Title: Modern Spanish Lyrics
Editor: E. C. Hills
S. Griswold Morley
Release date: June 14, 2005 [eBook #16059]
Most recently updated: December 11, 2020
Language: English, Spanish
Credits: Produced by Juliet Sutherland, Miranda van de Heijning,
Renald Levesque and the Online Distributed Proofreading
Team.
The present volume aims to furnish American students of Spanish with a convenient selection of the Castilian lyrics best adapted to class reading. It was the intention of the editors to include no poem which did not possess distinct literary value. On the other hand, some of the most famous Spanish lyrics do not seem apt to awaken the interest of the average student: it is for this reason that scholars will miss the names of certain eminent poets of the siglo de oro. The nineteenth century, hardly inferior in merit and nearer to present-day readers in thought and language, is much more fully represented. No apology is needed for the inclusion of poems by Spanish-American writers, for they will bear comparison both in style and thought with the best work from the mother Peninsula.
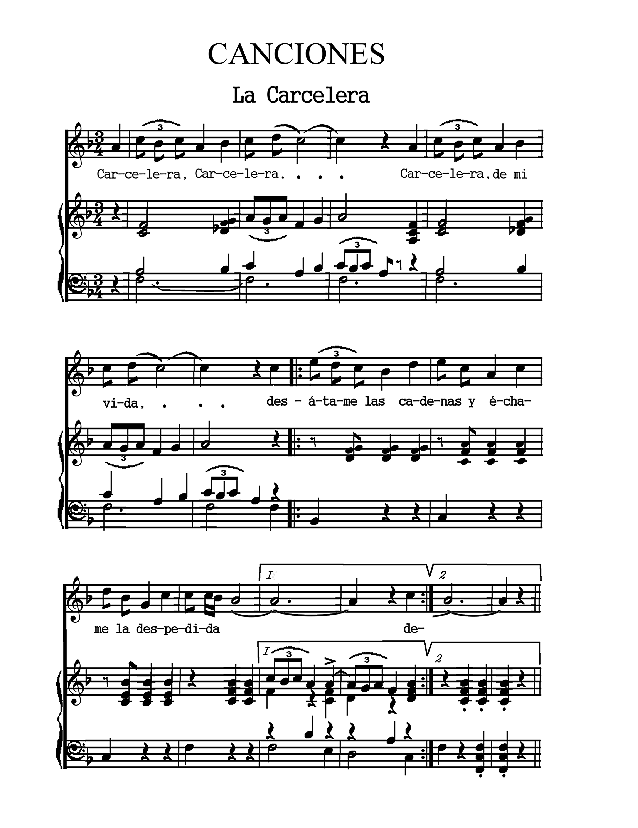
The Spanish poems are presented chronologically, according to the dates of their authors. The Spanish-American poems are arranged according to countries and chronologically within those divisions. Omissions are indicated by rows of dots and are due in all cases to the necessity of bringing the material within the limits of a small volume. Three poems (the Fiesta de toros of Moratín, the Castellano leal of Rivas and the Leyenda of Zorrilla) are more narrative than lyric. The romances iv selected are the most lyrical of their kind. A few songs have been added to illustrate the relation of poetry to music.
The editors have been constantly in consultation in all parts of the work, but the preparation of the Prosody, the Notes (including articles on Spanish-American literature) and the part of the Introduction dealing with the nineteenth century, was undertaken by Mr. Hills, while Mr. Morley had in charge the Introduction prior to 1800, and the Vocabulary. Aid has been received from many sources. Special thanks are due to Professor J.D.M. Ford and Dr. A.F. Whittem of Harvard University, Don Ricardo Palma of Peru, Don Rubén Darío of Nicaragua, Don Rufino Blanco-Fombona of Venezuela, Professor Carlos Bransby of the University of California, and Dr. Alfred Coester of Brooklyn, N.Y.
E.C.H.
S.G.M.
CONTENTS
I. Spanish Lyric Poetry to 1800
II. Spanish Lyric Poetry of the Nineteenth Century
III. Spanish Versification
Abenámar
Fonte-frida
El conde Arnaldos
La constancia
El amante desdichado
El prisionero
VINCENTE (GIL) (1470-1540?)
Canción
TERESA DE JESÚS (SANTA) (1515-1582)
Letrilla (que llevaba por registro en su breviario)
LEÓN (FRAY LUIS DE) (1527-1591)
Vida retirada
Á Cristo crucificado
VEGA (LOPE DE) (1562-1635)
Canción de la Virgen
Mañana
QUEVEDO (FRANCISCO DE) (1580-1645)
Epístola satírica al conde de Olivares
Letrilla satírica
VILLEGAS (ESTEBAN MANUEL DE) (1589-1669)
Cantilena: De un pajarillo
CALDERÓN DE LA BARCA (PEDRO) (1600-1681)
"Estas que fueron pompa y alegría,"
Consejo de Crespo á su hijo
GONZÁLEZ (FRAY DIEGO) (1733-1794)
El murciélago alevoso
viMORATÍN (NICOLÁS F. DE) (1737-1780)
Fiesta de toros en Madrid
JOVELLANOS (GASPAR M. DE) (1744-1811)
Á Arnesto
MELÉNDEZ VALDÉS (JUAN) (1754-1817)
Rosana en los fuegos
QUINTANA (MANUEL JOSÉ) (1772-1857)
Oda á España, después de la revolución de marzo
SOLÍS (DIONISIO) (1774-1834)
La pregunta de la niña
GALLEGO (JUAN NICASIO) (1777-1853)
El Dos de Mayo
MARTÍNEZ DE LA ROSA (FRANCISCO) (1787-1862)
El nido
RIVAS (DUQUE DE) (1791-1865)
Un castellano leal
AROLAS (PADRE JUAN) (1805-1849)
"Sé más feliz que yo"
ESPRONCEDA (JOSÉ DE) (1808-1842)
Canción del pirata
Á la patria
ZORRILLA (JOSÉ) (1817-1893)
Oriental
Indecisión
La fuente
Á buen juez, mejor testigo
TRUEBA (ANTONIO DE) (1821-1889)
Cantos de pájaro
La perejilera
SELGAS (JOSÉ) (1821-1882)
La modestia
ALARCÓN (PEDRO ANTONIO DE) (1833-1891)
El Mont-Blanc
El secreto
BÉCQUER (GUSTAVO A.) (1836-1870)
Rimas: II
VII
LIII
LXXIII
viiQUEROL (VINCENTE WENCESLAO) (1836-1889)
En Noche-Buena
CAMPOAMOR (RAMÓN DE) (1817-1901)
Proximidad del bien
¡Quién supiera escribir!
El mayor castigo
NÚÑEZ DE ARCE (GASPAR) (1834-1903)
¡Excelsior!
Tristezas
¡Sursum Corda!
PALACIO (MANUEL DEL) (1832-1895)
Amor oculto
BARTRINA (JOAQUÍN MARÍA) (1850-1880)
Arabescos
REINA (MANUEL) (1860-)
La poesía
ECHEVERRÍA (O. ESTEBAN) (1805-1851)
Canción de Elvira
ANDRADE (OLEGARIO VICTOR) (1838-1882)
Atlántida
Prometeo
OBLIGADO (RAFAEL) (1852-)
En la ribera
ORTIZ (JOSÉ JOAQUÍN) (1814-1892)
Colombia y España
CARO (JOSÉ EUSEBIO) (1817-1853)
El ciprés
MARROQUÍN (JOSÉ MANUEL) (1827-)
Los cazadores y la perrilla
CARO (MIGUEL ANTONIO) (1843-1909)
Vuelta á la patria
viiiARRIETA (DIÓGENES A.) (1848-)
En la tumba de mi hijo
GUTIÉRREZ PONCE (IGNACIO) (1850-)
Dolora
GARAVITO A. (JOSÉ MARÍA) (1860-)
Volveré mañana
HEREDIA (JOSÉ MARÍA) (1803-1839)
En el teocalli de Cholula
El Niágara
"PLÁCIDO" (GABRIEL DE LA CONCEPCIÓN VALDÉS) (1809-1844)
Plegaria á Dios
AVELLANEDA (GERTRUDIS GÓMEZ DE) (1814-1873)
Á Wáshington
Al partir
OLMEDO (JOSÉ JOAQUÍN) (1780-1847)
La victoria de Junín
PESADO (JOSÉ JOAQUÍN DE) (1801-1861)
Serenata
CALDERÓN (FERNANDO) (1809-1845)
La rosa marchita
ACUÑA (MANUEL) (1849-1873)
Nocturno: Á Rosario
PEZA (JUAN DE DIOS) (1852-1910)
Reír llorando
Fusiles y muñecas
BELLO (ANDRÉS) (1781-1865)
Á la victoria de Bailén
La agricultura de la zona tórrida
PÉREZ BONALDE (JUAN ANTONIO) (1846-1892)
Vuelta á la patria
MARTÍN DE LA GUARDIA (HERACLIO) (1830-)
Ultima ilusión
VOCABULARY[a]
[Transcriber's note a: The vocabulary section has
not been submitted for transcription.}
It has been observed that epic poetry, which is collective and objective in its nature, always reaches its full development in a nation sooner than lyric poetry, which is individual and subjective. Such is certainly the case in Spain. Numerous popular epics of much merit existed there in the Middle Ages.1 Of a popular lyric there are few traces in the same period; and the Castilian lyric as an art-form reached its height in the sixteenth, and again in the nineteenth, centuries. It is necessary always to bear in mind the distinction between the mysterious product called popular poetry, which is continually being created but seldom finds its way into the annals of literature, and artistic poetry. The chronicler of the Spanish lyric is concerned with the latter almost exclusively, though he will have occasion to mention the former not infrequently as the basis of some of the best artificial creations.
Footnote 1: (return) The popular epics were written in assonating lines of variable length. There were also numerous monkish narrative poems (mester de clereçia) in stanzas of four Alexandrine lines each, all riming (cuaderna vía).
If one were to enumerate ab origine the lyric productions of the Iberian Peninsula he might begin with the vague references of Strabo to the songs of its primitive inhabitants,xii and then pass on to Latin poets of Spanish birth, such as Seneca, Lucan and Martial. The later Spaniards who wrote Christian poetry in Latin, as Juvencus and Prudentius, might then be considered. But in order not to embrace many diverse subjects foreign to the contents of this collection, we must confine our inquiry to lyric production in the language of Castile, which became the dominating tongue of the Kingdom of Spain.
Such a restriction excludes, of course, the Arabic lyric, a highly artificial poetry produced abundantly by the Moors during their occupation of the south of Spain; it excludes also the philosophical and religious poetry of the Spanish Jews, by no means despicable in thought or form. Catalan poetry, once written in the Provençal manner and of late happily revived, also lies outside our field.
Even the Galician poetry, which flourished so freely under the external stimulus of the Provençal troubadours, can be included only with regard to its influence upon Castilian. The Galician dialect, spoken in the northwest corner of the Peninsula, developed earlier than the Castilian of the central region, and it was adopted by poets in other parts for lyric verse. Alfonso X of Castile (reigned 1252-1284) could write prose in Castilian, but he must needs employ Galician for his Cantigas de Santa María. The Portuguese nobles, with King Diniz (reigned 1279-1325) at their head, filled the idle hours of their bloody and passionate lives by composing strangely abstract, conventional poems of love and religion in the manner of the Provençal canso, dansa, balada and pastorela, which had had such a luxuriant growth in Southern France in the eleventh and twelfth centuries. A highly elaborated metrical system mainlyxiii distinguishes these writers, but some of their work catches a pleasing lilt which is supposed to represent the imitation of songs of the people. The popular element in the Galician productions is slight, but it was to bear important fruit later, for its spirit is that of the serranas of Ruiz and Santillana, and of villancicos and eclogues in the sixteenth century.
It was probably in the neighborhood of 1350 that lyrics began to be written in Castilian by the cultured classes of Leon and Castile, who had previously thought Galician the only proper tongue for that use, but the influence of the Galician school persisted long after. The first real lyric in Castilian is its offspring. This is the anonymous Razón feyta d'amor or Aventura amorosa (probably thirteenth century), a dainty story of the meeting of two lovers. It is apparently an isolated example, ahead of its time, unless, as is the case with the Castilian epic, more poems are lost than extant. The often quoted Cántica de la Virgen of Gonzalo de Berceo (first half of thirteenth century), with its popular refrain Eya velar, is an oasis in the long religious epics of the amiable monk of S. Millán de la Cogolla. One must pass into the succeeding century to find the next examples of the true lyric. Juan RUIZ, the mischievous Archpriest of Hita (flourished ca. 1350), possessed a genius sufficiently keen and human to infuse a personal vigor into stale forms. In his Libro de buen amor he incorporated lyrics both sacred and profane, Loores de Santa María and Cánticas de serrana, plainly in the Galician manner and of complex metrical structure. The serranas are particularly free and unconventional. The Chancellor Pero LÓPEZ DE AYALA (1332-1407), wise statesman, brilliant historian and xiv trenchant satirist, wrote religious songs in the same style and still more intricate in versification. They are included in the didactic poem usually called El rimado de palacio.
Poetry flourished in and about the courts of the monarchs of the Trastamara family; and what may be supposed a representative collection of the work done in the reigns of Henry II (1369-1379), John I (1379-1388), Henry III (1388-1406) and the minority of John II (1406-1454), is preserved for us in the Cancionero which Juan Alfonso de Baena compiled and presented to the last-named king. Two schools of versifiers are to be distinguished in it. The older men, such as Villasandino, Sánchez de Talavera, Macías, Jerena, Juan Rodríguez del Padrón and Baena himself, continued the artificial Galician tradition, now run to seed. In others appears the imitation of Italian models which was to supplant the ancient fashion. Francisco Imperial, a worshiper of Dante, and other Andalusians such as Ruy Páez de Ribera, Pero González de Uceda and Ferrán Manuel de Lando, strove to introduce Italian meters and ideas. They first employed the Italian hendecasyllable, although it did not become acclimated till the days of Boscán. They likewise cultivated the metro de arte mayor, which later became so prominent (see below, p. lxxv ff.). But the interest of the poets of the Cancionero de Baena is mainly historical. In spite of many an illuminating side-light on manners, of political invective and an occasional glint of imagination, the amorous platitudes and wire-drawn love-contests of the Galician school, the stiff allegories of the Italianates leave us cold. It was a transition period and the most talented were unable to master the undeveloped poetic language.xv
The same may be said, in general, of the whole fifteenth century. Although the language became greatly clarified toward 1500 it was not yet ready for masterly original work in verse. Invaded by a flood of Latinisms, springing from a novel and undigested humanism, encumbered still with archaic words and set phrases left over from the Galicians, it required purification at the hands of the real poets and scholars of the sixteenth century. The poetry of the fifteenth is inferior to the best prose of the same epoch; it is not old enough to be quaint and not modern enough to meet a present-day reader upon equal terms.
These remarks apply only to artistic poetry. Popular poetry,—that which was exemplified in the Middle Ages by the great epics of the Cid, the Infantes de Lara and other heroes, and in songs whose existence can rather be inferred than proved,—was never better. It produced the lyrico-epic romances (see Notes, p. 253), which, as far as one may judge from their diction and from contemporary testimony, received their final form at about this time, though in many cases of older origin. It produced charming little songs which some of the later court poets admired sufficiently to gloss. But the cultured writers, just admitted to the splendid cultivated garden of Latin literature, despised these simple wayside flowers and did not care to preserve them for posterity.
The artistic poetry of the fifteenth century falls naturally into three classes, corresponding to three currents of influence; and all three frequently appear in the work of one man, not blended, but distinct. One is the conventional love-poem of the Galician school, seldom containing a fresh or personal note. Another is the stilted allegory with xvi erotic or historical content, for whose many sins Dante was chiefly responsible, though Petrarch, he of the Triunfi, and Boccaccio cannot escape some blame. Third is a vein of highly moral reflections upon the vanity of life and certainty of death, sometimes running to political satire. Its roots may be found in the Book of Job, in Seneca and, nearer at hand, in the Proverbios morales of the Jew Sem Tob (ca. 1350), in the Rimado de Palacio of Ayala, and in a few poets of the Cancionero de Baena.
John II was a dilettante who left the government of the kingdom to his favorite, Álvaro de Luna. He gained more fame in the world of letters than many better kings by fostering the study of literature and gathering about him a circle of "court poets" nearly all of noble birth. Only two names among them all imperatively require mention. Iñigo LÓPEZ DE MENDOZA, MARQUIS OF SANTILLANA (1398-1458) was the finest type of grand seigneur, protector of letters, student, warrior, poet and politician. He wrote verse in all three of the manners just named, but he will certainly be longest remembered for his serranillas, the fine flower of the Provençal-Galician tradition, in which the poet describes his meeting with a country lass. Santillana combined the freshest local setting with perfection of form and left nothing more to be desired in that genre. He also wrote the first sonnets in Castilian, but they are interesting only as an experiment, and had no followers. Juan de MENA (1411-1456) was purely a literary man, without other distinction of birth or accomplishment. His work is mainly after the Italian model. The Laberinto de fortuna, by which he is best known, is a dull allegory with much of Dante's apparatus. There are historical passages where xvii the poet's patriotism leads him to a certain rhetorical height, but his good intentions are weighed down by three millstones: slavish imitation, the monotonous arte mayor stanza and the deadly earnestness of his temperament. He enjoyed great renown and authority for many decades.
Two anonymous poems of about the same time deserve mention. The Danza de la muerte, the Castilian representative of a type which appeared all over Europe, shows death summoning mortals from all stations of life with ghastly glee. The Coplas de Mingo Revulgo, promulgated during the reign of Henry IV (1454-1474), are a political satire in dialogue form, and exhibit for the first time the peculiar peasant dialect that later became a convention of the pastoral eclogues and also of the country scenes in the great drama.
The second half of the century continues the same tendencies with a notable development in the fluidity of the language and an increasing interest in popular poetry. Gómez Manrique (d. 1491?) was another warrior of a literary turn whose best verses are of a severely moral nature. His nephew JORGE MANRIQUE (1440-1478) wrote a single poem of the highest merit; his scanty other works are forgotten. The Coplas por la muerte de su padre, beautifully translated by Longfellow, contain some laments for the writer's personal loss, but more general reflections upon the instability of worldly glory. It is not to be thought that this famous poem is in any way original in idea; the theme had already been exploited to satiety, but Manrique gave it a superlative perfection of form and a contemporary application which left no room for improvement.
There were numerous more or less successful love-poets xviii of the conventional type writing in octosyllabics and the inevitable imitators of Dante with their unreadable allegories in arte mayor. The repository for the short poems of these writers is the Cancionero general of Hernando de Castillo (1511). It was reprinted many times throughout the sixteenth century. Among the writers represented in it one should distinguish, however, Rodrigo de Cota. His dramatic Diálogo entre el amor y un viejo has real charm, and has saved his name from the oblivion to which most of his fellows have justly been consigned. The bishop Ambrosio Montesino (Cancionero, 1508) was a fervent religious poet and the precursor of the mystics of fifty years later.
The political condition of Spain improved immensely in the reign of Ferdinand and Isabella (1479-1516) and the country entered upon a period of internal homogeneity and tranquility which might be expected to foster artistic production. Such was the case; but literature was not the first of the arts to reach a highly refined state. The first half of the sixteenth century is a period of humanistic study, and the poetical works coming from it were still tentative. JUAN DEL ENCINA (1469-1533?) is important in the history of the drama, for his églogas, representaciones and autos are practically the first Spanish dramas not anonymous. As a lyric poet Encina excels in the light pastoral; he was a musician as well as a poet, and his bucolic villancicos and glosas in stanzas of six-and eight-syllable lines are daintily written and express genuine love of nature. The Portuguese GIL VICENTE (1470-1540?) was a follower of Encina at first, but a much bigger man. Like most of his compatriots of the sixteenth century he wrote in both Portuguese and Castilian, though better in the former tongue. He was close to the xix people in his thinking and writing and some of the songs contained in his plays reproduce the truest popular savor.
The intimate connection between Spain and Italy during the period when the armies of the Emperor Charles V (Charles I of Spain: reigned 1516-1555) were overrunning the latter country gave a new stimulus to the imitation of Italian meters and poets which we have seen existed in a premature state since the reign of John II. The man who first achieved real success in the hendecasyllable, combined in sonnets, octaves, terza rima and blank verse, was Juan BOSCÁN ALMOGAVER (1490?-1542), a Catalan of wealth and culture. Boscán was handicapped by writing in a tongue not native to him and by the constant holding of foreign models before his eyes, and he was not a man of genius; yet his verse kept to a loftier ideal than had appeared for a long time and his effort to lift Castilian poetry from the slough of convention into which it had fallen was successful. During the rest of the century the impulse given by Boscán divided Spanish lyrists into two opposing hosts, the Italianates and those who clung to the native meters (stanzas of short, chiefly octosyllabic, lines, for the arte mayor had sunk by its own weight).
The first and greatest of Boscán's disciples was his close friend GARCILASO DE LA VEGA (1503-1536) who far surpassed his master. He was a scion of a most noble family, a favorite of the emperor, and his adventurous career, passed mostly in Italy, ended in a soldier's death. His poems, however (églogas, canciones, sonnets, etc.), take us from real life into the sentimental world of the Arcadian pastoral. Shepherds discourse of their unrequited loves and mourn amid surroundings of an idealized Nature.xx
The pure diction, the Vergilian flavor, the classic finish of these poems made them favorites in Spain from the first, and their author has always been regarded as a master.
With Garcilaso begins the golden age of Spanish poetry and of Spanish literature in general, which may be said to close in 1681 with the death of Calderón. It was a period of external greatness, of conquest both in Europe and beyond the Atlantic, but it contained the germs of future decay. The strength of the nation was exhausted in futile warfare, and virile thought was stifled by the Inquisition, supported by the monarchs. Hence the luxuriant literature of the time runs in the channels farthest from underlying social problems; philosophy and political satire are absent, and the romantic drama, novel and lyric flourish. But in all external qualities the poetry written during this period has never been equaled in Spain. Its polish, color and choiceness of language have been the admiration and model of later Castilian poets.
The superficial nature of this literature is exhibited in the controversy excited by the efforts of Boscán and Garcilaso to substitute Italian forms for the older Spanish ones. The discussion dealt with externals; with meters, not ideas. Both schools delighted in the airy nothings of the conventional love lyric, and it matters little at this distance whether they were cast in lines of eleven or eight syllables.
The contest was warm at the time, however. Sá de Miranda (1495-1558), the chief exponent of the Italian school in Portugal, wrote effectively also in Castilian. Gutierre de Cetina (1518?-1572?) and Fernando de Acuña (1500?-1580?) are two others who supported the new measures. One whose example had more influence is xxi Diego Hurtado de Mendoza (1503-1575), a famous diplomat, humanist and historian. He entertained his idle moments with verse, writing cleverly in the old style but turning also toward the new. His sanction for the latter seems to have proved decisive.
Cristóbal de CASTILLEJO (1490-1556) was the chief defender of the native Spanish forms. He employed them himself in light verse with cleverness, clearness and finish, and also attacked the innovators with all the resources of a caustic wit. In this patriotic task he was for a time aided by an organist of the cathedral at Granada, Gregorio Silvestre (1520-1569), of Portuguese birth. Silvestre, however, who is noted for the delicacy of his poems in whatever style, was later attracted by the popularity of the Italian meters and adopted them.
This literary squabble ended in the most natural way, namely, in the co-existence of both manners in peace and harmony. Italian forms were definitively naturalized in Spain, where they have maintained their place ever since. Subsequent poets wrote in either style or both as they felt moved, and no one reproached them. Such was the habit of Lope de Vega, Góngora, Quevedo and the other great writers of the seventeenth century.
A Sevillan Italianate was Fernando de HERRERA (1534?-1597), admirer and annotator of Garcilaso. Although an ecclesiastic, his poetic genius was more virile than that of his soldier master. He wrote Petrarchian sonnets to his platonic lady; but his martial, patriotic spirit appears in his canciones, especially in those on the battle of Lepanto and on the expedition of D. Sebastian of Portugal in Africa. In these stirring odes Herrera touches a sonorous, grandiloquent xxii chord which rouses the reader's enthusiasm and places the writer in the first rank of Spanish lyrists. He is noteworthy also in that he made an attempt to create a poetic language by the rejection of vulgar words and the coinage of new ones. Others, notably Juan de Mena, had attempted it before, and Góngora afterward carried it to much greater lengths; but the idea never succeeded in Castilian to an extent nearly so great as it did in France, for example; and to-day the best poetical diction does not differ greatly from good conversational language.
Beside Herrera stands a totally different spirit, the Salamancan monk Luis DE LEÓN (1527-1591). The deep religious feeling which is one strong trait of Spanish character has its representatives in Castilian literature from Berceo down, but León was the first to give it fine artistic expression. The mystic sensation of oneness with the divine, of aspiration to heavenly joys, breathes in all his writings. He was also a devoted student of the classics, and his poems (for which he cared nothing and which were not published till 1631) show Latin rather than Italian influence. There is nothing in literature more pure, more serene, more direct or more polished than La vida del campo, Noche serena and others of his compositions.
The other great mystics cared less for literature, either as a study or an accomplishment. The poems of Saint Theresa (1515-1582) are few and mostly mediocre. San Juan de la Cruz, the Ecstatic Doctor (1542-1591), wrote the most exalted spiritual poems in the language; like all the mystics, he was strongly attracted by the Song of Songs which was paraphrased by Pedro Malón de Chaide (1530-1596?). It is curious to note that the stanza adopted in the great xxiii mystical lyrics is one invented by Garcilaso and used in his amatory fifth Canción. It has the rime-scheme of the Spanish quintilla, but the lines are the Italian eleven-and seven-syllable (cf. pp. 9-12). Religious poems in more popular forms are found in the Romancero espiritual (1612) of José de Valdivielso, and in Lope de Vega's Rimas sacras (1614) and Romancero espiritual (1622).
There were numerous secular disciples of Garcilaso at about the same period. The names most deserving mention are those of Francisco de la Torre (d. 1594?), Luis Barahona de Soto (1535?-1595) and Francisco de Figueroa (1536?-1620), all of whom wrote creditably and sometimes with distinction in the Italian forms. Luis de Camoens (1524?-1580), author of the great Portuguese epic Os Lusiadas, employed Castilian in many verses with happy result.
These figures lead to the threshold of the seventeenth century which opened with a tremendous literary output in many lines. Cervantes was writing his various novels; the romance of roguery took on new life with Guzmán de Alfarache (1599); the drama, which had been developing rather slowly and spasmodically, burst suddenly into full flower with Lope de Vega and his innumerable followers. The old meter of the romance was adopted as a favorite form by all sorts and conditions of poets and was turned from its primitive epic simplicity to the utmost variety of subjects, descriptive, lyric and satiric.
From out this flood of production—for every dramatist was in a measure a lyric poet, and dramatists were legion—we can select for consideration only the men most prominent as lyrists. First in the impulse which he gave to literature for more than a century following stands Luis de ARGOTE Y xxiv GÓNGORA (1561-1627), a Cordovan who chose to be known by his mother's name. His life was mainly that of a disappointed place-hunter. His abrupt change of literary manner has made some say that there were in him two poets, Góngora the Good and Góngora the Bad. He began by writing odes in the manner of Herrera and romances and villancicos which are among the clearest and best. They did not bring their author fame, however, and he seems deliberately to have adopted the involved metaphoric style to which Marini gave his name in Italy. Góngora is merely the Spanish representative of the movement, which also produced Euphuism in England and préciosité in France. But he surpassed all previous writers in the extreme to which he carried the method, and his Soledades and Polifemo are simply unintelligible for the inversions and strained metaphors with which they are overloaded.
His influence was enormous. Gongorism, or culteranismo, as it was called at the time, swept the minor poets with it, and even those who fought the movement most vigorously, like Lope and Quevedo, were not wholly free from the contagion. The second generation of dramatists was strongly affected. Yet there are few lyric poets worth mentioning among Góngora's disciples for the reason that such a pernicious system meant certain ruin to those who lacked the master's talent. The most important names are the Count of Villamediana (1580-1622), a satirist whose sharp tongue caused his assassination, and Paravicino y Arteaga (1580-1633), a court preacher.
Obviously, such an innovation could not pass without opposition from clear-sighted men. LOPE DE VEGA (1562-1635) attacked it whenever opportunity offered, and his xxv verse seldom shows signs of corruption. It is impossible to consider the master-dramatist at length here. He wrote over 300 sonnets, many excellent eclogues, epistles, and, in more popular styles, glosses, letrillas, villancicos, romances, etc. Lope more than any other poet of his time kept his ear close to the people, and his light poems are full of the delicious breath of the country.
The other principal opponent of Gongorism was Francisco GÓMEZ DE QUEVEDO Y VILLEGAS (1580-1645), whose wit and independence made him formidable. In 1631 he published the poems of Luis de León and Francisco de la Torre as a protest against the baleful mannerism in vogue. But he himself adopted a hardly less disagreeable style, called conceptism, which is supposed to have been invented by Alonso de Ledesma (1552-1623). It consists in a strained search for unusual thoughts which entails forced paradoxes, antitheses and epigrams. This system, combined with local allusions, double meanings and current slang, in which Quevedo delighted, makes his poems often extremely difficult of comprehension. His romances de jaques, written in thieves' jargon, are famous in Spain. Quevedo wrote too much and carelessly and tried to cover too many fields, but at his best his caustic wit and fearless vigor place him high.
There were not lacking poets who kept themselves free from taint of culteranismo, though they did not join in the fight against it. The brothers Argensola (LUPERCIO LEONARDO DE ARGENSOLA, 1559-1613, BARTOLOMÉ LEONARDO DE ARGENSOLA, 1562-1631), of Aragonese birth, turned to Horace and other classics as well as to Italy for their inspiration. Their pure and dignified sonnets, odes and translations rank high. Juan MARTÍNEZ DE JÁUREGUI xxvi (1583-1641) wrote a few original poems, but is known mainly for his excellent translation of Tasso's Aminta. He too succumbed to Gongorism at times. The few poems of Francisco de RIOJA (1586?-1659) are famous for the purity of their style and their tender melancholy tone. A little apart is Esteban Manuel de VILLEGAS (1589-1669), an admirer of the Argensolas, "en versos cortos divino, insufrible en los mayores," who is known for his attempts in Latin meters and his successful imitations of Anacreon and Catullus.
The lyrics of CALDERÓN (1600-1681) are to be found mostly in his comedias and autos. There are passages which display great gifts in the realm of pure poetry, but too often they are marred by the impertinent metaphors characteristic of culteranismo.
His name closes the most brilliant era of Spanish letters. The decline of literature followed close upon that of the political power of Spain. The splendid empire of Charles V had sunk, from causes inherent in the policies of that over-ambitious monarch, through the somber bigotry of Philip II, the ineptitude of Philip III, the frivolity of Philip IV, to the imbecility of Charles II; and the death of the last of the Hapsburg rulers in 1700 left Spain in a deplorably enfeebled condition physically and intellectually. The War of the Succession (1701-1714) exhausted her internal strength still more, and the final acknowledgment of Philip V (reigned 1701-1746) brought hardly any blessing but that of peace. Under these circumstances poetry could not thrive; and in truth the eighteenth century in Spain is an age devoted more to the discussion of the principles of literature than to the production of it. At first the decadent remnants of xxvii the siglo de oro still survived, but later the French taste, following the principles formulated by Boileau, prevailed almost entirely. The history of Spanish poetry in the eighteenth century is a history of the struggle between these two forces and ends in the triumph of the latter.
The effects of Gongorism lasted long in Spain, which, with its innate propensity to bombast, was more fertile soil for it than other nations. Innumerable poetasters of the early eighteenth century enjoyed fame in their day and some possessed talent; but the obscure and trivial style of the age from which they could not free themselves deprived them of any chance of enduring fame. One may mention, as the least unworthy, Gabriel Álvarez de Toledo (1662-1714) and Eugenio Gerardo Lobo (1679-1750).
Some one has said that the poetry of Spain, with the exception of the romances and the drama of the siglo de oro, has always drawn its inspiration from some other country. Add to the exceptions the medieval epic and the statement would be close to the truth. First Provence through the medium of Galicia; then Italy and with it ancient Rome; and lastly France and England, on more than one occasion, have molded Spanish poetry. The power of the French classical literature, soon dominant in Europe, could not long be stayed by the Pyrenees; and Pope, Thomson and Young were also much admired. Philip V, a Frenchman, did not endeavor to crush the native spirit in his new home, but his influence could not but be felt. He established a Spanish Academy on the model of the French in 1714.
It was some time before the reaction, based on common sense and confined to the intellectuals, could take deep root, and, as was natural, it went too far and condemned much of xxviii the siglo de oro entire. The Diario de los literatos, a journal of criticism founded in 1737, and the Poética of Ignacio de Luzán, published in the same year, struck the first powerful blows. Luzán (1702-1754) followed in general the precepts of Boileau, though he was able to praise some of the good points in the Spanish tradition. His own poems are frigid. The Sátira contra los malos escritores de su tiempo (1742) of Jorge Pitillas (pseudonym of José Gerardo de Hervás, d. 1742) was an imitation of Boileau which had great effect. Blas Antonio Nasarre (1689-1751), Agustín Montiano (1697-1765) and Luis José Velázquez (1722-1772) were critics who, unable to compose meritorious plays or verse themselves, cut to pieces the great figures of the preceding age.
Needless to say, the Gallicizers were vigorously opposed, but so poor were the original productions of the defenders of the national manner that their side was necessarily the losing one. Vicente García de la Huerta (1734-1787) was its most vehement partisan, but he is remembered only for a tragedy, Raquel.
Thus it is seen that during a century of social and industrial depression Spain did not produce a poet worthy of the name. The condition of the nation was sensibly bettered under Charles III (reigned 1759-1788) who did what was possible to reorganize the state and curb the stifling domination of the Roman Church and its agents the Jesuits and the Inquisition. The Benedictine Feijóo (1675-1764) labored faithfully to inoculate Spain, far behind the rest of Europe, with an inkling of recent scientific discoveries. And the budding prosperity, however deceitful it proved, was reflected in a more promising literary generation.xxix
Nicolás FERNÁNDEZ DE MORATÍN (1737-1780) followed the French rules in theory and wrote a few mediocre plays in accordance with them; but he showed that at heart he was a good poet and a good Spaniard by his ode Á Pedro Romero, torero insigne, some romances and his famous quintillas, the Fiesta de toros en Madrid. Other followers of the French, in a genre not, strictly speaking, lyric at all, were the two fabulists, Samaniego and Iriarte. F. María de SAMANIEGO (1745-1801) gave to the traditional stock of apologues, as developed by Phaedrus, Lokmân and La Fontaine, a permanent and popular Castilian form. Tomás de IRIARTE (1750-1791), a more irritable personage who spent much time in literary polemics, wrote original fables (Fábulas literarias, 1781) directed not against the foibles of mankind in general, but against the world of writers and scholars.
The best work which was done under the classical French influence, however, is to be found in the writers of the so-called Salamancan school, which was properly not a school at all. The poets who are thus classed together, Cadalso, Diego González, Jovellanos, Forner, Meléndez Valdés, Cienfuegos, Iglesias, were personal friends thrown together in the university or town of Salamanca, but they were not subjected to a uniform literary training and possessed no similarity of style or aim as did the men of the later Sevillan school.
José de CADALSO (1741-1782), a dashing soldier of great personal charm killed at the siege of Gibraltar, is sometimes credited with founding the school of Salamanca. He was a friend of most of the important writers of his time and composed interesting prose satires; his verse (Noches lúgubres, etc.) is not remarkable. FRAY DIEGO GONZÁLEZ xxx (1733-1794) is one of the masters of idiomatic Castilian in the century. He admired Luis de León and imitated him in paraphrases of the Psalms. The volume of his verse is small but unsurpassed in surety of taste and evenness of finish. The Murciélago alevoso has passed into many editions and become a favorite in Spain. The pure and commanding figure of JOVELLANOS (1744-1811) dominated the whole group which listened to his advice with respect. It was not always sure, for he led Diego González and Meléndez Valdés astray by persuading them to attempt philosophical poetry instead of the lighter sort for which they were fitted. He was in fact a greater man than poet, but his satires and Epístola al duque de Veragua are strong and dignified.
Juan MELÉNDEZ VALDÉS (1754-1817) was on the contrary a greater poet than man. Brilliant from the first, he was petted by Cadalso and Jovellanos who strove to develop his talent. In 1780 he won a prize offered by the Academy for an eclogue. In 1784 his comedy Las bodas de Camacho, on a subject suggested by Jovellanos (from an episode in Don Quijote, II, 19-21), won a prize offered by the city of Madrid, but failed on the stage. His first volume of poems was published in 1785; later editions appeared in 1797 and 1820. He attached himself to the French party at the time of the invasion in 1808, incurred great popular odium and died in France. He is the most fluent, imaginative poet of the eighteenth century and is especially successful in the pastoral and anacreontic styles. Fresh descriptions of nature, enchanting pictures of love, form an oasis in an age of studied reasonableness. His language has been criticized for its Gallicisms. José IGLESIAS DE LA CASA (1748-1791), a native of Salamanca and a priest, wrote much light satirical xxxi verse, epigrams, parodies and letrillas in racy Castilian; he was less successful in the graver forms. Nicasio ÁLVAREZ DE CIENFUEGOS (1764-1809) passes as a disciple of Meléndez; he was a passionate, uneven writer whose undisciplined thought and habit of coining words lead to obscurity. Politically he opposed the French with unyielding vigor, barely escaped execution at their hands and died in exile. The verse of Cienfuegos prepared the way for Quintana. Differing from him in clarity and polish are Fr. Sánchez Barbero (1764-1819) and Leandro F. de Moratín, the dramatist (1760-1828).
One curious result of rationalistic doctrines was the "prosaism" into which it led many minor versifiers. These poetasters, afraid of overstepping the limits of good sense, tabooed all imagination and described in deliberately prosy lines the most commonplace events. The movement reached its height at the beginning of the reign of Charles IV (1788-1808) and produced such efforts as a poem to the gout, a nature-poem depicting barn-yard sounds, and even Iriarte's La música (1780), in which one may read in carefully constructed silvas the definition of diatonic and chromatic scales.
Early in the nineteenth century the armies of Napoleon invaded Spain. There ensued a fierce struggle for the mastery of the Peninsula, in which the latent strength and energy of the Spaniards became once more evident. The xxxii French devastated parts of the country, but they brought with them many new ideas which, together with the sharpness of the conflict, served to awaken the Spanish people from their torpor and to give them a new realization of national consciousness. During this period of stress and strife two poets, Quintana and Gallego, urged on and encouraged their fellow countrymen with patriotic songs.
Manuel José QUINTANA (1772-1857) had preëminently the "gift of martial music," and great was the influence of his odes Al armamento de las provincias contra los franceses and Á España después de la revolución de marzo. He also strengthened the patriotism of his people by his prose Vidas de españoles célebres (begun in 1806): the Cid, the Great Captain (Gonzalo de Córdoba), Pizarro and others of their kind. In part a follower of the French philosophers of the eighteenth century, Quintana sang also of humanity and progress, as in his ode on the invention of printing. In politics Quintana was a liberal; in religious beliefs, a materialist. Campoamor has said of Quintana that he sang not of faith or pleasures, but of duties. His enemies have accused him of stirring the colonies to revolt by his bitter sarcasm directed at past and contemporaneous Spanish rulers, but this is doubtless an exaggeration. It may be said that except in his best patriotic poems his verses lack lyric merit and his ideas are wanting in insight and depth; but his sincerity of purpose was in the main beyond question and he occasionally gave expression to striking boldness of thought and exaltation of feeling. In technique Quintana was a follower of the Salamancan school.
The cleric Juan Nicasio GALLEGO (1777-1853) rivaled Quintana as a writer of patriotic verses. A liberal in politics xxxiii like Quintana, Gallego also took the side of his people against the French invaders and against the servile Spanish rulers. He is best known by the ode El dos de mayo, in which he exults over the rising of the Spanish against the French on the second of May, 1808; the ode Á la defensa de Buenos Aires against the English; and the elegy Á la muerte de la duquesa de Frías in which he shows that he is capable of deep feeling. Gallego was a close friend of Quintana, whose salon in Madrid he frequented. Gallego wrote little, but his works are more correct in language and style than those of Quintana. It is interesting that although the writings of these two poets evince a profound dislike and distrust of the French, yet both were in their art largely dominated by the influence of French neo-classicism. This is but another illustration of the relative conservatism of belles-lettres.
In the year 1793 there had been formed in Seville by a group of young writers an Academia de Letras Humanas to foster the cultivation of letters. The members of this academy were admirers of Herrera, the Spanish Petrarchist and patriotic poet of the sixteenth century, and they strove for a continuation of the tradition of the earlier Sevillan group. The more important writers of the later Sevillan school were Arjona, Blanco, Lista and Reinoso. Manuel María de ARJONA (1771-1820), a priest well read in the Greek and Latin classics, was an imitator of Horace. José María BLANCO (1775-1841), known in the history of English literature as Blanco White, spent much time in England and wrote in English as well as in Castilian. Ordained a Catholic priest he later became an Unitarian. The best-known and most influential writer of the group was Alberto xxxiv LISTA (1775-1848), an educator and later canon of Seville. Lista was a skilful artist and like Arjona an admirer and imitator of Horace; but his ideas lacked depth. His best-known poem is probably a religious one, Á la muerte de Jesús, which abounds in true poetic feeling. Lista exerted great influence as a teacher and his Lecciones de literatura española did much to stimulate the study of Spanish letters. Félix José REINOSO (1772-1814), also a priest, imitated Milton in octava rima. As a whole the influence of the Sevillan school was healthful. By insisting upon purity of diction and regularity in versification, the members of the school helped somewhat to restrain the license and improve the bad taste prevailing in the Spanish literature of the time. The Catalonian Manuel de CABANYES (1808-1833) remained unaffected by the warring literary schools and followed with passionate enthusiasm the precepts of the ancients and particularly of Horace.
In the third decade of the nineteenth century romanticism, with its revolt against the restrictions of classicism, with its free play of imagination and emotion, and with lyricism as its predominant note, flowed freely into Spain from England and France. Spain had remained preëminently the home of romanticism when France and England had turned to classicism, and only in the second half of the eighteenth century had Spanish writers given to classicism a reception that was at the best lukewarm. Now romanticism was welcomed back with open arms, and Spanish writers turned eagerly for inspiration not only to Chateaubriand, Victor Hugo and Byron, but also to Lope de Vega and Calderón. Spain has always worshiped the past, for Spain was once great, and the appeal of romanticism was xxxv therefore the greater as it drew its material largely from national sources.
In 1830 a club known as the Parnasillo was formed in Madrid to spread the new literary theories, much as the Cénacle had done in Paris. The members of the Parnasillo met in a wretched little café to avoid public attention. Here were to be found Bretón de los Herreros, Estébanez Calderón, Mesonero Romanos, Gil y Zárate, Ventura de la Vega, Espronceda and Larra. The influence of Spanish epic and dramatic poetry had been important in stimulating the growth of romanticism in England, Germany and France. In England, Robert Southey translated into English the poem and the chronicle of the Cid and Sir Walter Scott published his Vision of Don Roderick; in Germany, Herder's translation of some of the Cid romances and the Schlegel brothers' metrical version of Calderón's dramas had called attention to the merit of the earlier Spanish literature; and in France, Abel Hugo translated into French the Romancero and his brother Victor made Spanish subjects popular with Hernani and Ruy Blas and the Légendes des siècles. But Spain, under the despotism of Ferdinand VII, the "Tyrant of Literature," remained apparently indifferent or even hostile to its own wonderful creations, and clung outwardly to French neo-classicism.2 Böhl von Faber,3 the German consul at Cadiz, who was influenced by the Schlegel brothers, had early called attention to the merit of the Spanish literature of the Golden Age and had even had some of Calderón's plays performed at xxxvi Cadiz. And in 1832 Durán published his epoch-making Romancero. In 1833 Ferdinand VII died and the romantic movement was hastened by the home-coming of a number of men who had fled the despotism of the monarch and had spent some time in England and France, where they had come into contact with the romanticists of those countries. Prominent amongst these were Martínez de la Rosa, Antonio Alcalá Galiano, the Duke of Rivas and Espronceda.
Footnote 2: (return) Cf. l'Épopée castillane, Ramón Menéndez Pidal, Paris, 1910, pp. 249-252.
Footnote 3: (return) The father of Fernán Caballero.
In this period of transition one of the first prominent men of letters to show the effects of romanticism was Francisco MARTÍNEZ DE LA ROSA (1787-1862). Among his earlier writings are a Poética and several odes in honor of the heroes of the War of Independence against the French. After his exile in Paris he returned home imbued with romanticism, and his two plays, Conjuración de Venecia (1834) and Abén Humeya (1836: it had already been given in French at Paris in 1830), mark the first public triumph of romanticism in Spain. But Martínez de la Rosa lacked force and originality and his works merely paved the way for the greater triumph of the Duke of Rivas. Ángel de Saavedra, DUQUE DE RIVAS (1791-1865), a liberal noble, insured the definite triumph of romanticism in Spain by the successful performance of his drama Don Álvaro (1835). At first a follower of Moratín and Quintana, he turned, after several years of exile in England, the Isle of Malta and France, to the new romantic school, and casting off all classical restraints soon became the acknowledged leader of the Spanish romanticists. Among his better works are the lyric Al faro de Malta, the legendary narrative poem El moro expósito and his Romances históricos. The Romances are more sober in tone and less fantastic,—and it should be xxxvii added, less popular to-day,—than the legends of Zorrilla. After a tempestuous life the Duke of Rivas settled quietly into the place of director of the Spanish Academy, which post he held till his death.
José de ESPRONCEDA (1808-1842) was preëminently a disciple of Byron, with Byron's mingling of pessimism and aspiration, and like him in revolt against the established order of things in politics and social organization. His passionate outpourings, his brilliant imagery and the music of his verse give to Espronceda a first place amongst the Spanish lyrical poets of the nineteenth century. Some of his shorter lyrics (e.g. Canto á Teresa) are inspired by his one-time passion for Teresa with whom after her marriage to another he eloped from London to Paris. The poet's best known longer works are the Diablo mundo and the Estudiante de Salamanca, which are largely made up of detached lyrics in which the subjective note is strikingly prominent. Espronceda was one of those fortunate few who shine in the world of letters although they work little. Both in lyric mastery and in his spirit of revolt, Espronceda holds the place in Spanish literature that is held in English by Byron. He is the chief Spanish exponent of a great revolutionary movement that swept over the world of letters in the first half of the nineteenth century.
José ZORRILLA (1817-1893) first won fame by the reading of an elegy at the burial of Larra. Zorrilla was a most prolific and spontaneous writer of verses, much of which is unfinished in form and deficient in philosophical insight. But in spite of his carelessness and shallowness he rivaled Espronceda in popularity. His verses are not seldom melodramatic or childish, but they are rich in coloring and poetic xxxviii fancy and they form a vast enchanted world in which the Spaniards still delight to wander. His versions of old Spanish legends are doubtless his most enduring work and their appeal to Spanish patriotism is not less potent to-day than when they were written. Zorrilla's dramatic works were successful on the stage by reason of their primitive vigor, especially Don Juan Tenorio, El Zapatero y el rey and Traidor, inconfeso y mártir. This "fantastic and legendary poet" went to Mexico in 1854 and he remained there several years. After that date he wrote little and the little lacked merit.
Gertrudis Gómez de AVELLANEDA (1814-1873) was born in Cuba but spent most of her life in Spain. Avellaneda was a graceful writer of lyrics in which there was feeling and melody but little depth of thought. With her the moving impulse was love, both human and divine. Her first volume of poems (1841) probably contains her best work. Her novels Sab and Espatolino were popular in their day but are now fallen into oblivion. Some of her plays, especially Baltasar and Munio, do not lack merit. Avellaneda is recognized as the foremost poet amongst the women of nineteenth-century Spain.
Two of the most successful dramatists of this period, García Gutiérrez and Hartzenbusch, were also lyric poets. Antonio GARCÍA GUTIÉRREZ (1813-1884), the author of El trovador, published two volumes of mediocre verses. Juan Eugenio HARTZENBUSCH (1806-1880) was, like Fernán Caballero, the child of a German father and a Spanish mother. Though an eminent scholar and critic, he did not hesitate in his Amantes de Teruel to play to the popular passion for sentimentality. He produced some lyric verse of worth. Manuel BRETÓN DE LOS HERREROS (1796-1873) was primarily a humorist and satirist, who turned from xxxix lyric verse to drama as his best medium of expression. He delighted in holding up to ridicule the excesses of romanticism. Mention should be made here of two poets who had been, like Espronceda, pupils of Alberto Lista. The eclectic poet MARQUÉS DE MOLINS (Mariano Roca de Togores: 1812-1889) wrote passively in all the literary genres of his time. VENTURA DE LA VEGA (1807-1865) was born in Argentina, but came to Spain at an early age. He was a well-balanced, cautious writer of mediocre verses that are rather neo-classic than romantic.
A marked reaction against the grandiose exaggerations of later romanticism appears in the works of José SELGAS y Carrasco (1824-1882), a clever writer of simple, sentimental verses. At one time his poetry was highly praised and widely read, but for the most part it is to-day censured as severely as it was once praised. Among the contemporaries of Selgas were the writer of simple verses and one-time popular tales, Antonio de TRUEBA (1821-1889) and Eduardo BUSTILLO, the author of Las cuatro estaciones and El ciego de Buenavista. Somewhat of the tradition of the Sevillan school persisted in the verses of Manuel CAÑETE and Narciso CAMPILLO (1838-1900) and in those of the poet and literary critic José AMADOR DE LOS RÍOS.
The Sevillan Gustavo Adolfo BÉCQUER (1836-1870) wrote perhaps the most highly polished Spanish verse of the nineteenth century. His Rimas are charged with true poetic fancy and the sweetest melody, but the many inversions of word-order that were used to attain to perfection of metrical form detract not a little from their charm. His writings are contained in three small volumes in which are found, together with the Rimas, a collection of prose legends. His xl prose work is filled with morbid mysticism or fairy-like mystery. His dreamy prose is often compared to that of Hoffmann and his verses to those of Heine, although it is doubtful if he was largely influenced by either of these German writers. Bécquer sings primarily of idealized human love. His material life was wretched and it would seem that his spirit took flight into an enchanted land of its own creation. Most human beings love to forget at times their sordid surroundings and wander in dreamland; hence the enduring popularity of Bécquer's works and especially of the Rimas. Bécquer has been widely imitated throughout the Spanish-speaking world, but with little success. In this connection it should be noted that the Spanish poets who have most influenced the Spanish literature of the nineteenth century, both in the Peninsula and in America, are the Tyrtaean poet Quintana, the two leading romanticists Espronceda and Zorrilla and the mystic Bécquer.
Like most writers in Latin lands, Juan VALERA y Alcalá Galiano (1824-1905) and Marcelino MENÉNDEZ Y PELAYO (1856-1912) began their literary career with a volume or two of lyric verses. Valera's verses have perfect metrical form and evince high scholarship, but they are too learned to be popular. The lyrics of Menéndez y Pelayo have also more merit in form than in inspiration and are lacking in human interest. Both authors turned soon to more congenial work: Valera became the most versatile and polished of all nineteenth century Spanish writers of essays and novels; and Menéndez y Pelayo became Spain's greatest scholar in literary history. The popular novelist, Pedro Antonio de ALARCÓN (1833-1891), wrote lyrics in which there is a curious blending of humor and skepticism. xli The foremost Spanish poet of the closing years of the nineteenth century was Ramón de CAMPOAMOR y Campoosorio (1817-1901) who is recognized as the initiator in Spain of a new type of verse in his Doloras and Pequeños poemas. The doloras are, for the most part, metrical fables or epigrams, dramatic or anecdotal in form, in which the author unites lightness of touch with depth of feeling. The pequeño poema is merely an enlarged dolora. Campoamor disliked Byron and he disliked still more the sonorous emptiness that is characteristic of too much Spanish poetry.4 In philosophy he revered Thomas à Kempis; in form he aimed at conciseness and directness rather than at artistic perfection. His poetry lacks enthusiasm and coloring, but it has dramatic interest.
Footnote 4: (return) Menéndez y Pelayo (Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Am., I, p. lv) says: "Al fin españoles somos, y á tal profusión de luz y á tal estrépito de palabras sonoras no hay entre nosotros quien resista."
The poets Manuel del PALACIO (1832-1895) and Federico BALART (1831-1905), though quite unlike in genius, won the esteem of their contemporaries. Palacio wrote excellent sonnets and epigrams. In his Leyendas y poemas he proved his mastery of Spanish diction; he had, moreover, the saving grace of humor which was so noticeably lacking in Zorrilla's legends. The poet and literary critic, Balart, achieved fame with his Dolores, in which he mourns with sincere grief the death of his beloved wife. Mention should also be made of the following poets who deserve recognition in this brief review of the history of Spanish lyric poetry: Vicente Wenceslao QUEROL (1836-1889), a Valencian, whose El eclipse, Cartas á María, and La fiesta de Venus, evince a remarkable technical skill and an unusual correctness of diction; xlii Teodoro LLORENTE (cf. p. 279); José GALIANO ALCALÁ whose verses have delicate feeling and lively imagination; Emilio FERRARI (b. 1853), the author of Abelardo é Hipatia and Aspiración; the pessimistic poets, Joaquín María de BARTRINA (1850-1880) and Gabino TEJADO; Salvador RUEDA (b. 1857), author of El bloque, En tropel and Cantos de la vendimia; and the poet and dramatist, Eduardo MARQUINA.
After the death of Campoamor in the first year of the twentieth century, the title of doyen of Spanish letters fell by universal acclaim to Gaspar NÚÑEZ DE ARCE (1834-1903). Núñez de Arce was a lyric poet, a dramatist and a writer of polemics, but first of all a man of action. With him the solution of political and sociological problems was all-important, and his literary writings were mostly the expression of his sociological and political views. Núñez de Arce is best known for his Gritos del combate (1875), in which he sings of liberty but opposes anarchy with energy and courage. As a satirist he attacks the excesses of radicalism as well as the vices and foibles common to mankind.5 As a poet he is neither original nor imaginative, and often his ideas are unduly limited; but he writes with a manly vigor that is rare amongst Spanish lyric poets, most of whom have given first place to the splendors of rhetoric.
Footnote 5: (return) Speaking of Núñez de Arce's satire, Juan Valera says humorously, in Florilegio de poesías castellanas del siglo XIX, Madrid, 1902, Vol. I, p. 247: «Está el poeta tan enojado contra la sociedad, contra nuestra descarriada civilización y contra los crímenes y maldades de ahora, y nos pinta tan perverso, tan vicioso y tan infeliz al hombre de nuestros días, atormentado por dudas, remordimientos, codicias y otras viles pasiones, que, á mi ver, lejos de avergonzarse este hombre de descender del mono, debiera ser el mono quien se avergonzara de haberse humanado.»
Most writers on the history of European literatures have xliii called attention to the fact that at the beginning of the nineteenth century there was a great outpouring of lyricism, which infused itself into prose as well as verse. When this movement had exhausted itself there came by inevitable reaction a period of materialism, when realism succeeded romanticism and prose fiction largely replaced verse. And now sociological and pseudo-scientific writings threaten the very existence of idealistic literature. And yet through it all there has been no dearth of poets. Browning in England and Campoamor in Spain, like many before them, have given metrical form to the expression of their philosophical views. And other poets, who had an intuitive aversion to science, have taken refuge in pure idealism and have created worlds after their own liking. To-day prose is recognized as the best medium for the promulgation of scientific or political teachings, and those who are by nature poets are turning to art for art's sake. Poetry is less didactic than formerly, and it is none the less beautiful and inspiring.
The Notes to this volume contain historical sketches of the literatures of Argentina (p. 279), Colombia (p. 285), Cuba (p. 291), Ecuador and Peru (p. 296), Mexico (p. 307), and Venezuela (p. 315). It is to be regretted that lack of space has excluded an account of the literatures of other Spanish-American countries, and especially of Chile and Uruguay.
Spanish versification is subject to the following general laws:
(1) There must be a harmonious flow of syllables, in which harsh combinations of sounds are avoided. This xliv usually requires that stressed syllables be separated by one or more unstressed syllables.6
Footnote 6: (return) By stress is meant secondary as well as primary syllabic stress. Thus, en nuestra vida has primary stress on vi-, and secondary stress on nues-.
(2) Verse must be divided into phrases, each of which can be uttered easily as one breath-group. The phrases are normally of not less than four nor more than eight syllables, with a rhythmic accent on the next to the last syllable of each phrase.7 Phrases of a fixed number of syllables must recur at regular intervals. There may or may not be a pause at the end of the phrase.
Footnote 7: (return) The unstressed syllable may be lacking, or there may be two unstressed syllables, after the rhythmic accent. See under Syllabication.
(a) In the n-syllable binary line the phrases may recur at irregular intervals. In lines with regular ternary movement phrasing is largely replaced by rhythmic pulsation (cf. p. lxx).
(3) There must be rime of final syllables, or final vowels, recurring at regular intervals.
(a) In some metrical arrangements of foreign origin the rimes recur at irregular intervals, or there is no rime at all. See the silva and versos sueltos under Strophes.
Whether normal Spanish verse has, or ever had, binary movement, with the occasional substitution of a "troche" for an "iambic," or vice-versa, is in dispute.8 That is, whether in Spanish verse, with the usual movement, (1) the alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables is essential, or whether (2) the xlv mere balancing of certain larger blocks of syllables is sufficient. For instance, in this line of Luis de León:
ya muestra en esperanza el fruto cierto,
is there regular rhythmic pulsation, much less marked than in English verse, doubtless,—but still an easily discernible alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables? If so, there must be secondary stress on es-. Or is ya muestra en esperanza one block, and el fruto cierto another, with no rhythmic stresses except those on -anza and cierto?
Footnote 8: (return) There are in Spanish certain types of verses in which there is regular ternary movement throughout. These are treated separately. Cf. p. lxx.
The truth seems to be that symmetry of phrases (the balancing of large blocks of syllables) is an essential and important part of modern Spanish versification; but that, in musical verse of the ordinary type, there is also a subtle and varied binary movement, while in some recitative verse (notably the dramatic romance verse) the binary movement is almost or quite negligible.9
Footnote 9: (return)A count of Spanish verses (none from drama), by arbitrarily assuming three contiguous atonic syllables to be equal to-[/-]-(with secondary stress on the middle syllable), gave the following results (cf. Romanic Review, Vol. III, pp. 301-308):
Common syllabic arrangements of 8-syllable lines:
(1) / _ / _ / _ / (_): Esta triste voz oí.
(2) _ / _ / _ _ / (_): Llorando dicen así.
(3) _ / _ _ / _ / (_): Mi cama las duras peñas.
Of 933 lines, 446 (nearly one-half) were in class (1); 257 in class (2); and 191 in class (3). The remaining lines did not belong to any one of these three classes.
Common syllabic arrangements of 11-syllable lines:
(1) _ / _ / _ / _ / _ / (_): Verás con cuánto amor llamar porfía.
(2) / _ / _ _ / _ / _ / (_): Cuántas veces el ángel me decía.
(3) / _ _ / _ / _ / _ / (_): Este matiz que al cielo desafía.
Of 402 lines, 216 (slightly more than one-half) were in class (1); 94 were in class (2); and 75 in class (3). The remaining lines did not belong to any one of these three classes. Note that, in these arrangements of the 11-syllable lines, the irregularities in rhythm are found only in the first four syllables.
Some poets have used at times a quite regular binary movement in Spanish verse; but they have had few or no followers, as the effect was too monotonous to please the Spanish ear. Thus, Solís:
Siempre orillas de la fuente
Busco rosas á mi frente,
Pienso en él y me sonrío,
Y entre mí le llamo mío,
Me entristezco de su ausencia,
Y deseo en su presencia
La más bella parecer.
The Colombian poet, José Eusebio Caro, wrote much verse thus, under the influence of the English poets.
On the other hand, some recent "decadent" poets have written verses in which the principle of symmetry of phrases, or of a fixed number of syllables, is abandoned, and rhythm and rime are considered sufficient to make the lines musical. Thus, Leopoldo Lugones (born 1875?), of Argentina, in verses which he calls «libres» (cf. Lunario sentimental, Buenos Aires, 1909):
Luna, quiero cantarte
¡Oh ilustre anciana de las mitologías!
Con todas las fuerzas de mi arte.
Deidad que en los antiguos días
Imprimiste en nuestro polvo tu sandalia,
No alabaré el litúrgico furor de tus orgías
Ni su erótica didascalia,
Para que alumbres sin mayores ironías,
Al polígloto elogio de las Guías,
Noches sentimentales de mises en Italia.
(Himno á la luna)
This is largely a harking back to primitive conditions, for in the oldest Castilian narrative verse the rule of "counted syllables" apparently did not prevail. Cf. the Cantar de mío Cid, where there is great irregularity in the number of syllables. And, although xlvii in the old romances the half-lines of eight syllables largely predominate, many are found with seven or nine syllables, and some with even fewer or more. The adoption of the rule of "counted syllables" in Spanish may have been due to one or more of several causes: to the influence of medieval Latin rhythmic songs;10 to French influence; or merely to the development in the Spanish people of a feeling for artistic symmetry.
Other poets of to-day write verses in which the line contains a fixed number of syllables or any multiple of that number. Thus, Julio Sesto (Blanco y Negro, Nov. 5, 1911):
¡Cómo desembarcan..., cómo desembarcan
esas pobres gentes...!
Desde la escalera de la nave todo Nueva York abarcan
de un vistazo: muelles, río, casas, puentes...
Y después que todos sus cinco sentidos
ponen asombrados en ver la ciudad,
como agradecidos,
miran á la estatua de la Libertad.
¡Ella es la Madona, ella es la Madona,
que de la Siberia saca á los esclavos,
que á los regicidas la vida perdona,
y que salva á muchos de contribuyentes, pobres, perseguidos,
subditos y esclavos!...
(La tierra prometida)
Spanish poets have often tried to write verses in classical meters with the substitution of stress for quantity. Thus, Villegas in the following hexameters:
Seis veces el verde soto coronó su cabeza
de nardo, de amarillo trebol, de morada viöla,
en tanto que el pecho frío de mi casta Licoris
al rayo del ruëgo mío deshizo su hielo.11
Footnote 11: (return) Apparently trebol instead of trébol. These lines are quoted by Eugenio Mele, in La poesia barbara in Ispagna, Bari, 1910.
José Eusebio Caro wrote similar hexameters, and, strange to say, made alternate lines assonate:
¡Céfiro rápido lánzate! ¡rápido empújame y vivo!
¡Más redondas mis velas pon: del proscrito á los lados,
haz que tus silbos susurren dulces y dulces suspiren!
¡Haz que pronto del patrio suelo se aleje mi barco!
(En alta mar)
The number of these direct imitations is large; but few succeeded. They are, at best, foreign to the spirit of Castilian poetry.
In singing Spanish verses two facts are of especial interest: that, where the rules of prosody require synalepha, hiatus sometimes occurs (especially in opera), thus:
Recógete—ese pañuelo.
(Olmedo, Folk-lore de Castilla, p. 133)
Y el pájaro—era verde.
(Ledesma, Cancionero salmantino, p. 53)
And that musical accents do not necessarily coincide with syllabic stresses, even at the end of a phrase. Thus,
¡Cuántas vèces, vida mìa,
Te asomàrás al balcòn!12
¡Cuerpo buèno, alma divìna,
Qué de fàtigas me cuèstas!
¡Bendiga Dios ese cuerpò,
Tan llenísimo de gracià!
(Hernández, Flores de España)
Footnote 12: (return) The grave accent mark (`) indicates a strong musical accent.
SYLLABICATION
In most modern Spanish verse there is a fixed number of syllables in a line up to and including the last stressed syllable.13 In counting these syllables consideration must be given to the following facts:
Footnote 13: (return)The number of unstressed syllables at the end of a line is not fixed. See p. lvi.
In order to have the correct number of syllables, poets sometimes (1) shorten a word or (2) shift the accent:
(1) ¿Ya qué mi puro espirtu sucias carnes...
(Cabanyes, Á Cintio)
(2) Puede querer...? Abralé...
(Zorrilla, Don Juan Tenorio, primera parte, III, 6)
Deben de ser angeles.
(Lope de Vega, El mejor alcalde el rey, II)
Note the artificial separation of lines in some dramatic romance-verse:
... Soy un cate-
Cúmeno muy diligente.
(Calderón, El José de las mujeres, II)
De una vil hermana, de un
Falso amigo, de un infame
Criado...
(Calderón, No hay burlas con el amor, III)
(1) SYNERESIS
Within a word two or three contiguous vowels usually combine to form a diphthong or a triphthong respectively (this is called "syneresis"): bai|le, rey, oi|go, ciu|dad, cui|da|do, es|tu|diar, es|tu|diáis, dien|te, lim|pio, gra|cio|so, muy, bien, pue|de, buey, etc. Exceptions:
(a) A stressed "weak" vowel (i, u) may not combine with a "strong" vowel (a, e, o) to form a diphthong: dí|a, l rí|e, frí|o, ra|íz, le|í|do, o|í|do, con|ti|nú|a, con|ti|nú|e, con|ti|nú|o, ba|úl, sa|bí|a, sa|brí|ais, ca|í|ais, etc.14
Footnote 14: (return) Note that in these combinations the weak vowel receives the accent mark. Some Spanish-American poets have sinned grievously, by reason of their local pronunciation, in diphthongizing a strong vowel with a following stressed weak vowel, as maiz, a|taud, oi|do, for ma|íz, a|ta|úd, o|í|do, respectively, etc.
Exceptions are rare:
Su|pe | que | se|ría | di|cho|so |
(Calderón, No hay burlas con el amor, III)
Cf. also rendíos, etc., where the o of os combines with the í by synalepha.
(b) uá, uó, are usually disyllabic, except after c, g, and j: a|dü|a|na, sü|a|ve; but cua|tro, san|ti|guó, Juan, etc. Syneresis may occur: sua|ve.
(c) úi is usually disyllabic, except in muy: flú|i|do.
(d) Two unstressed strong vowels, if they follow the stress, regularly form a diphthong; but if they precede they may form a diphthong or they may be dissyllabic, usually at the option of the poet.
Que | del | em|pí|reo en | el | ce|nit | fi|na|ba.15
Las | mar|mó|reas|, y aus|te|ras | es|cul|tu|ras.
La | ne|gra ad|ver|si|dad|, con | fé|rrea | ma|no.
El | tiem|po en|tre | sus | plie|gues | ro|e|do|res.
liTe | van | á ar|mar | do | ca|e|rás | in|cau|ta.
La | fe|al|dad | del vi|cio|; pe|ro hu|yó|se...16
En | tan | frá|gil | rea|li|dad.
La | sub|li|me | poe|sí|a | re|ver|be|ra.
Footnote 15: (return) Note that here poetic usage differs from the rules for syllabication that obtain in prose. Thus, in empíreo the í receives the accent mark, since it is held to be in the antepenultimate syllable, but in verse empíreo is regularly trisyllabic.
Footnote 16: (return) The ea of fealdad is normally disyllabic by analogy with feo. Cf. (f) below.
(e) Two strong vowels, if one is stressed, are usually disyllabic:
pa|se|a, re|cre|o, ca|no|a, etc.
A|rran|ca a|rran|ca|, Dios | mí|o,
De | la | men|te | del | po|e|ta
Es|te | pen|sa|mien|to im|pí|o
Que en | un | de|li|rio | cre|ó.
¿Qué | se hi|cie|ron | tus | mu|ros | to|rre|a|dos,
Oh | mi | pa|tria | que|ri|da?
¿Dón|de | fue|ron | tus | hé|roes | es|for|za|dos,
Tu es|pa|da | no | ven|ci|da?
A|na|cre|on|te, el | vi|no y | la a|le|grí|a.
Sa|e|ta | que | vo|la|do|ra...
De o|ro | la | na|o | ga|di|ta|na a|por|ta.
Y | no | se es|me|re en | lo|ar|la.
Don|de á | ca|er | vol|ve|rá.
Syneresis is rare, but may occur,—except in éa, éo and óa,—provided the second vowel does not receive a rhythmic accent:
Es|cri|ba|no al | caer | el | sol.
Caen | es|ta|llan|do | de | los | fuer|tes | gon|ces.
Cual | na|ve | real | en | triun|fo em|pa|ve|sa|da.
(f) In some words vowels that would normally form a diphthong are usually disyllabic by analogy with other forms derived from the same stem: fi|é, fi|ó (cf. fí|o), ri|ó, ri|e|ron (cf. rí|o), con|ti|nu|é (cf. con|ti|nú|o), di|a|rio (cf. dí|a), bri|o|so (cf. brí|o), hu|í, hu|i|mos (cf. hu|yo), etc.
Syneresis is rare, but possible, as in brio|so for bri|o|so.
(g) Prefixes, except a-, usually form separate syllables: pre|in|ser|to, re|im|pri|mir, re|hu|sar; but aho|gar. If the syllable after a-is stressed, dieresis usually occurs:
Á | los | que a|ho|ra a|cla|ma.
En | la | sub|li|me | so|le|dad | a|ho|ra...
(2) DIERESIS
By poetic license vowels that normally form one syllable may often be dissolved into separate syllables (this is called "dieresis") at the will of the poet: glo|rio|so or glo|rï|o|so, rui|do or rü|i|do, etc.17 See also (1), d, above.
Footnote 17: (return) Note that the dieresis mark is generally used in dieresis of two weak vowels, or of strong and weak vowels where the strong vowel is stressed.
But dieresis is impossible if the diphthong is ie or ue from Latin [e] and [o] respectively, as in bien, siente, huevo, puedo.
(3) SYNALEPHA
The final vowel or diphthong of one word and the initial vowel or diphthong of an immediately following word in the same line usually combine to form one syllable (this is called "synalepha")18 as in:
Cuan|do | re|cuer|do | la | pie|dad | sin|ce|ra
Con | que en | mi e|dad | pri|me|ra
En|tra|ba en | nues|tras | vie|jas | ca|te|dra|les.
La | cien|cia au|daz|, cuan|do | de | ti | se a|le|ja.
¡És|ta es | Es|pa|ña! A|tó|ni|ta y | mal|tre|cha...
Que | mi | can|tar | so|no|ro
A|com|pa|ñó has|ta a|quí|; no a|pri|sio|na|do...
Footnote 18: (return)Note that the union of vowels in separate words is called synalepha, while the union of vowels within a word is called syneresis. But synalepha may occur in combinations of vowels in which syneresis would be impossible. Compare te|ní|a and ca|no|a with:
A|sí al | man|ce|bo in|te|rrum|pe (p. 94, l. 13).
Ni | la | mi|ra|da | que | lan|zó al | sos|la|yo (p. 219, l. 8).
The vowels of three words may thus combine if the middle word is a (or ha) (see also (4), a):
Le | di|jo és|te á u|na | mu|jer.
Sal|va á es|ta | so|cie|dad | des|ven|tu|ra|da.
(4) HIATUS
(a) Hiatus (i.e. the final vowel of one word and the initial vowel of the immediately following word form separate syllables)19 is caused by the interposition of a weak unstressed vowel, as in:
En | sus | re|cuer|dos | de | hiel.
De | sus | á|la|mos | y | huer|tos.
Y hoy | en | sus | can|ta|res | llo|ra.
Footnote 19: (return) Note that hiatus between words is equivalent to dieresis within a word.
Note that, similarly, the vowels of three words may not combine, if the middle word is y, é (or he), ó (or oh), ú:
O|las| de | pla|ta y | a|zul.
Que | la al|ma | no|che | ó el | bri|llan|te | di|a.
¿Quién | cal|ma|rá, | ¡Oh Es|pa|ña! | tus | pe|sa|res?
And in all such expressions as: o|cio|so é | i|rri|ta|do, Se|vi|lla | ú O|vie|do, etc.
Except when a vowel is repeated:
Si he es|cu|cha|do | cuan|do ha|bla|bas.
(Calderón, No hay burlas con el amor, III)
In modern Spanish, h, being silent, has no effect, but in older Spanish, h for Latin f, being then pronounced, prevented synalepha, as in:
Hiatus was common in Old Spanish, except when the first of two words was the definite article, a personal pronoun-object or the preposition de; or when the vowels were the same.
(b) Hiatus is usual when the initial vowel of the second word has a strong accent (usually the rhythmic accent at the end of a line or phrase):
Pues | en | fin | me | de|jó | una (Calderón).
Ta|les | fue|ron | ya | és|tos | cual | her|mo|so (Herrera).
Tal | de | lo | al|to | tem|pes|tad | des|he|cha (Maury).
No hay | pla|ce|res | en | su | al | ma.
Cuan|do | po|bre | de | a|ños | y | pe|sa|res
Con|ti|go | se | fué | mi | hon|ra.
De | gra|na|das | es|pi|gas|; tú | la | u|va...
Por|que es | pa|ra el | ser | que | a|ma.
Muy | más | her|mo|sa | la | ha|llan
El | ne|va|do | cue|llo | al|za
Por|que | tam|bién | e|ra| u|so.
Que en | la | bo|ca, y | só|lo | u|no.
Gen|te en | es|te | mon|te | an|da...
Ya | que | de | tu | vis|ta | hu|ye.
(Calderón)
Gi|gan|te | o|la | que el | vien|to...20
Footnote 20: (return) Synalepha is usually to be avoided when it would bring together two stressed syllables as in gigante ola, querido hijo, etc.
But synalepha is possible (especially of de o-):
To|do e|le|va|ba | mi á|ni|mo in|tran|qui|lo.
Yo | le | da|ré|; mas | no en | el | ar|pa | de o|ro...
And synalepha is the rule, if stress on the initial syllable is weak:
If the vowels are the same, they usually combine into one:
Del | sol | en | la al|ta | cum|bre
Tem|blar | en | tor|no | de él|: un | ar|co in|men|so...
(5) FINAL SYLLABLES
In estimating the number of syllables in a Spanish verse-line one final unstressed syllable after the last stressed syllable is counted whether it be present or not; or, if there be two unstressed syllables at the end of the line, only one is counted.21 Thus the following are considered 8-syllable lines although, in fact, one line has nine syllables and another has only seven:
La | sal|pi|ca | con | es|com|bros
De | cas|ti|llos | y | de al|cá|za|res...
Pa|ra | vol|ver | á | bro|tar...
Footnote 21: (return) In Spanish, a word stressed on the final syllable is called agudo; a word with one syllable after the stress is called grave or llano; one with two syllables after the stress, esdrújulo: farol, pluma, pájaro.
This system of counting syllables obtains in Spanish because there is one and only one unstressed syllable at the end of most verse-lines. It would, perhaps, be more logical to stop the count with the last stressed syllable, as the French do. For instance, a Spanish 11-syllable line would be called a "feminine" 10-syllable line by the French; but the French language has only one vowel (e) that may occur in a final unstressed syllable, while in Spanish there are several (a, e, o, rarely i, u).
RIME
Spanish poetry may be in rimed verse or in blank verse. (1) Rimed verse may have "consonance," in which there is rime of the last stressed vowel and of any consonants and vowels that may follow in the line, as in:
En las presas
Yo divido
Lo cogido
Por igual:
Sólo quiero
Por riqueza
La belleza
Sin rival.
Madre mía, yo soy niña;
No se enfade, no me riña,
Si fiada en su prudencia
Desahogo mi conciencia,
¡Cuán solitaria la nación que un día
Poblara inmensa gente!
¡La nación cuyo imperio se extendía
Del ocaso al oriente!
¡Oh tú, que duermes en casto lecho,
De sinsabores ajeno el pecho,
Y á los encantos de la hermosura
Unes las gracias del corazón,
Deja el descanso, doncella pura,
Y oye los ecos de mi canción!
In a diphthong consisting of a strong and a weak vowel the weak vowel may be disregarded in rime. Cf. above: prudencia, conciencia; corazón, canción; igual, rival.
(2) Or rimed verse may have "assonance," in which there is rime of the last accented vowel and of any final vowel that may follow in the line, but not of consonants.22
Footnote 22: (return)Assonance is rare in popular English verse, but it occurs in some household rimes; e. g.:
Little Tommy Tucker,
He cried for his supper.
What shall little Tommy Tucker have for his supper?
Black-eyed beans and bread and butter.
Here the assonance is ú-er (final unstressed -er in standard present-day English represents vocalic r).
Assonance of alternate lines is the usual rime of the romances, as in:
Cabellos de mi cabeza
lléganme al corvejón;
los cabellos de mi barba
por manteles tengo yo:
las uñas de las mis manos
por cuchillo tajador.
Here the assonance is o.
¡Abenámar, Abenámar,
moro de la morería,
el día que tú naciste
grandes señales había!
Estaba la mar en calma,
la luna estaba crecida:
moro que en tal signo nace,
no debe decir mentira.
Here the assonance is í-a.23
Footnote 23: (return) The romances viejos were originally in lines of approximately sixteen syllables, and every line then had assonance.
Del salón en el ángulo obscuro,
De su dueño tal vez olvidada,
Silenciosa y cubierta de polvo
Veíase el arpa.
¡Cuánta nota dormía en sus cuerdas,
Como el pájaro duerme en las ramas,
Esperando la mano de nieve
Qué sabe arrancarlas!
Here the assonance is á-a.
The following rules for assonance should be noted:
(a) In modern Spanish a word stressed on the final syllable may not assonate with one stressed on a syllable preceding the final.24
Footnote 24: (return) In the old romances and in the medieval epic, á could assonate with á-a. In singing these old verses every line was probably made to end in an unstressed vowel by adding paragogic e to a final stressed syllable. Thus, son was sung as sone, dar as dare, temí as temíe, etc. Cf. Men. Pel., Ant. V, 65; XI, 86, 92; and Men. Pid., Cantar de mío Cid, I, 65 f.
(b) A word stressed on the penult may assonate with one lx stressed on the antepenult. Vowels between the stressed syllable and the final syllable are disregarded, as in cruza, cúpula (ú-a), bañe, márgenes, árabes (á-e).
(c) In stressed diphthongs and triphthongs only the vowels receiving the stress assonate, as in vale, aire (á-e), cabellos, suelo (é-o), envolviendo, aposento (é-o), guardias, alta (á-a), pleito, siento (é-o), mucho, triunfo (ú-o).
(d) In unstressed diphthongs and triphthongs only the strong vowels assonate, as in turba, lluvia (ú-a), licencia, quisierais (é-a), pido, continuo (í-o). Similarly, e or o, before another strong vowel, is disregarded in an unstressed diphthong, as in modo, erróneo (ó-o), crece, héroe (é-e).
(e) In final unstressed syllables, i and u (not in diphthongs) assonate with e and o, respectively, as in verde, débil (é-e), amante, fácil (á-e), líquido, espíritu (í-o).
(3) In Spanish blank verse (versos sueltos, libres, blancos) there is usually no rime; or if there be rime it is merely incidental. Blank verse usually consists of 11-syllable lines.
¡Oh! ¡cuánto rostro veo, á mi censura,
De palidez y de rubor cubierto!
Ánimo, amigos, nadie tema, nadie,
Su punzante aguijón; que yo persigo
En mi sátira el vicio, no al vicioso,
Blank verse is little used in Spanish. It occurs chiefly in serious satirical or philosophical poems. But separate versos sueltos are introduced into some varieties of compositions, such as the romance, seguidilla, silva, etc.25
Footnote 25: (return) The versos sueltos are, with regard to the absence of rime, in imitation of classic Greek and Latin verse. They came into Spain by way of Italy during the Renaissance movement. Abjured by the romanticists, they were restored to favor by Núñez de Arce.
VERSE-MEASURES
A. VERSE WITH BINARY MOVEMENT26
Footnote 26: (return) The term "binary" is used here to distinguish ordinary Spanish verse from that with regular ternary movement. Cf. p. lxx.
In modern Spanish this verse is commonly found in lines of seven, eight or eleven syllables. It may occur in lines of any length; but in lines of five or six syllables the binary and ternary movements are generally mingled. In Old Spanish binary lines of approximately 8+8 and 7+7 syllables were common, and lines of 6+6, or of nine, syllables were then, as now, also occasionally used.27
Footnote 27: (return) Verses of three or four syllables are best treated as half-lines, with inner rime (versos leonínos).
The most popular measure, and the one of most importance in the history of Spanish verse, is the 8+8-syllable line of the old romances, which was later divided into two 8-syllable lines, and became the most common measure in the drama and in popular songs. This line usually has only one rhythmic accent, which falls on the seventh syllable.28
Footnote 28: (return) By "rhythmic accent" is meant the musical accent on the last stressed syllable of a phrase and not syllabic stresses that may occur within a phrase.
Mis arreos son las armas,
mi descanso el pelear,
mi cama las duras peñas,
mi dormir siempre velar
Rarely 8-syllable lines are written with a fixed accent on the third syllable (cf. p. 51, l. 10 f.).29 There is then sometimes pie quebrado in alternate lines, as in:
Hijo mío mucho amado,
Para mientes;
No contrastes á las gentes
Mal su grado.
Ama: é serás amado;
Y podrás
Hazer lo que no harás
Desamado.30
Footnote 29: (return) They are less common in Spanish than in Italian:Sai tu dirme, o fanciullino,
In qual pasco gita sia
La vezzosa Egeria mia
Ch'io pur cerco dal mattino?
(Paolo A. Rolli)
Footnote 30: (return) Note the example of hiatus in this older Spanish.
Next to the popular 8-syllable line the most important measure in modern Spanish verse is that of eleven syllables, with binary movement, which came to Spain from Italy in the fifteenth century, and was generally accepted by the writers of the Siglo de Oro. This 11-syllable line, though of foreign origin, has held the boards as the chief erudite measure in Spanish verse for four centuries, and taken all in all it is the noblest metrical form for serious poems in modern Spanish. A striking peculiarity of the line is its flexibility. It is not divided into hemistichs as were its predecessors, the 14-syllable Alexandrine and the 12-syllable arte mayor verse; but it consists of two phrases and the position of the inner rhythmic accent is usually variable.
A well constructed line of this type has a rhythmic accent on the sixth syllable, or a rhythmic accent on the fourth syllable (usually with syllabic stress on the eighth), beside the necessary accent in the tenth position. Generally the inner accent falls on the sixth syllable approximately twice as often as on the fourth.
Y con diversas flòres va esparcièndo... (León)
Y para envejecèrse florecièron... (Calderón)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Cuna y sepùlcro en un botón hallàron... (Calderón)
Se mira al mùndo á nuestros pies tendìdo... (Zorrilla)
Logically, the close of the first phrase should coincide with the end of the word that receives the inner rhythmic accent, and this is usually so, as in:
¿Qué tengo yò, | que mi amistad procùras?... (Lope)
Son la verdad y Diòs, | Dios verdadèro... (Quevedo)
But in some lines the rhetorical and the rhythmic accents do not coincide, as in:
... pero huyóse
El pudor á vivìr en las cabànas... (Jovellanos)
Del plectro sabiamènte meneàdo... (León)
Que á mi puerta, cubièrto de rocìo... (Lope)
The 11-syllable line may be used alone. Cf. the sonnets of Lope de Vega (p. 14) and Calderón (p. 18), the Epístola satírica of Quevedo (p. 15), the blank verse of Jovellanos (p. 38) and Núñez de Arce (p. 144), et al. The neo-classic poets of the eighteenth century and some of the earlier romanticists even used it in redondillas or assonated:lxiv
En pago de este amor que, mal mi grado,
Hasta el crimen me lleva en su delirio,
Y á no verse por ti menospreciado
Mi virtud elevara hasta el martirio...
¿Por qué de nuevo pálida tristeza
Tus rosadas mejillas descolora?
¿Por qué tu rostro en lágrimas se inunda?
¿Por qué suspiras, niña, y te acongojas?
(Bretón de los Herreros, ¿Quién es ella?)
But the poets of the Siglo de Oro and the neo-classic poets generally used it in combination with 7-syllable lines, as in Leon's verses:
¡Qué descansada vida
la del que huye el mundanal rüido,
y sigue la escondida
senda por donde han ido
los pocos sabios que en el mundo han sido!
Strophes of three 11-syllable lines and one 5-syllable line (versos sáficos) are not uncommon in highly lyric poems. Usually, in the long lines, the inner accent falls on the fourth syllable, with syllabic stress on the eighth, and with cesura after the fifth syllable. Thus:31
Dulce vecino de la verde selva,
Huésped eterno del Abril florido,
Vital aliento de la madre Venus,
Céfiro blando.
(Villegas, Al céfiro)
Footnote 31: (return)Mele (op. cit) states that the Sapphic ode was introduced into Spain from Italy by Antonio Agustín, bishop of Tarragona, in the first half of the sixteenth century, and quotes these lines by Agustín:
Júpiter torna, como suele, rico:
Cuerno derrama Jove copiöso,
Ya que bien puede el pegaseo monte
Verse y la cumbre.
The romanticists used the versos sáficos with rime. Thus, Zorrilla:
Huye la fuente al manantial ingrata,
El verde musgo en derredor lamiendo,
Y el agua limpia en su cristal retrata
Cuanto va viendo.
In the Sapphic strophe of Francisco de la Torre (d. 1594), the short line has seven syllables, and the long line may have inner rhythmic accent on the sixth, or on the fourth syllable. Thus:
El frío Bóreas y el helado Noto
Apoderados de la mar insana
Anegaron agora en este puerto
Una dichosa nave.
(¡Tirsi, Tirsi! vuelve y endereza)
The Sapphic strophe of Francisco de la Torre has been not infrequently imitated. Thus, Bécquer:
Volverán las obscuras golondrinas
En tu balcón sus nidos á colgar,
Y, otra vez, con el ala á sus cristales
Jugando llamarán.
Footnote 32: (return) These long lines are especially cantabile, as most are accented on the third and sixth syllables. Only one is accented on the fourth and eighth.
The 7-syllable line is commonly used in combination with those of eleven syllables (see above). In the seventeenth century, particularly, the 7-syllable line was used in anacreontics, lxvi artistic romances, quintillas, etc., in imitation of the Italian settenario, as in Villegas' Cantilena beginning:
Yo vi sobre un tomillo
Quejarse un pajarillo,
Viendo su nido amado,
De quien era caudillo,
De un labrador robado.
In present-day songs the 7-syllable line is rather rare, except in combination with lines of five syllables, as in:
Camino de Valencia,
Camino largo...
And:
Á la puerta del cielo
Venden zapatos...
In these lines there is no fixed inner rhythmic accent.
The Old Spanish Alexandrine verse-line was composed of two 7-syllable half-lines. In the thirteenth and fourteenth centuries numerous monkish narrative poems (mester de clereçía) were written in this measure:
En el nonbre del Padre,—que fizo toda cosa,
E de don Jhesu Christo,—Fijo dela Gloriosa,
Et del Spiritu Sancto,—que egual dellos posa,
De un confessor sancto—quiero fer vna prosa...
(Gonzalo de Berceo)
The old Alexandrine fell before the rising popularity of the arte mayor verse early in the fifteenth century. In the eighteenth century a 13-syllable Alexandrine appears in Spanish in imitation of the classic French line. This later Spanish Alexandrine is not composed of two distinct half-lines. lxvii It also has, like its French prototype, alternate couplets of masculine and feminine lines (versos agudos and versos llanos or graves). Thus, Iriarte:
En cierta catedral una campana había
Que sólo se tocaba algún solemne día
Con el más recio son, con pausado compás,
Cuatro golpes ó tres solía dar, no más.
There is an inner rhythmic accent on the sixth syllable. Iriarte also revived the older Alexandrine, but without hiatus:
Cuando veo yo algunos,—que de otros escritores
Á la sombra se arriman,—y piensan ser autores...
Recent poets have revived the old Alexandrine.33 Thus, Rubén Darío uses it, even retaining the hiatus between the half-lines; but instead of grouping the lines in quatrains with monorime, as the old monks did, he uses assonance in alternate lines, which is, so far as I know, without precedent:
Es con voz de la Biblia—ó verso de Withman
Que habría que llegar—hasta ti, ¡cazador!
Primitivo y moderno,—sencillo y complicado,
Con un algo de Wáshington—y mucho de Nemrod...
Footnote 33: (return) For their use of this line with ternary movement, see p. lxxix.
Lines of five or six syllables usually have a mingled binary and ternary movement:
Una barquera
Hallé bizarra,
De pocos años
Y muchas gracias.
(N. Moratín)
Salí á las diez
Á ver á Clori
(No lo acerté):
Horas menguadas
Debe de haber...
(L. Moratín)
Lines of 5+5 syllables (versos asclepiadeos) are occasionally written:
Id en las alas—del raudo céfiro,
Humildes versos,—de las floridas
Vegas que diáfano—fecunda el Arlas,
Adonde lento—mi patrio río
Ve los alcázares—de Mantua excelsa.
(L. Moratín)
The Mexican poet Pesado used the same line in his Serenata:
¡Oh tú que duermes—en casto lecho,
De sinsabores—ajeno el pecho,
Y á los encantos—de la hermosura
Unes las gracias—del corazón,
Deja el descanso,—doncella pura,
Y oye los ecos—de mi canción!
The same measure appears in a patriotic song, Himno de Riego:
En las cabezas—él proclamó
La suspirada—constitución,
Y enarbolando—marcial pendón,
Á los leales—acaudilló...34
Footnote 34: (return)It should be noted that these latter verses, like most Spanish patriotic songs, are sung with ternary movement, thus:
Èn las cabèzas—èl proclamò...
This 10-syllable measure is cantabile, and its phrases are too short and too regular to make good recitative verse.
Versos alcaicos differ from the asclepiadeos in that the former have, in a strophe, two lines of 5 + 5, one of nine, and one of ten syllables. Thus, in these lines of Victorio Giner (who probably introduced this strophe into Spain in the second half of the nineteenth century):
Y si los nautas, cantando el piélago,
Con remos hieren y espumas alzan,
Se aduerme á los ecos sus penas
Y á los ecos su batel avanza.
Juan Luis Estelrich (Poesías, 1900) uses versos alcaicos with the first two lines of each strophe esdrújulo, in imitation of Carducci:
Carmen, tu nombre trae al espíritu
Vuelo de aromas, susurro de árboles,
Los píos consorcios del cielo,
Y el cantar melodioso del Lacio.
(Á Carmen Valera.)35
Footnote 35: (return) Cf. Mele, op. cit.
Romances in lines of 6 + 6 (or 6 + 5) syllables occur in popular Spanish verse, as in the Asturian romance of Don Bueso, beginning:
Camina don Bueso—mañanita fría
á tierra de moros—á buscar amiga...
(Men. Pel., Ant. X, 56: cf. also Ant. XI, 102)
This measure was also used in endechas, as in Los comendadores de Córdoba (fifteenth century), beginning:
¡Los comendadores,—por mi mal os vi!
Yo vi á vosotros,—vosotros á mí...
The 9-syllable line was not well received in Spain, and it has been little used. Iriarte, in his desire to vary the metrical constructions of his fables, used it at least once:
Sobre una mesa, cierto día,
Dando estaba conversación
Á un Abanico y á un Manguito
Un Paraguas ó Quitasol...
There is certainly no fixed inner rhythmic accent in these lines. The fact seems to be that the 9-syllable line is too long to be uttered comfortably in one phrase, or breath-group, and it is too short to be regularly divided into parts by cesura.
B. VERSE WITH TERNARY MOVEMENT
Verse with regular ternary movement may occur in lines of any length, but it is commonly found only in lines of ten, eleven or twelve syllables. Many ternary lines of five and six syllables are found, but they are almost invariably mingled with binary lines. This rondel antiguo (Nebrija, quoted by Men. Pel., Ant. V. 66) is ternary throughout, it would seem:
Despide plazer
y pone tristura;
crece en querer
vuestra hermosura.
For mixed movements, see the serranilla on p. 45, l. 9 f.
In lines with regular ternary movement, properly speaking, every primary stress receives a rhythmic accent, and lxxi these accents are always separated by two atonic syllables, as in:
Yo no sè como bàilan aquì,
Que en mi tièrra no bàilan ansì...
Rarely one finds 6-syllable and 9-syllable lines with regular ternary movement, and these are probably never of popular origin. Thus:
Serèna la lùna
Alùmbra en el cièlo,
Domìna en el suèlo
Profùnda quietùd...
(Espronceda, El reo de muerte, II)
Y luègo el estrèpito crèce
Confùso y mezclàdo en un sòn,
Que rònco en las bòvedas hòndas
Tronàndo furiòso zumbò...
(Espronceda, Estudiante de Salamanca)
Formerly the Spanish 10-syllable line occurred usually in combination with other lines, as in:
En la calle de Atòcha, ¡litòn!
Que vìve mi dàma;
Yo me llàmo Bartòlo, ¡litòn!
Litòque, vitòque, y36 èlla Catànla.
—En la càlle del Sòrdo, ¡litòn!
Que vìve mi mòzo,
Pues á cuànto le pìdo, ¡litòn!
Litòque, vitòque, que sièmpre está sòrdo.
Footnote 36: (return) There is hiatus here.
(Quiñones de Benavente, Entremeses, bailes, loas y sainetes, quoted by Milá y Fontanals, Obras completas, Vol. V, p. 324 f.)
Calderón used it in the Viña del Señor:
Á la vìña, á la vìña, zagàles;
Zagàles, venìd, venìd á la vìña.
Á la vìña, á la vìña, zagàles,
Y vàya de jìra, de bùlla y de bàile.
Zagàles, venìd, venìd á la vìña,
Y vàya de bàile, de bùlla y de jìra.
A recent number of the Ilustración Española y Americana (15 Enero, 1911) contains lines of similar construction by Don Rafael Torromé:
Al miràr su carìta sonriènte,
Tan dùlce y tan buèna,
Siempre obsèrvo que mi àlma presiènte,
Con duèlo y con pèna,
Que más tàrde este mùndo inclemènte
Trocarà en sentimièntos de hièna
Los pùros afèctos de su àlma inocènte.
Iriarte did not hesitate to write fables in these 10-syllable lines alone:
De sus hìjos la tòrpe Avetùrda
El pesàdo volàr conocìa...
And the romanticists of the nineteenth century used it not infrequently:
Con inmòvil, irònica muèca
Inclinàron formàndo en redòr...
(Espronceda, Est. de Sal.)
Del salòn en el àngulo obscùro,
De su duèño tal vèz olvidàda,
Silenciòsa y cubièrta de pòlvo,
Veìase el àrpa.
(Bécquer, Rima VII)
In the nineteenth century this line came to be popular in patriotic songs which are sung by the multitude, while the crash of the drum marks the rhythmic accents:
Entonèmos festìvos cantàres,
Pues el dìa felìz ha llegàdo,
Que del yùgo servìl aliviàdo
Goza yà el Españòl libertàd.
(La Constitución)
Al combàte corrèd, Bayamèses,
Que la pàtria os contèmpla orgullòsa;
No temàis una muèrte gloriòsa,
Que morìr por la pàtria es vivìr.
(Cuban national hymn, cf. p. 251)
The commoner form of verse with 11-syllable ternary lines is that popularly called "de gaita gallega" (Men. Pel., Ant., V, p. cxcv; X, 141. Cf. also Milá, op. cit.), the assumption being that this verse is intimately related to that type of popular Galician poetry known as the muiñeira, which was sung to the music of the bagpipe. These lines are typical of the "endecasílabos de gaita gallega":
Tànto bailè á la puèrta del cùra,
Tànto bailè que me diò calentùra;
Tànto bailè á la puèrta del hòrno,
Tànto bailè que me dièron un bòllo.37
Footnote 37: (return) Many Galician muiñeiras have been collected: cf. Milá, op. cit.; Carolina Michaëlis de Vasconcellos, Cancioneiro de Ajuda, Vol. II, Halle, 1904; José Pérez Ballesteros, Cancionero popular gallego, Madrid, 1885.
Menéndez y Pelayo (Ant. X, 141) gives, in his collection of Romances tradicionales de Asturias, the following one in ternary 11-syllable lines:
La tentación
—¡Ày, probe Xuàna de cuèrpo garrido!
¡Ày, probe Xuàna de cuèrpo galàno!
¿Dònde le dèxas al tù buen amigo?
¿Dònde le dèxas al tù buen amàdo?
—¡Muèrto le dèxo á la orìlla del rìo,
muèrto le dèxo á la orìlla del vàdo!
—¿Cuànto me dàs, volverètelo vìvo?
¿Cuànto me dàs, volverètelo sàno?
—Dòyte las àrmas y dòyte el rocìno,
dòyte las àrmas y dòyte el cabàllo.
—No hè menestèr ni armàs ni rocìno,
no hè menestèr ni armàs ni cabàllo...
It should be noted that this poem has assonance of the odd and of the even lines. Men. Pel. says of this popular 11-syllable romance that «su aparición en la poesía popular castellana es un fenómeno singular, aun en Asturias misma, y hasta ahora no se ha presentado más ejemplo que éste.» Note the apparent shifting of stress in armas. Iriarte and L. Moratin did not scorn to use this line.
Iriarte:
Cièrta criàda la càsa barrìa
Còn una escòba muy sùcia y muy vièja...
Moratin (in the chorus of Padres del Limbo):
Hùyan los àños con ràpido vuèlo;
Gòce la tièrra duràble consuèlo;
Mìre á los hòmbres piadòso el Señòr...
The 11-syllable line of ternary movement has had less vogue in artistic verse than those of ten and twelve syllables.38
Footnote 38: (return)In Las hijas del Cid E. Marquina has used a flexible 11-syllable ternary line beginning with either [\-] – – [\-] or – [\-] – [\-]:
Sus nòmbres jùntos los llèvo en el alma,
Jùntos los guàrda tambièn mi memòria.
These are blank verses with occasional assonance.
The Spanish ternary 12-syllable line was formerly used chiefly in combination with lines of ten or eleven syllables. Some examples of mingled 10-and 12-syllable lines have already been given above. Another is:
Mancebìto, perdòne las hèmbras,
Que còmen y bèben y no tienen rèntas.
—Pues, mocìtas, maldìtas sean èllas,
Ó còsan ó làbren ó càiganse muèrtas.
A song of mingled 11-and 12-syllable lines begins thus:
Al pàsar la bàrca, me dìjo el barquèro:
Mòza bonìta no pàga dinero.39
Footnote 39: (return) Cf. Milá, op. cit. In singing pasar, there is apparently a shifting of stress which is not uncommon in songs.
Efforts have been made from time to time to use the ternary movements in erudite verse, but these, for the most part, have proven futile. The most serious and the most successful attempt appears in the use of the copla de arte mayor in the fifteenth century. The copla (metro, versos) de arte mayor consists of mingled 12-and 11-syllable lines arranged in strophes of eight lines, each with consonantal rime according to some definite scheme. The arte mayor verse attained to its most perfect form and its greatest lxxvi popularity in El laberinto de la fortuna (1444?), by Juan de Mena, of which the following is a strophe:
Amores me dieron corona de amores
porque mi nombre por más bocas ande;
entonçes no era mi mal menos grande,
quando me dauan plazer sus dolores;
vençen el seso sus dulçes errores,
mas non duran sienpre, segund luego plazen;
pues me fizieron del mal que vos fazen,
sabed al amor desamar, amadores.
(Strophe 106)
The old arte mayor verse has these distinguishing characteristics:
The line is divided into hemistichs, each of which may have four, five or six syllables, thus:
(1) (-) - - - [/-] (-) | (-) - - - [/-] (-),
except that the final syllable of the first hemistich and the initial syllable of the second may not both be lacking. These arrangements may also occur (the third is rare):
(2) (-) - - - [/-] - - | - - - [/-] (-)
(3) (-) - - - [/-] | - - - - - [/-] (-).
Examples of types:
(1) Las grandes fazañas | de nuestros mayores... (Str. 4)
Vayan de gente | sabidos en gente... (Str. 3)
Reconocerán | maguer que feroce... (Str. 274)
Assí que qualquiera | cuerpo ya muerto... (Str. 244)
Cuya virtud | maguer que reclama...
Sufren que passen | males e viçios... (Str. 232)
(2) E ví á Pitágoras | que defendía... (Str. 118)
Bien como médico | mucho famoso... (Str. 178)
(3) Quando el señor | es en neçessidad... (Str. 258)
The initial unstressed syllable of the first hemistich is lacking in approximately one-third of the lines of the Laberinto. These lines resemble the 11-syllable gaita gallega verse, and the others resemble the popular Galician 12-syllable ternary line, for in both the final unstressed syllable of the first hemistich may fall,40 which seems to indicate that the appearance of the arte mayor verse in Castilian was due to Galician influence.
Footnote 40: (return)Cf. these Galician muiñeiras, cited by Milá y Fontanals (Romanía, VI, p. 47 f.):
Càndo te vèxo | na bèira do rìo,
Quèda o meu còrpo | tembràndo de frìo;
Càndo te vèxo | d'o mònte n'altùra,
A tòdo o mon córpo | lle dà calentùra.
Ìsca d'ahì | galìña maldìta,
Ìsca d'ahì | non me màte la pìta;
Ìsca d'ahì | galìña ladròna,
Ìsca d'ahì | pra càs de tua dòna.
Again, as in many Galician songs of this type, the ternary movement of the old arte mayor verse is not strictly regular. Approximately nine-tenths of the lines in the Laberinto may be read with regular ternary movement:
(-) [/-] - - [/-] (-) | (-) [/-] - - [/-] (-),
by giving a rhythmic accent to a syllable with secondary stress or to a middle syllable in a group of atonics, in a not inconsiderable number of lines, as in:
Pòr las altùras, | collàdos y cèrros...
Assì que tu ères | la gòvernadòra...
In the remaining lines the commonest movement is:
(-) - [/-] - [/-] (-) | (-) - [/-] - [/-] (-),
as in:
Aquel claro padre, aquel dulce fuente... lxxviii
In the second half of the sixteenth century and in the seventeenth century, the arte mayor verse was out of fashion, although it appeared occasionally, as in these lines of Lope de Vega (a variety of the Sapphic strophe), with inner rime:
Amor poderoso en cielo y en tierra,
dulcísima guerra de nuestros sentidos,
¡oh, cuántos perdidos con vida inquiëta
tu imperio sujeta!
(From first act of Dorotea)
In the nineteenth century it was restored to favor by the romanticists.41 Good examples are: Espronceda, El templario; Avellaneda, Las siete palabras; and Zorrilla, Á un torreón (part). Some writers used it even in the drama (cf. Gil y Zárate, Guzmán el bueno). The modern arte mayor verse is written in 12-syllable lines, usually with regular ternary movement. Thus:
¡Oh Antìlla dichòsa! | ¿qué màgicos sònes,
Qué lùz inefàble, | qué extràña alegrìa,
Del cièlo destièrran los nègros crespònes,
Prestàndo á esta nòche | la pòmpa del dìa?
¿Por qué tan ufàna, | tan bèlla la lùna
Con fàz refulgènte | comiènza su gìro,
Y no hày leve sòmbra | que crùce importùna
Su tròno esmaltàdo | de plàta y zafìro?
(Avellaneda, Serenata de Cuba)
Footnote 41: (return) Iriarte, of course, had written a fable or two in arte mayor verse. Cf. Fábula XXXIX.
Soldàdos, la Pàtria | nos llàma á la lìd;
Jurèmos por èlla | vencèr ó morìr;
Serènos, alègres, | valièntes, osàdos,
Cantèmos, soldàdos, | el hìmno á la lìd:
Ya nuèstros acèntos | el òrbe se admìre,
Y en nòsotros42 mìre | los hìjos del Cìd;
Ya nuèstros acèntos | el òrbe se admìre,
Y en nòsotros mìre | los hìjos del Cìd.
(Himno de Riego: cf. p. 242)
Footnote 42: (return) Note in nosotros the shifting of stress, which the musical notation indicates clearly.
Lines of fourteen and fifteen syllables with ternary movement are never popular, and in artistic verse they are exceedingly rare. Avellaneda used these measures in Soledad del alma:
Sàle la auròra risuèña, de flòres vestìda,
Dàndole al cièlo y al càmpo variàdo colòr;
Tòdo se anìma sintièndo brotàr nueva vìda,
Càntan las àves, y el àura suspìra de amòr.
Huyèron velòces—cual nùbes que el viènto arrebàta—
Los brèves momèntos de dìcha que el cièlo me diò...
¿Por què mi existència, ya inùtil, su cùrso dilàta,
Si el tèrmino ansiàdo á su espàlda perdìdo dejò?
Some recent poets have attempted to write ternary Alexandrine verse. Thus, the Peruvian poet, José S. Chocano (1867-):
Los Estados Unidos, como argolla de bronce,
contra un clavo sujetan de la América un pie;
y la América debe, si pretende ser libre,
imitarles primero, é igualarles después.
Imitemos ¡oh Musa! las crujientes estrofas
que en el Norte se arrastran con la gracia de un tren,
y que giren las rimas como ruedas veloces
y que caigan los versos como varas de riel.
(La epopeya del Pacífico)
STROPHES
There are certain conventional combinations of line and rime known by special names. Those used in modern Spanish may best be considered under the heads (I) Assonance, (II) Consonantal Rime, and (III) No Rime.
I. (1) The romance is the most characteristic and national of all Spanish meters. The proper romance consists of 8-syllable lines with assonance in alternate lines43 (cf. pp. 1-8, 42, etc.). The structure of the romance line has already been treated (p. lxi). In the old romances there was no division into stanzas, but poets from the end of the sixteenth century on regularly employ a pause after every fourth line, thereby creating a series of quatrains (pp. 42, 60, etc.), except in the drama (p. 19).
Footnote 43: (return) Historically, of i6-syllable lines, all assonating.
(2) Alternate assonance may be employed with lines of any length. With 11-syllable lines the verse is called romance heroico or real. Lines of seven syllables make versos anacreónticos. The name endecha is given to some assonated verse of either six (p. 124) or seven syllables. When the first three lines of a stanza are of seven syllables and the last of eleven, the verse is called endecha real. For examples of alternate assonance in lines of various lengths, see pp. 122 (2 examples), 123, 137, 160, 177.
An estribillo, or refrain, may be used in any assonating verse (p. 45).
(3) The use of alternate assonance in lines of fourteen syllables (pp. 211, 212) is a none too happy device of the author.
(4) The seguidilla is usually a stanza of seven lines of seven and five syllables in length, in this order: 7, 5, 7, 5; 5, 7, 5. There is usually a pause after the fourth line; lines 2 and 4 have one assonance and lines 5 and 7 another. The assonances change from one stanza to another. See pp. 112 and 120. In some seguidillas the stanzas consist only of the first four lines described.
II. The native Spanish strophes are usually combinations of 8-syllable or shorter lines. The 11-syllable line, itself an importation from Italy, brought with it many well-known Italian strophes. In none of the pure Italian forms are lines ending in agudos or esdrújulos permissible.
(1) The redondilla mayor consists of four 8-syllable lines with the rime-scheme abba (pp. 149, 167), or, less commonly, abab (p. 136). It is a common and characteristic Spanish meter. The redondilla menor has the same form expressed in lines of less than eight syllables. The same rime-schemes are found with lines of seven or of eleven (pp. 117, 207) syllables, and with combinations of eleven and seven (p. 134), or eleven and five (p. 86) syllables; but they are not properly called redondillas.
(2) The quintilla is a 5-line strophe, usually of 8-syllable lines. Only two rimes are used in one stanza, and not more than two lines having the same rime should stand together (pp. 26, 114). Quintillas are sometimes written with lines of other lengths. Examples with eleven and seven syllables are found on pp. 128, 133 and 148. The stanza used in Vida retirada (p. 9) is termed lira: cf. Introduction, p. xxiii.
(3) The décima (or espinela) is a 10-line strophe of 8-syllable lines which may be considered as two quintillas; but there should be a pause after the fourth line, and the rime-scheme is usually as follows: abbaaccddc.
(4) The arte mayor line has already been described (p. lxxv). The copla de arte mayor is a stanza of eight such lines, usually having the rime-scheme abbaacca.
(5) The octava rima (Ital. ottava rima) is an Italian form. Each stanza has eight 11-syllable lines with the rime-scheme abababcc. Examples are found of octaves employing short lines. A variety of the octava rima is the octava bermudina with the rime-scheme abbcdeec, the lines in c ending in agudos.
(6) The soneto (sonnet) is formed of fourteen 11-syllable lines. In the Siglo de Oro it appears as a much stricter form than the English sonnet of the corresponding period. The quatrains have the regular construction abba, and the tiercets almost always follow one of two types: either cde, cde, or cdcdcd. See pp. 14, 18, 148, etc.
(7) Tercetos (Italian terza rima), the verse used by Dante in the Divina Commedia, are formed of 11-syllable lines in groups of three, with the rime-scheme aba, bcb, cdc, etc., ending yzyz. See p. 15.
(8) The term canción, which means any lyrical composition, is also applied specifically to a verse form in which the poet invents a typical strophe, with a certain length of line and order of rimes, and adheres to this type of stanza throughout the whole poem. The lines are of eleven and seven syllables,—the Italian structure. Of such nature are the poems on pp. 8, 20, 71, 137 (bottom), 174, 190.
The same procedure is employed with lines of any length, lxxxiii but the poem is not then called canción. For strophes in 10-syllable lines, see p. 199; in 8-syllable lines, pp. 16, 51, 83, 151; in 7-syllables, p. 202.
(9) The silva is a free composition of 11-and 7-syllable lines. Most of the lines rime, but without any fixed order, and lines are often left unrimed. See pp. 46, 54, 152, 214 (bottom), etc. A similar freely riming poem in lines of seven syllables is Villegas' Cantilena (p. 17).
(10) The Asclepiadean verse (p. lxviii) and the Sapphic (p. lxiv) and Alcaic (p. lxix) strophes have already been described. These may be rimed, or in blank verse.
(11) Numerous conventional names are given to poems for some other characteristic than their metrical structure. Thus a glosa (gloss) is a poem "beginning with a text, a line of which enters into each of the stanzas expounding it." A letra may be a short gloss. The name letrilla is applied sometimes to a little poem in short lines which may be set to music (p. 9), and sometimes to a strophic poem with a refrain (p. 16). A madrigal is a short silva upon a light topic, an expanded conceit. The term cantilena is given to any short piece of verse intended to be set to music (p. 17). Serranillas, in which is described the meeting of a gentleman with a rustic maiden, are famous for the examples written by Juan Ruiz and the Marquis of Santillana. A villancico is a popular poem with a refrain, usually dealing with an episode celebrated in a church festival (p. 13).
III. Versos sueltos, libres or blancos (blank verse) are formed, as in English, of 11-syllable lines, with occasionally a shorter line thrown in. There is no rime, but sometimes a couplet may mark the close of an idea. See pp. 38 and 144, and cf. also p. lx.
ABENÁMAR
Abenámar, Abenámar,
moro de la morería,
el día que tú naciste
grandes señales había!
5Estaba la mar en calma,
la luna estaba crecida:
moro que en tal signo nace,
no debe decir mentira.—
Allí respondiera el moro,
10bien oiréis lo que decía:
—Yo te la diré, señor,
aunque me cueste la vida,
porque soy hijo de un moro
y una cristiana cautiva;
15siendo yo niño y muchacho
mi madre me lo decía:
que mentira no dijese,
que era grande villanía:
2por tanto pregunta, rey,
que la verdad te diría.
—Yo te agradezco, Abenámar
aquesa tu cortesía.
¿Qué castillos son aquéllos?
5¡Altos son y relucían!
—El Alhambra era, señor,
y la otra la mezquita;
los otros los Alixares,
labrados á maravilla.
10El moro que los labraba
cien doblas ganaba al día,
y el día que no los labra
otras tantas se perdía.
El otro es Generalife,
15huerta que par no tenía;
el otro Torres Bermejas,
castillo de gran valía.—
Allí habló el rey don Juan,
bien oiréis lo que decía:
20—Si tú quisieses, Granada,
contigo me casaría;
daréte en arras y dote
á Córdoba y á Sevilla.
—Casada soy, rey don Juan,
25casada soy, que no viuda;
el moro que á mí me tiene
3muy grande bien me quería.
Fonte-frida, fonte-frida,
fonte-frida y con amor,
do todas las avecicas
van tomar consolación,
5sino es la tortolica
que está viuda y con dolor.
Por allí fuera á pasar
el traidor de ruiseñor:
las palabras que le dice
10llenas son de traición:
—Si tú quisieses, señora,
yo sería tu servidor.
—Vete de ahí, enemigo,
malo, falso, engañador,
15que ni poso en ramo verde,
ni en prado que tenga flor;
que si el agua hallo clara,
turbia la bebía yo;
que no quiero haber marido,
20porque hijos no haya, no:
no quiero placer con ellos,
ni menos consolación.
¡Déjame, triste enemigo,
malo, falso, mal traidor,
25que no quiero ser tu amiga,
ni casar contigo, no.
EL CONDE ARNALDOS
¡Quién hubiese tal ventura
sobre las aguas del mar,
como hubo el conde Arnaldos
la mañana de San Juan!
5Con un falcón en la mano
la caza iba á cazar,
vió venir una galera
que á tierra quiere llegar.
Las velas traía de seda,
10la jarcia de un cendal,
marinero que la manda
diciendo viene un cantar
que la mar facía en calma,
los vientos hace amainar,
15los peces que andan nel hondo
arriba los hace andar,
las aves que andan volando
nel mástel las faz posar.
Allí fabló el conde Arnaldos,
20bien oiréis lo que dirá:
—Por Dios te ruego, marinero,
dígasme ora ese cantar.—
Respondióle el marinero,
tal respuesta le fué á dar:
25—Yo no digo esta canción
sino á quien conmigo va.
LA CONSTANCIA
Mis arreos son las armas,
mi descanso el pelear,
mi cama las duras peñas,
mi dormir siempre velar.
5Las manidas son escuras,
los caminos por usar,
el cielo con sus mudanzas
ha por bien de me dañar,
andando de sierra en sierra
10por orillas de la mar,
por probar si en mi ventura
hay lugar donde avadar.
Pero por vos, mi señora,
todo se ha de comportar.
EL AMANTE DESDICHADO
En los tiempos que me vi
más alegre y placentero,
yo me partiera de Burgos
para ir á Valladolid:
encontré con un Palmero,
20quien me habló, y dijo así:
—¿Dónde vas tú, el desdichado?
¿Dónde vas? ¡triste de ti!
¡Oh persona desgraciada,
en mal punto te conocí!
256Muerta es tu enamorada,
muerta es, que yo la vi;
las andas en que la llevan
de negro las vi cubrir,
los responsos que le dicen
5yo los ayudé á decir:
siete condes la lloraban,
caballeros más de mil,
llorábanla sus doncellas,
llorando dicen así:
10—¡Triste de aquel caballero
que tal pérdida pierde aquí!—
Desque aquesto oí, mezquino,
en tierra muerto caí,
y por más de doce horas
15no tornara, triste, en mí.
Desque hube retornado,
á la sepultura fuí,
con lágrimas de mis ojos
llorando decía así:
20—Acógeme, mi señora,
acógeme á par de ti.—
Al cabo de la sepultura
esta triste voz oí:
—Vive, vive, enamorado,
25vive, pues que yo morí:
Dios te dé ventura en armas,
y en amor otro que sí,
que el cuerpo come la tierra,
y el alma pena por ti.—
EL PRISIONERO
Por el mes era de mayo
cuando hace la calor,
cuando canta la calandria,
y responde el ruiseñor,
5cuando los enamorados
van á servir al amor,
sino yo, triste, cuitado,
que vivo en esta prisión,
que ni sé cuándo es de día
10ni cuándo las noches son,10
sino por un avecilla
que me cantaba al albor.
Matómela un ballestero,
¡déle Dios mal galardón!
15Cabellos de mi cabeza15
lléganme al corvejón;
los cabellos de mi barba
por manteles tengo yo:
las uñas de las mis manos
20por cuchillo tajador.
Si lo hacía el buen rey,
hácelo como señor:
si lo hace el carcelero,
hácelo como traidor.
25Mas ¡quién ahora me diese
un pájaro hablador,
8siquiera fuese calandria,
ó tordico ó ruiseñor:
criado fuese entre damas
y avezado á la razón,
que me lleve una embajada
5á mi esposa Leonor,
que me envíe una empanada,
no de truchas ni salmón,
sino de una lima sorda
y de un pico tajador:
10la lima para los hierros,
y el pico para el torreón!—
Oídolo había el rey,
mandóle quitar la prisión.
CANCIÓN
Muy graciosa es la doncella:
15¡cómo es bella y hermosa!
Digas tú, el marinero
que en las naves vivías,
si la nave ó la vela ó la estrella
es tan bella.
20Digas tú, el caballero
que las armas vestías,
si el caballo ó las armas ó la guerra
es tan bella.
9Digas tú, el pastorcico
que el ganadico guardas,
si el ganado ó los valles, ó la sierra
es tan bella.
VIDA RETIRADA
¡Qué descansada vida
la del que huye el mundanal rüido,
y sigue la escondida
15senda por donde han ido
los pocos sabios que en el mundo han sido!
Que no le enturbia el pecho
10de los soberbios grandes el estado,
ni del dorado techo
se admira, fabricado
del sabio moro, en jaspes sustentado.
No cura si la fama
5canta con voz su nombre pregonera,
ni cura si encarama
la lengua lisonjera
lo que condena la verdad sincera.
¿Qué presta á mi contento
10si soy del vano dedo señalado?
si en busca de este viento
ando desalentado
con ansias vivas, y mortal cuidado?
¡Oh campo, oh monte, oh río!
15¡oh secreto seguro deleitoso!
roto casi el navío,
á vuestro almo reposo
huyo de aqueste mar tempestüoso.
Un no rompido sueño,
20un día puro, alegre, libre quiero;
no quiero ver el ceño
vanamente severo
de quien la sangre ensalza ó el dinero.
Despiértenme las aves
25con su cantar süave no aprendido,
no los cuidados graves
de que es siempre seguido
quien al ajeno arbitrio está atenido.
11Vivir quiero conmigo,
gozar quiero del bien que debo al cielo,
á solas sin testigo,
libre de amor, de celo,
de odio, de esperanzas, de recelo.
5Del monte en la ladera
por mi mano plantado tengo un huerto
que con la primavera
de bella flor cubierto
ya muestra en esperanza el fruto cierto.
10Y como codiciosa
de ver y acrecentar su hermosura,
desde la cumbre airosa
una fontana pura
hasta llegar corriendo se apresura.
15Y luego sosegada
el paso entre los árboles torciendo,
el suelo de pasada
de verdura vistiendo,
y con diversas flores va esparciendo.
20El aire el huerto orea,
y ofrece mil olores al sentido,
los árboles menea
con un manso rüido
que del oro y del cetro pone olvido.
25Ténganse su tesoro
los que de un flaco leño se confían:
no es mío ver el lloro
de los que desconfían
12cuando el cierzo y el ábrego porfían.
La combatida antena
cruje, y en ciega noche el claro día
se torna, al cielo suena
confusa vocería,
5y la mar enriquecen á porfía.
Á mí una pobrecilla
mesa de amable paz bien abastada
me baste, y la vajilla
de fino oro labrada
10sea de quien la mar no teme airada.
Y mientras miserable-
mente se están los otros abrasando
en sed insaciable
del no durable mando,
15tendido yo á la sombra esté cantando;
Á la sombra tendido
de yedra y lauro eterno coronado,
puesto el atento oído
al son dulce acordado
20del plectro sabiamente meneado.
Á CRISTO CRUCIFICADO
No me mueve, mi Dios, para quererte
El cielo que me tienes prometido,
Ni me mueve el infierno tan temido
13Para dejar por eso de ofenderte.
Tú me mueves, Señor; muéveme el verte
Clavado en una cruz y escarnecido;
Muéveme ver tu cuerpo tan herido;
Muévenme tus afrentas y tu muerte.
5Muéveme, al fin, tu amor, y en tal manera,
Que aunque no hubiera cielo, yo te amara.
Y aunque no hubiera infierno, te temiera.
No me tienes que dar porque te quiera;
Pues aunque lo que espero no esperara.
10Lo mismo que te quiero te quisiera.
CANCIÓN DE LA VIRGEN
Pues andáis en las palmas,
Ángeles santos,
Que se duerme mi niño,
Tened los ramos.
15Palmas de Belén
Que mueven airados
Los furiosos vientos,
Que suenan tanto,
No le hagáis ruido,
20Corred más paso;
Que se duerme mi niño,
Tened los ramos.
El niño divino,
14Que está cansado
De llorar en la tierra,
Por su descanso
Sosegar quiere un poco
Del tierno llanto;
5Que se duerme mi niño,
Tened los ramos.
Rigurosos hielos
Le están cercando,
Ya veis que no tengo
10Con que guardarlo:
Ángeles divinos,
Que vais volando,
Que se duerme mi niño,
Tened los ramos.
MAÑANA
¿Qué tengo yo, que mi amistad procuras?
¿Qué interés se te sigue, Jesús mío,
Que á mi puerta, cubierto de rocío,
Pasas las noches del invierno escuras?
¡Oh cuánto fueron mis entrañas duras,
20Pues no te abrí! ¡Qué extraño desvarío,
Si de mi ingratitud el hielo frío
Secó las llagas de tus plantas puras!
¡Cuántas veces el ángel me decía:
«Alma, asómate agora á la ventana;
25Verás con cuánto amor llamar porfía!»
15Y ¡cuántas, hermosura soberana,
«Mañana le abriremos,» respondía!
Para lo mismo responder mañana.
EPÍSTOLA SATÍRICA Y CENSORIA
Contra las costumbres presentes de los castellanos,
escrita al Conde-Duque de Olivares.
No he de callar, por más que con el dedo,
Ya tocando la boca, ó ya la frente,
5Silencio avises ó amenaces miedo.
¿No ha de haber un espíritu valiente?
¿Siempre se ha de sentir lo que se dice?
¿Nunca se ha de decir lo que se siente?
Hoy sin miedo que libre escandalice
10Puede hablar el ingenio, asegurado
De que mayor poder le atemorice.
En otros siglos pudo ser pecado
Severo estudio y la verdad desnuda,
Y romper el silencio el bien hablado.
15Pues sepa quien lo niega y quien lo duda
Que es lengua la verdad de Dios severo
Y la lengua de Dios nunca fué muda.
Son la verdad y Dios, Dios verdadero:
Ni eternidad divina los separa,
20Ni de los dos alguno fué primero.
LETRILLA SATÍRICA
Poderoso caballero
Es don Dinero.
Madre, yo al oro me humillo:
Él es mi amante y mi amado,
5Pues de puro enamorado,
De contino anda amarillo;
Que pues, doblón ó sencillo,
Hace todo cuanto quiero,
Poderoso caballero
10Es don Dinero.
Nace en las Indias honrado,
Donde el mundo le acompaña;
Viene á morir en España
Y es en Génova enterrado.
15Y pues quien le trae al lado
Es hermoso, aunque sea fiero,
Poderoso caballero
Es don Dinero.
Es galán y es como un oro,
20Tiene quebrado el color,
Persona de gran valor,
Tan cristiano como moro;
Pues que da y quita el decoro
Y quebranta cualquier fuero,
25Poderoso caballero
Es don Dinero.
17Son sus padres principales
Y es de nobles descendiente,
Porque en las venas de Oriente
Todas las sangres son reales:
Y pues es quien hace iguales
5Al duque y al ganadero,
Poderoso caballero
Es don Dinero.
CANTILENA: DE UN PAJARILLO
Yo vi sobre un tomillo
Quejarse un pajarillo,
10Viendo su nido amado,
De quien era caudillo,
De un labrador robado.
Vile tan congojado
Por tal atrevimiento
15Dar mil quejas al viento,
Para que al cielo santo
Lleve su tierno llanto,
Lleve su triste acento.
Ya con triste armonía,
20Esforzando el intento,
Mil quejas repetía;
Ya cansado callaba,
18Y al nuevo sentimiento
Ya sonoro volvía.
Ya circular volaba,
Ya rastrero corría,
Ya pues de rama en rama
5Al rústico seguía;
Y saltando en la grama,
Parece que decía:
«Dame, rústico fiero,
Mi dulce compañía»;
10Y que le respondía
El rústico: «No quiero.»
SONETO
Estas que fueron pompa y alegría
Despertando al albor de la mañana,
Á la tarde serán lástima vana
15Durmiendo en brazos de la noche fría.
Este matiz que al cielo desafía,
Iris listado de oro, nieve y grana,
Será escarmiento de la vida humana:
¡Tanto se emprende en término de un día!
20Á florecer las rosas madrugaron,
Y para envejecerse florecieron:
Cuna y sepulcro en un botón hallaron.
Tales los hombres sus fortunas vieron:
En un día nacieron y expiraron;
25Que pasados los siglos, horas fueron.
CONSEJO DE CRESPO A SU HIJO
EL ALCALDE DE ZALAMEA (11, 21)
Por la gracia de Dios, Juan,
Eres de linaje limpio
Más que el sol, pero villano:
Lo uno y lo otro te digo,
5Aquello, porque no humilles
Tanto tu orgullo y tu brío,
Que dejes, desconfiado,
De aspirar con cuerdo arbitrio
Á ser más; lo otro, porque
10No vengas, desvanecido,
Á ser menos: igualmente
Usa de entrambos designios
Con humildad; porque siendo
Humilde, con recto juicio
15Acordarás lo mejor;
Y como tal, en olvido
Pondrás cosas que suceden
Al revés en los altivos.
¡Cuántos, teniendo en el mundo
20Algún defecto consigo,
Le han borrado por humildes!
Y ¡a cuántos, que no han tenido
Defecto, se le han hallado,
Por estar ellos mal vistos!
25Sé cortés sobremanera,
20Sé liberal y esparcido;
Que el sombrero y el dinero
Son los que hacen los amigos;
Y no vale tanto el oro
Que el sol engendra en el indio
5Suelo que conduce el mar,
Como ser uno bienquisto.
No hables mal de las mujeres:
La más humilde, te digo
Que es digna de estimación,
10Porque, al fin, dellas nacimos.
EL MURCIÉLAGO ALEVOSO
INVECTIVA
Estaba Mirta bella
Cierta noche formando en su aposento,
Con gracioso talento,
Una tierna canción, y porque en ella
15Satisfacer á Delio meditaba,
Que de su fe dudaba,
Con vehemente expresión le encarecía
El fuego que en su casto pecho ardía.
Y estando divertida,
20Un murciélago fiero, ¡suerte insana!
Entró por la ventana;
21Mirta dejó la pluma, sorprendida,
Temió, gimió, dio voces, vino gente;
Y al querer diligente
Ocultar la canción, los versos bellos
De borrones llenó, por recogellos.
5Y Delio, noticioso
Del caso que en su daño había pasado,
Justamente enojado
Con el fiero murciélago alevoso,
Que había la canción interrumpido,
10Y á su Mirta afligido,
En cólera y furor se consumía,
Y así á la ave funesta maldecía:
«Oh monstruo de ave y bruto,
Que cifras lo peor de bruto y ave,
15Visión nocturna grave,
Nuevo horror de las sombras, nuevo luto,
De la luz enemigo declarado,
Nuncio desventurado
De la tiniebla y de la noche fría,
20¿Qué tienes tú que hacer donde está el día?
«Tus obras y figura
Maldigan de común las otras aves,
Que cánticos süaves
Tributan cada día á la alba pura;
25Y porque mi ventura interrumpiste,
Y á su autor afligiste,
Todo el mal y desastre te suceda
Que á un murciélago vil suceder pueda.
22«La lluvia repetida,
Que viene de lo alto arrebatada,
Tan sólo reservada
Á las noches, se oponga á tu salida;
Ó el relámpago pronto reluciente
5Te ciegue y amedrente;
Ó soplando del Norte recio el viento,
No permita un mosquito á tu alimento.
«La dueña melindrosa,
Tras el tapiz do tienes tu manida,
10Te juzgue, inadvertida,
Por telaraña sucia y asquerosa,
Y con la escoba al suelo te derribe;
Y al ver que bulle y vive,
Tan fiera y tan ridícula figura,
15Suelte la escoba y huya con presura.
«Y luego sobrevenga
El juguetón gatillo bullicioso,
Y primero medroso
Al verte, se retire y se contenga,
20Y bufe y se espeluce horrorizado,
Y alce el rabo esponjado,
Y el espinazo en arco suba al cielo,
Y con los pies apenas toque el suelo.
«Mas luego recobrado,
25Y del primer horror convalecido,
El pecho al suelo unido,
Traiga el rabo del uno al otro lado,
Y cosido en la tierra, observe atento;
23Y cada movimiento
Que en ti llegue á notar su perspicacia,
Le provoque al asalto y le dé audacia.
«En fin sobre ti venga,
Te acometa y ultraje sin recelo,
5Te arrastre por el suelo, 5
Y á costa de tu daño se entretenga;
Y por caso las uñas afiladas
En tus alas clavadas,
Por echarte de sí con sobresalto,
10Te arroje muchas veces á lo alto 10
«Y acuda á tus chillidos
El muchacho, y convoque á sus iguales,
Que con los animales
Suelen ser comúnmente desabridos;
15Que á todos nos dotó naturaleza 15
De entrañas de fiereza,
Hasta que ya la edad ó la cultura
Nos dan humanidad y más cordura.
«Entre con algazara
20La pueril tropa, al daño prevenida, 20
Y lazada oprimida
Te echen al cuello con fiereza rara;
Y al oirte chillar alcen el grito
Y te llamen maldito;
25Y creyéndote al fin del diablo imagen, 25
Te abominen, te escupan y te ultrajen.
«Luego por las telillas
De tus alas te claven al postigo,
24Y se burlen contigo,
Y al hocico te apliquen candelillas,
Y se rían con duros corazones
De tus gestos y acciones,
Y á tus tristes querellas ponderadas
5Correspondan con fiesta y carcajadas.
«Y todos bien armados
De piedras, de navajas, de aguijones,
De clavos, de punzones,
De palos por los cabos afilados
10(De diversión y fiesta ya rendidos),
Te embistan atrevidos,
Y te quiten la vida con presteza,
Consumando en el modo su fiereza.
«Te puncen y te sajen,
15Te tundan, te golpeen, te martillen,
Te piquen, te acribillen,
Te dividan, te corten y te rajen,
Te desmiembren, te partan, te degüellen,
Te hiendan, te desuellen,
20Te estrujen, te aporreen, te magullen,
Te deshagan, confundan y aturrullen.
«Y las supersticiones
De las viejas creyendo realidades,
Por ver curiosidades,
25En tu sangre humedezcan algodones,
Para encenderlos en la noche obscura,
Creyendo sin cordura
Que verán en el aire culebrinas
25Y otras tristes visiones peregrinas.
«Muerto ya, te dispongan
El entierro, te lleven arrastrando,
Gori, gori, cantando,
Y en dos filas delante se compongan,
5Y otros, fingiendo voces lastimeras,
Sigan de plañideras,
Y dirijan entierro tan gracioso
Al muladar más sucio y asqueroso;
«Y en aquella basura
10Un hoyo hondo y capaz te faciliten,
Y en él te depositen,
Y allí te den debida sepultura;
Y para hacer eterna tu memoria,
Compendiada tu historia
15Pongan en una losa duradera,
Cuya letra dirá de esta manera:
Epitafio
FIESTA DE TOROS EN MADRID
Madrid, castillo famoso
Que al rey moro alivia el miedo,
Arde en fiestas en su coso
Por ser el natal dichoso
5De Alimenón de Toledo.
Su bravo alcaide Aliatar,
De la hermosa Zaida amante,
Las ordena celebrar
Por si la puede ablandar
10El corazón de diamante.
Pasó, vencida á sus ruegos,
Desde Aravaca á Madrid;
Hubo pandorgas y fuegos,
Con otros nocturnos juegos
15Que dispuso el adalid.
Y en adargas y colores,
En las cifras y libreas,
Mostraron los amadores,
Y en pendones y preseas,
20La dicha de sus amores.
Vinieron las moras bellas
De toda la cercanía,
Y de lejos muchas de ellas:
Las más apuestas doncellas
2527Que España entonces tenía.
Aja de Jetafe vino,
Y Zahara la de Alcorcón,
En cuyo obsequio muy fino
Corrió de un vuelo el camino
5El moraicel de Alcabón;
Jarifa de Almonacid,
Que de la Alcarria en que habita
Llevó á asombrar á Madrid
Su amante Audalla, adalid
10Del castillo de Zorita.
De Adamuz y la famosa
Meco llegaron allí
Dos, cada cual más hermosa,
Y Fátima la preciosa,
15Hija de Alí el alcadí.
El ancho circo se llena
De multitud clamorosa,
Que atiende á ver en la arena
La sangrienta lid dudosa,
20Y todo en torno resuena.
La bella Zaida ocupó
Sus dorados miradores
Que el arte afiligranó,
Y con espejos y flores
25Y damascos adornó.
Añafiles y atabales,
Con militar armonía,
Hicieron salva, y señales
28De mostrar su valentía
Los moros más principales.
No en las vegas de Jarama
Pacieron la verde grama
Nunca animales tan fieros,
5Junto al puente que se llama,
Por sus peces, de Viveros,
Como los que el vulgo vió
Ser lidiados aquel día;
Y en la fiesta que gozó,
10la popular alegría
Muchas heridas costó.
Salió un toro del toril
Y á Tarfe tiró por tierra,
Y luego á Benalguacil;
15Después con Hamete cierra
El temerón de Conil.
Traía un ancho listón
Con uno y otro matiz
Hecho un lazo por airón,
20Sobre la inhiesta cerviz
Clavado con un arpón.
Todo galán pretendía
Ofrecerle vencedor
Á la dama que servía:
25Por eso perdió Almanzor
El potro que más quería.
El alcaide muy zambrero
De Guadalajara, huyó
29Mal herido al golpe fiero,
Y desde un caballo overo
El moro de Horche cayó.
Todos miran á Aliatar,
Que, aunque tres toros ha muerto,
5No se quiere aventurar,
Porque en lance tan incierto
El caudillo no ha de entrar.
Mas viendo se culparía,
Va á ponérsele delante:
10La fiera le acometía,
Y sin que el rejón la plante
Le mató una yegua pía.
Otra monta acelerado:
Le embiste el toro de un vuelo,
15Cogiéndole entablerado;
Rodó el bonete encarnado
Con las plumas por el suelo.
Dió vuelta hiriendo y matando
Á los de á pie que encontrara,
20El circo desocupando,
Y emplazándose, se para,
Con la vista amenazando.
Nadie se atreve á salir:
La plebe grita indignada,
25Las damas se quieren ir,
Porque la fiesta empezada
No puede ya proseguir.
Ninguno al riesgo se entrega
30Y está en medio el toro fijo,
Cuando un portero que llega
De la puerta de la Vega,
Hincó la rodilla, y dijo:
Sobre un caballo alazano,
5Cubierto de galas y oro, 5
Demanda licencia urbano
Para alancear á un toro
Un caballero cristiano.
Mucho le pesa á Aliatar;
10Pero Zaida dió respuesta 10
Diciendo que puede entrar,
Porque en tan solemne fiesta
Nada se debe negar.
Suspenso el concurso entero
15Entre dudas se embaraza, 15
Cuando en un potro ligero
Vieron entrar en la plaza
Un bizarro caballero,
Sonrosado, albo color,
20Belfo labio, juveniles 20
Alientos, inquieto ardor,
En el florido verdor
De sus lozanos abriles.
Cuelga la rubia guedeja
25Por donde el almete sube, 25
Cual mirarse tal vez deja
Del sol la ardiente madeja
Entre cenicienta nube;
31Gorguera de anchos follajes,
De una cristiana primores;
En el yelmo los plumajes
Por los visos y celajes
Vergel de diversas flores;
5En la cuja gruesa lanza,
Con recamado pendón,
Y una cifra á ver se alcanza,
Que es de desesperación,
Ó á lo menos de venganza.
10En el arzón de la silla
Ancho escudo reverbera
Con blasones de Castilla,
Y el mote dice á la orilla:
Nunca mi espada venciera.
15Era el caballo galán,
El bruto más generoso,
De más gallardo ademán:
Cabos negros, y brioso,
Muy tostado, y alazán,
20Larga cola recogida
En las piernas descarnadas,
Cabeza pequeña, erguida,
Las narices dilatadas,
Vista feroz y encendida.
25Nunca en el ancho rodeo
Que da Betis con tal fruto
Pudo fingir el deseo
Más bella estampa de bruto,
32Ni más hermoso paseo.
Dió la vuelta al rededor;
Los ojos que le veían
Lleva prendados de amor:
¡Alá te salve! decían,
5¡Déte el Profeta favor! 5
Causaba lástima y grima
Su tierna edad floreciente:
Todos quieren que se exima
Del riesgo, y él solamente
10Ni recela ni se estima. 10
Las doncellas, al pasar,
Hacen de ámbar y alcanfor
Pebeteros exhalar,
Vertiendo pomos de olor,
15De jazmines y azahar. 15
Mas cuando en medio se para,
Y de más cerca le mira
La cristiana esclava Aldara,
Con su señora se encara,
20Y así la dice, y suspira: 20
—Señora, sueños no son;
Así los cielos, vencidos
De mi ruego y aflicción,
Acerquen á mis oídos
25Las campanas de León, 25
Como ese doncel, que ufano
Tanto asombro viene á dar
Á todo el pueblo africano,
33Es Rodrigo de Bivar,
El soberbio castellano.—
Sin descubrirle quién es,
La Zaida desde una almena
Le habló una noche cortés,
5Por donde se abrió después
El cubo de la Almudena;
Y supo que, fugitivo
De la corte de Fernando,
El cristiano, apenas vivo,
10Está á Jimena adorando
Y en su memoria cautivo.
Tal vez á Madrid se acerca
Con frecuentes correrías
Y todo en torno la cerca;
15Observa sus saetías,
Arroyadas y ancha alberca.
Por eso le ha conocido:
Que en medio de aclamaciones,
El caballo ha detenido
20Delante de sus balcones,
Y la saluda rendido.
La mora se puso en pie
Y sus doncellas detrás:
El alcaide que lo ve,
25Enfurecido además,
Muestra cuán celoso esté.
Suena un rumor placentero
Entre el vulgo de Madrid:
34No habrá mejor caballero,
Dicen, en el mundo entero,
Y algunos le llaman Cid.
Crece la algazara, y él,
Torciendo las riendas de oro,
5Marcha al combate crüel:
Alza el galope, y al toro
Busca en sonoro tropel.
El bruto se le ha encarado
Desde que le vió llegar,
10De tanta gala asombrado,
Y al rededor le ha observado
Sin moverse de un lugar.
Cual flecha se disparó
Despedida de la cuerda,
15De tal suerte le embistió;
Detrás de la oreja izquierda
La aguda lanza le hirió.
Brama la fiera burlada;
Segunda vez acomete,
20De espuma y sudor bañada,
Y segunda vez la mete
Sutil la punta acerada.
Pero ya Rodrigo espera
Con heroico atrevimiento,
25El pueblo mudo y atento:
Se engalla el toro y altera,
Y finje acometimiento.
La arena escarba ofendido,
35Sobre la espalda la arroja
Con el hueso retorcido;
El suelo huele y le moja
En ardiente resoplido.
La cola inquieto menea,
5La diestra oreja mosquea,
Vase retirando atrás,
Para que la fuerza sea
Mayor, y el ímpetu más.
El que en esta ocasión viera
10De Zaida el rostro alterado,
Claramente conociera
Cuanto le cuesta cuidado
El que tanto riesgo espera.
Mas ¡ay, que le embiste horrendo
15El animal espantoso!
Jamás peñasco tremendo
Del Cáucaso cavernoso
Se desgaja, estrago haciendo,
Ni llama así fulminante
20Cruza en negra obscuridad
Con relámpagos delante,
Al estrépito tronante
De sonora tempestad,
Como el bruto se abalanza
25Con terrible ligereza;
Mas rota con gran pujanza
La alta nuca, la fiereza
Y el último aliento lanza.
36La confusa vocería
Que en tal instante se oyó
Fué tanta, que parecía
Que honda mina reventó,
Ó el monte y valle se hundía.
5Á caballo como estaba
Rodrigo, el lazo alcanzó
Con que el toro se adornaba:
En su lanza le clavó
Y á los balcones llegaba.
10Y alzándose en los estribos,
Le alarga á Zaida, diciendo:
—Sultana, aunque bien entiendo
Ser favores excesivos,
Mi corto don admitiendo;
15Si no os dignáredes ser
Con él benigna, advertid
Que á mí me basta saber
Que no le debo ofrecer
Á otra persona en Madrid.—
20Ella, el rostro placentero,
Dijo, y turbada:—Señor,
Yo le admito y le venero,
Por conservar el favor
De tan gentil caballero.—
25Y besando el rico don,
Para agradar al doncel,
Le prende con afición
Al lado del corazón
37Por brinquiño y por joyel.
Pero Aliatar el caudillo
De envidia ardiendo se ve,
Y, trémulo y amarillo,
Sobre un tremecén rosillo
5Lozaneándose fué.
Y en ronca voz:—Castellano,
Le dice, con más decoros
Suelo yo dar de mi mano,
Si no penachos de toros,
10Las cabezas del cristiano.
Y si vinieras de guerra
Cual vienes de fiesta y gala,
Vieras que en toda la tierra,
Al valor que dentro encierra
15Madrid, ninguno se iguala.—
—Así, dijo el de Bivar,
Respondo—; y la lanza al ristre
Pone, y espera á Aliatar;
Mas sin que nadie administre
20Orden, tocaron á armar.
Ya fiero bando con gritos
Su muerte ó prisión pedía,
Cuando se oyó en los distritos
Del monte de Leganitos
25Del Cid la trompetería.
Entre la Monclova y Soto
Tercio escogido emboscó,
Que, viendo como tardó,
38Se acerca, oyó el alboroto,
Y al muro se abalanzó.
Y si no vieran salir
Por la puerta á su señor,
Y Zaida á le despedir,
5Iban la fuerza á embestir:
Tal era ya su furor.
El alcaide, recelando
Que en Madrid tenga partido,
Se templó disimulando,
10Y por el parque florido
Salió con él razonando.
Y es fama que, á la bajada,
Juró por la cruz el Cid
De su vencedora espada
15De no quitar la celada
Hasta que gane á Madrid.
Á ARNESTO
¿Quis tam patiens ut teneat se?
JUVENAL
Déjame, Arnesto, déjame que llore
Los fieros males de mi patria, deja
Que su rüina y perdición lamente;
20Y si no quieres que en el centro obscuro
De esta prisión la pena me consuma,
Déjame al menos que levante el grito
39Contra el desorden: deja que á la tinta
Mezclando miel y acíbar, siga indócil
Mi pluma el vuelo del bufón de Aquino.
¡Oh! ¡cuánto rostro veo, á mi censura,
De palidez y de rubor cubierto!
5Ánimo, amigos, nadie tema, nadie,
Su punzante aguijón; que yo persigo
En mi sátira el vicio, no al vicioso.
Ya la notoriedad es el más noble
Atributo del vicio, y nuestras Julias,
10Más que ser malas quieren parecerlo.
Hubo un tiempo en que andaba la modestia
Dorando los delitos; hubo un tiempo
En que el recato tímido cubría
La fealdad del vicio; pero huyóse
15El pudor á vivir en las cabañas.
¡Oh infamia! ¡oh siglo! ¡oh corrupción! Matronas
Castellanas, ¿quién pudo vuestro claro
Pundonor eclipsar? ¿Quién de Lucrecias
En Laís os volvió? ¿Ni el proceloso
20Océano, ni, lleno de peligros,
El Lilibeo, ni las arduas cumbres
De Pirene pudieron guareceros
Del contagio fatal? Zarpa preñada
De oro la nao gaditana, aporta
25Á las orillas gálicas, y vuelve
40Llena de objetos fútiles y vanos;
Y entre los signos de extranjera pompa
Ponzoña esconde y corrupción, compradas
Con el sudor de las iberas frentes;
Y tú, mísera España, tú la esperas
5Sobre la playa, y con afán recoges
La pestilente carga, y la repartes
Alegre entre tus hijos. Viles plumas,
Gasas y cintas, flores y penachos
Te trae en cambio de la sangre tuya;
10De tu sangre ¡oh baldón! y acaso, acaso
De tu virtud y honestidad. Repara
Cual la liviana juventud los busca.
Mira cual va con ellos engreída
La impudente doncella; su cabeza,
15Cual nave real en triunfo empavesada,
Vana presenta del favonio al soplo
La mies de plumas y de airones, y anda
Loca, buscando en la lisonja el premio
De su indiscreto afán. ¡Ay triste! guarte,
20Guarte, que está cercano el precipicio.
El astuto amador ya en asechanza
Te atisba y sigue con lascivos ojos;
La adulación y la caricia el lazo
Te van á armar, do caerás incauta,
25En él tu oprobio y perdición hallando.
¡Ay cuánto, cuánto de amargura y lloro
Te costarán tus galas! ¡Cuán tardío
Será y estéril tu arrepentimiento!
41Ya ni el rico Brasil, ni las cavernas
Del nunca exhausto Potosí no bastan
Á saciar el hidrópico deseo,
La ansiosa sed de vanidad y pompa.
Todo lo agotan: cuesta un sombrerillo
5Lo que antes un Estado, y se consume
En un festín la dote de una infanta;
Todo lo tragan; la riqueza unida
Va á la indigencia; pide y pordiosea
El noble, engaña, empeña, malbarata,
10Quiebra y perece, y el logrero goza
Los pingües patrimonios, premio un día
Del generoso afán de altos abuelos.
¡Oh ultraje! ¡oh mengua! todo se trafica:
Parentesco, amistad, favor, influjo,
15Y hasta el honor, depósito sagrado,
Ó se vende ó se compra. Y tú, belleza,
Don el más grato que dió al hombre el cielo,
No eres ya premio del valor, ni paga
Del peregrino ingenio; la florida
20Juventud, la ternura, el rendimiento
Del constante amador ya no te alcanzan.
Ya ni te das al corazón, ni sabes
De él recibir adoración y ofrendas.
Ríndeste al oro. La vejez hedionda,
25La sucia palidez, la faz adusta,
Fiera y terrible, con igual derecho
Vienen sin susto á negociar contigo.
Daste al barato, y tu rosada frente,
42Tus suaves besos y tus dulces brazos,
Corona un tiempo del amor más puro,
Son ya una vil y torpe mercancía.
ROSANA EN LOS FUEGOS
Del sol llevaba la lumbre,
Y la alegría del alba,
5En sus celestiales ojos
La hermosísima Rosana,
Una noche que á los fuegos
Salió la fiesta de Pascua
Para abrasar todo el valle
10En mil amorosas ansias.
Por do quiera que camina
Lleva tras sí la mañana,
Y donde se vuelve rinde
La libertad de mil almas.
15El céfiro la acaricia
Y mansamente la halaga,
Los Amores la rodean
Y las Gracias la acompañan.
Y ella, así como en el valle
20Descuella la altiva palma
Cuando sus verdes pimpollos
Hasta las nubes levanta;
Ó cual vid de fruto llena
43Que con el olmo se abraza,
Y sus vástagos extiende
Al arbitrio de las ramas;
Así entre sus compañeras
El nevado cuello alza,
5Sobresaliendo entre todas
Cual fresca rosa entre zarzas.
Todos los ojos se lleva
Tras sí, todo lo avasalla;
De amor mata á los pastores
10Y de envidia á las zagalas.
Ni las músicas se atienden,
Ni se gozan las lumbradas;
Que todos corren por verla
Y al verla todos se abrasan.
15¡Qué de suspiros se escuchan!
¡Qué de vivas y de salvas!
No hay zagal que no la admire
Y no se esmere en loarla.
Cual absorto la contempla
20Y á la aurora la compara
Cuando más alegre sale
Y el cielo en albores baña;
Cual al fresco y verde aliso
Que crece al margen del agua,
25Cuando más pomposo en hojas
En su cristal se retrata;
Cual á la luna, si muestra
Llena su esfera de plata,
44Y asoma por los collados
De luceros coronada.
Otros pasmados la miran
Y mudamente la alaban,
Y cuanto más la contemplan
5Muy más hermosa la hallan.
Que es como el cielo su rostro
Cuando en la noche callada
Brilla con todas sus luces
Y los ojos embaraza.
10¡Ay, qué de envidias se encienden!
¡Ay, qué de celos que causa
En las serranas del Tormes
Su perfección sobrehumana!
Las más hermosas la temen,
15Mas sin osar murmurarla;
Que como el oro más puro
No sufre una leve mancha.
Bien haya tu gentileza,
Una y mil veces bien haya,
20Y abrase la envidia al pueblo,
Hermosísima aldeana.
Toda, toda eres perfecta,
Toda eres donaire y gracia,
El amor vive en tus ojos
25Y la gloria está en tu cara.
La libertad me has robado,
Yo la doy por bien robada,
Mas recibe el don benigna
45Que mi humildad te consagra.
Esto un zagal la decía
Con razones mal formadas,
Que salió libre á los fuegos
Y volvió cautivo á casa.
5Y desde entonces perdido
El día á sus puertas le halla;
Ayer le cantó esta letra
Echándole la alborada:
Linda zagaleja
10De cuerpo gentil,
Muérome de amores
Desde que te vi.
Tu talle, tu aseo,
Tu gala y donaire,
15No tienen, serrana,
Igual en el valle.
Del cielo son ellos
Y tú un serafín:
Muérome de amores
20Desde que te vi.
De amores me muero,
Sin que nada baste
Á darme la vida
Que allá te llevaste,
25Si ya no te dueles,
Benigna, de mí;
Que muero de amores
Desde que te vi.
ODA Á ESPAÑA, DESPUÉS DE LA REVOLUCIÓN
DE MARZO
¿Qué era, decidme, la nación que un día
Reina del mundo proclamó el destino,
La que á todas las zonas extendía
Su cetro de oro y su blasón divino?
5Volábase á occidente,
Y el vasto mar Atlántico sembrado
Se hallaba de su gloria y su fortuna.
Do quiera España: en el preciado seno
De América, en el Asia, en los confines
10Del África, allí España. El soberano
Vuelo de la atrevida fantasía
Para abarcarla se cansaba en vano;
La tierra sus mineros le rendía,
Sus perlas y coral el Oceano,
15Y donde quier que revolver sus olas
Él intentase, á quebrantar su furia
Siempre encontraba costas españolas.
Ora en el cieno del oprobio hundida,
Abandonada á la insolencia ajena,
20Como esclava en mercado, ya aguardaba
La ruda argolla y la servil cadena.
¡Qué de plagas! ¡oh Dios! Su aliento impuro,
La pestilente fiebre respirando,
47Infestó el aire, emponzoñó la vida;
La hambre enflaquecida
Tendió sus brazos lívidos, ahogando
Cuanto el contagio perdonó; tres veces
De Jano el templo abrimos,
5Y á la trompa de Marte aliento dimos;
Tres veces ¡ay! Los dioses tutelares
Su escudo nos negaron, y nos vimos
Rotos en tierra y rotos en los mares.
¿Qué en tanto tiempo viste
10Por tus inmensos términos, oh Iberia?
¿Qué viste ya sino funesto luto,
Honda tristeza, sin igual miseria,
De tu vil servidumbre acerbo fruto?
Así rota la vela, abierto el lado,
15Pobre bajel á naufragar camina,
De tormenta en tormenta despeñado,
Por los yermos del mar; ya ni en su popa
Las guirnaldas se ven que antes le ornaban,
Ni en señal de esperanza y de contento
20La flámula rïendo al aire ondea.
Cesó en su dulce canto el pasajero,
Ahogó su vocería
El ronco marinero,
Terror de muerte en torno le rodea,
25Terror de muerte silencioso y frío;
Y él va á estrellarse al áspero bajío.
Llega el momento, en fin; tiende su mano
El tirano del mundo al occidente,
48Y fiero exclama: «El occidente es mío.»
Bárbaro gozo en su ceñuda frente
Resplandeció, como en el seno obscuro
De nube tormentosa en el estío
Relámpago fugaz brilla un momento
5Que añade horror con su fulgor sombrío.
Sus guerreros feroces
Con gritos de soberbia el viento llenan;
Gimen los yunques, los martillos suenan,
Arden las forjas. ¡Oh vergüenza! ¿Acaso
10Pensáis que espadas son para el combate
Las que mueven sus manos codiciosas?
No en tanto os estiméis: grillos, esposas,
Cadenas son que en vergonzosos lazos
Por siempre amarren tan inertes brazos.
15Estremecióse España
Del indigno rumor que cerca oía,
Y al grande impulso de su justa saña
Rompió el volcán que en su interior hervía.
Sus déspotas antiguos
20Consternados y pálidos se esconden;
Resuena el eco de venganza en torno,
Y del Tajo las márgenes responden:
«¡Venganza!» ¿Dónde están, sagrado río,
Los colosos de oprobio y de vergüenza
25Que nuestro bien en su insolencia ahogaban;
Su gloria fué, nuestro esplendor comienza;
Y tú, orgulloso y fiero,
Viendo que aun hay Castilla y castellanos,
49Precipitas al mar tus rubias ondas,
¡Oh triunfo! ¡Oh gloria! ¡Oh celestial momento!
¿Con que puede ya dar el labio mío
El nombre augusto de la patria al viento?
5Yo le daré; mas no en el arpa de oro5
Que mi cantar sonoro
Acompañó hasta aquí; no aprisionado
En estrecho recinto, en que se apoca
El numen en el pecho
10Y el aliento fatídico en la boca.10
Desenterrad la lira de Tirteo,
Y el aire abierto á la radiante lumbre
Del sol, en la alta cumbre
Del riscoso y pinífero Fuenfría,
15Allí volaré yo, y allí cantando15
Con voz que atruene en rededor la sierra,
Lanzaré por los campos castellanos
Los ecos de la gloría y de la guerra.
¡Guerra, nombre tremendo, ahora sublime,
20Único asilo y sacrosanto escudo20
Al ímpetu sañudo
Del fiero Atila que á occidente oprime!
¡Guerra, guerra, españoles! En el Betis
Ved del Tercer Fernando alzarse airada
25La augusta sombra; su divina frente
Mostrar Gonzalo en la imperial Granada;
Blandir el Cid su centelleante espada,
Y allá sobre los altos Pirineos,
50Del hijo de Jimena
Animarse los miembros giganteos.
En torvo ceño y desdeñosa pena
Ved como cruzan por los aires vanos;
Y el valor exhalando que se encierra
5Dentro del hueco de sus tumbas frías,
En fiera y ronca voz pronuncian: «¡Guerra!
¡Pues qué! ¿Con faz serena
Vierais los campos devastar opimos,
Eterno objeto de ambición ajena,
10Herencia inmensa que afanando os dimos?
Despertad, raza de héroes: el momento
Llegó ya de arrojarse á la victoria;
Que vuestro nombre eclipse nuestro nombre,
Que vuestra gloría humille nuestra gloria.
15No ha sido en el gran día
El altar de la patria alzado en vano
Por vuestra mano fuerte.
Juradlo, ella os lo manda: ¡Antes la muerte
Que consentir jamás ningún tirano!»
20Sí, yo lo juro, venerables sombras;
Yo lo juro también, y en este instante
Ya me siento mayor. Dadme una lanza,
Ceñidme el casco fiero y refulgente;
Volemos al combate, á la venganza;
25Y el que niegue su pecho á la esperanza,
Hunda en el polvo la cobarde frente.
Tal vez el gran torrente
De la devastación en su carrera
51Me llevará. ¿Qué importa? ¿Por ventura
No se muere una vez? ¿No iré, expirando,
Á encontrar nuestros ínclitos mayores?
«¡Salud, oh padres de la patria mía,
Yo les diré, salud! La heroica España
5De entre el estrago universal y horrores
Levanta la cabeza ensangrentada,
Y vencedora de su mal destino,
Vuelve á dar á la tierra amedrentada
Su cetro de oro y su blasón divino.»
LA PREGUNTA DE LA NIÑA
Madre mía, yo soy niña;
No se enfade, no me riña,
Si fiada en su prudencia
Desahogo mi conciencia,
Y contarle solicito
15Mi desdicha ó mi delito,
Aunque muerta de rubor.
Pues Blasillo el otro día,
Cuando mismo anochecía,
Y cantando descuidada
20Conducía mi manada,
En el bosque, por acaso,
Me salió solito al paso,
Más hermoso que el amor.
52Se me acerca temeroso,
Me saluda cariñoso,
Me repite que soy linda,
Que no hay pecho que no rinda,
Que si río, que si lloro,
5Á los hombres enamoro,
Y que mato con mirar.
Con estilo cortesano
Se apodera de mi mano,
Y entre dientes, madre mía,
10No sé bien qué me pedía;
Yo entendí que era una rosa,
Pero él dijo que era otra cosa,
Que yo no le quise dar.
¿Sabe usted lo que decía
15El taimado que quería?
Con vergüenza lo confieso,
Mas no hay duda que era un beso
Y fue tanto mi sonrojo,
Que irritada de su arrojo,
20No sé como no morí.
Mas mi pecho enternecido
De mirarle tan rendido,
Al principio resistiendo,
Él instando, yo cediendo,
25Fue por fin tan importuno,
Que en la boca, y sólo uno,
Que me diera permití.
Desde entonces, si le miro,
53Yo no sé por qué suspiro,
Ni por qué si á Clori mira
Se me abrasa el rostro en ira;
Ni por qué, si con cuidado
Se me pone junto al lado,
5Me estremezco de placer.
Siempre orillas de la fuente
Busco rosas á mi frente,
Pienso en él y me sonrío,
Y entre mí le llamo mío,
10Me entristezco de su ausencia,
Y deseo en su presencia
La más bella parecer.
Confundida, peno y dudo,
Y por eso á usted acudo;
15Dígame, querida madre,
Si sentía por mi padre
Este plácido tormento,
Esta dulce que yo siento
Deliciosa enfermedad.
20Diga usted con qué se cura
Ó mi amor, ó mi locura,
Y si puede por un beso,
Sin que pase á más exceso,
Una niña enamorarse,
25Y que trate de casarse
Á los quince de su edad.
EL DOS DE MAYO
Noche, lóbrega noche, eterno asilo
Del miserable que, esquivando el sueño,
En tu silencio pavoroso gime:
No desdeñes mi voz; letal beleño
5Presta á mis sienes, y en tu horror sublime
Empapada la ardiente fantasía,
Da á mi pincel fatídicos colores
Con que el tremendo día
Trace al furor de vengadora tea,
10Y el odio irrite de la patria mía,
Y escándalo y terror al orbe sea.
¡Día de execración! La destructora
Mano del tiempo le arrojó al averno;
Mas ¿quién el sempiterno
15Clamor con que los ecos importuna
La madre España en enlutado arreo
Podrá atajar? Junto al sepulcro frío,
Al pálido lucir de opaca luna,
Entre cipreses fúnebres la veo:
20Trémula, yerta, desceñido el manto,
Los ojos moribundos
Al cielo vuelve, que le oculta el llanto;
Roto y sin brillo el cetro de dos mundos
Yace entre el polvo, y el león guerrero
2555Lanza á sus pies rugido lastimero.
¡Ay, que cual débil planta
Que agota en su furor hórrido viento,
De víctimas sin cuento
Lloró la destrucción Mantua afligida!
5Yo vi, yo vi su juventud florida
Correr inerme al huésped ominoso.
¿Mas qué su generoso
Esfuerzo pudo? El pérfido caudillo
En quien su honor y su defensa fía,
10La condenó al cuchillo.
¿Quién ¡ay! la alevosía,
La horrible asolación habrá que cuente,
Que, hollando de amistad los santos fueros,
Hizo furioso en la indefensa gente
15Ese tropel de tigres carniceros?
Por las henchidas calles
Gritando se despeña
La infame turba que abrigó en su seno,
Rueda allá rechinando la cureña,
20Acá retumba el espantoso trueno,
Allí el joven lozano,
El mendigo infeliz, el venerable
Sacerdote pacífico, el anciano
Que con su arada faz respeto imprime,
25Juntos amarra su dogal tirano.
En balde, en balde gime,
De los duros satélites en torno,
La triste madre, la afligida esposa.
56Con doliente clamor, la pavorosa
Fatal descarga suena,
Que á luto y llanto eterno la condena.
¡Cuánta escena de muerte! ¡cuánto estrago!
¡Cuántos ayes doquier! Despavorido
5Mirad ese infelice
Quejarse al adalid empedernido
De otra cuadrilla atroz. «¡Ah! ¿Qué te hice?»
Exclama el triste en lágrimas deshecho:
«Mi pan y mi mansión partí contigo,
10Te abrí mis brazos, te cedí mi lecho,
Templé tu sed, y me llamé tu amigo;
¿Y ahora pagar podrás nuestro hospedaje
Sincero, franco, sin doblez ni engaño,
Con dura muerte y con indigno ultraje?»
15¡Perdido suplicar! ¡inútil ruego!
El monstruo infame á sus ministros mira,
Y con tremenda voz gritando: «¡fuego!»
Tinto en su sangre el desgraciado expira.
Y en tanto ¿dó se esconden?
20¿Dó están ¡oh cara patria! tus soldados,
Que á tu clamor de muerte no responden?
Presos, encarcelados
Por jefes sin honor, que, haciendo alarde
De su perfidia y dolo,
25Á merced de los vándalos te dejan,
Como entre hierros el león, forcejean
Con inútil afán. Vosotros sólo,
Fuerte Daoiz, intrépido Velarde,
57Que osando resistir al gran torrente
Dar supisteis en flor la dulce vida
Con firme pecho y con serena frente;
Si de mi libre musa
Jamás el eco adormeció á tiranos,
5Ni vil lisonja emponzoñó su aliento,
Allá del alto asiento,
Al que la acción magnánima os eleva,
El himno oid que á vuestro nombre entona,
Mientras la fama alígera le lleva
10Del mar de hielo á la abrasada zona.
Mas ¡ay! que en tanto sus funestas alas
Por la opresa metrópoli tendiendo,
La yerma asolación sus plazas cubre,
Y al áspero silbar de ardientes balas,
15Y al ronco son de los preñados bronces,
Nuevo fragor y estrépito sucede.
¿Oís cómo, rompiendo
De moradores tímidos las puertas,
Caen estallando de los fuertes gonces?
20¡Con qué espantoso estruendo
Los dueños buscan, que medrosos huyen!
Cuanto encuentran destruyen,
Bramando, los atroces forajidos,
Que el robo infame y la matanza ciegan.
25¿No veis cuál se despliegan,
Penetrando en los hondos aposentos,
De sangre y oro y lágrimas sedientos?
Rompen, talan, destrozan
58Cuanto se ofrece á su sangrienta espada.
Aquí, matando al dueño, se alborozan,
Hieren allí su esposa acongojada;
La familia asolada
Yace expirando, y con feroz sonrisa
5Sorben voraces el fatal tesoro.
Suelta, á otro lado, la madeja de oro,
Mustio el dulce carmín de su mejilla,
Y en su frente marchita la azucena,
Con voz turbada y anhelante lloro,
10De su verdugo ante los pies se humilla
Tímida virgen, de amargura llena;
Mas con furor de hiena,
Alzando el corvo alfanje damasquino,
Hiende su cuello el bárbaro asesino.
15¡Horrible atrocidad!... Treguas ¡oh musa!
Que ya la voz rehusa
Embargada en suspiros mi garganta.
Y en ignominia tanta,
¿Será que rinda el español bizarro
20La indómita cerviz á la cadena?
No, que ya en torno suena
De Palas fiera el sanguinoso carro,
Y el látigo estallante
Los caballos flamígeros hostiga.
25Ya el duro peto y el arnés brillante
Visten los fuertes hijos de Pelayo.
Fuego arrojó su ruginoso acero:
«¡Venganza y guerra!» resonó en su tumba;
59«¡Venganza y guerra!» repitió Moncayo;
Y al grito heroico que en los aires zumba,
«¡Venganza y guerra!» claman Turia y Duero.
Guadalquivir guerrero
Alza al bélico son la regia frente,
5Y del Patrón valiente
Blandiendo altivo la nudosa lanza,
Corre gritando al mar: «¡Guerra y venganza!»
¡Oh sombras infelices
De los que aleve y bárbara cuchilla
10Robó á los dulces lares!
¡Sombras inultas que en fugaz gemido
Cruzáis los anchos campos de Castilla!
La heroica España, en tanto que al bandido
Que á fuego y sangre, de insolencia ciego,
15Brindó felicidad, á sangre y fuego
Le retribuye el don, sabrá piadosa
Daros solemne y noble monumento.
Allí en padrón cruento
De oprobio y mengua, que perpetuo dure,
20La vil traición del déspota se lea,
Y altar eterno sea
Donde todo Español al monstruo jure
Rencor de muerte que en sus venas cunda,
Y á cien generaciones se difunda.
EL NIDO
¿Dónde vas, zagal cruel,
Dónde vas con ese nido,
Riyendo tú mientras pían
Esos tristes pajarillos?
5Su madre los dejó solos
En este momento mismo,
Para buscarles sustento
Y dárselo con su pico...
Mírala cuán azorada
10Echa menos á sus hijos,
Salta de un árbol en otro,
Va, torna, vuela sin tino:
Al cielo favor demanda
Con acento dolorido;
15Mientras ellos en tu mano
Baten el ala al oirlo...
¡Tú también tuviste madre,
Y la perdiste aun muy niño,
Y te encontraste en la tierra
20Sin amparo y sin abrigo!—
Las lágrimas se le saltan
Al cuitado pastorcillo,
Y vergonzoso y confuso
Deja en el árbol el nido.
UN CASTELLANO LEAL
ROMANCE PRIMERO
«Holá, hidalgos y escuderos
De mi alcurnia y mi blasón,
Mirad como bien nacidos
De mi sangre y casa en pro.
5«Esas puertas se defiendan;
Que no ha de entrar, vive Dios,
Por ellas, quien no estuviere
Más limpio que lo está el sol.
«No profane mi palacio
10Un fementido traidor
Que contra su Rey combate
Y que á su patria vendió.
«Pues si él es de Reyes primo,
Primo de Reyes soy yo;
15Y conde de Benavente
Si él es duque de Borbón;
«Llevándole de ventaja
Que nunca jamás manchó
La traición mi noble sangre,
20Y haber nacido español.»
Así atronaba la calle
62Una ya cascada voz,
Que de un palacio salía
Cuya puerta se cerró;
Y á la que estaba á caballo
Sobre un negro pisador,
5Siendo en su escudo las lises
Más bien que timbre baldón,
Y de pajes y escuderos
Llevando un tropel en pos
Cubiertos de ricas galas,
10El gran duque de Borbón:
El que lidiando en Pavía,
Más que valiente, feroz,
Gozóse en ver prisionero
Á su natural señor;
15Y que á Toledo ha venido,
Ufano de su traición,
Para recibir mercedes
Y ver al Emperador.
ROMANCE SEGUNDO
En una anchurosa cuadra
20Del alcázar de Toledo,
Cuyas paredes adornan
Ricos tapices flamencos,
Al lado de una gran mesa,
Que cubre de terciopelo
25Napolitano tapete
Con borlones de oro y flecos;
63Ante un sillón de respaldo
Que entre bordado arabesco
Los timbres de España ostenta
Y el águila del imperio,
De pie estaba Carlos Quinto,
5Que en España era primero,
Con gallardo y noble talle,
Con noble y tranquilo aspecto.
De brocado de oro y blanco
Viste tabardo tudesco,
10De rubias martas orlado,
Y desabrochado y suelto,
Dejando ver un justillo
De raso jalde, cubierto
Con primorosos bordados
15Y costosos sobrepuestos,
Y la excelsa y noble insignia
Del Toisón de oro, pendiendo
De una preciosa cadena
En la mitad de su pecho.
20Un birrete de velludo
Con un blanco airón, sujeto
Por un joyel de diamantes
Y un antiguo camafeo,
Descubre por ambos lados,
25Tanta majestad cubriendo,
Rubio, cual barba y bigote,
Bien atusado el cabello.
64Apoyada en la cadera
La potente diestra ha puesto,
Que aprieta dos guantes de ámbar
Y un primoroso mosquero,
Y con la siniestra halaga
5De un mastín muy corpulento,
Blanco y las orejas rubias,
El ancho y carnoso cuello.
Con el Condestable insigne,
Apaciguador del reino,
10De los pasados disturbios
Acaso está discurriendo;
Ó del trato que dispone
Con el Rey de Francia preso,
Ó de asuntos de Alemania
15Agitada por Lutero;
Cuando un tropel de caballos
Oye venir á lo lejos
Y ante el alcázar pararse,
Quedando todo en silencio.
20En la antecámara suena
Rumor impensado luego,
Ábrese al fin la mampara
Y entra el de Borbón soberbio,
Con el semblante de azufre
25Y con los ojos de fuego,
Bramando de ira y de rabia
Que enfrena mal el respeto;
65Y con balbuciente lengua,
Y con mal borrado ceño,
Acusa al de Benavente,
Un desagravio pidiendo.
Del español Condestable
5Latió con orgullo el pecho,
Ufano de la entereza
De su esclarecido deudo.
Y aunque advertido procura
Disimular cual discreto,
10Á su noble rostro asoman
La aprobación y el contento.
El Emperador un punto
Quedó indeciso y suspenso,
Sin saber qué responderle
15Al francés, de enojo ciego.
Y aunque en su interior se goza
Con el proceder violento
Del conde de Benavente,
De altas esperanzas lleno
20Por tener tales vasallos,
De noble lealtad modelos,
Y con los que el ancho mundo
Será á sus glorias estrecho,
Mucho al de Borbón le debe
25Y es fuerza satisfacerlo:
Le ofrece para calmarlo
Un desagravio completo.
66Y, llamando á un gentil-hombre,
Con el semblante severo
Manda que el de Benavente
Venga á su presencia presto.
ROMANCE TERCERO
Sostenido por sus pajes
5Desciende de su litera
El conde de Benavente
Del alcázar á la puerta.
Era un viejo respetable,
Cuerpo enjuto, cara seca,
10Con dos ojos como chispas,
Cargados de largas cejas,
Y con semblante muy noble,
Mas de gravedad tan seria
Que veneración de lejos
15Y miedo causa de cerca.
Eran su traje unas calzas
De púrpura de Valencia,
Y de recamado ante
Un coleto á la leonesa:
20De fino lienzo gallego20
Los puños y la gorguera,
Unos y otra guarnecidos
Con randas barcelonesas:
Un birretón de velludo
25Con su cintillo de perlas,
Y el gabán de paño verde
Con alamares de seda.
67Tan sólo de Calatrava
La insignia española lleva;
Que el Toisón ha despreciado
Por ser orden extranjera.
Con paso tardo, aunque firme,
Sube por las escaleras,
Y al verle, las alabardas
Un golpe dan en la tierra;
Golpe de honor, y de aviso
10De que en el alcázar entra
Un Grande, á quien se le debe
Todo honor y reverencia.
Al llegar á la antesala,
Los pajes que están en ella
15Con respeto le saludan
Abriendo las anchas puertas.
Con grave paso entra el conde
Sin que otro aviso preceda,
Salones atravesando
20Hasta la cámara regia.
Pensativo está el Monarca,
Discurriendo como pueda
Componer aquel disturbio
Sin hacer á nadie ofensa.
25Mucho al de Borbón le debe,
Aun mucho más de él espera,
68Y al de Benavente mucho
Considerar le interesa.
Dilación no admite el caso,
No hay quien dar consejo pueda
Y Villalar y Pavía
5Á un tiempo se le recuerdan.
En el sillón asentado
Y el codo sobre la mesa,
Al personaje recibe,
Que comedido se acerca.
Grave el conde le saluda
Con una rodilla en tierra,
Mas como Grande del reino
Sin descubrir la cabeza.
El Emperador benigno
15Que alce del suelo le ordena,
Y la plática difícil
Con sagacidad empieza.
Y entre severo y afable
Al cabo le manifiesta
20Que es el que á Borbón aloje
Voluntad suya resuelta.
Con respeto muy profundo,
Pero con la voz entera,
Respóndele Benavente,
25Destocando la cabeza:
«Soy, señor, vuestro vasallo,
Vos sois mi rey en la tierra,
69Á vos ordenar os cumple
De mi vida y de mi hacienda.
«Vuestro soy, vuestra mi casa,
De mí disponed y de ella,
Pero no toquéis mi honra
5Y respetad mi conciencia.
«Mi casa Borbón ocupe
Puesto que es voluntad vuestra,
Contamine sus paredes,
Sus blasones envilezca;
10«Que á mí me sobra en Toledo
Donde vivir, sin que tenga
Que rozarme con traidores,
Cuyo solo aliento infesta.
Y en cuanto él deje mi casa,
15Antes de tornar yo á ella,
Purificaré con fuego
Sus paredes y sus puertas.»
Dijo el conde, la real mano
Besó, cubrió su cabeza,
20Y retiróse bajando
Á do estaba su litera.
Y á casa de un su pariente
Mandó que le condujeran,
Abandonando la suya
25Con cuanto dentro se encierra.
Quedó absorto Carlos Quinto
De ver tan noble firmeza,
Estimando la de España
Más que la imperial diadema.
70ROMANCE CUARTO
Muy pocos días el duque
Hizo mansión en Toledo,
Del noble conde ocupando
Los honrados aposentos.
5Y la noche en que el palacio
Dejó vacío, partiendo,
Con su séquito y sus pajes,
Orgulloso y satisfecho,
Turbó la apacible luna
10Un vapor blanco y espeso
Que de las altas techumbres
Se iba elevando y creciendo:
Á poco rato tornóse
En humo confuso y denso
15Que en nubarrones obscuros
Ofuscaba el claro cielo;
Después en ardientes chispas,
Y en un resplandor horrendo
Que iluminaba los valles
20Dando en el Tajo reflejos,
Y al fin su furor mostrando
En embravecido incendio
Que devoraba altas torres
Y derrumbaba altos techos.
25Resonaron las campanas,
Conmovióse todo el pueblo,
71De Benavente el palacio
Presa de las llamas viendo.
El Emperador confuso
Corre á procurar remedio,
En atajar tanto daño
5Mostrando tenaz empeño.
En vano todo: tragóse
Tantas riquezas el fuego,
Á la lealtad castellana
Levantando un monumento.
10Aun hoy unos viejos muros
Del humo y las llamas negros
Recuerdan acción tan grande
En la famosa Toledo.
SÉ MÁS FELIZ QUE YO
Sobre pupila azul, con sueño leve,
15Tu párpado cayendo amortecido,
Se parece á la pura y blanca nieve
Que sobre las violetas reposó:
Yo el sueño del placer nunca he dormido:
Sé más feliz que yo.
20Se asemeja tu voz en la plegaria
Al canto del zorzal de indiano suelo
Que sobre la pagoda solitaria
72Los himnos de la tarde suspiró:
Yo sólo esta oración dirijo al cielo:
Sé más feliz que yo.
Es tu aliento la esencia más fragante
De los lirios del Arno caudaloso
5Que brotan sobre un junco vacilante
Cuando el céfiro blando los meció:
Yo no gozo su aroma delicioso:
Sé más feliz que yo.
El amor, que es espíritu de fuego,
10Que de callada noche se aconseja
Y se nutre con lágrimas y ruego,
En tus purpúreos labios se escondió:
Él te guarde el placer y a mí la queja:
Sé más feliz que yo.
15Bella es tu juventud en sus albores
Como un campo de rosas del Oriente;
Al ángel del recuerdo pedí flores
Para adornar tu sien, y me las dió;
Yo decía al ponerlas en tu frente:
20Sé más feliz que yo.
Tu mirada vivaz es de paloma;
Como la adormidera del desierto
Causas dulce embriaguez, hurí de aroma
Que el cielo de topacio abandonó:
25Mi suerte es dura, mi destino incierto:
Sé más feliz que yo.
CANCIÓN DEL PIRATA
Con diez cañones por banda,
Viento en popa á toda vela,
No corta el mar, sino vuela
Un velero bergantín:
5Bajel pirata que llaman,
Por su bravura, el Temido,
En todo mar conocido
Del uno al otro confín.
La luna en el mar rïela,
10En la lona gime el viento,
Y alza en blando movimiento
Olas de plata y azul;
Y ve el capitán pirata,
Cantando alegre en la popa,
15Asia á un lado, al otro Europa,
Y allá á su frente Stambul,
«Navega, velero mío,
Sin temor;
Que ni enemigo navío,
20Ni tormenta, ni bonanza
Tu rumbo á torcer alcanza,
Ni á sujetar tu valor.
«Veinte presas
74Hemos hecho
Á despecho
Del inglés,
Y han rendido
Sus pendones
5Cien naciones
Á mis pies.»
Que es mi barco mi tesoro,
Que es mi Dios la libertad,
Mi ley la fuerza y el viento,
10Mi única patria la mar.
«Allá muevan feroz guerra
Ciegos reyes
Por un palmo más de tierra:
Que yo tengo aquí por mío
15Cuanto abarca el mar bravío,
Á quien nadie impuso leyes.
«Y no hay playa,
Sea cual quiera,
Ni bandera
20De esplendor,
Que no sienta
Mi derecho,
Y dé pecho
Á mi valor.»
25Que es mi barco mi tesoro...
«Á la voz de «¡barco viene!»
75Es de ver
Cómo vira y se previene
Á todo trapo á escapar;
Que yo soy el rey del mar,
Y mi furia es de temer.
5«En las presas
Yo divido
Lo cogido
Por igual:
Sólo quiero
10Por riqueza
La belleza
Sin rival.»
Que es mi barco mi tesoro...
«¡Sentenciado estoy á muerte!
15Yo me río:
No me abandone la suerte,
Y al mismo que me condena
Colgaré de alguna entena,
Quizá en su propio navío.
20«Y si caigo,
¿Qué es la vida?
Por perdida
Ya la di,
Cuando el yugo
25Del esclavo,
Como un bravo,
Sacudí.»
Que es mi barco mi tesoro...
76«Son mi música mejor
Aquilones:
El estrépito y temblor
De los cables sacudidos,
5Del negro mar los bramidos
Y el rugir de mis cañones.
«Y del trueno
Al son violento
Y del viento
10Al rebramar,
Yo me duermo
Sosegado,
Arrullado
Por el mar.»
15Que es mi barco mi tesoro,
Que es mi Dios la libertad,
Mi ley la fuerza y el viento,
Mi única patria la mar.
Á LA PATRIA
¡Cuan solitaria la nación que un día
20Poblara inmensa gente!
¡La nación cuyo imperio se extendía
Del ocaso al oriente!
¡Lágrimas viertes, infeliz, ahora,
Soberana del mundo,
25Y nadie de tu faz encantadora
77Borra el dolor profundo!
Obscuridad y luto tenebroso
En ti vertió la muerte,
Y en su furor el déspota sañoso
Se complació en tu suerte.
No perdonó lo hermoso, patria mía;
Cayó el joven guerrero,
Cayó el anciano, y la segur impía
Manejó placentero.
So la rabia cayó la virgen pura
10Del déspota sombrío,
Como eclipsa la rosa su hermosura
En el sol del estío.
¡Oh vosotros, del mundo habitadores,
Contemplad mi tormento!
15¿Igualarse podrán ¡ah! qué dolores
Al dolor que yo siento?
Yo, desterrado de la patria mía,
De una patria que adoro,
Perdida miro su primer valía
20Y sus desgracias lloro.....
Tendió sus brazos la agitada España,
Sus hijos implorando;
Sus hijos fueron, mas traidora saña
78Desbarató su bando.
¿Qué se hicieron tus muros torreados,
Oh mi patria querida?
¿Dónde fueron tus héroes esforzados,
Tu espada no vencida?
¡Ay! de tus hijos en la humilde frente
Está el rubor grabado:
Á sus ojos, caídos tristemente,
El llanto está agolpado.
Un tiempo España fué; cien héroes fueron
10En tiempos de ventura,
Y las naciones tímidas la vieron
Vistosa en hermosura.
Cual cedro que en el Líbano se ostenta,
Su frente se elevaba;
15Como el trueno á la virgen amedrenta,
Su voz las aterraba.
Mas hora, como piedra en el desierto,
Yaces desamparada,
Y el justo desgraciado vaga incierto
20Allá en tierra apartada.
Cubren su antigua pompa y poderío
Pobre hierba y arena,
Y el enemigo que tembló á su brío
79Burla y goza en su pena.
Vírgenes, destrenzad la cabellera
Y dadla al vago viento;
Acompañad con arpa lastimera
Mi lúgubre lamento.
ORIENTAL
Corriendo van por la vega
10Á las puertas de Granada
Hasta cuarenta gomeles
Y el capitán que los manda.
Al entrar en la ciudad,
Parando en su yegua blanca,
15Le dijo éste á una mujer
Que entre sus brazos lloraba:
—Enjuga el llanto, cristiana,
No me atormentes así,
Que tengo yo, mi sultana,
20Un nuevo Edén para ti.
Tengo un palacio en Granada,
Tengo jardines y flores,
Tengo una fuente dorada
80Con más de cien surtidores.
Y en la vega del Genil
Tengo parda fortaleza,
Que será reina entre mil
Cuando encierre tu belleza.
5Y sobre toda una orilla
Extiendo mi señorío;
Ni en Córdoba ni en Sevilla
Hay un parque como el mío.
Allí la altiva palmera
10Y el encendido granado,
Junto á la frondosa higuera
Cubren el valle y collado.
Allí el robusto nogal,
Allí el nópalo amarillo,
15Allí el sombrío moral
Crecen al pie del castillo.
Y olmos tengo en mi alameda
Que hasta el cielo se levantan,
Y en redes de plata y seda
20Tengo pájaros que cantan.
Y tú mi sultana eres,
Que desiertos mis salones
Están, mi harén sin mujeres,
Mis oídos sin canciones.
25Yo te daré terciopelos
Y perfumes orientales;
De Grecia te traeré velos
Y de Cachemira chales.
81Y te daré blancas plumas
Para que adornes tu frente,
Más blancas que las espumas
De nuestros mares de oriente;
Y perlas para el cabello,
5Y baños para el calor,
Y collares para el cuello;
Para los labios... ¡amor!—
—¿Qué me valen tus riquezas,
Respondióle la cristiana,
10Si me quitas á mi padre,
Mis amigos y mis damas?
Vuélveme, vuélveme, moro,
Á mi padre y á mi patria,
Que mis torres de León
15Valen más que tu Granada.—
Escuchóla en paz el moro,
Y manoseando su barba,
Dijo, como quien medita,
En la mejilla una lágrima:
20Si tus castillos mejores
Que nuestros jardines son,
Y son más bellas tus flores,
Por ser tuyas, en León,
Y tú diste tus amores
25Á alguno de tus guerreros,
Hurí del Edén, no llores;
Vete con tus caballeros.—
Y dándola su caballo
82Y la mitad de su guardia
El capitán de los moros
Volvió en silencio la espalda.
INDECISIÓN
¡Bello es vivir, la vida es la armonía!
Luz, peñascos, torrentes y cascadas,
5Un sol de fuego iluminando el día,
Aire de aromas, flores apiñadas:
Y en medio de la noche majestuosa
Esa luna de plata, esas estrellas,
Lámparas de la tierra perezosa,
10Que se ha dormido en paz debajo de ellas.
¡Bello es vivir! Se ve en el horizonte
Asomar el crepúsculo que nace;
Y la neblina que corona el monte
En el aire flotando se deshace;
15Y el inmenso tapiz del firmamento
Cambia su azul en franjas de colores;
Y susurran las hojas en el viento,
Y desatan su voz los ruiseñores.
Si hay huracanes y aquilón que brama,
20Si hay un invierno de humedad vestido,
Hay una hoguera á cuya roja llama
Se alza un festín con su discorde ruido.
Y una pintada y fresca primavera,
83Con su manto de luz y orla de flores,
Que cubre de verdor la ancha pradera
Donde brotan arroyos saltadores.
¡Bello es vivir, la vida es la armonía!
Luz, peñascos, torrentes y cascadas,
5Un sol de fuego iluminando el día,
Aire de aromas, flores apiñadas.
Arranca, arranca, Dios mío,
De la mente del poeta
Este pensamiento impío
10Que en un delirio creó;
Sin un instante de calma,
En su olvido y amargura,
No puede soñar su alma
Placeres que no gozó.
15¡Ay del poeta! su llanto
Fué la inspiración sublime
Con que arrebató su canto
Hasta los cielos tal vez;
Solitaria flor que el viento
20Con impuro soplo azota,
Él arrastra su tormento
Escrito sobre la tez.
Porque tú, ¡oh Dios! le robaste
Cuanto los hombres adoran;
25Tú en el mundo le arrojaste
Para que muriera en él;
84Tú le dijiste que el hombre
Era en la tierra su hermano;
Mas él no encuentra ese nombre
En sus recuerdos de hiel.
Tú le has dicho que eligiera
5Para el viaje de la vida
Una hermosa compañera
Con quien partir su dolor;
Mas ¡ay! que la busca en vano;
Porque es para el ser que ama
10Como un inmundo gusano
Sobre el tallo de una flor.
Canta la luz y las flores,
Y el amor en las mujeres,
Y el placer en los amores,
15Y la calma en el placer:
Y sin esperanza adora
Una belleza escondida,
Y hoy en sus cantares llora
Lo que alegre cantó ayer.
20Él con los siglos rodando
Canta su afán á los siglos,
Y los siglos van pasando
Sin curarse de su afán.
¡Maldito el nombre de gloria
25Que en tu cólera le diste!
Sentados en su memoria
Recuerdos de hierro están.
El día alumbra su pena,
85La noche alarga su duelo,
La aurora escribe en el cielo
Su sentencia de vivir:
Fábulas son los placeres,
No hay placeres en su alma,
5No hay amor en las mujeres,
Tarda la hora de morir.
Hay sol que alumbra, mas quema:
Hay flores que se marchitan,
Hay recuerdos que se agitan
10Fantasmas de maldición.
Si tiene una voz que canta,
Al arrancarla del pecho
Deja fuego en la garganta,
Vacío en el corazón.
¡Bello es vivir! Sobre gigante roca
Se mira el mundo á nuestros pies tendido,
La frente altiva con las nubes toca...
Todo creado para el hombre ha sido.
¡Bello es vivir! Que el hombre descuidado
20En los bordes se duerme de la vida,
Y de locura y sueños embriagado
En un festín el porvenir olvida.
¡Bello es vivir! Vivamos y cantemos:
El tiempo entre sus pliegues roedores
25Ha de llevar el bien que no gocemos,
Y ha de apagar placeres y dolores.
Cantemos de nosotros olvidados,
86Hasta que el son de la fatal campana
Toque á morir... Cantemos descuidados,
Que el sol de ayer no alumbrará mañana.
LA FUENTE
Huye la fuente al manantial ingrata
El verde musgo en derredor lamiendo,
5Y el agua limpia en su cristal retrata
Cuanto va viendo.
El césped mece y las arenas moja
Do mil caprichos al pasar dibuja,
Y ola tras ola murmurando arroja,
10Riza y empuja.
Lecho mullido la presenta el valle,
Fresco abanico el abedul pomposo,
Cañas y juncos retirada calle,
Sombra y reposo.
15Brota en la altura la fecunda fuente;
¿Y á qué su empeño, si al bajar la cuesta
Halla del río en el raudal rugiente
Tumba funesta?
Á BUEN JUEZ MEJOR TESTIGO
Tradición de Toledo
I
Entre pardos nubarrones
20Pasando la blanca luna,
87Con resplandor fugitivo,7
La baja tierra no alumbra.
La brisa con frescas alas
Juguetona no murmura,
Y las veletas no giran
5Entre la cruz y la cúpula.
Tal vez un pálido rayo
La opaca atmósfera cruza,
Y unas en otras las sombras
Confundidas se dibujan.
10Las almenas de las torres
Un momento se columbran,
Como lanzas de soldados
Apostados en la altura.
Reverberan los cristales
15La trémula llama turbia,
Y un instante entre las rocas
Rïela la fuente oculta.
Los álamos de la vega
Parecen en la espesura
20De fantasmas apiñados
Medrosa y gigante turba;
Y alguna vez desprendida
Gotea pesada lluvia,
Que no despierta á quien duerme,
25Ni á quien medita importuna.
Yace Toledo en el sueño
Entre las sombras confusa,
Y el Tajo á sus pies pasando
88Con pardas ondas la arrulla.
El monótono murmullo
Sonar perdido se escucha,
Cual si por las hondas calles
Hirviera del mar la espuma.
5¡Qué dulce es dormir en calma
Cuando á lo lejos susurran
Los álamos que se mecen,
Las aguas que se derrumban!
Se sueñan bellos fantasmas
10Que el sueño del triste endulzan,
Y en tanto que sueña el triste,
No le aqueja su amargura.
Tan en calma y tan sombría
Como la noche que enluta
15La esquina en que desemboca
Una callejuela oculta,
Se ve de un hombre que aguarda
La vigilante figura,
Y tan á la sombra vela
20Que entre la sombra se ofusca.
Frente por frente á sus ojos
Un balcón á poca altura
Deja escapar por los vidrios
La luz que dentro le alumbra;
25Mas ni en el claro aposento,
Ni en la callejuela obscura
El silencio de la noche
Rumor sospechoso turba.
89Pasó así tan largo tiempo,
Que pudiera haberse duda
De si es hombre, ó solamente
Mentida ilusión nocturna;
Pero es hombre, y bien se ve,
5Porque con planta segura
Ganando el centro á la calle
Resuelto y audaz pregunta:
—¿Quién va?—y á corta distancia
El igual compás se escucha
10De un caballo que sacude
Las sonoras herraduras.
¿Quién va? repite, y cercana
Otra voz menos robusta
Responde:—Un hidalgo ¡calle!
15Y el paso el bruto apresura.
—Téngase el hidalgo,—el hombre
Replica, y la espada empuña.
—Ved más bien si me haréis calle
(Repusieron con mesura)
20Que hasta hoy á nadie se tuvo
Ibán de Vargas y Acuña.
—Pase el Acuña y perdone:—
Dijo el mozo en faz de fuga,
Pues teniéndose el embozo
25Sopla un silbato, y se oculta.
Paró el jinete á una puerta,
Y con precaución difusa
Salió una niña al balcón
90Que llama interior alumbra.
—¡Mi padre!—clamó en voz baja,
Y el viejo en la cerradura
Metió la llave pidiendo
Á sus gentes que le acudan.
5Un negro por ambas bridas
Tomó la cabalgadura,
Cerróse detrás la puerta
Y quedó la calle muda.
En esto desde el balcón,
10Como quien tal acostumbra,
Un mancebo por las rejas
De la calle se asegura.
Asió el brazo al que apostado
Hizo cara á Ibán de Acuña,
15Y huyeron, en el embozo
Velando la catadura.
II
Clara, apacible y serena
Pasa la siguiente tarde,
Y el sol tocando su ocaso
20Apaga su luz gigante:
Se ve la imperial Toledo
Dorada por los remates,
Como una ciudad de grana
Coronada de cristales.
25El Tajo por entre rocas
Sus anchos cimientos lame,
91Dibujando en las arenas
Las ondas con que las bate.
Y la ciudad se retrata
En las ondas desiguales,
Como en prendas de que el río
5Tan afanoso la bañe.
Á lo lejos en la vega
Tiende galán por sus márgenes,
De sus álamos y huertos
El pintoresco ropaje,
10Y porque su altiva gala
Más á los ojos halague,
La salpica con escombros
De castillos y de alcázares.
Un recuerdo es cada piedra
15Que toda una historia vale,
Cada colina un secreto
De príncipes ó galanes.
Aquí se bañó la hermosa
Por quien dejó su rey culpable
20Amor, fama, reino y vida
En manos de musulmanes.
Allí recibió Galiana
Á su receloso amante
En esa cuesta que entonces
25Era un plantel de azahares.
Allá por aquella torre,
Que hicieron puerta los árabes,
Subió el Cid sobre Babieca
92Con su gente y su estandarte.
Más lejos se ve el castillo
De San Servando, ó Cervantes
Donde nada se hizo nunca
Y nada al presente se hace.
5Á este lado está la almena
Por do sacó vigilante
El conde Don Peranzules
Al rey, que supo una tarde
Fingir tan tenaz modorra,
10Que, político y constante,
Tuvo siempre el brazo quedo
Las palmas al horadarle.
Allí está el circo romano,
Gran cifra de un pueblo grande,
15Y aquí la antigua Basílica
De bizantinos pilares,
Que oyó en el primer concilio
Las palabras de los Padres
Que velaron por la Iglesia
20Perseguida ó vacilante.
La sombra en este momento
Tiende sus turbios cendales
Por todas esas memorias
De las pasadas edades,
25Y del Cambrón y Visagra
Los caminos desiguales,
Camino á los Toledanos
Hacia las murallas abren.
93Los labradores se acercan
Al fuego de sus hogares,
Cargados con sus aperos,
Cansados de sus afanes.
Los ricos y sedentarios
5Se tornan con paso grave,
Calado el ancho sombrero,
Abrochados los gabanes;
Y los clérigos y monjes
Y los prelados y abades
10Sacudiendo el leve polvo
De capelos y sayales.
Quédase sólo un mancebo
De impetuosos ademanes,
Que se pasea ocultando
15Entre la capa el semblante.
Los que pasan le contemplan
Con decisión de evitarle,
Y él contempla á los que pasan
Como si á alguien aguardase.
20Los tímidos aceleran
Los pasos al divisarle,
Cual temiendo de seguro
Que les proponga un combate;
Y los valientes le miran
25Cual si sintieran dejarle
Sin que libres sus estoques
En riña sonora dancen.
Una mujer también sola
94Se viene el llano adelante,
La luz del rostro escondida
En tocas y tafetanes.
Mas en lo leve del paso,
Y en lo flexible del talle,
5Puede á través de los velos
Una hermosa adivinarse.
Vase derecha al que aguarda,
Y él al encuentro la sale
Diciendo... cuanto se dicen
10En las citas los amantes.
Mas ella, galanterías
Dejando severa aparte,
Así al mancebo interrumpe
En voz decisiva y grave:
«Abreviemos de razones,
Diego Martínez; mi padre,
Que un hombre ha entrado en su ausencia
Dentro mi aposento sabe:
Y así quien mancha mi honra,
20Con la suya me la lave;
Ó dadme mano de esposo,
Ó libre de vos dejadme.»
Miróla Diego Martínez
Atentamente un instante,
25Y echando á un lado el embozo,
Repuso palabras tales:
«Dentro de un mes, Inés mía,
95Parto á la guerra de Flandes;
Al año estaré de vuelta
Y contigo en los altares.
Honra que yo te desluzca,
Con honra mía se lave;
5Que por honra vuelven honra
Hidalgos que en honra nacen.
—Júralo,—exclamó la niña.
—Más que mi palabra vale
No te valdrá un juramento.
10—Diego, la palabra es aire.
—¡Vive Dios que estás tenaz!
Dalo por jurado y baste.
—No me basta; que olvidar
Puedes la palabra en Flandes.
15—¡Voto á Dios! ¿qué más pretendes?
—Que á los pies de aquella imagen
Lo jures como cristiano
Del santo Cristo delante.»
Vaciló un punto Martínez,
20Mas porfiando que jurase,
Llevóle Inés hacia el templo
Que en medio la vega yace.
Enclavado en un madero,
En duro y postrero trance,
25Ceñida la sien de espinas,
Descolorido el semblante,
Víase allí un crucifijo
Teñido de negra sangre,
96Á quien Toledo devota
Acude hoy en sus azares.
Ante sus plantas divinas
Llegaron ambos amantes,
Y haciendo Inés que Martínez
5Los sagrados pies tocase,
Preguntóle:
—Diego, ¿juras
Á tu vuelta desposarme?
Contestó el mozo:
—¡Sí juro!
Y ambos del templo se salen.
III
Pasó un día y otro día,
Un mes y otro mes pasó,
Y un año pasado había,
Mas de Flandes no volvía
Diego, que á Flandes partió.
15Lloraba la bella Inés
Su vuelta aguardando en vano,
Oraba un mes y otro mes
Del crucifijo á los pies
Do puso el galán su mano.
20Todas las tardes venía
Después de traspuesto el sol,
Y á Dios llorando pedía
La vuelta del español,
Y el español no volvía.
2597Y siempre al anochecer,
Sin dueña y sin escudero,
En un manto una mujer
El campo salía á ver
Al alto del Miradero.
5¡Ay del triste que consume
Su existencia en esperar!
¡Ay del triste que presume
Que el duelo con que él se abrume
Al ausente ha de pesar!
10La esperanza es de los cielos
Precioso y funesto don,
Pues los amantes desvelos
Cambian la esperanza en celos,
Que abrasan el corazón.
15Si es cierto lo que se espera,
Es un consuelo en verdad;
Pero siendo una quimera,
En tan frágil realidad
Quien espera desespera.
20Así Inés desesperaba
Sin acabar de esperar,
Y su tez se marchitaba,
Y su llanto se secaba
Para volver á brotar.
25En vano á su confesor
Pidió remedio ó consejo
Para aliviar su dolor;
Que mal se cura el amor
98Con las palabras de un viejo.
En vano á Ibán acudía,
Llorosa y desconsolada;
El padre no respondía;
Que la lengua le tenía
5Su propia deshonra atada.
Y ambos maldicen su estrella,
Callando el padre severo
Y suspirando la bella,
Porque nació mujer ella,
10Y el viejo nació altanero.
Dos años al fin pasaron
En esperar y gemir,
Y las guerras acabaron,
Y los de Flandes tornaron
15Á sus tierras á vivir.
Pasó un día y otro día,
Un mes y otro mes pasó,
Y el tercer año corría;
Diego á Flandes se partió,
20Mas de Flandes no volvía.
Era una tarde serena,
Doraba el sol de occidente
Del Tajo la vega amena,
Y apoyada en una almena
25Miraba Inés la corriente.
Iban las tranquilas olas
Las riberas azotando
Bajo las murallas solas,
99Musgo, espigas y amapolas
Ligeramente doblando.
Algún olmo que escondido
Creció entre la hierba blanda,
Sobre las aguas tendido
5Se reflejaba perdido
En su cristalina banda.
Y algún ruiseñor colgado
Entre su fresca espesura
Daba al aire embalsamado
10Su cántico regalado
Desde la enramada obscura.
Y algún pez con cien colores,
Tornasolada la escama,
Saltaba á besar las flores,
15Que exhalan gratos olores,
Á las puntas de una rama.
Y allá en el trémulo fondo
El torreón se dibuja
Como el contorno redondo
20Del hueco sombrío y hondo
Que habita nocturna bruja.
Así la niña lloraba
El rigor de su fortuna,
Y así la tarde pasaba
25Y al horizonte trepaba
La consoladora luna.
Á lo lejos por el llano
En confuso remolino
100Vió de hombres tropel lejano
Que en pardo polvo liviano
Dejan envuelto el camino.
Bajó Inés del torreón,
Y llegando recelosa
5Á las puertas del Cambrón,
Sintió latir zozobrosa
Más inquieto el corazón.
Tan galán como altanero
Dejó ver la escasa luz
10Por bajo el arco primero
Un hidalgo caballero
En un caballo andaluz;
Jubón negro acuchillado,
Banda azul, lazo en la hombrera,
15Y sin pluma al diestro lado
El sombrero derribado
Tocando con la gorguera;
Bombacho gris guarnecido,
Bota de ante, espuela de oro,
20Hierro al cinto suspendido,
Y á una cadena prendido
Agudo cuchillo moro.
Vienen tras este jinete
Sobre potros jerezanos
25De lanceros hasta siete,
Y en adarga y coselete
Diez peones castellanos.
Asióse á su estribo Inés
101Gritando:—¡Diego, eres tú!—
Y él viéndola de través
Dijo—¡Voto á Belcebú,
Que no me acuerdo, quién es!—
Dió la triste un alarido
5Tal respuesta al escuchar,
Y á poco perdió el sentido,
Sin que más voz ni gemido
Volviera en tierra á exhalar.
Frunciendo ambas á dos cejas
10Encomendóla á su gente,
Diciendo:—¡Malditas viejas
Que á las mozas malamente
Enloquecen con consejas!—
Y aplicando el capitán
15Á su potro las espuelas
El rostro á Toledo dan,
Y á trote cruzando van
Las obscuras callejuelas.
IV
Así por sus altos fines
20Dispone y permite el cielo
Que puedan mudar al hombre
Fortuna, poder y tiempo.
Á Flandes partió Martínez
De soldado aventurero,
25Y por su suerte y hazañas
Allí capitán le hicieron.
102Según alzaba en honores
Alzábase en pensamientos,
Y tanto ayudó en la guerra
Con su valor y altos hechos,
Que el mismo rey á su vuelta
5Le armó en Madrid caballero,
Tomándole á su servicio
Por capitán de lanceros.
Y otro no fué que Martínez
Quien ha poco entró en Toledo,
10Tan orgulloso y ufano
Cual salió humilde y pequeño.
Ni es otro á quien se dirige,
Cobrado el conocimiento,
La amorosa Inés de Vargas,
15Que vive por él muriendo.
Mas él, que olvidando todo
Olvidó su nombre mesmo,
Puesto que hoy Diego Martínez
Es el capitán Don Diego,
20Ni se ablanda á sus caricias,
Ni cura de sus lamentos;
Diciendo que son locuras
De gentes de poco seso;
Que ni él prometió casarse
25Ni pensó jamás en ello.
¡Tanto mudan á los hombres
Fortuna, poder y tiempo!
En vano porfiaba Inés
103Con amenazas y ruegos;
Cuanto más ella importuna
Está Martínez severo.
Abrazada á sus rodillas
Enmarañado el cabello,
5La hermosa niña lloraba
Prosternada por el suelo.
Mas todo empeño es inútil,
Porque el capitán Don Diego
No ha de ser Diego Martínez
10Como lo era en otro tiempo.
Y así llamando á su gente,
De amor y piedad ajeno,
Mandóles que á Inés llevaran
De grado ó de valimiento.
15Mas ella antes que la asieran,
Cesando un punto en su duelo,
Así habló, el rostro lloroso
Hacia Martínez volviendo:
«Contigo se fué mi honra,
20Conmigo tu juramento;
Pues buenas prendas son ambas,
En buen fiel las pesaremos.»
Y la faz descolorida
En la mantilla envolviendo,
25Á pasos desatentados
Salióse del aposento.
V
Era entonces de Toledo
Por el rey gobernador
El justiciero y valiente
Don Pedro Ruiz de Alarcón.
5Muchos años por su patria
El buen viejo peleó;
Cercenado tiene un brazo,
Mas entero el corazón.
La mesa tiene delante,
10Los jueces en derredor,
Los corchetes á la puerta
Y en la derecha el bastón.
Está, como presidente
Del tribunal superior,
15Entre un dosel y una alfombra
Reclinado en un sillón,
Escuchando con paciencia
La casi asmática voz
Con que un tétrico escribano
20Solfea una apelación.
Los asistentes bostezan
Al murmullo arrullador,
Los jueces medio dormidos
Hacen pliegues al ropón,
25Los escribanos repasan
Sus pergaminos al sol,
105Los corchetes á una moza
Guiñan en un corredor,
Y abajo en Zocodover
Gritan en discorde son
Los que en el mercado venden
5Lo vendido y el valor.
Una mujer en tal punto,
En faz de grande aflicción,
Rojos de llorar los ojos,
Ronca de gemir la voz,
10Suelto el cabello y el manto,
Tomó plaza en el salón
Diciendo á gritos: «¡Justicia,
Jueces; justicia, señor!»
Y á los pies se arroja humilde
15De Don Pedro de Alarcón,
En tanto que los curiosos
Se agitan al rededor.
Alzóla cortés Don Pedro
Calmando la confusión
20Y el tumultuoso murmullo
Que esta escena ocasionó,
Diciendo:
—Mujer, ¿qué quieres?
—Quiero justicia, señor.
—¿De qué?
—De una prenda hurtada.
25—¿Qué prenda?
—Mi corazón.
106—¿Tú le diste?
—Le presté.
—¿Y no te le han vuelto?
—No.
—¿Tienes testigos?
—Ninguno.
—¿Y promesa?
—¡Sí, por Dios!
Que al partirse de Toledo
5Un juramento empeñó.
—¿Quién es él?
—Diego Martínez.
—¿Noble?
—Y capitán, señor.
—Presentadme al capitán,
Que cumplirá si juró.—
10Quedó en silencio la sala,
Y á poco en el corredor
Se oyó de botas y espuelas
El acompasado son.
Un portero, levantando
15El tapiz, en alta voz
Dijo:—El capitán Don Diego.—
Y entró luego en el salón
Diego Martínez, los ojos
Llenos de orgullo y furor.
20—¿Sois el capitán Don Diego,
Díjole Don Pedro, vos?—
Contestó altivo y sereno
107Diego Martínez:
—Yo soy.
—¿Conocéis á esta muchacha?
—Ha tres años, salvo error.
—¿Hicísteisla juramento
De ser su marido?—
—No.
5—¿Juráis no haberlo jurado?
—Sí juro.—
—Pues id con Dios.
—¡Miente!—clamó Inés llorando
De despecho y de rubor.
—Mujer, ¡piensa lo que dices!...
10—Digo que miente, juró.
—¿Tienes testigos?
—Ninguno.
—Capitán, idos con Dios,
Y dispensad que acusado
Dudara de vuestro honor.—
15Tornó Martínez la espalda
Con brusca satisfacción,
É Inés, que le vió partirse,
Resuelta y firme gritó:
—Llamadle, tengo un testigo.
20Llamadle otra vez, señor.—
Volvió el capitán Don Diego,
Sentóse Ruiz de Alarcón,
La multitud aquietóse
Y la de Vargas siguió:
25108—Tengo un testigo á quien nunca
Faltó verdad ni razón.
—¿Quién?
—Un hombre que de lejos
Nuestras palabras oyó,
Mirándonos desde arriba.
5—¿Estaba en algún balcón?
—No, que estaba en un suplicio
Donde ha tiempo que expiró.
—¿Luego es muerto?
—No, que vive.
—Estáis loca, ¡vive Dios!
10¿Quién fué?
—El CRISTO de la Vega
Á cuya faz perjuró.—
Pusiéronse en pie los jueces
Al nombre del Redentor,
Escuchando con asombro
15Tan excelsa apelación.
Reinó un profundo silencio
De sorpresa y de pavor,
Y Diego bajó los ojos
De vergüenza y confusión.
20Un instante con los jueces
Don Pedro en secreto habló,
Y levantóse diciendo
Con respetuosa voz:
«La ley es ley para todos,
25Tu testigo es el mejor,
109Mas para tales testigos
No hay más tribunal que Dios.
Haremos... lo que sepamos;
Escribano, al caer el sol
Al CRISTO que está en la vega
5Tomaréis declaración.»
VI
Es una tarde serena,
Cuya luz tornasolada
Del purpurino horizonte
Blandamente se derrama.
10Plácido aroma las flores
Sus hojas plegando exhalan,
Y el céfiro entre perfumes
Mece las trémulas alas.
Brillan abajo en el valle
15Con suave rumor las aguas,
Y las aves en la orilla
Despidiendo al día cantan.
Allá por el Miradero
Por el Cambrón y Visagra
20Confuso tropel de gente
Del Tajo á la vega baja.
Vienen delante Don Pedro
De Alarcón, Ibán de Vargas,
Su hija Inés, los escribanos,
25Los corchetes y los guardias;
Y detrás monjes, hidalgos,
110Mozas, chicos y canalla.
Otra turba de curiosos
En la vega les aguarda,
Cada cual comentariando
El caso según le cuadra.
5Entre ellos está Martínez
En apostura bizarra,
Calzadas espuelas de oro,
Valona de encaje blanca,
Bigote á la borgoñona,
10Melena desmelenada,
El sombrero guarnecido
Con cuatro lazos de plata,
Un pie delante del otro,
Y el puño en el de la espada.
15Los plebeyos de reojo
Le miran de entre las capas,
Los chicos al uniforme
Y las mozas á la cara.
Llegado el gobernador
20Y gente que le acompaña,
Entraron todos al claustro
Que iglesia y patio separa.
Encendieron ante el CRISTO
Cuatro cirios y una lámpara,
25Y de hinojos un momento
Le rezaron en voz baja.
Está el CRISTO de la Vega
La cruz en tierra posada,
111Los pies alzados del suelo
Poco menos de una vara;
Hacia la severa imagen
Un notario se adelanta,
De modo que con el rostro
5Al pecho santo llegaba.
Á un lado tiene á Martínez,
Á otro lado á Inés de Vargas,
Detrás al gobernador
Con sus jueces y sus guardias.
10Después de leer dos veces
La acusación entablada,
El notario á Jesucristo
Así demandó en voz alta:
—«Jesús, Hijo de María,
15Ante nos esta mañana
Citado como testigo
Por boca de Inés de Vargas,
¿Juráis ser cierto que un día
Á vuestras divinas plantas
20Juró á Inés Diego Martínez
Por su mujer desposarla?»
Asida á un brazo desnudo
Una mano atarazada
Vino á posar en los autos
25La seca y hendida palma,
Y allá en los aires «¡Sí JURO!»
Clamó una voz más que humana.
Alzó la turba medrosa
112La vista á la imagen santa...
Los labios tenía abiertos,
Y una mano desclavada.
CONCLUSIÓN
Las vanidades del mundo
Renunció allí mismo Inés,
5Y espantado de sí propio
Diego Martínez también.
Los escribanos temblando
Dieron de esta escena fe,
Firmando como testigos
10Cuantos hubieron poder.
Fundóse un aniversario
Y una capilla con él,
Y Don Pedro de Alarcón
El altar ordenó hacer,
15Donde hasta el tiempo que corre,
Y en cada un año una vez,
Con la mano desclavada
El crucifijo se ve.
CANTOS DE PÁJARO
Tengo yo un pajarillo
20Que el día pasa
Cantando entre las flores
113De mi ventana;
Y un canto alegre
Á todo pasajero
Dedica siempre.
Tiene mi pajarillo
5Siempre armonías
Para alegrar el alma
Del que camina...
¡Oh cielo santo,
Por qué no harán los hombres
10Lo que los pájaros!
Cuando mi pajarillo
Cantos entona,
Pasajeros ingratos
Cantos le arrojan:
15Mas no por eso
Niega sus armonías
Al pasajero.
Tiende las leves alas,
Cruza las nubes
20Y canta junto al cielo
Con voz más dulce:
«Paz á los hombres
Y gloria al que en la altura
Rige los orbes!»
25Y yo sigo el ejemplo
Del ave mansa
Que canta entre las flores
De mi ventana,
114Porque es sabido
Que poetas y pájaros
Somos lo mismo.
LA PEREJILERA
Al salir el sol dorado
Esta mañana te vi
5Cogiendo, niña, en tu huerto
Matitas de perejil.
Para verte más de cerca
En el huerto me metí,
Y sabrás que eché de menos
10Mi corazón al salir.
Tú debiste de encontrarle,
Que en el huerto le perdí.
«Dámele, perejilera,
Que te le vengo á pedir.»
LA MODESTIA
Por las flores proclamado
Rey de una hermosa pradera,
Un clavel afortunado
Dió principio á su reinado
Al nacer la primavera.
20Con majestad soberana
Llevaba y con noble brío
115El regio manto de grana,
Y sobre la frente ufana
La corona de rocío.
Su comitiva de honor
Mandaba, por ser costumbre,
5El céfiro volador,
Y había en su servidumbre
Hierbas y malvas de olor.
Su voluntad poderosa,
Porque también era uso,
10Quiso una flor para esposa,
Y regiamente dispuso
Elegir la más hermosa.
Como era costumbre y ley,
Y porque causa delicia
15En la numerosa grey,
Pronto corrió la noticia
Por los estados del rey.
Y en revuelta actividad
Cada flor abre el arcano
20De su fecunda beldad,
Por prender la voluntad
Del hermoso soberano.
Y hasta las menos apuestas
Engalanarse se vían
25Con harta envidia, dispuestas
Á ver las solemnes fiestas
Que celebrarse debían.
Lujosa la Corte brilla:
116El rey, admirado, duda,
Cuando ocultarse sencilla
Vió una tierna florecilla
Entre la hierba menuda.
Y por si el regio esplendor
5De su corona le inquieta,
Pregúntale con amor:
—«¿Cómo te llamas?»—«Violeta,»
Dijo temblando la flor.
—«¿Y te ocultas cuidadosa
10Y no luces tus colores,
Violeta dulce y medrosa,
Hoy que entre todas las flores
Va el rey á elegir esposa?»
Siempre temblando la flor,
15Aunque llena de placer,
Suspiró y dijo: «Señor,
Yo no puedo merecer
Tan distinguido favor.»
El rey, suspenso, la mira
20Y se inclina dulcemente;
Tanta modestia le admira;
Su blanda esencia respira,
Y dice alzando la frente:
«Me depara mi ventura
25117Esposa noble y apuesta;
Sepa, si alguno murmura,
Que la mejor hermosura
Es la hermosura modesta.»
EL MONT-BLANC
¡Heme al fin en la cumbre soberana!...
15¡Nieve perpetua..., soledad doquiera!...
¿Quién sino el hombre, en su soberbia insana,
Á hollar estos desiertos se atreviera?
Aquí enmudece hasta la voz del viento...;
Profundo mar parece el horizonte...,
20Única playa el alto firmamento...,
Anclada nave el solitario monte.
118¡Nada en torno de mí!... ¡Todo á mis plantas!
Obscuros bosques, relucientes ríos,
Lagos, campiñas, páramos, gargantas...
¡Europa entera yace á los pies míos!
¡Y cuán pequeña la terrestre vida,
5Cuán relegado el humanal imperio
Se ve desde estos hielos donde anida
El Monte Blanco, el rey del hemisferio!
¡De aquí tiende su cetro sobre el mundo!
El Danubio opulento, el Po anchuroso,
10El luengo Rhin y el Ródano profundo,
Hijos son de los hijos del Coloso.
Debajo de él... los Alpes se eslabonan
Como escabeles de su trono inmenso:
Debajo de él... las nubes se amontonan
15Cual humo leve de quemado incienso.
¡Sobre él... los cielos nada más! La tarde
Le invidia al verlo de fulgor ceñido...
Llega la noche, y aún su frente arde
Con reflejos de un sol por siempre hundido.
20Allá turnan con raudo movimiento
Una y otra estación... Él permanece
Mudo, inmóvil, estéril. ¡Monumento
De la implacable eternidad parece!
Ni el oso atroz ni el traicionero lobo
25Huellan jamás su excelsitud nevada...
Huérfano vive del calor del globo...
¡En él principia el reino de la nada!
Por eso, ufano de su horror profundo,
119Dichoso aquí mi corazón palpita...
¡Aquí solo con Dios..., fuera del mundo!
¡Solo, bajo la bóveda infinita!
¡Y qué süave, deleitosa calma
Brinda á mi pecho esta región inerte!...
5Así concibe fatigada el alma
El tardo bien de la benigna muerte.
¡Morir aquí! De los poblados valles
No retornar á la angustiosa vida:
No escuchar más los lastimosos ayes
10De la cuitada humanidad caída:
Desparecer, huyendo de la tierra,
Desde esta cima que se acerca al cielo:
Por siempre desertar de aquella guerra,
De eterna libertad tendiendo el vuelo...
15Tal ansia acude al corazón llagado,
Al mirarte, ¡oh Mont-Blanc!, erguir la frente
Sobre un mísero mundo atribulado
Por el cierzo y el rayo y el torrente.
¡Tú nada temes! De tu imperio yerto
20Sólo Dios es señor, fuerza y medida:
¡Cómo el ancho Océano y el Desierto,
Tú vives sólo de tu propia vida!
La tierra acaba en tu glacial palacio;
Tuya es la azul inmensidad aérea:
25Tú ves más luz, más astros, más espacio...;
¡Parte eres ya de la mansión etérea!
¡Adiós! Retorno al mundo... Acaso un día
Ya de la tierra el corazón no lata,
120Y sobre su haz inanimada y fría
Tiendas tu manto de luciente plata...
Será entonces tu reino silencioso
Cuanto hoy circunda y cubre el Oceano...
¡Adiós!... Impera en tanto desdeñoso
5Sobre la insania del orgullo humano.
EL SECRETO
«¡Yo no quiero morirme!»
—Dice la niña,
Tendiendo hacia su madre
Dos manecitas
10Calenturientas,
Cual dos blancos jazmines
Que el viento seca...
Un silencio de muerte
La madre guarda...
15¡Ay! ¡si hablara, vertiera
Mares de lágrimas!
Besa á la niña,
¡Y aun le fingen sus labios
Una sonrisa!
20Del cuello de la madre
La hija se cuelga
Y, pegada á su oído,
Pálida y trémula,
Con sordo acento,
25Dícele horrorizada:
121—«Oye un secreto:
¿Sabes por qué á morirme
Le temo tanto?
Porque luego me llevan,
Toda de blanco,
5Al cementerio...,
¡Y de verme allí sola
Va á darme miedo!»
—«Hija de mis entrañas!
(Grita la madre)
10Dios querrá que me vivas...;
Y, aunque te mate,
Descuida, hermosa;
Que tú en el cementerio
No estarás sola.»
RIMAS
II
Saeta que voladora
Cruza, arrojada al azar,
Sin adivinarse dónde
Temblando se clavará;
Hoja que del árbol seca
20Arrebata el vendaval,
Sin que nadie acierte el surco
Donde á caer volverá;
122Gigante ola que el viento
Riza y empuja en el mar,
Y rueda y pasa, y no sabe
Qué playa buscando va;
Luz que en cercos temblorosos
5Brilla, próxima á expirar,
Ignorándose cuál de ellos
El último brillará;
Eso soy yo, que al acaso
Cruzo el mundo, sin pensar
10De dónde vengo, ni adónde
Mis pasos me llevarán.
VII
Del salón en el ángulo obscuro,
De su dueño tal vez olvidada,
Silenciosa y cubierta de polvo
15Veíase el arpa.
¡Cuánta nota dormía en sus cuerdas
Como el pájaro duerme en las ramas,
Esperando la mano de nieve
Que sabe arrancarlas!
20¡Ay! pensé; ¡cuántas veces el genio
Así duerme en el fondo del alma,
Y una voz, como Lázaro, espera
Que le diga: «Levántate y anda!»
LIII
Volverán las obscuras golondrinas
25123En tu balcón sus nidos á colgar,
Y, otra vez, con el ala á sus cristales
Jugando llamarán;
Pero aquellas que el vuelo refrenaban
Tu hermosura y mi dicha á contemplar,
5Aquellas que aprendieron nuestros nombres...
Ésas... ¡no volverán!
Volverán las tupidas madreselvas
De tu jardín las tapias á escalar,
Y otra vez á la tarde, aun más hermosas,
10Sus flores se abrirán;
Pero aquellas, cuajadas de rocío,
Cuyas gotas mirábamos temblar
Y caer, como lágrimas del día...
Ésas... ¡no volverán!
LXXIII
Cerraron sus ojos
Que aun tenía abiertos;
Taparon su cara
Con un blanco lienzo;
5y unos sollozando,
Otros en silencio,
De la triste alcoba
Todos se salieron.
La luz, que en un vaso
10Ardía en el suelo,
Al muro arrojaba
La sombra del lecho;
Y entre aquella sombra
Veíase á intervalos
15Dibujarse rígida
La forma del cuerpo.
Despertaba el día
Y á su albor primero
Con sus mil rüidos
20Despertaba el pueblo.
Ante aquel contraste
De vida y misterios,
De luz y tinieblas,
Medité un momento:
25«¡Dios mío, qué solos
Se quedan los muertos!»
125De la casa en hombros
Lleváronla al templo,
Y en una capilla
Dejaron el féretro.
5Allí rodearon
Sus pálidos restos
De amarillas velas
Y de paños negros.
Al dar de las ánimas
10El toque postrero,
Acabó una vieja
Sus últimos rezos;
Cruzó la ancha nave,
Las puertas gimieron,
15Y el santo recinto
Quedóse desierto.
De un reloj se oía
Compasado el péndulo,
Y de algunos cirios
20El chisporroteo.
Tan medroso y triste,
Tan obscuro y yerto
Todo se encontraba...
Que pensé un momento:
25«¡Dios mío, qué solos
Se quedan los muertos!»
126De la alta campana
La lengua de hierro,
Le dió, volteando,
Su adiós lastimero.
5El luto en las ropas,
Amigos y deudos
Cruzaron en fila,
Formando el cortejo.
Del último asilo,
10Obscuro y estrecho,
Abrió la piqueta
El nicho á un extremo.
Allí la acostaron,
Tapiáronle luego,
15Y con un saludo
Despidióse el duelo.
La piqueta al hombro,
El sepulturero
Cantando entre dientes
20Se perdió á lo lejos.
La noche se entraba,
Reinaba el silencio;
Perdido en las sombras,
Medité un momento:
25«¡Dios mío, qué solos
Se quedan los muertos!»
127En las largas noches
Del helado invierno,
Cuando las maderas
Crujir hace el viento
5Y azota los vidrios
El fuerte aguacero,
De la pobre niña
Á solas me acuerdo.
Allí cae la lluvia
10Con un son eterno;
Allí la combate
El soplo del cierzo.
¡Del húmedo muro
Tendida en el hueco,
15Acaso de frío
Se hielan sus huesos!...
EN NOCHE-BUENA
Á mis ancianos padres
I
Un año más en el hogar paterno
Celebramos la fiesta del Dios-Niño,
Símbolo augusto del amor eterno,
Cuando cubre los montes el invierno
5Con su manto de armiño.
II
Como en el día de la fausta boda
Ó en el que el santo de los padres llega,
La turba alegre de los niños juega,
Y en la ancha sala la familia toda
10De noche se congrega.
III
La roja lumbre de los troncos brilla
Del pequeño dormido en la mejilla,
Que con tímido afán su madre besa;
Y se refleja alegre en la vajilla
15De la dispuesta mesa.
IV
Á su sobrino, que lo escucha atento,
129Mi hermana dice el pavoroso cuento,
Y mi otra hermana la canción modula
Que, ó bien surge vibrante, ó bien ondula
Prolongada en el viento.
V
Mi madre tiende las rugosas manos
5Al nieto que huye por la blanda alfombra;
Hablan de pie mi padre y mis hermanos,
Mientras yo, recatándome en la sombra,
Pienso en hondos arcanos.
VI
Pienso que de los días de ventura
10Las horas van apresurando el paso,
Y que empaña el oriente niebla obscura,
Cuando aun el rayo trémulo fulgura
Último del ocaso.
VII
¡Padres míos, mi amor! ¡Cómo envenena
15Las breves dichas el temor del daño!
Hoy presidís nuestra modesta cena,
Pero en el porvenir... yo sé que un año
Vendrá sin Noche-Buena.
VIII
Vendrá, y las que hoy son risas y alborozo
20Serán muda aflicción y hondo sollozo.
No cantará mi hermana, y mi sobrina
No escuchará la historia peregrina
Que le da miedo y gozo.
130IX
No dará nuestro hogar rojos destellos
Sobre el limpio cristal de la vajilla,
Y, si alguien osa hablar, será de aquellos
Que hoy honran nuestra fiesta tan sencilla
5Con sus blancos cabellos.
X
Blancos cabellos cuya amada hebra
Es cual corona de laurel de plata,
Mejor que esas coronas que celebra
La vil lisonja, la ignorancia acata,
10Y el infortunio quiebra.
XI
¡Padres míos, mi amor! Cuando contemplo
La sublime bondad de vuestro rostro,
Mi alma a los trances de la vida templo,
Y ante esa imagen para orar me postro,
15Cual me postro en el templo.
XII
Cada arruga que surca ese semblante
Es del trabajo la profunda huella,
Ó fue un dolor de vuestro pecho amante.
La historia fiel de una época distante
20Puedo leer yo en ella.
XIII
La historia de los tiempos sin ventura
131En que luchasteis con la adversa suerte,
Y en que, tras negras horas de amargura,
Mi madre se sintió más noble y pura
Y mi padre más fuerte.
XIV
Cuando la noche toda en la cansada
5Labor tuvisteis vuestros ojos fijos,
Y, al venceros el sueño á la alborada,
Fuerzas os dió posar vuestra mirada
En los dormidos hijos.
XV
Las lágrimas correr una tras una
10Con noble orgullo por mi faz yo siento,
Pensando que hayan sido por fortuna,
Esas honradas manos mi sustento
Y esos brazos mi cuna.
XVI
¡Padres míos, mi amor! Mi alma quisiera
15Pagaros hoy la que en mi edad primera
Sufristeis sin gemir lenta agonía,
Y que cada dolor de entonces fuera
Germen de una alegría.
XVII
Entonces vuestro mal curaba el gozo
20De ver al hijo convertirse en mozo,
Mientras que al verme yo en vuestra presencia
Siento mi dicha ahogada en el sollozo
De una temida ausencia.
132XVIII
Si el vigor juvenil volver de nuevo
Pudiese á vuestra edad, ¿por qué estas penas?
Yo os daría mi sangre de mancebo,
Tornando así con ella á vuestras venas
5Esta vida que os debo.
XIX
Que de tal modo la aflicción me embarga
Pensando en la posible despedida,
Que imagino ha de ser tarea amarga
Llevar la vida, como inútil carga,
10Después de vuestra vida.
XX
Ese plazo fatal, sordo, inflexible,
Miro acercarse con profundo espanto,
Y en dudas grita el corazón sensible:
—«Si aplacar al destino es imposible,
15¿Para qué amarnos tanto?»
XXI
Para estar juntos en la vida eterna
Cuando acabe esta vida transitoria:
Si Dios, que el curso universal gobierna,
Nos devuelve en el cielo esta unión tierna,
20Yo no aspiro á más gloria.
XXII
PROXIMIDAD DEL BIEN
En el tiempo en que el mundo informe estaba,
Creó el Señor, cuando por dicha extrema
5El paraíso terrenal formaba,
Un fruto que del mal era el emblema
Y otro fruto que el bien simbolizaba.
Del miserable Adán al mismo lado
10El Señor colocó del bien el fruto;
Pero Adán nunca el bien halló, ofuscado,
Porque es del hombre mísero atributo
Huir del bien, del mal siempre arrastrado.
¡QUIÉN SUPIERA ESCRIBIR!
I
—Escribidme una carta, señor Cura.
5—Ya sé para quién es.
—¿Sabéis quién es, porque una noche obscura
Nos visteis juntos?—Pues.
—Perdonad; mas...—No extraño ese tropiezo.
La noche... la ocasión...
10Dadme pluma y papel. Gracias. Empiezo:
Mi querido Ramón:
—¿Querido?... Pero, en fin, ya lo habéis puesto...
—Si no queréis...—¡Sí, sí!
—¡Qué triste estoy! ¿ No es eso?—Por supuesto.
15—¡Qué triste estoy sin ti!
Una congoja, al empezar, me viene...
—¿Cómo sabéis mi mal?
—Para un viejo, una niña siempre tiene
El pecho de cristal.
20¿Qué es sin ti el mundo? Un valle de amargura.
¿Y contigo? Un edén.
—Haced la letra clara, señor Cura;
Que lo entienda eso bien.
135—El beso aquel que de marchar á punto
Te di...—¿Cómo sabéis?...
—Cuando se va y se viene y se está junto
Siempre... no os afrentéis.
Y si volver tu afecto no procura,
Tanto me harás sufrir...
—¿Sufrir y nada más? No, señor Cura,
¡Que me voy á morir!
—¿Morir? ¿Sabéis que es ofender al cielo?...
10—Pues, sí, señor, ¡morir!
—Yo no pongo morir.—¡Qué hombre de hielo!
¡Quién supiera escribir!
II
¡Señor Rector, señor Rector! en vano
Me queréis complacer,
15Si no encarnan los signos de la mano
Todo el ser de mi ser.
Escribidle, por Dios, que el alma mía
Ya en mí no quiere estar;
Que la pena no me ahoga cada día...
20Porque puedo llorar.
Que mis labios, las rosas de su aliento,
No se saben abrir;
Que olvidan de la risa el movimiento
Á fuerza de sentir.
136Que mis ojos, que él tiene por tan bellos,
Cargados con mi afán,
Como no tienen quien se mire en ellos,
Cerrados siempre están.
Que es, de cuantos tormentos he sufrido,5
La ausencia el más atroz;
Que es un perpetuo sueño de mi oído
El eco de su voz...
Que siendo por su causa, el alma mía
10¡Goza tanto en sufrir!...
Dios mío ¡cuántas cosas le diría
Si supiera escribir!...
III
EPÍLOGO
¡EXCELSIOR!
¿Por qué los corazones miserables,
Por qué las almas viles,
En los fieros combates de la vida
10Ni luchan ni resisten?
El espíritu humano es más constante
Cuanto más se levanta:
Dios puso el fango en la llanura, y puso
La roca en la montaña.
TRISTEZAS
Cuando recuerdo la piedad sincera
20Con que en mi edad primera
138Entraba en nuestras viejas catedrales,
Donde postrado ante la cruz de hinojos
Alzaba á Dios mis ojos,
Soñando en las venturas celestiales;
Hoy que mi frente atónito golpeo,
5Y con febril deseo
Busco los restos de mi fe perdida,
Por hallarla otra vez, radiante y bella
Como en la edad aquella,
¡Desgraciado de mí! diera la vida.
¡Con qué profundo amor, niño inocente,
Prosternaba mi frente
En las losas del templo sacrosanto!
Llenábase mi joven fantasía
De luz, de poesía,
15De mudo asombro, de terrible espanto.
Aquellas altas bóvedas que al cielo
Levantaban mi anhelo;
Aquella majestad solemne y grave;
Aquel pausado canto, parecido
20Á un doliente gemido,
Que retumbaba en la espaciosa nave;
Las marmóreas y austeras esculturas
De antiguas sepulturas,
139Aspiración del arte á lo infinito;
La luz que por los vidrios de colores
Sus tibios resplandores
Quebraba en los pilares de granito;
Haces de donde en curva fugitiva,
5Para formar la ojiva,
Cada ramal subiendo se separa,
Cual del rumor de multitud que ruega,
Cuando á los cielos llega,
Surge cada oración distinta y clara;
10En el gótico altar inmoble y fijo
El santo crucifijo,
Que extiende sin vigor sus brazos yertos,
Siempre en la sorda lucha de la vida,
Tan áspera y reñida,
15Para el dolor y la humildad abiertos;
El místico clamor de la campana
Que sobre el alma humana
De las caladas torres se despeña,
Y anuncia y lleva en sus aladas notas
20Mil promesas ignotas
Al triste corazón que sufre ó sueña;
Todo elevaba mi ánimo intranquilo
Á más sereno asilo:
140Religión, arte, soledad, misterio...
Todo en el templo secular hacía
Vibrar el alma mía,
Como vibran las cuerdas de un salterio.
Y á esta voz interior que sólo entiende
5Quien crédulo se enciende
En fervoroso y celestial cariño,
Envuelta en sus flotantes vestiduras
Volaba á las alturas,
Virgen sin mancha, mi oración de niño.
Su rauda, viva y luminosa huella
Como fugaz centella
Traspasaba el espacio, y ante el puro
Resplandor de sus alas de querube,
Rasgábase la nube
15Que me ocultaba el inmortal seguro.
¡Oh anhelo de esta vida transitoria!
¡Oh perdurable gloria!
¡Oh sed inextinguible del deseo!
¡Oh cielo, que antes para mí tenías
20Fulgores y armonías,
Y hoy tan obscuro y desolado veo!
Ya no templas mis íntimos pesares,
Ya al pie de tus altares
141Como en mis años de candor no acudo. page
Para llegar á ti perdí el camino,
Y errante peregrino
Entre tinieblas desespero y dudo.
Voy espantado sin saber por dónde;
5Grito, y nadie responde
Á mi angustiada voz; alzo los ojos
Y á penetrar la lobreguez no alcanzo;
medrosamente avanzo,
Y me hieren el alma los abrojos.
Hijo del siglo, en vano me resisto
Á su impiedad, ¡oh Cristo!
Su grandeza satánica me oprime.
Siglo de maravillas y de asombros,
Levanta sobre escombros
15Un Dios sin esperanza, un Dios que gime.
¡Y ese Dios no eres tú! No tu serena
Faz, de consuelos llena,
Alumbra y guía nuestro incierto paso.
Es otro Dios incógnito y sombrío:
20Su cielo es el vacío,
Sacerdote el error, ley el Acaso.
¡Ay! No recuerda el ánimo suspenso
Un siglo más inmenso,
142Más rebelde á tu voz, más atrevido;
Entre nubes de fuego alza su frente,
Como Luzbel, potente;
Pero también, como Luzbel, caído.
Á medida que marcha y que investiga
5Es mayor su fatiga,
Es su noche más honda y más obscura,
Y pasma, al ver lo que padece y sabe,
Cómo en su seno cabe
Tanta grandeza y tanta desventura.
10Como la nave sin timón y rota
Que el ronco mar azota,
Incendia el rayo y la borrasca mece
En piélago ignorado y proceloso,
Nuestro siglo—coloso,
15Con la luz que le abrasa, resplandece.
¡Y está la playa mística tan lejos!...
Á los tristes reflejos
Del sol poniente se colora y brilla.
El huracán arrecia, el bajel arde,
20Y es tarde, es ¡ay! muy tarde
Para alcanzar la sosegada orilla.
¿Qué es la ciencia sin fe? Corcel sin freno,
Á todo yugo ajeno,
143Que al impulso del vértigo se entrega,
Y á través de intrincadas espesuras,
Desbocado y á obscuras,
Avanza sin cesar y nunca llega.
¡Llegar! ¿Adónde?... El pensamiento humano
5En vano lucha, en vano
Su ley oculta y misteriosa infringe.
En la lumbre del sol sus alas quema,
Y no aclara el problema,
No penetra el enigma de la Esfinge.
10¡Sálvanos, Cristo, sálvanos, si es cierto
Que tu poder no ha muerto!
Salva á esta sociedad desventurada,
Que bajo el peso de su orgullo mismo
Rueda al profundo abismo
15Acaso más enferma que culpada.
¡SURSUM CORDA!
INTRODUCCIÓN
Á mi buen amigo el ilustre poeta Manuel Reina
I. Á ESPAÑA
Nunca mi labio á la servil lisonja
5Parias rindió. Ni el éxito ruidoso,
Ni la soberbia afortunada, oyeron
Falaz encomio de mi humilde Musa.
Dióme su austeridad la honrada tierra
Donde nací, y el presuroso tiempo
10Que arrastra y lleva en sus revueltas olas
Las grandezas humanas al olvido,
Á mi pesar me enseña que en el mundo
Tan sólo á dos excelsas majestades
Puedo, sin mengua, levantar mi canto;
15La Verdad y el Dolor.
En estas horas
De febril inquietud, ¿quién, Patria mía,
Merece como tú la pobre ofrenda
De mi respeto y de mi amor? Postrada
En los escombros de tu antigua gloria,
20La negra adversidad, con férrea mano,
145Comprime los latidos de tu pecho
Y el aire que respiras envenena.
Como tigre feroz clavó sus garras
La catástrofe en ti, y en tus heridas
Entrañas sacia su voraz instinto.
5¿Quién, al mirar tus lástimas, no llora?
¿Puede haber hombre tan perverso y duro,
Ni aun concebido en crapulosa orgía
Por hembra impura, que impasible vea
Morir sin fe, desesperado y solo,
10Al dulce bien que le llevó en su seno?
¡No existe, no!
Perdona si movido
Por la ciega pasión, allá en lejanos
Y borrascosos días, cuando airada
Mi voz como fatídico anatema
15Tronó en la tempestad, quizás injusto
Contigo pude ser. Pero hoy, que sufres,
Hoy que, Job de la Historia, te retuerces
En tu lecho de angustia, arrepentido
Y llena el alma de mortal congoja,
20Acudo ansioso á consolar tus penas,
Á combatir con los inmundos buitres,
Ávidos del festín, que en torno giran
De tu ulcerado cuerpo, y si lo mandas,
¡Oh, noble mártir! á morir contigo.
25Pero ¿quién habla de morir? ¿Acaso
No eres, Patria, inmortal? Tendrás eclipses
Como los tiene el sol. Sombras tenaces,
146Cual hiperbórea noche larga y fría,
Sobre ti pesarán, mientras no llegue
Tu santa redención. ¡Hora dichosa
En que verás con júbilo y ternura
Nacer el alba, el tenebroso espacio
5Inundarse de luz, la tierra encinta
Estremecerse en éxtasis materno,
De armonías, aromas y colores
Poblarse el aire, y palpitar en todo
La plenitud eterna de la vida!
10¡Ten esperanza y fe! Descubridora
De mundos, madre de indomada prole,
Tú no puedes morir, ¡Dios no lo quiere!
Aun tienes que cumplir altos destinos.
Busca en el seno de la paz bendita
15Reparador descanso, hasta que cobren
Tus músculos salud, y en cuanto sientas
El hervor de tu sangre renovada,
Ponte en pie, sacudiendo tu marasmo,
Que como losa del sepulcro, oprime
20Tu enferma voluntad. Surge del fondo
De tu aislamiento secular, y marcha
Con paso firme y corazón resuelto
Sin mirar hacia atrás, siempre adelante.
Sean la escuela y el taller y el surco
25Los solos campos de batalla en donde
Tu razón y tus fuerzas ejercites.
Entra en las lides del trabajo y vence,
Que entonces de laureles coronada,
147Más fecunda, más próspera y más grande,
Seguirás, fulgurando, tu camino
Por los arcos triunfales de la Historia.
II. Á AMÉRICA
¡Ésta es España! Atónita y maltrecha
Bajo el peso brutal de su infortunio,
5Inerte yace la matrona augusta
Que en otros siglos fatigó á la fama.
La que surcó los mares procelosos
Buscándote atrevida en el misterio,
Hasta que un día, deslumbrando al mundo,
10Surgiste, como Venus, de las ondas.
Cegada por tu espléndida hermosura,
Al engarzarte en su imperial diadema
España te oprimió; mas no la culpes,
Porque ¿cuándo la bárbara conquista
15Justa y humana fué? También clemente
Te dió su sangre, su robusto idioma,
Sus leyes y su Dios. ¡Te lo dió todo,
Menos la libertad! Pues mal pudiera
Darte el único bien que no tenía.
20AMOR OCULTO
Ya de mi amor la confesión sincera
Oyeron tus calladas celosías,
Y fué testigo de las ansias mías
La luna, de los tristes compañera.
5Tu nombre dice el ave placentera
 quien visito yo todos los días,
Y alegran mis soñadas alegrías
El valle, el monte, la comarca entera.
Sólo tú mi secreto no conoces,
10Por más que el alma con latido ardiente,
Sin yo quererlo, te lo diga a voces;
Y acaso has de ignorarlo eternamente,
Como las ondas de la mar veloces
La ofrenda ignoran que les da la fuente.
ARABESCOS Y COMPOSICIONES ÍNTIMAS
Oyendo hablar á un hombre, fácil es
Acertar dónde vió la luz del sol;
Si os alaba á Inglaterra, será inglés,
Si os habla mal de Prusia, es un francés,
Y si habla mal de España, es español.
149Si cumplir con lealtad
Nuestra última voluntad
Es sagrada obligación,
Cuando mis ojos se cierren,
5He de mandar que me entierren
Dentro de tu corazón.
Para matar la inocencia,
Para envenenar la dicha,
Es un gran puñal la pluma
10Y un gran veneno la tinta.
LA POESÍA
Á Teodoro Llorente
Como el raudal que corre en la pradera
Copia en su espejo pájaros y flores,
La alada mariposa de colores,
El verde arbusto y la radiante esfera,
La sublime poesía reverbera
20Combates, glorias, risas y dolores,
150Odio y amor, tinieblas y esplendores,
El cielo, el campo, el mar... ¡la vida entera!
¡Así Homero es la lid; Virgilio, el día;
Esquilo, la tormenta bramadora;
Anacreonte, el vino y la alegría;
5Dante, la noche con su negro arcano;
Calderón, el honor; Milton, la aurora;
Shakespeare, el triste corazón humano!
CANCIÓN DE ELVIRA
Creció acaso arbusto tierno
Á orillas de un manso río,
Y su ramaje sombrío
Muy ufano se extendió;
5Mas en el sañudo invierno
Subió el río cual torrente,
Y en su túmida corriente
El tierno arbusto llevó.
Reflejando nieve y grana,
10Nació garrida y pomposa
En el desierto una rosa,
Gala del prado y amor;
Mas lanzó con furia insana
Su soplo inflamado el viento,
15Y se llevó en un momento
Su vana pompa y frescor.
Así dura todo bien...
152Así los dulces amores,
Como las lozanas flores,
Se marchitan en su albor;
Y en el incierto vaivén
De la fortuna inconstante,
5Nace y muere en un instante
La esperanza del amor.
ATLÁNTIDA
Canto al porvenir de la raza latina en América
VII
¡Siglos pasaron sobre el mundo, y siglos
Guardaron el secreto!
Lo presintió Platón cuando sentado
10En las rocas de Engina contemplaba
Las sombras que en silencio descendían
Á posarse en las cumbres del Himeto;
Y el misterioso diálogo entablaba
Con las olas inquietas
15¡Que á sus pies se arrastraban y gemían!
Adivinó su nombre, hija postrera
Del tiempo, destinada
Á celebrar las bodas del futuro
En sus campos de eterna primavera,
20¡Y la llamó la Atlántida soñada!
153Pero Dios reservaba
La empresa ruda al genio renaciente
De la latina raza, ¡domadora
De pueblos, combatiente
5De las grandes batallas de la historia!
Y cuando fué la hora,
Colón apareció sobre la nave
Del destino del mundo portadora—
Y la nave avanzó. Y el Océano,
10Huraño y turbulento,
Lanzó al encuentro del bajel latino
Los negros aquilones,
¡Y á su frente rugiendo el torbellino,
Jinete en el relámpago sangriento!
15Pero la nave fué, y el hondo arcano
Cayó roto en pedazos;
¡Y despertó la Atlántida soñada
De un pobre visionario entre los brazos!
Era lo que buscaba
20El genio inquieto de la vieja raza,
Debelador de tronos y coronas,
¡Era lo que soñaba!
¡Ámbito y luz en apartadas zonas!
Helo armado otra vez, no ya arrastrando
25El sangriento sudario del pasado
Ni de negros recuerdos bajo el peso,
Sino en pos de grandiosas ilusiones,
¡La libertad, la gloria y el progreso!
154¡Nada le falta ya! lleva en el seno
El insondable afán del infinito,
¡Y el infinito por doquier lo llama
De las montañas con el hondo grito
5Y de los mares con la voz de trueno!
Tiene el altar que Roma
Quiso en vano construir con los escombros
Del templo egipcio y la pagoda indiana,
¡Altar en que profese eternamente
10Un culto solo la conciencia humana!
¡Y el Andes, con sus gradas ciclopeas,
Con sus rojas antorchas de volcanes,
Será el altar de fulgurantes velos
En que el himno inmortal de las ideas
15La tierra entera elevará á los cielos!
VIII
¡Campo inmenso á su afán! Allá dormidas
Bajo el arco triunfal de mil colores
Del trópico esplendente,
Las Antillas levantan la cabeza
20De la naciente luz á los albores,
Como bandadas de aves fugitivas
Que arrullaron al mar con sus extrañas
Canciones plañideras,
Y que secan al sol las blancas alas
25¡Para emprender el vuelo á otras riberas!
¡Allá Méjico está! sobre dos mares
155Alzada cual granítica atalaya,
¡Parece que aun espía
La castellana flota que se acerca
Del golfo azteca á la arenosa playa!
Y más allá Colombia adormecida
5Del Tequendama al retemblar profundo,
¡Colombia la opulenta
Que parece llevar en las entrañas
La inagotable juventud del mundo!
¡Salve, zona feliz! región querida
10Del almo sol que tus encantos cela,
Inmenso hogar de animación y vida,
¡Cuna del gran Bolívar! ¡Venezuela!
Todo en tu suelo es grande,
Los astros que te alumbran desde arriba
15Con eterno, sangriento centelleo,
El genio, el heroísmo,
¡Volcán que hizo erupción con ronco estruendo
En la cumbre inmortal de San Mateo!
Tendida al pie del Ande,
20Viuda infeliz sobre entreabierta huesa,
Yace la Roma de los Incas, rota
La vieja espada en la contienda grande,
La frente hundida en la tiniebla obscura,
¡Mas no ha muerto el Perú! que la derrota
25Germen es en los pueblos varoniles
De redención futura—
156entonces cuando llegue,
Para su suelo, la estación propicia
Del trabajo que cura y regenera,
Y brille al fin el sol de la justicia
Tras largos días de vergüenza y lloro,
5¡El rojo manto que á su espalda flota
Las mieses bordarán con flores de oro!
¡Bolivia! la heredera del gigante
Nacido al pie del Ávila, su genio
Inquieto y su valor constante
10Tiene para las luchas de la vida;
Sueña en batallas hoy, pero no importa,
Sueña también en anchos horizontes
En que en vez de cureñas y cañones
¡Sienta rodar la audaz locomotora
15Cortando valles y escalando montes!
Y Chile el vencedor, fuerte en la guerra,
Pero más fuerte en el trabajo, vuelve
Á colgar en el techo
Las vengadoras armas, convencido
20De que es estéril siempre la victoria
De la fuerza brutal sobre el derecho.
El Uruguay que combatiendo entrega
Su seno á las caricias del progreso,
El Brasil que recibe
25Del mar Atlante el estruendoso beso
Y á quien sólo le falta
El ser más libre, para ser más grande,
157¡Y la región bendita,
Sublime desposada de la gloria,
Que baña el Plata y que limita el Ande!
¡De pie para cantarla! que es la patria,
La patria bendecida,
5Siempre en pos de sublimes ideales,
¡El pueblo joven que arrulló en la cuna
El rumor de los himnos inmortales!
Y que hoy llama al festín de su opulencia
Á cuantos rinden culto
10Á la sagrada libertad, hermana
Del arte, del progreso y de la ciencia—
¡La patria! que ensanchó sus horizontes
Rompiendo las barreras
Que en otrora su espíritu aterraron,
15¡Y á cuyo paso en los nevados montes
Del Génesis los ecos despertaron!
¡La patria! que, olvidada
De la civil querella, arrojó lejos
El fratricida acero
20Y que lleva orgullosa
La corona de espigas en la frente,
¡Menos pesada que el laurel guerrero!
¡La patria! en ella cabe
Cuanto de grande el pensamiento alcanza,
25En ella el sol de redención se enciende,
Ella al encuentro del futuro avanza,
Y su mano, del Plata desbordante
¡La inmensa copa á las naciones tiende!
158IX
¡Ámbito inmenso, abierto
De la latina raza al hondo anhelo!
¡El mar, el mar gigante, la montaña
En eterno coloquio con el cielo...
5Y más allá desierto!
Acá ríos que corren desbordados,
Allí valles que ondean
Como ríos eternos de verdura,
Los bosques á los bosques enlazados,
10¡Doquier la libertad, doquier la vida
Palpitando en el aire, en la pradera
Y en explosión magnífica encendida!
¡Atlántida encantada
Que Platón presintió! promesa de oro
15Del porvenir humano—Reservado
Á la raza fecunda,
Cuyo seno engendró para la historia
Los Césares del genio y de la espada—
Aquí va á realizar lo que no pudo
20Del mundo antiguo en los escombros yertos
¡La más bella visión de sus visiones!
¡Al himno colosal de los desiertos
La eterna comunión de las naciones!
PROMETEO
VII
¡Arriba, pensadores! que en la lucha
Se templa y fortalece
Vuestra raza inmortal, nunca domada,
Que lleva por celeste distintivo
5La chispa de la audacia en la mirada
Y anhelos infinitos en el alma;
¡En cuya frente altiva
Se confunden y enlazan
El laurel rumoroso de la gloria
10Y del dolor la mustia siempre-viva!
¡Arriba, pensadores!
¡Que el espíritu humano sale ileso
Del cadalso y la hoguera!
Vuestro heraldo triunfal es el progreso
15Y la verdad la suspirada meta
De vuestro afán gigante.
¡Arriba! ¡que ya asoma el claro día
En que el error y el fanatismo expiren
Con doliente y confuso clamoreo!
20¡Ave de esa alborada es el poeta,
Hermano de las águilas del Cáucaso,
Que secaron piadosas con sus alas
La ensangrentada faz de Prometeo!
EN LA RIBERA
Ven, sigue de la mano
Al que te amó de niño;
Ven, y juntos lleguemos hasta el bosque
Que está en la margen del paterno río.
5¡Oh, cuánto eres hermosa,
mi amada, en este sitio!
Sólo por ti, y á reflejar tu frente,
Corriendo baja el Paraná tranquilo.
Para besar tu huella
10Fue siempre tan sumiso,
Que, en viéndote llegar, hasta la playa
Manda sus olas sin hacer rüido.
Por eso, porque te ama,
Somos grandes amigos;
15Luego, sabe decirte aquellas cosas
Que nunca brotan de los labios míos.
El año que tú faltas,
La flor de sus seíbos,
Como cansada de esperar tus sienes,
20Cuelga sus ramos de carmín marchitos.
161Por la tersa corriente,
Risueños y furtivos,
Como sueltas guirnaldas, no navegan
Los verdes camalotes florecidos.
Sólo inclinan los sauces
Su ramaje sombrío,
Y las aves más tristes, en sus copas
Gimiendo tejen sus ocultos nidos.
Pero llegas..., y el agua,
10El bosque, el cielo mismo,
Es como una explosión de mil colores,
Y el aire rompe en sonorosos himnos.
Así la primavera,
Del trópico vecino
15Desciende, y canta, repartiendo flores,
Y colgando en las vides los racimos.
¡Cuál suenan gratamente,
Acordes, en un ritmo,
Del agua el melancólico murmullo
20Y el leve susurrar de tu vestido!
¡Oh, si me fuera dado
Guardar en mis oídos,
Para siempre, esta música del alma,
Esta unión de tu ser y de mis ríos!
COLOMBIA Y ESPAÑA
¡Oh! ¡reposad en vuestras quietas tumbas,
Augustos padres de la patria mía,
Pues bien lo merecéis! La grande obra
De redención al fin está cumplida;
5Y no llegue á turbar vuestro reposo
El tumulto de lucha fratricida.
Hoy á vuestros sepulcros hace sombra
La bandera del iris, enlazada
Á la de los castillos y leones;
10Que el odio no es eterno
En los pobres humanos corazones;
Y llegó el día en que la madre España
Estrechase á Colombia entre sus brazos,
Depuesta ya la saña;
15No sierva, no señora;
Libres las dos como las hizo el cielo.
163¡Ah! ¿ni cómo podría
Hallarse la hija siempre separada
Del dulce hogar paterno,
Ni consentir la cariñosa madre
Que tal apartamiento fuera eterno?
5En esos años de la ausencia fiera,
El recuerdo de España
Seguíanos doquiera.
Todo nos es común: su Dios, el nuestro;
La sangre que circula por sus venas
10Y el hermoso lenguaje;
Sus artes, nuestras artes; la armonía
De sus cantos, la nuestra; sus reveses
Nuestros también, y nuestras
Las glorias de Bailén y de Pavía.
15Si á veces distraídos
Fijábamos los ojos
Á contemplar las hijas de Colombia;
En el porte elegante,
En el puro perfil de su semblante,
20En su mirada ardiente y en el dejo
Meloso de la voz, eran retrato
De sus nobles abuelas;
Copia feliz de gracia soberana,
En que agradablemente se veía
25El decoro y nobleza castellana
Y el donaire y la sal de Andalucía;
164Y entonces exclamábamos: Un nombre
Terrible, España, tienes; ¡pero suena
Qué dulcemente al corazón del hombre!
¡Oh! ¡que esta santa alianza eterna sea,
Y el pendón de Castilla y de Colombia
5Unidos siempre el universo vea!
Y que al ¡viva Colombia! que repiten
El áureo Tajo, y Ebro y Manzanares,
¡Responda el eco que rodando vaya
Por los tranquilos mares
10Á la ibérica playa
De ¡viva España! con que el Ande atruena
El Cauca, el Orinoco, el Magdalena!
EL CIPRÉS
¡Árbol sagrado, que la obscura frente,
Inmóvil, majestuoso,
15Sobre el sepulcro humilde y silencioso
Despliegas hacia el cielo tristemente!
Tú, sí, tú solamente
Al tiempo en que se duerme el rey del mundo
Tras las altas montañas de occidente,
20Me ves triste vagando
Entre las negras tumbas,
Con los ojos en llanto humedecidos,
165Mi orfandad y miseria lamentando.
Y cuando ya de la apacible luna
La luz de perla en tu verdor se acoge,
Sólo tu tronco escucha mis gemidos,
Sólo tu pie mis lágrimas recoge.
5¡Ay! hubo un tiempo en que feliz y ufano
Al seno paternal me abandonaba;
En que con blanda mano
Una madre amorosa
De mi niñez las lágrimas secaba...
10¡Y hoy, huérfano, del mundo desechado,
Aquí en mi patria misma
Solitario viajero,
Desde lejos contemplo acongojado
Sobre los techos de mi hogar primero
15El humo blanquear del extranjero!
Entre el bullicio de los pueblos busco
Mis tiernos padres para mí perdidos;
¡Vanamente!... Los rostros de los hombres
Me son desconocidos.
20Y sus manes, empero, noche y día
Presentes á mis ojos afligidos
Contino están; contino sus acentos
Vienen á resonar en mis oídos.
¡Sí, funeral ciprés! Cuando la noche
25Con su callada sombra te rodea,
Cuando escondido el solitario buho
166En tus obscuros ramos aletea;
La sombra de mi padre por tus hojas
Vagando me parece,
Que á velar por los días de su hijo
Del reino de los muertos se aparece.
5Y si el viento sacude impetüoso
Tu elevada cabeza,
Y á su furor con susurrar medroso
Respondes pavoroso;
En los tristes silbidos
10Que en torno de ti giran,
Á los paternos manes
Escucho, que dulcísimos suspiran.
¡Árbol augusto de la muerte! ¡Nunca
Tus verdores abata el bóreas ronco!
15¡Nunca enemiga, venenosa sierpe
Se enrosque en torno de tu pardo tronco!
¡Jamás el rayo ardiente
Abrase tu alta frente!
¡Siempre inmoble y sereno
20Por las cóncavas nubes
Oigas rodar el impotente trueno!
Vive, sí, vive; y cuando ya mis ojos
Cerrar el dedo de la muerte quiera;
Cuando esconderse mire en occidente
25Al sol por vez postrera,
Moriré sosegado
Á tu tronco abrazado.
167Tú mi sepulcro ampararás piadoso
De las roncas tormentas;
Y mi ceniza entonce agradecida,
En restaurantes jugos convertida,
Por tus delgadas venas penetrando,
5Te hará reverdecer, te dará vida.
Quizá sabiendo el infeliz destino
Que oprimió mi existencia desdichada,
Sobre mi pobre tumba abandonada
Una lágrima vierta el peregrino.
LOS CAZADORES Y LA PERRILLA
Es flaca sobremanera
Toda humana previsión,
Pues en más de una ocasión
Sale lo que no se espera.
Seguíale gran cuadrilla
De ejercitados monteros,
20De ojeadores, ballesteros
Y de mozos de traílla;
168Van todos apercibidos
De las armas necesarias,
Y llevan de castas varias
Perros diestros y atrevidos,
5Caballos de noble raza,
Cornetas de monte: en fin,
Cuanto exige Moratín
En su poema La Caza.
Levantan pronto una pieza,
10Un jabalí corpulento,
Que huye veloz, rabo á viento,
Y rompiendo la maleza.
Todos siguen con gran bulla
Tras la cerdosa alimaña,
15Pero ella se da tal maña
Que á todos los aturrulla;
Y aunque gastan todo el día
En paradas, idas, vueltas,
Y carreras y revueltas,
20Es vana tanta porfía.
Oigan lo que aconteció,
Y aunque es suceso que admira,
No piensen, no, que es mentira,
Que lo cuenta quien lo vio:
Al pie de uno de los cerros
Que batieron aquel día,
Una viejilla vivía,
Que oyó ladrar a los perros;
Con ella iba una perrilla...
Mas sin pasar adelante,
15Es preciso que un instante
Gastemos en describilla:
Flaco era el animalejo,
El más flaco de los canes,
Era el rastro, eran los manes
De un cuasi-semi-ex-gozquejo;
170Sarnosa era... digo mal;
No era una perra sarnosa,
Era una sarna perrosa
Y en figura de animal;
Era, otrosí, derrengada;
La derribaba un resuello;
Puede decirse que aquello
No era perra ni era nada.
Á ver, pues, la batahola
10La vieja al cerro subía,
De la perra en compañía,
Que era lo mismo que ir sola.
Por donde iba, hizo la suerte
Que se hubiese el jabalí
15Escondido, por si así
Se libraba de la muerte;
La vieja entonces al ver
Que escapaba por la loma,
¡Sus! dijo por pura broma,
Y la perra echó á correr.
171Y aquella perra extenuada,
Sombra de perra que fué,
De la cual se dijo que
No era perra ni era nada;
LA VUELTA A LA PATRIA
Mirad al peregrino
10¡Cuán doliente y trocado!
Apoyándose lento en su cayado
¡Qué solitario va por su camino!
En su primer mañana,
Alma alegre y cantora
15Abandonó el hogar, como á la aurora
Deja su nido la avecilla ufana.
Aire y luz, vida y flores,
Buscó en la vasta y fría
Región que la inocente fantasía
20Adornaba con mágicos fulgores.
172Ve el mundo, oye el rüido
De las grandes ciudades,
Y sólo vanidad de vanidades
Halla doquier su espíritu afligido
Materia da á su llanto
Cuanto el hombre le ofrece;
Ya la risa en sus labios no florece,
Y olvidó la nativa voz del canto.
Hízose pensativo;
10Las nubes y las olas
Sus confidentes son, y trata á solas
El sitio más repuesto y más esquivo.
Á su penar responde
En la noche callada,
15La estrella que declina fatigada
Y en el materno piélago se esconde.
¡Vuelve, vuelve á tu centro!
Natura al infelice
Clama; ¡vuelve! una voz también le dice
20Que habla siempre con él, amiga, adentro,
¡Ay triste! En lontananza
Ve los pasados días,
Y en gozar otra vez sus alegrías
Concentra reanimado la esperanza.
173¡Imposible! ¡Locura!...
¿Cuándo pudo á su fuente
Retroceder el mísero torrente
Que probó de los mares la amargura?
Ya sube la colina
Con mal seguro paso;
Del sol poniente al resplandor escaso
El valle de la infancia se domina.
¡Ay! Ese valle umbrío
10Que la paterna casa
Guarece; ese rumor con que acompasa
Sus blandos tumbos el sagrado río;
Esa aura embalsamada
Que sus sienes orea,
15¿A un corazón enfermo que desea
Su antigua soledad, no dicen nada?
El pobre peregrino
Ni oye, ni ve, ni siente;
De la Patria la imagen en su mente
20No existe ya, sino ideal divino.
Invisible le toca
Y sus párpados cierra
Ángel piadoso, y la ilusión destierra,
Y el dulce sonreir vuelve á su boca.
174¡Qué muda despedida!
¿Quién muerto le creyera?
¡Mirando está la Patria verdadera!
¡Está durmiendo el sueño de la vida!
EN LA TUMBA DE MI HIJO
¡Espejismos del alma dolorida!...
¡Hermosas esperanzas de la vida
Que disipa la muerte con crueldad!
Para engañar las penas nos forjamos
Imágenes de dicha, y luego damos
10Á la Ilusión el nombre de Verdad.
Aquí te llamo y nadie me responde:
Sorda y cruel, la tierra que te esconde
Ni el eco de mi voz devolverá.
Así la Eternidad: sombría y muda,
15El odio ni el amor, la fe y la duda
En sus abismos nada alcanzarán.
DOLORA
El ángel de mi cielo, mi María,
Que á la primera vuelta de las flores
Tres años cumplirá, medrosa un día
10Buscó refugio en mis abiertos brazos,
Y cuando entre caricias y entre abrazos,
Que prodigué, con paternal empeño,
Hubo al fin disipado sus temores,
Trocando así en sonrisas sus clamores,
15Cerró los ojos en tranquilo sueño.
En silencio quedó la estancia mía;
Y sintiéndome ansioso
De no turbar el infantil reposo
De mi bien, en mi pecho reclinado,
20Inmóviles mis miembros mantenía,
Y mi amoroso corazón latía
Al ritmo de su aliento sosegado.
176Sobre su faz serena,
Regadas como límpido rocío
En el cáliz de pálida azucena,
Brillaban gotas del reciente lloro,
5Y las guedejas de oro
Del undoso cabello
Caían arropando su albo cuello.
Así nos sorprendió mi tierna esposa.
Que á la par temerosa
10De interrumpir mi sueño de ventura,
Con paso leve recorrió el estrado
Y sin sentirla yo, vino á mi lado.
Aquella dulce calma
Que reinaba entre mí y en torno mío,
15Llenóme al fin de arrobamiento el alma.
Y se quedó mi mente
Enajenada en éxtasis creciente.
VOLVERÉ MAÑANA
I
—¡Adiós! ¡adiós! Lucero de mis noches,
—Dijo un soldado al pie de una ventana,—
10¡Me voy!... pero no llores, alma mía,
Que volveré mañana.
Ya se asoma la estrella de la aurora,
Ya se divisa en el oriente el alba,
Y en mi cuartel tambores y cornetas
15Están tocando diana.
II
Horas después, cuando la negra noche
Cubrió de luto el campo de batalla,
Á la luz del vivac pálida y triste,
Un joven expiraba.
20Alguna cosa de ella el centinela
178Al mirarlo morir, dijo en voz baja...
Alzó luego el fusil, bajó los ojos
Y se enjugó dos lágrimas.
III
EN EL TEOCALLI DE CHOLULA
¡Cuánto es bella la tierra que habitaban
Los aztecas valientes! En su seno
En una estrecha zona concentrados
Con asombro se ven todos los climas
5Que hay desde el polo al ecuador. Sus llanos
Cubren á par de las doradas mieses
Las cañas deliciosas. El naranjo
Y la piña y el plátano sonante,
Hijos del suelo equinoccial, se mezclan
10Á la frondosa vid, al pino agreste,
Y de Minerva al árbol majestuoso.
Nieve eternal corona las cabezas
De Iztaccíhual purísimo, Orizaba
Y Popocatepec; sin que el invierno
15Toque jamás con destructora mano
Los campos fertilísimos, do ledo
Los mira el indio en púrpura ligera
Y oro teñirse, reflejando el brillo
Del Sol en occidente, que sereno
20180En hielo eterno y perennal verdura
Á torrentes vertió su luz dorada,
Y vió á naturaleza conmovida
Con su dulce calor hervir en vida.
Era la tarde: su ligera brisa
5Las alas en silencio ya plegaba
Y entre la hierba y árboles dormía,
Mientras el ancho sol su disco hundía
Detrás de Iztaccíhual. La nieve eterna
Cual disuelta en mar de oro, semejaba
10Temblar en torno de él: un arco inmenso
Que del empíreo en el cenit finaba
Como espléndido pórtico del cielo
De luz vestido y centellante gloria,
De sus últimos rayos recibía
15Los colores riquísimos. Su brillo
Desfalleciendo fué: la blanca luna
Y de Venus la estrella solitaria
En el cielo desierto se veían.
¡Crepúsculo feliz! Hora más bella
20Que la alma noche ó el brillante día.
¡Cuánto es dulce tu paz al alma mía!
Hallábame sentado en la famosa
Choluteca pirámide. Tendido
El llano inmenso que ante mí yacía,
25Los ojos á espaciarse convidaba.
¡Qué silencio! ¡qué paz! ¡Oh! ¿quién diría
Que en estos bellos campos reina alzada
181La bárbara opresión, y que esta tierra
Brota mieses tan ricas, abonada
Con sangre de hombres, en que fué inundada
Por la superstición y por la guerra?...
Bajó la noche en tanto. De la esfera
5El leve azul, obscuro y más obscuro
Se fué tornando: la movible sombra
De las nubes serenas, que volaban
Por el espacio en alas de la brisa,
Era visible en el tendido llano.
10Iztaccíhual purísimo volvía
Del argentado rayo de la luna
El plácido fulgor, y en el oriente
Bien como puntos de oro centellaban
Mil estrellas y mil... ¡Oh! yo os saludo,
15Fuentes de luz, que de la noche umbría
Ilumináis el velo,
Y sois del firmamento poesía.
Al paso que la luna declinaba,
Y al ocaso fulgente descendía
20Con lentitud, la sombra se extendía
Del Popocatepec, y semejaba
Fantasma colosal. El arco obscuro
Á mí llegó, cubrióme, y su grandeza
Fué mayor y mayor, hasta que al cabo
25En sombra universal veló la tierra.
Volví los ojos al volcán sublime,
182Que velado en vapores transparentes,
Sus inmensos contornos dibujaba
De occidente en el cielo.
¡Gigante del Anáhuac! ¿cómo el vuelo
De las edades rápidas no imprime
5Alguna huella en tu nevada frente?
Corre el tiempo veloz, arrebatando
Años y siglos como el norte fiero
Precipita ante sí la muchedumbre
De las olas del mar. Pueblos y reyes
10Viste hervir á tus pies, que combatían
Cual hora combatimos, y llamaban
Eternas sus ciudades, y creían
Fatigar á la tierra con su gloria.
Fueron: de ellos no resta ni memoria.
15¿Y tú eterno serás? Tal vez un día
De tus profundas bases desquiciado
Caerás; abrumará tu gran ruina
Al yermo Anáhuac; alzaránse en ella
Nuevas generaciones y orgullosas,
20Que fuiste negarán...
Todo perece
Por ley universal. Aun este mundo
Tan bello y tan brillante que habitamos,
Es el cadáver pálido y deforme
De otro mundo que fue...
En tal contemplación embebecido
Sorprendióme el sopor. Un largo sueño,
183De glorias engolfadas y perdidas
En la profunda noche de los tiempos,
Descendió sobre mí. La agreste pompa
De los reyes aztecas desplegóse
Á mis ojos atónitos. Veía
5Entre la muchedumbre silenciosa
De emplumados caudillos levantarse
El déspota salvaje en rico trono,
De oro, perlas y plumas recamado;
Y al son de caracoles belicosos
10Ir lentamente caminando al templo
La vasta procesión, do la aguardaban
Sacerdotes horribles, salpicados
Con sangre humana rostros y vestidos.
Con profundo estupor el pueblo esclavo
15Las bajas frentes en el polvo hundía,
Y ni mirar á su señor osaba,
De cuyos ojos férvidos brotaba
La saña del poder.
Tales ya fueron
Tus monarcas, Anáhuac, y su orgullo:
20Su vil superstición y tiranía
En el abismo del no ser se hundieron.
Sí, que la muerte, universal señora,
Hiriendo á par al déspota y esclavo,
Escribe la igualdad sobre la tumba.
25Con su manto benéfico el olvido
Tu insensatez oculta y tus furores
Á la raza presente y la futura.
184Esta inmensa estructura
Vió á la superstición más inhumana
En ella entronizarse. Oyó los gritos
De agonizantes víctimas, en tanto
Que el sacerdote, sin piedad ni espanto,
5Les arrancaba el corazón sangriento;
Miró el vapor espeso de la sangre
Subir caliente al ofendido cielo
Y tender en el sol fúnebre velo,
Y escuchó los horrendos alaridos
10Con que los sacerdotes sofocaban
El grito del dolor.
Muda y desierta
Ahora te ves, Pirámide. ¡Más vale
Que semanas de siglos yazgas yerma,
Y la superstición á quien serviste
15En el abismo del infierno duerma!
Á nuestros nietos últimos, empero,
Sé lección saludable; y hoy al hombre
Que ciego en su saber fútil y vano
Al cielo, cual Titán, truena orgulloso,
20Sé ejemplo ignominioso
De la demencia y del furor humano.
EL NIÁGARA
Templad mi lira, dádmela, que siento
En mi alma estremecida y agitada
Arder la inspiración. ¡Oh! ¡cuánto tiempo
25185En tinieblas pasó, sin que mi frente
Brillase con su luz!... Niágara undoso,
Tu sublime terror sólo podría
Tornarme el don divino, que ensañada
Me robó del dolor la mano impía.
Torrente prodigioso, calma, calla
Tu trueno aterrador: disipa un tanto
Las tinieblas que en torno te circundan;
Déjame contemplar tu faz serena,
Y de entusiasmo ardiente mi alma llena.
10Yo digno soy de contemplarte: siempre
Lo común y mezquino desdeñando,
Ansié por lo terrífico y sublime.
Al despeñarse el huracán furioso,
Al retumbar sobre mi frente el rayo,
15Palpitando gocé: vi al Océano,
Azotado por austro proceloso,
Combatir mi bajel, y ante mis plantas
Vórtice hirviendo abrir, y amé el peligro.
Mas del mar la fiereza
20En mi alma no produjo
La profunda impresión que tu grandeza.
Sereno corres, majestuoso; y luego
En ásperos peñascos quebrantado,
Te abalanzas violento, arrebatado,
25Como el destino irresistible y ciego.
¿Qué voz humana describir podría
186De la sirte rugiente
La aterradora faz? El alma mía
En vago pensamiento se confunde
Al mirar esa férvida corriente,
Que en vano quiere la turbada vista
5En su vuelo seguir al borde obscuro
Del precipicio altísimo: mil olas,
Cual pensamiento rápidas pasando,
Chocan, y se enfurecen,
Y otras mil y otras mil ya las alcanzan,
10Y entre espuma y fragor desaparecen.
¡Ved! ¡llegan, saltan! El abismo horrendo
Devora los torrentes despeñados:
Crúzanse en él mil iris, y asordados
Vuelven los bosques el fragor tremendo.
15En las rígidas peñas
Rómpese el agua: vaporosa nube
Con elástica fuerza
Llena el abismo en torbellino, sube,
Gira en torno, y al éter
20Luminosa pirámide levanta,
Y por sobre los montes que le cercan
Al solitario cazador espanta.
Mas ¿qué en ti busca mi anhelante vista
Con inútil afán? ¿Por qué no miro
25Al rededor de tu caverna inmensa
Las palmas ¡ay! las palmas deliciosas,
187Que en las llanuras de mi ardiente patria
Nacen del sol á la sonrisa, y crecen,
Y al soplo de las brisas del Océano
Bajo un cielo purísimo se mecen?
Este recuerdo á mi pesar me viene...
5Nada ¡oh Niágara! falta á tu destino,
Ni otra corona que el agreste pino
Á tu terrible majestad conviene.
La palma y mirto y delicada rosa
Muelle placer inspiren y ocio blando
10En frívolo jardín: á ti la suerte
Guardó más digno objeto, más sublime.
El alma libre, generosa, fuerte,
Viene, te ve, se asombra,
El mezquino deleite menosprecia
15Y aun se siente elevar cuando te nombra.
¡Omnipotente Dios! En otros climas
Vi monstruos execrables,
Blasfemando tu nombre sacrosanto,
Sembrar error y fanatismo impío,
20Los campos inundar con sangre y llanto,
De hermanos atizar la infanda guerra,
Y desolar frenéticos la tierra.
Vilos, y el pecho se inflamó á su vista
En grave indignación. Por otra parte
25Vi mentidos filósofos, que osaban
Escrutar tus misterios, ultrajarte,
188Y de impiedad al lamentable abismo
Á los míseros hombres arrastraban.
Por eso te buscó mi débil mente
En la sublime soledad: ahora
Entera se abre á ti; tu mano siente
5En esta inmensidad que me circunda,
Y tu profunda voz hiere mi seno
De este raudal en el eterno trueno.
¡Asombroso torrente!
¡Cómo tu vista el ánimo enajena
10Y de terror y admiración me llena!
¿Dó tu origen está? ¿Quién fertiliza
Por tantos siglos tu inexhausta fuente?
¿Qué poderosa mano
Hace que al recibirte
15No rebose en la tierra el Océano?
Abrió el Señor su mano omnipotente;
Cubrió tu faz de nubes agitadas,
Dió su voz á tus aguas despeñadas,
Y ornó con su arco tu terrible frente.
20¡Ciego, profundo, infatigable corres,
Como el torrente obscuro de los siglos
En insondable eternidad!... ¡Al hombre
Huyen así las ilusiones gratas,
Los florecientes días,
25Y despierta al dolor!... ¡Ay! agostada
189Yace mi juventud; mi faz, marchita;
Y la profunda pena que me agita
Ruga mi frente de dolor nublada.
Nunca tanto sentí como este día
Mi soledad y mísero abandono
5Y lamentable desamor... ¿Podría
En edad borrascosa
Sin amor ser feliz? ¡Oh! si una hermosa
Mi cariño fijase,
Y de este abismo al borde turbulento
10Mi vago pensamiento
Y ardiente admiración acompañase!
¡Cómo gozara, viéndola cubrirse
De leve palidez, y ser más bella
En su dulce terror, y sonreirse
15Al sostenerla mis amantes brazos...
Delirios de virtud... ¡Ay! ¡Desterrado,
Sin patria, sin amores,
Sólo miro ante mí llanto y dolores!
¡Niágara poderoso!
20¡Adiós! ¡adiós! Dentro de pocos años
Ya devorado habrá la tumba fría
Á tu débil cantor. ¡Duren mis versos
Cual tu gloria inmortal! ¡Pueda piadoso,
Viéndote algún viajero,
25Dar un suspiro á la memoria mía!
Y al abismarse Febo en occidente,
190Feliz yo vuele do el Señor me llama,
Y al escuchar los ecos de mi fama,
Alce en las nubes la radiosa frente.
PLEGARIA Á DIOS
¡Ser de inmensa bondad! ¡Dios poderoso!
 vos acudo en mi dolor vehemente...
5Extended vuestro brazo omnipotente;
Rasgad de la calumnia el velo odioso;
Y arrancad este sello ignominioso
Con que el mundo manchar quiere mi frente.
¡Rey de los Reyes! ¡Dios de mis abuelos!
10¡Vos solo sois mi defensor! ¡Dios mío!...
Todo lo puede quien al mar sombrío
Olas y peces dio, luz á los cielos,
Fuego al sol, giro al aire, al norte hielos,
Vida á las plantas, movimiento al río.
Todo lo podéis vos; todo fenece,
Ó se reanima á vuestra voz sagrada;
Fuera de vos, Señor, el todo es nada
Que en la insondable eternidad perece;
Y aun esa misma nada os obedece,
20Pues de ella fué la humanidad creada.
191Yo no os puedo engañar, Dios de clemencia;
Y pues vuestra eternal sabiduría
Ve al través de mi cuerpo el alma mía
Cual del aire á la clara transparencia,
5Estorbad que humillada la inocencia
Bata sus palmas la calumnia impía.
Estorbadlo, Señor, por la preciosa
Sangre vertida, que la culpa sella
Del pecado de Adán, ó por aquella
10Madre cándida, dulce y amorosa,
Cuando envuelta en pesar, mustia y llorosa,
Siguió tu muerte como helíaca estrella.
Á WÁSHINGTON
No en lo pasado a tu virtud modelo,
20Ni copia al porvenir dará la historia,
Ni otra igual en grandeza á tu memoria
192Difundirán los siglos en su vuelo.
Miró la Europa ensangrentar su suelo
Al genio de la guerra y la victoria,
Pero le cupo á América la gloria
De que al genio del bien le diera el cielo.
5Que audaz conquistador goce en su ciencia
Mientras al mundo en páramo convierte,
Y se envanezca cuando á siervos mande;
¡Mas los pueblos sabrán en su conciencia
Que el que los rige libres sólo es fuerte;
10Que el que los hace grandes sólo es grande!
AL PARTIR
¡Perla del mar! ¡Estrella de Occidente!
¡Hermosa Cuba! Tu brillante cielo
La noche cubre con su opaco velo,
Como cubre el dolor mi triste frente.
15¡Voy á partir!... La chusma diligente
Para arrancarme del nativo suelo
Las velas iza, y pronta á su desvelo
La brisa acude de tu zona ardiente.
¡Adiós, patria feliz, Edén querido!
20Doquier que el hado en su furor me impela,
Tu dulce nombre halagará mi oído.
¡Adiós!... ¡ya cruje la turgente vela...
El ancla se alza... el buque estremecido
Las olas corta y silencioso vuela!
LA VICTORIA DE JUNÍN
Canto á Bolívar
El trueno horrendo, que en fragor revienta
Y sordo retumbando se dilata
Por la inflamada esfera,
Al Dios anuncia que en el cielo impera.
Y el rayo que en Junín rompe y ahuyenta
La hispana muchedumbre,
Que más feroz que nunca amenazaba
Á sangre y fuego eterna servidumbre,
Y el canto de victoria
10Que en ecos mil discurre, ensordeciendo
El hondo valle y enriscada cumbre,
Proclaman á Bolívar en la tierra
Árbitro de la paz y de la guerra.
Las soberbias pirámides que al cielo
15El arte humano osado levantaba
194Para hablar á los siglos y naciones,
Templos, do esclavas manos
Deificaban en pompa á sus tiranos,
Ludibrio son del tiempo, que con su ala
Débil las toca, y las derriba al suelo,
5Después que en fácil juego el fugaz viento
Borró sus mentirosas inscripciones;
Y bajo los escombros confundido
Entre las sombras del eterno olvido
¡Oh de ambición y de miseria ejemplo!
10El sacerdote yace, el dios y el templo.
Mas los sublimes montes, cuya frente
Á la región etérea se levanta,
Que ven las tempestades á su planta
Brillar, rugir, romperse, disiparse;
15Los Andes... las enormes, estupendas
Moles sentadas sobre bases de oro,
La tierra con su peso equilibrando,
Jamás se moverán. Ellos, burlando
De ajena envidia y del protervo tiempo
20La furia y el poder, serán eternos
De Libertad y de Victoria heraldos,
Que con eco profundo
Á la postrera edad dirán del mundo:
«Nosotros vimos de Junín el campo;
25Vimos que al desplegarse
Del Perú y de Colombia las banderas,
Se turban las legiones altaneras,
195Huye el fiero español despavorido,
Ó pide paz rendido.
Venció Bolívar: el Perú fué libre;
Y en triunfal pompa Libertad sagrada
En el templo del Sol fué colocada.»
¿Quién es aquel que el paso lento mueve
Sobre el collado que á Junín domina?
¿Que el campo desde allí mide, y el sitio
Del combatir y del vencer desina?
¿Que la hueste contraria observa, cuenta,
10Y en su mente la rompe y desordena,
Y á los más bravos á morir condena,
Cual águila caudal que se complace
Del alto cielo en divisar su presa
Que entre el rebaño mal segura pace?
15¿Quién el que ya desciende
Pronto y apercibido á la pelea?
Preñada en tempestades le rodea
Nube tremenda: el brillo de su espada
Es el vivo reflejo de la gloria;
20Su voz un trueno; su mirada un rayo.
¿Quién aquel que, al trabarse la batalla,
Ufano como nuncio de victoria,
Un corcel impetuoso fatigando,
Discurre sin cesar por toda parte?...
25¿Quién, sino el hijo de Colombia y Marte?
Sonó su voz: «Peruanos,
196Mirad allí los duros opresores
De vuestra patria. Bravos colombianos,
En cien crudas batallas vencedores,
Mirad allí los enemigos fieros
Que buscando venís desde Orinoco:
5Suya es la fuerza, y el valor es vuestro,
Vuestra será la gloria;
Pues lidiar con valor y por la patria
Es el mejor presagio de victoria.
Acometed: que siempre
10De quien se atreve más el triunfo ha sido:
Quien no espera vencer, ya está vencido.»
Dice; y al punto, cual fugaces carros
Que, dada la señal, parten, y en densos
De arena y polvo torbellinos ruedan,
15Arden los ejes, se estremece el suelo,
Estrépito confuso asorda el cielo,
Y en medio del afán cada cual teme
Que los demás adelantarse puedan;
Así los ordenados escuadrones,
20Que del iris reflejan los colores
Ó la imagen del sol en sus pendones,
Se avanzan á la lid. ¡Oh! ¡quién temiera,
Quién, que su ímpetu mismo los perdiera!
Tal el héroe brillaba
25Por las primeras filas discurriendo.
Se oye su voz, su acero resplandece
197Do más la pugna y el peligro crece;
Nada le puede resistir... Y es fama,
¡Oh portento inaudito!
Que el bello nombre de Colombia escrito
Sobre su frente en torno despedía
5Rayos de luz tan viva y refulgente,
Que deslumbrado el español desmaya,
Tiembla, pierde la voz, el movimiento:
Sólo para la fuga tiene aliento.
Así, cuando en la noche algún malvado
10Va á descargar el brazo levantado,
Si de improviso lanza un rayo el cielo,
Se pasma, y el puñal trémulo suelta;
Hielo mortal á su furor sucede;
Tiembla y horrorizado retrocede.
15Ya no hay más combatir. El enemigo
El campo todo y la victoria cede.
Huye cual ciervo herido; y á donde huye
Allí encuentra la muerte. Los caballos
Que fueron su esperanza en la pelea,
20Heridos, espantados, por el campo
Ó entre las filas vagan, salpicando
El suelo en sangre que su crin gotea;
Derriban al jinete, lo atropellan,
Y las catervas van despavoridas,
25Ó unas en otras con terror se estrellan.
Crece la confusión, crece el espanto,
198Y al impulso del aire, que vibrando
Sube en clamores y alaridos lleno,
Tremen las cumbres que respeta el trueno.
Y discurriendo el vencedor en tanto
Por cimas de cadáveres y heridos,
5Postra al que huye, perdona á los rendidos.
¡Padre del universo, sol radioso,
Dios del Perú, modera omnipotente
El ardor de tu carro impetüoso,
Y no escondas tu luz indeficiente!...
10¡Una hora más de luz!... Pero esta hora
No fué la del Destino. El dios oía
El voto de su pueblo, y de la frente
El cerco de diamantes desceñía.
En fugaz rayo el horizonte dora,
15En mayor disco menos luz ofrece,
Y veloz tras los Andes se obscurece.
LA SERENATA
¡Oh, tú, que duermes en casto lecho,
De sinsabores ajeno el pecho,
Y á los encantos de la hermosura
Unes las gracias del corazón,
5Deja el descanso, doncella pura,
Y oye los ecos de mi canción!
¿Quién en la tierra la dicha alcanza?
Iba mi vida sin esperanza,
Cual nave errante sin ver su estrella,
10Cuando me inundas en claridad;
Y desde entonces, gentil doncella,
Me revelaste felicidad.
¡Oh, si las ansias decir pudiera
Que siente el alma, desde que viera
15Ese semblante que amor inspira
Y los hechizos de tu candor!
Mas, rudo el labio, torpe la lira,
Decir no puede lo que es amor.
200Del Iris puede pintarse el velo;
Del sol los rayos, la luz del cielo;
La negra noche, la blanca aurora;
Mas no tus gracias ni tu poder,
Ni menos puede de quien te adora
5Decirse el llanto y el padecer.
Amor encuentra doquier que vuelva
La vista en torno; la verde selva,
Florido el prado y el bosque umbrío,
La tierna hierba, la hermosa ñor,
10Y la cascada, y el claro río,
Todos me dicen: amor, amor.
Cuando te ausentas, el campo triste
De luto y sombras luego se viste;
Mas si regresas, la primavera
15Hace sus galas todas lucir:
¡Oh, nunca, nunca de esta ribera,
Doncella hermosa, quieras partir!
LA ROSA MARCHITA
¿Eres tú, triste rosa,
La que ayer difundía
20Balsámica ambrosía,
Y tu altiva cabeza levantando
201Eras la reina de la selva umbría?
¿Por qué tan pronto, dime,
Hoy triste y desolada
Te encuentras de tus galas despojada?
Ayer viento süave
5Te halagó cariñoso;
Ayer alegre el ave
Su cántico armonioso
Ejercitaba, sobre ti posando;
Tú, rosa, le inspirabas,
10Y á cantar sus amores le excitabas.
Tal vez el fatigado peregrino,
Al pasar junto á ti, quiso cortarte:
Tal vez quiso llevarte
Algún amante á su ardoroso seno;
15Pero al ver tu hermosura,
La compasión sintieron,
Y su atrevida mano detuvieron.
Hoy nadie te respeta:
El furioso aquilón te ha deshojado.
20Ya nada te ha quedado
¡Oh reina de las flores!
De tu brillo y tus colores.
La fiel imagen eres
De mi triste fortuna:
25¡Ay! todos mis placeres,
Todas mis esperanzas una á una
202Arrancándome ha ido
Un destino funesto, cual tus hojas
Arrancó el huracán embravecido!
¿Y qué, ya triste y sola,
No habrá quien te dirija una mirada?
5¿Estarás condenada
Á eterna soledad y amargo lloro?
No, que existe un mortal sobre la tierra,
Un joven infeliz, desesperado,
Á quien horrible suerte ha condenado
10Á perpetuo gemir: ven, pues, ¡oh rosa!
Ven á mi amante seno, en él reposa
Y ojalá de mis besos la pureza
Resucitar pudiera tu belleza.
NOCTURNO
Á Rosario
I
¡Pues bien! yo necesito
Decirte que te adoro,
203Decirte que te quiero
Con todo el corazón;
Que es mucho lo que sufro,
Que es mucho lo que lloro,
Que ya no puedo tanto,
5Y al grito en que te imploro
Te imploro y te hablo en nombre
De mi última ilusión.
II
Yo quiero que tú sepas
Que ya hace muchos días
10Estoy enfermo y pálido
De tanto no dormir;
Que ya se han muerto todas
Las esperanzas mías;
Que están mis noches negras,
15Tan negras y sombrías,
Que ya no sé ni dónde
Se alzaba el porvenir.
III
De noche, cuando pongo
Mis sienes en la almohada
20Y hacia otro mundo quiero
Mi espíritu volver,
Camino mucho, mucho,
Y al fin de la jornada
Las formas de mi madre
25204Se pierden en la nada,
Y tú de nuevo vuelves
En mi alma á aparecer.
IV
Comprendo que tus besos
Jamás han de ser míos;
5Comprendo que en tus ojos
No me he de ver jamás;
Y te amo, y en mis locos
Y ardientes desvarios
Bendigo tus desdenes,
10Adoro tus desvíos,
Y en vez de amarte menos,
Te quiero mucho más.
V
Á veces pienso en darte
Mi eterna despedida,
15Borrarte en mis recuerdos
Y hundirte en mi pasión;
Mas si es en vano todo
Y el alma no te olvida,
¡Qué quieres tú que yo haga,
20Pedazo de mi vida;
Qué quieres tú que yo haga
Con este corazón!
VI
Y luego que ya estaba
205Concluido tu santuario,
Tu lámpara encendida,
Tu velo en el altar,
El sol de la mañana
Detrás del campanario,
5Chispeando las antorchas,
Humeando el incensario,
Y abierta allá á lo lejos
La puerta del hogar...
VII
¡Qué hermoso hubiera sido
10Vivir bajo aquel techo,
Los dos unidos siempre
Y amándonos los dos;
Tu siempre enamorada,
Yo siempre satisfecho,
15Los dos una sola alma,
Los dos un solo pecho,
Y en medio de nosotros
Mi madre como un Dios!
VIII
¡Figúrate qué hermosas
20Las horas de esa vida!
¡Qué dulce y bello el viaje
Por una tierra así!
Y yo soñaba en eso,
Mi santa prometida.
206Y al delirar en eso 25
Con la alma estremecida,
Pensaba yo en ser bueno
Por ti, no más por ti.
IX
Bien sabe Dios que ése era
5Mi más hermoso sueño,
Mi afán y mi esperanza,
Mi dicha y mi placer;
¡Bien sabe Dios que en nada
Cifraba yo mi empeño,
10Sino en amarte mucho
Bajo el hogar risueño
Que me envolvió en sus besos
Cuando me vio nacer!
X
REIR LLORANDO
¡Cuántos hay que, cansados de la vida,
Enfermos de pesar, muertos de tedio,
Hacen reir como el actor suicida,
Sin encontrar, para su mal, remedio!
¡Ay! ¡Cuántas veces al reir se llora!
¡Nadie en lo alegre de la risa fíe,
Porque en los seres que el dolor devora
El alma llora cuando el rostro ríe!
FUSILES Y MUÑECAS
Juan y Margot, dos ángeles hermanos,
Que embellecen mi hogar con sus cariños,
Se entretienen con juegos tan humanos
20Que parecen personas desde niños.
208Mientras Juan, de tres años, es soldado
Y monta en una caña endeble y hueca,
Besa Margot con labios de granado
Los labios de cartón de su muñeca.
Lucen los dos sus inocentes galas,
Y alegres sueñan en tan dulces lazos:
Él, que cruza sereno entre las balas;
Ella, que arrulla un niño entre sus brazos.
Puesto al hombro el fusil de hoja de lata,
10El kepis de papel sobre la frente,
Alienta al niño en su inocencia grata
El orgullo viril de ser valiente.
Quizá piensa, en sus juegos infantiles,
Que en este mundo que su afán recrea,
15Son como el suyo todos los fusiles
Con que la torpe humanidad pelea.
Que pesan poco, que sin odios lucen,
Que es igual el más débil al más fuerte,
Y que, si se disparan, no producen
20Humo, fragor, consternación y muerte.
¡Oh misteriosa condición humana!
Siempre lo opuesto buscas en la tierra:
Ya delira Margot por ser anciana,
Y Juan que vive en paz ama la guerra.
209Mirándolos jugar, me aflijo y callo;
¡Cuál será sobre el mundo su fortuna?
Sueña el niño con armas y caballo,
La niña con velar junto á la cuna.
El uno corre de entusiasmo ciego,
La niña arrulla á su muñeca inerme,
Y mientras grita el uno: Fuego, Fuego,
La otra murmura triste: Duerme, Duerme.
Á mi lado ante juegos tan extraños
10Concha, la primogénita, me mira:
¡Es toda una persona de seis años
Que charla, que comenta y que suspira!
¿Por qué inclina su lánguida cabeza
Mientras deshoja inquieta algunas flores?
15¿Será la que ha heredado mi tristeza?
¿Será la que comprende mis dolores?
Cuando me rindo del dolor al peso,
Cuando la negra duda me avasalla,
Se me cuelga del cuello, me da un beso,
20Se le saltan las lágrimas, y calla.
Sueltas sus trenzas claras y sedosas,
Y oprimiendo mi mano entre sus manos,
Parece que medita en muchas cosas
Al mirar como juegan sus hermanos...
210¡Inocencia! ¡Niñez! ¡Dichosos nombres!
Amo tus goces, busco tus cariños;
¡Cómo han de ser los sueños de los hombres
Más dulces que los sueños de los niños!
Á ROOSEVELT
Es con voz de la Biblia ó verso de Walt Whitman
Que habría que llegar hasta ti, ¡cazador!
Primitivo y moderno, sencillo y complicado,
Con un algo de Wáshington y mucho de Nemrod.
5Eres los Estados Unidos,
Eres el futuro invasor
De la América ingenua que tiene sangre indígena,
Que aun reza á Jesucristo y aun habla en español.
Eres soberbio y fuerte ejemplar de tu raza;
10Eres culto, eres hábil; te opones á Tolstoy.
Y domando caballos ó asesinando tigres,
Eres un Alejandro Nabucodonosor.
(Eres un profesor de Energía
Como dicen los locos de hoy.)
Crees que la vida es incendio,
Que el progreso es erupción,
Que en donde pones la bala
212El porvenir pones.
No.
Los Estados Unidos son potentes y grandes.
Cuando ellos se estremecen hay un hondo temblor
Que pasa por las vértebras enormes de los Andes.
5Si clamáis, se oye como el rugir de un león.
Ya Hugo á Grant lo dijo: «Las estrellas son vuestras.»
(Apenas brilla alzándose el argentino sol
Y la estrella chilena se levanta...) Sois ricos;
Juntáis al culto de Hércules el culto de Mamnón;
10Y alumbrando el camino de la fácil conquista,
La Libertad levanta su antorcha en Nueva York.
Mas la América nuestra que tenía poetas
Desde los viejos tiempos de Netzhualcoyolt,
Que ha guardado las huellas de los pies del gran Baco,
15Que el alfabeto pánico en un tiempo aprendió,
Que consultó los astros, que conoció la atlántida
Cuyo nombre nos llega resonando en Platón,
Que desde los remotos momentos de su vida
Vive de luz, de fuego, de perfume y de amor,
20La América del grande Moctezuma, del Inca,
La América fragante de Cristóbal Colón,
La América católica, la América española,
La América en que dijo el noble Guatemoc:
«Yo no estoy en un lecho de rosas»; esa América
25Que tiembla de huracanes y que vive de amor,
Hombres de ojos sajones y alma bárbara, vive
Y sueña. Y ama y vibra; y es la hija del Sol.
213Tened cuidado. ¡Vive la América española!
Hay mil cachorros sueltos del león español.
Se necesitaría, Roosevelt, ser Dios mismo,
El Riflero terrible y el fuerte cazador,
Para poder tenernos en vuestras férreas garras.
Á LA VICTORIA DE BAILÉN
Rompe el León soberbio la cadena
Con que atarle pensó la felonía,
Y sacude con noble bizarría
Sobre el robusto cuello la melena.
La espuma del furor sus labios llena
Y á los rugidos que indignado envía
El tigre tiembla en la caverna umbría,
Y todo el bosque atónito resuena.
El León despertó; ¡temblad, traidores!
10Lo que vejez creísteis, fué descanso;
Las juveniles fuerzas guarda enteras
Perseguid, alevosos cazadores,
Á la tímida liebre, al ciervo manso;
No insultéis al monarca de las fieras
LA AGRICULTURA DE LA ZONA TÓRRIDA
¡Salve, fecunda zona,
215Que al sol enamorado circunscribes
El vago curso, y cuanto ser se anima
En cada vario clima,
Acariciada de su luz, concibes!
Tú tejes al verano su guirnalda
5De granadas espigas; tú la uva
Das á la hirviente cuba:
No de purpúrea flor, ó roja, ó gualda,
Á tus florestas bellas
Falta matiz alguno; y bebe en ellas
10Aromas mil el viento;
Y greyes van sin cuento
Paciendo tu verdura, desde el llano
Que tiene por lindero el horizonte,
Hasta el erguido monte,
15De inaccesible nieve siempre cano.
Tú das la caña hermosa,
De do la miel se acendra,
Por quien desdeña el mundo los panales:
Tú en urnas de coral cuajas la almendra
20Que en la espumante jícara rebosa:
Bulle carmín viviente en tus nopales,
Que afrenta fuera al múrice de Tiro;
Y de tu añil la tinta generosa
Émula es de la lumbre del zafiro;
25El vino es tuyo, que la herida agave
Para los hijos vierte
Del Anáhuac feliz; y la hoja es tuya
Que, cuando de süave
216Humo en espiras vagarosas huya,
Solazará el fastidio al ocio inerte.
Tú vistes de jazmines
El arbusto sabeo,
Y el perfume le das que en los festines
5La fiebre insana templará á Lieo.
Para tus hijos la procera palma
Su vario feudo cría,
Y el ananás sazona su ambrosía:
Su blanco pan la yuca,
10Sus rubias pomas la patata educa,
Y el algodón despliega al aura leve
Las rosas de oro y el vellón de nieve.
Tendida para ti la fresca parcha
En enramadas de verdor lozano,
15Cuelga de sus sarmientos trepadores
Nectáreos globos y franjadas flores;
Y para ti el maíz, jefe altanero
De la espigada tribu, hinche su grano;
Y para ti el banano
20Desmaya al peso de su dulce carga;
El banano, primero
De cuantos concedió bellos presentes
Providencia á las gentes
Del ecuador feliz con mano larga.
25No ya de humanas artes obligado
El premio rinde opimo:
No es á la podadera, no al arado
Deudor de su racimo;
217Escasa industria bástale, cual puede
Hurtar á sus fatigas mano esclava:
Crece veloz, y cuando exhausto acaba,
Adulta prole en torno le sucede.
¡Oh! ¡Los que afortunados poseedores
5Habéis nacido de la tierra hermosa
En que reseña hacer de sus favores,
Como para ganaros y atraeros,
Quiso naturaleza bondadosa!
Romped el duro encanto
10Que os tiene entre murallas prisioneros.
El vulgo de las artes laborioso,
El mercader que, necesario al lujo,
Al lujo necesita,
Los que anhelando van tras el señuelo
15Del alto cargo y del honor ruidoso,
La grey de aduladores parasita,
Gustosos pueblen ese infecto caos;
El campo es vuestra herencia: en él gozaos.
¿Amáis la libertad? El campo habita:
20No allá donde el magnate
Entre armados satélites se mueve,
Y de la moda, universal señora,
Va la razón al triunfal carro atada,
Y á la fortuna la insensata plebe,
25Y el noble al aura popular adora.
¿Ó la virtud amáis? ¡Ah! ¡Que el retiro,
218La solitaria calma
En que, juez de sí misma, pasa el alma
Á las acciones muestra,
Es de la vida la mejor maestra!
¿Buscáis durables goces,
5Felicidad, cuanta es al hombre dada
Y á su terreno asiento, en que vecina
Está la risa al llanto, y siempre ¡ah! siempre,
Donde halaga la flor, punza la espina?
Id á gozar la suerte campesina;
10La regalada paz, que ni rencores,
Al labrador, ni envidias acibaran;
La cama que mullida le preparan
El contento, el trabajo, el aire puro;
Y el sabor de los fáciles manjares,
15Que dispendiosa gula no le aceda;
Y el asilo seguro
De sus patrios hogares
Que á la salud y al regocijo hospeda.
El aura respirad de la montaña,
20Que vuelve al cuerpo laso
El perdido vigor, que á la enojosa
Vejez retarda el paso,
Y el rostro á la beldad tiñe de rosa.
¿Es allí menos blanda por ventura
25De amor la llama, que templó el recato?
¿Ó menos aficiona la hermosura
Que de extranjero ornato
Y afeites impostores no se cura?
219¿Ó el corazón escucha indiferente
El lenguaje inocente
Que los afectos sin disfraz expresa
Y á la intención ajusta la promesa?
No del espejo al importuno ensayo
5La risa se compone, el paso, el gesto;
No falta allí carmín al rostro honesto
Que la modestia y la salud colora,
Ni la mirada que lanzó al soslayo
Tímido amor, la senda al alma ignora.
10¿Esperaréis que forme
Más venturosos lazos himeneo,
Do el interés barata,
Tirano del deseo,
Ajena mano y fe por nombre ó plata,
15Que do conforme gusto, edad conforme,
Y elección libre, y mutuo ardor los ata?
¡Oh jóvenes naciones, que ceñida
Alzáis sobre el atónito Occidente
De tempranos laureles la cabeza!
20Honrad al campo, honrad la simple vida
Del labrador y su frugal llaneza.
Así tendrán en vos perpetuamente
La libertad morada,
Y freno la ambición, y la ley templo.
25Las gentes á la senda
De la inmortalidad, ardua y fragosa,
Se animarán, citando vuestro ejemplo.
220Lo emulará celosa
Vuestra posteridad, y nuevos nombres
Añadiendo la fama
Á los que ahora aclama,
«Hijos son éstos, hijos
5(Pregonará á los hombres)
De los que vencedores superaron
De los Andes la cima:
De los que en Boyacá, los que en la arena
De Maipo y en Junín, y en la campaña
10Gloriosa de Apurima,
Postrar supieron al león de España.»
VUELTA Á LA PATRIA
Á mi hermana Elodia
¡Tierra! grita en la prora el navegante,
Y confusa y distante,
Una línea indecisa
15Entre brumas y ondas se divisa.
Poco á poco del seno
Destacándose va, del horizonte,
Sobre el éter sereno
La cumbre azul de un monte;
20Y así como el bajel se va acercando,
Va extendiéndose el cerro
221Y unas formas extrañas va tomando:
Formas que he visto cuando
Soñaba con la dicha en mi destierro.
Ya la vista columbra
Las riberas bordadas de palmares,
5Y una brisa cargada con la esencia
De silvestres violetas y azahares
En mi memoria alumbra
El recuerdo feliz de mi inocencia,
Cuando pobre de años y pesares
10Y rico de ilusiones y alegría,
Bajo las palmas retozar solía
Oyendo el arrullar de las palomas,
Bebiendo luz y respirando aromas.
Hay algo en esos rayos brilladores
15Que juegan por la atmósfera azulada,
Que me habla de ternuras y de amores
De una dicha pasada;
Y el viento al suspirar entre las cuerdas
Parece que me dice:—¿No te acuerdas?...
20Ese cielo, ese mar, esos cocales,
Ese monte que dora
El sol de las regiones tropicales...
¡Luz! ¡luz al fin! los reconozco ahora;
Son ellos, son los mismos de mi infancia,
25Y esas playas que al sol del mediodía
Brillan á la distancia,
¡Oh inefable alegría!
222Son las riberas de la patria mía.
Ya muerde el fondo de la mar hirviente
Del ancla el férreo diente;
Ya se acercan los botes desplegando
Al aire puro y blando
La enseña tricolor del pueblo mío.5 5
¡Á tierra! ¡á tierra! ¡Ó la emoción me ahoga,
Ó se adueña de mi alma el desvarío!
Llevado en alas de mi ardiente anhelo,
Me lanzo presuroso al barquichuelo
10Que á las riberas del hogar me invita.
Todo es grata armonía: los suspiros
De la onda de zafir que el remo agita,
De las marinas aves
Los caprichosos giros,
15Y las notas süaves
Y el timbre lisonjero,
Y la magia que toma,
Hasta en labios del tosco marinero,
El dulce son de mi nativo idioma.
¡Volad, volad veloces,
Ondas, aves y voces!
Id á la tierra en donde el alma tengo,
Y decidle que vengo
Á reposar, cansado caminante,
25Del hogar á la sombra un solo instante
Decidle que en mi anhelo, en mi delirio
223Por llegar á la orilla, el pecho siente
De Tántalo el martirio;
Decidle, en fin, que mientra estuve ausente
Ni un día, ni un instante la he olvidado,
Y llevadle este beso que os confío,
5Tributo adelantado
Que desde el fondo de mi ser le envío.
¡Boga, boga remero! ¡Así! ¡Llegamos!
¡Oh, emoción hasta ahora no sentida!
Ya piso el santo suelo en que probamos
10El almíbar primero de la vida.
Tras ese monte azul, cuya alta cumbre
Lanza reto de orgullo
Al zafir de los cielos,
Está el pueblo gentil donde al arrullo
15Del maternal amor rasgué los velos
Que me ocultaban la primera lumbre.
¡En marcha, en marcha, postillón; agita
El látigo inclemente!
Y á más andar el coche diligente
20Por la orilla del mar se precipita.
No hay peña ni ensenada que en mi mente
No venga á despertar una memoria;
Ni hay ola que en la arena humedecida
No escriba con espuma alguna historia
25De los felices tiempos de mi vida.
Todo me habla de sueños y cantares,
De paz, de amor y de tranquilos bienes;
224Y el aura fugitiva de los mares
Que viene, leda, á acariciar mis sienes,
Me susurra al oído
Con misterioso acento: ¡Bienvenido!
ÚLTIMA ILUSIÓN
Cayó empuñando el invencible acero
5Que coronó de lauros la victoria,
Terror de extraños, de su patria gloria,
En traidora asechanza el caballero.
"—Llevad mi espada al pueblo por quien muero,
Y airado el pueblo vengue mi memoria...
10Este anillo á... mi amor... La negra historia
Á mi madre callad."—Dijo el guerrero.

Carcelera, Carcelera,
Carcelera de mi vida,
desátame las cadenas
y échame la despedida.

Ya se murió el burro que acarreaba la vinagre;
Ya lo llevó Dios de esta vida miserable.
|:Que tu ru ru ru ru
Que tu ru ru ru ru.:|
Él era valiente, él era mohino;
Él era el alivio de todo Villarino.
|:Que tu ru ru ru ru
Que tu ru ru ru ru.:|

Yo tengo una cachuchita
que me la dió un cachuchero,
el que quiera cachuchita
que se gaste su dinero.
Vámonos, china del alma,
vámonos á Gibraltar
para ver á los moritos
que se quieren embarcar!
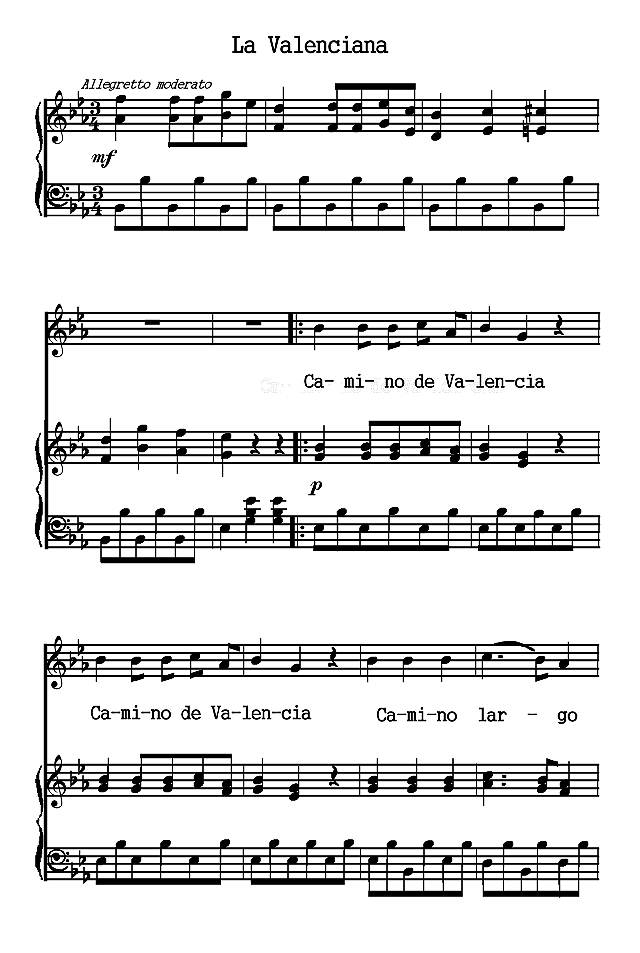
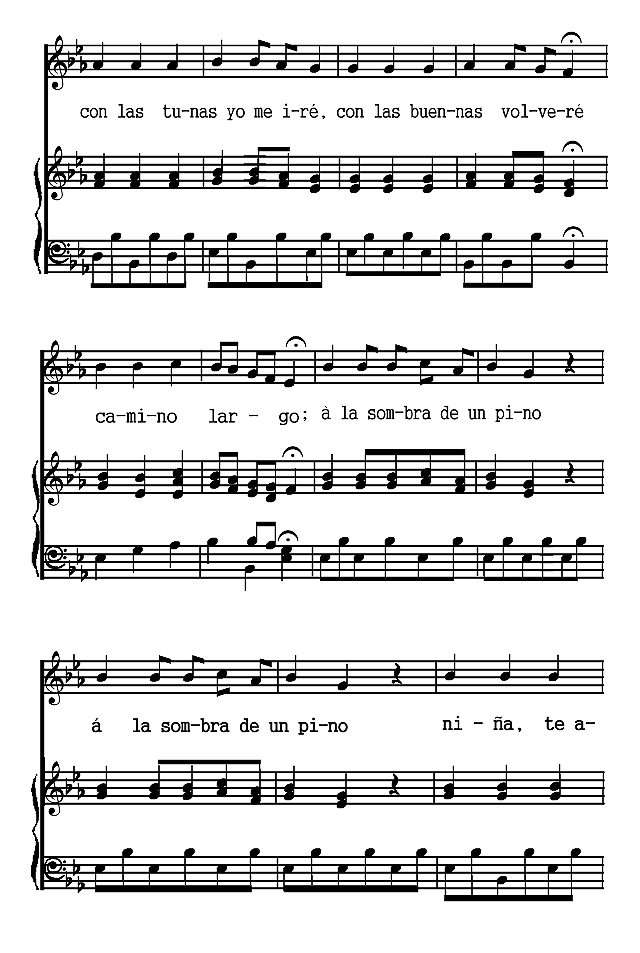
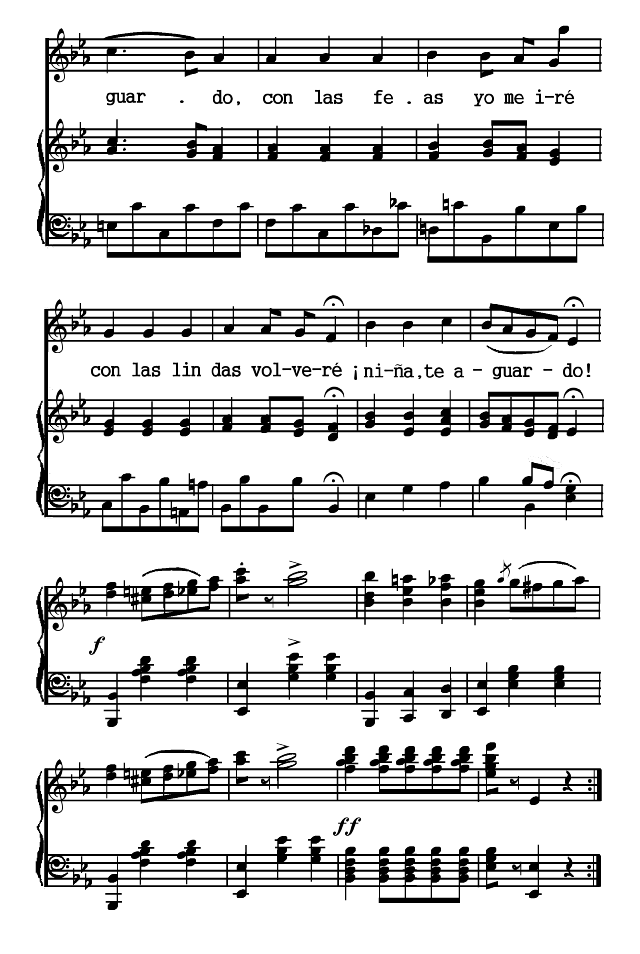
Camino de Valencia,
camino de Valencia,
camino largo,
con las tunas yo me iré,
con las bueñas volveré,
camino largo;
á la sombra de un pino,
á la sombra de un pino,
niña, te aguardo,
con las feas yo me iré,
con las lindas volveré,
¡niña, te aguardo!
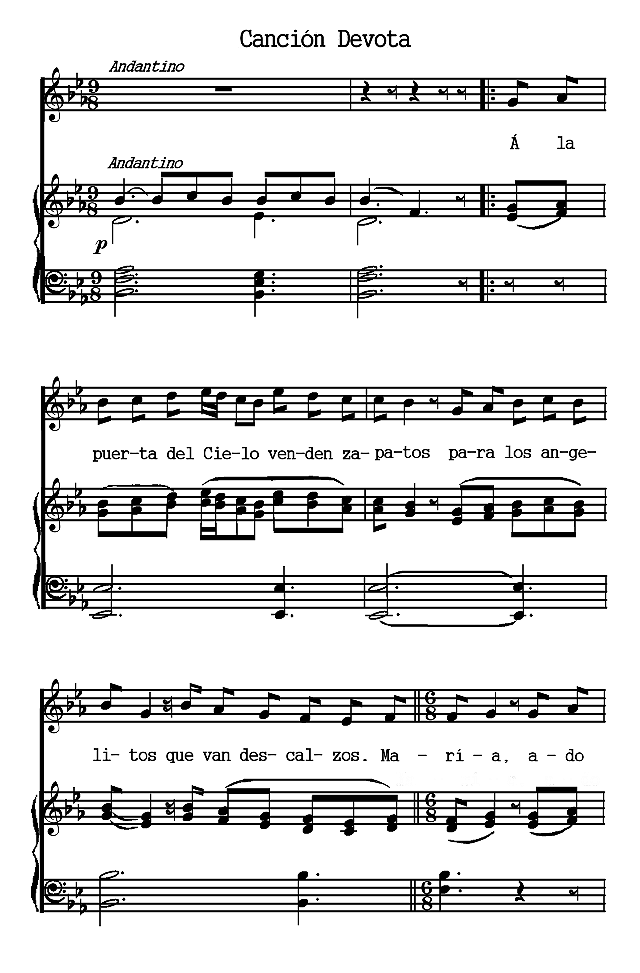
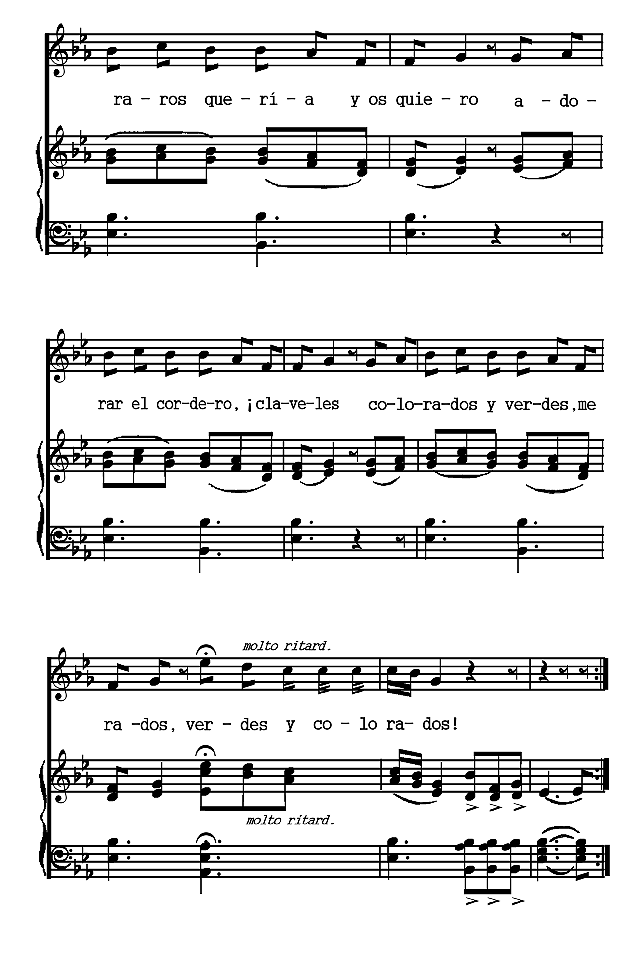
Á la puerta del Cielo venden zapatos
para los angelitos que van descalzos.
María, adoraros quería
y os quiero, adorar el cordero,
¡claveles, colorados y verdes,
morados, verdes y colorados!
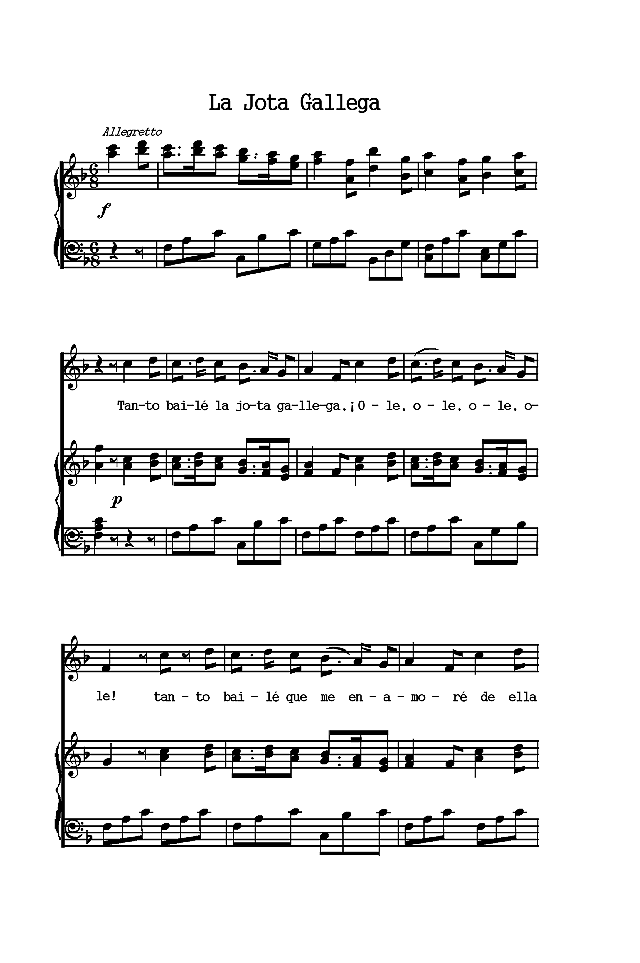



Tanto bailé la jota gallega,
¡ole, ole, ole, ole!
tanto bailé que me enamoré de ella,
¡ole, ole, ole!
tanto bailé que me enamoré,
¡ole, ole, ole, ole!
tanto bailé que me enamoré,
¡ole, ole, ole, ole!
tanto bailé la jota gallega,
¡ole, ole, ole, ole!
tanto bailé que me enamoré de ella,
¡ole, ole, ole!
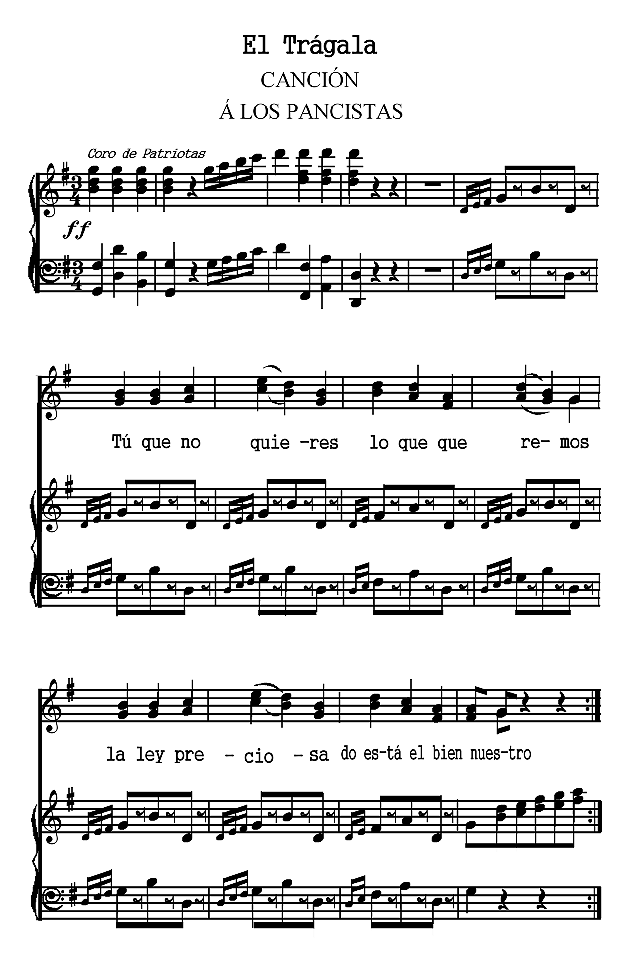
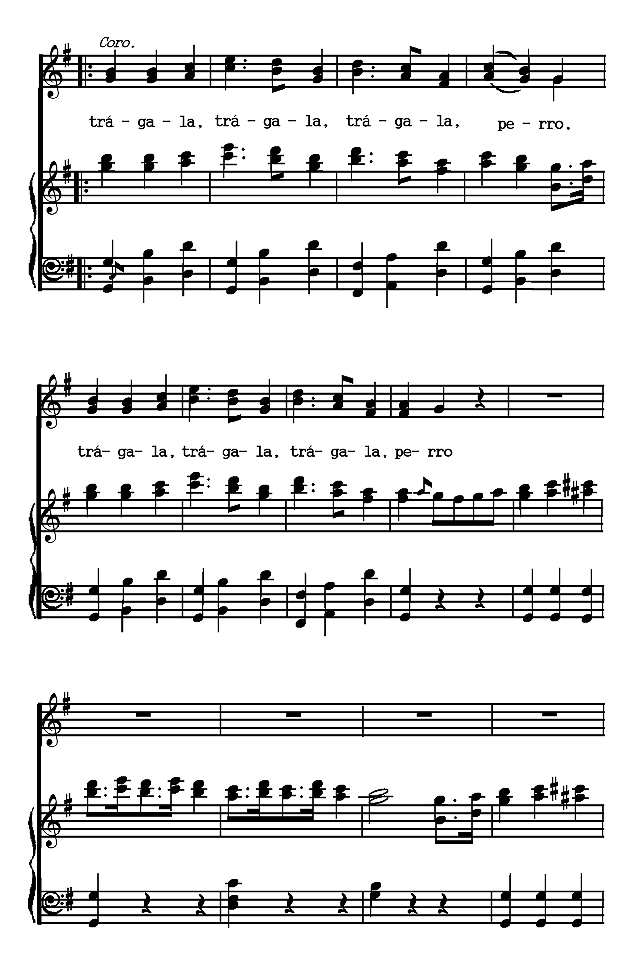
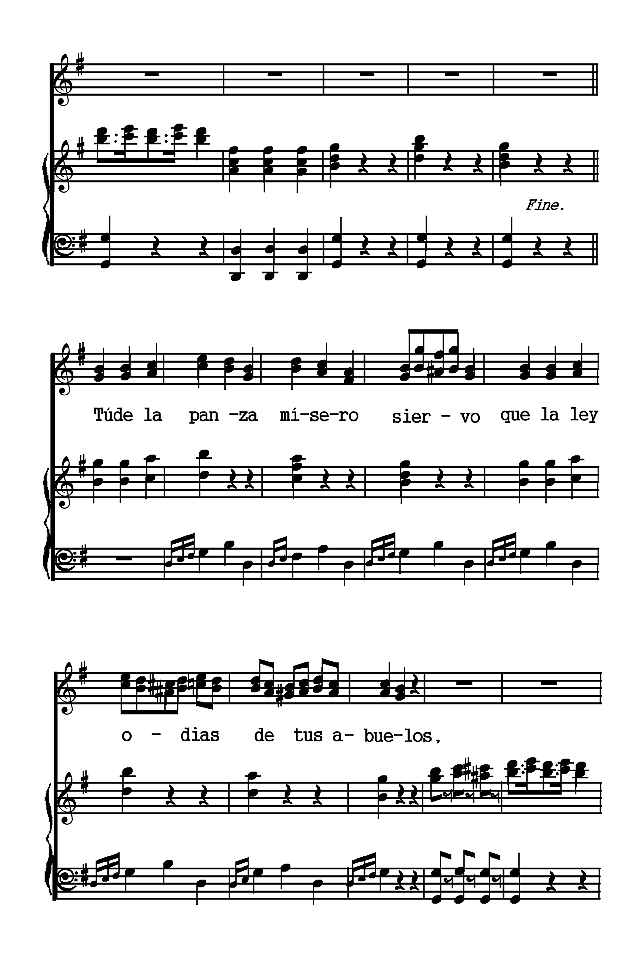
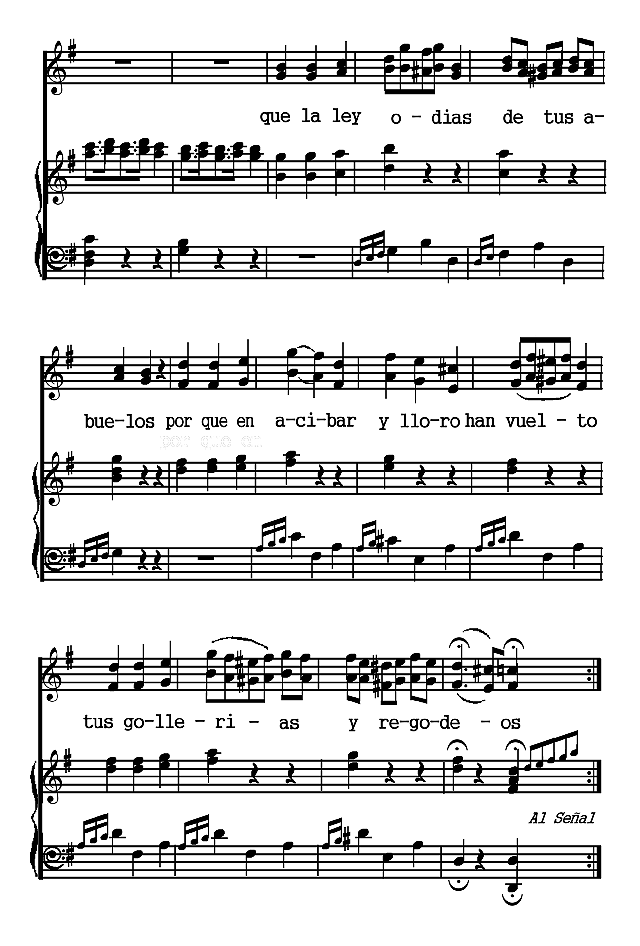
Tú que no quieres lo que queremos,
la ley preciosa do está el bien nuestro,
trágala, trágala, trágala, perro,
trágala, trágala, trágala, perro.
Tú de la panza mísero siervo
que la ley odias de tus abuelos,
por que en acíbar y lloro han vuelto
tus gollerías y regodeos.
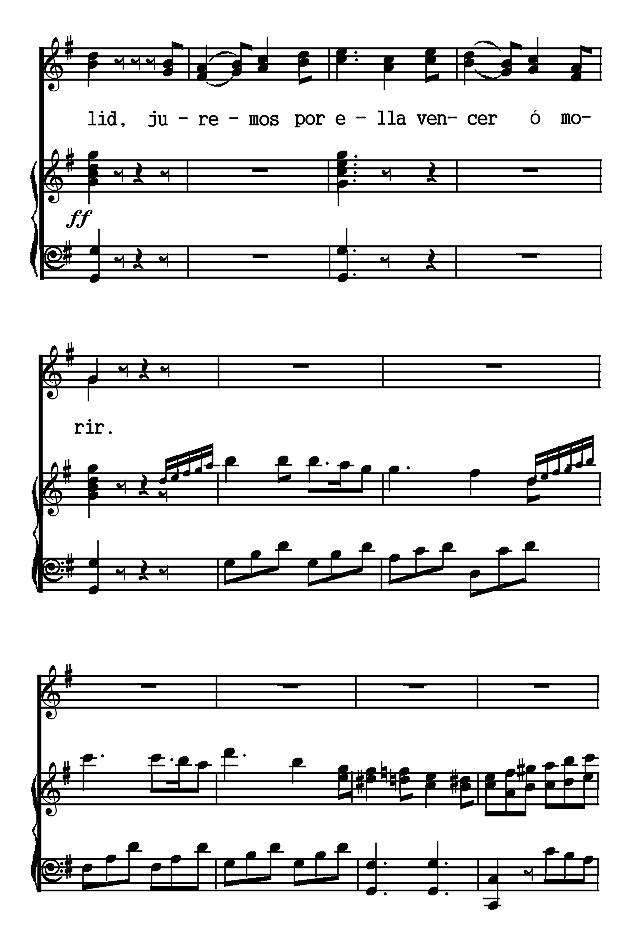
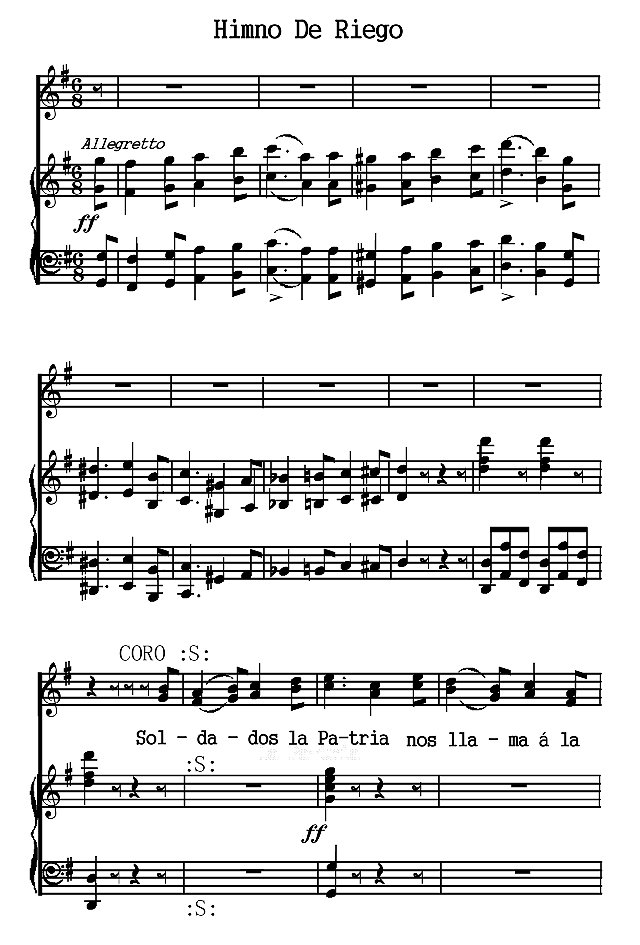

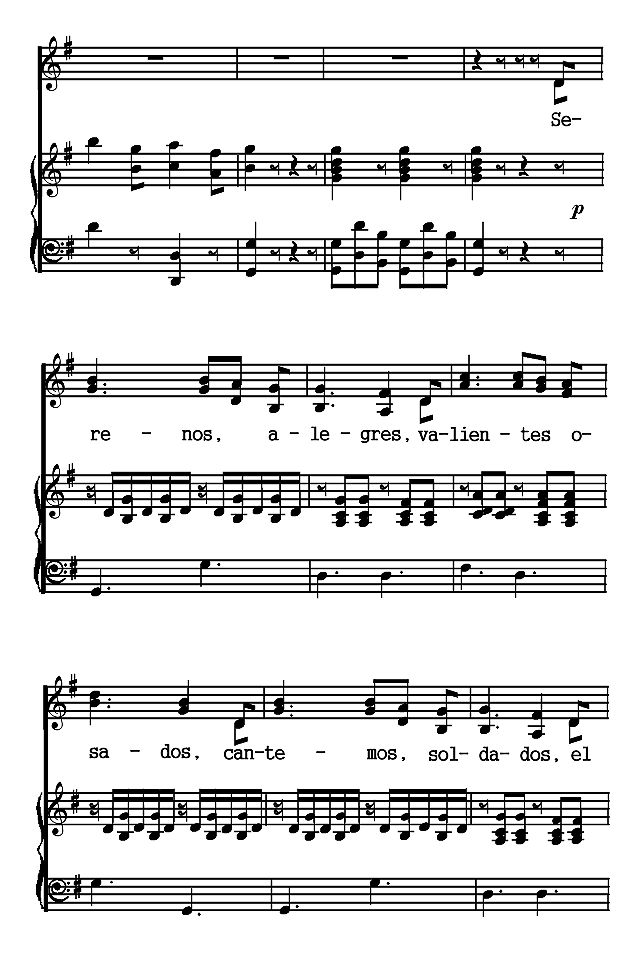

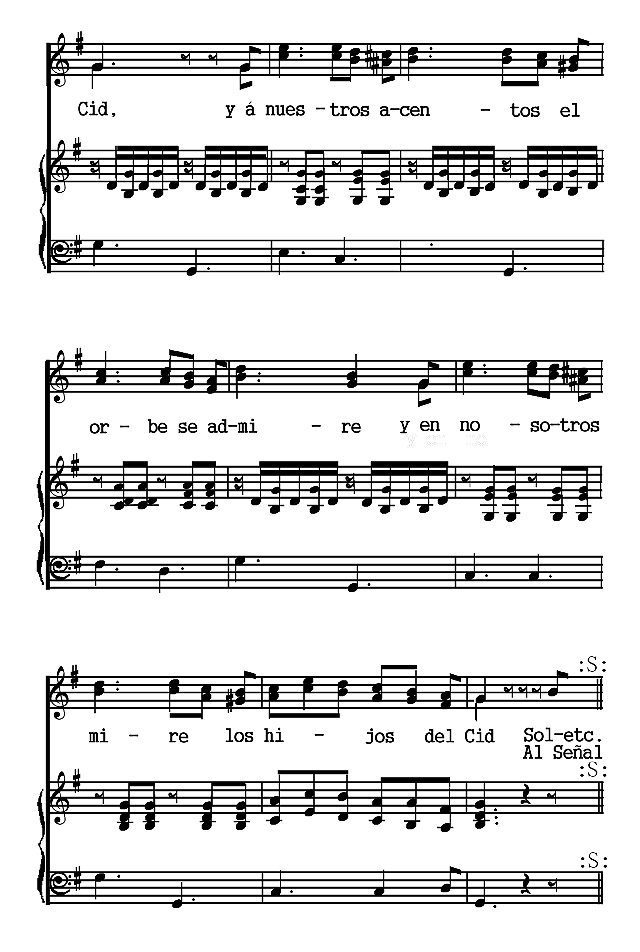
Soldados, la Patria nos llama á la lid,
juremos por ella vencer ó morir. Serenos,
alegres, valientes, osados,
cantemos, soldados, el himno á la lid,
y á nuestros acentos
el orbe se admire y en nosotros
mire los hijos del Cid,
y á nuestros acentos
el orbe se admire y en nosotros
mire los hijos del Cid.
Sol-etc.




Mexicanos al grito de guerra
El acero aprestad y el bridón,
y retiemble en sus centros la tierra
al sonoro rugir del cañon.
Y retiemble en sus centros la tierra
al sonoro rugir del cañón.
Ciña ¡oh patria! tus sienes de oliva
De la paz el arcángel divino,
Que en el ciélo tu eterno destino
por el dedo de Dios se escribió.
Mas si osare un extraño enemigo
profanar con su planta tu suelo
piensa ¡oh patria querida! que el cielo
un soldado en cada hijo te dió,
un soldado en cada hijo te dió.

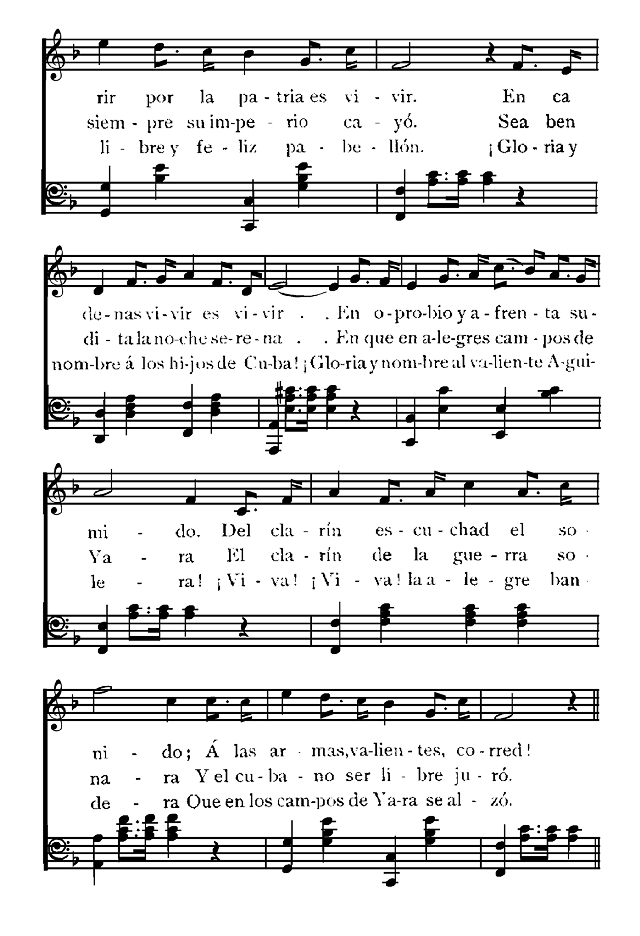
1. ¡Al combate corred Bayameses!
Que la patria os contempla orgullosa;
No temáis una muerte gloriosa,
Que morir por la patria es vivir.
En cadenas vivir es vivir
En oprobio y afrenta sumido.
Del clarín escuchad el sonido;
Á las armas, valientes, corred!
2. No temáis al gobierno extranjero
Que es cobarde cual todo tirano,
No resiste el empuje cubano,
Para siempre su imperio cayó.
Sea bendita la noche serena
En que en alegres campos de Yara
El clarín de la guerra sonara
Y el cubano ser libre juró.
3. No se nuble jamás esa estrella
Que las hijas de Cuba bordaron
Y que nobles cubanos alzaron
En su libre y feliz pabellón.
¡Gloria y nombre á los hijos de Cuba!
¡Gloria y nombre al valiente Aguilera!
¡Viva! ¡Viva! la alegre bandera
Que en los campos de Yara se alzó.
The heavy figures refer to pages of the text; the light figures to lines.
ROMANCES. The Spanish romances viejos, which correspond in form and spirit to the early English and Scotch ballads, exist in great number and variety. Anonymous and widely known among the people, they represent as well as any literary product can the spirit of the Spanish nation of the period, in the main stern and martial, but sometimes tender and plaintive. Most of them were written in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries; the earliest to which a date can be assigned is Cercada tiene á Baeza, which must have been composed soon after 1368. Others may have their roots in older events, but have undergone constant modification since that time. The romance popular is still alive in Spain and many have recently been collected from oral tradition (cf. Menéndez y Pelayo, Antología, vol. X).
The romances were once thought to be relics of very old lyrico-epic songs which, gathering material in the course of time, became the long epics that are known to have existed in Spain in the twelfth to fourteenth centuries (such as the Poema del Cid, and the lost cantares of Bernardo del Carpio, the Infantes de Lara and Fernán González). But modern investigation has shown conclusively that no such age can be ascribed to the romances in their present form, and that in so far as they have any relation with the epic cycles just cited they are rather descendants of them than ancestors,—striking passages remembered by the people and handed down by them in constantly changing form. Many are obviously later in origin; such are the romances fronterizos, springing from episodes of the Moorish wars, and the romances novelescos, which deal with romantic incidents of daily life. The romances juglarescos are longer poems, mostly concerned with 254 Charlemagne and his peers, veritable degenerate epics, composed by itinerant minstrels to be sung in streets and taverns to throngs of apprentices and rustics. They have not the spontaneity and vigor which characterize the better romances viejos.
A few of the romances were printed in the Cancionero general of 1511, and more in loose sheets (pliegos sueltos) not much later in date; but the great collections which contain nearly all the best we know were the Cancionero de romances "sin año," (shortly before 1550), the Cancionero de romances of 1550 and the Silva de varios romances (3 parts, 1550). The most comprehensive modern collection is that of A. Durán, Romancero general, 2 vols., Madrid, 1849-1851 (vols. 10 and 16 of the Biblioteca de Autores españoles). The best selected is the Primavera y flor de romances of Wolf and Hofmann (Berlin, 1856), reprinted in vols. VIII and IX of Menéndez y Pelayo's Antología de poetas líricos castellanos. This contains nearly all the oldest and best romances, and includes poems from pliegos sueltos and the second part of the Silva, which were not known to Durán. Menéndez y Pelayo, in his Apéndices á la Primavera y flor (Antol. vol. IX) has given still more texts, notably from the third part of the Silva, one of the rarest books in the world. The fundamental critical works on the romances are: F. Wolf, Ueber die Romanzenpoesie der Spanier (in Studien, Berlin, 1859); Milá y Fontanals, De la poesía heroico-popular castellana (1874); and Menéndez y Pelayo, Tratado de los romances viejos (vols. XI and XII of the Antología, Madrid, 1903-1906).
The romances, as usually printed, are in octosyllabic lines, with a fixed accent on the seventh syllable of each and assonance in alternate lines.
Many English translators have tried their hand at Spanish ballads, as Thomas Rodd (1812), J. C. Lockhart (1823), John Bowring (1824), J.Y. Gibson (1887) and others. Lockhart's versions are the best known and the least literal.
In the six romances included in this collection the lyrical quality 255 predominates above the narrative (cf. the many rimes in-or in Fonte-frida and El prisionero). Abenámar is properly a frontier ballad, and La constancia, perhaps, belongs with the Carolingian cycle; but the rest are detached poems of a romantic nature. (See S.G. Morley's Spanish Ballads, New York, 1911.)
1.—Abenámar is one of a very few romances which are supposed to have their origin in Moorish popular poetry. The Christian king referred to is Juan II, who defeated the Moors at La Higueruela, near Granada, in 1431. It is said that on the morning of the battle he questioned one of his Moorish allies, Yusuf Ibn Alahmar, concerning the conspicuous objects of Granada. The poem was utilized by Chateaubriand for two passages of Les aventures du dernier Abencérage.
1. Abenámar = Ibn Alahmar: see above.
9. The verbal forms in-ara and-iera were used then as now as the equivalent of the pluperfect or the preterit indicative.
11. la: la verdad is probably understood. Cf. p. 2, l. I.
2.—1. diría = diré. In the romances the conditional often replaces the future, usually to fit the assonance.
5. relucían: in the old ballads the imperfect indicative is often used to express loosely past time or even present time.
6. El Alhambra: in the language of the old ballads el, not la, is used before a feminine noun with initial-a or e-, whether the accent be on the first syllable or not.
25. viuda in old Spanish was pronounced viuda and assonated in í-a. This expletive que is common in Spanish: do not translate.
27. grande merely strengthens bien.
3.—Fonte-frida is a poem of erotic character, much admired for its suave melancholy. Probably it is merely an allegorical fragment of a longer poem now lost. It is one of those printed in the Cancionero general of 1511. It was well translated by Bowring. There is also a metrical version in Ticknor, I, III. This theme is found in the Physiologus, a 256 medieval bestiary. One of these animal stories relates that the turtle-dove has but one mate and if this mate dies the dove remains faithful to its memory. Cf. Mod. Lang. Notes, June, 1904 (Turtel-Taube), and February, 1906.
3. In avecicas and tortolica the diminutive ending-ica seems to be quite equivalent to-ito. Cf. Knapp's Span. Gram., 760a.
4. van tomar = van á tomar.
7. fuera: note that fué (or fuera) á pasar = pasó. This usage is now archaic, although it is still sometimes used by modern poets: see p. 136, l. 18.
18. bebía: see note, p. 2, l. 5.
19. haber, in the ballads, often = tener. See also haya in the following line.
4.—El Conde Arnaldos. Lockhart says of "Count Arnaldos," "I should be inclined to suppose that
'More is meant than meets the ear,'
—that some religious allegory is intended to be shadowed forth." Others have thought the same, and the strong mystic strain in Spanish character may bear out the opinion. In order that the reader may judge for himself he should have before him the mysterious song itself, which, omitted in the earliest version, is thus given in the Cancionero de romances of 1550, to follow line 18 of the poem:
—Galera, la mi galera,
Dios te me guarde de mal,
de los peligros del mundo
sobre aguas de la mar,
de los llanos de Almería,
del estrecho de Gibraltar,
y del golfo de Venecia,
y de los bancos de Flandes,
y del golfo de León,
donde suelen peligrar.
Popular poems which merely extol the power of music over animals are not uncommon.
1. ¡Quién hubiese! would that one might have! or would that I might have! Note ¡quién me diese! (p. 7, 1. 25), would that some one would give me!: this is the older meaning of quién in these expressions. Note also ¡Quién supiera escribir! (p.134), would that I could write! where the modern usage occurs.
22. dígasme = dime This use of the pres. subj. with the force of an imperative is not uncommon in older Spanish.
24.le fué á dar: see note, p. 3,1. 7.
5.—La constancia. These few lines, translated by Lockhart as "The Wandering Knight's Song," are only part of a lost ballad which began:
Á las armas, Moriscote,
si las has en voluntad.
Six lines of it have recently been recovered (Menéndez y Pelayo, Antología, IX, 211). It seems to have dealt with an incursion of the French into Spain, and the lines here given are spoken by the hero Moriscote, when called upon to defend his country. Don Quijote quotes the first two lines of this ballad, Part I, Cap. II.
8. de me dañar = de dañarme.
13. vos was formerly used in Spanish as usted is now used,—in formal address.
El amante desdichado. Named by Lockhart "Valladolid." It is one of the few old romances which have kept alive in oral tradition till the present day, and are still repeated by the Spanish peasantry (cf. Antología, X, 132, 192).
7.—El prisionero. Twelve lines of this poem were printed in 1511. It seems to be rather troubadouresque than popular in origin, but it became very well known later. Lockhart's version is called "The Captive Knight and the Blackbird."
16. This line is too short by one syllable, or has archaic hiatus. See Versification,(4) a.
19. las mis manos: in old Spanish the article was often used before a possessive adjective that preceded its noun. This usage is now archaic or dialectic.
21. hacía is here exactly equivalent to hace in 1. 23: see note, p. 2, 1. 5.
25. quien...me diese: see note, p. 4, 1. I.
8.—12. Oídolo había = lo había oído.
13. This line is too long by one syllable.
14. Gil Vicente (1470?-1540?), a Portuguese poet who wrote dramas in both Portuguese and Castilian. A strong creative artist and thinker, Vicente is the greatest dramatist of Portugal and one of the great literary figures of the Peninsula. This Canción to the Madonna occurs in El auto de la Sibila Casandra, a religious pastoral drama. Vicente himself wrote music for the song, which was intended to accompany a dance. John Bowring made a very good metrical translation of the song (Ancient Poetry and Romances of Spain, 1824, p. 315). Another may be found in Ticknor's History of Spanish Literature, I, 259.
16. digas tú: see note, p. 4, I. 22. el marinero: omit el in translation. In the Spanish of the ballads the article is regularly used with a noun in the vocative.
24. pastorcico: see note, p. 3, I. 3.
9.—Santa Teresa de Jesús (1515-1582), born at Ávila; became a Carmelite nun and devoted her life to reforming her Order and founding convents and monasteries. Saint Theresa believed herself inspired of God, and her devotional and mystic writings have a tone of authority. Her chief works in prose are the Castillo interior and the Camino de perfección. She is one of the greatest of Spanish mystics, and her influence is still potent (cf. Juan Valera, Pepita Jiménez; Huysmans, En route; et al.). Cf. Bibl. de Aut. Esp., vols. 53 259 and 55, for her works. This Letrilla has been translated by Longfellow ("Santa Teresa's Book-Mark," Riverside ed., 1886, VI., 216.)
9.—Fray Luis Ponce de León (1527-1591), born at Belmonte; educated at the University of Salamanca; became an Augustinian monk. While a professor at the same university he was accused by the Inquisition and imprisoned from 1572 to 1576, while his trial proceeded. He was acquitted, and he taught till his death, which occurred just after he had been chosen Vicar-General of his Order. The greatest of the mystic poets, he wrote as well religious works in prose (Los nombres de Cristo, La perfecta casada), and in verse translated Virgil, Horace and other classical authors and parts of the Old Testament. In gentleness of character and in the purity in which he wrote his native tongue, he resembles the Frenchman Pascal. His poems are in vol. 37 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. Cf. Ticknor, Period II, Cap. IX, and Introduction, p. xxii. La vida retirada is written in imitation of Horace's Beatus ille.
9.—17 to 10.—3. In these lines there is much poetic inversion of word-order. The logical order would be: Que ('for') el estado de los soberbios grandes no le enturbia el pecho, ni se admira del dorado techo, en jaspes sustentado, fabricado del sabio moro.
5. pregonera, as its gender indicates, modifies voz.
12.—10. In the sixteenth century great fortunes were made by Spaniards who exploited the mines of their American colonies across the seas.
11. Note, this unusual enjambement; but the mente of adverbs still has largely the force of a separate word.
Soneto: Á Cristo Crucificado. This famous sonnet has been ascribed to Saint Theresa and to various other writers, but without sufficient proof. Cf. Fouché-Delbosc in Revue Hispanique, II, 120-145; and ibid., VI, 56-57. The poem was translated by J.Y. Gibson (The Cid Ballads, etc., 1887, II, 144), and there is also a version attributed to Dryden.
13.—Lope Félix de Vega Carpio (1562-1635) was the most fertile playwright ever known to the world. Alone he created the Spanish drama almost out of nothing. Born at Madrid, where he spent most of his life, Lope was an infant prodigy who fulfilled the promise of his youth. His first play was written at the age of thirteen. He fought against the Portuguese in the expedition of 1583 and took part in the disastrous Armada of 1588. His life was marked by unending literary success, numerous love-affairs and occasional punishments therefor. In 1614 he was ordained priest. For the last twenty years of his life he was the acknowledged dictator of Spanish letters.
Lope's writings include some 2000 plays, of which perhaps 500 are extant, epics, pastorals, parodies, short stories and minor poems beyond telling. He undertook to write in every genre attempted by another and seldom scored a complete failure. His Obras completas are being published by the Spanish Academy (1890-); vol. 1 contains his life by Barrera. Most of his non-dramatic poems are in vol. 38 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp.; others are in vols. 16 and 35. There is a Life in English by H.A. Rennert (1904). Cf. also Introduction, p. xxiv.
Canción de la Virgen is a lullaby sung by the Madonna to her sleeping child in a palm grove. The song occurs in Lope's pastoral, Los pastores de Belén (1612). In Ticknor (II, 177), there is a metrical translation of the Canción.
The palm has great significance in the Roman Catholic Church. On Palm Sunday,—the last Sunday of Lent,—branches of the palm-tree are blessed and are carried in a solemn procession, in commemoration of the triumphal entry of Jesus into Jerusalem (cf. John, xii).
14. Ticknor translates these lines as follows:
Holy angels and blest,
Through these palms as you sweep,
Hold their branches at rest,
For my babe is asleep.
The literal meaning is: Since you are moving among the palms, holy angels, hold the branches, for my child sleeps. When the wind blows through the palm-trees their leaves rustle loudly.
14.—Mañana: translated by Longfellow (Riverside ed., 1886, VI, 204).
15.—Francisco Gómez de Quevedo y Villegas (1580-1645), the greatest satirist in Spanish literature, was one of the very few men of his time who dared criticize the powers that were. He was born in the province of Santander and was a precocious student at Alcalá. His brilliant mind and his honesty led him to Sicily and Naples, as a high official under the viceroy, and to Venice and elsewhere on private missions; his plain-speaking tongue and ready sword procured him numerous enemies and therefore banishments. He was confined in a dungeon from 1639 to 1643 at the instance of Olivares, at whom some of his sharpest verses were directed.
Quevedo was a statesman and lover of his country driven into pessimism by the ineptitude which he saw about him. He wrote hastily on many subjects and lavished a bitter, biting wit on all. His best-known works in prose are the picaresque novel popularly called El gran tacaño (1626) and the Sueños (1627). His Obras completas are in course of publication at Seville (1898-); his poems are in vol. 69 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. Cf. E. Mérimée, Essai sur la vie et les oeuvres de Francisco de Quevedo (Paris, 1886), and Introduction, p. xxv. For a modern portrayal of one side of Quevedo's character, see Bréton de los Herreros, ¿Quién es ella?
Epístola satírica: this epistle was addressed to Don Gaspar de Guzmán, Conde-Duque de Olivares (d. 1645), the favorite and prime minister of Philip IV. It is a remarkably bold protest, for it was published in 1639 when Olivares was at the height of his power. His disgrace did not occur till 1643.
8. Note the double meaning of sentir,—'to feel' and 'to regret.'
9. libre modifies ingenio. Translate: its freedom.
16. Que es lengua la verdad de Dios severo = que la verdad es lengua de Dios severo.
16.—Letrilla Satírica was published in 1640.
.14 Genoa was then, as now, an important seaport and commercial center. As the Spaniards bought many manufactured articles from Genoa, much of their money was "buried" there.
17.—Esteban Manuel de Villegas (d. 1669) was a lawyer who wrote poetry only in his extreme youth. His Eróticas ó Amatorias were published in 1617, and he says himself that they were written at fourteen and polished at twenty. Later the cares of life prevented him from increasing the poetical fame that he gained thus early. He had a reputation for excessive vanity, due partly to the picture of the rising sun which he placed upon the title-page of his poems with the motto Me surgente, quid istae? Istae referred to Lope, Quevedo and others. Villegas' poems may be found in vol. 42 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. Cf. Menéndez y Pelayo, Hist. de los heterodoxos españoles, III, 859-875.
There is a parody of this well-known cantilena by Iglesias in the Bibl. de Aut. Esp., vol. 61, p. 477.
18.—Pedro Calderón de la Barca Henao de la Barreda y Riaño (1600-1681) was the greatest representative of the second generation of playwrights in the Siglo de oro. He took some part in the nation's foreign wars, but his life was spent mostly without event at court as the favorite dramatist of the aristocracy. He became a priest in 1651 and was made chaplain of honor to Philip IV in 1663. There are extant over two hundred of his dramatic works, comedias, autos, entremeses, etc. Calderón constructed his plots more carefully than Lope and was stronger in exalted lyric and religious passages; but he was more mannered, more tainted with Gongorism and less skilled in creating characters.
His Comedias are contained in vols. 7, 9, 12 and 14 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp.; a few of his autos are in vol. 58, and some of his poems are in vols. 14 and 35. Cf. also Poesías inéditas, Madrid, 1881; Menéndez y Pelayo, Calderón y su teatro, Madrid, 1884; R.C. Trench, Calderón, London, 1880.
The sonnet, Estas que fueron..., is found in El príncipe constante, II.
20.—Diego Tadeo González (1733-1794) was born at Ciudad-Rodrigo. He entered the order of Augustinians at eighteen, and filled various important offices within the Order during his life. His duties took him to Seville, Salamanca and Madrid. From youth he showed a particular bent for poetry, and Horace and Luis de León were his admiration. He was an intimate friend of Jovellanos, who induced him to forsake light subjects and attempt a didactic poem, Las edades, which was left unfinished. Fray Diego's modest and lovable character and his friendly relations with other men of letters made him an attractive figure. His poems are in vol. 61 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. Cf. Introduction, p. xxx.
11.— Mirta was a lady with whom the author long corresponded and to whom he addressed many poems. Delio (l. 15) was the name by which Fray Diego González was known among his literary intimates: Jovellanos was called "Jovino"; Meléndez Valdés, "Batilo"; etc.
21.—4. recogellos = recogerlos.
12. á la ave: a more usual construction would be al ave, although the sound wouhd be approximately the same in either case. See also below in line 24, á la alba.
22—4. reluciente:, modified by an adverb, here = reluciendo.
6. recio: a predicate adjective with the force of an adverb.
26.—Nicolás Fernández de Moratín (1737-1780) was born in Madrid of a noble Asturian family. He studied for the law and practised it in Madrid, but irregularly, devoting most 264 of his time to literary work. Besides his poems in the national style (see Introduction, p. xxix) he wrote an epic on the burning of the ships of Cortés and several plays in the French manner, of which only one, Hormesinda (1770), ever had a stage production. His works, with his Life written by his son Leandro, are printed in vol. 2 of the Bibl. de Ant. Esp.
Fiesta de toros en Madrid. Baedeker's guide-book to Spain and Portugal says: "Bull-fights were instituted for the encouragement of proficiency in the use of martial weapons and for the celebration of festal occasions, and were a prerogative of the aristocracy down to the sixteenth century. As the mounted caballero encountered the bull, armed only with a lance, accidents were very frequent. No less than ten knights lost their lives at a single Fiesta de Toros in 1512. The present form of the sport, so much less dangerous for the man and so much more cruel for the beast, was adopted about the beginning of the seventeenth century. The construction, in 1749, of the first great Plaza de Toros in Madrid definitely converted the once chivalrous sport into a public spectacle, in which none took part but professional Toreros." The padded picador of to-day, astride a blinded, worn-out old hack, is the degenerate successor of the knight of old. In the seventeenth century bull-fights in Madrid were sometimes given in the Plaza Mayor (or Plaza de la Constitución).
6. Aliatar: this, like most of the names of persons in this poem, is fictitious; but in form these words are of Arabic origin, and it is probable that Moratin borrowed most of them from the romances moriscos. The names of places, it should be noticed, are also Arabic, but the places still retain these names. See Alimenón, and all names of places, in the Vocab.
28.—19. Hecho un lazo por airón, tied in a knot [to look] like a crest of plumes. This was doubtless the forerunner of 265 the modern banderilla (barbed dart ornamented with streamers of colored paper).
30.—26-28. Cual... nube = cual la ardiente madeja del sol deja mirarse tal vez entre cenicienta nube.
31.—12. blasones de Castilla: as at this time (in the reign of Alfonso VI) León and Castile were united, the blasones were probably two towers (for Castile) and two lions (for León), each one occupying a corner of the shield.
14. Nunca mi espada venciera apparently means: Never did he conquer my sword. This may refer to any adversary, or to some definite adversary in a previous combat.
26. The best bulls raised for bull-fights come from the valley of the Guadalquivir.
32.—22-26. Así... acerquen á..., Como, may... bring to..., just as surely as.
33.—8. Fernando I: see in Vocab.
35.—28. The stanzas of pages 34 and 35 are probably known to every Spaniard: schoolboys commit them to memory for public recitation.
36.—15. dignáredes = dignareis. In modern Spanish the d (from Lat. t) of the 2d pers. plur. verb endings has fallen.
38.—4. Y... despedir = y [si no vieran] á Zaida que le despedía.
13. cruz: the cross of a sword is the guard which, crossing the hilt at right angles, gives the sword the shape of a cross. The cross swords were held in especial veneration by the medieval Christians.
Gaspar Melchor de Jovellanos (or Jove-Llanos) (1744-1811) was one of the loftiest characters and most unselfish statesmen ever produced by Spain. Educated for the law, he filled with distinction important judicial offices in Seville and Madrid. In 1780 he was made a member of the Council of Orders. He attached himself to the fortunes of Count Cabarrús, and when that statesman fell from power in 1790, Jovellanos was 266 exiled to his home in Gijón (Asturias). There he devoted himself to the betterment of his native province. In 1797 the favorite, Godoy, made him ministro de gracia y justicia; but he could not be other than an enemy of the corrupt "Prince of the Peace," and in 1798 he was again sent home. In 1801 he was seized and imprisoned in Majorca and was not released till the invasion of Spain by the French in 1808. He refused flattering offers of office under the French, and was the most active member of the Junta Central which organized the Spanish cortes. Unjustly criticized for his labors he retired home, whence he was driven by a sudden incursion of the French. He died a few days after in an inn at Vega (Asturias).
Jovellanos' best literary work is really his political prose, such as the Informe sobre un proyecto de ley agraria (1787) and Defensa de la junta central (1810). His Delincuente honrado (1773), a comédie larmoyante after the manner of Diderot's Fils naturel, had wide success on the stage. His works are in vols. 46 and 50 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. Cf. E. Mérimée, Jovellanos, in the Revue hispanique, I, pp. 34-68.
¿Quis tam patiens ut teneat se? who is so long-suffering as to control himself?
21. prisión: see mention above of Jovellanos' imprisonment in Majorca.
39.—2. It is scarcely accurate to call Juvenal a bufón, since he was rather a scornful, austere satirist of indignation.
40.—26. cuánto de is an unusual expression; but if the line read: ¡Ay, cuánta amargura y cuánto lloro, it would lack one syllable.
41.—4-6. cuesta... infanta. Evidently the world has changed little in a hundred years!
42.—Juan Meléndez Valdés (1754-1817) was born in the district of Badajoz (Estremadura). He studied law at Salamanca, where he was guided in letters by Cadalso. In 1780 267 he won a prize offered by the Academy for the best eclogue. He then accepted a professorship at Salamanca offered him by Jovellanos. Literary success led him to petition a position under the government which, involving as it did loss of independence, proved fatal to his character. He filled honorably important judicial posts in Saragossa and Valladolid, but court intrigue and the caprices of Godoy brought him many trials and undeserved punishments. In 1808 he accepted a position under the French, and nearly lost his life from popular indignation. Later his vacillations were pitiful: he wrote spirited poems now for the French and now against them. When they were finally expelled in 1813, he left the country with them and died in poverty and sorrow in Montpellier.
Most of his poems are in vol. 63 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp.; others have been published in the Revue hispanique, vols. I. and IV. Cf. his Life by Quintana in Bibl. de Aut. Esp., vol. 19; E. Mérimée, Meléndez Valdés, in Revue hispanique, I, 166-195; Introduction, p. xxx.
44.—5. Muy más: this use of muy is not uncommon in the older classics, but the usual expression now is mucho más.
28. benigna: see note, p. 22, l. 6.
46.—Manuel José Quintana (1772-1857) was born in Madrid. He went to school in Cordova and later studied law at Salamanca. He fled from Madrid upon the coming of the French. In the reign of Ferdinand VII he was for a time confined in the Bastile of Pamplona on account of his liberal ideas. After the liberal triumph of 1834 he held various public offices, including that of Director General of Public Instruction. In 1855 he was publicly crowned in the Palace of the Senate.
See Introduction, p. xxxii; Ticknor, III, 332-334; Blanco García, La literatura española en el siglo XIX, 2d ed., Madrid, 1899, I, 1-13; Menéndez y Pelayo, D. Manuel José Quintana, 268 La poesía lírica al principiar el siglo XIX, Madrid, 1887; E. Piñeyro, M.-J. Quintana, Chartres, 1892; Juan Valera, Florilegio de poesías castellanas, Madrid, 1903, V, 32-38. His works are in vols. 19 and 67 of Bibl. de Aut. Esp.
The Spanish people, goaded by the subservience of Charles IV and his prime minister and favorite, Godoy, to the French, rose in March, 1808, swept away Godoy, forced the king to abdicate and placed his son Ferdinand upon the throne. It was believed that this change of rulers would check French influence in the Peninsula, but Ferdinand was forced by Napoleon into a position more servile than that occupied formerly by Charles.
2. Note the free word-order in Spanish which permits, as in this line, the subject to follow the verb, the object to precede.
14. Oceano: note the omission of the accent on e, that the word may rime with soberano and vano; but here oceano still has four syllables.
47.—28. tirano del mundo = Napoleon Bonaparte.
48.—24. By los colosos de oprobio y de vergüenza are probably meant Charles IV and Godoy.
49.—29. hijo de Jimena: see Jimena and Bernardo del Carpio, in Vocab.
50.—2. En... y, with a... and in.
51.—Dionisio Solís y Villanueva (1774-1834) was born in Cordova: he never rose higher in life than to be prompter in a theater. He fought against the French, and he was exiled for a time by Ferdinand VII. Solís wrote some plays and translated many from other languages into Spanish. The best that can be said of Solís as a poet is that his work is spontaneous and in parts pleasing. Cf. Blanco García, I, 50 and 61-63; Valera, Florilegio, V, 44-46.
53.—18-19. Esta... enfermedad = esta dulce deliciosa enfermedad que yo siento.
25. si puede (here meaning if it is possible) is understood before que trate.
54.—Juan Nicasio Gallego (1777-1853) was born at Zamora. He was ordained a priest: later he went to court, and was appointed Director of His Majesty's Pages. He frequented the salon of his friend Quintana, and was elected deputy from Cadiz. In 1814, during the reign of Ferdinand VII, Gallego was imprisoned for his liberal ideas and later was banished from Spain. He spent some years in France and returned to Spain in 1828. Later he was appointed Perpetual Secretary of the Spanish Academy.
See Introduction, p. xxxii; Blanco García, I, 13 f.; Valera, Florilegio, V, 38-44. His poems are in vol. 67 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. There is also an edition of his poems by the Academia de la Lengua, Madrid, 1854.
El Dos de Mayo: on the second of May, 1808, the Spanish people, unarmed and without strong leaders, rose against Napoleon's veteran troops. Aided by the English, they drove out the French after a long and bloody war, thus proving to the world that the old Spanish spirit of independence was still alive. This war is known to the Spaniards as the Guerra de la independencia and to the English as the Peninsular War. The popular uprising began with the seizure of a powder magazine in Madrid by Velarde and Daoiz (see in Vocab.). These men and their followers were killed and the magazine was retaken by the French, but the incident roused the Spanish people to action.
9. al furor, in the glare.
55.—4. Mantua: a poetic appellation of Madrid. Cf. article by Prof. Milton A. Buchanan in Romanic Review, 1910, p. 211 f. See also p. xxxiii, Introduction to this volume.
11-12. ¿Quién habrá... que cuente, who may there be to tell...
58.—26 to 59.—3. Note how the poet refers to the various parts of the Spanish peninsula: hijos de Pelayo = the 270 Spaniards in general, or perhaps those of northernmost Spain; Moncayo = Aragon, Navarre and Castile; Turia = Valencia; Duero = Old Castile, Leon and Portugal; and Guadalquivir = Andalusia. See Pelayo and Moncayo and these names of rivers in Vocab.
5. Patrón = Santiago, or St. James, the patron saint of Spain. According to the legend James "the Greater," son of Zebedee, preached in Spain, and after his death his body was taken there and buried at Santiago de Campostela. It was believed that he often appeared in the battle-fields fighting with the Spaniards against the Moslems.
14-15. á... brindó felicidad, drank in fire and blood a toast to her prosperity.
60.—Francisco Martínez de la Rosa (1787-1862) was born at Granada. During the War of Independence he was sent to England to plead for the support of that country against the French. Later he was exiled by Ferdinand VII, and was for five years a prisoner of state in a Spanish prison on the African coast. After his release he became prominent in politics, and was forced to flee to France. In 1834 he was called into power by the queen regent, Maria Cristina. He represented his country at Paris, and later at Rome, and held several important posts as cabinet minister.
See Introduction, p. xxxvi; Menéndez y Pelayo, Estudios de crítica literaria, Madrid, 1884, pp. 223, f.; Blanco García, I, 115-128; Juan Valera, Florilegio, V, 56-63. His Obras completas, 2 vols., ed. Baudry, were published at Paris in 1845. Several of his articles of literary criticism are in vols. 5, 7, 20 and 61 of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp.
3. riyendo = riendo.
61.—Angel de Saavedra, Duque de Rivas (1791-1865) was born at Cordova. He prepared for a military career. By reason of his liberal ideas he was compelled to leave Spain and went to England, France and the Island of Malta. He returned271 to Spain in 1834 and became a cabinet minister, but was again forced to flee the country. Later he was welcomed back and represented Spain at Naples. He retired from politics and was appointed Director of the Spanish Academy.
See Introduction, p. xxxvi; Blanco García, I, 129-153; Juan Valera, Florilegio, V, 184-195. His Obras completas, in 5 vols., were published by the Spanish Academy, Madrid, 1854-1855, with introductory essays by Pastor Díaz and Cañete. His works were also published in the Colección de Escritores castellanos, 1894-.
4. De... pro = en pro de mi sangre y casa.
62.—3. á la que: translate, before which.
10. duque de Borbón is the subject of estaba, l. 3.
18. Empérador = Charles V.
64.—8. Condestable = Velasco, Constable of Spain, who in 1521 defeated the comuneros who had rebelled against the rule of Charles V.
65.—22. Y con los que, with whom.
23. estrecho stands in antithesis to ancho: for his glory the broad world will be narrow.
66.—18-19. Y... leonesa = y un coleto á la leonesa de recamado ante.
68.—20-21. Que... resuelta = que es voluntad suya resuelta (el) que aloje á Borbón.
69.—22. de un su pariente is archaic. The regular expression to-day would be de un pariente suyo.
71.—Juan Arolas (1805-1849) was born in Barcelona, but spent most of his life in Valencia. In 1821, when sixteen years old, Arolas, much against the wishes of his parents, joined a monastic order. Arolas wrote in all the literary genres of his time, but he distinguished himself most as a poet by his romantic "oriental" and love poems.
Cf. El P. Arolas, su vida y sus versos, Madrid, 1898, by José R. Lomba y Pedraja; Blanco García, I, 186-189; Juan Valera, 272 Florilegio, V, 121-130. A new edition of Arolas' verses was published at Valencia in 1883.
73.—José de Espronceda (1808-1842), Spain's greatest romantic poet, was born in Almendralejo (Badajoz). At the Colegio de San Mateo Espronceda was considered a precocious but wayward pupil. His poetic gifts won for him the lasting friendship of his teacher, Alberto Lista. At an early age he became a member of a radical secret society, Los Numantinos. Sent into exile to a monastery in Guadalajara, he there composed the fragmentary heroic poem Pelayo. After his release he went to Lisbon and then to London. Enamored of Teresa, though another's wife, he fled with her to Paris, where he took an active part in the revolution of 1830. Espronceda returned to Spain in 1833, and engaged in journalism and politics. Worn out by his tempestuous life, he died at the early age of thirty-four years.
See Introduction, p. xxxvii; E. Rodríguez Solís, Espronceda, su tiempo, su vida y sus obras, Madrid, 1883; Blanco García, I, 154-171; Juan Valera, Florilegio, V, 197-207; Antonio Cortón, Espronceda, Madrid, 1906; Philip H. Churchman, Espronceda's Blanca de Borbón, Revue hisp., 1907; and Byron and Espronceda, ibid., 1909. For his poems, see Obras poéticas, in the Biblioteca amena é instructiva, Barcelona, 1882; Obras poéticas y escritos en prosa, colección ordenada por D. Patricio de la Escosura, Madrid, 1884.
79.—José de Zorrilla (1817-1893) was born in Valladolid. After receiving his secondary education in the Jesuit Semanario de Nobles he began the study of law; but he soon turned to the more congenial pursuit of belles-lettres. In 1855 he went to Mexico where he resided eleven years. Though a most productive writer, Zorrilla spent most of his life in penury until, in his old age, he received from the government an annual pension of 30,000 reales. He became a member of the Spanish Academy in 1885, and four years later he was "crowned" 273 in Granada. Zorrilla died in Madrid in his seventy-sixth year.
See Introduction, p. xxxvii; an autobiography, Recuerdos del tiempo viejo, 3 vols.; Fernández Flórez, D. José Zorrilla, in Autores dramáticos contemporáneos, 1881, vol. I; Blanco García, I, 197-216; Juan Valera, Florilegio, V, 258-270. For his works, see Poesías, 8 vols., Madrid, 1838-1840; Obras, edition Baudry, 3 vols., Paris, 1852; Poesías escogidas, published by the Academia de la lengua, Madrid, 1894; Obras dramáticas y líricas, Madrid, 1895.
85.—10. Fantasmas = como fantasmas.
86.—Á Buen Juez Mejor Testigo, A Good Judge, But a Better Witness. In Berceo's Milagros de Nuestra Señora there is a similar legend of a crucifix summoned as witness.
91.—4-5. Como... bañe: this passage is obscure, but the meaning seems to be, as a pledge that the river should so zealously bathe it.
18. la hermosa, according to tradition, was Florinda, daughter of Count Julian. Roderick (Roderico or Rodrigo), the last king of the Goths in Spain, saw Florinda bathing in the Tagus, conceived a passion for her and dishonored her. In revenge Julian is said to have brought the Saracens into Spain.
27. puerta: this may refer to the Puerta Visagra Antigua, an ancient Arabic gate of the ninth century, now closed.
92.—12. Las... horadarle = al horadarle las palmas (al rey). According to tradition Alfonso, who became afterward King Alfonso VI of Leon and Castile, when a refugee at the court of Alimenón, the Moorish king of Toledo, overheard the Moorish sovereign and his advisers talking about the defences of the city. The Moors said that the Christians, by a siege, could probably starve Toledo into submission. Upon perceiving Alfonso near at hand apparently asleep, the Moors, to prove whether he was really asleep or not, poured molten 274 lead into his hand, and he had sufficient will power to remain motionless while the lead burned a hole through it.
Mariana (Historia de España, Libro IX, Cap. VIII) relates this story, but rejects it and says that the real cause of Alfonso's nickname ("el rey de la mano horadada") was his extreme generosity.
13. circo romano: to the east of the Hospital de San Juan Bautista of Toledo lies the suburb of Covachuelas, the houses of which conceal the ruins of a Roman amphitheater.
15. Basílica: in the lower Vega, to the northwest of Toledo, is the hermitage of El Cristo de la Vega, formerly known as the Basílica de Santa Leocadia, which dated from the fourth century. This edifice was the meeting-place of several Church councils. The ancient building was destroyed by the Moors and has been repeatedly rebuilt.
95.—21. el templo: the Ermita del Cristo de la Vega. See preceding note.
27. Víase = veíase: vía, for veía, is not uncommon in poetry.
105.—3-5. Gritan... valor = los que en el mercado venden, gritan en discorde son lo vendido y el valor (= what they have for sale and its price).
107.—13-14. y... honor = y dispensad que (yo) dudara de vuestro honor acusado.
108.—10. See note, p. 92, l. 15.
112.—16. cada un año = cada año.
Antonio de Trueba (1821-1889) was born at Montellano (Viscaya). At the age of fifteen or sixteen years he removed to Madrid and engaged in commerce. In 1862 he was appointed Archivist and Chronicler of the Señorío de Vizcaya, which post he held for ten years. Trueba, best known as a writer of short stories, published two volumes of mediocre verses which achieved considerable popularity during the author's lifetime, but are now nearly forgotten.
Cf. Notas autobiográficas in La Ilustración Española y 275 Americana, Enero 30, 1889; Blanco García, II, 26-28 and 301-308; Juan Valera, Florilegio, V, 307-311. For his verses, see El libro de los cantares (1851) and El libro de las montañas (1867).
113.—14. Cantos: note the double meaning of canto.
114.—José Selgas y Carrasco (1821-1882) was born in Murcia. A writer on the staff of the satirical and humorous journal, El Padre Cobos, Selgas won the attention of the public by his ironical and reactionary articles and was elevated to an important political office by Martínez Campos. He is the author of two volumes of verses, La Primavera (1850) and El estío.
See Introduction, p. xxxix; and Blanco García, II, 19-23 and 244-250. For Selgas' verses, see his Poesías, Madrid, 1882-1883.
117.—Pedro Antonio de Alarcón (1833-1891) was born in Guadix. He studied law, served as a volunteer in an African war and became a writer on the staff of several revolutionary journals. His writings, which at first were sentimental or radical, became more subdued in tone and more conservative with his advancing years. In 1877 he was elected to membership in the Spanish Academy. Primarily a journalist and novelist, Alarcón published a volume of humorous and descriptive verses, some of which have merit.
Cf. Blanco García, II, 62-63 and 452-467; and articles in the Nuevo Teatro Crítico (Sept., Oct. and Nov., 1891). For his verses, see Poesías serias y humorísticas, 3d ed., Madrid, 1885.
121.—Gustavo Adolfo Bécquer (1836-1870) was born in Seville, and became an orphan in his tenth year. When eighteen years of age he went penniless to Madrid, where he earned a precarious living by writing for journals and by doing literary hack-work.
See Introduction, p. xxxix; Blanco García, II, 79-86 and 274-277. 276 For his works, see his Obras, 5th ed., Madrid, 1898 (with a Prólogo by Correa: the Rimas are in vol. III).
122.—12-13. Del salón... olvidada = en el ángulo obscuro del salón, tal vez olvidada de su dueño. Bécquer, in his striving after complicated metrical arrangements, often inverts the word-order in his verse. See also Introduction, Versification, p. lxxii.
19. arrancarlas: las refers to Cuánta nota, which seems to have here the force of a plural.
24. See Introduction, Versification, p. lxv.
124.—14. intérvalo: the standard form is intervalo.
126.—12. El nicho á un extremo: the meaning is, one end of the recess, in which the coffin will be placed. The graveyards of Spain and Spanish America have lofty walls with niches or recesses large enough to contain coffins. After receiving the coffin, the niche is sealed with a slab that bears the epitaph of the deceased.
128.—The Valencian Vicente W. Querol (1836-1889) gave most of his time to commerce, but he occasionally wrote verses that had the merit of correctness of language and strong feeling.
Cf. Blanco Garcia, II, 376-378. For his verses, see Rimas (Prólogo by Pedro A. de Alarcón), 1877; La fiesta de Venus, in the Almanaque de la Ilustración, 1878.
7. Ó en el que = ó en el día en que: the reference is to the anniversaries of the wedding day and the saints' days of the parents.
129.—19. las que... son, what is...
131.—15-16. la que... agonía = la lenta agonía que sufristeis...
133.—Ramón de Campoamor y Campoosorio (1817-1901) was born in Navia (Asturias). He studied medicine but soon turned to poetry and politics. A pronounced conservative, he won favor with the government and received appointment 277 to several important offices including that of governor of Alicante and Valencia.
Cf. Introduction, p. xli; Juan Valera, Obras poéticas de Campoamor, in Estudios críticos sobre literatura, Seville, 1884; Peseux-Richard, in the Revue hispanique, I, 236 f.; Blanco García, II, Cap. V. For his works, see Doloras y cantares, 16th ed., Madrid, 1882; Los pequeños poemas, Madrid, 1882-1883; Poética, 1883; El drama universal, 3d ed., Madrid, 1873; El licenciado Torralba, Madrid, 1888; Obras escogidas, Leipzig, 1885-1886; Obras completas, 8 vols., Madrid, 1901-03.
135.—3. se va y se viene y se está: note the use of se in the sense of people, or an indefinite we.
5. Y... procura = y si tu afecto no procura volver.
136.—18. See note, p. 3, l. 7.
137.—Valladolid was the birthplace of Gaspar Núñez de Arce (1834-1903). When a child, he removed with his family to Toledo. At the age of nineteen years he entered upon a journalistic career in Madrid. As a member of the Progresista party, Núñez de Arce was appointed Civil Governor of Barcelona, and afterward he became a cabinet minister.
Cf. Introduction, p. xlii; Menéndez y Pelayo's essay in Estudios de crítica literaria, 1884; Juan Valera's essay on the Gritos del combate, Revista europea, 1875, no. 60; Blanco García, Cap. XVIII; José del Castillo, Núñez de Arce, Apuntes para su biografía, Madrid, 1904. For his works, see Gritos del combate, 8th ed., 1891; Obras dramáticas, Madrid, 1879. Most of his longer poems are in separate pamphlets, published by M. Murillo and Fernando Fe, Madrid, 1895-1904.
137.—Tristezas shows unmistakably the influence of the French poet Alfred de Musset, and especially perhaps of his Rolla and Confession d'un enfant du siècle.
138.—16 f. Compare with the author's La duda and Miserere, and Bécquer's La ajorca de oro.
142.—1-3. The poet seems to compare the nineteenth century, amidst the flames of furnaces and engines, to the fallen archangel in hell.
16. mística, that is, of communion with God, heavenly.
144.—¡Sursum Corda!: the lines given are merely the introduction to the poem, and form about one fourth of the entire work. They were written soon after the Spanish-American War. See Sursum Corda!, Madrid, 1904; and also Juan Valera's Florilegio, IV, 413 f.
8. The plains of Old Castile may well be called "austere."
145.—10-16. Cf. Á España (1860) and Á Castelar (1873).
147.—11-19. There are few stronger lines than these in all Spanish poetry.
148.—Manuel del Palacio (1832-1895) was born in Lérida. His parents removed to Granada, and there he joined a club of young men known as La Cuerda. Going to Madrid, he devoted himself to journalism and politics, first as a radical and later as a conservative.
Cf. Blanco Garcia, II, 40. For his works, see his Obras, Madrid, 1884; Veladas de otoño, 1884; Huelgas diplomáticas, 1887.
5. el ave placentera: a well-known Spanish-American poet calls this a mere ripio (stop-gap), and says it may mean one bird as well as another.
The Catalan Joaquín María Bartrina (born at Reus in 1850) published in 1876 a volume of pessimistic and iconoclastic verses, entitled Algo. After his death (1880) his works were published under the title of Obras en prosa y verso, escogidas y coleccionadas por J. Sardá, Barcelona, 1881. Cf. Blanco García, II, 349-350.
148.—15-19. These lines give expression to the pessimism that has obtained in Spain for two centuries past.
149.—14. The reference is, of course, to the paintings, of which there are many, of "The Last Supper" of Jesus.
Manuel Reina (1860-) was born in Puente Genil. Like 279 Bartrina, Reina is an imitator of Núñez de Arce, in that he sings of the degeneracy of mankind. He undertook, with but little success, to revive the eleven-syllable romance of the neo-classic Spanish tragedy of the eighteenth century.
Cf. Blanco García, II, 354-355. For his verses, see Andantes y allegros and Cromos y acuarelas, cantos de nuestra época, con un prólogo de D. José Fernández Bremón.
The Valencian Teodoro Llorente (b. 1836) is best known for his translations of the works of modern poets. He is also the author of verses (Amorosas, Versos de la juventud, et al.).
151.—Argentina. The development of letters was slower in Argentina than in Mexico, Peru and Colombia, since Argentina was colonized and settled later than the others. During the colonial period there was little literary production in the territory now known as Argentina. Only one work of this period deserves mention. This is Argentina y conquista del río de la Plata, etc. (Lisbon, 1602), by Martín del Barco Centenera, a long work in poor verses and of little historical value. During the first decade of the nineteenth century there was an outpouring of lyric verses in celebration of the defeat of the English by the Spaniards at Buenos Aires, but to all of these Gallego's ode Á la defensa de Buenos Aires is infinitely superior.
During the revolutionary period the best-known writers, all of whom may be roughly classified as neo-classicists, were: Vicente López Planes (1784-1856), author of the Argentine national hymn; Esteban Luca (1786-1824); Juan C. Lafinur (1797-1824); Juan Antonio Miralla (d. 1825); and, lastly, the most eminent poet of this period, Juan Cruz Varela (1794-1839), author of the dramas Dido and Argía, and of the ode Triunfo de Ituzaingó (Poesías, Buenos Aires, 1879).
The first Argentine poet of marked ability, and one of the greatest that his country has produced, was the romanticist (who introduced romanticism into Argentina directly from 280 France), Esteban Echeverría (1805-1851), author of Los Consuelos (1834), Rimas (1837) and La cautiva. The latter poem is distinctively "American," as it is full of local color. Juan Valera, in his letter to Rafael Obligado (Cartas americanas, primera serie), says truly that Echeverría "marks the point of departure of the Argentine national literature." (Obras completas, 5 vols., Buenos Aires, 1870-74).
Other poets of the early period of independence are: the literary critic, Juan María Gutiérrez (1809-1878), one-time rector of the University of Buenos Aires and editor of an anthology, América poética (Valparaíso, 1846); Dr. Claudio Mamerto Cuenca (1812-1866; cf. Obras poéticas escogidas, Paris, 1889); and José Mármol (1818-1871), author of El peregrino and of the best of Argentine novels, Amalia (Obras poéticas y dramáticas, coleccionadas por José Domingo Cortés, 3d ed., Paris, 1905).
In parenthesis be it said that Argentina also claims as her own the poet Ventura de la Vega (1807-1865), who was born in Buenos Aires, as Mexico claims Juan Ruiz de Alarcón, and as Gertrudis Gómez de Avellaneda is claimed by Cuba.
As in Spain Ferdinand VII had driven into exile most of the prominent writers of his period, so the despotic president, Juan Manuel Rosas (1793-1877: fell from power in 1852), drove from Argentina many men of letters, including Varela, Echeverría and Mármol.
Down to the middle of the nineteenth century it may be said that the Spanish-American writers followed closely the literary movements of the mother country. Everywhere across the sea there were imitators of Meléndez Valdés and Cienfuegos, of Quintana, of Espronceda and Zorrilla. During the early years of romanticism some Spanish-American poets,—notably the Argentine Echeverría,—turned for inspiration directly to the French writers of the period; but, in the main, the Spanish influence was predominant. The Spanish-American 281281 verses, for the most part, showed insufficient preparation and were marred by many inaccuracies of diction; but here and there a group of writers appeared,—as in Colombia,—who rivaled in artistic excellence the poets of Spain. In the second half of the nineteenth century the Spanish-American writers became more independent in thought and speech. It is true that many imitated the mysticism of Bécquer or the pessimism of Núñez de Arce, but many more turned for inspiration to native subjects or to the literary works of other lands than Spain, and particularly of France and Italy.
The extreme in local color was reached in the "literatura gauchesca," which consists of collections of popular or semi-popular ballads in the dialect of the gauchos, or cowboys and "ranchers," of the Pampas. The best of these collections,—Martín Fierro (1872), by José Fernández,—is more artistic than popular. This long poem, which in its language reminds the English reader of Lowell's Biglow Papers, is the best-known and the most widely read work by an Argentine author.
The greatest Argentine poets of the second half of the century have been Andrade and Obligado. Olegario Víctor Andrade (1838-1882), the author of Prometeo and Atlántida, is generally recognized as one of the foremost modern poets of Spanish America, and probably the greatest poet that Argentina has as yet given to the world. In art, Andrade was a disciple of Victor Hugo; in philosophy, he was a believer in modern progress and freedom of thought; but above all else was his loyal patriotism to Argentina. Andrade's verses have inspiration and enthusiasm, but they are too didactic and they are marred by occasional incorrectness of speech. Atlantida, a hymn to the future of the Latin race in America, is the poet's last and noblest work (Obras, Buenos Aires, 1887).
It is said of Rafael Obligado (1852-) that he is more 282 elegant and correct than Andrade, but his muse has less inspiration. He has, moreover, the distinction of showing almost no French influence, which is rare to-day among Spanish-American writers. Juan Valera regrets Obligado's excessive "Americanism," and laments the fact that the poet uses many words of local origin that he, Valera, does not understand. The poet's better works are, for the most part, descriptions of the beauties of nature or the legendary tales of his native land (Poesías, Buenos Aires, 1885).
Among recent poets, two have especially distinguished themselves. Leopoldo Díaz (1868-) began as a disciple of Heredia, and has become a pronounced Hellenist, now a rare phenomenon in Spanish America. Besides many sonnets imbued with classicism, he has written odes to the conquistadores and to Atlántida conquistada. Like Darío, Blanco-Fombona and many other Spanish-American poets of to-day, Diaz resides in Europe; but, unlike the others, he lives in Morges instead of Paris (Sonetos, Buenos Aires, 1888; Bajo-relieves, Buenos Aires, 1895; et al.). A complete "modernista" (he would probably scorn the title of "decadent") is Leopoldo Lugones (1875?-), whose earlier verses are steeped in an erotic sensualism rare in the works of Spanish-American poets. He seeks to be original and writes verses on every conceivable theme and in all kinds of metrical arrangements. Thus, in Lunario sentimental there are verses, essays and dramatic sketches, all addressed to the moon. For an example of his versos libres, see Introduction to this volume, p. xlvi (Las montañas de oro, Los crepúsculos del jardín; Lunario sentimental, Buenos Aires, 1909; Odas seculares, Buenos Aires, 1910).
For studies of Argentine literature, see Blanco García, Hist. Lit. Esp., III, pp. 380 f.; Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Am., IV, pp. lxxxix f.; Juan Valera, Poesía argentina, in Cartas americanas, primera serie, Madrid, 1889, pp. 51-119; 283 Literatura argentina, Buenos Aires, 1903; Poetas argentinos, Buenos Aires, 1904; Antología argentina, B.T. Martínez, Buenos Aires, 1890-91; Compendio de literatura argentina, E. Alonso Criado, Buenos Aires, 1908; Miscelánea, by Santiago Estrada; La lira argentina, Buenos Aires, 1824. Other important works, treating of Spanish-American literature, are: Biblioteca hispano-americana (1493-1810), José Toribio Medina, 6 vols., Santiago de Chile, 1898-1902; Bibliography of Spanish-American Literature, Alfred Coester, Romanic Review, III, 1; Escritores hispano-americanos, Manuel Cañete, Madrid, 1884; Escritores y poetas sud-americanos, Francisco Sosa, Mex., 1890; Juicio crítico de poetas hispano-americanos, M.L. Amunátegui, Santiago de Chile, 1861; La joven literatura hispano-americana, Manuel Ugarte, Paris, 1906.
Echeverría: see preceding note.
Canción de Elvira. This Gutiérrez calls the "song of the American Ophelia."
152.—Andrade: see note to p. 151.
18. Á celebrar las bodas, to be the bride.
153.—3. The Argentines, especially, seem to take delight in calling themselves a Latin, rather than a Spanish, race. This may be due to the fact that fully one third of the population of Argentine is Italian. Both Juan Valera and Menéndez y Pelayo have chided the Argentines for speaking of themselves as a raza latino-americana, instead of hispano-americana.
15. arcano, secret, seems to have the force here of a secret ark, or secret sanctuary, which is broken open that its secrets may be disclosed.
154.—6-10. These lines refer, of course, to the Christian religion, spoken of symbolically as an altar, which has replaced the heterogeneous pagan cults of ancient Rome, and which the Spaniards first brought to America.
11. ciclopeas: note the omission of the accent on o that the word may rime with ideas.
155.—5. Tequendama: see in the Vocab. Several Colombian poets, including Don José Joaquín Ortiz and Doña Agripina Montes del Valle, have written odes to this famous waterfall. See Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Am., II; and Parnaso colombiano, II, Bogotá, 1887.
17-18. A revolutionary hero, Antonio Ricaurte (b. 1786), blew up the Spanish powder magazine on the summit of a hill near San Mateo, and lost his life in the explosion. See Mateo in Vocab.
156.—5. The colors of the Peruvian flag are red and white, mainly red. The red,—symbolical of bloodshed,—shall be largely replaced by the golden color of ripening grain,—symbolical of industry.
8. Caracas, where Bolivar was born, lies at the foot of Mount Ávila.
11. This line, and line 16, would indicate that Atlántida was written soon after the war, begun in 1876, between Chile and the allied forces of Bolivia and Peru, in which Chile was victorious.
12-15. When this was written there was little immediate prospect of other railways than the narrow-gage road from Oruro to the Chilean frontier, about five hundred miles in length; but now Bolivia has the promise of becoming the railway center of lines connecting both Argentina and Chile with Peru. These lines are now completed or building.
27. Andrade died in 1882, and seven years after his death, in 1889, the emperor Dom Pedro II was deposed, and a republican form of government was adopted by Brazil.
157.—3. Andrade now sings of his own country, hence ¡De pie para cantarla!
8. There is a larger immigration of Europeans into Argentina than into any other South-American country. The 285 immigrants come mostly from northern Italy and from Spain.
12-16. As the Atlántida was the last poetic work of Andrade, these lines may refer to the treaty of 1881 between Argentina and Chile, by which Argentina acquired all the territory east of the Andes, including Patagonia and the eastern part of Tierra del Fuego.
By the conquest and settlement of the broad plains (pampas) and the frozen region of the south, a new world was created, much as in the United States of America a new world was created by the acquirement and settlement of the western plains, mountain lands and Pacific coast.
21. Vast areas in Argentina are given over to the cultivation of wheat, barley and oats.
159.—These are the last stanzas of Prometeo, a poem in which the author addresses the human mind and urges it to break its bonds and free itself from tyranny and prejudice: see also in Vocab.
160.—Obligado: see note to p. 151.
162.—Colombia. Colombia was formerly known as Nueva Granada, and its inhabitants are still sometimes called Granadinos. An older and larger Colombia was organized in 1819, toward the close of the revolutionary war; but this state was later divided into three independent countries, viz., Venezuela, Nueva Granada and Ecuador. In 1861 Nueva Granada assumed the name of Estados Unidos de Colombia, and only recently the Colombian part of the Isthmus of Panama established itself as an independent republic. The present Colombia has, therefore, only about one third the area of the older state of the same name. In treating of literature, the terms Colombia and Colombian are restricted to the present-day Colombia and the older Nueva Granada. The capital of the Republic is Santa Fe de Bogotá, to-day generally known simply as Bogotá. It is at an elevation of 8700 feet 286 above the level of the sea, and has a cool and equable climate.
It is generally conceded that the literary production of Colombia has excelled that of any other Spanish-American country. Menéndez y Pelayo (Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Am., III, Introd.) speaks of Bogotá as the "Athens of South America," and says further: "the Colombian Parnassus to-day excels in quality, if not in quantity, that of any other region of the New World." And Juan Valera in his Cartas americanas (primera serie, p. 121 f.) says: "Of all the people of South America the Bogotanos are the most devoted to letters, sciences and arts"; and again: "In spite of the extraordinary ease with which verses are made in Colombia, and although Colombia is a democratic republic, her poetry is aristocratic, cultivated and ornate." Blanco García characterizes Colombia as one of the most Spanish of American countries.
During the colonial period, however, Nueva Granada produced few literary works. Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, the conquistador of New Granada, wrote memoirs, entitled Ratos de Suesca (1573?), of little historical value. The most important work of the period is the chronicles in verse of Juan de Castellanos (b. 1522? in the Spanish province of Seville). This work is largely epic in character; and, with its 150,000 lines, it is the longest poem in the Spanish language. Though for the most part prosaic and inexact, yet it has some passages of high poetic worth, and it throws much light on the lives of the early colonists. The first three parts of the poem, under the title of Elegías de varones ilustres de Indias (the first part only was published in 1589), occupies all of vol. IV of the Bibl. de Aut. Esp. The fourth part is contained in two volumes of the Colección de Escritores Castellanos, under the title of Historia del Nuevo Reino de Granada.
In the seventeenth century the colonists were still too busy with the conquest and settlement of the country to spare time 287 for the cultivation of letters. A long epic poem, the Poema heroico de San Ignacio de Loyola, with much Gongorism and little merit, was published at Madrid in 1696, after the death of the author, the Colombian Hernando Domínguez Camargo. A few short lyrics by the same author also appeared in the Ramillete de varias flores poéticas (Madrid, 1676) of Jacinto Evia of Ecuador.
Early in the eighteenth century Sor Francisca Josefa de la Concepción, "Madre Castillo" (d. 1742), wrote an account of her life and her Sentimientos espirituales, in which there is much of the mysticism of Saint Theresa.
About 1738 the printing-press was brought to Bogotá by the Jesuits, and after this date there was an important intellectual awakening. Many colleges and universities had already been founded,—the first in 1554. The distinguished Spanish botanist José Celestino Mutis, in 1762, took the chair of mathematics and astronomy in the Colegio del Rosario, and under him were trained many scientists, including Francisco José de Caldas. An astronomical observatory was established, the first in America. In 1777 a public library was organized, and a theater in 1794. And of great influence was the visit of Humboldt in 1801. Among the works published in the second half of the eighteenth century mention should be made of the Lamentaciones de Pubén by the canon José María Grueso (1779-1835) and El placer público de Santa Fe (Bogotá, 1804) by José María Salazar (1785-1828).
During the revolutionary period two poets stand preeminent. Dr. José Fernández Madrid (d. 1830) was a physician and statesman, and for a short time president of the Republic. His lyrics are largely the expression of admiration for Bolivar and of hatred toward Spain: his verses are usually sonorous and correct (Poesías, Havana, 1822; London, 1828). The "Chénier" of Colombia was Luis Vargas Tejada (1802-1829), the author of patriotic verses, some of which were directed 288 against Bolivar, and of neo-classic tragedies. He died by drowning at the age of twenty-seven (Poesías, Bogotá, 1855).
The four most noted poets of Colombia are J.E. Caro, Arboleda, Ortiz and Gutiérrez González. A forceful lyric poet was José Eusebio Caro (1817-1853), a philosopher and statesman, a man of moral greatness and a devout Christian. In the bloody political struggles of his day he sacrificed his estate and his life to his conception of right. He sang of God, love, liberty and nature with exaltation; but all his writings evince long meditation. Like many Spanish-American poets of his day Caro was influenced by Byron. In his earlier verses he had imitated the style of Quintana (cf. El ciprés); but later, under the influence of romantic poets, he attempted to introduce into Spanish prosody new metrical forms. Probably as a result of reading English poetry, he wrote verses of 8 and 11 syllables with regular alternation of stressed and unstressed syllables, which is rare in Spanish. So fond did he become of lines with regular binary movement throughout that he recast several of his earlier verses (Obras escogidas, Bogotá, 1873; Poesías, Madrid, 1885).
Julio Arboleda (1817-1861), "Don Julio," was one of the most polished and inspired poets of Colombia. He was an intimate friend of Caro and like him a journalist and politician. He was a good representative of the chivalrous and aristocratic type of Colombian writers of the first half of the nineteenth century. His best work is the narrative poem Gonzalo de Oyón which, though incomplete, is the noblest epic poem that a native Spanish-American poet has yet given to the world. After studying in Europe he engaged in journalism and politics. He took part in several civil wars. A candidate for the presidency of the Republic, he was assassinated before election (Poesías, colección formada sobre los manuscritos originales, con prólogo por M.A. Caro, New York, 1883).
The educator and journalist José Joaquín Ortiz (1814-1892) 289 imitated Quintana in form but not in ideas. Though a defender of neo-classicism, he did not entirely reject romanticism. Ortiz was an ultra-catholic, sincere and ascetic. His verses are impetuous and grandiloquent, but often lacking depth of thought (Poesías, Bogotá, 1880).
The poet Gregorio Gutiérrez González, "Antioco" (1820-1872), was a jurist and politician. He began as an imitator of Espronceda and Zorrilla and is the author of several sentimental poems (Á Julia, ¿Por qué no canto? Una lágrima, et al.) that are the delight of Colombian young ladies. His fame will doubtless depend on the rustic Georgic poem, Memoria sobre el cultivo del maíz en Antioquia. This work is an interesting and remarkably poetic description of the homely life and labors of the Antioquian country folk (Poesías, Bogotá, 1881; Paris, 1908).
The minor poets of this generation are legion. Among these are: Manuel María Madiedo (b. 1815), a sociologist; Germán Gutiérrez de Piñeres (1816-1872), author of melancholy verses; José María Rojas Garrido (1824-1883), a noted orator, one-time president of Colombia; Joaquín Pablo Posada (1825-1880), perhaps the most clever versifier of Spanish America, but whose décimas were mostly written in quest of money; Ricardo Carrasquilla (b. 1827), an educator and author of genial verses; José Manuel Marroquín (b. 1827), a poet and author of articles on customs and a foremost humorist of South America (he was president when Colombia lost Panama); José María Samper (b. 1828), a most voluminous writer; Rafael Núñez (1825-1897), a philosopher and skeptic, and one-time president of the Republic; Santiago Pérez (1830-1900), educator, journalist and one-time president; José María Vergara y Vergara (1831-1872), a Catholic poet and author of a volume of sentimental verses (Libro de los cantares); Rafael Pombo (1833-1912), an eminent classical scholar and literary critic, and "perpetual secretary" of the Colombian Academy; 290 Diego Fallón (b. 1834), son of an English father, and author of several highly finished and beautiful poems; Pinzón Rico (b. 1834), author of popular, romantic songs; César Conto (b. 1836), a jurist and educator; Jorge Isaacs (1837-1895), better known as author of the novel María; and Felipe Pérez (b. 1834).
In the second half of the nineteenth century, the most eminent man of letters in Colombia has been Miguel Antonio Caro (1843-1909), a son of J.E. Caro. A neo-Catholic and "traditionalist," a learned literary critic and a poet, the younger Caro, like Bello before him and like his distinguished contemporary Rufino José Cuervo, has worked for purity of diction and classical ideals in literature. Caro is also the translator of several classic works, including one of Virgil which is recognized as the best in Spanish.
Other poets of the closing years of the century are: Diógenes Arrieta (b. 1848), a journalist and educator; Ignacio Gutiérrez Ponce (1850), a physician; Antonio Gómez Restrepo (b. 1856), a lawyer and politician; José María Garavito A. (b. 1860); José Rivas Groot (b. 1864), an educator and literary critic, and editor of La lira nueva; Joaquín González Camargo (b. 1865), a physician; Agripina Montes del Valle (b. about the middle of the nineteenth century) noted for her ode to the Tequendama waterfall, and Justo Pastor Ríos (1870-), a philosophic poet and liberal journalist.
The "modernista" poet José Asunción Silva (1860-1896) was a sweet singer, but he brought no message. He was fond of odd forms, such as lines of 8+8, 8+8+8 and 8+8+4 syllables (Poesías, con Prólogo de Miguelde Unamuno, Barcelona, 1908).
References: Cf.: Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., III, p. 1 f.; Blanco García, III, 332 f.; Juan Valera, Cartas Am., primera serie, p. 121 f.; Historia de la literatura (1538-1820) en Nueva Granada, José María Vergara y Vergara, Bogotá, 1867; Apuntes sobre bibliografía colombiana, 291 con muestras escogidas en prosa y verso, Isidoro Laverde Amaya, Bogotá, 1882; Parnaso colombiano, J.M. Vergara y Vergara, 3 vols.; La lira granadina, J.M. Vergara y Vergara, Bogotá, 1865; Parnaso colombiano, Julio Áñez, con Prólogo de José Rivas Groot, 2 vols., Bogotá, 1886-87; La lira nueva, J.M. Rivas Groot, Bogotá, 1886; Antología colombiana, Emiliano Isaza, Paris, 1895.
Ortiz: see preceding note.
Colombia y España: In this poem, dated July 20, 1882, the poet begins by recalling the war of independence that he witnessed as a boy and the heroic figure of Bolivar; then he laments the fratricidal struggles that rent the older and larger Colombia; and, finally, in the verses that are here given, he rejoices over the friendly treaty just made by the mother country, Spain, and Colombia, her daughter.
8. The colors of the Colombian flag are yellow, blue and red.
9. The colors of the Spanish flag are red and yellow. On the Spanish arms two castles (for Castilla) and two lions (for León) are pictured.
164.—J.E. Caro: see note to p. 162.
167.—Marroquin: see note to p. 162.
Los cazadores y la perrilla: compare with Goldsmith's "Elegy on the Death of a Mad Dog."
168.—7. Moratín: see note to p. 26. La caza is in Bibl. de Aut. Esp., II, 49 f.
169.—16. describilla, archaic or poetic for describirla.
171.—M.A. Caro: see note to p. 162.
174.—14-16. sombría... alcanzarán = (siendo la Eternidad) sombría y eterna, ni el odio ni el amor, ni la fe ni la duda, alcanzarán nada en sus abismos.
179.—Cuba. Although the literary output of Cuba is greater than that of some other Spanish-American countries, yet during the colonial period there was in Cuba a dearth of both prose and verse. The Colegio Semanario de San Carlos 292 y San Ambrosio was founded in 1689 as a theological seminary and was reorganized with lay instruction in 1769. The University of Havana was established by a papal bull in 1721 and received royal sanction in 1728; but for many years it gave instruction only in theological subjects. The first book printed in Cuba dates from 1720. Not till the second half of the eighteenth century did poets of merit appear in the island. Manuel de Zequeira y Arango (1760-1846) wrote chiefly heroic odes (Poesías, N.Y., 1829; Havana, 1852). Inferior to Zequeira was Manuel Justo de Rubalcava (1769-1805), the author of bucolic poems and sonnets (Poesías, Santiago de Cuba, 1848).
The Cuban poet Don José María Heredia (1803-1839) is better known in Europe and in the United States than Bello and Olmedo, since his poems are universal in their appeal. He is especially well known in the United States, where he lived in exile for over two years (1823-1825), at first in Boston and later in New York, and wrote his famous ode to Niagara. Born in Cuba, he studied in Santo Domingo and in Caracas (1812-1817), as well as in his native island. Accused of conspiracy against the Spanish government, he fled to the United States in 1823, and there eked out a precarious existence by giving private lessons. In 1825 he went to Mexico, where he was well received and where he held several important posts, including those of member of Congress and judge of the superior court. In Heredia's biography two facts should be stressed: that he studied for five years in Caracas, the city that produced Bolivar and Bello, respectively the greatest general and the greatest scholar of Spanish America; and that he spent only twelve years, all told, in Cuba. As he lived for fourteen years in Mexico, that country also claims him as her own, while Caracas points to him with pride as another child of her older educational system.
Heredia was most unhappy in the United States. He admired 293 the political institutions of this country; but he disliked the climate of New York, and he despaired of learning English. Unlike Bello and Olmedo he was not a classical scholar. His acquaintance with the Latin poets was limited, and seldom does a Virgilian or Horatian expression occur in his verses. Rather did he stand for the manner of Chateaubriand in France and Cienfuegos in Spain. Though strictly speaking not a romantic poet, he was a close precursor of that movement. His language is not seldom incorrect or lacking in sobriety and restraint; but his numbers are musical and his thought springs directly from imaginative exaltation.
Heredia's poorest verses are doubtless his early love-songs: his best are those in which the contemplation of nature leads the poet to meditation on human existence, as in Niágara, El Teocalli de Cholula, En una tempestad and Al sol. In these poems the predominant note is that of gentle melancholy. In Cuba his best known verses are the two patriotic hymns: Á Emilia and El himno del desterrado. These were written before the poet was disillusioned by his later experiences in the turbulent Mexico of the second and third decades of the nineteenth century, and they are so virulent in their expression of hatred of Spain that Menéndez y Pelayo refused to include them in his Anthology. Heredia undertook to write several plays, but without success. Some translations of dramatic works, however, were well received, and especially those of Ducis' Abufar, Chénier's Tibère, Jouy's Sila, Voltaire's Mahomet and Alfieri's Saul. The Garnier edition (Paris, 1893) of Heredia's Poesías contains an interesting introduction by the critic Elías Zerolo (Poesías, N.Y., 1825; Toluca, 1832; N.Y., 1875; Paris, 1893).
The mulatto poet Gabriel de la Concepción Valdés, better known by his pen-name "Plácido" (1809-1844), an uncultivated comb-maker, wrote verses which were mostly commonplace and often incorrect; but some evince remarkable 294 sublimity and dignity (cf. Plegaria á Dios). Cf. Poesías, Matanzas, 1838; Matanzas, 1842; Veracruz, 1845; Paris, 1857; Havana, 1886. The greatest Cuban poetess, and perhaps the most eminent poetess who has written in the Castilian language, is Gertrudis Gómez de Avellaneda y Arteaga (1814-1873). Since Avellaneda spent most of her life in Spain, an account of her life and work is given in the Introduction to this volume, p. xxxviii. Next only to Heredia, the most popular Cuban poet is José Jacinto Milanés y Fuentes (1814-1863), who gave in simple verse vivid descriptions of local landscapes and customs. A resigned and touching sadness characterizes his best verse (Obras, 4 vols., Havana, 1846; N.Y., 1865).
A lawyer, educator and patriot, Rafael María Mendive y Daumy (1821-1886) wrote musical verse in which there is spontaneity and true poetic feeling (Pasionarias, Havana, 1847; Poesías, Madrid, 1860; Havana, 1883). Joaquín Lorenzo Luaces (1826-1867) was more learned than most Cuban poets and fond of philosophizing. Some of his verse has force and gives evidence of careful study; but much is too pedantic to be popular (Poesías, Havana, 1857). A poet of sorrow, Juan Clemente Zenea,—"Adolfo de la Azucena" (1832-1871),—wrote verses that are marked by tender melancholy (Poesías, Havana, 1855; N.Y., 1872, 1874).
Heredia was not the only Cuban poet to suffer persecution. Of the seven leading Cuban poets, often spoken of as "the Cuban Pleiad," Avellaneda removed to Spain, where she married and spent her life in tranquillity; and Joaquín Luaces avoided trouble by living in retirement and veiling his patriotic songs with mythological names. On the other hand José Jacinto Milanés lost his reason at the early age of thirty years, José María Heredia and Rafael Mendive fled the country and lived in exile; while Gabriel Valdés and Juan Clemente Zenea were shot by order of the governor-general.
Since the disappearance of the "Pleiad," the most popular 295 Cuban poets have been Julián del Casal, a skeptic and a Parnassian poet who wrote pleasing but empty verses (Hojas al viento, Nieve, Bustos y Rimas); and Francisco Sellén, whose philosophy is to conceal suffering and to put one's hand to the plow again (Libro íntimo, Havana, 1865; Poesías, N.Y., 1890). José Martí (1853-1895) spent most of his life in exile; but he returned to Cuba and died in battle against the Spanish forces. He wrote excellent prose, but few verses (Flor y lava, Paris, 1910(?)).
References: Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Am., II, p. 1 f.; Blanco García, III, p. 290 f.; E.C. Hills, Bardos cubanos (contains a bibliography), Boston, 1901; Aurelio Mitjans, Estudio sobre el movimiento científico y literario en Cuba, Havana, 1890; Bachiller y Morales, Apuntes para la historia de las letras y de la instrucción pública de la Isla de Cuba, Havana, 1859; La poesía lírica en Cuba, M. González del Valle, Barcelona, 1900; Cuba poética, Havana, 1858; Parnaso cubano, Havana, 1881.
Heredia: see preceding note.
5. This is quite true. On the coast of central and southern Mexico the climate is tropical; on the central plateau it is temperate; and on the mountain slopes, as at the foot of Popocatepetl, it is frigid.
13-14. Iztaccíhual and Popocatepec are the popular names of these mountains, but their official names are Iztaccíhuatel and Popocatépetel. These words are of Nahuatlan origin: see in Vocab.
16—18. do... teñirse = donde el indio ledo los mira teñirse en púrpura ligera y oro.
181.—3. This poem was written in the fourth decade of the nineteenth century, when Mexico was torn by civil war. There was peace only when some military leader assumed despotic power.
21. Note that the moon set behind Popocatepec, a little to the south of west from Cholula, while the sun sank behind 296 Iztaccíhual, a little to the north of west from the city. This might well occur in summer.
182.—14. Fueron (lit. they were), they are no more. In this Latinism the preterit denotes that a thing or condition that once existed no longer exists. Cf. fuit Ilium (Æneid, II, 325), "Troy is no more."
186.—4-5. Que... seguir = que, en su vuelo, la turbada vista quiere en vano seguir.
190.—"Plácido": see note to p. 179.
Plegaria á Dios: this beautiful prayer was written a few days before the poet's death. It is said that "Plácido" recited aloud the last stanza on his way to the place of execution, and that he slipped to a friend in the crowd a scrap of cloth on which the prayer was written.
191.—4. del... transparencia = á (in) la clara transparencia del aire.
Avellaneda: see Introduction, p. xxxviii.
19. No... modelo = (la historia) no [dió] modelo á tu virtud en lo pasado.
21. otra = otra copia.
192.—1-2. Miró... victoria = la Europa miró al genio de la guerra y la victoria ensangrentar su suelo. The genio was Napoleon Bonaparte.
4. Al... cielo = el cielo le diera al genio del bien. Note that le is dative and al genio accusative. This otherwise admirable sonnet is marred by the numerous inversions of the word-order.
193.—Ecuador is a relatively small and mountainous country, lying, as the name implies, directly on the equator. The two principal cities are Guayaquil, a port on the Pacific coast, and Quito, the capital. Quito is beautifully situated on a plateau 9300 feet above the level of the sea. The climate is mild and salubrious, and drier than at Bogotá. The early Spanish colonists repeatedly wrote of the beautiful scenery and the "eternal spring" of Quito.
All of the present Ecuador belonged to the Virreinato del Perú till 1721, after which date Quito and the contiguous territory were governed from Bogotá. In 1824 Guayaquil and southern Ecuador were forcibly annexed to the first Colombia by Bolivar. Six years later Ecuador separated from Colombia and organized as a separate state.
In the territory now known as Ecuador the first colleges were established about the middle of the sixteenth century, by the Franciscans, for the natives, and by the Jesuits, as elsewhere in America, for the sons of Spaniards. Several chronicles by priests and other explorers were written during the early years of the colonial period; but no poet appears before the seventeenth century. In 1675 the Jesuit Jacinto de Evia published at Madrid his Ramillete de varias flores poéticas which contains, beside those by Evia, verses by Antonio Bastidas, a Jesuit teacher, and by Hernando Domínguez Camargo, a Colombian. The verses are mediocre or worse, and, as the date would imply, are imbued with culteranism.
The best verses of the eighteenth century were collected by the priest Juan de Velasco (1727-1819) and published in six volumes under the title of El ocioso de Faenza. These volumes contain poems by Bautista Aguirre of Guayaquil, José Orozco (La conquista de Menorca, an epic poem in four cantos), Ramón Viescas (sonnets, romances, décimas, etc.) and others, most of whom were Jesuits.
The expulsion of the Jesuits in 1767 caused the closure of several colleges in Ecuador, and for a time seriously hampered the work of classical education. But even before the edict of expulsion scientific study had been stimulated by the coming of French and Spanish scholars to measure a degree of the earth's surface at the equator. The coming of Humboldt in 1801 still further encouraged inquiry and research. The new spirit was given concrete expression by Dr. Francisco Eugenio de Santa Cruz y Espejo, a physician of native descent, in 298 El nuevo Luciano, a work famous in the literary and the political history of South America. In this work Dr. Espejo attacked the prevailing educational and economic systems of the colonies, and his doctrine did much to start the movement toward secession from the mother country.
Although the poetry of Ecuador is of relatively little importance as compared with that of several other American countries, yet Ecuador gave to the world one of the greatest of American poets, José Joaquín de Olmedo. In the Americas that speak Castilian, Olmedo has only two peers among the classic poets, the Venezuelan Bello and the Cuban Heredia. Olmedo was born in Guayaquil in 1780, when that city still formed part of the Virreinato del Perú. Consequently, two countries claim him,—Peru, because he was born a Peruvian, and because, furthermore, he received his education at the Universidad de San Marcos in Lima; and Ecuador, since Guayaquil became permanently a part of that republic, and Olmedo identified himself with the social and political life of that country. In any case, Olmedo, as a poetic genius, looms suddenly on the horizon of Guayaquil, and for a time after his departure there was not only no one to take his place, but there were few followers of note.
Olmedo ranks as one of the great poetic artists of Spanish literature at the beginning of the nineteenth century. He is of the same semi-classic school as Quintana, and like him devoted to artistic excellence and lyric grandiloquence. The poems of Olmedo are few in number for so skilled an artist, and thoroughly imbued with the Græco-Latin classical spirit. His prosody nears perfection; but is marred by an occasional abuse of verbal endings in rime, and the inadvertent employment of assonance where there should be none, a fault common to most of the earlier Spanish-American poets. Olmedo's greatest poem is La victoria de Junín, which is filled with sweet-sounding phrases and beautiful images, but is logically 299 inconsistent and improbable. Even Bolivar, the "Libertador," censured Olmedo in a letter for using the machina of the appearance at night before the combined Colombian and Peruvian armies of Huaina-Capac the Inca, "showing himself to be a talkative mischief-maker where he should have been lighter than ether, since he comes from heaven," and instead of desiring the restoration of the Inca dynasty, preferring "strange intruders who, though avengers of his blood, are descendants of those who destroyed his empire."
The Canto al general Flores is considered by some critics to be the poet's most finished work, though of less substance and inspiration than La victoria de Junín. This General Flores was a successful revolutionary leader during the early days of the Republic; and he was later as bitterly assailed by Olmedo as he is here praised. Of a different type is the philosophic poem, Á un amigo en el nacimiento de su primogénito, which is filled with sincere sympathy and deep meditation as to the future. With the coming of middle age Olmedo's poetic vein had apparently been exhausted, and the Peruvian bard Felipe Pardo addressed to him an ode in which he sought, though to no avail, to stimulate the older poet to renewed activity (Poesías, Valparaíso, 1848, Paris, 1853; Poesías inéditas, Lima, 1861).
For a time after Olmedo's muse had become mute, little verse of merit was produced in Ecuador. Gabriel García Moreno (1821-1875), once president of the Republic and a champion of Catholicism, wrote a few strong satires in the style of Jovellanos. Dolores Veintemilla de Galindo (1831-1857), who committed suicide on account of domestic infelicity, left a short poem, Quejas, which is unique in the older Spanish-American literature by reason of its frank confession of feeling. The reflexive and didactic poet Numa P. Llona (1832-___) was the author of passionate outpourings of doubt and despair after the fashion of Byron and Leopardi 300 (Poesías, Paris, 1870; Cantos americanos, Paris, 1866; Cien sonetos, Quito, 1881). The gentle, melancholy bard, Julio Zalumbide (1833-1887), at first a skeptic and afterwards a devout believer in Christianity, wrote musical verse in correct language but of little force. Juan León Mera (1832-1894) was one of the most prominent literary historians and critics of the Republic. Besides his Poesías (2d ed., Barcelona, 1893), León Mera left a popular novel, Cumandá (Quito, 1876; Madrid, 1891), an Ojeada histórico-crítica sobre la poesía ecuatoriana (2d ed., Barcelona, 1893), and a volume of Cantares del Pueblo (Quito, 1892), published by the Academia del Ecuador, which contains, in addition to many semi-popular songs in Castilian, a few in the Quichua language.
A younger generation that has already done some good work in poetry includes Vicente Pedrahita, Luis Cordero, Quintiliano Sánchez and Remigio Crespo y Toral.
References: Men. Pel., Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., III, p. lxxxiii f.; Blanco García, III, 350 f.; Ensayo sobre la literatura ecuatoriana, Dr. Pablo Herrera, Quito, 1860; Ojeada histórico-crítica sobre la poesía ecuatoriana, Juan León Mera, Quito, 1868, 2d ed., Barcelona, 1893; Escritores españoles é hispano-americanos, Cañete, Madrid, 1884; Lira ecuatoriana, Vicente Emilio Molestina, Guayaquil, 1865; Nueva lira ecuat., Juan Abel Echeverría, Quito, 1879; Parnaso ecuat., Manuel Gallegos Naranjo, Quito, 1879; América poética, Juan María Gutiérrez, Valparaíso, 1846 (the best of the early anthologies: contains a few poems by Olmedo); Antología ecuat., published by the Academy of Ecuador, with a second volume entitled Cantares del pueblo ecuat. (Edited by Juan León Mera), both Quito, 1892.
Peru. The literature of Ecuador is so closely associated with that of Peru, that the one cannot be properly treated without some account of the other. The Virreinato del Perú was the wealthiest and most cultivated Spanish colony in South America, and in North America only Mexico rivaled it in influence. Lima, an attractive city, thoroughly Andalusian 301 in character and appearance, was the site of important institutions of learning, such as the famed Universidad de San Marcos. It had, moreover, a printing-press toward the close of the sixteenth century, a public theater by 1602, and a gazette by the end of the seventeenth century. The spread of learning in colonial Peru may be illustrated by the fact that the Jesuits alone, at the time of their expulsion in 1767, had twelve colleges and universities in Peru, the oldest of which dated from the middle of the sixteenth century and offered courses in philosophy, law, medicine and theology.
The Peruvians seem to have been content with their lot as a favored Spanish colony, and they declared for independence only when incited to do so and aided by Bolivar of Colombia and San Martin of Buenos Aires. After the revolution, Peru was torn by internal discord rather more than other Spanish-American countries during the period of adolescence; and it was its misfortune to lose territory after territory. Bolivar took northern Peru, including the valuable seaport of Guayaquil, and made it a part of the first Colombia; and largely through the influence of Bolivar much of Upper Peru was made a separate republic, that of Bolivia. Lastly, Chile, for centuries a dependency of Peru, became independent and even wrested a considerable stretch of the litoral from her former mistress. It is hard to realize that Peru, to-day relatively weak among the American countries, was once the heart of a vast Inca empire and later the colony whose governors ruled the territories of Argentina and Chile to the south, and of Ecuador and Colombia to the north. With the decline of wealth and political influence there has come to Peru a decadence in letters. Lima is still a center of cultivation, a city in which the Castilian language and Spanish customs have been preserved with remarkable fidelity; but its importance is completely eclipsed by such growing commercial centers as Buenos Aires, 302 Montevideo and Santiago de Chile, and by relatively small and conservative towns such as Bogotá.
In the sixteenth century Garcilasso Inga de la Vega (his mother was an "Inga," or Inca, princess), who had been well trained in the Latin classics by Spanish priests, wrote in excellent prose his famous works, Florida del Inca, Comentarios reales and Historia general del Perú. The second work, partly historical and largely imaginary, purports to be a history of the ancient Incas, and pictures the old Peru as an earthly paradise. This work has had great influence over Peruvian and Colombian poets. Menéndez y Pelayo (Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., III, Introd.) considers Garcilasso, or Garcilaso, and Alarcón the two truly classic writers that America has given to Spanish literature.
In the Golden Age of Spanish letters several Peruvian poets were known to Spaniards. Cervantes, in the Canto de Calíope and Lope de Vega in the Laurel del Apolo make mention of several Peruvians who had distinguished themselves by their verses.
An unknown poetess of Huanuco, Peru, who signed herself "Amarilis," wrote a clever silva in praise of Lope, which the latter answered in the epistle Belardo á Amarilis. This silva of "Amarilis" is the best poetic composition of the early colonial period. Another poetess of the period, also anonymous, wrote in terza rima a Discurso en loor de la poesía, which mentions by name most of the Peruvian poets then living.
Toward the close of the sixteenth century and in the early decades of the seventeenth century, several Spanish scholars, mostly Andalusians of the Sevillan school, went to Peru, and there continued literary work. Among these were Diego Mexía, who made the happiest of Spanish translations of Ovid's Heroides; Diego de Ojeda, the best of Spanish sacred-epic poets, author of the Cristiada; Juan Gálvez; Luis de Belmonte, author of La Hispálica; Diego de Avalos y Figueroa 303 whose Miscelánea austral (Lima, 1603) contains a long poem in ottava rima entitled Defensa de damas; and others. These men exerted great influence, and to them was largely due the peculiarly Andalusian flavor of Peruvian poetry.
The best Gongoristic Poetics came from Peru. This is the Apologético en favor de D. Luis de Góngora (Lima, 1694), by Dr. Juan de Espinosa Medrano.
In the eighteenth century the poetic compositions of Peru were chiefly "versos de circunstancias" by "poetas de ocasión." Many volumes of these were published, but no one reads them to-day. Their greatest fault is excessive culteranism, which survived in the colonies a half-century after it had passed away from the mother country. The most learned man of the eighteenth century in Peru was Pedro de Peralta Barnuevo, the erudite author of some fifty volumes of history, science and letters. His best known poem is the epic Lima fundada (Lima, 1732). He wrote several dramas, one of which, Rodoguna, is Corneille's play adapted to the Spanish stage, and has the distinction of being one of the first imitations of the French stage in Spanish letters. All in all, the literary output of Peru during the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries is disappointingly small in quantity and poor in quality, in view of the important position held by this flourishing colony. The Peruvian writers, then and now, lack in sustained effort.
During and immediately following the revolutionary period, the greatest poet is Olmedo, who was born and educated in Peru and became a citizen first of the primitive Colombia and then of Ecuador, only as his native city, Guayaquil, formed a part of one political division after another. It is customary, however, to consider Olmedo a poet of Ecuador, and it is so done in this volume.
After Olmedo, the commanding figure among the classical poets of Peru is Felipe Pardo y Aliaga (1806-1868). Pardo was educated in Spain, where he studied with Alberto Lista. 304 From his teacher he acquired a fondness for classical studies and a conservatism in letters that he retained throughout his life. In his later years he was induced to adopt some of the metrical forms invented or revived by the romanticists, but in spirit he remained a conservative and a classicist. He had a keen sense of wit and a lively imagination which made even his political satires interesting reading. Besides his Poesías y escritos en prosa (Paris, 1869), Pardo left a number of comedies portraying local types and scenes which are clever attempts at imitation of Spanish drama. As with all the earlier poets of Spanish America, literature was only a side-play to Pardo, although it probably took his time and attention even more than the law, which was his profession. A younger brother, José (1820-1873), wrote a few short poems, but his verses are relatively limited and amateurish. Manuel Ascensión Segura (1805-1871) wrote clever farces filled with descriptions of local customs, somewhat after the type of the modern género chico (Artículos, poesías y comedias, Lima, 1866).
The romantic movement came directly from Spain to Peru and obtained a foothold only well on toward the close of the first half of the century. The leader of the Bohemian romanticists of Lima was a Spaniard from Santander, Fernando Velarde. Around him clustered a group of young men who imitated Espronceda and Zorrilla and Velarde with great enthusiasm. For an account of the "Bohemians" of the fourth and fifth decades in Lima [Numa Pompilio Llona (b. 1832), Nicolás Corpancho (1830-1863), Luis Benjamín Cisneros (b. 1837), Carlos Augusto Salaverry (1830-1891), Manuel Ascensión Segura (b. 1805), Clemente Althaus (1835-1881), Adolfo García (1830-1883), Constantino Carrasco (1841-1877) and others, see the introduction to the Poesías (Lima, 1887) of Ricardo Palma (1833-___: till 1912 director of the national library of Peru).]
Not often could the romanticists of America go back to 305 indigenous legend for inspiration as their Spanish cousins so often did; but this Constantino Carrasco undertook to do in his translation of the famous Quichua drama, Ollanta. It was long claimed, and many still believe, that this is an ancient indigenous play; but to-day the more thoughtful critics are inclined to consider it an imitation of the Spanish classical drama, perhaps written in the Quichua language by some Spanish priest (Valdés?). The 8-syllable lines, the rime-scheme and the spirit of the play all suggest Spanish influence. In parenthesis it should be added that Quichua verse is still cultivated artificially in Peru and Ecuador.
The two men of that generation who have most distinguished themselves are Pedro Paz-Soldán y Unanue, "Juan de Arona" (1839-1894), a poet of satire and humor; and Ricardo Palma (1833-___) a leading scholar and literary critic, best known for his prose Tradiciones peruanas (Lima, 1875 and 1899).
The strongest representative of the present-day "modernistas" in Peru is José Santos Chocano (1867-___), a disciple of Darío. Chocano writes with much grandiloquence. His many sonnets are mostly prosaic, but some are finished and musical (cf. La magnolia). He is more Christian (cf. Evangeleida) than most of his contemporaries, and he sings of the conquistadores with true admiration [cf. En la aldea, Lima, 1895; Iras santas, Lima, 1895; Alma América (Prólogo de Miguel de Unamuno), Madrid, 1906; La selva virgen, Paris, 1901; Fiat lux, Paris, 1908].
A younger man is Edilberto Zegarra Ballón of Arequipa (1880-___), author of Vibraciones, Poemas, el al. His verse is simpler and less rugged than that of the more virile Chocano.
References: Men. Pel., Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., III, p. cxlix f.; Blanco García, III, 362 f.; Diccionario histórico y biográfico del Perú, formado y redactado por Manuel de Mendíburu, 9 vols., Lima, 1874-80; Colección de documentos literarios del Perú, 11 vols., Manuel de Odriozola, 306 Lima, 1863-74; América poética, Juan María Gutiérrez, Valparaíso, 1846; Parnaso peruano, J.D. Cortés, Paris, 1875; La Bohemia limeña de 1848 á 1860, Prólogo de Poesías de Ricardo Palma, Lima, 1887; Lira americana, Ricardo Palma, Paris, 1865.
193.—Olmedo: see preceding note.
8. Á, with.
194.—15-17. The following is a translation of a note to these lines which is given in Poesías de Olmedo, Garnier Hermanos, Paris, 1896: "Physicists have attempted to explain the equilibrium that is maintained by the earth in spite of the difference of mass in its two hemispheres" (northern and southern). "May not the enormous weight of the Andes be one of the data with which this curious problem of physical geography can be solved?"
195.—4. The religion of the ancient Peruvians, before they were converted to Christianity by the Spaniards, was based on the worship of the sun. The chief temple of the sun was at Cuzco.
25. Bolivar was a native of Caracas, Venezuela; but, when this poem was written, Colombia comprised most of the present States of Venezuela, Colombia, Panama and Ecuador. Moreover, Colombia is probably used somewhat figuratively by the poet to designate the "land of Columbus."
26. The Peruvians and the Colombians were allies. It is an interesting fact that in the war for independence waged by the Spanish Americans against Spain, the leaders of the Americans were nearly all of Spanish descent, while the majority of the rank and file of the American soldiery was Indian. To this day, a majority of the population of Spanish America, excepting only Chile, Argentina and the West Indian Islands, is indigenous, and their poets still sing of "indigenous America," but they sing in the Spanish tongue! See p. 211, l. 7.
196.—21. See note to p. 162, l. 8. The Peruvian flag has an image of the sun in its center.
23. It is reported that the first onslaught of the Spanish-American cavalry failed, partly by reason of their impetuousness, and that they would probably have been defeated if Bolivar had not rallied them and led them on to victory.
198.—10. The battle of Junin began at about five o'clock in the afternoon, and it is said that only night saved the Spaniards from complete destruction.
11. El dios oía: destiny did not permit the god to stay his course for an hour, but the god left behind him his circlet of diamonds (the stars).
199.—Mexico. The Virreinato de Nueva España was a favored colony, where Spanish culture took deepest root. It had the first institution of learning in America (opened in 1553 by decree of Charles I) and the first printing-press (1540?). Some 116 books were printed in Mexico City during the sixteenth century, most of which were catechisms or grammars and dictionaries in the native languages. In the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries several Spanish poets, mostly Sevillans, went to Mexico. Among these were Diego Mexía (went to Mexico in 1596); Gutierre de Cetina, Juan de la Cueva, and Mateo Alemán (published Ortografía castellana in Mexico in 1609). Certámenes poéticos ("poetic contests") were held in Mexico, as in other Spanish colonies, from time to time. The first of importance occurred in Mexico City in 1583, to which seven bishops lent the dignity of their presence and in which three hundred poets (?) competed. After the discovery and conquest of the Philippines, great opulence came to Mexico on account of its being on a direct route of Pacific trade between Europe and Asia, and Mexico became an emporium of Asiatic goods (note introduction of Mexican dollar into China).
The first native poet deserving of the name was Francisco 308 de Terrazas (cf. Cervantes, Canto de Calíope, 1584), who left in manuscript sonnets and other lyrics and an unfinished epic poem, Nuevo mundo y conquista. It is interesting that in the works of Terrazas and other native poets of the sixteenth century the Spaniards are called "soberbios," "malos," etc. Antonio Saavedra Guzmán was the first in Mexico to write in verse a chronicle of the conquest (El peregrino indiano, Madrid, 1599). Coloquios espirituales (published posthumously in 1610), autos of the "morality" type, with much local color and partly in dialect, were written by Fernán González Eslava, whom Pimentel considers the best sacred dramatic poet of Mexico. Sacred dramatic representations had been given in Spanish and in the indigenous languages almost from the time of the conquest. According to Beristain, at least two plays of Lope were done into Nahuatl by Bartolomé de Alba, of native descent, and performed, viz.: El animal profeta y dichoso parricida and La madre de la Mejor.
The first poet whose verses are genuinely American, exotic and rich in color like the land in which written (a rare quality in the Spanish poetry of the period), was Bernardo de Balbuena (1568-1627: born in Spain; educated in Mexico). Balbuena had a strong descriptive faculty, but his work lacked restraint (cf. Grandeza mexicana, Mex., 1604; Madrid, 1821, 1829 and 1837; N.Y., 1828; Mex., 1860). The great dramatist, Juan Ruiz de Alarcón (1581?-1639), was born and educated in Mexico; but as he wrote in Spain, and his dramas are Spanish in feeling, he is best treated as a Spanish poet.
Next only to Avellaneda the most distinguished Spanish-American poetess is the Mexican nun, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz (1651-1695), whose worldly name was Juana Inés de Asbaje y Ramírez de Cantillana. Sor Juana had intellectual curiosity in an unusual degree and early began the study of Latin and other languages. When still a young girl she became a maid-in-waiting in the viceroy's palace, where her beauty 309 and wit attracted much attention; but she soon renounced the worldly life of the court and joined a religious order. In the convent of San Jerónimo she turned for solace to books, and in time she accumulated a library of four thousand volumes. Upon being reproved by a zealous bishop for reading worldly books, she sold her entire library and gave the proceeds to the poor. Sor Juana's better verses are of two kinds: those that give evidence of great cleverness and mental acuteness, and those that have the ring of spontaneity and sincerity. As an exponent of erotic mysticism, she is most interesting. In the most passionate of her erotic verses there is an apparent sincerity which makes it difficult for the lay reader to believe that she had not been profoundly influenced by human love,—as when she gives expression to the feelings of a loving wife for a dead husband, or laments the absence of a lover or tells of a great jealousy. In addition to her lyrics Sor Juana wrote several autos and dramas. Her poems were first published under the bombastic title of Inundación castálida de la única poetisa, Musa décima, Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz, Madrid, 1689 (vol. II, Seville, 1691; vol. III, Madrid, 1700).
During the first half of the eighteenth century the traditions of the preceding century persisted; but in the second half there came the neo-classic reaction. Among the best of the prosaic poets of the century are: Miguel de Reyna Zeballos (La elocuencia del silencio, Madrid, 1738); Francisco Ruiz de León (Hernandía, 1755, based on the Conquista de México by Solís); and the priest Jorge José Sartorio (1746-1828: Poesías sagradas y profanas, 7 vols., Puebla, 1832). The Franciscan Manuel de Navarrete (1768-1809) is considered by Pimentel superior to Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz as a philosophic poet (the writer of this article does not so consider him) and is called the "restorer of lyric and objective poetry in Mexico" (cf. Pim., Hist. Poesía Mex., p. 442). Navarrete wrote in a variety of styles. His verses are harmonious, but altisonante 310 and often incorrect. His best lyrics, like those of Cienfuegos, have the personal note of the romanticists to follow (Entretenimientos poéticos, Mex., 1823, Paris, 1835; Poesías, Mex., 1905).
There were no eminent Mexican poets during the revolutionary period. Andrés Quintana Roo (1787-1851) was a lawyer and journalist and president of the congress which made the first declaration of independence. Pimentel (p. 309) calls him an eminent poet and one of the best of the period. Two of the most important in the period are: Manuel Sánchez de Tagle (1782-1847), a statesman given to philosophic meditation, but a poor versifier (Poesías, 1852); and Francisco Ortega (1793-1849), an ardent republican, who opposed Iturbide when the latter had himself proclaimed emperor of Mexico in 1821 (Poesías líricas, 1839; cf. Á Iturbide en su coronación). To these should be added Joaquín María del Castillo y Lanzas (1781-1878), one-time minister to the United States (Ocios juveniles, Philadelphia, 1835); and the priest Anastasio María Ochoa (1783-1833), who translated French, Italian, and Latin (Ovid's Heroides) works, and wrote some humorous verses (Poesías, N.Y., 1828: contains two dramas).
Next to Alarcón, the greatest dramatist that Mexico has produced is Manuel Eduardo de Gorostiza (1789-1851), who wrote few lyric verses, but many dramas in verse and prose. His plays, which are full of humorous contrasts, were written during his residence in Spain and are, for the most part, typically Spanish in all respects. Gorostiza, in manner and style, is considered a bridge between Moratín and Bretón. His best comedy is La indulgencia para todos (cf. Teatro original, Paris, 1822; Teatro escogido, Bruxelles, 1825; Obras dramáticas, Bibl. Aut. Mex., vols. 22, 24, 26, 45, Mex.,-1899).
Romanticism came into Mexico through Spain. It was probably introduced by Ignacio Rodríguez Galván (1816-1842), 311 a translator, lyric poet, and dramatist. His lyrics have the merit of sincerity; pessimism is the prevailing tone and there is much invective. His Profecías de Guatimoc is considered the masterpiece of Mexican romanticism (Obras, 2 vols., Mex., 1851; Paris, 1883). Another well-known romantic lyricist and dramatist is Fernando Calderón (1809-1845), who was more correct in form than Rodríguez Galvan (Poesías, Mex., 1844 and 1849; Paris, 1883; Mex., 1902).
The revival of letters in Mexico is generally attributed to the conservative poets Pesado and Carpio, both of whom sought to be classic, although they were not altogether so in practise. Probably the best known Mexican poet, though certainly not the most inspired, is José Joaquín Pesado (1801-1861). He translated much from Latin, French and Italian, and in some cases failed to acknowledge his indebtedness (cf. Pimentel, p. 694). His best translations are of the Psalms. The Aztecas, which were published as a translation of, or an adaptation from, indigenous legends, are mostly original with Pesado in all probability. He is an unusually even writer, and some of his verses are good (cf. certain sonnets: Mi amada en la misa del alba, which reminds one of Meléndez Valdés in Rosana en los fuegos; Elegía al ángel de la guardia de Elisa; and parts of La revelación in octavas reales). Montes de Oca and Menéndez y Pelayo consider Pesado the greatest of Mexican poets; but Pimentel does not (p. 694). Cf. Poesías originales y traducciones, Mex., 1839-40 (most complete), 1886 (introduction of Montes de Oca); Biografía de Pesado, by José María Roa Bárcena, Mex., 1878. Manuel Carpio (1791-1860) began to write verses after he had reached the age of forty years, and there is, consequently, a certain ripeness of thought and also a lack of feeling in his poetry. His verses are chiefly narrative or descriptive and generally treat of biblical subjects. His language is usually correct, but often prosaic (Poesías, Mex., 1849).
Minor poets of this period are: Alejandro Arango (1821-1883), an imitator of León (Versos, 1879; Ensayo histórico sobre Fr. Luis de León, Mex., 1866); Ignacio Ramírez (1818-1879), of Indian race, who was a free lance in religion and politics, and largely responsible for the separation of Church and State in Mexico (Poesías, Mex., 1889, and Lecciones de literatura, Mex., 1884); and Ignacio M. Altamarino (1834-1893), an erotic and descriptive poet (Obras, Mex., 1899).
The most popular Mexican poets during the second half of the nineteenth century have been Acuña, Flores, Peza and Gutiérrez Nájera. A materialistic iconoclast, Manuel Acuña (1849-1873) was uneven and incorrect in language, but capable of deep poetic feeling. In his Poesías (Garnier, Paris, 8th ed.) there are two short poems that may live: Nocturno, a passionate expression of disappointment in love; and Ante un cadáver, a poem of dogmatic materialism. Acuña committed suicide at the age of twenty-four years. Manuel María Flores (1840-1885), an erotic poet largely influenced by Musset, is very popular in Mexico (Pasionarias, Paris, 1911). Probably the most widely read poet of the period is Juan de Dios Peza (1852-1910). His verses are often incorrect and weak, as he improvised much; but they are interesting, as they usually treat of homely topics (Poesías completas: El arpa del amor, 1891; Hogar y patria, 1891; Leyendas, 1898; Flores del alma; Recuerdos y esperanzas, 1899, Garnier, Paris). The romantic pessimist, Manuel Gutiérrez Nájera (d. 1888), was tormented throughout life by the vain quest of happiness and the thirst of truth. His verses, which are often elegiac or fantastic, are highly admired by the younger generation of Mexican poets. In a letter to the writer of this article, Blanco-Fombona praises Gutiérrez Nájera above all other Mexican poets (Poesías, Paris, 1909, 2 vols.).
References: Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., I, p. xiv f.: Blanco García, III, 304 f.; Francisco Pimentel, Historia crítica de la 313 poesía en México, Mex., 1892; Biblioteca hispano-americana septentrional, D. José Mariano Beristain de Souza, Mex., 1816-21, 3 vols. (has more than 4000 titles),—reprinted by Fortino Hipólito de Vera, Amecameca, 1883; Bibliografía mexicana del siglo XVI (catálogo razonado de los libros impresos in México de 1539 á 1600); Biografías de mexicanos distinguidos, D. Francisco Sosa, Mex., 1884; Poetas yucatecos y tabasqueños, D. Manuel Sánchez Mármol y D. Alonso de Regil y Peón, Mérida de Yucatán, 1861; Poetisas mexicanas, Bogotá, 1889; Colección de poesias mexicanas, Paris, 1836; El parnaso mexicano, 36 vols., R.B. Ortega, Mex., 1886; Biblioteca de autores mexicanos, some 75 vols. to 1911, Mex.; Antología de poetas mexicanos, publ. by Acad. Mex., Mex., 1894; Poetas mexicanos, Carlos G. Amézaga, Buenos Aires, 1896; Los trovadores de México, Barcelona, 1900.
Pesado: see preceding note.
La Serenata: see Introduction, Versification, p. lxviii.
200.—6-11. These lines of Pesado are similar to those found in the first stanzas of Su alma by Milanés. See Hills' Bardos cubanos (Boston, 1901), p. 69.
Calderón: see note to p. 199.
202.—Acuña: see note to p. 199.
204.—15. The language is obscure, but the meaning seems to be: borrarte (á ti que estás) en mis recuerdos.
19. The forced synalepha of yo haga is discordant and incorrect.
204.—23 to 205.—8. That is, when the altar was ready for the marriage ceremony, and the home awaited the bride. The reference, apparently, is to a marriage at an early hour in the morning,—a favored time for marriages in Spanish lands.
206.—1. la alma, by poetic license, since el alma would make the line too long by one syllable.
207.—Peza: see note to p. 199.
211.—Darío: with the appearance in 1888 of a small volume of prose and verse entitled Azul, by Rubén Darío (1864-) of Nicaragua, there triumphed in Spanish America the "movement 314 of emancipation," the "literary revolution," which the "decadents" had already initiated in France. As romanticism had been a revolt against the empty formalism of later neo-classicism, so "decadence" was a reaction against the hard, marmoreal forms of the "Parnasse," and in its train there came inevitably a general attack on poetic traditions. This movement was hailed with joy by the young men of Latin America, who are by nature more emotional and who live in a more voluptuous environment than their cousins in Spain; for they had come to chafe at the coldness of contemporary Spanish poetry, at its lack of color and its "petrified metrical forms." With the success of the movement there was for a time a reign of license, when poet vied with poet in defying the time-honored rules, not only of versification, but also of vocabulary and syntax. But as in France, so in Spanish America, "decadence" has had its day, although traces of its passing are everywhere in evidence, and the best that was in it still lingers.
To-day the Spanish-American poets are turning their attention more and more to the study of sociological problems or to the cementing of racial solidarity. These notes ring clear in some recent poems of Darío, and of José S. Chocano of Peru and Rufino Blanco-Fombona of Venezuela. The lines given in the text are an ode which was addressed to Mr. Roosevelt when he was president of the United States from 1901 to 1909. The meter of the poem is mainly the Old Spanish Alexandrine, but with a curious intermingling of lines of nine, ten and eight syllables, and with assonance of the even lines throughout. In all fairness it should be stated here that Señor Darío, in a recent letter to the writer of these Notes, said: "I do not think to-day as I did when I wrote those verses" (Darío: Epístolas y poemas, 1885; Abrojos, 1887; Azul, 1888; Cantos de vida y esperanza, Madrid, 1905; El canto errante, Madrid, 1907).
212.—8. Argentina and Chile are the most progressive of the Spanish-American States. The Argentine flag is blue and white, with a sun in the center; the flag of Chile has a white and a red bar, and in one corner a white star on a blue background.
11. This refers, of course, to the colossal bronze Statue of Liberty by the French sculptor, Frédéric Bartholdi, which stands in New York harbor.
14. In a letter to the writer of these Notes, Senor Darío explains this passage as follows: "Bacchus, or Dionysius, after the conquest of India (I refer to the semi-historical and not to the mythological Bacchus) is supposed to have gone to other and unknown countries. I imagine that those unknown countries were America. Pan, who accompanied Bacchus on his journey, taught those new men the alphabet. All this is related to the tradition of the arrival of bearded men, strangely dressed, in the American countries.... These traditions exist in the South as well as the North."
16. Que consultó los astros: the ancient Peruvians and Mexicans had made considerable progress in the study of astronomy.
214.—Venezuela. During the colonial period the development of literary culture was slower in the Capitanía de Caracas than in Colombia, Peru and Mexico. The Colegio de Santa Rosa, which was founded at Caracas in 1696, was made a university in 1721. Not till 1806 was the first printing-press set up in the colony.
Poetry in Venezuela begins with Bello, for the works of his predecessors had little merit. Andrés Bello (1781-1865) was the most consummate master of poetic diction among Spanish-American poets, although he lacked the brilliancy of Olmedo and the spontaneity of Heredia. Born in Caracas and educated in the schools of his native city, Bello was sent to England in the year 1810 to further the cause of the revolution, and he remained in that country till 1829, when he was called to 316 Chile to take service in the Department of Foreign Affairs. His life may, therefore, be divided into three distinct periods. In Caracas he studied chiefly the Latin and Spanish classics and the elements of international law, and he made metrical translations of Virgil and Horace. Upon arriving in England at the age of twenty-nine years, he gave himself with enthusiasm to the study of Greek, Italian and French, as well as to English. Bello joined with the Spanish and Hispano-American scholars in London in the publication of several literary reviews, notably the Censor americano (1820), the Biblioteca americana (1823) and the Repertorio americano (1826-27), and in these he published many of his most important works. Here appeared his studies of Old French and of the Song of My Cid, his excellent translation of fourteen cantos of Boiardo's Orlando innamorato, several important articles on Spanish syntax and prosody, and the best of all his poems, the Silvas americanas.
In 1829, when already forty-eight years of age, Bello removed to Chile, and there entered upon the happiest period of his life. Besides working in a government office, he gave private lessons until in 1831 he was made rector of the College of Santiago. In the year 1843 the University of Chile was established at Santiago and Bello became its first rector. He held this important post till his death twenty-two years later at the ripe age of eighty-four. During this third and last period of his life Bello completed and published his Spanish Grammar and his Principles of International Law, works which, with occasional slight revisions, have been used as standard text-books in Spanish America and to some extent in Spain, to the present day. The Grammar, especially, has been extraordinarily successful, and the edition with notes by José Rufino Cuervo is still the best text-book of Spanish grammar we have. In the Grammar Bello sought to free Castilian from Latin terminology; but he desired, most of all, 317 to correct the abuses so common to writers of the period and to establish linguistic unity in Spanish America.
Bello wrote little original verse during these last years of his life. At one time he became exceedingly fond of Victor Hugo and even tried to imitate him; but his classical training and methodical habits made success impossible. His best poetic work during his residence in Chile, however, are translations of Victor Hugo, and his free metrical rendering of La Prière pour tous (from the Feuilles d'automne), is amongst his finest and most popular verses.
It is interesting that Andrés Bello, the foremost of Spanish-American scholars in linguistics and in international law, should also have been a preëminent poet, and yet all critics, except possibly a few of the present-day "modernistas," place his American Silvas amongst the best poetic compositions of all Spanish America. The Silvas are two in number: the Alocución á la poesía and the Silva á la agricultura de la zona tórrida. The first is fragmentary: apparently the poet despaired of completing it, and he embodied in the second poem an elaboration of those passages of the first work which describe nature in the tropics. The Silvas are in some degree imitations of Virgil's Georgics, and they are the best of Spanish imitations. Menéndez y Pelayo, who is not too fond of American poets, is willing to admit (Ant., II, p. cxlii) that Bello is, "in descriptive and Georgic verse, the most Virgilian of our (Spanish) poets." Caro, in his splendid biography of Bello (in Miguel Antonio Caro's introduction to the Poesías de Andrés Bello, Madrid, 1882) classifies the Silvas as "scientific poetry," which is quite true if this sort of poetry gives an esthetic conception of nature, expressed in beautiful terms and adorned with descriptions of natural objects. It is less true of the Alocución, which is largely historical, in that it introduces and sings the praises of towns and persons that won fame in the revolutionary wars. The Silva á la agricultura, 318 which is both descriptive and moral, may be best described in the words of Caro. It is, says this distinguished critic, "an account of the beauty and wealth of nature in the tropics, and an exhortation to those who live in the equator that, instead of wasting their strength in political and domestic dissensions, they should devote themselves to agricultural pursuits." Bello's interest in nature had doubtless been stimulated by the coming of Humboldt to Caracas in the first decade of the nineteenth century. In his attempt to express his feeling for nature in poetic terms, he probably felt the influence not only of Virgil, but also of Arriaza, and of the several poems descriptive of nature written in Latin by Jesuit priests, such as the once famous Rusticatio Mexicana by Father Landivar of Guatemala. And yet there is very little in the Silvas that is directly imitative. The Silva á la agricultura de la zona tórrida, especially, is an extraordinarily successful attempt to give expression in Virgilian terms to the exotic life of the tropics, and in this it is unique in Spanish literature. The beautiful descriptive passages in this poem, the noble ethical precepts and the severely pure diction combine to make it a classic that will long hold an honored place in Spanish-American letters (Obras completas, Santiago de Chile, 1881-93).
During the revolutionary period the most distinguished poets, after Bello, of that part of the greater Colombia which later formed the separate republic of Venezuela, were Baralt and Ros de Olano. Rafael María Baralt (1810-1860) took part in the revolutionary movement of secession from the first Colombia; but later he removed to Spain and became a Spanish citizen. His verses are usually correct, but lack feeling. He is best known as a historian and maker of dictionaries. Baralt was elected to membership in the Spanish Academy (Poesías, Paris, 1888).
General Antonio Ros de Olano (1802-1887) also removed to 319 Spain and won high rank in the Spanish army. He joined the romantic movement and became a follower of Espronceda. Besides a volume of verses (Poesías, Madrid, 1886), Ros de Olano wrote El doctor Lañuela (1863) and other novels. Both Baralt and Ros de Olano were identified with literary movements in Spain rather than in Venezuela.
José Heriberto García de Quevedo (1819-1871) was a cultivated and ambitious scholar who collaborated with Zorrilla in María, Ira de Dios and Un cuento de amores. Among his better works are the three philosophical poems: Delirium, La segunda vida and El proscrito (Obras poéticas y literarias, Paris, 1863). Among the lesser writers of this period are Antonio Maitín (1804-1874), the best of Venezuelan romanticists (cf. El canto fúnebre, a poem of domestic love); Abigail Lozano (1821-1866), a romanticist and author of musical but empty verses ("versos altisonantes"); José Ramón Yepes (1822-1881), an army officer and the author of legends in verse, besides the inevitable Poesías; Eloy Escobar (1824-1889), an elegiac poet; and Francisco G. Pardo (1829-1872), a mediocre imitator of Zorrilla.
Next to Bello alone, the most distinguished poet of Venezuela is José Pérez Bonalde (1846-1892), who was a good German scholar and left, besides his original verses, excellent translations of German poets. His metrical versions of Heine, especially, exerted considerable influence over the growth of literary feeling in Spanish America (Estrofas, N.Y., 1877; El poema del Niágara, N.Y., 1880). At least two other writers of the second half of the nineteenth century deserve mention: Miguel Sánchez Pesquera and Jacinto Gutiérrez Coll.
Among the present-day writers of Venezuela, Luis López Méndez was one of the first to introduce into Spanish America a knowledge of the philosophy and metrical theories of Paul Verlaine. Manuel Díaz Rodríguez (1868-___) has written little verse; but he is the best known Venezuelan novelist of 320 to-day [Sangre patricia, Camino de perfección (essays), Ídolos rotos, Cuentos, 2 vols., Confidencias de Psiquis, Cuentos de color, Sensaciones de viaje, De mis romerías]. The most influential of the younger writers is Rufino Blanco-Fombona, who was expelled from his native country by the present andino ("mountaineer") government and now lives in exile in Paris. At first a disciple of Musset and then of Heine and Maupassant, he is now an admirer of Darío and a pronounced modernista. His Letras y letrados de Hispano-America is the best recent work of literary criticism by a Spanish-American author. Blanco-Fombona is a singer of youthful ambition, force and robust love. His verses have rich coloring, but are at times erotic or lacking in restraint (prose works: Cuentos de poeta, Maracaibo, 1900; Más allá de los horizontes, Madrid, 1903; Cuentos americanos, Madrid, 1904; El hombre de hierro, Caracas, 1907; Letras y letrados de Hispano-America, Paris, 1908. Verses: Patria, Caracas, 1895; Trovadores y trovas, Caracas, 1899; Pequeña ópera lírica, Madrid, 1904; Cantos de la prisión, Paris, 1911).
References: Menéndez y Pelayo, Ant. Poetas Hisp.-Amer., II, p. cx f.; Blanco García, III, p. 321 f.; Reseña histórica de la literatura venezolana (1888) and Estado actual de la literatura en Venezuela (1892), both by Julio Calcaño, Caracas; La literatura venezolana en el siglo XIX, Gonzalo Picón Febres, Caracas, 1906; Parnaso venezolano, 12 vols., Julio Calcaño, Caracas, 1892; Biblioteca de escritores venezolanos, José María Rojas, Paris, 1875; Parnaso venezolano, Barcelona, 1906.
Bello: see preceding note.
1. The Lion symbolizes Spain, since from the medieval kingdom of Leon modern Spain sprang. The battle of Bailén (see in Vocab.) took place in 1808 when Bello was twenty-seven years of age and still loyal to Spain.
214.—16 to 215.—3. Que... concibes = que circunscribes el vago curso al (= del) sol enamorado, y (tú), acariciada de su 321 luz, concibes cuanto ser (= every being that) se anima en cada vario clima.
18. The use of quien referring to inanimate objects is now archaic.
216.—19 to 217.—3. It is said that the banana gives nourishment to more human beings than does any other plant. The fruit is taken when it is still green, before the starch has turned to sugar, and it is boiled, or baked, or it is ground and made into a coarse bread.
6-8. En que... bondadosa! = en que (la) naturaleza bondadosa quiso hacer reseña de sus favores...
9. The student should compare this and the following lines with Vida retirada by Fray Luis de León, p. 9.
19. The rime requires habita, instead of habitad.
22-23. Y... atada = y la razón va atada al triunfal carro de la moda, universal señora.
219.—10-16. ¿Esperaréis... ata? = ¿esperaréis que (el) himeneo forme más venturosos lazos do el interés, tirano del deseo, barata ajena mano y fe por nombre ó plata, que do conforme gusto, conforme edad, y (= both) elección libre y (= and) mutuo ardor ata los lazos? Note that, by poetic license, ata agrees in number with the nearest subject, although it has two.
220.—8-11. As this poem was written after the Spanish-American colonies had revolted against the mother country, Bello no longer rejoices at the success of Spanish arms nor grieves over their losses, as he had done when he wrote Á la victoria de Bailén.
Pérez Bonalde: see note to p. 214.
222.—5. The Venezuelan flag is yellow, blue and red with seven small white stars in the center.
225.—La carcelera: the words and music of this song and of the first that follows are taken from the Cancionero salmantino (Dámaso Ledesma), Madrid, 1907.
227.—La cachucha: the words and music of this song and 322 of the five that immediately follow are taken from Poesías populares (Tomás Segarra), Leipzig, 1862.
238.—El trágala: (lit., the swallow it) a song with which the Spanish liberals taunted the partizans of an absolute government.
242.—Himno de Riego: a song to the liberal general, Rafael de Riego (1784-1823), who initiated the revolution of 1820 in Spain and proclaimed at Cabezas de San Juan the constitution of 1812. Cf. Versification, p. lxxix.
251.—Himno Nacional de Cuba, called also the Himno de Bayamo, on account of the importance of Bayamo (see in Vocab.) in the Cuban revolution of 1868. Note the ternary movement of this song, and see Versification, p. lxxiii.