was inspired with new
Vigour and Life, and saw every thing in nobler and more pleasing Views
than before; I breathed a purer Æther in a Sky which was a continued
Azure, gilded with perpetual Sunshine. The two Summits of the Mountain
rose on each Side, and formed in the midst a most delicious Vale, the
Habitation of the Muses, and of such as had composed Works worthy of
Immortality.
Apollo was seated upon a Throne of Gold, and for a
Canopy an aged Laurel spread its Boughs and its Shade over his Head.
His Bow and Quiver lay at his Feet. He held his Harp in his Hand,
whilst the Muses round about him celebrated with Hymns his Victory
over the Serpent
Python, and sometimes sung in softer Notes the
Loves of
Leucothoe and
Daphnis.
Homer,
Virgil, and
Milton
were seated the next to them. Behind were a great Number of others,
among whom I was surprized to see some in the Habit of
Laplanders,
who, notwithstanding the Uncouthness of their Dress, had lately
obtained a Place upon the Mountain. I saw
Pindar walking all alone,
no one daring to accost him, till
Cowley join'd himself to him; but
growing weary of one who almost walked him out of breath, he left him
for
Horace and
Anacreon, with whom he seemed infinitely delighted.
'A little further I saw another Groupe of Figures; I made up to them,
and found it was
Socrates dictating to
Xenophon, and the Spirit of
Plato; but most of all,
Musoeus had the greatest Audience about
him. I was at too great a Distance to hear what he said, or to
discover the Faces of his Hearers; only I thought I now perceived
Virgil, who had joined them, and stood in a Posture full of
Admiration at the Harmony of his Words.
'Lastly, At the very Brink of the Hill I saw
Boccalini sending
Dispatches to the World below of what happened upon
Parnassus; but I
perceived he did it without leave of the Muses, and by stealth, and
was unwilling to have them revised by
Apollo. I could now from this
Height and serene Sky behold the infinite Cares and Anxieties with
which Mortals below sought out their way through the Maze of Life. I
saw the Path of Virtue lie strait before them, whilst Interest, or
some malicious Demon, still hurry'd them out of the Way. I was at once
touched with Pleasure at my own Happiness, and Compassion at the sight
of their inextricable Errors. Here the two contending Passions rose so
high, that they were inconsistent with the sweet Repose I enjoy'd, and
awaking with a sudden start, the only Consolation I could admit of for
my Loss,
was the Hopes that this Relation of my Dream will not
displease you.'
2
T.
Room is made for this paper, in the original issue,
by printing it in smaller type.
This Advertisement follows:
A Letter written October 14, dated Middle Temple, has been
overlooked, by reason it was not directed to the Spectator at the
usual Places; and the Letter of the 18th, dated from the same Place,
is groundless, the Author of the Paper of Friday last not having
ever seen the Letter of the 14th. In all circumstances except the
Place of Birth of the Person to whom the Letters were written, the
Writer of them is misinformed.
Contents
|
Tuesday, October 21, 1712 |
Steele |
Pudet me et miseret qui harum mores contabat mihi
Monuisse frustra—
Ter.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am obliged to you for printing the Account I lately sent you of a
Coquet who disturbed a sober Congregation in the City of
London.
That Intelligence ended at her taking Coach, and bidding the Driver go
where he knew. I could not leave her so, but dogged her, as hard as
she drove, to
Paul's Church-Yard, where there was a Stop of Coaches
attending Company coming out of the Cathedral. This gave me
opportunity to hold up a Crown to her Coachman, who gave me the
Signal, that he would hurry on, and make no Haste, as you know the Way
is when they favour a Chase. By his many kind Blunders, driving
against other Coaches, and slipping off some of his Tackle, I could
keep up with him, and lodged my fine Lady in the Parish of St.
James's. As I guessed when I first saw her at Church, her Business
is to win Hearts and throw 'em away, regarding nothing but the
Triumph. I have had the Happiness, by tracing her through all with
whom I heard she was acquainted, to find one who was intimate with a
Friend of mine, and to be introduced to her Notice. I have made so
good use of my Time, as to procure from that Intimate of hers one of
her Letters, which she writ to her when in the Country. This Epistle
of her own may serve to alarm the World against her in ordinary Life,
as mine, I hope, did those, who shall behold her at Church. The Letter
was written last Winter to the Lady who gave it me; and I doubt not
but you will find it the Soul of an happy self-loving Dame, that takes
all the Admiration she can meet with, and returns none of it in Love
to her Admirers.'
Dear Jenny,
"I am glad to find you are likely to be dispos'd of in Marriage so
much to your Approbation as you tell me. You say you are afraid only
of me, for I shall laugh at your Spouse's Airs. I beg of you not to
fear it, for I am too nice a Discerner to laugh at any, but whom
most other People think fine Fellows; so that your Dear may bring
you hither as soon as his Horses are in Case enough to appear in
Town, and you be very safe against any Raillery you may apprehend
from me; for I am surrounded with Coxcombs of my own making, who are
all ridiculous in a manner: your Good-man, I presume, can't exert
himself. As Men
who cannot raise their Fortunes, and are uneasy
under the Incapacity of shining in Courts, rail at Ambition; so do
awkard1 and insipid Women, who cannot warm the Hearts and charm
the Eyes of Men, rail at Affectation: But she that has the Joy of
seeing a Man's Heart leap into his Eyes at beholding her, is in no
Pain for want of Esteem among a Crew of that Part of her own Sex,
who have no Spirit but that of Envy, and no Language but that of
Malice. I do not in this, I hope, express my self insensible of the
Merit of
Leodacia, who lowers her Beauty to all but her Husband,
and never spreads her Charms but to gladden him who has a Right in
them: I say, I do Honour to those who can be Coquets, and are not
such; but I despise all who would be so, and in Despair of arriving
at it themselves, hate and vilify all those who can. But, be that as
it will, in Answer to your De
Sir e of knowing my History: One of my
chief present Pleasures is in Country-Dances: and, in Obedience to
me, as well as the Pleasure of coming up to me with a good Grace,
shewing themselves in their Address to others in my Presence, and
the like Opportunities, they are all Proficients that Way: And I had
the Happiness of being the other Night where we made six Couple, and
every Woman's Partner a profess'd Lover of mine. The wildest
Imagination cannot form to it self on any Occasion, higher Delight
than I acknowledge my self to have been in all that Evening. I chose
out of my Admirers a Set of Men who most love me, and gave them
Partners of such of my own Sex who most envy'd me.
"My way is, when any Man who is my Admirer pretends to give himself
Airs of Merit, as at this Time a certain Gentleman you know did, to
mortify him by favouring in his Presence the most insignificant
Creature I can find. At this Ball I was led into the Company by
pretty Mr.
Fanfly, who, you know, is the most obsequious,
well-shaped, well-bred Woman's Man in Town. I at first Entrance
declared him my Partner if I danced at all; which put the whole
Assembly into a Grin, as forming no Terrours from such a Rival. But
we had not been long in the Room, before I overheard the meritorious
Gentleman above-mention'd say with an Oath, There is no Raillery in
the Thing, she certainly loves the Puppy. My Gentleman, when we were
dancing, took an Occasion to be very soft in his Oglings upon a Lady
he danced with, and whom he knew of all Women I love most to
outshine. The Contest began who should plague the other most. I, who
do not care a Farthing for him, had no hard Task to out-vex him. I
made
Fanfly, with a very little Encouragement, cut Capers
Coupee, and then sink with all the Air and Tenderness imaginable.
When he perform'd this, I observed the Gentleman you know of fall
into the same way, and imitate as well as he could the despised
Fanfly. I cannot well give you, who are so grave a Country Lady,
the Idea of the Joy we have when we see a stubborn Heart breaking,
or a Man of Sense turning Fool for our sakes; but this happened to
our Friend, and I expect his Attendance whenever I go to Church, to
Court, to the Play, or the Park. This is a Sacrifice due to us Women
of Genius, who have the Eloquence of Beauty, an easie Mein. I mean
by an easie Mein, one which can be on Occasion easily affected: For
I must tell you, dear
Jenny, I hold one Maxim, which is an
uncommon one, to wit, That our greatest Charms are owing to
Affectation. 'Tis to That that our Arms can lodge so quietly just
over our Hips, and the Fan can play without any Force or Motion but
just of the Wrist. 'Tis to Affectation we owe the pensive Attention
of
Deidamia at a Tragedy, the scornful Approbation of
Dulciamara
at a Comedy, and the lowly Aspect of
Lanquicelsa at a Sermon.
"To tell you the plain Truth, I know no Pleasure but in being
admir'd, and have yet never failed of attaining the Approbation of
the Man whose Regard I had a Mind to. You see all the Men who make a
Figure in the World (as wise a Look as they are pleased to put upon
the Matter) are moved by the same Vanity as I am. What is there in
Ambition, but to make other People's Wills depend upon yours? This
indeed is not to be aim'd at by one who has a Genius no higher than
to think of being a very good Housewife in a Country Gentleman's
Family. The Care of Poultrey and Piggs are great Enemies to the
Countenance: The vacant Look of a fine Lady is not to be preserved,
if she admits any thing to take up her Thoughts but her own dear
Person. But I interrupt you too long from your Cares, and my self
from my Conquests."
I am, Madam, Your most humble Servant.
'Give me leave, Mr. SPECTATOR, to add her Friend's Answer to this
Epistle, who is a very discreet ingenious Woman.'
Dear Gatty,
"I take your Raillery in very good Part, and am obliged to you for
the free Air with which you speak of your own Gayeties.
But this is
but a barren superficial Pleasure;
indeed2,
Gatty, we are
made for Man, and in serious Sadness I must tell you, whether you
yourself know it or no, all these Gallantries tend to no other End
but to be a Wife and Mother as fast as you can."
I am, Madam, Your most humble3 Servant.
T.
Spelt generally in the first issue
awkard
, in the first
reprint
aukward
.
for indeed,
obedient
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 22, 1712 |
Steele |
Immortale odium et nunquam sanabile vulnus.
Inde furor vulgo, quod Numina vicinorum
Odit uterque locus, quum solos credit habendos
Esse Deos quos ipse colat.
Juv.

Of all the monstrous Passions and Opinions which have crept into the
World, there is none so wonderful as that those who profess the common
Name of
Christians
, should pursue each other with Rancour and Hatred
for Differences in their Way of following the Example of their Saviour.
It seems so natural that all who pursue the Steps of any Leader should
form themselves after his Manners, that it is impossible to account for
Effects so different from what we might expect from those who profess
themselves Followers of the highest Pattern of Meekness and Charity, but
by ascribing such Effects to the Ambition and Corruption of those who
are so audacious, with Souls full of Fury, to serve at the Altars of the
God of Peace.
The Massacres to which the Church of
Rome
has animated the ordinary
People, are dreadful Instances of the Truth of this Observation; and
whoever reads the History of the
Irish
Rebellion, and the Cruelties
which ensued thereupon, will be sufficiently convinced to what Rage poor
Ignorants may be worked up by those who profess Holiness, and become
Incendiaries, and under the Dispensation of Grace, promote Evils
abhorrent to Nature.
This Subject and Catastrophe, which deserve so well to be remarked by
the Protestant World, will, I doubt not, be considered by the Reverend
and Learned Prelate that Preaches to-morrow before many of the
Descendants, of those who perished on that lamentable Day, in a manner
suitable to the Occasion, and worthy his own great Virtue and Eloquence.
I shall not dwell upon it any further, but only transcribe out of a
little Tract, called,
The Christian Hero
, published in 1701, what I
find there in Honour of the renowned Hero
William
III. who rescued
that Nation from the Repetition of the same Disasters. His late Majesty,
of glorious Memory, and the most Christian King, are considered at the
Conclusion of that Treatise as Heads of the Protestant and Roman
Catholick World in the following Manner.
'There were not ever, before the Entrance of the Christian Name into
the World, Men who have maintained a more renowned Carriage, than the
two great Rivals who possess the full Fame of the present Age, and
will be the Theme and Examination of the future. They are exactly
form'd by Nature for those Ends to which Heaven seems to have sent
them amongst us: Both animated with a restless De
Sir e of Glory, but
pursue it by different Means, and with different Motives. To one it
consists in an extensive undisputed Empire over his Subjects, to the
other in their rational and voluntary Obedience: One's Happiness is
founded in their want of Power, the other's in their want of De
Sir e to
oppose him. The one enjoys the Summit of Fortune with the Luxury of a
Persian, the other with the Moderation of a
Spartan: One is made
to oppress, the other to relieve the Oppressed: The one is satisfy'd
with the Pomp and Ostentation of Power to prefer and debase his
Inferiours, the other delighted only with the Cause and Foundation of
it to cherish and protect 'em. To one therefore Religion is but a
convenient Disguise, to the other a vigorous Motive of Action.
'For without such Ties of real and solid Honour, there is no way of
forming a Monarch, but after the Machiavillian Scheme, by which a
Prince must ever seem to have all Virtues, but really to be Master of
none, but is to be liberal, merciful and just, only as they serve his
Interests; while, with the noble Art of Hypocrisy, Empire would be to
be extended, and new Conquests be made by new Devices, by which prompt
Address
his Creatures might insensibly give Law in the Business of
Life, by leading Men in the Entertainment of it
1.
'Thus when Words and Show are apt to pass for the substantial things
they are only to express, there would need no more to enslave a
Country but to adorn a Court; for while every Man's Vanity makes him
believe himself capable of becoming Luxury, Enjoyments are a ready
Bait for Sufferings, and the Hopes of Preferment Invitations to
Servitude; which Slavery would be colour'd with all the Agreements, as
they call it, imaginable. The noblest Arts and Artists, the finest
Pens and most elegant Minds, jointly employ'd to set it off, with the
various Embellishments of sumptuous Entertainments, charming
Assemblies, and polished Discourses; and those apostate Abilities of
Men, the adored Monarch might profusely and skilfully encourage, while
they flatter his Virtue, and gild his Vice at so high a rate, that he,
without Scorn of the one, or Love of the other, would alternately and
occasionally use both: So that his Bounty should support him in his
Rapines, his Mercy in his Cruelties.
'Nor is it to give things a more severe Look than is natural, to
suppose such must be the Consequences of a Prince's having no other
Pursuit than that of his own Glory; for, if we consider an Infant born
into the World, and beholding it self the mightiest thing in it, it
self the present Admiration and future Prospect of a fawning People,
who profess themselves great or mean, according to the Figure he is to
make amongst them, what Fancy would not be debauched to believe they
were but what they professed themselves, his mere Creatures, and use
them as such by purchasing with their Lives a boundless Renown, which
he, for want of a more just Prospect, would place in the Number of his
Slaves, and the Extent of his Territories? Such undoubtedly would be
the tragical Effects of a Prince's living with no Religion, which are
not to be surpassed but by his having a false one.
'If Ambition were spirited with Zeal, what would follow, but that his
People should be converted into an Army, whose Swords can make Right
in Power, and solve Controversy in Belief? And if Men should be
stiff-neck'd to the Doctrine of that visible Church, let them be
contented with an Oar and a Chain, in the midst of Stripes and
Anguish, to contemplate on him,
whose Yoke is easy, and whose Burthen
is light.
'With a Tyranny begun on his own Subjects, and Indignation that others
draw their Breath independent of his Frown or Smile, why should he not
proceed to the Seizure of the World? And if nothing but the Thirst of
Sway were the Motive of his Actions, why should Treaties be other than
mere Words, or solemn national Compacts be any thing but an Halt in
the March of that Army, who are never to lay down their Arms, till all
Men are reduc'd to the necessity of hanging their Lives on his wayward
Will; who might supinely, and at leisure, expiate his own Sins by
other Mens Sufferings, while he daily meditates new Slaughter, and new
Conquest?
'For mere Man, when giddy with unbridled Power, is an insatiate Idol,
not to be appeased with Myriads offer'd to his Pride, which may be
puffed up by the Adulation of a base and prostrate World, into an
Opinion that he is something more than human, by being something less:
And, alas, what is there that mortal Man will not believe of himself,
when complimented with the Attributes of God? Can he then conceive
Thoughts of a Power as
Omnipresent as his! But should there be such
a Foe of Mankind now upon Earth, have our Sins so far provoked Heaven,
that we are left utterly naked to his Fury? Is there no Power, no
Leader, no Genius, that can conduct and animate us to our Death or our
Defence? Yes; our great God never gave one to feign by his Permission,
but he gave to another also to reign by his Grace.
'All the Circumstances of the illustrious Life of our Prince, seem to
have conspired to make him the Check and Bridle of Tyranny; for his
Mind has been strengthened and confirmed by one continual Struggle,
and Heaven has educated him by Adversity to a quick Sense of the
Distresses and Miseries of Mankind, which he was born to redress: In
just scorn of the trivial Glories and light Ostentations of Power,
that glorious Instrument of Providence moves, like that, in a steddy,
calm, and silent Course, independent either of Applause or Calumny;
which renders him, if not in a political, yet in a moral, a
philosophick, an heroick, and a Christian Sense, an absolute Monarch;
who satisfy'd with this unchangeable, just, and ample Glory, must
needs turn all his Regards from himself to the Service of others; for
he begins his Enterprize with his own Share in the Success of them;
for Integrity bears in it self its Reward, nor can that which depends
not on Event ever know Disappointment.
'With the undoubted Character of a glorious Captain, and (what he much
more values than the most splendid Titles) that of a sincere and
honest Man, he is the Hope and Stay of
Europe, an universal Good not
to be engrossed by us only, for distant Potentates implore his
Friendship, and injur'd Empires court his Assistance. He rules the
World, not by an Invasion of the People of the Earth, but the Address
of its Princes; and if that World should be again rous'd from the
Repose which his prevailing Arms had given it, why should we not hope
that there is an Almighty, by whose Influence the terrible Enemy that
thinks himself prepar'd for Battel, may find he is but ripe for
Destruction? and that there may be in the Womb of Time great
Incidents, which may make the Catastrophe of a prosperous Life as
unfortunate as the particular Scenes of it were successful? For there
does not want a skilful Eye and resolute Arm to observe and grasp the
Occasion: A Prince, who from
2
—Fuit Ilium et ingens
Gloria—
Virg.
T.
The extract is from very near the close of Steele's
Christian Hero
. At this part a few lines have been omitted. In the
original the paragraph closed thus:
'... the Entertainment of it, and making their great Monarch the
Fountain of all that's delicate and refined, and his Court the Model
for Opinions in Pleasure, as well as the Pattern in Dress; which might
prevail so far upon an undiscerning world as (to accomplish it or its
approaching Slavery) to make it receive a superfluous Babble for an
Universal Language.'
Here Steele abruptly breaks with
Fuit Ilium
—the glory
has departed—on the sentence:
'A Prince who from just Notion of his Duty to that Being to whom he
must be accountable, has in the Service of his Fellow Creatures a
noble Contempt of Pleasures, and Patience of Labours, to whom 'tis
Hereditary to be the Guardian and Asserter of the native Rights and
Liberties of Mankind;'
A few more clauses to the sentence formed the summary of William's
character before the book closed with a prayer that Heaven would guard
his important life.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 23, 1712 |
Addison |
Heu Pietas! heu prisca Fides!
Virg.

We last night received a Piece of ill News at our Club, which very
sensibly afflicted every one of us. I question not but my Readers
themselves will be troubled at the hearing of it.
keep them no longer
in Suspence,
Sir
Roger De Coverly
is dead.
He departed this Life
at his House in the Country, after a few Weeks Sickness.
Sir
Andrew
Freeport
has a Letter from one of his Correspondents in those Parts,
that informs him the old Man caught a Cold at the County-Sessions, as he
was very warmly promoting an Address of his own penning, in which he
succeeded according to his Wishes, But this Particular comes from a
Whig-Justice of Peace, who was always
Sir
Roger's
Enemy and Antagonist.
I have Letters both from the Chaplain and Captain
Sentry
which mention
nothing of it, but are filled with many Particulars to the Honour of the
good old Man. I have likewise a Letter from the Butler, who took so much
care of me last Summer when I was at the Knight's House. As my Friend
the Butler mentions, in the Simplicity of his Heart, several
Circumstances the others have passed over in Silence, I shall give my
Reader a Copy of his Letter, without any Alteration or Diminution.
Honoured Sir ,
'Knowing that you was my old Master's good Friend, I could not forbear
sending you the melancholy News of his Death, which has afflicted the
whole Country, as well as his poor Servants, who loved him, I may say,
better than we did our Lives. I am afraid he caught his Death the last
County Sessions, where he would go to see Justice done to a poor Widow
Woman, and her Fatherless Children, that had been wronged by a
neighbouring Gentleman; for you know,
Sir , my good Master was always
the poor Man's Friend. Upon his coming home, the first Complaint he
made was, that he had lost his Roast-Beef Stomach, not being able to
touch a
Sir loin, which was served up according to Custom; and you know
he used to take great Delight in it. From that time forward he grew
worse and worse, but still kept a good Heart to the last.
Indeed we
were once in great
Hope2 of his Recovery, upon a kind Message
that was sent him from the Widow Lady whom he had made love to the
Forty last Years of his Life; but this only proved a Light'ning before
Death. He has bequeathed to this Lady, as a token of his Love, a great
Pearl Necklace, and a Couple of Silver Bracelets set with Jewels,
which belonged to my good old Lady his Mother: He has bequeathed the
fine white Gelding, that he used to ride a hunting upon, to his
Chaplain, because he thought he would be kind to him, and has left you
all his Books. He has, moreover, bequeathed to the Chaplain a very
pretty Tenement with good Lands about it. It being a very cold Day
when he made his Will, he left for Mourning, to every Man in the
Parish, a great Frize-Coat, and to every Woman a black Riding-hood. It
was a most moving Sight to see him take leave of his poor Servants,
commending us all for our Fidelity, whilst we were not able to speak a
Word for weeping. As we most of us are grown Gray-headed in our Dear
Master's Service, he has left us Pensions and Legacies, which we may
live very comfortably upon, the remaining part of our Days.
He has bequeath'd a great deal more in Charity, which is not yet come
to my Knowledge, and it is peremptorily said in the Parish, that he
has left Mony to build a Steeple to the Church; for he was heard to
say some time ago, that if he lived two Years longer,
Coverly Church
should have a Steeple to it. The Chaplain tells every body that he
made a very good End, and never speaks of him without Tears. He was
buried according to his own Directions, among the Family of the
Coverly's, on the Left Hand of his Father
Sir Arthur. The Coffin
was carried by Six of his Tenants, and the Pall held up by Six of the
Quorum: The whole Parish follow'd the Corps with heavy Hearts, and
in their Mourning Suits, the Men in Frize, and the Women in
Riding-Hoods. Captain
Sentry, my Master's Nephew, has taken Possession
of the Hall-House, and the whole Estate. When my old Master saw him a
little before his Death, he shook him by the Hand, and wished him Joy
of the Estate which was falling to him, de
Sir ing him only to make good
Use of it, and to pay the several Legacies, and the Gifts of Charity
which he told him he had left as Quitrents upon the Estate. The
Captain truly seems a courteous Man, though he says but little. He
makes much of those whom my Master loved, and shews great Kindness to
the old House-dog, that you know my poor Master was so fond of. It
would have gone to your Heart to have heard the Moans the dumb
Creature made on the Day of my Master's Death. He has ne'er joyed
himself since; no more has any of us. 'Twas the melancholiest Day for
the poor People that ever happened in
Worcestershire. This being all
from,
Honoured Sir ,
Your most Sorrowful Servant,
Edward Biscuit.
P. S. 'My Master de
Sir ed, some Weeks before he died, that a Book
which comes up to you by the Carrier should be given to
Sir Andrew
Freeport, in his Name.'
This Letter, notwithstanding the poor Butler's Manner of writing it,
gave us such an Idea of our good old Friend, that upon the reading of it
there was not a dry Eye in the Club.
Sir
Andrew
opening the Book,
found it to be a Collection of Acts of Parliament. There was in
particular the Act of Uniformity, with some Passages in it marked by
Sir
Roger's
own Hand.
Sir
Andrew
found that they related to two or three
Points, which he had disputed with
Sir
Roger
the last time he appeared
at the Club.
Sir
Andrew
, who would have been merry at such an Incident
on another Occasion, at the sight of the old Man's Hand-writing burst
into Tears, and put the Book into his Pocket. Captain
Sentry
informs
me, that the Knight has left Rings and Mourning for every one in the
Club.
O.
In No. 1 of the
Bee
(for February, 1733) Eustace Budgell,
who set up that publication, and who probably was the intimate friend of
Addison's to whom he there refers, said of
Sir
Roger de Coverley,
'Mr. Addison was so fond of this character that a little before he
laid down the Spectator (foreseeing that some nimble gentleman would
catch up his pen the moment he quitted it) he said to an intimate
friend, with a certain warmth in his expression which he was not often
guilty of, By God, I'll kill Sir Roger, that nobody else may murder
him.'
Accordingly the whole
Spectator
No. 517 consists of nothing but an
account of the old knight's death, and some moving circumstances which
attended it. Steele had by this date resolved on bringing his
Spectator
to a close, and Addison's paper on the death of
Sir
Roger, the first of
several which are to dispose of all members of the
Spectator's
Club and
break up the Club itself, was the first clear warning to the public that
he had such an intention.
Hopes
Contents
|
Friday, October 24, 1712 |
Steele1 |
—Miserum est alienæ incumbere famæ,
Ne collapsa ruant subductis tecta columnis.
Juv.

This being a Day of Business with me, I must make the present
Entertainment like a Treat at an House-warming, out of such Presents as
have been sent me by my Guests. The first Dish which I serve up is a
Letter come fresh to my Hand.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
It is with inexpressible Sorrow that I hear of the Death of good
Sir
Roger, and do heartily condole with you upon so melancholy an
Occasion. I think you ought to have blacken'd the Edges of a Paper
which brought us so ill News, and to have had it stamped likewise in
Black. It is expected of you that you should write his Epitaph, and,
if possible, fill his Place in the Club with as worthy and diverting a
Member. I question not but you will receive many Recommendations from
the publick of such as will appear Candidates for that Post.
Since I am talking of Death, and have mentioned an Epitaph, I must
tell you,
Sir , that I have made discovery of a Church-Yard in which I
believe you might spend an Afternoon, with great Pleasure to your self
and to the Publick: It. belongs to the Church of
Stebon-Heath,
commonly called
Stepney. Whether or no it be that the People of that
Parish have a particular Genius for an Epitaph, or that there be some
Poet among them who undertakes that Work by the Great, I can't tell;
but there are more remarkable Inscriptions in that place than in any
other I have met with, and I may say without Vanity, that there is not
a Gentleman in
England better read in Tomb-stones than my self, my
Studies having laid very much in Church-yards. I shall beg leave to
send you a Couple of Epitaphs, for a Sample of those I have just now
mentioned. They are written in a different manner; the first being in
the diffused and luxuriant, the second in the close contracted Style.
The first has much of the Simple and Pathetick; the second is
something Light, but Nervous. The first is thus:
Here Thomas Sapper lyes interred. Ah why!
Born in New England, did in London dye;
Was the third Son of Eight, begot upon
His Mother Martha by his Father John.
Much favoured by his Prince he 'gan to be,
But nipt by Death at th' Age of Twenty Three.
Fatal to him was that we Small-pox name,
By which his Mother and two Brethren came
Also to breathe their last nine Years before,
And now have left their Father to deplore
The loss of all his Children, with his Wife,
Who was the Joy and Comfort of his Life.
The Second is as follows:
Here lies the body of Daniel Saul,
Spittle-fields weaver, and that's all.
'I will not dismiss you, whilst I am upon this Subject, without
sending a short Epitaph which I once met with, though I cannot
possibly recollect the Place. The Thought of it is serious, and in my
Opinion, the finest that I ever met with upon this Occasion. You know,
Sir , it is usual, after having told us the Name of the Person who lies
interr'd to lanch out into his Praises.
This Epitaph takes a quite
contrary Turn, having been made by the Person himself some time before
his Death.
Hic jacet R. C.
in expectatione diei supremi. Qualis erat dies
iste indicabit.2
Here lieth
R. C. in expectation of the last Day. What sort
of a Man he was, that Day will discover.
I am, Sir , &c.
following Letter is dated from
Cambridge
.
Sir ,
'Having lately read among your Speculations, an Essay upon
Phisiognomy, I cannot but think that if you made a Visit to this
ancient University, you might receive very considerable Lights upon
that Subject, there being scarce a young Fellow in it who does not
give certain Indications of his particular Humour and Disposition
conformable to the Rules of that Art. In Courts and Cities every body
lays a Constraint upon his Countenance, and endeavours to look like
the rest of the World; but the Youth of this Place, having not yet
formed themselves by Conversation, and the Knowledge of the World,
give their Limbs and Features their full Play.
'As you have considered Human Nature in all its Lights, you must be
extremely well apprized, that there is a very close Correspondence
between the outward and the inward Man; that scarce the least Dawning,
the least Parturiency towards a Thought can be stirring in the Mind of
Man, without producing a suitable Revolution in his Exteriors, which
will easily discover it self to an Adept in the Theory of the Phiz.
Hence it is, that the intrinsick Worth and Merit of a Son of Alma
Mater is ordinarily calculated from the Cast of his Visage, the
Contour of his Person, the Mechanism of his Dress, the Disposition of
his Limbs, the Manner of his Gate and Air, with a number of
Circumstances of equal Consequence and Information: The Practitioners
in this Art often make use of a Gentleman's Eyes to give 'em Light
into the Posture of his Brains; take a Handle from his Nose, to judge
of the Size of his Intellects; and interpret the over-much Visibility
and Pertness of one Ear, as an infallible mark of Reprobation, and a
Sign the Owner of so saucy a Member fears neither God nor Man. In
conformity to this Scheme, a contracted Brow, a lumpish down-cast
Look, a sober sedate Pace, with both Hands dangling quiet and steddy
in Lines exactly parallel to each Lateral Pocket of the Galligaskins,
is Logick, Metaphysicks and Mathematicks in Perfection. So likewise
the Belles Lettres are typified by a Saunter in the Gate; a Fall of
one Wing of the Peruke backward, an Insertion of one Hand in the Fobb,
and a negligent Swing of the other, with a Pinch of right and fine
Barcelona between Finger and Thumb, a due Quantity of the same upon
the upper Lip, and a Noddle-Case loaden with Pulvil. Again, a grave
solemn stalking Pace is Heroick Poetry, and Politicks; an Unequal one,
a Genius for the Ode, and the modern Ballad: and an open Breast, with
an audacious Display of the Holland Shirt, is construed a fatal
Tendency to the Art Military.
'I might be much larger upon these Hints, but I know whom I write to.
If you can graft any Speculation upon them, or turn them to the
Advantage of the Persons concerned in them, you will do a Work very
becoming the British Spectator, and oblige'
Your very Humble Servant,
Tom. Tweer.
Of the two letters which form this number the second is by
John Henley, known afterwards as 'Orator Henley,' of whom see a note to
[Volume 2 link:
.]
The European Magazine for July, 1787, says that the exact
copy of this Epitaph, which is on a Thomas Crouch, who died in 1679,
runs thus:
Aperiet Deus tumulos et educet nos de sepulchris
Qualis eram, dies isti hæc cum venerit, scies.
By John Henley.
Contents
|
Saturday, October 25, 1712 |
Addison |
Inde Hominum pecudumque genus, vitæque volantum,
Et quæ marmoreo fert Monstra sub æquore pontus.
Virg.

Though there is a great deal of Pleasure in contemplating the material
World, by which I mean that System of Bodies into which Nature has so
curiously wrought the Mass of dead Matter, with the several Relations
which those Bodies bear to one another; there is still, methinks,
something more wonderful and surprizing in Contemplations on the World
of Life, by which I mean all those Animals with which every Part of the
Universe is furnished. The Material World is only the Shell of the
Universe: The World of Life are its Inhabitants.
If we consider those parts of the Material World which lie the nearest
to us, and are therefore subject to our Observations and Enquiries, it
is amazing to consider the Infinity of Animals with which it is stocked.
Every part of Matter is peopled: Every green Leaf swarms with
Inhabitants. There is scarce a single Humour in the Body of a Man, or of
any other Animal, in which our Glasses do not discover Myriads of living
Creatures. The Surface of Animals is also covered with other Animals,
which are in the same manner the Basis of other Animals, that live upon
it; nay, we find in the most solid Bodies, as in Marble it self,
innumerable Cells and Cavities that are crouded with such imperceptible
Inhabitants, as are too little for the naked Eye to discover. On the
other hand, if we look into the more bulky parts of Nature, we see the
Seas, Lakes and Rivers teeming with numberless kinds of living
Creatures: We find every Mountain and Marsh, Wilderness and Wood,
plentifully stocked with Birds and Beasts, and every part of Matter
affording proper Necessaries and Conveniencies for the Livelihood of
Multitudes which inhabit it.
Author of the
Plurality of Worlds
draws a very good Argument
from this Consideration, for the
peopling
of every Planet; as indeed
it seems very probable from the Analogy of Reason, that if no Part of
Matter, which we are acquainted with, lies waste and useless, those
great Bodies which are at such a Distance from us should not be desart
and unpeopled, but rather that they should be furnished with Beings
adapted to their respective Situations.
Existence is a Blessing to those Beings only which are endowed with
Perception, and is in a manner thrown away upon dead Matter, any further
than as it is subservient to Beings which are conscious of their
Existence. Accordingly we find, from the Bodies which lie under our
Observation, that Matter is only made as the Basis and Support of
Animals, and that there is no more of the one, than what is necessary
for the Existence of the other.
Infinite Goodness
of so communicative a nature, that it seems to
delight in the conferring of Existence upon every Degree of
Perceptive
Being. As this is a Speculation, which I have often pursued with
great Pleasure to my self, I shall enlarge farther upon it, by
considering that part of the Scale of Beings which comes within our
Knowledge.
There are some living Creatures which are raised but just above dead
Matter. To mention only that Species of Shell-fish, which are form'd in
the Fashion of a Cone, that grow to the Surface of several Rocks, and
immediately die upon their being sever'd from the Place where they grow.
There are many other Creatures but one Remove from these, which have no
other Sense besides that of Feeling and Taste. Others have still an
additional one of Hearing; others of Smell, and others of Sight. It is
wonderful to observe, by what a gradual Progress the World of Life
advances through a prodigious Variety of Species, before a Creature is
form'd that is compleat in all its Senses; and even among these there is
such a different Degree of Perfection in the Sense which one Animal
enjoys beyond what appears in another, that though the Sense in
different Animals be distinguished by the same common Denomination, it
seems almost of a different Nature. If after this we look into the
several inward Perfections of Cunning and Sagacity, or what we generally
call Instinct, we find them rising after the same Manner, imperceptibly
one above another, and receiving additional Improvements, according to
the Species in which they are implanted. This Progress in Nature is so
very gradual, that the most perfect of an inferior Species comes very
near to the most imperfect of that which is immediately above it.
The exuberant and overflowing Goodness of the Supreme Being, whose Mercy
extends to all his Works, is plainly seen, as I have before hinted, from
his having made so very little Matter, at least what falls within our
Knowledge, that does not swarm with Life: Nor is his Goodness less seen
in the Diversity, than in the Multitude of living Creatures. Had he only
made one Species of Animals, none of the rest would have enjoyed the
Happiness of Existence; he has, therefore,
specified
in his Creation
every degree of Life, every Capacity of Being. The whole Chasm in
Nature, from a Plant to a Man, is filled up with diverse Kinds of
Creatures, rising one over another, by such a gentle and easy Ascent,
that the little Transitions and Deviations from one Species to another,
are almost insensible. This intermediate Space is so well husbanded and
managed, that there is scarce a degree of Perception which does not
appear in some one part of the World of Life. Is the Goodness, or Wisdom
of the divine Being, more manifested in this his Proceeding?
There is a Consequence, besides those I have already mentioned, which
seems very naturally deducible from the foregoing Considerations. If the
Scale of Being rises by such a regular Progress, so high as Man, we may
by a parity of Reason suppose that it still proceeds gradually through
those Beings which are of a Superior Nature to him; since there is an
infinitely greater space and room for different Degrees of Perfection,
between the Supreme Being and Man, than between Man and the most
despicable Insect. This
of so great a variety of Beings
which are superior to us, from that variety which is inferior to us, is
made by Mr.
Lock
, in a Passage which I shall here set down, after
having premised, that notwithstanding there is such infinite room
between Man and his Maker for the Creative Power to exert it self in, it
is impossible that it should ever be filled up, since there will be
still an infinite Gap or Distance between the highest created Being, and
the Power which produced him.
That there should be more Species
of intelligent Creatures above
us, than there are of sensible and material below us, is probable to
me from hence; That in all the visible corporeal World, we see no
Chasms, or no Gaps. All quite down from us, the descent is by easy
steps, and a continued Series of things, that in each remove differ
very little one from the other. There are Fishes that have Wings, and
are not Strangers to the airy Region: and there are some Birds, that
are Inhabitants of the Water; whose Blood is cold as Fishes, and their
Flesh so like in taste, that the Scrupulous are allowed them on
Fish-days. There are Animals so near of kin both to Birds and Beasts,
that they are in the middle between both: Amphibious Animals link the
Terrestrial and Aquatick together; Seals live at Land and at Sea, and
Porpoises have the warm Blood and Entrails of a Hog; not to mention
what is confidently reported of Mermaids or Sea-Men. There are some
Brutes, that seem to have as much Knowledge and Reason, as some that
are called Men; and the Animal and Vegetable Kingdoms are so nearly
join'd, that if you will take the lowest of one, and the highest of
the other, there will scarce be perceived any great difference between
them: and so on till we come to the lowest and the most inorganical
parts of Matter, we shall find every where that the several Species
are linked together, and differ but in almost insensible degrees. And
when we consider the infinite Power and Wisdom of the Maker, we have
reason to think that it is suitable to the magnificent Harmony of the
Universe, and the great Design and infinite Goodness of the Architect,
that the Species
of Creatures should also, by gentle degrees, ascend
upward from us towards his infinite Perfection, as we see they
gradually descend from us downwards: Which if it be probable, we have
reason then to be persuaded, that there are far more Species
of
Creatures above us, than there are beneath; we being in degrees of
Perfection much more remote from the infinite Being of God, than we
are from the lowest State of Being, and that which approaches nearest
to nothing. And yet of all those distinct Species, we have no clear
distinct Ideas
3.
In this System of Being, there is no Creature so wonderful in its
Nature, and which so much deserves our particular Attention, as Man, who
fills up the middle Space between the Animal and Intellectual Nature,
the visible and invisible World, and is that Link in the Chain of
Beings, which has been often termed the
nexus utriusque Mundi
. So that
he who in one respect is associated with Angels and Arch-Angels, may
look upon a Being of infinitei Perfection as his Father, and the highest
Order of Spirits as his Brethren,
in another respect say to
Corruption, thou art my Father, and to the Worm, thou art my Mother and
my Sister
.
Fontenelle,
Entretiens sur la Pluralité des Mondes
.
Troisième Soir.
Preceptive
and in first reprint.
Essay concerning Human Understanding
, Bk. III. ch. vi. §
12.
Job
. xvii. 14.
Contents
|
Monday, October 27, 1712 |
Francham1 |
Quis desiderio sit pudor aut modus
Tant chari capitis!
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The just Value you have expressed for the Matrimonial State, is the
Reason that I now venture to write to you, without Fear of being
ridiculous; and confess to you, that though it is three Months since I
lost a very agreeable Woman, who was my Wife, my Sorrow is still
fresh; and I am often, in the midst of Company, upon any Circumstance
that revives her Memory, with a Reflection what she would say or do on
such an Occasion: I say, upon any Occurrence of that Nature, which I
can give you a Sense of, though I cannot express it wholly, I am all
over Softness, and am obliged to retire, and give Way to a few Sighs
and Tears, before I can be easy. I cannot but recommend the Subject of
Male Widowhood to you, and beg of you to touch upon it by the first
Opportunity. To those who have not lived like Husbands during the
Lives of their Spouses, this would be a tasteless Jumble of Words; but
to such (of whom there are not a few) who have enjoyed that State with
the Sentiments proper for it, you will have every Line, which hits the
Sorrow, attended with a Tear of Pity and Consolation. For I know not
by what Goodness of Providence it is, that every Gush of Passion is a
step towards the Relief of it; and there is a certain Comfort in the
very Act of Sorrowing, which, I suppose, arises from a secret
Consciousness in the Mind, that the Affliction it is under flows from
a virtuous Cause. My Concern is not indeed so outragious as at the
first Transport; for I think it has subsided rather into a soberer
State of Mind, than any actual Perturbation of Spirit. There might be
Rules formed for Men's Behaviour on this great Incident, to bring them
from that Misfortune into the Condition I am at present; which is, I
think, that my Sorrow has converted all Roughness of Temper into
Meekness, Good-nature, and Complacency: But indeed, when in a serious
and lonely Hour I present my departed Consort to my Imagination, with
that Air of Perswasion in her Countenance when I have been in Passion,
that sweet Affability when I have been in good Humour, that tender
Compassion when I have had any thing which gave me Uneasiness; I
confess to you I am inconsolable, and my Eyes gush with Grief as if I
had seen her but just then expire. In this Condition I am broken in
upon by a charming young Woman, my Daughter, who is the Picture of
what her Mother was on her Wedding-Day. The good Girl strives to
comfort me; but how shall I let you know that all the Comfort she
gives me is to make my Tears flow more easily? The Child knows she
quickens my Sorrows, and rejoices my Heart at the same Time. Oh, ye
Learned! tell me by what Word to speak a Motion of the Soul, for which
there is no name. When she kneels and bids me be comforted, she is my
Child; when I take her in my Arms, and bid her say no more, she is my
very Wife, and is the very Comforter I lament the Loss of. I banish
her the Room, and weep aloud that I have lost her Mother, and that I
have her.
'
Mr. SPECTATOR, I wish it were possible for you to have a Sense of
these pleasing Perplexities; you might communicate to the guilty part
of Mankind, that they are incapable of the Happiness which is in the
very Sorrows of the Virtuous.
'But pray spare me a little longer; give me Leave to tell you the
Manner of her Death. She took leave of all her Family, and bore the
vain Application of Medicines with the greatest Patience imaginable.
When the Physician told her she must certainly die, she de
Sir ed, as
well as she could, that all who were present, except my self, might
depart the Room. She said she had nothing to say, for she was
resigned, and I knew all she knew that concerned us in this World; but
she de
Sir ed to be alone, that in the presence of God only she might,
without Interruption, do her last Duty to me, of thanking me for all
my Kindness to her; adding, that she hoped in my last Moments I should
feel the same Comfort for my Goodness to her, as she did in that she
had acquitted herself with Honour, Truth and Virtue to me.
'I curb my self, and will not tell you that this Kindness cut my Heart
in twain, when I expected an Accusation for some passionate Starts of
mine, in some Parts of our Time together, to say nothing, but thank me
for the Good, if there was any Good suitable to her own Excellence!
All that I had ever said to her, all the Circumstances of Sorrow and
Joy between us, crowded upon my Mind in the same Instant; and when
immediately after I saw the Pangs of Death come upon that dear Body
which I had often embraced with Transport, when I saw those cherishing
Eyes begin to be ghastly, and their last Struggle to be to fix
themselves on me, how did I lose all patience? She expired in my Arms,
and in my Distraction I thought I saw her Bosom still heave. There was
certainly Life yet still left; I cried she just now spoke to me: But
alas! I grew giddy, and all things moved about me from the Distemper
of my own Head; for the best of Women was breathless, and gone for
ever.
'Now the Doctrine I would, methinks, have you raise from this Account
I have given you is, That there is a certain Equanimity in those who
are good and just, which runs into their very Sorrow, and disappoints
the Force of it. Though they must pass through Afflictions in common
with all who are in human Nature, yet their conscious Integrity shall
undermine their Affliction; nay, that very Affliction shall add Force
to their Integrity, from a Reflection of the Use of Virtue in the Hour
of Affliction. I sat down with a Design to put you upon giving us
Rules how to overcome such Griefs as these, but I should rather advise
you to teach Men to be capable of them.
'You Men of Letters have what you call the fine Taste in their
Apprehensions of what is properly done or said: There is something
like this deeply grafted in the Soul of him who is honest and faithful
in all his Thoughts and Actions. Every thing which is false, vicious
or unworthy, is despicable to him, though all the World should approve
it. At the same time he has the most lively Sensibility in all
Enjoyments and Sufferings which it is proper for him to have, where
any Duty of Life is concerned. To want Sorrow when you in Decency and
Truth should be afflicted, is, I should think, a greater Instance of a
Man's being a Blockhead, than not to know the Beauty of any Passage in
Virgil. You have not yet observed,
Mr. SPECTATOR, that the fine
Gentlemen of this Age set up for Hardness of Heart, and Humanity has
very little share in their Pretences. He is a brave Fellow who is
always ready to kill a Man he hates, but he does not stand in the same
Degree of Esteem who laments for the Woman he loves. I should fancy
you might work up a thousand pretty Thoughts, by reflecting upon the
Persons most susceptible of the sort of Sorrow I have spoken of; and I
dare say you will find upon Examination, that they are the wisest and
the bravest of Mankind who are most capable of it.
I am,
Sir ,
Your most humble Servant,
F. J.
Norwich,
7∞ Octobris,
1712.
T.
The Mr. Francham who wrote this letter was of Norwich,
whence it is dated.
Contents
|
Tuesday, October 28, 1712 |
Steele |
Vera redit facies, dissimulata perit.
P. Arb.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
I have been for many Years loud in this Assertion, That there are very
few that can see or hear, I mean that can report what they have seen
or heard; and this thro' Incapacity or Prejudice, one of which
disables almost every Man who talks to you from representing things as
he ought. For which Reason I am come to a Resolution of believing
nothing I hear; and I contemn the Men given to Narration under the
Appellation of a Matter of Fact Man: And according to me, a Matter of
Fact Man is one whose Life and Conversation is spent in the Report of
what is not Matter of Fact.
I remember when Prince
Eugene was here, there was no knowing his
Height or Figure, till you,
Mr. SPECTATOR, gave the Publick
Satisfaction in that Matter. In Relations, the Force of the Expression
lies very often more in the Look, the Tone of Voice, or the Gesture,
than the Words themselves; which being repeated in any other Manner by
the Undiscerning, bear a very different Interpretation from their
original Meaning. I must confess, I formerly have turn'd this Humour
of mine to very good Account; for whenever I heard any Narration
utter'd with extraordinary vehemence, and grounded upon considerable
Authority, I was always ready to lay any Wager that it was not so.
Indeed I never pretended to be so rash, as to fix the Matter in any
particular Way in Opposition to theirs; but as there are a hundred
Ways of any thing happening, besides that it has happen'd, I only
controverted its falling out in that one Manner as they settled it,
and left it to the Ninety nine other Ways, and consequently had more
Probability of Success. I had arrived at a particular skill in warming
a Man so far in his Narration, as to make him throw in a little of the
Marvelous, and then, if he has much Fire, the next Degree is the
Impossible. Now this is always the Time for fixing the Wager. But this
requires the nicest Management, otherwise very probably the Dispute
may arise to the old Determination by Battle. In these Conceits I have
been very fortunate, and have won some Wagers of those who have
professedly valued themselves upon Intelligence, and have put
themselves to great Charge and Expence to be misinformed considerably
sooner than the Rest of the World.
Having got a comfortable Sum by this my Opposition to publick Report,
I have brought my self now to so great a Perfection in Inattention,
more especially to Party Relations, that at the same time I seem with
greedy Ears to devour up the Discourse, I certainly don't know one
Word of it, but pursue my own Course of Thought, whether upon Business
or Amusement, with much Tranquility: I
say Inattention, because a late
Act of Parliament has secur'd all Party-Lyars from the Penalty of a
Wager
1, and consequently made it unprofitable to attend them.
However, good Breeding obliges a Man to maintain the Figure of the
keenest Attention, the true Posture of which in a Coffee-house I take
to consist in leaning over a Table, with the Edge of it pressing hard
upon your Stomach; for the more Pain the Narration is received with,
the more gracious is your bending over: Besides that the Narrator
thinks you forget your Pain by the Pleasure of hearing him.
Fort
Knock has occasioned several very perplexed and inelegant Heats
and Animosities; and there was one t'other day in a Coffee-house where
I was, that took upon him to clear that Business to me, for he said he
was there. I knew him to be that sort of Man that had not strength of
Capacity to be inform'd of any thing that depended merely upon his
being an Eye-Witness, and therefore was fully satisfied he could give
me no Information, for the very same Reason he believed he could, for
he was there. However, I heard him with the same Greediness as
Shakespear describes in the following Lines:
I saw a Smith stand on his Hammer, thus,
With open Mouth swallowing a Taylor's News.
I confess of late I have not been so much amazed at the Declaimers in
Coffee-houses as I formerly was, being satisfied that they expect to
be rewarded for their Vociferations. Of these Liars there are two
Sorts. The Genius of the first consists in much Impudence and a strong
Memory; the others have added to these Qualifications a good
Understanding and smooth Language. These therefore have only certain
Heads, which they are as eloquent upon as they can, and may be call'd
Embellishers; the others repeat only what they hear from others as
literally as their Parts or Zeal will permit, and are called Reciters.
Here was a Fellow in Town some Years ago, who used to divert himself
by telling a Lie at
Charing-Cross in the Morning at eight of
the
Clock, and then following it through all Parts of the Town till eight
at Night; at which time he came to a Club of his Friends, and diverted
them with an Account what Censure it had at
Will's in
Covent-Garden, how dangerous it was believed to be at
Child's, and what
Inference they drew from it with Relation to Stocks at
Jonathan's. I
have had the Honour to travel with this Gentleman I speak of in Search
of one of his Falshoods; and have been present when they have
described the very Man they have spoken to, as him who first reported
it, tall or short, black or fair, a Gentleman or a Raggamuffin,
according as they liked the Intelligence. I have heard one of our
ingenious Writers of News say, that when he has had a Customer come
with an Advertisement of an Apprentice or a Wife run away, he has
de
Sir ed the Advertiser to compose himself a little, before he dictated
the Description of the Offender: For when a Person is put into a
publick Paper by a Man who is angry with him, the real Description of
such Person is hid in the Deformity with which the angry Man described
him; therefore this Fellow always made his Customers describe him as
he would the Day before he offended, or else he was sure he would
never find him out. These and many other Hints I could suggest to you
for the Elucidation of all Fictions; but I leave it to your own
Sagacity to improve or neglect this Speculation.
I am, Sir ,
Your most obedient,
Humble Servant.
Postscript
to the
Spectator,
.
N. B. There are in the Play of the
Self-Tormentor
of
Terence's,
which is allowed a most excellent Comedy, several Incidents which would
draw Tears from any Man of Sense, and not one which would move his
Laughter.
T.
By 7 Anne, cap. 17, all wagers laid upon a contingency
relating to the war with France were declared void.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 29, 1712 |
Steele |
—Adjuro nunquam eam me deserturum,
Non, si capiundos mihi sciam esse inimicos omneis homines.
Hanc mihi expetivi, contigit: conveniunt mores: valeant
Qui inter nos dissidium volunt: hanc, nisi mors,
Mi adimet nemo.
Ter.

I should esteem my self a very happy Man, if my Speculations could in
the least contribute to the rectifying the Conduct of my Readers in one
of the most important Affairs of Life, to wit their Choice in Marriage.
This State is the Foundation of Community, and the chief Band of
Society; and I do not think I can be too frequent on Subjects which may
give Light to my unmarried Readers, in a particular which is so
essential to their following Happiness or Misery. A virtuous
Disposition, a good Understanding, an agreeable Person, and an easy
Fortune, are the things which should be chiefly regarded on this
Occasion. Because my present View is to direct a young Lady, who, I
think, is now in doubt whom to take of many Lovers, I shall talk at this
time to my female Reader. The Advantages, as I was going to say, of
Sense, Beauty and Riches, are what are certainly the chief Motives to a
prudent young Woman of Fortune for changing her Condition; but as she is
to have her Eye upon each of these, she is to ask herself whether the
Man who has most of these Recommendations in the Lump is not the most
de
Sir
able. He that has excellent Talents, with a moderate Estate, and an
agreeable Person, is preferable to him who is only rich, if it were only
that good Faculties may purchase Riches, but Riches cannot purchase
worthy Endowments. I do not mean that Wit, and a Capacity to entertain,
is what should be highly valued, except it is founded upon Good-nature
and Humanity. There are many ingenious Men, whose Abilities do little
else but make themselves and those about them uneasy: Such are those who
are far gone in the Pleasures of the Town, who cannot support Life
without quick Sensations and gay Reflections, and are Strangers to
Tranquility, to right Reason, and a calm Motion of Spirits without
Transport or Dejection.
ingenious Men, of all Men living, are most
to be avoided by her who would be happy in
a
Husband. They are
immediately sated with Possession, and must necessarily fly to new
Acquisitions of Beauty, to pass away the whiling Moments and Intervals
of Life; for with them every Hour is heavy that is not joyful. But there
is a sort of Man of Wit and Sense, that can reflect upon his own Make,
and that of his Partner, with the Eyes of Reason and Honour, and who
believes he offends against both these, if he does not look upon the
Woman (who chose him to be under his Protection in Sickness and Health)
with the utmost Gratitude, whether from that Moment she is shining or
defective in Person or Mind: I say, there are those who think themselves
bound to supply with Good-nature the Failings of those who love them,
and who always think those the Objects of Love and Pity, who came to
their Arms the Objects of Joy and Admiration.
Of this latter sort is
Lysander
, a Man of Wit, Learning, Sobriety and
Good-nature, of Birth and Estate below no Woman to accept, and of whom
it might be said, should he succeed in his present Wishes, his Mistress
rais'd his Fortune, but not that she made it. When a Woman is
deliberating with herself whom she shall chuse of many near each other
in other Pretensions, certainly he of best Understanding is to be
preferr'd. Life hangs heavily in the repeated Conversation of one who
has no Imagination to be fired at the several Occasions and Objects
which come before him, or who cannot Strike out of his Reflections new
Paths of pleasing Discourse. Honest
Will Thrash
and his Wife, tho' not
married above four Months, have scarce had a Word to say to each other
this six weeks; and one cannot form to one's self a sillier Picture,
than these two Creatures in solemn Pomp and Plenty unable to enjoy their
Fortunes, and at a full stop among a Crowd of Servants, to whose Taste
of Life they are beholden for the little Satisfactions by which they can
be understood to be so much as barely in Being. The Hours of the Day,
the Distinctions of Noon and Night, Dinner and Supper, are the greatest
Notices they are capable of. This is perhaps representing the Life of a
very modest Woman, joined to a dull Fellow, more insipid than it really
deserves; but I am sure it is not to exalt the Commerce with an
ingenious Companion too high, to say that every new Accident or Object
which comes into such a Gentleman's way, gives his Wife new Pleasures
and Satisfactions. The Approbation of his Words and Actions is a
continual new Feast to her, nor can she enough applaud her good Fortune
in having her Life varied every hour, her Mind more improv'd, and her
Heart more glad from every Circumstance which they meet with. He will
lay out his Invention in forming new Pleasures and Amusements, and make
the Fortune she has brought him subservient to the Honour and Reputation
of her and hers. A Man of Sense who is thus oblig'd, is ever contriving
the Happiness of her who did him so great a Distinction; while the Fool
is ungrateful without Vice, and never returns a Favour because he is not
sensible of it. I would, methinks, have so much to say for my self, that
if I fell into the hands of him who treated me ill, he should be
sensible when he did so: His Conscience should be of my side, whatever
became of his Inclination. I do not know but it is the insipid Choice
which has been made by those who have the Care of young Women, that the
Marriage State it self has been liable to so much Ridicule. But a
well-chosen Love, mov'd by Passion on both sides, and perfected by the
Generosity of one Party, must be adorn'd with so many handsome Incidents
on the other side, that every particular Couple would be an example in
many Circumstances to all the rest of the Species. I shall end the Chat
upon this Subject with a couple of Letters, one from a Lover who is very
well acquainted with the way of Bargaining on these Occasions; and the
other from his Rival, who has a less Estate, but great Gallantry of
Temper. As for my Man of Prudence, he makes love, as he says, as if he
were already a Father, and laying aside the Passion, comes to the Reason
of the Thing.
Madam,
My Counsel
2 has perused the Inventory of your Estate, and
consider'd what Estate you have, which it seems is only yours, and to
the Male-Heirs of your Body; but, in Default of such Issue, to the
right Heirs of your Uncle
Edward for ever. Thus, Madam, I am advis'd
you cannot (the Remainder not being in you) dock the Entail; by which
means my Estate, which is Fee-Simple, will come by the Settlement
propos'd to your Children begotten by me, whether they are Males or
Females; but my Children begotten upon you will not inherit your
Lands, except I beget a Son. Now, Madam, since things are so, you are
a Woman of that Prudence, and understand the World so well, as not to
expect I should give you more than you can give me.
I am, Madam,
(with great Respect)
Your most obedient humble Servant, T. W.
The other Lover's Estate is less than this Gentleman's, but he express'd
himself as follows.
Madam,
I
have given in my Estate to your Counsel
3, and de
Sir ed my own
Lawyer to insist upon no Terms which your Friends can propose for your
certain Ease and Advantage: For indeed I have no notion of making
Difficulties of presenting you with what cannot make me happy without
you.
I am, Madam,
Your most devoted humble Servant, B. T.
You must know the Relations have met upon this, and the Girl being
mightily taken with the latter Epistle, she is laugh'd out, and Uncle
Edward
is to be dealt with to make her a suitable Match to the worthy
Gentleman who has told her he does not care a farthing for her. All I
hope for is, that the Lady
Fair
will make use of the first light Night
to show
B. T.
she understands a Marriage is not to be considered as a
common Bargain.
T.
an
and in first reprint.
Spelt
Council
in the first issue and first reprint.
Spelt
Council
in the first issue and first reprint.
Contents
|
Thursday, October 30, 1712 |
Addison |
—Nunc augur Apollo,
Nunc Lyciæ sortes, nunc et Jove missus ab ipso
Interpres Divûm fert horrida jussa per auras.
Scilicet is superis labor—
Virg.

I am always highly delighted with the discovery of any rising Genius
among my Countrymen. For
reason I have read over, with great
pleasure, the late Miscellany published by Mr.
Pope
, in which
there are many excellent Compositions of that ingenious Gentleman. I
have had a pleasure of the same kind, in perusing a Poem that is just
publish'd
on the Prospect of Peace
, and which, I hope, will meet with
such a Reward from its Patrons, as so noble a Performance deserves. I
was particularly
pleased to find that the Author had not amused
himself with Fables out of the Pagan Theology, and that when he hints at
any thing of
this
nature, he alludes to it only as to a Fable.
Many of our Modern Authors, whose Learning very often extends no farther
than
Ovid's Metamorphosis
, do not know how to celebrate a Great Man,
without mixing a parcel of School-Boy Tales with the Recital of his
Actions. If you read a Poem on a fine Woman, among the Authors of this
Class, you shall see that it turns more upon
Venus
or
Helen
, that on
the Party concerned. I have known a Copy of Verses on a great Hero
highly commended; but upon asking to hear some of the beautiful
Passages, the Admirer of it has repeated to me a Speech of
Apollo
, or
a Description of
Polypheme
. At other times when I have search'd for
the Actions of a great Man, who gave a Subject to the Writer, I have
been entertained with the Exploits of a River-God, or have been forced
to attend a Fury in her mischievous Progress, from one end of the Poem
to the other. When we are at School it is necessary for us to be
acquainted with the System of Pagan Theology, and may be allowed to
enliven a Theme, or point an Epigram with an Heathen God; but when we
would write a manly Panegyrick, that should carry in it all the Colours
of Truth, nothing can be more ridiculous than to have recourse to our
Jupiters
and
Junos
.
No Thought is beautiful which is not just, and no Thought can be just
which is not founded in Truth, or at least in that which passes for
such.
In Mock-Heroick Poems, the Use of the Heathen Mythology is not only
excusable but graceful, because it is the Design of such Compositions to
divert, by adapting the fabulous Machines of the Ancients to low
Subjects, and at the same time by ridiculing such kinds of Machinery in
modern Writers. If any are of opinion, that there is a Necessity of
admitting these Classical Legends into our serious Compositions, in
order to give them a more Poetical Turn; I would recommend to their
Consideration the Pastorals of Mr.
Philips
. One would have thought it
impossible for this Kind of Poetry to have subsisted without Fawns and
Satyrs, Wood Nymphs, and Water Nymphs, with all the Tribe of rural
Deities. But we see he has given a new Life, and a more natural Beauty
to this way of Writing by substituting in the place of these Antiquated
Fables, the superstitious Mythology which prevails among the Shepherds
of our own Country.
Virgil
and
Homer
might compliment their Heroes, by interweaving the
Actions of Deities with their Atchievements; but for a Christian Author
to write in the Pagan Creed, to make Prince
Eugene
a Favourite of
Mars
, or to carry on a Correspondence between
Bellona
and the
Marshal
de Villars
, would be downright Puerility, and unpardonable in
a Poet that is past Sixteen. It is want of sufficient Elevation in a
Genius to describe Realities, and place them in a shining Light, that
makes him have recourse to such trifling antiquated Fables; as a Man may
write a fine Description of
Bacchus
or
Apollo
, that does not know
how to draw the Character of any of his Contemporaries.
In order therefore to put a stop to this absurd Practice, I shall
publish the following Edict, by virtue of that Spectatorial Authority
with which I stand invested.
'Whereas the Time of a General Peace is, in all appearance, drawing
near, being inform'd that there are several ingenious Persons who intend
to shew their Talents on so happy an Occasion, and being willing, as
much as in me lies, to prevent that Effusion of Nonsense, which we have
good Cause to apprehend; I do hereby strictly require every Person, who
shall write on this Subject, to remember that he is a Christian, and not
to Sacrifice his Catechism to his Poetry. In order to it, I do expect of
him in the first place, to make his own Poem, without depending upon
Phœbus
for any part of it, or calling out for Aid upon any one of the
Muses by Name. I do likewise positively forbid the sending of
Mercury
with any particular Message or Dispatch relating to the Peace, and shall
by no means suffer
Minerva
to take upon her the Shape of any
Plenipotentiary concerned in this Great Work. I do further declare, that
I shall not allow the Destinies to have had an hand in the Deaths of the
several thousands who have been slain in the late War, being of opinion
that all such Deaths may be very well accounted for by the Christian
System of Powder and Ball. I do therefore strictly forbid the Fates to
cut the Thread of Man's Life upon any pretence whatsoever, unless it be
for the sake of the Rhyme. And whereas I have good Reason to fear, that
Neptune
will have a great deal of Business on his Hands, in several
Poems which we may now suppose are upon the Anvil, I do also prohibit
his Appearance, unless it be done in Metaphor, Simile, or any very short
Allusion, and that even here he be not permitted to enter, but with
great Caution and Circumspection. I de
Sir
e that the same Rule may be
extended to his whole Fraternity of Heathen Gods, it being my design to
condemn every Poem to the Flames in which
Jupiter
Thunders, or
exercises any other Act of Authority which does not belong to him: In
short, I expect that no Pagan Agent shall be introduc'd, or any Fact
related which a Man cannot give Credit to with a good Conscience.
Provided always, that nothing herein contained shall extend, or be
construed to extend, to several of the Female Poets in this Nation, who
shall be still left in full Possession of their Gods and Goddesses, in
the same manner as if this Paper had never been written.
O.
In this year, 1712, Bernard Lintot, having observed the success of
Tonson's volumes of Miscellanies, produced a Miscellany edited by Pope
(now 24 years old), and containing the first sketch of his
Rape of the
Lock,
translations from Statius and Ovid, and other pieces. Addison's
delight with the discovery of rising genius leads him to dispose in a sentence
of 'that ingenious gentleman' who had just published a
Rape of the Lock,
and proceed to warm praise of his personal friends, Thomas Tickell and
Ambrose Philips. In his Poem to his Excellency the Lord Privy Seal on
the Prospect of Peace, Tickell invites Strafford to 'One hour, oh! listen
while the Muses sing.'
that
Contents
|
Friday, October 31, 1712 |
1 |
Nos populo damus—
Sen.

When I first of all took it in my Head to write Dreams and Visions, I
determin'd to Print nothing of that nature, which was not of my own
Invention. But several laborious Dreamers have of late communicated to
me Works of this Nature, which, for their Reputations and my own, I have
hitherto suppressed. Had I printed every one that came to my Hands, my
Book of Speculations would have been little else but a Book of Visions.
Some of my Correspondents have indeed been so very modest, as to offer
at an Excuse for their not being in a Capacity to dream better. I have
by me, for example, the Dream of a young Gentleman not past Fifteen. I
have likewise by me the Dream of a Person of Quality, and another called
the Lady's Dream. In these, and other Pieces of the same nature, it is
suppos'd the usual Allowances will be made to the Age, Condition and Sex
of the Dreamer. To prevent this Inundation of Dreams, which daily flows
in upon me, I shall apply to all Dreamers of Dreams, the Advice which
Epictetus
has couched, after his manner, in a very simple and concise
Precept.
Never tell thy Dreams, says that Philosopher, for tho' thou
thy self may'st take a Pleasure in telling thy Dream, another will take
no Pleasure in hearing it.
After this short Preface, I must do Justice
to two or three Visions which I have lately publish'd, and which I have
owned to have been written by other Hands. I shall add a Dream to these,
which comes to me from
Scotland
, by one who declares himself of that
Country, and for all I know may be second-sighted. There is, indeed,
something in it of the Spirit of
John Bunyan
; but at the same time a
certain Sublime, which that Author was never master of. I shall publish
it, because I question not but it will fall in with the Taste of all my
popular Readers, and amuse the Imaginations of those who are more
profound; declaring at the same time, that this is the last Dream which
I intend to publish this Season.
Sir ,
'I was last Sunday in the Evening led into a serious Reflection on
the Reasonableness of Virtue, and great Folly of Vice, from an
excellent Sermon I had heard that Afternoon in my Parish-Church. Among
other Observations, the Preacher shew'd us that the Temptations which
the Tempter propos'd, were all on a Supposition, that we are either
Madmen or Fools, or with an Intention to render us such; that in no
other Affair we would suffer ourselves to be thus imposed upon, in a
Case so plainly and clearly against our visible Interest. His
illustrations and Arguments carried so much Persuasion and Conviction
with them, that they remained a considerable while fresh, and working
in my Memory; till at last the Mind, fatigued with Thought, gave way
to the forcible Oppressions of Slumber and Sleep, whilst Fancy,
unwilling yet to drop the Subject, presented me with the following
Vision.
'Methought I was just awoke out of a Sleep, that I could never
remember the beginning of; the Place where I found my self to be, was
a wide and spacious Plain, full of People that wandered up and down
through several beaten Paths, whereof some few were strait, and in
direct lines, but most of them winding and turning like a Labyrinth;
but yet it appear'd to me afterwards, that these last all met in one
Issue, so that many that seemed to steer quite contrary Courses, did
at length meet and face one another, to the no little Amazement of
many of them.
'In the midst of the Plain there was a great Fountain: They called it
the Spring of Self-Love; out of it issued two Rivulets to the
Eastward and Westward, the Name of the first was Heavenly-Wisdom,
its Water was wonderfully clear, but of a yet more wonderful Effect;
the other's Name was Worldly-Wisdom, its Water was thick, and yet
far from dormant or stagnating, for it was in a continual violent
Agitation; which kept the Travellers whom I shall mention by and by,
from being sensible of the Foulness and Thickness of the Water; which
had this Effect, that it intoxicated those who drunk it, and made 'em
mistake every Object that lay before them: both Rivulets were parted
near their Springs into so many others, as there were strait and
crooked Paths, which they attended all along to their respective
Issues.
'I observ'd from the several Paths many now and then diverting, to
refresh and otherwise qualify themselves for their Journey, to the
respective Rivulets that ran near them; they contracted a very
observable Courage and Steadiness in what they were about, by drinking
these Waters. At the end of the Perspective of every strait Path, all
which did end in one Issue and Point, appeared a high Pillar, all of
Diamond, casting Rays as bright as those of the Sun into the Paths;
which Rays had also certain sympathizing and alluring Virtues in them,
so that whosoever had made some considerable progress in his Journey
onwards towards the Pillar, by the repeated impression of these Rays
upon him, was wrought into an habitual Inclination and Conversion of
his Sight towards it, so that it grew at last in a matter natural to
him to look and gaze upon it, whereby he was kept steddy in the strait
Paths, which alone led to that radiant Body, the beholding of which
was now grown a Gratification to his Nature.
'At the Issue of the crooked Paths there was a great black Tower, out
of the Centre of which streamed a long Succession of Flames, which did
rise even above the Clouds; it gave a very great Light to the whole
Plain, which did sometimes outshine the Light, and opprest the Beams
of the Adamantine Pillar; tho' by the Observation I made afterwards,
it appeared that it was not for any Diminution of Light, but that this
lay in the Travellers, who would sometimes step out of the strait
Paths, where they lost the full Prospect of the Radiant Pillar, and
saw it but side-ways: but the great Light from the black Tower, which
was somewhat particularly scorching to them, would generally light and
hasten them to their proper Climate again.
'Round about the black Tower there were, methoughts, many thousands of
huge mis-shapen ugly Monsters; these had great Nets, which they were
perpetually plying and casting towards the crooked Paths, and they
would now and then catch up those that were nearest to them: these
they took up streight, and whirled over the Walls into the flaming
Tower, and they were no more seen nor heard of.
'They would sometimes cast their Nets towards the right Paths to catch
the Stragglers, whose Eyes for want of frequent drinking at the Brook
that ran by them grew dim, whereby they lost their way; these would
sometimes very narrowly miss being catched away, but I could not hear
whether any of these had ever been so unfortunate, that had been
before very hearty in the strait Paths.
'I considered all these strange Sights with great Attention, till at
last I was interrupted by a Cluster of the Travellers in the crooked
Paths, who came up to me, bid me go along with them, and presently
fell to singing and dancing; they took me by the Hand, and so carried
me away along with them. After I had follow'd them a considerable
while, I perceiv'd I had lost the black Tower of Light, at which I
greatly wonder'd; but as I looked and gazed round about me, and saw
nothing, I begun to fancy my first Vision had been but a Dream, and
there was no such thing in reality: but then I consider'd, that if I
could fancy to see what was not, I might as well have an Illusion
wrought on me at present, and not see what was really before me. I was
very much confirmed in this Thought, by the Effect I then just
observ'd the Water of Worldly-Wisdom had upon me; for as I had drunk
a little of it again, I felt a very sensible Effect in my Head;
methought it distracted and disorder'd all there: this made me stop of
a sudden, suspecting some Charm or Inchantment. As I was casting about
within my self what I should do, and whom to apply to in this Case; I
spy'd at some distance off me a Man beckning, and making signs to me
to come over to him. I cry'd to him, I did not know the Way. He then
called to me audibly, to step at least out of the Path I was in; for
if I staid there any longer I was in danger to be catched in a great
Net that was just hanging over me, and ready to catch me up; that he
wonder'd I was so blind, or so distracted, as not to see so imminent
and visible a Danger; assuring me, that as soon as I was out of that
Way, he would come to me to lead me into a more secure Path. This I
did, and he brought me his Palm full of the Water of
Heavenly-Wisdom, which was of very great use to me, for my Eyes were
streight cleared, and I saw the great black Tower just before me; but
the great Net which I spy'd so near me, cast me in such a Terror, that
I ran back as far as I could in one Breath, without looking behind me:
then my Benefactor thus bespoke me, You have made the wonderful'st
Escape in the World, the Water you used to drink is of a bewitching
Nature, you would else have been mightily shocked at the Deformities
and Meanness of the Place; for beside the Set of blind Fools, in whose
Company you was, you may now observe many others who are only
bewitched after another no less dangerous manner. Look a little that
way, there goes a Crowd of Passengers, they have indeed so good a
Head, as not to suffer themselves to be blinded by this bewitching
Water; the black Tower is not vanished out of their sight, they see it
whenever they look up to it; but see how they go side-ways, and with
their Eyes downwards, as if they were mad, that they may thus rush
into the Net, without being beforehand troubled at the Thought of so
miserable a Destruction. Their Wills are so perverse, and their Hearts
so fond of the Pleasures of the Place, that rather than forgo them
they will run all Hazards, and venture upon all the Miseries and Woes
before them.
'See there that other Company, tho' they should drink none of the
bewitching Water, yet they take a Course bewitching and deluding; see
how they chuse the crookedest Paths, whereby they have often the black
Tower behind them, and sometimes see the radiant Column side-ways,
which gives them some weak Glimpse of it. These Fools content
themselves with that, not knowing whether any other have any more of
its Influence and Light than themselves: this Road is called that of
Superstition or Human Invention; they grossly over-look that which
the Rules and Laws of the Place prescribe to them, and contrive some
other Scheme and Set of Directions and Prescriptions for themselves,
which they hope will serve their turn. He shewed me many other kind of
Fools, which put me quite out of humour with the Place. At last he
carried me to the right Paths, where I found true and solid Pleasure,
which entertained me all the way, till we came in closer sight of the
Pillar, where the Satisfaction increased to that measure that my
Faculties were not able to contain it; in the straining of them I was
violently waked, not a little grieved at the vanishing of so pleasing
a Dream.
Glascow, Sept. 29.
The dream in this Paper is taken to have been the joint
production of Alexander Dunlop, Professor of Greek in Glasgow
University, and a Mr. Montgomery, who traded to Sweden, and of whom it
is hinted that he disordered his wits by falling in love with Queen
Christina. Alexander Dunlop, born (1684) in America, where his father
was an exile till the Revolution, as Greek Professor at Glasgow,
published a Grammar, which was used for many years in Scottish
Universities. He died in 1742.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 1, 1712 |
John Hughes |
It is my Custom to take
frequent
Opportunities of enquiring from time
to time, what Success my Speculations meet with in the Town. I am glad
to find in particular, that my Discourses on Marriage have been well
received. A Friend of mine gives me to understand, from
Doctors-Commons
, that more Licences have been taken out there of late
than usual. I am likewise informed of several pretty Fellows, who have
resolved to commence Heads of Families by the first favourable
Opportunity: One of them writes me word, that he is ready to enter into
the Bonds of Matrimony, provided I will give it him under my Hand (as I
now do) that a Man may shew his Face in good Company after he is
married, and that he need not be ashamed to treat a Woman with Kindness,
who puts herself into his Power for Life.
I have other Letters on this Subject, which say that I am attempting to
make a Revolution in the World of Gallantry, and that the Consequence of
it will be, that a great deal of the sprightliest Wit and Satyr of the
last Age will be lost. That a bashful Fellow, upon changing his
Condition, will be no longer puzzled how to stand the Raillery of his
facetious Companions;
he need not own he married only to plunder an
Heiress of her Fortune, nor pretend that he uses her ill, to avoid the
ridiculous
Name of a fond Husband.
Indeed if I may speak my Opinion of great part of the Writings which
once prevail'd among us under the Notion of Humour, they are such as
would tempt one to think there had been an Association among the Wits of
those times to rally Legitimacy out of our Island. A State of Wedlock
was the common Mark for all the Adventurers in Farce and Comedy, as well
as the Essayers in Lampoon and Satyr, to shoot at, and nothing was a
more standing Jest in all Clubs of fashionable Mirth, and gay
Conversation. It was determined among those airy Criticks, that the
Appellation of a
Sober Man
should signify a
Spiritless Fellow
. And I
am apt to think it was about the same Time, that
Good-Nature
, a Word
so peculiarly elegant in our Language that some have affirmed it cannot
well be expressed in any other, came first to be render'd suspicious,
and in danger of being transferred from its original Sense to so distant
an Idea as that of
Folly
.
I must confess it has been my Ambition, in the course of my Writings, to
restore, as well as I was able, the proper Ideas of things. And as I
have attempted this already on the Subject of Marriage, in several
Papers, I shall here add some further Observations which occur to me on
the same Head. Nothing seems to be thought, by our fine Gentlemen, so
indispensable an Ornament in fashionable Life, as Love.
A Knight
Errant
, says
Don Quixot, without a Mistress, is like a Tree without
Leaves
and a Man of Mode among us, who has not some Fair One to sigh
for, might as well pretend to appear dressed, without his Periwig. We
have Lovers in Prose innumerable. All our Pretenders to Rhyme are
professed Inamorato's; and there is scarce a Poet, good or bad, to be
heard of, who has not some real or supposed
Sacharissa
to improve his
Vein.
If Love be any Refinement,
Conjugal Love
must be certainly so in a
much higher Degree. There is no comparison between the frivolous
Affectation of attracting the Eyes of Women with whom you are only
captivated by Way of Amusement, and of whom perhaps you know nothing
more than their Features, and a regular and uniform Endeavour to make
your self valuable, both as a Friend and Lover, to one whom you have
chosen to be the Companion of your Life. The first is the Spring of a
thousand Fopperies, silly Artifices, Falshoods, and perhaps Barbarities;
or at best arises no higher than to a kind of Dancing-School Breeding,
to give the Person a more sparkling Air. The latter is the Parent of
substantial Virtues and agreeable Qualities, and cultivates the Mind
while it improves the Behaviour. The Passion of Love to a Mistress, even
where it is most sincere, resembles too much the Flame of a Fever; that
to a Wife is like the Vital Heat.
I have often thought, if the Letters written by Men of Goodnature to
their Wives, were to be compared with those written by Men of Gallantry
to their Mistresses, the former, notwithstanding any Inequality of
Style, would appear to have the Advantage. Friendship, Tenderness and
Constancy, drest in a Simplicity of Expression, recommend themselves by
a more native Elegance, than passionate Raptures, extravagant Encomiums,
and slavish Adoration. If we were admitted to search the Cabinet of the
beautiful
Narcissa
, among Heaps of Epistles from several Admirers,
which are there preserv'd with equal Care, how few should we find but
would make any one Sick in the Reading, except her who is flattered by
them? But in how different a Style must the wise
Benevolus
, who
converses with that good Sense and good Humour among all his Friends,
write to a Wife who is the worthy Object of his utmost Affection?
Benevolus
, both in Publick and Private, on all Occasions of Life,
appears to have every good Quality and de
Sir
able Ornament. Abroad he is
reverenced and esteemed; at home beloved and happy. The Satisfaction he
enjoys there, settles into an habitual Complacency, which shines in his
Countenance, enlivens his Wit, and seasons his Conversation: Even those
of his Acquaintance, who have never seen him in his Retirement, are
Sharers in the Happiness of it; and it is very much owing to his being
the best and best beloved of Husbands, that he is the most stedfast of
Friends, and the most agreeable of Companions.
There is a sensible Pleasure in contemplating such beautiful Instances
of Domestick Life. The Happiness of the Conjugal State appears
heighten'd to the highest degree it is capable of, when we see two
Persons of accomplished Minds, not only united in the same Interests and
Affections, but in their Taste of the same Improvements, Pleasures and
Diversions.
Pliny
, one of the finest Gentlemen, and politest Writers
of the Age in which he lived, has left us, in his Letter to
Hispulla
,
his Wife's Aunt, one of the most agreeable Family-Pieces of this Kind I
have ever met with. I
end this Discourse with a Translation of it;
and I believe the Reader will be of my opinion, that
Conjugal Love
is
drawn in it with a Delicacy which makes it appear to be, as I have
represented it, an Ornament as well as a Virtue.
Pliny to Hispulla2.
'As I remember the great Affection which was between you and your
excellent Brother, and know you love his Daughter as your own, so as
not only to express the Tenderness of the best of Aunts, but even to
supply that of the best of Fathers; I am sure it will be a pleasure to
you to hear that she proves worthy of her Father, worthy of you, and
of your Ancestors. Her Ingenuity is admirable; her Frugality
extraordinary. She loves me, the surest Pledge of her Virtue; and adds
to this a wonderful Disposition to Learning, which she has acquir'd
from her Affection to me. She reads my Writings, studies them, and
even gets them by heart. You'd smile to see the Concern she is in when
I have a Cause to plead, and the Joy she shews when it is over. She
finds means to have the first News brought her of the Success I meet
with in Court, how I am heard, and what Decree is made. If I recite
any thing in publick, she cannot refrain from placing her self
privately in some Corner to hear, where with the utmost delight she
feasts upon my Applauses. Sometimes she sings my Verses, and
accompanies them with the Lute, without any Master, except Love, the
best of Instructors. From these Instances I take the most certain
Omens of our perpetual and encreasing Happiness; since our Affection
is not founded on my Youth and Person, which must gradually decay, but
she is in love with the immortal Part of me, my Glory and Reputation.
Nor indeed could less be expected from one who had the Happiness to
receive her Education from you, who in your House was accustomed to
every thing that was virtuous and decent, and even began to love me by
your Recommendation. For, as you had always the greatest Respect for
my Mother, you were pleased from my Infancy to form me, to commend me,
and kindly to presage I should be one day what my Wife fancies I am.
Accept therefore our united Thanks; mine, that you have bestowed her
on me, and hers, that you have given me to her, as a mutual Grant of
Joy and Felicity.'
scandalous
Bk iv. ep. 19.
Contents
|
Monday, November 3, 1712 |
Steele |
—Fortius utere Loris.
Ovid.

I am very loth to come to Extremities with the young Gentlemen mention'd
in the following Letter, and do not care to chastise them with my own
Hand, till I am forc'd by Provocations too great to be suffer'd without
the absolute Destruction of my Spectatorial Dignity. The Crimes of these
Offenders are placed under the Observation of one of my chief Officers,
who is posted just at the entrance of the Pass between
London
and
Westminster
. As I have great Confidence in the Capacity, Resolution
and Integrity of the Person deputed by me to give an Account of
Enormities, I doubt not but I shall soon have before me all proper
Notices which are requisite for the Amendment of Manners in Publick, and
the Instruction of each Individual of the Human Species in what is due
from him, in respect to the whole Body of Mankind. The present Paper
shall consist only of the above-mentioned Letter, and the Copy of a
Deputation which I have given to my trusty Friend Mr.
John Sly
;
wherein he is charged to notify to me all that is necessary for my
Animadversion upon the Delinquents mentioned by my Correspondent, as
well as all others described in the said Deputation.
To the SPECTATOR-GENERAL of Great Britain.
'I grant it does look a little familiar, but I must call you
Dear Dumb,
'Being got again to the farther End of the Widow's Coffeehouse, I
shall from hence give you some account of the Behaviour of our
Hackney-Coachmen since my last. These indefatigable Gentlemen, without
the least Design, I dare say, of Self-Interest or Advantage to
themselves, do still ply as Volunteers Day and Night for the Good of
their Country. I will not trouble you with enumerating many
Particulars, but I must by no means omit to inform you of an Infant
about six foot high, and between twenty and thirty Years of Age, who
was seen in the Arms of a Hackney Coach-man driving by Will's
Coffee-house in Covent-Garden, between the Hours of four and five in
the Afternoon of that very Day, wherein you publish'd a Memorial
against them. This impudent young Cur, tho' he could not sit in a
Coach-box without holding, yet would he venture his Neck to bid
defiance to your Spectatorial Authority, or to any thing that you
countenanced. Who he was I know not, but I heard this Relation this
Morning from a Gentleman who was an Eye-Witness of this his Impudence;
and I was willing to take the first opportunity to inform you of him,
as holding it extremely requisite that you should nip him in the Bud.
But I am my self most concerned for my Fellow-Templers,
Fellow-Students, and Fellow-Labourers in the Law, I mean such of them
as are dignified and distinguish'd under the Denomination of
Hackney-Coachmen. Such aspiring Minds have these ambitious young Men,
that they cannot enjoy themselves out of a Coach-Box. It is however an
unspeakable Comfort to me, that I can now tell you, that some of them
are grown so bashful as to study only in the Nighttime, or in the
Country. The other Night I spied one of our young Gentlemen very
diligent at his Lucubrations in Fleet-Street; and by the way, I
should be under some concern, lest this hard Student should one time
or other crack his Brain with studying, but that I am in hopes Nature
has taken care to fortify him in proportion to the great Undertakings
he was design'd for. Another of my Fellow-Templers, on Thursday
last, was getting up into his Study at the Bottom of Grays-Inn-Lane,
in order, I suppose, to contemplate in the fresh Air. Now, Sir , my
Request is, that the great Modesty of these two Gentlemen may be
recorded as a Pattern to the rest; and if you would but give them two
or three Touches with your own Pen, tho' you might not perhaps prevail
with them to desist entirely from their Meditations, yet I doubt not
but you would at least preserve them from being publick Spectacles of
Folly in our Streets. I say, two or three Touches with your own Pen;
for I have really observed, Mr. Spec, that those Spectators which
are so prettily laced down the sides with little c's, how instructive
soever they may be, do not carry with them that Authority as the
others. I do again therefore deSir e, that for the sake of their dear
Necks, you will bestow one Penful of your own Ink upon them. I know
you are loth to expose them; and it is, I must confess, a thousand
Pities that any young Gentleman, who is come of honest Parents, should
be brought to publick Shame: And indeed I should be glad to have them
handled a little tenderly at the first; but if fair means will not
prevail, there is then no other Way to reclaim them, but by making use
of some wholesome Severities; and I think it is better that a Dozen or
two of such good-for-nothing Fellows should be made Examples of, than
that the Reputation of some Hundreds of as hopeful young Gentlemen as
my self should suffer thro' their Folly. It is not, however, for me to
direct you what to do; but, in short, if our Coachmen will drive on
this Trade, the very first of them that I do find meditating in the
Street, I shall make Bold to take the Number of his Chambers, together
with a Note of his Name, and dispatch them to you, that you may
chastise him at your own Discretion.
I am, Dear Spec.
For ever Yours,
Moses Greenbag,
Esq., if you please.
P. S. 'Tom Hammercloth, one of our Coachmen, is now pleading at the
Bar at the other end of the Room, but has a little too much Vehemence,
and throws out his Arms too much to take his Audience with a good
Grace.
To my Loving and Well-beloved
John Sly,
Haberdasher of Hats and
Tobacconist, between the Cities of
London
and
Westminster.
Whereas frequent Disorders, Affronts, Indignities, Omissions, and
Trespasses, for which there are no Remedies by any Form of Law, but
which apparently disturb and disquiet the Minds of Men, happen near the
Place of your Residence; and that you are, as well by your commodious
Situation as the good Parts with which you are endowed, properly
qualified for the Observation of the said Offences; I do hereby
authorize and depute you from the hours of Nine in the Morning, till
Four in the Afternoon, to keep a strict Eye upon all Persons and Things
that are convey'd in Coaches, carried in Carts, or walk on Foot from the
City of
London
to the City of
Westminster
, or from the City of
Westminster
to the City of
London
, within the said Hours. You are
therefore not to depart from your Observatory at the end of
Devereux-Court
during the said space of each Day; but to observe the
Behaviour of all Persons who are suddenly transported from stamping on
Pebbles to sit at ease in Chariots, what Notice they take of their
Foot-Acquaintance, and send me the speediest Advice, when they are
guilty of overlooking, turning from, or appearing grave and distant to
their old Friends. When Man and Wife are in the same Coach, you are to
see whether they appear pleased or tired with each other, and whether
they carry the due Mein in the Eye of the World between Fondness and
Coldness. You are carefully to behold all such as shall have Addition of
Honour or Riches, and Report whether they preserve the Countenance they
had before such Addition. As to Persons on Foot, you are to be attentive
whether they are pleased with their Condition, and are dress'd suitable
to it; but especially to distinguish such as appear discreet, by a
low-heel Shoe, with the decent Ornament of a Leather-Garter: To write
down the Name of such Country Gentlemen as, upon the Approach of Peace,
have left the Hunting for the Military Cock of the Hat: Of all who
strut, make a Noise, and swear at the Drivers of Coaches to make haste,
when they see it impossible they should pass: Of all young Gentlemen in
Coach-boxes, who labour at a Perfection in what they are sure to be
excelled by the meanest of the People. You are to do all that in you
lies that Coaches and Passengers give way according to the Course of
Business, all the Morning in Term-Time towards
Westminster
, the rest
of the Year towards the
Exchange
. Upon these Directions, together with
other secret Articles herein inclosed, you are to govern your self, and
give Advertisement thereof to me at all convenient and spectatorial
Hours, when Men of Business are to be seen. Hereof you are not to fail.
Given under my Seal of Office.
The
SPECTATOR.
T.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 4, 1712 |
|
Facile invenies, et pejorem, et pejus moratam,
Meliorem neque tu reperes, neque sol videt.
Plautus in Sticho.

I am so tender of my Women-Readers, that I cannot defer the Publication
of any thing which concerns their Happiness or Quiet. The Repose of a
married Woman is consulted in the first of the following Letters, and
the Felicity of a Maiden Lady in the second. I
it a Felicity to
have the Addresses of an agreeable Man: and I think I have not any where
seen a prettier Application of a Poetical Story than that of his, in
making the Tale of
Cephalus
and
Procris
the History-Picture of a Fan
in so gallant a manner as he addresses it
. But see the Letters.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Tis now almost three months since I was in Town about some Business;
and the Hurry of it being over, took Coach one Afternoon, and drove to
see a Relation, who married about six Years ago a wealthy Citizen. I
found her at home, but her Husband gone to the
Exchange, and
expected back within an Hour at the farthest. After the usual
Salutations of Kindness, and a hundred Questions about Friends in the
Country, we sat down to Piquet, played two or three Games, and drank
Tea. I should have told you that this was my second time of seeing her
since Marriage, but before she lived at the same Town where I went to
School; so that the Plea of a Relation, added to the Innocence of my
Youth, prevailed upon her good Humour to indulge me in a Freedom of
Conversation as often, and oftner, than the strict Discipline of the
School would allow of. You may easily imagine after such an
Acquaintance we might be exceeding merry without any Offence, as in
calling to mind how many Inventions I had been put to in deluding the
Master, how many Hands forged for Excuses, how many times been sick in
perfect Health; for I was then never sick but at School, and only then
because out of her Company. We had whiled away three Hours after this
manner, when I found it past Five; and not expecting her Husband would
return till late, rose up, told her I should go early next Morning for
the Country: She kindly answered she was afraid it would be long
before she saw me again; so I took my leave and parted. Now,
Sir , I
had not been got home a Fortnight, when I received a Letter from a
Neighbour of theirs, that ever since that fatal Afternoon the Lady had
been most inhumanly treated, and the Husband publickly stormed that he
was made a Member of too numerous a Society. He had, it seems,
listened most of the time my Cousin and I were together. As jealous
Ears always hear double, so he heard enough to make him mad; and as
jealous Eyes always see thro' Magnifying Glasses, so he was certain it
could not be I whom he had seen, a beardless Stripling, but fancied he
saw a gay Gentleman of the
Temple, ten Years older than my self; and
for that reason, I presume, durst not come in, nor take any Notice
when I went out. He is perpetually asking his Wife if she does not
think the time long (as she said she should) till she see her Cousin
again. Pray,
Sir , what can be done in this Case? I have writ to him to
assure him I was at his House all that afternoon expecting to see him:
His Answer is, 'tis only a Trick of hers, and that he neither can nor
will believe me. The parting Kiss I find mightily nettles him, and
confirms him in all his Errors.
Ben. Johnson, as I remember, makes a
Foreigner in one of his Comedies,
admire the desperate Valour of the
bold English,
who let out their Wives to all Encounters. The
general Custom of Salutation should Excuse the Favour done me, or you
should lay down Rules when such Distinctions are to be given or
omitted. You cannot imagine,
Sir , how troubled I am for this unhappy
Lady's Misfortune; and beg you would insert this Letter, that the
Husband may reflect upon this Accident coolly. It is no small Matter,
the Ease of a virtuous Woman for her whole Life: I know she will
conform to any Regularities (tho' more strict than the common Rules of
our Country require) to which his particular Temper shall incline him
to oblige her. This Accident puts me in mind how generously
Pisistratus the
Athenian Tyrant behaved himself on a like
Occasion, when he was instigated by his Wife to put to death a young
Gentleman, because being passionately fond of his Daughter, he kissed
her in publick as he met her in the Street;
What (says he)
shall we
do to those who are our Enemies, if we do thus to those who are our
Friends? I will not trouble you much longer, but am exceedingly
concern'd lest this Accident may cause a virtuous Lady to lead a
miserable Life with a Husband, who has no Grounds for his Jealousy but
what I have faithfully related, and ought to be reckon'd none. 'Tis to
be fear'd too, if at last he sees his Mistake, yet People will be as
slow and unwilling in disbelieving Scandal as they are quick and
forward in believing it. I shall endeavour to enliven this plain
honest Letter, with
Ovid's Relation about
Cybele's Image. The Ship
wherein it was aboard was stranded at the mouth of the
Tyber, and
the Men were unable to move it, till
Claudia, a Virgin, but
suspected of Unchastity, by a slight Pull hawled it in. The Story is
told in the fourth Book of the
Fasti.
Parent of Gods, began the weeping Fair,
Reward or punish, but oh! hear my Pray'r.
If Lewdness e'er defil'd my Virgin Bloom,
From Heav'n with Justice I receive my Doom;
But if my Honour yet has known no Stain,
Thou, Goddess, thou my Innocence maintain;
Thou, whom the nicest Rules of Goodness sway'd,
Vouchsafe to follow an unblemish'd Maid.
She spoke, and touch'd the Cord with glad Surprize,
(The truth was witness'd by ten thousand Eyes)
The pitying Goddess easily comply'd,
Follow'd in triumph, and adorn'd her Guide;
While Claudia, blushing still far past Disgrace,
March'd silent on with a slow solemn Pace:
Nor yet from some was all Distrust remov'd,
Tho' Heav'n such Virtue by such Wonders prov'd.
I am,
Sir ,
Your very humble Servant,
Philagnotes.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You will oblige a languishing Lover, if you will please to print the
enclosed Verses in your next Paper. If you remember the
Metamorphosis, you know
Procris, the fond Wife of
Cephalus, is
said to have made her Husband, who delighted in the Sports of the
Wood, a Present of an unerring Javelin. In process of time he was so
much in the Forest, that his Lady suspected he was pursuing some
Nymph, under the pretence of following a Chace more innocent. Under
this Suspicion she hid herself among the Trees, to observe his
Motions. While she lay conceal'd, her Husband, tired with the Labour
of Hunting, came within her hearing. As he was fainting with Heat, he
cried out,
Aura veni; Oh charming Air approach.
'The unfortunate Wife, taking the Word
Air to be the name of a
Woman, began to move among the Bushes; and the Husband believing it a
Deer, threw his Javelin and kill'd her. This History painted on a Fan,
which I presented to a Lady, gave occasion to my growing poetical.
Come gentle Air! th' Æolian Shepherd said,
While Procris panted in the secret Shade;
Come gentle Air! the fairer Delia cries,
While at her Feet her Swain expiring lies.
Lo the glad Gales o'er all her Beauties stray,
Breathe on her Lips, and in her Bosom play.
In Delia's Hand this Toy is fatal found,
Nor did that fabled Dart more surely wound.
Both Gifts destructive to the Givers prove,
Alike both Lovers fall by those they love:
Yet guiltless too this bright Destroyer lives,
At random wounds, nor knows the Wound she gives.
She views the Story with attentive Eyes,
And pities Procris, while her Lover dies.
This second letter and the verses were from Pope.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 5, 1712 |
Steele |
Dum potuit solite gemitum virtute repressit.
Ovid.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I who now write to you, am a Woman loaded with Injuries, and the
Aggravation of my Misfortune is, that they are such which are
overlooked by the Generality of Mankind, and tho' the most afflicting
imaginable, not regarded as such in the general Sense of the World. I
have hid my Vexation from all Mankind; but have now taken Pen, Ink,
and Paper, and am resolv'd to unbosom my self to you, and lay before
you what grieves me and all the Sex. You have very often mentioned
particular Hardships done to this or that Lady; but, methinks, you
have not in any one Speculation directly pointed at the partial
Freedom Men take, the unreasonable Confinement Women are obliged to,
in the only Circumstance in which we are necessarily to have a
Commerce with them, that of Love. The Case of Celibacy is the great
Evil of our Nation; and the Indulgence of the vicious Conduct of Men
in that State, with the Ridicule to which Women are exposed, though
ever so virtuous, if long unmarried, is the Root of the greatest
Irregularities of this Nation. To shew you,
Sir , that tho' you never
have given us the Catalogue of a Lady's Library as you promised, we
read good Books of our own chusing, I shall insert on this occasion a
Paragraph or two out of
Echard's Roman History. In the 44th Page of
the second Volume the Author observes, that
Augustus, upon his
Return to
Rome at the end of a War, received Complaints that too
great a Number of the young Men of Quality were unmarried. The Emperor
thereupon assembled the whole
Equestrian Order; and having separated
the Married from the Single, did particular Honours to the former, but
he told the latter, that is to say, Mr. SPECTATOR, he told the
Batchelors,
"That their Lives and Actions had been so peculiar, that he knew not
by what Name to call 'em; not by that of Men, for they performed
nothing that was manly; not by that of Citizens, for the City might
perish notwithstanding their Care; nor by that of Romans, for they
designed to extirpate the Roman Name."
Then proceeding to shew his tender Care and hearty Affection for his
People, he further told them,
"That their Course of Life was of such pernicious Consequence to the
Glory and Grandeur of the Roman Nation, that he could not chuse
but tell them, that all other Crimes put together could not equalize
theirs: For they were guilty of Murder, in not suffering those to be
born which should proceed from them; of Impiety, in causing the
Names and Honours of their Ancestors to cease; and of Sacrilege, in
destroying their Kind, which proceeded from the immortal Gods, and
Human Nature, the principal thing consecrated to 'em: Therefore in
this Respect they dissolved the Government, in disobeying its Laws;
betrayed their Country, by making it barren and waste; nay and
demolished their City, in depriving it of Inhabitants. And he was
sensible that all this proceeded not from any kind of Virtue or
Abstinence, but from a Looseness and Wantonness, which ought never
to be encouraged in any Civil Government."
There are no Particulars dwelt upon that let us into the Conduct of
these young Worthies, whom this great Emperor treated with so much
Justice and Indignation; but any one who observes what passes in this
Town, may very well frame to himself a Notion of their Riots and
Debaucheries all Night, and their apparent Preparations for them all
Day. It is not to be doubted but these
Romans never passed any of
their Time innocently but when they were asleep, and never slept but
when they were weary and heavy with Excesses, and slept only to
prepare themselves for the Repetition of them. If you did your Duty as
a SPECTATOR, you would carefully examine into the Number of Births,
Marriages, and Burials; and when you had deducted out of your Deaths
all such as went out of the World without marrying, then cast up the
number of both Sexes born within such a Term of Years last past, you
might from the single People departed make some useful Inferences or
Guesses how many there are left unmarried, and raise some useful
Scheme for the Amendment of the Age in that particular. I have not
Patience to proceed gravely on this abominable Libertinism; for I
cannot but reflect, as I am writing to you, upon a certain lascivious
Manner which all our young Gentlemen use in publick, and examine our
Eyes with a Petulancy in their own, which is a downright Affront to
Modesty. A disdainful Look on such an Occasion is return'd with a
Countenance rebuked, but by averting their Eyes from the Woman of
Honour and Decency to some flippant Creature, who will, as the Phrase
is, be kinder. I must set down things as they come into my Head,
without standing upon Order. Ten thousand to one but the gay Gentleman
who stared, at the same time is an House-keeper; for you must know
they have got into a Humour of late of being very regular in their
Sins, and a young Fellow shall keep his four Maids and three Footmen
with the greatest Gravity imaginable. There are no less than six of
these venerable House-keepers of my Acquaintance. This Humour among
young Men of Condition is imitated by all the World below them, and a
general Dissolution of Manners arises from the one Source of
Libertinism, without Shame or Reprehension in the Male Youth. It is
from this one Fountain that so many Beautiful helpless young Women are
sacrific'd and given up to Lewdness, Shame, Poverty and Disease. It is
to this also that so many excellent young Women, who might be Patterns
of conjugal Affection and Parents of a worthy Race, pine under unhappy
Passions for such as have not Attention enough to observe, or Virtue
enough to prefer them to their common Wenches. Now,
Mr. SPECTATOR, I
must be free to own to you, that I my self suffer a tasteless insipid
Being, from a Consideration I have for a Man who would not, as he has
said in my hearing, resign his Liberty, as he calls it, for all the
Beauty and Wealth the whole Sex is possessed of. Such Calamities as
these would not happen, if it could possibly be brought about, that by
fining Batchelors as Papists Convict, or the like, they were
distinguished to their disadvantage from the rest of the World, who
fall in with the Measures of Civil Society. Lest you should think I
speak this as being, according to the senseless rude Phrase, a
malicious old Maid, I shall acquaint you I am a Woman of Condition not
now three and twenty, and have had Proposals from at least ten
different Men, and the greater Number of them have upon the Upshot
refused me. Something or other is always amiss when the Lover takes to
some new Wench: A Settlement is easily excepted against; and there is
very little Recourse to avoid the vicious Part of our Youth, but
throwing one's self away upon some lifeless Blockhead, who tho' he is
without Vice, is also without Virtue. Now-a-days we must be contented
if we can get Creatures which are not bad, good are not to be
expected. Mr. SPECTATOR, I sat near you the other Day, and think I did
not displease you Spectatorial Eyesight; which I shall be a better
Judge of when I see whether you take notice of these Evils your own
way, or print this Memorial dictated from the disdainful heavy Heart
of,
Sir ,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
Rachael Welladay.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 6, 1712 |
Addison |
Singula quæque locum teneant sortita decenter.
Hor.

Upon the hearing of several late Disputes concerning Rank and
Precedence, I could not forbear amusing my self with some Observations,
which I have made upon the Learned World, as to this great Particular.
By the Learned World I here mean at large, all those who are any way
concerned in Works of Literature, whether in the Writing, Printing or
Repeating Part. To begin with the Writers; I have observed that the
Author of a
Folio
, in all Companies and Conversations, sets himself
above the Author of a
Quarto
; the Author of a
Quarto
above the
Author of an
Octavo
; and so on, by a gradual Descent and
Subordination, to an Author in
Twenty Fours
. This Distinction is so
well observed, that in an Assembly of the Learned, I have seen a
Folio
Writer place himself in an Elbow-Chair, when the Author of a
Duo-decimo
has, out of a just Deference to his superior Quality,
seated himself upon a Squabb. In a word, Authors are usually ranged in
Company after the same manner as their Works are upon a Shelf.
The most minute Pocket-Author hath beneath him the Writers of all
Pamphlets, or Works that are only stitched. As for the Pamphleteer, he
takes place of none but of the Authors of single Sheets, and of that
Fraternity who publish their Labours on certain Days, or on every Day of
the Week. I do not find that the Precedency among the Individuals, in
this latter Class of Writers, is yet settled.
For my own part, I have had so strict a regard to the Ceremonial which
prevails in the Learned World, that I never presumed to take place of a
Pamphleteer till my daily Papers were gathered into those two first
Volumes, which have already appeared. After which, I naturally jumped
over the Heads not only of all Pamphleteers, but of every
Octavo
Writer in
Great Britain
, that had written but one Book. I am also
informed by my Bookseller, that six
Octavo's
have at all times been
look'd upon as an Equivalent to a
Folio
, which I take notice of the
rather, because I would not have the Learned World surprized, if after
the Publication of half a dozen Volumes I take my Place accordingly.
When my scattered Forces are thus rallied, and reduced into regular
Bodies, I flatter my self that I shall make no despicable Figure at the
Head of them.
Whether these Rules, which have been received time out of Mind in the
Common-Wealth of Letters, were not originally established with an Eye to
our Paper Manufacture, I shall leave to the Discussion of others, and
shall only remark further in this place, that all Printers and
Booksellers take the Wall of one another, according to the
abovementioned Merits of the Authors to whom they respectively belong.
I come now to that point of Precedency which is settled among the three
Learned Professions, by the Wisdom of our Laws. I need not here take
Notice of the Rank which is allotted to every Doctor in each of these
Professions, who are all of them, though not so high as Knights, yet a
Degree above Squires; this last Order of Men being the illiterate Body
of the Nation, are consequently thrown together into a Class below the
three Learned Professions. I mention this for the sake of several Rural
'Squires, whose Reading does not rise so high as to
the Present State
of England
, and who are often apt to usurp that Precedency which by the
Laws of their Country is not due to them. Their Want of Learning, which
has planted them in this Station, may in some measure extenuate their
Misdemeanour; and our Professors ought to pardon them when they offend
in this Particular, considering that they are in a State of Ignorance,
or, as we usually say, do not know their Right Hand from their Left.
There is another Tribe of Persons who are Retainers to the Learned
World, and who regulate themselves upon all Occasions by several Laws
peculiar to their Body. I mean the Players or Actors of both Sexes.
Among these it is a standing and uncontroverted Principle, that a
Tragedian always takes place of a Comedian; and 'tis very well known the
merry Drolls who make us laugh are always placed at the lower End of the
Table, and in every Entertainment give way to the Dignity of the Buskin.
It is a Stage Maxim,
Once a King, and always a King
. For this Reason
it would be thought very absurd in Mr. Bullock, notwithstanding the
Height and Gracefulness of his Person, to sit at the Right Hand of an
Hero, tho' he were but five Foot high. The same Distinction is observed
among the Ladies of the Theatre. Queens and Heroines preserve their Rank
in private Conversation, while those who are Waiting-Women and Maids of
Honour upon the Stage, keep their Distance also behind the Scenes.
I shall only add, that by a Parity of Reason, all Writers of Tragedy
look upon it as their due to be seated, served, or saluted before Comick
Writers: Those who deal in Tragi-Comedy usually taking their Seats
between the Authors of either Side. There has been a long Dispute for
Precedency between the Tragick and Heroick Poets.
Aristotle
would have
the latter yield the
Pas
to the former, but Mr.
Dryden
and many
others would never submit to this Decision. Burlesque Writers pay the
same Deference to the Heroick, as Comick Writers to their Serious
Brothers in the Drama.
By this short Table of Laws, Order is kept up, and Distinction preserved
in the whole Republick of Letters.
O.
Contents
|
Friday, November 7, 1712 |
Addison |
Sic visum Veneri; cui placet impares
Formas atque animos sub juga ahenea
Sævo mittere cum joco.
Hor.

It is very usual for those who have been severe upon Marriage, in some
part or other of their Lives to enter into the Fraternity which they
have ridiculed, and to see their Raillery return upon their own Heads. I
scarce ever knew a Woman-hater that did not, sooner or later, pay for
it. Marriage, which is a Blessing to another Man, falls upon such a one
as a Judgment.
Mr.
Congreve's Old Batchelor
is set forth to us
with much Wit and Humour, as an Example of this kind. In short, those
who have most distinguished themselves by railing at the Sex in general,
very often make an honourable Amends, by chusing one of the most
worthless Persons of it, for a Companion and Yoke-fellow.
Hymen
takes
his Revenge in kind, on those who turn his Mysteries into Ridicule.
My Friend
Will Honeycomb
, who was so unmercifully witty upon the
Women, in a couple of Letters, which I lately communicated to the
Publick, has given the Ladies ample Satisfaction by marrying a Farmer's
Daughter; a piece of News which came to our Club by the last Post. The
Templer
is very positive that he has married a Dairy-maid: But
Will,
in his Letter to me on this Occasion, sets the best Face upon the Matter
that he can, and gives a more tollerable Account of his Spouse. I must
confess I suspected something more than ordinary, when upon opening the
Letter I found that
Will
was fallen off from his former Gayety, having
changed
Dear Spec.
which was his usual Salute at the Beginning of the
Letter, into
My Worthy Friend
, and subscribed himself in the latter
End of it at full length
William Honeycomb
. In short, the gay, the
loud,
vain
Will Honeycomb
, who had made Love to every great
Fortune that has appeared in Town for
above
thirty Years together,
and boasted of Favours from Ladies whom he had never seen, is at length
wedded to a plain Country Girl.
His Letter gives us the Picture of a converted Rake. The sober Character
of the Husband is dashed with the Man of the Town, and enlivened with
those little Cant-phrases which have made my Friend
Will
often thought
very pretty Company. But let us hear what he says for himself.
My Worthy Friend,
I question not but you, and the rest of my Acquaintance, wonder that
I, who have lived in the Smoak and Gallantries of the Town for thirty
Years together, should all on a sudden grow fond of a Country Life.
Had not my Dog
of a3 Steward run away as he did, without making
up his Accounts, I had still been immersed in Sin and Sea-Coal. But
since my late forced Visit to my Estate, I am so pleased with it, that
I am resolved to live and die upon it. I am every Day abroad among my
Acres, and can scarce forbear filling my Letter with Breezes, Shades,
Flowers, Meadows, and purling Streams. The Simplicity of Manners,
which I have heard you so often speak of, and which appears here in
Perfection, charms me wonderfully. As an Instance of it, I must
acquaint you, and by your means the whole Club, that I have lately
married one of my Tenants Daughters. She is born of honest Parents,
and though she has no Portion, she has a great deal of Virtue. The
natural Sweetness and Innocence of her Behaviour, the Freshness of her
Complection, the unaffected Turn of her Shape and Person, shot me
through and through every time I saw her, and did more Execution upon
me in Grogram, than the greatest Beauty in Town or Court had ever done
in Brocade. In short, she is such an one as promises me a good Heir to
my Estate; and if by her means I cannot leave to my Children what are
falsely called the Gifts of Birth; high Titles and Alliances: I hope
to convey to them the more real and valuable Gifts of Birth; strong
Bodies, and Healthy Constitutions. As for your fine Women, I need not
tell thee that I know them. I have had my share in their Graces, but
no more of that. It shall be my Business hereafter to live the Life of
an honest Man, and to act as becomes the Master of a Family. I
question not but I shall draw upon me the Raillery of the Town, and be
treated to the Tune of the
Marriage-Hater match'd; but I am prepared
for it. I have been as witty upon others in my time. To tell thee
truly, I saw such a Tribe of Fashionable young fluttering Coxcombs
shot up, that I did not think my Post of an
homme de ruelle any
longer tenable. I felt a certain Stiffness in my Limbs, which entirely
destroyed that Jauntyness of Air I was once Master of. Besides, for I
may now confess my Age to thee, I have been eight and forty above
these Twelve Years. Since my Retirement into the Country will make a
Vacancy in the Club, I could wish you would fill up my Place with my
Friend
Tom Dapperwit. He has an infinite deal of Fire, and knows the
Town. For my own part, as I have said before, I shall endeavour to
live hereafter suitable to a Man in my Station, as a prudent Head of a
Family, a good Husband, a careful Father (when it shall so happen) and
as
Your most Sincere Friend,
and Humble Servant,
William Honeycomb.
O.
Heartwell in the play of the
Old Batchelor
. Addison here
continues the winding up of the
Spectator
by finally disposing of
another member of the club.
about
the
Contents
|
Saturday, November 8, 1712 |
Addison |
Qui mare et terras variisque mundum
Temperat horis:
Unde nil majus generatur ipso,
Nec viget quicquam simile aut secundum.
Hor.

Simonides
ask'd by
Dionysius
the Tyrant what God was, de
Sir
ed a
Day's time to consider of it before he made his Reply. When the Day was
expired, he de
Sir
ed two Days; and afterwards, instead of returning his
Answer, demanded still double the Time to consider of it. This great
Poet and Philosopher, the more he contemplated the Nature of the Deity,
found that he waded but the more out of his Depth; and that he lost
himself in the Thought, instead of finding an End of it
.
If we consider the Idea which wise Men, by the Light of Reason, have
framed of the Divine Being, it amounts to this: That he has in him all
the Perfection of a Spiritual Nature; and since we have no Notion of any
kind of spiritual Perfection but what we discover in our own Souls, we
joyn Infinitude to each kind of these Perfections, and what is a Faculty
in an human Soul becomes an Attribute in God.
We
exist in Place and
Time, the Divine Being fills the Immensity of Space with his Presence,
and Inhabits Eternity.
We
are possessed of a little Power and a little
Knowledge, the Divine Being is Almighty and Omniscient. In short, by
adding Infinity to any kind of Perfection we enjoy, and by joyning all
these different kinds of Perfections in one Being, we form our Idea of
the great Sovereign of Nature.
Though every one who thinks must have made this Observation, I shall
Mr.
Locke's
Authority to the same purpose, out of his
Essay on
Human Understanding.
If we examine the Idea
we have of the incomprehensible Supreme
Being, we shall find, that we come by it the same way; and that the
complex Ideas
we have both of God and separate Spirits, are made up
of the simple Ideas
we receive from Reflection:
e. g. having from
what we experiment in our selves, got the Ideas
of Existence and
Duration, of Knowledge and Power, of Pleasure and Happiness, and of
several other Qualities and Powers, which it is better to have, than
to be without; when we would frame an Idea
the most suitable we can
to the Supreme Being, we enlarge every one of these with our Idea
of
Infinity; and so putting them together, make our Complex Idea of
God.
2
It is not impossible that there may be many kinds of Spiritual
Perfection, besides those which are lodged in an human Soul; but it is
impossible that we should have Ideas of any kinds of Perfection, except
those of which we have some small Rays and short imperfect Strokes in
our selves. It would be therefore a very high Presumption to determine
whether the Supream Being has not many more Attributes than those which
enter into our Conceptions of him. This is certain, that if there be any
kind of Spiritual Perfection which is not marked out in an human Soul,
it belongs in its Fulness to the Divine Nature.
Several eminent Philosophers have imagined that the Soul, in her
separate State, may have new Faculties springing up in her, which she is
not capable of exerting during her present Union with the Body; and
whether these Faculties may not correspond with other Attributes in the
Divine Nature, and open to us hereafter new Matter of Wonder and
Adoration, we are altogether ignorant.
, as I have said before, we
ought to acquiesce in, that the Sovereign Being, the great Author of
Nature, has in him all possible Perfection, as well in
Kind
as in
Degree
; to speak according to our Methods of
conceiving
. I shall
only add under this Head, that when we have raised our Notion of this
Infinite Being as high as it is possible for the Mind of Man to go, it
will fall infinitely short of what He really is.
There is no end of his
Greatness
: The most exalted Creature he has made, is only capable of
adoring it, none but himself can comprehend it.
The Advice of
Son of
Sir ach
is very just and sublime in this
Light.
By his Word all things consist. We may speak much, and yet come
short: wherefore in sum, he is all. How shall we be able to magnify
him? For he is great above all his Works. The Lord is terrible and
very great; and marvellous in his Power. When you glorify the Lord,
exalt him as much as you can; for even yet will he far exceed. And
when you exalt him, put forth all your strength, and be not weary; for
you can never go far enough. Who hath seen him, that he might tell us?
And who can magnify him as he is? There are yet hid greater things
than these be, for we have seen but a few of his Works.4
I have here only considered the Supreme Being by the Light of Reason and
Philosophy. If we would see him in all the Wonders of his Mercy we must
have recourse to Revelation, which represents him to us, not only as
infinitely Great and Glorious, but as infinitely Good and Just in his
Dispensations towards Man. But as this is a Theory which falls under
every one's Consideration, tho' indeed it can never be sufficiently
considered, I shall here only take notice of that habitual Worship and
Veneration which we ought to pay to this Almighty Being. We should often
refresh our Minds with the Thought of him, and annihilate our selves
before him, in the Contemplation of our own Worthlessness, and of his
transcendent Excellency and Perfection. This would imprint in our Minds
such a constant and uninterrupted Awe and Veneration as that which I am
here recommending, and which is in reality a kind of incessant Prayer,
and reasonable Humiliation of the Soul before him who made it.
This would effectually kill in us all the little Seeds of Pride, Vanity
and Self-conceit, which are apt to shoot up in the Minds of such whose
Thoughts turn more on those comparative Advantages which they enjoy over
some of their Fellow-Creatures, than on that infinite Distance which is
placed between them and the Supreme Model of all Perfection. It would
likewise quicken our De
Sir
es and Endeavours of uniting our selves to him
by all the Acts of Religion and Virtue.
Such an habitual Homage to the Supreme Being would, in a particular
manner, banish from among us that prevailing Impiety of using his Name
on the most trivial Occasions.
I find the following Passage in an excellent Sermon, preached at the
Funeral of
Gentleman who was an Honour to his Country, and a more
diligent as well as successful Enquirer into the Works of Nature, than
any other our Nation has ever produced
.
'He had the profoundest Veneration for the Great God of Heaven and
Earth that I have ever observed in any Person. The very Name of God
was never mentioned by him without a Pause and a visible Stop in his
Discourse; in which, one that knew him most particularly above twenty
Years, has told me, that he was so exact, that he does not remember to
have observed him once to fail in it.'
Every one knows the Veneration which was paid by the
Jews
to a Name so
great, wonderful and holy. They would not let it enter even into their
religious Discourses. What can we then think of those who make use of so
tremendous a Name in the ordinary Expressions of their Anger, Mirth, and
most impertinent Passions? Of those who admit it into the most familiar
Questions and Assertions, ludicrous Phrases and Works of Humour? not to
mention those who violate it by solemn Perjuries? It would be an Affront
to Reason to endeavour to set forth the Horror and Prophaneness of such
a Practice. The very mention of it exposes it sufficiently to those in
whom the Light of Nature, not to say Religion, is not utterly
extinguished.
O.
This story is taken from Book I. of Cicero
De Naturâ
Deorum.
Human Understanding
, Book II. ch. xxiii. § 33.
conceiving him.
Ecclus
. xliii. 26-32.
Bishop Burnet's sermon at the funeral of the Hon. Robert
Boyle (who died in 1691).
Contents
|
Monday, November 10, 1712 |
Steele |
—Fungor vice cotis, acutum
Reddere quæ ferrum valet, exsors ipsa secandi.
Hor.

It is a very honest Action to be studious to produce other Men's Merit;
and I make no scruple of saying I have as much of this Temper as any Man
in the World. It would not be a thing to be bragged of, but that it is
what any Man may be Master of who will take Pains enough for it. Much
Observation of the Unworthiness in being pained at the Excellence of
another, will bring you to a Scorn of yourself for that Unwillingness:
And when you have got so far, you will find it a greater Pleasure than
you ever before knew, to be zealous in promoting the Fame and Welfare of
the Praise-worthy. I do not speak this as pretending to be a mortified
self-denying Man, but as one who has turned his Ambition into a right
Channel. I
to my self the Merit of having extorted excellent
Productions from a Person of the greatest Abilities
, who would not
have let them appear by any other Means; to have animated a few young
Gentlemen into worthy Pursuits, who will be a Glory to our Age; and at
all Times, and by all possible Means in my Power, undermined the
Interests of Ignorance, Vice, and Folly, and attempted to substitute in
their Stead, Learning, Piety, and good Sense. It is from this honest
Heart that I find myself honoured as a Gentleman-Usher to the Arts and
Sciences. Mr.
Tickell
and Mr.
Pope
have, it seems, this Idea of me.
The former has writ me an excellent Paper of Verses in Praise, forsooth,
of my self; and
other enclosed for my perusal an admirable Poem
,
which, I hope, will shortly see the Light. In the mean time I cannot
suppress any Thought of his, but insert his Sentiment about the dying
Words of
Adrian
. I won't determine in the Case he mentions; but have
thus much to say in favour of his Argument, that many of his own Works
which I have seen, convince me that very pretty and very sublime
Sentiments may be lodged in the same Bosom without diminution to its
Greatness.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I was the other day in Company with five or six Men of some Learning;
where chancing to mention the famous Verses which the Emperor
Adrian
spoke on his Death-bed, they were all agreed that 'twas a Piece of
Gayety unworthy that Prince in those Circumstances. I could not but
dissent from this Opinion: Methinks it was by no means a gay, but a
very serious Soliloquy to his Soul at the Point of his Departure: in
which Sense I naturally took the Verses at my first reading them when
I was very young, and before I knew what Interpretation the World
generally put upon them:
'Animula vagula, blandula,
Hospes Comesque corporis,
Quæ nunc abibis in loca?
Pallidula, rigida, nudula,
Nec (ut soles) dabis Joca!
'Alas, my Soul! thou pleasing Companion of this Body, thou fleeting
thing that art now deserting it! whither art thou flying? to what
unknown Region? Thou art all trembling, fearful, and pensive. Now
what is become of thy former Wit and Humour? thou shall jest and be
gay no more.
'I confess I cannot apprehend where lies the Trifling in all this; 'tis
the most natural and obvious Reflection imaginable to a dying Man: and
if we consider the Emperor was a Heathen, that Doubt concerning the
Future Fate of his Soul will seem so far from being the Effect of Want
of Thought, that 'twas scarce reasonable he should think otherwise;
not to mention that here is a plain Confession included of his Belief
in its Immortality. The diminutive Epithets of
Vagula, Blandula, and
the rest, appear not to me as Expressions of Levity, but rather of
Endearment and Concern; such as we find in
Catullus, and the Authors
of
Hendeca-syllabi after him, where they are used to express the
utmost Love and Tenderness for their Mistresses—If
you think me right
in my Notion of the last Words of
Adrian, be pleased to insert this
in the
Spectator; if not, to suppress it.'
3
I am, &c.
To
the supposed Author of the
Spectator.
In Courts licentious, and a shameless Stage,
How long the War shall Wit with Virtue wage?
Enchanted by this prostituted Fair,
Our Youth run headlong in the fatal Snare;
In height of Rapture clasp unheeded Pains,
And suck Pollution thro' their tingling Veins.
Thy spotless Thoughts unshock'd the Priest may hear,
And the pure Vestal in her Bosom wear.
To conscious Blushes and diminish'd Pride,
Thy Glass betrays what treach'rous Love would hide;
Nor harsh thy Precepts, but infused by stealth,
Please while they cure, and cheat us into Health.
Thy Works in Chloe's
Toilet gain a part,
And with his Tailor share the the Fopling's Heart:
Lash'd in thy Satire, the penurious Cit
Laughs at himself, and finds no harm in Wit:
From Felon Gamesters the raw Squire is free,
And Britain
owes her rescu'd Oaks to thee.
His Miss the frolick Viscount dreads to toast,
Or his third Cure the shallow Templar boast;
And the rash Fool who scorn'd the beaten Road,
Dares quake at Thunder, and confess his God.
The brainless Stripling,—who, expell'd to Town,
Damn'd the stiff College and pedantick Gown,
Aw'd by thy Name, is dumb, and thrice a Week
Spells uncouth Latin,
and pretends to Greek.
A sauntring Tribe! such born to wide Estates,
With Yea and No in Senates hold Debates:
At length despis'd, each to his Fields retires,
First with the Dogs, and King amidst the Squires;
From Pert to Stupid sinks supinely down,
In Youth a Coxcomb, and in Age a Clown.
Such Readers scorned, thou wings't thy daring Flight
Above the Stars, and tread'st the Fields of Light;
Fame, Heav'n and Hell, are thy exalted Theme,
And Visions such as Jove
himself might dream;
Man sunk to Slav'ry, tho' to Glory born,
Heaven's Pride when upright, and depraved his Scorn.
Such Hints alone could British Virgil
lend,
And thou alone deserve from such a Friend:
A Debt so borrow'd, is illustrious Shame,
And Fame when shar'd with him is double Fame.
So flush'd with Sweets, by Beauty's Queen bestow'd,
With more than mortal Charms. Æneas
glow'd.
Such genrous Strifes Eugene
and Marlbro'
try,
And as in Glory, so in Friendship vie.
Permit these Lines by Thee to live—nor blame
A Muse that pants and languishes for Fame;
That fears to sink when humbler Themes she sings,
Lost in the Mass of mean forgotten things.
Receiv'd by Thee, I prophesy my Rhymes
The Praise of Virgins in succeeding Times:
Mix'd with thy Works, their Life no Bounds shall see,
But stand protected, as inspir'd by thee.
So some weak Shoot, which else would poorly rise,
Jove's
Tree adopts, and lifts him to the Skies;
Through the new Pupil fost'ring Juices flow,
Thrust forth the Gems, and give the Flow'rs to blow
Aloft; immortal reigns the Plant unknown,
With borrow'd Life, and Vigour not his own.4
To the Spectator-General.
Mr. John Sly
humbly sheweth,
'That upon reading the Deputation given to the said Mr.
John Sly,
all Persons passing by his Observatory behaved themselves with the
same Decorum, as if your Honour your self had been present.
That your said Officer is preparing, according to your Honour's secret
Instructions, Hats for the several kind of Heads that make Figures in
the Realms of
Great Britain, with Cocks significant of their Powers
and Faculties.
That your said Officer has taken due Notice of your Instructions and
Admonitions concerning the Internals of the Head from the outward Form
of the same. His Hats for Men of the Faculties of Law and Physick do
but just turn up, to give a little Life to their Sagacity; his
military Hats glare full in the Face; and he has prepared a familiar
easy Cock for all good Companions between the above-mentioned
Extreams. For this End he has consulted the most Learned of his
Acquaintance for the true Form and Dimensions of the
Lepidum Caput,
and made a Hat fit for it.
Your said Officer does further represent, That the young Divines about
Town are many of them got into the Cock Military, and de
Sir es your
Instructions therein.
That the Town has been for several Days very well behaved; and further
your said Officer saith not.
T.
Addison.
The Temple of Fame.
Pope republished this in his
Letters
in 1735, adding a
metrical translation of Adrian's lines:
Ah, fleeting spirit! wandering fire,
That long hast warm'd my tender breast,
Must thou no more this frame inspire?
No more a pleasing, cheerful guest?
Whither, ah, whither art thou flying,
To what dark, undiscovered shore?
Thou seem'st all trembling, shivering, dying,
And wit and humour are no more.
Two days after the insertion of this letter from Pope, Steele wrote to
the young poet (Nov. 12):
'I have read over your "Temple of Fame" twice; and cannot find
anything amiss of weight enough to call a fault, but see in it a
thousand thousand beauties. Mr. Addison shall see it to-morrow: after
his perusal of it I will let you know his thoughts. I deSir e you would
let me know whether you are at leisure or not? I have a design which I
shall open a month or two hence, with the assistance of a few like
yourself. If your thoughts are unengaged I shall explain myself
further.'
This design was the
Guardian
, which Steele was about to establish as
the successor to the
Spectator
; and here we find him at work on the
foundations of his new journal while the finishing strokes are being
given to the
Spectator
. Pope in his reply to Steele said (Nov. 16):
'I shall be very ready and glad to contribute to any design that tends
to the advantage of mankind, which, I am sure, all yours do. I wish I
had but as much capacity as leisure, for I am perfectly idle (a sign I
have not much capacity). If you will entertain the best opinion of me,
be pleased to think me your friend. Assure Mr. Addison of my most
faithful service; of every one's esteem he must be assured already.'
About a fortnight later, returning to the subject of Adrian's verses,
Pope wrote to Steele in reply to subsequent private discussion of the
subject (Nov. 29):
'I am sorry you published that notion about Adrian's verses as mine;
had I imagined you would use my name, I should have expressed my
sentiments with more modesty and diffidence. I only wrote to have your
opinion, and not to publish my own, which I distrusted.'
Then after defending his view of the poem, and commenting upon the Latin
diminutives, he adds,
'perhaps I should be much better pleased if I were told you called me
"your little friend," than if you complimented me with the title of "a
great genius," or "an eminent hand," as Jacob [Tonson] does all his
authors.'
Steele's genial reply produced from Pope, as final result of the above
letter to the
Spectator
, one of the most popular of his short pieces.
Steele wrote (Dec. 4):
'This is to deSir e of you that you would please to make an ode as of a
cheerful dying spirit; that is to say, the Emperor Adrian's "animula
vagula," put into two or three stanzas for music. If you will comply
with this, and send me word so, you will very particularly oblige
Richard Steele.'
This was written two days before the appearance of the last number of
his
Spectator
. Pope answered,
'I do not send you word I will do, but have already done the thing you
deSir e of me,'
and sent his poem of three stanzas, called
The Dying Christian To His
Soul.
Vital spark of heavenly flame, &c.
These two letters were published by Warburton, but are not given by Pope
in the edition of his correspondence, published in 1737, and the poem
has no place in the collected works of 1717. It has been said that if
the piece had been written in 1712 Steele would have inserted it in the
Spectator
. But it was not received until the last number of the
Spectator
had been published. Three months then elapsed before the
appearance of the
Guardian
, to which Pope contributed eight papers.
Pope, on his part, would be naturally unwilling to connect with the poem
the few words he had sent with it to Steele, saying,
'You have it (as Cowley calls it) just warm from the brain. It came to
me the first moment I waked this morning. Yet, you will see, it was
not so absolutely inspiration, but that I had in my head not only the
verses of Adrian, but the fine fragment of Sappho, &c.'
The &c. being short for Thomas Flatman, whose name would not have stood
well by that of Sappho, though he was an accomplished man in his day,
who gave up law for poetry and painting, and died in 1688, one of the
best miniature painters of his time, and the author of
Songs and
Poems,
published in 1674, which in ten years went through three
editions. Flatman had written:
When on my sick-bed I languish,
Full of sorrow, full of anguish,
Fainting, gasping, trembling, crying,
Panting, groaning, speechless, dying;
Methinks I hear some gentle spirit say,
"Be not fearful, come away!"
From Thomas Tickell.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 11, 1712 |
Steele |
Immo duas dabo, inquit ille, una si parum est:
Et si duarum pænitebit, addentur duæ.
Plaut.

To the SPECTATOR.
Sir ,
'You have often given us very excellent Discourses against that
unnatural Custom of Parents, in forcing their Children to marry
contrary to their Inclinations. My own Case, without further Preface,
I will lay before you, and leave you to judge of it. My Father and
Mother both being in declining Years, would fain see me, their eldest
Son, as they call it settled. I am as much for that as they can be;
but I must be settled, it seems, not according to my own, but their
liking. Upon this account I am teaz'd every Day, because I have not
yet fallen in love, in spite of Nature, with one of a neighbouring
Gentleman's Daughters; for out of their abundant Generosity, they give
me the choice of four.
Jack, begins my Father, Mrs.
Catherine is a
fine Woman—Yes,
Sir , but she is rather too old—She will make the
more discreet Manager, Boy. Then my Mother plays her part. Is not Mrs.
Betty exceeding fair? Yes, Madam, but she is of no Conversation; she
has no Fire, no agreeable Vivacity; she neither speaks nor looks with
Spirit. True, Son; but for those very Reasons, she will be an easy,
soft, obliging, tractable Creature. After all, cries an old Aunt, (who
belongs to the Class of those who read Plays with Spectacles on) what
think you, Nephew, of proper Mrs.
Dorothy? What do I think? why I
think she cannot be above six foot two inches high. Well, well, you
may banter as long as you please, but Height of Stature is commanding
and majestick. Come, come, says a Cousin of mine in the Family, I'll
fit him;
Fidelia is yet behind—Pretty Miss
Fiddy must please
you—Oh! your very humble Servant, dear Cos. she is as much too young
as her eldest Sister is too old. Is it so indeed, quoth she, good Mr.
Pert? You who are but barely turned of twenty two, and Miss Fiddy in
half a Year's time will be in her Teens, and she is capable of
learning any thing. Then she will be so observant; she'll cry perhaps
now and then, but never be angry. Thus they will think for me in this
matter, wherein I am more particularly concerned than any Body else.
If I name any Woman in the World, one of these Daughters has certainly
the same Qualities. You see by these few Hints,
Mr. SPECTATOR, what
a comfortable Life I lead. To be still more open and free with you, I
have been passionately fond of a young Lady (whom give me leave to
call
Miranda) now for these three Years. I have often urged the
Matter home to my Parents with all the Submission of a Son, but the
Impatience of a Lover. Pray,
Sir , think of three Years; what
inexpressible Scenes of Inquietude, what Variety of Misery must I have
gone thro' in three long whole Years?
Miranda's Fortune is equal to
those I have mention'd; but her Relations are not Intimates with mine.
Ah! there's the Rub.
Miranda's Person, Wit, and Humour, are what the
nicest Fancy could imagine; and though we know you to be so elegant a
Judge of Beauty, yet there is none among all your various Characters
of fine Women preferable to
Miranda. In a Word, she is never guilty
of doing any thing but one amiss, (if she can be thought to do amiss
by me) in being as blind to my Faults, as she is to her own
Perfections.
I am, Sir ,
Your very humble obedient Servant,
Dustererastus.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'When you spent so much time as you did lately in censuring the
ambitious young Gentlemen who ride in Triumph through Town and Country
in Coach-boxes, I wished you had employed those Moments in
consideration of what passes sometimes within-side of those Vehicles.
I am sure I suffered sufficiently by the Insolence and Ill-breeding of
some Persons who travelled lately with me in a Stage-Coach out of
Essex to
London. I am sure, when you have heard what I have to
say, you will think there are Persons under the Character of Gentlemen
that are fit to be no where else but in the Coach-box.
Sir , I am a
young Woman of a sober and religious Education, and have preserved
that Character; but on Monday was Fortnight it was my Misfortune to
come to
London. I was no sooner clapt in the Coach, but to my great
Surprize, two Persons in the Habit of Gentlemen attack'd me with such
indecent Discourse as I cannot repeat to you, so you may conclude not
fit for me to hear. I had no relief but the Hopes of a speedy End of
my short Journey.
Sir , form to your self what a Persecution this must
needs be to a virtuous and a chaste Mind; and in order to your proper
handling such a Subject, fancy your Wife or Daughter, if you had any,
in such Circumstances, and what Treatment you would think then due to
such Dragoons. One of them was called a Captain, and entertained us
with nothing but silly stupid Questions, or lewd Songs, all the way.
Ready to burst with Shame and Indignation, I repined that Nature had
not allowed us as easily to shut our Ears as our Eyes. But was not
this a kind of Rape? Why should there be Accessaries in Ravishment any
more than Murder? Why should not every Contributor to the Abuse of
Chastity suffer Death? I am sure these shameless Hell-hounds deserved
it highly. Can you exert your self better than on such an Occasion? If
you do not do it effectually, I 'll read no more of your Papers. Has
every impertinent Fellow a Privilege to torment me, who pay my
Coach-hire as well as he?
Sir , pray consider us in this respect as the
weakest Sex, and have nothing to defend our selves; and I think it as
Gentleman-like to challenge a Woman to fight, as to talk obscenely in
her Company, especially when she has not power to stir. Pray let me
tell you a Story which you can make fit for publick View. I knew a
Gentleman, who having a very good Opinion of the Gentlemen of the
Army, invited ten or twelve of them to sup with him; and at the same
time invited two or three Friends, who were very severe against the
Manners and Morals of Gentlemen of that Profession. It happened one of
them brought two Captains of his Regiment newly come into the Army,
who at first Onset engaged the Company with very lewd Healths and
suitable Discourse. You may easily imagine the Confusion of the
Entertainer, who finding some of his Friends very uneasy, de
Sir ed to
tell them a Story of a great Man, one Mr,
Locke (whom I find you
frequently mention) that being invited to dine with the then Lords
Hallifax, Anglesey, and
Shaftsbury; immediately after Dinner,
instead of Conversation, the Cards were called for, where the bad or
good Success produced the usual Passions of Gaming. Mr.
Locke
retiring to a Window, and writing, my Lord
Anglesey de
Sir ed to know
what he was writing:
Why, my Lords, answered he,
I could not sleep
last Night for the Pleasure and Improvement I expected from the
Conversation of the greatest Men of the Age. This so sensibly stung
them, that they gladly compounded to throw their Cards in the Fire if
he would his Paper, and so a Conversation ensued fit for such Persons.
This Story prest so hard upon the young Captains, together with the
Concurrence of their superior Officers, that the young Fellows left
the Company in Confusion.
Sir , I know you hate long things; but if you
like it, you may contract it, or how you will; but I think it has a
Moral in it.
But,
Sir , I am told you are a famous Mechanick as well as a Looker-on,
and therefore humbly propose you would invent some Padlock, with full
Power under your Hand and Seal, for all modest Persons, either Men or
Women, to clap upon the Mouths of all such impertinent impudent
Fellows: And I wish you would publish a Proclamation, that no modest
Person who has a Value for her Countenance, and consequently would not
be put out of it, presume to travel after such a Day without one of
them in their Pockets. I fancy a smart
Spectator upon this Subject
would serve for such a Padlock; and that publick Notice may be given
in your Paper where they may be had with Directions, Price 2
d. and
that part of the Directions may be, when any Person presumes to be
guilty of the above-mentioned Crime, the Party aggrieved may produce
it to his Face, with a Request to read it to the Company. He must be
very much hardened that could outface that Rebuke; and his further
Punishment I leave you to prescribe.
Your humble Servant,
Penance Cruel.
T.
To this number is appended the advertisement:
This Day is Published,
a very neat Pocket Edition of the 3rd and 4th Volumes of the
Spectator in 12∞. To which is added a compleat Index to the whole 4
volumes. Printed for S. Buckley at the Dolphin in Little Britain
and J. Tonson at Shakespear's Head over against Catherine Street in
the Strand.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 12, 1712 |
Steele |
—Rarus enim fermè sensus communis in illa
Fortunâ—
Juv.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am a young Woman of Nineteen, the only Daughter of very wealthy
Parents; and have my whole Life been used with a Tenderness which did
me no great Service in my Education. I have perhaps an uncommon De
Sir e
for Knowledge of what is suitable to my Sex and Quality; but as far as
I can remember, the whole Dispute about me has been, whether such a
thing was proper for the Child to do, or not? Or whether such or such
Food was the more wholsome for the young Lady to eat? This was ill for
my Shape, that for my Complexion, and t'other for my Eyes. I am not
extravagant when I tell you, I do not know that I have trod upon the
very Earth since I was ten Years old: A Coach or Chair I am obliged to
for all my Motions from one Place to another ever since I can
remember. All who had to do to instruct me, have ever been bringing
Stories of the notable things I have said and the Womanly manner of my
behaving my self upon such and such an Occasion. This has been my
State, till I came towards Years of Womanhood; and ever since I grew
towards the Age of Fifteen, I have been abused after another Manner.
Now, forsooth, I am so killing, no one can safely speak to me. Our
House is frequented by Men of Sense, and I love to ask Questions when
I fall into such Conversation; but I am cut short with something or
other about my bright Eyes. There is,
Sir , a Language particular for
talking to Women in; and none but those of the very first good
Breeding (who are very few, and who seldom come into my way) can speak
to us without regard to our Sex. Among the generality of those they
call Gentlemen, it is impossible for me to speak upon any subject
whatsoever, without provoking somebody to say,
Oh! to be sure fine
Mrs. such-a-one must be very particularly acquainted with all that;
all the World will contribute to her Entertainment and Information.
Thus,
Sir , I am so handsome, that I murder all who approach me; so
wise, that I want no new Notices; and so well bred, that I am treated
by all that know me like a Fool, for no one will answer as if I were
their Friend or Companion. Pray,
Sir , be pleased to take the part of
us Beauties and Fortunes into your Consideration, and do not let us be
thus flattered out of our Senses. I have got an Hussey of a Maid, who
is most craftily given to this ill Quality. I was at first diverted
with a certain Absurdity the Creature was guilty of in every thing she
said: She is a Country Girl, and in the Dialect of the Shire she was
born in, would tell me that every body reckon'd her Lady had the
purest Red and White in the World: Then she would tell me, I was the
most like one
Sisly Dobson in their Town, who made the Miller make
away with himself, and walk afterwards in the Corn-Field where they
used to meet. With all this, this cunning Hussey can lay Letters in my
way, and put a Billet in my Gloves, and then stand in it she knows
nothing of it. I do not know, from my Birth to this Day, that I have
been ever treated by any one as I ought; and if it were not for a few
Books which I delight in, I should be at this Hour a Novice to all
common Sense. Would it not be worth your while to lay down Rules for
Behaviour in this Case, and tell People, that we Fair-ones expect
honest plain Answers as well as other People? Why must I, good
Sir ,
because I have a good Air, a fine Complexion, and am in the Bloom of
my Years, be mis-led in all my Actions? and have the Notions of Good
and Ill confounded in my Mind, for no other Offence, but because I
have the Advantages of Beauty and Fortune? Indeed,
Sir , what with the
silly Homage which is paid to us by the sort of People I have above
spoken of, and the utter Negligence which others have for us, the
Conversation of us young Women of Condition is no other than what must
expose us to Ignorance and Vanity, if not Vice. All this is humbly
submitted to your Spectatorial Wisdom, by,
Sir , Your humble Servant,
Sharlot Wealthy.
Will's Coffee-house.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Pray,
Sir , it will serve to fill up a Paper, if you put in this;
which is only to ask, whether that Copy of Verses, which is a
Paraphrase of
Isaiah, in one of your Speculations, is not written by
Mr.
Pope? Then you get on another Line, by putting in, with proper
Distances, as at the end of a Letter,
I am, Sir ,
Your humble Servant,
Abraham Dapperwit.
Mr. Dapperwit,
I am glad to get another Line forward, by saying that excellent Piece is
Mr.
Pope's
; and so, with proper Distances,
I am, Sir ,
Your humble Servant
,
S—r.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I was a wealthy Grocer in the City, and as fortunate as diligent; but
I was a single Man, and you know there are Women. One in particular
came to my Shop, who I wished might, but was afraid never would, make
a Grocer's Wife. I thought, however, to take an effectual Way of
Courting, and sold to her at less Price than I bought, that I might
buy at less Price than I sold. She, you may be sure, often came, and
helped me to many Customers at the same Rate, fancying I was obliged
to her. You must needs think this was a good living Trade, and my
Riches must be vastly improved. In fine, I was nigh being declared
Bankrupt, when I declared my self her Lover, and she herself married.
I was just in a Condition to support my self, and am now in Hopes of
growing rich by losing my Customers.
Yours,
Jeremy Comfit.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I am in the Condition of the Idol you was once pleased to mention, and
Bar-keeper of a Coffee-house. I believe it is needless to tell you the
Opportunities I must give, and the Importunities I suffer. But there
is one Gentleman who besieges me as close as the French did
Bouchain. His Gravity makes him work cautious, and his regular
Approaches denote a good Engineer. You need not doubt of his Oratory,
as he is a Lawyer; and especially since he has had so little Use of it
at Westminster, he may spare the more for me.
What then can weak Woman do? I am willing to surrender, but he would
have it at Discretion, and I with Discretion. In the mean time, whilst
we parly, our several Interests are neglected. As his Siege grows
stronger, my Tea grows weaker; and while he pleads at my Bar, none
come to him for Counsel but in Forma Pauperis. Dear Mr. SPECTATOR,
advise him not to insist upon hard Articles, nor by his irregular
DeSir es contradict the well-meaning Lines of his Countenance. If we
were agreed we might settle to something, as soon as we could
determine where we should get most, by the Law, at the Coffee-house,
or at Westminster.
Your humble Servant,
Lucinda Parly.
A Minuit from Mr. John Sly.
The World is pretty regular for about forty Rod East, and ten West of
the Observatory of the said Mr. Sly; but he is credibly informed,
that when they are got beyond the Pass into the Strand, or those who
move City-ward are got within Temple-Bar, they are just as they were
before. It is there-fore humbly proposed that Moving-Centries may be
appointed all the busy Hours of the Day between the Exchange and
Westminster, and report what passes to your Honour, or your
subordinate Officers, from Time to Time.
Ordered
,
That Mr.
Sly
name the said Officers, provided he will answer for their
Principles and Morals.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 13, 1712 |
Addison |
Spem longam reseces—
Hor.

My
turned upon the Subject of
Hope in general. I design this Paper as a Speculation upon that vain and
foolish Hope, which is misemployed on Temporal Objects, and produces
many Sorrows and Calamities in human Life.
It is a Precept several times inculcated by
Horace
, that we should not
entertain an Hope of any thing in Life which lies at a great Distance
from us. The Shortness and Uncertainty of our Time here, makes such a
kind of Hope unreasonable and absurd. The Grave lies unseen between us
and the Object which we reach after: Where one Man lives to enjoy the
Good he has in view, ten thousand are cut off in the Pursuit of it.
It happens likewise unluckily, that one Hope no sooner dies in us but
another rises up in its stead. We are apt to fancy that we shall be
happy and satisfied if we possess ourselves of such and such particular
Enjoyments; but either by reason of their Emptiness, or the natural
Inquietude of the Mind, we have no sooner gained one Point but we extend
our Hopes to another. We still find new inviting Scenes and Landskips
lying behind those which at a Distance terminated our View.
The natural Consequences of such Reflections are these; that we should
take Care not to let our Hopes run out into too great a Length; that we
should sufficiently weigh the Objects of our Hope, whether they be such
as we may reasonably expect from them what we propose in their Fruition,
and whether they are such as we are pretty sure of attaining, in case
our Life extend itself so far. If we hope for things which are at too
great a Distance from, us, it is possible that we may be intercepted by
Death in our Progress towards them. If we hope for things of which we
have not thoroughly considered the value, our Disappointment will be
greater than our Pleasure in the Fruition of them. If we hope for what
we are not likely to possess, we act and think in vain, and make Life a
greater Dream and Shadow than it really is.
Many of the Miseries and Misfortunes of Life proceed from our Want of
Consideration, in one or all of these Particulars. They are the Rocks on
which the sanguine Tribe of Lovers daily split, and on which the
Bankrupt, the Politician, the Alchymist and Projector are cast away in
every Age. Men
warm Imaginations and towring Thoughts are apt to
overlook the Goods of Fortune
which are
near them, for something
that glitters in the Sight at a distance; to neglect solid and
substantial Happiness, for what is showy and superficial; and to contemn
that Good which lies within their reach, for that which they are not
capable of attaining. Hope calculates its Schemes for a long and durable
Life; presses forward to imaginary Points of Bliss; and grasps at
Impossibilities; and consequently very often ensnares Men into Beggary,
Ruin and Dishonour.
What I
here said, may serve as a Moral to an
Arabian
Fable, which
I find translated into
French
by Monsieur
Galland
.
The Fable has in it such a wild, but natural Simplicity, that I question
not but my Reader will be as much pleased with it as I have been, and
that he will consider himself, if he reflects on the several Amusements
of Hope which have sometimes passed in his Mind, as a near Relation to
the
Persian
Glass-Man.
Alnaschar, says the Fable, was a very idle Fellow, that never would
set his Hand to any Business during his Father's Life. When his Father
died, he left him to the value of an hundred Drachmas in Persian
Mony. Alnaschar, in order to make the best of it, laid it out in
Glasses, Bottles, and the finest Earthen Ware. These he piled up in a
large open Basket, and having made choice of a very little Shop,
placed the Basket at his Feet, and leaned his Back upon the Wall, in
Expectation of Customers. As he sat in this Posture with his Eyes upon
the Basket, he fell into a most amusing Train of Thought, and was
over-heard by one of his Neighbours, as he talked to himself in the
following manner: This Basket, says he, cost me at the Wholesale
Merchant's an Hundred Drachmas, which is all I have in the World. I
shall quickly make two hundred of it, by selling it in Retail. These
two hundred Drachmas will in a very little while rise to four
Hundred, which of course will amount in time to four Thousand. Four
Thousand Drachmas cannot fail of making Eight Thousand. As soon as by
this means I am Master of Ten Thousand, I will lay aside my Trade of a
Glass-Man, and turn Jeweller. I shall then deal in Diamonds, Pearls,
and all sorts of rich Stones. When I have got together as much Wealth
as I can well deSir e, I will make a Purchase of the finest House I can
find, with Lands, Slaves, Eunuchs and Horses. I shall then begin to
enjoy my self, and make a noise in the World. I will not, however,
stop there, but still continue my Traffick, till I have got together
an Hundred Thousand Drachmas. When I have thus made my self Master of
an hundred thousand Drachmas, I shall naturally set my self on the
foot of a Prince, and will demand the Grand Visier's Daughter in
Marriage, after having represented to that Minister the Information
which I have received of the Beauty, Wit, Discretion, and other high
Qualities which his Daughter possesses. I will let him know at the
same time, that it is my Intention to make him a Present of a thousand
Pieces of Gold on our Marriage-Night. As soon as I have married the
Grand Visier's Daughter, I'll buy her ten black Eunuchs, the
youngest and best that can be got for Mony. I must afterwards make my
Father-in-Law a Visit with a great Train and Equipage. And when I am
placed at his Right-hand, which he will do of course, if it be only to
Honour his Daughter, I will give him the thousand Pieces of Gold which
I promised him, and afterwards, to his great Surprize, will present
him another Purse of the same Value, with some short Speech; as, Sir ,
you see I am a Man of my Word: I always give more than I promise.
When I have brought the Princess to my House, I shall take particular
care to breed in her a due Respect for me, before I give the Reins to
Love and Dalliance. To this end I shall confine her to her own
Apartment, make her a short Visit, and talk but little to her. Her
Women will represent to me, that she is inconsolable by reason of my
Unkindness, and beg me with Tears to caress her, and let her sit down
by me; but I shall still remain inexorable, and will turn my Back upon
her all the first Night. Her Mother will then come and bring her
Daughter to me, as I am seated upon my Sofa. The Daughter, with Tears
in her Eyes, will fling herself at my Feet, and beg of me to receive
her into my Favour: Then will I, to imprint in her a thorough
Veneration for my Person, draw up my Legs and spurn her from me with
my Foot, in such a manner that she shall fall down several Paces from
the Sofa.
Alnaschar was entirely swallowed up in this Chimerical Vision, and
could not forbear acting with his Foot what he had in his Thoughts: So
that unluckily striking his Basket of brittle Ware, which was the
Foundation of all his Grandeur, he kicked his Glasses to a great
distance from him into the Street, and broke them into ten thousand
Pieces.
O.
that lie
Arabian Nights,
translated by Antony Galland, who died
1715.
Contents
|
Friday, November 14, 1712 |
Addison |
O veræ Phrygiæ neque enim Phryges!
Virg.

As I was the other day standing in my Bookseller's Shop, a pretty young
Thing about Eighteen Years of Age, stept out of her Coach, and brushing
by me, beck'ned the Man of the Shop to the further end of his Counter,
where she whispered something to him with an attentive Look, and at the
same time presented him with a Letter: After which, pressing the End of
her Fan upon his Hand, she delivered the remaining part of her Message,
and withdrew. I observed, in the midst of her Discourse, that she
flushed, and cast an Eye upon me over her Shoulder, having been informed
by my Bookseller, that I was the Man of the short Face, whom she had so
often read of. Upon her passing by me, the pretty blooming Creature
smiled in my Face, and dropped me a Curtsie. She scarce gave me time to
return her Salute, before she quitted the Shop with an easie Scuttle,
and stepped again into her Coach, giving the Footman Directions to drive
where they were bid. Upon her Departure, my Bookseller gave me a Letter,
superscribed,
To the ingenious Spectator
, which the young Lady had
de
Sir
ed him to deliver into my own Hands, and to tell me that the speedy
Publication of it would not only oblige her self, but a whole Tea-Table
of my Friends. I opened it therefore, with a Resolution to publish it,
whatever it should contain, and am sure, if any of my Male Readers will
be so severely critical as not to like it, they would have been as well
pleased with it as my self, had they seen the Face of the pretty Scribe.
London, Nov. 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You are always ready to receive any useful Hint or Proposal, and
such, I believe, you will think one that may put you in a way to
employ the most idle part of the Kingdom; I mean that part of Mankind
who are known by the Name of the Womens-Men or Beaus, &c. Mr.
SPECTATOR, you are sensible these pretty Gentlemen are not made for
any Manly Imployments, and for want of Business are often as much in
the Vapours as the Ladies. Now what I propose is this, that since
Knotting is again in fashion, which has been found a very pretty
Amusement, that you would recommend it to these Gentlemen as something
that may make them useful to the Ladies they admire. And since 'tis
not inconsistent with any Game, or other Diversion, for it may be done
in the Playhouse, in their Coaches, at the Tea-Table, and, in short,
in all Places where they come for the sake of the Ladies (except at
Church, be pleased to forbid it there, to prevent Mistakes) it will be
easily complied with. 'Tis beside an Imployment that allows, as we see
by the Fair Sex, of many Graces, which will make the Beaus more
readily come into it; it shews a white Hand and Diamond Ring to great
advantage; it leaves the Eyes at full liberty to be employed as
before, as also the Thoughts, and the Tongue. In short, it seems in
every respect so proper, that 'tis needless to urge it further, by
speaking of the Satisfaction these Male-Knotters will find, when they
see their Work mixed up in a Fringe, and worn by the fair Lady for
whom and with whom it was done. Truly, Mr. SPECTATOR, I cannot but
be pleased I have hit upon something that these Gentlemen are capable
of; for 'tis sad so considerable a part of the Kingdom (I mean for
Numbers) should be of no manner of use. I shall not trouble you
farther at this time, but only to say, that I am always your Reader,
and generally your Admirer, C. B.
P. S. 'The sooner these fine Gentlemen are set to Work the better;
there being at this time several fine Fringes that stay only for more
Hands.'
I shall, in the next place, present my Reader with the Description of a
Set of Men who are common enough in the World, tho' I do not remember
that I have yet taken notice of them, as they are drawn in the following
Letter.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Since you have lately, to so good purpose, enlarged upon Conjugal
Love, it's to be hoped you'll discourage every Practice that rather
proceeds from a regard to Interest, than to Happiness. Now you cannot
but observe, that most of our fine young Ladies readily fall in with
the Direction of the graver sort, to retain in their Service, by some
small Encouragement, as great a Number as they can of supernumerary
and insignificant Fellows, which they use like Whifflers, and commonly
call Shoeing-Horns. These are never designed to know the length of
the Foot, but only, when a good Offer comes, to whet and spur him up
to the Point. Nay, 'tis the Opinion of that grave Lady, Madam
Matchwell, that it's absolutely convenient for every prudent Family
to have several of these Implements about the House, to clap on as
Occasion serves, and that every Spark ought to produce a Certificate
of his being a Shoeing-Horn, before he be admitted as a Shoe. A
certain Lady, whom I could name, if it was necessary, has at present
more Shoeing-Horns of all Sizes, Countries, and Colours, in her
Service, than ever she had new Shoes in her Life. I have known a Woman
make use of a Shoeing-Horn for several Years, and finding him
unsuccessful in that Function, convert him at length into a Shoe. I am
mistaken if your Friend Mr. William Honeycomb, was not a cast
Shoeing-Horn before his late Marriage. As for my self, I must frankly
declare to you, that I have been an errant Shoeing-Horn for above
these twenty Years. I served my first Mistress in that Capacity above
five of the Number, before she was shod. I confess, though she had
many who made their Applications to her, I always thought my self the
best Shoe in her Shop, and it was not till a Month before her Marriage
that I discovered what I was. This had like to have broke my Heart,
and raised such Suspicions in me, that I told the next I made Love to,
upon receiving some unkind Usage from her, that I began to look upon
my self as no more than her Shoeing-Horn. Upon which, my Dear, who was
a Coquet in her Nature, told me I was Hypocondriacal, and that I might
as well look upon my self to be an Egg or a Pipkin. But in a very
short time after she gave me to know that I was not mistaken in my
self. It would be tedious to recount to you the Life of an unfortunate
Shoeing-Horn, or I might entertain you with a very long and melancholy
Relation of my Sufferings. Upon the whole, I think, Sir , it would very
well become a Man in your Post, to determine in what Cases a Woman may
be allowed, with Honour, to make use of a Shoeing-Horn, as also to
declare whether a Maid on this side Five and Twenty, or a Widow who
has not been three Years in that State, may be granted such a
Privilege, with other Difficulties which will naturally occur to you
upon that Subject.
I am, Sir ,
With the most profound Veneration,
Yours, &c.
O.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 15, 1712 |
J. Hughes |

To the SPECTATOR.
Sir ,
'It has been usual to remind Persons of Rank, on great Occasions in
Life, of their Race and Quality, and to what Expectations they were
born; that by considering what is worthy of them, they may be
withdrawn from mean Pursuits, and encouraged to laudable Undertakings.
This is turning Nobility into a Principle of Virtue, and making it
productive of Merit, as it is understood to have been originally a
Reward of it.
'It is for the like reason, I imagine, that you have in some of your
Speculations asserted to your Readers the
Dignity of Human Nature.
But you cannot be insensible that this is a controverted Doctrine;
there are Authors who consider Human Nature in a very different View,
and Books of Maxims have been written to shew the
Falsity of all
Human Virtues. The Reflections which are made on this Subject usually
take some Tincture from the Tempers and Characters of those that make
them. Politicians can resolve the most shining Actions among Men into
Artifice and Design; others, who are soured by Discontent, Repulses,
or ill Usage, are apt to mistake their Spleen for Philosophy; Men of
profligate Lives, and such as find themselves incapable of rising to
any Distinction among their Fellow-Creatures, are for pulling down all
Appearances of Merit, which seem to upbraid them: and Satirists
describe nothing but Deformity. From all these Hands we have such
Draughts of Mankind as are represented in those burlesque Pictures,
which the
Italians call
Caracatura's; where the Art consists in
preserving, amidst distorted Proportions and aggravated Features, some
distinguishing Likeness of the Person, but in such a manner as to
transform the most agreeable Beauty into the most odious Monster.
'It is very disingenuous to level the best of Mankind with the worst,
and for the Faults of Particulars to degrade the whole Species. Such
Methods tend not only to remove a Man's good Opinion of others, but to
destroy that Reverence for himself, which is a great Guard of
Innocence, and a Spring of Virtue.
'It is true indeed that there are surprizing Mixtures of Beauty and
Deformity, of Wisdom and Folly, Virtue and Vice, in the Human Make;
such a Disparity is found among Numbers of the same Kind, and every
Individual, in some Instances, or at some Times, is so unequal to
himself, that
Man seems to be the most wavering and inconsistent
Being in the whole Creation. So that the Question in Morality,
concerning the Dignity of our Nature, may at first sight appear like
some difficult Questions in Natural Philosophy, in which the Arguments
on both Sides seem to be of equal Strength. But as I began with
considering this Point as it relates to Action, I
shall here borrow an
admirable Reflection from Monsieur
Pascal, which I think sets it in
its proper Light.
'
It is of dangerous Consequence, says he,
to represent to Man how
near he is to the Level of Beasts, without shewing him at the same
time his Greatness.
It is likewise dangerous to let him see his
Greatness, without his Meanness.
It is more dangerous yet to leave
him ignorant of either; but very beneficial that he should be made
sensible of both.1
Whatever Imperfections we may have in our Nature, it is the Business
of Religion and Virtue to rectify them, as far as is consistent with
our present State. In the mean time, it is no small Encouragement to
generous Minds to consider that we shall put them all off with our
Mortality. That sublime Manner of Salutation with which the
Jews
approached their Kings,
O King, live for ever!
may be addressed to the lowest and most despised Mortal among us,
under all the Infirmities and Distresses with which we see him
surrounded. And whoever believes the
Immortality of the Soul, will
not need a better Argument for the Dignity of his Nature, nor a
stronger Incitement to Actions suitable to it.
'I am naturally led by this Reflection to a Subject I have already
touched upon in a former Letter, and cannot without pleasure call to
mind the Thoughts of
Cicero to this purpose, in the close of his
Book concerning
Old Age. Every one who is acquainted with his
Writings, will remember that the elder
Cato is introduced in that
Discourse as the Speaker, and
Scipio and
Lelius as his Auditors.
This venerable Person is represented looking forward as it were from
the Verge of extreme Old Age, into a future State, and rising into a
Contemplation on the unperishable Part of his Nature, and its
Existence after Death. I shall collect Part of his Discourse. And as
you have formerly offered some Arguments for the Soul's Immortality,
agreeable both to Reason and the Christian Doctrine, I believe your
Readers will not be displeased to see how the same great Truth shines
in the Pomp of
Roman Eloquence.
"This, says
Cato, my firm Persuasion, that since the human Soul
exerts it self with so great Activity, since it has such a
Remembrance of the Past, such a Concern for the Future, since it is
enriched with so many Arts, Sciences and Discoveries, it is
impossible but the Being which contains all these must be Immortal.
"The
elder Cyrus, just before his Death, is represented by
Xenophon speaking after this Manner."
'
Think not, my dearest Children, that when I depart from you I
shall be no more, but remember, that my Soul, even while I lived
among you, was invisible to you; yet by my Actions you were
sensible it existed in this Body. Believe it therefore existing
still, though it be still unseen. How quickly would the Honours of
illustrious Men perish after Death, if their Souls performed
nothing to preserve their Fame? For my own part, I never could
think that the Soul while in a mortal Body, lives, but when
departed out of it, dies; or that its Consciousness is lost when
it is discharged out of an unconscious Habitation. But when it is
freed from all corporeal Alliance, then it truly exists. Further,
since the Human Frame is broken by Death, tell us what becomes of
its Parts? It is visible whither the Materials of other Beings are
translated, namely to the Source from whence they had their Birth.
The Soul alone, neither present nor departed, is the Object of our
Eyes.'
2
"Thus
Cyrus. But to proceed. No one shall persuade me,
Scipio,
that your worthy Father, or your Grandfathers
Paulus and
Africanus, or
Africanus his Father, or Uncle, or many other
excellent Men whom I need not name, performed so many Actions to be
remembered by Posterity, without being sensible that Futurity was
their Right. And, if I may be allowed an old Man's Privilege, to
speak of my self, do you think I would have endured the Fatigue of
so many wearisome Days and Nights both at home and abroad, if I
imagined that the same Boundary which is set to my Life must
terminate my Glory? Were it not more de
Sir able to have worn out my
days in Ease and Tranquility, free from Labour, and without
Emulation? But I know not how, my Soul has always raised it self,
and looked forward on Futurity, in this View and Expectation, that
when it shall depart out of Life, it shall then live for ever; and
if this were not true, that the Mind is immortal, the Souls of the
most worthy would not, above all others, have the strongest Impulse
to Glory.
"What besides this is the Cause that the wisest Men die with the
greatest Æquanimity, the ignorant with the greatest Concern? Does it
not seem that those Minds which have the most extensive Views,
foresee they are removing to a happier Condition, which those of a
narrower Sight do not perceive? I, for my part, am transported with
the Hope of seeing your Ancestors, whom I have honoured and loved,
and am earnestly de
Sir ous of meeting not only those excellent
Persons whom I have known, but those too of whom I have heard and
read, and of whom I myself have written: nor would I be detained
from so pleasing a Journey. O happy Day, when I shall escape from
this Croud, this Heap of Pollution, and be admitted to that Divine
Assembly of exalted Spirits! When I shall go not only to those great
Persons I have named, but to my
Cato, my Son, than whom a better
Man was never born, and whose Funeral Rites I my self performed,
whereas he ought rather to have attended mine. Yet has not his Soul
deserted me, but, seeming to cast back a Look on me, is gone before
to those Habitations to which it was sensible I should follow him.
And though I might appear to have born my Loss with Courage, I was
not unaffected with it, but I comforted myself in the Assurance that
it would not be long before we should meet again, and be divorced no
more.
I am, Sir , &c."'
I question not but my Reader will be very much pleased to hear, that
the Gentleman who has obliged the World with the foregoing Letter, and
who was the Author of the [Volume 2 link: 210th] Speculation on the Immortality of the
Soul, the [Volume 2 link: 375th on Virtue in Distress, the 525th on Conjugal Love, and
two or three other very fine ones among those which are not lettered at
the end, will soon publish a noble Poem, Intitled An Ode to the Creator
of the World,
occasioned by the Fragments of
Orpheus.
Pensées
. Part I. Art. iv. 7.
Cyropædia
, Book viii.
Contents
|
Monday, November 17, 1712 |
Addison |
—Ultra
Finem tendere opus.
Hor.

Surprize is so much the Life of Stories, that every one aims at it, who
endeavours to please by telling them. Smooth Delivery, an elegant Choice
of Words, and a sweet Arrangement, are all beautifying
Graces
, but not
the particulars in this Point of Conversation which either long command
the Attention, or strike with the Violence of a sudden Passion, or
occasion the burst of Laughter which accompanies Humour. I have
sometimes fancied that the Mind is in this case like a Traveller who
sees a fine Seat in Haste; he acknowledges the Delightfulness of a Walk
set with Regularity, but would be uneasy if he were obliged to pass it
over, when the first View had let him into all its Beauties from one End
to the other.
However, a knowledge of the Success which Stories will have when they
are attended with a Turn of Surprize, as it has happily made the
Characters of some, so has it also been the Ruin of the Characters of
others. There is a Set of Men who outrage Truth, instead of affecting us
with a Manner in telling it; who over-leap the Line of Probability, that
they may be seen to move out of the common Road; and endeavour only to
make their Hearers stare, by imposing upon them with a kind of Nonsense
against the Philosophy of Nature, or such a Heap of Wonders told upon
their own Knowledge, as it is not likely one Man should ever have met
with.
I have been led to this Observation by a Company into which I fell
accidentally. The Subject of
Antipathies
was a proper Field wherein
such false Surprizes might expatiate, and there were those present who
appeared very fond to shew it in its full Extent of traditional History.
Some of them, in a learned manner, offered to our Consideration the
miraculous Powers which the Effluviums of Cheese have over Bodies whose
Pores are dispos'd to receive them in a noxious manner; others gave an
account of such who could indeed bear the sight of Cheese, but not the
Taste; for which they brought a Reason from the Milk of their Nurses.
Others again discours'd, without endeavouring at Reasons, concerning an
unconquerable Aversion which some Stomachs have against a Joint of Meat
when it is whole, and the eager Inclination they have for it, when, by
its being cut up, the Shape which had affected them is altered. From
hence they passed to Eels, then to Parsnips, and so from one Aversion to
another, till we had work'd up our selves to such a pitch of
Complaisance, that when the Dinner was to come in, we enquired the name
of every Dish, and hop'd it would be no Offence to any in Company,
before it was admitted. When we had sat down, this Civility amongst us
turned the Discourse from Eatables to other sorts of Aversions; and the
eternal Cat, which plagues every Conversation of this nature, began then
to engross the Subject. One had sweated at the Sight of it, another had
smelled it out as it lay concealed in a very distant Cupboard; and he
who crowned the whole set of these Stories, reckon'd up the Number of
Times in which it had occasion'd him to swoon away. At last, says he,
that you may all be satisfy'd of my invincible Aversion to a Cat, I
shall give an unanswerable Instance: As I was going through a Street of
London
, where I had never been till then, I felt a general Damp and
Faintness all over me, which I could not tell how to account for, till I
chanced to cast my Eyes upwards, and found that I was passing under a
Sign-Post on which the Picture of a Cat was hung.
The Extravagance of this Turn in the way of Surprize, gave a stop to the
Talk we had been carrying on: Some were silent because they doubted, and
others because they were conquered in their own Way; so that the
Gentleman had Opportunity to press the Belief of it upon us, and let us
see that he was rather exposing himself than ridiculing others.
I must freely own that I did not all this while disbelieve every thing
that was said; but yet I thought some in the Company had been
endeavouring who should pitch the Bar farthest; that it had for some
time been a measuring Cast, and at last my Friend of the Cat and
Sign-post had thrown beyond them all.
I then consider'd the Manner in which this Story had been received, and
the Possibility that it might have pass'd for a Jest upon others, if he
had not labour'd against himself. From hence, thought I, there are two
Ways which the well-bred World generally takes to correct such a
Practice, when they do not think fit to contradict it flatly.
The first of these is a general Silence, which I would not advise any
one to interpret in his own behalf. It is often the Effect of Prudence
in avoiding a Quarrel, when they see another drive so fast, that there
is no stopping him without being run against; and but very seldom the
Effect of Weakness in believing suddenly. The generality of Mankind are
not so grossly ignorant, as some over-bearing Spirits would persuade
themselves; and if the Authority of a Character or a Caution against
Danger make us suppress our Opinions, yet neither of these are of force
enough to suppress our Thoughts of them. If a Man who has endeavoured to
amuse his Company with Improbabilities could but look into their Minds,
he would find that they imagine he lightly esteems of their Sense when
he thinks to impose upon them, and that he is less esteemed by them for
his Attempt in doing so. His endeavour to glory at their Expence becomes
a Ground of Quarrel, and the Scorn and Indifference with which they
entertain it begins the immediate Punishment: And indeed (if we should
even go no further) Silence, or a negligent Indifference has a deeper
way of wounding than Opposition; because Opposition proceeds from an
Anger that has a sort of generous Sentiment for the Adversary mingling
along with it, while it shews that there is some Esteem in your Mind for
him; in short, that you think him worth while to contest with: But
Silence, or a negligent Indifference, proceeds from Anger, mixed with a
Scorn that shews another he is thought by you too contemptible to be
regarded.
The other Method which the World has taken for correcting this Practice
of false Surprize, is to over-shoot such Talkers in their own Bow, or to
raise the Story with further Degrees of Impossibility, and set up for a
Voucher to them in such a manner as must let them see they stand
detected. Thus I have heard a Discourse was once managed upon the
Effects of Fear. One of the Company had given an account how it had
turn'd his Friend's Hair grey in a Night, while the Terrors of a
Shipwrack encompassed him. Another taking the Hint from hence, began,
upon his own Knowledge, to enlarge his Instances of the like nature to
such a Number, that it was not probable he could ever have met with
them; and as he still grounded these upon different Causes, for the sake
of Variety, it might seem at last, from his Share of the Conversation,
almost impossible that any one who can feel the Passion of Fear should
all his Life escape so common an Effect of it. By this time some of the
Company grew negligent, or de
Sir
ous to contradict him: But one rebuked
the rest with an appearance of Severity, and with the known old Story in
his Head, assured them they need not scruple to believe that the Fear of
any thing can make a Man's Hair grey, since he knew one whose Perriwig
had suffered so by it. Thus he stopped the Talk, and made them easy.
Thus is the same Method taken to bring us to Shame, which we fondly take
to increase our Character. It is indeed a kind of Mimickry, by which
another puts on our Air of Conversation to show us to our selves: He
seems to look ridiculous before you, that you may remember how near a
Resemblance you bear to him, or that you may know he will not lie under
the Imputation of believing you. Then it is that you are struck dumb
immediately with a conscientious Shame for what you have been saying,
Then it is that you are inwardly grieved at the Sentiments which you
cannot but perceive others entertain concerning you. In short, you are
against your self; the Laugh of the Company runs against you; the
censuring World is obliged to you for that Triumph which you have
allowed them at your own Expence; and Truth, which you have injured, has
a near way of being revenged on you,
by the bare Repetition of your
Story you become a frequent Diversion for the
Publick
.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The other Day, walking in
Pancras Churchyard, I thought of your
Paper wherein you mention Epitaphs, and am of opinion this has a
Thought in it worth being communicated to your Readers.
Here Innocence and Beauty lies, whose Breath
Was snatch'd by early, not untimely Death.
Hence did she go, just as she did begin
Sorrow to know, before she knew to sin.
Death, that does Sin and Sorrow thus prevent,
Is the next Blessing to a Life well spent.
I am, Sir , Your Servant.
Publick. I am, Sir , your Servant.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 18, 1712 |
Budgell |
Heteroclyta sunto.—Quæ Genus.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am a young Widow of a good Fortune and Family, and just come to
Town; where I find I have Clusters of pretty Fellows come already to
visit me, some dying with Hopes, others with Fears, tho' they never
saw me. Now what I would beg of you, would be to know whether I may
venture to use these pert Fellows with the same Freedom as I did my
Country Acquaintance. I de
Sir e your Leave to use them as to me shall
seem meet, without Imputation of a Jilt; for since I make Declaration
that not one of them shall have me, I think I ought to be allowed the
Liberty of insulting those who have the Vanity to believe it is in
their power to make me break that Resolution. There are Schools for
learning to use Foils, frequented by those who never design to fight;
and this useless way of aiming at the Heart, without design to wound
it on either side, is the Play with which I am resolved to divert my
self: The Man who pretends to win, I shall use like him who comes into
a Fencing-School to pick a Quarrel. I hope, upon this Foundation, you
will give me the free use of the natural and artificial Force of my
Eyes, Looks, and Gestures. As for verbal Promises, I will make none,
but shall have no mercy on the conceited Interpreters of Glances and
Motions. I am particularly skill'd in the downcast Eye, and the
Recovery into a sudden full Aspect, and away again, as you may have
seen sometimes practised by us Country Beauties beyond all that you
have observed in Courts and Cities. Add to this,
Sir , that I have a
ruddy heedless Look, which covers Artifice the best of any thing. Tho'
I can dance very well, I affect a tottering untaught way of walking,
by which I appear an easy Prey and never exert my instructed Charms
till I find I have engaged a Pursuer. Be pleased,
Sir , to print this
Letter; which will certainly begin the Chace of a rich Widow: The many
Foldings, Escapes, Returns and Doublings which I make, I shall from
time to time communicate to you, for the better Instruction of all
Females who set up, like me, for reducing the present exorbitant Power
and Insolence of Man.'
I am, Sir ,
Your faithful Correspondent,
Relicta Lovely.
Dear Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I depend upon your profess'd Respect for virtuous Love, for your
immediate answering the Design of this Letter; which is no other than
to lay before the World the Severity of certain Parents who de
Sir e to
suspend the Marriage of a discreet young Woman of eighteen, three
Years longer, for no other reason but that of her being too young to
enter into that State. As to the consideration of Riches, my
Circumstances are such, that I cannot be suspected to make my
Addresses to her on such low Motives as Avarice or Ambition. If ever
Innocence, Wit and Beauty, united their utmost Charms, they have in
her. I wish you would expatiate a little on this Subject, and admonish
her Parents that it may be from the very Imperfection of Human Nature
it self, and not any personal Frailty of her or me, that our
Inclinations baffled at present may alter; and while we are arguing
with our selves to put off the Enjoyment of our present Passions, our
Affections may change their Objects in the Operation. It is a very
delicate Subject to talk upon; but if it were but hinted, I am in
hopes it would give the Parties concern'd some Reflection that might
expedite our Happiness. There is a Possibility, and I hope I may say
it without Imputation of Immodesty to her I love with the highest
Honour; I say, there is a Possibility this Delay may be as painful to
her as it is to me. If it be as much, it must be more, by reason of
the severe Rules the Sex are under in being denied even the Relief of
Complaint. If you oblige me in this, and I succeed, I promise you a
Place at my Wedding, and a Treatment suitable to your Spectatorial
Dignity.'
Your most humble Servant,
Eustace.
Sir ,
'I Yesterday heard a young Gentleman, that look'd as if he was just
come to the Town, and a Scarf, upon Evil-speaking; which Subject, you
know, Archbishop
Tillotson has so nobly handled in a Sermon in his
Folio. As soon as ever he had named his Text, and had opened a
little the Drift of his Discourse, I was in great hopes he had been
one of
Sir ROGER'S Chaplains. I have conceived so great an Idea of the
charming Discourse above, that I should have thought one part of my
Sabbath very well spent in hearing a Repetition of it. But alas! Mr.
SPECTATOR, this Reverend Divine gave us his Grace's Sermon, and yet I
don't know how; even I, that I am sure have read it at least twenty
times, could not tell what to make of it, and was at a loss sometimes
to guess what the Man aim'd at. He was so just indeed, as to give us
all the Heads and the Sub-divisions of the Sermon; and farther I think
there was not one beautiful Thought in it but what we had. But then,
Sir , this Gentleman made so many pretty Additions; and he could never
give us a Paragraph of the Sermon, but he introduced it with something
which, methought, look'd more like a Design to shew his own Ingenuity,
than to instruct the People. In short, he added and curtailed in such
a manner that he vexed me; insomuch that I could not forbear thinking
(what, I confess, I ought not to have thought of in so holy a Place)
that this young Spark was as justly blameable as
Bullock or
Penkethman when they mend a noble Play of
Shakespear or
Johnson.
Pray,
Sir , take this into your Consideration; and if we must be
entertained with the Works of any of those great Men, de
Sir e these
Gentlemen to give them us as they find them, that so, when we read
them to our Families at home, they may the better remember they have
heard them at Church.'
Sir ,
Your humble Servant.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 19, 1712 |
Steele |
—Non Deficit Alter—
Virg.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'There is no Part of your Writings which I have in more Esteem than
your Criticism upon
Milton. It is an honourable and candid Endeavour
to set the Works of our Noble Writers in the graceful Light which they
deserve. You will lose much of my kind Inclination towards you, if you
do not attempt the Encomium of
Spencer also, or at least indulge my
Passion for that charming Author so far as to print the loose Hints I
now give you on that Subject.
'Spencer's general Plan is the Representation of six Virtues,
Holiness, Temperance, Chastity, Friendship, Justice and Courtesy, in
six Legends by six Persons. The six Personages are supposed under
proper Allegories suitable to their respective Characters, to do all
that is necessary for the full Manifestation of the respective Virtues
which they are to exert.
'These one might undertake to shew under the several Heads, are
admirably drawn; no Images improper, and most surprizingly beautiful.
The Red-cross Knight runs through the whole Steps of the Christian
Life;
Guyon does all that Temperance can possibly require;
Britomartis (a Woman) observes the true Rules of unaffected
Chastity;
Arthegal is in every Respect of Life strictly and wisely
just;
Calidore is rightly courteous.
'In short, in
Fairy-Land, where Knights Errant have a full Scope to
range, and to do even what
Ariosto's or
Orlando's could not do in
the World without breaking into Credibility,
Spencer's Knights have,
under those six Heads, given a full and a truly Poetical System of
Christian, Public, and Low Life.
'His Legend of Friendship is more diffuse, and yet even there the
Allegory is finely drawn, only the Heads various, one Knight could not
there support all the Parts.
'To do honour to his Country, Prince
Arthur is an Universal Hero; in
Holiness, Temperance, Chastity, and Justice super-excellent. For the
same Reason, and to compliment Queen
Elizabeth,
Gloriana, Queen of
Fairies, whose Court was the Asylum of the Oppressed, represents that
Glorious Queen. At her Commands all these Knights set forth, and only
at her's the Red-cross Knight destroys the Dragon.
Guyon overturns
the Bower of Bliss,
Arthegal (i. e.
Justice) beats down
Geryoneo
(i. e.
Phil. II. King of
Spain) to rescue
Belge (i. e.
Holland) and he beats the
Grantorto (the same
Philip in another
Light) to restore
Irena (i. e.
Peace to Europe.)
'Chastity being the first Female Virtue,
Britomartis is a
Britain;
her Part is fine, though it requires Explication. His stile is very
Poetical; no Puns, Affectations of Wit, forced Antitheses, or any of
that low Tribe.
'His old Words are all true
English, and numbers exquisite; and
since of Words there is the
Multa Renascentur, since they are all
proper, such a Poem should not (any more than
Milton's) subsist all
of it of common ordinary Words. See Instances of Descriptions.
'Causeless Jealousy in
Britomartis, V. 6, 14, in its Restlessness.
Like as a wayward Child whose sounder Sleep
Is broken with some fearful Dream's Affright,
With froward Will doth set himself to weep,
Ne can be stil'd for all his Nurse's Might,
But kicks, and squalls, and shrieks for fell Despight;
Now scratching her, and her loose Locks misusing,
Now seeking Darkness, and now seeking Light;
Then craving Suck, and then the Suck refusing:
Such was this Lady's Loves in her Love's fond accusing.
Curiosity occasioned by Jealousy, upon occasion of her Lover's
Absence.
Ibid, Stan. 8, 9.
Then as she looked long, at last she spy'd
One coming towards her with hasty Speed,
Well ween'd she then, e'er him she plain descry'd,
That it was one sent from her Love indeed;
Whereat her Heart was fill'd with Hope and Dread,
Ne would she stay till he in Place could come,
But ran to weet him forth to know his Tidings somme;
Even in the Door him meeting, she begun,
And where is he, thy Lord, and how far hence?
Declare at once; and hath he lost or won?
Care and his
House are described thus, IV. 6, 33, 34, 35.
|
Not far away, not meet for any Guest,
They spy'd a little Cottage, like some poor Man's Nest. |
| 34 |
There entring in, they found the Good-Man's self,
Full busily unto his Work ybent,
Who was so weel a wretched wearish Elf,
With hollow Eyes and raw-bone Cheeks forspent,
As if he had in Prison long been pent.
Full black and griesly did his Face appear,
Besmear'd with Smoke that nigh his Eye-sight blent,
With rugged Beard and Hoary shaggy Heare,
The which he never wont to comb, or comely shear. |
| 35 |
Rude was his Garment and to Rags all rent,
Ne better had he, ne for better cared;
His blistred Hands amongst the Cinders brent,
And Fingers filthy, with long Nails prepared,
Right fit to rend the Food on which he fared.
His Name was Care; a Blacksmith by his Trade,
That neither Day nor Night from working spared,
But to small purpose Iron Wedges made:
These be unquiet Thoughts that careful Minds invade. |
'Homer's Epithets were much admired by Antiquity: See what great
Justness and Variety there is in these Epithets of the Trees in the
Forest where the Red-cross Knight lost
Truth, B. I. Cant. i. St. 8,
9.
The sailing Pine, the Cedar proud and tall,
The Vine-prop Elm, the Poplar never dry,
The Builder Oak, sole King of Forests all.
The Aspine good for Staves, the Cypress Funeral.
The Laurel, Meed of mighty Conquerors,
And Poets sage; the Fir that weepeth still,
The Willow worn of forlorn Paramours,
The Yew obedient to the Bender's Will.
The Birch for Shafts, the Sallow for the Mill;
The Myrrhe sweet bleeding in the bitter Wound,
The warlike Beech, the Ash for nothing ill,
The fruitful Olive, and the Plantane round,
The Carver Helm, the Maple seldom inward sound.
'I shall trouble you no more, but de
Sir e you to let me conclude with
these Verses, though I think they have already been quoted by you;
They are Directions to young Ladies opprest with Calumny. VI. 6, 14.
The best (said he) that I can you advise,
Is to avoid the Occasion of the Ill;
For when the Cause whence Evil doth arise
Removed is, the Effect surceaseth still.
Abstain from Pleasure, and restrain your Will,
Subdue DeSir e, and bridle loose Delight,
Use scanted Diet, and forbear your Fill,
Shun Secrecy, and talk in open Sight;
So shall you soon repair your present evil Plight.
T.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 20, 1712 |
John Hughes |
Format enim Natura prius nos intus ad omnem
Fortunarum habitum; juvat, aut impellit ad iram,
Aut ad humum mærore gravi deducit et angit;
Post effert animi motus interprete Lingua.
Hor.

My Friend the
Templar
, whom I have so often mentioned in these
Writings, having determined to lay aside his Poetical Studies, in order
to a closer Pursuit of the Law,
put together, as a Farewell Essay,
some Thoughts concerning
Pronunciation and Action,
which he has
given me leave to communicate to the Publick. They are chiefly collected
from his Favourite Author,
Cicero
, who is known to have been an
intimate Friend of
Rostius
the Actor,
a good Judge of
Dramatick
Performances, as well as the most Eloquent Pleader of the Time in
which he lived.
Cicero concludes his celebrated Books
de Oratore
with some Precepts
for Pronunciation and Action, without which Part he affirms that the
best Orator in the World can never succeed; and an indifferent one, who
is Master of this, shall gain much greater Applause. What could make a
stronger Impression, says he, than those Exclamations of
Gracchus
:
Whither shall I turn? Wretch that I am! To what Place betake my self?
Shall I go to the Capitol?—Alas! it is overflowed with my Brother's
Blood. Or shall I retire to my House? Yet there I behold my Mother
plung'd in Misery, weeping and despairing!
These Breaks and Turns of Passion, it seems, were so enforced by the
Eyes, Voice, and Gesture of the Speaker, that his very Enemies could not
refrain from Tears. I insist, says
Tully
, upon this the rather,
because our Orators, who are as it were Actors of the Truth it self,
have quitted this manner of speaking; and the Players, who are but the
Imitators of Truth, have taken it up.
I shall therefore pursue the Hint he has here given me, and for the
Service of the
British Stage
I shall copy some of the Rules which this
great
Roman
Master has laid down; yet, without confining my self
wholly to his Thoughts or Words: and to adapt this Essay the more to the
Purpose for which I intend it, instead of the Examples he has inserted
in his Discourse, out of the ancient Tragedies, I shall make use of
parallel Passages out of the most celebrated of our own.
The Design of Art is to assist Action as much as possible in the
Representation of Nature; for the Appearance of Reality is that which
moves us in all Representations, and these have always the greater
Force, the nearer they approach to Nature, and the less they shew of
Imitation.
Nature herself has assigned to every Emotion of the Soul, its peculiar
Cast of the Countenance, Tone of Voice, and Manner of Gesture; and the
whole Person, all the Features of the Face and Tones of the Voice,
answer, like Strings upon musical Instruments, to the Impressions made
on them by the Mind. Thus the Sounds of the Voice, according to the
various Touches which raise them, form themselves into an Acute or
Grave, Quick or Slow, Loud or Soft Tone. These too may be subdivided
into various kinds of Tones, as the gentle, the rough, the contracted,
the diffuse, the continued, the intermitted, the broken, abrupt,
winding, softned, or elevated. Every one of these may be employed with
Art and Judgment; and all supply the Actor, as Colours do the Painter,
with an expressive Variety.
Anger exerts its peculiar Voice in an acute, raised, and hurrying sound.
The passionate Character of
King Lear
, as it is admirably drawn by
Shakespear
, abounds with the strongest Instances of this kind.
—Death! Confusion!
Fiery!—what Quality?—why Gloster! Gloster!
I'd speak with the Duke of Cornwall and his Wife.
Are they informed of this? My Breath and Blood!
Fiery? the fiery Duke?—&c.
Sorrow and Complaint demand a Voice quite different, flexible, slow,
interrupted, and modulated in a mournful Tone; as in that pathetical
Soliloquy of Cardinal
Wolsey
on his Fall.
Farewel!—a long Farewel to all my Greatness!
This is the State of Man!—to-day he puts forth
The tender Leaves of Hopes; to-morrow Blossoms,
And bears his blushing Honours thick upon him,
The third Day comes a Frost, a killing Frost,
And when he thinks, good easie Man, full surely
His Greatness is a ripening, nips his Root,
And then he falls as I do.
We have likewise a fine Example of this in the whole Part of
Andromache
in the
Distrest-Mother
, particularly in these Lines.
I'll go, and in the Anguish of my Heart
Weep o'er my Child—If he must die, my Life
Is wrapt in his, I shall not long survive.
'Tis for his sake that I have suffer'd Life,
Groan'd in Captivity, and out-liv'd Hector.
Yes, my Astyanax, we'll go together!
Together to the Realms of Night we'll go;
There to thy ravish'd Eyes thy Sir e I'll show,
And point him out among the Shades below.
Fear expresses it self in a low, hesitating and abject Sound. If the
Reader considers the following Speech of
Lady Macbeth
, while her
husband is about the Murder of
Duncan
and his Grooms, he will imagine
her even affrighted with the Sound of her own Voice, while she is
speaking it.
Alas! I am afraid they have awak'd,
And 'tis not done; th' Attempt, and not the Deed,
Confounds us—Hark!—I laid the Daggers ready,
He could not miss them. Had he not resembled
My Father as he slept, I had done it.
Courage
a louder tone, as in that Speech of Don
Sebastian
.
Here satiate all your Fury:
Let Fortune empty her whole Quiver on me,
I have a Soul that like an ample Shield
Can take in all, and Verge enough for more.
Pleasure
into a luxurious, mild, tender, and joyous
Modulation; as in the following Lines in
Caius Marius
.
Lavinia! O there's Musick in the Name,
That softning me to infant Tenderness,
Makes my Heart spring, like the first Leaps of Life.
And Perplexity is different from all these; grave, but not bemoaning,
with an earnest uniform Sound of Voice; as in that celebrated Speech of
Hamlet
.
To be, or not to be?—that is the Question:
Whether 'tis nobler in the Mind to suffer
The Slings and Arrows of outrageous Fortune,
Or to take Arms against a Sea of Troubles,
And by opposing end them. To die, to sleep;
No more; and by a Sleep to say we end
The Heart-ach, and the thousand natural Shocks
That Flesh is Heir to; 'tis a Consummation
Devoutly to be wish'd. To die, to sleep—
To sleep; perchance to dream! Ay, there's the Rub.
For in that sleep of Death what Dreams may come,
When we have shuffled off this Mortal Coil,
Must give us pause—There's the Respect
That makes Calamity of so long Life;
For who would bear the Whips and Scorns of Time,
Th' Oppressor's Wrongs, the proud Man's contumely,
The Pangs of despis'd Love, the Law's Delay,
The Insolence of Office, and the Spurns
That patient Merit of th' unworthy takes,
When he himself might his Quietus make
With a bare Bodkin? Who would Fardles bear,
To groan and sweat under a weary Life?
But that the Dread of something after Death,
The undiscover'd Country, from whose Bourn
No Traveller returns, puzzles the Will,
And makes us rather chuse those Ills we have,
Than fly to others that—we know not of.
As all these Varieties of Voice are to be directed by the Sense, so the
Action is to be directed by the Voice, and with a beautiful Propriety,
as it were to enforce it. The Arm, which by a strong Figure
Tully
calls
The Orator's Weapon
, is to be sometimes raised and extended; and
the Hand, by its Motion, sometimes to lead, and sometimes to follow the
Words, as they are uttered. The Stamping of the Foot too has its proper
Expression in Contention, Anger, or absolute Command. But the Face is
the Epitome of the whole Man, and the Eyes are as it were the Epitome of
the Face; for which Reason, he says, the best Judges among the
Romans
were not extremely pleased, even with
Roscius
himself in his Masque.
No Part of the Body, besides the Face, is capable of as many Changes as
there are different Emotions in the Mind, and of expressing them all by
those Changes. Nor is this to be done without the Freedom of the Eyes;
therefore
Theophrastus
call'd one, who barely rehearsed his Speech
with his Eyes fix'd, an
absent Actor
.
As the Countenance admits of so great Variety, it requires also great
Judgment to govern it. Not that the Form of the Face is to be shifted on
every Occasion, lest it turn to Farce and Buffoonery; but it is certain
that the Eyes have a wonderful Power of marking the Emotions of the
Mind, sometimes by a stedfast Look, sometimes by a careless one, now by
a sudden Regard, then by a joyful Sparkling, as the Sense of the Words
is diversified: for Action is, as it were, the Speech of the Features
and Limbs, and must therefore conform itself always to the Sentiments of
the Soul. And it may be observed, that in all which relates to the
Gesture, there is a wonderful Force implanted by Nature, since the
Vulgar, the Unskilful, and even the most Barbarous are chiefly affected
by this. None are moved by the Sound of Words, but those who understand
the Language; and the Sense of many things is lost upon Men of a dull
Apprehension: but Action is a kind of Universal Tongue; all Men are
subject to the same Passions, and consequently know the same Marks of
them in others, by which they themselves express them.
Perhaps some of my Readers may be of Opinion, that the Hints I have here
made use of, out of
Cicero
, are somewhat too refined for the Players
on our Theatre: In answer to which, I venture to lay it down as a Maxim,
that without Good Sense no one can be a good Player, and that he is very
unfit to personate the Dignity of a
Roman
Hero, who cannot enter into
the Rules for Pronunciation and Gesture delivered by a
Roman
Orator.
There is another thing which my Author does not think too minute to
insist on, though it is purely mechanical: and that is the right
pitching
of the Voice. On this occasion he tells the Story of
Gracchus
, who employed a Servant with a little Ivory Pipe to stand
behind him, and give him the right Pitch, as often as he wandered too
far from the proper
. Every Voice, says
Tully
, has its
particular Medium and Compass, and the Sweetness of Speech consists in
leading it through all the Variety of Tones naturally, and without
touching any Extreme. Therefore, says he,
Leave the Pipe at home, but carry the Sense of this Custom with you.
Action and Pronunciation
Dramatical
, and in first reprint.
Dryden's.
Otway's.
Near the end of the
De Oratore.
Contents
|
Friday, November 21, 1712 |
Addison |
Et sibi præferri se gaudet.
Ovid.

When I have been present in Assemblies where my Paper has been talked
of, I have been very well pleased to hear those who would detract from
the Author of it observe, that the Letters which are sent to the
Spectator
are as good, if not better than any of his Works. Upon this
Occasion many Letters of Mirth are usually mentioned, which some think
the
Spectator
writ to himself, and which others commend because they
fancy he received them from his Correspondents: Such are those from the
Valetudinarian;
the Inspector of the Sign-Posts; the Master of the
Fan-Exercise: with that of the Hoop'd Petticoat; that of
Nicholas Hart
the annual Sleeper; that from
Sir
John Envill;
that upon the
London
Cries; with multitudes of the same nature. As I love nothing more than
to mortify the Ill-natured, that I may do it effectually, I must
acquaint them, they have very often praised me when they did not design
it, and that they have approved my Writings when they thought they had
derogated from them. I have heard several of these unhappy Gentlemen
proving, by undeniable Arguments, that I was not able to pen a Letter
which I had written the Day before. Nay, I have heard some of them
throwing out ambiguous Expressions, and giving the Company reason to
suspect that they themselves did me the Honour to send me such or such a
particular Epistle, which happened to be talked of with the Esteem or
Approbation of those who were present. These rigid Criticks are so
afraid of allowing me any thing which does not belong to me, that they
will not be positive whether the Lion, the wild Boar, and the
Flower-pots in the Play-house, did not actually write those Letters
which came to me in their Names. I must therefore inform these
Gentlemen, that I often chuse this way of casting my Thoughts into a
Letter, for the following Reasons; First, out of the Policy of those who
try their Jest upon another, before they own it themselves. Secondly,
because I would extort a little Praise from such who will never applaud
any thing whose Author is known and certain. Thirdly, because it gave me
an Opportunity of introducing a great variety of Characters into my
Work, which could not have been done, had I always written in the Person
of the
Spectator
. Fourthly, because the Dignity Spectatorial would
have suffered, had I published as from my self those several ludicrous
Compositions which I have ascribed to fictitious Names and Characters.
And lastly, because they often serve to bring in, more naturally, such
additional Reflections as have been placed at the End of them.
There are others who have likewise done me a very particular Honour,
though undesignedly. These are such who will needs have it, that I have
translated or borrowed many of my Thoughts out of Books which are
written in other Languages. I have heard of a Person, who is more famous
for his Library than his Learning, that has asserted this more than once
in his private Conversation. Were it true, I am sure he could not speak
it from his own Knowledge; but had he read the Books which he has
collected, he would find this Accusation to be wholly groundless. Those
who are truly learned will acquit me in this Point, in which I have been
so far from offending, that I have been scrupulous perhaps to a Fault in
quoting the Authors of several Passages which I might have made my own.
But as this Assertion is in reality an Encomium on what I have
published, I ought rather to glory in it, than endeavour to confute it.
Some are so very willing to alienate from me that small Reputation which
might accrue to me from any of these my Speculations, that they
attribute some of the best of them to those imaginary Manuscripts with
which I have introduced them. There are others, I must confess, whose
Objections have given me a greater Concern, as they seem to reflect,
under this Head, rather on my Morality than on my Invention. These are
they who say an Author is guilty of Falshood, when he talks to the
Publick of Manuscripts which he never saw, or describes Scenes of Action
or Discourse in which he was never engaged. But these Gentlemen would do
well to consider, there is not a Fable or Parable which ever was made
use of, that is not liable to this Exception; since nothing; according
to this Notion, can be related innocently, which was not once Matter of
Fact. Besides, I think the most ordinary Reader may be able to discover,
by my way of writing, what I deliver in these Occurrences as Truth, and
what as Fiction.
Since I am unawares engaged in answering the several Objections which
have been made against these my Works, I must take Notice that there are
some who affirm a Paper of this Nature should always turn upon diverting
Subjects, and others who find Fault with every one of them that hath not
an immediate Tendency to the Advancement of Religion or Learning. I
shall leave these Gentlemen to dispute it out among themselves; since I
see one half of my Conduct patronized by each side. Were I serious on an
improper Subject, or trifling in a serious one, I should deservedly draw
upon me the Censure of my Readers; or were I conscious of any thing in
my Writings that is not innocent at least, or that the greatest part of
them were not sincerely designed to discountenance Vice and Ignorance,
and support the Interest of true Wisdom and Virtue, I should be more
severe upon my self than the Publick is disposed to be. In the mean
while I de
Sir
e my Reader to consider every particular Paper or Discourse
as a distinct Tract by itself, and independent of every thing that goes
before or after it.
I shall end this Paper with the following Letter, which was really sent
me, as some others have been which I have published, and for which I
must own my self indebted to their respective Writers.
Sir ,
I was this Morning in a Company of your Well-wishers, when we read
over, with great Satisfaction, Tully's Observations on Action
adapted to the British Theatre: Though, by the way, we were very
sorry to find that you have disposed of another Member of your Club.
Poor Sir Roger is dead, and the worthy Clergyman dying. Captain
Sentry has taken Possession of a fair Estate; Will. Honeycomb has
married a Farmer's Daughter; and the Templar withdraws himself into
the Business of his own Profession. What will all this end in? We are
afraid it portends no Good to the Publick. Unless you very speedily
fix a Day for the Election of new Members, we are under Apprehensions
of losing the British Spectator. I hear of a Party of Ladies who
intend to address you on this Subject, and question not, if you do not
give us the Slip very suddenly, that you will receive Addresses from
all Parts of the Kingdom to continue so useful a Work. Pray deliver us
out of this Perplexity, and among the Multitude of your Readers you
will particularly oblige
Your most Sincere Friend and Servant,
Philo-Spec.
O.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 22, 1712 |
Addison |
—Facies non omnibus una
Nec diversa tamen—
Ov.

Those who were skillful in Anatomy among the Ancients, concluded from
the outward and inward Make of an Human Body, that it was the Work of a
Being transcendently Wise and Powerful. As the World grew more
enlightened in this Art, their Discoveries gave them fresh Opportunities
of admiring the Conduct of Providence in the Formation of an Human Body.
Galen
was converted by his Dissections, and could not but own a
Supreme Being upon a Survey of this his Handy-work. There were, indeed,
many Parts of which the old Anatomists did not know the certain Use; but
as they saw that most of those which they examined were adapted with
admirable Art to their several Functions, they did not question but
those, whose Uses they could not determine, were contrived with the same
Wisdom for respective Ends and Purposes. Since the Circulation of the
Blood has been found out, and many other great Discoveries have been
made by our modern Anatomists, we see new Wonders in the Human Frame,
and discern several important Uses for those Parts, which Uses the
Ancients knew nothing of. In short, the Body of Man is such a Subject as
stands the utmost Test of Examination. Though it appears formed with the
nicest Wisdom, upon the most superficial Survey of it, it still mends
upon the Search, and produces our Surprize and Amazement in proportion
as we pry into it. What I have here said of an Human Body, may be
applied to the Body of every Animal which has been the Subject of
Anatomical Observations.
The Body of an Animal is an Object adequate to our Senses. It is a
particular System of Providence, that lies in a narrow Compass. The Eye
is able to command it, and by successive Enquiries can search into all
its Parts. Could the Body of the whole Earth, or indeed the whole
Universe, be thus submitted to the Examination of our Senses, were it
not too big and disproportioned for our Enquiries, too unwieldy for the
Management of the Eye and Hand, there is no question but it would appear
to us as curious and well-contrived a Frame as that of an Human Body. We
should see the same Concatenation and Subserviency, the same Necessity
and Usefulness, the same Beauty and Harmony in all and every of its
Parts, as what we discover in the Body of every single Animal.
The more extended our Reason is, and the more able to grapple with
immense Objects, the greater still are those Discoveries which it makes
of Wisdom and Providence in the Work of the Creation. A
Sir
Isaac
Newton
, who stands up as the Miracle of the Present Age, can look
through a whole Planetary System; consider it in its Weight, Number, and
Measure; and draw from it as many Demonstrations of infinite Power and
Wisdom, as a more confined Understanding is able to deduce from the
System of an Human Body.
But to return to our Speculations on Anatomy. I shall here consider the
Fabrick and Texture of the Bodies of Animals in one particular View;
which, in my Opinion, shews the Hand of a thinking and all-wise Being in
their Formation, with the Evidence of a thousand Demonstrations. I think
we may lay this down as an incontested Principle, that Chance never acts
in a perpetual Uniformity and Consistence with it self. If one should
always fling the same number with ten thousand Dice, or see every Throw
just five times less, or five times more in Number than the Throw which
immediately preceded it, who would not imagine there is some invisible
Power which directs the Cast? This is the Proceeding which we find in
the Operations of Nature. Every kind of Animal is diversified by
different Magnitudes, each of which gives rise to a different Species.
Let a Man trace the Dog or Lion-Kind, and he will observe how many of
the Works of Nature are published, if I may use the Expression, in a
variety of Editions. If we look into the Reptile World, or into those
different Kinds of Animals that fill the Element of Water, we meet with
the same Repetitions among several Species, that differ very little from
one another, but in Size and Bulk. You find the same Creature that is
drawn at large, copied out in several Proportions, and ending in
Miniature. It would be tedious to produce Instances of this regular
Conduct in Providence, as it would be superfluous to those who are
versed in the natural History of Animals. The magnificent Harmony of the
Universe is such, that we may observe innumerable
Divisions
running
upon the same
Ground
. I might also extend this Speculation to the dead
Parts of Nature, in which we may find Matter disposed into many
similar
Systems, as well in our Survey of Stars and Planets, as of
Stones, Vegetables, and other sublunary Parts of the Creation. In a
Word, Providence has shewn the Richness of its Goodness and Wisdom, not
only in the Production of many Original Species, but in the Multiplicity
of Descants which it has made on every Original Species in particular.
But to pursue this Thought still farther; Every living Creature,
considered in it self, has many very complicated Parts, that are exact
copies of some other Parts which it possesses, and which are complicated
in the same Manner. One
Eye
would have been sufficient for the
Subsistence and Preservation of an Animal; but in order to better his
Condition, we see another placed with a Mathematical Exactness in the
same most advantageous Situation, and in every particular of the same
Size and Texture. Is it possible for Chance to be thus delicate and
uniform in her Operations? Should a Million of Dice turn up twice
together the same Number, the Wonder would be nothing in comparison with
this. But when we see this Similitude and Resemblance in the Arm, the
Hand, the Fingers; when we see one half of the Body entirely correspond
with the other in all those minute Strokes, without which a Man might
have very well subsisted; nay, when we often see a single Part repeated
an hundred times in the same Body, notwithstanding it consists of the
most intricate weaving of numberless Fibres, and these Parts differing
still in Magnitude, as the Convenience of their particular Situation
requires; sure a Man must have a strange Cast of Understanding, who does
not discover the Finger of God in so wonderful a Work. These Duplicates
in those Parts of the Body, without which a Man might have very well
subsisted, though not so well as with them, are a plain Demonstration of
an all-wise Contriver; as those more numerous Copyings, which are found
among the Vessels of the same Body, are evident Demonstrations that they
could not be the Work of Chance. This Argument receives additional
Strength, if we apply it to every Animal and Insect within our
Knowledge, as well as to those numberless living Creatures that are
Objects too minute for a Human Eye; and if we consider how the several
Species in this whole World of Life resemble one another in very many
Particulars, so far as is convenient for their respective States of
Existence; it is much more probable that an hundred Million of Dice
should be casually thrown a hundred Million of Times in the same number,
than that the Body of any single Animal should be produced by the
fortuitous Concourse of Matter. And that the like Chance should arise in
innumerable Instances, requires a degree of Credulity that is not under
the direction of Common Sense.
We may carry this Consideration yet
further, if we reflect on the two Sexes in every living Species, with
their Resemblances to each other, and those particular Distinctions that
were necessary for the keeping up of this great World of Life.
There are many more Demonstrations of a Supreme Being, and of his
transcendent Wisdom, Power, and Goodness in the Formation of the Body of
a living Creature,
which I refer my Reader to other Writings,
particularly to the Sixth Book of the Poem, entitled
Creation
, where
the Anatomy of the human Body is described with great Perspicuity and
Elegance. I have been particular on the Thought which runs through this
Speculation, because I have not seen it enlarged upon by others.
O.
Blackmore's.
Contents
|
Monday, November 24, 1712 |
Steele |
Nunquam ita quisquam bene subducta ratione ad vitam fuit
Quia res, Ætas usus semper aliquid apportet novi
Aliquid moneat, ut illa, quæ te scire credas, nescias
Et, quæ tibi putaris prima, in experiundo ut repudies.
Ter.

There are, I think, Sentiments in the following Letter from my Friend
Captain
Sentry
, which discover a rational and equal Frame of Mind, as
well prepared for an advantageous as an unfortunate Change of Condition.
Coverley-Hall, Nov. 15, Worcestershire.
Sir ,
'I am come to the Succession of the Estate of my honoured Kinsman Sir
Roger De Coverley; and I assure you I find it no easy Task to keep up
the Figure of Master of the Fortune which was so handsomely enjoyed by
that honest plain Man. I cannot (with respect to the great Obligations
I have, be it spoken) reflect upon his Character, but I am confirmed
in the Truth which I have, I think, heard spoken at the Club, to wit,
That a Man of a warm and well-disposed Heart with a very small
Capacity, is highly superior in human Society to him who with the
greatest Talents is cold and languid in his Affections. But, alas! why
do I make a difficulty in speaking of my worthy Ancestor's Failings?
His little Absurdities and Incapacity for the Conversation of the
politest Men are dead with him, and his greater Qualities are even now
useful to him. I know not whether by naming those Disabilities I do
not enhance his Merit, since he has left behind him a Reputation in
his Country which would be worth the Pains of the wisest Man's whole
Life to arrive at. By the way I must observe to you, that many of your
Readers have mistook that Passage in your Writings, wherein Sir Roger
is reported to have enquired into the private Character of the young
Woman at the Tavern. I know you mentioned that Circumstance as an
Instance of the Simplicity and Innocence of his Mind, which made him
imagine it a very easy thing to reclaim one of those Criminals, and
not as an Inclination in him to be guilty with her. The less
discerning of your Readers cannot enter into that Delicacy of
Description in the Character: But indeed my chief Business at this
time is to represent to you my present State of Mind, and the
Satisfactions I promise to my self in the Possession of my new
Fortune. I have continued all Sir Roger's Servants, except such as it
was a Relief to dismiss into little Beings within my Manor: Those who
are in a List of the good Knight's own Hand to be taken care of by me,
I have quartered upon such as have taken new Leases of me, and added
so many Advantages during the Lives of the Persons so quartered, that
it is the Interest of those whom they are joined with, to cherish and
befriend them upon all Occasions. I find a considerable Sum of ready
Money, which I am laying out among my Dependants at the common
Interest, but with a Design to lend it according to their Merit,
rather than according to their Ability. I shall lay a Tax upon such as
I have highly obliged, to become Security to me for such of their own
poor Youth, whether Male or Female, as want Help towards getting into
some Being in the World. I hope I shall be able to manage my Affairs
so, as to improve my Fortune every Year, by doing Acts of Kindness. I
will lend my Money to the Use of none but indigent Men, secured by
such as have ceased to be indigent by the Favour of my Family or my
self. What makes this the more practicable, is, that if they will do
any one Good with my Money, they are welcome to it upon their own
Security: And I make no Exception against it, because the Persons who
enter into the Obligations, do it for their own Family. I have laid
out four thousand Pounds this way, and it is not to be imagined what a
Crowd of People are obliged by it. In Cases where Sir Roger has
recommended, I have lent Money to put out Children, with a Clause
which makes void the Obligation, in case the Infant dies before he is
out of his Apprenticeship; by which means the Kindred and Masters are
extremely careful of breeding him to Industry, that he may repay it
himself by his Labour, in three Years Journeywork after his Time is
out, for the Use of his Securities. Opportunities of this kind are all
that have occurred since I came to my Estate; but I assure you I will
preserve a constant Disposition to catch at all the Occasions I can to
promote the Good and Happiness of my Neighbourhood.
'But give me leave to lay before you a little Establishment which has
grown out of my past Life, that I doubt not, will administer great
Satisfaction to me in that Part of it, whatever that is, which is to
come.
'There is a Prejudice in favour of the Way of Life to which a Man has
been educated, which I know not whether it would not be faulty to
overcome: It is like a Partiality to the Interest of one's own Country
before that of any other Nation. It is from an Habit of Thinking,
grown upon me from my Youth spent in Arms, that I have ever held
Gentlemen, who have preserved Modesty, Good-nature, Justice, and
Humanity in a Soldier's Life, to be the most valuable and worthy
Persons of the human Race. To pass through imminent Dangers, suffer
painful Watchings, frightful Alarms, and laborious Marches for the
greater part of a Man's Time, and pass the rest in a Sobriety
conformable to the Rules of the most virtuous civil Life, is a Merit
too great to deserve the Treatment it usually meets with among the
other part of the World. But I assure you, Sir , were there not very
many who have this Worth, we could never have seen the glorious Events
which we have in our Days. I need not say more to illustrate the
Character of a Soldier, than to tell you he is the very contrary to
him you observe loud, sawcy, and over-bearing in a red Coat about
Town. But I was going to tell you, that in Honour of the Profession of
Arms, I have set apart a certain Sum of Money for a Table for such
Gentlemen as have served their Country in the Army, and will please
from Time to Time to sojourn all, or any Part of the Year, at
Coverley. Such of them as will do me that Honour, shall find Horses,
Servants, and all things necessary for their Accommodation and
Enjoyment of all the Conveniences of Life in a pleasant various
Country. If Colonel Camperfelt be in Town, and his Abilities are not
employ'd another way in the Service, there is no Man would be more
welcome here. That Gentleman's thorough Knowledge in his Profession,
together with the Simplicity of his Manners, and Goodness of his
Heart, would induce others like him to honour my Abode; and I should
be glad my Acquaintance would take themselves to be invited or not, as
their Characters have an Affinity to his.
'I would have all my Friends know, that they need not fear (though I
am become a Country Gentleman) I will trespass against their
Temperance and Sobriety. No, Sir , I shall retain so much of the good
Sentiments for the Conduct of Life, which we cultivated in each other
at our Club, as to contemn all inordinate Pleasures: But particularly
remember, with our beloved Tully, that the Delight in Food consists
in DeSir e, not Satiety. They who most passionately pursue Pleasure,
seldomest arrive at it. Now I am writing to a Philosopher, I cannot
forbear mentioning the Satisfaction I took in the Passage I read
Yesterday in the same Tully. A Nobleman of Athens made a
Compliment to Plato the Morning after he had supped at his House,
Your Entertainments do not only please when you give them, but also
the Day after.
I am, My worthy Friend,
Your most obedient humble Servant,
William Sentry.
Contents
|
Tuesday, November 25, 1712 |
Steele |
Quin potius Pacem Æternam pactosque Hymenæos
Exercemus—
Virg.

I cannot but think the following Letter from the Emperor of
China
to
the Pope of
Rome
, proposing a Coalition of the
Chinese
and
Roman
Churches, will be acceptable to the Curious. I must confess I my self
being of opinion that the Emperor has as much Authority to be
Interpreter to him he pretends to expound, as the Pope has to be Vicar
to the Sacred Person he takes upon him to represent, I was not a little
pleased with their Treaty of Alliance. What Progress the Negotiation
between his Majesty of
Rome
, and his Holiness of
China
makes (as we
daily Writers say upon Subjects where we are at a Loss) Time will let us
know. In the mean time, since they agree in the Fundamentals of Power
and Authority, and differ only in Matters of Faith, we may expect the
Matter will go on without Difficulty.
Copia di Littera del Re della China al Papa, interpretata dal Padre
Segretario dell' India della Compagna di Giesu
1.
A Voi Benedetto sopra i benedetti PP, ed interpretatore grande de
Pontifici e Pastore Xmo dispensatore dell' oglio de i Rè d' Europe
Clemente XI.
'Il Favorite amico di Dio Gionata 7∞ Potentissimo sopra tutti i
potentissimi della terra, Altissmo sopra tutti gl' Altissmi sotto il
sole e la luna, che sede nella sede di smeraldo della China sopra
cento scalini d'oro, ad interpretare la lingua di Dio a tutti i
descendenti fedeli d'Abramo, che da la vita e la morte a cento
quindici regni, ed a cento settante Isole, scrive con la penna dello
Struzzo vergine, e manda salute ed accresimento di vecchiezza.
'Essendo arrivato il tempo in cui il fiore della reale nostro gioventu
deve maturare i Frutti della nostra vecchiezza, e confortare con quell
i desiderii dei populi nostri divoti, e propogare il seme di quella
pianta che deve proteggerli, habbiamo Stabilito d'accompagnarci con
una virgine eccelsa ed amorosa allattata alia mammella della leonessa
forte e dell' Agnella mansueta. Percio essendo ci stato figurato
sempre il vostro populo Europeo Romano par paese di donne invitte, i
forte, e caste; allongiamo la nostra mano potente, a stringere una di
loro, e questa sara una vostra nipote, o nipote di qualche altro gran
Sacerdote Latino, che sia guardata dall' occhio dritto di Dio. Sara
seminata in lei l'Autorita di Sarra, la Fedelta d'Esther, e la
Sapienza di Abba; la vogliamo con l'occhio della colomba che guarda il
cielo, e la terra e con la bocca dello Conchiglia che si pasce della
ruggiada del matino. La sua eta non passi ducento corsi della Luna, la
sua statura sia alta quanto la spicca dritta del grano verde, e la sua
grossezza quanto un manipolo di grano secco. Noi la mandaremmo a
vestire per li nostri mandatici Ambasciadori, e chi la conduranno a
noi, e noi incontraremmo alla riva del fiume grande facendola salire
su nostro cocchio. Ella potra adorare appresso di noi il suo Dio, con
venti quatro altre vergini a sua ellezzione, e potra cantare con loro
come la Tortora alla Primavera.
'Sodisfando O Padre e amico nostro questa nostro brama, sarete
caggione di unire in perpetua amicitia cotesti vostri Regni d'Europa
al nostro dominante Imperio, e si abbracciranno le vostri leggi come
l'edera abbraccia la pianta, e noi medesemi Spargeremo del nostro seme
reale in coteste Provinci, riscaldando i letti di vostri Principi con
il fuoco amoroso delle nostre Amazoni, d'alcune delle quali i nostri
mandatici Ambasciadori vi porteranno le Somiglianze depinte. Vi
Confirmiamo di tenere in pace le due buone religiose famiglie delli
Missionarii gli' Figlioli d'Ignazio, e li bianchi e neri figlioli di
Dominico; il cui consiglio degl' uni e degl' altri ci serve di scorta
nel nostro regimento e di lume ad interpretare le divine Legge come
appuncto fa lume l'oglio che si getta in Mare. In tanto Alzandoci dal
nostro Trono per Abbracciarvi, vi dichiariamo nostro congiunto e
Confederato; ed ordiniamo che questo foglio sia segnato col nostro
Segno Imperiale dalla nostra Citta, Capo del Mondo, il quinto giorno
della terza lunatione l'anno quarto del nostro Imperio.
'Sigillo e un sole nelle cui faccia e anche quella della Luna ed
intorno tra i Raggi vi sono traposte alcune Spade.
'Dico il Traduttore che secondo il Ceremonial di questo Lettere e
recedentissimo specialmente Fessere scritto con la penna della Struzzo
vergine con la quella non soglionsi scrivere quei Re che le pregiere a
Dio e scrivendo a qualche altro Principe del Mondo, la maggior Finezza
che usino, e scrivergli con la penna del Pavone.
A Letter from the Emperor of
China to the Pope, interpreted by a
Father Jesuit, Secretary to the
Indies.
To you blessed above the Blessed, great Emperor of Bishops, and
Pastor of Christians, Dispenser of the Oil of the Kings of Europe,
Clement XI.
"The Favourite Friend of God
Gionnata the VIIth, most Powerful above
the most Powerful of the Earth, Highest above the Highest under the
Sun and Moon, who sits on a Throne of Emerald of
China, above 100
Steps of Gold, to interpret the Language of God to the faithful, and
who gives Life and Death to 115 Kingdoms, and 170 Islands; he writes
with the Quill of a Virgin
Ostrich, and sends Health and Increase of
old Age.
"Being arrived at the time of our Age, in which the Flower of our
Royal Youth ought to ripen into Fruit towards old Age, to comfort
therewith the De
Sir e of our devoted People, and to propagate the Seed
of that Plant which must protect them; We have determined to accompany
our selves with an high Amorous Virgin, suckled at the Breast of a
wild Lioness, and a meek Lamb; and imagining with our selves that your
European Roman People is the Father of many unconquerable and chaste
Ladies: We stretch out our powerful Arm to embrace one of them, and
she shall be one of your Neices, or the Neice of some other great
Latin Priest, the Darling of God's Right Eye. Let the Authority of
Sarah be sown in her, the Fidelity of
Esther, and the Wisdom of
Abba. We would have her Eye like that of a
Dove, which may look
upon Heaven and Earth, with the Mouth of a Shell-Fish to feed upon the
Dew of the Morning; Her Age must not exceed 200 Courses of the Moon;
let her Stature be equal to that of an Ear of green Corn, and her
Girth a Handful.
"We will send our
Mandarine's Embassadors to clothe her, and to
conduct her to us, and we will meet her on the Bank of the great
River, making her to leap up into our Chariot. She may with us worship
her own God; together with twenty four Virgins of her own chusing; and
she may sing with them, as the
Turtle in the Spring. You, O Father
and Friend, complying with this our De
Sir e, maybe an occasion of
uniting in perpetual Friendship our high Empire with your
European
Kingdoms, and we may embrace your Laws, as the
Ivy embraces the
Tree; and we our selves may scatter our Royal Blood into your
Provinces, warming the chief of your Princes with the amorous Fire of
our
Amazons, the resembling Pictures of some of which our said
Mandarine's Embassadors shall convey to you.
"We exhort you to keep in Peace two good Religious Families of
Missionaries, the black Sons of
Ignatius, and the white and black
Sons of
Dominicus; that the Counsel, both of the one and the other,
may serve as a Guide to us in our Government, and a Light to interpret
the Divine Law, as the Oil cast into the Sea produces Light.
"To conclude, we rising up in our Throne to embrace you, we declare
you our Ally and Confederate; and have ordered this Leaf to be sealed
with our Imperial Signet, in our Royal City the Head of the World, the
8th Day of the third Lunation, and the 4th Year of our Reign."
Letters from
Rome
say, the whole Conversation both among Gentlemen and
Ladies has turned upon the Subject of this Epistle, ever since it
arrived. The Jesuit who translated it says, it loses much of the Majesty
of the Original in the
Italian
. It seems there was an Offer of the
same nature made by a Predecessor of the present Emperor to
Lewis
the
XIIIth of France, but no Lady of that Court would take the Voyage, that
Sex not being at that time so much used in politick Negotiations. The
manner of treating the Pope is, according to the
Chinese
Ceremonial,
very respectful: For the Emperor writes to him with the Quill of a
Virgin
Ostrich
, which was never used before but in Writing Prayers.
Instructions are preparing for the Lady who shall have so much Zeal as
to undertake this Pilgrimage, and be an Empress for the sake of her
Religion. The Principal of the
Indian
Missionaries has given in a List
of the reigning Sins in
China
, in order to prepay the Indulgences
necessary to this Lady and her Retinue, in advancing the Interests of
the
Roman Catholic Religion
in those Kingdoms.
To the Spectator-General.
May it please your Honour,
'I have of late seen French Hats, of a prodigious Magnitude, pass by
my Observatory.
John Sly.
T.
No suggestion has been made as to the authorship of this
squib on the Jesuits in China.
Contents
|
Wednesday, November 26, 1712 |
Steele |
Omnia patefacienda ut ne quid omnino quod venditor norit, emptor
ignoret.
Tull.

It gives me very great Scandal to observe, where-ever I go, how much
Skill, in buying all manner of Goods, there is necessary to defend
yourself from being cheated in whatever you see exposed to Sale. My
Reading makes such a strong impression upon me, that I should think my
self a Cheat in my Way, if I should translate any thing from another
Tongue, and not acknowledge it to my Readers. I understood from common
Report,
Mr.
Cibber
was introducing a
French
Play upon our
Stage, and thought my self concerned to let the Town know what was his,
and what foreign
. When I came to the Rehearsal, I found the House so
partial to one of their own Fraternity, that they gave every thing which
was said such Grace, Emphasis, and Force in their Action, that it was no
easy matter to make any Judgment of the Performance. Mrs.
Oldfield
,
who, it seems, is the Heroick Daughter, had so just a Conception of her
Part, that her Action made what she spoke appear decent, just, and
noble. The Passions of Terrour and Compassion, they made me believe were
very artfully raised, and the whole Conduct of the Play artful and
surprizing. We Authors do not much relish the Endeavours of Players in
this kind; but have the same Disdain as Physicians and Lawyers have when
Attorneys and Apothecaries give Advice.
Cibber
himself took the
liberty to tell me, that he expected I would do him Justice, and allow
the Play well-prepared for his
Spectators
, whatever it was for his
Readers. He added very many Particulars not uncurious concerning the
manner of taking an Audience, and laying wait not only for their
superficial Applause, but also for insinuating into their Affections and
Passions, by the artful Management of the Look, Voice, and Gesture of
the Speaker. I could not but consent that the Heroick Daughter appeared
in the Rehearsal a moving Entertainment wrought out of a great and
exemplary Virtue.
The Advantages of Action, Show, and Dress on these Occasions are
allowable, because the Merit consists in being capable of imposing upon
us to our Advantage and Entertainment. All that I was going to say about
the Honesty of an Author in the Sale of his Ware, was that he ought to
own all that he had borrowed from others, and lay in a clear light all
that he gives his
Spectators
for their Money, with an Account of the
first Manufacturers. But I intended to give the Lecture of this Day upon
the common and prostituted Behaviour of Traders in ordinary Commerce.
The Philosopher made it a Rule of Trade, that your Profit ought to be
the common Profit; and it is unjust to make any Step towards Gain,
wherein the Gain of even those to whom you sell is not also consulted. A
Man may deceive himself if he thinks fit, but he is no better than a
Cheat who sells any thing without telling the Exceptions against it, as
well as what is to be said to its Advantage. The scandalous abuse of
Language and hardening of Conscience, which may be observed every Day in
going from one Place to another, is what makes a whole City to an
unprejudiced Eye a Den of Thieves. It was no small pleasure to me for
this reason to remark, as I passed by
Cornhill
,
the Shop of that
worthy, honest, tho' lately unfortunate, Citizen, Mr.
John Moreton
, so well known in the Linnen Trade, is fitting up a-new. Since a Man
has been in a distressed Condition, it ought to be a great Satisfaction
to have passed thro' it in such a Manner as not to have lost the
Friendship of those who suffered with him, but to receive an honourable
Acknowledgment of his Honesty from those very Persons to whom the Law
had consigned his Estate.
The Misfortune of this Citizen is like to prove of a very general
Advantage to those who shall deal with him hereafter: For the Stock with
which he now sets up being the Loan of his Friends, he cannot expose
that to the Hazard of giving Credit, but enters into a Ready-Money
Trade, by which Means he will both buy and sell the best and cheapest.
He imposes upon himself a Rule of affixing the Value of each Piece he
sells to the Piece it self; so that the most ignorant Servant or Child
will be as good a Buyer at his Shop as the most skilful in the Trade.
For all which, you have all his Hopes and Fortune for your Security. To
encourage Dealing after this Way, there is not only the avoiding the
most infamous Guilt in ordinary Bartering; but this Observation, That he
who buys with ready Money saves as much to his Family, as the State
exacts out of his Land for the Security and Service of his Country; that
is to say, in plain
English
, Sixteen will do as much as Twenty
Shillings.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'My Heart is so swelled with grateful Sentiments on account of some
Favours which I have lately received, that I must beg leave to give
them Utterance amongst the Croud of other anonymous Correspondents;
and writing, I hope, will be as great a Relief to my forced Silence,
as it is to your natural Taciturnity—My generous Benefactor will not
suffer me to speak to him in any Terms of Acknowledgment, but ever
treats me as if he had the greatest Obligations, and uses me with a
Distinction that is not to be expected from one so much my Superiour
in Fortune, Years, and Understanding. He insinuates, as if I had a
certain Right to his Favours from some Merit, which his particular
Indulgence to me has discovered but that is only a beautiful Artifice
to lessen the Pain an honest Mind feels in receiving Obligations, when
there is no probability of returning them.
'A gift is doubled when accompanied with such a Delicacy of Address;
but what to me gives it an inexpressible Value, is its coming from the
Man I most esteem in the World. It pleases me indeed, as it is an
Advantage and Addition to my Fortune; but when I consider it is an
Instance of that good Man's Friendship, it overjoys, it transports me;
I look on it with a Lover's Eye, and no longer regard the Gift, but
the Hand that gave it. For my Friendship is so entirely void of any
gainful Views, that it often gives me Pain to think it should have
been chargeable to him; and I cannot at some melancholy Hours help
doing his Generosity the Injury of fearing it should cool on this
account, and that the last Favour might be a sort of Legacy of a
departing Friendship.
'I Confess these Fears seem very groundless and unjust, but you must
forgive them to the Apprehension of one possessed of a great Treasure,
who is frighted at the most distant Shadow of Danger.
'Since I have thus far open'd my Heart to you, I will not conceal the
secret Satisfaction I feel there of knowing the Goodness of my Friend
will not be unrewarded. I am pleased with thinking the Providence of
the Almighty hath sufficient Blessings in store for him, and will
certainly discharge the Debt, though I am not made the happy
Instrument of doing it.
'However, nothing in my power shall be wanting to shew my Gratitude; I
will make it the Business of my Life to thank him, and shall esteem
(next to him) those my best Friends, who give me greatest Assistance
in this good Work. Printing this Letter would be some little Instance
of my Gratitude; and your Favour herein will very much oblige
Your most humble Servant, &c.
W. C.
Nov. 24th.
T.
Ximena
, or the
Heroic Daughter
, a Tragedy taken from
the
Cid
of Corneille, by Colley Gibber. The play was not published
until after Steele's pamphlet,
The Crisis,
had exposed him to
political and (as it necessarily followed in those days) personal
detraction. Cibber then dedicated his play to Steele, referring to the
custom of his calumniators, since they could not deny his literary
services, to transfer all the merit of them to Addison, upon whom he had
so generously heaped more than the half of his own fame, and said:
"Your Enemies therefore, thus knowing that your own consent had partly
justified their insinuations, saved a great deal of their malice from
being ridiculous, and fairly left you to apply to such your singular
conduct what Mark Antony says of Octavius in the play:
'Fool that I was! upon my Eagle's wings
I bore this Wren, 'till I was tired with soaring,
And now, he mounts above me.'"
True-hearted Steele never read his relation to his friend in this
fashion. With how fine a disregard of conventional dignity is the latter
part of this paper given by Steele to the kind effort to help in setting
a fallen man upon his legs again!
See [Volume 2 link:
] To this Mr. Moreton was addressed the letter
signed W. S., from
Sir
William Scawen.
Contents
|
Thursday, November 27, 1712 |
Addison |
Si vulnus tibi monstratâ radice vel herbâ
Non fieret levius, fugeres radice vel herbâ
Proficiente nihil curarier—
Hor.

It is very difficult to praise a Man without putting him out of
Countenance. My following Correspondent has found out this uncommon Art,
and, together with his Friends, has celebrated some of my Speculations
after such a concealed but diverting manner, that if any of my Readers
think I am to blame in Publishing my own Commendations, they will allow
I should have deserved their Censure as much, had I suppressed the
Humour in which they are convey'd to me.
Sir ,
'I am often in a private Assembly of Wits of both Sexes, where we
generally descant upon your Speculations, or upon the Subjects on
which you have treated. We were last
Tuesday talking of those two
Volumes which you have lately published. Some were commending one of
your Papers, and some another; and there was scarce a single Person in
the Company that had not a favourite Speculation. Upon this a Man of
Wit and Learning told us, he thought it would not be amiss if we paid
the
Spectator the same Compliment that is often made in our publick
Prints to
Sir William Read, Dr.
Grant, Mr.
Moor the Apothecary
1; and other eminent Physicians, where it is usual for the Patients
to publish the Cures which have been made upon them, and the several
Distempers under which they laboured. The Proposal took, and the Lady
where we visited having the two last Volumes in large Paper
interleav'd for her own private use, ordered them to be brought down,
and laid in the Window, whither every one in the Company retired, and
writ down a particular Advertisement in the Style and Phrase of the
like ingenious Compositions which we frequently meet with at the end
of our News-Papers. When we had finish'd our Work, we read them with a
great deal of Mirth at the Fire-side, and agreed,
Nemine
contradicente, to get them transcrib'd, and sent to the
Spectator.
The Gentleman who made the Proposal enter'd the following
Advertisement before the Title-Page, after which the rest succeeded in
order.
Remedium efficax et universum; or, An effectual Remedy adapted to
all Capacities; shewing how any Person may Cure himself of
Ill-Nature, Pride, Party-Spleen, or any other Distemper incident to
the human System, with an easie way to know when the Infection is
upon him. This Panacea is as innocent as Bread, agreeable to the
Taste, and requires no Confinement. It has not its Equal in the
Universe, as Abundance of the Nobility and Gentry throughout the
Kingdom have experienced.
N. B. 'No Family ought to be without it.
Over the two Spectators on Jealousy, being the two first in the
third Volume.
I William Crazy, aged Threescore and seven, having been for
several Years afflicted with uneasie Doubts, Fears and Vapours,
occasion'd by the Youth and Beauty of Mary my Wife, aged twenty
five, do hereby for the Benefit of the Publick give Notice, that I
have found great Relief from the two following Doses, having taken
them two Mornings together with a Dish of Chocolate. Witness my
Hand, &c.
For the Benefit of the Poor.
'In charity to such as are troubled with the Disease of Levée-
Haunting, and are forced to seek their Bread every Morning at the
Chamber Doors of great Men, I
A. B. do testifie, that for many
Years past I laboured under this fashionable Distemper, but was
cured of it by a Remedy which I bought of Mrs.
Baldwin, contain'd
in an Half-Sheet of Paper, marked [Volume 1 link:
No. 193]. where any one may be
provided with the same Remedy at the price of a single Penny.
An infallible Cure for
Hypocondriack Melancholys.
[Volume 1 links: No.
173.
184.
191.] [Volume 2 links:
203.
209.
221.
233.
235.
239.
245.
247.
251.]
Probatum est.
Charles Easy.
'I
Christopher Query having been troubled with a certain Distemper
in my Tongue, which shewed it self in impertinent and superfluous
Interrogatories, have not asked one unnecessary Question since my
Perusal of the Prescription marked [Volume 2 link:
No. 228.]
'The
Britannick Beautifyer, being an Essay on Modesty, [Volume 2 link:
No. 231.
which gives such a delightful Blushing Colour to the Cheeks of those
that are White or Pale, that it is not to be distinguished from a
natural fine Complection, nor perceived to be artificial by the
nearest Friend: Is nothing of Paint, or in the least hurtful. It
renders the Face delightfully handsome; is not subject to be rubbed
off, and cannot be parallelled by either Wash, Powder, Cosmetick,
&c. It is certainly the best Beautifier in the World.
Martha Gloworm.
'I
Samuel Self, of the Parish of
St. James's, having a
Constitution which naturally abounds with Acids, made use of a Paper
of Directions marked [Volume 1 link: No.
No. 177.] recommending a healthful Exercise
called
Good-Nature, and have found it a most excellent Sweetner of
the Blood.
'Whereas I,
Elizabeth Rainbow, was troubled with that Distemper in
my Head, which about a Year ago was pretty Epidemical among the
Ladies, and discover'd it self in the Colour of their Hoods, having
made use of the Doctor's Cephalick Tincture, which he exhibited to
the Publick in one of his last Year's Papers, I recover'd in a very
few Days.
'I
George Gloom have for a long time been troubled with the
Spleen, and being advis'd by my Friends to put my self into a Course
of Steele, did for that end make use of Remedies convey'd to me
several Mornings, in short Letters, from the Hands of the invisible
Doctor. They were marked at the bottom
Nathaniel Henroost, Alice
Threadneedle, Rebecca Nettletop, Tom. Loveless, Mary Meanwell,
Thomas Smoaky, Anthony Freeman, Tom Meggot, Rustick Sprightly, &c.
which have had so good an Effect upon me, that I now find my self
chearful, lightsome and easie; and therefore do recommend them to
all such as labour under the same Distemper.
Not having room to insert all the Advertisements which were sent me, I
have only picked out some few from the Third Volume, reserving the
Fourth for another Opportunity.
O.
Sir
William Read, a doctor who could hardly read, was one of the
most pertinacious advertisers of his time. He advertised in the
Tatler
that
he had been 35 years in the practice of
'couching cataracts, taking off all sorts of wens, curing wry necks
and hair lips without blemish, though never so deformed.'
His wife assisted him, and after his death carried on his business,
advertising that,
'The Lady Read, in Durham Yard, in the Strand, having obtained a
peculiar method of couching cataracts and curing all diseases of the
eyes, by Sir William Read's method and medicines, and having had above
15 years' experience ... Note. Sir William Read has left only with his
lady the true receipt of his Styptich Water,' &c., &c.
Dr. Grant was another advertising oculist, illiterate and celebrated,
originally a tinker or cobbler, afterwards a Baptist preacher in
Southwark.
Mr. Moore sold a powder which, according to his advertisements, brought
off worms of incredible length.
Contents
|
Friday, November 28, 1712 |
1 |
—Vitiis nemo sine nascitur, optimus illo
Qui minimis urgetur—
Hor.

Nov. 27, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I have read this Day's Paper with a great deal of Pleasure, and could
send you an Account of several Elixirs and Antidotes in your third
Volume, which your Correspondents have not taken Notice of in their
Advertisements; and at the same time must own to you, that I have
seldom seen a Shop furnished with such a Variety of Medicaments, and
in which there are fewer Soporifics. The several Vehicles you have
invented for conveying your unacceptable Truths to us, are what I most
particularly admire, as I am afraid they are Secrets which will die
with you. I do not find that any of your Critical Essays are taken
Notice of in this Paper, notwithstanding I look upon them to be
excellent Cleansers of the Brain, and could venture to superscribe
them with an Advertisement which I have lately seen in one of our
News-Papers, wherein there is an Account given of a Sovereign Remedy
for restoring the Taste of all such Persons whose Palates have been
vitiated by Distempers, unwholesome Food, or any the like Occasions.
But to let fall the Allusion, notwithstanding your Criticisms, and
particularly the Candour which you have discovered in them, are not
the least taking Part of your Works, I find your Opinion concerning
Poetical Justice, as it is expressed in the first Part of your
[Volume 1 link:
Fortieth Spectator], is controverted by some eminent Criticks; and as
you now seem, to our great Grief of Heart, to be winding up your
Bottoms, I hoped you would have enlarged a little upon that Subject.
It is indeed but a single Paragraph in your Works, and I believe those
who have read it with the same Attention I have done, will think there
is nothing to be objected against it. I have however drawn up some
additional Arguments to strengthen the Opinion which you have there
delivered, having endeavoured to go to the Bottom of that Matter,
which you may either publish or suppress as you think fit.
'
Horace in my Motto says, that all Men are vicious, and that they
differ from one another, only as they are more or less so.
Boileau
has given the same Account of our Wisdom, as
Horace has of our
Virtue.
Tous les homines sont fous, et, malgré tous leurs soins,
Ne different entre eux, que du plus et du moins.
'All Men, says he, are Fools, and, in spite of their Endeavours to the
contrary, differ from one another only as they are more or less so.
'Two or three of the old
Greek Poets have given the same turn to a
Sentence which describes the Happiness of Man in this Life;
'That Man is most happy who is the least miserable.
'It will not perhaps be unentertaining to the Polite Reader to observe
how these three beautiful Sentences are formed upon different Subjects
by the same way of thinking; but I shall return to the first of them.
'Our Goodness being of a comparative, and not an absolute nature,
there is none who in strictness can be called a Virtuous Man. Every
one has in him a natural Alloy, tho' one may be fuller of Dross than
another: For this reason I cannot think it right to introduce a
perfect or a faultless Man upon the Stage; not only because such a
Character is improper to move Compassion, but because there is no such
a thing in Nature. This might probably be one Reason why the SPECTATOR
in one of his Papers took notice of that late invented Term called
Poetical Justice, and the wrong Notions into which it has led some
Tragick Writers. The most perfect Man has Vices enough to draw down
Punishments upon his Head, and to justify Providence in regard to any
Miseries that may befal him. For this reason I cannot think, but that
the Instruction and Moral are much finer, where a Man who is virtuous
in the main of his Character falls into Distress, and sinks under the
Blows of Fortune at the End of a Tragedy, than when he is represented
as Happy and Triumphant. Such an Example corrects the Insolence of
Human Nature, softens the Mind of the Beholder with Sentiments of Pity
and Compassion, comforts him under his own private Affliction, and
teaches him not to judge Mens Virtues by their Successes. I cannot
think of one real Hero in all Antiquity so far raised above Human
Infirmities, that he might not be very naturally represented in a
Tragedy as plunged in Misfortunes and Calamities. The Poet may still
find out some prevailing Passion or Indiscretion in his Character, and
shew it in such a Manner, as will sufficiently acquit the Gods of any
Injustice in his Sufferings. For as
Horace observes in my Text, the
best Man is faulty, tho' not in so great a degree as those whom we
generally call vicious Men.
'If such a strict Poetical Justice, as some Gentlemen insist upon, was
to be observed in this Art, there is no manner of Reason why it should
not extend to Heroick Poetry, as well as Tragedy. But we find it so
little observed in
Homer, that his
Achilles is placed in the
greatest point of Glory and Success, though his Character is Morally
Vicious, and only Poetically Good, if I may use the Phrase of our
modern Criticks. The
Æneid is filled with Innocent, unhappy Persons.
Nisus and
Eurialus, Lausus and
Pallas come all to unfortunate
Ends. The Poet takes Notice in particular, that in the Sacking of
Troy, Ripheus fell, who was the most just Man among the
Trojans.
—Cadit et Ripheus justissimus unus,
Qui fuit in Teucris et servantissimus Æqui:
Dijs aliter visum est—
'And that
Pantheus could neither be preserved by his transcendent
Piety, nor by the holy Fillets of
Apollo, whose Priest he was.
—nec Te tua plurima Pantheu
Labentem pietas, nec Apollinis infula texit.
(Æn. 1. 2.)
'I might here mention the Practice of ancient Tragick Poets, both
Greek and
Latin; but as this Particular is touched upon in the
Paper above-mentioned, I shall pass it over in Silence. I could
produce Passages out of
Aristotle in favour of my Opinion, and if in
one Place he says that an absolutely Virtuous Man should not be
represented as unhappy, this does not justifie any one who shall think
fit to bring in an absolutely virtuous Man upon the Stage. Those who
are acquainted with that Author's Way of Writing, know very well, that
to take the whole extent of his Subject into his Divisions of it, he
often makes use of such Cases as are imaginary, and not reducible to
Practice: He himself declares that such Tragedies as ended unhappily
bore away the Prize in Theatrical Contentions, from those which ended
happily; and for the [Volume 1 link:
Fortieth Speculation], which I am now considering,
as it has given Reasons why these are more apt to please an Audience,
so it only proves that these are generally preferable to the other,
tho' at the same time it affirms that many excellent Tragedies have
and may be written in both kinds.
'I shall conclude with observing, that though the Spectator
above-mentioned is so far against the Rule of Poetical Justice, as to
affirm, that good Men may meet with an unhappy Catastrophe in Tragedy,
it does not say that ill Men may go off unpunished. The Reason for
this Distinction is very plain, namely, because the best of Men are
vicious enough to justify Providence for any Misfortunes and
Afflictions which may befal them, but there are many Men so criminal
that they can have no Claim or Pretence to Happiness. The best of Men
may deserve Punishment, but the worst of Men cannot deserve
Happiness.'
Unacknowledged, but doubtless by Addison, who took this
indirect way of answering Dennis. Addison's hand is further shown by the
addition made to the reprint.
Contents
|
Saturday, November 29, 1712 |
Addison |
Quamvis digressu veteris confusus amici,
Laudo tamen—
Juv.

I believe most People begin the World with a Resolution to withdraw from
it into a serious kind of Solitude or Retirement, when they have made
themselves easie in it. Our Unhappiness is, that we find out some Excuse
or other for deferring such our good Resolutions till our intended
Retreat is cut off by Death. But among all kinds of People there are
none who are so hard to part with the World, as those who are grown old
in the heaping up of Riches. Their Minds are so warped with their
constant Attention to Gain, that it is very difficult for them to give
their Souls another Bent, and convert them towards those Objects, which,
though they are proper for every Stage of Life, are so more especially
for the last.
Horace
describes an old Usurer as so charmed with the
Pleasures of a Country Life, that in order to make a Purchase he called
in all his Mony; but what was the Event of it? Why in a very few Days
after he put it out again. I am engaged in this Series of Thought by a
Discourse which I had last Week with my worthy Friend
Sir
Andrew
Freeport
, a Man of so much natural Eloquence, good Sense, and Probity of
Mind, that I always hear him with a particular Pleasure. As we were
sitting together, being the sole remaining Members of our Club,
Sir
Andrew
gave me an Account of the many busie Scenes of Life in which he
had been engaged, and at the same time reckoned up to me abundance of
those lucky Hits, which at another time he would have called pieces of
good Fortune; but in the Temper of Mind he was then, he termed them
Mercies, Favours of Providence, and Blessings upon an honest Industry.
Now, says he, you must know my good Friend, I am so used to consider my
self as Creditor and Debtor, that I often state my Accounts after the
same manner with regard to Heaven and my own Soul. In this case, when I
look upon the Debtor-side, I find such innumerable Articles, that I want
Arithmetick to cast them up; but when I look upon the Creditor-side, I
find little more than blank Paper. Now though I am very well satisfied
that it is not in my power to ballance Accounts with my Maker, I am
resolved however to turn all my future Endeavours that way. You must not
therefore be surprized, my Friend, if you hear that I am betaking my
self to a more thoughtful kind of Life, and if I meet you no more in
this Place.
I could not but approve so good a Resolution, notwithstanding the Loss I
shall suffer by it.
Sir
Andrew
has since explained himself to me more at
large in the following Letter, which is just come to my hands.
Good Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Notwithstanding my Friends at the Club have always rallied me, when I
have talked of retiring from Business, and repeated to me one of my
own Sayings,
That a Merchant has never enough till he has got a
little more; I can now inform you, that there is one in the World who
thinks he has enough, and is determined to pass the Remainder of his
Life in the Enjoyment of what he has. You know me so well, that I need
not tell you, I mean, by the Enjoyment of my Possessions, the making
of them useful to the Publick. As the greatest part of my Estate has
been hitherto of an unsteady and volatile nature, either tost upon
Seas or fluctuating in Funds; it is now fixed and settled in
Substantial Acres and Tenements. I have removed it from the
Uncertainty of Stocks, Winds and Waves, and disposed of it in a
considerable Purchase. This will give me great Opportunity of being
charitable in my way, that is, in setting my poor Neighbours to Work,
and giving them a comfortable Subsistence out of their own Industry.
My Gardens, my Fish-ponds, my Arable and Pasture Grounds shall be my
several Hospitals, or rather Work-houses, in which I propose to
maintain a great many indigent Persons, who are now starving in my
Neighbourhood. I have got a fine Spread of improveable Lands, and in
my own Thoughts am already plowing up some of them, fencing others;
planting Woods, and draining Marshes. In fine, as I have my share in
the Surface of this Island, I am resolved to make it as beautiful a
Spot as any in her Majesty's Dominions; at least there is not an Inch
of it which shall not be cultivated to the best Advantage, and do its
utmost for its Owner. As in my Mercantile Employment I so disposed of
my Affairs, that from whatever Corner of the Compass the Wind blew, it
was bringing home one or other of my Ships; I hope, as a Husbandman,
to contrive it so, that not a Shower of Rain, or a Glimpse of
Sunshine, shall fall upon my Estate without bettering some part of it,
and contributing to the Products of the Season. You know it has been
hitherto my Opinion of Life, that it is thrown away when it is not
some way useful to others. But when I am riding out by my self, in the
fresh Air on the open Heath that lies by my House, I find several
other Thoughts growing up in me. I am now of opinion that a Man
of my
Age may find Business enough on himself, by setting his Mind in
order, preparing it for another World, and reconciling it to the
Thoughts of Death. I must therefore acquaint you, that besides those
usual Methods of Charity, of which I have before spoken, I am at this
very Instant finding out a convenient Place where I may build an
Alms-house, which I intend to endow very handsomely, for a Dozen
superannuated Husbandmen. It
will be a great pleasure to me to say my
Prayers twice a-day with Men of my own
Years1, who all of them, as
well as my self, may have their Thoughts taken up how they shall die,
rather than how they shall live. I remember an excellent Saying that I
learned at School,
Finis coronat opus. You know best whether it be
in
Virgil or in
Horace, it is my business to apply it. If your
Affairs will permit you to take the Country Air with me sometimes, you
shall find an Apartment fitted up for you, and shall be every day
entertained with Beef or Mutton of my own feeding; Fish out of my own
Ponds; and Fruit out of my own Garden
s. You shall have free Egress
and Regress about my House, without having any Questions asked you,
and in a Word such an hearty Welcome as you may expect from
Your most sincere Friend
and humble Servant,
Andrew Freeport.
The Club, of which I am Member, being entirely dispersed, I shall
consult my Reader next Week, upon a Project relating to the Institution
of a new one.
O.
Age
.
Contents
|
Monday, December 1, 1712 |
Addison |
Quid dignum tanto feret hic promissor Hiatu?
Hor.

Since the late Dissolution of the Club whereof I have often declared my
self a Member, there are very many Persons who by Letters, Petitions,
and Recommendations, put up for the next Election. At the same time I
must complain, that several indirect and underhand Practices have been
made use of upon this Occasion. A certain Country Gentleman begun to
tapp
upon the first Information he received of
Sir
Roger's
Death; when
he sent me up word, that if I would get him chosen in the Place of the
Deceased, he would present me with a Barrel of the best
October
I had
ever drank in my Life. The Ladies are in great Pain to know whom I
intend to elect in the Room of
Will. Honeycombe.
Some of them indeed are
of Opinion that Mr.
Honeycombe
did not take sufficient care of their
Interests in the Club, and are therefore de
Sir
ous of having in it
hereafter a Representative of their own Sex. A Citizen who subscribes
himself
Y. Z.
tells me that he has one and twenty Shares in the
African
Company, and offers to bribe me with the odd one in case he
may succeed
Sir
Andrew Freeport
, which he thinks would raise the Credit
of that Fund. I have several Letters, dated from
Fenny Man's
, by
Gentlemen who are Candidates for Capt.
Sentry's
Place, and as many from
a Coffee-House in
Paul's
Church-yard of such who would fill up the
Vacancy occasioned by the Death of my worthy Friend the Clergyman, whom
I can never mention but with a particular Respect.
Having maturely weighed these several Particulars, with the many
Remonstrances that have been made to me on this Subject, and considering
how invidious an Office I shall take upon me, if I make the whole
Election depend upon my single Voice, and being unwilling to expose my
self to those Clamours, which, on such an Occasion, will not fail to be
raised against me for Partiality, Injustice, Corruption, and other
Qualities which my Nature abhors, I have formed to my self the Project
of a Club as follows.
I have thoughts of issuing out Writs to all and every of the Clubs that
are established in the Cities of
London
and
Westminster
, requiring
them to chuse out of their respective Bodies a Person of the greatest
Merit, and to return his name to me before
Lady-day
, at which time I
intend to sit upon Business.
By this means I may have Reason to hope, that the Club over which I
shall preside will be the very Flower and Quintescence of all other
Clubs. I have communicated this my Project to none but a particular
Friend of mine, whom I have celebrated twice or thrice for his Happiness
in that kind of Wit which is commonly known by the Name of a Punn. The
only Objection he makes to it is, that I shall raise up Enemies to my
self if I act with so regal an Air; and that my Detractors, instead of
giving me the usual Title of SPECTATOR, will be apt to call me the
King
of Clubs
.
But to proceed on my intended Project: It is very well known that I at
first set forth in this Work with the Character of a silent Man; and I
think I have so well preserved my Taciturnity, that I do not remember to
have violated it with three Sentences in the space of almost two Years.
As a Monosyllable is my Delight, I have made very few Excursions in the
Conversations which I have related beyond a Yes or a No. By this Means
my Readers have lost many good things which I have had in my Heart,
though I did not care for uttering them.
Now in order to diversify my Character, and to shew the World how well I
can talk if I have a Mind, I have Thoughts of being very loquacious in
the Club which I have now under Consideration. But that I may proceed
the more regularly in this Affair, I design, upon the first Meeting of
the said Club, to have
my Mouth opened
in form; intending to regulate
my self in this Particular by a certain Ritual which I have by me, that
contains all the Ceremonies which are practised at the opening of the
Mouth of a Cardinal. I have likewise examined the forms which were used
of old by
Pythagoras
, when any of his Scholars, after an
Apprenticeship of Silence, was made free of his Speech. In the mean
time, as I have of late found my Name in foreign Gazettes upon less
Occasions, I question
but in their next Articles from
Great
Britain
, they will inform the World that
the
Spectator's
Mouth is to
be opened on the twenty-fifth of
March
next
. I may perhaps
publish a very useful Paper at that Time of the Proceedings in that
Solemnity, and of the Persons who shall assist at it. But of this more
hereafter.
O.
On the twelfth of the following March appeared the first
number of Steele's
Guardian
. Addison's attempt to revive the
Spectator
was not made until June, 1714.
Contents
|
Tuesday, December 2, 1712 |
|
Sic Honor et Nomen divinis vatibus atque
Carminibus venit.
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
When Men of worthy and excelling Genius's have obliged the World with
beautiful and instructive Writings, it is in the nature of Gratitude
that Praise should be returned them, as one proper consequent Reward
of their Performances. Nor has Mankind ever been so degenerately sunk,
but they have made this Return, and even when they have not been
wrought up by the generous Endeavour so as to receive the Advantages
designed by it. This Praise, which arises first in the Mouth of
particular Persons, spreads and lasts according to the Merit of
Authors; and when it thus meets with a full Success changes its
Denomination, and is called
Fame. They who have happily arrived at
this, are, even while they live, enflamed by the Acknowledgments of
others, and spurred on to new Undertakings for the Benefit of Mankind,
notwithstanding the Detraction which some abject Tempers would cast
upon them: But when they decease, their Characters being freed from
the Shadow which
Envy laid them under, begin to shine out with
greater Splendour; their Spirits survive in their Works; they are
admitted into the highest Companies, and they continue pleasing and
instructing Posterity from Age to Age. Some of the best gain a
Character, by being able to shew that they are no Strangers to them;
and others obtain a new Warmth to labour for the Happiness and Ease of
Mankind, from a Reflection upon those Honours which are paid to their
Memories.
The Thought of this took me up as I turned over those Epigrams which
are the Remains of several of the
Wits of
Greece, and perceived
many dedicated to the Fame of those who had excelled in beautiful
poetick Performances. Wherefore, in pursuance to my Thought, I
concluded to do something along with them to bring their Praises into
a new Light and Language, for the Encouragement of those whose modest
Tempers may be deterr'd by the Fear of Envy or Detraction from fair
Attempts, to which their Parts might render them equal. You will
perceive them as they follow to be conceived in the form of Epitaphs,
a sort of Writing which is wholly set apart for a short pointed Method
of Praise.
On Orpheus, written by Antipater.
No longer, Orpheus, shall thy sacred Strains
Lead Stones, and Trees, and Beasts along the Plains;
No longer sooth the boistrous Wind to sleep,
Or still the Billows of the raging Deep:
For thou art gone, the Muses mourn'd thy Fall
In solemn Strains, thy Mother most of all.
Ye Mortals, idly for your Sons ye moan,
If thus a Goddess could not save her own.
Observe here, that if we take the Fable for granted, as it was
believed to be in that Age when the Epigram was written, the Turn
appears to have Piety to the Gods, and a resigning Spirit in its
Application. But if we consider the Point with respect to our present
Knowledge, it will be less esteem'd; though the Author himself,
because he believ'd it, may still be more valued than any one who
should now write with a Point of the same Nature.
On Homer, by Alpheus of Mytilene.
Still in our Ears Andromache complains,
And still in sight the Fate of Troy remains;
Still Ajax fights, still Hector's dragg'd along,
Such strange Enchantment dwells in Homer's Song;
Whose Birth cou'd more than one poor Realm adorn,
For all the World is proud that he was born.
The Thought in the first part of this is natural, and depending upon
the Force of Poesy: In the latter part it looks as if it would aim at
the History of seven Towns contending for the Honour of
Homer's
Birth-place; but when you expect to meet with that common Story, the
Poet slides by, and raises the whole
World for a kind of
Arbiter,
which is to end the Contention amongst its several Parts.
On Anacreon by Antipater.
This Tomb be thine, Anacreon; all around
Let Ivy wreath, let Flourets deck the Ground,
And from its Earth, enrich'd with such a Prize,
Let Wells of Milk and Streams of Wine arise:
So will thine Ashes yet a Pleasure know,
If any Pleasure reach the Shades below.
The Poet here written upon, is an easy gay Author, and he who writes
upon him has filled his own Head with the Character of his Subject. He
seems to love his Theme so much, that he thinks of nothing but
pleasing him as if he were still alive, by entering into his Libertine
Spirit; so that the Humour is easy and gay, resembling
Anacreon in
its Air, raised by such Images, and pointed with such a Turn as he
might have used. I give it a place here, because the Author may have
design'd it for his Honour; and I take an Opportunity from it to
advise others, that when they would praise, they cautiously avoid
every looser Qualification, and fix only where there is a real
Foundation in Merit.
On Euripides, by Ion.
Divine Euripides, this Tomb we see
So fair, is not a Monument for thee,
So much as thou for it, since all will own
Thy Name and lasting Praise adorns the Stone.
The Thought here is fine, but its Fault is, that it is general, that
it may belong to any great Man, because it points out no particular
Character. It would be better, if when we light upon such a Turn, we
join it with something that circumscribes and bounds it to the
Qualities of our Subject. He who gives his Praise in gross, will often
appear either to have been a Stranger to those he writes upon, or not
to have found any thing in them which is Praise-worthy.
On Sophocles, by Simonides.
Winde, gentle Ever-green, to form a Shade
Around the Tomb where Sophocles is laid;
Sweet Ivy winde thy Boughs, and intertwine
With blushing Roses and the clustring Vine:
Thus will thy lasting Leaves, with Beauties hung,
Prove grateful Emblems of the Lays he sung;
Whose Soul, exalted like a God of Wit,
Among the Muses and the Graces writ.
This Epigram I have open'd more than any of the former: The Thought
towards the latter End seemed closer couched, so as to require an
Explication. I fancied the Poet aimed at the Picture which is
generally made of
Apollo and the
Muses, he sitting with his Harp
in the Middle, and they around him. This look'd beautiful to my
Thought, and because the Image arose before me out of the Words of the
Original as I was reading it, I venture to explain them so.
On Menander, the Author unnamed.
The very Bees, O sweet Menander, hung
To taste the Muses Spring upon thy Tongue;
The very Graces made the Scenes you writ
Their happy Point of fine Expression hit.
Thus still you live, you make your Athens shine,
And raise its Glory to the Skies in thine.
This Epigram has a respect to the Character of its Subject; for
Menander writ remarkably with a Justness and Purity of Language. It
has also told the Country he was born in, without either a set or a
hidden Manner, while it twists together the Glory of the Poet and his
Nation, so as to make the Nation depend upon his for an Encrease of
its own.
I will offer no more Instances at present, to shew that they who
deserve Praise have it returned them from different Ages. Let these
which have been laid down, shew Men that Envy will not always prevail.
And to the End that Writers may more successfully enliven the
Endeavours of one another, let them consider, in some such Manner as I
have attempted, what may be the justest Spirit and Art of Praise. It
is indeed very hard to come up to it. Our Praise is trifling when it
depends upon Fable; it is false when it depends upon wrong
Qualifications; it means nothing when it is general; it is extreamly
difficult to hit when we propose to raise Characters high, while we
keep to them justly. I shall end this with transcribing that excellent
Epitaph of Mr.
Cowley, wherein, with a kind of grave and
philosophick Humour, he very beautifully speaks of himself (withdrawn
from the World, and dead to all the Interests of it) as of a Man
really deceased. At the same time it is an Instruction how to leave
the Publick with a good Grace.
Epitaphium Vivi Authoris.
Hic, O Viator, sub Lare parvulo
Couleius hic est conditus, hic jacet
Defunctus Humani Laboris
Sorte, supervacuaque Vita,
Non Indecora pauperie nitens,
Et non inerti Nobilis Otio,
Vanoque dilectis popello
Divitiis animosus hostis.
Possis ut illum dicere mortuum
En Terra jam nunc Quantula sufficit?
Exempta sit Curis, Viator,
Terra sit illa lævis, precare.
Hic sparge Flores, sparge breves Rosas,
Nam Vita gaudet Mortua Floribus,
Herbisque Odoratis Corona
Vatis adhuc Cinerem Calentem.
[The Publication of these Criticisms having procured me the following
Letter from a very ingenious Gentleman, I cannot forbear inserting it in
the Volume, though it did not come soon enough to have a place in any of
my single Papers.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Having read over in your Paper, No. 551. some of the Epigrams made by
the Grecian Wits, in commendation of their celebrated Poets, I could
not forbear sending you another, out of the same Collection; which I
take to be as great a Compliment to Homer, as any that has yet been
paid him.
Who first transcribed the famous Trojan War,
And wise Ulysses' Acts, O Jove, make known:
For since 'tis certain, Thine those Poems are,
No more let Homer boast they are his own.
If you think it worthy of a Place in your Speculations, for ought I
know (by that means) it may in time be printed as often in English,
as it has already been in Greek, I am (like the rest of the World)
Sir ,
Your great Admirer,
G. R.
4th Dec.
The Reader may observe that the Beauty of this Epigram is different from
that of any in the foregoing. An Irony is look'd upon as the finest
Palliative of Praise; and very often conveys the noblest Panegyrick
under the Appearance of Satire. Homer is here seemingly accused and
treated as a Plagiary; but what is drawn up in the form of an Accusation
is certainly, as my Correspondent observes, the greatest Compliment that
could have been paid to that Divine Poet.
Dear Mr. SPECTATOR,
I am a Gentleman of a pretty good Fortune, and of a Temper impatient
of any thing which I think an Injury; however I always quarrelled
according to Law, and instead of attacking my Adversary by the
dangerous Method of Sword and Pistol, I made my Assaults by that more
secure one of Writ or Warrant. I cannot help telling you, that either
by the Justice of my Causes, or the Superiority of my Counsel, I have
been generally successful; and to my great Satisfaction I can say it,
that by three Actions of Slander, and half a dozen Trespasses, I have
for several Years enjoy'd a perfect Tranquility in my Reputation and
Estate. By these means also I have been made known to the Judges, the
Serjeants of our Circuit are my intimate Friends, and the Ornamental
Counsel pay a very profound Respect to one who has made so great a
Figure in the Law. Affairs of Consequence having brought me to Town, I
had the Curiosity t'other day to visit Westminster-Hall; and having
placed my self in one of the Courts, expected to be most agreeably
entertained. After the Court and Counsel were, with due Ceremony,
seated, up stands a learned Gentleman, and began, When this Matter
was last stirr'd before your Lordship: The next humbly moved to
quash an Indictment; another complain'd that his Adversary had
snapp'd a Judgment; the next informed the Court that his Client
was stripp'd of his Possession; another begg'd Leave to acquaint
his Lordship, that they had been saddled with Costs. At last up got
a grave Serjeant, and told us his Client had been hung up a whole
Term by a Writ of Error. At this I could bear it no longer, but came
hither, and resolv'd to apply my self to your Honour to interpose with
these Gentlemen, that they would leave off such low and unnatural
Expressions: For surely tho' the Lawyers subscribe to hideous French
and false Latin, yet they should let their Clients have a little
decent and proper English for their Money. What Man that has a Value
for a good Name would like to have it said in a publick Court, that
Mr. such-a-one was stripp'd, saddled or hung up? This being what
has escaped your Spectatorial Observation, be pleas'd to correct such
an illiberal Cant among profess'd Speakers, and you'll infinitely
oblige
Your humble Servant,
Philonicus.
Joe's Coffee-house,
Novemb. 28.
Contents
|
Wednesday, December 3, 1712 |
Steele |
—Quæ prægravat artes
Infra se positas extinctus amabitur idem.
Hor.

As I was tumbling about the Town the other Day in an Hackney-Coach, and
delighting my self with busy Scenes in the Shops of each Side of me, it
came into my Head, with no small Remorse, that I had not been frequent
enough in the Mention and Recommendation of the industrious Part of
Mankind. It very
, upon this Occasion, touched my Conscience in
particular, that I had not acquitted my self to my Friend Mr.
Peter
Motteux
. That industrious Man of Trade, and formerly Brother of the
Quill, has dedicated to me a Poem upon Tea. It would injure him, as a
Man of Business, if I did not let the World know that the Author of so
good Verses writ them before he was concern'd in Traffick. In order to
expiate my Negligence towards him, I immediately resolv'd to make him a
Visit. I found his spacious Warehouses fill'd and adorn'd with Tea,
China
and
Indian
Ware. I could observe a beautiful Ordonnance of the
whole; and such different and considerable Branches of Trade carried on,
in the same House, I exulted in seeing dispos'd by a Poetical Head. In
one place were exposed to view Silks of various Shades and Colours, rich
Brocades, and the wealthiest Products of foreign Looms.
Here you might see the finest Laces held up by the fairest Hands, and
there examin'd by the beauteous Eyes of the Buyers, the most delicate
Cambricks, Muslins, and Linnens. I could not but congratulate my Friend
on the humble, but, I hoped, beneficial Use he had made of his Talents,
and wished I could be a Patron to his Trade, as he had been pleased to
make me of his Poetry. The honest Man has, I know, that modest De
Sir
e of
Gain which is peculiar to those who understand better Things than
Riches: and I dare say he would be contented with much less than what is
called Wealth at that Quarter of the Town which he inhabits, and will
oblige all his Customers with Demands agreeable to the Moderation of his
De
Sir
es.
Among other Omissions of which I have been also guilty, with relation to
Men of Industry of a superior Order, I must acknowledge my Silence
towards a Proposal frequently enclosed to me by Mr.
Renatus Harris,
Organ-Builder
. The ambition of this Artificer is to erect an Organ in
St.
Paul's
Cathedral, over the West Door, at the Entrance into the
Body of the Church, which in Art and Magnificence shall transcend any
Work of that kind ever before invented. The Proposal in perspicuous
Language sets forth the Honour and Advantage such a Performance would be
to the
British
Name, as well as that it would apply the Power of
Sounds in a manner more amazingly forcible than, perhaps, has yet been
known, and I am sure to an End much more worthy. Had the vast Sums which
have been laid out upon Opera's without Skill or Conduct, and to no
other Purpose but to suspend or vitiate our Understandings, been
disposed this Way, we should now perhaps have an Engine so formed as to
strike the Minds of half a People at once in a Place of Worship with a
Forgetfulness of present Care and Calamity, and a Hope of endless
Rapture, Joy, and Hallelujah hereafter.
When I am doing this Justice, I am not to forget the best Mechanick of
my Acquaintance, that useful Servant to Science and Knowledge, Mr.
John
Rowley
; but I think I lay a great Obligation on the Publick, by
acquainting them with his Proposals for a Pair of new Globes. After his
Preamble, he promises in the said Proposals that,
In the Celestial Globe,
'Care shall be taken that the fixed Stars be placed according to their
true Longitude and Latitude, from the many and correct Observations of
Hevelius, Cassini, Mr.
Flamsteed, Reg. Astronomer, Dr.
Halley
Savilian Professor of Geometry in
Oxon; and from whatever else can
be procured to render the Globe more exact, instructive, and useful.
'That all the Constellations be drawn in a curious, new, and
particular manner; each Star in so just, distinct, and conspicuous a
Proportion, that its true Magnitude may be readily known by bare
Inspection, according to the different
Light and
Sizes of the
Stars. That the Track or Way of such Comets as have been well
observ'd, but not hitherto expressed in any Globe, be carefully
delineated in this.
In the Terrestrial Globe.
'That
by reason the Descriptions formerly made, both in the
English
and2 Dutch great Globes, are erroneous,
Asia, Africa, and
America, be drawn in a Manner wholly new; by which means it is to be
noted, that the Undertakers will be obliged to alter the Latitude of
some Places in 10 Degrees, the Longitude of others in 20 Degrees:
besides which great and necessary Alterations, there be many
remarkable Countries, Cities, Towns, Rivers, and Lakes, omitted in
other Globes, inserted here according to the best Discoveries made by
our late Navigators. Lastly, That the Course of the Trade-Winds, the
Monsoons, and other Winds periodically shifting between the
Tropicks, be visibly express'd.
'Now in Regard that this Undertaking is of so universal Use, as the
Advancement of the most necessary Parts of the Mathematicks, as well
as tending to the Honour of the
British Nation, and that the Charge
of carrying it on is very expensive; it is de
Sir ed that all Gentlemen
who are willing to promote so great a Work, will be pleased to
subscribe on the following Conditions.
- The Undertakers engage to furnish each Subscriber with a Celestial
and Terrestrial Globe, each of 30 Inches Diameter, in all Respects
curiously adorned, the Stars gilded, the Capital Cities plainly
distinguished, the Frames, Meridians, Horizons, Hour Circles and
Indexes so exactly finished up, and accurately divided, that a Pair of
these Globes will really appear in the Judgment of any disinterested
and intelligent Person, worth Fifteen Pounds more than will be
demanded for them by the Undertakers.
-
Whosoever will be pleas'd to subscribe, and pay Twenty Five
Pounds in the Manner following for a Pair of these Globes, either for
their own Use, or to present them to any College in the Universities,
or any publick Library or School, shall have his Coat of Arms, Name,
Title, Seat, or Place of Residence, &c., inserted in some convenient
Place of the Globe.
-
That every Subscriber do at first pay down the Sum of Ten
Pounds, and Fifteen Pounds more upon the delivery of each Pair of
Globes perfectly fitted up. And that the said Globes be deliver'd
within Twelve Months after the Number of Thirty Subscribers be
compleated; and that the Subscribers be served with Globes in the
Order in which they subscribed.
-
That a Pair of these Globes shall not hereafter to be sold to any
Person but the Subscribers under Thirty Pounds.
-
That if there be not thirty Subscribers within four Months after
the first of December, 1712, the Money paid shall be return'd on
Demand by Mr. John Warner Gold-smith near Temple-Bar, who shall
receive and pay the same according to the above-mention'd Articles.
T.
See note on p. 288, 289, vol. ii. [Volume 2 links:
of
.]
or
Contents
|
Thursday, December 4, 1712 |
Addison |
Nec lusisse pudet, sed non incidere ludum.
Hor.

The Project which I published on
Monday
last has brought me in several
Packets of Letters. Among the rest I have receiv'd one from a certain
Projector, wherein after having represented, that in all probability the
Solemnity of
opening my Mouth
will draw together a great Confluence of
Beholders, he proposes to me the hiring of
Stationer's-Hall
for the
more convenient exhibiting of that Publick Ceremony. He undertakes to be
at the Charge of it himself, provided he may have the erecting of
Galleries on every side, and the letting of them out upon that Occasion.
I have a Letter also from a Bookseller, petitioning me in a very humble
manner, that he may have the Printing of the Speech which I shall make
to the Assembly upon the first opening of my Mouth. I am informed from
all Parts, that there are great Canvassings in the several Clubs about
Town, upon the chusing of a proper Person to sit with me on those
arduous Affairs, to which I have summoned them. Three Clubs have already
proceeded to Election, whereof one has made a double Return. If I find
that my Enemies shall take Advantage of my Silence to begin Hostilities
upon me, or if any other Exigency of Affairs may so require, since I see
Elections in so great a forwardness, we may possibly meet before the Day
appointed; or if matters go on to my Satisfaction, I may perhaps put off
the Meeting to a further Day; but of this Publick Notice shall be given.
In the mean time, I must confess that I am not a little gratify'd and
oblig'd by that Concern which appears in this great City upon my present
Design of laying down this Paper. It is likewise with much Satisfaction,
that I find some of the most outlying Parts of the Kingdom alarm'd upon
this Occasion, having receiv'd Letters to expostulate with me about it,
from several of my Readers of the remotest Boroughs of
Great Britain
.
Among these I am very well pleased with a Letter dated from
Berwick
upon Tweed
, wherein my Correspondent compares the Office which I have
for some time executed in these Realms to the Weeding of a great Garden;
which, says he, it is not sufficient to weed once for all, and
afterwards to give over, but that the Work must be continued daily, or
the same Spots of Ground which are cleared for a while, will in a little
time be over-run as much as ever. Another Gentleman lays before me
several Enormities that are already sprouting, and which he believes
will discover themselves in their Growth immediately after my
Disappearance. There is no doubt, says he, but the Ladies Heads will
shoot up as soon as they know they are no longer under the
Spectator's
Eye; and I have already seen such monstrous broad-brimmed Hats under the
Arms of Foreigners, that I question not but they will overshadow the
Island within a Month or two after the dropping of your Paper. But among
all the Letters which are come to my hands, there is none so handsomely
written as the following one, which I am the more pleased with, as it is
sent me from Gentlemen who belong to a Body which I shall always Honour,
and where (I cannot speak it without a secret Pride) my Speculations
have met with a very kind Reception. It is usual for Poets, upon the
publishing of their Works, to print before them such Copies of Verses as
have been made in their Praise. Not that you must imagine they are
pleased with their own Commendations, but because the elegant
Compositions of their Friends should not be lost. I must make the same
Apology for the Publication of the ensuing Letter, in which I have
suppressed no Part of those Praises that are given my Speculations with
too lavish and good-natured an Hand; though my Correspondents can
witness for me, that at other times I have generally blotted out those
Parts in the Letters which I have received from them.
O.
Oxford, Nov. 25.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'In spight of your Invincible Silence you have found out a Method of
being the most agreeable Companion in the World: That kind of
Conversation which you hold with the Town, has the good Fortune of
being always pleasing to the Men of Taste and Leisure, and never
offensive to those of Hurry and Business. You are never heard, but at
what
Horace calls
dextro tempore, and have the Happiness to
observe the politick Rule, which the same discerning Author gave his
Friend, when he enjoin'd him to deliver his Book to
Augustus.
Si validus, si lætus erit, si denique poscet.
You never begin to talk, but when People are de
Sir ous to hear you;
and I defy any one to be out of humour till you leave off. But I am
led unawares into Reflections, foreign to the original Design of this
Epistle; which was to let you know, that some unfeigned Admirers of
your inimitable Papers, who could, without any Flattery, greet you
with the Salutation used to the Eastern Monarchs,
viz. O Spec, live
for ever, have lately been under the same Apprehensions, with Mr.
Philo-Spec; that the haste you have made to dispatch your best
Friends portends no long Duration to your own short Visage. We could
not, indeed, find any just Grounds for Complaint in the Method you
took to dissolve that venerable Body: No, the World was not worthy of
your Divine.
Will. Honeycomb could not, with any Reputation, live
single any longer. It was high time for the
Templar to turn himself to
Coke: And
Sir Roger's dying was the wisest thing he ever did in his
Life. It was, however, matter of great Grief to us, to think that we
were in danger of losing so Elegant and Valuable an Entertainment. And
we could not, without Sorrow, reflect that we were likely to have
nothing to interrupt our Sips in a Morning, and to suspend our Coffee
in mid-air, between our Lips and Right Ear, but the ordinary Trash of
News-Papers. We resolved, therefore, not to part with you so. But
since, to make use of your own Allusion, the Cherries began now to
crowd the Market, and their Season was almost over, we consulted our
future Enjoyments, and endeavoured to make the exquisite Pleasure that
delicious Fruit gave our Taste as lasting as we could, and by drying
them protract their stay beyond its natural Date. We own that thus
they have not a Flavour equal to that of their juicy Bloom; but yet,
under this Disadvantage, they pique the Palate, and become a Salver
better than any other Fruit at its first Appearance. To speak plain,
there are a Number of us who have begun your Works afresh, and meet
two Nights in the Week in order to give you a Rehearing. We never come
together without drinking your Health, and as seldom part without
general Expressions of Thanks to you for our Night's Improvement. This
we conceive to be a more useful Institution than any other Club
whatever, not excepting even that of
ugly Faces. We have one
manifest Advantage over that renowned Society, with respect to Mr.
Spectator's Company. For though they may brag, that you sometimes
make your personal Appearance amongst them, it is impossible they
should ever get a Word from you. Whereas you are with us the Reverse
of what
Phædria would have his Mistress be in his Rival's Company,
Present in your Absence. We make you talk as much and as long as we
please; and let me tell you, you seldom hold your Tongue for the whole
Evening. I promise my self you will look with an Eye of Favour upon a
Meeting which owes its Original to a mutual Emulation among its
Members, who shall shew the most profound Respect for your Paper; not
but we have a very great Value for your Person: and I dare say you can
no where find four more sincere Admirers, and humble Servants, than
T. F., G. S., J. T., E. T.
Contents
|
Friday, December 5, 1712 |
John Hughes |
—tentanda Via est, quâ me quoque possim
Tollere humo, Victorque virûm volitare per Ora.
Virg.

I am obliged for the following Essay, as well as for that which lays
down Rules out of
Tully
for Pronunciation and Action, to the Ingenious
Author of a Poem just Published, Entitled,
An Ode to the Creator of the
World, occasioned by the Fragments of
Orpheus.
It is a Remark made, as I remember, by a celebrated
French
Author,
that
no Man ever pushed his Capacity as far as it was able to extend
.
I shall not enquire whether this Assertion be strictly true. It may
suffice to say, that Men of the greatest Application and Acquirements
can look back upon many vacant Spaces, and neglected Parts of Time,
which have slipped away from them unemployed; and there is hardly any
one considering Person in the World, but is apt to fancy with himself,
at some time or other, that if his Life were to begin again, he could
fill it up better.
The Mind is most provoked to cast on it self this ingenuous Reproach,
when the Examples of such Men are presented to it, as have far outshot
the generality of their Species, in Learning, Arts, or any valuable
Improvements.
One of the most extensive and improved Genius's we have had any Instance
of in our own Nation, or in any other, was that of
Sir
Francis Bacon
Lord
Verulam.
This great Man, by an extraordinary Force of Nature,
Compass of Thought, and indefatigable Study, had amassed to himself such
stores of Knowledge as we cannot look upon without Amazement. His
Capacity seems to have grasped All that was revealed in Books before his
Time; and not satisfied with that, he began to strike out new Tracks of
Science, too many to be travelled over by any one Man, in the Compass of
the longest Life. These, therefore, he could only mark down, like
imperfect Coastings in Maps, or supposed Points of Land, to be further
discovered, and ascertained by the Industry of After-Ages, who should
proceed upon his Notices or Conjectures.
The Excellent Mr.
Boyle
was the Person, who seems to have been
designed by Nature to succeed to the Labours and Enquiries of that
extraordinary Genius I have just mentioned. By innumerable Experiments
He, in a great Measure, filled up those Planns and Out-Lines of Science,
which his Predecessor had sketched out. His Life was spent in the
Pursuit of Nature, through a great Variety of Forms and Changes, and in
the most rational, as well as devout Adoration of its Divine Author.
It would be impossible to name many Persons who have extended their
Capacities so far as these two, in the Studies they pursued; but my
learned Readers,
this Occasion, will naturally turn their Thoughts to
a
Third
, who is yet living, and is likewise the Glory of our own
Nation. The Improvements which others had made in Natural and
Mathematical Knowledge have so vastly increased in his Hands, as to
afford at once a wonderful Instance how great the Capacity is of a Human
Soul, and how inexhaustible the Subject of its Enquiries; so true is
that Remark in Holy Writ, that,
though a wise Man seek to find out the
Works of God from the Beginning to the End, yet shall he not be able to
do it
.
I cannot help mentioning here one Character more, of a different kind
indeed from these, yet such a one as may serve to shew the wonderful
Force of Nature and of Application, and is the most singular Instance of
an Universal Genius I have ever met with. The Person I mean is
Leonardo
da Vinci
, an
Italian
Painter, descended from a noble Family in
Tuscany
, about the beginning of the sixteenth Century. In his
Profession of History-Painting he was so great a Master, that some have
affirmed he excelled all who went before him
. It is certain
, that he
raised the Envy of
Michael Angelo
, who was his Contemporary, and that
from the Study of his Works
Raphael
himself learned his best Manner of
Designing. He was a Master too in Sculpture and Architecture, and
skilful in Anatomy, Mathematicks, and Mechanicks. The Aquæduct from the
River
Adda
to
Milan
, is mentioned as a Work of his Contrivance. He
had learned several Languages, and was acquainted with the Studies of
History, Philosophy, Poetry, and Musick. Though it is not necessary to
my present Purpose, I cannot but take notice, that all who have writ of
him mention likewise his Perfections of Body. The Instances of his
Strength are almost incredible. He is described to have been of a
well-formed Person, and a Master of all genteel Exercises. And lastly,
we are told that his moral Qualities were agreeable to his natural and
intellectual Endowments, and that he was of an honest and generous Mind,
adorned with great Sweetness of Manners. I might break off the Account
of him here, but I imagine it will be an Entertainment to the Curiosity
of my Readers, to find so remarkable a Character distinguished by as
remarkable a Circumstance at his Death. The Fame of his Works having
gained him an universal Esteem, he was invited to the Court of
France
,
where, after some time, he fell sick; and
Francis the First
coming to
see him, he raised himself in his Bed to acknowledge the Honour which
was done him by that Visit. The King embraced him, and
Leonardo
fainting at the same Instant, expired in the Arms of that great Monarch.
It is impossible to attend to such Instances as these, without being
raised into a Contemplation on the wonderful Nature of an Human Mind,
which is capable of such Progressions in Knowledge, and can contain such
a Variety of Ideas without Perplexity or Confusion. How reasonable is it
from hence to infer its Divine Original? And whilst we find unthinking
Matter endued with a Natural Power to last for ever, unless annihilated
by Omnipotence, how absurd would it be to imagine, that a Being so much
Superior to it should not have the same Privilege?
At the same time it is very surprizing, when we remove our Thoughts from
such Instances as I have mentioned, to consider those we so frequently
meet with in the Accounts of barbarous Nations among the
Indians
;
where we find Numbers of People who scarce shew the first Glimmerings of
Reason, and seem to have few Ideas above those of Sense and Appetite.
These, methinks, appear like large Wilds, or vast uncultivated Tracts of
Human Nature; and when we compare them with Men of the most exalted
Characters in Arts and Learning, we find it difficult to believe that
they are Creatures of the same Species.
Some are of Opinion that the Souls of Men are all naturally equal, and
that the great Disparity we so often observe, arises from the different
Organization or Structure of the Bodies to which they are United. But
whatever constitutes this first Disparity, the next great Difference
which we find between Men in their several Acquirements is owing to
accidental Differences in their Education, Fortunes, or Course of Life.
The Soul is a kind of rough Diamond, which requires Art, Labour, and
Time to polish it. For want of which, many a good natural Genius is
lost, or lies unfashioned, like a Jewel in the Mine.
One of the strongest Incitements to excel in such Arts and
Accomplishments as are in the highest Esteem among Men, is the natural
Passion which the Mind of Man has for Glory; which, though it may be
faulty in the Excess of it, ought by no means to be discouraged. Perhaps
some Moralists are too severe in beating down this Principle, which
seems to be a Spring implanted by Nature to give Motion to all the
latent Powers of the Soul, and is always observed to exert it self with
the greatest Force in the most generous Dispositions. The Men whose
Characters have shone the brightest among the ancient
Romans
, appear
to have been strongly animated by this Passion.
Cicero
, whose Learning
and Services to his Country are
well known, was enflamed by it to an
extravagant degree, and warmly presses
Lucceius
, who was composing
a History of those Times, to be very particular and zealous in relating
the Story of his Consulship; and to execute it speedily, that he might
have the Pleasure
enjoying in his Life-time some Part of the
Honour
which he foresaw wou'd be paid to his Memory. This was the Ambition
of a great Mind; but he is faulty in the Degree of it, and cannot
refrain from solliciting the Historian upon this Occasion to neglect the
strict Laws of History, and, in praising him,
even to exceed the Bounds
of Truth
. The younger
Pliny
appears to have had the same Passion for
Fame, but accompanied with greater Chastness and Modesty. His Ingenuous
manner of owning it to a Friend, who had prompted him to undertake some
great Work, is exquisitely beautiful, and raises him to a certain
Grandeur above the Imputation of Vanity.
I must confess
,
he,
that nothing employs my Thoughts more than the DeSir e I have of
perpetuating my Name; which in my Opinion is a Design worthy of a Man,
at least of such a one, who being conscious of no Guilt, is not afraid
to be remember'd by Posterity
.
I think I ought not to conclude, without interesting all my Readers in
the Subject of this Discourse: I shall therefore lay it down as a Maxim,
that though all are not capable of shining in Learning or the Politer
Arts; yet
every one is capable of excelling in something
. The Soul has
in this Respect a certain vegetative Power, which cannot lie wholly
idle. If it is not laid out and cultivated into a regular and beautiful
Garden, it will of it self shoot up in Weeds or Flowers of a wilder
Growth.
Footnote 1:
Newton.
Footnote 2:
Epist. ad Diversos
, v. 12.
Footnote 3:
Glory
Footnote 4:
Lib. v. ep. 8, to Titinius Capito. In which, also, Pliny
quotes the bit of Virgil taken for the motto of this paper.
Contents
|
Saturday, December 6, 1712 |
Steele |
—Respue quod non es—
Pers.

All the Members of the imaginary Society, which were described in my
First Papers, having disappear'd one after another, it is high time for
the
Spectator
himself to go off the Stage. But, now I am to take my
Leave, I am under much greater Anxiety than I have known for the Work of
any Day since I undertook this Province. It is much more difficult to
converse with the World in a real than a personated Character. That
might pass for Humour in the
Spectator
, which would look like
Arrogance in a Writer who sets his Name to his Work. The Fictitious
Person might contemn those who disapproved him, and extoll his own
Performances, without giving Offence. He might assume a mock-Authority,
without being looked upon as vain and conceited. The Praises or Censures
of himself fall only upon the Creature of his Imaginations; and if any
one finds fault with him, the Author may reply with the Philosopher of
old,
Thou dost but beat the Case of
Anaxarchus. When I speak in my own
private Sentiments, I cannot but address my self to my Readers in a more
submissive manner, and with a just Gratitude, for the kind Reception
which they have given to these Dayly Papers that have been published for
almost the space of Two Years last past.
I hope the Apology I have made as to the Licence allowable to a feigned
Character, may excuse any thing which has been said in these Discourses
of the
Spectator
and his Works; but the Imputation of the grossest
Vanity would still dwell upon me, if I did not give some Account by what
Means I was enabled to keep up the Spirit of so long and approved a
Performance. All the Papers marked with a C, an L, an I, or an O, that
is to say, all the Papers which I have distinguished by any Letter in
the name of the Muse
CLIO
, were given me by the Gentleman, of whose
Assistance I formerly boasted in the Preface and concluding Leaf of my
Tatlers.
I am indeed much more proud of his long-continued Friendship,
than I should be of the Fame of being thought the Author of any Writings
which he himself is capable of producing. I remember when I finished the
Tender Husband
, I told him there was nothing I so ardently wished, as
that we might some time or other publish a Work written by us both,
which should bear the Name of
the Monument
, in Memory of our
Friendship. I heartily wish what I have done here, were as Honorary to
that Sacred Name, as Learning, Wit, and Humanity render those Pieces
which I have taught the Reader how to distinguish for his. When the Play
above-mentioned was last Acted, there were so many applauded Stroaks in
it which I had from the same Hand, that I thought very meanly of my self
that I had never publickly acknowledged them. After I have put other
Friends upon importuning him to publish Dramatick, as well as other
Writings he has by him, I shall end what I think I am obliged to say on
this Head, by giving my Reader this Hint for the better judging of my
Productions, that the best Comment upon them would be an Account when
the Patron to the
Tender Husband
was in
England
, or Abroad.
The Reader will also find some Papers which are marked with the Letter
X, for which he is obliged to the Ingenious Gentleman who diverted the
Town with the Epilogue to the
Distressed Mother
. I might have owned
these several Papers with the free Consent of these Gentlemen, who did
not write them with a design of being known for the Authors. But as a
candid and sincere Behaviour ought to be preferred to all other
Considerations, I would not let my Heart reproach me with a
Consciousness of having acquired a Praise which is not my Right.
The other Assistances which I have had, have been conveyed by Letter,
sometimes by whole Papers, and other times by short Hints from unknown
Hands. I have not been able to trace Favours of this kind, with any
Certainty, but to the following Names, which I place in the Order
wherein I received the Obligation, tho' the first I am going to name,
can hardly be mentioned in a List wherein he would not deserve the
Precedence. The Persons to whom I am to make these Acknowledgments are
Mr.
Henry Martyn
, Mr.
Pope
, Mr.
Hughs
, Mr.
Carey
of
New-College
in
Oxford
, Mr.
Tickell
of
Queen's
in the same
University, Mr.
Parnelle
, and Mr.
Eusden
of
Trinity
in
Cambridge.
Thus, to speak in the Language of my late Friend
Sir
Andrew
Freeport
, I have Ballanced my Accounts with all my Creditors for Wit and
Learning. But as these excellent Performances would not have seen the
Light without the means of this Paper, I may still arrogate to my self
the Merit of their being communicated to the Publick.
I have nothing more to add, but having swelled this Work to five hundred
and fifty five Papers, they will be disposed into seven Volumes, four of
which are already publish'd, and the three others in the Press. It will
not be demanded of me why I now leave off, tho' I must own my self
obliged to give an Account to the Town of my Time hereafter; since I
retire when their Partiality to me is so great, that an Edition of the
former Volumes of
Spectators
of above Nine thousand each Book is
already sold off, and the Tax on each half-Sheet has brought into the
Stamp-Office one Week with another above
£20.
a-Week arising from this
single Paper, notwithstanding it at first reduced it to less than half
the number that was usually Printed before this Tax was laid.
I humbly beseech the Continuance of this Inclination to favour what I
may hereafter produce, and hope I have in many Occurrences of Life
tasted so deeply of Pain and Sorrow, that I am Proof against much more
prosperous Circumstances than any Advantages to which my own Industry
can possibly exalt me.
I am,
My Good-natured Reader,
Your most Obedient,
Most Obliged Humble Servant,
Richard Steele.
Vos valete et plaudite
. Ter.
regards an ingenious Sett of Gentlemen, who
have done me the Honour to make me one of their Society.
Dec. 4, 1712.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The Academy of
Painting, lately established in
London, having
done you and themselves the Honour to chuse you one of their
Directors; that Noble and Lovely Art, which before was entitled to
your Regards, as a
Spectator, has an additional Claim to you, and
you seem to be under a double Obligation to take some Care of her
Interests.
'The Honour of our Country is also concerned in the matter I am going
to lay before you: we (and perhaps other Nations as well as we) have a
National false Humility as well as a National Vain-Glory; and tho' we
boast our selves to excel all the World in things wherein we are
out-done abroad, in other things we attribute to others a Superiority
which we our selves possess. This is what is done, particularly, in
the Art of
Portrait or
Face-Painting.
'
Painting is an Art of a vast Extent, too great by much for any
mortal Man to be in full possession of, in all its Parts; 'tis enough
if any one succeed in painting Faces, History, Battels, Landscapes,
Sea-Pieces, Fruit, Flowers, or Drolls, &c.
Nay, no Man ever was
excellent in all the Branches (tho'
many3 in Number) of these
several Arts, for a distinct Art I take upon me to call every one of
those several Kinds of Painting.
'And as one Man may be a good Landscape-Painter, but unable to paint a
Face or a History tollerably well, and so of the rest; one Nation may
excel in some kinds of Painting, and other kinds may thrive better in
other Climates.
'
Italy may have the Preference of all other Nations for
History-Painting;
Holland for Drolls, and a neat finished Manner of
Working;
France, for Gay, Janty, Fluttering Pictures; and
England
for Portraits: but to give the Honour of every one of these kinds of
Painting to any one of those Nations on account of their Excellence in
any of these parts of it, is like adjudging the Prize of Heroick,
Dramatick, Lyrick or Burlesque Poetry, to him who has done well in any
one of them.
'Where there are the greatest Genius's, and most Helps and
Encouragements, 'tis reasonable to suppose an Art will arrive to the
greatest Perfection: By this Rule let us consider our own Country with
respect to Face-Painting. No Nation in the World delights so much in
having their own, or Friends, or Relations Pictures; whether from
their National Good-Nature, or having a love to Painting, and not
being encouraged in the great Article of Religious Pictures, which the
Purity of our Worship refuses the free use of, or from whatever other
Cause. Our Helps are not inferior to those of any other People, but
rather they are greater; for what the Antique Statues and Bas-reliefs
which
Italy enjoys are to the History-Painters, the Beautiful and
noble Faces with which
England is confessed to abound, are to
Face-Painters; and besides we have the greatest number of the Works of
the best Masters in that kind of any People, not without a competent
number of those of the most excellent in every other part of Painting.
And for Encouragement, the Wealth and Generosity of the
English
Nation affords that in such a degree, as Artists have no reason to
complain.
'And accordingly in Fact, Face-Painting is no where so well performed
as in
England: I know not whether it has lain in your way to observe
it, but I have, and pretend to be a tolerable Judge. I have seen what
is done abroad, and can assure you, that the Honour of that Branch of
Painting is justly due to us. I appeal to the judicious Observers for
the Truth of what I assert. If Foreigners have oftentimes or even for
the most part excelled our Natives, it ought to be imputed to the
Advantages they have met with
here, join'd to their own Ingenuity
and Industry; nor has any one Nation distinguished themselves so as to
raise an Argument in favour of their Country: but it is to be
observed, that neither
French nor
Italians, nor any one of either
Nation, notwithstanding all our Prejudices in their favour have, or
ever had, for any considerable time, any Character among us as
Face-Painters.
'This Honour is due to our own Country; and has been so for near an
Age: So that instead of going to
Italy, or elsewhere, one that
designs for Portrait-Painting ought to study in
England. Hither such
should come from
Holland, France, Italy, Germany, &c. as he that
intends to practice any other kind of Painting, should go to those
Parts where 'tis in greatest Perfection. 'Tis said the Blessed Virgin
descended from Heaven, to sit to St
Luke; I dare venture to affirm,
that if she should de
Sir e another
Madonna to be painted by the Life,
she would come to
England; and am of opinion that your present
President,
Sir Godfrey Kneller, from his Improvement since he
arrived in this Kingdom, would perform that Office better than any
Foreigner living. I am, with all possible Respect,
Sir
Your most Humble, and
Most Obedient Servant, &c.
The ingenious Letters sign'd the
Weather-Glass,
with several others,
were received, but came too late
.(
Postscript.
It
not come to my Knowledge, when I left off the
Spectator
, that I
owe several excellent Sentiments and agreeable Pieces in this Work to
Mr.
Ince of Grey's-Inn
.
R. Steele
.)
Footnote 1:
Transposed in the volume to this place. In the number it
stood last; following the next letter.
Footnote 2:
Give me leave before I conclude to insert a Letter which
Footnote 3:
few
Footnote 4:
Mr. Richard Ince, a good Greek scholar, who became
Comptroller of Army Accounts, and inherited a fortune, died in 1758.
Contents
Dedication of the Eighth Volume of The Spectator
ToWilliam Honeycomb Esq.1.
The Seven former Volumes of the
Spectator
having been Dedicated to
some of the most celebrated Persons of the Age, I take leave to Inscribe
this Eighth and Last to You, as to a Gentleman who hath ever been
ambitious of appearing in the best Company.
You are now wholly retired from the busie Part of Mankind, and at
leisure to reflect upon your past Achievements; for which reason, I look
upon You as a Person very well qualified for a Dedication.
I may possibly disappoint my Readers, and your self too, if I do not
endeavour on this Occasion to make the World acquainted with your
Virtues. And here,
Sir
, I shall not compliment You upon your Birth,
Person, or Fortune; nor any other the like Perfections, which You
possess whether You will or no: But shall only touch upon those, which
are of your own acquiring, and in which every one must allow You have a
real Merit.
Your janty Air and easy Motion, the Volubility of your Discourse, the
Suddenness of your Laugh, the Management of your Snuff-Box, with the
Whiteness of your Hands and Teeth (which have justly gained You the Envy
of the most polite part of the Male World, and the Love of the greatest
Beauties in the Female) are intirely to be ascribed to your own personal
Genius and Application.
You are formed for these Accomplishments by a happy Turn of Nature, and
have finished your self in them by the utmost Improvements of Art. A Man
that is defective in either of these Qualifications (whatever may be the
secret Ambition of his Heart) must never hope to make the Figure You
have done, among the fashionable part of his Species. It is therefore no
wonder, we see such Multitudes of aspiring young Men fall short of You
in all these Beauties of your Character, notwithstanding the Study and
Practice of them is the whole Business of their Lives. But I need not
tell You that the free and disengaged Behaviour of a fine Gentleman
makes as many aukward Beaux, as the Easiness of your Favourite
Waller
hath made insipid Poets.
At present You are content to aim all your Charms at your own Spouse,
without further Thought of Mischief to any others of the Sex. I know you
had formerly a very great Contempt for that Pedantick Race of Mortals
who call themselves Philosophers; and yet, to your Honour be it spoken,
there is not a Sage of them all could have better acted up to their
Precepts in one of the most important Points of Life: I mean in that
Generous Dis-regard of Popular Opinion, which you showed some Years ago,
when you chose for your Wife an obscure young Woman, who doth not indeed
pretend to an ancient Family, but has certainly as many Fore-fathers as
any Lady in the Land, if she could but reckon up their Names.
I must own I conceived very extraordinary hopes of you from the Moment
that you confessed your Age, and from eight and forty (where you had
stuck so many Years) very ingenuously step'd into your Grand
Climacterick. Your Deportment has since been very venerable and
becoming. If I am rightly informed, You make a regular Appearance every
Quarter-Sessions among your Brothers of the
Quorum
; and if things go
on as they do, stand fair for being a Colonel of the Militia. I am told
that your Time passes away as agreeably in the Amusements of a Country
Life, as it ever did in the Gallantries of the Town: And that you now
take as much pleasure in the Planting of young Trees, as you did
formerly in the Cutting down of your Old ones. In short, we hear from
all Hands that You are thoroughly reconciled to your dirty Acres, and
have not too much Wit to look into your own Estate.
After having spoken thus much of my Patron, I must take the Privilege of
an Author in saying something of my self. I shall therefore beg leave to
add, that I have purposely omitted setting those Marks to the End of
every Paper, which appeared in my former Volumes, that You may have an
Opportunity of showing Mrs.
Honeycomb
the Shrewdness of your
Conjectures, by ascribing every Speculation to its proper Author: Though
You know how often many profound Criticks in Style and Sentiments have
very judiciously erred in this Particular, before they were let into the
Secret. I am,
Sir ,
Your most Faithful,
Humble Servant,
The SPECTATOR.
(
The
Bookseller
to the
Reader.
In the Six hundred and thirty second
Spectator,
the Reader will find
an Account of the Rise of this Eighth and Last Volume.
I have not been able to prevail upon the several Gentlemen who were
concerned in this Work to let me acquaint the World with their Names.
Perhaps it will be unnecessary to inform the Reader, that no other
Papers, which have appeared under the Title of
Spectator.)
Footnote 1:
This Dedication to Addison's supplementary
Spectator
,
begun a year and a half after the close of Steele's, is thought to be by
Eustace Budgell.
Contents
|
Friday, June 18, 1714 |
Addison1 |
To be continued every
Monday, Wednesday
, and
Friday.
Qualis ubi in lucem coluber, mala gramina, pastus,
Frigida sub terra tumidum quem bruma tegebat;
Nunc positis novus exuviis, nitidusque juventa,
Lubrica convolvit sublato pectore terga
Arduus ad solem, et linguis micat ore trisulcis.
Virg.

Upon laying down the Office of SPECTATOR, I acquainted the World with my
Design of electing a new Club, and of opening my Mouth in it after a
most solemn Manner. Both the Election and the Ceremony are now past; but
not finding it so easy as I at first imagined, to break thro' a Fifty
Years Silence, I would not venture into the World under the character of
a Man who pretends to talk like other People, till I had arrived at a
full Freedom of Speech.
I shall reserve for another time the History of such Club or Clubs of
which I am now a Talkative, but unworthy Member; and shall here give an
Account of this surprising Change which has been produced in me, and
which I look upon to be as remarkable an Accident as any recorded in
History, since that which happened to the Son of
Croesus
, after having
been many Years as much Tongue-tied as my self.
Upon the first opening of my Mouth, I made a Speech consisting of about
half a Dozen well-turned Periods; but grew so very hoarse upon it, that
for three Days together, instead of finding the use of my Tongue, I was
afraid that I had quite lost it. Besides, the unusual Extension of my
Muscles on this Occasion, made my Face ake on both Sides to such a
Degree, that nothing but an invincible Resolution and Perseverance could
have prevented me from falling back to my Monosyllables. I afterwards
made several Essays towards speaking; and that I might not be startled
at my own Voice, which has happen'd to me more than once, I used to read
aloud in my Chamber, and have often stood in the Middle of the Street to
call a Coach, when I knew there was none within hearing.
When I was thus grown pretty well acquainted with my own Voice, I laid
hold of all Opportunities to exert it. Not caring however to speak much
by my self, and to draw upon me the whole Attention of those I conversed
with, I used, for some time, to walk every Morning in the
Mall
, and
talk in Chorus with a Parcel of
Frenchmen.
I found my Modesty greatly
relieved by the communicative Temper of this Nation, who are so very
sociable, as to think they are never better Company, than when they are
all opening at the same time.
I then fancied I might receive great Benefit from Female Conversation,
and that I should have a Convenience of talking with the greater
Freedom, when I was not under any Impediment of thinking: I therefore
threw my self into an Assembly of Ladies, but could not for my Life get
in a Word among them; and found that if I did not change my Company, I
was in Danger of being reduced to my primitive Taciturnity.
The Coffee-houses have ever since been my chief Places of Resort, where
I have made the greatest Improvements; in order to which I have taken a
particular Care never to be of the same Opinion with the Man I conversed
with. I was a Tory at
Button's
, and a Whig at
Childe's
; a Friend to
the
Englishman
, or an Advocate for the
Examiner
, as it best served
my Turn; some fancy me a great Enemy to the
French
King, though, in
reality, I only make use of him for a Help to Discourse. In short, I
wrangle and dispute for Exercise; and have carried this Point so far
that I was once like to have been run through the Body for making a
little too free with my Betters.
In a Word, I am quite another Man to what I was.
—Nil fuit unquam
Tam dispar sibi—
My old Acquaintance scarce know me; nay I was asked the other Day by a
Jew
at
Jonathan's
, whether I was not related to a dumb Gentleman,
who used to come to that Coffee-house? But I think I^never was better
pleased in my Life than about a Week ago, when, as I was battling it
across the Table with a young Templar, his Companion gave him a Pull by
the Sleeve, begging him to come away, for that the old Prig would talk
him to Death.
Being now a very good Proficient in Discourse, I shall appear in the
World with this Addition to my Character, that my Countrymen may reap
the Fruits of my new-acquired Loquacity.
Those who have been present at public Disputes in the University, know
that it is usual to maintain Heresies for Argument's sake. I have heard
a Man a most impudent Socinian for Half an Hour, who has been an
Orthodox Divine all his Life after. I have taken the same Method to
accomplish my self in the Gift of Utterance, having talked above a
Twelve-month, not so much for the Benefit of my Hearers as of my self.
But since I have now gained the Faculty, I have been so long
endeavouring after, I intend to make a right Use of it, and shall think
my self obliged, for the future, to speak always in Truth and Sincerity
of Heart. While a Man is learning to fence, he practises both on Friend
and Foe; but when he is a Master in the Art, he never exerts it but on
what he thinks the right Side.
That this last Allusion may not give my Reader a wrong Idea of my Design
in this Paper, I must here inform him, that the Author of it is of no
Faction, that he is a Friend to no Interests but those of Truth and
Virtue, nor a Foe to any but those of Vice and Folly. Though I make more
Noise in the World than I used to do, I am still resolved to act in it
as an indifferent SPECTATOR. It is not my Ambition to encrease the
Number either of Whigs or Tories, but of wise and good Men, and I could
heartily wish there were not Faults common to both Parties which afford
me sufficient Matter to work upon, without descending to those which are
peculiar to either.
If in a Multitude of Counsellors there is Safety, we ought to think our
selves the securest Nation in the World. Most of our Garrets are
inhabited by Statesmen, who watch over the Liberties of their Country,
and make a Shift to keep themselves from starving by taking into their
Care the Properties of their Fellow-Subjects.
As these Politicians of both Sides have already worked the Nation into a
most unnatural Ferment, I shall be so far from endeavouring to raise it
to a greater Height, that on the contrary, it shall be the chief
Tendency of my Papers, to inspire my Countrymen with a mutual Good-will
and Benevolence. Whatever Faults either Party may be guilty of, they are
rather inflamed than cured by those Reproaches, which they cast upon one
another. The most likely Method of rectifying any Man's Conduct, is, by
recommending to him the Principles of Truth and Honour, Religion and
Virtue; and so long as he acts with an Eye to these Principles, whatever
Party he is of, he cannot fail of being a good
Englishman
, and a Lover
of his Country.
As for the Persons concerned in this Work, the Names of all of them, or
at least of such as de
Sir
e it, shall be published hereafter: Till which
time I must entreat the courteous Reader to suspend his Curiosity, and
rather to consider what is written, than who they are that write it.
Having thus adjusted all necessary Preliminaries with my Reader, I shall
not trouble him with any more prefatory Discourses, but proceed in my
old Method, and entertain him with Speculations on every useful Subject
that falls in my Way.
Footnote 1:
Addison's papers are marked on the authority of Tickell.
Contents
|
From Friday, June 18, to Monday, June 21, 1714 |
Addison |
Quippe domum timet ambiguam, Tyriosque bilingues.
Virg.

There is nothing, says Plato, so delightful, as the hearing or the
speaking of Truth
. For this Reason there is no Conversation so
agreeable as that of the Man of Integrity, who hears without any
Intention to betray, and speaks without any Intention to deceive.
Among all the Accounts which are given of
Cato
, I do not remember one
that more redounds to his Honour than the following Passage related by
Plutarch.
As an Advocate was pleading the Cause of his Client before
one of the Prætors, he could only produce a single Witness in a Point
where the Law required the Testimony of two Persons; upon which the
Advocate insisted on the Integrity of that Person whom he had produced:
but the Prætor told him, That where the Law required two Witnesses he
would not accept of one, tho' it were
Cato
himself. Such a Speech from
a Person who sat at the Head of a Court of Justice, while
Cato
was
still living, shews us, more than a thousand Examples, the high
Reputation this great Man had gained among his Contemporaries upon the
Account of his Sincerity.
When such an inflexible Integrity is a little softened and qualified by
the Rules of Conversation and Good-breeding, there is not a more shining
Virtue in the whole Catalogue of Social Duties. A Man however ought to
take great Care not to polish himself out of his Veracity, nor to refine
his Behaviour to the Prejudice of his Virtue.
Subject is exquisitely treated in the most elegant Sermon of the
great
British
Preacher
. I shall beg Leave to transcribe out of it
two or three Sentences, as a proper Introduction to a very curious
Letter, which I shall make the chief Entertainment of this Speculation.
'The old English Plainness and Sincerity, that generous Integrity of
Nature, and Honesty of Disposition, which always argues true Greatness
of Mind, and is usually accompanied with undaunted Courage and
Resolution, is in a great Measure lost among us.
'The Dialect of Conversation is now-a-days so swelled with Vanity and
Compliment, and so surfeited (as I may say) of Expressions of Kindness
and Respect, that if a Man that lived an Age or two ago should return
into the World again, he would really want a Dictionary to help him to
understand his own Language, and to know the true intrinsick Value of
the Phrase in Fashion; and would hardly, at first, believe at what a
low Rate the highest Strains and Expressions of Kindness imaginable do
commonly pass in current Payment; and when he should come to
understand it, it would be a great while before he could bring himself
with a good Countenance and a good Conscience, to converse with Men
upon equal Terms and in their own Way.'
I have by me a Letter which I look upon as a great Curiosity, and which
may serve as an Exemplification to the foregoing Passage, cited out of
this most excellent Prelate. It is
to have been written in King
Charles
II.'s Reign by the Ambassador of
Bantam
, a little after
his Arrival in
England.
Master,
'The People, where I now am, have Tongues further from their Hearts
than from London to Bantam, and thou knowest the Inhabitants of
one of these Places does not know what is done in the other. They call
thee and thy Subjects Barbarians, because we speak what we mean; and
account themselves a civilized People, because they speak one thing
and mean another: Truth they call Barbarity, and Falsehood Politeness.
Upon my first landing, one who was sent from the King of this Place to
meet me told me, That he was extremely sorry for the Storm I had met
with just before my Arrival. I was troubled to hear him grieve and
afflict himself upon my Account; but in less than a Quarter of an Hour
he smiled, and was as merry as if nothing had happened. Another who
came with him told me by my Interpreter, He should be glad to do me
any Service that lay in his Power. Upon which I deSir 'd him to carry
one of my Portmantaus for me, but instead of serving me according to
his Promise, he laughed, and bid another do it. I lodged, the first
Week, at the House of one, who deSir ed me to think my self at home,
and to consider his House as my own. Accordingly, I the next Morning
began to knock down one of the Walls of it, in order to let in the
fresh Air, and had packed up some of the Houshold-Goods, of which I
intended to have made thee a Present: But the false Varlet no sooner
saw me falling to Work, but he sent Word to deSir e me to give over,
for that he would have no such Doings in his House. I had not been
long in this Nation, before I was told by one, for whom I had asked a
certain Favour from the Chief of the King's Servants, whom they here
call the Lord-Treasurer, That I had eternally obliged him. I was so
surpriz'd at his Gratitude, that I could not forbear saying, What
Service is there which one Man can do for another, that can oblige him
to all Eternity! However I only asked him, for my Reward, that he
would lend me his eldest Daughter during my Stay in this Country; but
I quickly found that he was as treacherous as the rest of his
Countrymen.
'At my first going to Court, one of the great Men almost put me out of
Countenance, by asking ten thousand Pardons of me for only treading
by Accident upon my Toe. They call this kind of Lye a Compliment; for
when they are Civil to a great Man, they tell him Untruths, for which
thou wouldst order any of thy Officers of State to receive a hundred
Blows upon his Foot. I do not know how I shall negociate any thing
with this People, since there is so little Credit to be given to 'em.
When I go to see the King's Scribe, I am generally told that he is not
at home, tho' perhaps I saw him go into his House almost the very
Moment before. Thou wouldest fancy that the whole Nation are
Physicians, for the first Question they always ask me, is, how I do:
I have this Question put to me above a hundred times a Day. Nay, they
are not only thus inquisitive after my Health, but wish it in a more
solemn Manner, with a full Glass in their Hands, every time I sit with
them at Table, tho' at the same time they would perswade me to drink
their Liquors in such Quantities as I have found by Experience will
make me sick. They often pretend to pray for thy Health also in the
same Manner; but I have more Reason to expect it from the Goodness of
thy Constitution, than the Sincerity of their Wishes. May thy Slave
escape in Safety from this doubled-tongued Race of Men, and live to
lay himself once more at thy Feet in thy Royal City of Bantam.'
Footnote 1:
Tillotson. The Sermon 'Of Sincerity Towards God and Man.'
Works
,
Vol. II., p. 6, folio ed.
Footnote 2:
In 1682.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 23, 1714 |
Addison |
Qui fit, Mæcenas, ut nemo, quam sibi sortem
Seu ratio dederit, seu fors objecerit, illa
Contentus vivat: laudet diversa sequentes?
O Fortunati mercatores, gravis annis
Miles ait, multo jam fractus membra labore!
Contra mercator, navim jactantibus austris,
Militia est potior. Quid enim? concurritur? horæ
Momenta cita mors venit, aut victoria læta.
Agricolam laudat juris legumque peritus,
Sub galli cantum consultor ubi ostia pulsat.
Ille, datis vadibus, qui rure extractus in urbem est,
Solos felices viventes clamat in urbe.
Cætera de genere hoc (adeo sunt multa) loquacem
Delassare valent Fabium. Ne te morer, audi
Quo rem deducam. Si quis Deus, en ego dicat,
Jam faciam quod vultis: eris tu, qui modo miles,
Mercator: tu consultus modo, rusticus. Hinc vos,
Vos hinc mutatis discedite partibus. Eja,
Quid statis? Nolint. Atque licet esse beatis.
Hor.

It is a celebrated Thought of
Socrates
, that if all the Misfortunes of
Mankind were cast into a publick Stock, in order to be equally
distributed among the whole Species, those who now think themselves the
most unhappy, would prefer the Share they are already possess'd of,
before that which would fall to them by such a Division.
Horace
has
carried this Thought a great deal further in the Motto of my Paper,
which implies that the Hardships or Misfortunes we lye under, are more
easy to us than those of any other Person would be, in case we could
change Conditions with him.
As I was ruminating on these two Remarks, and seated in my Elbow-Chair,
I insensibly fell asleep; when, on a sudden, methought there was a
Proclamation made by
Jupiter
, that every Mortal should bring in his
Griefs and Calamities, and throw them together in a Heap. There was a
large Plain appointed for this Purpose. I took my Stand in the Center of
it, and saw with a great deal of Pleasure the whole human Species
marching one after another and throwing down their several Loads, which
immediately grew up into a prodigious Mountain that seemed to rise above
the Clouds.
There was a certain Lady of a thin airy Shape, who was very active in
this Solemnity. She carried a magnifying Glass in one of her Hands, and
was cloathed in a loose flowing Robe, embroidered with several Figures
of Fiends and Spectres, that discovered themselves in a Thousand
chimerical Shapes, as her Garment hovered in the Wind. There was
something wild and distracted in her Look. Her Name was
Fancy.
She led
up every Mortal to the appointed Place, after having very officiously
assisted him in making up his Pack, and laying it upon his Shoulders. My
Heart melted within me to see my Fellow-Creatures groaning under their
respective Burthens, and to consider that prodigious Bulk of human
Calamities which lay before me.
There were however several Persons who gave me great Diversion upon this
Occasion. I observed one bringing in a Fardel very carefully concealed
under an old embroidered Cloak, which, upon his throwing it into the
Heap, I discovered to be Poverty. Another, after a great deal of
puffing, threw down his Luggage; which, upon examining, I found to be
his Wife.
There were Multitudes of Lovers saddled with very whimsical Burthens
composed of Darts and Flames; but, what was very odd, tho' they sighed
as if their Hearts would break under these Bundles of Calamities, they
could not perswade themselves to cast them into the Heap when they came
up to it; but after a few faint efforts, shook their Heads and marched
away as heavy loaden as they came. I saw Multitudes of old Women throw
down their Wrinkles, and several young ones who stripped themselves of a
tawny Skin. There were very great Heaps of red Noses, large Lips, and
rusty Teeth. The Truth of it is, I was surpriz'd to see the greatest
Part of the Mountain made up of bodily Deformities. Observing one
advancing towards the Heap with a larger Cargo than ordinary upon his
Back, I found upon his near Approach, that it was only a natural Hump,
which he disposed of with great Joy of Heart among this Collection of
humane Miseries. There were likewise Distempers of all Sorts, tho' I
could not but observe, that there were many more Imaginary than real.
One little Packet I could not but take Notice of, which was a
Complication of all the Diseases incident to humane Nature, and was in
the Hand of a great many fine People: This was called the Spleen. But
what most of all surprized me, was a Remark I made, that there was not a
single [illegible] Folly thrown into the whole Heap: At which I was very
much astonished, having concluded within my self, that every one would
take this Opportunity of getting rid of his Passions, Prejudices, and
Frailties.
I took Notice in particular of a very profligate Fellow, who I did not
Question came loaden with his Crimes, but upon searching into his
Bundle, I found that instead of throwing his Guilt from him, he had only
laid down his Memory. He was followed by another worthless Rogue who
flung away his Modesty instead of his Ignorance.
When the whole Race of Mankind had thus cast their Burthens, the
Phantome
which had been so busie on this Occasion, seeing me an idle
Spectator
of what passed, approached towards me. I grew uneasy at her
Presence, when of a sudden she held her magnifying Glass full before my
Eyes. I no sooner saw my Face in it, but was startled at the Shortness
of it, which now appeared to me in its utmost Aggravation. The
immoderate Breadth of the Features made me very much out of Humour with
my own Countenance, upon which I threw it from me like a Mask. It
happened very luckily, that one who stood by me had just before thrown
down his Visage, which, it seems, was too long for him. It was indeed
extended to a most shameful length; I believe the very Chin was,
modestly speaking, as long as my whole Face. We had both of us an
Opportunity of mending our selves, and all the Contributions being now
brought in, every Man was at Liberty to exchange his Misfortune for
those of another Person. But as there arose many new Incidents in the
Sequel of my Vision, I shall reserve them for the Subject of my next
Paper.
Contents
|
Friday, June 25, 1714 |
Addison |
Quid causæ est, meritò quin illis Jupiter ambas
Iratus buccas inflet: neque se fore posthac
Tam facilem dicat, votis ut præbeat aurem?
Hor.

In my last Paper, I gave my Reader a Sight of that Mountain of Miseries,
which was made up of those several Calamities that afflict the Minds of
Men. I saw, with unspeakable Pleasure, the whole Species thus delivered
from its Sorrows: though at the same time, as we stood round the Heap,
and surveyed the several Materials of which it was composed, there was
scarce a Mortal in this vast Multitude who did not discover what he
thought Pleasures and Blessings of Life; and wondered how the Owners of
them ever came to look upon them as Burthens and Grievances.
As we were regarding very attentively this Confusion of Miseries, this
Chaos of Calamity,
Jupiter
issued out a second Proclamation, that
every one was now at Liberty to exchange his Affliction, and to return
to his Habitation with any such other Bundle as should be delivered to
him.
Upon this,
Fancy
began again to bestir her self, and parcelling out
the whole Heap with incredible Activity, recommended to every one his
particular Packet. The Hurry and Confusion at this time was not to be
expressed. Some Observations, which I made upon the Occasion, I shall
communicate to the Publick. A venerable grey-headed Man, who had laid
down the Cholick, and who I found wanted an Heir to his Estate, snatched
up an undutiful Son that had been thrown into the Heap by his angry
Father. The graceless Youth, in less than a quarter of an Hour, pulled
the old Gentleman by the Beard, and had like to have knocked his Brains
out; so that meeting the true Father, who came towards him in a Fit of
the Gripes, he begg'd him to take his Son again, and give him back his
Cholick; but they were incapable either of them to recede from the
Choice they had made. A poor Gally-Slave, who had thrown down his
Chains, took up the Gout in their stead, but made such wry Faces, that
one might easily perceive he was no great Gainer by the Bargain. It was
pleasant enough to see the several Exchanges that were made, for
Sickness against Poverty, Hunger against want of Appetite, and Care
against Pain.
The Female World were very busie among themselves in bartering for
Features; one was trucking a Lock of grey Hairs for a Carbuncle, another
was making over a short Waste for a Pair of round Shoulders, and a third
cheapning a bad Face for a lost Reputation: But on all these Occasions,
there was not one of them who did not think the new Blemish, as soon as
she had got it into her Possession, much more disagreeable than the old
one. I made the same Observation on every other Misfortune or Calamity,
which every one in the Assembly brought upon himself, in lieu of what he
had parted with; whether it be that all the Evils which befall us are in
some Measure suited and proportioned to our Strength, or that every Evil
becomes more supportable by our being accustomed to it, I shall not
determine.
I could not for my Heart forbear pitying the poor hump-back'd Gentleman
mentioned in the former Paper, who went off a very well-shaped Person
with a Stone in his Bladder; nor the fine Gentleman who had struck up
this Bargain with him, that limped thro' a whole Assembly of Ladies, who
used to admire him, with a Pair of Shoulders peeping over his Head.
I must not omit my own particular Adventure. My Friend with the long
Visage had no sooner taken upon him my short Face, but he made such a
grotesque Figure in it, that as I looked upon him I could not forbear
laughing at my self, insomuch that I put my own Face out of Countenance.
The poor Gentleman was so sensible of the Ridicule, that I found he was
ashamed of what he had done: On the other Side I found that I my self
had no great Reason to triumph, for as I went to touch my Forehead I
missed the Place, and clapped my Finger upon my upper Lip. Besides, as
my Nose was exceeding Prominent, I gave it two or three unlucky Knocks
as I was playing my Hand about my Face, and aiming at some other Part of
it. I saw two other Gentlemen by me, who were in the same ridiculous
Circumstances. These had made a foolish Swop between a Couple of thick
bandy Legs, and two long Trapsticks that had no Calfs to them. One of
these looked like a Man walking upon Stilts, and was so lifted up into
the Air above his ordinary Height, that his Head turned round with it,
while the other made such awkward Circles, as he attempted to walk, that
he scarce knew how to move forward upon his new Supporters: Observing
him to be a pleasant Kind of Fellow, I stuck my Cane in the Ground, and
told him I would lay him a Bottle of Wine, that he did not march up to
it on a Line, that I drew for him, in a Quarter of an Hour.
The Heap was at last distributed among the two Sexes, who made a most
piteous Sight, as they wandered up and down under the Pressure of their
several Burthens. The whole Plain was filled with Murmurs and
Complaints, Groans and Lamentations.
Jupiter
at length, taking
Compassion on the poor Mortals, ordered them a second time to lay down
their Loads, with a Design to give every one his own again. They
discharged themselves with a great deal of Pleasure, after which, the
Phantome, who had led them into such gross Delusions, was commanded to
disappear. There was sent in her stead a Goddess of a quite different
Figure: Her Motions were steady and composed, and her Aspect serious but
cheerful. She every now and then cast her Eyes towards Heaven, and fixed
them upon
Jupiter:
Her name was
Patience.
She had no sooner placed
her self by the Mount of Sorrows, but, what I thought very remarkable,
the whole Heap sunk to such a Degree, that it did not appear a third
part so big as it was before. She afterwards returned every Man his own
proper Calamity, and teaching him how to bear it in the most commodious
Manner, he marched off with it contentedly, being very well pleased that
he had not been left to his own Choice, as to the kind of Evils which
fell to his Lot.
Besides the several Pieces of Morality to be drawn out of this Vision, I
learnt from it, never to repine at my own Misfortunes, or to envy the
Happiness of another, since it is impossible for any Man to form a right
Judgment of his Neighbour's Sufferings; for which Reason also I have
determined never to think too lightly of another's Complaints, but to
regard the Sorrows of my Fellow Creatures with Sentiments of Humanity
and Compassion.
Contents
|
Monday, June 28, 1714 |
Addison |
—Verba intermissa retentat.
Ov.
Met.
Every one has heard of the Famous Conjurer, who, according to the
Opinion of the Vulgar, has studied himself
dumb
; for which Reason, as
it is believed, he delivers out all his Oracles in Writing. Be that as
it will, the blind
Tiresias
was not more famous in
Greece
, than this
dumb Artist has been, for some Years last past, in the Cities of
London
and
Westminster.
Thus much for the profound Gentleman who
honours me with the following Epistle.
From my Cell, June 24, 1714.
Sir ,
'Being informed that you have lately got the Use of your Tongue, I
have some Thoughts of following your Example, that I may be a
Fortune-teller properly speaking. I am grown weary of my
Taciturnity, and having served my Country many Years under the Title
of the dumb Doctor, I shall now prophesie by Word of Mouth, and (as
Mr. Lee says of the Magpie, who you know was a great Fortune-teller
among the Ancients) chatter Futurity. I have hitherto chosen to
receive Questions and return Answers in Writing, that I might avoid
the Tediousness and Trouble of Debates, my Querists being generally of
a Humour to think, that they have never Predictions enough for their
Mony. In short, Sir , my Case has been something like that of those
discreet Animals the Monkeys, who, as the Indians tell us, can speak
if they would, but purposely avoid it that they may not be made to
work. I have hitherto gained a Livelyhood by holding my Tongue, but
shall now open my Mouth in order to fill it. If I appear a little
Word-bound in my first Solutions and Responses, I hope it will not be
imputed to any Want of Foresight, but to the long Disuse of Speech. I
doubt not by this Invention to have all my former Customers over
again, for if I have promised any of them Lovers or Husbands, Riches
or good Luck, it is my Design to confirm to them vivâ voce, what I
have already given them under my Hand. If you will honour me with a
Visit, I will compliment you with the first opening of my Mouth, and
if you please you may make an entertaining Dialogue out of the
Conversation of two dumb Men. Excuse this Trouble, worthy Sir , from
one who has been a long time
Your Silent Admirer,
Cornelius Agrippa.'
I have received the following Letter, or rather
Billet-doux
, from a
pert young Baggage, who congratulates with me upon the same Occasion.
June 23, 1714.
Dear Mr. Prate-apace,
'I am a Member of a Female Society who call ourselves the Chit-Chat
Club, and am ordered by the whole Sisterhood, to congratulate you upon
the Use of your Tongue. We have all of us a mighty Mind to hear you
talk, and if you will take your Place among us for an Evening, we have
unanimously agreed to allow you one Minute in ten, without
Interruption.
I am, Sir ,
Your Humble Servant,
S. T.
P. S. 'You may find us at my Lady Betty Clack's, who will leave
Orders with her Porter, that if an elderly Gentleman, with a short
Face, enquires for her, he shall be admitted and no Questions asked.
As this particular Paper shall consist wholly of what I have received
from my Correspondents, I shall fill up the remaining Part of it with
other congratulatory Letters of the same Nature.
Oxford, June 25, 1714.
Sir ,
'We are here wonderfully pleased with the Opening of your Mouth, and
very frequently open ours in Approbation of your Design; especially
since we find you are resolved to preserve your Taciturnity as to all
Party Matters. We do not question but you are as great an Orator as
Sir Hudibras, of whom the Poet sweetly sings,
—He could not ope
His Mouth, but out there flew a Trope.
'If you will send us down the Half-dozen well-turned Periods, that
produced such dismal Effects in your Muscles, we will deposite them
near an old Manuscript of
Tully's Orations, among the Archives of
the University; for we all agree with you, that there is not a more
remarkable Accident recorded in History, since that which happened to
the Son of
Croesus, nay, I believe you might have gone higher, and
have added
Balaam's Ass. We are impatient to see more of your
Productions, and expect what Words will next fall from you, with as
much attention as those, who were set to watch the speaking Head which
Friar
Bacon formerly erected in this Place.
We are,
Worthy Sir ,
Your most humble Servants,
B. R. T. D., &c.
Honest Spec.
Middle-Temple, June 24.
'I am very glad to hear that thou beginnest to prate; and find, by thy
Yesterday's Vision, thou art so used to it, that thou canst not
forbear talking in thy Sleep. Let me only advise thee to speak like
other Men, for I am afraid thou wilt be very Queer, if thou dost not
intend to use the Phrases in Fashion, as thou callest them in thy
Second Paper. Hast thou a Mind to pass for a
Bantamite, or to make
us all
Quakers? I do assure thee, Dear
Spec, I am not Polished out
of my Veracity, when I subscribe my self
Thy Constant Admirer,
and humble Servant,
Frank Townly.
Contents
|
Wednesday, June 30, 1714 |
Addison |
—Paulatim abolere Sichæum
Incipit, et vivo tentat prævertere amore
Jampridem resides animos desuetaque corda.
Virg.

Sir ,
'I am a tall, broad-shoulder'd, impudent, black Fellow, and, as I
thought, every way qualified for a rich Widow: But, after having tried
my Fortune for above three Years together, I have not been able to get
one single Relict in the Mind. My first Attacks were generally
successful, but always broke off as soon as they came to the Word
Settlement. Though I have not improved my Fortune this way, I have
my Experience, and have learnt several Secrets which may be of use to
those unhappy Gentlemen, who are commonly distinguished by the Name of
Widow-hunters, and who do not know that this Tribe of Women are,
generally speaking, as much upon the Catch as themselves. I shall here
communicate to you the Mysteries of a certain Female Cabal of this
Order, who call themselves the
Widow-Club. This Club consists of
nine experienced Dames, who take their Places once a Week round a
large oval Table.
- Mrs. President is a Person who has disposed of six Husbands, and is
now determined to take a seventh; being of Opinion that there is as
much Vertue in the Touch of a seventh Husband as of a seventh Son. Her
Comrades are as follow.
- Mrs. Snapp, who has four Jointures, by four different
Bed-fellows, of four different Shires. She is at present upon the
Point of Marriage with a Middlesex Man, and is said to have an
Ambition of extending her Possessions through all the Counties in
England on this Side the Trent.
- Mrs. Medlar, who after two Husbands and a Gallant, is now
wedded to an old Gentleman of Sixty. Upon her making her Report to the
Club after a Weeks Cohabitation, she is still allowed to sit as a
Widow, and accordingly takes her Place at the Board.
- The Widow Quick, married within a Fortnight after the Death of
her last Husband. Her Weeds have served her thrice, and are still as
good as new.
- Lady Catherine Swallow. She was a Widow at Eighteen, and has
since buried a second Husband and two Coachmen.
- The Lady Waddle. She was married in the 15th Year of her Age to
Sir Simon Waddle, Knight, aged Threescore and Twelve, by whom she
had Twinns nine Months after his Decease. In the 55th Year of her Age
she was married to James Spindle, Esq.; a Youth of One and Twenty,
who did not out-live the Honey-Moon.
- Deborah Conquest. The Case of this Lady is something
particular. She is the Relict of Sir Sampson Conquest, some time
Justice of the Quorum. Sir Sampson was seven Foot high, and two
Foot in Breadth from the Tip of one Shoulder to the other. He had
married three Wives, who all of them died in Child-bed. This terrified
the whole Sex, who none of them durst venture on Sir Sampson. At
length Mrs. Deborah undertook him, and gave so good an Account of
him, that in three Years time she very fairly laid him out, and
measured his Length upon the Ground. This Exploit has gained her so
great a Reputation in the Club, that they have added Sir Sampson's
three Victories to hers, and give her the Merit of a fourth Widowhood;
and she takes her Place accordingly.
- The Widow Wildfire, Relict of Mr. John Wildfire,
Fox-hunter, who broke his Neck over a six Bar Gate. She took his Death
so much to Heart, that it was thought it would have put an End to her
Life, had she not diverted her Sorrows by receiving the Addresses of a
Gentleman in the Neighbourhood, who made Love to her in the second
Month of her Widowhood. This Gentleman was discarded in a Fortnight
for the sake of a young Templar, who had the Possession of her for
six Weeks after, till he was beaten out by a broken Officer, who
likewise gave up his Place to a Gentleman at Court. The Courtier was
as short-liv'd a Favourite as his Predecessors, but had the Pleasure
to see himself succeeded by a long Series of Lovers, who followed the
Widow Wildfire to the 37th Year of her Age, at which time there
ensued a Cessation of ten Years, when John Felt, Haberdasher, took
it in his Head to be in love with her, and it is thought will very
suddenly carry her off.
- The last is pretty Mrs. Runnet, who broke her first Husband's
Heart before she was Sixteen, at which Time she was entred of the
Club, but soon after left it, upon Account of a Second, whom she made
so quick a Dispatch of, that she returned to her Seat in less than a
Twelvemonth. This young Matron is looked upon as the most rising
Member of the Society, and will probably be in the President's Chair
before she dies.
'These Ladies, upon their first Institution, resolved to give the
Pictures of their deceased Husbands to the Club-Room, but two of them
bringing in their Dead at full Length, they cover'd all the Walls;
Upon which they came to a second Resolution, that every Matron should
give her own Picture, and set it round with her Husbands in Miniature.
As they have most of them the Misfortune to be troubled with the
Cholick, they have a noble Celler of Cordials and strong Waters. When
they grow Maudlin, they are very apt to commemorate their former
Partners with a Tear. But ask them which of their Husbands they
Condole, they are not able to tell you, and discover plainly that they
do not Weep so much for the Loss of a Husband, as for the want of One.
'The principal Rule, by which the whole Society are to govern
themselves is this, To cry up the Pleasures of a single Life upon all
Occasions, in order to deter the rest of their Sex from Marriage, and
engross the whole Male World to themselves.
'They are obliged, when any one makes Love to a Member of the Society,
to communicate his Name, at which Time the whole Assembly sit upon his
Reputation, Person, Fortune, and good Humour; and if they find him
qualified for a Sister of the Club, they lay their Heads together how
to make him sure. By this Means they are acquainted with all the
Widow-hunters about Town, who often afford them great Diversion. There
is an honest
Irish Gentleman, it seems, who knows nothing of this
Society, but at different times has made Love to the whole Club.
Their Conversation often turns upon their former Husbands, and it is
very diverting to hear them relate their several Arts and Stratagems,
with which they amused the Jealous, pacified the Chokrick, or wheedled
the Good-natured Man, till at last, to use the Club Phrase,
They sent
him out of the House with his Heels foremost.
The Politicks, which are most cultivated by this Society of
She-
Machiavils, relate chiefly to these two Points: How to treat a
Lover, and How to manage a Husband. As for the first Set of Artifices,
they are too numerous to come within the Compass of your Paper, and
shall therefore be reserved for a Second Letter.
The Management of a Husband is built upon the following Doctrines,
which are Universally assented to by the whole Club. Not to give him
his Head at first. Not to allow him too great Freedoms and
Familiarities. Not to be treated by him like a raw Girl, but as a
Woman that knows the World. Not to Lessen anything of her former
Figure. To celebrate the Generosity, or any other Vertue, of a
deceased Husband, which she would recommend to his Successor. To turn
away all his old Friends and Servants, that she may have the Dear Man
to her self. To make him disinherit the undutiful Children of any
former Wife. Never to be thoroughly convinced of his Affection, till he
has made over to her all his Goods and Chattels.
'After so long a Letter, I am, without more Ceremony,
Your Humble Servant, &c.
Contents
|
Friday, July 2, 1714 |
Addison |
—Præsens, absens ut sies.
Ter.

It is a hard and nice Subject for a Man to speak of himself, says
Cowley
;
it grates his own Heart to say anything of Disparagement,
and the Reader's Ears to hear any thing of Praise from him.
Let the
Tenour of his Discourse be what it will upon this Subject, it generally
proceeds from
Vanity.
An ostentatious Man will rather relate a Blunder
or an Absurdity he has committed, than be debarred from talking of his
own dear Person.
Some very great Writers have been guilty of this Fault. It is observed
of
Tully
in particular, that his Works run very much in the First
Person, and that he takes all Occasions of doing himself Justice.
'Does he think, says Brutus, that his Consulship deserves more
Applause than my putting Cæsar to Death, because I am not
perpetually talking of the Ides of March, as he is of the Nones of
December?'
I need not acquaint my learned Reader, that in the Ides of
March,
Brutus
destroyed
Caesar
, and that
Cicero
quashed the Conspiracy of
Cataline
in the Calends of
December
. How shocking soever this great
Man's talking of himself might have been to his Contemporaries, I must
confess I am never better pleased than when he is on this Subject. Such
Openings of the Heart give a Man a thorough Insight into his Personal
Character, and illustrate several Passages in the History of his Life:
Besides that, there is some little Pleasure in discovering the Infirmity
of a great Man, and seeing how the Opinion he has of himself agrees with
what the World entertains of him.
The Gentlemen of
Port-Royal
, who were more eminent for their Learning
and their Humility than any other in
France
, banish'd the way of
speaking in the First Person out of all their Works, as arising from
Vain-Glory and Self-Conceit. To shew their particular Aversion to it,
they branded this Form of Writing with the Name of an
Egotism
; a
Figure not to be found among the ancient Rhetoricians.
The most violent Egotism which I have met with in the Course of my
Reading, is that of Cardinal
Wolsey, Ego et Rex meus, I and my King
;
as perhaps the most eminent Egotist that ever appeared in the World, was
Montagne
the Author of the celebrated Essays. This lively old
Gascon
has woven all his bodily Infirmities into his Works, and after having
spoken of the Faults or Virtues of any other Man, immediately publishes
to the World how it stands with himself in that Particular. Had he kept
his own Counsel he might have passed for a much better Man, though
perhaps he would not have been so diverting an Author. The Title of an
Essay promises perhaps a Discourse upon
Virgil
or
Julius Cæsar
; but
when you look into it, you are sure to meet with more upon Monsieur
Montagne
, than of either of them. The younger
Scaliger
, who seems to
have been no great Friend to this Author, after having acquainted the
World that his Father sold Herrings, adds these Words;
La grande
fadaise de Montague, qui a escrit, qu'il aimoit mieux le vin blanc—que
diable a-t-on a faire de scavoir ce qu'il aime? For my Part, says
Montague, I am a great Lover of your White Wines—What the Devil
signifies it to the Publick, says Scaliger, whether he is a Lover of
White Wines or of Red Wines?
I cannot here forbear mentioning a Tribe of Egotists for whom I have
always had a mortal Aversion, I mean the Authors of Memoirs, who are
never mentioned in any Works but their own, and who raise all their
Productions out of this single Figure of Speech.
Most of our modern Prefaces savour very strongly of the Egotism. Every
insignificant Author fancies it of Importance to the World, to know that
he writ his Book in the Country, that he did it to pass away some of his
idle Hours, that it was published at the Importunity of Friends, or that
his natural Temper, Studies or Conversations, directed him to the Choice
of his Subject.
—Id populus curat scilicet.
Such Informations cannot but be highly improving to the Reader.
In Works of Humour, especially when a Man writes under a fictitious
Personage, the talking of one's self may give some Diversion to the
Publick; but I would advise every other Writer never to speak of
himself, unless there be something very considerable in his Character:
Tho' I am sensible this Rule will be of little Use in the World, because
there is no Man who fancies his Thoughts worth publishing, that does not
look upon himself as a considerable Person.
I shall close this Paper with a Remark upon such as are Egotists in
Conversation: These are generally the vain or shallow part of Mankind,
People being naturally full of themselves when they have nothing else in
them. There is one kind of Egotists which is very common in the World,
tho' I do not remember that any Writer has taken Notice of them; I mean
those empty conceited Fellows, who repeat as Sayings of their own, or
some of their particular Friends, several Jests which were made before
they were born, and which every one who has conversed in the World has
heard a hundred times over. A forward young Fellow of my Acquaintance
was very guilty of this Absurdity: He would be always laying a new Scene
for some old Piece of Wit, and telling us, That as he and
Jack
such-a-one were together, one or t'other of them had such a Conceit on
such an Occasion; upon which he would laugh very heartily, and wonder
the Company did not join with him. When his Mirth was over, I have often
reprehended him out of
Terence, Tuumne, obsecro te, hoc dictum erat?
vetus credidi
. But finding him still incorrigible, and having a
Kindness for the young Coxcomb, who was otherwise a good-natured Fellow,
I recommended to his Perusal the
Oxford
and
Cambridge
Jests, with
several little Pieces of Pleasantry of the same Nature. Upon the reading
of them, he was under no small Confusion to find that all his Jokes had
passed through several Editions, and that what he thought was a new
Conceit, and had appropriated to his own Use, had appeared in Print
before he or his ingenious Friends were ever heard of. This had so good
an Effect upon him, that he is content at present to pass for a Man of
plain Sense in his ordinary Conversation, and is never facetious but
when he knows his Company.
Footnote 1:
Essay 2.
Contents
—Magni nominis Umbra—
Lucan.

I shall entertain my Reader with two very curious Letters. The first of
them comes from a chimerical Person, who I believe never writ to any
Body before.
Sir ,
'I am descended from the Ancient Family of the
Blanks, a Name well
known among all Men of Business. It is always read in those little
white Spaces of Writing which want to be filled up, and which for that
Reason are called
blank Spaces, as of right appertaining to our
Family: For I consider my self as the Lord of a Mannor, who lays his
Claim to all Wastes or Spots of Ground that are unappropriated. I am a
near Kinsman to
John a Styles and
John a Nokes; and they, I am
told, came in with the Conquerour. I am mentioned oftner in both
Houses of Parliament than any other Person in Great Britain. My Name
is written, or more properly speaking, not written, thus, . I am one that can turn my Hand to every thing, and appear under
any Shape whatsoever. I can make my self Man, Woman, or Child. I am
sometimes metamorphosed into a Year of our Lord, a Day of the Month,
or an Hour of the Day. I very often represent a Sum of Mony, and am
generally the first Subsidy that is granted to the Crown. I have now
and then supplied the Place of several Thousands of Land Soldiers, and
have as frequently been employed in the Sea Service.
'Now,
Sir , my Complaint is this, that I am only made use of to serve a
Turn, being always discarded as soon as a proper Person is found out
to fill up my Place.
'If you have ever been in the Play-house before the Curtain rises, you
see most of the Front Boxes filled with Men of my Family, who
forthwith turn out and resign their Stations upon the Appearance of
those for whom they are retained.
'But the most illustrious Branch of the
Blanks are those who are
planted in high Posts, till such time as Persons of greater
Consequence can be found out to supply them. One of these
Blanks is
equally qualified for all Offices; he can serve in time of Need for a
Soldier, a Politician, a Lawyer, or what you please. I have known in
my Time many a Brother
Blank that has been born under a lucky
Planet, heap up great Riches, and swell into a Man of Figure and
Importance, before the Grandees of his Party could agree among
themselves which of them should step into his Place. Nay, I have known
a
Blank continue so long in one of these vacant Posts, (for such it
is to be reckoned all the Time a
Blank is in it) that he has grown
too formidable and dangerous to be removed.
'But to return to my self, since I am so very commodious a Person, and
so very necessary in all well-regulated Governments, I de
Sir e you will
take my Case into Consideration, that I may be no longer made a Tool
of, and only employed to stop a Gap. Such Usage, without a Pun, makes
me look very blank. For all which Reasons I humbly recommend my self
to your Protection, and am
Your most obedient Servant,
'Blank.
'P. S. I herewith send you a Paper, drawn up by a Country Attorney
employed by two Gentlemen, whose Names he was not acquainted with, and
who did not think fit to let him into the Secret which they were
transacting. I heard him call it a Blank Instrument, and read it after
the following Manner. You may see by this single Instance of what Use
I am to the busy World.
'I T. Blank, Esq., of Blank Town, in the County of Blank, do own my self indebted in the Sum of Blank, to Goodman Blank, for
the Service he did me in procuring for me the Goods following, Blank: And I do hereby promise the said Blank to pay unto him the
said Sum of Blank, on the Blank Day of the Month of Blank next
ensuing, under the Penalty and Forfeiture of Blank.
I shall take Time to consider the Case of this my imaginary
Correspondent, and in the mean while shall present my Reader with a
Letter which seems to come from a Person that is made up of Flesh and
Blood.
Good Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am married to a very honest Gentleman that is exceedingly
good-natured, and at the same time very cholerick. There is no
standing before him when he is in a Passion; but as soon as it is over
he is the best-humour'd Creature in the World. When he is angry, he
breaks all my China-Ware that chances to lie in his Way, and the next
Morning sends me in twice as much as he broke the Day before. I may
positively say, that he has broke me a Child's Fortune since we were
first marry'd together.
'As soon as he begins to fret, down goes every thing that is within
Reach of his Cane. I once prevailed upon him never to carry a Stick in
his Hand, but this saved me nothing; for upon seeing me do something
that did not please him, he kicked down a great Jarr, that cost him
above Ten Pound but the Week before. I then laid the Fragments
together in a Heap, and gave him his Cane again, deSir ing him that if
he chanced to be in Anger, he would spend his Passion upon the China
that was broke to his Hand: But the very next Day upon my giving a
wrong Message to one of the Servants, he flew into such a Rage, that
he swept down a Dozen Tea-Dishes, which, to my Misfortune, stood very
convenient for a Side-Blow.
I then removed all my China into a Room which he never frequents; but
I got nothing by this neither, for my Looking-Glasses immediately went
to Rack.
'In short, Sir , whenever he is in a Passion he is angry at every thing
that is brittle; and if on such Occasions he had nothing to vent his
Rage upon, I do not know whether my Bones would be in Safety. Let me
beg of you, Sir , to let me know whether there be any Cure for this
unaccountable Distemper; or if not, that you will be pleased to
publish this Letter: For my Husband having a great Veneration for your
Writings, will by that means know you do not approve of his Conduct. I
am,
Your most humble Servant, &c.
Contents
—Adsit
Regula, peccatis quæ pœnas irroget æquas:
Ne Scutica dignum horribili sectere flagello.
Hor.

It is the Work of a Philosopher to be every Day subduing his Passions,
and laying aside his Prejudices. I endeavour at least to look upon Men
and their Actions only as an impartial Spectator, without any regard to
them as they happen to advance or cross my own private Interest. But
while I am thus employed my self, I cannot help observing, how those
about me suffer themselves to be blinded by Prejudice and Inclination,
how readily they pronounce on every Man's Character, which they can give
in two Words, and make him either good for nothing, or qualified for
every thing. On the contrary, those who search thoroughly into humane
Nature, will find it much more difficult to determine the Value of their
Fellow-Creatures, and that Mens Characters are not thus to be given in
general Words. There is indeed no such thing as a Person entirely good
or bad; Virtue and Vice are blended and mixed together, in a greater or
less Proportion, in every one; and if you would search for some
particular good Quality in its most eminent Degree of Perfection, you
will often find it in a Mind, where it is darkned and eclipsed by an
hundred other irregular Passions.
Men have either no Character at all, says a celebrated Author, or it is
that of being inconsistent with themselves. They find it easier to join
Extremities, than to be uniform and of a Piece. This is finely
illustrated in
Xenophon's
Life of
Cyrus
the Great. That Author tells
us, that
Cyrus
having taken a most beautiful Lady named
Panthea
, the
Wife of
Abradatas
, committed her to the Custody of
Araspas
, a young
Persian
Nobleman, who had a little before maintain'd in Discourse,
that a Mind truly virtuous was incapable of entertaining an unlawful
Passion. The young Gentleman had not long been in Possession of his fair
Captive, when a Complaint was made to
Cyrus
, that he not only
sollicited the Lady
Panthea
to receive him in the Room of her absent
Husband, but that finding his Entreaties had no Effect, he was preparing
to make use of Force.
Cyrus
, who loved the young Man, immediately sent
for him, and in a gentle Manner representing to him his Fault, and
putting him in Mind of his former Assertion, the unhappy Youth,
confounded with a quick Sense of his Guilt and Shame, burst out into a
Flood of Tears, and spoke as follows.
Oh
Cyrus,
I am convinced that I hare two Souls. Love has taught me
this Piece of Philosophy. If I had but one Soul, it could not at the
same time pant after Virtue and Vice, wish and abhor the same thing. It
is certain therefore we have two Souls: When the good Soul rules, I
undertake noble and virtuous Actions; but when the bad Soul
predominates, I am forced to do Evil. All I can say at present is, that
I find my good Soul, encouraged by your Presence, has got the Better of
my bad.
I know not whether my Readers will allow of this Piece of Philosophy;
but if they will not, they must confess we meet with as different
Passions in one and the same Soul, as can be supposed in two. We can
hardly read the Life of a great Man who lived in former Ages, or
converse with any who is eminent among our Contemporaries, that is not
an Instance of what I am saying.
But as I have hitherto only argued against the Partiality and Injustice
of giving our Judgment upon Men in gross, who are such a Composition of
Virtues and Vices, of Good and Evil; I might carry this Reflection still
farther, and make it extend to most of their Actions. If on the one
Hand, we fairly weighed every Circumstance, we should frequently find
them obliged to do that Action we at first sight condemn, in order to
avoid another we should have been much more displeased with. If on the
other Hand we nicely examined such Actions as appear most dazzling to
the Eye, we should find most of them either deficient and lame in
several Parts, produced by a bad Ambition, or directed to an ill End.
The very same Action may sometimes be so oddly circumstanced, that it is
difficult to determine whether it ought to be rewarded or punish'd.
Those who compiled the Laws of
England
were so sensible of this, that
they have laid it down as one of their first Maxims,
It is better
suffering a Mischief than an Inconvenience
; which is as much as to say
in other Words, That since no Law can take in or provide for all Cases,
it is better private Men should have some Injustice done them, than that
a public Grievance should not be redressed. This is usually pleaded in
Defence of all those Hardships which fall on particular Persons in
particular Occasions, which could not be foreseen when a Law was made.
To remedy this however as much as possible, the Court of Chancery was
erected, which frequently mitigates and breaks the Teeth of the Common
Law, in Cases of Men's Properties, while in Criminal Cases there is a
Power of pardoning still lodged in the Crown.
Notwithstanding this, it is perhaps impossible in a large Government to
distribute Rewards and Punishments strictly proportioned to the Merits
of every Action. The
Spartan
Commonwealth was indeed wonderfully exact
in this Particular; and I do not remember in all my Reading to have met
with so nice an Example of Justice as that recorded by
Plutarch
, with
which I shall close my Paper for this Day.
The City of
Sparta
being unexpectedly attacked by a powerful Army of
Thebans
, was in very great Danger of falling into the Hands of their
Enemies. The Citizens suddenly gathering themselves into a Body, fought
with a Resolution equal to the Necessity of their Affairs, yet no one so
remarkably distinguished himself on this Occasion, to the Amazement of
both Armies, as
Isadas
the Son of
Phœbidas
, who was at that time in
the Bloom of his Youth, and very remarkable for the Comeliness of his
Person. He was coming out of the Bath when the Alarm was given, so that
he had not time to put on his Cloaths, much less his Armour; however
transported with a De
Sir
e to serve his Country in so great an Exigency,
snatching up a Spear in one Hand, and a Sword in the other, he flung
himself into the thickest Ranks of his Enemies. Nothing could withstand
his Fury: in what Part soever he fought he put the Enemies to Flight
without receiving a single Wound. Whether, says
Plutarch
, he was the
particular Care of some God, who rewarded his Valour that Day with an
extraordinary Protection, or, that his Enemies, struck with the
Unusualness of his Dress, and Beauty of his Shape, supposed him
something more than Man, I shall not determine.
The Gallantry of this Action was judged so great by the
Spartans
, that
the
Ephori
, or chief Magistrates, decreed he should be presented with
a Garland; but as soon as they had done so, fined him a thousand
Drachmas for going out to the Battle unarmed.
Contents
|
Friday, July 9, 1714 |
Addison |
—Deum namque ire per omnes
Terrasque, tractusque maris, cœlumque profundum.
Virg.

I was Yesterday about Sun-set walking in the open Fields, 'till the
Night insensibly fell upon me. I at first amused my self with all the
Richness and Variety of Colours, which appeared in the Western Parts of
Heaven: In Proportion as they faded away and went out, several Stars and
Planets appeared one after another 'till the whole Firmament was in a
Glow. The Blewness of the
Æther
was exceedingly heightened and
enlivened by the Season of the Year, and by the Rays of all those
Luminaries that passed through it. The
Galaxy
appeared in its most
beautiful White. To compleat the Scene, the full Moon rose at length in
that clouded Majesty, which
Milton
takes Notice of, and opened to the
Eye a new Picture of Nature, which was more finely shaded, and disposed
among softer Lights than that which the Sun had before discovered to us.
As I was surveying the Moon walking in her Brightness and taking her
Progress among the Constellations, a Thought rose in me which I believe
very often perplexes and disturbs Men of serious and contemplative
Natures.
David
himself fell into it in that Reflection,
When I consider the Heavens the Work of thy Fingers, the Moon and the
Stars which thou hast ordained; what is man that thou art mindful of
him, and the son of man that thou regardest him!
In the same manner when I considered that infinite Host of Stars, or, to
speak more Philosophically, of Suns, which were then shining upon me,
with those innumerable Sets of Planets or Worlds, which were moving
round their respective Suns; When I still enlarged the Idea, and
supposed another Heaven of Suns and Worlds rising still above this which
we discovered, and these still enlightened by a superior Firmament of
Luminaries, which are planted at so great a Distance, that they may
appear to the Inhabitants of the former as the Stars do to us; In short,
whilst I pursued this Thought, I could not but reflect on that little
insignificant Figure which I my self bore amidst the Immensity of God's
Works.
Were the Sun, which enlightens this Part of the Creation, with all the
Host of Planetary Worlds, that move about him, utterly extinguished and
annihilated, they would not be missed more than a grain of Sand upon the
Sea-shore. The Space they possess is so exceedingly little, in
Comparison of the whole, that it would scarce make a
Blank
in the
Creation. The Chasm would be imperceptible to an Eye, that could take in
the whole Compass of Nature, and pass from one end of the Creation to
the other, as it is possible there may be such a Sense in our selves
hereafter, or in Creatures which are at present more exalted than our
selves. We see many Stars by the help of Glasses, which we do not
discover with our naked Eyes; and the finer our Telescopes are, the more
still are our Discoveries.
Huygenius
carries this Thought so far, that
he does not think it impossible there may be Stars whose Light is not
yet travelled down to us, since their first Creation. There is no
Question but the Universe has certain Bounds set to it; but when we
consider that it is the Work of infinite Power, prompted by infinite
Goodness, with an infinite Space to exert it self in, how can our
Imagination set any Bounds to it?
To return therefore to my first Thought, I could not but look upon
myself with secret Horrour, as a Being that was not worth the smallest
Regard of one who had so great a Work under his Care and
Superintendency. I was afraid of being overlooked amidst the Immensity
of Nature, and lost among that infinite Variety of Creatures, which in
all Probability swarm through all these immeasurable Regions of Matter.
In order to recover my self from this mortifying Thought, I considered
that it took its Rise from those narrow Conceptions, which we are apt to
entertain of the Divine Nature. We our selves cannot attend to many
different Objects at the same Time. If we are careful to inspect some
Things, we must of Course neglect others. This Imperfection which we
observe in our selves, is an Imperfection that cleaves in some Degree to
Creatures of the highest Capacities, as they are Creatures, that is,
Beings of finite and limited Natures. The Presence of every created
Being is confined to a certain Measure of Space, and consequently his
Observation is stinted to a certain number of Objects. The Sphere in
which we move, and act, and understand, is of a wider Circumference to
one Creature than another, according as we rise one above another in the
Scale of Existence. But the widest of these our Spheres has its
Circumference. When therefore we reflect on the Divine Nature, we are so
used and accustomed to this Imperfection in our selves, that we cannot
forbear in some measure ascribing it to him in whom there is no shadow
of Imperfection. Our Reason indeed assures us that his Attributes are
Infinite, but the Poorness of our Conceptions is such, that it cannot
forbear setting Bounds to every Thing it contemplates, till our Reason
comes again to our Succour, and throws down all those little Prejudices
which rise in us unawares, and are natural to the Mind of Man.
We shall therefore utterly extinguish this melancholy Thought, of our
being overlooked by our Maker in the Multiplicity of his Works, and the
Infinity of those Objects among which he seems to be incessantly
employed, if we consider, in the first Place, that he is Omnipresent;
and, in the second, that he is Omniscient.
If we consider him in his Omnipresence: His Being passes through,
actuates, and supports the whole Frame of Nature. His Creation, and
every Part of it, is full of him. There is nothing he has made, that is
either so distant, so little, or so inconsiderable, which he does not
essentially inhabit. His Substance is within the Substance of every
Being, whether material, or immaterial, and as intimately present to it
as that Being is to it self. It would be an Imperfection in him, were he
able to remove out of one Place into another, or to withdraw himself
from any Thing he has created, or from any Part of that Space which is
diffused and spread abroad to Infinity. In short, to speak of him in the
Language of the old Philosopher, he is a Being whose Centre is every
where, and his Circumference no where.
In the second Place, he is Omniscient as well as Omnipresent. His
Omniscience indeed necessarily and naturally flows from his
Omnipresence; he cannot but be conscious of every Motion that arises in
the whole material World, which he thus essentially pervades, and of
every Thought that is stirring in the intellectual World, to every Part
of which he is thus intimately united. Several Moralists have considered
the Creation as the Temple of God, which he has built with his own
Hands, and which is filled with his Presence. Others have considered
infinite Space as the Receptacle, or rather the Habitation of the
Almighty: But the noblest and most exalted Way of considering this
infinite Space is that of
Sir
Isaac Newton
, who calls it the
Sensorium
of the Godhead. Brutes and Men have their
Sensoriola
, or
little
Sensoriums
, by which they apprehend the Presence and perceive
the Actions of a few Objects, that lie contiguous to them. Their
Knowledge and Observation turns within a very narrow Circle. But as God
Almighty cannot but perceive and know every Thing in which he resides,
Infinite Space gives Room to Infinite Knowledge, and is, as it were, an
Organ to Omniscience.
Were the Soul separate from the Body, and with one Glance of Thought
should start beyond the Bounds of the Creation, should it for Millions
of Years continue its Progress through Infinite Space with the same
Activity, it would still find it self within the Embrace of its Creator,
and encompassed round with the Immensity of the Godhead. Whilst we are
in the Body he is not less present with us, because he is concealed from
us.
O that I knew where I might find him! says Job. Behold I go
forward, but he is not there; and backward, but I cannot perceive him.
On the left hand, where he does work, but I cannot behold him: he
hideth himself on the right hand, that I cannot see him.
In short, Reason as well as Revelation assures us, that he cannot be
absent from us, notwithstanding he is undiscovered by us.
In this Consideration of God Almighty's Omnipresence and Omniscience
every uncomfortable Thought vanishes. He cannot but regard every Thing
that has Being, especially such of his Creatures who fear they are not
regarded by him. He is privy to all their Thoughts, and to that Anxiety
of Heart in particular, which is apt to trouble them on this Occasion:
For, as it is impossible he should overlook any of his Creatures, so we
may be confident that he regards, with an Eye of Mercy, those who
endeavour to recommend themselves to his Notice, and in an unfeigned
Humility of Heart think themselves unworthy that he should be mindful of
them.
Contents
Militia Species Amor est.
Ovid.

As my Correspondents begin to grow pretty numerous, I think my self
obliged to take some Notice of them, and shall therefore make this Paper
a Miscellany of Letters. I have, since my reassuming the Office of
SPECTATOR, received abundance of Epistles from Gentlemen of the Blade,
who, I find, have been so used to Action that they know not how to lie
still: They seem generally to be of Opinion, that the Fair at home ought
to reward them for their Services abroad, and that, till the Cause of
their Country calls them again into the Field, they have a sort of Right
to Quarter themselves upon the Ladies. In Order to favour their
Approaches, I am de
Sir
ed by some to enlarge upon the Accomplishments of
their Profession, and by others to give them my Advice in the carrying
on of their Attacks. But let us hear what the Gentlemen say for
themselves.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Tho' it may look somewhat perverse amidst the Arts of Peace, to talk
too much of War, it is but Gratitude to pay the last Office to its
Manes, since even Peace it self is, in some Measure, obliged to it
for its Being.
'You have, in your former Papers, always recommended the Accomplished
to the Favour of the Fair; and, I hope, you will allow me to represent
some Part of a Military Life not altogether unnecessary to the forming
a Gentleman. I need not tell you that in
France, whose Fashions we
have been formerly so fond of, almost every one derives his Pretences
to Merit from the Sword; and that a Man has scarce the Face to make
his Court to a Lady, without some Credentials from the Service to
recommend him. As the Profession is very ancient, we have Reason to
think some of the greatest Men, among the old
Romans, derived many
of their Virtues from it, their Commanders being frequently, in other
Respects, some of the most shining Characters of the Age.
'The Army not only gives a Man Opportunities of exercising those two
great Virtues
Patience and
Courage, but often produces them in
Minds where they had scarce any Footing before. I must add, that it is
one of the best Schools in the World to receive a general Notion of
Mankind in, and a certain Freedom of Behaviour, which is not so easily
acquired in any other Place. At the same Time I must own, that some
Military Airs are pretty extraordinary, and that a Man who goes into
the Army a Coxcomb will come out of it a Sort of Publick Nuisance: But
a Man of Sense, or one who before had not been sufficiently used to a
mixed Conversation, generally takes the true Turn. The Court has in
all Ages been allowed to be the Standard of Good-breeding; and I
believe there is not a juster Observation in Monsieur
Rochefoucault,
than that
A Man who has been bred up wholly to
Business, can never get the Air of a Courtier at Court, but
will immediately catch it in the Camp.
The Reason of this most certainly is, that the very Essence of
Good-Breeding and Politeness consists in several Niceties, which are
so minute that they escape his Observation, and he falls short of the
Original he would copy after; but when he sees the same Things charged
and aggravated to a Fault, he no sooner endeavours to come up to the
Pattern which is set before him, than, though he stops somewhat short
of that, he naturally rests where in reality he ought. I was two or
three Days ago, mightily pleased with the Observation of an humourous
Gentleman upon one of his Friends, who was in other Respects every way
an accomplished Person, That
he wanted nothing but a Dash of the
Coxcomb in him; by which he understood a little of that Alertness and
Unconcern in the common Actions of Life, which is usually so visible
among Gentlemen of the Army, and which a Campaign or two would
infallibly have given him.
'You will easily guess,
Sir , by this my Panegyrick upon a Military
Education, that I am my self a Soldier, and indeed I am so; I
remember, within three Years after I had been in the Army, I was
ordered into the Country a Recruiting. I had very particular Success
in this Part of the Service, and was over and above assured, at my
going away, that I might have taken a young Lady, who was the most
considerable Fortune in the County, along with me. I preferred the
Pursuit of Fame at that time to all other Considerations, and tho' I
was not absolutely bent on a Wooden Leg, resolved at least to get a
Scar or two for the good of
Europe. I have at present as much as I
de
Sir e of this Sort of Honour, and if you could recommend me
effectually, should be well enough contented to pass the Remainder of
my Days in the Arms of some dear kind Creature, and upon a pretty
Estate in the Country: This, as I take it, would be following the
Example of
Lucius Cincinnatus, the old
Roman Dictator, who at the
End of a War left the Camp to follow the Plow. I am,
Sir , with all
imaginable Respect,
Your most Obedient,
Humble Servant,
Will. Warly.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I am an Half-pay Officer, and am at present with a Friend in the
Country. Here is a rich Widow in the Neighbourhood, who has made Fools
of all the Fox-hunters within fifty Miles of her. She declares she
intends to marry, but has not yet been asked by the Man she could
like. She usually admits her humble Admirers to an Audience or two,
but, after she has once given them Denial will never see them more. I
am assured by a Female Relation, that I shall have fair Play at her;
but as my whole Success Depends on my first Approaches, I de
Sir e your
Advice, whether I had best
Storm or proceed by way of
Sap.
I am, Sir , Yours, &c.
'
P. S. I had forgot to tell you, that I have already carried one of
her Outworks, that is, secured her Maid.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I have assisted in several Sieges in the
Low-Countries, and being
still willing to employ my Talents, as a Soldier and Engineer, lay
down this Morning at Seven a Clock before the Door of an obstinate
Female, who had for some time refused me Admittance. I made a Lodgment
in an outer Parlour about Twelve: The Enemy retired to her
Bed-Chamber, yet I still pursued, and about two a-Clock this Afternoon
she thought fit to Capitulate. Her Demands are indeed somewhat high,
in Relation to the Settlement of her Fortune. But being in Possession
of the House, I intend to insist upon
Carte-Blanche, and am in
hopes, by keeping off all other Pretenders for the Space of twenty
four Hours, to starve her into a Compliance. I beg your speedy Advice,
and am,
Sir , Yours, Peter Push.
From my Camp in
Red-Lion Square,
Saturday 4, in the Afternoon.
Contents
|
Wednesday, July 14, 1714 |
Addison |
—Inceptus clamor frustratur hiantes.
Virg.

I have received private Advice from some of my Correspondents, that if I
would give my Paper a general Run, I should take care to season it with
Scandal. I have indeed observed of late, that few Writings sell which
are not filled with great Names and illustrious Titles. The Reader
generally casts his Eye upon a new Book, and if he finds several Letters
separated from one another by a Dash,
buys it up, and peruses it with
great Satisfaction. An
M
and an
h
, a
T
and an
r
, with a
short Line between them, has sold many an Insipid Pamphlet. Nay I have
known a whole Edition go off by vertue of two or three well written
&c—'s.
A sprinkling of
Words
Faction, Frenchman, Papist, Plunderer,
and
the like significant Terms, in an Italick Character, have also a very
good Effect upon the Eye of the
Purchaser
; not to mention
Scribler, Lier, Rogue, Rascal, Knave,
and
Villain
, without which it
is impossible to carry on a Modern Controversie.
Our Party-writers are so sensible of the secret Vertue of an Innuendo to
recommend their Productions, that of late they never mention the Q—n or
P—l at length, though they speak of them with Honour, and with that
Deference which is due to them from every private Person. It gives a
secret Satisfaction to a Peruser of these mysterious Works, that he is
able to decipher them without help, and, by the Strength of his own
natural Parts, to fill up a Blank-Space, or make out a Word that has
only the first or last Letter to it.
Some of our Authors indeed, when they would be more Satyrical than
ordinary, omit only the Vowels of a great Man's Name, and fall most
unmercifully upon all the Consonants. This way of Writing was first of
all introduced by
T—m Br—wn
, of facetious Memory, who, after having
gutted a proper Name of all its intermediate Vowels, used to plant it in
his Works, and make as free with it as he pleased, without any Danger of
the Statute.
That I may imitate these celebrated Authors, and publish a Paper which
shall be more taking than ordinary, I have here drawn up a very curious
Libel, in which a Reader of Penetration will find a great deal of
concealed Satyr, and if he be acquainted with the present Posture of
Affairs, will easily discover the Meaning of it.
'If there are
four
Persons in the Nation who endeavour to bring all
things into Confusion, and ruin their native Country, I think every
honest
Engl—shm—n
ought to be upon his Guard. That there are such,
every one will agree with me, who hears me name *** with his first
Friend and Favourite ***, not to mention *** nor ***. These People may
cry Ch—rch, Ch—rch, as long as they please, but, to make use of a homely
Proverb, The Proof of the P—dd-ng is in the eating. This I am sure of,
that if a
certain Prince
should concur with a
certain Prelate
, (and
we have Monsieur Z—n's Word for it) our Posterity would be in a sweet
P—ckle. Must the
British
Nation suffer forsooth, because my Lady
Q—p—t—s
has been disobliged? Or is it reasonable that our
English
Fleet, which used to be the Terror of the Ocean, should lie Windbound
for the sake of a ——. I love to speak out and declare my Mind clearly,
when I am talking for the Good of my Country. I will not make my Court
to an ill Man, tho' he were a B—y or a T—t. Nay, I would not stick to
call so wretched a Politician, a Traitor, an Enemy to his Country, and a
Bl—nd—rb—ss, &c., &c.
The remaining Part of this Political Treatise, which is written after
the manner of the most celebrated Authors in
Great Britain
, I may
communicate to the Publick at a more convenient Season. In the mean
while I shall leave this with my curious Reader, as some ingenious
Writers do their Enigmas, and if any sagacious Person can fairly
unriddle it, I will print his Explanation, and, if he pleases, acquaint
the World with his Name.
I hope this short Essay will convince my Readers, it is not for want of
Abilities that I avoid State-tracts, and that if I would apply my Mind
to it, I might in a little time be as great a Master of the Political
Scratch as any the most eminent Writer of the Age. I shall only add,
that in order to outshine all this Modern Race of
Syncopists
, and
thoroughly content my
English
Readers, I intend shortly to publish a
SPECTATOR, that shall not have a single Vowel in it.
Footnote 1:
For 'Marlborough' and 'Treasurer.'
Footnote 2:
Reader.
Contents
|
Friday, July 16, 1714 |
Addison |
—Dum recitas, incipit esse Tuus—
Mart.

I was Yesterday in a Coffee-House not far from the
Royal Exchange
,
where I observed three Persons in close Conference over a Pipe of
Tobacco; upon which, having filled one for my own use, I lighted it at
the little Wax Candle that stood before them; and after having thrown in
two or three Whiffs amongst them, sat down and made one of the Company.
I need not tell my Reader, that lighting a Man's Pipe at the same
Candle, is looked upon among Brother-smokers as an Overture to
Conversation and Friendship. As we here lay our Heads together in a very
amicable Manner, being intrenched under a Cloud of our own raising, I
took up the last SPECTATOR, and casting my Eye over it,
The
SPECTATOR,
says I,
is very witty to-Day;
upon which a lusty lethargick old
Gentleman, who sat at the Upper-end of the Table, having gradually blown
out of his Mouth a great deal of Smoke, which he had been collecting for
some Time before,
Ay,
says he,
more witty than wise I am afraid.
His
Neighbour who sat at his right Hand immediately coloured, and being an
angry Politician, laid down his Pipe with so much Wrath that he broke it
in the Middle, and by that Means furnished me with a Tobacco-stopper. I
took it up very sedately, and looking him full in the Face, made use of
it from Time to Time all the while he was speaking:
This fellow,
says
he,
can't for his Life keep out of Politicks. Do you see how he abuses four great Men here?
I fix'd my Eye very attentively on the Paper, and
asked him if he meant those who were represented by Asterisks.
Asterisks,
says he,
do you call them? they are all of them Stars. He
might as well have put Garters to 'em. Then pray do but mind the two or
three next Lines? Ch—rch and P—dd-ing in the same Sentence! Our Clergy
are very much beholden to him.
Upon this the third Gentleman, who was
of a mild Disposition, and, as I found, a Whig in his Heart, de
Sir
ed him
not to be too severe upon the
Spectator
neither; For, says he,
you find
he is very cautious of giving Offence, and has therefore put two Dashes
into his Pudding.
A Fig for his Dash,
says the angry Politician.
In
his next Sentence he gives a plain Innuendo, that our Posterity will be
in a sweet P—ckle. What does the Fool mean by his Pickle? Why does not
he write it at length, if he means honestly?
I have read over the whole
Sentence,
says I;
but I look upon the Parenthesis in the Belly of it
to be the most dangerous Part, and as full of Insinuations as it can
hold.
But who,
says I,
is my Lady Q—p—t—s?
Ay, Answer that if you can,
Sir ,
says the furious Statesman to the poor Whig that sate over-against
him. But without giving him Time to reply,
I do assure you,
says he,
were I my Lady
Q—p—t—s,
I would sue him for
Scandalum Magnatum.
What is the World come to? Must every Body be allowed to—?
He had by
this time filled a new Pipe and applying it to his Lips, when we
expected the last Word of his Sentence, put us off with a Whiff of
Tobacco; which he redoubled with so much Rage and Trepidation, that he
almost stifled the whole Company. After a short Pause, I owned that I
thought the
Spectator
had gone too far in writing so many Letters of my
Lady
Q—p—t—s'
s Name;
but however
, says I,
he has made a little
Amends for it in his next Sentence, where he leaves a blank Space
without so much as a Consonant to direct us? I mean
, says I,
after
those Words
, The Fleet, that used to be the Terrour of the Ocean,
should be Wind-bound for the sake of a ——;
after which ensues a Chasm,
that in my Opinion looks modest enough.
Sir
, says my Antagonist,
you
may easily know his Meaning by his Gaping; I suppose he designs his
Chasm, as you call it, for an Hole to creep out at, but I believe it
will hardly serve his Turn. Who can endure to see the great Officers of
State, the
B—y's
and
T—t's
treated after so scurrilous a Manner?
I
can't for my Life
, says I,
imagine who they are the
Spectator
means?
No!
says he,—
Your humble Servant, Sir !
Upon which he flung himself
back in his Chair after a contemptuous Manner, and smiled upon the old
lethargick Gentleman on his left Hand, who I found was his great
Admirer. The Whig however had begun to conceive a Good-will towards me,
and seeing my Pipe out, very generously offered me the Use of his Box;
but I declined it with great Civility, being obliged to meet a Friend
about that Time in another Quarter of the City.
At my leaving the Coffee-house, I could not forbear reflecting with my
self upon that gross Tribe of Fools who may be termed the
Overwise
,
and upon the Difficulty of writing any thing in this censorious Age,
which a weak Head may not construe into private Satyr and personal
Reflection.
A Man who has a good Nose at an Innuendo, smells Treason and Sedition in
the most innocent Words that can be put together, and never sees a Vice
or Folly stigmatized, but finds out one or other of his Acquaintance
pointed at by the Writer. I remember an empty pragmatical Fellow in the
Country, who upon reading over
the whole Duty of Man
, had written the
Names of several Persons in the Village at the Side of every Sin which
is mentioned by that excellent Author; so that he had converted one of
the best Books in the World into a Libel against the 'Squire,
Church-wardens, Overseers of the Poor, and all other the most
considerable Persons in the Parish. This Book with these extraordinary
marginal Notes fell accidentally into the Hands of one who had never
seen it before; upon which there arose a current Report that Somebody
had written a Book against the 'Squire and the whole Parish. The
Minister of the Place having at that Time a Controversy with some of his
Congregation upon the Account of his Tythes, was under some Suspicion of
being the Author, 'till the good Man set his People right by shewing
them that the satyrical Passages might be applied to several others of
two or three neighbouring Villages, and that the Book was writ against
all the Sinners in England.
Contents
|
Monday, July 19, 1714 |
Addison |
Reges dicuntur multis urgere culullis
Et torquere mero, quem perspexisse laborent,
An sit amicitia dignus—
Hor.

No Vices are so incurable as those which Men are apt to glory in. One
would wonder how Drunkenness should have the good Luck to be of this
Number.
Anacharsis
, being invited to a Match of Drinking at
Corinth
,
demanded the Prize very humorously, because he was drunk before any of
the rest of the Company: for, says he, when we run a Race, he who
arrives at the Goal first is entitled to the Reward. On the contrary, in
this thirsty Generation, the Honour falls upon him who carries off the
greatest Quantity of Liquor, and knocks down the rest of the Company. I
was the other Day with honest
Will. Funnell
the
West Saxon
, who was
reckoning up how much Liquor had past through him in the last twenty
Years of his Life, which, according to his Computation, amounted to
twenty three Hogsheads of October, four Ton of Port, half a Kilderkin of
small Beer, nineteen Barrels of Cider, and three Glasses of Champaign;
besides which, he had assisted at four hundred Bowls of Punch, not to
mention Sips, Drams, and Whets without Number. I question not but every
Reader's Memory will suggest to him several ambitious young Men, who are
as vain in this Particular as
Will. Funnell
, and can boast of as
glorious Exploits.
Our modern Philosophers observe, that there is a general Decay of
Moisture in the Globe of the Earth. This they chiefly ascribe to the
Growth of Vegetables, which incorporate into their own Substance many
fluid Bodies that never return again to their former Nature: But, with
Submission, they ought to throw into their Account those innumerable
rational Beings which fetch their Nourishment chiefly out of Liquids;
especially when we consider that Men, compared with their
Fellow-Creatures, drink much more than comes to their Share.
But however highly this Tribe of People may think of themselves, a
drunken Man is a greater Monster than any that is to be found among all
the Creatures which God has made; as indeed there is no Character which
appears more despicable and deformed, in the Eyes of all reasonable
Persons, than that of a Drunkard.
Bonosus
, one of our own Countrymen,
who was addicted to this Vice, having set up for a Share in the Roman
Empire, and being defeated in a great Battle, hang'd himself. When he
was seen by the Army in this melancholy Situation, notwithstanding he
had behaved himself very bravely, the common Jest was, That the Thing
they saw hanging upon the Tree before them, was not a Man but a Bottle.
This Vice has very fatal Efects on the Mind, the Body, and Fortune of
the Person who is devoted to it.
In regard to the Mind, it first of all discovers every Flaw in it. The
sober Man, by the Strength of Reason, may keep under and subdue every
Vice or Folly to which he is most inclined; but Wine makes every latent
Seed sprout up in the Soul, and shew it self. It gives Fury to the
Passions, and Force to those Objects which are apt to produce them.
When a young Fellow complained to an old Philosopher that his Wife was
not handsome,
Put less Water in your Wine, says the Philosopher, and
you'll quickly make her so
. Wine heightens Indifference into Love, Love
into Jealousy, and Jealousy into Madness. It often turns the
Good-natured Man into an Ideot, and the Cholerick into an Assassin. It
gives Bitterness to Resentment, it makes Vanity insupportable, and
displays every little Spot of the Soul in its utmost Deformity. Nor does
this Vice only betray the hidden Faults of a Man, and shew them in the
most odious Colours, but often occasions Faults to which he is not
naturally subject. There is more of Turn than of Truth in a Saying of
Seneca, That Drunkenness does not produce but discover Faults. Common
Experience teaches us the contrary. Wine throws a Man out of himself,
and infuses Qualities into the Mind, which she is a Stranger to in her
sober Moments. The Person you converse with, after the third Bottle, is
not the same Man who at first sat down at Table with you. Upon this
Maxim is founded one of the prettiest Sayings I ever met with, which is
ascribed to Publius Syrus,
Qui ebrium ludificat ladit absentem; He who
jests upon a Man that is Drunk, injures the Absent.
Thus does Drunkenness act in direct Contradiction to Reason, whose
Business it is to clear the Mind of every Vice which is crept into it,
and to guard it against all the Approaches of any that endeavours to
make its Entrance. But besides these ill Effects which this Vice
produces in the Person who is actually under its Dominion, it has also a
bad Influence on the Mind even in its sober Moments, as it insensibly
weakens the Understanding, impairs the Memory, and makes those Faults
habitual which are produced by frequent Excesses.
I should now proceed to shew the ill Effects which this Vice has on the
Bodies and Fortunes of Men; but these I shall reserve for the Subject of
some future Paper.
Contents
—Nugaque canora—
Hor.

There is scarce a Man living who is not actuated by Ambition. When this
Principle meets with an honest Mind and great Abilities, it does
infinite Service to the World; on the contrary, when a Man only thinks
of distinguishing himself, without being thus qualified for it, he
becomes a very pernicious or a very ridiculous Creature. I shall here
confine my self to that petty kind of Ambition, by which some Men grow
eminent for odd Accomplishments and trivial Performances. How many are
there whose whole Reputation depends upon a Punn or a Quibble? You may
often see an Artist in the Streets gain a Circle of Admirers, by
carrying a long Pole upon his Chin or Forehead in a perpendicular
Posture. Ambition has taught some to write with their Feet, and others
to walk upon their Hands. Some tumble into Fame, others grow immortal by
throwing themselves through a Hoop.
Cætera de genere hoc adeo sunt multa, loquacem
Delassare valent Fabium—
I am led into this Train of Thought by an Adventure I lately met with.
I
the other Day at a Tavern, where the Master of the House
accommodating us himself with every thing we wanted, I accidentally fell
into a Discourse with him; and talking of a certain great Man, who shall
be nameless, he told me, That he had sometimes the Honour
to treat him
with a Whistle;
(adding by the way of Parenthesis)
For you must know,
Gentlemen, that I whistle the best of any Man in
Europe. This naturally
put me upon de
Sir
ing him to give us a Sample of his Art; upon which he
called for a Case-Knife, and applying the Edge of it to his Mouth,
converted it into a musical Instrument, and entertained me with an
Italian
Solo. Upon laying down the Knife, he took up a Pair of clean
Tobacco Pipes; and after having slid the small End of them over the
Table in a most melodious Trill, he fetched a Tune out of them,
whistling to them at the same time in Consort. In short, the
Tobacco-Pipes became
Musical Pipes
in the Hands of our Virtuoso; who
confessed to me ingenuously, he had broke such Quantities of them, that
he had almost broke himself, before he had brought this Piece of Musick
to any tolerable Perfection. I then told him I would bring a Company of
Friends to dine with him the next Week, as an Encouragement to his
Ingenuity; upon which he thanked me, saying, That he would provide
himself with a new Frying-Pan against that Day. I replied, That it was
no matter; Roast and Boiled would serve our Turn. He smiled at my
Simplicity, and told me, That it was his Design to give us a Tune upon
it. As I was surprised at such a Promise, he sent for an old Frying-Pan,
and grating it upon the Board, whistled to it in such a melodious
Manner, that you could scarce distinguish it from a Base-Viol. He then
took his Seat with us at the Table, and hearing my Friend that was with
me humm over a Tune to himself, he told him if he would sing out he
would accompany his Voice with a Tobacco-Pipe. As my Friend has an
agreeable Base, he chose rather to sing to the Frying-Pan; and indeed
between them they made up a most extraordinary Consort. Finding our
Landlord so great a Proficient in Kitchen-Musick, I asked him if he was
Master of the Tongs and Key. He told Me that he had laid it down some
Years since, as a little unfashionable: but that if I pleased he would
give me a Lesson upon the Gridiron. He then informed me that he had
added two Bars to the Gridiron, in order to give it a greater Compass of
Sound; and I perceived was as well pleased with the Invention, as
Sappho
could have been upon adding two Strings to the Lute. To be
short, I found that his whole Kitchen was furnished with musical
Instruments; and could not but look upon this Artist as a kind of
Burlesque Musician.
He afterwards of his own Accord fell into the Imitation of several
Singing-Birds. My Friend and I toasted our Mistresses to the
Nightingale, when all of a sudden we were surpriz'd with the musick of
the Thrush. He next proceeded to the Sky-Lark, mounting up by a proper
Scale of Notes, and afterwards falling to the Ground with a very easy
and regular Descent. He then contracted his Whistle to the Voice of
several Birds of the smallest Size. As he is a Man of a larger Bulk and
higher Stature than ordinary, you would fancy him a Giant when you
look'd upon him, and a Tom Tit when you shut your Eyes. I must not omit
acquainting my Reader, that this accomplished Person was formerly the
Master of a Toy-shop near
Temple-Bar
; and that the famous
Charles
Mathers
was bred up under him. I am told that the Misfortunes which he
has met with in the World, are chiefly owing to his great Application to
his Musick; and therefore cannot but recommend him to my Readers as one
who deserves their Favour, and may afford them great Diversion over a
Bottle of Wine, which he sells at the Queen's Arms, near the End of the
little Piazza in
Covent-Garden.
Footnote 1:
Named Daintry. He was of the trained bands, and commonly
known as Captain Daintry.
Contents
|
Friday, July 23, 1714 |
Addison |
—Cœlum quid querimus ultra?
Luc.

As the Work I have engaged in, will not only consist of Papers of Humour
and Learning, but
several Essays Moral and Divine, I shall publish
the following one, which is founded on a former SPECTATOR
, and sent
me by a particular Friend, not questioning but it will please such of my
Readers, as think it no Disparagement to their Understandings to give
way sometimes to a serious Thought.
Sir ,
In your Paper of
Friday the 9th Instant, you had Occasion to
consider the Ubiquity of the Godhead, and at the same time, to shew,
that as he is present to every thing, he cannot but be attentive to
every thing, and privy to all the Modes and Parts of its Existence;
or, in other Words, that his Omniscience and Omnipresence are
coexistent, and run together through the whole Infinitude of Space.
This Consideration might furnish us with many Incentives to Devotion
and Motives to Morality, but as this Subject has been handled by
several excellent Writers, I shall consider it in a Light wherein I
have not seen it placed by others.
- First, How disconsolate is the Condition of an intellectual Being
who is thus present with his Maker, but at the same time receives no
extraordinary Benefit or Advantage from this his Presence!
-
Secondly, How deplorable is the Condition of an intellectual Being,
who feels no other Effects from this his Presence but such as proceed
from Divine Wrath and Indignation!
-
Thirdly, How happy is the Condition of that intellectual Being, who
is sensible of his Maker's Presence from the secret Effects of his
Mercy and Loving-kindness!
First, How disconsolate is the Condition of an intellectual Being,
who is thus present with his Maker, but at the same time receives no
extraordinary Benefit or Advantage from this his Presence!
Every
Particle of Matter is actuated by this Almighty Being which passes
through it. The Heavens and the Earth, the Stars and Planets, move and
gravitate by Vertue of this great Principle within them. All the dead
Parts of Nature are invigorated by the Presence of their Creator, and
made capable of exerting their respective Qualities. The several
Instincts, in the brute Creation, do likewise operate and work towards
the several Ends which are agreeable to them, by this Divine Energy.
Man only, who does not co-operate with this holy Spirit, and is
unattentive to his Presence, receives none of those Advantages from
it, which are perfective of his Nature, and necessary to his
Well-being. The Divinity is with him, and in him, and everywhere about
him, but of no Advantage to him. It is the same thing to a Man without
Religion, as if there were no God in the World. It is indeed
impossible for an infinite Being to remove himself from any of his
Creatures, but tho' he cannot withdraw his Essence from us, which
would argue an Imperfection in him, he can withdraw from us all the
Joys and Consolations of it. His Presence may perhaps be necessary to
support us in our Existence; but he may leave this our Existence to it
self, with regard to its Happiness or Misery. For, in this Sense, he
may cast us away from his Presence, and take his holy Spirit from us.
This single Consideration one would think sufficient to make us open
our Hearts to all those Infusions of Joy and Gladness which are so
near at Hand, and ready to be poured in upon us; especially when we
consider,
Secondly, The deplorable Condition of an intellectual Being who
feels no other Effects from his Maker's Presence, but such as proceed
from Divine Wrath and Indignation!
We may assure our selves, that the great Author of Nature will not
always be as one who is indifferent to any of his Creatures. Those who
will not feel him in his Love, will be sure at length to feel him in
his Displeasure. And how dreadful is the Condition of that Creature,
who is only sensible of the Being of his Creator by what he suffers
from him! He is as essentially present in Hell as in Heaven, but the
Inhabitants of those accursed Places behold him only in his Wrath, and
shrink within the Flames to conceal themselves from him. It is not in
the Power of Imagination to conceive the fearful Effects of
Omnipotence incensed.
But I shall only consider the Wretchedness of an intellectual Being,
who, in this Life, lies under the Displeasure of him, that at all Times
and in all Places is intimately united with him. He is able to disquiet
the Soul, and vex it in all its Faculties. He can hinder any of the
greatest Comforts of Life from refreshing us, and give an Edge to every
one of its slightest Calamities. Who then can bear the Thought of being
an Out-cast from his Presence, that is, from the Comforts of it, or of
feeling it only in its Terrors? How pathetick is that Expostulation of
Job, when, for the Tryal of his Patience, he was made to look upon
himself in this deplorable Condition!
Why hast thou set me as a Mark against thee, so that I am
become a Burthen to my self?
But,
Thirdly, how happy is the Condition of that intellectual Being,
who is sensible of his Maker's Presence from the secret Effects of his
Mercy and Loving-kindness.
The Blessed in Heaven behold him Face to Face; that is, are as
sensible of his Presence as we are of the Presence of any Person whom
we look upon with our Eyes. There is doubtless a Faculty in Spirits,
by which they apprehend one another, as our Senses do material
Objects; and there is no Question but our Souls, when they are
disembodied, or placed in glorified Bodies, will by this Faculty, in
whatever Part of Space they reside, be always sensible of the Divine
Presence. We, who have this Veil of Flesh standing between us and the
World of Spirits, must be Content to know that the Spirit of God is
present with us, by the Effects which he produces in us. Our outward
Senses are too gross to apprehend him; we may however taste and see
how gracious he is, by his Influence upon our Minds, by those Virtuous
Thoughts which he awakens in us, by those secret Comforts and
Refreshments which he conveys into our Souls, and by those ravishing
Joys and inward Satisfactions, which are perpetually springing up, and
diffusing themselves among all the Thoughts of good Men. He is lodged
in our very Essence, and is as a Soul within the Soul, to irradiate
its Understanding, rectifie its Will, purifie its Passions, and
enliven all the Powers of Man. How happy therefore is an intellectual
Being, who, by Prayer and Meditation, by Virtue and good Works, opens
this Communication between God and his own Soul! Tho' the whole
Creation frowns upon him, and all Nature looks black about him, he has
his Light and Support within him, that are able to cheer his Mind, and
bear him up in the Midst of all those Horrors which encompass him. He
knows that his Helper is at Hand, and is always nearer to him than any
thing else can be, which is capable of annoying or terrifying him. In
the Midst of Calumny or Contempt, he attends to that Being who
whispers better things within his Soul, and whom he looks upon as his
Defender, his Glory, and the Lifter up of his Head. In his deepest
Solitude and Retirement, he knows that he is in Company with the
greatest of Beings; and perceives within himself such real Sensations
of his Presence, as are more delightful than any thing that can be met
with in the Conversation of his Creatures. Even in the Hour of Death,
he considers the Pains of his Dissolution to be nothing else but the
breaking down of that Partition, which stands betwixt his Soul, and
the Sight of that Being, who is always present with him, and is about
to manifest it self to him in Fullness of Joy.
If we would be thus Happy, and thus Sensible of our Maker's Presence,
from the secret Effects of his Mercy and Goodness, we must keep such a
Watch over all our Thoughts, that, in the Language of the Scripture, his
Soul may have Pleasure in us. We must take care not to grieve his Holy
Spirit, and endeavour to make the Meditations of our Hearts always
acceptable in his Sight, that he may delight thus to reside and dwell in
us. The Light
of Nature could direct
Seneca to this Doctrine, in a
very remarkable Passage among his Epistles:
Sacer inest in
nobis spiritus bonorum malorumque custos, et Observator, et
quemadmodum nos illum tractamus, ita et ille nos.2
There is a Holy Spirit residing in us, who watches and observes both
Good and Evil Men, and will treat us after the same Manner that we
treat him. But I
shall conclude this Discourse with those more
emphatical Words in Divine Revelation,
If a Man
love me, he will keep my Word, and my Father will love him,
and we will come unto him, and make our Abode with him.3
Footnote 1:
No.
, and see Nos.
,
, and
.
Footnote 2:
Ep. 41. To Lucilius. 'Deum in viro bono sedere.'
Footnote 3:
John
xiv. 23.
Contents
|
Monday, July 26, 1714 |
Z. Pearce1 |
—Quod medicorum est
Promittant medici—
Hor.

I am the more pleased with these my Papers, since I find they have
encouraged several Men of Learning and Wit to become my Correspondents:
I Yesterday received the following Essay against Quacks, which I shall
here communicate to my Readers for the Good of the Publick, begging the
Writer's Pardon for those Additions and Retrenchments which I have made
in it.
The De
Sir
e of Life is so natural and strong a Passion, that I have long
since ceased to wonder at the great Encouragement which the Practice of
Physick finds among us. Well-constituted Governments have always made
the Profession of a Physician both honourable and advantageous.
Homer's
Machaon
and
Virgil's Japis
were Men of Renown, Heroes in War, and
made at least as much Havock among their Enemies as among their Friends.
Those who have little or no Faith in the Abilities of a Quack will apply
themselves to him, either because he is willing to sell Health at a
reasonable Profit, or because the Patient, like a drowning Man, catches
at every Twig, and hopes for Relief from the most Ignorant, when the
most able Physicians give him none. Though Impudence and many Words are
as necessary to these Itinerary
Galens
as a laced Hat or a Merry
Andrew
, yet they would turn very littl to the Advantage of the Owner,
if there were not some inward Disposition in the sick Man to favour the
Pretensions of the Mountebank. Love of Life in the one, and of Mony in
the other, creates a good Correspondence between them.
There is scarce a City in
Great-Britain
but has one of this Tribe, who
takes it into his Protection, and on the Market-Day harangues the good
People of the Place with Aphorisms and Receipts. You may depend upon it,
he comes not there for his own private Interest, but out of a particular
Affection to the Town. I remember one of those Public-spirited Artists
at
Hammersmith
, who told his Audience 'that he had been born and bred
there, and that having a special Regard for the Place of his Nativity,
he was determined to make a Present of five Shillings to as many as
would accept of it.' The whole Crowd stood agape, and ready to take the
Doctor at his Word; when putting his Hand into a long Bag, as every one
was expecting his Crown-Piece, he drew out an handful of little Packets,
each of which he informed the
Spectators
was constantly sold at five
Shillings and six pence, but that he would bate the odd five Shillings
to every Inhabitant of that Place: The whole Assembly immediately closed
with this generous Offer, and took off all his Physick, after the Doctor
had made them vouch for one another, that there were no Foreigners among
them, but that they were all
Hammersmith
-Men.
There is another Branch of Pretenders to this Art, who, without either
Horse or Pickle-Herring, lie snug in a Garret, and send down Notice to
the World of their extraordinary Parts and Abilities by printed Bills
and Advertisements. These seem to have derived their Custom from an
Eastern
Nation which
Herodotus
speaks of, among whom it was a Law,
that whenever any Cure was performed, both the Method of the Cure, and
an Account of the Distemper, should be fixed in some Publick Place; but
as Customs will corrupt, these our Moderns provide themselves of Persons
to attest the Cure, before they publish or make an Experiment of the
Prescription. I have heard of a Porter, who serves as a Knight of the
Post under one of these Operators, and tho' he was never sick in his
Life, has been cured of all the Diseases in the Dispensary. These are
the Men whose Sagacity has invented Elixirs of all sorts, Pills and
Lozenges, and take it as an Affront if you come to them before you are
given over by every Body else. Their Medicines
are infallible, and
never fail of Success
, that is of enriching the Doctor, and setting the
Patient effectually at Rest.
I lately dropt into a Coffee-house at
Westminster
, where I found the
Room hung round with Ornaments of this Nature. There were Elixirs,
Tinctures, the
Anodine Fotus, English
Pills, Electuaries, and, in
short, more Remedies than I believe there are Diseases. At the Sight of
so many Inventions, I could not but imagine my self in a kind of Arsenal
or Magazine, where store of Arms were reposited against any sudden
Invasion. Should you be attack'd by the Enemy Side-ways, here was an
infallible Piece of defensive Armour to cure the Pleurisie: Should a
Distemper beat up your Head Quarters, here you might purchase an
impenetrable Helmet, or, in the Language of the Artist, a Cephalic
Tincture: If your main Body be assaulted, here are various Kinds of
Armour in Case of various Onsets. I began to congratulate the present
Age upon the Happiness Men might reasonably hope for in Life, when Death
was thus in a manner Defeated; and when Pain it self would be of so
short a Duration, that it would but just serve to enhance the Value of
Pleasure: While I was in these Thoughts, I unluckily called to mind a
Story of an Ingenious Gentleman of the last Age, who lying violently
afflicted with the Gout, a Person came and offered his Service to Cure
him by a Method, which he assured him was Infallible; the Servant who
received the Message carried it up to his Master, who enquiring whether
the Person came on Foot or in a Chariot; and being informed that he was
on Foot:
Go, says he, send the Knave about his Business: Was his Method
as infallible as he pretends, he would long before now have been in his
Coach and Six.
In like manner I concluded, that had all these
Advertisers arrived to that Skill they pretend to, they would have had
no Need for so many Years successively to publish to the World the Place
of their Abode, and the Virtues of their Medicines. One of these
Gentlemen indeed pretends to an effectual Cure for Leanness: What
Effects it may have had upon those who have try'd it I cannot tell; but
I am credibly informed, that the Call for it has been so great, that it
has effectually cured the Doctor himself of that Distemper. Could each
of them produce so good an Instance of the Success of his Medicines,
they might soon persuade the World into an Opinion of them.
I observe that most of the Bills agree in one Expression,
viz.
that
(
with God's Blessing
) they perform such and such Cures: This
Expression is certainly very proper and emphatical, for that is all they
have for it. And if ever a Cure is performed on a Patient where they are
concerned, they can claim no greater Share in it than
Virgil's Japis
in the curing of
Æneas
; he tried his Skill, was very assiduous about
the Wound, and indeed was the only visible Means that relieved the Hero;
but the Poet assures us it was the particular Assistance of a Deity that
speeded the Operation. An
English
Reader may see the whole Story in
Mr.
Dryden's
Translation.
Prop'd on his Lance the pensive Heroe stood,
And heard, and saw unmov'd, the Mourning Crowd.
The fam'd Physician tucks his Robes around,
With ready Hands, and hastens to the Wound.
With gentle Touches he performs his Part,
This Way and that, solliciting the Dart,
And exercises all his Heavenly Art.
All softning Simples, known of Sov'reign Use,
He presses out, and pours their noble Juice;
These first infus'd, to lenifie the Pain,
He tugs with Pincers, but he tugs in vain.
Then to the Patron of his Art he pray'd;
The Patron of his Art refus'd his Aid.
But now the Goddess Mother, mov'd with Grief,
And pierc'd with Pity, hastens her Relief.
A Branch of Healing Dittany she brought,
Which in the Cretan Fields with Care she sought;
Rough is the Stem, which woolly Leaves surround;
The Leafs with Flow'rs, the Flow'rs with Purple crown'd:
Well known to-wounded Goats; a sure Relief
To draw the pointed Steel, and ease the Grief.
This Venus brings, in Clouds involv'd; and brews
Th' extracted Liquor with Ambrosian Dews,
And od'rous Panacee: Unseen she stands,
Temp'ring the Mixture with her heav'nly Hands:
And pours it in a Bowl, already crown'd
With Juice of medc'nal Herbs, prepared to bathe the Wound.
The Leech, unknowing of superior Art,
Which aids the Cure, with this foments the Part;
And in a Moment ceas'd the raging Smart.
Stanched is the Blood, and in the bottom stands:
The Steel, but scarcely touched with tender Hands,
Moves up, and follows of its own Accord;
And Health and Vigour are at once restor'd.
Japis first perceiv'd the closing Wound;
And first the Footsteps of a God he found.
Arms, Arms! he cries, the Sword and Shield prepare,
And send the willing Chief, renew'd to War.
This is no mortal Work, no cure of mine,
Nor Art's effect, but done by Hands Divine.
Footnote 1:
Dr. Zachary Pearce, Bishop of Rochester, with alterations
by Addison.
Contents
—Castigata remordent—
Juv.

My Paper on the Club of Widows has brought me in several Letters; and,
among the rest, a long one from Mrs. President, as follows.
Smart Sir ,
'You are pleased to be very merry, as you imagine, with us Widows: And
you seem to ground your Satyr on our receiving Consolation so soon
after the Death of our Dears, and the Number we are pleased to admit
for our Companions; but you never reflect what Husbands we have
buried, and how short a Sorrow the Loss of them was capable of
occasioning. For my own Part, Mrs. President as you call me, my First
Husband I was marry'd to at Fourteen, by my Uncle and Guardian (as I
afterwards discovered) by way of Sale, for the Third part of my
Fortune. This Fellow looked upon me as a meer Child, he might breed up
after his own Fancy; if he kissed my Chamber-Maid before my Face, I
was supposed so ignorant, how could I think there was any Hurt in it?
When he came home Roaring Drunk at five in the Morning, 'twas the
Custom of all Men that live in the World. I was not to see a Penny of
Money, for, poor Thing, how could I manage it? He took a handsome
Cousin of his into the House, (as he said) to be my Housekeeper, and
to govern my Servants; for how should I know how to rule a Family? and
while she had what Money she pleased, which was but reasonable for the
Trouble she was at for my Good, I was not to be so censorious as to
dislike Familiarity and Kindness between near Relations. I was too
great a Coward to contend, but not so ignorant a Child to be thus
imposed upon. I resented his Contempt as I ought to do, and as most
poor passive blinded Wives do, 'till it pleased Heaven to take away my
Tyrant, who left me free Possession of my own Land, and a large
Jointure. My Youth and Money brought me many Lovers, and several
endeavoured to establish an Interest in my Heart while my Husband was
in his last Sickness; the Honourable Edward Waitfort was one of the
first who addressed to me, advised to it by a Cousin of his that was
my intimate Friend, and knew to a Penny what I was worth. Mr.
Waitfort is a very agreeable Man, and every Body would like him as
well as he does himself, if they did not plainly see that his Esteem
and Love is all taken up, and by such an Object, as 'tis impossible to
get the better of. I mean himself. He made no doubt of marrying me
within Four or Five Months, and begun to proceed with such an assured
easie Air, that piqued my Pride not to banish him; quite contrary, out
of pure Malice, I heard his first Declaration with so much innocent
Surprize, and blushed so prettily, I perceived it touched his very
Heart, and he thought me the best-natured Silly poor thing on Earth.
When a Man has such a Notion of a Woman, he loves her better than he
thinks he does. I was overjoy'd to be thus revenged on him, for
designing on my Fortune; and finding it was in my Power to make his
Heart ake, I resolved to compleat my Conquest, and entertain'd several
other Pretenders. The first Impression of my undesigning Innocence was
so strong in his Head, he attributed all my Followers to the
inevitable Force of my Charms, and from several Blushes and side
Glances, concluded himself the Favourite; and when I used him like a
Dog for my Diversion, he thought it was all Prudence and Fear, and
pitied the Violence I did my own Inclinations to comply with my
Friends, when I marry'd Sir Nicholas Fribble of Sixty Years of Age.
You know, Sir , the Case of Mrs. Medlar, I hope you would not have
had me cry out my Eyes for such a Husband. I shed Tears enough for my
Widowhood a Week after my Marriage, and when he was put in his Grave,
reckoning he had been two Years dead, and my self a Widow of that
Standing, I married three Weeks afterwards John Sturdy, Esq., his
next Heir. I had indeed some Thoughts of taking Mr. Waitfort, but I
found he could stay, and besides he thought it indecent to ask me to
marry again 'till my Year was out, so privately resolving him for my
Fourth, I took Mr. Sturdy for the present. Would you believe it,
Sir , Mr. Sturdy was just Five and Twenty, about Six Foot high, and
the stoutest Fox-hunter in the Country, and I believe I wished ten
thousand times for my old Fribble again; he was following his Dogs
all the Day, and all the Night keeping them up at Table with him and
his Companions: however I think my self obliged to them for leading
him a Chase in which he broke his Neck. Mr. Waitfort began his
Addresses anew, and I verily believe I had married him now, but there
was a young Officer in the Guards, that had debauched two or three of
my Acquaintance, and I could not forbear being a little vain of his
Courtship. Mr. Waitfort heard of it, and read me such an insolent
Lecture upon the Conduct of Women, I married the Officer that very
Day, out of pure Spight to him. Half an Hour after I was married I
received a Penitential Letter from the Honourable Mr. Edward
Waitfort, in which he begged Pardon for his Passion, as proceeding
from the Violence of his Love: I triumphed when I read it, and could
not help, out of the Pride of my Heart, shewing it to my new Spouse:
and we were very merry together upon it. Alas! my Mirth lasted a short
time; my young Husband was very much in Debt when I marry'd him, and
his first Action afterwards was to set up a gilt Chariot and Six, in
fine Trappings before and behind. I had married so hastily, I had not
the Prudence to reserve my Estate in my own Hands; my ready Money was
lost in two Nights at the Groom Porter's; and my Diamond Necklace,
which was stole I did not know how, I met in the Street upon Jenny
Wheadle's Neck. My Plate vanished Piece by Piece, and I had been
reduced to downright Pewter, if my Officer had not been deliciously
killed in a Duel, by a Fellow that had cheated him of Five Hundred
Pounds, and afterwards, at his own Request, satisfy'd him and me too,
by running him through the Body. Mr. Waitfort was still in Love, and
told me so again; and to prevent all Fears of ill Usage, he deSir 'd me
to reserve every thing in my own Hands: But now my Acquaintance begun
to wish me Joy of his Constancy, my Charms were declining, and I could
not resist the Delight I took in shewing the young Flirts about Town,
it was yet in my Power to give Pain to a Man of Sense: This, and some
private Hopes he would hang himself, and what a Glory would it be for
me, and how I should be envy'd, made me accept of being third Wife to
my Lord Friday. I proposed from my Rank and his Estate, to live in
all the Joys of Pride, but how was I mistaken? he was neither
extravagant, nor ill-natured, nor debauched? I suffered however more
with him than with all my others. He was splenatick. I was forced to
sit whole Days hearkening to his imaginary Ails; it was impossible to
tell what would please him; what he liked when the Sun shined, made
him sick when it rained; he had no Distemper, but lived in constant
Fear of them all: my good Genius dictated to me to bring him
acquainted with Doctor Gruel; from that Day he was always contented,
because he had Names for all his Complaints; the good Doctor furnished
him with Reasons for all his Pains, and Prescriptions for every Fancy
that troubled him; in hot Weather he lived upon Juleps, and let Blood
to prevent Fevers; when it grew cloudy he generally apprehended a
Consumption; to shorten the History of this wretched Part of my Life,
he ruined a good Constitution by endeavouring to mend it, and took
several Medicines, which ended in taking the grand Remedy, which cured
both him and me of all our Uneasinesses. After his Death, I did not
expect to hear any more of Mr. Waitfort, I knew he had renounced me
to all his Friends, and been very witty upon my Choice, which he
affected to talk of with great Indifferency; I gave over thinking of
him, being told that he was engaged with a pretty Woman and a great
Fortune; it vexed me a little, but not enough to make me neglect the
Advice of my Cousin Wishwell, that came to see me the Day my Lord
went into the Country with Russel; she told me experimentally,
nothing put an unfaithful Lover and a dear Husband so soon out of ones
Head, as a new one; and, at the same time, propos'd to me a Kinsman of
hers; You understand enough of the World (said she) to know Money is
the most valuable Consideration; he is very rich, and I am sure cannot
live long; he has a Cough that must carry him off soon. I knew
afterwards she had given the self-same Character of me to him; but
however I was so much persuaded by her, I hastned on the Match, for
fear he should die before the time came; he had the same Fears, and
was so pressing, I married him in a Fortnight, resolving to keep it
private a Fortnight longer. During this Fortnight Mr. Waitfort came
to make me a Visit; he told me he had waited on me sooner, but had
that Respect for me, he would not interrupt me in the first Day of my
Affliction for my dead Lord; that as soon as he heard I was at Liberty
to make another Choice, he had broke off a Match very advantageous for
his Fortune, just upon the Point of Conclusion, and was forty times
more in Love with me than ever. I never received more Pleasure in my
Life than from this Declaration, but I composed my Face to a grave
Air, and said the News of his Engagement had touched me to the Heart,
that in a rash jealous Fit, I had married a Man I could never have
thought on if I had not lost all hopes of him. Good-natured Mr.
Waitfort had like to have dropped down dead at hearing this, but
went from me with such an Air as plainly shewed me he laid all the
Blame upon himself, and hated those Friends that had advised him to
the Fatal Application; he seemed as much touched by my Misfortune as
his own, for he had not the least Doubt I was still passionately in
Love with him. The Truth of the Story is, my new Husband gave me
Reason to repent I had not staid for him; he had married me for my
Money, and I soon found he loved Money to Distraction; there was
nothing he would not do to get it, nothing he would not suffer to
preserve it; the smallest Expence keep him awake whole Nights, and
when he paid a Bill, 'twas with as many Sighs, and after as many
Delays, as a Man that endures the Loss of a Limb. I heard nothing but
Reproofs for Extravagancy whatever I did. I saw very well that he
would have starved me, but for losing my Jointures; and he suffered
Agonies between the Grief of seeing me have so good a Stomach, and the
Fear that if he made me fast, it might prejudice my Health. I did not
doubt he would have broke my Heart, if I did not break his, which was
allowed by the Law of Self-defence. The Way was very easy. I resolved
to spend as much Money as I could, and before he was aware of the
Stroke, appeared before him in a two thousand Pound Diamond Necklace;
he said nothing, but went quietly to his Chamber, and, as it is
thought, composed himself with a Dose of Opium. I behaved my self so
well upon the Occasion, that to this Day I believe he died of an
Apoplexy. Mr. Waitfort was resolved not to be too late this time,
and I heard from him in two Days. I am almost out of my Weed at this
present Writing, and am very doubtful whether I'll marry him or no. I
do not think of a Seventh, for the ridiculous Reason you mention, but
out of pure Morality that I think so much Constancy should be
rewarded, tho' I may not do it after all perhaps. I do not believe all
the unreasonable Malice of Mankind can give a Pretence why I should
have been constant to the Memory of any of the Deceased, or have spent
much time in grieving for so insolent, insignificant, negligent,
extravagant, splenatick, or covetous Husband; my first insulted me, my
second was nothing to me, my third disgusted me, the fourth would have
ruined me, the fifth tormented me, and the sixth would have starved
me. If the other Ladies you name would thus give in their Husbands
Pictures at length, you would see they have had as little Reason as my
self to lose their Hours in weeping and wailing.
Contents
|
Friday, July 30, 1714 |
Addison |
Non possidentem multa vocaveris
Rectè Beatum, recliùs occupat
Nomen Beati, qui Deorum
Muneribus sapienter uti
Duramque callet pauperiem pati.
Hor.

I was once engaged in Discourse with a
Rosicrusian
about
the great
Secret
. As this kind of Men (I mean those of them who are not professed
Cheats) are over-run with Enthusiasm and Philosophy, it was very amusing
to hear this religious Adept descanting on his pretended Discovery. He
talked of the Secret as of a Spirit which lived within an Emerald, and
converted every thing that was near it to the highest Perfection it is
capable of. It gives a Lustre, says he, to the Sun, and Water to the
Diamond. It irradiates every Metal, and enriches Lead with all the
Properties of Gold. It heightens Smoak into Flame, Flame into Light, and
Light into Glory. He further added, that a single Ray of it dissipates
Pain, and Care, and Melancholy from the Person on whom it falls. In
short, says he, its Presence naturally changes every Place into a kind
of Heaven. After he had gone on for some Time in this unintelligible
Cant, I found that he jumbled natural and moral Ideas together into the
same Discourse, and that his great Secret was nothing else but
Content.
This Virtue does indeed produce, in some measure, all those Effects
which the Alchymist usually ascribes to what he calls the Philosopher's
Stone; and if it does not bring Riches, it does the same thing, by
banishing the De
Sir
e of them. If it cannot remove the Disquietudes
arising out of a Man's Mind, Body, or Fortune, it makes him easie under
them. It has indeed a kindly Influence on the Soul of Man, in respect of
every Being to whom he stands related. It extinguishes all Murmur,
Repining, and Ingratitude towards that Being who has allotted him his
Part to act in this World. It destroys all inordinate Ambition, and
every Tendency to Corruption, with regard to the Community wherein he is
placed. It gives Sweetness to his Conversation, and a perpetual Serenity
to all his Thoughts.
Among the many Methods which might be made use of for the acquiring of
this Virtue, I shall only mention the two following. First of all, A Man
should always consider how much he has more than he wants; and Secondly,
How much more unhappy he might be than he really is.
First of all, A Man should always consider how much he has more than he
wants. I am wonderfully pleased with the Reply which
Aristippus
made
to one who condoled him upon the Loss of a Farm,
Why
, said he,
I have
three Farms still, and you have but one; so that I ought rather to be
afflicted for you, than you for me.
On the contrary, foolish Men are
more apt to consider what they have lost than what they possess; and to
fix their Eyes upon those who are richer than themselves, rather than on
those who are under greater Difficulties. All the real Pleasures and
Conveniences of Life lie in a narrow Compass; but it is the Humour of
Mankind to be always looking forward, and straining after one who has
got the Start of them in Wealth and Honour. For this Reason, as there
are none can be properly called rich, who have not more than they want;
there are few rich Men in any of the politer Nations but among the
middle Sort of People, who keep their Wishes within their Fortunes, and
have more Wealth than they know how to enjoy. Persons of a higher Rank
live in a kind of splendid Poverty, and are perpetually wanting, because
instead of acquiescing in the solid Pleasures of Life, they endeavour to
outvy one another in Shadows and Appearances. Men of Sense have at all
times beheld with a great deal of Mirth this silly Game that is playing
over their Heads, and by contracting their De
Sir
es, enjoy all that
secret Satisfaction which others are always in quest of. The Truth is,
this ridiculous Chace after imaginary Pleasures cannot be sufficiently
exposed, as it is the great Source of those Evils which generally undo a
Nation. Let a Man's Estate be what it will, he is a poor Man if he does
not live within it, and naturally sets himself to Sale to any one that
can give him his Price. When
Pittacus
, after the Death of his Brother,
who had left him a good Estate, was offered a great Sum of Money by the
King of
Lydia
, he thanked him for his Kindness, but told him he had
already more by Half than he knew what to do with. In short, Content is
equivalent to Wealth, and Luxury to Poverty; or, to give the Thought a
more agreeable Turn,
Content is natural Wealth
, says
Socrates
; to
which I shall add,
Luxury is artificial Poverty.
I shall therefore
recommend to the Consideration of those who are always aiming after
superfluous and imaginary Enjoyments, and will not be at the Trouble of
contracting their De
Sir
es, an excellent Saying of
Bion
the
Philosopher; namely,
That no Man has so much Care, as he who endeavours
after the most Happiness.
In the second Place, every one ought to reflect how much more unhappy he
might be than he really is. The former Consideration took in all those
who are sufficiently provided with the Means to make themselves easie;
this regards such as actually lie under some Pressure or Misfortune.
These may receive great Alleviation from such a Comparison as the
unhappy Person may make between himself and others, or between the
Misfortune which he suffers, and greater Misfortunes which might have
befallen him.
I like the Story of the honest
Dutchman
, who, upon breaking his
Leg
by a Fall from the Mainmast, told the Standers-by, It was a great Mercy
that 'twas not his
Neck.
To which, since I am got into Quotations,
give me leave to add the Saying of an old Philosopher, who, after having
invited some of his Friends to dine with him, was ruffled by his Wife
that came into the Room in a Passion, and threw down the Table that
stood before them;
Every one,
says he,
has his Calamity, and he is a
happy Man that has no greater than this
. We find an Instance to the
same Purpose in the Life of Doctor
Hammond
, written by Bishop
Fell.
As this good Man was troubled with a Complication of Distempers, when he
had the Gout upon him, he used to thank God that it was not the Stone;
and when he had the Stone, that he had not both these Distempers on him
at the same time.
I cannot conclude this Essay without observing that there was never any
System besides that of Christianity, which could effectually produce in
the Mind of Man the Virtue I have been hitherto speaking of. In order to
make us content with our present Condition, many of the ancient
Philosophers tell us that our Discontent only hurts our selves, without
being able to make any Alteration in our Circumstances; others, that
whatever Evil befalls us is derived to us by a fatal Necessity, to which
the Gods themselves are subject; whilst others very gravely tell the Man
who is miserable, that it is necessary he should be so to keep up the
Harmony of the Universe, and that the
Scheme
of Providence would be
troubled and perverted were he otherwise. These, and the like
Considerations, rather silence than satisfy a Man. They may shew him
that his Discontent is unreasonable, but are by no means sufficient to
relieve it. They rather give Despair than Consolation. In a Word, a Man
might reply to one of these Comforters, as
Augustus
did to his Friend
who advised him not to grieve for the Death of a Person whom he loved,
because his Grief could not fetch him again:
It is for that very
Reason,
said the Emperor,
that I grieve.
On the contrary, Religion bears a more tender Regard to humane Nature.
It prescribes to every miserable Man the Means of bettering his
Condition; nay, it shews him, that the bearing of his Afflictions as he
ought to do will naturally end in the Removal of them: It makes him
easie here, because it can make him happy hereafter.
Upon the whole, a contented Mind is the greatest Blessing a Man can
enjoy in this World; and if in the present Life his Happiness arises
from the subduing of his De
Sir
es, it will arise in the next from the
Gratification of them.
Contents
|
Monday, August 2, 1714 |
Addison |
—Nec merti esse locum—
Virg.

A lewd young Fellow seeing an aged Hermit go by him barefoot,
Father
,
says he,
you are in a very miserable Condition if there is not another
World. True, Son,
said the Hermit;
but what is thy Condition if there
is?
Man is a Creature designed for two different States of Being, or
rather, for two different Lives. His first Life is short and transient;
his second permanent and lasting. The Question we are all concerned in
is this, In which of these two Lives it is our chief Interest to make
our selves happy? Or, in other Words, Whether we should endeavour to
secure to our selves the Pleasures and Gratifications of a Life which is
uncertain and precarious, and at its utmost Length of a very
inconsiderable Duration; or to secure to our selves the Pleasures of a
Life which is fixed and settled, and will never end? Every Man, upon the
first hearing of this Question, knows very well which Side of it he
ought to close with. But however right we are in Theory, it is plain
that in Practice we adhere to the wrong Side of the Question. We make
Provisions for this Life as tho' it were never to have an End, and for
the other Life as tho' it were never to have a Beginning.
Should a Spirit of superior Rank who is a Stranger to human Nature,
accidentally alight upon the Earth, and take a Survey of its
Inhabitants; what would his Notions of us be? Would not he think that we
are a Species of Beings made for quite different Ends and Purposes than
what we really are? Must not he imagine that we were placed in this
World to get Riches and Honours? Would not he think that it was our Duty
to toil after Wealth, and Station, and Title? Nay, would not he believe
we were forbidden Poverty by Threats of eternal Punishment, and enjoined
to pursue our Pleasures under Pain of Damnation? He would certainly
imagine that we were influenced by a Scheme of Duties quite opposite to
those which are indeed prescribed to us. And truly, according to such an
Imagination, he must conclude that we are a Species of the most obedient
Creatures in the Universe; that we are constant to our Duty; and that we
keep a steddy Eye on the End for which we were sent hither.
But how great would be his Astonishment, when he learnt that we were
Beings not designed to exist in this World above threescore and ten
Years? and that the greatest Part of this busy Species fall short even
of that Age? How would he be lost in Horrour and Admiration, when he
should know that this Sett of Creatures, who lay out all their
Endeavours for this Life, which scarce deserves the Name of Existence,
when, I say, he should know that this Sett of Creatures are to exist to
all Eternity in another Life, for which they make no Preparations?
Nothing can be a greater Disgrace to Reason, than that Men, who are
perswaded of these two different States of Being, should be perpetually
employed in providing for a Life of three-score and ten Years, and
neglecting to make Provision for that, which after many Myriads of Years
will be still new, and still beginning; especially when we consider that
our endeavours for making ourselves great, or rich, or honourable, or
whatever else we place our Happiness in, may after all prove
unsuccessful; whereas if we constantly and sincerely endeavour to make
our selves happy in the other Life, we are sure that our Endeavours will
succeed, and that we shall not be disappointed of our Hope.
The following Question is started by one of the Schoolmen. Supposing the
whole Body of the Earth were a great Ball or Mass of the finest Sand,
and that a single Grain or Particle of this Sand should be annihilated
every thousand Years. Supposing then that you had it in your Choice to
be happy all the while this prodigious Mass of Sand was consuming by
this slow Method till there was not a Grain of it left, on Condition you
were to be miserable for ever after; or, supposing that you might be
happy for ever after, on Condition you would be miserable till the whole
Mass of Sand were thus annihilated at the Rate of one Sand in a thousand
Years: Which of these two Cases would you make your Choice?
It must be confessed in this Case, so many Thousands of Years are to the
Imagination as a kind of eternity, tho' in reality they do not bear so
great a Proportion to that Duration which is to follow them, as a Unite
does to the greatest Number which you can put together in Figures, or as
one of those Sands to the supposed Heap. Reason therefore tells us,
without any Manner of Hesitation, which would be the better Part in this
Choice. However, as I have before intimated, our Reason might in such a
Case be so overset by the Imagination, as to dispose some Persons to
sink under the Consideration of the great Length of the first Part of
this Duration, and of the great Distance of that second Duration which
is to succeed it. The Mind, I say, might give it self up to that
Happiness which is at Hand, considering that it is so very near, and
that it would last so very long. But when the Choice we actually have
before us is this, Whether we will chuse to be happy for the space of
only three-score and ten, nay perhaps of only twenty or ten Years, I
might say of only a Day or an Hour, and miserable to all Eternity; or,
on the contrary, miserable for this short Term of Years, and happy for a
whole Eternity: What Words are sufficient to express that Folly and want
of Consideration which in such a Case makes a wrong Choice?
I here put the Case even at the worst, by supposing (what seldom
happens) that a Course of Virtue makes us miserable in this Life: But if
we suppose (as it generally happens) that Virtue would make us more
happy even in this Life than a contrary Course of Vice; how can we
sufficiently admire the Stupidity or Madness of those Persons who are
capable of making so absurd a Choice?
Every wise Man therefore will consider this Life only as it may conduce
to the Happiness of the other, and chearfully sacrifice the Pleasures of
a few Years to those of an Eternity.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 4, 1714 |
Addison |
Nitor in adversum; nec me, qui coetera, vincit
Impetus; et rapido contrarius euchor Orbi.
Ovid.

I remember a young Man of very lively Parts, and of a sprightly Turn in
Conversation, who had only one Fault, which was an inordinate De
Sir
e of
appearing fashionable. This ran him into many Amours, and consequently
into many Distempers. He never went to Bed till two a-Clock in the
Morning, because he would not be a queer Fellow; and was every now and
then knocked down by a Constable, to signalize his Vivacity. He was
initiated into Half a Dozen Clubs before he was One and twenty, and so
improved in them his natural Gayety of Temper, that you might frequently
trace him to his Lodgings by a range of broken Windows, and other the
like Monuments of Wit and Gallantry. To be short, after having fully
established his Reputation of being a very agreeable Rake, he died of
old Age at Five and twenty.
There is indeed nothing which betrays a Man into so many Errors and
Inconveniences, as the De
Sir
e of not appearing singular; for which
Reason it is very necessary to form a right Idea of Singularity, that we
may know when it is laudable, and when it is vicious. In the first
Place, every Man of Sense will agree with me, that Singularity is
laudable, when, in Contradiction to a Multitude, it adheres to the
Dictates of Conscience, Morality, and Honour. In these Cases we ought to
consider, that it is not Custom, but Duty, which is the Rule of Action;
and that we should be only so far
sociable
, as we are reasonable
Creatures. Truth is never the less so, for not being attended to; and it
is the Nature of Actions, not the Number of Actors, by which we ought to
regulate our Behaviour. Singularity in Concerns of this Kind is to be
looked upon as heroick Bravery, in which a Man leaves the Species only
as he soars above it. What greater Instance can there be of a weak and
pusillanimous Temper, than for a Man to pass his whole Life in
Opposition to his own Sentiments? or not to dare to be what he thinks he
ought to be?
Singularity therefore is only vicious when it makes Men act contrary to
Reason, or when it puts them upon distinguishing themselves by Trifles.
As for the first of these, who are singular in any thing that is
irreligious, immoral, or dishonourable, I believe every one will easily
give them up. I shall therefore speak of those only who are remarkable
for their Singularity in things of no Importance, as in Dress,
Behaviour, Conversation, and all the little Intercourses of Life. In
these Cases there is a certain Deference due to Custom; and
notwithstanding there may be a Colour of Reason to deviate from the
Multitude in some Particulars, a Man ought to sacrifice his private
Inclinations and Opinions to the Practice of the Publick. It must be
confessed that good Sense often makes a Humourist; but then it
unqualifies him for being of any Moment in the World, and renders him
ridiculous to Persons of a much inferiour Understanding.
I have heard of a Gentleman in the North of
England
, who was a
remarkable Instance of this foolish Singularity. He had laid it down as
a Rule within himself, to act in the most indifferent Parts of Life
according to the most abstracted Notions of Reason and Good Sense,
without any Regard to Fashion or Example. This Humour broke out at first
in many little Oddnesses: He had never any stated Hours for his Dinner,
Supper or Sleep; because, said he, we ought to attend the Calls of
Nature, and not set our Appetites to our Meals, but bring our Meals to
our Appetites. In his Conversation with Country Gentlemen, he would not
make use of a Phrase that was not strictly true: He never told any of
them, that he was his humble Servant, but that he was his Well-wisher;
and would rather be thought a Malecontent, than drink the King's Health
when he was not a-dry. He would thrust his Head out of his
Chamber-Window every Morning, and after having gaped for fresh Air about
half an Hour, repeat fifty Verses as loud as he could bawl them for the
Benefit of his Lungs; to which End he generally took them out of
Homer
; the
Greek
Tongue, especially in that Author, being more deep
and sonorous, and more conducive to Expectoration, than any other. He
had many other Particularities, for which he gave sound and
philosophical Reasons. As this Humour still grew upon him, he chose to
wear a Turban instead of a Perriwig; concluding very justly, that a
Bandage of clean Linnen about his Head was much more wholsome, as well
as cleanly, than the Caul of a Wig, which is soiled with frequent
Perspirations. He afterwards judiciously observed, that the many
Ligatures in our
English
Dress must naturally check the Circulation of
the Blood; for which Reason, he made his Breeches and his Doublet of one
continued Piece of Cloth, after the Manner of the
Hussars.
In short,
by following the pure Dictates of Reason, he at length departed so much
from the rest of his Countrymen, and indeed from his whole Species, that
his Friends would have clapped him into
Bedlam
, and have begged his
Estate; but the Judge being informed that he did no Harm, contented
himself with issuing out a Commission of Lunacy against him, and putting
his Estate into the Hands of proper Guardians.
The Fate of this Philosopher puts me in Mind of a Remark in Monsieur
Fontinell's
Dialogues of the Dead.
The Ambitious and the Covetous
(says he)
are Madmen to all Intents and Purposes, as much as those who
are shut up in dark Rooms; but they have the good Luck to have Numbers
on their Side; whereas the Frenzy of one who is given up for a Lunatick,
is a Frenzy
hors d'oeuvre; that is, in other Words, something which is
singular in its Kind, and does not fall in with the Madness of a
Multitude.
The Subject of this Essay was occasioned by a Letter which I received
not long since, and which, for want of Room at present, I shall insert
in my next Paper.
Contents
—Hoc tolerabile, si non
Et furere incipias—
Juv.

The Letter mentioned in my last Paper is as follows.
Sir ,
'You have so lately decryed that Custom, too much in use among most
People, of making themselves the Subjects of their Writings and
Conversation, that I had some difficulty to perswade my self to give
you this Trouble, till I had considered that tho' I should speak in
the First Person, yet I could not be justly charged with Vanity, since
I shall not add my Name; as also, because what I shall write will not,
to say the best, redound to my Praise; but is only designed to remove
a Prejudice conceived against me, as I hope, with very little
Foundation. My short History is this.
I have lived for some Years last past altogether in
London, till
about a Month ago an Acquaintance of mine, for whom I have done some
small Services in Town, invited me to pass part of the Summer with him
at his House in the Country. I accepted his Invitation, and found a
very hearty Welcome. My Friend, an honest plain Man, not being
qualified to pass away his Time without the Reliefs of Business, has
grafted the Farmer upon the Gentleman, and brought himself to submit
even to the servile Parts of that Employment, such as inspecting his
Plough, and the like. This necessarily takes up some of his Hours
every Day; and as I have no Relish for such Diversions, I used at
these Times to retire either to my Chamber, or a shady Walk near the
House, and entertain my self with some agreeable Author. Now you must
know, Mr. SPECTATOR, that when I read, especially if it be Poetry, it
is very usual with me, when I meet with any Passage or Expression
which strikes me much, to pronounce it aloud, with that Tone of the
Voice which I think agreeable to the Sentiments there expressed; and
to this I generally add some Motion or Action of the Body. It was not
long before I was observed by some of the Family in one of these
heroick Fits, who thereupon received Impressions very much to my
Disadvantage. This however I did not soon discover, nor should have
done probably, had it not been for the following Accident. I had one
Day shut my self up in my Chamber, and was very deeply engaged in the
Second Book of
Milton's Paradise Lost. I walked to and fro with the
Book in my Hand, and, to speak the Truth, I fear I made no little
Noise; when presently coming to the following Lines,
—On a sudden open fly,
With impetuous Recoil and jarring Sound,
Th' infernal Doors, and on their Hinges grate
Harsh Thunder, &c.
'I in great Transport threw open the Door of my Chamber, and found the
greatest Part of the Family standing on the Out-side in a very great
Consternation. I was in no less Confusion, and begged Pardon for
having disturbed them; addressing my self particularly to comfort one
of the Children, who received an unlucky fall in this Action, whilst
he was too intently surveying my Meditations through the Key-hole. To
be short, after this Adventure I easily observed that great Part of
the Family, especially the Women and Children, looked upon me with
some Apprehensions of Fear; and my Friend himself, tho' he still
continued his Civilities to me, did not seem altogether easie: I took
Notice, that the Butler was never after this Accident ordered to leave
the Bottle upon the Table after Dinner. Add to this, that I frequently
overheard the Servants mention me by the Name of the crazed Gentleman,
the Gentleman a little touched, the mad
Londoner, and the like. This
made me think it high Time for me to shift my Quarters, which I
resolved to do the first handsome Opportunity; and was confirmed in
this Resolution by a young Lady in the Neighbourhood who frequently
visited us, and who one Day, after having heard all the fine Things I
was able to say, was pleased with a scornful Smile to bid me go to
sleep.
'The first Minute I got to my Lodgings in Town I set Pen to Paper to
de
Sir e your Opinion, whether, upon the Evidence before you, I am mad
or not. I can bring Certificates that I behave my self soberly before
Company, and I hope there is at least some Merit in withdrawing to be
mad. Look you,
Sir , I am contented to be esteemed a little touched, as
they phrase it, but should be sorry to be madder than my Neighbours;
therefore, pray let me be as much in my Senses as you can afford. I
know I could bring your self as an Instance of a Man who has confessed
talking to himself; but yours is a particular Case, and cannot justify
me, who have not kept Silence any Part of my Life. What if I should
own my self in Love? You know Lovers are always allowed the Comfort of
Soliloquy.—But I will say no more upon this Subject, because I have
long since observed, the ready Way to be thought Mad is to contend
that you are not so; as we generally conclude that Man drunk, who
takes Pains to be thought sober. I will therefore leave my self to
your Determination; but am the more de
Sir ous to be thought in my
Senses, that it may be no Discredit to you when I assure you that I
have always been very much
Your Admirer.
P.S. If I must be mad, I deSir e the young Lady may believe it is for
her.
The humble Petition of John a Nokes
and John a Stiles,
Sheweth.
'That your Petitioners have had Causes depending in
Westminster-Hall
above five hundred Years, and that we despair of ever seeing them
brought to an Issue: That your Petitioners have not been involved in
these Law Suits, out of any litigious Temper of their own, but by the
Instigation of contentious Persons; that the young Lawyers in our Inns
of Court are continually setting us together by the Ears, and think
they do us no Hurt, because they plead for us without a Fee; That many
of the Gentlemen of the Robe have no other Clients in the World
besides us two; That when they have nothing else to do, they make us
Plaintiffs and Defendants, tho' they were never retained by either of
us; That they traduce, condemn, or acquit us, without any manner of
Regard to our Reputations and good Names in the World. Your
Petitioners therefore (being thereunto encouraged by the favourable
Reception which you lately gave to our Kinsman
Blank) do humbly
pray, that you will put an End to the Controversies which have been so
long depending between us your said Petitioners, and that our Enmity
may not endure from Generation to Generation; it being our Resolution
to live hereafter as it becometh Men of peaceable Dispositions.
And your Petitioners (as in Duty bound) shall ever Pray, &c.
Contents
—Eque feris humana in corpora transit,
Inque feras Noster—
Ovid.

There has been very great Reason, on several Accounts, for the learned
World to endeavour at settling what it was that might be said to compose
personal Identity.
Mr.
Lock
, after having premised that the Word
Person
properly
signifies a thinking intelligent Being that has Reason and Reflection,
and can consider it self as it self; concludes That it is Consciousness
alone, and not an Identity of Substance, which makes this personal
Identity of Sameness. Had I the same Consciousness (says that Author)
that I saw the Ark and
Noah's
Flood, as that I saw an Overflowing of
the
Thames
last Winter; or as that I now write; I could no more doubt
that I who write this now, that saw the
Thames
overflow last Winter,
and that viewed the Flood at the general Deluge, was the same
Self
,
place that
Self
in what Substance you please, than that I who write
this am the same
My self
now whilst I write, (whether I consist of all
the same Substance material or immaterial or no) that I was Yesterday;
For as to this Point of being the same
Self
, it matters not whether
this present
Self
be made up of the same or other Substances.
I was mightily pleased with a Story in some Measure applicable to this
Piece of Philosophy, which I read the other Day in the
Persian Tales
,
as they are lately very well translated by Mr.
Philips
; and with an
Abridgement whereof I shall here present my Readers.
I shall only premise that these Stories are writ after the Eastern
Manner, but somewhat more correct.
'
Fadlallah
, a Prince of great Virtues, succeeded his Father
Bin-Ortoc
, in the Kingdom of
Mousel
. He reigned over his faithful
Subjects for some time, and lived in great Happiness with his beauteous
Consort Queen
Zemroude
; when there appeared at his Court a young
Dervis
of so lively and entertaining a Turn of Wit, as won upon the
Affections of every one he conversed with. His Reputation grew so fast
every Day, that it at last raised a Curiosity in the Prince himself to
see and talk with him. He did so, and far from finding that common Fame
had flatter'd him, he was soon convinced that every thing he had heard
of him fell short of the Truth.
'
Fadlallah
immediately lost all Manner of Relish for the Conversation
of other Men; and as he was every Day more and more satisfied of the
Abilities of this Stranger, offered him the first Posts in his Kingdom.
The young
Dervis
, after having thanked him with a very singular
Modesty, de
Sir
ed to be excused, as having made a Vow never to accept of
any Employment, and preferring a free and independent State of Life to
all other Conditions.
'The King was infinitely charmed with so great an Example of Moderation;
and tho' he could not get him to engage in a Life of Business, made him
however his chief Companion and first Favourite.
'As they were one Day hunting together, and happened to be separated
from the rest of the Company, the
Dervis
entertained
Fadlallah
with
an Account of his Travels and Adventures. After having related to him
several Curiosities which he had seen in the
Indies
,
It was in this
Place
, says he,
that I contracted an Acquaintance with an old
Brachman,
who was skilled in the most hidden Powers of Nature: He died
within my Arms, and with his parting Breath communicated to me one of
the most valuable of his Secrets, on Condition I should never reveal it
to any Man
. The King immediately reflecting on his young Favourite's
having refused the late Offers of Greatness he had made him, told him he
presumed it was the Power of making Gold.
No Sir
, says the
Dervis
,
it is somewhat more wonderful than that; it is the Power of
re-animating a dead Body, by flinging my own Soul into it
.
'While he was yet speaking a Doe came bounding by them; and the King,
who had his Bow ready, shot her through the Heart; telling the
Dervis
,
that a fair Opportunity now offered for him to show his Art. The young
Man immediately left his own Body breathless on the Ground, while at the
same Instant that of the Doe was re-animated, she came to the King,
fawned upon him, and after having play'd several wanton Tricks, fell
again upon the Grass; at the same Instant the Body of the
Dervis
recovered its Life. The King was infinitely pleased at so uncommon an
Operation, and conjured his Friend by every thing that was sacred to
communicate it to him. The
Dervis
at first made some Scruple of
violating his Promise to the dying
Brachman
; but told him at last that
he found he could conceal nothing from so excellent a Prince; after
having obliged him therefore by an Oath to Secrecy, he taught him to
repeat two Cabalistick Words, in pronouncing of which the whole Secret
consisted. The King, impatient to try the Experiment, immediately
repeated them as he had been taught, and in an Instant found himself in
the Body of the Doe. He had but little Time to contemplate himself in
this new Being; for the treacherous
Dervis
shooting his own Soul into
the Royal Corps, and bending the Prince's own Bow against him, had laid
him dead on the Spot, had not the King, who perceiv'd his Intent, fled
swiftly to the Woods.
'The
Dervis
, now triumphant in his Villany, returned to
Mousel
, and
filled the Throne and Bed of the unhappy
Fadlallah
.
'The first thing he took Care of, in order to secure himself in the
Possession of his new-acquired Kingdom, was to issue out a Proclamation,
ordering his Subjects to destroy all the Deer in the Realm. The King had
perished among the rest, had he not avoided his Pursuers by re-animating
the Body of a Nightingale which he saw lie dead at the Foot of a Tree.
In this new Shape he winged his Way in Safety to the Palace, where
perching on a Tree which stood near his Queen's Apartment, he filled the
whole Place with so many melodious and Melancholy Notes as drew her to
the Window. He had the Mortification to see that instead of being
pitied, he only moved the Mirth of his Princess, and of a young Female
Slave who was with her. He continued however to serenade her every
Morning, 'till at last the Queen, charmed with his Harmony, sent for the
Bird-catchers, and ordered them to employ their utmost Skill to put that
little Creature into her Possession. The King, pleased with an
Opportunity of being once more near his beloved Consort, easily suffered
himself to be taken; and when he was presented to her, tho' he shewed a
Fearfulness to be touched by any of the other Ladies, flew of his own
Accord, and hid himself in the Queen's Bosom.
Zemroude
was highly
pleased at the unexpected Fondness of her new Favourite, and ordered him
to be kept in an open Cage in her own Apartment. He had there an
Opportunity of making his Court to her every Morning, by a thousand
little Actions which his Shape allowed him. The Queen passed away whole
Hours every Day in hearing and playing with him.
Fadlallah
could even
have thought himself happy in this State of Life, had he not frequently
endured the inexpressible Torment of seeing the
Dervis
enter the
Apartment and caress his Queen even in his Presence.
The Usurper, amidst his toying with the Princess, would often endeavour
to ingratiate himself with her Nightingale; and while the enraged
Fadlallah
peck'd at him with his Bill, beat his Wings, and shewed all
the Marks of an impotent Rage, it only afforded his Rival and the Queen
new Matter for their Diversion.
Zemroude
was likewise fond of a little Lap-Dog which she kept in her
Apartment, and which one Night happened to die.
The King immediately found himself inclined to quit the shape of the
Nightingale, and enliven this new Body. He did so, and the next Morning
Zemroude
saw her favourite Bird lie dead in the Cage. It is impossible
to express her Grief on this Occasion, and when she called to mind all
its little Actions, which even appeared to have somewhat in them like
Reason, she was inconsolable for her Loss.
Her Women immediately sent for the
Dervis
, to come and comfort her,
who after having in vain represented to her the Weakness of being
grieved at such an Accident, touched at last by her repeated Complaints;
Well Madam
, says he,
I will exert the utmost of my Art to please you.
Your Nightingale shall again revive every Morning and serenade you as
before
. The Queen beheld him with a Look which easily shewed she did
not believe him; when laying himself down on a Sofa, he shot his Soul
into the Nightingale, and
Zemroude
was amazed to see her Bird revive.
'The King, who was a
Spectator
of all that passed, lying under the Shape
of a Lap-Dog, in one Corner of the Room, immediately recovered his own
Body, and running to the Cage with the utmost Indignation, twisted off
the Neck of the false Nightingale.
'
Zemroude
was more than ever amazed and concerned at this second
Accident, 'till the King entreating her to hear him, related to her his
whole Adventure.
'The Body of the
Dervis
, which was found dead in the Wood, and his
Edict for killing all the Deer, left her no Room to doubt of the Truth
of it: But the Story adds, That out of an extream Delicacy (peculiar to
the Oriental Ladies) she was so highly afflicted at the innocent
Adultery in which she had for some time lived with the
Dervis
, that no
Arguments even from
Fadlallah
himself could compose her Mind. She
shortly after died with Grief, begging his Pardon with her last Breath
for what the most rigid Justice could not have interpreted as a Crime.
'The King was so afflicted with her Death, that he left his Kingdom to
one of his nearest Relations, and passed the rest of his Days in
Solitude and Retirement.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 11, 1714 |
Addison |
—Odora canum vis—
Virg.

In the Reign of King
Charles
I., the Company of Stationers, into whose
Hands the Printing of the Bible is committed by Patent, made a very
remarkable
Erratum
or Blunder in one of their Editions: For instead of
Thou shalt not commit Adultery
, they printed off several thousands of
Copies with
Thou shalt commit Adultery
. Archbishop
Laud
, to punish
this their Negligence, laid a considerable Fine upon that Company in the
Star-Chamber.
By the Practice of the World, which prevails in this degenerate Age, I
am afraid that very many young Profligates, of both Sexes, are possessed
of this spurious Edition of the Bible, and observe the Commandment
according to that faulty Reading.
Adulterers, in the first Ages of the Church, were excommunicated for
ever, and unqualified all their Lives from bearing a Part in Christian
Assemblies, notwithstanding they might seek it with Tears, and all the
Appearances of the most unfeigned Repentance.
I might here mention some ancient Laws among the Heathens which punished
this Crime with Death: and others of the same Kind, which are now in
Force among several Governments that have embraced the Reformed
Religion. But because a Subject of this Nature may be too serious for my
ordinary Readers, who are very apt to throw by my Papers, when they are
not enlivened with something that is diverting or uncommon; I shall here
publish the Contents of a little Manuscript lately fallen into my Hands,
and which pretends to great Antiquity, tho' by Reason of some modern
Phrases and other Particulars in it, I can by no means allow it to be
genuine, but rather the Production of a Modern Sophist.
It is well known by the Learned, that there was a Temple upon Mount
Ætna
dedicated to
Vulcan
, which was guarded by Dogs of so exquisite
a Smell, (say the Historians) that they could discern whether the
Persons who came thither were chast or otherwise. They used to meet and
faun upon such as were chast, caressing them as the Friends of their
Master
Vulcan
; but flew at those who were polluted, and never ceased
barking at them till they had driven them from the Temple.
My Manuscript gives the following Account of these Dogs, and was
probably designed as a Comment upon this Story.
'These Dogs were given to
Vulcan
by his Sister
Diana
, the Goddess of
Hunting and of Chastity, having bred them out of some of her Hounds, in
which she had observed this natural Instinct and Sagacity. It was
thought she did it in Spight to
Venus
, who, upon her Return home,
always found her Husband in a good or bad Humour, according to the
Reception which she met with from his Dogs. They lived in the Temple
several Years, but were such snappish Curs that they frighted away most
of the Votaries. The Women of
Sicily
made a solemn Deputation to the
Priest, by which they acquainted him, that they would not come up to the
Temple with their annual Offerings unless he muzzled his Mastiffs; and
at last comprimised the Matter with him, that the Offering should always
be brought by a Chorus of young Girls, who were none of them above seven
Years old. It was wonderful (says the Author) to see how different the
Treatment was which the Dogs gave to these little Misses, from that
which they had shown to their Mothers. It is said that the Prince of
Syracuse
, having married a young Lady, and being naturally of a
jealous Temper, made such an Interest with the Priests of this Temple,
that he procured a Whelp from them of this famous Breed. The young Puppy
was very troublesome to the fair Lady at first, insomuch that she
sollicited her Husband to send him away, but the good Man cut her short
with the old
Sicilian
Proverb,
Love me love my Dog
. From which Time
she lived very peaceably with both of them. The Ladies of
Syracuse
were very much annoyed with him, and several of very good Reputation
refused to come to Court till he was discarded. There were indeed some
of them that defied his Sagacity, but it was observed, though he did not
actually bite them, he would growle at them most confoundedly. To return
to the Dogs of the Temple: After they had lived here in great Repute for
several Years, it so happened, that as one of the Priests, who had been
making a charitable Visit to a Widow who lived on the Promontory of
Lilybeum
, return'd home pretty late in the Evening, the Dogs flew at
him with so much Fury, that they would have worried him if his Brethren
had not come in to his Assistance: Upon which, says my Author, the Dogs
were all of them hanged, as having lost their original Instinct.
I cannot conclude this Paper without wishing, that we had some of this
Breed of Dogs in
Great Britain
, which would certainly do
Justice
, I
should say
Honour
, to the Ladies of our Country, and shew the World
the difference between Pagan Women and those who are instructed in
sounder Principles of Virtue and Religion.
Contents
|
Friday, August 13, 1714 |
Addison |
—Si verbo audacia detur,
Non metuam magni dixisse palatia Coeli.
Ovid.
Met.
Sir ,
'
I considered in my two last Letters
1 that awful and tremendous
Subject, the Ubiquity or Omnipresence of the Divine Being. I have
shewn that he is equally present in all Places throughout the whole
Extent of infinite Space.
'This Doctrine is so agreeable to Reason, that we meet with it in the
Writings of the enlightened Heathens, as I might show at large, were
it not already done by other Hands. But tho' the Deity be thus
essentially present through all the Immensity of Space, there is one
Part of it in which he discovers himself in a most transcendent and
visible Glory. This is that Place which is marked out in Scripture
under the different Appellations of
Paradise, the third Heaven, the
Throne of God, and
the Habitation of his Glory. It is here where
the glorified Body of our Saviour resides, and where all the celestial
Hierarchies, and the innumerable Hosts of Angels, are represented as
perpetually surrounding the Seat of God with
Hallelujahs and Hymns
of Praise. This is that Presence of God which some of the Divines call
his Glorious, and others his Majestatick Presence. He is indeed as
essentially present in all other Places as in this, but it is here
where he resides in a sensible Magnificence, and in the midst of those
Splendors which can affect the Imagination of created Beings.
'It is very remarkable that this Opinion of God Almighty's Presence in
Heaven, whether discovered by the Light of Nature, or by a general
Tradition from our first Parents, prevails among all the Nations of
the World, whatsoever different Notions they entertain of the Godhead.
If you look into
Homer, that is, the most ancient of the
Greek
Writers, you see the supreme Powers seated in the Heavens, and
encompassed with inferior Deities, among whom the Muses are
represented as singing incessantly about his Throne. Who does not here
see the main Strokes and Outlines of this great Truth we are speaking
of? The same Doctrine is shadowed out in many other Heathen Authors,
tho' at the same time, like several other revealed Truths, dashed and
adulterated with a mixture of Fables and human Inventions. But to pass
over the Notions of the
Greeks and
Romans, those more enlightened
Parts of the Pagan World, we find there is scarce a People among the
late discovered Nations who are not trained up in an Opinion, that
Heaven is the Habitation of the Divinity whom they worship.
As in
Solomon's Temple there was the
Sanctum Sanctorum, in which a
visible Glory appeared among the Figures of the Cherubims, and into
which none but the High Priest himself was permitted to enter, after
having made an Atonement for the Sins of the People; so if we consider
the whole Creation as one great Temple, there is in it this Holy of
Holies, into which the High-Priest of our Salvation entered, and took
his Place among Angels and Archangels, after having made a Propitiation
for the Sins of Mankind.
'With how much Skill must the Throne of God be erected? With what
glorious Designs is that Habitation beautified, which is contrived and
built by him who inspired
Hyram with Wisdom? How great must be the
Majesty of that Place, where the whole Art of Creation has been
employed, and where God has chosen to show himself in the most
magnificent manner? What must be the Architecture of Infinite Power
under the Direction of Infinite Wisdom? A Spirit cannot but be
transported, after an ineffable manner, with the sight of those Objects,
which were made to affect him by that Being who knows the inward Frame
of a Soul, and how to please and ravish it in all its most secret Powers
and Faculties. It is to this Majestic Presence of God, we may apply
those beautiful Expressions in holy Writ:
Behold even to the Moon, and
it shineth not; yea the Stars are not pure in his sight. The Light of
the Sun, and all the Glories of the World in which we live, are but as
weak and sickly Glimmerings, or rather Darkness itself, in Comparison of
those Splendors which encompass the Throne of God.
'As the
Glory of this Place is transcendent beyond Imagination, so
probably is the
Extent of it. There is Light behind Light, and Glory
within Glory. How far that Space may reach, in which God thus appears in
perfect Majesty, we cannot possibly conceive. Tho' it is not infinite,
it may be indefinite; and though not immeasurable in its self, it may be
so with regard to any created Eye or Imagination. If he has made these
lower Regions of Matter so inconceivably wide and magnificent for the
Habitation of mortal and perishable Beings, how great may we suppose the
Courts of his House to be, where he makes his Residence in a more
especial manner, and displays himself in the Fulness of his Glory, among
an innumerable Company of Angels, and Spirits of just Men made perfect?
'This is certain, that our Imaginations cannot be raised too high, when
we think on a Place where Omnipotence and Omniscience have so signally
exerted themselves, because that they are able to produce a Scene
infinitely more great and glorious than what we are able to imagine. It
is not impossible but at the Consummation of all Things, these outward
Apartments of Nature, which are now suited to those Beings who inhabit
them, may be taken in and added to that glorious Place of which I am
here speaking; and by that means made a proper Habitation for Beings who
are exempt from Mortality, and cleared of their Imperfections: For so
the Scripture seems to intimate when it speaks of new Heavens and of a
new Earth, wherein dwelleth Righteousness.
'I have only considered this Glorious Place, with Regard to the Sight
and Imagination, though it is highly probable that our other Senses may
here likewise enjoy their highest Gratifications. There is nothing which
more ravishes and transports the Soul, than Harmony; and we have great
Reason to believe, from the Descriptions of this Place in Holy
Scripture, that this is one of the Entertainments of it. And if the Soul
of Man can be so wonderfully affected with those Strains of Musick,
which Human Art is capable of producing, how much more will it be raised
and elevated by those, in which is exerted the whole Power of Harmony!
The Senses are Faculties of the Human Soul, though they cannot be
employed, during this our vital Union, without proper Instruments in the
Body. Why therefore should we exclude the Satisfaction of these
Faculties, which we find by Experience are Inlets of great Pleasure to
the Soul, from among those Entertainments which are to make up our
Happiness hereafter? Why should we suppose that our Hearing and Seeing
will not be gratify'd with those Objects which are most agreeable to
them, and which they cannot meet with in these lower Regions of Nature;
Objects,
which neither Eye hath seen, nor Ear heard, nor can it enter
into the Heart of Man to conceive? I knew a Man in Christ (says St
Paul, speaking of himself)
above fourteen Years ago (whether in the
Body, I cannot tell, or whether out of the Body, I cannot tell: God
knoweth) such a one caught up to the third Heaven. And I knew such a
Man, (whether in the Body, or out of the Body, I cannot tell: God
knoweth,) how that he was caught up into Paradise, and heard unspeakable
Words, which it is not possible for a Man to utter. By this is meant,
that what he heard was so infinitely different from any thing which he
had heard in this World, that it was impossible to express it in such
Words as might convey a Notion of it to his Hearers.
'It is very natural for us to take Delight in Enquiries concerning any
Foreign Country, where we are some Time or other to make our Abode; and
as we all hope to be admitted into this Glorious Place, it is both a
laudable and useful Curiosity, to get what Informations we can of it,
whilst we make Use of Revelation for our Guide. When these everlasting
Doors shall be open to us, we may be sure that the Pleasures and
Beauties of this Place will infinitely transcend our present Hopes and
Expectations, and that the glorious Appearance of the Throne of God,
will rise infinitely beyond whatever we are able to conceive of it. We
might here entertain our selves with many other Speculations on this
Subject, from those several Hints which we find of it in the Holy
Scriptures; as whether there may not be different Mansions and
Apartments of Glory, to Beings of different Natures; whether as they
excel one another in Perfection, they are not admitted nearer to the
Throne of the Almighty, and enjoy greater Manifestations of his
Presence; whether there are not solemn Times and Occasions, when all the
Multitude of Heaven celebrate the Presence of their Maker in more
extraordinary Forms of Praise and Adoration; as
Adam, though he had
continued in a State of Innocence, would, in the Opinion of our Divines,
have kept Holy the Sabbath-Day, in a more particular Manner than any
other of the Seven. These, and the like Speculations, we may very
innocently indulge, so long as we make use of them to inspire us with a
De
Sir e of becoming Inhabitants of this delightful Place.
'I have in this, and in two foregoing Letters, treated on the most
serious Subject that can employ the Mind of Man, the Omnipresence of the
Deity; a Subject which, if possible, should never depart from our
Meditations. We have considered the Divine Being, as he inhabits
Infinitude, as he dwells among his Work, as he is present to the Mind of
Man, and as he discovers himself in a more glorious Manner among the
Regions of the Blest. Such a Consideration should be kept awake in us at
all Times, and in all Places, and possess our Minds with a perpetual Awe
and Reverence. It should be interwoven with all our Thoughts and
Perceptions, and become one with the Consciousness of our own Being. It
is not to be reflected on in the Coldness of Philosophy, but ought to
sink us into the lowest Prostration before him, who is so astonishingly
Great, Wonderful, and Holy.'
Footnote 1:
: See Nos.
,
,
, and
.
Contents
|
Monday, August 16, 1714 |
Addison |
Sunt bona, sunt quædam mediocria, sunt mala plura
Quæ legis.
Mart.

I am at present sitting with a Heap of Letters before me, which I have
received under the Character of SPECTATOR; I have Complaints from
Lovers, Schemes from Projectors, Scandal from Ladies, Congratulations,
Compliments, and Advice in abundance.
I have not been thus long an Author, to be insensible of the natural
Fondness every Person must have for their own Productions; and I begin
to think I have treated my Correspondents a little too uncivilly in
Stringing them all together on a File, and letting them lye so long
unregarded. I shall therefore, for the future, think my self at least
obliged to take some Notice of such Letters as I receive, and may
possibly do it at the end of every Month.
In the mean time, I intend my present Paper as a short Answer to most of
those which have been already sent me.
The Publick however is not to expect I should let them into all my
Secrets; and though I appear abstruse to most People, it is sufficient
if I am understood by my particular Correspondents.
My Well-wisher
Van Nath
is very arch, but not quite enough so to
appear in Print.
Philadelphus
will, in a little time, see his Query fully answered by a
Treatise which is now in the Press.
It was very improper at that time to comply with Mr.
G.
Miss
Kitty
must excuse me.
The Gentleman who sent me a Copy of Verses on his Mistress's Dancing, is
I believe too thoroughly in Love to compose correctly.
I have too great a Respect for both the Universities to praise one at
the Expence of the other.
Tom Nimble
is a very honest Fellow, and I de
Sir
e him to present my
humble Service to his Cousin
Fill Bumper
.
I am obliged for the Letter upon Prejudice.
I may in due time animadvert on the Case of
Grace Grumble
.
The Petition of
P. S. granted.
That of
Sarah Loveit, refused.
The Papers of
A. S.
are returned.
I thank
Aristippus
for his kind Invitation.
My Friend at
Woodstock
is a bold Man, to undertake for all within Ten
Miles of him.
I am afraid the Entertainment of
Tom Turnover
will hardly be relished
by the good Cities of
London
and
Westminster.
I must consider further of it, before I indulge
W. F
. in those
Freedoms he takes with the Ladies Stockings.
I am obliged to the ingenious Gentleman, who sent me an Ode on the
Subject of a late SPECTATOR, and shall take particular Notice of his
last Letter.
When the Lady who wrote me a Letter, dated
July
the 20th, in relation
to some Passages in a
Lover
, will be more particular in her
Directions, I shall be so in my Answer.
The poor Gentleman, who fancies my Writings could reclaim an Husband who
can abuse such a Wife as he describes, has I am afraid too great an
Opinion of my Skill.
Philanthropos
is, I dare say, a very well-meaning Man, but a little
too prolix in his Compositions.
Constantius
himself must be the best Judge in the Affair he mentions.
The Letter dated from
Lincoln
is received.
Arethusa
and her Friend may hear further from me.
Celia
is a little too hasty.
Harriot
is a good Girl, but must not Curtsie to Folks she does not
know.
I must ingeniously confess my Friend
Sampson Bentstaff
has quite
puzzled me, and writ me a long Letter which I cannot comprehend one Word
of.
Collidan
must also explain what he means by his
Drigelling.
I think it beneath my
Spectatorial
Dignity, to concern my self in the
Affair of the boiled Dumpling.
I shall consult some
Litterati
on the Project sent me for the
Discovery of the Longitude.
I know not how to conclude this Paper better, than by inserting a Couple
of Letters which are really genuine, and which I look upon to be two of
the smartest Pieces I have received from my Correspondents of either Sex.
Brother Spec.
'While you are surveying every Object that falls in your way, I am
wholly taken up with one. Had that Sage, who demanded what Beauty was,
lived to see the dear Angel I love, he would not have asked such a
Question. Had another seen her, he would himself have loved the Person
in whom Heaven has made Virtue visible; and were you your self to be
in her ompany, you could never, with all your Loquacity, say enough of
her good Humour and Sense. I send you the Outlines of a Picture, which
I can no more finish than I can sufficiently admire the dear Original.
I am
Your most Affectionate Brother,
Constantio Spec.
Good Mr. Pert,
'I will allow you nothing till you resolve me the following Question.
Pray what's the Reason that while you only talk now upon Wednesdays,
Fridays, and Mondays, you pretend to be a greater Tatler, than
when you spoke every Day as you formerly used to do? If this be your
plunging out of your Taciturnity, pray let the Length of your Speeches
compensate for the Scarceness of them.
I am,
Good Mr. Pert,
Your Admirer, if you will be long enough for Me,
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 18, 1714 |
|
—Tenet insanabile multos
Scribendi Cacœthes—
Juv.

There is a certain Distemper, which is mentioned neither by
Galen
nor
Hippocrates
, nor to be met with in the
London Dispensary
.
Juvenal
,
in the Motto of my Paper, terms it a
Cacœthes
; which is a hard Word
for a Disease called in plain
English
, the
Itch of Writing.
This
Cacœthes
is as Epidemical as the Small-Pox, there being very few who
are not seized with it some time or other in their Lives. There is,
however, this Difference in these two Distempers, that the first, after
having indisposed you for a time, never returns again; whereas this I am
speaking of, when it is once got into the Blood, seldom comes out of it.
The
British
Nation is very much afflicted with this Malady, and tho'
very many Remedies have been applied to Persons infected with it, few of
them have ever proved successful. Some have been cauterized with Satyrs
and Lampoons, but have received little or no Benefit from them; others
have had their Heads fastned for an Hour together between a Cleft Board,
which is made use
as a Cure for the Disease when it appears in its
greatest Malignity
. There is indeed one kind of this Malady which
has been sometimes removed, like the Biting of a
Tarantula
, with the
sound of a musical Instrument, which is commonly known by the Name of a
Cat-Call. But if you have a Patient of this kind under your Care, you
may assure your self there is no other way of recovering him
effectually, but by forbidding him the use of Pen, Ink and Paper.
But to drop the Allegory before I have tired it out, there is no Species
of Scriblers more offensive, and more incurable, than your Periodical
Writers, whose Works return upon the Publick on certain Days and at
stated Times. We have not the Consolation in the Perusal of these
Authors, which we find at the reading of all others, (namely) that we
are sure if we have but Patience, we may come to the End of their
Labours. I have often admired a humorous Saying of
Diogenes
, who
reading a dull Author to several of his Friends, when every one began to
be tired, finding he was almost come to a blank leaf at the End of it,
cried,
Courage, Lads, I see Land
. On the contrary, our Progress
through that kind of Writers I am now speaking of is never at an End.
One Day makes Work for another, we do not know when to promise our
selves Rest.
It is a melancholy thing to consider, that the Art of Printing, which
might be the greatest Blessing to Mankind, should prove detrimental to
us, and that it should be made use of to scatter Prejudice and Ignorance
through a People, instead of conveying to them Truth and Knowledge.
I was lately reading a very whimsical Treatise, entitled,
William
Ramsey's
Vindication of Astrology. This profound Author, among many
mystical Passages, has the following one:
The Absence of the Sun is not the Cause of Night, forasmuch
as his Light is so great that it may illuminate the Earth all
over at once as clear as broad Day, but there are tenebrificous
and dark Stars, by whose Influence Night is brought on, and
which do ray out Darkness and Obscurity upon the Earth, as
the Sun does Light.
I consider Writers in the same View this sage Astrologer does the
Heavenly Bodies. Some of them are Stars that scatter Light as others do
Darkness. I could mention several Authors who are tenebrificous Stars of
the first Magnitude, and point out a Knot of Gentlemen, who have been
dull in Consort, and may be looked upon as a dark Constellation. The
Nation has been a great while benighted with several of these
Antiluminaries. I suffered them to ray out their Darkness as long as I
was able to endure it, till at length I came to a Resolution of rising
upon them, and hope in a little time to drive them quite out of the
British
Hemisphere.
Footnote 1:
Put in the Pillory.
Contents
|
Friday, August 20, 1714 |
Addison |
Ipse thymum pinosque ferens de montibus altis,
Tecta serat latè circum, cui talia Curæ:
Ipse labore manum duro terat, ipse feraces
Figat humo plantas, et amicos irriget Imbres.
Virg.

Every Station of Life has Duties which are proper to it. Those who are
determined by Choice to any particular kind of Business, are indeed more
happy than those who are determined by Necessity, but both are under an
equal Obligation of fixing on Employments, which may be either useful to
themselves or beneficial to others. No one of the Sons of
Adam
ought
to think himself exempt from that Labour and Industry which were
denounced to our first Parent, and in him to all his Posterity. Those to
whom Birth or Fortune may seem to make such an Application unnecessary,
ought to find out some Calling or Profession for themselves, that they
may not lie as a Burden on the Species, and be the only useless Parts of
the Creation.
Many of our Country Gentlemen in their busie Hours apply themselves
wholly to the Chase, or to some other Diversion which they find in the
Fields and Woods. This gave occasion to one of our most eminent
English
Writers to represent every one of them as lying under a kind
of Curse pronounced to them in the Words of
Goliah, I will give thee to
the Fowls of the Air, and to the Beasts of the Field.
Tho' Exercises of this kind, when indulged with Moderation, may have a
good Influence both on the Mind and Body, the Country affords many other
Amusements of a more noble kind.
Among these I know none more delightful in itself, and beneficial to the
Publick, than that of
Planting.
I could mention a Nobleman whose
Fortune has placed him in several Parts of
England
, and who has always
left these visible Marks behind him, which show he has been there: He
never hired a House in his Life, without leaving all about it the Seeds
of Wealth, and bestowing Legacies on the Posterity of the Owner. Had all
the Gentlemen of
England
made the same Improvements upon their
Estates, our whole Country would have been at this time as one great
Garden. Nor ought such an Employment to be looked upon as too inglorious
for Men of the highest Rank. There have been Heroes in this Art, as well
as in others. We are told in particular of
Cyrus
the Great, that he
planted all the Lesser
Asia.
There is indeed something truly
magnificent in this kind of Amusement: It gives a nobler Air to several
Parts of Nature; it fills the Earth with a Variety of beautiful Scenes,
and has something in it like Creation. For this Reason the Pleasure of
one who Plants is something like that of a Poet, who, as
Aristotle
observes, is more delighted with his Productions than any other Writer
or Artist whatsoever.
Plantations have one Advantage in them which is not to be found in most
other Works, as they give a Pleasure of a more lasting Date, and
continually improve in the Eye of the Planter, When you have finished a
Building or any other Undertaking of the like Nature, it immediately
decays upon your Hands; you see it brought to its utmost Point of
Perfection, and from that time hastening to its Ruin. On the contrary,
when you have finished your Plantations, they are still arriving at
greater Degrees of Perfection as long as you live, and appear more
delightful in every succeeding Year than they did in the foregoing.
But I do not only recommend this Art to Men of Estates as a pleasing
Amusement, but as it is a kind of Virtuous Employment, and may therefore
be inculcated by moral Motives; particularly from the Love which we
ought to have for our Country, and the Regard which we ought to bear to
our Posterity. As for the first, I need only mention what is frequently
observed by others, that the Increase of Forest-Trees does by no Means
bear a Proportion to the Destruction of them, insomuch that in a few
Ages the Nation may be at a Loss to supply it self with Timber
sufficient for the Fleets of
England.
I know when a Man talks of
Posterity in Matters of this Nature, he is looked upon with an Eye of
Ridicule by the cunning and selfish part of Mankind. Most People are of
the Humour of an old Fellow of a College, who, when he was pressed by
the Society to come into something that might redound to the good of
their Successors, grew very peevish,
We are always doing
, says he,
something for Posterity, but I would fain see Posterity do something
for us.
But I think Men are inexcusable, who fail in a Duty of this Nature,
since it is so easily discharged. When a Man considers that the putting
a few Twigs into the Ground, is doing good to one who will make his
appearance in the World about Fifty Years hence, or that he is perhaps
making one of his own Descendants easy or rich, by so inconsiderable an
Expence, if he finds himself averse to it, he must conclude that he has
a poor and base Heart, void of all generous Principles and Love to
Mankind.
There is one Consideration, which may very much enforce what I have here
said. Many honest Minds that are naturally disposed to do good in the
World, and become Beneficial to Mankind, complain within themselves that
they have not Talents for it. This therefore is a good Office, which is
suited to the meanest Capacities, and which may be performed by
Multitudes, who have not Abilities sufficient to deserve well of their
Country and to recommend themselves to their Posterity, by any other
Method. It is the Phrase of a Friend of mine, when any useful Country
Neighbour dies, that
you may trace him:
which I look upon as a good
Funeral Oration, at the Death of an honest Husbandman, who hath left the
Impressions of his Industry behind him, in the Place where he has lived.
Upon the foregoing Considerations, I can scarce forbear representing the
Subject of this Paper as a kind of Moral Virtue: Which, as I have
already shown, recommends it self likewise by the Pleasure that attends
it. It must be confessed, that this is none of those turbulent Pleasures
which is apt to gratifie a Man in the Heats of Youth; but if it be not
so Tumultuous, it is more lasting. Nothing can be more delightful than
to entertain ourselves with Prospects of our own making, and to walk
under those Shades which our own Industry has raised. Amusements of this
Nature compose the Mind, and lay at Rest all those Passions which are
uneasie to the Soul of Man, besides that they naturally engender good
Thoughts, and dispose us to laudable Contemplations. Many of the old
Philosophers passed away the greatest Parts of their Lives among their
Gardens.
Epicurus
himself could not think sensual Pleasure attainable
in any other Scene. Every Reader who is acquainted with
Homer,
Virgil
and
Horace
, the greatest Genius's of all Antiquity, knows
very well with how much Rapture they have spoken on this Subject; and
that
Virgil
in particular has written a whole Book on the Art of
Planting.
This Art seems to have been more especially adapted to the Nature of Man
in his Primaeval State, when he had Life enough to see his Productions
flourish in their utmost Beauty, and gradually decay with him. One who
lived before the Flood might have seen a Wood of the tallest Oakes in
the Accorn. But I only mention this Particular, in order to introduce in
my next Paper, a History which I have found among the Accounts of
China
, and which may be looked upon as an Antediluvian Novel.
Contents
|
Monday, August 23, 1714 |
Addison |
Hec gelidi fontes, hic mollia prata, Lycori,
Hic Nemus, hic toto tecum consumerer ævo.
Virg.

Hilpa
was one of the 150 Daughters of
Zilpah
, of the Race of
Cohu
,
by whom some of the Learned think is meant
Cain
. She was exceedingly
beautiful, and when she was but a Girl of threescore and ten Years of
Age, received the Addresses of several who made Love to her. Among these
were two Brothers,
Harpath
and
Shalum
;
Harpath
, being the
First-born, was Master of that fruitful Region which lies at the Foot of
Mount
Tirzah
, in the Southern Parts of
China
.
Shalum
(which is to
say the Planter in the
Chinese
Language) possessed all the
neighbouring Hills, and that great Range of Mountains which goes under
the Name of
Tirzah
.
Harpath
was of a haughty contemptuous Spirit;
Shalum
was of a gentle Disposition, beloved both by God and Man.
It is said that, among the Antediluvian Women, the Daughters of
Cohu
had their Minds wholly set upon Riches; for which Reason the beautiful
Hilpa
preferr'd
Harpath
to
Shalum
, because of his numerous Flocks
and Herds, that covered all the low Country which runs along the Foot of
Mount
Tirzah
, and is watered by several Fountains and Streams breaking
out of the Sides of that Mountain.
Harpath
made so quick a Dispatch of his Courtship, that he married
Hilpa
in the hundredth Year of her Age; and being of an insolent
Temper, laughed to Scorn his Brother
Shalum
for having pretended to
the beautiful
Hilpa
, when he was Master of nothing but a long Chain of
Rocks and Mountains. This so much provoked
Shalum
, that he is said to
have cursed his Brother in the Bitterness of his Heart, and to have
prayed that one of his Mountains might fall upon his Head if ever he
came within the Shadow of it.
From this Time forward
Harpath
would never venture out of the Vallies,
but came to an untimely End in the 250th Year of his Age, being drowned
in a River as he attempted to cross it This River is called to this Day,
from his Name who perished in it, the River
Harpath
, and, what is very
remarkable, issues out of one of those Mountains which
Shalum
wished
might fall upon his Brother, when he cursed him in the Bitterness of his
Heart.
Hilpa
was in the 160th Year of her Age at the Death of her Husband,
having brought him but 50 Children, before he was snatched away, as has
been already related. Many of the Antediluvians made Love to the young
Widow, tho' no one was thought so likely to succeed in her Affections as
her first Lover
Shalum
, who renewed his Court to her about ten Years
after the Death of
Harpath
; for it was not thought decent in those
Days that a Widow should be seen by a Man within ten Years after the
Decease of her Husband.
Shalum
falling into a deep Melancholy, and resolving to take away that
Objection which had been raised against him when he made his first
Addresses to
Hilpa
, began immediately, after her Marriage with
Harpath
, to plant all that mountainous Region which fell to his Lot in
the Division of this Country. He knew how to adapt every Plant to its
proper Soil, and is thought to have inherited many traditional Secrets
of that Art from the first Man. This Employment turn'd at length to his
Profit as well as to his Amusement: His Mountains were in a few Years
shaded with young Trees, that gradually shot up into Groves, Woods, and
Forests, intermixed with Walks, and Launs, and Gardens; insomuch that
the whole Region, from a naked and desolate Prospect, began now to look
like a second Paradise. The Pleasantness of the Place, and the agreeable
Disposition of
Shalum
, who was reckoned one of the mildest and wisest
of all who lived before the Flood, drew into it Multitudes of People,
who were perpetually employed in the sinking of Wells, the digging of
Trenches, and the hollowing of Trees, for the better Distribution of
Water through every Part of this spacious Plantation.
The Habitations of
Shalum
looked every Year more beautiful in the Eyes
of
Hilpa
, who, after the Space of 70 Autumns, was wonderfully pleased
with the distant Prospect of
Shalum
's Hills, which were then covered
with innumerable Tufts of Trees and gloomy Scenes that gave a
Magnificence to the Place, and converted it into one of the finest
Landskips the Eye of Man could behold.
The
Chinese
record a Letter which
Shalum
is said to have written to
Hilpa
, in the Eleventh Year of her Widowhood. I shall here translate
it, without departing from that noble Simplicity of Sentiments, and
Plainness of Manners which appears in the Original.
Shalum
was at this Time 180 Years old, and
Hilpa
170.
Shalum, Master of Mount Tirzah, to Hilpa, Mistress of the
Vallies.
In the 788th Year of the Creation.
'What have I not suffered, O thou Daughter of Zilpah, since thou
gavest thy self away in Marriage to my Rival? I grew weary of the
Light of the Sun, and have been ever since covering my self with Woods
and Forests. These threescore and ten Years have I bewailed the Loss
of thee on the Tops of Mount Tirzah, and soothed my Melancholy among
a thousand gloomy Shades of my own raising. My Dwellings are at
present as the Garden of God; every Part of them is filled with
Fruits, and Flowers, and Fountains. The whole Mountain is perfumed for
thy Reception. Come up into it, O my Beloved, and let us People this
Spot of the new World with a beautiful Race of Mortals; let us
multiply exceedingly among these delightful Shades, and fill every
Quarter of them with Sons and Daughters. Remember, O thou Daughter of
Zilpah, that the Age of Man is but a thousand Years; that Beauty is
the Admiration but of a few Centuries. It flourishes as a Mountain
Oak, or as a Cedar on the Top of Tirzah, which in three or four
hundred Years will fade away, and never be thought of by Posterity,
unless a young Wood springs from its Roots. Think well on this, and
remember thy Neighbour in the Mountains.
Having here inserted this Letter, which I look upon as the only
Antediluvian
Billet-doux
now extant, I shall in my next Paper give the
Answer to it, and the Sequel of this Story.
Contents
|
Wednesday, August 25, 1714 |
Addison |
Ipsi lætitia voces ad sidera jactant
Intonsi montes: ipsæ jam carmina rupes,
Ipsæ sonant arbusta—
Virg.

The Sequel of the Story of
Shalum
and
Hilpa.
The Letter inserted in my last had so good an Effect upon
Hilpa,
that
she answered it in less than a Twelvemonth, after the following Manner.
Hilpa, Mistress of the Vallies, to Shalum, Master of Mount Tirzah.
In the 789th Year of the Creation.
'What have I to do with thee, O Shalum? Thou praisest Hilpa's
Beauty, but art thou not secretly enamoured with the Verdure of her
Meadows? Art thou not more affected with the Prospect of her green
Vallies, than thou wouldest be with the Sight of her Person? The
Lowings of my Herds, and the Bleatings of my Flocks, make a pleasant
Eccho in thy Mountains, and sound sweetly in thy Ears. What tho' I am
delighted with the Wavings of thy Forests, and those Breezes of
Perfumes which flow from the Top of Tirzah: Are these like the
Riches of the Valley?
'I know thee, O Shalum; thou art more wise and happy than any of the
Sons of Men. Thy Dwellings are among the Cedars; thou searchest out
the Diversity of Soils, thou understandest the Influences of the
Stars, and markest the Change of Seasons. Can a Woman appear lovely in
the Eyes of such a one? Disquiet me not, O Shalum; let me alone,
that I may enjoy those goodly Possessions which are fallen to my Lot.
Win me not by thy enticing Words. May thy Trees increase and multiply;
mayest thou add Wood to Wood, and Shade to Shade; but tempt not
Hilpa to destroy thy Solitude, and make thy Retirement populous.
The
Chinese
say, that a little time afterwards she accepted of a Treat
in one of the neighbouring Hills to which
Shalum
had invited her. This
Treat lasted for two Years, and is said to have cost
Shalum
five
hundred Antelopes, two thousand Ostriches, and a thousand Tun of Milk;
but what most of all recommended it, was that Variety of delicious
Fruits and Pot-herbs, in which no Person then living could any way equal
Shalum
.
He treated her in the Bower which he had planted amidst the Wood of
Nightingales. This Wood was made up of such Fruit-Trees and Plants as
are most agreeable to the several Kinds of Singing Birds; so that it had
drawn into it all the Musick of the Country, and was filled from one End
of the Year to the other with the most agreeable Consort in Season.
He shewed her every Day some beautiful and surprising Scene in this new
Region of Woodlands; and as by this Means he had all the Opportunities
he could wish for of opening his Mind to her, he succeeded so well, that
upon her Departure she made him a kind of Promise, and gave him her Word
to return him a positive Answer in less than fifty Years.
She had not been long among her own People in the Vallies, when she
received new Overtures, and at the same Time a most splendid Visit from
Mishpach
, who was a mighty Man of old, and had built a great City,
which he called after his own Name. Every House was made for at least a
thousand Years, nay there were some that were leased out for three
Lives; so that the Quantity of Stone and Timber consumed in this
Building is scarce to be imagined by those who live in the present Age
of the World. This great Man entertained her with the Voice of musical
Instruments which had been lately invented, and danced before her to the
Sound of the Timbrel. He also presented her with several domestick
Utensils wrought in Brass and Iron, which had been newly found out for
the Conveniency of Life. In the mean time
Shalum
grew very uneasie
with himself, and was sorely displeased at
Hilpa
for the Reception
which she had given to
Mishpach
, insomuch that he never wrote to her
or spoke of her during a whole Revolution of
Saturn
; but finding that
this Intercourse went no further than a Visit, he again renewed his
Addresses to her, who during his long Silence is said very often to have
cast a wishing Eye upon Mount
Tirzah
.
Her Mind continued wavering about twenty Years longer between
Shalum
and
Mishpach
; for tho' her Inclinations favoured the former, her
Interest pleaded very powerfully for the other. While her Heart was in
this unsettled Condition, the following Accident happened which
determined her Choice. A high Tower of Wood that stood in the City of
Mishpach
having caught Fire by a Flash of Lightning, in a few Days
reduced the whole Town to Ashes.
Mishpach
resolved to rebuild the
Place whatever it should cost him; and having already destroyed all the
Timber of the Country, he was forced to have Recourse to
Shalum
, whose
Forests were now two hundred Years old. He purchased these Woods with so
many Herds of Cattle and Flocks of Sheep, and with such a vast Extent of
Fields and Pastures, that
Shalum
was now grown more wealthy than
Mishpach
; and therefore appeared so charming in the Eyes of
Zilpah's
Daughter, that she no longer refused him in Marriage. On the Day in
which he brought her up into the Mountains he raised a most prodigious
Pile of Cedar and of every sweet smelling Wood, which reached above 300
Cubits in Height; He also cast into the Pile Bundles of Myrrh and
Sheaves of Spikenard, enriching it with every spicy Shrub, and making it
fat with the Gums of his Plantations. This was the Burnt-Offering which
Shalum
offered in the Day of his Espousals: The Smoke of it ascended
up to Heaven, and filled the whole Country with Incense and Perfume.
Contents
|
Friday, August 27, 1714 |
John Byrom1 |
—Quæ in vita usurpant homines, cogitant, curant, vident, Quæque
agunt vigilantes, agitantque, ea cuique in somno accidunt.
Cic.
de Div.
By the last Post I received the following Letter, which is built upon a
Thought that is new, and very well carried on; for which Reasons I shall
give it to the Publick without Alteration, Addition, or Amendment.
Sir ,
'It was a good Piece of Advice which Pythagoras gave to his
Scholars, That every Night before they slept they should examine what
they had been a doing that Day, and so discover what Actions were
worthy of Pursuit to-morrow, and what little Vices were to be
prevented from slipping unawares into a Habit. If I might second the
Philosopher's Advice, it should be mine, That in a Morning before my
Scholar rose, he should consider what he had been about that Night,
and with the same Strictness, as if the Condition he has believed
himself to be in, was real. Such a Scrutiny into the Actions of his
Fancy must be of considerable Advantage, for this Reason, because the
Circumstances which a Man imagines himself in during Sleep, are
generally such as entirely favour his Inclinations good or bad, and
give him imaginary Opportunities of pursuing them to the utmost; so
that his Temper will lye fairly open to his View, while he considers
how it is moved when free from those Constraints which the Accidents
of real Life put it under. Dreams are certainly the Result of our
waking Thoughts, and our daily Hopes and Fears are what give the Mind
such nimble Relishes of Pleasure, and such severe Touches of Pain, in
its Midnight Rambles. A Man that murders his Enemy, or deserts his
Friend in a Dream, had need to guard his Temper against Revenge and
Ingratitude, and take heed that he be not tempted to do a vile thing
in the Pursuit of false, or the Neglect of true Honour. For my Part, I
seldom receive a Benefit, but in a Night or two's Time I make most
noble Returns for it; which tho' my Benefactor is not a whit the
better for, yet it pleases me to think that it was from a Principle of
Gratitude in me, that my Mind was susceptible of such generous
Transport while I thought my self repaying the Kindness of my Friend:
And I have often been ready to beg Pardon, instead of returning an
Injury, after considering, that when the Offender was in my Power I
had carried my Resentments much too far.
'I think it has been observed in the Course of your Papers, how much
one's Happiness or Misery may depend upon the Imagination: Of which
Truth those strange Workings of Fancy in Sleep are no inconsiderable
Instances; so that not only the Advantage a Man has of making
Discoveries of himself, but a Regard to his own Ease or Disquiet, may
induce him to accept of my Advice. Such as are willing to comply with
it, I shall put into a way of doing it with pleasure, by observing
only one Maxim which I shall give them, viz. To go to Bed with a Mind
entirely free from Passion, and a Body clear of the least
Intemperance.
'They indeed who can sink into Sleep with their Thoughts less calm or
innocent than they should be, do but plunge themselves into Scenes of
Guilt and Misery; or they who are willing to purchase any Midnight
Disquietudes for the Satisfaction of a full Meal, or a Skin full of
Wine; these I have nothing to say to, as not knowing how to invite
them to Reflections full of Shame and Horror: But those that will
observe this Rule, I promise them they shall awake into Health and
Cheerfulness, and be capable of recounting with Delight those glorious
Moments wherein the Mind has been indulging it self in such Luxury of
Thought, such noble Hurry of Imagination. Suppose a Man's going
supperless to Bed should introduce him to the Table of some great
Prince or other, where he shall be entertained with the noblest Marks
of Honour and Plenty, and do so much Business after, that he shall
rise with as good a Stomach to his Breakfast as if he had fasted all
Night long; or suppose he should see his dearest Friends remain all
Night in great Distresses, which he could instantly have disengaged
them from, could he have been content to have gone to Bed without
t'other Bottle: Believe me, these Effects of Fancy are no contemptible
Consequences of commanding or indulging one's Appetite.
'I forbear recommending my Advice upon many other Accounts, till I
hear how you and your Readers relish what I have already said, among
whom if there be any that may pretend it is useless to them, because
they never dream at all, there may be others, perhaps, who do little
else all Day long. Were every one as sensible as I am what happens to
him in his Sleep, it would be no Dispute whether we past so
considerable a Portion of our Time in the Condition of Stocks and
Stones, or whether the Soul were not perpetually at Work upon the
Principle of Thought. However, 'tis an honest Endeavour of mine to
perswade my Countrymen to reap some Advantage from so many unregarded
Hours, and as such you will encourage it.
'I shall conclude with giving you a Sketch or two of my Way of
proceeding.
'If I have any Business of consequence to do to-morrow, I am scarce
dropt asleep to-night but I am in the midst of it, and when awake I
consider the whole Procession of the Affair, and get the Advantage of
the next Day's Experience before the Sun has risen upon it.
'There is scarce a great Post but what I have some Time or other been
in; but my Behaviour while I was Master of a College, pleases me so
well, that whenever there is a Province of that Nature vacant, I
intend to step in as soon as I can.
'I have done many Things that would not pass Examination, when I have
had the Art of Flying, or being invisible; for which Reason I am glad
I am not possessed of those extra-ordinary Qualities.
'Lastly, Mr. SPECTATOR, I have been a great Correspondent of yours,
and have read many of my Letters in your Paper which I never wrote
you. If you have a Mind I should really be so, I have got a Parcel of
Visions and other Miscellanies in my Noctuary, which I shall send you
to enrich your Paper with on proper Occasions.
I am, &c.
John Shadow.
Oxford, Aug. 20.
Footnote 1:
John Byrom, born at Manchester, in 1691, was quarrelled
with by his family for marrying a young lady without fortune, and lived
by an ingenious way of teaching short-hand, till the death of an elder
brother gave him the family estate. He died in 1763. In 1714 he had just
been elected Fellow of Trinity College, Cambridge. In 1723 he was
admitted a Fellow of the Royal Society, and contributed to its
Transactions a paper upon his own System of short-hand. In his later
years he wrote much rhyme.
Contents
|
Monday, August 30, 1714 |
John Byrom |
—Intus, et in Cute novi—
Pers.

Tho' the Author of the following Vision is unknown to me, I am apt to
think it may be the Work of that ingenious Gentleman, who promised me,
in the last Paper, some Extracts out of his Noctuary.
Sir
'I was the other Day reading the Life of Mahomet. Among many other
Extravagancies, I find it recorded of that Impostor, that in the
fourth Year of his Age the Angel Gabriel caught him up, while he was
among his Play-fellows, and, carrying him aside, cut open his Breast,
plucked out his Heart, and wrung out of it that black Drop of Blood,
in which, say the Turkish Divines, is contained the Fomes Peccati,
so that he was free from Sin ever after. I immediately said to my
self, tho' this Story be a Fiction, a very good Moral may be drawn
from it, would every Man but apply it to himself, and endeavour to
squeeze out of his Heart whatever Sins or ill Qualities he finds in
it.
'While my Mind was wholly taken up with this Contemplation, I
insensibly fell into a most pleasing Slumber, when methought two
Porters entered my Chamber, carrying a large Chest between them. After
having set it down in the middle of the Room they departed. I
immediately endeavour'd to open what was sent me, when a Shape, like
that in which we paint our Angels, appeared before me, and forbad me.
Enclosed, said he, are the Hearts of several of your Friends and
Acquaintance; but before you can be qualified to see and animadvert on
the Failings of others, you must be pure your self; whereupon he drew
out his Incision Knife, cut me open, took out my Heart, and began to
squeeze it. I was in a great Confusion, to see how many things, which
I had always cherished as Virtues, issued out of my Heart on this
Occasion. In short, after it had been thoroughly squeezed, it looked
like an empty Bladder, when the Phantome, breathing a fresh Particle
of Divine Air into it, restored it safe to its former Repository: and
having sewed me up, we began to examine the Chest.
'The Hearts were all enclosed in transparent Phials, and preserved in
a Liquor which looked like Spirits of Wine. The first which I cast my
Eye upon, I was afraid would have broke the Glass which contained it.
It shot up and down, with incredible Swiftness, thro' the Liquor in
which it swam, and very frequently bounced against the Side of the
Phial. The Fomes, or Spot in the Middle of it, was not large, but of
a red fiery Colour, and seemed to be the Cause of these violent
Agitations. That, says my Instructor, is the Heart of Tom.
Dread-Nought, who behaved himself well in the late Wars, but has for
these Ten Years last past been aiming at some Post of Honour to no
Purpose. He is lately retired into the Country, where, quite choaked
up with Spleen and Choler, he rails at better Men than himself, and
will be for ever uneasie, because it is impossible he should think his
Merit sufficiently rewarded. The next Heart that I examined was
remarkable for its Smallness; it lay still at the Bottom of the Phial,
and I could hardly perceive that it beat at all. The Fomes was quite
black, and had almost diffused it self over the whole Heart. This,
says my Interpreter, is the Heart of Dick Gloomy, who never thirsted
after any thing but Money. Notwithstanding all his Endeavours, he is
still poor. This has flung him into a most deplorable State of
Melancholy and Despair. He is a Composition of Envy and Idleness,
hates Mankind, but gives them their Revenge by being more uneasie to
himself, than to any one else.
'The Phial I looked upon next contained a large fair Heart, which beat
very strongly. The Fomes or Spot in it was exceeding small; but I
could not help observing, that which way soever I turned the Phial it
always appeared uppermost and in the strongest Point of Light. The
Heart you are examining, says my Companion, belongs to Will. Worthy.
He has, indeed, a most noble Soul, and is possessed of a thousand good
Qualities. The Speck which you discover is Vanity.
'Here, says the Angel, is the Heart of Freelove, your intimate
Friend. Freelove and I, said I, are at present very cold to one
another, and I do not care for looking on the Heart of a Man, which I
fear is overcast with Rancour. My Teacher commanded me to look upon
it; I did so, and to my unspeakable Surprize, found that a small
swelling Spot, which I at first took to be Ill-Will towards me, was
only Passion, and that upon my nearer Inspection it wholly
disappeared; upon which the Phantome told me Freelove was one of the
best-natured Men alive.
'This, says my Teacher, is a Female Heart of your Acquaintance. I
found the Fomes in it of the largest Size, and of a hundred
different Colours, which were still varying every Moment. Upon my
asking to whom it belonged, I was informed that it was the Heart of
Coquetilla.
'I set it down, and drew out another, in which I took the Fomes at
first Sight to be very small, but was amazed to find, that as I looked
stedfastly upon it, it grew still larger. It was the Heart of
Melissa, a noted Prude who lives the next Door to me.
'I show you this, says the Phantome, because it is indeed a Rarity,
and you have the Happiness to know the Person to whom it belongs. He
then put into my Hands a large Chrystal Glass, that enclosed an Heart,
in which, though I examined it with the utmost Nicety, I could not
perceive any Blemish. I made no Scruple to affirm that it must be the
Heart of Seraphina, and was glad, but not surprized, to find that it
was so. She is, indeed, continued my Guide, the Ornament, as well as
the Envy, of her Sex; at these last Words, he pointed to the Hearts of
several of her Female Acquaintance which lay in different Phials, and
had very large Spots in them, all of a deep Blue. You are not to
wonder, says he, that you see no Spot in an Heart, whose Innocence has
been Proof against all the Corruptions of a depraved Age. If it has
any Blemish, it is too small to be discovered by Human Eyes.
'I laid it down, and took up the Hearts of other Females, in all of
which the Fomes ran in several Veins, which were twisted together,
and made a very perplexed Figure. I asked the Meaning of it, and was
told it represented Deceit.
'I should have been glad to have examined the Hearts of several of my
Acquaintance, whom I knew to be particularly addicted to Drinking,
Gaming, Intreaguing, &c., but my Interpreter told me I must let that
alone till another Opportunity, and flung down the Cover of the Chest
with so much violence, as immediately awoke me.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 1, 1714 |
H. Grove1 |
Dicitis, omnis in Imbecillitate est et Gratia, et Caritas.
Cicero
de Nat. Deor. L.
Man may be considered in two Views, as a Reasonable, and as a Sociable
Being; capable of becoming himself either happy or miserable, and of
contributing to the Happiness or Misery of his Fellow Creatures.
Suitably to this double Capacity, the Contriver of Human Nature hath
wisely furnished it with two Principles of Action, Self-love and
Benevolence; designed one of them to render Man wakeful to his own
personal Interest, the other to dispose him for giving his utmost
Assistance to all engaged in the same Pursuit. This is such an Account
of our Frame, so agreeable to Reason, so much for the Honour of our
Maker, and the Credit of our Species, that it may appear somewhat
unaccountable what should induce Men to represent human Nature as they
do under Characters of Disadvantage, or, having drawn it with a little
and sordid Aspect, what Pleasure they can possibly take in such a
Picture. Do they reflect that 'tis their Own, and, if we will believe
themselves, is not more odious than the Original?
One of the first that talked in this lofty Strain of our Nature was
Beneficence
, would his Followers say, is all founded in
Weakness; and, whatever be pretended, the Kindness that passeth between
Men and Men is by every Man directed to himself. This, it must be
confessed, is of a Piece with the rest of that hopeful Philosophy, which
having patch'd Man up out of the four Elements, attributes his Being to
Chance, and derives all his Actions from an unintelligible Declination
of Atoms. And for these glorious Discoveries the Poet is beyond Measure
transported in the Praises of his Hero, as if he must needs be something
more than Man, only for an Endeavour to prove that Man is in nothing
superior to Beasts.
In this School was Mr.
Hobs
instructed to speak after the same Manner,
if he did not rather draw his Knowledge from an Observation of his own
Temper; for he somewhere unluckily lays down this as a Rule,
'That from the Similitudes of Thoughts and Passions of one Man to the
Thoughts and Passions of another, whosoever looks into himself and
considers what he doth when he thinks, hopes, fears, &c., and upon
what Grounds; he shall hereby read and know what are the Thoughts and
Passions of all other Men upon the like Occasions.'
Now we will allow Mr.
Hobs
to know best how he was inclined; But in
earnest, I should be heartily out of Conceit with my self, if I thought
my self of this unamiable Temper, as he affirms, and should have as
little Kindness for my self as for any Body in the World. Hitherto I
always imagined that kind and benevolent Propensions were the original
Growth of the Heart of Man, and, however checked and over-topped by
counter Inclinations that have since sprung up within us, have still
some Force in the worst of Tempers, and a considerable Influence on the
best. And, methinks, it's a fair Step towards the Proof of this, that
the most beneficent of all Beings is He who hath an absolute Fulness of
Perfection in Himself, who gave Existence to the Universe, and so cannot
be supposed to want that which He communicated, without diminishing from
the Plenitude of his own Power and Happiness. The Philosophers before
mentioned have indeed done all that in them lay to invalidate this
Argument; for, placing the Gods in a State of the most elevated
Blessedness, they describe them as Selfish as we poor miserable Mortals
can be, and shut them out from all Concern for Mankind, upon the Score
of their having no Need of us.
But if He that sitteth in the Heavens wants not us, we stand in
continual Need of Him; and surely, next to the Survey of the immense
Treasures of his own Mind, the most exalted Pleasure He receives is from
beholding Millions of Creatures, lately drawn out of the Gulph of
Non-existence, rejoycing in the various Degrees of Being and Happiness
imparted to them. And as this is the true, the glorious Character of the
Deity, so in forming a reasonable Creature He would not, if possible,
suffer his Image to pass out of his Hands unadorned with a Resemblance
of Himself in this most lovely Part of his Nature. For what Complacency
could a Mind, whose Love is as unbounded as his Knowledge, have in a
Work so unlike Himself? a Creature that should be capable of knowing and
conversing with a vast Circle of Objects, and love none but Himself?
What Proportion would there be between the Head and the Heart of such a
Creature, its Affections, and its Understandings? Or could a Society of
such Creatures, with no other Bottom but Self-Love on which to maintain
a Commerce, ever flourish? Reason, 'tis certain, would oblige every Man
to pursue the general Happiness, as the Means to procure and establish
his own; and yet if, besides this Consideration, there were not a
natural Instinct, prompting Men to de
Sir
e the Welfare and Satisfaction
of others, Self-Love, in Defiance of the Admonitions of Reason, would
quickly run all Things into a State of War and Confusion.
As nearly interested as the Soul is in the Fate of the Body; our
provident Creator saw it necessary, by the constant Returns of Hunger
and Thirst, those importunate Appetites, to put it in Mind of its
Charge; knowing, that if we should eat and drink no oftner than cold
abstracted Speculation should put us upon these Exercises, and then
leave it to Reason to prescribe the Quantity, we should soon refine our
selves out of this bodily Life. And indeed, 'tis obvious to remark, that
we follow nothing heartily, unless carried to it by Inclinations which
anticipate our Reason, and, like a Biass, draw the Mind strongly towards
it. In order, therefore, to establish a perpetual Intercourse of
Benefits amongst Mankind, their Maker would not fail to give them this
generous Prepossession of Benevolence, if, as I have said, it were
possible. And from whence can we go about to argue its Impossibility? Is
it inconsistent with Self-Love? Are their Motions contrary? No more than
the diurnal Rotation of the Earth is opposed to its Annual; or its
Motion round its own Center, which may be improved as an Illustration of
Self-Love, to that which whirls it about the common Center of the World,
answering to universal Benevolence. Is the Force of Self-Love abated, or
its Interest prejudiced by Benevolence? So far from it, that
Benevolence, though a distinct Principle, is extreamly serviceable to
Self-Love, and then doth most Service when 'tis least designed.
But to descend from Reason to Matter of Fact; the Pity which arises on
Sight of Persons in Distress, and the Satisfaction of Mind which is the
Consequence of having removed them into a happier State, are instead of
a thousand Arguments to prove such a thing as a disinterested
Benevolence. Did Pity proceed from a Reflection we make upon our
Liableness to the same ill Accidents we see befall others, it were
nothing to the present Purpose; but this is assigning an artificial
Cause of a natural Passion, and can by no Means be admitted as a
tolerable Account of it, because Children and Persons most Thoughtless
about their own Condition, and incapable of entering into the Prospects
of Futurity, feel the most violent Touches of Compassion.
And then as to that charming Delight which immediately follows the
giving Joy to another, or relieving his Sorrow, and is, when the Objects
are numerous, and the kindness of Importance really inexpressible, what
can this be owing to but a Consciousness of a Man's having done some
thing Praise-worthy, and expressive of a great Soul? Whereas, if in all
this he only Sacrificed to Vanity and Self-Love, as there would be
nothing brave in Actions that make the most shining Appearance, so
Nature would not have rewarded them with this divine Pleasure; nor could
the Commendations, which a Person receives for Benefits done upon
selfish Views, be at all more Satisfactory, than when he is applauded
for what he doth without Design; because in both Cases the Ends of
Self-Love are equally answered.
The Conscience of approving ones self a Benefactor to Mankind is the
noblest Recompence for being so; doubtless it is, and the most
interested cannot propose anything so much to their own Advantage,
notwithstanding which, the Inclination is nevertheless unselfish. The
Pleasure which attends the Gratification of our Hunger and Thirst, is
not the Cause of these Appetites; they are previous to any such
Prospect; and so likewise is the De
Sir
e of doing Good; with this
Difference, that being seated in the intellectual Part, this last,
though Antecedent to Reason, may yet be improved and regulated by it,
and, I will add, is no otherwise a Virtue than as it is so.
Thus have I contended for the Dignity of that Nature I have the Honour
to partake of, and, after all the Evidence produced, think I have a
Right to conclude, against the Motto of this Paper, that there is such a
thing as Generosity in the World. Though if I were under a Mistake in
this, I should say as
Cicero
in Relation to the Immortality of the
Soul, I willingly err, and should believe it very much for the Interest
of Mankind to lye under the same Delusion. For the contrary Notion
naturally tends to dispirit the Mind, and sinks it into a Meanness fatal
to the Godlike Zeal of doing good. As on the other hand, it teaches
People to be Ungrateful, by possessing them with a Perswasion concerning
their Benefactors, that they have no Regard to them in the Benefits they
bestow. Now he that banishes Gratitude from among Men, by so doing stops
up the Stream of Beneficence. For though in conferring Kindnesses, a
truly generous Man doth not aim at a Return, yet he looks to the
Qualities of the Person obliged, and as nothing renders a Person more
unworthy of a Benefit, than his being without all Resentment of it, he
will not be extreamly forward to Oblige such a Man.
Footnote 1:
The Rev. Henry Grove was a Presbyterian minister, who kept
school at Taunton. He was born there in 1683, became a teacher at the
age of 23 (already married), and worked for the next 18 years in the
Taunton Academy, his department Ethics and Pneumatology. He spent his
leisure in religious controversy, writing an
Essay on the Terms of
Christian Communion
, a
Discourse on Saving Faith
, an
Essay on the
Soul's Immortality
, and miscellanies in prose and verse, including Nos.
,
,
, and
, of the
Spectator.
He received also £20 a year
for ministering to two small congregations in the neighbourhood of
Taunton. His wife died in 1736, and he in the year following. His works
appeared in 1740 in 4 vols. 8vo.
Contents
|
Friday, September 3, 1714 |
|
Persequitur scelus ille suum: labefactaque tandem
Ictibus innumeris adductaque funibus arbor
Corruit.
Ovid.

Sir ,
'I am so great an Admirer of Trees, that the Spot of Ground I have
chosen to build a small Seat upon, in the Country, is almost in the
midst of a large Wood. I was obliged, much against my Will, to cut
down several Trees, that I might have any such thing as a Walk in my
Gardens; but then I have taken Care to leave the Space, between every
Walk, as much a Wood as I found it. The Moment you turn either to the
Right or Left, you are in a Forest, where Nature presents you with a
much more beautiful Scene than could have been raised by Art.
'Instead of
Tulips or
Carnations, I can shew you
Oakes in my
Gardens of four hundred Years standing, and a Knot of
Elms that
might shelter a Troop of Horse from the Rain.
'It is not without the utmost Indignation, that I observe several
prodigal young Heirs in the Neighbourhood, felling down the most
glorious Monuments of their Ancestors Industry, and ruining, in a Day,
the Product of Ages.
'I am mightily pleased with your Discourse upon Planting, which put me
upon looking into my Books to give you some Account of the Veneration
the Ancients had for Trees. There is an old Tradition, that
Abraham
planted a
Cypress, a
Pine, and a
Cedar, and that these three
incorporated into one Tree, which was cut down for the building of the
Temple of
Solomon.
'
Isidorus, who lived in the Reign of
Constantius, assures us, that
he saw, even in his Time, that famous
Oak in the Plains of
Mambré,
under which
Abraham is reported to have dwelt, and adds, that the
People looked upon it with a great Veneration, and preserved it as a
Sacred Tree.
'The Heathens still went farther, and regarded it as the highest Piece
of Sacrilege to injure certain Trees which they took to be protected
by some Deity. The Story of
Erisicthon, the Grove of
Dodona, and
that at
Delphi, are all Instances of this Kind.
'If we consider the Machine in
Virgil, so much blamed by several
Criticks, in this Light, we shall hardly think it too violent.
'
Æneas, when he built his Fleet, in order to sail for
Italy, was
obliged to cut down the Grove on Mount
Ida, which however he durst
not do till he had obtained leave from
Cybele, to whom it was
dedicated. The Goddess could not but think her self obliged to protect
these Ships, which were made of Consecrated Timber, after a very
extraordinary Manner, and therefore de
Sir ed
Jupiter, that they might
not be obnoxious to the Power of Waves or Winds.
Jupiter would not
grant this, but promised her, that as many as came safe to
Italy
should be transformed into Goddesses of the Sea; which the Poet tells
us was accordingly executed.
And now at length the number'd Hours were come,
Prefix'd by Fate's irrevocable Doom,
When the great Mother of the Gods was free
To save her Ships, and finish Jove's Decree.
First, from the Quarter of the Morn, there sprung
A Light that sign'd the Heavens, and shot along:
Then from a Cloud, fring'd round with Golden Fires,
Were Timbrels heard, and Berecynthian Quires:
And last a Voice, with more than Mortal Sounds,
Both Hosts in Arms oppos'd, with equal Horror wounds.
O Trojan Race, your needless Aid forbear;
And know my Ships are my peculiar Care.
With greater Ease the bold Rutulian may,
With hissing Brands, attempt to burn the Sea,
Than singe my sacred Pines. But you my Charge,
Loos'd from your crooked Anchors launch at large,
Exalted each a Nymph: Forsake the Sand,
And swim the Seas, at Cybele's Command.
No sooner had the Goddess ceas'd to speak,
When lo, th' obedient Ships their Haulsers break;
And, strange to tell, like Dolphins in the Main,
They plunge their Prows, and dive, and spring again:
As many beauteous Maids the Billows sweep,
As rode before tall Vessels on the Deep.
(Dryden's Virg.)
'The common Opinion concerning the Nymphs, whom the Ancients called
Hamadryads, is more to the Honour of Trees than any thing yet
mentioned. It was thought the Fate of these Nymphs had so near a
Dependance on some Trees, more especially Oaks, that they lived and
died together. For this Reason they were extremely grateful to such
Persons who preserved those Trees with which their Being subsisted.
Apollonius tells us a very remarkable Story to this Purpose, with
which I shall conclude my Letter.
'A certain Man, called
Rhœcus, observing an old Oak ready to fall,
and being moved with a sort of Compassion towards the Tree, ordered
his Servants to pour in fresh Earth at the Roots of it, and set it
upright. The
Hamadryad or Nymph who must necessarily have perished
with the Tree, appeared to him the next Day, and after having returned
him her Thanks, told him, she was ready to grant whatever he should
ask. As she was extreamly Beautiful,
Rhœcus de
Sir ed he might be
entertained as her Lover. The
Hamadryad, not much displeased with
the Request, promis'd to give him a Meeting, but commanded him for
some Days to abstain from the Embraces of all other Women, adding that
she would send a Bee to him, to let him know when he was to be Happy.
Rhœcus was, it seems, too much addicted to Gaming, and happened to
be in a Run of ill Luck when the faithful Bee came buzzing about him;
so that instead of minding his kind Invitation, he had like to have
killed him for his Pains. The
Hamadryad was so provoked at her own
Disappointment, and the ill Usage of her Messenger, that she deprived
Rhœcus of the Use of his Limbs. However, says the Story, he was not
so much a Criple, but he made a shift to cut down the Tree, and
consequently to fell his Mistress.
Contents
|
Monday, September 6, 1714 |
Addison |
—Assiduo labuntur tempora motu
Non secus ac flumen. Neque enim consistere flumen,
Nec levis hora potest: sed ut unda, impellitur unda,
Urgeturque prior venienti, urgetque priorem,
Tempora sic fugiunt pariter, pariterque sequuntur;
Et nova sunt semper. Nam quod fuit ante, relictum est;
Fitque quod haud fuerat: momentaque cuncta novantur.
Ov.
Met.
The following Discourse comes from the same Hand with the Essays upon
Infinitude.
We consider infinite Space as an Expansion without a Circumference: We
consider Eternity, or infinite Duration, as a Line that has neither a
Beginning nor an End. In our Speculations of infinite Space, we consider
that particular Place in which we exist, as a kind of Center to the
whole Expansion. In our Speculations of Eternity, we consider the Time
which is present to us as the Middle, which divides the whole Line into
two equal Parts. For this Reason, many witty Authors compare the present
Time to an Isthmus or narrow Neck of Land, that rises in the midst of an
Ocean, immeasurably diffused on either Side of it.
Philosophy, and indeed common Sense, naturally throws Eternity under two
Divisions; which we may call in
English
, that Eternity which is past,
and that Eternity which is to come. The learned Terms of
Æternitas a
Parte ante
, and
Æternitas a Parte post
, may be more amusing to the
Reader, but can have no other Idea affixed to them than what is conveyed
to us by those Words, an Eternity that is past, and an Eternity that is
to come. Each of these Eternities is bounded at the one Extream; or, in
other Words, the former has an End, and the latter a Beginning.
Let us first of all consider that Eternity which is past, reserving that
which is to come for the Subject of another Paper. The Nature of this
Eternity is utterly inconceivable by the Mind of Man: Our Reason
demonstrates to us that it
has been
, but at the same Time can frame no
Idea of it, but what is big with Absurdity and Contradiction. We can
have no other Conception of any Duration which is past, than that all of
it was once present; and whatever was once present, is at some certain
Distance from us, and whatever is at any certain Distance from us, be
the Distance never so remote, cannot be Eternity. The very Notion of any
Duration's being past, implies that it was once present; for the Idea of
being once present, is actually included in the Idea of its being past.
This therefore is a Depth not to be sounded by human Understanding. We
are sure that there has been an Eternity, and yet contradict our selves
when we measure this Eternity by any Notion which we can frame of it.
If we go to the Bottom of this Matter, we shall find, that the
Difficulties we meet with in our Conceptions of Eternity proceed from
this single Reason, That we can have no other Idea of any kind of
Duration, than that by which we our selves, and all other created
Beings, do exist; which is, a successive Duration made up of past,
present, and to come. There is nothing which exists after this Manner,
all the Parts of whose Existence were not once actually present, and
consequently may be reached by a certain Number of Years applied to it.
We may ascend as high as we please, and employ our Being to that
Eternity which is to come, in adding Millions of Years to Millions of
Years, and we can never come up to any Fountain-Head of Duration, to any
Beginning in Eternity: But at the same time we are sure, that whatever
was once present does lye within the Reach of Numbers, though perhaps we
can never be able to put enough of them together for that Purpose. We
may as well say, that any thing may be actually present in any Part of
infinite Space, which does not lye at a certain Distance from us, as
that any Part of infinite Duration was once actually present, and does
not also lye at some determined Distance from us. The Distance in both
Cases may be immeasurable and indefinite as to our Faculties, but our
Reason tells us that it cannot be so in it self. Here therefore is that
Difficulty which Human Understanding is not capable of surmounting. We
are sure that something must have existed from Eternity, and are at the
same Time unable to conceive, that any thing which exists, according to
our Notion of Existence, can have existed from Eternity.
It is hard for a Reader, who has not rolled this Thought in his own
Mind, to follow in such an abstracted Speculation; but I have been the
longer on it, because I think it is a demonstrative Argument of the
Being and Eternity of a God: And tho' there are many other
Demonstrations which lead us to this great Truth, I do not think we
ought to lay aside any Proofs in this Matter which the Light of Reason
has suggested to us, especially when it is such a one as has been urged
by Men famous for their Penetration and Force of Understanding, and
which appears altogether conclusive to those who will be at the Pains to
examine it.
Having thus considered that Eternity which is past, according to the
best Idea we can frame of it, I shall now draw up those several Articles
on this Subject which are dictated to us by the Light of Reason, and
which may be looked upon as the Creed of a Philosopher in this great
Point.
First
, It is certain that no Being could have made it self; for if so,
it must have acted before it was, which is a Contradiction.
Secondly
, That therefore some Being must have existed from all
Eternity.
Thirdly
, That whatever exists after the manner of created Beings, or
according to any Notions which we have of Existence, could not have
existed from Eternity.
Fourthly
, That this eternal Being must therefore be the great Author
of Nature,
The Ancient of Days
, who, being at an infinite Distance in
his Perfections from all finite and created Beings, exists in a quite
different Manner from them, and in a Manner of which they can have no
Idea.
I know that several of the School-men, who would not be thought ignorant
of any thing, have pretended to explain the Manner of God's Existence,
by telling us, That he comprehends infinite Duration in every Moment;
That Eternity is with him a
Punctum stans
, a fixed Point; or, which is
as good Sense, an
Infinite Instance;
That nothing with Reference to
his Existence is either past or to come: To which the ingenious Mr.
Cowley
alludes in his Description of Heaven,
Nothing is there to come, and nothing past,
But an Eternal Now does always last.
For my own Part, I look upon these Propositions as Words that have no
Ideas annexed to them; and think Men had better own their Ignorance than
advance Doctrines by which they mean nothing, and which indeed are
self-contradictory. We cannot be too modest in our Disquisitions, when
we meditate on Him who is environed with so much Glory and Perfection,
who is the Source of Being, the Fountain of all that Existence which we
and his whole Creation derive from him. Let us therefore with the utmost
Humility acknowledge, that as some Being must necessarily have existed
from Eternity, so this Being does exist after an incomprehensible
manner, since it is impossible for a Being to have existed from Eternity
after our Manner or Notions of Existence. Revelation confirms these
natural Dictates of Reason in the Accounts which it gives us of the
Divine Existence, where it tells us, that he is the same Yesterday,
To-day, and for Ever; that he is the
Alpha
and
Omega
, the Beginning
and the Ending; that a thousand Years are with him as one Day, and one
Day as a Thousand Years; by which and the like Expressions, we are
taught, that his Existence, with Relation to Time or Duration, is
infinitely different from the Existence of any of his Creatures, and
consequently that it is impossible for us to frame any adequate
Conceptions of it.
In the first Revelation which he makes of his own Being, he entitles
himself,
I am that I am
; and when
Moses
de
Sir
es to know what Name he
shall give him in his Embassy to
Pharaoh
, he bids him say that
I am
hath sent you. Our great Creator, by this Revelation of himself, does in
a manner exclude every thing else from a real Existence, and
distinguishes himself from his Creatures, as the only Being which truly
and really exists. The ancient Platonick Notion, which was drawn from
Speculations of Eternity, wonderfully agrees with this Revelation which
God has made of himself. There is nothing, say they, which in Reality
exists, whose Existence, as we call it, is pieced up of past, present,
and to come. Such a flitting and successive Existence is rather a Shadow
of Existence, and something which is like it, than Existence it self. He
only properly exists whose Existence is intirely present; that is, in
other Words, who exists in the most perfect Manner, and in such a Manner
as we have no Idea of.
I shall conclude this Speculation with one useful Inference. How can we
sufficiently prostrate our selves and fall down before our Maker, when
we consider that ineffable Goodness and Wisdom which contrived this
Existence for finite Natures? What must be the Overflowings of that good
Will, which prompted our Creator to adapt Existence to Beings, in whom
it is not necessary? Especially when we consider that he himself was
before him in the compleat Possession of Existence and of Happiness, and
in the full Enjoyment of Eternity. What Man can think of himself as
called out and separated from nothing, of his being made a conscious, a
reasonable and a happy Creature, in short, of being taken in as a Sharer
of Existence, and a kind of Partner in Eternity, without being swallowed
up in Wonder, in Praise, in Adoration! It is indeed a Thought too big
for the Mind of Man, and rather to be entertained in the Secrecy of
Devotion, and in the Silence of the Soul, than to be expressed by Words.
The Supreme Being has not given us Powers or Faculties sufficient to
extol and magnifie such unutterable Goodness.
It is however some Comfort to us, that we shall be always doing what we
shall be never able to do, and that a Work which cannot be finished,
will however be the Work of an Eternity.
Footnote 1:
See Nos.
,
,
, and
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 8, 1714 |
Budgell |
—Tenerorum lusor amorum—
Ovid.

I have just receiv'd a Letter from a Gentleman, who tells me he has
observed, with
small Concern, that my Papers have of late been very
barren in relation to Love
; a Subject which when agreeably handled,
can scarce fail of being well receiv'd by both Sexes.
If my Invention therefore should be almost exhausted on this Head, he
offers to serve under me in the Quality of a
Love Casuist;
for which
Place he conceives himself to be throughly qualified, having made this
Passion his Principal Study, and observed it in all its different Shapes
and Appearances, from the Fifteenth to the Forty Fifth Year of his Age.
He assures me with an Air of Confidence, which I hope proceeds from his
real Abilities, that he does not doubt of giving Judgment to the
Satisfaction of the Parties concerned, on the most nice and intricate
Cases which can happen in an Amour; as,
-
How great the Contraction of the Fingers must be before it amounts to a
Squeeze by the Hand.
-
What can be properly termed an absolute Denial from a Maid, and what
from a Widow.
-
What Advances a Lover may presume to make, after having received a Patt
upon his Shoulder from his Mistress's Fan.
-
Whether a Lady, at the first Interview, may allow an Humble Servant to
kiss her Hand.
-
How far it may be permitted to caress the Maid in order to succeed with
the Mistress.
-
What Constructions a Man may put upon a Smile, and in what Cases a Frown
goes for nothing.
-
On what Occasions a sheepish Look may do Service, &c.
As a farther Proof of his Skill, he has also sent me several Maxims in
Love, which he assures me are the Result of a long and profound
Reflection, some of which I think my self obliged to communicate to the
Publick, not remembering to have seen them before in any Author.
-
'There are more Calamities in the World arising from Love than from
Hatred.
-
Love is the Daughter of Idleness, but the Mother of Disquietude.
-
Men of grave Natures (says Sir Francis Bacon) are the most
constant; for the same Reason Men should be more constant than Women.
-
The Gay Part of Mankind is most amorous, the Serious most loving.
-
A Coquet often loses her Reputation, whilst she preserves her Virtue.
-
A Prude often preserves her Reputation when she has lost her Virtue.
-
Love refines a Man's Behaviour, but makes a Woman's ridiculous.
-
Love is generally accompanied with Good-will in the Young, Interest
in the Middle-aged, and a Passion too gross to Name in the Old.
-
The Endeavours to revive a decaying Passion generally extinguish the
Remains of it.
-
A Woman who from being a Slattern becomes over-neat, or from being
over-neat becomes a Slattern, is most certainly in Love.
I shall make use of this Gentleman's Skill as I see Occasion; and since
I am got upon the Subject of Love, shall conclude this Paper with a Copy
of Verses which were lately sent me by an unknown Hand, as I look upon
them to be above the ordinary Run of Sonneteers.
Author tells me they were written in one of his despairing Fits; and
I find entertains some Hope that his Mistress may pity such a Passion as
he has described, before she knows that she is herself
Corinna.
Conceal, fond Man, conceal the mighty Smart,
Nor tell Corinna
she has fir'd thy Heart.
In vain would'st thou complain, in vain pretend
To ask a Pity which she must not lend.
She's too much thy Superior to comply,
And too too fair to let thy Passion dye.
Languish in Secret, and with dumb Surprize
Drink the resistless Glances of her Eyes.
At awful Distance entertain thy Grief,
Be still in Pain, but never ask Relief.
Ne'er tempt her Scorn of thy consuming State;
Be any way undone, but fly her Hate.
Thou must submit to see thy Charmer bless
Some happier Youth that shall admire her less;
Who in that lovely Form, that Heavenly Mind,
Shall miss ten thousand Beauties thou could'st find;
Who with low Fancy shall approach her Charms,
While half enjoy'd she sinks into his Arms.
She knows not, must not know, thy nobler Fire,
Whom she, and whom the Muses do inspire;
Her Image only shall thy Breast employ,
And fill thy captiv'd Soul with Shades of joy;
Direct thy Dreams by Night, thy Thoughts by Day;
And never, never, from thy Bosom stray2.
Footnote 1:
See Nos.
,
,
,
, and
.
Footnote 2:
These verses were by Gilbert Budgell, second brother of
Eustace.
Contents
|
Friday, September 10, 1714 |
Addison |
—Studium sine divite Vena—
Hor.

I look upon the Play-house as a World within it self. They have lately
furnished the Middle Region of it with a new Sett of Meteors, in order
to give the Sublime to many modern Tragedies. I
there last Winter at
the first Rehearsal of the new Thunder
, which is much more deep and
sonorous than any hitherto made use of. They have a
Salmoneus
behind
the Scenes, who plays it off with great Success. Their Lightnings are
made to flash more briskly than heretofore; their Clouds are also better
furbelow'd, and more voluminous; not to mention a violent Storm locked
up in a great Chest that is designed for the
Tempest.
They are also
provided with above a Dozen Showers of Snow, which, as I am informed,
are the Plays of many unsuccessful Poets artificially cut and shreaded
for that Use. Mr.
Rimer's Edgar
is to fall in Snow at the next acting
of King
Lear
, in order to heighten, or rather to alleviate, the
Distress of that unfortunate Prince; and to serve by way of Decoration
to a Piece which that great Critick has written against.
I do not indeed wonder that the Actors should be such professed Enemies
to those among our Nation who are commonly known by the Name of
Criticks, since it is a Rule among these Gentlemen to fall upon a Play,
not because it is ill written, but because it takes. Several of them lay
it down as a Maxim, That whatever Dramatick Performance has a long Run,
must of Necessity be good for nothing; as though the first Precept in
Poetry were
not to please
. Whether this Rule holds good or not, I
shall leave to the Determination of those who are better Judges than my
self: If it does, I am sure it tends very much to the Honour of those
Gentlemen who have established it; few of their Pieces having been
disgraced by a Run of three Days, and most of them being so exquisitely
written, that the Town would never give them more than one Night's
Hearing.
I have a great Esteem for a true Critick, such as
Aristotle
and
Longinus
among the
Greeks
,
Horace
and
Quintilian
among the
Romans
,
Boileau
and
Dacier
among the
French
. But it is our
Misfortune, that some who set up for professed Criticks among us are so
stupid, that they do not know how to put ten Words together with
Elegance or common Propriety, and withal so illiterate, that they have
no Taste of the learned Languages, and therefore criticise upon old
Authors only at second-hand. They judge of them by what others have
written, and not by any Notions they have of the Authors themselves. The
Words Unity, Action, Sentiment, and Diction, pronounced with an Air of
Authority, give them a Figure among unlearned Readers, who are apt to
believe they are very deep, because they are unintelligible. The Ancient
Criticks are full of the Praises of their Contemporaries; they discover
Beauties which escaped the Observation of the Vulgar, and very often
find out Reasons for palliating and excusing such little Slips and
Oversights as were committed in the Writings of eminent Authors. On the
contrary, most of the Smatterers in Criticism who appear among us, make
it their Business to vilifie and depreciate every new Production that
gains Applause, to descry imaginary Blemishes, and to prove by
far-fetch'd Arguments, that what pass for Beauties in any celebrated
Piece are Faults and Errors. In short, the Writings of these Criticks
compared with those of the Ancients, are like the Works of the Sophists
compared with those of the old Philosophers.
Envy and Cavil are the natural Fruits of Laziness and Ignorance; which
was probably the Reason, that in the Heathen Mythology
Momus
is said
to be the Son of
Nox
and
Somnus
, of Darkness and Sleep. Idle Men,
who have not been at the Pains to accomplish or distinguish themselves,
are very apt to detract from others; as ignorant Men are very subject to
decry those Beauties in a celebrated Work which they have not Eyes to
discover. Many of our Sons of
Momus
, who dignify themselves by the
Name of Criticks, are the genuine Descendants of these two illustrious
Ancestors. They are often led into those numerous Absurdities, in which
they daily instruct the People, by not considering that,
1st
, There is
sometimes a greater Judgment shewn in deviating from the Rules of Art,
than in adhering to them; and,
2dly
, That there is more Beauty in the
Works of a great Genius who is ignorant of all the Rules of Art, than in
the Works of a little Genius, who not only knows, but scrupulously
observes them.
First, We may often take Notice of Men who are perfectly acquainted with
all the Rules of good Writing, and notwithstanding chuse to depart from
them on extraordinary Occasions. I could give Instances out of all the
Tragick Writers of Antiquity who have shewn their Judgment in this
Particular; and purposely receded from an established Rule of the Drama,
when it has made way for a much higher Beauty than the Observation of
such a Rule would have been. Those who have surveyed the noblest Pieces
of Architecture and Statuary both ancient and modern, know very well
that there are frequent Deviations from Art in the Works of the greatest
Masters, which have produced a much nobler Effect than a more accurate
and exact way of Proceeding could have done. This often arises from what
the
Italians
call the
Gusto Grande
in these Arts, which is what we
call the Sublime in Writing.
In the next Place, our Criticks do not seem sensible that there is more
Beauty in the Works of a great Genius who is ignorant of the Rules of
Art, than in those of a little Genius who knows and observes them. It is
of these Men of Genius that
Terence
speaks, in Opposition to the
little artificial Cavillers of his Time;
Quorum æmulari exoptat negligentiam
Potiùs, quàm istorum obscuram diligentiam.
A Critick may have the same Consolation in the ill Success of his Play,
as Dr.
South
tells us a Physician has at the Death of a Patient, That
he was killed
secundum artem
. Our inimitable
Shakespear
is a
Stumbling-Block to the whole Tribe of these rigid Criticks. Who would
not rather read one of his Plays, where there is not a single Rule of
the Stage observed, than any Production of a modern Critick, where there
is not one of them violated?
Shakespear
was indeed born with all the
Seeds of Poetry, and may be compared to the Stone in
Pyrrhus's
Ring,
which, as
Pliny
tells us, had the Figure of
Apollo
and the Nine
Muses in the Veins of it, produced by the spontaneous Hand of Nature,
without any Help from Art.
Footnote 1:
John Dennis's invention, of which he said with exultation,
'That's my thunder.'
Contents
|
Monday, September 13, 1714 |
Byrom |
Quale per incertam Lunam sub luce maligna
Est iter in Sylvis:—
Virg.

My dreaming Correspondent, Mr.
Shadow
, has sent me a second Letter,
with several curious Observations on Dreams in general, and the Method
to render Sleep improving: An Extract of his Letter will not, I presume,
be disagreeable to my Readers.
'Since we have so little Time to spare, that none of it may be lost, I
see no Reason why we should neglect to examine those imaginary Scenes
we are presented with in Sleep, only because they have less Reality in
them than our waking Meditations. A Traveller would bring his Judgment
in Question who should despise the Directions of his Map for want of
real Roads in it, because here stands a
Dott instead of a Town, or a
Cypher instead of a City, and it must be a long Day's Journey to
travel thro' two or three Inches. Fancy in Dreams gives us much such
another Landskip of Life as that does of Countries, and tho' its
Appearances may seem strangely jumbled together, we may often observe
such Traces and Footsteps of noble Thoughts, as, if carefully pursued,
might lead us into a proper Path of Action. There is so much Rapture
and Extasie in our fancied Bliss, and something so dismal and shocking
in our fancied Misery, that tho' the Inactivity of the Body has given
Occasion for calling Sleep the Image of
Death, the Briskness of the
Fancy affords us a strong Intimation of something within us that can
never die.
'I have wondered, that
Alexander the Great, who came into the World
sufficiently dreamt of by his Parents, and had himself a tolerable
Knack at dreaming, should often say, that
Sleep was one thing which made him sensible he was Mortal.
I who have not such Fields of Action in the Daytime to divert my
Attention from this Matter, plainly perceive, that in those Operations
of the Mind, while the Body is at rest, there is a certain Vastness of
Conception very suitable to the Capacity, and demonstrative of the
Force of that Divine Part in our Composition which will last for ever.
Neither do I much doubt but had we a true Account of the Wonders the
Hero last mentioned performed in his Sleep, his conquering this little
Globe would hardly be worth mentioning. I may affirm, without Vanity,
that when I compare several Actions in
Quintus Curtius with some
others in my own Noctuary, I appear the greater Hero of the two.
I shall close this Subject with observing, that while we are awake we
are at Liberty to fix our Thoughts on what we please, but in Sleep we
have not the Command of them. The Ideas which strike the Fancy, arise
in us without our Choice, either from the Occurrences of the Day past,
the Temper we lye down in, or it may be the Direction of some superior
Being.
It is certain the Imagination may be so differently affected in Sleep,
that our Actions of the Day might be either rewarded or punished with
a little Age of Happiness or Misery. St.
Austin was of Opinion, that
if in
Paradise there was the same Vicissitude of sleeping and waking
as in the present World, the Dreams of its Inhabitants would be very
happy.
And so far at present our Dreams are in our Power, that they are
generally conformable to our waking Thoughts, so that it is not
impossible to convey our selves to a Consort of Musick, the
Conversation of Distant Friends, or any other Entertainment which has
been before lodged in the Mind.
My Readers, by applying these Hints will find the Necessity of making
a
good Day of it, if they heartily wish themselves a good Night.
I have often consider'd
Marcia's Prayer, and
Lucius's Account of
Cato, in this Light.
| Marc. |
O ye immortal Powers, that guard the Just,
Watch round his Couch, and soften his Repose,
Banish his Sorrows, and becalm his Soul
With easie Dreams; remember all his Virtues;
And shew Mankind that Goodness is your Care. |
| Luc. |
Sweet are the Slumbers of the virtuous Man!
O Marcia, I have seen thy Godlike Father:
Some Pow'r invisible supports his Soul,
And bears it up in all its wonted Greatness.
A kind refreshing Sleep is fall'n upon him:
I saw him stretcht at Ease, his Fancy lost
In pleasing Dreams; as I drew near his Couch,
He smil'd, and cry'd, Cæsar, thou canst not hurt me. |
Mr.
Shadow
acquaints me in a Postscript, that he has no manner of
Title to the Vision which succeeded his first Letter; but adds, that as
the Gentleman who wrote it Dreams very sensibly, he shall be glad to
meet him some Night or other, under the great Elm Tree, by which
Virgil
has given us a fine Metaphorical Image of Sleep, in order to
turn over a few of the Leaves together, and oblige the Publick with an
Account of the Dreams that lie under them.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 15, 1714 |
|
—Absentem qui rodit amicum,
Qui non defendit, alio culpante; solutos
Qui captat risus hominum, famamque dicacis,
Fingere qui non visa potest, commissa tacere
Qui nequit, hic niger est: hunc tu Romane caveto.
Hor.

Were all the Vexations of Life put together, we should find that a great
Part of them proceed from those Calumnies and Reproaches which we spread
abroad concerning one another.
There is scarce a Man living who is not, in some Degree, guilty of this
Offence; tho', at the same time, however we treat one another, it must
be confessed, that we all consent in speaking ill of the Persons who are
notorious for this Practice. It generally takes its Rise either from an
Ill-will to Mankind, a private Inclination to make our selves esteemed,
an Ostentation of Wit, a Vanity of being thought in the Secrets of the
World, or from a De
Sir
e of gratifying any of these Dispositions of Mind
in those Persons with whom we converse.
The Publisher of Scandal is more or less odious to Mankind, and criminal
in himself, as he is influenced by any one or more of the foregoing
Motives. But whatever may be the Occasion of spreading these false
Reports, he ought to consider, that the Effect of them is equally
prejudicial and pernicious to the Person at whom they are aimed. The
Injury is the same, tho' the Principle from whence it proceeds may be
different.
As every one looks upon himself with too much Indulgence, when he passes
a Judgment on his own Thoughts or Actions, and as very few would be
thought guilty of this abominable Proceeding, which is so universally
practised, and, at the same time, so universally blamed, I shall lay
down three Rules by which I would have a Man examine and search into his
own Heart, before he stands acquitted to himself of that evil
Disposition of Mind which I am here mentioning.
- First of all, Let him consider whether he does not take Delight in
hearing the Faults of others.
-
Secondly, Whether he is not too apt to believe such little blackning
Accounts, and more inclined to be credulous on the uncharitable than
on the good-natured Side.
-
Thirdly, Whether he is not ready to spread and propagate such
Reports as tend to the Disreputation of another. These are the several
Steps by which this Vice proceeds, and grows up into Slander and
Defamation.
In the first Place, A Man who takes delight in hearing the Faults of
others, shows sufficiently that he has a true Relish of Scandal, and
consequently
Seeds of this Vice within him. If his mind is gratified
with hearing the Reproaches
which
are cast on others, he will find
the same Pleasure in relating them, and be the more apt to do it, as he
will naturally imagine every one he converses with is delighted in the
same manner with himself. A Man should endeavour therefore to wear out
of his Mind this criminal Curiosity, which is perpetually heightened and
inflamed by listening to such Stories as tend to the Disreputation of
others.
In the second Place, a Man should consult his own Heart, whether he be
not apt to
believe
such little blackening Accounts, and more enclined
to be credulous on the uncharitable, than on the good-natured Side.
Such a Credulity is very vicious in it self, and generally arises from a
Man's Consciousness of his own secret Corruptions.
is a pretty Saying
of
Thales, Falshood is just as far distant from Truth, as the Ears are
from the Eyes.
By which he would intimate, that a wise Man should
not easily give Credit to the Reports of Actions which he has not seen.
I
, under this Head, mention two or three remarkable Rules to be
observed by the Members of the celebrated Abbey
de la Trape
, as they
are Published in a little
French
Book
.
The Fathers are there ordered, never to give an Ear to any Accounts of
Base or Criminal Actions; to turn off all such Discourse if possible;
but in Case they hear any thing of this Nature so well attested that
they cannot disbelieve it, they are then to suppose, that the criminal
Action may have proceeded from a good Intention in him who is guilty of
it. This is perhaps carrying Charity to an Extravagance, but it is
certainly much more Laudable, than to suppose, as the ill-natured part
of the World does, that indifferent, and even Good Actions, proceed from
bad Principles and wrong Intentions.
In the third Place, a Man should examine his Heart, whether he does not
find in it a secret Inclination to propagate such Reports, as tend to
the Disreputation of another.
When the Disease of the Mind, which I have hitherto been speaking of,
arises to this Degree of Malignity it discovers its self in its worst
Symptoms, and is in danger of becoming incurable. I need not therefore
insist upon the Guilt in this last Particular, which every one cannot
but disapprove, who is not void of Humanity, or even common Discretion.
I shall only add, that whatever Pleasure any Man may take in spreading
Whispers of this Nature, he will find an infinitely greater Satisfaction
in conquering the Temptation he is under, by letting the Secret die
within his own Breast.
Footnote 1:
that
Footnote 2:
Stobaji, Serm. 61.
Footnote 3:
Felibien,
Description de l'Abbaye de la Trappe
, Paris,
1671, reprinted in 1682. It is a letter from M. Felibien to the Duchess
of Liancon.
Contents
|
Friday, September 17, 1714 |
|
—Non ut placidis cœant immitia, non ut
Serpentes avibus geminentur, tigribus agni—
Hor.

If ordinary Authors would condescend to write as they think, they would
at least be allow'd the Praise of being intelligible. But they really
take Pains to be ridiculous; and, by the studied Ornaments of Style,
perfectly disguise the little Sense they aim at. There is a Grievance of
this Sort in the Common-wealth of Letters, which I have for some time
resolved to redress, and accordingly I have set this Day apart for
Justice. What I mean is, the
Mixture of inconsistent Metaphors,
which
is a Fault but too often found in learned Writers, but in all the
unlearned without Exception.
In order to set this Matter in a clear Light to every Reader, I shall in
the first Place observe, that a Metaphor is a Simile in one Word, which
serves to convey the Thoughts of the Mind under Resemblances and Images
which affect the Senses. There is not any thing in the World, which may
not be compared to several Things, if considered in several distinct
Lights; or, in other Words, the same thing may be expressed by different
Metaphors. But the Mischief is, that an unskilful Author shall run these
Metaphors so absurdly into one another, that there shall be no Simile,
no agreeable Picture, no apt Resemblance, but Confusion, Obscurity, and
Noise. Thus I have known a Hero compared to a Thunderbolt, a Lion, and
the Sea; all and each of them proper Metaphors for impetuosity, Courage
or Force. But by bad Management it hath so happened, that the
Thunder-bolt hath overflowed its Banks; the Lion hath been darted
through the Skies, and the Billows have rolled out of the
Libyan
Desart.
The Absurdity in this Instance is obvious. And yet every time that
clashing Metaphors are put together, this Fault is committed more or
less. It hath already been said, that Metaphors are Images of things
which affect the Senses. An Image therefore, taken from what acts upon
the Sight, cannot, without Violence, be applied to the Hearing; and so
of the rest. It is no less an impropriety to make any Being in Nature or
Art to do things in its Metaphorical State, which it could not do in its
Original. I shall illustrate what I have said by an Instance which I
have read more than once in Controversial Writers.
The heavy Lashes
,
saith a celebrated Author,
that have dropped from your Pen
, &c. I
suppose this Gentleman having frequently heard of
Gall dropping from a
Pen
, and
being lashed in a Satyr,
he was resolved to have them both
at any Rate, and so uttered this compleat Piece of Nonsense. It will
most effectually discover the Absurdity of these monstrous Unions, if we
will suppose these Metaphors or Images actually Painted. Imagine then a
Hand holding a Pen, and several Lashes of Whip-cord falling from it, and
you have the true Representation of this sort of Eloquence. I believe,
by this very Rule, a Reader may be able to judge of the Union of all
Metaphors whatsoever, and determine which are Homogeneous and which
Heterogeneous: or to speak more plainly, which are Consistent, and which
Inconsistent.
There is yet one Evil more which I must take notice of, and that is the
running of Metaphors into tedious Allegories; which, though an Error on
the better Hand, causes Confusion as much as the other. This becomes
abominable, when the Lustre of one Word leads a Writer out of his Road,
and makes him wander from his Subject for a Page together. I remember a
young Fellow, of this Turn, who having said by Chance that his Mistress
had a
World
of Charms, thereupon took Occasion to consider her as one
possessed of Frigid and Torrid Zones, and pursued her from the one Pole
to the other. I shall conclude this Paper with a Letter written in that
enormous Style, which I hope my Reader hath by this time set his Heart
against. The Epistle hath heretofore received great Applause; but after
what hath been said, let any Man commend it if he dare.
Sir ,
'After the many heavy Lashes that have fallen from your Pen, you
may justly expect in return all the Load that my Ink can lay upon
your Shoulders. You have Quartered all the foul Language upon me,
that could be raked out of the Air of Billingsgate, without
knowing who I am, or whether I deserved to be Cupped and Scarified
at this rate. I tell you once for all, turn your Eyes where you
please, you shall never Smell me out. Do you think that the
Panicks, which you sow about the Parish, will ever build a
Monument to your Glory? No, Sir , you may Fight these Battles as long
as you will, but when you come to Ballance the Account you will find
that you have been Fishing in troubled Waters, and that an Ignis
fatuus hath bewildered you, and that indeed you have built upon a
sandy Foundation, and brought your Hogs to a fair Market.
I am, Sir ,
Yours, &c.
Contents
|
Monday, September 20, 1714 |
|
Molle meum levibus Cor est violabile Telis.
Ovid.

The Case of my Correspondent who sends me the following Letter has
somewhat in it so very whimsical, that I know not how to entertain my
Readers better than by laying it before them.
Sir ,
'I am fully convinced that there is not upon Earth a more impertinent
Creature than an importunate Lover: We are daily complaining of the
Severity of our Fate, to People who are wholly unconcerned in it; and
hourly improving a Passion, which we would persuade the World is the
Torment of our Lives. Notwithstanding this Reflection,
Sir , I cannot
forbear acquainting you with my own Case. You must know then,
Sir ,
that even from my Childhood, the most prevailing Inclination I could
perceive in my self, was a strong De
Sir e to be in Favour with the Fair
Sex. I am at present in the one and twentieth Year of my Age, and
should have made Choice of a She Bed-fellow many Years since, had not
my Father, who has a pretty good Estate of his own getting, and passes
in the World for a prudent Man, being pleased to lay it down as a
Maxim, That nothing spoils a young Fellow's Fortune so much as
marrying early; and that no Man ought to think of Wedlock 'till six
and twenty. Knowing his Sentiments upon this Head, I thought it in
vain to apply my self to Women of Condition, who expect Settlements;
so that all my Amours have hitherto been with Ladies who had no
Fortunes: But I know not how to give you so good an Idea of me, as by
laying before you the History of my Life.
'I can very well remember, that at my School-mistresses, whenever we
broke up, I was always for joining my self with the Miss who
Lay in,
and was constantly one of the first to make a Party in the Play of
Husband and Wife. This Passion for being well with the Females still
increased as I advanced in Years. At the Dancing-School I contracted
so many Quarrels by struggling with my Fellow-Scholars for the Partner
I liked best, that upon a Ball Night, before our Mothers made their
Appearance, I was usually up to the Nose in Blood. My Father, like a
discreet Man, soon removed me from this Stage of Softness to a School
of Discipline, where I learnt
Latin and Greek. I underwent several
Severities in this Place, 'till it was thought convenient to send me
to the University; though, to confess the Truth, I should not have
arrived so early at that Seat of Learning, but from the Discovery of
an Intrigue between me and my Master's House-Keeper; upon whom I had
employed my Rhetorick so effectually, that, though she was a very
elderly Lady, I had almost brought her to consent to marry me. Upon my
Arrival at
Oxford, I found Logick so dry, that, instead of giving
Attention to the Dead, I soon fell to addressing the Living. My first
Amour was with a pretty Girl whom I shall call
Parthenope: Her
Mother sold Ale by the Town-Wall. Being often caught there by the
Proctor, I was forced at last, that my Mistress's Reputation might
receive no Blemish, to confess my Addresses were honourable. Upon this
I was immediately sent Home; but
Parthenope soon after marrying a
Shoe-maker, I was again suffered to return. My next Affair was with my
Taylor's Daughter, who deserted me for the sake of a young Barber.
Upon my complaining to one of my particular Friends of this
Misfortune,
the cruel Wagg made a meer Jest of my Calamity, and asked
me with a Smile,
Where the Needle
should turn but to the Pole?
1
After this I was deeply in Love with a Milliner, and at last with my
Bed-maker, upon which I was sent away, or in the University Phrase,
Rusticated for ever.
'Upon my coming home, I settled to my Studies so heartily, and
contracted so great a Reservedness by being kept from the Company I
most affected, that my Father thought he might venture me at the
Temple.
'Within a Week after my Arrival I began to shine again, and became
enamour'd with a mighty pretty Creature, who had every thing but Mony
to recommend her. Having frequent Opportunities of uttering all the
soft things which an Heart formed for Love could inspire me with, I
soon gained her Consent to treat of Marriage; but unfortunately for us
all, in the Absence of my Charmer I usually talked the same Language
to her elder Sister, who is also very pretty. Now I assure you, Mr.
SPECTATOR, this did not proceed from any real Affection I had
conceived for her; but being a perfect Stranger to the Conversation of
Men, and strongly addicted to associate with the Women, I knew no
other Language but that of Love. I should however be very much obliged
to you, if you could free me from the Perplexity I am at present in. I
have sent Word to my old Gentleman in the Country, that I am
desperately in Love with the younger Sister! and her Father, who knew
no better, poor Man! acquainted him by the same Post, that I had for
some time made my Addresses to the Elder. Upon this old Testy sends me
up Word, that he has heard so much of my Exploits, that he intends
immediately to order me to the
South-Sea. Sir , I have occasionally
talked so much of dying, that I begin to think there is not much in
it; and if the old Squire persists in his Design, I do hereby give him
Notice that I am providing my self with proper Instruments for the
Destruction of despairing Lovers; let him therefore look to it, and
consider that by his Obstinacy he may himself lose the Son of his
Strength, the World an hopeful Lawyer, my Mistress a passionate Lover,
and you, Mr. SPECTATOR,
Your constant Admirer,
Jeremy Lovemore.
Middle-Temple,
Sept. 18.
Footnote 1:
Sign of a Barber's shop.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 22, 1714 |
Byrom |
—Metis sine Pondere ludit—
Petr.

Since I received my Friend
Shadow's
Letter, several of my
Correspondents have been pleased to send me an Account how they have
been employed in Sleep, and what notable Adventures they have been
engaged in during that Moonshine in the Brain. I shall lay before my
Readers an Abridgment of some few of their Extravagancies, in hopes that
they will in Time accustom themselves to dream a little more to the
Purpose.
One who styles himself
Gladio
, complains heavily that his Fair One
charges him with Inconstancy, and does not use him with half the
Kindness which the Sincerity of his Passion may demand; the said
Gladio
having by Valour and Stratagem put to Death Tyrants,
Inchanters, Monsters, Knights, &c. without Number, and exposed himself
to all manner of Dangers for her Sake and Safety. He de
Sir
es in his
Postscript to know, whether, from a constant Success in them, he may not
promise himself to succeed in her Esteem at last.
Another who is very prolix in his Narrative writes me Word, that having
sent a Venture beyond Sea, he took Occasion one Night to fancy himself
gone along with it, and grown on a sudden the richest Man in all the
Indies.
Having been there about a Year or two, a Gust of Wind that
forced open his Casement blew him over to his native Country again,
where awaking at Six a Clock, and the Change of the Air not agreeing
with him, he turned to his Left Side in order to a second Voyage: but
e'er he could get on Shipboard, was unfortunately apprehended for
stealing a Horse, try'd and condemn'd for the Fact, and in a fair way of
being executed, if some Body stepping hastily into his Chamber had not
brought him a Reprieve. This Fellow too wants Mr.
Shadow's
Advice,
who, I dare say, would bid him be content to rise after his first Nap,
and learn to be satisfied as soon as Nature is.
The next is a publick-spirited Gentleman, who tells me, That on the
Second of September at Night the whole City was on Fire, and would
certainly have been reduced to Ashes again by this Time, if he had not
flown over it with the
New River
on his Back, and happily extinguished
the Flames before they had prevailed too far. He would be informed
whether he has not a Right to petition the Lord Mayor and Alderman for a
Reward.
A Letter dated September the Ninth acquaints me, That the Writer being
resolved to try his Fortune, had fasted all that Day; and that he might
be sure of dreaming upon something at Night, procured an handsome Slice
of Bride-Cake, which he placed very conveniently under his Pillow. In
the Morning his Memory happen'd to fail him, and he could recollect
nothing but an odd Fancy that he had eaten his Cake; which being found
upon Search reduced to a few Crums, he is resolved to remember more of
his Dreams another Time, believing from this that there may possibly be
somewhat of Truth in them.
I have received numerous Complaints from several delicious Dreamers,
de
Sir
ing me to invent some Method of silencing those noisy Slaves, whose
Occupations lead them to take their early Rounds about the City in a
Morning, doing a deal of Mischief; and working strange Confusion in the
Affairs of its Inhabitants. Several Monarchs have done me the Honour to
acquaint me, how often they have been shook from their respective
Thrones by the rattling of a Coach or the rumbling of a Wheel-barrow.
And many private Gentlemen, I find, have been baulk'd of vast Estates by
Fellows not worth Three-pence. A fair Lady was just upon the Point of
being married to a young, handsome, rich, ingenious Nobleman, when an
impertinent Tinker passing by, forbid the Banns; and an hopeful Youth,
who had been newly advanced to great Honour and Preferment, was forced
by a neighbouring Cobler to resign all for an old Song. It has been
represented to me, that those inconsiderable Rascals do nothing but go
about dissolving of Marriages and spoiling of Fortunes, impoverishing
rich and ruining great People, interrupting Beauties in the midst of
their Conquests, and Generals in the Course of their Victories. A
boisterous Peripatetick hardly goes through a Street without waking half
a Dozen Kings and Princes to open their Shops or clean Shoes, frequently
transforming Sceptres into Paring-Shovels, and Proclamations into Bills.
I have by me a Letter from a young Statesman, who in five or six Hours
came to be Emperor of
Europe
, after which he made War upon the Great
Turk, routed him Horse and Foot, and was crowned Lord of the Universe in
Constantinople:
the Conclusion of all his Successes is, that on the
12th Instant, about Seven in the Morning, his Imperial Majesty was
deposed by a Chimney— Sweeper.
On the other hand, I have Epistolary Testimonies of Gratitude from many
miserable People, who owe to this clamorous Tribe frequent Deliverances
from great Misfortunes.
Small-coalman
, by waking of one of these
distressed Gentlemen, saved him from ten Years Imprisonment. An honest
Watchman bidding aloud Good-morrow to another, freed him from the Malice
of many potent Enemies, and brought all their Designs against him to
nothing. A certain Valetudinarian confesses he has often been cured of a
sore Throat by the Hoarseness of a Carman, and relieved from a Fit of
the Gout by the Sound of
old Shoes
. A noisy Puppy that plagued a sober
Gentleman all Night long with his Impertinence, was silenced by a
Cinder-Wench with a Word speaking.
Instead therefore of suppressing this Order of Mortals, I would propose
it to my Readers to make the best Advantage of their Morning
Salutations. A famous
Macedonian
Prince, for fear of forgetting
himself in the midst of his good Fortune, had a Youth to wait on him
every Morning, and bid him remember that he was a Man. A Citizen who is
waked by one of these Criers, may regard him as a kind of Remembrancer,
come to admonish him that it is time to return to the Circumstances he
has overlooked all the Night-time, to leave off fancying himself what he
is not, and prepare to act suitably to the Condition he is really placed
in.
People may dream on as long as they please, but I shall take no Notice
of any Imaginary Adventures that do not happen while the Sun is on this
Side of the Horizon. For which Reason I stifle
Fritilla's
Dream at
Church last
Sunday
, who while the rest of the Audience were enjoying
the Benefit of an excellent Discourse, was losing her Money and Jewels
to a Gentleman at Play, till after a strange Run of ill Luck she was
reduced to pawn three lovely pretty Children for her last Stake. When
she had thrown them away her Companion went off, discovering himself by
his usual Tokens, a cloven Foot and a strong Smell of Brimstone; which
last proved only a Bottle of Spirits, which a good old Lady applied to
her Nose, to put her in a Condition of hearing the Preacher's third Head
concerning Time.
If a Man has no Mind to pass abruptly from his imagined to his real
Circumstances, he may employ himself a while in that new kind of
Observation which my Onicrocritical Correspondent has directed him to
make of himself. Pursuing the Imagination through all its
Extravagancies, whether in Sleeping or Waking, is no improper Method of
correcting and bringing it to act in Subordinancy to Reason, so as to be
delighted only with such Objects as will affect it with Pleasure, when
it is never so cool and sedate.
Footnote 1:
Thomas Britton. (Old Note.) Why he in particular?
Contents
|
Friday, September 24, 1714 |
Addison |
Jamne igitur laudas, quod de sapientibus alter
Ridebat, quoties a limine moverat unum
Protuleratque pedem: flebat contrarius alter?
Juv.

Mankind may be divided into the Merry and the Serious, who, both of
them, make a very good Figure in the Species, so long as they keep their
respective Humours from degenerating into the neighbouring Extreme;
there being a natural Tendency in the one to a melancholy Moroseness,
and in the other to a fantastick Levity.
The merry Part of the World are very amiable, whilst they diffuse a
Chearfulness through Conversation at proper Seasons and on proper
Occasions; but, on the contrary, a great Grievance to Society, when they
infect every Discourse with insipid Mirth, and turn into Ridicule such
Subjects as are not suited to it. For though Laughter is looked upon by
the Philosophers as the Property of Reason, the Excess of it has been
always considered as the Mark of Folly.
On the other Side, Seriousness has its Beauty whilst it is attended with
Chearfulness and Humanity, and does not come in unseasonably to pall the
good Humour of those with whom we converse.
These two Sets of Men, notwithstanding they each of them shine in their
respective Characters, are apt to bear a natural Aversion and Antipathy
to one another.
What is more usual, than to hear Men of serious Tempers and austere
Morals, enlarging upon the Vanities and Follies of the young and gay
Part of the Species; whilst they look with a kind of Horror upon such
Pomps and Diversions as are innocent in themselves, and only culpable
when they draw the Mind too much?
I could not but smile upon reading a Passage in the Account which Mr.
Baxter
gives of his own Life, wherein he represents it as a great
Blessing, that in his Youth he very narrowly escaped getting a Place at
Court.
It must indeed be confessed that Levity of Tamper takes a Man off his
Guard, and opens a Pass to his Soul for any Temptation that assaults it.
It favours all the Approaches of Vice, and weakens all the Resistance of
Virtue. For which Reason a renowned Statesman in Queen
Elizabeth's
Days, after having retir'd from Court and publick Business, in order to
give himself up to the Duties of Religion; when any of his old Friends
used to visit him, had still this Word of Advice in his Mouth,
Be
serious.
An eminent
Italian
Author of this Cast of Mind, speaking of the great
Advantage of a serious and composed Temper, wishes very gravely, that
for the Benefit of Mankind he had
Trophonius's
Cave in his Possession;
which, says he, would contribute more to the Reformation of Manners than
all the Work-houses and Bridewells in
Europe.
We have a very particular Description of this Cave in
Pausanias
, who
tells us, that it was made in the Form of a huge Oven, and had many
particular Circumstances, which disposed the Person who was in it to be
more pensive and thoughtful than ordinary; insomuch that no Man was ever
observed to laugh all his Life after, who had once made his Entry into
this Cave. It was usual in those Times, when any one carried a more than
ordinary Gloominess in his Features, to tell him that he looked like one
just come out of
Trophonius's
Cave.
On the other hand, Writers of a more merry Complexion have been no less
severe on the opposite Party; and have had one Advantage above them,
that they have attacked them with more Turns of Wit and Humour.
After all, if a Man's Temper were at his own Disposal, I think he would
not chuse to be of either of these Parties; since the most perfect
Character is that which is formed out of both of them. A Man would
neither chuse to be a Hermit nor a Buffoon: Humane Nature is not so
miserable, as that we should be always melancholy; nor so happy, as that
we should be always merry. In a Word, a Man should not live as if there
was no God in the World; nor, at the same Time, as if there were no Men
in it.
Contents
|
Monday, September 27, 1714 |
|
—Ubique
Luctus, ubique pavor—
Virg.

It has been my Custom, as I grow old, to allow my self in some little
Indulgencies which I never took in my Youth. Among others is that of an
Afternoon's Napp, which I fell into in the Fifty fifth Year of my Age,
and have continued for the three Years last past. By this means I enjoy
a double Morning, and rise twice a-day fresh to my Speculations. It
happens very luckily for me, that some of my Dreams have proved
instructive to my Countrymen, so that I may be said to sleep, as well as
to wake, for the Good of the Publick. I was Yesterday meditating on the
Account with which I have already entertained my Readers concerning the
Cave of
Trophonius.
I was no sooner fallen into my usual Slumber, but
I dreamt that this Cave was put into my Possession, and that I gave
publick Notice of its Virtue, inviting every one to it, who had a mind
to be a serious Man for the remaining Part of his Life. Great Multitudes
immediately resorted to me. The first who made the Experiment was a
Merry-Andrew
, who was put into my Hands by a neighbouring Justice of
Peace, in order to reclaim him from that profligate kind of Life. Poor
Pickle-herring had not taken above one Turn in it, when he came out of
the Cave, like a Hermit from his Cell, with a penitential Look, and a
most rueful Countenance. I then put in a young laughing Fop, and,
watching for his Return, asked him, with a Smile, how he liked the
Place? He replied, Pr'ythee Friend be not impertinent; and stalked by me
as grave as a Judge. A Citizen then de
Sir
ed me to give free Ingress and
Egress to his Wife, who was dressed in the gayest coloured Ribbons I had
ever seen. She went in with a Flirt of her Fan and a smirking
Countenance, but came out with a Severity of a Vestal, and throwing from
her several Female Gugaws, told me with a Sigh, that she resolved to go
into deep Mourning, and to wear Black all the rest of her Life. As I had
many Coquets recommended to me by their Parents, their Husbands, and
their Lovers, I let them in all at once, de
Sir
ing them to divert
themselves together as well as they could. Upon their emerging again
into Day-light, you would have fancied my Cave to have been a Nunnery,
and that you had seen a solemn Procession of Religious marching out, one
behind another, in the most profound Silence and the most exemplary
Decency. As I was very much delighted with so edifying a Sight, there
came towards me a great Company of Males and Females laughing, singing,
and dancing, in such a manner that I could hear them a great while
before I saw them. Upon my asking their Leader, what brought them
thither? they told me all at once, that they were
French
Protestants
lately arrived in
Great-Britain
, and that finding themselves of too
Gay a Humour for my Country, they applyed themselves to me in order to
compose them for
British
Conversation. I told them, that to oblige
them I would soon spoil their Mirth; upon which I admitted a whole Shole
of them, who, after having taken a Survey of the Place, came out in a
very good Order, and with Looks entirely
English.
I afterwards put in
a
Dutch
Man, who had a great Fancy to see the
Kelder
, as he called
it, but I could not observe that it had made any manner of Alteration in
him.
A Comedian who had gained great Reputation in Parts of Humour, told me,
that he had a mighty Mind to act
Alexander
the Great, and fancied that
he should succeed very well in it, if he could strike two or three
laughing Features out of his Face: He tried the Experiment, but
contracted so very solid a Look by it, that I am afraid he will be fit
for no Part hereafter but a
Timon
of
Athens
, or a Mute in the
Funeral.
I then clapt up an empty fantastic Citizen, in order to qualifie him for
an Alderman. He was succeeded by a young Rake of the
Middle-Temple
,
who was brought to me by his Grandmother; but to her great Sorrow and
Surprize, he came out a
Quaker.
Seeing my self surrounded with a Body
of
Free-thinkers
, and Scoffers at Religion, who were making themselves
merry at the sober Looks and thoughtful Brows of those who had been in
the Cave; I thrust them all in, one after another, and locked the Door
upon 'em. Upon my opening it, they all looked, as if they had been
frighted out of their Wits, and were marching away with Ropes in their
Hands to a Wood that was within Sight of the Place. I found they were
not able to bear themselves in their first serious Thoughts; but knowing
these would quickly bring them to a better Frame of Mind, I gave them
into the Custody of their Friends 'till that happy Change was wrought in
them.
The last that was brought to me was a young Woman, who at the first
Sight of my short Face fell into an immoderate fit of Laughter, and was
forced to hold her Sides all the while her Mother was speaking to me.
Upon this I interrupted the old Lady, and taking her Daughter by the
Hand, Madam, said I, be pleased to retire into my Closet, while your
Mother tells me your Case. I then put her into the Mouth of the Cave,
when the Mother, after having begg'd Pardon for the Girl's Rudeness,
told me, that she often treated her Father and the gravest of her
Relations in the same manner; that she would sit giggling and laughing
with her Companions from one End of a Tragedy to the other; nay, that
she would sometimes burst out in the Middle of a Sermon, and set the
whole Congregation a staring at her. The Mother was going on, when the
young Lady came out of the Cave to us with a composed Countenance, and a
low Curtsie. She was a Girl of such exuberant Mirth, that her Visit to
Trophonius
only reduced her to a more than ordinary Decency of
Behaviour, and made a very pretty Prude of her. After having performed
innumerable Cures, I looked about me with great Satisfaction, and saw
all my Patients walking by themselves in a very Pensive and musing
Posture, so that the whole Place seem'd covered with Philosophers. I was
at length resolv'd to go into the Cave my self, and see what it was that
had produced such wonderful Effects upon the Company; but as I was
stooping at the Entrance, the Door being something low, I gave such a
Nodd in my Chair, that I awaked. After having recovered my self from my
first Startle, I was very well pleas'd at the Accident which had
befallen me, as not knowing but a little Stay in the Place might have
spoiled my
Spectators
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, September 29, 1714 |
Addison |
—Solemque suum, sua sidera norunt—
Virg.

I have always taken a particular Pleasure in examining the Opinions
which Men of different Religions, different Ages, and different
Countries, have entertained concerning the Immortality of the Soul, and
the State of Happiness which they promise themselves in another World.
For whatever Prejudices and Errors human Nature lies under; we find that
either Reason, or Tradition from our first Parents, has discovered to
all People something in these great Points which bears Analogy to Truth,
and to the Doctrines opened to us by Divine Revelation. I
lately
discoursing on this Subject with a learned Person who has been very much
conversant among the Inhabitants of the more Western Parts of
Africk.
Upon his conversing with several in that Country, he tells me that
their Notion of Heaven or of a future State of Happiness is this, That
every thing we there wish for will immediately present it self to us. We
find, say they, our Souls are of such Nature that they require Variety,
and are not capable of being always delighted with the same Objects. The
Supreme Being therefore, in Compliance with this Taste of Happiness
which he has planted in the Soul of Man, will raise up from time to
time, say they, every Gratification which it is in the Humour to be
pleased with. If we wish to be in Groves or Bowers, among running
Streams or Falls of Water, we shall immediately find our selves in the
midst of such a Scene as we de
Sir
e. If we would be entertained with
Musick and the Melody of Sounds, the Consort rises upon our Wish, and
the whole Region about us is filled with Harmony. In short, every De
Sir
e
will be followed by Fruition, and whatever a Man's Inclination directs
him to will be present with him. Nor is it material whether the Supreme
Power creates in Conformity to our Wishes, or whether he only produces
such a Change in our Imagination, as makes us believe our selves
conversant among those Scenes which delight us. Our Happiness will be
the same, whether it proceed from external Objects, or from the
Impressions of the Deity upon our own private Fancies. This is the
Account which I have received from my learned Friend. Notwithstanding
this System of Belief be in general very chimerical and visionary, there
is something sublime in its manner of considering the Influence of a
Divine Being on a Human Soul. It has also, like most other Opinions of
the Heathen World upon these important Points, it has, I say, its
Foundation in Truth, as it supposes the Souls of good Men after this
Life to be in a State of perfect Happiness, that in this State there
will be no barren Hopes, nor fruitless Wishes, and that we shall enjoy
every thing we can de
Sir
e. But the particular Circumstance which I am
most pleas'd with in this Scheme, and which arises from a just
Reflection upon Human Nature, is that Variety of Pleasures which it
supposes the Souls of good Men will be possessed of in another World.
This I think highly probable, from the Dictates both of Reason and
Revelation. The Soul consists of many Faculties, as the Understanding,
and the Will, with all the Senses both outward and inward; or to speak
more Philosophically, the Soul can exert herself in many different Ways
of Action. She can understand, will, imagine, see, and hear, love, and
discourse, and apply herself to many other the like Exercises of
different Kinds and Natures; but what is more to be considered, the Soul
is capable of receiving a most exquisite Pleasure and Satisfaction from
the Exercise of any of these its Powers, when they are gratified with
their proper Objects; she can be entirely happy by the Satisfaction of
the Memory, the Sight, the Hearing, or any other Mode of Perception.
Every Faculty is as a distinct Taste in the Mind, and hath Objects
accommodated to its proper Relish. Doctor
Tillotson
somewhere says
that he will not presume to determine in what consists the Happiness of
the Blest, because God Almighty is capable of making the Soul happy by
Ten thousand different Ways. Besides those several Avenues to Pleasure
which the Soul is endowed with in this Life; it is not impossible,
according to the Opinions of many eminent Divines, but there may be new
Faculties in the Souls of good Men made perfect, as well as new Senses
in their glorified Bodies. This we are sure of, that there will be new
Objects offer'd to all those Faculties which are essential to us.
We are likewise to take Notice that every particular Faculty is capable
of being employed on a very great Variety of Objects. The Understanding,
for Example, may be happy in the Contemplation of Moral, Natural,
Mathematical, and other Kinds of Truth. The Memory likewise may turn
itself to an infinite Multitude of Objects, especially when the Soul
shall have pass'd through the Space of many Millions of Years, and shall
reflect with Pleasure on the Days of Eternity. Every other Faculty may
be consider'd in the same Extent.
We cannot question but that the Happiness of a Soul will be adequate to
its Nature, and that it is not endowed with any Faculties which are to
lie useless and unemploy'd. The Happiness is to be the Happiness of the
whole Man, and we may easily conceive to our selves the Happiness of the
Soul, whilst any one of its Faculties is in the Fruition of its chief
Good. The Happiness may be of a more exalted Nature in Proportion as the
Faculty employed is so, but as the whole Soul acts in the Exertion of
any of its particular Powers, the whole Soul is happy in the Pleasure
which arises from any of its particular Acts. For notwithstanding, as
has been before hinted,
as it has been taken Notice of by one of the
greatest modern Philosophers
, we divide the Soul into several Powers
and Faculties, there is no such Division in the Soul it self, since it
is the whole Soul that remembers, understands, wills, or imagines. Our
manner of considering the Memory, Understanding, Will, Imagination, and
the like Faculties, is for the better enabling us to express our selves
in such abstracted Subjects of Speculation, not that there is any such
Division in the Soul it self.
Seeing then that the Soul has many different Faculties, or in other
Words, many different Ways of acting; that it can be intensely pleas'd,
or made happy by all these different Faculties, or Ways of acting; that
it may be endow'd with several latent Faculties, which it is not at
present in a Condition to exert; that we cannot believe the Soul is
endow'd with any Faculty which is of no Use to it; that whenever any one
of these Faculties is transcendently pleased, the Soul is in a State of
Happiness; and in the last Place considering that the Happiness of
another World is to be the Happiness of the whole Man; who can question
but that there is an infinite Variety in those Pleasures we are speaking
of; and that this Fulness of Joy will be made up of all those Pleasures
which the Nature of the Soul is capable of receiving.
We shall be the more confirmed in this Doctrine, if we observe the
Nature of Variety, with regard to the Mind of Man. The Soul does not
care to be always in the same bent. The Faculties relieve one another by
Turns, and receive an additional Pleasure from the Novelty of those
Objects about which they are conversant.
Revelation likewise very much confirms this Notion, under the different
Views which it gives us of our future Happiness. In the Description of
the Throne of God, it represents to us all those Objects which are able
to gratify the Senses and Imagination: In very many Places it intimates
to us all the Happiness which the Understanding can possibly receive in
that State, where all Things shall be revealed to us, and we shall know,
even as we are known; the Raptures of Devotion, of Divine Love, the
Pleasure of conversing with our Blessed Saviour, with an innumerable
Host of Angels, and with the Spirits of Just Men made Perfect, are
likewise revealed to us in several Parts of the Holy Writings. There are
also mentioned those Hierarchies or Governments, in which the Blest
shall be ranged one above another, and in which we may be sure a great
Part of our Happiness will likewise consist; for it will not be there as
in this World, where every one is aiming at Power and Superiority; but
on the contrary, every one will find that Station the most proper for
him in which he is placed, and will probably think that he could not
have been so happy in any other Station. These and many other
Particulars are marked in Divine Revelation, as the several Ingredients
of our Happiness in Heaven, which all imply such a Variety of Joys and
such a Gratification of the Soul in all its different Faculties, as I
have been here mentioning.
Some of the Rabbins tell us, that the Cherubims are a Set of Angels who
know most, and the Seraphims a Set of Angels who love most. Whether this
Distinction be not altogether Imaginary, I shall not here examine; but
it is highly probable that among the Spirits of good Men, there may be
some who will be more pleased with the Employment of one Faculty than of
another, and this perhaps according to those innocent and virtuous
Habits or Inclinations which have here taken the deepest Root.
I might here apply this Consideration to the Spirits of wicked Men, with
relation to the Pain which they shall suffer in every one of their
Faculties, and the respective Miseries which shall be appropriated to
each Faculty in particular. But leaving this to the Reflection of my
Readers, I shall conclude, with observing how we ought to be thankful to
our great Creator, and rejoice in the Being which he has bestowed upon
us, for having made the Soul susceptible of Pleasure by so many
different Ways.
We see by what a Variety of Passages, Joy and Gladness may enter into
the Thoughts of Man; how wonderfully a human Spirit is framed, to imbibe
its proper Satisfactions, and taste the Goodness of its Creator. We may
therefore look into our selves with Rapture and Amazement, and cannot
sufficiently express our Gratitude to him, who has encompassed us with
such a Profusion of Blessings, and opened in us so many Capacities of
enjoying them.
There cannot be a stronger Argument that God has designed us for a State
of future Happiness, and for that Heaven which he has revealed to us,
than that he has thus naturally qualified the Soul for it, and made it a
Being capable of receiving so much Bliss. He would never have made such
Faculties in vain, and have endowed us with Powers that were not to be
exerted on such Objects as are suited to them. It is very manifest, by
the inward Frame and Constitution of our Minds, that he has adapted them
to an infinite Variety of Pleasures and Gratifications, which are not to
be met with in this Life. We should therefore at all times take Care
that we do not disappoint this his gracious Purpose and Intention
towards us, and make those Faculties which he formed as so many
Qualifications for Happiness and Rewards, to be the Instruments of Pain
and Punishment.
Footnote 1:
Addison's father, who wrote an account of West Barbary,
died in 1703.
Footnote 2:
Locke.
Contents
|
Friday, October 1, 1714 |
Henry Grove |
following Essay comes from an Hand which has entertained my Readers
once before
.
Notwithstanding a narrow contracted Temper be that which obtains most in
the World, we must not therefore conclude this to be the genuine
Characteristick of Mankind; because there are some who delight in
nothing so much as in doing Good, and receive more of their Happiness at
second hand, or by rebound from others, than by direct and immediate
Sensation. Now tho' these Heroic Souls are but few, and to Appearance so
far advanced above the groveling Multitude, as if they were of another
Order of Beings, yet in Reality their Nature is the same, moved by the
same Springs, and endowed with all the same essential Qualities, only
cleared, refined, and cultivated.
Water is the same fluid Body in Winter and in Summer; when it stands
stiffened in Ice as when it flows along in gentle Streams gladdening a
thousand Fields in its Progress. 'Tis a Property of the Heart of Man to
be diffusive: Its kind Wishes spread abroad over the Face of the
Creation; and if there be those, as we may observe too many of them, who
are all wrapt up in their own dear selves, without any visible Concern
for their Species, let us suppose that their Good-nature is frozen, and
by the prevailing Force of some contrary Quality restrained in its
Operations. I shall therefore endeavour to assign some of the principal
Checks upon this generous Propension of the Human Soul, which will
enable us to judge whether, and by what Method, this most useful
Principle may be unfettered, and restored to its native Freedom of
Exercise.
The first and leading Cause is an unhappy Complexion of Body. The
Heathens, ignorant of the true Source of Moral Evil, generally charged
it on the Obliquity of Matter, which, being eternal and independent, was
incapable of Change in any of its Properties, even by the Almighty Mind,
who, when He came to fashion it into a World of Beings, must take it as
he found it. This Notion, as most others of theirs, is a Composition of
Truth and Error. That Matter is eternal, that from the first Union of a
Soul to it, it perverted its Inclinations, and that the ill Influence it
hath upon the Mind is not to be corrected by God himself, are all very
great Errors, occasioned by a Truth as evident, that the Capacities and
Dispositions of the Soul depend, to a great Degree, on the bodily
Temper. As there are some Fools, others are Knaves, by Constitution; and
particularly, it may be said of many, that they are born with an
illiberal Cast of Mind; the Matter that composes them is tenacious as
Birdlime, and a kind of Cramp draws their Hands and their Hearts
together, that they never care to open them unless to grasp at more.
'Tis a melancholy Lot this; but attended with one Advantage above
theirs, to whom it would be as painful to forbear good Offices, as it is
to these Men to perform them; that whereas Persons naturally Beneficent
often mistake Instinct for Virtue, by reason of the Difficulty of
distinguishing when one rules them and when the other, Men of the
opposite Character may be more certain of the Motive that predominates
in every Action. If they cannot confer a Benefit with that Ease and
Frankness which are necessary to give it a Grace in the Eye of the
World, in requital, the real Merit of what they do is inhanc'd by the
Opposition they surmount in doing it. The Strength of their Virtue is
seen in rising against the Weight of Nature, and every time they have
the Resolution to discharge their Duty, they make a Sacrifice of
Inclination to Conscience, which is always too grateful to let its
Followers go without suitable Marks of its Approbation. Perhaps the
entire Cure of this ill Quality is no more possible, than of some
Distempers that descend by Inheritance. However, a great deal may be
done by a Course of Beneficence obstinately persisted in; this, if any
thing, being a likely way of establishing a moral Habit, which shall be
somewhat of a Counterpoise to the Force of Mechanism. Only it must be
remembred, that we do not intermit, upon any Pretence whatsoever, the
Custom of doing Good, in regard if there be the least Cessation, Nature
will watch the Opportunity to return, and in a short time to recover the
Ground it was so long in quitting: For there is this Difference between
mental Habits, and such as have their Foundation in the Body; that these
last are in their Nature more forcible and violent, and, to gain upon
us, need only not to be opposed; whereas the former must be continually
reinforced with fresh Supplies, or they will languish and die away. And
this suggests the Reason why good Habits, in general, require longer
time for their Settlement than bad, and yet are sooner displaced; the
Reason is, that vicious Habits (as Drunkenness for Instance) produce a
Change in the Body, which the others not doing, must be maintained the
same way they are acquired, by the mere Dint of Industry, Resolution,
and Vigilance.
Another Thing which suspends the Operations of Benevolence, is the Love
of the World; proceeding from a false Notion Men have taken up, that an
Abundance of the World is an essential Ingredient into the Happiness of
Life. Worldly Things are of such a Quality as to lessen upon dividing,
so that the more Partners there are, the less must fall to every Man's
private Share. The Consequence of this is, that they look upon one
another with an evil Eye, each imagining all the rest to be embarked in
an Interest, that cannot take Place but to his Prejudice. Hence are
those eager Competitions for Wealth or Power; hence one Man's Success
becomes another's Disappointment; and, like Pretenders to the same
Mistress, they can seldom have common Charity for their Rivals. Not that
they are naturally disposed to quarrel and fall out, but 'tis natural
for a Man to prefer himself to all others, and to secure his own
Interest first. If that which Men esteem their Happiness were like the
Light, the same sufficient and unconfined Good, whether Ten Thousand
enjoy the Benefit of it, or but One, we should see Mens Good-will, and
kind Endeavours, would be as universal.
Homo qui Erranti comiter monstrat Viam,
Quasi Lumen de suo Lumine accendat, facit,
Nihilominus ipsi luceat, cum illi accenderit.
But, unluckily, Mankind agree in making Choice of Objects, which
inevitably engage them in perpetual Differences. Learn therefore, like a
wise Man, the true Estimate of Things. De
Sir
e not more of the World than
is necessary to accommodate you in passing through it; look upon every
thing beyond, not as useless only, but burthensome. Place not your Quiet
in Things, which you cannot have without putting others beside them, and
thereby making them your Enemies; and which, when attain'd, will give
you more Trouble to keep, than Satisfaction in the Enjoyment. Virtue is
a Good of a nobler kind; it grows by Communication, and so little
resembles earthly Riches, that the more Hands it is lodged in, the
greater is every Man's particular Stock. So, by propagating and mingling
their Fires, not only all the Lights of a Branch together cast a more
extensive Brightness, but each single Light burns with a stronger Flame.
And lastly, take this along with you, that if Wealth be an Instrument of
Pleasure, the greatest Pleasure it can put into your Power, is that of
doing Good. 'Tis worth considering, that the Organs of Sense act within
a narrow Compass, and the Appetites will soon say they have enough:
which of the two therefore is the happier Man? He, Who confining all his
Regard to the Gratification of his own Appetites, is capable but of
short Fits of Pleasure? Or the Man, who, reckoning himself a Sharer in
the Satisfactions of others, especially those which come to them by his
Means, enlarges the Sphere of his Happiness?
The last Enemy to Benevolence I shall mention is Uneasiness of any Kind.
A guilty, or a discontented Mind, a Mind ruffled by ill Fortune,
disconcerted by its own Passions, sowered by Neglect, or fretting at
Disappointments, hath not Leisure to attend to the Necessity or
Reasonableness of a Kindness de
Sir
ed, nor a Taste for those Pleasures
which wait on Beneficence, which demand a calm and unpolluted Heart to
relish them. The most miserable of all Beings is the most envious; as,
on the other hand, the most communicative is the happiest. And if you
are in search of the Seat of perfect Love and Friendship, you will not
find it till you come to the Region of the Blessed, where Happiness,
like a refreshing Stream, flows from Heart to Heart in an endless
Circulation, and is preserv'd sweet and untainted by the Motion. 'Tis
old Advice, if you have a Favour to request of any one, to observe the
softest times of Address, when the Soul, in a Flush of good Humour,
takes a Pleasure to shew it self pleased. Persons conscious of their own
integrity, satisfied with themselves, and their Condition, and full of
Confidence in a Supreme Being, and the Hope of Immortality, survey all
about them with a Flow of Good-will. As Trees which like their Soil,
they shoot out in Expressions of Kindness and bend beneath their own
precious Load, to the hand of the Gatherer. Now if the Mind be not thus
easie, 'tis an infallible Sign that it is not in its natural State;
Place the Mind in its right Posture, it will immediately discover its
innate Propension to Beneficence.
Footnote 1:
No.
Contents
|
Monday, October 4, 1714 |
Budgell |
—Facit hoc illos Hyacinthos—
Juv.

The following Letter comes from a Gentleman, who, I find, is very
dilgent in making his Observations, which I think too material not to be
communicated to the Publick.
Sir ,
'In order to
execute the Office of Love-Casuist to
Great Britain,
with which I take my self to be invested by your Paper of September 8
1, I shall make some further Observations upon the two Sexes in
general, beginning with that which always ought to have the upper
Hand. After having observed with much Curiosity the Accomplishments
which are apt to captivate female Hearts, I find that there is no
Person so irresistable as one who is a Man of Importance, provided it
be in Matters of no Consequence. One who makes himself talked of, tho'
it be for the particular Cock of his Hat, or for prating aloud in the
Boxes at a Play, is in a fair way of being a Favourite. I have known a
young Fellow make his Fortune by knocking down a Constable; and may
venture to say, tho' it may seem a Paradox, that many a Fair One has
died by a Duel in which both the Combatants have survived.
About three Winters ago I took Notice of a young Lady at the Theatre,
who convceived of a Passion for a notorious Rake that headed a Party
of Cat-calls; and am credibly informed, that the Emperor of the
Mohocks married a rich Widow within three Weeks after having rendered
himself formidable in the Cities of
London and
Westminster.
Scowring and breaking Windows have done frequent Execution upon the
Sex; but there is no Sett of these Male Charmers who make their way
more successfully, than those who have gained themselves a Name for
Intrigue, and have ruined the greatest Number of Reputations. There is
a strange Curiosity in the female World to be acquainted with the dear
Man who has been loved by others, and to know what it is that makes
him so agreeable. His Reputation does more than half his Business.
Every one that is ambitious of being a Woman of Fashion, looks out for
Opportunities of being in his Company; so that to use the old Proverb,
When his Name is up he may lie a-Bed.
'I was very sensible of the great Advantage of being a Man of
Importance upon these Occasions on the Day of the King's Entry, when I
was seated in a Balcony behind a Cluster of very pretty Country
Ladies, who had one of these showy Gentlemen in the midst of them. The
first Trick I caught him at was bowing to several Persons of Quality
whom he did not know; nay, he had the Impudence to hem at a Blue
Garter who had a finer Equipage than ordinary, and seemed a little
concerned at the Impertinent Huzzas of the Mob, that hindered his
Friend from taking Notice of him. There was indeed one who pull'd off
his Hat to him, and upon the Ladies asking who it was, he told them,
it was a Foreign Minister that he had been very merry with the Night
before; whereas in Truth, it was the City Common Hunt.
'He was never at a Loss when he was asked any Person's Name, tho' he
seldom knew any one under a Peer. He found Dukes and Earls among the
Aldermen, very good-natured Fellows among the Privy-Counsellors, with
two or three agreeable old Rakes among the Bishops and Judges.
'In short, I collected from his whole Discourse, that he was
acquainted with every Body, and knew no Body. At the same Time, I am
mistaken if he did not that Day make more Advances in the Affections
of his Mistress, who sat near him, than he could have done in half a
Year's Courtship.
'
Ovid has finely touched this Method of making Love, which I shall
here give my Reader in Mr.
Dryden's Translation.
(Page the Eleventh.)
Thus Love in Theatres did first improve,
And Theatres are still the Scene of Love:
Nor shun the Chariots, and the Coursers Race;
The Circus is no inconvenient Place.
Nor Need is there of talking on the Hand,
Nor Nods, nor Sighs, which Lovers understand;
But boldly next the Fair your Seat provide,
Close as you can to hers, and Side by Side:
Pleas'd or unpleas'd, no Matter; crowding sit;
For so the Laws of publick Shows permit.
Then find Occasion to begin Discourse,
Enquire whose Chariot this, and whose that Horse;
To whatsoever Side she is inclin'd,
Suit all your Inclinations to her Mind;
Like what she likes, from thence your Court begin,
And whom she favours, wish that he may win.
(Again, Page the Sixteenth.)
O when will come the Day, by Heav'n design'd,
When thou, the best and fairest of Mankind,
Drawn by white Horses, shall in Triumph ride,
With conquer'd Slaves attending on thy Side;
Slaves, that no longer can be safe in flight,
O glorious Object! O surprizing Sight!
O Day of publick Joy, too good to end in Night!
On such a Day, if thou, and next to thee
Some Beauty sits, the Spectacle to see;
If she enquire the Names of conquer'd Kings,
Of Mountains, Rivers, and their hidden Springs;
Answer to all thou knowest; and, if Need be,
Of Things unknown seem to speak knowingly:
This is Euphrates, crown'd with Reeds; and there
Flows the swift Tigris, with his Sea-green hair,
Invent new Names of Things unknown before;
Call this Armenia, that, the Caspian Shore:
Call this a Mede, and that a Parthian Youth;
Talk probably; no Matter for the Truth.
Footnote 1:
No.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 6, 1714 |
Byrom |
Ducite ab Urbe Domum, mea Carmina, ducite Daphnim.
Virg.

The following Copy of Verses comes
one of my Correspondents, and
has something in it so Original, that I do not much doubt but it will
divert my Readers
.
| I |
My Time, O ye Muses, was happily spent,
When Phebe went with me wherever I went;
Ten thousand sweet Pleasures I felt in my Breast:
Sure never fond Shepherd like Colin was blest!
But now she is gone, and has left me behind,
What a marvellous Change on a sudden I find?
When things were as fine as could possibly be,
I thought 'twas the Spring; but alas! it was she. |
| II |
With such a Companion, to tend a few Sheep,
To rise up and play, or to lye down and sleep:
I was so good-humour'd, so chearful and gay,
My Heart was as light as a Feather all Day.
But now I so cross and so peevish am grown;
So strangely uneasie as ever was known.
My Fair one is gone, and my Joys are all drown'd,
And my Heart—I am sure it weighs more than a Pound. |
| III |
The Fountain that wont to run sweetly along,
And dance to soft Murmurs the Pebbles among,
Thou know'st, little Cupid, if Phebe was there,
'Twas Pleasure to look at, 'twas Musick to hear:
But now she is absent, I walk by its Side,
And still as it murmurs do nothing but chide,
Must you be so chearful, while I go in Pain?
Peace there with your Bubbling, and hear me complain. |
| IV |
When my Lambkins around me would oftentimes play,
And when Phebe and I were as joyful as they,
How pleasant their Sporting, how happy the Time,
When Spring, Love and Beauty were all in their Prime?
But now in their Frolicks when by me they pass,
I fling at their Fleeces an handful of Grass;
Be still then, I cry, for it makes me quite mad,
To see you so merry, while I am so sad. |
| V |
My Dog I was ever well pleased to see
Come wagging his Tail to my Fair one and me;
And Phebe was pleas'd too, and to my Dog said,
Come hither, poor Fellow; and patted his Head.
But now, when he's fawning, I with a sour Look
Cry, Sir rah; and give him a Blow with my Crook:
And I'll give him another; for why should not Tray
Be as dull as his Master, when Phebe's away? |
| VI |
When walking with Phebe, what Sights have I seen?
How fair was the Flower, how fresh was the Green?
What a lovely appearance the Trees and the Shade,
The Corn-fields and Hedges, and ev'ry thing made?
But now she has left me, tho' all are still there,
They none of 'em now so delightful appear:
'Twas nought but the Magick, I find, of her Eyes,
Made so many beautiful Prospects arise. |
| VII |
Sweet Musick went with us both all the Wood thro',
The Lark, Linnet, Throstle, and Nightingale too;
Winds over us whisper'd, Flocks by us did bleat,
And chirp went the Grasshopper under our Feet.
But now she is absent, tho' still they sing on,
The Woods are but lonely, the Melody's gone:
Her Voice in the Consort, as now I have found,
Gave ev'ry thing else its agreeable Sound. |
| VIII |
Rose, what is become of thy delicate Hue?
And where is the Violet's beautiful Blue?
Does ought of its Sweetness the Blossom beguile,
That Meadow, those Dasies, why do they not smile?
Ah! Rivals, I see what it was that you drest
And made your selves fine for; a Place in her Breast:
You put on your Colours to pleasure her Eye,
To be pluckt by her Hand, on her Bosom to die. |
| IX |
How slowly Time creeps, till my Phebe return!
While amidst the soft Zephyr's cold Breezes I burn;
Methinks if I knew whereabouts he would tread,
I could breathe on his Wings, and 'twould melt down the Lead.
Fly swifter, ye Minutes, bring hither my Dear,
And rest so much longer for't when she is here.
Ah Colin! old Time is full of Delay,
Nor will budge one Foot faster for all thou canst say. |
| X |
Will no pitying Power that hears me complain,
Or cure my Disquiet, or soften my Pain?
To be cur'd, thou must, Colin, thy Passion remove;
But what Swain is so silly to live without Love?
No, Deity, bid the dear Nymph to return,
For ne'er was poor Shepherd so sadly forlorn.
Ah! What shall I do? I shall die with Despair;
Take heed, all ye Swains, how ye love one so fair. |
Footnote 1:
It is said that John Byrom wrote these verses in honour of
Joanna, daughter of his friend, Dr. Richard Bentley, Master of Trinity.
Contents
Tu ne quæsieris (scire nefas) quem mihi, quem tibi,
Finem Dii dederint, Leuconoe; nec Babylonios
Tentaris numeros—
Hor.

The De
Sir
e of knowing future Events is one of the strongest Inclinations
in the Mind of Man. Indeed an Ability of foreseeing probable Accidents
is what, in the Language of Men, is called Wisdom and Prudence: But, not
satisfied with the Light that Reason holds out, Mankind hath endeavoured
to penetrate more compendiously into Futurity. Magick, Oracles, Omens,
lucky Hours, and the various Arts of Superstition, owe their Rise to
this powerful Cause. As this Principle is founded in Self-Love, every
Man is sure to be sollicitous in the first Place about his own Fortune,
the Course of his Life, and the Time and Manner of his Death.
If we consider that we are free Agents, we shall discover the Absurdity
of Enquiries. One of our Actions, which we might have performed or
neglected, is the Cause of another that succeeds it, and so the whole
Chain of Life is link'd together. Pain, Poverty, or Infamy, are the
natural Product of vicious and imprudent Acts; as the contrary Blessings
are of good ones; so that we cannot suppose our Lot to be determined
without Impiety. A great Enhancement of Pleasure arises from its being
unexpected; and Pain is doubled by being foreseen. Upon all these, and
several other Accounts, we ought to rest satisfied in this Portion
bestowed on us; to adore the Hand that hath fitted every Thing to our
Nature, and hath not more display'd his Goodness in our Knowledge than
in our Ignorance.
It is not unworthy Observation, that superstitious Enquiries into future
Events prevail more or less, in proportion to the Improvement of liberal
Arts and useful Knowledge in the several Parts of the World. Accordingly
we find, that magical Incantations remain in
Lapland
, in the more
remote Parts of
Scotland
they have their second Sight, and several of
our own Countrymen see abundance of Fairies. In
Asia
this Credulity is
strong; and the greatest Part of refined Learning there consists in the
Knowledge of Amulets, Talismans, occult Numbers, and the like.
While I was at
Grand Cairo
, I fell into the Acquaintance of a
good-natured Mussulman, who promised me many good Offices, which he
designed to do me when he became the Prime Minister, which was a Fortune
bestowed on his Imagination by a Doctor very deep in the curious
Sciences. At his repeated Sollicitations I went to learn my Destiny of
this wonderful Sage. For a small Sum I had his Promise, but was requir'd
to wait in a dark Apartment till he had run thro' the preparatory
Ceremonies. Having a strong Propensity, even then, to Dreaming, I took a
Nap upon the Sofa where I was placed, and had the following Vision, the
Particulars whereof I picked up the other Day among my Papers.
I found my self in an unbounded Plain, where methought the whole World,
in several Habits and with different Tongues, was assembled. The
Multitude glided swiftly along, and I found in my self a strong
Inclination to mingle in the Train. My Eyes quickly singled out some of
the most splendid Figures. Several in rich Caftans and glittering
Turbans bustled through the Throng, and trampled over the Bodies of
those they threw down; till to my great Surprize I found that the great
Pace they went only hastened them to a Scaffold or a Bowstring. Many
beautiful Damsels on the other Side moved forward with great Gaiety;
some danced till they fell all along; and others painted their Faces
till they lost their Noses. A Tribe of Creatures with busie Looks
falling into a Fit of Laughter at the Misfortunes of the unhappy Ladies,
I turn'd my Eyes upon them. They were each of them filling his Pockets
with Gold and Jewels, and when there was no Room left for more, these
Wretches looking round with Fear and Horror, pined away before my Face
with Famine and Discontent.
This Prospect of human Misery struck me dumb for some Miles. Then it was
that, to disburthen my Mind, I took Pen and Ink, and did every Thing
that hath since happen'd under my Office of SPECTATOR. While I was
employing my self for the Good of Mankind, I was surpriz'd to meet with
very unsuitable Returns from my Fellow-Creatures. Never was poor Author
so beset with Pamphleteers, who sometimes marched directly against me,
but oftner shot at me from strong Bulwarks, or rose up suddenly in
Ambush. They were of all Characters and Capacities, some with Ensigns of
Dignity, and others in Liveries; but what most surpriz'd me, was to see
two or three in black Gowns among my Enemies. It was no small Trouble to
me, sometimes to have a Man come up to me with an angry Face, and
reproach me for having lampooned him, when I had never seen or heard of
him in my Life. With the Ladies it was otherwise: Many became my Enemies
for not being particularly pointed out; as there were others who
resented the Satyr which they imagined I had directed against them. My
great Comfort was in the Company of half a Dozen Friends, who, I found
since, were the Club which I have so often mentioned in my Papers. I
laughed often at
Sir Roger
in my Sleep, and was the more diverted with
Will Honeycomb
's Gallantries, (when we afterwards became acquainted)
because I had foreseen his Marriage with a Farmer's Daughter. The Regret
which arose in my Mind upon the Death of my Companions, my Anxieties for
the Publick, and the many Calamities still fleeting before my Eyes, made
me repent my Curiosity; when the Magician entered the Room, and awakened
me, by telling me (when it was too late) that he was just going to
begin.
N. B.
I have only deliver'd the Prophecy of that Part of my Life which
is past, it being inconvenient to divulge the second Part 'till a more
proper Opportunity.
Contents
|
Monday, October 11, 1714 |
Budgell |
Exuerint sylvestrem animum, cultuque frequenti
In quascunque voces artes, haud tarda sequentur.
Virg.

Having perused the following Letter, and finding it to run upon the
Subject of Love, I referred it to the Learned
Casuist
, whom I have
retained in my Service for Speculations of that Kind. He return'd it to
me the next Morning with his Report annexed to it, with both of which I
shall here present my Reader.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'
Finding that you have Entertained an useful Person in your Service in
quality of
Love-Casuist1, I apply my self to you, under a very
great Difficulty, that hath for some Months perplexed me. I have a
Couple of humble Servants, one of which I have no Aversion to; the
other I think of very kindly. The first hath the Reputation of a Man
of good Sense, and is one of those People that your Sex are apt to
Value. My Spark is reckoned a Coxcomb among the Men, but is a
Favourite of the Ladies. If I marry the Man of Worth, as they call
him, I shall oblige my Parents and improve my Fortune; but with my
dear Beau I promise my self Happiness, altho' not a Jointure. Now I
would ask you, whether I should consent to lead my Life with a Man
that I have only no Objection to, or with him against whom all
Objections to me appear frivolous. I am determined to follow the
Casuist's Advice, and I dare say he will not put me upon so serious
a thing as Matrimony, contrary to my Inclination.'
I am, &c.
Fanny Fickle.
P.S. 'I forgot to tell you, that the pretty Gentleman is the most
complaisant Creature in the World, and is always of my Mind; but the
other, forsooth, fancies he hath as much Wit as my self, slights my
Lap-Dog, and hath the Insolence to contradict me when he thinks I am
not in the Right. About half an Hour ago, he maintained to my Face,
that a Patch always implies a Pimple.'
As I look upon it to be my Duty rather to side with the Parents than the
Daughter, I shall propose some Considerations to my Gentle Querist,
which may encline her to comply with those, under whose Direction she
is: And at the same time, convince her, that it is not impossible but
she may, in time, have a true Affection for him who is, at present,
indifferent to her: Or, to use the old Family Maxim, that
If she
marries first, Love will come after.
The only Objection, that she seems to insinuate against the Gentleman
proposed to her, is his want of Complaisance, which, I perceive, she is
very willing to return. Now, I can discover from this very Circumstance,
that she and her Lover, whatever they may think of it, are very good
Friends in their Hearts. It is difficult to determine, whether Love
delights more in giving Pleasure or Pain. Let Miss
Fickle
ask her own
Heart, if she doth not take a Secret Pride in making this Man of good
Sense look very silly. Hath she ever been better pleas'd, than when her
Behaviour hath made her Lover ready to hang himself? Or doth she ever
rejoice more, than when she thinks she hath driven him to the very Brink
of a purling Stream? Let her consider, at the same time, that it is not
impossible but her Lover may have discovered her Tricks, and hath a Mind
to give her as good as she brings. I remember a handsome young Baggage
that treated a hopeful
Greek
of my Acquaintance, just come from
Oxford
, as if he had been a
Barbarian.
The first Week, after she had
fixed him, she took a Pinch of Snuff out of his Rival's Box, and
apparently touched the Enemy's little Finger. She became a profest Enemy
to the Arts and Sciences, and scarce ever wrote a Letter to him without
wilfully mis-spelling his Name. The young Scholar, to be even with her,
railed at
Coquettes
as soon as he had got the Word; and did not want
Parts to turn into Ridicule her Men of Wit and Pleasure of the Town.
After having irritated one another for the Space of five Months, she
made an Assignation with him fourscore Miles from
London.
But as he
was very well acquainted with her Pranks, he took a Journey the quite
contrary Way. Accordingly they met, quarrell'd, and in a few Days were
Married. Their former Hostilities are now the Subject of their Mirth,
being content at present with that Part of Love only which bestows
Pleasure.
Women, who have been married some time, not having it in their Heads to
draw after them a numerous Train of Followers, find their Satisfaction
in the Possession of one Man's Heart. I know very well, that Ladies in
their Bloom de
Sir
e to be excused in this Particular. But when Time hath
worn out their natural Vanity and taught them Discretion, their Fondness
settles on its proper Object. And it is probably for this Reason, that
among Husbands, you will find more that are fond of Women beyond their
Prime, than of those who are actually in the Insolence of Beauty. My
Reader will apply the same Observation to the other Sex.
I need not insist upon the Necessity of their pursuing one common
Interest, and their united Care, for their Children; but shall only
observe, by the Way, that married Persons are both more warm in their
Love, and more hearty in their Hatred, than any others whatsoever.
Mutual Favours and Obligations, which may be supposed to be greater here
than in any other State, naturally beget an Intense Affection in
generous Minds. As, on the contrary, Persons who have bestowed such
Favours, have a particular Bitterness in their Resentments, when they
think themselves ill treated by those of whom they have deserved so
much.
Besides, Miss
Fickle
may consider, that as there are often many Faults
conceal'd before Marriage, so there are sometimes many Virtues
unobserv'd.
To this we may add the great Efficacy of Custom, and constant
Conversation, to produce a mutual Friendship and Benevolence in two
Persons. It is a nice Reflection, which I have heard a Friend of mine
make, that you may be sure a Woman loves a Man, when she uses his
Expressions, tells his Stories, or imitates his Manner. This gives a
secret Delight; for Imitation is a kind of artless Flattery, and
mightily favours the powerful Principle of Self-love. It is certain,
that married Persons, who are possest with a mutual Esteem, not only
catch the Air and way of Talk from one another, but fall into the same
Traces of thinking and liking. Nay, some have carried the Remark so far
as to assert, that the Features of Man and Wife grow, in time, to
resemble one another. Let my fair Correspondent therefore consider, that
the Gentleman recommended will have a good deal of her own Face in two
or three Years; which she must not expect from the Beau, who is too full
of his dear self to copy after another. And I dare appeal to her own
Judgment, if that Person will not be the handsomest, that is the most
like her self.
We have a remarkable Instance to our present Purpose in the History of
King
Edgar
, which I shall here relate, and leave it with my fair
Correspondent to be applied to her self.
This great Monarch, who is so famous in
British
Story, fell in Love,
as he made his Progress through his Kingdom, with a certain Duke's
Daughter who lived near
Winchester
, and was the most celebrated Beauty
of the Age. His Importunities and the Violence of his Passion were so
great, that the Mother of the young Lady promised him to bring her
Daughter to his Bed the next Night, though in her Heart she abhorr'd so
infamous an Office. It was no sooner dark than she convey'd into his
Room a young Maid of no disagreeable Figure, who was one of her
Attendants, and did not want Address to improve the Opportunity for the
Advancement of her Fortune. She made so good use of her Time, that when
she offered to rise a little before Day, the King could by no means
think of parting with her. So that finding herself under a Necessity of
discovering who she was, she did it in so handsome a Manner, that his
Majesty was exceeding gracious to her, and took her ever after under his
Protection; insomuch that our Chronicles tell us he carried her along
with him, made her his first Minister of State, and continued true to
her alone, 'till his Marriage with the beautiful
Elfrida.
Footnote 1:
See Nos.
,
,
,
,
.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 13, 1714 |
|
—longum cantu solata laborem
Arguto Conjux percurrit pectine Telas.
Virg.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I have a couple of Nieces under my Direction, who so often run
gadding abroad, that I don't know where to have them. Their Dress,
their Tea, and their Visits take up all their Time, and they go to Bed
as tired with doing nothing, as I am after quilting a whole
Under-Petticoat. The only time they are not idle, is while they read
your
Spectators; which being dedicated to the Interests of Virtue, I
de
Sir e you to recommend the long neglected Art of Needle-work. Those
Hours which in this Age are thrown away in Dress, Play, Visits, and
the like, were employ'd, in my time, in writing out Receipts, or
working Beds, Chairs, and Hangings for the Family. For my Part, I have
ply'd my Needle these fifty Years, and by my good Will would never
have it out of my Hand. It grieves my Heart to see a couple of proud
idle Flirts sipping their Tea, for a whole Afternoon, in a Room hung
round with the Industry of their Great Grandmother. Pray,
Sir , take
the laudable Mystery of Embroidery into your serious Consideration,
and as you have a great deal of the Virtue of the last Age in you,
continue your Endeavours to reform the present.'
I am, &c.
In Obedience to the Commands of my venerable Correspondent, I have duly
weigh'd this important Subject, and promise my self, from the Arguments
here laid down,
all the fine Ladies of
England
will be ready, as
soon as their Mourning is over
, to appear covered with the Work of
their own Hands.
What a delightful Entertainment must it be to the Fair Sex, whom their
native Modesty, and the Tenderness of Men towards them, exempts from
Publick Business, to pass their Hours in imitating Fruits and Flowers,
and transplanting all the Beauties of Nature into their own Dress, or
raising a new Creation in their Closets and Apartments. How pleasing is
the Amusement of walking among the Shades and Groves planted by
themselves, in surveying Heroes slain by their Needle, or little Cupids
which they have brought into the World without Pain!
This is, methinks, the most proper way wherein a Lady can shew a fine
Genius, and I cannot forbear wishing, that several Writers of that Sex
had chosen to apply themselves rather to Tapestry than Rhime. Your
Pastoral Poetesses may vent their Fancy in Rural Landskips, and place
despairing Shepherds under silken Willows, or drown them in a Stream of
Mohair. The Heroick Writers may work up Battles as successfully, and
inflame them with Gold or stain them with Crimson. Even those who have
only a Turn to a Song or an Epigram, may put many valuable Stitches into
a Purse, and crowd a thousand Graces into a Pair of Garters.
If I may, without breach of good Manners, imagine that any pretty
Creature is void of Genius, and would perform her Part herein but very
awkardly, I must nevertheless insist upon her working, if it be only to
keep her out of Harm's way.
Another Argument for busying good Women in Works of Fancy, is, because
it takes them off from Scandal, the usual Attendant of Tea-Tables, and
all other unactive Scenes of Life. While they are forming their Birds
and Beasts, their Neighbours will be allowed to be the Fathers of their
own Children: And
Whig
and
Tory
will be but seldom mentioned, where
the great Dispute is, whether Blue or Red is the more proper Colour. How
much greater Glory would
Sophronia
do the General, if she would chuse
rather to work the Battle of
Blenheim
in Tapestry, than signalize her
self with so much Vehemence against those who are
Frenchmen
in their
Hearts.
A Third Reason that I shall mention, is the Profit that is brought to
the Family where these pretty Arts are encouraged. It is manifest that
this way of Life not only keeps fair Ladies from running out into
Expences, but is at the same time an actual Improvement. How memorable
would that Matron be, who should have it Inscribed upon her Monument,
'that she Wrought out the whole Bible in Tapestry, and died in a good
old Age, after having covered three hundred Yards of Wall in the
Mansion-House.'
The Premises being consider'd, I humbly submit the following Proposals
to all Mothers in
Great Britain
.
-
That no young Virgin whatsoever be allow'd to receive the Addresses
of her first Lover, but in a Suit of her own Embroidering.
-
That before every fresh Servant, she be oblig'd to appear with a
new Stomacher at the least.
-
That no one be actually married, till she hath the Child-bed
Pillows, &c. ready Stitched, as likewise the Mantle for the Boy quite
finished.
These Laws, if I mistake not, would effectually restore the decay'd Art
of Needle-work, and make the Virgins of
Great Britain
exceedingly
Nimble-finger'd in their Business.
There is a memorable Custom of the
Grecian
Ladies in this particular,
preserv'd in
Homer
, which I hope will have a very good Effect with my
Country-women. A Widow in Ancient Times could not, without Indecency,
receive a second Husband, till she had Woven a Shrowd for her deceased
Lord, or the next of Kin to him. Accordingly, the Chaste
Penelope
having, as she thought, lost
Ulysses
at Sea, she employed her time in
preparing a Winding-sheet for
Laertes
, the Father of her Husband. The
Story of her Web being very Famous, and yet not sufficiently known in
its several Circumstances, I shall give it to my Reader, as
Homer
makes one of her Wooers relate it.
Sweet Hope she gave to every Youth apart,
With well-taught Looks, and a deceitful Heart:
A Web she wove of many a slender Twine,
Of curious Texture, and perplext Design;
My Youths, she cry'd, my Lord but newly dead,
Forbear a while to court my widow'd Bed,
'Till I have wov'n, as solemn Vows require,
This Web, a Shrowd for poor Ulysses' Sir e.
His Limbs, when Fate the Hero's Soul demands,
Shall claim this Labour of his Daughter's Hands:
Lest all the Dames of Greece my Name despise,
While the great King without a Covering lies.
Thus she. Nor did my Friends mistrust the Guile.
All Day she sped the long laborious Toil:
But when the burning Lamps supply'd the Sun,
Each Night unravell'd what the Day begun.
Three live-long Summers did the Fraud prevail.
The Fourth her Maidens told th' amazing Tale.
These Eyes beheld, as close I took my Stand,
The backward Labours of her faithless Hand:
'Till watch'd at length, and press'd on every Side,
Her Task she ended, and commenc'd a Bride.
Footnote 1:
Public Mourning for Q. Anne, who died Aug. 1, 1714.
Contents
Dicite Iö Pæan, et Iö bis dicite Pæan:
Decidit in casses præda petita meos.
Ovid.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Having in your Paper of
Monday last published my Report on the
Case of Mrs.
Fanny Fickle, wherein I have taken Notice, that Love
comes after Marriage; I hope your Readers are satisfied of this Truth,
that as Love generally produces Matrimony, so it often happens that
Matrimony produces Love.
'It perhaps requires more Virtues to make a good Husband or Wife, than
what go the finishing any the most shining Character whatsoever.
'Discretion seems absolutely necessary, and accordingly we find that
the best Husbands have been most famous for their Wisdom.
Homer, who
hath drawn a perfect Pattern of a prudent Man, to make it the more
compleat, hath celebrated him for the just Returns of Fidelity and
Truth to his
Penelope; insomuch that he refused the Caresses of a
Goddess for her sake, and to use the Expression of the best of Pagan
Authors,
vetulam suam prætulit Immortalitati, his old Woman was
dearer to him than Immortality.
'Virtue is the next necessary Qualification for this domestick
Character, as it naturally produces Constancy and mutual Esteem. Thus
Brutus and
Porcia were more remarkable for Virtue and Affection
than any others of the Age in which they lived.
'Good-Nature is a third necessary Ingredient in the Marriage-State,
without which it would inevitably sower upon a thousand Occasions.
When Greatness of Mind is joined with this amiable Quality, it
attracts the Admiration and Esteem of all who behold it. Thus
Cæsar,
not more remarkable for his Fortune and Valour than for his Humanity,
stole into the Hearts of the
Roman People, when breaking through the
Custom, he pronounced an Oration at the Funeral of his first and best
beloved Wife.
'Good-Nature is insufficient, unless it be steady and uniform, and
accompanied with an Evenness of Temper, which is, above all things, to
be preserved in this Friendship contracted for Life. A Man must be
easie within himself, before he can be so to his other self.
Socrates, and
Marcus Aurelius, are Instances of Men, who, by the
Strength of Philosophy, having entirely composed their Minds, and
subdued their Passions, are celebrated for good Husbands,
notwithstanding the first was yoked with
Xantippe, and the other
with
Faustina. If the wedded Pair would but habituate themselves for
the first Year to bear with one another's Faults, the Difficulty would
be pretty well conquer'd. This mutual Sweetness of Temper and
Complacency, was finely recommended in the Nuptial Ceremonies among
the Heathens, who, when they sacrificed to
Juno at that Solemnity,
always tore out the Gaul from the Entrails of the Victim, and cast it
behind the Altar.
'I shall conclude this Letter with a Passage out of Dr.
Plot's
Natural History of Staffordshire, not only as it will serve to fill
up your present Paper; but if I find my self in the Humour, may give
Rise to another; I having by me an old Register, belonging to the
Place here under-mentioned.'
Sir Philip de Somervile held the Manors of Whichenovre,
Scirescot, Ridware, Netherton, and Cowlee, all in Com.
Stafford, of the Earls of Lancaster, by this memorable Service.
The said Sir Philip shall find, maintain, and sustain, one Bacon
Flitch, hanging in his Hall at Whichenovre ready arrayed all
times of the Year, but in Lent, to be given to every Man or Woman
married, after the Day and the Year of their Marriage be past, in
Form following.
Whensoever that any one such before named will come to enquire for
the Bacon, in their own Person, they shall come to the Bailiff, or
to the Porter of the Lordship of Whichenovre, and shall say to
them in the manner as ensueth;
'Bayliff, or Porter, I doo you to know, that I am come for my self,
to demand one Bacon Flyke hanging in the Hall of the Lord of
Whichenovre, after the Form thereunto belonging.'
After which Relation, the Bayliff or Porter shall assign a Day to
him, upon Promise by his Faith to return, and with him to bring
Twain of his Neighbours. And in the mean Time the said Bailiff shall
take with him Twain of the Freeholders of the Lordship of
Whichenovre, and they three shall go to the Manor of Rudlow,
belonging to Robert Knightleye, and there shall summon the
aforesaid Knightleye, or his Bayliff, commanding him to be ready
at Whichenovre the Day appointed, at Prime of Day, with his
Carriage, that is to say, a Horse and a Saddle, a Sack and a Pryke,
for to convey the said Bacon and Corn a Journey out of the County of
Stafford, at his Costages. And then the said Bailiff shall, with
the said Freeholders, summon all the Tenants of the said Manor, to
be ready at the Day appointed, at Whichenovre, for to do and
perform the Services which they owe to the Bacon. And at the Day
assigned, all such as owe Services to the Bacon, shall be ready at
the Gate of the Manor of Whichenovre, from the Sun-rising to Noon,
attending and awaiting for the coming of him who fetcheth the Bacon.
And when he is come, there shall be delivered to him and his
Fellows, Chapelets; and to all those which shall be there, to do
their Services due to the Bacon. And they shall lead the said
Demandant with Trumps and Tabours, and other manner of Minstrels to
the Hall-Door, where he shall find the Lord of Whichenovre, or his
Steward, ready to deliver the Bacon in this Manner.
He shall enquire of him, which demandeth the Bacon, if he have
brought twain of his Neighbours with him: Which must answer, They
be here ready. And then the Steward shall cause these two
Neighbours to swear, if the said Demandant be a wedded Man, or have
been a Man wedded; and if since his Marriage one Year and a Day be
past; and if he be a Free-man, or a Villain. And if his said
Neighbours make Oath, that he hath for him all these three Points
rehearsed; then shall the Bacon be taken down and brought to the
Hall-Door, and shall there be laid upon one half Quarter of Wheat,
and upon one other of Rye. And he that demandeth the Bacon shall
kneel upon his Knee, and shall hold his right Hand upon a Book,
which Book shall be laid upon the Bacon and the Corn, and shall make
Oath in this manner.
'Here ye, Sir Philip de Somervile, Lord of Whichenovre,
mayntener and gyver of this Baconne: That I A sithe I Wedded B
my Wife, and sithe I had hyr in my kepyng, and at my Wylle, by a
Year and a Day after our Marriage, I would not have chaunged for
none other; farer ne fowler; richer, ne pourer; ne for none other
descended of greater Lynage; slepyng ne wakyng, at noo tyme. And if
the seyd B were sole and I sole I would take her to be my Wife
before all the Wymen of the Worlde, of what condiciones soever they
be: good or evylle, as help me God ond his Seyntes, and this Flesh
and all Fleshes.'
And his Neighbours shall make Oath, that they trust verily he hath
said truly. And if it be found by his Neighbours before-named that
he be a Free-man, there shall be delivered to him half a Quarter of
Wheat and a Cheese; and if he be a Villain, he shall have half a
Quarter of Rye without Cheese. And then shall Knightleye the Lord
of Rudlow be called for, to carry all these Things tofore
rehearsed; and the said Corn shall be laid on one Horse and the
Bacon above it: and he to whom the Bacon appertaineth shall ascend
upon his Horse; and shall take the Cheese before him if he have a
Horse. And if he have none, the Lord of Whichenovre shall cause
him to have one Horse and Saddle, to such time as he be past his
Lordship: and so shall they depart the Manor of Whichenovre with
the Corn and the Bacon, tofore him that hath won it, with Trumpets,
Tabourets, and other manner of Minstrelsie. And all the Free Tenants
of Whichenovre shall Conduct him to be passed the Lordship of
Whichenovre. And then shall they all return; except him, to whom
appertained to make the Carriage and Journey without the County of
Stafford, at the Costs of his Lord of Whichenovre.
Contents
|
Monday, October 18, 1714 |
Addison1 |
—Perjuria ridet Amantum—
Ovid.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'According to my Promise, I herewith transmit to you a List of several
Persons, who from time to time demanded the
Flitch of Bacon of
Sir
Philip de Somervile and his Descendants; as it is preserved in an
ancient Manuscript under the Title of
The Register of
Whichenovre-Hall, and of the Bacon Flitch there maintained.
'In the Beginning of this Record is recited the Law or Institution in
Form, as it is already printed in your
last Paper: To which are added
Two By-Laws, as a Comment upon the General Law, the Substance whereof
is, that the Wife shall take the same Oath as the Husband,
mutatis
mutandis; and that the Judges shall, as they think meet, interrogate
or cross-examine the Witnesses. After this proceeds the Register in
Manner following.
'Aubry de Falstaff,
Son of Sir John Falstaff,
Kt. with Dame Maude
his Wife, were the first that demanded the Bacon, he having bribed
twain of his Father's Companions to swear falsly in his Behoof whereby
he gained the Flitch: But he and his said Wife falling immediately
into a Dispute how the said Bacon should be dressed, it was by Order
of the Judges taken from him, and hung up again in the Hall.
'Alison
the Wife of Stephen Freckle,
brought her said Husband along
with her, and set forth the good Conditions and Behaviour of her
Consort, adding withal that she doubted not but he was ready to attest
the like of her, his Wife; whereupon he, the said Stephen,
shaking
his Head, she turned short upon him, and gave him a Box on the Ear.
'Philip de Waverland,
having laid his Hand upon the Book, when the
Clause, Were I sole and she sole,
was rehearsed, found a secret
Compunction rising in his Mind, and stole it off again.
'Richard de Loveless,
who was a Courtier, and a very wellbred Man,
being observed to hesitate at the Words after our Marriage,
was
thereupon required to explain himself. He reply'd, by talking very
largely of his exact Complaisance while he was a Lover; and alledg'd,
that he had not in the least disobliged his Wife for a Year and a Day
before Marriage,
which he hoped was the same Thing.
'Rejected.
'Joceline Jolly, Esq.,
making it appear by unquestionable Testimony,
That he and his Wife had presented full and entire Affection for the
Space of the first Month, commonly called the Honey-Moon;
he had in
Consideration thereof one Rasher bestowed upon him.
'After this, says the Record, many Years passed over before any
Demandant appeared at
Whichenovre-Hall; insomuch that one would have
thought that the whole Country were turned
Jews, so little was their
Affection to the Flitch of Bacon.
'The next Couple enrolled had like to have carried it, if one of the
Witnesses had not deposed, That dining on a
Sunday with the
Demandant, whose Wife had sate below the Squire's Lady at Church, she
the said Wife dropped some Expressions, as if she thought her Husband
deserved to be knighted; to which he returned a passionate
Pish! The
Judges taking the Premises into Consideration, declared the aforesaid
Behaviour to imply an unwarrantable Ambition in the Wife, and Anger in
the Husband.
'It is recorded as a sufficient Disqualification of a certain Wife,
that speaking of her Husband, she said,
God forgive him.
'It is likewise remarkable, that a Couple were rejected upon the
Deposition of one of their Neighbours, that the Lady had once told her
Husband, that
it was her Duty to obey; to which he replied,
Oh! my
Dear, you are never in the wrong.
'The violent Passion of one Lady for her Lap-Dog; the turning away of
the old House-Maid by another; a Tavern-Bill torn by the Wife, and a
Taylor's by the Husband; a Quarrel about the Kissing-Crust; spoiling
of Dinners, and coming in late of Nights; are so many several Articles
which occasioned the Reprobation of some Scores of Demandants, whose
Names are recorded in the aforesaid Register.
'Without enumerating other particular Persons, I shall content my self
with observing, that the Sentence pronounced against one
Gervase
Poacher is, that
he might have had Bacon to his Eggs, if he had not
heretofore scolded his Wife when they were over boiled. And the
Deposition against
Dorothy Dolittle runs in these Words;
That she
had so far usuped the Dominion of the Coalfire, (the Stirring whereof
her Husband claimed to himself) that by her good Will she never would
suffer the Poker out of her Hand.
'I find but two Couples, in this first Century, that were successful:
The first, was a Sea-Captain and his Wife, who since the Day of their
Marriage, had not seen one another till the Day of the Claim. The
Second, was an honest Pair in the Neighbourhood; The Husband was a Man
of plain good Sense, and a peaceable Temper; the Woman was dumb.'
Footnote 1:
Lord Macaulay, in a letter published p. 1433 ... of Mr.
Bohn's edition of Lowndes's
Bibliographer's Manual
, calls this paper
'undoubtedly Addison's, and one of his best,' although not claimed,
because he could not own it without admitting what Lord Macaulay rightly
considered quite as obvious, his authorship of
. Addison wrote,
evidently, some other of these unappropriated papers.
Contents
|
Wednesday, October 20, 1714 |
|
—Farrago libelli—
Juv.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I
have for some Time de
Sir ed to appear in your Paper, and have
therefore chosen a Day
1 to steal into the SPECTATOR, when I take it
for granted you will not have many spare Minutes for Speculations of
your own. As I was the other Day walking with an honest
Country-Gentleman, he very often was expressing his Astonishment to
see the Town so mightily crowded with Doctors of Divinity: Upon which
I told him he was very much mistaken if he took all those Gentlemen he
saw in Scarfs to be Persons of that Dignity; for, that a young Divine,
after his first Degree in the University, usually comes hither only to
show himself; and on that Occasion is apt to think he is but half
equipp'd with a Gown and Cassock for his publick Appearance, if he
hath not the additional Ornament of a Scarf of the first Magnitude to
intitle him to the Appellation of Doctor from his Landlady and the Boy
at
Childs. Now since I know that this Piece of Garniture is looked
upon as a Mark of Vanity or Affectation, as it is made use of among
some of the little spruce Adventurers of the Town, I should be glad if
you would give it a Place among those Extravagancies you have justly
exposed in several of your Papers: being very well assured that the
main Body of the Clergy, both in the Country and the Universities, who
are almost to a Man untainted with it, would be very well pleased to
see this Venerable Foppery well exposed. When my Patron did me the
Honour to take me into his Family, (for I must own my self of this
Order) he was pleased to say he took me as a Friend and Companion; and
whether he looked upon the Scarf like the Lace and Shoulder-knot of a
Footman, as a Badge of Servitude and Dependance, I do not know, but he
was so kind as to leave my wearing of it to my own Discretion; and not
having any just Title to it from my Degrees, I am content to be
without the Ornament. The Privileges of our Nobility to keep a certain
Number of Chaplains are undisputed, though perhaps not one in ten of
those reverend Gentlemen have any Relation to the noble Families their
Scarfs belong to; the Right generally of creating all Chaplains except
the Domestick, where there is one, being nothing more than the
Perquisite of a Steward's Place, who, if he happens to out-live any
considerable Number of his noble Masters, shall probably, at one and
the same Time, have fifty Chaplains, all in their proper
Accoutrements, of his own Creation; though perhaps there hath been
neither Grace nor Prayer said in the Family since the Introduction of
the first Coronet.'
I am, &c.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I wish you would write a Philosophical Paper about Natural
Antipathies, with a Word or two concerning the Strength of
Imagination. I can give you a List upon the first Notice, of a
Rational
China Cup, of an Egg that walks upon two Legs, and a Quart
Pot that sings like a Nightingale. There is in my Neighbourhood a very
pretty prattling Shoulder of Veal, that squawls out at the Sight of a
Knife. Then as for Natural Antipathies, I know a General Officer who
was never conquered but by a smother'd Rabbit; and a Wife that
domineers over her Husband by the Help of a Breast of Mutton. A Story
that relates to my self on this Subject may be thought not
unentertaining, especially when I assure you that it is literally
true. I had long made Love to a Lady, in the Possession of whom I am
now the happiest of Mankind, whose Hand I shou'd have gained with much
Difficulty without the Assistance of a Cat. You must know then, that
my most dangerous Rival had so strong an Aversion to this Species,
that he infallibly swooned away at the Sight of that harmless
Creature. My Friend Mrs.
Lucy, her Maid, having a greater Respect
for me and my Purse than she had for my Rival, always took Care to pin
the Tail of a Cat under the Gown of her Mistress, whenever she knew of
his coming; which had such an Effect, that every Time he entred the
Room, he looked more like one of the Figures in Mrs.
Salmon's
Wax-work, than a de
Sir able Lover. In short, he grew Sick of her
Company; which the young Lady taking Notice of, (who no more knew why,
than he did) she sent me a Challenge to meet her in
Lincoln's-Inn
Chappel, which I joyfully accepted, and have (amongst other Pleasures)
the Satisfaction of being praised by her for my Stratagem, I am, &c.'
From the Hoop.
Tom. Nimble.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The Virgins of
Great Britain are very much oblig'd to you for
putting them upon such tedious Drudgeries in Needlework as were fit
only for the
Hilpa's and the
Nilpa's that lived before the Flood.
Here's a stir indeed with your Histories in Embroidery, your Groves
with Shades of Silk and Streams of Mohair! I would have you to know,
that I hope to kill a hundred Lovers before the best Housewife in
England can stitch out a Battel, and do not fear but to provide Boys
and Girls much faster than your Disciples can embroider them. I love
Birds and Beasts as well as you, but am content to fancy them when
they are really made. What do you think of Gilt Leather for Furniture?
There's your pretty Hangings for a Chamber
2; and what is more, our
own Country is the only Place in
Europe where Work of that kind is
tolerably done. Without minding your musty Lessons: I am this Minute
going to
Paul's Church-Yard to bespeak a Skreen and a Set of
Hangings; and am resolved to encourage the Manufacture of my Country.'
Yours,
Cleora.
Footnote 1:
Oct. 20, 1714, was the day of the Coronation of George I.
Footnote 2:
There was at this time a celebrated manufactory of tapestry
at Chelsea.
Contents
Sic, cum transierint mei
Nullo cum strepitu dies,
Plebeius moriar senex.
Illi mors gravis incubat,
Qui, notus nimis omnibus,
Ignotus moritur sibi.
Seneca.

I have often wondered that the
Jews
should contrive such a worthless
Greatness for the Deliverer whom they expected, as to dress him up in
external Pomp and Pageantry, and represent him to their Imagination, as
making Havock amongst his Creatures, and acted with the poor Ambition of
a
Cæsar
or an
Alexander
. How much more illustrious doth he appear in
his real Character, when considered as the Author of universal
Benevolence among Men, as refining our Passions, exalting our Nature,
giving us vast Ideas of Immortality, and teaching us a Contempt of that
little showy Grandeur, wherein the
Jews
made the Glory of their
Messiah to consist!
Nothing
(says
Longinus
)
can be Great, the Contempt of which is
Great
. The Possession of Wealth and Riches cannot give a Man a Title to
Greatness, because it is looked upon as a Greatness of Mind, to contemn
these Gifts of Fortune, and to be above the De
Sir
e of them. I have
therefore been inclined to think, that there are greater Men who lie
concealed among the Species, than those who come out, and draw upon
themselves the Eyes and Admiration of Mankind.
Virgil
would never have
been heard of, had not his Domestick Misfortunes driven him out of his
Obscurity, and brought him to
Rome
.
If we suppose that there are Spirits or Angels who look into the Ways of
Men, as it is highly probable there are, both from Reason and
Revelation; how different are the Notions which they entertain of us,
from those which we are apt to form of one another? Were they to give us
in their Catalogue of such Worthies as are now living, how different
would it be from that, which any of our own Species would draw up?
We are dazled with the Splendour of Titles, the Ostentation of Learning,
the Noise of Victories; They, on the contrary, see the Philosopher in
the Cottage, who possesses his Soul in Patience and Thankfulness, under
the Pressure of what little Minds call Poverty and Distress. They do not
look for great Men at the Head of Armies, or among the Pomps of a Court,
but often find them out in Shades and Solitudes, in the private Walks
and By-paths of Life. The Evening's Walk of a wise Man is more
illustrious in their Sight, than the March of a General at the Head of a
hundred thousand Men. A Contemplation of God's Works; a voluntary Act of
Justice to our own Detriment; a generous Concern for the Good of
Mankind; Tears that are shed in Silence for the Misery of others; a
private De
Sir
e or Resentment broken and subdued; in short, an unfeigned
Exercise of Humility, or any other Virtue; are such Actions as are
glorious in their Sight, and denominate Men great and reputable. The
most famous among us are often looked upon with Pity, with Contempt, or
with Indignation; while those who are most obscure among their own
Species, are regarded with Love, with Approbation and Esteem.
The Moral of the present Speculation amounts to this, That we should not
be led away by the Censures and Applauses of Men, but consider the
Figure that every Person will make, at that Time when Wisdom shall be
justified of her Children, and nothing pass for Great or Illustrious,
which is not an Ornament and Perfection to humane Nature.
The Story of
Gyges
the rich
Lydian
Monarch, is a memorable Instance
to our present Purpose. The Oracle being asked by
Gyges
, who was the
happiest Man, replied
Aglaüs
.
Gyges
, who expected to have heard
himself named on this Occasion, was much surprized, and very curious to
know who this
Aglaüs
should be. After much Enquiry he was found to be
an obscure Countryman, who employ'd all his Time in cultivating a
Garden, and a few Acres of Land about his House.
Cowley's
agreeable Relation of this Story shall close this Day's
Speculation.
Thus Aglaüs (a Man unknown to Men,
But the Gods knew, and therefore lov'd him then)
Thus liv'd obscurely then without a Name,
Aglaüs, now consign'd t' eternal Fame.
For Gyges, the rich King, wicked and great,
Presum'd at wise Apollo's Delphick Seat,
Presum'd to ask, Oh thou, the whole World's Eye,
See'st thou a Man that happier is than I?
The God, who scorned to flatter Man, reply'd,
Aglaüs happier is. But Gyges cry'd,
In a proud Rage, Who can that Aglaüs be?
We've heard as yet of no such King as he.
And true it was, through the whole Earth around,
No King of such a Name was to be found.
Is some old Hero of that Name alive,
Who his high Race does from the Gods derive?
Is it some mighty Gen'ral, that has done
Wonders in Fight, and God-like Honours won?
Is it some Man of endless Wealth? said he:
None, none of these; who can this Aglaüs be?
After long Search, and vain Enquiries past,
In an obscure Arcadian Vale at last,
(Th' Arcadian Life has always shady been)
Near Sopho's Town (which he but once had seen)
This Aglaüs, who Monarchs Envy drew,
Whose Happiness the Gods stood Witness to,
This mighty Aglaüs was lab'ring found,
With his own Hands, in his own little Ground.
So, gracious God, (if it may lawful be,
Among those foolish Gods to mention thee)
So let me act, on such a private Stage,
The last dull Scenes of my declining Age;
After long Toils and Voyages in vain,
This quiet Port let my toss'd Vessel gain;
Of heav'nly Rest, this Earnest to me lend,
Let my Life sleep, and learn to love her End.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Perfide! sed duris genuit te cautibus horrens
Caucasus, Hircanæque admórunt ubera tigres.
Virg.

I am willing to postpone every thing, to do any the least Service for
the Deserving and Unfortunate. Accordingly I have caused the following
Letter to be inserted in my Paper the Moment that it came to my Hands,
without altering one Tittle in an Account which the Lady relates so
handsomely her self.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I flatter my self, you will not only pity, but, if possible, redress
a Misfortune my self and several others of my Sex lie under. I hope
you will not be offended, nor think I mean by this to justifie my own
imprudent Conduct, or expect You should. No! I am sensible how
severely, in some of your former Papers, you have reproved Persons
guilty of the like Mismanagements. I was scarce Sixteen, and, I may
say without Vanity, Handsome, when courted by a false perjured Man;
who, upon Promise of Marriage, rendered me the most unhappy of Women.
After he had deluded me from my Parents, who were People of very good
Fashion, in less than three Months he left me. My Parents would not
see, nor hear from me; and had it not been for a Servant, who had
lived in our Family, I must certainly have perished for want of Bread.
However, it pleased Providence, in a very short time, to alter my
miserable Condition. A Gentleman saw me, liked me, and married me. My
Parents were reconciled; and I might be as happy in the Change of my
Condition, as I was before miserable, but for some things, that you
shall know, which are insupportable to me; and I am sure you have so
much Honour and Compassion as to let those Persons know, in some of
your Papers, how much they are in the wrong. I have been married near
five Years, and do not know that in all that time I ever went abroad
without my Husband's Leave and Approbation. I am obliged, through the
Importunities of several of my Relations, to go abroad oftner than
suits my Temper. Then it is, I labour under insupportable Agonies.
That Man, or rather Monster, haunts every Place I go to. Base Villain!
By reason I will not admit his nauseous wicked Visits and
Appointments, he strives all the ways he can to ruin me. He left me
destitute of Friend or Money, nor ever thought me worth enquiring
after, till he unfortunately happened to see me in a Front Box,
sparkling with Jewels. Then his Passion returned. Then the Hypocrite
pretended to be a Penitent. Then he practised all those Arts that
helped before to undo me. I am not to be deceived a second time by
him. I hate and abhor his odious Passion; and, as he plainly perceives
it, either out of Spight or Diversion, he makes it his Business to
expose me. I never fail seeing him in all publick Company, where he is
always most industriously spightful. He hath, in short, told all his
Acquaintance of our unhappy Affair, they tell theirs; so that it is no
Secret among his Companions, which are numerous. They, to whom he
tells it, think they have a Title to be very familiar. If they bow to
me, and I out of good Manners return it, then I am pester'd with
Freedoms that are no ways agreeable to my self or Company. If I turn
my Eyes from them, or seem displeased, they sower upon it, and whisper
the next Person; he his next; 'till I have at last the Eyes of the
whole Company upon me. Nay, they report abominable Falshoods, under
that mistaken Notion, She that will grant Favours to one Man, will to
a hundred. I beg you will let those who are guilty, know, how
ungenerous this way of Proceeding is. I am sure he will know himself
the Person aim'd at, and perhaps put a stop to the Insolence of
others. Cursed is the Fate of unhappy Women! that Men may boast and
glory in those things that we must think of with Shame and Horror! You
have the Art of making such odious Customs appear detestable. For my
Sake, and I am sure, for the Sake of several others, who dare not own
it, but, like me, lie under the same Misfortunes, make it as infamous
for a Man to boast of Favours, or expose our Sex, as it is to take the
Lie or a Box on the Ear, and not resent it.'
Your Constant Reader,
and Admirer,
Lesbia.
P. S. 'I am the more Impatient under this Misfortune, having receiv'd
fresh Provocation, last Wednesday, in the Abbey.'
I entirely agree with the amiable and unfortunate
Lesbia
, that an
Insult upon a Woman in her Circumstances, is as infamous in a Man, as a
tame Behaviour when the Lie or a Buffet is given; which Truth, I shall
beg leave of her to illustrate by the following Observation.
It is a Mark of Cowardice passively to forbear resenting an Affront, the
Resenting of which would lead a Man into Danger; it is no less a Sign of
Cowardice to affront a Creature, that hath not Power to avenge it self.
Whatever Name therefore this ungenerous Man may bestow on the helpless
Lady he hath injur'd, I shall not scruple to give him in return for it,
the Appellation of
Coward.
A Man, that can so far descend from his Dignity, as to strike a Lady,
can never recover his Reputation with either Sex, because no Provocation
is thought strong enough to justifie such Treatment from the Powerful
towards the Weak. In the Circumstances, in which poor
Lesbia
is
situated, she can appeal to no Man whatsoever to avenge an Insult, more
grievous than a Blow. If she could open her Mouth, the base Man knows,
that a Husband, a Brother, a generous Friend would die to see her
righted.
A generous Mind, however enrag'd against an Enemy, feels its Resentments
sink and vanish away, when the Object of its Wrath falls into its Power.
An estranged Friend, filled with Jealousie and Discontent towards a
Bosom-Acquaintance, is apt to overflow with Tenderness and Remorse, when
a Creature, that was once dear to him, undergoes any Misfortune. What
Name then shall we give to his Ingratitude, (who forgetting the Favours
he sollicited with Eagerness, and receiv'd with Rapture) can insult the
Miseries that he himself caused, and make Sport with the Pain to which
he owes his greatest Pleasure? There is but one Being in the Creation
whose Province it is to practise upon the Imbecillities of frail
Creatures, and triumph in the Woes which his own Artifices brought
about; and we well know, those who follow his Example, will receive his
Reward.
Leaving my fair Correspondent to the Direction of her own Wisdom and
Modesty; and her Enemy, and his mean Accomplices, to the Compunction of
their own Hearts; I shall conclude this Paper with a memorable Instance
of Revenge, taken by a
Spanish
Lady upon a guilty Lover, which may
serve to show what violent Effects are wrought by the most tender
Passion, when sower'd into Hatred; and may deter the Young and unwary
from unlawful Love. The Story, however Romantick it may appear, I have
heard affirmed for a Truth.
Not many Years ago an
English
Gentleman, who in a Rencounter by Night
in the Streets of
Madrid
had the Misfortune to kill his Man, fled into
a Church-Porch for Sanctuary. Leaning against the Door, he was surprized
to find it open, and a glimmering Light in the Church. He had the
Courage to advance towards the Light; but was terribly startled at the
sight of a Woman in White who ascended from a Grave with a bloody Knife
in her Hand. The Phantome marched up to him, and asked him what he did
there. He told her the Truth, without reserve, believing that he had met
a Ghost: Upon which, she spoke to him in the following Manner.
'Stranger, thou art in my Power: I am a Murderer as thou art. Know then,
that I am a Nun of a noble Family. A base perjur'd Man undid me, and
boasted of it. I soon had him dispatched; but not content with the
Murder, I have brib'd the Sexton to let me enter his Grave, and have now
pluck'd out his False Heart from his Body; and thus I use a Traitor's
Heart.' At these Words she tore it in Pieces, and trampled it under her
Feet.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, October 27, 1714 |
|
Murranum hic atavos et avorum antiqua sonantem
Nomina per regesque actum genus omne Latinos,
Præcipitem scopulo, atque ingentis turbine saxi
Excutit, effunditque solo.
Virg.

It is highly laudable to pay Respect to Men who are descended from
worthy Ancestors, not only out of Gratitude to those who have done Good
to Mankind, but as it is an Encouragement to others to follow their
Example. But this is an Honour to be receiv'd, not demanded, by the
Descendants of great Men; and they who are apt to remind us of their
Ancestors, only put us upon making Comparisons to their own
Disadvantage.
There is some Pretence for boasting of Wit, Beauty, Strength or Wealth,
because the Communication of them may give Pleasure or Profit to others;
but we can have no Merit, nor ought we to claim any Respect, because our
Fathers acted well, whether we would or no.
The following Letter ridicules the Folly I have mentioned, in a new,
and, I think, not disagreeable Light.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Were the Genealogy of every Family preserved, there would probably be
no Man valued or despis'd on Account of his Birth. There is scarce a
Beggar in the Streets, who would not find himself lineally descended
from some great Man; nor any one of the highest Title, who would not
discover several base and indigent Persons among his Ancestors. It
would be a pleasant Entertainment to see one Pedigree of Men appear
together, under the same Characters they bore when they acted their
respective Parts among the Living. Suppose therefore a Gentleman, full
of his illustrious Family, should, in the same manner as
Virgil
makes
Æneas look over his Descendants, see the whole Line of his
Progenitors pass in a Review before his Eyes, and with how many
varying Passions would he behold Shepherds and Soldiers, Statesmen and
Artificers, Princes and Beggars, walk in the Procession of five
thousand Years! How would his Heart sink or flutter at the several
Sports of Fortune in a Scene so diversified with Rags and Purple,
Handicraft Tools and Scepters, Ensigns of Dignity and Emblems of
Disgrace; and how would his Fears and Apprehensions, his Transports
and Mortifications, succeed one another, as the Line of his Genealogy
appear'd bright or obscure?
'In most of the Pedigrees hung up in old Mansion Houses, you are sure
to find the first in the Catalogue a great Statesman, or a Soldier
with an honourable Commission. The Honest Artificer that begot him,
and all his frugal Ancestors before him, are torn off from the Top of
the Register; and you are not left to imagine, that the noble Founder
of the Family ever had a Father. Were we to trace many boasted Lines
farther backwards, we should lose them in a Mob of Tradesmen, or a
Crowd of Rusticks, without hope of seeing them emerge again: Not
unlike the old
Appian Way, which after having run many Miles in
Length, loses it self in a Bog.
'I lately made a Visit to an old Country Gentleman, who is very far
gone in this sort of
Family Madness. I found him in his Study
perusing an old Register of his Family, which he had just then
discover'd, as it was branched out in the Form of a Tree, upon a Skin
of Parchment. Having the Honour to have some of his Blood in my Veins,
he permitted me to cast my Eye over the Boughs of this venerable
Plant; and asked my Advice in the Reforming of some of the superfluous
Branches.
'We passed slightly over three or four of our immediate Fore-fathers,
whom we knew by Tradition, but were soon stopped by an Alderman of
London, who, I perceived, made my Kinsman's Heart go pit-a-pat. His
Confusion increased when he found the Alderman's Father to be a
Grasier; but he recovered his Fright upon seeing
Justice of the
Quorum at the end of his Titles. Things went on pretty well, as we
threw our Eyes occasionally over the Tree, when unfortunately he
perceived a Merchant-Tailor perched on a Bough, who was said greatly
to have encreased the Estate; he was just a going to cut him off, if
he had not seen
Gent. after the Name of his Son; who was recorded to
have mortgaged one of the Manors his honest Father had purchased. A
Weaver, who was burnt for his Religion in the Reign of Queen
Mary,
was pruned away without Mercy; as was likewise a Yeoman, who died of a
Fall from his own Cart. But great was our Triumph in one of the Blood
who was beheaded for High-Treason; which nevertheless was not a little
allayed by another of our Ancestors, who was hanged for stealing
Sheep. The Expectations of my good Cousin were wonderfully raised by a
Match into the Family of a Knight, but unfortunately for us this
Branch proved Barren: On the other hand
Margery the Milk-maid being
twined round a Bough, it flourished out into so many Shoots, and bent
with so much Fruit, that the old Gentleman was quite out of
Countenance. To comfort me, under this Disgrace, he singled out a
Branch ten times more fruitful than the other, which, he told me, he
valued more than any in the Tree, and bad me be of good Comfort. This
enormous Bough was a Graft out of a
Welsh Heiress, with so many
Ap's upon it that it might have made a little Grove by it self. From
the Trunk of the Pedigree, which was chiefly composed of Labourers and
Shepherds, arose a huge Sprout of Farmers; this was branched out into
Yeomen; and ended in a Sheriff of the County, who was Knighted for his
good Service to the Crown, in bringing up an Address. Several of the
Names that seemed to disparage the Family, being looked upon as
Mistakes, were lopped off as rotten or withered; as, on the contrary,
no small Number appearing without any Titles, my Cousin, to supply the
Defects of the Manuscript, added
Esq; at the End of each of them.
'This Tree so pruned, dressed, and cultivated, was, within few Days,
transplanted into a large Sheet of Vellum and placed in the great
Hall, where it attracts the Veneration of his Tenants every
Sunday
Morning, while they wait till his Worship is ready to go to Church;
wondering that a Man who had so many Fathers before him, should not be
made a
Knight1, or at least a Justice of the Peace.'
Footnote 1:
Lord,
Contents
Contents, p. 8
—Studiis florentem ignobilis oti—
Virg.

It is reckoned a Piece of Ill-breeding for one Man to engross the whole
Talk to himself. For this Reason, since I keep three Visiting-Days in
the Week, I am content now and then to let my Friends put in a Word.
There are several Advantages hereby accruing both to my Readers and my
self. As first, Young and modest Writers have an Opportunity of getting
into Print: Again, The Town enjoys the Pleasure of Variety; and
Posterity will see the Humour of the present Age, by the help of these
little Lights into private and domestick Life. The Benefits I receive
from thence, are such as these: I gain more Time for future
Speculations; pick up Hints which I improve for the publick Good; give
Advice; redress Grievances; and, by leaving commodious Spaces between
the several Letters that I print, furnish out a
Spectator
with little
Labour and great Ostentation.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'I was mightily pleased with your Speculation of
Friday. Your
Sentiments are Noble, and the whole worked up in such a manner, as
cannot but strike upon every Reader. But give me leave to make this
Remark: That while you write so Pathetically on Contentment, and a
retired Life, you sooth the Passion of Melancholy, and depress the
Mind from Actions truly Glorious. Titles and Honours are the Reward of
Virtue: We therefore ought to be affected with them: And tho' light
Minds are too much puffed up with exterior Pomp, yet I cannot see why
it is not as truly Philosophical, to admire the glowing Ruby, or the
sparkling Green of an Emerald, as the fainter and less permanent
Beauties of a Rose or a Myrtle. If there are Men of extraordinary
Capacities who lye concealed from the World, I should impute it to
them as a Blot in their Character, did not I believe it owing to the
Meanness of their Fortune rather than of their Spirit.
Cowley, who
tells the Story of
Aglaüs with so much Pleasure, was no Stranger to
Courts, nor insensible of Praise.
What shall I do to be for ever known,
And make the Age to come my own?
was the Result of a laudable Ambition. It was not till after frequent
Disappointments, that he termed himself the Melancholy
Cowley; and
he praised Solitude, when he despair'd of shining in a Court. The Soul
of Man is an active Principle. He therefore, who withdraws himself
from the Scene before he has play'd his Part, ought to be hissed off
the Stage, and cannot be deemed Virtuous, because he refuses to answer
his End. I must own I am fired with an honest Ambition to imitate
every illustrious Example. The Battles of
Blenheim and
Ramillies
have more than once made me wish my self a Soldier. And when I have
seen those Actions so nobly celebrated by our Poets, I have secretly
aspir'd to be one of that distinguished Class. But in vain I wish, in
vain I pant with the De
Sir e of Action. I am chained down in Obscurity,
and the only Pleasure I can take is in seeing so many brighter
Genius's join their friendly Lights, to add to the Splendor of the
Throne. Farewel then dear
Spec, and believe me to be with great
Emulation, and no Envy,'
Your profess'd Admirer,
Will. Hopeless.
Middle-Temple, October 26, 1714.
Sir ,
'Tho' you have formerly made
Eloquence the Subject of one or more of
your Papers, I do not remember that you ever consider'd it as
possessed by a Set of People, who are so far from making
Quintilian's Rules their Practice, that, I dare say for them, they
never heard of such an Author, and yet are no less Masters of it than
Tully or
Demosthenes among the Ancients, or whom you please
amongst the Moderns. The Persons I am speaking of are our common
Beggars about this Town; and that what I say is true, I appeal to any
Man who has a Heart one Degree softer than a Stone. As for my part,
who don't pretend to more Humanity than my Neighbours, I have
oftentimes gone from my Chambers with Money in my Pocket, and returned
to them not only Pennyless, but destitute of a Farthing, without
bestowing of it any other way than on these seeming Objects of Pity.
In short, I have seen more Eloquence in a
Look from one of these
despicable Creatures, than in the
Eye of the fairest
She I ever
saw, yet no one is a greater Admirer of that Sex than my self. What I
have to de
Sir e of you is, to lay down some Directions in order to
guard against these powerful Orators, or else I know nothing to the
contrary but I must my self be forced to leave the Profession of the
Law, and endeavour to get the Qualifications necessary to that more
profitable one of Begging. But in which soever of these two Capacities
I shine, I shall always de
Sir e to be your constant Reader, and ever
will be'
Your most humble Servant,
J. B.
Sir ,
'Upon Reading a
Spectator last Week, where Mrs.
Fanny Fickle
submitted the Choice of a Lover for Life to your decisive
Determination, and imagining I might claim the Favour of your Advice
in an Affair of the like, but much more difficult Nature, I called for
Pen and Ink, in order to draw the Characters of Seven Humble Servants,
whom I have equally encouraged for some time. But alas! while I was
reflecting on the agreeable Subject, and contriving an advantageous
Description of the dear Person I was most inclined to favour, I
happened to look into my Glass. The sight of the Small-Pox, out of
which I am just recovered, tormented me at once with the loss of my
captivating Arts and my Captives. The Confusion I was in, on this
unhappy, unseasonable Discovery, is inexpressible. Believe me,
Sir , I
was so taken up with the Thoughts of your fair Correspondent's Case,
and so intent on my own Design, that I fancied myself as Triumphant in
my Conquests as ever.
'Now,
Sir , finding I was incapacitated to Amuse my self on that
pleasing Subject, I resolved to apply my self to you, or your
Casuistical Agent, for Advice in my present Circumstances. I am
sensible the Tincture of my Skin, and the Regularity of my Features,
which the Malice of my late Illness has altered, are irrecoverable;
yet don't despair, but that Loss, by your Assistance, may in some
measure be reparable, if you'll please to propose a way for the
Recovery of one only of my Fugitives.
'One of them is in a more particular Manner beholden to me than the
rest; he for some private Reasons being de
Sir ous to be a Lover
incognito, always addressed me with
Billet-Doux, which I was so
careful of in my Sickness, that I secured the Key of my Love-Magazine
under my Head, and hearing a noise of opening a Lock in my Chamber,
indangered my Life by getting out of Bed, to prevent, if it had been
attempted, the Discovery of that Amour.
'I have formerly made use of all those Artifices, which our Sex daily
practises over yours, to draw, as it were undesignedly, the eyes of a
whole Congregation to my Pew; I have taken a Pride in the number of
Admirers at my Afternoon Levée; but am now quite another Creature. I
think, could I regain the attractive Influence I once had, if I had a
Legion of Suitors, I should never be ambitious of Entertaining more
than one. I have almost contracted an Antipathy to the trifling
Discourses of Impertinent Lovers, though I must needs own, I have
thought it very odd of late, to hear Gentlemen, instead of their usual
Complacencies, fall into Disputes before me of Politicks, or else
weary me with the tedious Repetition of how thankful I ought to be,
and satisfied with my Recovery out of so dangerous a Distemper: This,
though I am very sensible of the Blessing, yet I cannot but dislike,
because such Advice from them rather seems to Insult than Comfort me,
and reminds me too much of what I was; which melancholy Consideration
I cannot yet perfectly surmount, but hope your Sentiments on this Head
will make it supportable.
'To shew you what a Value I have for your Dictates, these are to
certify the Persons concern'd, that unless one of them returns to his
Colours, (if I may so call them now) before the Winter is over, I'll
voluntarily confine my self to a Retirement, where I'll punish them
all with my Needle. I'll be reveng'd on them by deciphering them on a
Carpet, humbly begging Admittance, my self scornfully refusing it: If
you disapprove of this, as favouring too much of Malice, be pleased to
acquaint me with a Draught you like better, and it shall be faithfully
performed'
By the Unfortunate
Monimia.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Si mihi non animo fixum, immotumque sederet,
Ne cui me vinclo vellem sociare jugali,
Postquam primus amor deceptam morte fefellit;
Si non pertæsum thalami, tedæque fuisset:
Huic uni forsan potui succumbere culpæ.
Virg.

The following Account hath been transmitted to me by the Love Casuist.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'Having, in some former Papers, taken Care of the two States of
Virginity and Marriage, and being willing that all People should be
served in their Turn; I this Day drew out my Drawer of Widows, where I
met with several Cases, to each whereof I have returned satisfactory
Answers by the Post. The Cases are as follow:
'Q. Whether Amoret be bound by a Promise of Marriage to
Philander, made during her Husband's Life?
'Q. Whether Sempronia, having faithfully given a Promise to two
several Persons during the last Sickness of her Husband, is not
thereby left at Liberty to chase which of them she pleases, or to
reject them both for the sake of a new Lover?
'Cleora asks me, Whether she be obliged to continue single,
according to a Vow made to her Husband at the time of his presenting
her with a Diamond Necklace; she being informed by a very pretty young
Fellow of a good Conscience, that such Vows are in their Nature
sinful?
'Another enquires, Whether she hath not the Right of Widowhood, to
dispose of her self to a Gentleman of great Merit, who presses very
hard; her Husband being irrecoverably gone in a Consumption?
'An unreasonable Creature hath the Confidence to ask, Whether it be
proper for her to marry a Man who is younger than her eldest Son?
'A scrupulous well-spoken Matron, who gives me a great many good
Words, only doubts, Whether she is not obliged in Conscience to shut
up her two marriageable Daughters, till such time as she hath
comfortably disposed of her self?
'Sophronia, who seems by her Phrase and Spelling to be a Person of
Condition, sets forth, That whereas she hath a great Estate, and is
but a Woman, she deSir es to be informed, whether she would not do
prudently to marry Camillus, a very idle tall young Fellow, who hath
no Fortune of his own, and consequently hath nothing else to do but to
manage hers.'
Before I speak of Widows, I cannot but observe one thing, which I do not
know how to account for; a Widow is always more sought after, than an
old Maid of the same Age. It is common enough among ordinary People, for
a stale Virgin to set up a Shop in a Place where she is not known; where
the large Thumb Ring, supposed to be given her by her Husband, quickly
recommends her to some wealthy Neighbour, who takes a Liking to the
jolly Widow, that would have overlooked the venerable Spinster.
The Truth of it is, if we look into this Sett of Women, we find,
according to the different Characters or Circumstances wherein they are
left, that Widows may be divided into those who raise Love, and those
who raise Compassion.
But not to ramble from this Subject, there are two Things in which
consists chiefly the Glory of a Widow; The Love of her deceased Husband,
and the Care of her Children: To which may be added a third arising out
of the former, Such a prudent Conduct as may do Honour to both.
A Widow possessed of all these three Qualities, makes not only a
virtuous but a sublime Character.
There is something so great and so generous in this State of Life, when
it is accompanied with all its Virtues, that it is the Subject of one of
the finest among our modern Tragedies in the Person of
Andromache
; and
hath met with an universal and deserved Applause, when introduced upon
our
English
Stage by Mr.
Philips.
The most memorable Widow in History is Queen
Artemisia
, who not only
erected the famous
Mausoleum
, but drank up the Ashes of her dead Lord;
thereby enclosing them in a nobler Monument than that which she had
built, though deservedly esteemed one of the Wonders of Architecture.
This last Lady seems to have had a better Title to a second Husband than
any I have read of, since not one Dust of her First was remaining. Our
modern Heroines might think a Husband a very bitter Draught, and would
have good Reason to complain, if they might not accept of a second
Partner, till they had taken such a troublesome Method of losing the
Memory of the first.
I shall add to these illustrious Examples out of ancient Story, a
remarkable instance of the Delicacy of our Ancestors in Relation to the
State of Widowhood, as I
it recorded in
Cowell's
Interpreter.
At
East
and
West-Enborne,
in the County of
Berks,
if a Customary
Tenant die, the Widow shall have what the Law calls her
Free-Bench
in
all his Copy-hold Lands
, dum sola & casta fuerit;
that is
, while she
lives single and chaste;
but if she commit Incontinency, she forfeits
her Estate: Yet if she will come into the Court riding backward upon a
Black Ram, with his Tail in her Hand, and say the Words following, the
Steward is bound by the Custom to re-admit her to her
Free-Bench
.
Here I am,
Riding upon a Black Ram,
Like a Whore as I am;
And, for my Crincum Crancum,
Have lost my Bincum Bancum;
And, for my Tail's Game,
Have done this worldly Shame;
Therefore, I pray you Mr. Steward, let me have my Land again.
The like Custom there is in the Manor of
Torre
in
Devonshire
, and
other Parts of the
West.
It is not impossible but I may in a little Time present you with a
Register of
Berkshire
Ladies and other Western Dames, who rode
publickly upon this Occasion; and I hope the Town will be entertained
with a Cavalcade of Widows.
Footnote 1:
Frank Bank or Free bench are copyhold lands which the wife,
being married a spinster, had after her husband's death for dower.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, November 3, 1714 |
|
—Qui Deorum
Muneribus sapienter uti,
Duramque callet pauperiem pati,
Pejusque letho flagitium timet:
Non ille pro caris amicis
Aut patriâ timidus perire.
Hor.

It must be owned that Fear is a very powerful Passion, since it is
esteemed one of the greatest of Virtues to subdue it. It being implanted
in us for our Preservation, it is no Wonder it sticks close to us, as
long as we have any thing we are willing to preserve. But as Life, and
all its Enjoyments, would be scarce worth the keeping, if we were under
a perpetual Dread of losing them; it is the Business of Religion and
Philosophy to free us from all unnecessary Anxieties, and direct our
Fear to its proper Object.
If we consider the Painfulness of this Passion, and the violent Effects
it produces, we shall see how dangerous it is to give way to it upon
slight Occasions. Some have frightened themselves into Madness, others
have given up their Lives to these Apprehensions. The Story of a Man who
grew grey in the Space of one Night's Anxiety is very famous;
O! Nox, quam longa es, quæ facis una Senem.
These Apprehensions, if they proceed from a Consciousness of Guilt, are
the sad Warnings of Reason; and may excite our Pity, but admit of no
Remedy. When the Hand of the Almighty is visibly lifted against the
Impious, the Heart of mortal Man cannot withstand him. We have this
Passion
represented in the Punishment of the
Egyptians
,
tormented with the Plague of Darkness, in the
Apocryphal
Book. of
Wisdom
ascribed to
Solomon.
'For when unrighteous Men thought to oppress the holy Nation; they
being shut up in their Houses, the Prisoners of Darkness, and fetter'd
with the Bonds of a long Night, lay here exiled from the eternal
Providence. For while they supposed to lye hid in their secret Sins,
they were scattered under a dark Veil of Forgetfulness, being horribly
astonished and troubled with strange Apparitions—For Wickedness,
condemned by her own Witness, is very timorous, and being oppressed
with Conscience, always forecasteth grievous things. For Fear is
nothing else but a betraying of the Succours which Reason
offereth—For the whole World shined with clear Light, and none were
hindered in their Labour. Over them only was spread a heavy Night, an
Image of that Darkness which should afterwards receive them; but yet
were they unto themselves more grievous than the Darkness.'
1
To Fear, so justly grounded, no Remedy can be proposed; but a Man (who
hath no great Guilt hanging upon his Mind, who walks in the plain Path
of Justice and Integrity, and yet either by natural Complection, or
confirmed Prejudices, or Neglect of serious Reflection, suffers himself
to be moved by this abject and unmanly Passion) would do well to
consider, That there is nothing which deserves his Fear, but that
beneficent Being who is his Friend, his Protector, his Father. Were this
one Thought strongly fixed in the Mind, what Calamity would be dreadful?
What Load can Infamy lay upon us when we are sure of the Approbation of
him, who will repay the Disgrace of a Moment with the Glory of Eternity?
What Sharpness is there in Pain and Diseases, when they only hasten us
on to the Pleasures that will never fade? What sting is in Death, when
we are assured that it is only the Beginning of Life? A Man who lives
so, as not to fear to die, is inconsistent with himself, if he delivers
himself up to any incidental Anxiety.
The Intrepidity
a just good Man is so nobly set forth by
Horace
,
that it cannot be too often repeated.
The Man resolved and steady to his Trust,
Inflexible to Ill, and obstinately just,
May the rude Rabble's Insolence despise,
Their senseless Clamours and tumultuous Cries;
The Tyrant's Fierceness he beguiles,
And the stern Brow, and the harsh Voice defies,
And with superior Greatness smiles.
Not the rough Whirlwind, that deforms
Adria's
black Gulf, and vexes it with Storms,
The stubborn Virtue of his Soul can move;
Not the Red Arm of angry Jove,
That flings the Thunder from the Sky,
And gives it Rage to roar, and Strength to fly.
Should the whole Frame of Nature round him break,
In Ruin and Confusion hurl'd,
He, unconcerned, would hear the mighty Crack,
And Stand secure amidst a falling World.2
The Vanity of Fear may be yet farther illustrated, if we reflect,
First
, What we fear may not come to pass. No human Scheme can be so
accurately projected, but some little Circumstance intervening may spoil
it. He, who directs the Heart of Man at his Pleasure, and understands
the Thoughts long before, may by ten thousand Accidents, or an immediate
Change in the Inclinations of Men, disconcert the most subtle Project,
and turn it to the Benefit of his own Servants.
In the next Place we should consider, though the Evil we imagine should
come to pass, it may be much more supportable than it appeared to be. As
there is no prosperous State of Life without its Calamities, so there is
no Adversity without its Benefits, Ask the Great and Powerful, if they
do not feel the Pangs of Envy and Ambition. Enquire of the Poor and
Needy, if they have not tasted the Sweets of Quiet and Contentment. Even
under the Pains of Body; the Infidelity of Friends; or the
Misconstructions put upon our laudable Actions, our Minds (when for some
Time accustomed to these Pressures) are sensible of secret Flowings of
Comfort, the present Reward of a pious Resignation. The Evils of this
Life appear like Rocks and Precipices, rugged and barren at a Distance,
but at our nearer Approach, we find little fruitful Spots, and
refreshing Springs, mixed with the Harshness and Deformities of Nature.
In the last Place, we may comfort our selves with this Consideration;
that, as the Thing feared may not reach us, so we may not reach what we
fear: Our Lives may not extend to that dreadful Point which we have in
View. He who knows all our Failings, and will not suffer us to be
tempted beyond our Strength, is often pleased in his tender Severity, to
separate the Soul from its Body and Miseries together.
If we look forward to him for Help, we shall never be in Danger of
falling down those Precipices which our Imagination is apt to create.
Like those who walk upon a Line, if we keep our Eye fixed upon one
Point, we may step forward securely; whereas an imprudent or cowardly
Glance on either Side will infallibly destroy us.
Footnote 1:
Wisd. xvii.
passim.
Footnote 2:
Horace, Bk III.
Od.
3.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Qui bellus homo est, Cotta, pusillus homo est.
Martial.

Cicero
hath observed, that a Jest is never uttered with a better
Grace, than when it is accompanied with a serious Countenance. When a
pleasant Thought plays in the Features, before it discovers it self in
Words, it raises too great an Expectation, and loses the Advantage of
giving Surprize. Wit and Humour are no less poorly recommended by a
Levity of Phrase, and that kind of Language which may be distinguished
by the Name of
Cant.
Ridicule is never more strong, than when it is
concealed in Gravity. True Humour lies in the Thought, and arises from
the Representation of Images in odd Circumstances, and uncommon Lights.
A pleasant Thought strikes us by the Force of its natural Beauty; and
the Mirth of it is generally rather palled, than heightened by that
ridiculous Phraseology, which is so much in Fashion among the Pretenders
to Humour and Pleasantry. This Tribe of Men are like our Mountebanks;
they make a Man a Wit, by putting him in a fantastick Habit.
Our little Burlesque Authors, who are the Delight of ordinary Readers,
generally abound in these pert Phrases, which have in them more Vivacity
than Wit.
I lately saw an Instance of this kind of Writing, which gave me so
lively an Idea of it, that I could not forbear begging a Copy of the
Letter from the Gentleman who shew'd it to me. It is written by a
Country Wit, upon the Occasion of the Rejoycings on the Day of the
King's Coronation.
Dear Jack,
(Past two a Clock and a frosty Morning.)1
I have just left the Right Worshipful and his Myrmidons about a
Sneaker of Five Gallons. The whole Magistracy was pretty well
disguised before I gave 'em the Slip. Our Friend the Alderman was half
Seas over before the Bonfire was out. We had with us the Attorney, and
two or three other bright Fellows. The Doctor plays least in Sight.
At Nine a Clock in the Evening we set Fire to the Whore of
Babylon.
The Devil acted his Part to a Miracle. He has made his Fortune by it.
We equip'd the young Dog with a Tester a-piece. Honest old
Brown of
England was very drunk, and showed his Loyalty to the Tune of a
hundred Rockets. The Mob drank the King's Health, on their
Marrow-bones, in Mother
Day's Double. They whip'd us half a dozen
Hogsheads. Poor
Tom Tyler had like to have been demolished with the
End of a Sky-Rocket, that fell upon the Bridge of his Nose as he was
drinking the King's Health, and spoiled his Tip. The Mob were very
loyal 'till about Midnight, when they grew a little mutinous for more
Liquor. They had like to have dumfounded the Justice; but his Clerk
came in to his Assistance, and took them all down in Black and White.
When I had been huzza'd out of my Seven Senses, I made a Visit to the
Women, who were guzzling very comfortably. Mrs. Mayoress clip'd the
King's
English. Clack was the Word.
I forgot to tell thee, that every one of the Posse had his Hat cocked
with a Distich: The Senators sent us down a Cargo of Ribbon and Metre
for the Occasion.
Sir Richard to shew his Zeal for the Protestant Religion, is at the
Expence of a Tar-Barrel and a Ball. I peeped into the Knight's great
Hall, and saw a very pretty Bevy of Spinsters. My dear Relict was
amongst them, and ambled in a Country-Dance as notably as the best of
'em.
May all his Majesty's liege Subjects love him as well as his good
People of this his ancient Borough. Adieu.
Footnote 1:
(Two in the Morning is the Word, old Boy.)
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Torva Mimalloneis implerunt cornua bombis,
Et raptum vitulo caput ablatura superbo
Bassaris, et lyncem Mænas flexura corymbis,
Evion ingeminat reparabilis adsonat Echo.
Persius.

There are two Extreams in the Stile of Humour, one of which consists in
the Use of that little pert Phraseology which I took Notice of in my
last Paper; the other in the Affectation of strained and pompous
Expressions, fetched from the learned Languages. The first savours too
much of the Town; the other of the College.
As nothing illustrates better than Example, I shall here present my
Reader with a Letter of Pedantick Humour, which was written by a young
Gentleman of the University to his Friend; on the same Occasion, and
from the same Place, as the lively Epistle published in my
Dear Chum,
'It is now the third Watch of the Night, the greatest Part of which I
have spent round a capacious Bowl of
China, filled with the choicest
Products of both the
Indies. I was placed at a quadrangular Table,
diametrically opposite to the Mace-bearer. The Visage of that
venerable Herald was, according to Custom, most gloriously illuminated
on this joyful occasion. The Mayor and Aldermen, those Pillars of our
Constitution, began to totter; and if any one at the Board could have
so far articulated, as to have demanded intelligibly a Reinforcement
of Liquor, the whole Assembly had been by this time extended under the
Table.
'The Celebration of this Night's Solemnity was opened by the
Obstreperous Joy of Drummers, who, with their Parchment Thunder, gave
a signal for the Appearance of the Mob under their several Classes and
Denominations. They were quickly joined by the melodious Clank of
Marrow-bone and Cleaver, whilst a Chorus of Bells filled up the
Consort. A Pyramid of Stack-Faggots cheared the Hearts of the Populace
with the Promise of a Blaze: The Guns had no sooner uttered the
Prologue, but the Heavens were brightned with artificial Meteors, and
Stars of our own making; and all the
High-street lighted up from one
End to another, with a Galaxy of Candles. We collected a Largess for
the Multitude, who tippled Eleemosynary till they grew exceeding
Vociferous. There was a Paste-board Pontiff with a little swarthy
Dæmon at his Elbow, who, by his diabolical Whispers and Insinuations
tempted his Holiness into the Fire, and then left him to shift for
himself. The Mobile were very sarcastick with their Clubs, and gave
the old Gentleman several Thumps upon his triple Head-piece.
Tom
Tyler's Phiz is something damaged by the Fall of a Rocket, which hath
almost spoiled the Gnomon of his Countenance. The Mirth of the Commons
grew so very outragious, that it found Work for our Friend of the
Quorum, who, by the help of his
Amanuensis, took down all their
Names and their Crimes, with a Design to produce his Manuscript at the
next Quarter-Sessions,
&c. &c. &c.
'I shall subjoin to the foregoing Piece of a Letter, the following
Copy of Verses
translated from an
Italian Poet, who was the
Cleveland of his Age, and had Multitudes of Admirers. The Subject is
an Accident that happened under the Reign of Pope
Leo, when a
Firework, that had been prepared upon the Castle of St.
Angelo,
begun to play before its Time, being kindled by a Flash of Lightning.
The Author hath written his Poem
1 in the same kind of Style, as
that I have already exemplified in Prose. Every Line in it is a
Riddle, and the Reader must be forced to consider it twice or thrice,
before he will know that the
Cynick's Tenement is a
Tub, and
Bacchus his Cast-coat a
Hogs-head, &c.
'Twas Night, and Heav'n, a Cyclops, all the Day,
An Argus now did countless Eyes display;
In ev'ry Window Rome her Joy declares,
All bright, and studded with terrestrial Stars.
A blazing Chain of Lights her Roofs entwines.
And round her Neck the mingled Lustre shines,
The Cynick's rowling Tenement conspires,
With Bacchus his Cast-coat, to feed the Fires.
The Pile, still big with undiscover'd Shows,
The Tuscan Pile did last its Freight disclose,
Where the proud Tops of Rome's new Ætna rise,
Whence Giants sally, and invade the Skies.
Whilst now the Multitude expect the Time,
And their tir'd Eyes the lofty Mountain climb,
A thousand Iron Mouths their Voices try,
And thunder out a dreadful Harmony;
In treble Notes the small Artill'ry plays,
The deep-mouth'd Cannon bellows in the Bass.
The lab'ring Pile now heaves; and having giv'n
Proofs of its Travail sighs in Flames to Heav'n.
The Clouds invelop'd Heav'n from Human Sight,
Quench'd every Star, and put out ev'ry Light;
Now Real Thunder grumbles in the Skies,
And in disdainful Murmurs Rome defies;
Nor doth its answer'd Challenge Rome decline;
But whilst both Parties in full Consort join,
While Heav'n and Earth in Rival Peals resound,
The doubtful Cracks the Hearer's Sense confound;
Whether the Claps of Thunderbolts they hear,
Or else the Burst of Canon wounds their Ear;
Whether Clouds raged by struggling Metals rent,
Or struggling Clouds in Roman Metals pent.
But O, my Muse, the whole Adventure tell,
As ev'ry Accident in order fell.
Tall Groves of Trees the Hadrian Tow'r surround,
Fictitious Trees with Paper Garlands crown'd,
These know no Spring, but when their Bodies sprout
In Fire, and shoot their gilded Blossoms out;
When blazing Leaves appear above their Head,
And into branching Flames their Bodies spread.
Whilst real Thunder splits the Firmament,
And Heav'n's whole Roof in one vast Cleft is rent,
The three-fork'd Tongue amidst the Rupture lolls,
Then drops and on the Airy Turret falls.
The Trees now kindle, and the Garland burns,
And thousand Thunderbolts for one returns.
Brigades of burning Archers upward fly,
Bright Spears and shining Spear-men mount on high,
Flash in the Clouds, and glitter in the Sky.
A Seven-fold Shield of Spheres doth Heav'n defend,
And back again the blunted Weapons send;
Unwillingly they fall, and dropping down,
Pour out their Souls, their sulph'rous Souls, and groan.
With Joy, great Sir , we viewed this pompous Show,
While Heaven, that sate Spectator still 'till now,
It self turn'd Actor, proud to Pleasure you.
And so 'tis fit, when Leo's fires appear,
That Heav'n it self should turn an Engineer;
That Heav'n it self should all its Wonders show,
And Orbs above consent with Orbs below.
Footnote 1:
Translated from the Latin in Strada's
Prolusions.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, November 10, 1714 |
|
—Neque enim concludere versum
Dixeris esse satis: neque siquis scribat, uti nos,
Sermoni propiora, putes hunc esse Poetam.
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
You having, in your two last
Spectators, given the Town a couple of
Remarkable Letters, in very different Styles: I take this Opportunity
to offer to you some Remarks upon the
Epistolary way of writing in
Verse. This is a
Species of Poetry by it self; and has not so much
as been hinted at in any of the Arts of Poetry, that have ever fallen
into my Hands: Neither has it in any Age, or any Nation, been so much
cultivated, as the other several Kinds of Poesie. A Man of
Genius
may, if he pleases, write Letters in Verse upon all manner of
Subjects, that are capable of being embellished with Wit and Language,
and may render them new and agreeable by giving the proper Turn to
them. But in speaking, at present, of
Epistolary Poetry, I would be
understood to mean only such Writings in this Kind, as have been in
Use amongst the Ancients, and have been copied from them by some
Moderns. These may be reduced into two
Classes: In the one I shall
range Love-Letters, Letters of Friendship, and Letters upon mournful
Occasions: In the other I shall place such Epistles in Verse, as may
properly be called Familiar, Critical, and Moral; to which may be
added Letters of Mirth and Humour.
Ovid for the first, and
Horace
for the Latter, are the best Originals we have left.
'He that is ambitious of succeeding in the
Ovidian way, should first
examine his Heart well, and feel whether his Passions (especially
those of the gentler Kind) play easie, since it is not his Wit, but
the Delicacy and Tenderness of his Sentiments, that will affect his
Readers. His Versification likewise should be soft, and all his
Numbers flowing and querulous.
'The Qualifications requisite for writing Epistles, after the Model
given us by
Horace, are of a quite different Nature. He that would
excel in this kind must have a good Fund of strong Masculine Sense: To
this there must be joined a thorough Knowledge of Mankind, together
with an Insight into the Business, and the prevailing Humours of the
Age. Our Author must have his Mind well seasoned with the finest
Precepts of Morality, and be filled with nice Reflections upon the
bright and the dark sides of human Life: He must be a Master of
refined Raillery, and understand the Delicacies, as well as the
Absurdities of Conversation. He must have a lively Turn of Wit, with
an easie and concise manner of Expression; Every thing he says, must
be in a free and disengaged manner. He must be guilty of nothing that
betrays the Air of a Recluse, but appear a Man of the World
throughout. His Illustrations, his Comparisons, and the greatest part
of his Images must be drawn from common Life. Strokes of Satyr and
Criticism, as well as Panegyrick, judiciously thrown in (and as it
were by the by) give a wonderful Life and Ornament to Compositions of
this kind. But let our Poet, while he writes Epistles, though never so
familiar, still remember that he writes in Verse, and must for that
reason have a more than ordinary care not to fall into Prose, and a
vulgar Diction, excepting where the Nature and Humour of the Thing
does necessarily require it. In this Point
Horace hath been thought
by some Criticks to be sometimes careless, as well as too negligent of
his Versification; of which he seems to have been sensible himself.
'All I have to add is, that both these Manners of Writing may be made
as entertaining, in their Way, as any other Species of Poetry, if
undertaken by Persons duly qualify'd; and the latter sort may be
managed so as to become in a peculiar manner Instructive.
I am, &ct.'
I shall add an Observation or two to the Remarks of my ingenious
Correspondent, and, in the First place, take Notice, that Subjects of
the most sublime Nature are often treated in the Epistolary way with
Advantage, as in the famous Epistle of
Horace
to
Augustus.
The Poet
surprizes us with his Pomp, and seems rather betrayed into his Subject,
than to have aimed at it by Design: He appears like the Visit of a King
Incognito
, with a mixture of Familiarity, and Grandeur. In Works of
this kind, when the Dignity of the Subject hurries the Poet into
Descriptions and Sentiments, seemingly unpremeditated, by a sort of
Inspiration; it is usual for him to recollect himself, and fall back
gracefully into the natural Stile of a Letter.
I might here mention an Epistolary Poem, just published by Mr.
Eusden
on the King's Accession to the Throne: Wherein, amongst many other noble
and beautiful Strokes of Poetry, his Reader may see this Rule very
happily observed.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Friday, November 12, 1714 |
|
—dura
Exerce imperia, et ramos compesce fluentes.
Virg.

I have often thought, that if the several Letters, which are written to
me under the Character of SPECTATOR, and which I have not made use of,
were published in a Volume, they would not be an unentertaining
Collection. The Variety of the Subjects, Styles, Sentiments, and
Informations, which are transmitted to me, would lead a very curious, or
very idle Reader, insensibly along, through a great many Pages. I know
some Authors, who
pick up a
Secret History
out of such
Materials, and make a Bookseller an Alderman by the Copy
. I shall
therefore carefully preserve the Original Papers in a Room set apart for
that Purpose, to the end that they may be of Service to Posterity; but
shall at present content my self, with owning the Receipt of several
Letters, lately come to my Hands, the Authors whereof are impatient for
an Answer.
Charissa
, whose Letter is dated from
Cornhill
, de
Sir
es to be eased
in some Scruples relating to the Skill of Astrologers.
Referred to the
Dumb Man for an Answer.
J. C.
who proposes a Love-Case, as he calls it, to the Love-Casuist,
is hereby de
Sir
'd to speak of it to the Minister of the Parish; it being
a Case of Conscience.
The poor young Lady, whose Letter is dated
October
26, who complains of
a harsh Guardian, and an unkind Brother, can only have my good Wishes,
unless she pleases to be more particular.
The Petition of a certain Gentleman, whose Name I have forgot, famous
for renewing the Curls of decayed Perriwigs, is referred to the
Censor
of small Wares.
The Remonstrance of
T. C.
against the Profanation of the Sabbath by
Barbers, Shoe-cleaners,
&c.
had better be offer'd to
the Society of
Reformers.
A learned and laborious Treatise upon the Art of Fencing,
returned to
the Author.
To the Gentleman of
Oxford
, who de
Sir
es me to insert a Copy of
Latin
Verses which were denied a Place in the University Book. Answer.
Nonumque prematur in annum.
To my learned Correspondent who writes against Master's Gowns, and Poke
Sleeves, with a Word in Defence of large Scarves. Answer.
I resolve not
to raise Animosities amongst the Clergy.
To the Lady, who writes with Rage against one of her own Sex, upon the
Account of Party Warmth. Answer.
Is not the Lady she writes against
reckoned Handsome?
I de
Sir
e
Tom Truelove
, (who sends me a Sonnet upon his Mistress, with
a de
Sir
e to print it immediately) to consider, that it is long since I
was in Love.
I shall answer a very profound Letter from my old Friend the
Upholsterer, who is still inquisitive whether the King of
Sweden
be
living or dead, by whispering him in the Ear,
That I believe he is
alive.
Let Mr.
Dapperwit
consider,
What is that long Story of the Cuckoldom
to me?
At the earnest De
Sir
e of
Monimia's
Lover, who declares himself very
penitent, he is recorded in my Paper by the Name of
The Faithful
Castalio.
The Petition of
Charles Cocksure
, which the Petitioner styles
very
reasonable—Rejected.
The Memorial of
Philander
, which he de
Sir
es may be dispatched out of
Hand,
Postponed.
I de
Sir
e
S. R.
not to repeat the Expression
under the Sun
so often
in his next Letter.
The Letter of
P. S.
who de
Sir
es either to have it printed entire, or
committed to the Flames.
Not to be printed entire.
Footnote 1:
Charles Lillie published, in 1725, 'Original and Genuine
Letters sent 'to the
Tatler
and
Spectator
during the time those
Works were publishing, none of which have been before printed.'
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Monday, November 15, 1714 |
Tickell |
Hic Vir, hic est, tibi quem promitti sæpius audis.
Virg.

Having lately presented my Reader with a Copy of Verses full of the
False Sublime, I shall here communicate to him an excellent Specimen of
the True: Though it hath not yet been published, the judicious Reader
will readily discern it to be the Work of a Master: And if he hath read
that noble Poem on
The Prospect of Peace
, he will not be at a Loss to
guess at the Author.
The Royal Progress.
When
Brunswick
first appear'd, each honest Heart,
Intent on Verse, disdain'd the Rules of Art;
For him the Songsters, in unmeasur'd Odes,
Debas'd
Alcides,
and dethron'd the Gods,
In Golden Chains the Kings of
India
led,
Or rent the Turban from the
Sultan's
Head.
One, in old Fables, and the
Pagan
Strain,
With
Nymphs
and
Tritons,
wafts him o'er the Main;
Another draws fierce
Lucifer
in Arms,
And fills th' Infernal Region with Alarms;
A Third awakes some
Druid,
to foretel
Each future Triumph from his dreary Cell.
Exploded Fancies! that in vain deceive,
While the Mind nauseates what she can't believe.
My Muse th' expected1 Hero shall pursue
From Clime to Clime, and keep him still in View;
His shining March describe in faithful Lays,
Content to paint him, nor presume to praise;
Their Charms, if Charms they have, the Truth supplies,
And from the Theme unlabour'd Beauties rise.
By longing Nations for the Throne design'd,
And call'd to guard the Rights of Human-kind;
With secret Grief his God-like Soul repines,
And Britain's
Crown with joyless Lustre shines,
While Prayers and Tears his destin'd Progress stay,
And Crowds of Mourners choak their Sovereign's Way.
Not so he march'd, when Hostile Squadrons stood
In Scenes of Death, and fir'd his generous Blood;
When his hot Courser paw'd th'
Hungarian
Plain,
And adverse Legions stood the Shock in vain.
His Frontiers past, the
Belgian
Bounds he views,
And cross the level Fields his March pursues.
Here pleas'd the Land of Freedom to survey,
He greatly scorns the Thirst of boundless Sway.
O'er the thin Soil, with silent Joy he spies
Transplanted Woods, and borrow'd Verdure rise;
Where every Meadow won with Toil and Blood,
From haughty Tyrants, and the raging Flood,
With Fruits and Flowers the careful Hind supplies,
And cloathes the Marshes in a rich Disguise.
Such Wealth for frugal Hands doth Heaven decree,
And such thy Gifts, Celestial Liberty!
Through stately Towns, and many a fertile Plain,
The Pomp advances to the neighbouring Main.
Whole Nations crowd around with joyful Cries,
And view the Heroe with insatiate Eyes.
In
Haga's
Towers he waits, 'till Eastern Gales
Propitious rise to swell the
British
Sails.
Hither the Fame of
England's
Monarch brings
The Vows and Friendships of the neighb'ring Kings;
Mature in Wisdom, his extensive Mind
Takes in the blended Int'rests of Mankind,
The World's great Patriot. Calm thy anxious Breast,
Secure in him
, O Europe
take thy Rest;
Henceforth thy Kingdoms shall remain confined
By Rocks or Streams, the Mounds which Heav'n design'd:
The
Alps
their new-made Monarch shall restrain,
Nor shall thy Hills
, Pirene,
rise in vain
But see! to
Britain's
Isle the Squadrons stand,
And leave the sinking Towers, and lessening Land,
The Royal Bark bounds o'er the floating Plain,
Breaks thro' the Billows, and divides the Main,
O'er the vast Deep, Great Monarch, dart thine Eyes,
A watry Prospect bounded by the Skies:
Ten thousand Vessels, from ten thousand Shores,
Bring Gums and Gold, and either
India's
Stores:
Behold the Tributes hastening to thy Throne,
And see the wide Horizon all thy own.
Still is it thine; tho' now the cheerful Crew
Hail
Albion's
Cliffs, just whitening to the View.
Before the Wind with swelling Sails they ride,
Till
Thames
receives them in his opening Tide.
The Monarch hears the thundering Peals around,
From trembling Woods and ecchoing Hills rebound,
Nor misses yet, amid the deafening Train,
The Roarings of the hoarse-resounding Main.
As in the Flood he sails, from either Side
He views his Kingdom in its rural Pride;
A various Scene the wide-spread Landskip yields,
O'er rich Enclosures and luxuriant Fields:
A lowing Herd each fertile Pasture fills,
And distant Flocks stray o'er a thousand Hills.
Fair
Greenwich
hid in Woods, with new Delight,
(Shade above Shade) now rises to the Sight:
His Woods ordain'd to visit every Shore,
And guard the Island which they graced before.
The Sun now rowling down the Western Way,
A Blaze of Fires renews the fading Day;
Unnumbered Barks the Regal Barge infold,
Brightening the Twilight with its beamy Gold;
Less thick the finny Shoals, a countless Fry,
Before the Whale or kingly Dolphin fly.
In one vast Shout he seeks the crowded Strand,
And in a Peal of Thunder gains the Land.
Welcome, great Stranger, to our longing Eyes,
Oh! King deSir 'd, adopted
Albion
cries.
For thee the East breath'd out a prosperous Breeze,
Bright were the Suns, and gently swell'd the Seas.
Thy Presence did each doubtful Heart compose,
And Factions wonder'd that they once were Foes;
That joyful Day they lost each Hostile Name,
The same their Aspect, and their Voice the same.
So two fair Twins, whose Features were design'd
At one soft Moment in the Mother's Mind,
Show each the other with reflected Grace,
And the same Beauties bloom in either Face;
The puzzled Strangers which is which enquire,
Delusion grateful to the smiling Sir e.
From that fair Hill, where hoary Sages boast
To name the Stars, and count the heavenly Host,
By the next Dawn doth great
Augusta
rise,
Proud Town! the noblest Scene beneath the Skies.
O'er
Thames
her thousand Spires their Lustre shed,
And a vast Navy hides his ample Bed,
A floating Forest. From the distant Strand
A Line of Golden Carrs strikes o'er the Land
:
Britannia's
Peers in Pomp and rich Array,
Before their King, triumphant, lead the Way.
Far as the Eye can reach, the gawdy Train,
A bright Procession, shines along the Plain.
So haply through the Heav'n's wide pathless Ways
A Comet draws a long-extended Blaze;
From East to West burns through2 th' ethereal Frame,
And half Heav'n's Convex glitters with the Flame.
Now to the Regal Towers securely brought,
He plans Britannia's
Glories in his Thought;
Resumes the delegated Pow'r he gave,
Rewards the Faithful and restores the Brave.
Whom shall the Muse from out the shining Throng
Select to heighten and adorn her Song?
Thee,
Halifax.
To thy capacious Mind,
O Man approved, is
Britain's
Wealth consigned.
Her Coin (while
Nassau
fought) debas'd and rude,
By Thee in Beauty and in Truth renew'd,
An Arduous Work! again thy Charge we see,
And thy own Care once more returns to Thee.
O! form'd in every Scene to awe and please,
Mix Wit with Pomp, and Dignity with Ease:
Tho' call'd to shine aloft, thou wilt not scorn
To smile on Arts thy self did once adorn:
For this thy Name succeeding Time shall praise,
And envy less thy Garter, than thy Bays.
The Muse, if fir'd with thy enlivening Beams,
Perhaps shall aim at more exalted Themes,
Record our Monarch in a nobler Strain,
And sing the opening Wonders of his Reign;
Bright
Carolina
'
s heavenly Beauties trace,
Her valiant
Consort
,
and his blooming Race.
A Train of Kings their fruitful Love supplies,
A glorious Scene to
Albion'
s ravish'd Eyes;
Who sees by
Brunswick
'
s Hand her Sceptre sway'd,
And through his Line from Age to Age convey'd.
Footnote 1:
artless Muse the
Footnote 2:
he burns
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, November 17, 1714 |
|
—postquam se lumine puro
Implevit, stellasque vagas miratur et Astra
Fixa Polis, vidit quanta sub nocte jaceret
Nostra dies, risitque sui ludibria—
Lucan.

The following Letter having in it some Observations out of the common
Road, I shall make it the Entertainment of this Day.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The common Topicks against the Pride of Man which are laboured by
florid and declamatory Writers, are taken from the Baseness of his
Original, the Imperfections of his Nature, or the short Duration of
those Goods in which he makes his Boast. Though it be true that we can
have nothing in us that ought to raise our Vanity, yet a Consciousness
of our own Merit may be sometimes laudable. The Folly therefore lyes
here: We are apt to pride our selves in worthless, or perhaps shameful
Things; and, on the other hand, count that disgraceful which is our
truest Glory.
'Hence it is, that the Lovers of Praise take wrong Measures to attain
it. Would a vain Man consult his own Heart, he would find that if
others knew his Weaknesses as well as he himself doth, he could not
have the Impudence to expect the publick Esteem. Pride therefore flows
from want of Reflection, and Ignorance of our selves. Knowledge and
Humility come upon us together.
'The proper way to make an Estimate of our selves, is to consider
seriously what it is we value or despise in others. A Man who boasts
of the Goods of Fortune, a gay Dress or a new Title, is generally the
Mark of Ridicule. We ought therefore not to admire in our selves, what
we are so ready to laugh at in other Men.
'Much less can we with Reason pride our selves in those things, which
at some time of our Life we shall certainly despise. And yet, if we
will give our selves the Trouble of looking backward and forward on
the several Changes, which we have already undergone and hereafter
must try, we shall find that the greater Degrees of our Knowledge and
Wisdom, serve only to shew us our own Imperfections.
'As we rise from Childhood to Youth, we look with Contempt on the Toys
and Trifles which our Hearts have hitherto been set upon. When, we
advance to Manhood, we are held wise in proportion to our Shame and
Regret for the Rashness and Extravagance of Youth. Old Age fills us
with mortifying Reflections upon a Life, mis-spent in the Pursuit of
anxious Wealth or uncertain Honour. Agreeable to this Gradation of
Thought in this Life, it may be reasonably supposed, that in a future
State, the Wisdom, the Experience, and the Maxims of old Age, will be
looked upon by a separate Spirit in much the same Light, as an ancient
Man now sees the little Follies and Toyings of Infants. The Pomps, the
Honours, the Policies, and Arts of mortal Men, will be thought as
trifling as Hobby-Horses, Mock Battles, or any other Sports that now
employ all the Cunning, and Strength, and Ambition of rational Beings
from four Years old to nine or ten.
'If the Notion of a gradual Rise in Beings, from the meanest to the
most High, be not a vain Imagination, it is not improbable that an
Angel looks down upon a Man, as a Man doth upon a Creature which
approaches the nearest to the rational Nature. By the same Rule (if I
may indulge my Fancy in this Particular) a superior Brute looks with a
kind of Pride on one of an inferior Species. If they could reflect, we
might imagine from the Gestures of some of them, that they think
themselves the Sovereigns of the World, and that all things were made
for them. Such a Thought would not be more absurd in Brute Creatures,
than one which Men are apt to entertain, namely, That all the Stars in
the Firmament were created only to please their Eyes and amuse their
Imaginations. Mr.
Dryden, in his Fable of the
Cock and the Fox,
makes a Speech for his Hero the Cock, which is a pretty Instance for
this Purpose,
Then turning, said to Partlet, See, my Dear,
How lavish Nature hath adorn'd the Year;
How the pale Primrose and the Violet spring,
And Birds essay their Throats, disus'd to sing:
All these are ours, and I with Pleasure see
Man strutting on two Legs, and aping me.
'What I would observe from the Whole is this, That we ought to value
our selves upon those Things only which superior Beings think
valuable, since that is the only way for us not to sink in our own
Esteem hereafter.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Friday, November 19, 1714 |
|
—Fallentis Semita Vitæ.
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'In a former Speculation you have observed, that true Greatness doth
not consist in that Pomp and Noise wherein the Generality of Mankind
are apt to place it. You have there taken Notice, that Virtue in
Obscurity often appears more illustrious in the Eye of superior
Beings, than all that passes for Grandeur and Magnificence among Men.
When we look back upon the History of those who have born the Parts of
Kings, Statesmen, or Commanders, they appear to us stripped of those
out-side Ornaments that dazzled their Contemporaries; and we regard
their Persons as great or little, in Proportion to the Eminence of
their Virtues or Vices. The wise Sayings, generous Sentiments, or
disinterested Conduct of a Philosopher under mean Circumstances of
Life, set him higher in our Esteem than the mighty Potentates of the
Earth, when we view them both through the long Prospect of many Ages.
Were the Memoirs of an obscure Man, who lived up to the Dignity of his
Nature, and according to the Rules of Virtue, to be laid before us, we
should find nothing in such a Character which might not set him on a
Level with Men of the highest Stations. The following Extract out of
the private Papers of an honest Country-Gentleman will set this Matter
in a clear Light. Your Reader will perhaps conceive a greater Idea of
him from these Actions done in Secret, and without a Witness, than of
those which have drawn upon them the Admiration of Multitudes.
Memoirs.
"In my 22d Year I found a violent Affection for my Cousin
Charles's Wife growing upon me, wherein I was in danger of
succeeding, if I had not upon that Account begun my Travels into
foreign Countries.
"A little after my Return into England, at a private Meeting with
my Uncle Francis, I refused the Offer of his Estate, and prevailed
upon him not to disinherit his Son Ned.
"Mem. Never to tell this to Ned, lest he should think hardly of
his deceased Father; though he continues to speak ill of me for this
very Reason.
"Prevented a scandalous Law-suit betwixt my Nephew Harry and his
Mother, by allowing her under-hand, out of my own Pocket, so much
Money yearly as the Dispute was about.
"Procured a Benefice for a young Divine, who is Sister's Son to the
good Man who was my Tutor, and hath been dead Twenty Years.
"Gave Ten Pounds to poor Mrs.—, my Friend H—'s Widow.
"Mem. To retrench one Dish at my Table, till I have fetched it up
again.
"Mem. To repair my House and finish my Gardens in order to employ
poor People after Harvest time.
"Ordered John to let out Goodman D—'s Sheep that were pounded, by
Night: but not to let his Fellow-Servants know it.
"Prevailed upon M. T. Esq., not to take the Law of the Farmer's
Son for shooting a Partridge, and to give him his Gun again.
"Paid the Apothecary for curing an old Woman that confessed her self
a Witch.
"Gave away my favourite Dog for biting a Beggar.
"Made the Minister of the Parish and a Whig Justice of one Mind,
by putting them upon explaining their Notions to one another.
"Mem, To turn off Peter for shooting a Doe while she was eating
Acorns out of his Hand.
"When my Neighbour John, who hath often injured me, comes to make
his Request to Morrow:
"Mem. I have forgiven him.
"Laid up my Chariot and sold my Horses, to relieve the Poor in a
Scarcity of Corn.
"In the same Year remitted to my Tenants a Fifth Part of their
Rents.
"As I was airing to-day, I fell into a Thought that warmed my Heart,
and shall, I hope, be the better for it as long as I live.
"Mem. To charge my Son in private to erect no Monument for me; but
not to put this in my last Will.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Monday, November 22, 1714 |
Addison1 |
Sed mihi vel tellus optem prius ima dehiscat,
Vel pater omnipotens adigat me fulmine ad umbras,
Pallentes umbras Erebi noctemque profundam,
Ante, pudor, quam te violem aut tua jura resolvam.
Ille meos, primos qui me sibi junxit, amores
Abstulit: ille habeat secum, servetque sepulchro.
Virg.

I
obliged to my Friend, the
Love-Casuist
, for the following
Curious Piece of Antiquity, which I shall communicate to the Publick in
his own Words.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You may remember, that I lately transmitted to you an Account of an
ancient Custom, in the Manors of East
and West-Enborne,
in the
County of Berks,
and elsewhere. If a Customary Tenant die, the Widow
shall have what the Law calls her Free-Bench
in all his Copyhold
Lands, dum sola et casta fuerit,
that is, while she lives single
and chaste;
but if she commits Incontinency, she forfeits her Estate;
Yet if she will come into the Court riding backward upon a Black Ram,
with his Tail in her Hand, and say the Words following, the Steward is
bound by the Custom to re-admit her to her Free-Bench.
Here I am,
Riding upon a Black Ram,
Like a Whore as I am;
And, for my Crincum Crancum,
Have lost my Bincum Bancum;
And, for my Tail's Game,
Have done this worldly Shame;
Therefore, I pray you Mr. Steward, let me have my Land again.
'After having informed you that my Lord
Coke observes, that this is
the most frail and slippery Tenure of any in
England, I shall tell
you, since the Writing of that Letter, I have, according to my
Promise, been at great Pains in searching out the Records of the
Black Ram; and have at last met with the Proceedings of the
Court-Baron, held in that Behalf, for the Space of a whole Day. The
Record saith, that a strict Inquisition having been made into the
Right of the Tenants to their several Estates, by a crafty old
Steward, he found that many of the Lands of the Manor were, by default
of the several Widows, forfeited to the Lord, and accordingly would
have enter'd on the Premises: Upon which the good Women demanded the
Benefit of the Ram. The
Steward, after having perused their several
Pleas, adjourn'd the Court to
Barnaby-bright3, that they might
have Day enough before them.
'The Court being set, and filled with a great Concourse of People, who
came from all Parts to see the Solemnity, the first who entered was
the Widow
Frontly, who had made her Appearance in the last Year's
Cavalcade. The Register observes, that finding it an easy Pad-Ram, and
foreseeing she might have further Occasion for it, she purchased it of
the Steward.
'Mrs.
Sarah Dainty, Relict of Mr.
John Dainty, (who was the
greatest Prude in the Parish) came next in the Procession. She at
first made some Difficulty of taking the Tail in her Hand; and was
observed in pronouncing the Form of Penance, to soften the two most
emphatical Words into
Clincum Clancum: But the Steward took care to
make her speak plain
English before he would
let her have her Land
again.
'The third Widow that was
brought to this worldly Shame, being
mounted upon a vicious Ram, had the Misfortune to be thrown by him;
upon which she hoped to be excused from going thro' the rest of the
Ceremony: But the Steward being well versed in the Law, observed very
wisely upon this Occasion, that the breaking of the Rope does not
hinder the Execution of the Criminal.
'The fourth Lady upon Record was the Widow
Ogle, a famous Coquette,
who had kept half a Score young Fellows off and on for the Space of
two Years; but having been more kind to her Carter
John, she was
introduced with the Huzza's of all her Lovers about her.
'Mrs.
Sable appearing in her Weeds, which were very new and fresh,
and of the same Colour with her whimsical
Palfrey, made a very
decent Figure in the Solemnity.
'Another, who had been summoned to make her Appearance, was excused by
the Steward, as well knowing in his Heart, that the good Squire
himself had qualified her for the Ram.
'Mrs.
Quick having nothing to object against the Indictment, pleaded
her Belly. But it was remembred that she made the same Excuse the Year
before. Upon which the Steward observ'd, that she might so contrive
it, as never to do the Service of the Manor.
'The Widow
Fidget being cited into Court, insisted that she had done
no more since the Death of her Husband, than what she used to do in
his Life-time; and withal de
Sir 'd Mr. Steward to consider his own
Wife's Case, if he should chance to die before her.
'The next in order was a Dowager of a very corpulent Make, who would
have been excused as not finding any Ram that was able to carry her;
upon which the Steward commuted her Punishment, and ordered her to
make her Entry upon a black Ox.
'The Widow
Maskwell, a Woman who had long lived with a most
unblemished Character, having turned off her old Chamber-maid in a
Pet, was by that revengeful Creature brought in upon the black Ram
Nine times the same Day.
'Several Widows of the Neighbourhood, being brought upon their Tryal,
they shewed that they did not hold of the Manor, and were discharged
accordingly.
'A pretty young Creature who closed the Procession, came ambling in,
with so bewitching an Air, that the Steward was observ'd to cast a
Sheep's Eye upon her, and married her within a Month after the Death
of his Wife.
'
N. B. Mrs.
Touchwood appeared, according to Summons, but had
nothing laid to her Charge; having liv'd irreproachably since the
Decease of her Husband, who left her a Widow in the Sixty-ninth Year
of her Age.'
I am, Sir , &c.
Footnote 1:
See
to
.
Footnote 2:
See Nos.
,
,
,
, and
.
Footnote 3:
Then the 11th, now the 22nd of June, longest day of the
year.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, November 24, 1714 |
|
Audire, atque togam jubeo componere, quisquis
Ambitione mala, aut argenti pallet amore
Quisquis luxuria—
Hor.

Mankind is divided into two Parts, the Busie and the Idle. The Busie
World may be divided into the Virtuous and the Vicious. The Vicious
again into the Covetous, the Ambitious, and the Sensual. The idle Part
of Mankind are in a State inferior to any one of these. All the other
are engaged in the Pursuit of Happiness, though often misplaced, and are
therefore more likely to be attentive to such Means, as shall be
proposed to them for that End. The Idle, who are neither wise for this
World, nor the next, are emphatically called by
Dr. Tillotson, Fools
at large
. They propose to themselves no End, but run adrift with every
Wind. Advice therefore would be but thrown away upon them, since they
would scarce take the Pains to read it. I shall not fatigue any of this
worthless Tribe with a long Harangue; but will leave them with this
short Saying of
Plato
, that
Labour is preferable to Idleness, as
Brightness to Rust.
The Pursuits of the Active Part of Mankind, are either in the Paths of
Religion and Virtue; or, on the other Hand, in the Roads to Wealth,
Honours or Pleasure. I shall therefore compare the Pursuits of Avarice,
Ambition and sensual Delight, with their opposite Virtues; and shall
consider which of these Principles engages Men in a Course of the
greatest Labour, Suffering and Assiduity. Most Men, in their cool
Reasonings, are willing to allow that a Course of Virtue will in the End
be rewarded the most amply; but represent the Way to it as rugged and
narrow. If therefore it can be made appear, that Men struggle through as
many Troubles to be miserable, as they do to be happy, my Readers may
perhaps be perswaded to be Good, when they find they shall lose nothing
by it.
First
, for Avarice. The Miser is more Industrious than the Saint: The
Pains of getting, the Fears of losing, and the Inability of enjoying his
Wealth, have been the Mark of Satyr in all Ages. Were his Repentance
upon his Neglect of a good Bargain, his Sorrow for being over-reached,
his Hope of improving a Sum, and his Fear of falling into Want, directed
to their proper Objects; they would make so many different
Christian
Graces and Virtues. He may apply to himself a great Part of St.
Paul's
Catalogue of Sufferings.
In journeying often; in Perils of Water, in
Perils of Robbers, in Perils among false Brethren. In Weariness and
Painfulness, in Watchings often, in Hunger and Thirst, in Fastings
often,
—At how much less Expence might he
lay up to himself Treasures
in Heaven
; or if I may, in this Place, be allowed to add the Saying of
a great Philosopher, he may
provide such Possessions, as fear neither
Arms, nor Men, nor
Jove
himself.
In the second Place, if we look upon the Toils of Ambition, in the same
Light as we have considered those of Avarice, we shall readily own that
far less Trouble is requisite to gain lasting Glory, than the Power and
Reputation of a few Years; or, in other Words, we may with more Ease
deserve Honour, than obtain it. The Ambitious Man should remember
Cardinal
Woolsey's
Complaint.
'Had I served God, with the same Application, wherewith I served my
King, he would not have forsaken me in my old Age.'
The Cardinal here softens his Ambition by the specious Pretence of
serving his King
: Whereas his Words in the proper Construction, imply,
that if instead of being acted by Ambition, he had been acted by
Religion, he should have now felt the Comforts of it, when the whole
World turned its Back upon him.
Thirdly
, Let us compare the Pains of the Sensual, with those of the
Virtuous, and see which are heavier in the Balance. It may seem strange,
at the first View, that the Men of Pleasure should be advised to change
their Course, because they lead a painful Life. Yet when we see them so
active and vigilant in quest of Delight; under so many Disquiets, and
the Sport of such various Passions; let them answer, as they can, if the
Pains they undergo, do not outweigh their Enjoyments. The Infidelities
on the one Part between the two Sexes, and the Caprices on the other,
the Debasement of Reason, the Pangs of Expectation, the Disappointments
in Possession, the Stings of Remorse, the Vanities and Vexations
attending even the most refined Delights that make up this Business of
Life, render it so silly and uncomfortable, that no Man is thought wise
till he hath got over it, or happy, but in proportion as he hath cleared
himself from it.
The Sum of all is this. Man is made an active Being. Whether he walks in
the Paths of Virtue or Vice, he is sure to meet with many Difficulties
to prove his Patience, and excite his Industry. The same if not greater
Labour, is required in the Service of Vice and Folly, as of Virtue and
Wisdom: And he hath this easie Choice left him, whether with the
Strength he is Master of, he will purchase Happiness or Repentance.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Friday, November 26, 1714 |
|
—amores
A tenero meditatur Ungui—
Hor.

The
Love Casuist
hath referred to me the following Letter of Queries,
with his Answers to each Question, for my Approbation. I have
accordingly consider'd the several Matters therein contained, and hereby
confirm and ratifie his Answers, and require the gentle Querist to
conform her self thereunto.
Sir ,
'I was Thirteen the Ninth of November last, and must now begin to
think of settling my self in the World, and so I would humbly beg your
Advice, what I must do with Mr. Fondle, who makes his Addresses to
me. He is a very pretty Man, and hath the blackest Eyes and whitest
Teeth you ever saw. Though he is but a younger Brother, he dresses
like a Man of Quality, and no Body comes into a Room like him. I know
he hath refused great Offers, and if he cannot Marry me, he will never
have any Body else. But my Father hath forbid him the House, because
he sent me a Copy of Verses; for he is one of the greatest Wits in
Town. My eldest Sister, who, with her good Will, would call me Miss
as long as I live, must be married before me, they say. She tells
them, that Mr. Fondle makes a Fool of me, and will spoil the Child,
as she calls me, like a confident thing as she is. In short, I am
resolved to marry Mr. Fondle, if it be but to spite her. But because
I would do nothing that is imprudent, I beg of you to give me your
Answers to some Questions I will write down, and deSir e you to get
them printed in the SPECTATOR, and I do not doubt but you will give
such Advice, as, I am sure, I shall follow.
'When Mr. Fondle looks upon me for half an Hour together, and calls
me Angel, is he not in Love?
Answer, No.
'May not I be certain he will be a kind Husband, that has promised me
half my Portion in Pin-money, and to keep me a Coach and Six in the
Bargain.
No.
'Whether I, who have been acquainted with him this whole Year almost,
am not a better Judge of his Merit, than my Father and Mother, who
never heard him talk, but at Table?
No.
'Whether I am not old enough to chuse for my self?
No.
'Whether it would not have been rude in me to refuse a Lock of his
Hair?
No.
'Shou'd not I be a very barbarous Creature, if I did not pity a Man
that is always Sighing for my Sake?
No.
'Whether you would not advise me to run away with the poor Man?
No.
'Whether you do not think, that if I won't have him, he won't drown
himself?
No.
What shall I say to him the next time he asks me if I will marry him?
No.
The following Letter requires neither Introduction, nor Answer.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
I wonder that in the present Situation of Affairs, you can take
Pleasure in writing any thing but News; for, in a Word, who minds any
thing else? The Pleasure of increasing in Knowledge, and learning
something new every Hour of Life, is the noblest Entertainment of a
Rational Creature. I have a very good Ear for a Secret, and am
naturally of a communicative Temper; by which Means I am capable of
doing you great Services in this way. In order to make my self useful,
I am early in the Antichamber, where I thrust my Head into the thick
of the Press, and catch the News, at the opening of the Door, while it
is warm. Sometimes I stand by the Beef-Eaters, and take the Buz as it
passes by me. At other times I lay my Ear close to the Wall, and suck
in many a valuable Whisper, as it runs in a streight Line from Corner
to Corner. When I am weary with standing, I repair to one of the
neighbouring Coffee-houses, where I sit sometimes for a whole Day, and
have the News as it comes from Court fresh and fresh. In short, Sir , I
spare no Pains to know how the World goes. A Piece of News loses its
Flavour when it hath been an Hour in the Air. I love, if I may so
speak, to have it fresh from the Tree; and to convey it to my Friends
before it is faded. Accordingly my Expences in Coach-hire make no
small Article; which you may believe, when I assure you, that I post
away from Coffee-house to Coffee-house, and forestall the
Evening-Post by two Hours. There is a certain Gentleman who hath
given me the slip twice or thrice, and hath been beforehand with me at
Child's. But I have play'd him a Trick. I have purchas'd a pair of
the best Coach-horses I could buy for Money, and now let him out-strip
me if he can. Once more, Mr. SPECTATOR, let me advise you to deal in
News. You may depend upon my Assistance. But I must break off
abruptly, for I have twenty Letters to write.
Yours in haste,
Tho. Quid-nunc.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Monday, November 29, 1714 |
Henry Grove |
—Dulcique animos novitate tenebo—
Ov.
Met. 1. I.

I
seen a little Work of a learned Man
, consisting of
extemporary Speculations, which owed their Birth to the most trifling
Occurrences of Life. His usual Method was, to write down any sudden
Start of Thought which arose in his Mind upon the sight of an odd
Gesticulation in a Man, any whimsical Mimickry of Reason in a Beast, or
whatever appeared remarkable in any Object of the visible Creation. He
was able to moralize upon a Snuff-Box, would flourish eloquently upon a
Tucker or a Pair of Ruffles, and draw practical Inferences from a
full-bottomed Perriwig. This I thought fit to mention, by way of Excuse,
for my ingenious Correspondent, who hath introduced the following Letter
by an Image which, I will beg leave to tell him, is too ridiculous in so
serious and noble a Speculation.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'When I have seen young Puss playing her wanton Gambols, and with a
thousand antick Shapes express her own Gayety at the same time that
she moved mine, while the old Grannum hath sat by with a most
exemplary Gravity, unmov'd at all that past; it hath made me reflect
what should be the occasion of Humours so opposite in two Creatures,
between whom there was no visible Difference but that of Age; and I
have been able to resolve it into nothing else but the Force of
Novelty.
'In every Species of Creatures, those who have been least Time in the
World, appear best pleased with their Condition: For, besides that to
a new Comer the World hath a Freshness on it that strikes the Sense
after a most agreeable Manner, Being it self, unattended with any
great Variety of Enjoyments, excites a Sensation of Pleasure. But as
Age advances, every thing seems to wither, the Senses are disgusted
with their old Entertainments, and Existence turns flat and insipid.
We may see this exemplified in Mankind: The Child, let him be free
from Pain, and gratified in his Change of Toys, is diverted with the
smallest Trifle. Nothing disturbs the Mirth of the Boy, but a little
Punishment or Confinement. The Youth must have more violent Pleasures
to employ his Time; the Man loves the Hurry of an active Life, devoted
to the Pursuits of Wealth or Ambition; and Lastly, old Age, having
lost its Capacity for these Avocations, becomes its own insupportable
Burthen. This Variety may in part be accounted for by the Vivacity and
Decay of the Faculties; but I believe is chiefly owing to this, That
the longer we have been in Possession of Being, the less sensible is
the Gust we have of it; and the more it requires of adventitious
Amusements to relieve us from the Satiety and Weariness it brings
along with it.
'And as Novelty is of a very powerful, so of a most extensive
influence. Moralists have long since observed it to be the Source of
Admiration, which lessens in proportion to our Familiarity with
Objects, and upon a thorough Acquaintance is utterly extinguished. But
I think it hath not been so commonly remarked, that all the other
Passions depend considerably on the same Circumstance. What is it but
Novelty that awakens DeSir e, enhances Delight, kindles Anger, provokes
Envy, inspires Horror? To this Cause we must ascribe it, that Love
languishes with Fruition, and Friendship it self is recommended by
Intervals of Absence: Hence Monsters, by use, are beheld without
loathing, and the most enchanting Beauty without Rapture. That Emotion
of the Spirits in which Passion consists, is usually the Effect of
Surprize, and as long as it continues, heightens the agreeable or
disagreeable Qualities of its Object; but as this Emotion ceases (and
it ceases with the Novelty) things appear in another Light, and
affects us even less than might be expected from their proper Energy,
for having moved us too much before.
'It may not be an useless Enquiry how far the Love of Novelty is the
unavoidable Growth of Nature, and in what Respects it is peculiarly
adapted to the present State. To me it seems impossible, that a
reasonable Creature should rest absolutely satisfied in any
Acquisitions whatever, without endeavouring farther; for after its
highest Improvements, the Mind hath an Idea of an Infinity of things
still behind worth knowing, to the Knowledge of which therefore it
cannot be indifferent; as by climbing up a Hill in the midst of a wide
Plain, a Man hath his Prospect enlarged, and, together with that, the
Bounds of his DeSir es. Upon this Account, I cannot think he detracts
from the State of the Blessed, who conceives them to be perpetually
employed in fresh Searches into Nature, and to Eternity advancing into
the fathomless Depths of the Divine Perfections. In this Thought there
is nothing but what doth Honour to these glorified Spirits; provided
still it be remembred, that their DeSir e of more proceeds not from
their disrelishing what they possess; and the Pleasure of a new
Enjoyment is not with them measured by its Novelty (which is a thing
merely foreign and accidental) but by its real intrinsick Value. After
an Acquaintance of many thousand Years with the Works of God, the
Beauty and Magnificence of the Creation fills them with the same
pleasing Wonder and profound Awe, which Adam felt himself seized
with as he first opened his Eyes upon this glorious Scene. Truth
captivates with unborrowed Charms, and whatever hath once given
Satisfaction will always do it: In all which they have manifestly the
Advantage of us, who are so much govern'd by sickly and changeable
Appetites, that we can with the greatest Coldness behold the
stupendous Displays of Omnipotence, and be in Transports at the puny
Essays of humane Skill; throw aside Speculations of the sublimest
Nature and vastest Importance into some obscure Corner of the Mind, to
make Room for new Notions of no Consequence at all; are even tired of
Health, because not enlivened with alternate Pain, and prefer the
first Reading of an indifferent Author, to the second or third Perusal
of one whose Merit and Reputation are established.
Our being thus formed serves many useful Purposes in the present
State. It contributes not a little to the Advancement of Learning;
for, as Cicero takes Notice, That which makes Men willing to undergo
the Fatigues of Philosophical Disquisitions, is not so much the
Greatness of Objects as their Novelty. It is not enough that there is
Field and Game for the Chace, and that the Understanding is prompted
with a restless Thirst of Knowledge, effectually to rouse the Soul,
sunk into the State of Sloth and Indolence; it is also necessary that
there be an uncommon Pleasure annexed to the first Appearance of Truth
in the Mind. This Pleasure being exquisite for the Time it lasts, but
transient, it hereby comes to pass that the Mind grows into an
Indifference to its former Notions, and passes on after new
Discoveries, in hope of repeating the Delight. It is with Knowledge as
with Wealth, the Pleasure of which lies more in making endless
Additions, than in taking a Review of our old Store. There are some
Inconveniencies that follow this Temper, if not guarded against,
particularly this, that through a too great Eagerness of something new
we are many times impatient of staying long enough upon a Question
that requires some time to resolve it, or, which is worse, perswade
our selves that we are Masters of the Subject before we are so, only
to be at the Liberty of going upon a fresh Scent; in Mr. Lock's
Words, We see a little, presume a great deal, and so jump to the
Conclusion.
'A farther Advantage of our Inclination for Novelty, as at present
circumstantiated, is, that it annihilates all the boasted Distinctions
among Mankind. Look not up with Envy to those above thee. Sounding
Titles, stately Buildings, fine Gardens, gilded Chariots, rich
Equipages, what are they? They dazzle every one but the Possessor: To
him that is accustomed to them they are cheap and regardless Things:
They supply him not with brighter Images, or more sublime
Satisfactions than the plain Man may have, whose small Estate will
just enable him to support the Charge of a simple unencumbered Life.
He enters heedless into his Rooms of State, as you or I do under our
poor Sheds. The noble Paintings and costly Furniture are lost on him;
he sees them not: As how can it be otherwise, when by Custom, a
Fabrick infinitely more grand and finish'd, that of the Universe,
stands unobserved by the Inhabitants, and the everlasting Lamps of
Heaven are lighted up in vain, for any Notice that Mortals take of
them? Thanks to indulgent Nature, which not only placed her Children
originally upon a Level, but still, by the Strength of this Principle,
in a great Measure preserves it, in spite of all the Care of a Man, to
introduce artificial Distinctions.
'To add no more, Is not this Fondness for Novelty, which makes us out
of Conceit with all we already have, a convincing Proof of a future
State? Either Man was made in vain, or this is not the only World he
was made for: For there cannot be a greater Instance of Vanity, than
that to which Man is liable, to be deluded from the Cradle to the
Grave with fleeting Shadows of Happiness. His Pleasures, and those not
considerable neither, die in the Possession, and fresh Enjoyments do
not rise fast enough to fill up half his Life with Satisfaction. When
I see Persons sick of themselves any longer than they are called away
by something that is of Force to chain down the present Thought; when
I see them hurry from Country to Town, and then from the Town back
again into the Country, continually shifting Postures, and placing
Life in all the different Lights they can think of; Surely, say I to
my self, Life is vain, and the Man beyond Expression stupid or
prejudic'd, who from the Vanity of Life cannot gather, He is designed
for Immortality.
Footnote 1:
Meditations, &c.
by the Hon. Robert Boyle.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, December 1, 1714 |
|
Tantum inter densas umbrosa cacumine fagos
Assidue veniebat; ibi hæc incondita solus
Montibus et Sylvis studio jactabat inani.
Virg.

The following Account, which came to my Hands some time ago, may be no
disagreeable Entertainment to such of my Readers, as have tender Hearts
and nothing to do.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'A Friend of mine died of a Feaver last Week, which he caught by
walking too late in a dewy Evening amongst his Reapers. I must inform
you that his greatest Pleasure was in Husbandry and Gardening. He had
some Humours which seemed inconsistent with that good Sense he was
otherwise Master of. His Uneasiness in the Company of Women was very
remarkable in a Man of such perfect Good-breeding, and his avoiding
one particular Walk in his Garden, where he had used to pass the
greatest Part of his Time, raised abundance of idle Conjectures in the
Village where he lived. Upon looking over his Papers we found out the
Reason, which he never intimated to his nearest Friends. He was, it
seems, a passionate Lover in his Youth, of which a large Parcel of
Letters he left behind him are a Witness. I send you a Copy of the
last he ever wrote upon that Subject, by which you will find that he
concealed the true Name of his Mistress under that of
Zelinda.
A long Month's Absence would be insupportable to me, if the
Business I am employed in were not for the Service of my Zelinda,
and of such a Nature as to place her every Moment in my Mind. I have
furnished the House exactly according to your Fancy, or, if you
please, my own; for I have long since learned to like nothing but
what you do. The Apartment designed for your Use is so exact a Copy
of that which you live in, that I often think my self in your House
when I step into it, but sigh when I find it without its proper
Inhabitant. You will have the most delicious Prospect from your
Closet-window that England affords: I am sure I should think it
so, if the Landskip that shows such Variety did not at the same time
suggest to me the Greatness of the Space that lies between us.
The Gardens are laid out very beautifully; I have dressed up every
Hedge in Woodbines, sprinkled Bowers and Arbours in every Corner,
and made a little Paradise round me; yet I am still like the first
Man in his Solitude, but half blest without a Partner in my
Happiness. I have directed one Walk to be made for two Persons,
where I promise ten thousand Satisfactions to my self in your
Conversation. I already take my Evening's Turn in it, and have worn
a Path upon the Edge of this little Alley, while I soothed my self
with the Thought of your walking by my Side. I have held many
imaginary Discourses with you in this Retirement; and when I have
been weary have sat down with you in the midst of a Row of
Jessamines. The many Expressions of Joy and Rapture I use in these
silent Conversations have made me for some Time the Talk of the
Parish; but a neighbouring young Fellow, who makes Love to the
Farmer's Daughter, hath found me out, and made my Case known to the
whole Neighbourhood.
In planting of the Fruit-Trees I have not forgot the Peach you are
so fond of. I have made a Walk of Elms along the River Side, and
intend to sow all the Place about it with Cowslips, which I hope you
will like as well as that I have heard you talk of by your Father's
House in the Country.
Oh! Zelinda, What a Scheme of Delight have I drawn up in my
Imagination! What Day-Dreams do I indulge my self in! When will the
Six Weeks be at an End, that lye between me and my promised
Happiness?
How could you break off so abruptly in your last, and tell me you
must go and dress for the Play? If you loved as I do, you would find
no more Company in a Crowd, than I have in my Solitude.
I am, &c.
'On the Back of this Letter is written, in the Hand of the Deceased,
the following Piece of History.
Mem. Having waited a whole Week for an Answer to this Letter, I
hurried to Town, where I found the Perfidious Creature married to my
Rival. I will bear it as becomes a Man, and endeavour to find out
Happiness for my self in that Retirement, which I had prepared in
vain for a false ungrateful Woman.
I am,
&c.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Labitur et labetur in omne volubilis avum.
Hor.

Mr. SPECTATOR,
'There
are none of your Speculations which please me more than those
upon Infinitude and Eternity
1. You have already considered that
Part of Eternity which is past, and I wish you would give us your
Thoughts upon that which is to come.
'Your Readers will perhaps receive greater Pleasure from this View of
Eternity than the former, since we have every one of us a Concern in
that which is to come: Whereas a Speculation on that which is past is
rather curious than useful.
'Besides, we can easily conceive it possible for successive Duration
never to have an End; tho', as you have justly observed, that Eternity
which never had a Beginning is altogether incomprehensible; That is,
we can conceive an Eternal Duration which
may be, though we cannot
an Eternal Duration which
hath been; or, if I may use the
Philosophical Terms, we may apprehend a
Potential though not an
Actual Eternity.
'This Notion of a future Eternity, which is natural to the Mind of
Man, is an unanswerable Argument that he is a Being designed for it;
especially if we consider that he is capable of being Virtuous or
Vicious here; that he hath Faculties improvable to all Eternity, and
by a proper or wrong Employment of them, may be happy or miserable
throughout that infinite Duration. Our Idea indeed of this Eternity is
not of an adequate or fixed Nature, but is perpetually growing and
enlarging itself toward the Object, which is too big for human
Comprehension. As we are now in the Beginnings of Existence, so shall
we always appear to our selves as if we were for ever entring upon it.
After a Million or two of Centuries, some considerable Things, already
past, may slip out of our Memory; which, if it be not strengthened in
a wonderful Manner, may possibly forget that ever there was a Sun or
Planets. And yet, notwithstanding the long Race that we shall then
have run, we shall still imagine ourselves just starting from the
Goal, and find no Proportion between that Space which we know had a
Beginning, and what we are sure will never have an End.
'But I shall leave this Subject to your Management, and question not
but you will throw it into such Lights as shall at once improve and
entertain your Reader.
'I
have enclos'd sent you a Translation
2 of the Speech of
Cato on
this Occasion, which hath accidentally fallen into my Hands, and which
for Conciseness, Purity, and Elegance of Phrase, cannot be
sufficiently admired.
Act V. Scen. I.
Cato solus &c.
Sic, sic se habere rem necesse prorsus est,
Ratione vincis, do lubens manus, Plato.
Quid enim dedisset, Quæ dedit frustra nihil,
Æternitatis insitam cupidinem
Natura? Quorsum hæc dulcis Expectatio;
Vitæque non explenda melioris sitis?
Quid vult sibi aliud iste redeundi in nihil
Horror, sub imis quemque agens precordiis?
Cur territa in se refugit anima, cur tremit
Attonita, quoties, morte ne pereat, timet?
Particula nempe est cuique nascenti indita
Divinior; quæ corpus incolens agit;
Hominique succinit, Tua est Æternitas,
Æternitas! O lubricum nimis aspici,
Mixtumque dulci Gaudium formidine?
Quæ demigrabitur alia hinc in corpora?
Quæ Terra mox incognita? Quis orbis novus
Manet incolendus? Quanta erit mutatio?
Hæc intuenti spatia mihi quaquà patent
Immensa: Sed caliginosa nox premit;
Nec luce clarâ vult videri singula.
Figendus hic pes; certa sunt hæc hactenus:
Si quod gubernet Numen Humanum genus,
(At, quod gubernet, esse clamant omnia)
Virtute non gaudere certè non potest:
Nec esse non Beata, quâ gaudet, potest.
Sed quâ Beata sede? Quove in tempore?
Hæc quanta quanta terra, tola est Cæsaris.
Quid dubius hæret animus usque adeo? Brevi
Hic nodum hic omnem expediet. Arma en induor
Ensi manum admovens,
In utramque partem facta; quæque vim inferant,
Et quæ propulsent! Dextera intentat necem;
Vitam sinistra: Vulnus hæc dabit manus;
Altera medelam vulneris: Hic ad exitum
Deducet, ictu simplici; hæc vetant mori.
Secura ridet anima mucronis minas,
Ensesque strictos, interire nescia.
Extinguet ætas sidera diuturnior:
Ætate languens ipse Sol, obscurius
Emittet Orbi consenescenti jubar:
Natura et ipsa sentiet quondam vices
Ætatis, annis ipsa deficiet gravis:
At tibi juventus, at tibi immortalitas,
Tibi parta Divûm est vita. Periment mutuis
Elementa sese, et interibunt ictibus:
Tu permanebis sola semper integra,
Tu cuncta rerum quassa, cuncta naufraga,
Jam portu in ipso tuta, contemplabere.
Compage rupta, corruent in se invicem,
Orbesque fractis ingerentur orbibus;
Illæsa tu sedebis extra Fragmina.
Act V. Scen. I
Cato alone &c.
It must be so—Plato, thou reason'st well—
Else whence this pleasing Hope, this fond DeSir e,
This Longing after Immortality?
Or whence this secret Dread, and inward Horror,
Of falling into Nought? Why shrinks the Soul
Back on her self, and startles at Destruction?
'Tis the Divinity that stirs within us;
'Tis Heaven it self, that points out an Hereafter,
And intimates Eternity to Man.
Eternity! thou pleasing, dreadful, Thought!
Through what Variety of untry'd Being,
Through what new Scenes and Changes must we pass!
The wide, th' unbounded Prospect, lyes before me;
But Shadows, Clouds, and Darkness rest upon it.
Here will I hold. If there's a Pow'r above us,
(And that there is all Nature cries aloud
Through all her Works) He must delight in Virtue;
And that which he delights in, must be happy.
But when! or where!—This World was made for Cæsar.
I'm weary of Conjectures—This must end 'em.
Laying his Hand on his Sword.
Thus am I doubly arm'd: my Death and Life,
My Bane and Antidote are both before me.
This in a Moment brings me to an End;
But This informs me I shall never die.
The Soul, secur'd in her Existence, smiles
At the drawn Dagger, and defies its Point.
The Stars shall fade away, the Sun himself
Grow dim with Age, and Nature sink in Years;
But thou shalt flourish in immortal Youth,
Unhurt amidst the War of Elements,
The Wrecks of Matter and the Crush of Worlds.
Footnote 1:
Nos.
,
,
, and
.
Footnote 2:
By Mr., afterwards Dr., Bland, who became Provost of Eton
and Dean of Durham.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
Experiar quid concedatur in illos,
Quorum Flaminia tegitur cinis atque Latinâ.
Juv.

Next to the People who want a Place, there are none to be pitied more
than those who are solicited for one. A plain Answer, with a Denial in
it, is looked upon as Pride, and a civil Answer as a Promise.
Nothing is more ridiculous than the Pretensions of People upon these
Occasions. Every thing a Man hath suffered, whilst his Enemies were in
play, was certainly brought about by the Malice of the opposite Party. A
bad Cause would not have been lost, if such an one had not been upon the
Bench; nor a profligate Youth disinherited, if he had not got drunk
every Night by toasting an outed Ministry. I remember a Tory, who having
been fined in a Court of Justice for a Prank that deserved the Pillory,
de
Sir
'd upon the Merit of it to be made a Justice of Peace when his
Friends came into Power; and shall never forget a Whig Criminal, who,
upon being indicted for a Rape, told his Friends,
You see what a Man
suffers for sticking to his Principles.
The Truth of it is, the Sufferings of a Man in a Party are of a very
doubtful Nature. When they are such as have promoted a good Cause, and
fallen upon a Man undeservedly, they have a Right to be heard and
recompensed beyond any other Pretensions. But when they rise out of
Rashness or Indiscretion, and the Pursuit of such Measures as have
rather ruined, than promoted the Interest they aim at, (which hath
always been the Case of many great Sufferers) they only serve to
recommend them to the Children of Violence or Folly.
I have by me a Bundle of Memorials presented by several Cavaliers upon
the Restauration of K.
Charles
II. which may serve as so many
Instances, to our present Purpose.
Among several Persons and Pretensions recorded by my Author, he mentions
one of a very great Estate, who, for having roasted an Ox whole, and
distributed a Hogshead upon K.
Charles's
Birth-day, de
Sir
ed to be
provided for, as his Majesty in his great Wisdom shall think fit.
Another put in to be Prince
Henry's
, Governor, for having dared to
drink his Health in the worst of Times.
A Third petitioned for a Colonel's Commission, for having Cursed
Oliver
Cromwell
, the Day before his Death, on a publick Bowling-Green.
But the most whimsical Petition I have met with is that of
B. B.
Esq.,
who de
Sir
'd the Honour of Knighthood, for having Cuckolded
Sir
T. W.
a
notorious
Roundhead.
There is likewise the Petition of one, who having let his Beard grow
from the Martyrdom of K.
Charles
the First, till the Restauration of
K.
Charles
the Second, de
Sir
ed, in Consideration thereof, to be made a
Privy-Counsellor.
I must not omit a Memorial setting forth, that the Memorialist had, with
great dispatch, carried a Letter from a certain Lord to a certain Lord,
wherein, as it afterwards appeared, Measures were concerted for the
Restauration, and without which he verily believes that happy Revolution
had never been effected; who thereupon humbly prays to be made
Post-Master-General.
A certain Gentleman, who seems to write with a great deal of Spirit, and
uses the Words
Gallantry
and
Gentleman-like
very often in his
Petition, begs that (in Consideration of his having worn his Hat for ten
Years past in the Loyal Cavalier-Cock, to his great Danger and
Detriment) he may be made a Captain of the Guards.
I shall close my Account of this Collection of Memorials, with the Copy
of one Petition at length, which I recommend to my Reader as a very
valuable Piece.
The Petition of E. H. Esq., humbly Sheweth,
'That your Petitioner's Father's Brother's Uncle, Colonel W. H. lost
the Third Finger of his Left Hand at Edge-hill Fight.
'That your Petitioner, notwithstanding the Smallness of his Fortune,
(he being a younger Brother) always kept Hospitality, and drank
Confusion to the Roundheads in half a Score Bumpers every Sunday in
the Year, as several honest Gentlemen (whose Names are underwritten)
are ready to testifie.
'That your Petitioner is remarkable in his Country for having dared to
treat Sir P. P. a cursed Sequestrator, and three Members of the
Assembly of Divines, with Brawn and Minced Pies upon New Year's Day.
'That your said humble Petitioner hath been five times imprisoned in
five several County-Goals, for having been a Ring-leader in five
different Riots; into which his Zeal for the Royal Cause hurried him,
when men of greater Estates had not the Courage to rise.
'That he, the said E. H. hath had six Duels and four and twenty
Boxing-Matches in Defence of his Majesty's Title; and that he received
such a Blow upon the Head at a Bonfire in Stratford upon Avon, as
he hath been never the better for from that Day to this.
'That your Petitioner hath been so far from improving his Fortune, in
the late damnable Times, that he verily believes, and hath good Reason
to imagine, that if he had been Master of an Estate, he had infallibly
been plundered and sequestred.
'Your Petitioner, in Consideration of his said Merits and Sufferings,
humbly requests that he may have the Place of Receiver of the Taxes,
Collector of the Customs, Clerk of the Peace, Deputy Lieutenant, or
whatsoever else he shall be thought qualified for.
And your Petitioner shall ever Pray, &c.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, December 8, 1714 |
|
—Favete linguis—
Hor.

Having no spare Time to write any thing of my own, or to correct what is
sent me by others, I have thought fit to publish the following Letters.
Oxford, November 22.
Sir ,
'If you would be so kind to me, as to suspend that Satisfaction, which
the Learned World must receive in reading one of your Speculations, by
publishing this Endeavour, you will very much oblige and improve one,
who has the Boldness to hope, that he may be admitted into the number
of your Correspondents.
'I have often wondered to hear Men of good Sense and good Nature
profess a Dislike to Musick, when, at the same time, they do not
scruple to own, that it has the most agreeable and improving
Influences over their Minds: It seems to me an unhappy Contradiction,
that those Persons should have an Indifference for an Art, which
raises in them such a Variety of sublime Pleasures.
'However, though some few, by their own or the unreasonable Prejudices
of others, may be led into a Distaste for those Musical Societies
which are erected merely for Entertainment, yet sure I may venture to
say, that no one can have the least Reason for Disaffection to that
solemn kind of Melody which consists of the Praises of our Creator.
'You have, I presume, already prevented me in an Argument upon this
Occasion (which some Divines have successfully advanced upon a much
greater) that Musical Sacrifice and Adoration has claimed a Place in
the Laws and Customs of the most different Nations; As the
Grecians
and
Romans of the Prophane, the
Jews and
Christians of the
Sacred World did as unanimously agree in this, as they disagreed in
all other Parts of their œconomy.
'I know there are not wanting some who are of Opinion that the pompous
kind of Musick which is in Use in foreign Churches is the most
excellent, as it most affects our Senses. But I am swayed by my
Judgment to the Modesty which is observed in the musical Part of our
Devotions. Methinks there is something very laudable in the Custom of
a
Voluntary before the first Lesson; by this we are supposed to be
prepared for the Admission of those Divine Truths, which we are
shortly to receive. We are then to cast all worldly Regards from off
our Hearts, all Tumults within are then becalmed, and there should be
nothing near the Soul but Peace and Tranquility. So that in this short
Office of Praise, the Man is raised above himself, and is almost lost
already amidst the Joys of Futurity.
'I have heard some nice Observers frequently commend the Policy of our
Church in this Particular, that it leads us on by such easie and
regular Methods, that we are perfectly deceived into Piety. When the
Spirits begin to languish (as they too often do) with a constant
Series of Petitions, she takes care to allow them a pious Respite, and
relieves them with the Raptures of an Anthem. Nor can we doubt that
the sublimest Poetry, softened in the most moving Strains of Musick,
can ever fail of humbling or exalting the Soul to any Pitch of
Devotion. Who can hear the Terrors of the Lord of Hosts described in
the most expressive Melody, without being awed into a Veneration? or
who can hear the kind and endearing Attributes of a merciful Father,
and not be softened into Love towards him!
'As the rising and sinking of the Passions, the casting soft or noble
Hints into the Soul, is the natural Privilege of Musick in general, so
more particularly of that kind which is employed at the Altar. Those
Impressions which it leaves upon the Spirits are more deep and
lasting, as the Grounds from which it receives its Authority are
founded more upon Reason. It diffuses a Calmness all around us, it
makes us drop all those vain or immodest
Thoughts which would be an
hindrance to us in the Performance of that great Duty of Thanksgiving
1, which, as we are informed by our Almighty Benefactor, is the most
acceptable Return which can be made for those infinite Stores of
Blessings which he daily condescends to pour down upon his Creatures.
When we make Use of this pathetical Method of addressing our selves to
him, we can scarce contain from Raptures! The Heart is warmed with a
Sublimity of Goodness. We are all Piety and all Love!
'How do the Blessed Spirits rejoice and wonder to behold unthinking
Man prostrating his Soul to his dread Sovereign in such a Warmth of
Piety as they themselves might not be ashamed of!
'I shall close these Reflections with a Passage taken out of the Third
Book of
Milton's Paradise Lost, where those harmonious Beings are
thus nobly described.
Then Crown'd again, their Gold'n Harps they took,
Harps ever tun'd, that glittering by their side
Like Quivers hung, and with Preamble sweet
Of Charming Symphony they introduce
The Sacred Song, and waken Raptures high;
No one exempt, no Voice but well could join
Melodious part, such Concord is in Heav'n
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'The Town cannot be unacquainted, that in divers Parts of it there are
vociferous Setts of Men who are called
Rattling Clubs; but what
shocks me most is, they have now the Front to invade the Church and
institute these Societies there, as a Clan of them have in late times
done, to such a degree of Insolence, as has given the Partition where
they reside in a Church near one of the City Gates, the Denomination
of the
Rattling Pew. These gay Fellows, from humble Lay Professions,
set up for Criticks without any Tincture of Letters or Reading, and
have the Vanity to think they can lay hold of something from the
Parson, which may be formed into Ridicule.
'It is needless to observe, that the Gentlemen who every
Sunday have
the hard Province of Instructing these Wretches in a way they are in
no present Disposition to take, have a fixt Character for Learning and
Eloquence, not to be tainted by the weak Efforts of this Contemptible
Part of their Audiences. Whether the Pulpit is taken by these
Gentlemen, or any Strangers their Friends, the way of the Club is
this: If any Sentiments are delivered too Sublime for their
Conception; if any uncommon Topick is entered on, or one in use new
modified with the finest Judgment and Dexterity; or any controverted
Point be never so elegantly handled; In short whatever surpasses the
narrow Limits of their Theology, or is not suited to their Taste, they
are all immediately upon their Watch, fixing their Eyes upon each
other, with as much Warmth as our Gladiators of
Hockley in the Hole,
and waiting like them for a Hit; if one touches, all take Fire, and
their Noddles instantly meet in the Centre of the Pew; then, as by
beat of Drum, with exact Discipline, they rear up into a full length
of Stature, and with odd Looks and Gesticulations confer together in
so loud and clamorous a manner, continued to the close of the
Discourse, and during the After-Psalm, as is not to be silenced but by
the Bells. Nor does this suffice them, without aiming to propagate
their Noise through all the Church, by Signals given to the adjoyning
Seats, where others designed for this Fraternity are sometimes placed
upon Tryal to receive them.
'The Folly as well as Rudeness of this Practice is in nothing more
conspicuous than this, that all that follows in the Sermon is lost;
for whenever our Sparks take alarm, they blaze out and grow so
Tumultuous that no After-Explanation can avail, it being impossible
for themselves or any near them to give an Account thereof. If any
thing really Novel is advanced, how averse soever it may be to their
way of thinking, to say nothing of Duty, Men of less Levity than these
would be led by a natural Curiosity to hear the whole.
'Laughter, where things Sacred are transacted, is far less pardonable
than Whining at a Conventicle; the last has at least a Semblance of
Grace, and where the Affectation is unseen may possibly imprint
wholesome Lessons on the Sincere; but the first has no Excuse,
breaking through all the Rules of Order and Decency, and manifesting a
Remissness of Mind in those important Matters, which require the
strictest Composure and Steadiness of Thought; A Proof of the greatest
Folly in the World.
'I shall not here enter upon the Veneration due to the Sanctity of the
Place, the Reverence owing to the Minister, or the Respect that so
great an Assembly as a whole Parish may justly claim. I shall only
tell them, that as the
Spanish Cobler, to reclaim a profligate Son,
bid him
have some regard to the Dignity of his Family, so they as
Gentlemen (for we Citizens assume to be such one Day in a Week) are
bound for the future to Repent of, and Abstain from, the gross Abuses
here mentioned, whereof they have been Guilty in Contempt of Heaven
and Earth, and contrary to the Laws in this Case made and provided.
I am, Sir ,
Your very humble Servant,
R. M.
Footnote 1:
A Proclamation appeared the day before this Paper,
ordaining a Thanksgiving for King George's Accession to be observed on
the 20th of January.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Friday, December 10, 1714 |
|
—Simplex Munditiis—
Hor.

I had occasion to go a few Miles out of Town, some Days since, in a
Stage-Coach, where I had for my Fellow-Tavellers a dirty Beau, and a
pretty young Quaker-Woman. Having no Inclination to Talk much at that
time, I placed my self backward, with a design to survey them, and pick
a Speculation out of my two Companions. Their different Figures were
sufficient of themselves to draw my Attention. The Gentleman was dressed
in a Suit, the Ground whereof had been Black, as I perceived from some
few Spaces, that had escaped the Powder,
was Incorporated with the
greatest part of his Coat: His Perriwig, which cost no small Sum
,
was after so slovenly a manner cast over his Shoulders, that it seemed
not to have been combed since the Year 1712; his Linnen, which was not
much concealed, was daubed with plain
Spanish
from the Chin to the
lowest Button, and the Diamond upon his Finger (which naturally dreaded
the Water) put me in Mind how it sparkled amidst the Rubbish of the
Mine, where it was first discovered. On the other hand, the pretty
Quaker appeared in all the Elegance of Cleanliness. Not a Speck was to
be found on her. A clear, clean oval Face, just edged about with little
thin Plaits of the purest Cambrick, received great Advantages from the
Shade of her black Hood; as did the Whiteness of her Arms from that
sober-coloured Stuff, in which she had Cloathed her self. The Plainness
of her Dress was very well suited to the Simplicity of her Phrases; all
which put together, though they could not give me a great Opinion of her
Religion, they did of her Innocence.
This Adventure occasioned my throwing together a few hints upon
Cleanliness
, which I shall consider as one of the
Half-Virtues
, as
Aristotle
calls them, and shall recommend it under the three following
Heads, As it is a Mark of Politeness; As it produces Love; and As it
bears Analogy to Purity of Mind.
First
, It is a Mark of Politeness. It is universally agreed upon, that
no one, unadorn'd with this Virtue, can go into Company without giving a
manifest Offence. The easier or higher any one's Fortune is, this Duty
arises proportionably. The different Nations of the World are as much
distinguished by their Cleanliness, as by their Arts and Sciences. The
more any Country is civilized, the more they consult this part of
Politeness. We need but compare our Ideas of a Female
Hottentot
and an
English
Beauty, to be satisfied of the Truth of what hath been
advanced.
In the next Place, Cleanliness may be said to be the Foster-Mother of
Love. Beauty indeed most commonly produces that Passion in the Mind, but
Cleanliness preserves it. An indifferent Face and Person, kept in
perpetual Neatness, had won many a Heart from a pretty Slattern. Age it
self is not unamiable, while it is preserved clean and unsullied: Like a
piece of Metal constantly kept smooth and bright, we look on it with
more Pleasure than on a new Vessel that is canker'd with Rust.
I might observe farther, that as Cleanliness renders us agreeable to
others, so it makes us easie to our selves; that it is an excellent
Preservative of Health; and that several Vices, destructive both to Mind
and Body, are inconsistent with the Habit of it. But these Reflections I
shall leave to the Leisure of my Readers, and shall observe in the Third
Place, that it bears a great Analogy with Purity of Mind, and naturally
inspires refined Sentiments and Passions.
We find from Experience, that through the Prevalence of Custom, the most
vicious Actions lose their Horror, by being made familiar to us. On the
contrary, those who live in the Neighbourhood of good Examples, fly from
the first Appearances of what is shocking. It fares with us much after
the same Manner, as to our Ideas. Our Senses, which are the Inlets to
all the Images conveyed to the Mind, can only transmit the Impression of
such things as usually surround them. So that pure and unsullied
Thoughts are naturally suggested to the Mind, by those Objects that
perpetually encompass us, when they are beautiful and elegant in their
kind.
In the East, where the Warmth of the Climate makes Cleanliness more
immediately necessary than in colder Countries, it is made one Part of
their Religion: The
Jewish
Law, (and the
Mahometan
, which in some
things copies after it) is filled with Bathings, Purifications, and
other Rites of the like Nature. Though there is the above-named
convenient Reason to be assigned for these Ceremonies, the chief
Intention undoubtedly was to typifie inward Purity and Cleanness of
Heart by those outward Washings. We read several Injunctions of this
Kind in the Book of
Deuteronomy
, which confirm this Truth; and which
are but ill accounted for by saying, as some do, that they were only
instituted for Convenience in the Desart, which otherwise could not have
been habitable for so many Years.
I shall conclude this Essay, with a Story which I have somewhere read in
an Account of
Mahometan
Superstitions.
A
Dervise
of great Sanctity one Morning had the Misfortune as he took
up a Chrystal Cup, which was consecrated to the Prophet, to let it fall
upon the Ground, and dash it in Pieces. His Son coming in, some time
after, he stretched out his Hands to bless him, as his manner was every
Morning; but the Youth going out stumbled over the Threshold and broke
his Arm. As the old Man wondered at these Events, a Caravan passed by in
its way from
Mecca.
The
Dervise
approached it to beg a Blessing; but
as he stroaked one of the Holy Camels, he received a Kick from the
Beast, that sorely bruised him. His Sorrow and Amazement increased upon
him, till he recollected that through Hurry and Inadvertency he had that
Morning come abroad without washing his Hands.
Footnote 1:
Duumvir's fair wig cost 40 guineas.
Tatler
, No. 54.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Monday, December 13, 1714 |
|
—Explebo numerum, reddarque tenebris—
Virg.

The Love of Symmetry and Order, which is natural to the Mind of Man,
betrays him sometimes into very whimsical Fancies.
This noble
Principle,
says a
French
Author,
loves to amuse it self on the most
trifling Occasions. You may see a profound Philosopher
, says he,
walk
for an Hour together in his Chamber, and industriously treading, at
every Step, upon every other Board in the Flooring.
Every Reader will
recollect several Instances of this Nature without my Assistance. I
it was
Gregorio Leti
who had published as many Books as he was
Years old
; which was a Rule he had laid down and punctually observed
to the Year of his Death. It was, perhaps, a Thought of the like Nature
which determined
Homer
himself to divide each of his Poems into as
many Books, as there are Letters in the
Greek
Alphabet.
Herodotus
has in the same manner adapted his Books to the Number of the
Muses
,
for which Reason many a Learned man hath wished there had been more than
Nine of that Sisterhood.
Several
Epic
Poets have religiously followed
Virgil
as to the Number
of his Books; and even
Milton
is thought by many to have changed the
Number of his Books from Ten to Twelve, for no other Reason; as
Cowley
tells us, it was his Design, had he finished his
Davideis
, to have
also imitated the
Æneid
in this Particular. I believe every one will
agree with me, that a Perfection of this Nature hath no Foundation in
Reason; and, with due Respect to these great Names, may be looked upon
as something whimsical.
I mention these great Examples in Defence of my Bookseller, who
occasioned this Eighth Volume of
Spectators
, because, as he said, he
thought Seven a very Odd Number. On the other Side, several grave
Reasons were urged on this important Subject; as in particular, that
Seven was the precise Number of the Wise Men, and that the most
Beautiful Constellation in the Heavens was composed of Seven Stars. This
he allowed to be true, but still insisted, that Seven was an Odd Number;
suggesting at the same time that if he were provided with a sufficient
Stock of leading Papers, he should find Friends ready enough to carry on
the Work. Having by this means got his Vessel launched and set afloat,
he hath committed the Steerage of it, from time to time, to such as he
thought capable of conducting it.
The Close of this Volume, which the Town may now expect in a little
time, may possibly ascribe each Sheet to its proper Author.
It were no hard Task to continue this Paper a considerable Time longer,
by the Help of large Contributions sent from unknown Hands.
I cannot give the Town a better Opinion of the
Spectator's
Correspondents, than by publishing the following Letter, with a very
fine Copy of Verses upon a Subject perfectly new.
Dublin, Nov. 30, 1714.
Mr. SPECTATOR,
'You lately recommended to your Female Readers, the good old Custom of
their Grandmothers, who used to lay out a great Part of their Time in
Needle-work: I entirely agree with you in your Sentiments, and think
it would not be of less Advantage to themselves, and their Posterity,
than to the Reputation of many of their good Neighbours, if they past
many of those Hours in this innocent Entertainment, which are lost at
the Tea-Table. I would, however, humbly offer to your Consideration,
the Case of the Poetical Ladies; who, though they may be willing to
take any Advice given them by the SPECTATOR, yet can't so easily quit
their Pen and Ink, as you may imagine. Pray allow them, at least now
and then, to indulge themselves in other Amusements of Fancy, when
they are tired with stooping to their Tapestry. There is a very
particular kind of Work, which of late several Ladies here in our
Kingdom are very fond of, which seems very well adapted to a Poetical
Genius: It is the making of
Grotto's. I know a Lady who has a very
Beautiful one, composed by her self, nor is there one Shell in it not
stuck up by her own Hands. I here send you a Poem to the fair
Architect, which I would not offer to herself, till I knew whether
this Method of a Lady's passing her Time were approved of by the
British SPECTATOR, which, with the Poem, I submit to your Censure,
who am,
Your Constant Reader, and Humble Servant,
A. B.
To Mrs. — on her Grotto.
A Grotto so compleat, with such Design,
What Hands, Calypso, cou'd have form'd but Thine?
Each chequer'd Pebble, and each shining Shell,
So well proportion'd, and dispos'd so well,
Surprizing Lustre from thy Thought receive,
Assuming Beauties more than Nature gave.
To Her their various Shapes, and glossy Hue,
Their curious Symmetry they owe to You.
Not fam'd Amphion's Lute,—whose powerful Call
Made Willing Stones dance to the Theban Wall,
In more harmonious Ranks cou'd make them fall.
Not Ev'ning Cloud a brighter Arch can show,
Nor richer Colours paint the heav'nly Bow.
Where can unpolished Nature boast a Piece,
In all her Mossie Cells exact as This?
At the gay parti-color'd Scene—we start,
For Chance too regular, too rude for Art,
Charmed with the sight, my ravish'd Breast is fir'd
With Hints like those which ancient Bards inspir'd;
All the feign'd Tales by Superstition told,
All the bright Train of fabled Nymphs of Old,
Th' enthusiastick Muse believes are true,
Thinks the Spot sacred, and its Genius You.
Lost in wild Rapture, wou'd she fain disclose,
How by degrees the pleasing Wonder rose:
Industrious in a faithful Verse to trace
The various Beauties of the lovely Place;
And while she keeps the glowing Work in View,
Thro' ev'ry Maze thy Artful Hand pursue.
Oh were I equal to the bold Design,
Or cou'd I boast such happy Art as Thine!
That cou'd rude Shells in such sweet Order place,
Give common Objects such uncommon Grace!
Like them my well-chose Words in ev'ry Line,
As sweetly temper'd should as sweetly shine.
So just a Fancy shou'd my Numbers warm,
Like the gay Piece shou'd the Description charm.
Then with superior Strength my Voice I'd raise,
The echoing Grotto shou'd approve my Lays,
Pleas'd to reflect the well-sung Founder's Praise.
Footnote 1:
His boast was that he had been the author of a book and
father of a child for 20 years successively.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Wednesday, December 15, 1714 |
Z. Pearce |
Omnia profecto, cum se à cœlestibus rebus referet ad humanas,
excelsius magnificentiusque et dicet et sentiet.
Cicer.

The following Discourse is printed, as it came to my Hands, without
Variation.
Cambridge, Dec. 12.
'It was a very common Enquiry among the Ancients why the Number of
excellent Orators, under all the Encouragements the most flourishing
States could give them, fell so far short of the Number of those who
excelled in all other Sciences. A Friend of mine used merrily to apply
to this Case an Observation of Herodotus, who says, That the most
useful Animals are the most fruitful in their Generation; whereas the
Species of those Beasts that are fierce and mischievous to Mankind are
but scarcely continued. The Historian instances in a Hare, which
always either breeds or brings forth; and a Lioness, which brings
forth but once, and then loses all Power of Conception. But, leaving
my Friend to his Mirth, I am of Opinion, that in these latter Ages we
have greater Cause of Complaint than the Ancients had. And since that
solemn Festival is approaching, which calls for all the Power of
Oratory, and which affords as noble a Subject for the Pulpit as any
Revelation has taught us, the Design of this Paper shall be to show,
that our Moderns have greater Advantages towards true and solid
Eloquence, than any which the celebrated Speakers of Antiquity
enjoy'd.
'The first great and substantial Difference is, that their
Common-Places, in which almost the whole Force of Amplification
consists, were drawn from the Profit or Honesty of the Action, as they
regarded only this present State of Duration. But Christianity, as it
exalts Morality to a greater Perfection, as it brings the
Consideration of another Life into the Question, as it proposes
Rewards and Punishments of a higher Nature, and a longer Continuance,
is more adapted to affect the Minds of the Audience, naturally
inclined to pursue what it imagines its greatest Interest and Concern.
If Pericles, as Historians report, could shake the firmest
Resolutions of his Hearers, and set the Passions of all Greece in a
Ferment, when the present Welfare of his Country, or the Fear of
hostile Invasions, was the Subject: What may be expected from that
Orator, who warns his Audience against those Evils which have no
Remedy, when once undergone, either from Prudence or Time? As much
greater as the Evils in a future State are than these at present, so
much are the Motives to Persuasion under Christianity greater than
those which meer moral Considerations could supply us with. But what I
now mention relates only to the Power of moving the Affections. There
is another Part of Eloquence, which is indeed its Master-piece; I mean
the Marvellous or Sublime. In this the Christian Orator has the
Advantage beyond Contradiction. Our Ideas are so infinitely enlarged
by Revelation, the Eye of Reason has so wide a Prospect into Eternity,
the Notions of a Deity are so worthy and refined, and the Accounts we
have of a State of Happiness or Misery so clear and evident, that the
Contemplation of such Objects will give our Discourse a noble Vigour,
an invincible Force, beyond the Power of any human Consideration.
Tully requires in his Perfect Orator some Skill in the Nature of
Heavenly Bodies, because, says he, his Mind will become more extensive
and unconfined; and when he descends to treat of human Affairs, he
will both think and write in a more exalted and magnificent Manner.
For the same Reason that excellent Master would have recommended the
Study of those great and glorious Mysteries which Revelation has
discovered to us; to which the noblest Parts of this System of the
World are as much inferiour, as the Creature is less excellent than
its Creator. The wisest and most knowing among the Heathens had very
poor and imperfect Notions of a future State. They had indeed some
uncertain Hopes, either received by Tradition, or, gathered by Reason,
that the Existence of virtuous Men would not be determined by the
Separation of Soul and Body: But they either disbelieved a future
State of Punishment and Misery, or upon the same Account that
Apelles painted Antigonus with one Side only towards the
Spectator, that the Loss of his Eye might not cast a Blemish upon the
whole Piece; so these represented the Condition of Man in its fairest
View, and endeavoured to conceal what they thought was a Deformity to
human Nature. I have often observed, that whenever the abovementioned
Orator in his Philosophical Discourses is led by his Argument to the
Mention of Immortality, he seems like one awaked out of Sleep, rous'd
and alarm'd with the Dignity of the Subject, he stretches his
Imagination to conceive something uncommon, and with the greatness of
his Thoughts, casts, as it were, a Glory round the Sentence; Uncertain
and unsettled as he was, he seems fired with the Contemplation of it.
And nothing but such a Glorious Prospect could have forced so great a
Lover of Truth, as he was, to declare his Resolution never to part
with his Persuasion of Immortality, though it should be proved to be
an erroneous one. But had he lived to see all that Christianity has
brought to Light, how would he have lavished out all the Force of
Eloquence in those noblest Contemplations which humane Nature is
capable of, the Resurrection and the Judgment that follows it? How had
his Breast glowed with Pleasure, when the whole Compass of Futurity
lay open and exposed to his View? How would his Imagination have
hurried him on in the Pursuit of the Mysteries of the Incarnation? How
would he have enter'd, with the Force of Lightning, into the
Affections of his Hearers, and fixed their Attention, in spite of all
the Opposition of corrupt Nature, upon those glorious Themes which his
Eloquence hath painted in such lively and lasting Colours?
'This Advantage Christians have; and it was with no small Pleasure I
lately met with a Fragment of Longinus, which is preserv'd, as a
Testimony of that Critick's Judgment, at the Beginning of a Manuscript
of the New Testament in the Vatican Library. After that Author has
number'd up the most celebrated Orators among the Grecians, he says,
Add to these Paul of Tarsus, the Patron of an Opinion not yet
fully proved. As a Heathen, he condemns the Christian Religion; and,
as an impartial Critick, he judges in Favour of the Promoter and
Preacher of it. To me it seems, that the latter Part of his Judgment
adds great Weight to his Opinion of St. Paul's Abilities, since,
under all the Prejudice of Opinions directly opposite, he is
constrained to acknowledge the Merit of that Apostle. And, no doubt,
such as Longinus describes St. Paul, such he appeared to the
Inhabitants of those Countries which he visited and blessed with those
Doctrines was divinely commissioned to preach. Sacred Story gives us,
in one Circumstance, a convincing Proof of his Eloquence, when the Men
of Lystra called him Mercury, because he was the chief Speaker,
and would have paid Divine Worship to him, as to the God who invented
and presided over Eloquence. This one Account of our Apostle sets his
Character, consider'd as an Orator only, above all the celebrated
Relations of the Skill and Influence of Demosthenes and his
Contemporaries. Their Power in Speaking was admired, but still it was
thought human: Their Eloquence warmed and ravished the Hearers, but
still it was thought the Voice of Man, not the Voice of God. What
Advantage then had St. Paul above those of Greece, or Rome? I
confess I can ascribe this Excellence to nothing but the Power of the
Doctrines he delivered, which may have still the same Influence on the
Hearers; which have still the Power, when preached by a skilful
Orator, to make us break out in the same Expressions, as the Disciples
who met our Saviour in their Way to Emmaus, made use of; Did not
our Hearts burn within us, when he talked to us by the Way, and while
he opened to us the Scriptures? I may be thought bold in my Judgment
by some; but I must affirm, That no one Orator has left us so visible
Marks and Footsteps of his Eloquence as our Apostle. It may perhaps be
wondered at, that in his Reasonings upon Idolatry at Athens, where
Eloquence was born and flourished, he confines himself to strict
Argument only; but my Reader may remember what many Authors of the
best Credit have assured us, That all Attempts upon the Affections and
Strokes of Oratory were expressly forbidden, by the Laws of that
Country, in Courts of Judicature. His want of Eloquence therefore
here, was the Effect of his exact Conformity to the Laws. But his
Discourse on the Resurrection to the Corinthians, his Harangue
before Agrippa upon his own Conversion and the Necessity of that of
others, are truly Great, and may serve as full Examples to those
excellent Rules for the Sublime, which the best of Criticks has left
us. The Sum of all this Discourse is, That our Clergy have no farther
to look for an Example of the Perfection they may arrive at, than to
St. Paul's Harangues; that when he, under the Want of several
Advantages of Nature (as he himself tells us) was heard, admired, and
made a Standard to succeeding Ages by the best Judge of a different
Persuasion in Religion, I say our Clergy may learn, That, however
instructive their Sermons are, they are capable of receiving a great
Addition; which St. Paul has given them a noble Example of, and the
Christian Religion has furnished them with certain Means of attaining
to.'
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Friday, December 17, 1714 |
|
It was the common Boast of the Heathen Philosophers, that by the
Efficacy of their several Doctrines, they made Humane Nature resemble
the Divine. How much mistaken soever they might be in the several Means
they proposed for this End, it must be owned that the Design was great
and glorious. The finest Works of Invention and Imagination are of very
little Weight, when put in the Balance with what refines and exalts the
rational Mind.
Longinus
excuses
Homer
very handsomely, when he says
the Poet made his Gods like Men, that he might make his Men appear like
the Gods: But it must be allowed that several of the ancient
Philosophers acted, as
Cicero
wishes
Homer
had done; they
endeavoured rather to make Men like Gods, than Gods like Men.
According to this general Maxim in Philosophy, some of them have
endeavoured to place Men in such a State of Pleasure, or Indolence at
least, as they vainly imagined the Happiness of the Supreme Being to
consist in. On the other Hand, the most virtuous Sect of Philosophers
have created a chimerical wise Man, whom they made exempt from Passion
and Pain, and thought it enough to pronounce him All-sufficient.
This last Character, when divested of the Glare of Humane Philosophy
that surrounds it, signifies no more, than that a Good and Wise Man
should so arm himself with Patience, as not to yield tamely to the
Violence of Passion and Pain; that he should learn so to suppress and
contract his De
Sir
es as to have few Wants; and that he should cherish so
many Virtues in his Soul, as to have a perpetual Source of Pleasure in
himself.
The Christian Religion requires, that, after having framed the best
Idea, we are able, of the Divine Nature, it should be our next Care to
conform our selves to it, as far as our Imperfections will permit. I
might mention several Passages in the sacred Writings on this Head, to
which I might add many Maxims and wise Sayings of Moral Authors among
the
Greeks
and
Romans
.
I shall only instance a remarkable Passage, to this Purpose, out of
Julian's Cæsars
. The Emperor having represented all the
Roman
Emperors, with
Alexander
the Great, as passing in Review before the
Gods, and striving for the Superiority, lets them all drop, excepting
Alexander
,
Julius Cæsar
,
Augustus Cæsar
,
Trajan
,
Marcus
Aurelius
, and
Constantine
. Each of these great Heroes of Antiquity
lays in his Claim for the upper Place; and, in Order to it, sets forth
his Actions after the most advantageous Manner. But the Gods, instead of
being dazzled with the Lustre of their Actions, enquire, by
Mercury
,
into the proper Motive and governing Principle that influenced them
throughout the whole Series of their Lives and Exploits.
Alexander
tells them, That his Aim was to conquer:
Julius Cæsar
, that his was to
gain the highest Post in his Country;
Augustus
, To govern well;
Trajan
, That His was the same as that of
Alexander
, namely, To
conquer. The Question, at length, was put to
Marcus Aurelius
, who
replied, with great Modesty, That
it had always been his Care to
imitate the Gods
. This Conduct seems to have gained him the most Votes
and best Place in the whole Assembly.
Marcus Aurelius
being afterwards
asked to explain himself declares, That, by imitating the Gods, he
endeavoured to imitate them in the Use of his Understanding, and of all
other Faculties; and, in particular, That it was always his Study to
have as few Wants as possible in himself, and to do all the Good he
could to others.
Among the many Methods by which Revealed Religion has advanced Morality,
this is one, That it has given us a more just and perfect Idea of that
Being whom every reasonable Creature ought to imitate. The young Man, in
a Heathen Comedy, might justify his Lewdness by the Example of
Jupiter
; as, indeed, there was scarce any Crime that might not be
countenanced by those Notions of the Deity which prevailed among the
common People in the Heathen World. Revealed Religion sets forth a
proper Object for Imitation, in that Being who is the Pattern, as well
as the Source, of all spiritual Perfection.
While we remain in this Life, we are subject to innumerable Temptations,
which, if listen'd to, will make us deviate from Reason and Goodness,
the only Things wherein we can imitate the Supreme Being. In the next
Life we meet with nothing to excite our Inclinations that doth not
deserve them. I shall therefore dismiss my Reader with this Maxim, viz.
Our Happiness in this World proceeds from the Suppression of our
DeSir es, but in the next World from the Gratification of them.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
|
Monday, December 20, 1714 |
Henry Grove |
Sentio Te sedem Hominum ac Domum contemplarique si tibi parva (ut
est) ita videtur, hæc cœlestia semper Spectato; illa humana
contemnito.
Cicero
Somn. Scip.
The following Essay comes from the ingenious Author of the Letter upon
Novelty
, printed in a late
Spectator:
The Notions are drawn from the
Platonick
way of Thinking, but as they contribute to raise the Mind,
and may inspire noble Sentiments of our own future Grandeur and
Happiness, I think it well deserves to be presented to the Publick.
If the Universe be the Creature of an intelligent Mind, this Mind could
have no immediate Regard to himself in producing it. He needed not to
make Tryal of his Omnipotence, to be informed what Effects were within
its Reach: The World as existing in his eternal Idea was then as
beautiful as now it is drawn forth into Being; and in the immense Abyss
of his Essence are contained far brighter Scenes than will be ever set
forth to View; it being impossible that the great Author of Nature
should bound his own Power by giving Existence to a System of Creatures
so perfect that he cannot improve upon it by any other Exertions of his
Almighty Will. Between Finite and Infinite there is an unmeasured
Interval, not to be filled up in endless Ages; for which Reason, the
most excellent of all God's Works must be equally short of what his
Power is able to produce as the most imperfect, and may be exceeded with
the same Ease.
This Thought hath made some imagine, (what, it must be confest, is not
impossible) that the unfathomed Space is ever teeming with new Births,
the younger still inheriting a greater Perfection than the elder. But as
this doth not fall within my present View, I shall content my self with
taking Notice, that the Consideration now mentioned proves undeniably,
that the Ideal Worlds in the Divine Understanding yield a Prospect
incomparably more ample, various and delightful than any Created World
can do: And that therefore as it is not to be supposed that God should
make a World merely of inanimate Matter, however diversified; or
inhabited only by Creatures of no higher an Order than Brutes; so the
End for which he designed his reasonable Offspring is the Contemplation
of his Works, the Enjoyment of himself, and in both to be happy, having,
to this Purpose, endowed them with correspondent Faculties and De
Sir
es.
He can have no greater Pleasure from a bare Review of his Works, than
from the Survey of his own Ideas, but we may be assured that he is well
pleased in the Satisfaction derived to Beings capable of it, and, for
whose Entertainment, he hath erected this immense Theatre. Is not this
more than an Intimation of our Immortality? Man, who when considered as
on his Probation for a happy Existence hereafter is the most remarkable
Instance of Divine Wisdom; if we cut him off from all Relation to
Eternity, is the most wonderful and unaccountable Composition in the
whole Creation. He hath Capacities to lodge a much greater Variety of
Knowledge than he will be ever Master of, and an unsatisfied Curiosity
to tread the secret Paths of Nature and Providence: But, with this, his
Organs, in their present Structure, are rather fitted to serve the
Necessities of a vile Body, than to minister to his Understanding; and
from the little Spot to which he is chained, he can frame but wandering
Guesses concerning the innumerable Worlds of Light that encompass him,
which, tho' in themselves of a prodigious Bigness, do but just glimmer
in the remote Spaces of the Heavens; and, when with a great deal of Time
and Pains he hath laboured a little way up the steep Ascent of Truth,
and beholds with Pity the groveling Multitude beneath, in a Moment, his
Foot slides, and he tumbles down headlong into the Grave.
Thinking on this, I am obliged to believe, in Justice to the Creator of
the World, that there is another State when Man shall be better situated
for Contemplation, or rather have it in his Power to remove from Object
to Object, and from World to World; and be accommodated with Senses, and
other Helps, for making the quickest and most amazing Discoveries. How
doth such a Genius as
Sir
Isaac Newton,
from amidst the Darkness that
involves human Understanding, break forth, and appear like one of
another Species! The vast Machine, we inhabit, lyes open to him, he
seems not unacquainted with the general Laws that govern it; and while
with the Transport of a Philosopher he beholds and admires the glorious
Work, he is capable of paying at once a more devout and more rational
Homage to his Maker. But alas! how narrow is the Prospect even of such a
Mind? and how obscure to the Compass that is taken in by the Ken of an
Angel; or of a Soul but newly escaped from its Imprisonment in the Body!
For my Part, I freely indulge my Soul in the Confidence of its future
Grandeur; it pleases me to think that I who know so small a portion of
the Works of the Creator, and with slow and painful Steps creep up and
down on the Surface of this Globe, shall e'er long shoot away with the
Swiftness of Imagination, trace out the hidden Springs of Nature's
Operations, be able to keep pace with the heavenly Bodies in the
Rapidity of their Career, be a
Spectator
of the long Chain of Events in
the natural and Moral Worlds, visit the several Apartments of the
Creation, know how they are furnished and how inhabited, comprehend the
Order, and measure the Magnitudes, and Distances of those Orbs, which to
us seem disposed without any regular Design, and set all in the same
Circle; observe the Dependance of the Parts of each System, and (if our
Minds are big enough to grasp the Theory) of the several Systems upon
one another, from whence results the Harmony of the Universe. In
Eternity a great deal may be done of this kind. I find it of use to
cherish this generous Ambition: for besides the secret Refreshment it
diffuses through my Soul, it engages me in an Endeavour to improve my
Faculties, as well as to exercise them conformably to the Rank I now
hold among reasonable Beings, and the Hope I have of being once advanced
to a more exalted Station.
The other, and that the Ultimate End of Man, is the Enjoyment of God,
beyond which he cannot form a Wish. Dim at best are the Conceptions we
have of the Supreme Being, who, as it were, keeps his Creatures in
Suspence, neither discovering, nor hiding himself; by which Means, the
Libertine hath a Handle to dispute his Existence, while the most are
content to speak him fair, but in their Hearts prefer every trifling
Satisfaction to the Favour of their Maker, and ridicule the good Man for
the Singularity of his Choice. Will there not a Time come, when the
Free-thinker shall see his impious Schemes overturned, and be made a
Convert to the Truths he hates; when deluded Mortals shall be convinced
of the Folly of their Pursuits, and the few Wise who followed the
Guidance of Heaven, and, scorning the Blandishments of Sense and the
sordid Bribery of the World, aspired to a celestial Abode, shall stand
possessed of their utmost Wish in the Vision of the Creator? Here the
Mind heaves a Thought now and then towards him, and hath some transient
Glances of his Presence: When, in the Instant it thinks it self to have
the fastest hold, the Object eludes its Expectations, and it falls back
tired and baffled to the Ground. Doubtless there is some more perfect
way of conversing with heavenly Beings. Are not Spirits capable of
Mutual Intelligence, unless immersed in Bodies, or by their
Intervention? Must superior Natures depend on inferior for the main
Privilege of sociable Beings, that of conversing with, and knowing each
other? What would they have done, had Matter never been created? I
suppose, not have lived in eternal Solitude. As incorporeal Substances
are of a nobler Order, so be sure, their manner of Intercourse is
answerably more expedite and intimate. This method of Communication, we
call Intellectual Vision, as somewhat Analogous to the Sense of Seeing,
which is the Medium of our Acquaintance with this visible World. And in
some such way can God make himself the Object of immediate Intuition to
the Blessed; and as he can, 'tis not improbable that he will, always
condescending, in the Circumstances of doing it, to the Weakness and
Proportion of finite Minds. His Works but faintly reflect the Image of
his Perfections, 'tis a Second-hand Knowledge: To have a just Idea of
him, it may be necessary that we see him as he is. But what is that?
'Tis something, that never entered into the Heart of Man to conceive;
yet what we can easily conceive, will be a Fountain of Unspeakable, of
Everlasting Rapture. All created Glories will fade and die away in his
Presence. Perhaps it will be my Happiness to compare the World with the
fair Exemplar of it in the Divine Mind; perhaps, to view the original
Plan of those wise Designs that have been executing in a long Succession
of Ages. Thus employed in finding out his Works, and contemplating their
Author! how shall I fall prostrate and adoring, my Body swallowed up in
the Immensity of Matter, my Mind in the Infinitude of his Perfections.
Contents
Contents, p. 8
end of Volume 3.
The Spectator
in three volumes: translations and index
for:
- Spectator Volume 1 (Nos. 1-202)
- Spectator Volume 2 (Nos. 203-416)
- Spectator Volume 3 (Nos 417-635).
A New Edition
Reproducing the Original Text
Both as First Issued
and as Corrected by its Authors
with Introduction, Notes, and Index
edited by Henry Morley
1891
Index
Additional Notes
[Volume 1 link:
The following letter, dated July 21, 1711, was sent by Addison to his
friend Mr. Wortley Montagu, with
of the
Spectator.
'Dear Sir,
'Being very well pleased with this day's Spectator I cannot forbear
sending you one of them, and desiring your opinion of the story in it.
When you have a son I shall be glad to be his Leontine, as my
circumstances will probably be like his. I have within this
twelvemonth lost a place of £200 per ann., an estate in the Indies of
£14,000, and what is worse than all the rest, my mistress. Hear this,
and wonder at my philosophy. I find they are going to take away my
Irish place from me too: to which I must add, that I have just
resigned my fellowship, and that stocks sink every day. If you have
any hints or subjects, pray send me up a paper full. I long to talk an
evening with you. I believe I shall not go for Ireland this summer,
and perhaps would pass a month with you if I knew where. Lady Bellasis
is very much your humble servant. Dick Steele and I often remember
you.'
I am, Dear Sir, Yours eternally.
The
Retrospective Review
, vol. xi. for 1825, in a cordially
appreciative review of the writings of Marvell, says,
'Captain Thompson was a very incorrect and injudicious editor of
Marvell's works. A very contemptible charge of plagiarism is also
preferred by the editor against Addison for the insertion of three
hymns in the
Spectator, Nos.
453,
461, and
465; no proof whatever is
vouchsafed that they belong to Marvell, and the hymn inserted in the
Spectator, No.
461, "When Israel freed from Pharaoh's land," is now
known to be the noble composition of Dr. Watts.'
Captain Edward Thompson's edition of Marvell in 3 volumes quarto was
printed for the editor in 1776. Its great blunder was immediately
disposed of in the
Gentleman's Magazine
for September, 1776, and
February, 1777, where it was shown for example that Dr. Watts had
claimed and transferred his version of the 114th Psalm (which Captain
Thompson supposed to have been claimed by 'Tickle') to his volume of
Divine Psalms and Hymns
, published in 1719. In the preface to that
volume Dr. Watts wrote,
'Where I have used three or four lines together of any author I have
acknowledged it in the notes.'
He did make frequent acknowledgment of lines or thoughts taken from
other poets in Psalms 6, 21, 63, 104, 139. But in a note to Ps. 114 he
absolutely spoke of the work as his own. Now the ground upon which
Thompson ascribed this piece to Marvell is precisely that on which he
also ascribed to Marvell Addison's poems in Nos.
and
of the
Spectator.
He found them all in the latter part of a book of extracts
of which he said that the first part was in Marvell's handwriting, 'and
the rest copied by his order.' It is very doubtful whether even the
first part of the MS. book, containing verse of Marvell's, was really in
Marvell's handwriting, and that the part written later was copied by his
order, is an unfounded assumption. Captain Thompson said of the MS. book
that it was many years in the care of Mr. Nettleton, and communicated to
the editor by Mr. Thomas Raikes.—Probably it was Mr. Nettleton who in
his youth had added to the book copies of Addison's and Dr. Watts's
verses from the
Spectator
, and Mallet's version of the old ballad of
William and Margaret, all of which pieces Captain Edward Thompson
therefore supposed to have been written by Marvell.
Contents
Translations of the Mottos
| No. | Source | Translation |
|---|
Vol.
1 |
| 1 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 143. |
One with a flash begins, and ends in smoke;
Another out of smoke brings glorious light,
And (without raising expectation high)
Surprises us with dazzling miracles.
(Roscommon) |
| 2 |
Juv.
Sat. vii. 167. |
Six more, at least, join their consenting voice. |
| 3 |
Luc.
1. iv. 959. |
—What studies please, what most delight,
And fill men's thoughts, they dream them o'er at night.
(Creech) |
| 4 |
Hor.
2 Sat. vi. 58. |
One of uncommon silence and reserve. |
| 5 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 5. |
Admitted to the sight, would you not laugh? |
| 6 |
Juv.
Sat. xiii. 54. |
'Twas impious then (so much was age revered)
For youth to keep their seats when an old man appear'd. |
| 7 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 208. |
Visions and magic spells can you despise,
And laugh at witches, ghosts, and prodigies? |
| 8 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 415. |
They march obscure, for Venus kindly shrouds
With mists their persons, and involves in clouds.
(Dryden) |
| 9 |
Juv.
Sat. xv. 163. |
Tiger with tiger, bear with bear, you'll find
In leagues offensive and defensive join'd.
(Tate) |
| 10 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 201. |
So the boat's brawny crew the current stem,
And, slow advancing, struggle with the stream:
But if they slack their hands, or cease to strive,
Then down the flood with headlong haste they drive.
(Dryden) |
| 11 |
Juv.
Sat. ii. 63. |
The doves are censured, while the crows are spared. |
| 12 |
Pers.
Sat. v. 92. |
I root th' old woman from thy trembling heart. |
| 13 |
Mart. |
Were you a lion, how would you behave? |
| 14 |
Ovid
Met. iv. 590. |
Wretch that thou art! put off this monstrous shape. |
| 15 |
Ovid
Ars Am. i. 159. |
Light minds are pleased with trifles. |
| 16 |
Hor.
1 Ep. i. ii. |
What right, what true, what fit we justly call,
Let this be all my care—for this is all.
(Pope) |
| 17 |
Juv.
x. 191. |
—A visage rough,
Deform'd, unfeatured. |
| 18 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 187. |
But now our nobles too are fops and vain,
Neglect the sense, but love the painted scene.
(Creech) |
| 19 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iv. 17. |
Thank Heaven, that made me of an humble mind;
To action little, less to words inclined! |
| 20 |
Hom. |
Thou dog in forehead.
(Pope) |
| 21 |
Hor.
1 Ep. v. 28. |
There's room enough, and each may bring his friend.
(Creech) |
| 22 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 5. |
—Whatever contradicts my sense
I hate to see, and never can believe.
(Roscommon) |
| 23 |
Virg.
Æn. ix. 420. |
Fierce Volscens foams with rage, and gazing round,
Descry'd not him who gave the fatal wound;
Nor knew to fix revenge.
(Dryden) |
| 24 |
Hor.
1 Sat. ix. 3. |
Comes up a fop (I knew him but by fame),
And seized my hand, and call'd me by name—
—My dear!—how dost? |
| 25 |
Virg.
Æn. xii. 46. |
And sickens by the very means of health. |
| 26 |
Hor.
1 Od. iv. 13. |
With equal foot, rich friend, impartial fate
Knocks at the cottage and the palace gate:
Life's span forbids thee to extend thy cares,
And stretch thy hopes beyond thy years:
Night soon will seize, and you must quickly go
To storied ghosts, and Pluto's house below. |
| 27 |
Hor.
1 Ep. i 20.
imitated |
Long as to him, who works for debt, the day;
Long as the night to her, whose love's away;
Long as the year's dull circle seems to run
When the brisk minor pants for twenty-one:
So slow th' unprofitable moments roll,
That lock up all the functions of my soul;
That keep me from myself, and still delay
Life's instant business to a future day:
That task, which as we follow, or despise,
The eldest is a fool, the youngest wise:
Which done, the poorest can no wants endure,
And which not done, the richest must be poor. |
| 28 |
Hor.
2 Od. x. 19. |
Nor does Apollo always bend his bow. |
| 29 |
Hor.
1 Sat. x. 23. |
Both tongues united, sweeter sounds produce,
Like Chian mixed with Palernian juice. |
| 30 |
Hor.
1 Ep. vi. 65. |
If nothing, as Mimnermus strives to prove,
Can e'er be pleasant without mirth and love,
Then live in mirth and love, thy sports pursue.
(Creech) |
| 31 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 266. |
What I have heard, permit me to relate. |
| 32 |
Hor.
1 Sat. v. 64. |
He wants no tragic vizor to increase
His natural deformity of face. |
| 33 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxx. 5. |
The graces with their zones unloosed;
The nymphs, with beauties all exposed
From every spring, and every plain;
Thy powerful, hot, and winged boy;
And youth, that's dull without thy joy;
And Mercury, compose thy train.
(Creech) |
| 34 |
Juv.
Sat. xv. 159. |
From spotted skins the leopard does refrain.
(Tate) |
| 35 |
Catull.
Carm. 39
in Enat. |
Nothing so foolish as the laugh of fools. |
| 36 |
Virg.
Æn. iii. 583. |
Things the most out of nature we endure. |
| 37 |
Virg.
Æn. vii. 805. |
Unbred to spinning, in the loom unskill'd.
(Dryden) |
| 38 |
Mart. |
One would not please too much. |
| 39 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 102.
imitated |
Much do I suffer, much, to keep in peace
This jealous, waspish, wrong-headed rhyming race.
(Pope) |
| 40 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 208.
imitated |
Yet lest you think I rally more than teach,
Or praise, malignant, arts I cannot reach,
Let me for once presume t' instruct the times,
To know the poet from the man of rhymes;
'Tis he, who gives my breast a thousand pains,
Can make me feel each passion that he feigns;
Enrage, compose, with more than magic art,
With pity, and with terror, tear my heart;
And snatch me o'er the earth, or through the air,
To Thebes, to Athens, when he will, and where.
(Pope) |
| 41 |
Ovid.
Met. i. 654. |
So found, is worse than lost.
(Addison) |
| 42 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 202.
imitated |
Loud as the wolves on Orca's stormy steep,
Howl to the roarings of the northern deep:
Such is the shout, the long applauding note,
At Quin's high plume, or Oldfield's petticoat:
Or when from court a birth-day suit bestow'd
Sinks the last actor in the tawdry load.
Booth enters—hark! the universal peal!—
But has he spoken?—Not a syllable—
What shook the stage, and made the people stare?
Cato's long wig, flower'd gown, and lacker'd chair.
(Pope) |
| 43 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 854. |
Be these thy arts; to bid contention cease,
Chain up stern wars, and give the nations peace;
O'er subject lands extend thy gentle sway,
And teach with iron rod the haughty to obey. |
| 44 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 123. |
Now hear what every auditor expects.
(Roscommon) |
| 45 |
Juv.
Sat. iii. 100 |
The nation is a company of players. |
| 46 |
Ovid
Met. 1 i. ver. 9. |
The jarring seeds of ill-concerted things. |
| 47 |
Mart. |
Laugh, if you are wise. |
| 48 |
Ovid
Met. xiv. 652. |
Through various shapes he often finds access. |
| 49 |
Mart. |
Men and manners I describe. |
| 50 |
Jun.
Sat. xix. 321 |
Good taste and nature always speak the same. |
| 51 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 127. |
He from the taste obscene reclaims our youth.
(Pope) |
| 52 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 78. |
To crown thy worth, she shall be ever thine,
And make thee father of a beauteous line. |
| 53 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 359. |
Homer himself hath been observed to nod.
(Roscommon) |
| 54 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xi. 28. |
Laborious idleness our powers employs. |
| 55 |
Pers.
Sat. v. 129 |
Our passions play the tyrants in our breasts. |
| 56 |
Lucan.
i. 454. |
Happy in their mistake. |
| 57 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 251 |
What sense of shame in woman's breast can lie,
Inured to arms, and her own sex to fly? |
| 58 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 361. |
Poems like pictures are. |
| 59 |
Seneca |
Busy about nothing. |
| 60 |
Pers.
Sat. iii. 85 |
Is it for this you gain those meagre looks,
And sacrifice your dinner to your books? |
| 61 |
Pers.
Sat. v. 19 |
'Tis not indeed my talent to engage
In lofty trifles, or to swell my page
With wind and noise.
(Dryden) |
| 62 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 309. |
Sound judgment is the ground of writing well.
(Roscommon) |
| 63 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. i. |
If in a picture, Piso, you should see
A handsome woman with a fish's tail,
Or a man's head upon a horse's neck,
Or limbs of beasts, of the most different kinds,
Cover'd with feathers of all sorts of birds;
Would you not laugh, and think the painter mad?
Trust me that book is as ridiculous,
Whose incoherent style, like sick men's dreams,
Varies all shapes, and mixes all extremes.
(Roscommon) |
| 64 |
Juv.
Sat. iii. 183 |
The face of wealth in poverty we wear. |
| 65 |
Hor.
1 Sat. x. 90. |
Demetrius and Tigellius, know your place;
Go hence, and whine among the school-boy race. |
| 66 |
Hor.
1 Od. vi. 21. |
Behold a ripe and melting maid
Bound 'prentice to the wanton trade:
Ionian artists, at a mighty price,
Instruct her in the mysteries of vice,
What nets to spread, where subtle baits to lay;
And with an early hand they form the temper'd clay.
(Roscommon) |
| 67 |
Sallust. |
Too fine a dancer for a virtuous woman. |
| 68 |
Ovid
Met. i. 355 |
We two are a multitude. |
| 69 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 54 |
This ground with Bacchus, that with Ceres suits;
That other loads the trees with happy fruits,
A fourth with grass, unbidden, decks the ground:
Thus Tmolus is with yellow saffron crown'd;
India black ebon and white iv'ry bears;
And soft Idume weeps her od'rous tears:
Thus Pontus sends her beaver stones from far:
And naked Spaniards temper steel for war:
Epirus for th' Elean chariot breeds
(In hopes of palms) a race of running steeds.
This is th' original contract; these the laws
Imposed by nature, and by nature's cause.
(Dryden) |
| 70 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 63. |
Sometimes the vulgar see and judge aright. |
| 71 |
Ovid
Epist. iv. 10 |
Love bade me write. |
| 72 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 208 |
Th' immortal line in sure succession reigns,
The fortune of the family remains,
And grandsires' grandsons the long list contains.
(Dryden) |
| 73 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 328. |
O Goddess! for no less you seem. |
| 74 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 88. |
The works unfinish'd and neglected lie. |
| 75 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvii. 23. |
All fortune fitted Aristippus well.
(Creech) |
| 76 |
Hor.
1 Ep. viii. 17. |
As you your fortune bear, we will bear you.
(Creech) |
| 77 |
Mart.
Epig. i. 87 |
What correspondence can I hold with you,
Who are so near, and yet so distant too? |
| 78 |
|
Could we but call so great a genius ours! |
| 79 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvi. 52. |
The good, for virtue's sake, abhor to sin.
(Creech) |
| 80 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ix. 27. |
Those that beyond sea go, will sadly find,
They change their climate only, not their mind.
(Creech) |
| 81 |
Stat.
Theb. ii. 128. |
As when the tigress hears the hunter's din,
Dark angry spots distain her glossy skin. |
| 82 |
Juv.
Sat iii. 33 |
His fortunes ruin'd, and himself a slave. |
| 83 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 464. |
And with the shadowy picture feeds his mind. |
| 84 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 6. |
Who can such woes relate, without a tear,
As stern Ulysses must have wept to hear? |
| 85 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 319. |
—When the sentiments and manners please,
And all the characters are wrought with ease,
Your tale, though void of beauty, force, and art,
More strongly shall delight, and warm the heart;
Than where a lifeless pomp of verse appears,
And with sonorous trifles charms our ears.
(Francis) |
| 86 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 447 |
How in the looks does conscious guilt appear!
(Addison) |
| 87 |
Virg.
Ecl. ii. 17 |
Trust not too much to an enchanting face.
(Dryden) |
| 88 |
Virg.
Ecl. iii. 16 |
What will not masters do, when servants thus presume? |
| 89 |
Pers.
Sat. v. 64 |
| Pers. | From thee both old and young with profit learn
The bounds of good and evil to discern. |
| Corn. | Unhappy he, who does this work adjourn,
And to to-morrow would the search delay:
His lazy morrow will be like to-day. |
| Pers. | But is one day of ease too much to borrow? |
| Corn. | Yes, sure; for yesterday was once to-morrow:
That yesterday is gone, and nothing gain'd;
And all thy fruitless days will thus be drain'd,
For thou hast more to-morrows yet to ask,
And wilt be ever to begin thy task;
Who, like the hindmost chariot-wheels, are curst,
Still to be near, but ne'er to reach the first. |
| (Dryden) |
|
| 90 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 90 |
In all the rage of impotent desire,
They feel a quenchless flame, a fruitless fire. |
| 91 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 244 |
—They rush into the flame;
For love is lord of all, and is in all the same.
(Dryden) |
| 92 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 61.
imitated |
—What would you have me do,
When out of twenty I can please not two?—
One likes the pheasant's wing, and one the leg;
The vulgar boil, the learned roast an egg;
Hard task, to hit the palate of such guests.
(Pope) |
| 93 |
Hor.
1 Od. xi. 6. |
Thy lengthen'd hopes with prudence bound
Proportion'd to the flying hour:
While thus we talk in careless ease,
The envious moments wing their flight;
Instant the fleeting pleasure seize,
Nor trust to-morrow's doubtful light.
(Francis) |
| 94 |
Mart.
Epig. xxiii. 10 |
The present joys of life we doubly taste,
By looking back with pleasure to the past. |
| 95 |
Seneca
Trag. |
Light sorrows loose the tongue, but great enchain.
(P.) |
| 96 |
Hor.
2 Sat. vii. 2. |
—The faithful servant, and the true. |
| 97 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 436. |
They prodigally threw their lives away. |
| 98 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 500 |
So studiously their persons they adorn. |
| 99 |
Hor.
1 Sat. vi. 63. |
You know to fix the bounds of right and wrong. |
| 100 |
Hor.
1 Sat. v. 44. |
The greatest blessing is a pleasant friend. |
| 101 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 5. |
Edward and Henry, now the boast of fame,
And virtuous Alfred, a more sacred name,
After a life of generous toils endured,
The Gaul subdued, or property secured,
Ambition humbled, mighty cities storm'd,
Or laws established, and the world reform'd:
Closed their long glories with a sigh to find
Th' unwilling gratitude of base mankind.
(Pope) |
| 102 |
Phædr.
Fab. xiv. 3. |
The mind ought sometimes to be diverted, that it may return the
better to thinking. |
| 103 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 240. |
Such all might hope to imitate with ease:
Yet while they strive the same success to gain,
Should find their labour and their hopes are vain.
(Francis) |
| 104 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 316. |
With such array Harpalyce bestrode
Her Thracian courser.
(Dryden) |
| 105 |
Ter.
Andr. Act i. Sc. I. |
I take to be a principal rule of life, not to be too much addicted to
any one thing.
Too much of anything is good for nothing.
(Eng. Prov.) |
| 106 |
Hor.
1 Od. xvii. 14. |
Here plenty's liberal horn shall pour
Of fruits for thee a copious show'r,
Rich honours of the quiet plain. |
| 107 |
Phædr.
Epilog. i. 2. |
The Athenians erected a large statue to Æsop, and placed him, though
a slave, on a lasting pedestal: to show that the way to honour lies
open indifferently to all. |
| 108 |
Phædr.
Fab. v. 2. |
Out of breath to no purpose, and very busy about nothing. |
| 109 |
Hor.
2 Sat. ii. 3. |
Of plain good sense, untutor'd in the schools. |
| 110 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 755. |
All things are full of Horror and affright,
And dreadful ev'n the silence of the night.
(Dryden) |
| 111 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 45. |
To search for truth in academic groves. |
| 112 |
Pythag. |
First, in obedience to thy country's rites,
Worship th' immortal gods. |
| 113 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 4. |
Her looks were deep imprinted in his heart. |
| 114 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 24. |
—The dread of nothing more
Than to be thought necessitous and poor.
(Pooly) |
| 115 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 356 |
Pray for a sound mind in a sound body. |
| 116 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 43 |
The echoing hills and chiding hounds invite. |
| 117 |
Virg.
Ecl. viii. 108 |
With voluntary dreams they cheat their minds. |
| 118 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 73. |
—The fatal dart
Sticks in his side, and rankles in his heart.
(Dryden) |
| 119 |
Virg.
Ecl. i. 20 |
The city men call Rome, unskilful clown,
I thought resembled this our humble town.
(Warton) |
| 120 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 415 |
—I deem their breasts inspired
With a divine sagacity— |
| 121 |
Virg.
Ecl. iii. 66 |
—All things are full of Jove. |
| 122 |
Publ. Syr.
Frag. |
An agreeable companion upon the road is as good as a coach. |
| 123 |
Hor.
4 Od. iv. 33. |
Yet the best blood by learning is refined,
And virtue arms the solid mind;
Whilst vice will stain the noblest race,
And the paternal stamp efface.
(Oldisworth) |
| 124 |
|
A great book is a great evil. |
| 125 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 832. |
This thirst of kindred blood, my sons, detest,
Nor turn your force against your country's breast.
(Dryden) |
| 126 |
Virg.
Æn. x. 108. |
Rutulians, Trojans, are the same to me.
(Dryden) |
| 127 |
Pers.
Sat. i. 1 |
How much of emptiness we find in things! |
| 128 |
Lucan.
i. 98. |
—Harmonious discord. |
| 129 |
Pers.
Sat. v. 71 |
Thou, like the hindmost chariot-wheels, art curst,
Still to be near, but ne'er to be the first.
(Dryden) |
| 130 |
Virg.
Æn. vii. 748. |
A plundering race, still eager to invade,
On spoil they live, and make of theft a trade. |
| 131 |
Virg.
Ecl. x. 63 |
Once more, ye woods, adieu. |
| 132 |
Tull. |
That man may be called impertinent, who considers not the
circumstances of time, or engrosses the conversation, or makes himself
the subject of his discourse, or pays no regard to the company he is
in. |
| 133 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxiv. 1. |
Such was his worth, our loss is such,
We cannot love too well, or grieve too much.
(Oldisworth) |
| 134 |
Ovid
Met. i. 521 |
And am the great physician call'd below.
(Dryden) |
| 135 |
Hor.
1 Sat. x. 9. |
Let brevity dispatch the rapid thought. |
| 136 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 112. |
A greater liar Parthia never bred. |
| 137 |
Tull.
Epist. |
Even slaves were always at liberty to fear, rejoice, and grieve at
their own, rather than another's, pleasure. |
| 138 |
Tull. |
He uses unnecessary proofs in an indisputable point. |
| 139 |
Tull. |
True glory takes root, and even spreads; all false pretences, like
flowers, fall to the ground; nor can any counterfeit last long. |
| 140 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 285. |
This way and that the anxious mind is torn. |
| 141 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 187. |
Taste, that eternal wanderer, that flies
From head to ears, and now from ears to eyes.
(Pope) |
| 142 |
Hor.
1 Od. xiii. 12. |
Whom love's unbroken bond unites. |
| 143 |
Martial
Epig. lxx. 6 |
For life is only life, when blest with health. |
| 144 |
Ter.
Eun. Act iii. Sc. 5. |
You shall see how nice a judge of beauty I am. |
| 145 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 29. |
Their folly pleads the privilege of wealth. |
| 146 |
Tull. |
No man was ever great without some degree of inspiration. |
| 147 |
Tull. |
Good delivery is a graceful management of the voice, countenance, and
gesture. |
| 148 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 212. |
Better one thorn pluck'd out, than all remain. |
| 149 |
Cæcil.
apud Tull. |
Who has it in her power to make men mad,
Or wise, or sick, or well: and who can choose
The object of her appetite at pleasure. |
| 150 |
Juv.
Sat. iii. 152 |
What is the scorn of every wealthy fool,
And wit in rags is turn'd to ridicule.
(Dryden) |
| 151 |
Tull.
de Fin. |
Where pleasure prevails, all the greatest virtues will lose their
power. |
| 152 |
Hom.
Il. 6, v. 146. |
Like leaves on trees the race of man is found.
(Pope) |
| 153 |
Tull.
de Senect. |
Life, as well as all other things, hath its bounds assigned by
nature; and its conclusion, like the last act of a play, is old age,
the fatigue of which we ought to shun, especially when our appetites
are fully satisfied. |
| 154 |
Juv.
Sat. ii. 83 |
No man e'er reach'd the heights of vice at first.
(Tate) |
| 155 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 451. |
These things which now seem frivolous and slight,
Will prove of serious consequence.
(Roscommon) |
| 156 |
Hor.
2 Od. viii. 5. |
—But thou,
When once thou hast broke some tender vow,
All perjured, dost more charming grow! |
| 157 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 187.
imitated |
—That directing power,
Who forms the genius in the natal hour:
That God of nature, who, within us still,
Inclines our action, not constrains our will.
(Pope) |
| 158 |
Martial
xiii. 2. |
We know these things to be mere trifles. |
| 159 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 604. |
The cloud, which, intercepting the clear light,
Hangs o'er thy eyes, and blunts thy mortal sight,
I will remove— |
| 160 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iv. 43. |
On him confer the Poet's sacred name,
Whose lofty voice declares the heavenly flame. |
| 161 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 527 |
Himself, in rustic pomp, on holydays,
To rural powers a just oblation pays;
And on the green his careless limbs displays:
The hearth is in the midst: the herdsmen, round
The cheerful fire, provoke his health in goblets crown'd.
He calls on Bacchus, and propounds the prize,
The groom his fellow-groom at buts defies,
And bends his bow, and levels with his eyes:
Or, stript for wrestling, smears his limbs with oil,
And watches with a trip his foe to foil.
Such was the life the frugal Sabines led;
So Remus and his brother king were bred,
From whom th' austere Etrurian virtue rose;
And this rude life our homely fathers chose;
Old Rome from such a race derived her birth,
The seat of empire, and the conquer'd earth.
(Dryden) |
| 162 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 126. |
Keep one consistent plan from end to end. |
| 163 |
Enn.
apud Tullium |
Say, will you thank me if I bring you rest,
And ease the torture of your troubled breast? |
| 164 |
Virg.
iv. Georg. 494 |
Then thus the bride: What fury seized on thee,
Unhappy man! to lose thyself and me?
And now farewell! involved in shades of night,
For ever I am ravish'd from thy sight:
In vain I reach my feeble hands to join
In sweet embraces, ah! no longer thine.
(Dryden) |
| 165 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 48. |
—If you would unheard-of things express,
Invent new words; we can indulge a muse,
Until the licence rise to an abuse.
(Creech) |
| 166 |
Ovid
Met. xv. 871. |
—Which nor dreads the rage
Of tempests, fire, or war, or wasting age.
(Welsted) |
| 167 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 128.
imitated |
There lived in Primo Georgii (they record)
A worthy member, no small fool, a lord;
Who, though the house was up, delighted sate,
Heard, noted, answer'd as in full debate;
In all but this, a man of sober life,
Fond of his friend, and civil to his wife;
Not quite a madman, though a pasty fell,
And much too wise to walk into a well.
Him the damn'd doctor and his friends immured;
They bled, they cupp'd, they purged, in short they cured,
Whereat the gentleman began to stare—
'My friends!' he cry'd: 'pox take you for your care!
That from a patriot of distinguish'd note,
Have bled and purged me to a simple vote.
(Pope) |
| 168 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 128. |
Forms the soft bosom with the gentlest art.
(Pope) |
| 169 |
Ter.
Andr. Act i. Sc. 1. |
His manner of life was this: to bear with everybody's humours; to
comply with the inclinations and pursuits of those he conversed with;
to contradict nobody; never to assume a superiority over others. This
is the ready way to gain applause without exciting envy. |
| 170 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 1. |
In love are all these ills: suspicions, quarrels,
Wrongs, reconcilements, war, and peace again.
(Coleman) |
| 171 |
Ovid
Met. vii. 826 |
Love is a credulous passion. |
| 172 |
Plato
apud Tull. |
As knowledge, without justice, ought to be called cunning, rather
than wisdom; so a mind prepared to meet danger, if excited by its own
eagerness, and not the public good, deserves the name of audacity,
rather than that of fortitude. |
| 173 |
Ovid
Met. v. 215. |
Hence with those monstrous features, and, O! spare
That Gorgon's look and petrifying stare.
(P.) |
| 174 |
Virg.
Ecl. vii. 69 |
The whole debate in memory I retain,
When Thyrsis argued warmly, but in vain.
(P.) |
| 175 |
Ovid
Rem. Am. v. 625. |
To save your house from neighb'ring fire is hard.
(Tate) |
| 176 |
Lucr.
iv. 1155. |
A little, pretty, witty, charming she! |
| 177 |
Juv.
Sat. xv. 140 |
Who can all sense of others' ills escape,
Is but a brute, at best, in human shape.
(Tate) |
| 178 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 133. |
Civil to his wife.
(Pope) |
| 179 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 341. |
Old age is only fond of moral truth,
Lectures too grave disgust aspiring youth;
But he who blends instruction with delight,
Wins every reader, nor in vain shall write.
(P.) |
| 180 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 14. |
The monarch's folly makes the people rue.
(P.) |
| 181 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 145. |
Moved by these tears, we pity and protect. |
| 182 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 180 |
The bitter overbalances the sweet. |
| 183 |
Hom. |
Sometimes fair truth in fiction we disguise;
Sometimes present her naked to men's eyes.
(Pope) |
| 184 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 360. |
—Who labours long may be allowed sleep. |
| 185 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 15. |
And dwells such fury in celestial breasts? |
| 186 |
Hor.
3 Od. i. 38. |
High Heaven itself our impious rage assails.
(P.) |
| 187 |
Hor.
1 Od. v. 2. |
Ah wretched they! whom Pyrrha's smile
And unsuspected arts beguile.
(Duncome) |
| 188 |
Tull. |
It gives me pleasure to be praised by you, whom all men praise. |
| 189 |
Virg.
Æn. x. 824. |
An image of paternal tenderness. |
| 190 |
Hor.
2 Od. viii. 18. |
A slavery to former times unknown. |
| 191 |
|
—Deluding vision of the night.
(Pope) |
| 192 |
Ter.
Andr. Act i. Sc. 1. |
—All the world
With one accord said all good things, and praised
My happy fortunes, who possess a son
So good, so liberally disposed.
(Colman) |
| 193 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 461 |
His lordship's palace view, whose portals proud
Each morning vomit forth a cringing crowd.
(Warton, &c.) |
| 194 |
Hor.
1 Od. xiii. 4. |
With jealous pangs my bosom swells. |
| 195 |
Hesiod |
Fools not to know that half exceeds the whole,
How blest the sparing meal and temperate bowl! |
| 196 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xi. 30. |
True happiness is to no place confined,
But still is found in a contented mind. |
| 197 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 15. |
On trifles some are earnestly absurd;
You'll think the world depends on every word.
What! is not every mortal free to speak?
I'll give my reasons, though I break my neck!
And what's the question? If it shines or rains;
Whether 'tis twelve or fifteen miles to Staines.
(Pitt) |
| 198 |
Hor.
4 Od. iv. 50. |
We, like 'weak hinds,' the brinded wolf provoke,
And when retreat is victory,
Rush on, though sure to die.
(Oldisworth) |
| 199 |
Ovid
Ep. iv. 10 |
Love bade me write. |
| 200 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 823. |
The noblest motive is the public good. |
| 201 |
Incerti Autoris
apud Aul. Gell. |
A man should be religious, not superstitious. |
| 202 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 25. |
Tho' ten times worse themselves, you'll frequent view
Those who with keenest rage will censure you.
(P.) |
Vol.
2 |
| 203 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 38 |
Illustrious parent! if I yet may claim
The name of son, O rescue me from shame;
My mother's truth confirm; all doubt remove
By tender pledges of a father's love. |
| 204 |
Hor.
1 Od. xix. 7. |
Her face too dazzling for the sight,
Her winning coyness fires my soul,
I feel a strange delight. |
| 205 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 205 |
Deluded by a seeming excellence. |
| 206 |
Hor.
3 Od. xvi. 21. |
They that do much themselves deny,
Receive more blessings from the sky.
(Creech) |
| 207 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 1 |
Look round the habitable world, how few
Know their own good, or, knowing it, pursue?
How rarely reason guides the stubborn choice,
Prompts the fond wish, or lifts the suppliant voice.
(Dryden, Johnson &c.) |
| 208 |
Ovid
Ars Am. 1. i. 99. |
To be themselves a spectacle they come. |
| 209 |
Simonides |
Of earthly goods, the best is a good wife;
A bad, the bitterest curse of human life. |
| 210 |
Cic.
Tusc. Quæst. |
There is, I know not how, in minds a certain presage, as it were, of
a future existence; this has the deepest root, and is most
discoverable, in the greatest geniuses and most exalted souls. |
| 211 |
Phædr.
1. 1. Prol. |
Let it be remembered that we sport in fabled stories. |
| 212 |
Hor.
2 Sat. vii. 92. |
—Loose thy neck from this ignoble chain,
And boldly say thou'rt free.
(Creech) |
| 213 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 608. |
A good intention. |
| 214 |
Juv.
3 Sat. 124 |
A long dependence in an hour is lost.
(Dryden) |
| 215 |
Ovid
de Ponto II. ix. 47. |
Ingenuous arts, where they an entrance find,
Soften the manners, and subdue the mind. |
| 216 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 1. |
Oh brave! oh excellent! if you maintain it!
But if you try, and can't go through with spirit,
And finding you can't bear it, uninvited,
Your peace unmade, all of your own accord,
You come and swear you love, and can't endure it,
Good night! all's over! ruin'd! and undone!
She'll jilt you, when she sees you in her power.
(Colman) |
| 217 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 326 |
Then unrestrain'd by rules of decency,
Th' assembled females raise a general cry. |
| 218 |
Hor.
Ep. xvii. Ep. xvii. |
—Have a care
Of whom you talk, to whom, and what, and where.
(Pooley) |
| 219 |
Ovid
Met. xiii. 141 |
These I scarce call our own. |
| 220 |
Virg.
Æn. xii. 228. |
A thousand rumours spreads. |
| 221 |
Hor.
3 Sat. I. 1. v. 6. |
From eggs, which first are set upon the board,
To apples ripe, with which it last is stored. |
| 222 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 183. |
Why, of two brothers, one his pleasure loves,
Prefers his sports to Herod's fragrant groves.
(Creech) |
| 223 |
Phædr.
iii. i. 5. |
O sweet soul! how good must you have been heretofore, when your
remains are so delicious! |
| 224 |
Hor.
1 Sat. vi. 23. |
Chain'd to her shining car, Fame draws along
With equal whirl the great and vulgar throng. |
| 225 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 365 |
Prudence supplies the want of every good. |
| 226 |
Hor. |
A picture is a poem without words. |
| 227 |
Theocritus |
Wretch that I am! ah, whither shall I go?
Will you not hear me, nor regard my woe?
I'll strip, and throw me from yon rock so high,
Where Olpis sits to watch the scaly fry.
Should I be drown'd, or 'scape with life away,
If cured of love, you, tyrant, would be gay. |
| 228 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 69. |
Th' inquisitive will blab; from such refrain:
Their leaky ears no secret can retain.
(Shard) |
| 229 |
Hor.
4 Od. ix. 4. |
Nor Sappho's amorous flames decay;
Her living songs preserve their charming art,
Her verse still breathes the passions of her heart.
(Francis) |
| 230 |
Tull. |
Men resemble the gods in nothing so much as in doing good to their
fellow-creatures. |
| 231 |
Mart.
viii. 78. |
O modesty! O piety! |
| 232 |
Sallust
Bel. Cat. |
By bestowing nothing he acquired glory. |
| 233 |
Virg.
Ecl. x. v. 60 |
As if by these my sufferings I could ease;
Or by my pains the god of love appease.
(Dryden) |
| 234 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 41. |
I wish this error in your friendship reign'd.
(Creech) |
| 235 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 81 |
Awes the tumultuous noises of the pit.
(Roscommon) |
| 236 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 398 |
With laws connubial tyrants to restrain. |
| 237 |
Seneca
in Oedip. |
They that are dim of sight see truth by halves. |
| 238 |
Pers.
Sat. iv. 50 |
No more to flattering crowds thine ear incline,
Eager to drink the praise which is not thine.
(Brewster) |
| 239 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 86. |
—Wars, horrid wars!
(Dryden) |
| 240 |
Mart.
Ep. i. 17 |
Of such materials, Sir, are books composed. |
| 241 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 466. |
All sad she seems, forsaken, and alone;
And left to wander wide through paths unknown.
(P.) |
| 242 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i 168 |
To write on vulgar themes, is thought an easy task. |
| 243 |
Tull.
Offic. |
You see, my son Marcus, virtue as if it were embodied, which if it
could be made the object of sight, would (as Plato says) excite in us
a wonderful love of wisdom. |
| 244 |
Hor.
2 Sat. vii. 101. |
A judge of painting you, a connoisseur. |
| 245 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 338 |
Fictions, to please, should wear the face of truth. |
| 246 |
|
No amorous hero ever gave thee birth,
Nor ever tender goddess brought thee forth:
Some rugged rock's hard entrails gave thee form,
And raging seas produced thee in a storm:
A soul well suiting thy tempestuous kind,
So rough thy manners, so untamed thy mind.
(Pope) |
| 247 |
Hesiod |
Their untired lips a wordy torrent pour. |
| 248 |
Tull.
Off. i. 16. |
It is a principal point of duty, to assist another most when he
stands most in need of assistance.' |
| 249 |
Frag. Vet. Poet. |
Mirth out of season is a grievous ill. |
| 250 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvii. 3. |
Yet hear what an unskilful friend can say:
As if a blind man should direct your way;
So I myself, though wanting to be taught,
May yet impart a hint that's worth your thought. |
| 251 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 625. |
—A hundred mouths, a hundred tongues,
And throats of brass inspired with iron lungs.
(Dryden) |
| 252 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 570. |
Exploring every place with curious eyes. |
| 253 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 76. |
I feel my honest indignation rise,
When with affected air a coxcomb cries,
The work I own has elegance and ease,
But sure no modern should presume to please. |
| 254 |
Frag. Vet. Poet. |
Virtuous love is honourable, but lust increaseth sorrow. |
| 255 |
Hor.
1 Ep. lib. 1. ver. 36.
imitated |
Know there are rhymes, which (fresh and fresh apply'd)
Will cure the arrant'st puppy of his pride.
(Pope) |
| 256 |
Hesiod |
Fame is an ill you may with ease obtain,
A sad oppression, to be borne with pain. |
| 257 |
Stobæus |
No slumber seals the eye of Providence,
Present to every action we commence. |
| 258 |
|
Divide and rule. |
| 259 |
Tull. |
What is becoming is honourable, and what is honourable is becoming. |
| 260 |
Hor.
3 Ep. ii. 55. |
Years following years steal something every day,
At last they steal us from ourselves away.
(Pope) |
| 261 |
Frag. Vet. Poet., |
Wedlock's an ill men eagerly embrace. |
| 262 |
Ovid
Trist. ii. 566.
adapted |
My paper flows from no satiric vein,
Contains no poison, and conveys no pain. |
| 263 |
Trebonius
apud Tull. |
I am glad that he whom I must have loved from duty, whatever he had
been, is such a one as I can love from inclination. |
| 264 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 103.
adapted |
In public walks let who will shine or stray,
I'll silent steal through life in my own way. |
| 265 |
Ovid
de Art. Am. iii. 7. |
But some exclaim: What frenzy rules your mind?
Would you increase the craft of womankind?
Teach them new wiles and arts? As well you may
Instruct a snake to bite, or wolf to prey.
(Congreve) |
| 266 |
Ter.
Eun. Act v. Sc. 4. |
This I conceive to be my master-piece, that I have discovered how
unexperienced youth may detect the artifices of bad women, and by
knowing them early, detest them for ever. |
| 267 |
Propert.
El. 34, lib. 2, ver. 95. |
Give place, ye Roman and ye Grecian wits. |
| 268 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 29. |
—unfit
For lively sallies of corporeal wit.
(Creech) |
| 269 |
Ovid
Ars Am. i. 241. |
Most rare is now our old simplicity.
(Dryden) |
| 270 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 262. |
For what's derided by the censuring crowd,
Is thought on more than what is just and good.
(Dryden)
There is a lust in man no power can tame,
Of loudly publishing his neighbour's shame;
On eagle's wings invidious scandals fly,
While virtuous actions are but born, and die.
(E. of Corke)
Sooner we learn, and seldomer forget,
What critics scorn, than what they highly rate.
(Hughes's Letters, vol. ii p 222.) |
| 271 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 701. |
Drawing a thousand colours from the light.
(Dryden) |
| 272 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 345. |
Great is the injury, and long the tale. |
| 273 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 156 |
Note well the manners. |
| 274 |
Hor.
1 Sat. ii. 37. |
All you who think the city ne'er can thrive
Till every cuckold-maker's flay'd alive,
Attend.
(Pope) |
| 275 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 300 |
A head, no hellebore can cure. |
| 276 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 42. |
Misconduct screen'd behind a specious name. |
| 277 |
Ovid
Met. lib. iv. ver. 428. |
Receive instruction from an enemy. |
| 278 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 250. |
I rather choose a low and creeping style. |
| 279 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 316 |
He knows what best befits each character. |
| 280 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvii. 35. |
To please the great is not the smallest praise.
(Creech) |
| 281 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 64. |
Anxious the reeking entrails he consults. |
| 282 |
Virg.
Æn. viii. 580. |
Hopes and fears in equal balance laid.
(Dryden) |
| 283 |
Pers.
Prolog. ver. 10 |
Necessity is the mother of invention.
(English Proverbs) |
| 284 |
Virg.
Ecl. vii. 17 |
Their mirth to share, I bid my business wait. |
| 285 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 227 |
But then they did not wrong themselves so much,
To make a god, a hero, or a king,
(Stript of his golden crown, and purple robe)
Descend to a mechanic dialect;
Nor (to avoid such meanness) soaring high,
With empty sound, and airy notions fly.
(Roscommon) |
| 286 |
Tacit.
Ann. I. xiv. c. 21. |
Specious names are lent to cover vices. |
| 287 |
Menand. |
Dear native land, how do the good and wise
Thy happy clime and countless blessings prize! |
| 288 |
Hor.
1 Ep. vi. 10. |
Both fear alike. |
| 289 |
Hor.
1 Od. iv. 15. |
Life's span forbids us to extend our cares,
And stretch our hopes beyond our years.
(Creech) |
| 290 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 97 |
Forgets his swelling and gigantic words.
(Roscommon) |
| 291 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 351 |
But in a poem elegantly writ,
I will not quarrel with a slight mistake,
Such as our nature's frailty may excuse.
(Roscommon) |
| 292 |
Tibul.
4 Eleg. ii. 8. |
Whate'er she does, where'er her steps she bends,
Grace on each action silently attends. |
| 293 |
Frag. Vet. Poet. |
The prudent still have fortune on their side. |
| 294 |
Tull.
ad Herennium |
The man who is always fortunate cannot easily have much reverence for
virtue. |
| 295 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 361 |
But womankind, that never knows a mean,
Down to the dregs their sinking fortunes drain:
Hourly they give, and spend, and waste, and wear,
And think no pleasure can be bought too dear.
(Dryden) |
| 296 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xix. 42. |
Add weight to trifles. |
| 297 |
Hor.
1 Sat. vi. 66. |
As perfect beauties somewhere have a mole.
(Creech) |
| 298 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 373. |
Honour is nowhere safe. |
| 299 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 166 |
Some country girl, scarce to a curtsey bred,
Would I much rather than Cornelia wed;
If supercilious, haughty, proud, and vain,
She brought her father's triumphs in her train.
Away with all your Carthaginian state;
Let vanquish'd Hannibal without-doors wait,
Too burly and too big to pass my narrow gate.
(Dryden) |
| 300 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 5. |
—Another failing of the mind,
Greater than this, of quite a different kind.
(Pooley) |
| 301 |
Hor.
4 Od. xiii. 26. |
That all may laugh to see that glaring light,
Which lately shone so fierce and bright,
End in a stink at last, and vanish into night.
(Anon.) |
| 302 |
Virg.
Æn. v. 343. |
Becoming sorrows, and a virtuous mind
More lovely in a beauteous form enshrined. |
| 303 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 363 |
—Some choose the clearest light,
And boldly challenge the most piercing eye.'
(Roscommon) |
| 304 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 2. |
A latent fire preys on his feverish veins. |
| 305 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 521. |
These times want other aids.
(Dryden) |
| 306 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 177 |
What beauty, or what chastity, can bear
So great a price, if stately and severe
She still insults?
(Dryden) |
| 307 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 39 |
—Often try what weight you can support,
And what your shoulders are too weak to bear.
(Roscommon) |
| 308 |
Hor.
5 Od. lib. ii. ver. 15. |
—Lalage will soon proclaim
Her love, nor blush to own her flame.
(Creech) |
| 309 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. ver. 264. |
Ye realms, yet unreveal'd to human sight,
Ye gods, who rule the regions of the night,
Ye gliding ghosts, permit me to relate
The mystic wonders of your silent state.
(Dryden) |
| 310 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 77. |
I'll tie the indissoluble marriage-knot. |
| 311 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 137 |
He sighs, adores, and courts her ev'ry hour:
Who wou'd not do as much for such a dower?
(Dryden) |
| 312 |
Tull. |
What duty, what praise, or what honour will he think worth enduring
bodily pain for, who has persuaded himself that pain is the chief
evil? Nay, to what ignominy, to what baseness will he not stoop, to
avoid pain, if he has determined it to be the chief evil? |
| 313 |
Juv.
Sat. vii. 237 |
Bid him besides his daily pains employ,
To form the tender manners of the boy,
And work him, like a waxen babe, with art,
To perfect symmetry in ev'ry part. |
| 314 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxiii, II. |
Attend thy mother's heels no more,
Now grown mature for man, and ripe for joy.
(Creech) |
| 315 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 191 |
Never presume to make a god appear,
But for a business worthy of a god.
(Roscommon) |
| 316 |
Virg.
Ecl. i. 28 |
Freedom, which came at length, though slow to come.
(Dryden) |
| 317 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 27. |
—Born to drink and eat.
(Creech) |
| 318 |
Virg.
Ecl. viii. 63 |
With different talents form'd, we variously excel. |
| 319 |
Hor.
1 Ep. i. 90. |
Say while they change on thus, what chains can bind
These varying forms, this Proteus of the mind?
(Francis) |
| 320 |
Ovid
Met. vi. 428 |
Nor Hymen nor the Graces here preside,
Nor Juno to befriend the blooming bride;
But fiends with fun'ral brands the process led,
And furies waited at the genial bed.
(Croxal) |
| 321 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 99 |
'Tis not enough a poem's finely writ;
It must affect and captivate the soul. |
| 322 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 110 |
Grief wrings her soul, and bends it down to earth.
(Francis) |
| 323 |
Virg. |
Sometimes a man, sometimes a woman. |
| 324 |
Pers.
Sat. ii. 61 |
O souls, in whom no heavenly fire is found,
Flat minds, and ever grovelling on the ground!
(Dryden) |
| 325 |
Ovid
Metam. iii. 432
from the fable of Narcissus |
What could, fond youth, this helpless passion move?
What kindled in thee this unpitied love?
Thy own warm blush within the water glows;
With thee the colour'd shadow comes and goes;
Its empty being on thyself relies;
Step thou aside, and the frail charmer dies.
(Addison) |
| 326 |
Hor.
Lib. iii. Od. xvi. 1. |
Of watchful dogs an odious ward
Right well one hapless virgin guard,
When in a tower of brass immured,
By mighty bars of steel secured,
Although by mortal rake-hells lewd
With all their midnight arts pursued,
Had not—
(Francis) vol. ii p. 77
(adapted)
Be to her faults a little blind,
Be to her virtues very kind,
And clap your padlock on her mind.
(Padlock) |
| 327 |
Virg.
Æn. vii. 48. |
A larger scene of action is display'd.
(Dryden) |
| 328 |
Petr. Arb. |
Delighted with unaffected plainness. |
| 328b |
Hor.
Epod. xvii. 24 |
Day chases night, and night the day,
But no relief to me convey.
(Duncome) |
| 329 |
Hor.
1 Ep. vi. 27. |
With Ancus, and with Numa, kings of Rome,
We must descend into the silent tomb. |
| 330 |
Juv.
Sat. xiv. 48 |
To youth the greatest reverence is due. |
| 331 |
Pers.
Sat. ii. 28 |
Holds out his foolish beard for thee to pluck. |
| 332 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 29. |
He cannot bear the raillery of the age.
(Creech) |
| 333 |
Virg. |
He calls embattled deities to arms. |
| 334 |
Cic.
de Gestu. |
You would have each of us be a kind of Roscius in his way; and you
have said that fastidious men are not so much pleased with what is
right, as disgusted at what is wrong. |
| 335 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 327 |
Keep Nature's great original in view,
And thence the living images pursue.
(Francis) |
| 336 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 80.
imitated |
One tragic sentence if I dare deride,
Which Betterton's grave action dignified,
Or well-mouth'd Booth with emphasis proclaims
(Tho' but, perhaps, a muster-roll of names),
How will our fathers rise up in a rage,
And swear, all shame is lost in George's age!
You'd think no fools disgraced the former reign,
Did not some grave examples yet remain,
Who scorn a lad should teach his father skill,
And, having once been wrong, will be so still.
(Pope) |
| 337 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 63. |
The jockey trains the young and tender horse,
While yet soft-mouth'd, and breeds him to the course.'
(Creech) |
| 338 |
Hor.
1 Ep. iii. 18. |
Made up of nought but inconsistencies. |
| 339 |
Virg.
Ecl. vi. 33 |
He sung the secret seeds of nature's frame,
How seas, and earth, and air, and active flame,
Fell through the mighty void, and in their fall,
Were blindly gather'd in this goodly ball.
The tender soil then stiff'ning by degrees,
Shut from the bounded earth the bounding seas,
The earth and ocean various forms disclose,
And a new sun to the new world arose.
(Dryden) |
| 340 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 10. |
What chief is this that visits us from far,
Whose gallant mien bespeaks him train'd to war? |
| 341 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 206. |
Resume your courage and dismiss your fear.
(Dryden) |
| 342 |
Tull. |
Justice consists in doing no injury to men; decency, in giving them
no offence. |
| 343 |
Ovid
Metam. xv. 165 |
—All things are but alter'd; nothing dies;
And here and there th' unbody'd spirit flies,
By time, or force, or sickness dispossess'd,
And lodges, where it lights, in man or beast.
(Dryden) |
| 344 |
Juv.
Sat. xi. 11 |
Such, whose sole bliss is eating; who can give
But that one brutal reason why they live?
(Congreve) |
| 345 |
Ovid
Metam. i. 76 |
A creature of a more exalted kind
Was wanting yet, and then was man design'd;
Conscious of thought, of more capacious breast,
For empire form'd and fit to rule the rest.
(Dryden) |
| 346 |
Tull. |
I esteem a habit of benignity greatly preferable to munificence. The
former is peculiar to great and distinguished persons; the latter
belongs to flatterers of the people, who tickle the levity of the
multitude with a kind of pleasure. |
| 347 |
Lucan
lib. i. 8 |
What blind, detested fury, could afford
Such horrid licence to the barb'rous sword! |
| 348 |
Hor.
2 Sat. iii. 13. |
To shun detraction, would'st thou virtue fly? |
| 349 |
Lucan
i. 454. |
Thrice happy they beneath their northern skies,
Who that worst fear, the fear of death, despise!
Hence they no cares for this frail being feel,
But rush undaunted on the pointed steel,
Provoke approaching fate, and bravely scorn
To spare that life which must so soon return.
(Rowe) |
| 350 |
Tull. |
That elevation of mind which is displayed in dangers, if it wants
justice, and fights for its own conveniency, is vicious. |
| 351 |
Virg.
Æn. xii. 59. |
On thee the fortunes of our house depend. |
| 352 |
Tull. |
If we be made for honesty, either it is solely to be sought, or
certainly to be estimated much more highly than all other things. |
| 353 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 6 |
Though low the subject, it deserves our pains. |
| 354 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 168 |
heir signal virtues hardly can be borne,
Dash'd as they are with supercilious scorn. |
| 355 |
Ovid
Trist. ii. 563. |
I ne'er in gall dipp'd my envenom'd pen,
Nor branded the bold front of shameless men. |
| 356 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 349 |
—The gods will grant
What their unerring wisdom sees they want;
In goodness, as in greatness, they excel;
Ah! that we loved ourselves but half as well!
(Dryden) |
| 357 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 6. |
Who can relate such woes without a tear? |
| 358 |
Hor.
4 Od. xii. 1. ult. |
'Tis joyous folly that unbends the mind.
(Francis) |
| 359 |
Virg.
Ecl. ii. 63 |
Lions the wolves, and wolves the kids pursue,
The kids sweet thyme,—and still I follow you
(Warton) |
| 360 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvii. 43. |
The man who all his wants conceals,
Gains more than he who all his wants reveals.
(Duncome) |
| 361 |
Virg.
Æn. vii. 514. |
The blast Tartarean spreads its notes around;
The house astonish'd trembles at the sound. |
| 362 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xix. 6. |
He praises wine; and we conclude from thence,
He liked his glass on his own evidence. |
| 363 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 368. |
All parts resound with tumults, plaints, and fears,
And grisly Death in sundry shapes appears.
(Dryden) |
| 364 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xi. 29. |
Anxious through seas and land to search for rest,
Is but laborious idleness at best.
(Francis) |
| 365 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 272 |
But most in spring: the kindly spring inspires
Reviving heat, and kindles genial fires.
adapted
Flush'd by the spirit of the genial year,
Be greatly cautious of your sliding hearts.
(Thompson's Spring, 160 &c.) |
| 366 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxii. 17. |
Set me where on some pathless plain
The swarthy Africans complain,
To see the chariot of the sun
So near the scorching country run:
The burning zone, the frozen isles,
Shall hear me sing of Celia's smiles;
All cold, but in her breast, I will despise,
And dare all heat, but that of Celia's eyes.
(Roscommon) |
| 367 |
Juv.
Sat. i. 18 |
In mercy spare us, when we do our best
To make as much waste paper as the rest. |
| 368 |
Eurip.
apud Tull. |
When first an infant draws the vital air,
Officious grief should welcome him to care:
But joy should life's concluding scene attend,
And mirth be kept to grace a dying friend. |
| 369 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 180 |
What we hear moves less than what we see.
(Roscommon) |
| 370 |
Shakspeare |
—All the world's a stage,
And all the men and women merely players. |
| 371 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 28 |
And shall the sage your approbation win,
Whose laughing features wore a constant grin? |
| 372 |
Ovid
Met. i. 759 |
To hear an open slander is a curse;
But not to find an answer is a worse.
(Dryden) |
| 373 |
Juv.
Sat. xiv. 109 |
Vice oft is hid in Virtue's fair disguise,
And in her borrow'd form escapes inquiring eyes. |
| 374 |
Lucan
ii. 57. |
He reckon'd not the past, while aught remain'd
Great to be done, or mighty to be gain'd.
(Rowe) |
| 375 |
Hor.
4 Od. ix. 45. |
We barbarously call them blest,
Who are of largest tenements possest,
While swelling coffers break their owner's rest.
More truly happy those who can
Govern that little empire, man;
Who spend their treasure freely, as 'twas given
By the large bounty of indulgent Heaven;
Who, in a fix'd unalterable state,
Smile at the doubtful tide of Fate,
And scorn alike her friendship and her hate.
Who poison less than falsehood fear,
Loath to purchase life so dear.
(Stepney) |
| 376 |
Pers.
Sat. vi. 11. |
From the Pythagorean peacock. |
| 377 |
Hor.
2 Od. xiii. 13. |
What each should fly, is seldom known;
We unprovided, are undone.
(Creech) |
| 378 |
Virg.
Ecl. ix. 48 |
Mature in years, to ready honours move.
(Dryden) |
| 379 |
Pers.
Sat. i. 27 |
—Science is not science till reveal'd.
(Dryden) |
| 380 |
Ovid
Ars Am. ii. 538. |
With patience bear a rival in thy love. |
| 381 |
Hor.
2 Od. iii. 1. |
Be calm, my Dellius, and serene,
However fortune change the scene,
In thy most dejected state,
Sink not underneath the weight;
Nor yet, when happy days begin,
And the full tide comes rolling in.
Let a fierce, unruly, joy,
The settled quiet of thy mind destroy.
(Anon.) |
| 382 |
Tull. |
The accused confesses his guilt. |
| 383 |
Juv.
Sat. i. 75 |
A beauteous garden, but by vice maintain'd. |
| 384 |
|
[no motto. html Ed.] |
| 385 |
Ovid.
1 Trist. iii 66. |
Breasts that with sympathizing ardour glow'd,
And holy friendship, such as Theseus vow'd. |
| 386 |
|
[motto, but translation missing. html Ed.] |
| 387 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 102. |
What calms the breast, and makes the mind serene. |
| 388 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 174 |
For thee I dare unlock the sacred spring,
And arts disclosed by ancient sages sing. |
| 389 |
Hor. |
Their pious sires a better lesson taught. |
| 390 |
Tull. |
It is not by blushing, but by not doing what is unbecoming, that we
ought to guard against the imputation of impudence. |
| 391 |
Pers.
Sat. ii. v. 3. |
Thou know'st to join
No bribe unhallow'd to a prayer of thine;
Thine, which can ev'ry ear's full test abide,
Nor need be mutter'd to the gods aside!
No, thou aloud may'st thy petitions trust!
Thou need'st not whisper; other great ones must;
For few, my friend, few dare like thee be plain,
And prayer's low artifice at shrines disdain.
Few from their pious mumblings dare depart,
And make profession of their inmost heart.
Keep me, indulgent Heaven, through life sincere,
Keep my mind sound, my reputation clear.
These wishes they can speak, and we can hear.
Thus far their wants are audibly exprest;
Then sinks the voice, and muttering groans the rest:
'Hear, hear at length, good Hercules, my vow!
O chink some pot of gold beneath my plough!
Could I, O could I, to my ravish'd eyes,
See my rich uncle's pompous funeral rise;
Or could I once my ward's cold corpse attend,
Then all were mine!' |
| 392 |
Petr. |
By fable's aid ungovern'd fancy soars,
And claims the ministry of heavenly powers. |
| 393 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 412 |
Unusual sweetness purer joys inspires. |
| 394 |
Tull. |
It is obvious to see that these things are very acceptable to
children, young women, and servants, and to such as most resemble
servants; but they can by no means meet with the approbation of people
of thought and consideration. |
| 395 |
Ovid
Rem. Amor. 10 |
'Tis reason now, 'twas appetite before. |
| 396 |
|
[motto, but translation missing. html Ed.] |
| 397 |
Ovid
Metam. xiii. 228 |
Her grief inspired her then with eloquence. |
| 398 |
Hor.
2 Sat. iii. 271. |
You'd be a fool
With art and wisdom, and be mad by rule.
(Creech) |
| 399 |
Pers.
Sat. iv. 23 |
None, none descends into himself to find
The secret imperfections of his mind.
(Dryden) |
| 400 |
Virg.
Ecl. iii. 93 |
There's a snake in the grass.
(English Proverbs) |
| 401 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 1. |
It is the capricious state of love to be attended with injuries,
suspicions, enmities, truces, quarrelling, and reconcilement. |
| 402 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 181 |
Sent by the Spectator to himself. |
| 403 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 142 |
Of many men he saw the manners. |
| 404 |
Virg.
Ecl. viii. 63 |
With different talents form'd, we variously excel. |
| 405 |
Hom. |
With hymns divine the joyous banquet ends;
The paæans lengthen'd till the sun descends:
The Greeks restored, the grateful notes prolong;
Apollo listens, and approves the song.
(Pope) |
| 406 |
Tull. |
These studies nourish youth; delight old age; are the ornament of
prosperity, the solacement and the refuge of adversity; they are
delectable at home, and not burdensome abroad, they gladden us at
nights, and on our journeys, and in the country. |
| 407 |
Ovid
Met. xiii. 127 |
Eloquent words a graceful manner want. |
| 408 |
Tull.
de Finibus. |
The affections of the heart ought not to be too much indulged, nor
servilely depressed. |
| 409 |
Lucr.
i. 933. |
To grace each subject with enlivening wit. |
| 410 |
Ter.
Eun. Act v. Sc. 4. |
When they are abroad, nothing so clean and nicely dressed, and when
at supper with a gallant, they do but piddle, and pick the choicest
bits: but to see their nastiness and poverty at home, their gluttony,
and how they devour black crusts dipped in yesterday's broth, is a
perfect antidote against wenching. |
| 411 |
Lucr.
i. 925. |
In wild unclear'd, to Muses a retreat,
O'er ground untrod before, I devious roam,
And deep enamour'd into latent springs
Presume to peep at coy virgin Naiads. |
| 412 |
Mart.
Ep. iv. 14 |
The work, divided aptly, shorter grows. |
| 413 |
Ovid
Met. ix. 207 |
The cause is secret, but the effect is known.
(Addison) |
| 414 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 410 |
But mutually they need each other's help.
(Roscommon) |
| 415 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 155 |
Witness our cities of illustrious name,
Their costly labour, and stupendous frame.
(Dryden) |
| 416 |
Lucr.
ix. 754. |
So far as what we see with our minds, bears similitude to what we see
with our eyes. |
Vol.
3. |
title, |
text |
| 417 |
Hor.
4 Od. iii. 1. |
He on whose birth the lyric queen
Of numbers smiled, shall never grace
The Isthmian gauntlet, or be seen
First in the famed Olympic race.
But him the streams that warbling flow
Rich Tibur's fertile meads along,
And shady groves, his haunts shall know
The master of th' Æolian song.
(Atterbury) |
| 418 |
Virg.
Ecl. iii. 89 |
The ragged thorn shall bear the fragrant rose. |
| 419 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 140. |
The sweet delusion of a raptured mind. |
| 420 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 100 |
And raise men's passions to what height they will. |
| 421 |
Ovid
Met. vi. 294 |
He sought fresh fountains in a foreign soil;
The pleasure lessen'd the attending toil.
(Addison) |
| 422 |
Tull.
Epist. |
I have written this, not out of the abundance of leisure, but of my
affection towards you. |
| 423 |
Hor.
3 Od. xxvi. 1. |
Once fit myself. |
| 424 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xi. 30. |
'Tis not the place disgust or pleasure brings:
From our own mind our satisfaction springs. |
| 425 |
Hor.
4 Od. vii. 9. |
The cold grows soft with western gales,
The summer over spring prevails,
But yields to autumn's fruitful rain,
As this to winter storms and hails;
Each loss the hasting moon repairs again.
(Sir. W. Temple) |
| 426 |
Virg.
Æn. iii. 56. |
O cursed hunger of pernicious gold!
What bands of faith can impious lucre hold.
(Dryden) |
| 427 |
Tull. |
We should be as careful of our words as our actions; and as far from
speaking as from doing ill. |
| 428 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 417 |
The devil take the hindmost.
(English Proverbs) |
| 429 |
Hor.
2 Od. ii. 19. |
From cheats of words the crowd she brings
To real estimates of things.
(Creech) |
| 430 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xvii. 62. |
—The crowd replies,
Go seek a stranger to believe thy lies.
(Creech) |
| 431 |
Tull. |
What is there in nature so dear to man as his own children? |
| 432 |
Virg.
Ecl. ix. 36 |
He gabbles like a goose amidst the swan-like quire.
(Dryden) |
| 433 |
Mart.
Epig. xiv. 183 |
To banish anxious thought and quiet pain,
Read Homer's frogs, or my more trifling strain. |
| 434 |
Virg.
Æn. xi. 659. |
So march'd the Thracian Amazons of old
When Thermedon with bloody billows roll'd;
Such troops as these in shining arms were seen,
When Theseus met in fight their maiden queen;
Such to the field Penthesilea led,
From the fierce virgin when the Grecians fled.
With such return'd triumphant from the war,
Her maids with cries attend the lofty car;
They clash with manly force their moony shields;
With female shouts resound the Phrygian fields.
(Dryden) |
| 435 |
Ovid
Met. iv. 378 |
Both bodies in a single body mix,
A single body with a double sex.
(Addison) |
| 436 |
Juv.
Sat. iii. 36 |
With thumbs bent back, they popularly kill.
(Dryden) |
| 437 |
Ter.
And. Act v. Sc. 4. |
Shall you escape with impunity; you who lay snares for young men of a
liberal education, but unacquainted with the world, and by force of
importunity and promises draw them in to marry harlots? |
| 438 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 62. |
—Curb thy soul,
And check thy rage, which must be ruled or rule.
(Creech) |
| 439 |
Ovid
Metam. xii. 57 |
Some tell what they have heard, or tales devise;
Each fiction still improved with added lies. |
| 440 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 213. |
Learn to live well, or fairly make your will.
(Pope) |
| 441 |
Hor.
3 Od. iii. 7. |
Should the whole frame of nature round him break,
In ruin and confusion hurl'd,
He, unconcern'd, would hear the mighty crack,
And stand secure amidst a falling world.
(Anon.) |
| 442 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 117. |
—Those who cannot write, and those who can,
All rhyme, and scrawl, and scribble to a man.
(Pope) |
| 443 |
Hor.
3 Od. xxiv. 32. |
Snatch'd from our sight, we eagerly pursue,
And fondly would recall her to our view. |
| 444 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 139 |
The mountain labours. |
| 445 |
Mart.
Epig. i. 118. |
You say, Lupercus, what I write
I'n't worth so much: you're in the right. |
| 446 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 308 |
What fit, what not; what excellent, or ill.
(Roscommon) |
| 447 |
|
Long exercise, my friend, inures the mind;
And what we once disliked we pleasing find. |
| 448 |
Juv.
Sat. ii. 82 |
In time to greater baseness you proceed. |
| 449 |
Mart.
iii. 68. |
A book the chastest matron may peruse. |
| 450 |
Hor.
1 Ep. i. 53. |
—Get money, money still,
And then let virtue follow, if she will.
(Pope) |
| 451 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 149. |
—Times corrupt and nature ill-inclined
Produced the point that left the sting behind;
Till, friend with friend, and families at strife,
Triumphant malice raged through private life.
(Pope) |
| 452 |
Pliny
apud Lillium |
Human nature is fond of novelty. |
| 453 |
Hor.
2 Od. xx. i. |
No weak, no common wing shall bear
My rising body through the air.
(Creech) |
| 454 |
Ter.
Heaut. Act i. Sc. 1. |
Give me leave to allow myself no respite from labour. |
| 455 |
Hor.
4 Od. ii. 27. |
—My timorous Muse
Unambitious tracts pursues;
Does with weak unballast wings,
About the mossy brooks and springs.
Like the laborious bee,
For little drops of honey fly,
And there with humble sweets contents her Industry.
(Cowley) |
| 456 |
Tull. |
The man whose conduct is publicly arraigned, is not suffered even to
be undone quietly. |
| 457 |
Hor.
2 Sat. iii. 9. |
Seeming to promise something wondrous great. |
| 458 |
Hor. |
False modesty. |
| 459 |
Hor.
1 Ep. iv. 5. |
—Whate'er befits the wise and good
(Creech) |
| 460 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 25 |
Deluded by a seeming excellence.
(Roscommon) |
| 461 |
Virg.
Ecl. ix. 34 |
But I discern their flatt'ry from their praise.
(Dryden) |
| 462 |
Hor.
1 Sat. v. 44. |
Nothing so grateful as a pleasant friend. |
| 463 |
Claud. |
In sleep, when fancy is let loose to play,
Our dreams repeat the wishes of the day.
Though farther toil his tired limbs refuse.
The dreaming hunter still the chace pursues,
The judge abed dispenses still the laws,
And sleeps again o'er the unfinish'd cause.
The dozing racer hears his chariot roll,
Smacks the vain whip, and shuns the fancied goal.
Me too the Muses, in the silent night,
With wonted chimes of jingling verse delight. |
| 464 |
Hor.
2 Od. x. 5. |
The golden mean, as she's too nice to dwell
Among the ruins of a filthy cell,
So is her modesty withal as great,
To baulk the envy of a princely seat.
(Norris) |
| 465 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 97. |
How you may glide with gentle ease
Adown the current of your days;
Nor vex'd by mean and low desires,
Nor warm'd by wild ambitious fires;
By hope alarm'd, depress'd by fear,
For things but little worth your care.
(Francis) |
| 466 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 409. |
And by her graceful walk the queen of love is known.
(Dryden) |
| 467 |
Tibull.
ad Messalam
1 Eleg. iv. 24. |
Whate'er my Muse adventurous dares indite,
Whether the niceness of thy piercing sight
Applaud my lays, or censure what I write,
To thee I sing, and hope to borrow fame,
By adding to my page Messala's name. |
| 468 |
Pliny
Epist. |
He was an ingenious, pleasant fellow, and one who had a great deal of
wit and satire, with an equal share of good humour. |
| 469 |
Tull. |
To detract anything from another, and for one man to multiply his own
conveniences by the inconveniences of another, is more against nature
than death, than poverty, than pain, and the other things which can
befall the body, or external circumstances. |
| 470 |
Mart.
2 Epig. lxxxvi. |
'Tis folly only, and defect of sense,
Turns trifles into things of consequence. |
| 471 |
Eurip. |
The wise with hope support the pains of life. |
| 472 |
Virg.
Æn. iii. 660. |
This only solace his hard fortune sends.
(Dryden) |
| 473 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xix. 12. |
Suppose a man the coarsest gown should wear,
No shoes, his forehead rough, his look severe,
And ape great Cato in his form and dress;
Must be his virtues and his mind express?
(Creech) |
| 474 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 6. |
Rude, rustic, and inelegant. |
| 475 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 1. |
The thing that in itself has neither measure nor consideration,
counsel cannot rule. |
| 476 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 41 |
Method gives light. |
| 477 |
Hor.
3 Od. iv. 5. |
—Does airy fancy cheat
My mind well pleased with the deceit?
I seem to hear, I seem to move,
And wander through the happy grove,
Where smooth springs flow, and murm'ring breeze,
Wantons through the waving trees.
(Creech) |
| 478 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 72 |
Fashion, sole arbitress of dress. |
| 479 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 398 |
To regulate the matrimonial life. |
| 480 |
Hor.
2 Sat. vii. 85. |
He, Sir, is proof to grandeur, pride, or pelf,
And, greater still, he's master of himself:
Not to and fro, by fears and factions hurl'd,
But loose to all the interests of the world;
And while the world turns round, entire and whole,
He keeps the sacred tenor of his soul.
(Pitt) |
| 481 |
Hor.
Sat. 1 vii. 19. |
Who shall decide when doctors disagree,
And soundest casuists doubt like you and me?
(Pope) |
| 482 |
Lucr.
iii. 11. |
As from the sweetest flower the lab'ring bee
Extracts her precious sweets. |
| 483 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 191 |
Never presume to make a god appear,
But for a business worthy of a god.
(Roscommon) |
| 484 |
Plin.
Epist. |
Nor has any one so bright a genius as to become illustrious
instantaneously, unless it fortunately meets with occasion and
employment, with patronage too, and commendation. |
| 485 |
Quin. Curt.
1. vii. c. 8. |
The strongest things are not so well established as to be out of
danger from the weakest. |
| 486 |
Hor.
1 Sat. ii. 37.
imitated |
All you who think the city ne'er can thrive,
Till ev'ry cuckold-maker's flay'd alive,
Attend—
(Pope) |
| 487 |
Petr. |
While sleep oppresses the tired limbs, the mind
Plays without weight, and wantons unconfined. |
| 488 |
Hor.
2 Sat. iii. 156. |
What doth it cost? Not much, upon my word.
How much, pray? Why, Two-pence. Two-pence, O Lord!
(Creech) |
| 489 |
Hom. |
The mighty force of ocean's troubled flood. |
| 490 |
Hor.
2 Od. xiv. 21. |
Thy house and pleasing wife.
(Creech) |
| 491 |
Virg.
Æn. iii. 318. |
A just reverse of fortune on him waits. |
| 492 |
Seneca |
Levity of behaviour is the bane of all that is good and virtuous. |
| 493 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 76. |
Commend not, till a man is throughly known:
A rascal praised, you make his faults your own.
(Anon.) |
| 494 |
Cicero |
What kind of philosophy is it to extol melancholy, the most
detestable thing in nature? |
| 495 |
Hor.
4 Od. iv. 57. |
—Like an oak on some cold mountain brow,
At every wound they sprout and grow:
The axe and sword new vigour give,
And by their ruins they revive.
(Anon.) |
| 496 |
Terent.
Heaut. Act i. Sc. 1. |
Your son ought to have shared in these things, because youth is best
suited to the enjoyment of them. |
| 497 |
Menander |
A cunning old fox this! |
| 498 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 514 |
Nor reins, nor curbs, nor cries, the horses fear,
But force along the trembling charioteer.
(Dryden) |
| 499 |
Pers.
Sat. i. 40 |
—You drive the jest too far.
(Dryden) |
| 500 |
Ovid
Met. vi. 182 |
Seven are my daughters of a form divine,
With seven fair sons, an indefective line.
Go, fools, consider this, and ask the cause
From which my pride its strong presumption draws.
(Croxal) |
| 501 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxiv. 19. |
'Tis hard: but when we needs must bear,
Enduring patience makes the burden light.
(Creech) |
| 502 |
Ter.
Heaut. Act iv. Sc. 1. |
Better or worse, profitable or disadvantageous, they see nothing but
what they list. |
| 503 |
Ter.
Eun. Act ii. Sc. 3. |
From henceforward I blot out of my thoughts all memory of womankind. |
| 504 |
Ter.
Eun. Act iii. Sc. 1. |
You are a hare yourself, and want dainties, forsooth. |
| 505 |
Ennius |
Augurs and soothsayers, astrologers,
Diviners, and interpreters of dreams,
I ne'er consult, and heartily despise:
Vain their pretence to more than human skill:
For gain, imaginary schemes they draw;
Wand'rers themselves, they guide another's steps;
And for poor sixpence promise countless wealth.
Let them, if they expect to be believed,
Deduct the sixpence, and bestow the rest. |
| 506 |
Mart.
4 Epig. xiii. 7. |
Perpetual harmony their bed attend,
And Venus still the well-match'd pair befriend!
May she, when time has sunk him into years,
Love her old man, and cherish his white hairs;
Nor he perceive her charms through age decay,
But think each happy sun his bridal day! |
| 507 |
Juv.
2 Sat. 46 |
Preserved from shame by numbers on our side. |
| 508 |
Corn. Nepos.
in Milt. c. 8 |
For all those are accounted and denominated tyrants, who exercise a
perpetual power in that state which was before free. |
| 509 |
Ter.
Heaut. Act iii. Sc. 3. |
Discharging the part of a good economist. |
| 510 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 1. |
If you are wise, add not to the troubles which attend the passion of
love, and bear patiently those which are inseparable from it. |
| 511 |
Ovid
Ars Am. i. 175 |
—Who could fail to find,
In such a crowd a mistress to his mind? |
| 512 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 344 |
Mixing together profit and delight. |
| 513 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 50. |
When all the god came rushing on her soul.
(Dryden) |
| 514 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 291 |
But the commanding Muse my chariot guides,
Which o'er the dubious cliff securely rides:
And pleased I am no beaten road to take,
But first the way to new discov'ries make.
(Dryden) |
| 515 |
Ter.
Heaut. Act ii. Sc. 3. |
I am ashamed and grieved, that I neglected his advice, who gave me
the character of these creatures. |
| 516 |
Juv.
Sat xv. 34 |
—A grutch, time out of mind, begun,
And mutually bequeath'd from sire to son:
Religious spite and pious spleen bred first,
The quarrel which so long the bigots nurst:
Each calls the other's god a senseless stock:
His own divine.
(Tate) |
| 517 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 878. |
Mirror of ancient faith!
Undaunted worth! Inviolable truth!
(Dryden) |
| 518 |
Juv.
Sat. viii. 76 |
'Tis poor relying on another's fame,
For, take the pillars but away, and all
The superstructure must in ruins fall.
(Stepney) |
| 519 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 728. |
Hence men and beasts the breath of life obtain,
And birds of air, and monsters of the main.
(Dryden) |
| 520 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxiv. 1. |
And who can grieve too much? What time shall end
Our mourning for so dear a friend?
(Creech) |
| 521 |
P. Arb. |
The real face returns, the counterfeit is lost. |
| 522 |
Ter.
Andr. Act iv. Sc. 2. |
I swear never to forsake her; no, though I were sure to make all men
my enemies. Her I desired; her I have obtained; our humours agree.
Perish all those who would separate us! Death alone shall deprive me
of her! |
| 523 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 376. |
Now Lycian lots, and now the Delian god,
Now Hermes is employ'd from Jove's abode,
To warn him hence, as if the peaceful state
Of heavenly powers were touch'd with human fate!
(Dryden) |
| 524 |
Sen. |
As the world leads, we follow. |
| 525 |
Eurip. |
That love alone, which virtue's laws control,
Deserves reception in the human soul. |
| 526 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 127 |
Keep a stiff rein.
(Addison) |
| 527 |
Plautus
in Stichor. |
You will easily find a worse woman; a better the sun never shone
upon. |
| 528 |
Ovid
Met. ix. 165 |
With wonted fortitude she bore the smart,
And not a groan confess'd her burning heart.
(Gay) |
| 529 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. 92 |
Let everything have its due place.
(Roscommon) |
| 530 |
Hor.
1 Od. xxxiii. 10. |
Thus Venus sports; the rich, the base,
Unlike in fortune and in face,
To disagreeing love provokes;
When cruelly jocose,
She ties the fatal noose,
And binds unequals to the brazen yokes.
(Creech) |
| 531 |
Hor.
1 Od. xii. 15. |
Who guides below, and rules above,
The great Disposer, and the mighty King:
Than he none greater, like him none
That can be, is, or was;
Supreme he singly fills the throne.
(Creech) |
| 532 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 304 |
I play the whetstone; useless, and unfit
To cut myself, I sharpen other's wit.
(Creech) |
| 533 |
Plaut. |
Nay, says he, if one is too little, I will give you two;
And if two will not satisfy you, I will add two more. |
| 534 |
Juv.
Sat. viii. 73 |
—We seldom find
Much sense with an exalted fortune join'd.
(Stepney) |
| 535 |
Hor.
1 Od. xi. 7. |
Cut short vain hope. |
| 536 |
Virg.
Æn. ix. 617. |
O! less than women in the shapes of men. |
| 537 |
Acts xvii. 28 |
For we are his offspring. |
| 538 |
Hor.
2 Sat. i. 1. |
To launch beyond all bounds. |
| 539 |
Quæ Genus |
Be they heteroclites. |
| 540 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 143. |
A second is not wanting. |
| 541 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. v. 108 |
For nature forms and softens us within,
And writes our fortune's changes in our face:
Pleasure enchants, impetuous rage transports,
And grief dejects, and wrings the tortured soul:
And these are all interpreted by speech.
(Roscommon) |
| 542 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 430 |
He heard,
Well pleased, himself before himself preferred.
(Addison) |
| 543 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 12 |
Similar, though not the same. |
| 544 |
Ter.
Adelph. Act v. Sc. 4. |
No man was ever so completely skilled in the conduct of life, as not
to receive new information from age and experience; insomuch that we
find ourselves really ignorant of what we thought we understood, and
see cause to reject what we fancied our truest interest. |
| 545 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 99. |
Let us in bonds of lasting peace unite,
And celebrate the hymeneal rite. |
| 546 |
Tull. |
Everything should be fairly told, that the buyer may not be ignorant
of anything which the seller knows. |
| 547 |
Hor.
2 Ep. ii. 149. |
Suppose you had a wound, and one that show'd
An herb, which you apply'd, but found no good;
Would you be fond of this, increase your pain,
And use the fruitless remedy again?
(Creech) |
| 548 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 68. |
There's none but has some fault, and he's the best,
Most virtuous he, that's spotted with the least.
(Creech) |
| 549 |
Juv.
Sat. iii. 1 |
Tho' grieved at the departure of my friend,
His purpose of retiring I commend. |
| 550 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 138 |
In what will all this ostentation end?
(Roscommon |
| 551 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 400 |
So ancient is the pedigree of verse,
And so divine a poet's function.
(Roscommon) |
| 552 |
Hor.
2 Ep. i. 13. |
For those are hated that excel the rest,
Although, when dead, they are beloved and blest.
(Creech) |
| 553 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xiv. 35. |
Once to be wild is no such foul disgrace,
But 'tis so still to run the frantic race.
(Creech) |
| 554 |
Virg.
Georg. iii. 9 |
New ways I must attempt, my grovelling name
To raise aloft, and wing my flight to fame.
(Dryden) |
| 555 |
Pers.
Sat. iv. 51 |
Lay the fictitious character aside. |
| 556 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 471. |
So shines, renew'd in youth, the crested snake,
Who slept the winter in a thorny brake;
And, casting off his slough when spring returns,
Now looks aloft, and with new glory burns:
Restored with pois'nous herbs, his ardent sides
Reflect the sun, and raised on spires he rides;
High o'er the grass hissing he rolls along,
And brandishes by fits his forky tongue.
(Dryden) |
| 557 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 665. |
He fears the ambiguous race, and Tyrians double-tongued. |
| 558 |
Hor.
1 Sat. i. 1. |
Whence is't, Mæcenas, that so few approve
The state they're placed in, and incline to rove;
Whether against their will by fate imposed,
Or by consent and prudent choice espoused?
Happy the merchant! the old soldier cries,
Broke with fatigues and warlike enterprise.
The merchant, when the dreaded hurricane
Tosses his wealthy cargo on the main,
Applauds the wars and toils of a campaign:
There an engagement soon decides your doom,
Bravely to die, or come victorious home.
The lawyer vows the farmer's life is best,
When at the dawn the clients break his rest.
The farmer, having put in bail t' appear,
And forced to town, cries they are happiest there:
With thousands more of this inconstant race,
Would tire e'en Fabius to relate each case.
Not to detain you longer, pray attend,
The issue of all this: Should Jove descend,
And grant to every man his rash demand,
To run his lengths with a neglectful hand;
First, grant the harass'd warrior a release,
Bid him to trade, and try the faithless seas,
To purchase treasure and declining ease:
Next, call the pleader from his learned strife,
To the calm blessings of a country life:
And with these separate demands dismiss
Each suppliant to enjoy the promised bliss:
Don't you believe they'd run? Not one will move,
Though proffer'd to be happy from above.
(Horneck) |
| 559 |
Hor.
1 Sat. i. 20. |
Were it not just that Jove, provoked to heat,
Should drive these triflers from the hallow'd seat,
And unrelenting stand when they entreat?
(Horneck) |
| 560 |
Ovid
Met. i. 747 |
He tries his tongue, his silence softly breaks.
(Dryden) |
| 561 |
Virg.
Æn. i. 724. |
But he
Works in the pliant bosom of the fair,
And moulds her heart anew, and blots her former care.
The dead is to the living love resign'd,
And all Æneas enters in her mind.
(Dryden) |
| 562 |
Ter.
Eun. Act i. Sc. 2. |
Be present as if absent. |
| 563 |
Lucan
i. 135. |
The shadow of a mighty name. |
| 564 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iii. 117. |
Let rules be fix'd that may our rage contain,
And punish faults with a proportion'd pain,
And do not flay him who deserves alone
A whipping for the fault that he hath done.
(Creech) |
| 565 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 221 |
For God the whole created mass inspires.
Through heaven and earth, and ocean's depths: he throws
His influence round, and kindles as he goes.
(Dryden) |
| 566 |
Ovid
Ars Am. ii. 233 |
Love is a kind of warfare. |
| 567 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 493. |
The weak voice deceives their gasping throats.
(Dryden) |
| 568 |
Mart.
Epig. i. 39 |
Reciting makes it thine. |
| 569 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 434 |
Wise were the kings who never chose a friend,
Till with full cups they had unmask'd his soul,
And seen the bottom of his deepest thoughts.
(Roscommon) |
| 570 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 322 |
Chiming trifles.
(Roscommon) |
| 571 |
Luc. |
What seek we beyond heaven? |
| 572 |
Hor.
1 Ep. ii. 115. |
Physicians only boast the healing art. |
| 573 |
Juv.
Sat. ii. 35 |
Chastised, the accusation they retort. |
| 574 |
Hor.
4 Od. ix. 45. |
Believe not those that lands possess,
And shining heaps of useless ore,
The only lords of happiness;
But rather those that know
For what kind fates bestow,
And have the heart to use the store
That have the generous skill to bear
The hated weight of poverty.
(Creech) |
| 575 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 223 |
No room is left for death.
(Dryden) |
| 576 |
Ovid
Met. ii. 72 |
I steer against their motions, nor am I
Borne back by all the current of the sky.
(Addison) |
| 577 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 613 |
This might be borne with, if you did not rave. |
| 578 |
Ovid
Met. xv. 167 |
Th' unbodied spirit flies
And lodges where it lights in man or beast.
(Dryden) |
| 579 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 132. |
Sagacious hounds. |
| 580 |
Ovid
Met. i. 175 |
This place, the brightest mansion of the sky,
I'll call the palace of the Deity.
(Dryden) |
| 581 |
Mart.
Epig. i. 17. |
Some good, more bad, some neither one nor t'other. |
| 582 |
Juv.
Sat. vii. 51 |
The curse of writing is an endless itch.
(Ch. Dryden) |
| 583 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 112 |
With his own hand the guardian of the bees,
For slips of pines may search the mountain trees,
And with wild thyme and sav'ry plant the plain,
Till his hard horny fingers ache with pain;
And deck with fruitful trees the fields around,
And with refreshing waters drench the ground.
(Dryden) |
| 584 |
Virg.
Ecl. x. 42 |
Come see what pleasures in our plains abound;
The woods, the fountains, and the flow'ry ground:
Here I could live, and love, and die with only you.
(Dryden) |
| 585 |
Virg.
Ecl. v. 68 |
The mountain-tops unshorn, the rocks rejoice;
The lowly shrubs partake of human voice.
(Dryden) |
| 586 |
Cic.
de Div. |
The things which employ men's waking thoughts and actions recur to
their imaginations in sleep. |
| 587 |
Pers.
Sat. iii. 30 |
I know thee to thy bottom; from within
Thy shallow centre to the utmost skin.
(Dryden) |
| 588 |
Cicero |
You pretend that all kindness and benevolence is founded in
weakness. |
| 589 |
Ovid
Met. viii. 774 |
The impious axe he plies, loud strokes resound:
Till dragg'd with ropes, and fell'd with many a wound,
The loosen'd tree comes rushing to the ground. |
| 590 |
Ovid
Met. xv. 179 |
E'en times are in perpetual flux, and run,
Like rivers from their fountains, rolling on.
For time, no more than streams, is at a stay;
The flying hour is ever on her way:
And as the fountains still supply their store,
The wave behind impels the wave before;
Thus in successive course the minutes run,
And urge their predecessor minutes on.
Still moving, ever new; for former things
Are laid aside, like abdicated kings;
And every moment alters what is done,
And innovates some act, till then unknown.
(Dryden) |
| 591 |
Ovid
Trist. 3 El. li. 73. |
Love the soft subject of his sportive Muse. |
| 592 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 409 |
Art without a vein.
(Roscommon) |
| 593 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 270. |
Thus wander travellers in woods by night,
By the moon's doubtful and malignant light.
(Dryden) |
| 594 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iv. 81. |
He that shall rail against his absent friends,
Or hears them scandalized, and not defends;
Sports with their fame, and speaks whate'er he can,
And only to be thought a witty man;
Tells tales, and brings his friends in disesteem;
That man's a knave; be sure beware of him.
(Creech) |
| 595 |
Hor.
Ars Poet. ver. 12 |
Nature, and the common laws of sense,
Forbid to reconcile antipathies;
Or make a snake engender with a dove,
And hungry tigers court the tender lambs.
(Roscommon) |
| 596 |
Ovid
Ep. xv. 79 |
Cupid's light darts my tender bosom move.
(Pope) |
| 597 |
Petr. |
The mind uncumber'd plays. |
| 598 |
Juv.
Sat. x. 28 |
Will ye not now the pair of sages praise,
Who the same end pursued by several ways?
One pity'd, one condemn'd, the woful times;
One laugh'd at follies, one lamented crimes.
(Dryden) |
| 599 |
Virg.
Æn. ii. 369. |
All parts resound with tumults, plaints, and fears.
(Dryden) |
| 600 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 641 |
Stars of their own, and their own suns they know.
(Dryden) |
| 601 |
Antonin.
lib. 9. |
Man is naturally a beneficent creature. |
| 602 |
Juv.
Sat. vi. 110 |
This makes them hyacinths. |
| 603 |
Virg.
Ecl. viii. 68 |
Restore, my charms,
My lingering Daphnis to my longing arms.
(Dryden) |
| 604 |
Hor.
1 Od. xi. 1. |
Ah, do not strive too much to know,
My dear Leuconoe,
What the kind gods design to do
With me and thee.
(Creech) |
| 605 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 51 |
They change their savage mind,
Their wildness lose, and, quitting nature's part,
Obey the rules and discipline of art.
(Dryden) |
| 606 |
Virg.
Georg. i. 293 |
Mean time at home
The good wife singing plies the various loom. |
| 607 |
Ovid
Ars Amor. i. 1 |
Now Iö Pæan sing, now wreaths prepare,
And with repeated Iös fill the air;
The prey is fallen in my successful toils.
(Anon.) |
| 608 |
Ovid
Ars Amor. i. 633 |
Forgiving with a smile
The perjuries that easy maids beguile.
(Dryden) |
| 609 |
Juv.
Sat. i. 86 |
The miscellaneous subjects of my book. |
| 610 |
Seneca |
Thus, when my fleeting days, at last,
Unheeded, silently, are past,
Calmly I shall resign my breath,
In life unknown, forgot in death:
While he, o'ertaken unprepared,
Finds death an evil to be fear'd,
Who dies, to others too much known,
A stranger to himself alone. |
| 611 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 366. |
Perfidious man! thy parent was a rock,
And fierce Hyrcanian tigers gave thee suck. |
| 612 |
Virg.
Æn. xii. 529. |
Murranus, boasting of his blood, that springs
From a long royal race of Latin kings,
Is by the Trojan from his chariot thrown,
Crush'd with the weight of an unwieldy stone.
(Dryden) |
| 613 |
Virg.
Georg. iv. 564 |
Affecting studies of less noisy praise.
(Dryden) |
| 614 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 15. |
Were I not resolved against the yoke
Of hapless marriage; never to be cursed
With second love, so fatal was the first,
To this one error I might yield again.
(Dryden) |
| 615 |
Hor.
4 Od. ix. 47. |
Who spend their treasure freely, as 'twas given
By the large bounty of indulgent Heaven:
Who in a fixt unalterable state
Smile at the doubtful tide of fate,
And scorn alike her friendship and her hate:
Who poison less than falsehood fear,
Loath to purchase life so dear;
But kindly for their friend embrace cold death,
And seal their country's love with their departing breath.
(Stepney) |
| 616 |
Mart.
Epig. i. 10. |
A pretty fellow is but half a man. |
| 617 |
Pers.
Sat. i. 99 |
Their crooked horns the Mimallonian crew
With blasts inspired; and Rassaris, who slew
The scornful calf, with sword advanced on high,
Made from his neck his haughty head to fly.
And Mænas, when, with ivy-bridles bound,
She led the spotted lynx, then Evion rang around,
Evion from woods and floods repeating Echo's sound.
(Dryden) |
| 618 |
Hor.
1 Sat. iv. 40. |
'Tis not enough the measured feet to close:
Nor will you give a poet's name to those
Whose humble verse, like mine, approaches prose. |
| 619 |
Virg.
Georg. ii. 369 |
Exert a rigorous sway,
And lop the too luxuriant boughs away. |
| 620 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 791. |
Behold the promised chief! |
| 621 |
Lucan
ix. 11. |
Now to the blest abode, with wonder fill'd,
The sun and moving planets he beheld;
Then, looking down on the sun's feeble ray,
Survey'd our dusky, faint, imperfect day,
And under what a cloud of night we lay.
(Rowe) |
| 622 |
Hor.
1 Ep. xviii. 103. |
A safe private quiet, which betrays
Itself to ease, and cheats away the days.
(Pooley) |
| 623 |
Virg.
Æn. iv. 24. |
But first let yawning earth a passage rend,
And let me thro' the dark abyss descend:
First let avenging Jove, with flames from high.
Drive down this body to the nether sky,
Condemn'd with ghosts in endless night to lie;
Before I break the plighted faith I gave;
No: he who had my vows shall ever have;
For whom I loved on earth, I worship in the grave.
(Dryden) |
| 624 |
Hor.
2 Sat. iii. 77. |
Sit still, and hear, those whom proud thoughts do swell,
Those that look pale by loving coin too well;
Whom luxury corrupts.
(Creech) |
| 625 |
Hor.
3 Od. vi. 23. |
Love, from her tender years, her thoughts employ'd. |
| 626 |
Ovid
Met. i. 1 |
With sweet novelty your taste I'll please.
(Eusden) |
| 627 |
Virg.
Ecl. ii. 3 |
He underneath the beechen shade, alone.
Thus to the woods and mountains made his moan.
(Dryden) |
| 628 |
Mor.
1 Ep. ii. 43. |
It rolls, and rolls, and will for ever roll. |
| 629 |
Juv.
1 Sat. i. 170. |
Since none the living dare implead,
Arraign them in the persons of the dead.
(Dryden) |
| 630 |
Hor.
3 Od. i. 2. |
With mute attention wait. |
| 631 |
Hor.
1 Od. v. 5. |
Elegant by cleanliness |
| 632 |
Virg.
Æn. vi. 545. |
The number I'll complete,
Then to obscurity well pleased retreat. |
| 633 |
Cicero |
The contemplation of celestial things will make a man both speak and
think more sublimely and magnificently when he descends to human
affairs. |
| 634 |
Soctrates
apud Xen. |
The fewer our wants, the nearer we resemble the gods. |
| 635 |
Cicero
Somn. Scip. |
I perceive you contemplate the seat and habitation of men; which if
it appears as little to you as it really is, fix your eyes perpetually
upon heavenly objects, and despise earthly. |
Contents
Some Advertisements from the Original Numbers of the Spectator
In
Books only were advertised; and they were:
- Dr. James Drake's Anthropologia Nova; or, a New System of Anatomy
- Sir William Petty's Political Arithmetic
- a translation of Bernard Lamy's Perspective made Easie
- The Compleat Geographer
- an Essay towards the Probable Solution of this Question, Where those birds do probably make their abode which are absent from our Climate at some certain Times and
Seasons of the Year. By a Person of Learning.
- The second edition of The Origin and Institution of Civil Government Discussed, by the Rev. Benjamin Hoadly, M.A., Rector of St. Peter's poor (who did not become a
Bishop until 1715)
- a third edition of The Works of the Right Rev. Ezekiel Hopkins, late Lord Bishop of Londonderry,
- and newly published,
a Collection of Debates, Reports, Orders and Resolutions of the House of
Commons, touching the right of Electing Members to serve in Parliament.
was without Advertisements. Nos.
to
still advertised only
Books.
placed five miscellaneous advertisements before the books,
one of 'The Number of Silk Gowns that are weekly sold at Mrs. Rogers's,
in Exchange Alley,' one of a House to Let at Sutton, one of Spanish
Snuff, and two of Clarets and Spanish (Villa Nova, Barcelona and
Galicia) Wines. The book advertisements predominating still,—with at
first only one or at most two general advertisements, as of Plain
Spanish Snuff; Yew and Holly Plants for sale; the drinking glasses and
decanters at the Flint Glass-House in Whitefryers; a large House to let
with a Dove House, Stables, and all other conveniences; the sale of a
deceased Gentleman's Furniture, or a Lieutenant's Commission lost or
mislaid,—we come to the first of the quack advertisements in
.
They are from separate houses, one of a 'Chrystal Cosmetick,' the other
'A most Incomparable Paste for the Hands, far exceeding anything ever
yet in Print: It makes them Delicately white, sleek and plump; fortifies
them against the Scorching heat of the Fire or Sun, and Sharpness of the
Wind. A Hand cannot be so spoilt but the use of it will recover them.'
In
the first advertisement is of a Consort of Vocal and
Instrumental Musick by the best Masters, which would be performed for
the benefit of Mrs. Moore, at the Desire of several Persons of Quality.
It was to be given 'at the Two Golden Balls, in Hart Street, the Upper
End of Bow Street, Covent Garden.'
The first advertisement in
is of a boarding school
for young gentlewomen, 'near the Windmill in Hampstead.' 'The famous
Water Theatre of the Ingenious Mr. Winstanly' was to be opened on the
ensuing Easter Monday, and
'There is a Parcel of extraordinary fine Bohee Tea to be sold at 26s.
per Pound, at the Sign of the Barber's Pole, next door to the
Brasier's Shop in Southampton Street in the Strand. N. B. The same is
to be sold from 10 to 12 in the Morning and from 2 to 4 in the
Afternoon.'
we have
'Just Published, and Printed very Correctly, with a neat Elzevir
Letter, in 12mo for the Pocket,
'Paradise Lost, a Poem in twelve Books, written by Mr. John Milton.
The Ninth Edition, adorn'd with Sculptures. Printed for Jacob Tonson
at Shakespear's Head over against Catherine Street in the Strand.'
'Right German Spaw-Waters at 13s. a dozen. Bohee 16, 20 and 24s. All
Sorts of Green, the lowest at 10s. Chocolate all Nut 2s. 6d. and 3s.
with sugar 1s. 8d. and 2s. The finest of Brazil Snuff at 35s. a Pound,
another sort at 20s. Barcelona, Havana and Old Spanish Snuff, Sold by
Wholesale with Encouragement to Retailers, by Robert Tate, at the Star
in Bedford Court, Covent Garden.
'This Day is Published,
'A Poem to the Right Honourable Mr. Harley, wounded by Guiscard.
Printed for Jacob Tonson, &c.' (
No. 35.)
The first advertisement of the performance at Drury Lane appeared in
, with an appended 'N. B. Advertisements for Plays will be continued,
from time to time, in this Paper.'
'A large Collection of Manuscript Sermons preach'd by several of the
most Eminent Divines, for some Years last past, are to be sold at the
Bookseller's Warehouse in Exeter Change in the Strand.'
'This Day is publish'd,
'
An Essay on Criticism. Printed for W. Lewis in Russell-street Covent
Garden; and Sold by W. Taylor, at the Ship in Pater Noster Row; T.
Osborn, in Grays-Inn near the Walks; J. Graves in St. James's-street;
and J. Morphew near Stationers' Hall. Price 1s.'
'Concerning the Small-Pox.
'R. Stroughton, Apothecary, at the Unicorn in Southwark, having about
Christmas last Published in the
Postman,
Tatler and
Courant, a
long Advertisement of his large Experience and great Success in curing
the Small-Pox, even of the worst Kind and Circumstances, having had a
Reputation for it almost 30 years, and can say than not 3 in 20
miscarry under his hands, doth now contract it; and only repeats, that
he thinks he has attain'd to as great a Certainty therein (and the
Measles which are near of Kin) as has been acquir'd in curing any one
disease (an Intermitting Feaver with the Bark only excepted) which he
conceives may at this time, when the Small-Pox so prevails, and is so
mortal, justify his Publications, being pressed by several so to do,
and hopes it may be for the Good of many: He has had many Patients
since his last Publication and but One of all dy'd. He hath also
Certificates from above 20 in a small time Cured, and of the worst
sort. What is here offered is Truth and Matter of Fact; and he will,
if desired, go with any one to the Persons themselves who have been
Cured, many of whom are People of Value and Figure: 'Tis by a correct
Management, more than a great deal of Physick, by which also the Face
and Eyes are much secured; tho' one Secret he has (obtained only by
Experience and which few or none know besides) that when they suddenly
strike in very rarely fails of raising them again in a few Hours, when
many other things, and proper too, have not answered. He does not
desire, nor aim at the supplanting of any Physician or Apothecary
concerned, but gives his assisting Advice if desired, and in such a
way not Dishonourable or Injurious to either.'
'Angelick Snuff: The most noble Composition in the World, removing all
manner of Disorders of the Head and all Swimming or Giddiness
proceeding from Vapours, &c., also Drowsiness, Sleepiness and other
lethargick Effects, perfectly curing Deafness to Admiration, and ill
Humours or Soreness in the Eyes, &c., strength'ning them when weak,
perfectly cures Catarrhs, or Defluxions of Rheum, and remedies the
Tooth-ach instantly; is excellently beneficial in Apoplectick Fits and
Falling-Sickness, and assuredly prevents those Distempers;
corroborates the Brain, comforts the Nerves, and revives the Spirits.
Its admirable Efficacy in all the above mention'd Diseases has been
experienc'd above a Thousand times, and very justly causes it to be
esteem'd the most beneficial Snuff in the World, being good for all
sorts of Persons. Price 1s. a Paper with Directions. Sold only at Mr.
Payn's Toyshop at the Angel and Crown in St Paul's Churchyard near
Cheapside.'
'For Sale by the Candle,
'On Friday next, the 25th Instant, at Lloyd's Coffee-house in
Lombard-Street at 4 a Clock in the Afternoon, only 1 Cask in a Lot,
viz. 74 Buts, 22 Hogsheads and 3 quarter Casks of new Bene-Carlos
Barcelona Wine, very deep, bright and strong, extraordinary good and
ordinary, at £10. per. But, £5. per Hogshead and 25s. per Quarter
Cask; neat, an entire Parcel, lately landed, now in Cellars on Galley
Key (fronting the Thames) between the Coffeehouse and Tower Dock. To
be tasted this Day the 23rd, and to Morrow the 24th Instant, from 7 a
Clock to 1, and from 2 to 7, and all Friday till the Time of Sale. To
be sold by Tho. Tomkins Broker in Seething-lane in Tower-street.'
'Loss of Memory or Forgetfulness, certainly Cured, By a grateful
Electuary, peculiarly adapted for that End; it strikes at the Prime
Cause (which few apprehend) of Forgetfulness, makes the Head clear and
easie, the Spirits free, active and undisturb'd; corroborates and
revives all the noble Faculties of the Soul, such as Thought,
Judgment, Apprehension, Reason and Memory; which last in particular it
so strengthens, as to render that Faculty exceeding quick and good
beyond Imagination; thereby enabling those whose Memory was before
almost totally lost, to remember the Minutest Circumstance of their
Affairs, &c. to a wonder. Price 2s. 6d. a Pot. Sold only at Mr.
Payne's at the Angel and Crown in St. Paul's Church Yard near
Cheapside with Directions.'
An Entertainment of Musick, consisting of a Poem called
The Passion of
Sappho: Written by Mr. Harison. And the
Feast of Alexander: Written by
Mr. Dryden; as they are set to Musick by Mr. Thomas Clayton (Author of
Arsinoe) will be performed at his House in York-Buildings to Morrow
the 29th Instant: Beginning at 8 in the Evening. Tickets at 5s. each,
may be had at Mr. Charles Lillie's, the Corner of Beauford-Buildings,
and at Mr. Elliott's, at St. James's Coffee-house. No Money receiv'd,
or Tickets given out at the House.
'
This Poem is sold by Jacob Tonson, at Shakspear's Head over against
Catherine-street in the Strand
1.
'
Any Master or Composer, who has any Piece of Musick which he desires
to bring in Publick, may have the same perform'd at Mr. Clayton'
s by
his Performers; and be rewarded in the Manner as the Authors of Plays
have Benefit Nights at the Play-house. The Letter subscribed A. A. May
the 25, is received.' (
No. 76.)
'To be Disposed of at a very reasonable Rate, a Compleat Riding Suit
for a Lady, of Blue Camlet, well laced with Silver, being a Coat,
Wastecoat, Petticoat, Hatt and Feather, never worn but twice; to be
seen at Mr. Harford's at the Acorn in York-street, Covent-garden.'
'The Delightful Chymical Liquor, for the Breath, Teeth and Gums, which
in a Moment makes the most Nauseous Breath smell delicately Fine and
Charming, and in very little Time infallibly Cures, so that an
offensive Breath will not return; It certainly makes the blackest and
most foul Teeth perfectly White, Clean and Beautiful to a Miracle;
Cures the Scurvy in the Gums, tho' never so inveterate, making the
Flesh grow again, when almost Eaten away, and infallibly fastens loose
Teeth to Admiration, even in Old People, who too often falsly think
their Age to be the Occasion: In short, for delightful Perfuming, and
quickly Curing an ill scented Breath, for presently making the
blackest Teeth most excellently White, certainly fastening them when
Loose, effectually preserving them from Rotting or Decaying, and
assuredly Curing the Scurvy in the Gums, it has not its Equal in the
Universe, as Abundance of the Nobility and Gentry throughout the
kingdom have Experienced. Is sold at Mr. Payn's, a Toyshop at the
Angel and Crown in St. Paul's Churchyard, near Cheapside, at 2s. 6d. a
Bottle with Directions.'
'In Dean Street, Sohoe, is a very good House to be Lett, with a very
good Garden, at Midsummer or Michaelmas; with Coachhouse and Stables
or without. Inquire at Robin's Coffeehouses near St. Anne's Church.'
'This Day is Publish'd
'A Representation of the Present State of Religion, with regard to the
late Excessive growth of Infidelity, Heresy, and Prophaneness:
Unanimously agreed upon by a Committee of both Houses of Convocation
of the Province of Canterbury, and afterwards pass'd in the lower
House, but rejected by the upper House. Members of the Committee. The
Bps. of Peterborough, Landaff, Bangor, St. Asaph, St. David's, Dr.
Atterbury, Prol. Dr. Stanhope, Dr. Godolphin, Dr. Willis, Dr. Gastrel,
Dr. Ashton, Dr. Smalridge, Dr. Altham, Dr. Sydel, Archdeacon of
Bridcock. Printed for Jonah Bowyer at the Rose in Ludgate-street.
Price 6s. At the same time will be Publish'd a Representation of the
present State of Religion, &c., as drawn up by the Bishops, and sent
down to the Lower House for their Approbation, Price 6d.'
'The Vapours in Women infallibly Cured in an Instant, so as never to
return again, by an admirable Chymical Secret, a few drops of which
takes off a Fit in a Moment, dispels Sadness, clears the Head, takes
away all Swimming, Giddiness, Dimness of Sight, Flushings in the Face,
&c., to a Miracle, and most certainly prevents the Vapours returning
again; for by Rooting out the very cause, it perfectly Cures as
Hundreds have experienc'd: It also strengthens the Stomach and Bowels,
and causes Liveliness and settled Health. Is sold only at Mrs.
Osborn's Toy-shop, at the Rose and Crown under St. Dunstan's Church in
Fleet-street, at 2s. 6d. the Bottle, with Directions.' (
No. 120.)
'An Admirable Confect, which assuredly Cures Stuttering or Stammering
in Children or grown Persons, tho' never so bad, causing them to speak
distinct and free, without any trouble or difficulty; it remedies all
manner of Impediments in the Speech, or disorders of the Voice of any
kind, proceeding from what cause soever, rendering those Persons
capable of speaking easily, free and with a clear Voice, who before
were not able to utter a Sentence without Hesitation; its stupendious
Effects, in so quickly and infallibly curing Stuttering, Stammering,
and all disorders of the Voice and difficulty in delivery of the
Speech are really Wonderful. Price 2s. 6d. a Pot, with Directions.
Sold only at Mr. Osborn's Toyshop at the Rose and Crown, under St.
Dunstan's Church, Fleet Street.'
Mr. Payn had also in his Toyshop 'an Infallible Electuary for Coughs and
Colds,' an 'Incomparably Pleasant Tincture to Restore the Sense of
Smelling,' and 'an Assured Cure for Leanness,' as well as
'The famous Bavarian Red Liquor:
Which gives such a delightful blushing Colour to the Cheeks of those
that are White or Pale, that it is not to be distinguished from a
natural fine Complexion, nor perceived to be artificial by the nearest
Friend. Is nothing of Paint, or in the least hurtful, but good in many
Cases to be taken inwardly. It renders the Face delightfully handsome
and beautiful; is not subject to be rubb'd off like Paint, therefore
cannot be discovered by the nearest friend. It is certainly the best
Beautifier in the World.'
So also after the Drury Lane advertisement of the play of
the night, is usually advertised: 'This Play is sold by Jacob Tonson,'
&c.
Contents
Index
The figures refer to Numbers of Papers, Fn. adds references to
[Foot]Notes.
- Spectator Volume 1: Nos. 1-202.
- Spectator Volume 2: Nos. 203-416.
- Spectator Volume 3: Nos. 417-635.
Wait
a few seconds after clicking on inter-volume links.
Click on your browser's
Back
button to come back here.
A -
B -
C -
D -
E -
F -
G -
H -
IJ -
K -
L -
M -
N -
O -
P -
Q -
R -
S -
T -
UV -
W -
X -
Y -
Z
| Abbey, Westminster | 26, 329 |
| Abel Drugger, Ben Jonson's | 28 Fn. 5 |
| Abigails (male) for ladies | 45 |
| Abracadabra | 221 Fn. 3 |
Absence
in love
of mind |
24, 241, 245
77 |
| Abstinence | 174,
195 |
| Academy for Politics | 305 |
| Acasto, the agreeable man | 386 |
| Accounts, keeping | 174 |
| Acetur's raillery | 422 |
| Acosta's defence of Jewish ceremonies | 213 |
| Acrostics | 60 Fn. 4 |
Act
of Deformity for the Ugly Club
of Uniformity, Toleration, Settlement
Stamp |
17
3 Fns. 3, 4, 5
445 Fn. 1 |
Action
the, in an Epic poem | 116, 292, 541, 588
267 |
| Actions | 174, 257 |
| Admiration | 73, 237, 256, 340, 413 |
| Adrian, Emperor, Pope on his last lines | 532 |
| Adversity | 237 |
| Advertisements1 | 2 n., 31 Fn. 1, 46 Fn. 2, 65 Fn. 2, 141 Fn. 2, 156 Fn. 1, 291 Fn. 7,
294 Fn. 2, 332 Fn. 1, 358 Fn. 1, 370 Fn. 6, 462 n., 489 Fn. 4, 514 Fn. 2, 533 Fn. 1, 547 Fn. 1 |
Advice
to a daughter, George Savile, Lord Halifax's | 34, 385, 475, 512
170 |
| Æneid in rhyme | 60 |
| Æschylus, Prometheus Bound of | 357 Fn. 5 |
| Æsop | 17 Fn. 2 |
Affectation
of vice, outlives the practice | 35, 38, 150, 205, 284, 404, 408, 460, 515
318 |
| Affection | 449 |
Affliction
not uncharitably to be called a judgment | 95, 163, 164, 501
483 |
| Aganippe, the fountain | 514 |
| Age | 6, 153, 260, 336 |
| Aglaüs, the happy man | 610 |
Agreeable, in conversation, the art of being
man
woman | 386
280, 386
21 |
| Alabaster, Dr. | 221 |
| Albacinda, the too fair and witty | 144 |
| Albertus Magnus | 56 Fn. 1 |
Alexander the Great
project of an opera upon him
William, Earl of Stirling | 32, 127, 337, 379
14
300 Fn. 1 |
Allegories
in Epics | 55, 421, 501
357 |
| Allusion | 421 |
| Almanza, battle of | 7 Fn. 1 |
| Alms | 232 |
| Alnaschar, the Persian glassman | 535 |
| Altar, poem in shape of an | 58 |
| Amanda rewarded | 375 |
| Amaryllis improved by good breeding | 144 |
| Amazons, the commonwealth of | 433, 434 |
| Ambition | 27, 125, 156, 180, 188, 200, 219, 224, 255, 257, 570, 613, 624 |
Americans,
who used painting for writing
their opinion of departed souls, in a vision |
416
56 |
| Amoret the jilt reclaimed | 401 |
| Amorous Club | 30 |
| Amusements | 93 |
| Anacharsis, the Corinthian drunkard, a saying of | 569 |
| Anagram | 58 Fn. 2, 60 |
| Anatomy, speculations on | 543 |
| Ancestry | 612 |
| Ancients, the | 61, 249, 358 |
| Andromache | 57 |
| Angels | 610 |
| Anger | 438 |
| Animals, structure and instincts of | 120, 121 |
| Anna Bella on the conversation between men and women | 53 |
| Anne Boleyn's last letter to Henry VIII. | 397 |
Anne, Queen
mourning for | 384 Fn. 1
606 |
| Annihilation | 210 |
| Anthony, Mark, his witty mirth | 386 |
| Antigonus painted by Apelles | 633 |
| Antimony, Basil Valentine on | 94 Fn. 1 |
| Antiochus in love with his mother-in-law | 229 |
| Antipathies | 538, 609 |
| Anti-starers appointed | 20 |
| Anxieties, unnecessary | 615 |
| Apes, some women considered as | 244 |
Apollo,
his temple on the top of Leucate
his throne |
233
514 |
| Apollodorus, a fragment of | 203 |
| Apostle spoons | 250 |
| Apothecaries | 195 |
Apparitions
Plato's opinion of | 12, 110
90 |
| Appearances | 86, 87, 360 |
| Appetites | 120, 208, 260 |
| Applause | 188, 442, 610 |
April,
described
the first of |
425
47 |
| Arabian Nights | 195, 535 |
| Arable, Mrs., in a stage coach | 132 |
| Aranda, Countess of, displeased with Gratian | 379 |
| Araspas and Panthea, story of | 564 |
| Arcadia, Sidney's | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Archduke Charles | 45 Fn. 1 |
| Architecture | 415 |
| Aretino | 23 Fn. 6 |
| Arguments, management of | 197, 239 |
| Argus | 250 |
| Arietta, the agreeable | 11 |
| Aristas and Aspasia, the happy couple | 128 |
| Aristenætus, letters of | 238 |
| Aristippus, saying of, on contentment | 574 |
| Aristophanes | 23 Fn. 2 |
| Aristotle | 39, 40 Fn. 1, 42, 86 Fn. 6, 166, 239, 267 Fns. 4, 5 & 9, 273 Fns. 1 & 12, 279 Fn. 1 285 Fn. 1 291 Fn. 2, 297 Fns. 3, 9 & 14, 315 Fn. 2 |
| Arithmetic, political | 200 |
| Arm, the orator's weapon | 541 |
Army,
losses in a campaign
wherein a good school |
180
566 |
| Arsinoe, the opera | 18 Fn. 1 |
Art,
general design of
and taste
works of
of Criticism, Pope's |
541
29
414
253 |
| Artillery, Milton's | 333 |
| Artist and author compared | 166 |
| Asaph (Bishop of St.), preface to sermons | 384 Fn. 1 |
| Aspasia, an excellent woman | 128 |
| Ass, schoolman's case of the, applied | 191, 196, 201 |
| Assizes, county, described | 122 |
| Association of honest men proposed | 126 |
| Assurance, modest | 75, 166, 185, 373 |
| Astræa, D'Urfe's | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Astrop Spa | 154 Fn. 3 |
| Atheists | 237, 381, 389, 483 |
| Atlantis, the New | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Attention, the true posture of | 521 |
Atticus,
his genius
as a friend |
150
385 |
| Audience at a play | 13, 190, 502 |
| August described | 425 |
| Augustus Cæsar | 528, 585 |
| Aurelia, a happy wife | 15 |
Author
and readers
and artist
and author
on himself
for what to be admired
inconvenience of his signing his name to his works
of folios takes precedence
for the stage
|
1
166
124
4, 9
355
451
529
51 |
| Avarice | 55, 224, 624 |
| Axe, poem in the shape of an | 58 |
| Babblers | 218 |
| Babes in the Wood | 85 |
| Babylon | 415 |
| Bachelors, an inquisition on | 320 |
| Bacon flitch at Whichenovre | 607 |
Bacon, Lord
quoted | 554
10, 19, 411, 447 |
| Bags of money transformed | 3 |
| Balance, Jupiter's, in Homer and Virgil | 463 |
| Baldness | 497 |
Ballads (old),
admiration of
Chevy Chace
Babes in the Wood |
85, 502 Fn. 1
70, 74
85 |
| Balloon | 45 Fn. 3 |
| Balzac | 355 |
| Bamboo, Benjamin, his philosophical use of a shrew | 482 |
| Bank of England | 2 Fn. 1 |
| Bankruptcy | 428, 456 |
| Bantam, the ambassador from, describes the English | 557 |
| Bantry Bay | 383 Fn. 1 |
Barbadoes,
Ligon's History of
appeals from |
11 Fn. 2
394 |
| Barbarity | 139 |
| Bareface, his success with the ladies | 156 |
| Barn Elms | 91 |
| Barnes, Joshua | 245 |
| Bar, oratory of the English | 407 |
| Barnaby-bright | 632 |
| Barr, Mr. | 388 |
| Barreaux, Jacques Vallée, Seigneur des | 513 Fn. 2 |
| Barrow, Isaac | 106 Fn. 4 |
| Bashfulness natural to the English | 148 |
| Basil Valentine and his son, history of | 426 |
| Bastards | 203 |
| Bastile, a prisoner in the | 116 |
| Battles, descriptions of | 428 |
| Bawlers | 148 |
| Baxter | 84, 445, 498 |
Bayle,
on libels
his dictionary |
451
92 Fn. 2, 121 Fn. 1, 198 Fn. 1 |
| Beagles | 116 Fn. 1 |
Bear garden,
visited
how to improve the |
436, 449
141 |
| Beards | 321 331 |
Beau
and Quaker
Beau's head dissected |
631
255 |
| Beaufort, Cardinal, Shakespeare's death of | 210 |
| Beaumont and Fletcher's Scornful Lady | 270 |
| Beauties | 4, 33, 87, 144, 155 |
| Beauty | 33, 133, 302, 406, 412, 510 |
| Beaver, the haberdasher and coffeehouse politician | 49 |
| Beef-steak Club | 9 Fn. 2 |
Beggars
Sir A. Freeport on | 430, 613
232 |
| Behn, Aphra | 22 Fn. 4, 51 Fn. 9 |
Beings,
scale of, considered
imaginary |
519
419 |
| Bel and the Dragon | 28 Fn. 6 |
| Bell Savage, etymology of | 28 |
| Belvidera, song upon, criticized | 470 |
| Beneficence | 292, 588, 601 |
| Bentley, Richard | 165 |
| Biblis, every woman's rival | 187 |
Bill,
for preserving female fame
of mortality |
326
289 |
| Bion, saying of, on search for happiness | 574 |
| Birch, Dr. Thomas | 364 Fn. 2 |
Birds
for the opera
better education of, by L. Tattle
how affected by colours |
5
36, 121
412 |
| Birthday, Queen Anne's | 294 |
| Biters | 47, 504 |
| Biton and Cleobis | 483 |
| Blackmore, Sir R. | 6 Fn. 1, 339 Fn. 8, 543 |
| Bland, Dr. | 628 |
| Blank, a letter from | 563 |
| Blank verse | 39 |
| Blast, Lady, her character | 457 |
| Bluemantle, Lady | 427 |
| Blushing | 390 |
| Boar killed by Mrs. Tofts in Armida | 22 Fn. 3 |
| Board-wages | 88 |
| Boccalini, Trajan | 291 Fn. 6, 335, 514 |
| Bodily exercises | 161 |
| Body, human, transcendent wisdom in construction of the | 543 |
| Boevey, Mrs. Catherine | 113 Fn. 1 |
| Boileau | 47, 209, 279 Fn. 11 |
| Boleyn, Anne, her letter to Henry VIII. | 397 |
| Bond, John | 286 Fn. 1 |
| Bonosus, a drunken Briton | 569 |
| Books | 37, 93, 123, 124, 163, 166 |
| Bossu, Réné le | 279 Fn. 4, 291 Fn. 2 |
| Bouhours, Dominique | 62 Fn. 4 |
| Boul, Mr., sale of his pictures | 226 |
| Bouts Rimés | 60 |
| Bow, English use of the | 161 |
| Boyle, Hon. Robert | 94, 121, 531, 554 |
| Bracton's law of Scolds | 479 Fn. 2 |
| Brady, Nicholas | 168 Fn. 3 |
| Breeding (good) | 66, 119, 169 |
| Bribery | 239, 394 |
British
Ladies and Picts
Princes, Hon. E. Howard's |
41
43 Fn. 7 |
| Brome, Dr. | 302 |
| Brooke and Hellier | 362 Fn. 5 |
| Brown, Tom, his new method of writing | 576 |
| Brunetta and Phillis | 80 |
| Bruno, Giordano | 389 |
| Bruyère's character of an absent man | 77 Fn. 2 |
| Buck, Timothy, answers the challenge of James Miller | 436 |
Buckingham,
Duke of, invention in glass
Sheffield, Duke of
Villiers, Duke of |
509
253 Fn. 5, 462 Fn. 3
371 |
Budgell,
Eustace
Gilbert |
67 Fn. 1, 517 |
| Buffoonery | 443 |
Bullock,
the Comedian
Gabriel, love letter of |
36 Fn. 4, 44
324 Fn. 3, 328 |
| Bully Dawson | 2 Fn. 5 |
| Bumpers in drinking | 474 |
| Burlesque | 249, 616, 625 |
Burnet's
Theory of the Earth
Travels |
38 Fn. 1, 143, 146
46 Fn. 4, 531 |
| Bury Fair | 154 Fn. 4 |
Business,
the man of
learned men most fit for |
27
469 |
| Bussy d'Amboise | 467 |
| Busy world, virtuous and vicious | 624 |
| Button-makers' petition | 175 Fn. 2 |
| Butts | 47, 175 |
| Byrom, John | 586 Fn. 1, 603 Fn. 1 |
| Cacœthes scribendi | 582 |
| Cælia, the pretty, advised to hold her tongue | 404 |
Cæsar,
Julius
edition of his Commentaries |
23 Fn. 3, 147, 169, 231, 224, 256, 374, 395
367 |
| Cairo, Spectator at | 1, 69 |
| Calamities | 312, 483, 558, 559 |
| Calamy, Edward | 106 Fn. 4 |
| Caligula | 16, 246 |
| Callipædia, Claude Quillet's | 23 Fn. 4 |
| Callisthenes | 422 |
| Calprenède's romances | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Calumny | 451, 594 |
| Cambray, Fenelon, Archbishop of | 69, 95 |
| Cambridge Ugly Club | 78 |
Camilla
Virgil's
the opera |
15
18 Fn. 1, 22 Fn. 3,443 |
| Camillus, behaviour of, to his son | 263 |
| Camisars, the | 160 |
| Camp, wherein a good school | 566 |
| Campbell, the dumb fortune-teller | 323 Fn. 4, 474 |
| Candour | 382 |
| Canidia, an old beauty | 301 |
| Cant | 147 |
| Capacities of children
to be considered in their education | 307 |
| Caprice | 191 |
| Carbuncle, Dr., his dye | 52 |
Care
who has most
man's chief |
574
122 |
| Caricatures | 537 |
| Carneades, his definition of Beauty | 144 |
| Cartesian theory of ideas | 417 |
| Cartoons, Raphael's | 226, 244 |
| Cases in love answered | 591, 607, 614 |
| Casimir, Liszinski, a Polish atheist, punishment of | 389 |
| Cassandra, romance of | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Cassius, Caius, temper of | 157 |
| Castle-builders | 167 |
Cat
a contributor to harmony
old and young, speculations on
-call, a dissertation on the |
361
626
361 |
| Catiline | 386 |
| Cato | 243, 255, 446, 557 |
| Catullus, his lampoon of Cæsar | 23 Fn. 3 |
| Cave of Trophonius | 598, 599 |
| Celibacy | 528 |
| Celinda on female jealousy | 178 |
Censor
of small wares
of marriages
-ship of the press |
16
308
445 Fn. 1 |
| Censure | 101, 610 |
| Ceremony | 119 |
| Chair, the mathematical | 25 |
| Chambermaids | 366 |
| Chancery | 564 |
Chaplains
to persons of quality
Sir Roger de Coverley's chaplain |
609
106 |
| Chapman, George | 467 Fn. 4 |
| Chardin, Sir John | 289 Fn. 4 |
| Charity schools | 294, 430 |
| Charlemagne and his secretary, story of | 181 |
| Charles I., book of Psalms in a picture of | 58 |
| Charles II., his familiarities | 78, 462 |
| Charles II. of Spain | 64 Fn. 2 |
| Charles VI. of Germany | 353 Fn. 3 |
| Charles XII. of Sweden, his march to the Ukraine | 43 Fn. 2 |
| Chastity | 99, 579 |
| Chaucer | 73 |
| Cheerfulness | 143, 381, 387 |
| Chemists' jargon | 426 |
| Cherubim and Seraphim | 600 |
| Chevy Chace criticized | 70, 74 |
| Chezluy, Jean, excused to Pharamond his absence from court | 480 |
| Children | 157, 246, 307, 426, 500 |
| in the Wood, on the Ballad of the | 85 |
| Child's Coffee-house | 1 Fn. 7 |
| China women and the vapours | 336 |
| Chinese | 60, 189, 414 |
| Chit-chat Club | 560 |
| Chocolate | 365 |
Chocolate-house
Cocoa Tree
White's | 1 Fn. 11, 88 Fn. 2 |
| Chremylus, story of, from Aristophanes | 464 |
| Christian religion | 186, 213, 574 |
| Christian Hero, Steele's | 37, 356 Fns. 2-8, 516 |
| Christmas | 268 |
| Chronograms | 60 Fn. 7 |
Church
and puppet show
behaviour at
music
work |
14
53, 242, 259, 460, 630
338
383 |
| Churchyard, the country, on Sunday | 112 |
| Cibber, Colley | 48 Fn. 2, 370, 546 |
| Cicero | 61, 68, 212, 404, 427, 436, 467 Fn. 1, 505, 531, 541, 554 |
| Citizens, the opportunity of | 346 |
| City lovers | 155 |
| Clarendon, Earl of | 349, 485 Fn. 1 |
| Clarinda, an Idol | 73 |
| Clark, Mrs. Margaret, remnant of a love-letter to | 342 |
| Clarke, Dr. Samuel | 367 Fn. 1 |
| Classics, editors of the | 470 |
| Clavius, Christopher | 307 Fn. 2 |
| Clay, Stephen | 133 Fn. 2 |
| Clayton, Thomas, the composer | 18 Fn. 1, 258 Fn. 2 |
| Cleanliness | 631 |
| Cleanthe, a French lady, novel of | 15 |
| Cleanthes misapplies his talents | 404 |
| Clelia, Scudéri's | 37 Fn. 2 |
Cleopatra
Caprenède's romance of | 400
37 Fn. 2 |
| Clergyman of the Spectator's Club | 2, 34 |
| Clergymen | 21, 306, 609, 633 |
| Clerks, parish, advice to | 372 |
| Cleveland, John | 286 Fn. 1 |
| Cliff, Nat., advertises for a lottery ticket | 191 |
| Clinch of Barnet | 24 Fn. 2, 31 |
| Clodpate, Justice, Cibber's | 48 |
| Cloe the idiot | 466 |
| Club Law | 239 |
Clubs
the Amorous
Beef-steak
Chit-chat
Everlasting
Fox-hunters'
Fringe-glove
Hebdomadal
Hen-pecked
Kitcat
Lazy
Lawyers'
Mohock
Moving
October
Rattling
She Romp
Sighing
Spectator's
Club at Oxford for re-reading the Spectator
Street Clubs
Twopenny
Ugly
White's
Widows' | 9, 474, 508
30
9 Fn. 2
560
72
474
30
43
474
9 Fn. 1
320
372
324
372
9 Fn. 3
630
217
30
1, 2, 34
553
9
9
17, 78
88 Fn. 2
561 |
| Coachmen, Hackney, gentlemen as | 515, 526 |
| Coat, fine, when a livery | 168 |
| Cocoa-tree Chocolate-house | 1 Fn. 11 |
Coffee-house
debates
idols
impertinents
liars
potentates at different hours
Child's
Grecian
Jonathan's
Lloyd's
Rainbow
St. James's
Serle's
Squire's
Will's
|
197, 476
155
87, 145
521
49
1 Fn. 7
1 Fn. 10
1 Fn. 13
46 Fn. 1
16 Fn. 1
1 Fn. 9, 24
49 Fn. 1
49 Fn. 1
1 Fn. 6, 49 Fn. 1 |
| Collier, Jeremy | 361 Fn. 3 |
| Colours | 412, 413, 416 |
| Colours taken at Blenheim | 136 |
| Comedies | 249, 446 |
| Comet, Newton on the | 101 |
| Comfort | 196, 501 |
| Commode, the | 98 Fn. 1 |
| Commendation | 348, 467 |
| Commentaries, Cæsar's, Clarke's edition of | 367 |
| Commerce | 21, 69 |
| Commercial friendship | 346 |
| Commines, Philip de | 491 |
| Commodus, Emperor | 127 |
| Common Prayer, the Book of | 147 |
| Commonwealth of Amazons | 433 |
| Companions | 424 |
| Comparisons in Homer and Milton | 303 |
| Compassion | 169, 397 |
| Complaisance at courts | 394 |
| Compliments | 103, 155 |
| Comus, god of revels | 425 |
| Concave figure, its advantage in architecture | 415 |
| Condé, Prince of | 86 |
| Conecte, Thomas, his preaching against women's commodes | 96 Fn. 4 |
| Confidants | 118 |
| Confidence dangerous to ladies | 395 |
| Conformity, occasional | 269 |
| Congreve | 40 Fn. 3, 189, 204, 443, 530 |
| Conquest, Deborah, of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Conquests, the vanity of | 180 |
| Conscience | 188 |
| Constancy in sufferings | 237 |
| Contemplation | 514 |
| Contempt | 150 |
| Content | 163, 574 |
| Conversation | 53, 68, 100, 103, 119, 143, 409, 574 |
| Copenhagen | 393 |
Coquets
heart of one dissected | 66, 172, 208, 390 |
| Cordeliers, story of St. Francis | 245 |
| Cornaro, Lewis | 195 |
| Corneille | 39 Fn. 4 |
| Cornelii, family of the | 192 |
| Corruption | 469 |
| Cotqueans | 482 |
| Cottilus, his equanimity | 143 |
Country dances
the Sir Roger de Coverley | 67
106 Fn. 1 |
Country
life
Wake, the, a farce
wakes described |
151, 161, 414, 424, 474, 583, 622
502
161 |
| Courage | 99, 152, 161, 350, 422 |
| Court life | 64, 76, 394, 403 |
| Courtship | 261 |
| Coverley, Sir Roger de | 2, 6, 34, 106-113, 115, 116, 118, 122, 125, 126, 130, 131, 174, 269, 295, 329, 331, 335, 359, 410, 424, 517 |
| Covetousness | 316 |
| Cowardice | 231, 611 |
| Cowley | 41, 62, 67, 81, 114, 123, 339, 551, 590, 610, 613 |
| Cowper, Lord | 38, 467 |
| Crab, chaplain to the Ugly Club | 78 |
| Crambo | 63 |
| Crastin, Dick, challenges Tom Tulip | 91 |
| Crazy, a man thought so for reading Milton aloud | 577 |
Creation
contemplation of
Milton's account of
Blackmore's poem on |
393
339
339 Fn. 8, 543 |
| Credit | 3, 218, 320 |
| Credulity in women | 190 |
| Cries of London | 251 |
| Critics | 87, 291, 409, 592 |
| Cross, Miss, half a tun less handsome than Madam Van Brisket | 32 |
| Cully-Mully-Puff | 362 |
| Cultismo | 379 Fn. 3, 409 |
| Cunning | 225 |
| Curiosity | 237, 439 |
| Custom | 437, 455, 474 |
| Cymon and Iphigenia | 71 |
| Cynæas reproves Pyrrhus | 180 |
| Cynthio and Flavia, broken courtship of | 399 |
| Cyrus | 564 |
| Czar Peter, compared with Louis XIV. | 139 |
| Dacier, André and Anna | 291 Fn. 2, 297 Fn. 1 |
| Dacinthus, a pleasant fellow | 462 |
| Dæmon, Plato's | 214 Fn. 4 |
| Daintry, Captain | 570 Fn. 1 |
| Dainty, Mrs. Mary, writes from the Infirmary | 429 |
| Dalton's Country Justice | 92 Fn. 2 |
| Damon, Strephon, and Gloriana | 423 |
| Dampier's Voyages | 121 |
| Dancing | 66, 67, 296, 334, 370, 376, 466 |
| Dangers past | 418 |
| Daphne's Chance Medley | 33 |
| Dapperwit, Tom | 482, 530 |
| Darkness, Egyptian | 615 |
| Day, several times of, in London life | 454 |
| Day-dream | 167 |
| Death | 7, 25, 133, 152, 289, 349 |
| Debt | 82 |
| Dedications | 188
of Spectator to Lord Somers
to Lord Halifax
to Henry Boyle
to the Duke of Marlborough
to Thomas, Earl of Wharton
to Earl of Sunderland
to Paul Methuen
to Will. Honeycomb |
| Defamation | 348, 427, 451 |
| Definitions | 373 |
| Deformity | 17, 87 |
| Delicacy | 104, 286, 292 |
Delight
essential to wit
vernal |
62
393 |
| Deluge, Whiston's Theory of the | 396 |
| Demetrius, a saying of | 237 |
| Demurrers, what women to be so called | 89 |
| Denham, Sir John | 82 Fn. 2 |
| Dennis, John | 47 Fn. 2, 273 Fn. 5, 548 Fn. 1 |
| Denying, sometimes a virtue | 458 |
| Dependence | 181, 214, 282 |
| Dervise Fadlallah, story of the | 631 |
| Descriptions, source of pleasure in | 416, 418 |
| Desire | 191, 400 |
| D'Estrades, negotiations of Count | 92 Fn. 2 |
| Detraction | 256, 348, 355 |
| Devotee described | 354 |
| Devotion | 93, 163, 201, 207, 415 |
| Diagoras, the atheist, in a storm | 483 Fn. 2 |
| Dial plate for absent lovers | 241 |
| Diana | 453 |
| Diet | 195 |
| Dieupart, Charles | 258 Fn. 2 |
| Diffidence | 87 |
| Dignitaries of the law | 21 |
| Dilatoriness | 469 |
| Diligence | 514 |
| Dionysius, a Club tyrant | 508 |
| Dionysius's ear | 439 |
| Disappointed love | 163 |
| Discontent | 214 |
| Discretion | 225, 607 |
| Dispensary, Garth's | 476 |
Dissection
of a beau's head
of a coquette's heart |
275
281 |
| Dissenters | 147, 259 |
| Dissimulation | 103 |
| Distempers, each does best with his own | 599 |
| Distinction, desire of | 219, 224 |
| Distrest Mother, a tragedy, commended | 290, 335, 338 Fn. 2 |
| Diversions, over-indulgence in | 447 |
| Divorce | 41 |
| Doctor in Moorfields, contrivance of a | 193 |
| Dogget the comedian | 235 Fn. 1, 370, 446, 502 Fn. 3 |
| Doggrel | 60 |
| Dogs | 116 Fn. 1, 474, 579 |
| Doily stuffs cheap and genteel | 283, 320 |
| Domestic life | 320, 455 |
| Donne, his description of Eliz. Drury | 41 Fn. 3 |
| Dorigny's engravings of the Cartoons | 226 Fn. 5 |
| Doris, Congreve's character of | 422 |
| Dorset, Lord, collected old ballads | 85 |
| Doves in company | 300 |
| Drama, its original a worship | 465 |
| Drawcansir | 16 Fn. 4 |
Dreams
of retirement
golden scales
seasons
Trophonius' Cave | 167, 487, 505, 524, 586, 593, 597
425
403
425
599 |
| Dress | 69, 150, 360, 435 |
| Drinking | 189, 195, 205, 458, 474, 569 |
| Drums in a marriage concert | 364 |
| Drury Lane Theatre | 1 Fn. 12 |
| Dry, Will., of clear head and few words | 476 |
| Dryden | 5 Fn. 1, 32 Fn. 3, 33, 37 Fn. 2, 40 Fns. 2 & 4, 55, 58, 62, 71, 77, 85, 116, 141, 162, 177, 222, 223 Fn. 2, 267 Fn. 13, 297 Fn. 5, 341, 365, 512, 572, 589, 621 |
| Du Bartas | 58 Fn. 4 |
| Duelling | 84, 97, 99 |
| Dugdale | 21 Fn. 3 |
| Dull fellows | 43 |
| Dullness, goddess of | 63 |
| Dumb conjurer, the | 560 |
| Dunces | 17 Fn. 3 |
| Dunlop, Alexander | 524 Fn. 1 |
| Duration, the idea of | 94 |
| D'Urfey, Thomas | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Dutch monuments for the dead | 26 |
| Dyer's News-letter | 43 Fn. 6, 127 |
| Earl of Essex, in a Tragedy | 48 Fn. 1 |
Earth
why covered with green
why called a mother |
387
246 |
| Ease | 196 |
| East-Enborne, custom for widows | 614, 623 |
| Eating, drinking, and sleeping | 317 |
| Echo, false wit | 59 |
| Edgar, King, amour of | 605 |
| Editors of the classics | 470 |
| Education | 53, 66, 108, 123, 157, 215, 224, 230, 313, 314, 337, 353, 376, 431, 445 |
| Egg, the scholar's | 58 |
| Eginhart and the daughter of Charlemagne | 181 Fn. 4 |
| Egotism | 562 |
| Egyptian darkness | 615 |
| Electra of Sophocles | 44 |
| Elihu's speech to Job | 336 |
| Elizabeth, Queen | 293 |
Eloquence
of St. Paul
of beggars |
633
613 |
| Embellishers | 521 |
| Emblematical persons | 419 |
| Emilia | 302 |
| Eminence, the tax on | 101 |
| Emperor of the Moon, Mrs. Behn's farce of the | 22 Fn. 4 |
| Emulation | 432 |
| Enborne, the custom for widows at | 614, 623 |
| Enemies | 125, 399 |
| England, advantages of being born in | 135 |
English
the people
the language |
135, 158, 387, 407, 419, 432, 435, 557
135, 163, 230, 405 |
| Envy | 19, 253 |
| Epaminondas | 133 |
| Ephesian lady, the | 11 Fn. 1, 198 |
| Ephraim, the Quaker, and the officer, in a stage coach | 132 Fn. 1 |
| Epic poem, construction of an | 267, 273, 291, 297, 315 |
| Epictetus | 53 Fn. 1, 219, 355, 397, 524 |
| Epigram on Hecatissa | 52 |
| Epilogues | 338 Fn. 2, 341 |
Epistles
poetical
recommendatory |
618
493 |
Epitaph
by Ben Jonson
on Countess of Pembroke
on a charitable man
extravagant and modest epitaphs |
33 Fn. 3
323
177 Fn. 7
26, 538, 539 |
| Equanimity | 137, 143, 196 |
| Equestrian order of ladies | 435, 437 |
| Equipage | 15, 144, 428 |
| Equity, schools of | 337 |
| Erasmus | 59, 239 |
| Erratum in an edition of the Bible | 579 |
| Error | 117, 460 |
| Escalus, an old beau | 318 |
| Esquires | 529 |
| Essays | 123, 476 |
| Estates, acquisition of | 222, 353 |
| Estcourt, Richard | 264 Fn. 1, 358, 370, 468 |
| Eternity | 159, 575, 590, 628 |
| Ether, the fields of | 420 |
| Etherege, Sir George | 2 Fn. 4, 44 Fn. 6, 51, 65 Fn. 1, 127 |
| Eubulus at the coffee-house | 49 |
| Eucrate, the friend of King Pharamond | 76, 84 |
| Eucratia | 144 |
| Eudosia | 7, 144 |
| Eudoxus and Leontine, their friendship, and education of their children | 123 |
| Eugene, Prince | 269 Fn. 1, 340 Fn. 2 |
| Eugenius, his charity | 177 |
| Euphrates, the | 415 |
| Eusden, Lawrence | 54, 78 Fn. 3, 87 |
| Evergreens, feminine | 395 |
| Everlasting Club, the | 72 |
| Evremont, M. de St. | 213, 349 |
| Example | 337 |
| Excess | 180 |
Exchange
the Royal
the new | 69, 454
96 Fn. 2 |
| Exchequer bills, Montagu's | 3 Fn. 9 |
| Exercise | 115, 116, 161, 195 |
| Extravagance | 161, 222, 243 |
| Eye, formation of the | 472 |
Eyes
a dissertation on
their influence |
250
19, 252 |
Fable
use of
of the Lion and Man
of the Children and Frogs
of Jupiter and the Countryman
of Pleasure and Pain
of a Drop of Water
of the Persian Glassman |
183
11
23
25
183
293
535 |
Face
the epitome of man
a good one a letter of recommendation
each should be pleased with his own |
541
221
559 |
| Fadlallah, story of | 578 |
| Fairs, Persian, for selling women | 511 |
| Fairy writing | 419 |
| Faith | 459, 465 |
| False wit | 25, 58, 60 |
| Falsehood | 63, 103, 156, 352 |
| Falstaff | 47 |
| Fame | 73, 139, 218, 255, 256, 257, 426, 439 |
| Familiarities in society | 429, 430 |
| Family madness in pedigrees | 612 |
| Famine in France | 180 |
| Fan exercise | 102 |
| Fancy | 411, 512, 558 |
| Fashion | 6, 64, 151, 175, 460, 478, 490 |
| Father's love | 490 |
| Faults, secret, discovered | 399 |
| Faustina, empress | 128 |
| Fawners | 304 |
| Fear | 25, 114, 152, 224, 471, 615 |
| Feasts | 195 |
| Feeling, the sense of | 411 |
Female
library proposed
oratory
rakes
virtues
domestic rule
game, preserving |
37, 242
247
337
81
320
326 |
| Fenelon | 95 |
| Festeau, the surgeon | 368 |
| Festivity of spirit | 358 |
| Feuille mort | 265 |
| Fiction | 419 |
| Fidelia, a good daughter | 499 |
| Fidelio transformed into a looking glass | 392 |
| Final causes | 413 |
| Fireworks at Rome, a poem on | 617 |
| Flattery | 49, 238, 460, 621 |
| Flavia and Cynthio | 398 |
| Flavia, rival to her mother | 91 |
| Flavilla, spoiled by marriage | 437 |
| Fleetwood, Dr. William | 384 Fn. 1 |
| Flesh painter out of place | 41 |
Fletcher's
Pilgrim, on a scene in
humorous lieutenant |
22 Fn. 6
266 |
| Flora | 425 |
| Flourilles, Chevalier de | 152 Fn. 2 |
| Flutter, Sir Fopling, comedy of | 65 |
| Flying, letter on | 462 |
| Foible, Sir Geoffrey | 190 |
| Follies, our own, mistaken for worth | 460 |
| Fondness | 449 |
| Fontenelle | 291 Fn. 2, 519, 576 |
| Fools | 47, 148, 485 |
| Footman, a too sober | 493 |
| Fop | 280 |
| Fopling Flutter, Sir, Etherege's | 65 |
| Foppington, Cibber's Lord | 48 |
| Forehead, an orator's | 231 |
| Fortius, whose faults are overlooked | 422 |
| Fortunatus, the trader | 433 |
Fortune
stealers
hunters
comedy of the | 282, 293, 294, 312
211
326
22 Fn. 5 |
| Fox-hunters | 474 |
| Francham, Mr., of Norwich | 520 |
| Francis, St. | 245 |
| Frankair, Charles, an envied and impudent speaker | 484 |
| Freart, M., on architecture | 415 |
| Freeman, Antony, his stratagem to escape from his wife's rule | 213 |
| Freeport, Sir Andrew | 2, 34, 82, 126, 174, 232, 549 |
| Free-thinkers | 3, 9, 27, 39, 55, 62, 70, 77, 234, 599 |
| Freher, Marquard | 181 Fn. 4 |
French
poets
privateer, cruelty of a | 102, 104, 435, 481
45
350 |
| Fribbles | 288 |
| Friends | 68, 346, 385, 399, 400, 490 |
| Fringe-glove Club | 30 |
| Fritilla, dreams at church | 597 |
| Frogs and Boys, fable of the | 23 Fn. 7 |
| Frolic | 358 |
| Froth, Mr., on public affairs | 43 Fn. 1 |
| Frugality | 107, 348, 467 |
| Fuller's English worthies | 221 Fn. 5 |
| Funeral, the, Steele's comedy | 51 Fn. 1 |
| Funnel, Will., a toper | 569 |
| Futurity, man's weak desire to know | 604 |
| Galen | 543 |
| Gallantry | 72, 142, 318 |
| Gambols | 41 |
| Game, Female | 326 |
| Gaming | 93, 140, 428, 447 |
| Gaper, the, a Dutch sign | 47 |
| Gardens | 5 Fn. 5, 414, 455, 477 |
| Garth, Sir Samuel | 249 Fn. 2, 273 Fn. 8 |
| Gazers | 263 |
| Genealogy, a letter on | 612 |
| Generosity | 107, 248, 346 |
| Genius | 160 |
| Gentleman | 75, 82 |
| Geography of a jest | 138 |
George I.
coronation | 3 Fn. 8
609, 630 |
| Georgics, Virgil's | 417 |
| Germanicus | 238 |
| Germany, politics of | 43 Fn. 5, 45 Fn. 1 |
| Gesture in oratory | 407 |
Ghosts
on the stage | 12, 419
36, 44 |
| Gigglers in church | 158 |
| Gildon, Charles | 267 Fn. 1 |
| Gipsies, Sir Roger de Coverley and the | 130 |
| Giving and forgiving | 189 |
| Gladiators | 436 |
| Gladio's dream of knight errantry | 597 |
| Gladness | 494 |
| Glaphyra, story of | 110 |
| Globe, Burnet's funeral oration on the | 146 |
| Globes, proposal for a new pair of | 552 |
| Gloriana, advice concerning a design on | 423 |
| Glory | 139, 172, 218, 238 |
| Gluttony | 195, 344 |
| Goat's milk | 408 |
| God | 7, 257, 381, 421, 441, 465, 489, 531, 543, 565, 571, 580, 634, 635 |
| Gold clears understanding | 239 |
| Good breeding | 119 |
| Goodfellow, Robin, on rule of drinking | 205 |
| Good Friday paper, a | 365 |
Good humour
infirmary for establishing | 100
429, 437, 440 |
| Good nature | 23, 76, 169, 177, 196, 243, 607 |
| Good sense | 437 |
| Goodwin, Dr. Thomas | 494 Fn. 2 |
| Goose and Watchman | 376 |
| Goosequill, William, clerk to Lawyers' Club | 372 |
| Gosling, George, advertises for lottery ticket | 191 |
| Gospel gossips | 46 |
| Gossiping | 310 |
Goths
in poetry
in taste |
62
409 |
| Government, forms of | 287 |
| Gracchus's pitch-pipe | 541 |
| Grace at meals | 458 |
| Gracefulness in action | 292 |
| Graham, Mr., his picture sale | 67 |
| Grammar schools | 353 |
| Grand Cyrus, Scuderi's | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Grandeur and minuteness | 420 |
| Grandmother, Sir Roger de Coverley's great, great, great, had the best receipts for a hasty pudding and a white pot | 109 |
| Grant, Dr., the oculist | 472, 547 Fn. 1 |
| Gratian, Balthazar | 293 Fn. 1, 379 Fn. 3 |
| Gratification | 454 |
| Gratitude | 453, 588 |
| Gravitation | 121 |
| Great and good not alike in meaning | 109 |
| Great men | 101, 196 |
Greatness
of mind
of objects |
312
412, 413 |
| Greaves, John | 1 Fn. 4 |
| Grecian Coffee-house | Fn. 10 |
Greeks
modern, who so called | 189, 313
239, 245 |
| Green, why the earth is covered with | 387 |
| Green-sickness | 431 |
| Grief, the grotto of | 501 |
| Grinning match | 137 |
| Grotto, verses on a | 632 |
| Grove, Rev. Henry | 588 Fn. 1 |
| Guardian, the | 532 Fn.3 , 550 Fn. 1 |
| Gumley, Mr., a diligent tradesman | 509 |
| Gyges and Aglaüs, tale of | 610 |
| Gymnosophists | 337 |
| Habits | 197 |
| Hadley, John | 428 |
Halifax
Charles Montagu, Earl of
George Savile, Marquis of |
3 Fn. 9, dedication
170 Fn. 1 |
| Hamadryads | 589 |
| Hamlet | 404 |
| Handel | 5 Fn. 2 |
| Handkerchief in tragedy | 44 |
| Handsome people | 144 |
| Hangings, the men in the | 22 |
| Hanover succession | 384 |
| Happiness | 15, 167, 575, 610 |
| Hardness in parents | 181 |
| Hard words should be mispronounced by well-bred ladies | 45 |
| Harehounds | 116 Fn. 1 |
| Harper, Robert | 480 Fn. 2 |
| Harrington's Oceana | 176 Fn. 1 |
| Harris, Mr., proposes an organ for St. Paul's | 552 |
| Harrison, John | 428 Fn. 1 |
| Hart, Nicholas, the annual sleeper | 184 Fn. 2 |
| Hatred | 125 |
| Hats | 187, 219 |
| Hayn2, Nicolino | 258 Fn. 2 |
| Haymarket Theatre | 1 Fn. 12 |
| Head-dress | 98, 319 |
| Health | 411 |
| Hearts, a vision of | 587 |
Heathen
philosophy
notions of a future state |
150
633 |
| Heaven | 447,465, 580, 590, 600 |
| Hebrew idiom in English | 405 |
| Hecatissa and the Ugly Club | 48 |
| Heidegger, J. J. | 14 Fn. 1, 31 |
| Heirs and elder brothers | 123 |
| Hell, the Platonic | 90 |
| Henley, Anthony | 494, 518 Fn. 1 |
Henpecked
husbands
bachelors |
176, 179, 479
486 |
| Herbert, George | 58 Fn. 4 |
| Heretics | 185 |
| Hermit, saying of a | 575 |
Hero
what makes a
in tragedy |
240, 312, 601
40 |
| Herod and Mariamne, story of | 171 |
| Herodotus | 483 |
| Hesiod | 200, 447 |
| Heteropticks | 250 |
| Heywood, James | 268 Fn. 1 |
| Hilpa, an antediluvian princess, story of | 584, 585 |
| Hirst, James, his love-letter | 71 Fn. 2 |
Historians
in conversation | 420, 483
136 |
History
a study recommended to newsmongers
secret | 133, 289, 420, 428
452
619 |
| Hobbes | 47 Fn. 1, 52, 249, 588 |
| Hobson's choice | 509 |
| Hockley in the Hole | 31 Fn. 2, 436 Fn. 1 |
| Homer | 70, 273, 357, 411, 417 |
| Honest men, association of | 126 |
| Honestus, the trader | 443 |
| Honeycomb, Will. | 2 Fn. 8, 4, 34, 41, 67, 77, 105, 131, 156, 265, 311, 325, 352, 359, 410, 475, 490, 511, 530, dedication |
| Honeycomb, Simon | 154 |
| Honour | 99, 219 |
| Horace | 394 |
| Howard, Hon. E., The British Princes | 43 Fn. 7 |
| Huarte, Juan | 307 Fn. 1 |
| Hudibras | 17, 54, 59, 145 |
| Hughes, John | 66 Fn. 1, 104, 141, 220, 231, 232, 252, 306 |
| Hummums, the | 347 Fn. 1 |
| Hunting | 116 Fn. 1, 583 |
| Hunt the squirrel, a country dance | 67 |
| Husbandman, funeral oration for a | 583 |
| Husbands | 149, 178, 179, 236, 530, 561, 607 |
| Hush note | 228 |
| Hush, Peter, the whisperer | 457 |
| Hyæna and spider | 187 |
| Hydaspes, the opera of | 13 Fn. 1 |
| Hymen, revengeful | 530 |
Hymn
to the Virgin, a book in eight words
to Venus by Sappho
David's, on Providence
on gratitude
on the glories of heaven and earth |
60
232
441
453
465 |
| Hypocrisy | 119, 243, 399, 458 |
| Iambic verse | 39 |
| James, a country footman polished by love | 71 |
| Jane, Mrs., a pickthank | 272 |
| Japis's care of Æneas | 572 |
| Ibrahim XII., tragedy of | 51 Fn. 8 |
| Ichneumon fly | 126 |
| Ideas, association of | 416 |
| Identity | 578 |
| Idiots | 47, 474 |
| Idleness | 316, 411, 624 |
| Idolatry | 211 |
| Idols | 73, 79, 87, 155, 534 |
| Jealousy | 170, 171, 178 |
| Jest | 138, 616 |
| Jesuits | 17 Fn. 3, 307, 545 |
| Jews | 213, 495, 531 |
| Jezebels | 175 |
| Ignatus, a fine gentleman, as opposed to an atheist | 75 |
| Ignorance, when amiable | 324 |
| Jilt, a penitent | 401 |
| Jilts | 187 |
| Iliad, effect of reading the | 417 |
| Ill nature | 23, 169, 185 |
| Imaginary beings in poetry | 357 Fns. 4 & 5, 419 |
| Imagination, Essays on | 411-421 |
| Imitators | 140 |
| Imma, daughter of Charlemagne, story of | 181 |
| Immortality | 110, 210, 537, 600, 633 |
| Impertinent persons | 148, 168, 432 |
| Implex fables | 297 Fn. 1 |
| Impudence | 2, 20, 231, 373, 390, 443 |
| Incantations in Macbeth | 141 |
| Ince, Richard | 555 |
| Inclination and reason | 447 |
| Inconsistency | 162, 50 |
| Indian kings, the | 50 |
| Indifference in marriage | 332 |
| Indigo the merchant | 136 |
| Indiscretion | 23 |
| Indisposition | 143 |
| Indolence | 100, 316, 320 |
| Industry | 116 |
| Infidelity | 186 |
| Infirmary for establishing good humour | 429, 437, 440, 474 |
| Ingratitude | 491 |
| Ingoltson, Charles, quack doctor | 444 |
| Initial letters | 2 Fn. 9, 567, 568 |
| Inkle and Yarico | 11 |
| Innocence | 34, 242 |
| Inns of Court | 49 |
| Inquisition on maids and bachelors | 320 |
| Inquisitiveness | 288 |
| Insipid couple, an | 522 |
| Insolence | 294 |
| Instinct | 120. 121, 181, 201, 519 |
| Insults | 150 |
| Integrity | 448, 557 |
| Intemperance | 195 |
| Intentions | 213, 257 |
| Interest, worldly | 185, 394 |
| Invention | 487 |
| John a Nokes and John a Stiles, petition of | 577 |
| Johnson, the player | 370 |
| Jolly, Frank, memorial from the Infirmary | 429 |
| Jonathan's Coffee-house | 1 Fn. 13 |
| Jonson, Ben. | 9, 28 Fn. 5, 33, 70 |
| Joseph I., Emperor | 43 Fn. 4, 45 Fn. 1, 353 Fn. 3 |
| Josephus | 110, 171 |
Journal
use of keeping a
of a deceased citizen for a week
of a lady
of three country maids
of the country Infirmary |
317
317
323
332
440 |
| Iras the witty | 404 |
| Irish widow-hunters | 561 |
| Irony | 438 |
| Iroquois chiefs in London | 50 |
| Irresolution | 151, 162 |
| Irus the rake | 264 |
| Isadas the Spartan | 564 |
Italian
writers
opera and singers |
5
1 Fn. 12, 5 Fn. 2, 13 Fn. 1, 18, 29, 258 |
| Itch of writing | 582 |
| Judgment the offspring of time | 514 |
| Judgments | 483, 548 |
| Julian, Emperor | 634 |
| July and June described | 425 |
| Jupiter's distribution of calamities | 558, 559 |
Justice
poetical | 479, 564
40, 548 |
Juvenal
Dryden's | 150, 209
37 Fn. 2 |
| text | links |
| Kennet, Dr., on the origin of country wakes | 161 Fn. 1 |
| Kensington Gardens | 477 |
| Kimbow, Tom | 24 |
| King Lear | 40 |
| Kings, logic of | 239 |
| Kissing dances | 67 |
| Kitcat Club | 9 Fn. 1 |
| Kitchen music | 570 |
| Kitty, a jilt | 187 |
| Knaves | 601 |
| Knotting, as an employment for beaus | 536 |
Knowledge
self | 287, 379
399 |
| Koran | 94 Fn. 4 |
| Labour | 115, 161, 624 |
| Lacedæmonians | 67, 188, 207 |
| Lackeys, The, of Ménager and Rechteren | 481 |
| Ladies | 143, 435, 437, 607 |
| Laertes, prodigal through shame of poverty | 114 |
| La Ferte, the dancing master | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Lætitia and Daphne, beauty and worth | 33 |
| Lampoons | 16, 23, 35, 224 |
| Lancashire Witches, the comedy | 141 |
Language
English, effect of the war on the
European
brutal |
165
405
400 |
| Lapirius, generosity of | 248 |
| Lapland odes | 366, 406 |
| Larvati | 32 Fn. 4 |
| Lath, Squire, would give an estate for better legs | 32 |
| Latimer | 465 |
| Latin, effect of, on a country audience | 221 |
| Latinus, King, pressed for a soldier | 22 Fn. 8, 53 |
| Laughers at public places | 168 |
| Laughter | 47, 52, 249, 494, 598, 630 |
| Lawyers | 21, 49, 456, 551 |
| Lazy Club, the | 323 |
| Leaf, population of a | 420 |
| Learned, precedency among the | 529 |
| Learning | 6, 105, 350, 353, 367, 469, 506 |
| Leather, gilt, for furniture | 609 |
| Le Conte, Father | 189 Fn. 4 |
| Lee, Nathaniel | 39 Fn. 6 |
| Leo X. | 497 |
| Leonora's library | 37, 163 |
| Leontine and Eudoxus | 123 |
| Leopold I., Emperor | 353 Fn. 3 |
| Leti, Gregorio | 632 |
Letters
| Absence of lovers | 241 |
| Academy of Painting, from the | 555 |
| Ambassador of Bantam | 557 |
| Apology for a man of wit and pleasure | 154 |
| Author turned dealer | 288 |
| Bankrupt, from a, and answer | 456 |
| Bashfulness | 231 |
| Beauty, from a | 87 |
| Beauty destroyed by the small pox | 306 |
| Behaviour at church | 236 |
| Belinda to the shades | 204 |
| Benefactor | 546 |
| Blank, from a | 563 |
| Bowing and curtseying at church | 460 |
| Brook and Hellier's wine | 362 |
| Butts | 175 |
| Captain Sentry on the character of Sir Roger de Coverley, and on his own situation | 544 |
| Castle-builder, from a | 167 |
| Cat-calls | 361 |
| Censuring Spectator | 158 |
| Character of jilts | 187 |
| Chloë from her lover, with an account of his dreams | 301 |
| Choleric gentleman | 563 |
| Clergyman, to a | 27 |
| Coquette, from a | 79 |
| Coquette, and answer | 254, 515 |
| Cotquean | 482 |
| Country manners and conversation | 474 |
| Countryman to his mistress | 324 |
| Coverley, from Sir Roger de | 264 |
| Crazy man, from a supposed | 577 |
| Cries of London | 251 |
| Cruel Husbands | 236 |
| Dancing | 334 |
| Decay of the club | 542 |
| Demonstrations of grief | 95 |
| Detraction | 348 |
| Devotion, formal | 79 |
| Dumb Doctor | 560 |
| Education | 330, 337, 353 |
| Emperor of China to the Pope | 545 |
| Envil, Sir John, from, married to a lady of quality | 299 |
| Epilogues, against comic, to a Tragedy | 338, 341 |
| Epitaphs, on | 518 |
| Estcourt, from Dick | 264 |
| Eye, on the | 252 |
| Fair sex | 298 |
| Fan exercise | 134 |
| Fashion | 66, 319 |
| Father to his son | 189 |
| Female equestrians | 104 |
| Fortune-hunters | 326 |
| Fortune-stealers | 311 |
| Freeport, Sir Andrew, his retiring | 549 |
| Gardening | 477 |
Greek
mottos
shopkeeper on his wife's Greek |
271, 296
278 |
| Hecatissa | 48 |
Hen-pecked
husband, determined to be free
keepers |
212
486 |
| Hoop petticoat | 127 |
| Horace to Claudius Nero | 493 |
| Husband, to a | 204 |
| Husband likely to be ruined by his wife's accomplishments | 328 |
| Idler, from an | 320 |
| Idols | 87 |
| Impertinents | 168 |
| Jealous husband | 527 |
| Kissing | 272 |
| Lady insulted by her seducer—reflections on the subject | 611 |
| Languishing lover, from a | 527 |
| Law | 480, 551 |
| Leonora | 163 |
| Lillie, Chas., from | 16 |
| Lion, from a | 136 |
| Lottery ticket | 242 |
| Lover, from a | 208 |
| Lover's leap, on the | 227 |
| Mary Tuesday, from | 24 |
| Masquerades | 8 |
| Mercenary practice of men in the choice of wives | 199 |
| Modesty, on | 484 |
| Money, love of | 450 |
| Monkey, from a | 343 |
| Mother and son | 263 |
| Mottos | 296 |
| Naked shoulders | 437 |
| Natural son, from a | 203 |
| New-married couple, from a | 364 |
| Nose-pulling | 268 |
| Octavia complains of the ingratitude of her husband | 322 |
| Oxford correspondents | 553 |
| Parish-clerk on evergreens | 284 |
| Parthenia, from | 140 |
| Patching | 268 |
| Pert baggage, from a | 560 |
| Playhouse | 36 |
| Pliny to Hispulla | 525 |
| Poachers | 168 |
| Poetical justice | 548 |
| Poor and proud Jezebel | 292 |
| Powell, the Puppet-showman, commendation of | 372 |
| Prayers of clergymen before sermon | 312 |
| Prude, from a | 364 |
| Punning | 396 |
| Quaker | 276 |
| Rudeness | 443 |
| Rustic amusements | 161 |
| Scholar in love, from a | 362 |
| Seduction | 208 |
| Servants | 202 |
| Severity of schoolmasters | 168 |
| Sexton of St. Paul's, Covent Garden | 14 |
| Short face, Sophia in love with a | 290 |
| Silent lover, from a | 304 |
| Sly, Mr., on hats | 532 |
| Smallpox, lady marked with | 613 |
| Soldiers, from several | 566 |
| Spenser, merits of | 540 |
| Splenetic cured | 134 |
| Stage-coach, behaviour in a | 242 |
| Steele, from | 274 |
| Swinging | 496 |
| Talebearers | 310 |
| Templars turned Hackney-coachmen | 498 |
| Theatre, on the—on a musical scheme | 258 |
| Three thrifty ladies | 332 |
| Travelling | 364 |
| Ugly Club | 52 |
| Unhappy condition of women of the town | 190 |
| Untoward wife | 194 |
| Valetudinarian | 25 |
| Visiting | 208 |
| Wagerers and whistlers | 145 |
| Widow with two lovers, and answer | 149 |
| Widows' Club | 573 |
| Will. Honeycomb | 131 |
| Women's Men | 158 |
| Women taking snuff | 344 |
| Zelinda from her lover—his death | 627 |
| |
| Letters, show temper of writers | 283 |
| Levées | 193 |
| Levity | 234, 253 |
| Liars | 103, 167, 234 |
| Libels | 35, 451 |
| Liberality | 292, 346 |
| Liberty | 287 |
| Library, female | 37, 79, 92, 140 |
| Liddy, Miss, reasons for differing in temper from her sister | 396 |
Life
(domestic)
(human) |
455
27, 93, 94, 143, 159, 202, 219, 222, 289, 317, 574, 575 |
| Light | 413 |
| Ligon's History of Barbadoes | 11 Fn. 2 |
| Lillie, Charles | 16, 46 Fn. 2, advertisement, 173 Fn. 3, 334 Fn. 1, 358 |
| Lilly's Latin Grammar | 221 Fn. 2 |
| Lindamira allowed to paint | 41 |
| Lion, the, in the Haymarket | 13 Fn. 1 |
| Lipogrammatists | 58 Fn. 1 |
| Liszynski, a Polish atheist | 389 |
| Livy | 409, 420 |
| Lloyd's coffee-house | 46 Fn. 1 |
| Locke, John | 37 Fn. 2, 62, 94, 121, 313, 373, 519, 557 |
| Logic of kings | 239 |
| Loiterers | 155 |
| Loller, Lady, from the country infirmary | 429 |
London
cries of | 69, 200, 403
251 |
| London and Wise, gardeners | 5 Fn. 5, 477 |
| Longings of Women | 326 |
| Longinus | 229, 279 Fn. 6, 326, 339 Fns. 2-4, 489 Fn. 1, 633 |
| Longitude | 428 Fn. 1 |
| Looking-glasses | 325 |
| Lorrain, Paul | 338 Fn. 3 |
| Lottery | 191, 199 |
Love
casuist, the | 4, 30, 47, 71, 118, 120, 142, 149, 161, 163, 199, 206, 241, 274, 304, 324, 325, 362, 366, 367, 376, 377, 397, 400, 475, 479, 506, 525, 561, 591, 596, 605, 607
591, 607, 614, 625 |
| Love for Love, the comedy | 189 |
| Loveless, Biddy | 196 |
| Lovemore, Jeremy | 596 |
| Lovers' Leaps, the | 225, 233 |
| Loungers, the, at Cambridge | 54 |
| Loyola, Oldham's | 17 Fn. 3 |
| Lucceius, character of | 206 |
| Lucian | 67, 283 |
| Ludgate | 82 Fn. 1 |
| Lulli, Jean Baptiste | 29 Fn. 3 |
| Lute-string, advanced price of | 21 |
| Luxury | 55, 195 |
| Lying, party | 507 |
| Lysander, character of | 522 |
| Macbeth, incantation in | 141 |
Machiavel
the she | 406
561 |
| Mademoiselle, the French Puppet | 277 |
| Magna Charta | 2 Fn. 2 |
| Mahomet's night journey | 94 Fn. 4 |
| Mahometans | 85, 460, 631 |
| Maids, inquisition on | 320 |
Male
jilts
widows
birds | 288
520
128 |
| Malebranche | 37 Fn. 2, 94 Fn. 3 |
| Malvolio, a mixed character | 238 |
| Man | 9, 115, 156, 162, 237, 238, 408, 441, 494, 519, 537, 564, 588, 624 |
| Man of Mode, Etherege's | 65 |
| Manilius, in retirement | 467 |
| Mankind | 444, 598 |
| Manley, Mrs. | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Manner | 292 |
| Manuscript Note Book of Addison's | 411 Fn. 2 |
| Maple, Will | 203 |
| Maraton and Yaratilda | 56 |
| March, month of, described | 425 |
| Marcia's prayer in Cato | 593 |
| Marcus, son of Cicero | 307 |
Mariamne
story of | 466
171 |
| Marius, Scipio's judgment of young | 157 |
| Marlborough, Duke of | 26 Fn. 5, 139, dedication, 353 Fn. 3 |
| Marriage | 89, 113, 149, 181, 326, 254, 261, 268, 308, 322, 430, 479, 482, 490, 506, 522, 525, 533, 607 |
| Martial | 52, 446 |
| Martyn, Henry | 180 Fn. 1, 200, 232 |
| Masquerades | 8, 14 Fn. 1 |
| Massacres | 185 |
Master
a good
a bad |
107
136, 201, 202 |
| Mathematics | 307 |
| Mather, Charles, toyman | 570 |
| Matter | 420, 519 |
| Matter-of-fact man | 521 |
| Maundrell's Journey to Jerusalem | 303 Fn. 2 |
May
dangerous to ladies | 425
365, 395 |
| Mazarine, Cardinal, and Quillet | 23 |
| Medals on the Spanish Armada | 293 |
| Mede's Clavis Apocalyptica | 92 Fn. 2 |
| Medicina Gymnastica, Fuller's | 115 Fn. 2 |
| Medlar, Mrs., of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Memory | 417, 471 |
| Men | 97, 145, 196, 264, 505, 510 |
| Menagiana | 60 Fn. 9 |
| Ménager and Count Rechteren at Utrecht | 481 |
| Merab, with too much beauty and wit | 144 |
| Merchants | 69, 174, 218, 428 |
| Mercurialis Hieronymus | 115 Fn. 3 |
| Mercy | 456 |
| Merit | 223, 340 |
| Merry men | 70 |
| Messiah, Pope's | 378 |
| Metamorphoses, Ovid's | 417 |
| Metaphor | 417, 421, 595 |
Methuen
Paul
treaty |
dedication
43 Fn. 1, 140, 240, 417, 421, 425 |
| Milton, Addison's papers on | 267, 273, 279, 285, 291, 297, 303, 309, 315, 321, 327, 333, 339, 345, 351, 357, 363, 369, 417, 425, 463 |
| Mimicry | 416 |
| Mind | 455, 554 |
| Minister of state, a watchful | 439 |
| Mint, arguments of the | 239 |
| Mirth | 196, 358, 381 |
| Mirza, Visions of | 159 |
| Mischief | 564 |
| Misers | 624 |
Miseries
the mountain of | 169
558, 559 |
| Misfortune, a good man's struggle with, Seneca on | 39 Fn. 1 |
| Misfortunes, not to be called judgments | 483 |
| Mixt wit | 62 |
| Mode | 6, 129, 145 |
| Moderation | 312 |
| Modern writers | 61, 249 |
| Modest assurance | 373 |
| Modesty | 6, 52, 154, 206, 231, 242, 296, 350, 354, 373, 390, 400, 435, 458, 484 |
| Mohocks | 324, 347 |
| Moles | 123 |
| Molière | 70 |
| Moll Peatley, a dance | 67 Fn. 3 |
| Money | 3, 422, 450, 456, 509 |
| Monks | 60 |
| Monmouth, Duke of | 2 Fn. 2 |
| Monosyllables, English liking for | 135 |
| Monsters | 412, 413, 418 |
| Montague, Charles, Earl of Halifax | 3 Fn. 9, dedication |
| Montgomery, Mr. | 524 |
| Monuments in Westminster Abbey | 26 |
| Montaigne | 562 |
| Moorfields | 505 |
| Moralists | 196 |
| Morality | 446, 459, 465 |
More
Henry
Sir Thomas |
86, 90 Fn. 1, 121
349 |
| Moreton, Mr. John | 546 Fn. 2 |
Mortality
bill of | 289
377 |
| Mosaic pavement | 358 Fn. 1 |
| Moses, tradition of | 237 |
Mother
story of the Rival Mother | 246
91 |
| Motion in gods and mortals | 369 |
| Motteux, Peter | 14 Fn. 1, 552 |
| Motto | 221 |
| Mountebank | 572 |
| Mourning | 64, 65, 575 |
| Mouth, a padlock for the | 533 |
| Much cry but little wool | 251 |
| Mulberry Garden, the | 96 |
| Muley Moluc, last moments of | 349 |
| Muses, the mountain of the | 514 |
| Music | 18, 29, 258, 278, 405, 416, 570, 630 |
| Naked-shouldered females | 437 |
| Names of authors to their works | 451 |
| Natural History | 22 |
| Nature | 153, 404, 408, 414, 588 |
| Needlework | 606, 609 |
| Negroes | 215 |
| Neighbourhoods | 49 |
| Nemesis, an old maid who discovers judgments | 483 |
| Nero's nurse | 246 |
| Nettletop, Rebecca | 190 |
| New, the, in art | 411, 412, 413, 415 |
| Newberry, Mr., his rebus | 59 |
| New River | 5 |
| New Style | 21 Fn. 1 |
| News | 425, 457, 625 |
| Newton, Sir Isaac | 37 Fn. 2, 543, 554, 565 |
| Nicholas Hart, the sleeper | 184 |
| Nicodemuncio to Olivia, on being made an April fool | 432 |
| Nicolini, the singer | 5, 13 Fn. 1, 235, 403 |
| Night | 425, 565, 582 |
| Nightingale | 383 |
| Nigralia, a party lady, forced to patch on the wrong side | 81 |
| No, a word useful to women | 625 |
| Nobility | 537 |
| Northern hive, Sir W. Temple's | 21 Fn. 4 |
| Nose-pullers | 268 |
| Notable men | 150 |
| Novell, Lydia, complains of a rich lover | 140 |
| Novels | 365 |
| Novelty | 412, 413, 626 |
| November described | 425 |
| Numbering of houses | 28 Fn. 2 |
| Nutmeg of Delight, the | 160 |
| Oates, Titus | 58 Fn. 4 |
| Obedience to parents | 189, 449 |
| Obscurity | 101, 406, 622 |
| Obsequiousness | 386 |
| Ocean | 489 |
| October Club | 9 Fn. 3 |
| Ogilby, John | 37 Fn. 2 |
| Ogler, the Complete | 46 |
| Oldfield, Mrs. | 546 |
| Oldham's Loyola | 17 Fn. 3 |
| Old Style | 21 Fn. 1 |
| Olearius, travels of | 426 Fn. 1 |
| Omens, superstitious dread of | 7 |
| Omniamanta | 144 |
| Omnipotence | 565 |
| Omnipresence | 572, 580 |
| Oneirocritic | 505 |
Opera
Italian
France |
1 Fn. 12, 5 Fn. 2, 13 Fn. 1, 18, 29, 314
29 Fn. 4 |
| Opinion, popular | 460 |
Oratory
female | 484, 633
247, 252 |
| Orbicilla | 390 |
| Order | 219 |
| Orestilla, the great fortune | 118 |
| Oroondates, Statira to | 199 |
| Osborn's Advice to his Son | 150 |
| Ostentation | 460 |
| Otway | 39 Fn. 7, 117, 456 |
| Overdo, Justice, Ben Jonson's | 48 |
| Ovid | 417, 439, 618 |
| Oxford scholar at a coffee-house | 46 |
| Padlocks for the mouth | 533 |
| Pages in gentlemen's houses | 214 Fn. 2 |
| Painter's part in a tragedy | 42 |
Painting
the art of
of the face |
83, 129, 226, 555
41 |
| Palmquist, Monsieur | 43 |
| Pamphilio, a good master | 137 |
| Pamphlets, defamatory | 541 |
Pantheon
Penkethman's
at Rome |
31 Fn. 3
415 |
| Paradin, Guillaume | 98 Fn. 3 |
| Paradise of Fools | 460 |
| Paradise Lost, Addison's papers on | 267, 273, 279, 285, 291, 297, 303, 309, 315, 321, 325, 327, 333, 339, 345, 354, 357, 363, 369 |
| Parents | 21, 150, 181, 189, 192, 235, 263, 313, 330, 449, 532, 539 |
| Parish clerks, advice to | 372 |
| Parker, Richard | 474 Fn. 3 |
| Parnassus, Vision of | 514 |
| Parnell, Thomas | 460 Fn. 1 |
| Parricide, how punished in China | 189 |
| Parthenia, letter of, upon the ladies' library | 140 |
Party
patches | 57, 125, 126, 243, 399, 432, 507
81 |
| Particles, English | 18 |
| Pascal | 116 Fn. 3 |
| Pasquinades | 23 Fn. 5 |
Passion
of the fan | 202, 438, 528
102 |
| Passions, the | 31, 71, 215, 224, 255, 408, 418, 564 |
| Pastorals, Philips's | 523 |
Patches
party use of | 50
81 |
| Patience | 312, 501, 559 |
| Patrons | 214 |
| Paul Lorrain | 338 |
| Paul, Saint | 633 |
| Paul's Cathedral, St., Indian kings on | 50 |
Peace
negotiations | 45
45 Fn. 1 |
| Pearce, Zachary | 572 |
| Pedants | 105, 286, 617 |
| Pedigrees, vanity of | 612 |
| Peepers | 53 |
| Peevish fellow, a | 438 |
| Penkethman, W. | 31 Fn. 3, 370 Fn. 5 |
| Penruddock's rising in the West | 313 Fn. 3 |
| Penseroso, Il | 425 |
| Pentathlum | 161 |
| People, the wealth of a country | 200 |
| Pericles | 81, 633 |
| Perrault, Charles | 279 Fn. 11, 303 Fn. 3 |
| Perry, Mrs. | 92 Fn. 1 |
| Persecution, religious | 459 |
Persian
education
soldier reproved |
99, 189, 337
427 |
| Persius | 379 |
Peter the Great
compared with Louis XIV. | 43 Fn. 2
139 |
Petronius
his story of the Ephesian lady
mood of, at death |
11 Fn. 1
349 |
Petticoat
politicians | 109, 127, 140
305 |
| Petty, Sir William | 200 |
| Phædra and Hippolitus, a tragedy | 18 Fn. 9 |
Pharamond
his edict against duelling
letter to | 76 Fn. 1, 84 Fn. 1
97
480 |
| Phidias | 415 |
| Philanthropy | 177 |
| Philantia, a votary | 79 |
| Philips, Ambrose | 223 Fn. 2, 229, 290 Fn. 2, 338 Fn. 2, 400, 523, 578 |
| Philopater on his daughter's dancing | 466 |
| Philosophers | 195, 634 |
| Philosophy | 7, 10, 22, 175, 201, 393, 420 |
| Phocion | 133, 188, 448 |
| Phœbe and Colin, a poem | 603 |
| Physic | 195 |
| Physicians | 16, 21, 25, 234 |
| Physiognomy | 86, 206, 518 |
| Pictures | 67, 83, 107, 109, 226, 244, 248, 416, 418 |
| Picts, what women are | 41 |
| Piety | 201 |
| Pindar | 160, 467 |
| Pindaric writing | 58 Fn. 5 |
| Pin money | 295 |
| Piper of Hamelin, the | 5 |
| Pisistratus | 527 |
| Pitchpipe | 228 |
| Pittacus, a saying of | 574 |
| Pity | 208, 397, 418, 442, 588 |
| Pix, Mary | 51 Fn. 8 |
| Places of trust | 469, 629 |
| Plain dealing | 460 |
| Planets | 420 |
| Planting | 583, 589 |
| Plato | 23 Fn. 2, 86 Fn. 12, 90, 183, 211 Fn. 2, 237, 507, 624 |
| Platonic love | 400 |
| Players | 141, 370, 502, 529 |
| Plays, modern | 22, 592 |
| Pleaders | 197 |
| Pleasant fellows | 462 |
| Pleasure | 146, 151, 152, 183, 312, 424, 600, 624 |
| Pleasures of Imagination, Essays on | 411-421 |
| Pliny | 230, 467 Fn. 1, 484 Fn. 1, 525, 554 |
| Plot, Robert | 447 Fn. 1 |
| Plutarch | 125 Fn. 1, 180, 188, 229, 483, 494, 507 |
| Poacher, request from a | 168 |
| Poetry | 39, 40, 44, 51, 58, 220, 253, 314, 405, 417, 418, 419, 421 |
| Poetical justice | 40, 548 |
| Polite imaginations | 411 |
| Politeness | 119 |
| Political arithmetic | 200 |
| Politicians | 43, 305, 403, 556, 567, 568 |
| Poll, a way of arguing | 239 |
| Polycarpus, beloved by all | 280 |
| Pompey | 293 |
| Pontignon, M. | 90 |
| Poor, the | 200, 232 Fn. 3, 430 |
Pope, Alexander
his Essay on Criticism
an idea from
commended
his Pastorals
his Messiah
Letter and Verses
on Adrian's dying words
his Miscellany |
65 Fn. 2
210 Fn. 1
253 Fn. 2
223 Fn. 2
378
527
532
523 |
| Popular applause | 188 |
| Porta, Baptista della, on Physiognomy | 86 Fn. 6 |
| Posterity | 101, 583 |
| Postman, newspaper | 1 Fn. 8 |
| Pottière, Dominic, a French privateer | 350 |
| Poverty | 150, 464 |
| Powell, junior, his Puppet-show | 14 Fn. 2, 31 Fn. 5, 372 |
| Powell, George, the actor | 31 Fn. 4, 40 |
| Power, despotic | 287 |
| Praise | 38, 73, 188, 238, 349, 467, 551 |
| Prayer | 207, 236, 312, 391 |
| Precedence | 119, 529 |
| Précieuses, the | 45 Fns. 2 & 4 |
| Prediction, vulgar arts of | 505 |
| Preface to the Bishop of St. Asaph's Sermons | 384 |
| Prejudice | 101, 263, 432 |
| Prepossession | 117 |
| Prerogative | 480 |
| Presumption | 187 |
| Pride | 33, 201, 394, 462 |
| Prince, Mr., dances of | 466 |
| Princes, good and bad | 139 |
| Printing | 166, 367, 582 |
| Prior | 141 |
| Procrastination | 151 |
| Procrustes, bed of | 58 |
| Prodicus | 183 |
| Professions, the three learned | 21 |
| Projector of town entertainments, a | 31 |
| Promisers | 448 |
| Pronunciation | 451 |
| Prospects | 411, 412, 418 |
| Prosperity | 237 |
| Prosper, Will. | 19, 20 |
| Proverbs of Solomon, in verse | 410 |
| Providence | 120, 237, 293, 441, 543 |
| Prudence | 293 |
| Prudes at the play | 208 |
Psalm
xxiii. translated
cxiv.
cxxxix.
singing in church |
441
461
399
205 |
| Psalmanazar, George | 14 Advertisement Fn. 1 |
| Pugg the Monkey, Adventures of | 343 |
| Pulvillios | 63 Fn. 1 |
| Punchinello | 14 |
| Punishments in school | 157 |
| Puns | 61, 396, 454, 504 |
| Puppet-show, Powell's | 14 Fn. 2 |
| Purcell, Henry | 29 Fn. 3 |
| Puzzle, Tom, in argument | 476 |
| Pyramids of Egypt | 415 |
| Pyrrhus, King | 180 |
| Pythagoras | 447, 586 |
| Quacks | 444, 547 Fn. 1, 572 |
| Quakers | 396 |
| Quality | 34, 219 |
| Queries in love | 625 |
| Quick, Mrs., of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Quidnunc, Tom | 625 |
| Quillet, Claude | 23 Fn. 4 |
| Quintilian | 168 |
| Quir, Peter de, on Puns | 396 |
| Quixote, Don, patron of Sigher's Club | 30 |
| Rabelais | 283 |
| Racine | 39 Fn. 4 |
| Rack | 239 |
| Radcliffe, Dr. John | 468 Fn. 4 |
| Raillery | 422 |
Rainbow
coffee-house | 415
16 Fn. 1 |
| Rakes | 336, 576 |
| Raleigh, Sir W. | 510 |
| Ramble from Richmond to the Exchange | 454 |
| Ramsey, Will., the astrologer, describes night | 582 |
| Rant | 40 |
| Rape of Proserpine, a French opera | 29 |
| Raphael | 226, 244, 467 |
| Rapin, Réné | 44 Fn. 3, 291 Fn. 2 |
| Rattling Club at church | 630 |
| Read, Sir Wm., oculist | 472, 547 Fn. 1 |
| Readers | 1, 62, 93, 94, 179 |
| Reason | 6, 120, 408, 447 |
| Rebus | 59 |
| Rechteren, Count, and M. Ménager | 481 Fn. 3 |
| Recitative | 29 |
| Reciters | 521 |
| Recluse, the | 282 |
| Recommendations, letters of, generally unjust and absurd | 493 |
| Recreations | 258 |
| Rehearsal, Buckingham's | 3 Fn. 7 |
| Religion | 201, 213, 292, 356, 447, 459, 471, 483, 494, 574 |
| Renatus Valentinus, story of | 426 |
| Rentfree, Sabina, letter on greensickness | 431 |
| Repository for fashions | 487 |
| Reproach | 594 |
| Reproof | 382 |
| Reputation | 218, 467 |
| Retirement | 4, 27, 249, 425, 467, 549, 613 |
| Revelation | 600 |
| Reveries | 167 |
| Revenge of a Spanish lady | 611 |
| Rhubarb, John, Esq., from the Infirmary | 429 |
| Rhyme, the Æneid in | 60 |
| Rhynsault, story of | 491 |
| Rich, Christopher | 258 Fn. 1 |
| Riches | 140, 145, 150, 280, 282, 283, 294, 456, 464, 574 |
| Richelieu, Cardinal | 305 |
| Ridicule | 150, 249, 445, 446 |
Riding
dress of ladies | 115
435 |
| Rinaldo and Armida, opera of | 5 Fn. 2, 14 |
| Riot | 180 |
| Rival Mother, story of the | 91 |
| Rivers, Colonel | 204 Fn. 3 |
| Roarers | 474 |
| Robin the Porter at Will's Coffeehouse | 398 |
| Rochester, John Wilmot, Earl of | 2 Fn. 3 |
Roman
ladies
education
understanding |
81
313
502 |
| Rope-dancing | 141 |
Rosalinda
a Whig partizan
reformation of
the handsome, to the Ugly Club |
81
87
87 |
| Rosamond, Clayton's opera of | 18 Fn. 1 |
| Rosamond's Bower | 281 |
| Roscommon, Earl of | 44 Fn. 4, 253 Fn. 4 |
| Rose Tavern, the | 2 Fn. 6 |
| Rosicrucius, story of sepulchre of | 379 |
| Royal Exchange neglected | 509 |
| Royal Progress, Tickell's poem of the | 620 |
| Royal Society | 121, 262 Fn. 4 |
| Runnet, Mrs., of the Widows' club | 561 |
| Ruricola, his son and daughter | 192 |
| Rusticity | 400 |
| Rusty Scabbard, on the fighters at the Bear garden | 449 |
| Rycaut, Sir Paul | 343 |
| Rymer | 267 Fn. 1 |
| Sabine ladies | 81 |
| St. Evremond, Sieur de | 33 Fn. 1 |
St. James's
Park
Coffee-house |
109 Fn. 9, 1 Fn. 1 |
| Sacheverell, Henry | 57 Fn. 4 |
| Salamanders, an Order of Ladies | 198 |
| Sallust | 409 |
| Salmon, Mrs., her waxwork | 28 Fn. 4, 31 Fn. 1 |
| Salutations | 259, 270, 460 |
| Sanctorius, the chair of | 25 Fn. 2 |
| Santer, Betty, letter from | 140 |
| Sapper, Thomas, his epitaph | 518 |
| Sappho | 223, 229, 233 |
| Sarasin, I. F. | 60 Fn. 11 |
| Satires | 209, 256, 451, 473, 568 |
| Satyricon of Petronius Arbiter, story from the | 11 Fn. 1 |
| Saudades | 204 |
| Saul, David, his epitaph | 518 |
| Saunter, Mrs., snuff-taker | 344 |
| Scale of being | 519 |
| Scaliger | 562 |
| Scandal | 426, 427, 562 |
| Scaramouch | 283 |
| Scarecrow the Beggar | 6 |
| Scarron, Paul | 17 Fn. 1 |
| Scarves, vanity of, in clergy | 609 |
| Scawen, Sir William | 546 Fn. 2 |
| Scheffer's Northern odes | 366, 406 |
| Scholar's egg | 58 |
| Schoolmasters | 157, 168, 313 |
| Schoolmen's case of the ass | 191 |
| Scipio | 157 |
| Scolds | 479, 482 |
| Scornful Lady, Comedy of the | 270 |
| Scott, Dr., on the Christian Life | 447 Fn. 6 |
| Scribblers | 445, 582 |
| Scudery | 37 Fn. ?3, 241 |
| Scurlock, Miss, letters to, adapted to the praise of marriage | 142 |
| Sea | 489 |
| Seasons, dream of the | 425 |
| Second sight in Scotland | 604 |
| Segrais, his threefold distinction of readers | 62 Fn. 7 |
| Self-conceit | 460 |
| Self-denial | 206, 248 |
| Self-examination | 399, 586 |
| Self-love | 17, 192, 238, 426, 588 |
| Self-murder | 231 |
| Self-tormentor of Terence | 521 |
| Semanthe, who paints well | 404 |
| Semiramis | 415 |
Sempronia
who admires the French
match-maker |
45
437 |
| Seneca | 37, 39 Fn. 1, 77 Fn. 1, 93, 569 |
| Sense | 6, 172, 259, 519 |
| Sentry, Captain | 2 Fn. 7, 34, 152, 197, 350, 517 |
| September described | 425 |
| Serle's Coffee-house | 49 Fn. 1 |
| Sermons | 633 |
| Servants | 88, 96, 107, 137, 202 |
| Settlement, Act of | 3 Fn. 5 |
| Seven | 632 |
| Severity in schools | 408 |
| Sexes | 43, 156, 400 |
| Sextant | 428 Fn. 1 |
| Sextus V., Pope | 23 |
| Shadows and realities | 5 |
| Shadwell | 35 Fn. 2 |
| Shakespeare | 49, 54, 141, 168, 419, 562 |
| Shalum and Hilpa, story of | 584 |
| Sheepishness | 484 |
| She-Machiavels | 561 |
| Sheffield, John, Duke of Buckingham | 253 Fn. 4, 462 Fn. 3 |
| Shepheard, Miss | 92 Fn. 1, 140, 163 |
| Shepherd, eminent for tossing eggs | 160 |
| Shepherd's pipe, poem in shape of a | 58 |
| Sherlock on Death | 37 Fn. 2, 289, 447 |
| She would if she could, a comedy | 51 |
| Ship in storm | 489 |
| Shoeing horns, men used as | 536 |
| Shoe-strings | 150 |
| Short face, the Spectator's | 17, 48 |
| Shovel, Sir Cloudesley, monument of | 26 Fn. 6 |
| Shows | 193, 235, 271 |
| Sickness, a thought in | 513 |
| Sidney, Sir Philip | 70, 400 |
Sight
second | 411, 472
604 |
| Sighers' Club | 30 |
| Signs of houses | 28 Fn. 2 |
Silence
the Spectator's | 514
4, 12 |
| Silk-worms, what women are | 454 |
| Similes | 160, 421, 455 |
| Simonides | 209 Fn. 1 |
| Sincerity | 103, 352 |
| Singing, verses on a lady's | 433 |
| Singularity | 576 |
| Sippet, Jack, who breaks appointments | 448 |
| Sir Martin Mar-all, Dryden's | 5 Fn. 1 |
| Skiomachia | 115 Fn. 3 |
| Slavery | 287 |
| Sleep | 586, 593, 597 |
| Sleeper, the annual | 184 |
| Slovens | 150 |
| Sly, haberdasher | 187 Fn. 1, 526, 532, 534, 545 |
| Smithfield bargain in marriage | 304 |
| Snap, Mrs., of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Snape, Dr., charity sermon by | 294 |
| Snarlers | 438 |
| Snuff | 344 Fn. 1 |
| Snuff-box | 138 |
| Society | 422 |
| Socrates | 23, 54, 67, 86, 133, 146, 183, 195, 207, 213, 239, 247, 408, 479, 486, 500, 558 |
| Soho Square | 2 Fn. 2 |
| Soldiers | 152, 544, 566 |
| Solitude | 4, 158, 264, 406, 425, 514 |
| Solomon's Song, paraphrase of part of | 388 |
| Somers, Sir John | dedication |
| Song with notes | 470 |
| Songs of Sion | 405 |
| Sophocles, Electra of | 44 |
| Sorites in logic | 239 |
| Sorrow | 95, 312, 397 |
| Soul, the | 56, 111, 116, 237, 413, 487, 600, 602 |
| Sounds | 416 |
| Southerne | 40 Fn. 2, 481 |
| Space, infinite | 564 |
| Spanish Friar, Dryden's | 267 Fn. 13 |
| Spanish Succession, War of the | 26 Fn. 5, 45 Fn. 1, 64 Fn. 2, 353 Fn. 3 |
| Sparkes, John, of Coventry | 436 Fn. 2 |
| Sparkish, Will., a modern husband | 479 |
| Sparrows for the opera | 5 |
| Spartans | 6, 307, 564 |
| Speakers, loud | 148 |
Spectator, the
his Club
himself
trade of the paper
stamp duty
Nahum Tate on the | 1 Fn. 15
2, 34
1, 4, 12, 34
46 Fn. 2, 499 Fn. 1, 533 Fn. 1
455 Fn. 1
488 |
| Speech, organs of | 231 |
| Spenser | 390, 419, 540 |
| Spies | 202, 439 |
| Spinamont on duels | 84 |
| Spirits | 12, 110, 419 |
| Spite in a beauty | 156 |
| Spleen | 53, 588 |
| Sprat, Dr. Thomas | 114 Fn. 3 |
| Spring | 393, 423 |
| Squeezing the hand | 119 |
| Squire's Coffee-house | 39 Fn. 1 |
| Squires | 529 |
| Staffordshire, Dr. Plot's Natural History of | 447 Fn. 1 |
| Stage, the | 370, 440, 446 |
Stage-coach
in a
-men |
131, 242, 513
474 |
| Staincoat Hole, at Cambridge | 397 |
| Stamp Act | 445 Fn. 1 |
| Starch, political | 305 |
| Starers | 20, 250 |
| Stars, the | 420, 565 |
| Stationers | 304, 579 |
| Statira, a pattern for women | 41 |
| Statuary | 416 |
Steele
censures a passage in his Funeral
love-letters
his paper omitted in the reprint
Cibber on his literary relation to Addison |
51
142
328 Fn. 1
546 Fn. 1 |
| Stepney, epitaphs at | 518 |
| Sternhold, Thomas | 205 Fn. 4 |
| Stint, Jack, and Will. Trap | 448 |
| Stock's Market | 462 |
| Stoics | 243, 307 |
| Stonesfield, the Roman pavement at | 358 Fn. 1 |
| Storm at sea | 489 |
| Strada | 241, 617 |
| Stratonica | 229 |
| Strife | 197 |
| Stripes for perverse wives | 479 |
| Strolling players | 48 |
| Stubbs, Rev. Philip | 147 Fn. 1 |
| Style, New and Old | 21 Fn. 1 |
| Subjects, value of, to a prince | 200 |
| Sublime in writing | 117, 152, 592, 633 |
| Sudden, Thomas, Esq., from the Infirmary | 429 |
| Sukey's adventure with Sir Roger and Will. Honeycomb | 410 |
| Syllogisms | 239 |
| Syrinx of Theocritus, the | 58 Fn. 3 |
| Summer in England | 393 |
| Sun, the | 250, 412 |
| Sunday in the country | 112 |
| Superiority | 6, 202, 219 |
| Superstition | 7, 201, 213 |
| Surgeon, Italian, advertisement of an | after No. 23 |
| Surprise | 62, 538 |
| Susanna(h)4, puppet-show of | 14 Fn. 2 |
| Swallow, Lady Catherine, of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Swearing | 233, 332, 371, 448, 531 |
| Swift | 23 Fn. 1, 50 Fn. 1, 226 Fn. 1, 265 Fn. 3, 324 Fn. 2 353 Fn. 1, 445 Fn. 1, 504 Fn. 1 |
| Swingers at Tunbridge Wells | 492 |
| Sydenham, Dr. Thomas | 25 Fn. 1 |
| Sylvester, Joshua | 58 Fn. 4 |
| Sylvia, in choice of husband, hesitates between riches and merit | 149 |
| Symmetry | 411, 632 |
| Syncopists, modern | 567 |
| Syncopius the passionate | 438 |
| Syracusan prince, the jealous | 579 |
| Tale-bearers | 19, 439 |
| Talents | 172 |
| Tartars, a conceit of the | 126 |
| Taste | 29, 140, 208, 379 Fn. 3, 409 Fn. 1, 447 |
| Tate, Nahum | 488 |
| Tattle, Letitia, her trained birds | 36 |
| Tavern Tyrants | 508 |
| Tax on eminence | 101 |
| Tears | 95 |
| Temper | 181, 424, 598 |
| Temperance | 195 |
| Templar, the | 2, 34 |
| Temple, Sir W. | 21 Fn. 4, 37 Fn. 2, 195 Fn. 4 |
| Ten | 221 |
| Terence | 170, 502 |
| Terror | 418 |
| Terset, Harry, and his lady, indolent | 100 |
| Tetractys | 221 Fn. 4 |
| Thales quoted | 594 |
| Thames described | 454 |
| That, remonstrance of | 80 |
| Theatres | 36, 40, 42, 44, 51, 65, 141 Fn. 2, 602 |
| Themista, a confidant | 118 |
| Themistocles | 311 |
| Theocritus | 58 Fn. 3 |
| Theodosius and Constantia | 164 |
| Theognis quoted | 464 |
| Theon, Pindar's saying of | 467 |
| Theory of the Earth, Burnet's, quoted | 146 |
| Thersites | 17 Fn. 2 |
| Thimbleton, Ralph, his calamity | 432 |
| Thinking aloud | 211 |
| Thirst | 22 |
| Thornhill, Mr., his duel | 84 Fn. 3 |
| Thrash, Will, and his wife, insipid | 522 |
| Throne of God | 580, 600 |
| Thunder, stage | 36, 44 |
| Tickell | 523 Fn. 1, 532 |
| Tillotson | 103 Fn. 1, 106 Fn. 4, 293, 352, 447, 600 |
| Tilt Yard, Whitehall | 109 Fn. 1 |
| Time | 83, 93, 316 |
| Titian | 292 |
| Title-page, Antony, stationer | 304 |
| Titles | 204, 219, 480 |
| Tofts, Mrs. | 18 Fn. 1, 22 Fn. 3 |
| Toleration, Act of | 3 Fn. 4 |
| Tom Touchy | 122 |
| Tom Trusty | 479 |
| Tom the Tyrant, at the coffee-house | 49 |
| Tombs in Westminster Abbey | 26 |
| Tomtits in the Opera | 5 |
| Tonson, Jacob | 9 Fn. 1 |
| Tories | 50, 58 Fn. 4 |
| Torture | 239, 418 |
| Townly, Frank, letter of | 560 |
| Trade | 2, 69, 109, 283, 443 |
| Tragedy | 39, 40, 42, 44, 279 Fn. 1 |
| Tranquillity | 196, 425 |
| Transmigration of souls | 211, 343, 408 |
| Trap, Mr., letter to Mr. Stint | 448 |
| Travel | 45, 93, 364, 474 |
| Trees | 414, 589 |
| Triflers | 432 |
| Trojans, modern | 239, 245 |
| Trophonius, cave of | 598, 599 |
| Trott, Nell, waiter on the Ugly Club | 17 |
| Truby's, Widow, water | 329 |
| Truepenny, Jack, the good-natured | 82 |
| Trunkmaker, at the play | 235 |
| Trust in God | 441 |
| Trusty, Tom, a servant, account of | 96 |
| Truth | 63, 103, 352, 507 |
| Tryphiodorus | 59 |
| Tumbling | 141 |
| Tunbridge Wells | 492, 496 |
| Tuperty, Mrs., a flirt | 202 |
| Turner, Sir William | 509 |
| Tyrants | 508 |
| Vainlove family, the | 454 |
Valentine, Basil
Currus Triumphalis
a legend of |
94 Fn. 1
426 Fn. 1 |
| Valerio resolves to be a poet | 404 |
| Valetudinarians | 100, 143, 395 |
| Vanini | 389 Fn. 4 |
| Vanity | 16, 255, 380, 460, 514 |
| Vapours in women | 115 |
| Variety | 408, 600 |
| Varillas, the cheerful | 100 |
| Venice Preserved, Otway's | 39 |
| Venus | 127, 417, 425 |
| Vernal delight | 393 |
| Versifying, artificial | 220 Fn. 4 |
| Vertot, the Abbé | 349 Fn. 2 |
| Ugly Club | 17, 32, 48, 52, 78 |
| Vice | 137, 151, 243, 624 |
| Victor, a genteel politician | 150 |
| Villacerse, death of Madame de | 368 |
| Villars, Abbé de | 379 Fn. 4 |
| Vinci, Leonardo da | 554 |
| Viner, Sir Robert, familiar with Charles II. | 462 Fn. 2 |
| Virgil | 70, 90, 273, 351, 404, 417, 514, 610 |
| Virtue | 93, 104, 219, 240, 243, 248, 266, 394, 399, 520 |
| Virtuoso, a female | 242 |
Vision
of Calamities
of Credit
of Fame
Hearts
Mirza
Misery
Mountain of the Muses
Painters
Scales
Seasons
Vanity
Wit, true and false |
558, 559
3
81
563
159
604
514
83
463
425
460
63 |
| Visits | 24, 45 Fn. 2, 208 |
| Understanding | 6, 420, 438 |
| Uniformity, Act of | 3 Fn. 3 |
| Universe, the | 420 |
| Unlearned, proposal for publishing works of the | 457 |
| Vocifer, how he passed for a fine gentleman | 75 |
| Volumes, dignity of | 124 |
| Voluntaries at church | 630 |
| Votaries | 79 |
| Vowels | 135 |
| Uranius has composure of soul | 143 |
| Usurpers, tavern | 508 |
| Utrecht, the Peace Negotiation at | 481 Fn. 3 |
| Vulcan's dogs | 579 |
| Waddle, Lady, of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Wagers | 145, 521 Fn. 1 |
| Wake, Colonel | 313 Fn. 3 |
| Wakes, country | 161 |
| Wall of China | 415 |
| Waller | 148, 158, 224 |
| Wall's Infant Baptism | 92 Fn. 2 |
| Want, fear of | 114 |
| War, the, in Queen Anne's reign | 26 Fn. 5, 43 Fns. 1-5, 45 Fn. 1, 64 Fn. 2, 353 Fn. 3, 521 Fn. 1 |
| War news, greed for | 452 |
| Wasps in public | 300 |
| Watchman and goose | 376 |
| Watts, Dr. Isaac | 461 Fn. 1 |
| Wax-work, Mrs. Salmon's, fifteen images burnt on Queen Elizabeth's birthday | 262 Fn. 3 |
| Way of the World, Congreve's | 204 |
| Wealth | 469, 506, 601 |
| Weaver on dancing | 466 |
| Wedlock | 525 |
| Weed, Ephraim | 450 |
| Weights showing true values | 463 |
| Wenham, Jane, the last condemned witch | 117 Fn. 4 |
| West Enborne in Berkshire, custom of | 614 |
| Westminster Abbey | 26, 329 |
| Westminster boy and colours taken at Blenheim | 139 |
| Wharton, Thomas, Earl of | dedication |
| Whichenovre in Staffordshire, custom of | 607 |
| Whigs | 50, 58 Fn. 4 |
| Whims | 371 |
| Whining | 630 |
| Whisperers | 148, 168, 457 |
| Whispering place of Dionysius | 439 |
| Whistling match | 179 |
| White, Moll, a witch | 117, 268 |
| Whittington and his Cat v. Rinaldo and Armida | 14 Fn. 2, 31 Fn. 5 |
| Who and Which, petition of | 78 |
| Widow, the perverse, Sir Roger's love for | 113, 115, 118 |
Widows
male | 311, 561, 573, 606, 614, 623
520 |
| Wife | 199, 479, 490, 525 |
Wigs
the lawyer's | 319, 631 Fn. 1
407 |
| Wildfire, widow, of the Widows' Club | 561 |
| Wilks the comedian | 370 |
| William III. | 468 Fn. 4, 516 |
| William, Sir Roger's huntsman | 118 |
| Willow Kate, Sir Roger's character of | 118 |
| Wills' Coffee-house | 1 Fn. 6 |
| Wimble, Will | 108, 109, 126, 131, 268 |
| Wine | 140, 147, 181, 362 Fn. 5 |
| Wings, verse in the form of | 58 |
| Winstanley's Water Theatre | 168 |
| Winter Gardens | 477 |
| Winter piece by Ambrose Philips | 393 |
| Wisdom | 225 |
| Wit, Addison's Essays on | 58-63, 6, 23, 35 Fn. 2, 38, 140, 151, 169, 179, 220, 270, 416, 422, 514, 522 |
| Wits | 404, 509 |
| Witchcraft | 61, 117 Fn. 4, 268, 419 |
| Wolsey | 624 |
| Woman's Man, the | 57, 156 |
Women
a republic of | 4, 10, 15, 33, 53, 57, 79, 81, 92, 95, 98, 104, 128, 154, 155, 156, 158, 159, 182, 208, 209, 243, 247, 252, 261, 265, 274, 320, 342, 343, 365, 390, 433, 486, 506, 510, 511, 606, 625
416 |
| Words | 373, 416 |
| Works of art | 414 |
| World, the | 27, 111, 387, 519 |
| Worriers | 304 |
| Wortley, Hon. E. | 71 Fn. 2 |
| Writers | 166, 379, 409, 417, 422, 568, 582 |
| Wycherley's Plain Dealer | 354 Fn. 2 |
| Yaratilda and Maraton, story of | 56 |
| Yarico, Inkle and, story of | 11 |
| Yawning, a Christmas game | 179 |
| Year, the, described | 425 |
| Youth | 153 |
The references without links are those for which I could not find the information mentioned. Possibly these are Spectators which originally had advertisements, but don't in this collection. html Ed.
Spelt "Hayn" here (the index) but "Haym" in the text of Spectator No. 258, to which the index entry refers. html Ed.
I could not find any reference to Scudery in No. 37, nor in any of the numbers in Volume 2. He is mentioned in Volume 3 (No. 241) as the author of some romances, so it is possible that he is the unnamed author of one or more of the titles listed in the Lady Leonora's Library in No. 37. html Ed.
Spelt in the
Spectator
No. 14, "Susanna", but in the Index, "Susannah". html Ed.
end of the Spectator series
![[Illustration: Richard Steele]](images/steele.jpg)
![[Illustration: Richard Steele]](images/steele.jpg)
![[Illustration]](images/addison.gif)

or Love-Feasts; and were first established in England by Pope Gregory the Great, who in an Epistle to Melitus the Abbot gave Order that they should be kept in Sheds or Arbories made up with Branches and Boughs of Trees round the Church.


shocking. Then he adds that our pity is excited by undeserved misfortune, and our terror by some resemblance between the sufferer and ourselves.'
"eats" says
"banquets on."'



