
Title: The Business of Being a Housewife
Author: Leona A. Malek
Release date: August 4, 2016 [eBook #52716]
Most recently updated: October 23, 2024
Language: English
Credits: Produced by Emmy, MWS and the Online Distributed
Proofreading Team at http://www.pgdp.net (This file was
produced from images generously made available by The
Internet Archive)


As meat is one of the most important items of American diet, its price is a matter of moment to every housewife. Comparisons between the cost of live animals and the price per pound of meat sometimes lead to the conclusion that the existing margin is too wide and that possibly the profits of the middleman are too large.
After fair analysis, the housewife realizes that a live animal is not all meat and, furthermore, that the meat carcass is not all steaks and rib roasts. A comparison, therefore, between the live cost of meat animals per pound and the cost per pound of a tenderloin is misleading, if it results in any conclusions relative to margins.
Then we must reckon with the wide difference in grades of meat. We cannot correctly estimate the cost of a steak cut from a prime beef by that of a steak from a grass-fed cow. There are several grades of meat, depending upon the nature and feeding, each wholesome and nutritious, but some demanding more special cooking than others.
About fifty-five per cent of a steer is meat; the remainder includes the hide and various other by-products, which, except the hide, are not worth in their primary state anywhere near as much per pound as they cost alive. The fifty-five per cent of the animal which is meat must, therefore, carry the greater portion of the original cost. That is why a steer carcass might be sold by the packer for twenty cents a pound and still fail to pay a profit, even though the live animal cost the packer only twelve cents a pound. The casual observer, noting a difference of eight cents a pound between the live animal and the carcass, might say a sixty-six per cent increase in price is unduly large; but a little deeper study develops that the return from the carcass in this instance would fail to equal the amount paid for the live steer.
When a retailer buys a carcass, he purchases neck meat as well as loins; chucks as well as rounds. Portions of the carcass have to be sold at or sometimes less than he paid per pound for the carcass. The choice cuts necessarily have to make up for the losses on the less desirable portions. It is not unreasonable, therefore, that the retailer should charge fifty or sixty cents a pound for choice steaks and fifteen cents a pound for boiling beef out of a carcass which he bought at the rate of twenty cents a pound.
Only the aggregate price which the retailer gets for all parts and portions of the carcass will show his margin over the initial cost. It is wholly improper, therefore, to compare sixty-cent steaks with twelve-cent cattle with a view to determining profit.
The same thing is true of hogs and of sheep. A hog is not all meat, nor is the meat all ham. A sheep is not all carcass and only a small part of the carcass cuts up into chops. One must know the aggregate return and something about the costs of doing business before a justifiable conclusion as to price margins can be determined.

THE home managers have in their hands the most important business of the nation. American women realize that to their duties as home makers, mothers, and guiding influences, is added an important economic responsibility. The manner in which the purchasing power of twenty million home managers is used has an inestimable effect upon the production, collection, and distribution of all products in the market.
This second edition of “The Business of Being a Housewife” is respectfully dedicated to the thousands of wise home managers who are determined to understand more fully their relation to the producers of the country and to the great industries, such as that of Armour and Company, who have made possible the providing of perfect food in perfect condition at any distance from the farm.
A study of the national and world situation on food production shows that old-time low food prices may never return. Formerly much of the food was raised by numerous individual families on Government land at nominal cost; today practically all food is raised on expensive land—the plains have been turned into villages and farms by the increasing population. Many men and expensive machinery and equipment are needed to produce our present high standard products.
It became economically unsound for so great a percentage of food producers to spend their time in producing meats and staples, only part of which could be consumed by themselves and their near neighbors, the rest going to waste. The great waste of the surplus products set the minds of men of genius to devising ways to preserve the foods of abundant harvests for the seasons of scarcity. The result is before us in the form of modern cold-storage plants, refrigerator cars, volume-curing and pickling of meat products, and volume-canning of fish, meats, fruits, and vegetables; great cereal factories, etc.
The standard of quality has been raised and the sanitary handling of foods greatly developed. While this has increased the prices a little, it has also increased the efficiency and earning power of the consumer and has tended towards the better health of the nation. The only way to equalize prices, for the high quality of foods demanded by discriminating home managers, is through efficient commercial handling and the conservation of every bit of material. While the efficiency of the Armour organization is regarded as of the highest standard, the organization is continually striving to still further increase this efficiency.
Armour and Company act as a great service link between the farmers and consumers. Through our agricultural department we reach out to the farmer and advise him in producing the best meat animals and farm products within his farm’s possibilities. We assist him to improve his soil and to feed his animals to the best advantage.
The raw material buyers for Armour and Company are all experts in their special lines. They search the markets to select the best products for each branch of our service. Then various corps of specialists analyze and prepare the foods in the most efficient, scientific, and satisfactory way for the consumer. Through able management the most expert service today goes into the translating of a meat animal into wholesome U.S. Government inspected meat, either fresh, smoked, dried, prepared, or canned.
Expensive experimenting with foods may be eliminated from your accounts by the simple method of buying by known brands. Label reading is today’s most important buying guide. A dealer soon learns the wants of his quality buyers, and, knowing your demand for high standard commercially prepared foods, he will be careful to select correspondingly good quality foods when replenishing his stock.
Every careful home maker demands that the meat she buys, whether fresh, smoked, dried, cured, or canned, bears a U. S. Government inspected-and-passed label, and should demand canned foods marketed under a reliable firm name.
Standards of purity and quality in the preparation of commercial foods have gradually raised, until now there is practically every food for every need in convenient sanitary packages at your corner market under a quality label guarantee.
Drudgery has been literally taken out of food preparation. Madam Home Manager’s time may now well be employed along more constructive lines than in shelling peas and stringing beans. Hers is the responsibility and privilege of selecting foods for her family’s menus in such combinations that every food-need of the body is supplied in proper proportion.
This is one of the most serious matters before us today, and the physicians of the entire country are deploring the fact that many of the children of the wealthy as well as of the poor are undernourished. Do you know foods? Prepared foods release you from less important tasks, that you may have time to learn food values. It rests with the responsible housewife to plan her own time so as to achieve the greatest returns in the health and efficiency of her family. Food knowledge means a better-fed nation.
A pantry stocked with a wide variety of quality foods and a working knowledge of individual needs and food values will make it possible for the home manager to prepare the proper foods within her budget limitations.
A simple budget, or account keeping system, is a necessity in every well-ordered, successful business. The world of today holds so many attractions that we must carefully select those necessities and comforts that will mean the most in real value to us, and then adhere to that selection. The only way to know that we are following our own plan is to have a simple accounting system. At the end of the month, we should look over the figures and decide upon the readjustments necessary. To insure progress and stability, our monthly accounts should show some savings and advancement expenditures.
We offer suggestions throughout this book, arranged to help the average housewife solve her knotty home-managing problems. We have been greatly assisted by the women editors of national women’s publications, prominent home economics teachers, and writers on vital home subjects. This array of talent aims to make this book of the greatest help possible to the American Housewife.
Many thousands of housewives have come to depend upon the Armour Oval Label as a buying guide for a wide variety of their pantry and refrigerator staples; they know they can depend upon the uniformity and quality of every Oval Label product.
Madam Home Manager receives the full benefit of our fifty-some years of experience in caring for foods. She has the Armour assurance of uniformity and quality and is guided in her buying by the distinguishing quality Oval Label.
We prepare and distribute with great efficiency, fresh, smoked, cured, dried, prepared, and canned meats, all Government inspected.
A full line of Armour shortenings and frying mediums, as well as our economical oleomargarines and delicious Cloverbloom Butter, may be secured from your dealer. Salad oil under the Oval Label, as well as peanut butter, will continue to meet with popular favor. The evaporated milk and identifiable or carton eggs are considered indispensable by the average home manager.
Cheese is becoming more and more favored for its high food value, and it is with satisfaction that many learn of the great variety of cheese sold under the Armour guarantee of quality.
Armour’s Pork and Beans, Peanut Butter, Evaporated Milk, Mince Meat, etc., are favorite products, and Madam Home Manager will be able to obtain the well-established Armour brands at her market.
Armour and Company maintain a well organized department of Food Economics as a medium of expression to the American housewife. This department is made up of trained and experienced dietitians, teachers of home economics, food chemists, practical home managers, writers and lecturers.
We are equipped and prepared to give every home maker the practical, technical and economic information she may need on any food or home managing subject.
It is the purpose of this book to assist Madam Home Manager in her mastery of the problems incident to the feeding of a family for health, happiness and efficiency.
To simplify the presentation of this very important material, we have divided the book into four sections: Section one covers the apportionment of the income; Section two deals with the wise selection of foods and the place of each class of food in the building of a well-balanced menu. Section three is devoted to fundamental cookery suggestions. Section four holds for the reader a wealth of general information to assist in simplifying the labor of cookery.
As this is a manual of household efficiency and economy, we have aimed to give the greatest possible number of helpful suggestions, referring the reader to a number of splendid cook books for recipes. (See Page 28)
Every home maker has a cherished ideal for the various members of her family. The rapidity with which that dream is realized depends upon how the family income and individual energy are used. To those who have never kept a record of expenditures, the first definite step toward establishing a substantial financial basis and assuring progress to the family is the keeping of an expense account. Each day, make an accurate accounting of all expenditures. Keep this carefully for four months, then, with that account as a basis, plan your expenditures for the next four months and live within that plan. The third quarter, keep your expense account again and then you will have the accurate information regarding the financial needs of your particular family. After a careful analysis, make up a year’s budget, cutting down non-essentials and adding to accounts that really mean an advance step toward your goal.
The following percentages will serve as a guide showing the possibilities of various incomes. Each family will find it necessary to adjust the figures according to special needs, local conditions and family ambitions. Special education is worth economy in many lines, as it offers future returns and is really an investment.
The food section of the Family Account Book is perhaps the most important. Without properly prepared food in proper combination, and quantity, we are not able to exercise our greatest earning ability, to grasp new situations as we should, or to invest our savings wisely. By keeping the food account according to the body building uses of the food purchased, we daily progress in our food knowledge and become adepts at using alternative foods.
When one really operates a budget plan to win, it is an advancement in itself. In cases of a large independent income it is wise to have your banker’s representative work out a budget for you. The budget outline, on page 6, is estimated for a family of five, one young child, two school children, mother and father. Where the family is smaller, the food and clothing accounts will change, the amount saved going either to savings, investments, or advancements.
| Family of Two | Family of Three | Family of Four | Family of Five | |||||
| Items | % of Income | Amount | % of Income | Amount | % of Income | Amount | % of Income | Amount |
| Food | 20 | $40.00 | 25 | $50.00 | 32½ | $65.00 | 40 | $80.00 |
| Shelter | 17½ | 35.00 | 20 | 40.00 | 22½ | 45.00 | 25 | 50.00 |
| Operating | 10 | 20.00 | 11 | 22.00 | 12½ | 25.00 | 13 | 26.00 |
| Clothing | 9 | 18.00 | 11 | 22.00 | 13 | 26.00 | 15 | 30.00 |
| Contingency | 43½ | 87.00 | 33 | 66.00 | 19½ | 39.00 | 7 | 14.00 |
| Total | 100% | $200.00 | 100% | $200.00 | 100% | $200.00 | 100% | $200.00 |

| Family of Three | Family of Four | Family of Five | ||||||
| Food | 30% | $60.00 | 35% | $70.00 | 40% | $80.00 | ||
| Shelter | 25 | 50.00 | 28 | 56.00 | 30 | 60.00 | ||
| Operating | 12 | 24.00 | 12 | 24.00 | 10 | 20.00 | ||
| Clothing | 15 | 30.00 | 17 | 34.00 | 15 | 30.00 | ||
| Contingency: | ||||||||
| Insurance | — | 18 | 36.00 | 8 | 16.00 | 5 | 10.00 | |
| Advancements | ||||||||
| Savings | ||||||||
| Amusements | ||||||||
| Investments | ||||||||
Itemized Accounting of Expenditures and Percentage Apportionment of Income.
Estimated for Family of Five on $300 a Month. Percentages of Expenditures for Food, Operating and Contingency vary according to income.
The accompanying is a family budget outline that is easily adjustable to entirely satisfactory use in your home. If the home manager, by means of her ingenuity or by doing work herself, saves on the regular scheduled expenditures, that money should go to her personal account. Preparedness is a big factor in the growth of the Home Manager’s credit column.
With this form as a guide, lay out your family budget outline, in any ordinary notebook eight by eleven inches. Substitute your own income and percentage figures, listing your needs under their proper heads. As this outline is general, it may contain some suggestions better fitted to your neighbor—just leave these items out of your budget and add any others in their proper class.
The analysis of your needs and expenses necessary to make up your very own budget is a great help toward keeping within your income bounds.
Attach a pencil to your account book and keep it where you will put down the day’s expenditures regularly each evening.
Make your budget a co-operative affair, soliciting suggestions from the family as to what investments, savings, etc., to make.
Food experts agree that 20 per cent. of the entire diet should consist of protein. In our country, meat is the favorite protein food. It provides a portion of the energy which is also furnished by carbohydrates and fats, but its chief purpose is to supply material for growth and repair of the body tissues which are constantly worn out in the performance of their various functions.
Much of the frontier, upon which vast numbers of cattle were formerly raised, is now cut up into small farms and town lots. Hereafter, we must raise the greater portion of our meat animals upon expensive land and feed. The cost of production has increased many fold and consequently meat is higher in price. Packers, through utilizing by-products, keep the cost of wholesome meat within the reach of the consumer.
(See page 2)
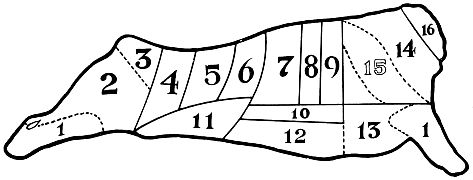
| Name of Cut | Water | Prot. | Fat | Ash | Carb. | Cal. per Lb. Unc’ked | Comp. Cost | Cook. Helps | How Used | ||
| 1. Shank | 42.9 | 12.8 | ... | .6 | None | ... | Least Expense | Sear, cook slowly | Stews and soups | ||
| 2. Round | 60.7 | 19.0 | 12.8 | ... | ... | ... | Economical | “ | “ | quickly | Steaks, and roasts, heel for pot roasts and stews |
| 3. Rump | 45.0 | 13.8 | 20.2 | .7 | ... | 1110 | Medium | “ | “ | slowly | Steaks, pot roasts, braising and corning |
| 4. Sirloin | 54.0 | 16.5 | 16.1 | .9 | ... | ... | Reasonable | “ | “ | quickly | Steaks |
| 5. Pin Bone | 52.4 | 19.1 | 17.9 | .8 | ... | 1110 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Steaks |
| v6. Porterhouse | 52.4 | 19.1 | 17.9 | .8 | ... | 1110 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Choicest steaks |
| v7, 8, 9. Prime Ribs | 43.8 | 13.9 | 21.2 | .7 | ... | 1155 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Best roasts |
| 10. Short Ribs | 57.4 | 15.6 | 13.0 | .7 | ... | ... | Economical | “ | “ | slowly | Roasts and stews |
| 11. Flank | 54.0 | 17.0 | 19.0 | .7 | ... | 1115 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Steaks, stews, braising |
| 12. Plate | 45.3 | 13.8 | 24.4 | .7 | ... | 1285 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Stews, soups, corning |
| 13. Brisket | 41.6 | 12.0 | 22.3 | .6 | ... | 1165 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Stews, pot roasts, soups |
| 14. Chuck | 62.7 | 18.5 | 18.0 | ... | ... | 1105 | “ | “ | “ | “ | Roasts, steaks, pot roasts, boiling, stews |
| 15. Shoulder Clod | 56.8 | 16.4 | ... | .9 | ... | ... | “ | “ | “ | “ | Steaks and pot roasts |
| 16. Neck | 45.9 | 14.5 | 11.9 | .7 | ... | ... | “ | “ | “ | “ | Soups, stews and corning |
Transcriber's Note: To make the table width smaller for this and the next tables on cuts of meat, words were shortened to abbreviations. See which words in the key below.
Every wise home manager should learn to cook to advantage every cut of meat.
This knowledge of correct cookery offers an opportunity for a wide variety of meat dishes.

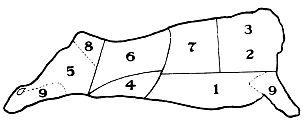
| Name of Cuts | Calories per lb. uncooked | Comp. Cost | Cooking Helps | How Used | ||
| 1. Breast | 740 | Reasonable | Sear— | cook | slowly | Roast—baked |
| 2. Shoulder | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | |
| 3. Chuck | 515 | Low | “ | “ | Roast—steak | |
| 4. Flank | 820 | “ | “ | “ | quickly | Steak—Casserole |
| 5. Leg | 755 | Reasonable | “ | “ | slowly | Roast—steaks |
| 6. Loin | 690 | “ | “ | “ | Steaks—roast | |
| 7. Rib | 480 | “ | “ | “ | quickly | Roast—chops |
| 8. Rump | 735 | Medium | “ | “ | slowly | Roast—pot roast—steak |
| 9. Shank | 580 | Low | “ | “ | Soup—stew | |
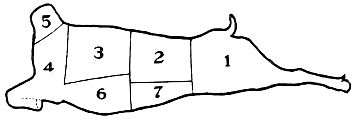
| Name of Cuts | Calories per lb. uncooked | Comp. Cost | Cooking Helps | How Used | |
| 1. Leg (hind) | 1105 | Reasonable | Sear, cook slowly | Roasts | |
| 2. Loin | 1795 | “ | “ | “ | Chops, roasts |
| 3. Rack (Corresponds with Rib Chops) | 1350 | “ | “ | “ | Chops, crown roasts |
| 4. Shoulder or Chuck | 910 | Medium | “ | “ | Stews |
| 5. Neck | 985 | Low | “ | “ | Stews, casserole |
| 6. Plate | 1560 | Low | “ | “ | Roasts, stews |
| 7. Flank | |||||
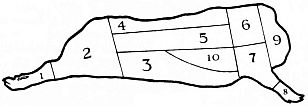
| Name of Cuts | Calories per lb. uncooked | Comp. Cost | Cooking Helps | How Used | |
| 1 and 8. Foot | 365 | Low | Long, slow cooking | Stewed, pickled, boiled or fried | |
| 2. Ham | 1345 | Reasonable | Long, slow cooking | Smoked, then boiled or baked whole; steaks—sautéed, broiled | |
| 3. Belly (bacon) | 1455 | Reasonable | Slow cooking | Smoked—broiled | |
| 4. Fat Back (salt pork) | 3860 | Medium | Slow cooking | Boiled with vegetables | |
| 5. Pork Loin | 1270 | Reasonable | Moderate heat | Chops and roasts | |
| 6. Boston Butt | 1340 | Low | Sear, cook slowly | Cheaper steaks and roasts | |
| 7. Green Picnic | 1480 | Medium | “ | “ | Steaks, roasts, boiling |
| 6 and 7. Shoulder | |||||
| 9. Neck | 3435 | Low | “ | “ | Stewed, baked or braised |
| 10. Spare Ribs | Low | “ | “ | Baked or boiled | |

Every home manager should have a thorough understanding of what U. S. Government Inspection of meat is—its significance and importance in her selection of meats. Practically everyone who has ever purchased meat has noticed a round purple stamp, the size of a half dollar, bearing the words “U. S. Inspected and Passed,” in the center of the commercial cuts displayed.
The government stamp on the meat you purchase is your absolute guarantee that the meat you are buying is wholesome. It signifies that the animal from which that piece of meat was cut had passed four separate inspections, and that the meat was found to be free from all disease and in perfect condition when it left the packing house.
Government meat inspection is one of the greatest protections to the American table. Only concerns doing interstate business offer this protection.
All meats have four inspections. The ante-mortem inspection is termed “on the hoof.” The three post-mortem inspections are made upon the glands of the neck, on the viscera and on the dressed carcass.
Only about 60 per cent of the meat consumed in the United States is United States Government inspected. When the public shall demand that all meats be inspected, we will have the much-needed nation-wide inspection, which will insure wholesome meats for all. Women’s organizations should make this movement a definite part of their regular programs and consider it a duty to buy only U. S. Government inspected meats.
The products of each packing house are identified by the letter and number and the U. S. Gov’t Inspection mark on each commercial cut.
Cold storage is a great factor in the present solution of the nation’s food problems. It is a means of holding certain foods over from the season of plenty to the season of scarcity. Since the first mechanical refrigeration was installed in the late eighties, Government investigators have been continually studying various methods of preserving food, without canning, and all insist that there is no modern method which equals cold storage. Understanding is fast eliminating the prejudice against use of supplies from cold storage plants of reputable houses.
The first cold-storage house was cooled by the use of a mixture of crushed ice and salt. The modern process is the ammonia brine method. As the liquid ammonia enters the pipes that carry the refrigeration through the cooler, it expands and is forced through the pipes as an ammonia gas. An absorption method is also frequently in use. Ammonia brine is by far the best method of cooling. It is cleanly, absolutely odorless and, through use, has proved its efficiency.
The establishment of scientific refrigeration plants has made possible a variety and abundance of food at any season on the American table.
Coolers are kept at an average temperature of 38° F. for foods kept a short time. The temperature of the freezer is normally ten above zero to ten below. Fresh meats are not allowed to stay in the coolers longer than one to two weeks. If they must be held longer, they are sent to the freezer. When meat is to be thawed, it is taken from the freezer and sent to the coolers. Once taken from the freezer and defrosted, neither meat nor any other food should ever go back. There are time limiting cold-storage laws in twenty states. Twelve months is the limit of time allowed in nineteen states.
Butter in cold storage is kept at a temperature of zero to five below. Its sweetness and delicate flavor is the same when taken from storage as when put in.
Eggs that are absolutely fresh and in perfect condition when placed in cold storage, will keep perfectly at a temperature between 29° F. and 31° F. for six to nine months. Eggs laid in April and May are kept for midwinter use, and the June pack is used in autumn and early winter when the supply is scarce and prices high.
The box of frozen poultry your dealer displays fresh from cold storage is most attractive and appetizing. A Nationally known name on the box guarantees the quality. Such poultry was especially selected and carefully fed some time before killing. It is fine-flavored and dainty. Always buy your frozen poultry in the frozen state and thaw it out at home. Directions for thawing are on page 13.

The great importance of meat as food lies in its high protein content. Protein is body building material. It forms one-fifth of our food requirements. Half of the protein requirement is furnished by meat. In lean meat the solid protein is very nearly in the pure form.
Meat is delicately constructed with small cells of tissue holding the flavory juices. These cells are held together by a connective tissue. In the cheaper cuts of meat, the cells or fibers holding the juices are long and the connective tissue thick. In the structure of the expensive steaks and loin cuts, the cells are short and the connective tissue thin. It is this difference in structure that makes it necessary to use entirely different methods of cooking for the tender cuts and for the cheaper ones. The same result—a tender, flavory, nutritious cut of meat—may be obtained with the cheaper cut as with the expensive loin cuts, if the proper method of cooking is employed.
One so often hears the remark, “I wish someone would invent a new animal.” The housewife is tired of ordering beef, mutton, pork or veal day after day. Too often she orders only the roasts, steaks or chops from these typical animals and then complains because her meat bill is high. This idea of lack of variety in fresh meats is all because of the unsound and uninteresting habit of buying the same cuts over and over again.
For every loin of beef there are several other cuts besides the extra portions, such as heart, liver, kidney, brain, etc. In these lie possibilities for many distinctive dishes and interesting flavors.
While there are not so many cuts of pork and lamb, there are great possibilities for variety in the preparation.
Nine out of ten home managers have believed for years, as do some even now, that the more expensive and most tender cuts of meat must naturally be most nutritious and that the cheaper, long fibered cuts are to be discarded or left for the butcher to dispose of, not realizing that their purchase of the tender cuts only, forces prices of these cuts high enough to cover the cost of the carcass. We are grateful that our leading dietitians of today are teaching women the truth: that the cheaper cuts of meat are exactly as nutritious as the tenderer cuts, if not more so, because the blood is drawn to the parts in which the muscles are constantly used, thus continually rebuilding the tissue.
In a dressed beef carcass of 700 pounds there are about 200 pounds of prime meat. The loin of the hind quarter, composed of sirloin, porterhouse, and club steaks, and the prime ribs of the fore quarter, are the commercial cuts most tender and easily prepared, and so are most in demand. Your butcher orders the cuts you demand. If you neglect the cheaper cuts and extra meat portions, he will not order them, and the expense of their production will be distributed over the cuts in demand.
An economically sound buying campaign would be a resolution by the housewives to use in its regular order every cut on a side of meat before reordering a cut. One of the extra meat portions could well be every third meat purchase.
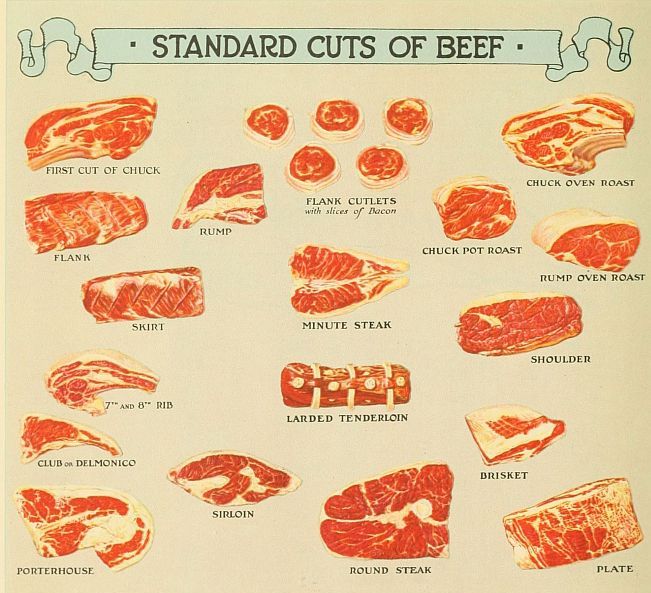
In order to secure the most satisfactory cuts of meat, marketing should be done in person. Before this can be done with any degree of satisfaction, the buyer should be familiar with the various cuts of beef, pork and mutton.
The meal is planned around the meat dish, as a rule; so it is most important to select the main meat dish with greatest care.
When buying beef, see that it is bright red in color, streaked with fat—and firm. The streaks of fat add to the food value and make a more flavory steak or roast. Veal is pink in color, but less firm. Mutton flesh is firm and dull red in color, the fat hard and white or slightly yellow. Pork is dark pink in color and the fat is less firm than beef or mutton.
The modern system of refrigeration has made world-wide distribution of fresh meat possible. Refrigerator cars, iced en route in such a manner that the contents are kept always in a current of cold air, make it possible to carry the products of the packing house to remote parts of the country and deliver them in sound condition.
The housewife in turn may have such products by being discriminating in her marketing, skillful in her cooking and careful in her serving.
By a knowledge of all the cuts of meat, the housewife can keep down her meat expenditures. She should also have her recipe file well stocked with tested recipes for the wide variety of popular meat dishes to be made with the less expensive cuts.
For those who do not include meat in their diet, there is a wide variety of non-meat protein foods to choose from. Eggs, cheese, milk, and beans will give the necessary protein for a complete diet.

Much of the vigor and force of Americans is attributed to the beef which is so generously included in the American diet. It is the favorite meat of a large percentage of people of every nation because it is easy to secure, is delicious of flavor and, properly cooked, is easily assimilated. The best cuts of beef for broiling are porterhouse, sirloin, and tenderloin steaks. For roasting, the prime ribs are preferred, while for the pot roast the rump, round, chuck, shoulder clod and brisket result in a tender piece of meat of delicious flavor when subject to slow, moist cooking.
| DISH | CUT |
Beef à la mode |
Round, rump, chuck, and brisket |
Beef roast |
Prime ribs, short ribs, sirloin, Spencer roll, sirloin strip, regular roll |
Boiled beef |
Flank, brisket, short ribs, neck |
Corned beef |
Flank, short ribs, brisket, rump |
Spiced beef |
Flank |
Braised brisket with vegetables |
Lean brisket (boned) |
English style flank |
Lean flank |
Glazed ribs with macaroni |
Lean short ribs |
Braised beef with ravioli |
Top sirloin |
Braised sirloin with truffles or rice croquettes |
Top sirloin larded |
Tenderloin with mushrooms |
Tenderloin |
Tenderloin steak, Parisian potatoes |
Tenderloin steak |
Porterhouse steak |
Porterhouse steak |
Minute steak |
Club steak |
Tenderloin steak sautéed with peppers |
Tenderloin steak |
Filet of beef with string beans |
Larded tenderloin |
Hamburg steak |
Neck, round, rump, clod (ground) |
Salisbury steak |
Neck, round, rump, clod (ground) |
English beef soup |
Shank, neck |
Beef soup stock |
Shank, neck |
Beef croquettes or loaf |
Left-over beef |
Beef collops |
Left-over beef |
Beef rissoles |
Left-over beef |
Beefsteak and mushroom pie |
Flank steak, round steak |
Tournedos of beef with olives |
Tenderloin |
Ragout of beef, creole sauce |
Neck, chuck, shoulder clod, plate |
Beef Stew |
Neck, chuck, shoulder clod, plate |
Pot roast of beef |
Chuck, brisket, round, Spencer roll, neck, shoulder clod |
Baked stuffed hanging tenderloin |
Hanging tenderloin |
Baked stuffed flank |
Flank steak |
| NAME OF CUTS | SAUCE | GARNISH | VEGETABLES |
Shank |
Mixed vegetable |
Parsley; jelly |
Boiled potatoes |
Round |
Maitre d’hotel butter |
Water cress |
Mashed potatoes, creamed carrots |
Rump |
Tomato sauce |
Corn fritters |
Lyonnaise potatoes |
Sirloin |
Parsley; butter sauce |
Peas or fried onions |
Baked potato, sliced tomatoes |
Pin bone |
Melted butter sauce |
Baked stuffed tomatoes |
Baked or au gratin potatoes |
Porterhouse |
Mushroom sauce |
Head lettuce |
Steamed potatoes, tomatoes |
Prime ribs |
Brown gravy |
Stewed apricots; parsley |
Mashed, baked squash |
Short ribs |
Horseradish sauce |
Radishes |
Lyonnaise, stewed corn |
Flank |
Dressing; meat gravy |
Bacon curls; parsley |
Hashed brown potatoes |
Plate |
Mint sauce |
Spinach |
Mashed potatoes, turnips |
Brisket |
Caper sauce |
Baked onions |
Potato croquettes |
Chuck |
Brown gravy |
Currant jelly |
Boiled potatoes, spinach |
Shoulder clod |
Apple sauce |
Parsley |
Browned potatoes |
Neck |
Tomato sauce |
Grape jelly |
Creamed potatoes, cucumbers |

Poultry is one of the most popular meats found upon the American table. Dry-picked poultry is the most sanitary and desirable. It is no simple matter to provide fresh poultry to our thickly populated cities. But with improved breeding, scientific feeding and the modern cold-storage houses and refrigerator cars, Armour and Company supply a large clientele with either fresh or cold-storage poultry of the highest quality. “Spring chickens,” so called because before the days of storage they could be obtained only in the spring—are from three to six months old. The older members of the chicken family are known as “fowl.”
A chicken’s feet are soft and smooth and the end of the breastbone is flexible. Poultry that is to be carried over from the season of plenty is carefully selected and specially fed and prepared. Only the choicest corn and milk fed poultry is worthy of the skill and science displayed in modern cold storage. Scientific methods of packing fresh poultry, and shipment in the refrigerator cars originated by the packers, assures the most select fresh poultry in season. The undrawn poultry is preferred to the drawn poultry in the market.
To thaw frozen poultry, submerge it in a pan of cold water and leave in the water until thawed—about four hours for a four-pound hen. Cook as soon as thawed.
To “draw,” it is only necessary to make an incision below the breastbone just large enough to insert the hand and remove the entire viscera at once. Separate the giblets, remove the gall bladder without breaking it, and clean the gizzard by cutting through the flesh and removing the inside sack intact; peel the fleshy part off the sack. Insert two fingers under the skin of the breast and draw out and discard crop and windpipe. Wash the inside of the bird by allowing clean cold water to run through it. Wipe inside and out. From this point the chicken is treated according to the method to be used in cooking. If it is to be “fried,” it is split in half lengthwise, if very young, or in smaller pieces if it is a fowl. For a roast, the chicken is left whole; for stewing, the fowl is entirely disjointed.
U. S. Dept, of Ag. Bulletins. Circulars 61-64. “Studies of Poultry from the Farm to the Consumer.” “How to Kill and Market Poultry” by M. E. Pennington. “Poultry as Food.”
| Chicken | Accompaniments |
| Roast | Mashed Potatoes—Creamed Onions |
| Fricasseed | Steamed Potatoes, Parsnips |
| Smothered | Corn Fritters, Peas |
| Fried | Mashed Potatoes, Jelly |
| Baked Stuffed | Glazed Sweet Potatoes |
| Broiled | Shoe String Potatoes, Combination Salad |
| Chicken à la King | Potato Chips, Tomato and Lettuce Salad |
| Chicken Patties | Mashed Potatoes, Jelly |
| Curried | Steamed Rice with Parsley |
| Cold Sliced | Au Gratin Potatoes, Jelly |
| Croquettes | Creamed Potatoes and Sweetbreads |
| Chicken Hash | Steamed Rice, Jelly |
| Chicken en Casserole | Carrots, Baked Onions and Potato Balls |
| Chicken Pie | Potatoes—Stewed Tomatoes |
| Chicken in Aspic Jelly | Potato Croquettes |
| Creamed | Baked Potatoes—Sliced Cucumbers |

Lamb and mutton afford welcome meat dishes. Lamb is most easily digested and very nutritious.
From a standpoint of economics, the increased use of lamb and mutton results in greater production of wool.
In the menu, lamb and mutton should hold a permanent place because of the number of attractive and wholesome dishes they afford. The crown roast of lamb is a decorative and delicious dish. The leg of lamb and shoulder roll are just of the right size to be convenient for the average family. With a sauce of tart jelly accompanying, they make an excellent special or company dinner dish. There are the loin chops; “French” and “American” rib chops, delicious morsels when broiled; the shoulder, which may be made into a mock duck that would deceive the most observant; the neck and other cuts, which make delicious stews, ragouts and broth. Twice a week is not too often to have lamb in the menu.
| DISH | CUT |
| Roast Lamb with Mint Sauce | Leg—shoulder roll—crown ribs |
| Braised Lamb with Currant Jelly | Shoulder |
| Boiled Lamb with Caper Sauce | Shoulder—leg |
| Sauté of Lamb | Shoulder |
| Epigramme of Lamb | Breast |
| Curried Lamb | Left-over |
| Ragout of Lamb | Left-over—chuck—neck |
| Irish Stew | Neck—breast |
| Roast Saddle of Mutton | Saddle |
| Broiled Chops | Loin or rib chops |
| Breaded Lamb Chops | Loin or rib chops |
| Lamb Steak | Steaks cut from leg |
| Lamb Croquettes | Left-over lamb or mutton |
| Barbecue of Lamb | Leg—Loin—Shoulder |
| Casserole of Lamb | Neck—shoulder—chuck |
The story of pork in the menu takes us back to the days when the Chinese people discovered the goodness of roast pork when the house burned and accidentally resulted in the first “burnt pig.” Every house in the village was soon in ashes to supply every inhabitant with the delicacy, and its popularity has steadily increased.
Like all meat, pork is classed among the protein foods and builds body tissue. Because of its high percentage of fat, it also supplies heat and energy to the body.
The U. S. Government Inspection stamp guarantees the wholesomeness of the pork you buy.
The digestibility of pork depends largely upon proper cooking—it should be thoroughly cooked in a slow oven. Smoked pork, in the form of ham and bacon, is very easily digested, this being due to the curing and smoking.
In planning the menu including pork, include vegetables containing considerable water, such as cabbage or greens, and tart fruit and spicy dessert. Such a combination will complete a meal rich in food value and satisfying to the appetite.
| DISH | CUT | |
| Sautéed Pork Chops | Chops | |
| Breaded Pork Chops with Tomato Sauce | Loin Chops | |
| Pork Steak | Steak cut from shoulder | |
| Roast Pork with Apple Sauce | Loin, Boston butt, shoulder, tenderloin, blade butt, green ham | |
| Stuffed Pork Tenderloin | Tenderloin | |
| Pork Tenderloin with Sweet Potatoes | Tenderloin | |
| Crown Roast of Pork | Crown prepared from ribs | |
| Spareribs and Sauer Kraut | Spareribs | |
| Boiled Pork with Vegetables | Neck, belly, hocks, feet, tails, jowl, snout, ears | |
| Breaded Pork Cutlets | Shoulder | |
| Roast Boston Butt | Boston butt | |
| Hot Pork Sandwiches | Roast pork | |
| Cold Pork Sandwiches | Boiled green ham | |
| Creamed Pork in Patties | —Lean loin, (use left-over) | |
| Pork Rissoles | ||
Fish is an easily assimilated protein food and is sufficient for the main dish of the meal occasionally. See cook books, referred to on page 28, for cookery methods.
Fresh fish of many varieties are available only to those who live near the great bodies of water. The national producer, however, by canning makes it possible for all housewives, regardless of residence, to have these valuable foods at any season. The process of canning is done with the utmost attention to every detail necessary to produce a perfect product.
The best quality of various kinds of fish are selected, canned, and transported to all parts of the country. The housewife has but to exercise her ability in attractive service and correct combination when using these foods. The nationally recognized brands of shrimp, sardines, lobster, clams, and salmon are found in every quality retail store throughout our country.

The extra meat portions are all the edible parts of the animal not included in the list of regular cuts. They are nutritious protein foods. A great variety of inexpensive and tasty dishes can be made with the various extra meat portions. This will add distinction and variety to your menus.
| Name | Wat’r | Prot. | Fat | Ash | Carb. | Cal. per lb. | Comp. Cost | Characteristics | Use |
| Tripe | 78.0 | 16.3 | 4.98 | .61 | ... | 480 | Economical | Needs careful cooking |
Pickled, breaded, à la Creole |
| Lungs | 79.7 | 16.4 | 3.2 | 1.0 | ... | 440 | “ | Easily cooked | Stew, casserole |
| Kidney | 76.7 | 16.6 | 4.8 | 1.2 | .4 | 500 | Medium | Easily cooked |
Stewed, sautéed, boiled, grilled |
| Tongue | 51.8 | 14.1 | 6.7 | .8 | ... | 545 | Reasonable | Easily prepared |
Boil’d, corn’d, bak’d, smok’d, or pickl’d |
| Brains | 86.6 | 8.8 | 9.3 | 1.1 | ... | 540 | Economical | Needs care in cooking |
Fried, sautéed, scrambled with eggs |
| Liver | 71.2 | 20.4 | 4.5 | 1.6 | 1.7 | 585 | Medium | Easily prepared |
Fried, baked, larded with onions |
| Tail | 67.9 | 26.3 | 6.3 | 1.2 | ... | 755 | Economical | Easily prepared |
Soup, jugged, boiled, braised |
| Suet | 13.7 | 4.7 | 81.8 | .3 | ... | 3540 | “ | Easily tried out or used |
For suet puddings and for cooking fat |
| Fillet | 59.2 | 16.2 | 24.4 | .8 | ... | 1330 | Reasonable | Easily cooked, very tender |
Generally larded, roasted in hot oven and served with mushroom sauce |
| Sweetbreads | 70.9 | 16.8 | 12.1 | 1.6 | ... | 825 | Medium | Needs care in cooking |
Creamed, bak’d in casserole, fr’d, salad |
| Heart | 53.2 | 14.8 | 24.7 | .9 | ... | 1320 | Economical | Needs careful, slow cooking |
Stuffed, braised, baked, fried |
| Name | Wat’r | Prot. | Fat | Ash | Carb. | Cal. per lb. | Comp. Cost | Characteristics | Use |
| Feet | 55.4 | 15.8 | 26.3 | .8 | ... | 1360 | Economical | Easily prepared |
Stewed, pickled, boiled, breaded and fried |
| Ears | 63.5 | 18.9 | 17.1 | .5 | ... | 1080 | “ | Needs slow cooking |
Stewed or boiled in head cheese |
| Head | 45.3 | 13.4 | 41.3 | .7 | ... | 1935 | “ | Needs slow cooking |
Boiled, roasted |
| Kidneys | 77.8 | 15.5 | 4.8 | 1.2 | ... | 490 | “ | Must be prepared carefully |
Sautéed, boiled or stewed |
| Heart | 75.6 | 17.1 | 6.3 | 1.0 | ... | 585 | Medium | Needs long, slow cooking |
Boiled, baked, braised |
| Liver | 71.4 | 21.3 | 4.5 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 615 | Economical | Easily prepared |
Fried, baked, larded with onion, fried with bacon |
| Brains | 75.8 | 11.7 | 10.3 | 1.6 | ... | 655 | “ | Needs care in cooking |
Rissoles, creamed, scrambled with eggs |
| Tongue | 58.7 | 17.7 | 19.8 | 3.6 | ... | 1165 | Reasonable | Needs care in cooking |
Sautéed, stewed, braised, boiled |
| Snouts | 47.5 | 13.90 | 38.1 | .5 | ... | 1809 | Economical | Long, slow cook’g necessary |
Stewed, or boiled with vegetables |
| Tail | 15.0 | 4.1 | 66.9 | .3 | ... | 2900 | “ | Long, slow cooking |
Boiled, soup, braised |
| Jowl | 16.0 | 5.9 | 78.8 | .2 | ... | 3435 | “ | Needs slow cooking |
Boiled with vegetables |
| Lungs | 83.3 | 11.9 | 4.0 | .9 | ... | 390 | “ |
| Name | Wat’r | Prot. | Fat | Ash | Carb. | Cal. per lb. | Comp. Cost | Characteristics | Use |
| Kidneys | 78.7 | 16.50 | 3.2 | 1.3 | ... | 440 | Medium | Easily cooked |
Sautéed, stewed, braised, en Brochette |
| Lungs | 75.9 | 20.2 | 2.8 | 1.20 | ... | 495 | Economical | Needs careful cooking |
Casseroles, baked |
| Heart | 69.5 | 16.9 | 12.6 | .9 | ... | 845 | Medium | Long, slow cooking |
Stuffed, baked, braised |
| Liver | 61.2 | 23.1 | 9.0 | 1.7 | 5.0 | 905 | “ | Easily prepared |
Sautéed, boiled, baked |
| Head | 67.2 | 14.43 | 16.12 | 0.94 | ... | 920 | Economical | Requires spec. care in prep. |
Baked, stewed, stewed with dumplings |
| Brains | 24.5 | 12.5 | 13.1 | 2.3 | ... | 550 | ” | Needs care in preparation |
Creamed, scrambled with eggs, fried, rissoles |
| Tongue | 45.8 | 28.8 | 22.8 | 4.2 | ... | 1465 | Reasonable | Easily cook’d, care necess’ry |
Boiled, braised, smoked |
| Milts | 78.2 | 17.65 | 2.18 | 1.37 | ... | 410 | Economical | Easily prepared |
Sautéed, fried with onions |
| Sweetbreads | 79.7 | 13.95 | 5.80 | 1.43 | ... | 490 | Medium | Need care in preparation |
Creamed, braised |
| Fries | 85.4 | 12.37 | 1.02 | 1.05 | ... | 270 | Economical | Easily prepared |
Fried |
| Feet | 66.3 | 23.90 | 11.26 | 0.55 | ... | 890 | “ | Needs long, slow cooking |
Boiled with dumplings, boiled with vegetables |

Ham and bacon are two of the most popular foods in the American market. These tasty staple foods serve a double purpose. While they are perhaps the most satisfactory stimulators of a dull appetite, they are such hearty foods that in proper combination they easily satisfy the most ravenous appetite.
Hams smoked in the stockinet covering retain their shape and keep moist and juicy to the last slice. The covering should be left on the raw ham and folded or tied over the cut surface so the ham will retain all the delicate nut flavor given by our special cure and expert handling.
The ideal ham is firm, moist, juicy, tender and of medium weight, not too fat or too lean. The stockinet covering keeps the selected ham moist and firm.
Ham in some form is a welcome part of either breakfast, luncheon or dinner several days every week.
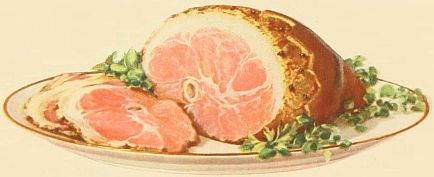
Bacon should be fine and firm—it is selected to suit varying tastes and may be purchased with either the fat or lean predominating or evenly distributed. Through the smoking process certain changes take place in meats which render them more easily digested, hence bacon is one of the most easily digested and savory forms of fat. As sources of heat and energy, bacon and ham rank high.
Even for a small family, it is wise to buy a whole ham. This kind of quantity buying is economical and the many ways to serve ham add variety to your menus. In planning the use of the whole ham, first use the slices for broiling, baked slice of ham, creamed ham and other dishes requiring slices or cubes of ham. Use the last half of the ham for baking in the piece.
Bacon in the piece or cartons of bacon should be kept on hand at all times. A breakfast of bacon and eggs is the accepted breakfast and may be quickly and easily prepared. A few strips of bacon add just the right flavor to the roast fowl, meat loaf, larded tenderloin, or casserole of vegetables or cereals.
The drippings from ham and bacon should be kept in a cold place and used for shortening in spice cakes and cookies, for flavor in sauces for vegetables and meats, for sautéing where the smoked meat flavor is desirable, in the dressing for vegetable salads, and in the stuffing for fowl.
Boiled Ham with Apple Rings—Cold or hot boiled ham served with a border of apple rings fried in deep fat.
Cold Ham with Sliced Pineapple—Ham sliced thin served with one slice of pineapple to each helping.
Boiled Ham and Spinach—Slices of boiled ham steamed over spinach, served with border of ham surrounding spinach.
Fritters—Ground ham in a fritter batter with corn.
Rissoles of Ham—Diced boiled ham in cream sauce, baked in a pastry case.
Ham Patties—Creamed boiled ham in patty shells.
Timbales—Creamed ham in timbale cases.
With Apricots—Cold boiled ham garnished with apricots.
Ham au Gratin—Cooked ham in cream sauce in casserole with layer of cheese and buttered crumbs.
Spiced Baked Ham—Whole ham rubbed with brown sugar, stuck with cloves and baked. (See page 30)
Ham Roast Stuffed—Boned ham, stuffed with pork forcemeat, tied, steamed and baked. Served with celery sauce.
Broiled Ham Steak—Slice of ham half an inch thick, cut from large part of ham.

Milk is nature’s own food. It contains all the food elements necessary for body growth, protein, mineral salts, carbohydrates, fats, vitamines and water. It is the indispensable food for the young. It lends itself to a great variety of uses in the correct diet of the individual. Modern housekeeping demands that a supply of a quality brand of canned milk be in every pantry.
As an addition to coffee or tea, evaporated milk has long been a recognized boon. Now, however, the convenience of this as a pantry staple for the country, town or city home cannot be overestimated. It is ever ready for the milk or cream call necessary to the completion of a perfect festive meal, or the easily digested milk toast or eggnog for the convalescent as well as the everyday baking need.
According to latest scientific experiments, the growth properties known as vitamines, so rich in milk, are in no way affected by the process of water elimination used to produce evaporated milk.
Evaporated milk is a product of the greatest importance to all families far removed from the source of a reliable fresh milk supply. It is just the pure milk with a large part of the moisture removed. It contains all the natural butter fats, mineral salts, proteins, and solids of the fresh milk. Nothing is changed in evaporated milk excepting the quantity of water in the fluid. For that reason, when canned milk is used to feed to children it is best to purchase a reliable brand of evaporated milk. Condensed milk is whole milk reduced by heating; it differs from evaporated milk in that it has 40% to 44% sugar added.
A high quality evaporated milk contains 26.16% solids and 69.24% water. A test of the keeping qualities of this product demonstrated that evaporated milk would keep sweet ten days after the can was opened. On souring it may be used the same as soured whole milk and with equally good results.
To use evaporated milk as whole milk, it should be diluted in the proportion of one cup of evaporated milk to two and one-quarter cups of water. This will give a product averaging a rich whole milk.
Evaporated milk is most satisfactory for cream soups; for sauces for vegetables, fish and meats. Whipped for puddings (undiluted). Used diluted, it gives splendid results in cakes, muffins, biscuits and other flour mixtures. As cream for coffee, cocoa and chocolate, cereals, fruits and puddings it adds food value and flavor. As a beverage diluted with water or for eggnog it is just as satisfactory as ordinary milk for children. For ice creams and custards, cream candies and fudge it adds a smoothness and creaminess.
Escalloped Ham with Peanut Butter—Dressing of crumbs, celery and seasoning, covered with slice of ham spread with peanut butter, buttered crumbs and baked until brown.
Ham Omelet—Cooked ham cut fine and folded into an omelet.
Croquettes of Ham with Green Peas—Ham ground, mixed with a thick white sauce, seasoned and formed in croquettes. Served on platter with creamed peas.
Tomato Stuffed with Ham—Minced ham and rice pressed into tomato shells and baked.
Sweet Peppers Stuffed with Ham—Cooked ham cut fine, mixed with crumbs and pressed into peppers.
Ham Sandwiches—Minced ham, chopped pickles and mayonnaise.
Ham Salad—Diced ham, diced celery, baked beans and mayonnaise. Served on lettuce.
Ham à la King—Diced cooked ham with green pepper, pimento and mushrooms in cream sauce.
Ham and Eggs, Ham Cutlets, Boiled Bacon, Bacon and Eggs, Bacon with Fowl, with Veal, with Flank Steak, with Fish, Bacon as seasoning in dressings, Casserole of Bacon and vegetables, Creamed Bacon, Omelet, Bacon Sandwiches, Club Sandwiches (Broiled bacon and white meat of chicken between slices of toast).

Cheese has an important mission in the dietary; served as an accompaniment, it adds food value, flavor and distinction. In large quantities it may take the place in food value of the meat dish. It must, of course, be served in combination with vegetables or cereal food to supply the proper bulk.
Cheese contains protein and fat. It builds tissue and creates heat and energy. For variety it may occasionally be served as the main food for a meal—and adds zest when used in salads and other table specialties.
In fuel value, one pound of cheese is equal to three and one-third pounds of baked beans—or three quarts of whole milk, twenty-five average size eggs, or of peanut butter approximately three-fourths pounds.
Popular cheese dishes are Spaghetti and Cheese, Macaroni and Cheese, Cauliflower and Cheese au Gratin, Potatoes au Gratin, Melted Cheese Sandwiches, Cheese Crackers, Eggs au Gratin, Cheese Croquettes, etc.
Peanut Butter is a highly concentrated, rich food, containing protein, carbohydrates and fat, all in large proportion. For this reason it may be used as a main dish in the menu in proper combination. Peanut loaf, peanut soufflé, peanut omelet, and peanut salad are fitting main dishes for the dinner or luncheon.
In order to properly balance in the diet, peanut butter must be combined with foods of more bulk and less food value. Salad dressing and peanut butter make excellent sandwiches. Combined with tomato pulp and milk, peanut butter forms delicious soup. It may be used to flavor and to shorten cookies and drop cakes. It also adds to custards or salads. Due to its popular flavor, it also lends itself for use in the making of delicious confections.
Beans are in the class with meat and cheese as protein food and may alternate with them as the main dish in the menu. They offer a variety to the menu served as bean loaf, soufflé, croquettes, relish, salad, or as purée.
The choicest commercially prepared pork and beans are made from selected double hand-picked Michigan pea beans with carefully selected government-inspected pork. They are cooked by the Appert Dry Steam Process, thereby blending and retaining all the delicious bean flavor.
This dry steam process renders the beans more easily digestible than is possible for home-cooked beans.
Eggs contain all of the elements necessary to life. Next to milk, selected eggs are the most economical source of animal protein and, like milk, contain the growth elements popularly known as fat soluble A. Vitamines.
The highly concentrated food value of eggs makes it necessary to combine them with such starchy foods as bread or potatoes so that there will be sufficient bulk food for the stomach to act upon. Eggs are an excellent substitute for meat and are as indispensable as sugar in cooking. It is necessary to cook eggs slowly and at a low temperature to have them easily digested.


Delicately seasoned sausage, made of carefully selected Government-inspected meats, has a very definite place as a staple food. Sausage is all food, no waste, and most appetizing. The correctly blended seasonings of high-grade sausage, fresh, smoked or dry, start the gastric juices and act as an aid to digestion.
Fresh pork sausage is very high in fuel value, the fat adding to the protein, heat and energy-producing material. This makes it essentially a cold-weather food. The drippings should always be saved to use as a sautéing medium or shortening.
Fresh sausage, either links or bulk. Fry and serve with toast, pancakes or muffins, mashed potatoes, rice or hominy, for breakfast, dinner or luncheon. Stuff potatoes and apples with fresh pork sausage, bake and serve as a nutritive luncheon novelty.
Tart fruit always adds to the meal of which fresh pork sausage is the main dish.
Bologna and Frankfurters have gained wide reputation as dependable meats satisfactory for all informal occasions. They are made of pork, beef, and mutton. They are carefully spiced with delicate mild spices.
Smoked sausage may be used for any meal. The Bologna is preferable for luncheon dishes and picnics; the Frankfurters for any hot meal.

Left-overs of either sausage may be made into such appetizing breakfast dishes as omelet, creamed sausage on toast or heated in the oven with mashed potatoes.

As dry sausage is a product which originated across the water, American housewives are rapidly learning to appreciate its higher food value. Fresh U. S. Gov’t inspected meat cuts are selected and combined with the choicest seasonings and subjected to unique curing processes, making this a most delicious food ready to eat. There is a wide variety to suit every taste. Recipes from Italy, France and the other foreign countries are followed or improved upon to make American dry sausage the superior food it is.
Dry sausage may be made into a great variety of appetizing dishes or served sliced, cold. It is wholesome and nutritious. An attractively garnished platter of Dry Sausage is a favorite for a cold meal.
Breakfast: Creamed dry sausage with apple-fritters; diced and cooked in pancakes; stuffed into potatoes before baking; or in fritters.
Luncheon: Dry sausage croquettes, dry sausage sandwich; cheese and dry sausage rarebit; omelet au summer sausage.
Dinner: Dry sausage dressing for fowl or meat, dry sausage stuffed in peppers, dry sausage with tomato sauce; potatoes stuffed with dry sausage and cheese; dry sausage meat loaf; casserole of dry sausage and hominy.

As the many advantages of ready-cooked canned meats have become more generally known, their universal use has constantly increased, so that to-day thousands of housewives maintain on their pantry shelves a variety of canned meats to supply all regular and emergency requirements.
Meat was first put up in cans to prolong its keeping qualities, especially during the hot weather season. So uniformly successful were these experiments that the original purpose has been almost forgotten, and canned meat now occupies an all-year-round prominent place in the national food supply.
When canned meats are sold under a nationally known brand name, such as Armour’s Veribest, you can be sure that the meats are carefully selected, U. S. Government inspected, and prepared, cooked and seasoned in sanitary, scrupulously clean kitchens by the most expert chefs. Complete sterilization, accompanied by a vacuum process of sealing, guarantees their perfect keeping qualities and enables the home manager to serve this meat on her table with all the deliciousness of meat prepared by the nation’s most expert cooks.
The cost per pound is a trifle higher than fresh meat, but it is already cooked, there is no shrinkage, it is 100% edible, and therefore can be served on the table at a relatively lower cost. Canned Meats served either hot or cold can be prepared in as many appetizing ways as fresh meat.
The housewife should always buy canned meats by brand name; for the label, plus the U. S. Government Inspection stamp, is the safest buying guide that can be found.
In every home where meals are served regularly it is a great convenience to have on the pantry shelf a complete supply of canned meats, for it takes the guesswork out of cookery, saves time and labor, and assures the home manager of a successful meat dish for any regular or emergency meal.
Any first-class dealer can supply you with a complete variety of high quality canned meats.
Always read the label when buying and be sure to look for the U. S. Government inspected and passed legend on every can of meat you buy.
Meat loaf is made from choice selected Government Inspected meats. Prepared commercially by chefs who daily use the same accurate measurements of beef and pork trimmings combined with macaroni, eggs, cheese and seasonings. The results are standard products. When whole, the loaves average about six pounds in weight.
Meat loaves are widely popular, time and energy savers for the housewife and may be purchased in any amount desired, from your butcher, grocer or delicatessen.
In more elaborate form are jellied loaves. Such meats as tongue, tripe, pigs’ feet, corned brisket of beef and ox lips are selected, cooked whole, covered with gelatine and molded into loaf form. They require no home preparation, are ready to slice and serve.
Luncheon meats are made of selected pork trimmings cut in somewhat larger portions than for the loaf meats. These meats, carefully seasoned, mixed and cooked, suggest a great variety of dishes.
As an appetizer, sandwich fillers, sliced cold on lettuce or in salad, luncheon meats have come into great favor.
| New England Style Veribest | Luncheon | Meat |
| Berliner Style | “ | “ |
| Minced Style | “ | “ |
Extract of Beef adds the distinctive touch to many meat and fish sauces, soups and gravies. It is a valued meat extender as it adds the meat flavor necessary to make a small amount of meat, flavor a large amount of cereal in a loaf or croquettes. Many salads and vegetable dishes are greatly improved by the addition of a bit of Extract of Beef to the sauce.
DRY SAUSAGE SMOKED Summer Sausage, Salami, Scandinavian, Mettwurst, Nola.
DRY SAUSAGE UNSMOKED Milan Salami, Coppa, Capicolli, Arles, Menage, Sopressata, Peperoni, Mortadella.
FRESH SAUSAGE Veribest Farm Style Pork Sausage, Blood Pudding, Bologna Style Sausage, Frankfurt Style Sausage, Garlic or Knoblach, Head Cheese, Liver Pudding, Pure Pork Sausage.
A wide variety of superior sausage is put up in cans for convenience in keeping. Available under the quality brand are the following:


A properly balanced diet contains a regular supply of fat. The ideal diet determined by weight, height, occupation and general health of the individual contains just sufficient quantity of fat and carbohydrates to give the required amount of heat and energy. In popular terms, one-fifth of the diet should consist of fat. Much of this may be fat of vegetables or meats, but some of it should be butter fat or its equivalent, especially for children because of the vitamines it contains. Scientists agree that oleo oil also contains the growth-promoting elements.
The necessity of fat in the diet has been proven by numerous experiments. Animals lacking certain fats do not grow and cannot reproduce. Disastrous results have attended nations where shortage of supplies made it impossible to include the necessary fat in the diet.
Fats supply a large part of the heat and energy required, an ounce giving two and one-half times as much heat and energy as an ounce of carbohydrates. Butter, oleomargarine, nut margarines, pure leaf lard, bacon, salt pork, the fats of beef, mutton, pork and fowl, vegetable fats and oils and peanut butter are our principal sources of fat. A certain percentage is found in all nuts, cereals and vegetables. For the average healthy person fats are not difficult to digest if not taken in too large quantities and if the fat is properly used in the food.
Butter, oleomargarine, nut margarine and peanut butter are the spreads in general use. In a well balanced diet these may be used interchangeably. The food value is principally in the heat and energy furnished, which is practically equal in all the spreads. Butter and highest grade oleomargarine contain certain growth elements not found in the nut butter, but milk or the average well varied diet corrects this.
Butter is one of the best sources of fat for the daily diet. High grade creamery butter, such as Cloverbloom, is made in the heart of the rich dairy districts, from sweet pasteurized cream.
Oleomargarine has a well recognized place among spreads, due to a growing understanding among intelligent housewives as to its composition and the ideal conditions under which it is made. It is made by churning pure, sweet animal oils and vegetable oils in pasteurized milk and salting to taste. Since the housewife knows that materials used in oleomargarine are used daily in one form or another in her home and that it is given Government Inspection, oleomargarine has become a most generally used spread.
The vegetable or nut margarines are made from pure cocoanut and peanut oils churned in pasteurized milk. They are daily growing in public favor. The low moisture content of nut margarine and the care in preparation make it a rich and tasty spread. Nut-ola is the popular Armour nut margarine.
Peanut butter, although used as a spread, has become universally known as one of our most excellent protein sources to replace meat. Easily digested, it is not only popular with adults, but a good food for children.
For shortening purposes, fats are used to improve the texture of the product. The fat in the mixture protects the starch grains from the moisture until the proper time in baking, allowing the leavening agent to act and the starch grains to swell, resulting in a light even-textured product.

It is possible to use a great variety of fats for cooking. Animal fats have been popular shortenings. Recent fat shortage has[22] acquainted us with the value of vegetable fats as shortening and in spreads. Armour’s vegetable fat is Vegetole. It contains the same fuel value and has the same shortening value as lard. Pure Leaf Lard or vegetable fats are the ideal shortenings. Salad Oil, highly refined vegetable fat, Oleomargarine, Nut-ola, butter, and drippings from bacon, ham, beef and pork are used with entire satisfaction for shortening purposes.
The fats best suited to deep frying and sautéing are those which have a very high burning point. For general “all purpose” satisfaction, pure leaf lard ranks first. There is an Armour product especially suited to every cookery need.
Bacon drippings may be substituted for lard in frying, baking, or in gravies, providing the drippings are clarified and not too strong. A great many people prefer the flavor of bacon drippings to any other shortening.
Beef suet drippings, for reheating meats or for frying or shortening purposes, take the place of lard and are much more economical.
Pork fat, left from roast, chops or ham, can be used in the same manner.
Mutton drippings need no longer be set aside, since the housewife has learned how to sweeten them.
Smoky kitchens indicate the improper use of fat in cooking. Too high a temperature causes a chemical change to take place which results in smoke and disagreeable odor, and also renders the fat less digestible.
Put cold fat into a cold pan before placing it over the heat. Bringing into contact with the hot pan frequently results in burning the fat.
For deep frying and sautéing, care should be taken not to heat the fat to too high a temperature, as burning decomposes the fat and renders it less digestible. In deep fat frying, place the food to be fried in the hot fat a small amount at a time. The addition of the cold food reduces the temperature of the fat.
Do not pile fried articles. Drain on unglazed paper.
Strain fat after using, save, and use again.
When fat is not hot enough, when mixture is too rich, when mixture is too moist, and when too much soda or baking powder has been used, deep-fried foods will take up too much fat and be greasy.
A piece of soft bread will brown in 40 seconds in deep fat that is just hot enough for cooked articles, or in 60 seconds in fat at the right temperature for uncooked foods.
Fat is too hot if it smokes.
To clarify the frying medium for second or third use, melt, add raw potato cut in quarter inch slices, and allow to heat gradually; when it ceases to bubble and the potatoes are well browned, strain through double cheesecloth, placed over the wire strainer into a pan.
Vegetable salad oil meets all the requirements for a rich, delicately flavored oil for salad dressing. Highly refined cottonseed oil and cocoanut oil are American products, made from highly refined vegetable oil. Both have proved entirely satisfactory and economical as salad oil. Highly refined cottonseed oil for frying has a high smoking point, and, properly used, gives off no unpleasant odor.
| NAME | SMOKING POINT | 100 CALORIES | USE | COMPARATIVE QUANTITIES TO USE |
| “Simon Pure” Leaf Lard | 468° F. | 1 scant tbsp. | Shortening, Deep Frying, Sautéing, or Pan Frying | Standard Shortening |
| White Cloud Shortening | 446° F. | 1 scant tbsp. | Shortening, Deep Frying, Sautéing | Same as “Simon Pure” |
| Vegetole | 473° F. | 1 scant tbsp. | Shortening, Deep Frying, Sautéing | “ |
| Veribest Oil | 510° F. | 1 scant tbsp. | Salad Dressing, Deep Frying, Sautéing, Shortening | A trifle less than of “Simon Pure” |
| Veribest Oleomargarine | 425° F. | 1 tbsp. | A satisfactory economy Spread and Shortening | To replace butter use 1/8th less for shortening; a bit more than of “Simon Pure” |
| Nut-ola | 420° F. | 1 tbsp. | An economy Spread | ” |
| Cloverbloom Butter | 400° F. | 1 tbsp. | The Ideal Spread and Shortening for cakes | For shortening use 1/5th more than “Simon Pure” Leaf Lard |
| Protein | Fat | Moisture | Carbohydrates | Salt and Ash | Calories per lb. |
|
| Butter | 1.00 | 80.5 | 15.5 | 3.00 | 3310 | |
| Oleomargarine | 1.0 | 85.5 | 11.00 | 2.5 | 3820 | |
| Nut-ola | 2.17 | 85.15 | 11.77 | 2.17 | 3610 | |
| Peanut Butter | 29.3 | 46.5 | 2.1 | 17.1 | 5.0 | 2825 |
| Pure Leaf Lard | 100.00 | 4220 | ||||
Salad and Cooking Oil |
100.00 | 4220 | ||||
| Vegetole | 100.00 | 4220 |

The dietetic value of fruits lies in the fruit sugar, mineral salts, and organic acids which they contain. Fruits are body regulators.
Fruit sugar or carbohydrates are the chief sources of fuel value in fruit. Most fruits also contain the substance which is necessary for jelly making. A fruit which does not contain pectin, such as pears and pineapple, must be combined with some fruit containing pectin. Apples, grapes, and currants contain great quantities of pectin.
Fresh fruit eaten the first thing in the morning acts as a cleanser. Care must be taken in the selection of fruit, it should be ripe, but not overripe. If overripe, it is liable to cause fermentation in the alimentary tract.
Science has perfected the drying process to such a degree that dried fruit has become a great convenience when the fresh product is not obtainable.
Because it is impossible to wholly consume all fruits at the harvesting time, great quantities are canned for later consumption. To retain the highest natural flavor and full fruit sugar value, it is necessary to can fruits and vegetables just as they ripen and immediately after picking. Commercial canning of fruits has reached such a high degree of excellence that the average home manager prefers to buy a reliable brand she knows to be uniform, rather than run the risk of having fruits spoil that she uses her own time and material to “put up.”
The wide variety of fruits on the market under reliable brand names makes it possible to serve practically any fruit at any season. Even the special types of fruits may be purchased canned, as Royal Anne Cherries, Muscat Grapes, Bartlett Pears, Egg Plums, etc.
| Apricots | Roast Lamb, Baked Ham |
| Pineapple | Boiled Ham, Cheese |
| Apples | Roast Pork |
| Pears (spiced) | Cold Beef, Cheese |
| Peaches (spiced) | Veal, Cheese |
All fruits combine in fruit salads, cocktails, ices.
Vegetables contain a large amount of water, cellulose, and mineral matter. They are included under the classification of carbohydrates, or mineral salts according to the predominance of starch or mineral matter. Leafy vegetables are rich in vitamines.
The mineral salts afford bone building material, while the large amount of cellulose which they contain furnishes bulk in the diet.
Canned vegetables are preserved by sterilization. Salt is used to bring out the flavor, acts as a preservative, and increases the mineral content.
Dried vegetables are being used in soups and ragouts. The dried vegetables have not yet reached as extensive use as have the dried fruits.
Commercially canned vegetables add year round variety to practically every American table. The selection of a reliable brand simplifies the marketing.
Tomatoes—Broiled Steak, Lamb Chops. Asparagus—Planked Steak, Roast Beef, Lamb Chops, Veal Chops. Spinach—Ham, Tongue, all meats, eggs, fish. Peas—Lamb Chops, Chicken, Meat croquettes. String Beans—Ham, Boiled Lamb, Chicken. Okra—Chicken, Tuna, Ham. Celery—Cheese Dishes.
All vegetables combine in vegetable casseroles and salads.
Mince Meat nearly conforms to the requisites of a perfect food. It contains protein from the meat content, carbohydrates, both sugar and starch in the form of fruits, and moisture. Spices and flavoring make it complete. Its fuel value is considerable. It should not merely be used as a holiday food, but as an all year round product.
Mince meat contains only the best and most wholesome ingredients. On the market are two varieties, the condensed and moist. Moist mince meat requires more attention because of its aptness to ferment. In making it, green apples and fresh cider are used. As cider makes vinegar and raisins and currants make wine, fermentation is possible. This does not mean that the mince meat is no longer good. The alcohol formed acts as a preservative.
Concentrated mince meat contains dried apples and boiled cider. In this respect only does it differ from moist mince meat. By the addition of water, the condensed becomes equal to moist. Condensing is done merely to aid in packing and delivery.
Pie Patties, Brown Bread and Mince Meat Sandwich, Pudding, Tomato stuffed with Mince Meat, Mince Meat Salad, Mince Meat Relish, Mince Meat Cookies.

Perhaps one of the greatest simple helps toward a well-ordered home is a well-stocked pantry. With this to rely upon, one is always ready for any demand that can interfere with the regular plans of the household.
Besides a carefully selected assortment of quality foods already prepared, a number of menus and the recipes to accompany them should be easily accessible, so that in case the home-manager herself is away from home or is ill, almost any member of the family can keep the meals going satisfactorily.
The pantry shelf should contain CANNED soups, fish, meats, milk, vegetables, fruits; jams, jellies, condiments, a few packages of cookies and crackers. A few cans of evaporated milk come in handy, even on the farm, now and then, and will keep until needed.
Let the Armour Housewives’ Choosing List be your guide in stocking this shelf. When a package is used, replace it at once so that the shelf will be ready for all staple and emergency calls, sure to come when least expected. During the warm months, many of the foods illustrated on pages 24-25 will be kept in the refrigerator.
| Proteins | Fats | Carbohydrates | Minerals | Water |
| Amount needed 1-5 of meal | Amount needed 1-5 of meal | Amount needed 3-5 of meal | At least 1 serving daily | Amount needed 1 quart daily |
| Build Muscle and Tissues | Supply Heat and Energy | Supply Heat and Energy | Body regulators, make bone, hair, teeth and nails | Body regulator, aids in digestion keeps body normal temperature |
| Milk Cheese Eggs Fish Beans Peas Poultry Fresh Meat Smoked “ Dried “ Canned “ Nuts Peanut Butter |
Butter Lard Oleomargarine Nut Margarine Salad Oil Vegetable Shortening |
Cereals Starchy Veg. Sugars Flours Syrups Candy |
Fruits (Canned, Fresh) Vegetables Milk Egg Yolks |
In all Vegetables “ “ Fruits “ “ Beverages |
| Vitamines | ||||
| Necessary to growth and reproduction | ||||
| Contained in Milk and Milk Products Egg Yolks Leafy Vegetables Yeast Glandular Meat Organs |
||||
| Place in menu, usually main dish. | Used as shortenings and spreads | Place in menu, vegetables, cereals, desserts | Place in menu, fruit and vegetables |

Cookery, to meet the present day standards, is necessarily an art and a science. (See page 46 for measures and abbreviations.)
Skill in blending flavors, and arranging dishes to please the eye as well as the palate, is an art of which every home manager may be proud. Still more important, however, is the scientific preparation of nutritious and economical dishes to supply the body needs of every member of the family.
In these pages devoted to cookery we have covered important cookery points which influence the palatability, digestibility, and combination of materials for best results. Our aim is to present to the American home manager a valuable cooking manual, not a recipe book. Below are listed many splendid books of recipes in your public library:
| Book | Author | Subject Matter |
Boston Cooking School Cook Book |
Fannie Merritt Farmer |
Foods, cookery, recipes |
Mrs. Rorer’s New Cook Book |
Mrs. S. T. Rorer |
Foods, cookery, recipes |
Practical Cooking and Serving |
Janet McKenzie Hill |
Cookery, recipes, serving |
Feeding the Family |
Mary Swartz Rose |
Foods—Their place in the menu and economical use |
Boston Cook Book |
Mary J. Lincoln |
Foods, cookery, recipes |
Home Canning, and Preserving |
A. Louise Andrea |
Use of dried foods |
Mrs. Allen’s Cook Book |
Ida C. Bailey Allen |
Foods, cookery, recipes |
Canning, Preserving, and Pickling |
Marian Harris Neil |
Canning, preserving, pickling |
Food and Household Management |
Kinne & Cooley |
Food values and home management |
Home Science Cook Book |
Anna Barrows and Mary J. Lincoln |
Appetizing and nourishing dishes and how to serve |
Practical Dietetics with Reference to Diet in Disease |
A. F. Patte |
Diets for sick and convalescent, food values, special recipes |
U. S. Government Bulletins, Department of Agriculture. Washington, D. C.
Farmers Bulletins, Department of Agriculture, Washington, D. C.
The Department of Agriculture issues bulletins on almost all foods, their care and use in the home, household appliances, canning, etc. These bulletins may be obtained by writing to the addresses above. Send for a catalogue of the bulletins and order the ones in which you are interested.
Prepare soup stock in a kettle which will retain heat. Fit with a tight cover, for the vapors must be held in to add to the flavor of the stock. Shank and neck of beef, pork or lamb, left-over morsels of meat, bones from steaks, roasts, chops and the carcasses of poultry, are good materials from which to make meat stock.
Crack and saw bones to uniform size, put into kettle and add cold water in the proportion of three cups of cold water to one pound of bones.

Let stand for one-half hour or until water is colored by juices, heat to boiling point. Skim off fat, reduce heat and let simmer or bubble slowly for four hours. The stock must be kept at low temperature in cooking so that the albumen or jelly of the meat will not coagulate, but be retained in the stock, giving it full flavor.
Cook until the meat is shredded and colorless. When nearly done, add vegetables and seasoning. Strain, set stock aside to cool—discard bones, reserving vegetables and meat portions, which are still rich in food value, for further use in pressed loaves. A bit of Extract of Beef will add the desired meat flavor.
Stock is used as the foundation for all meat and vegetable soups. Cream soups have white sauce as a foundation with the vegetable purée added.
So much time is consumed in preparing soup that the great variety of high quality canned soups are a welcome addition to Madam Home Manager’s Labor Savers.

(See pages 7, 8 and 9 for Meat Charts)
To be sure of success in meat cookery, know first the structure of the cut of meat you are to prepare, then use a standard tested method for making that cut tender, flavory and juicy.
Always have a good fire before placing meat over the heat, for all meat cookery requires the greatest heat first to seal the appetizing juices in. Your skill will be shown in your first ten minutes of handling.
The short fibered cuts comprising the loin cuts, porterhouse, and club steaks may be given the entire short cooking over a hot fire. Practically all the other cuts on the carcass require long moist cooking after the searing process.
All boiling pieces should be put into boiling water first and after ten minutes’ brisk boiling, the heat should be reduced so that the meat simmers until the connective tissue softens and the meat is tender and just right for carving. Too long brisk boiling makes the meat stringy. Roasts should be cooked on the same principle. Put into the hot oven for fifteen minutes, then reduce the heat and cook the cut slowly, basting frequently. Steaks and chops that are to be pan broiled, should be put on a hot pan and quickly turned so as to sear and brown evenly, then allowed to cook through, over the hot fire. As salt draws the juices out of meats it should not be added until after the first ten or fifteen minutes of cooking, when the meat is thoroughly seared.
This process of cooking subjects the meat, fish or poultry to the direct rays of the fire, quickly searing and browning the meat; this is the approved method of cooking tender steaks and chops, fish and spring chicken. An intense, even heat is necessary.
A very hot frying pan is used without addition of any fat; chops and steaks are cooked in this way.
Roasting is oven cooking in an uncovered pan. Baking differs only in the fact that the pan is covered, thus making the cooking self basting. Prime ribs, loin or leg, and fowl, are roasted; rump, short ribs and shoulder are frequently baked.
Wipe the meat, dredge with flour and brown the entire surface in a little fat, place the meat on a rack in a deep kettle and cover with boiling water. Cook with vegetables and seasoning, adding vegetables at intervals to allow for the perfect cooking of each class of vegetables by the time the meat is done. Place cover on kettle and simmer slowly about four hours. Serve with the thickened liquor.
Cooking in liquid at 212° F. is boiling. Meat should never be boiled rapidly, as the fibers become tough and the tissues dissolved. To have boiled meats tasty and juicy, plunge the meat into boiling water and cook for ten minutes, then lower the heat and cook slowly until tender. An excellent way to cook shank, clod, shoulder plate, brisket or neck. A fireless cooker is practical for this type of cookery. A pressure cooker makes it possible to cook a tough fowl or cut of meat in a very short time.
Cooking in a closely covered pan in the oven is termed braising; a small amount of water is used. The meat is usually sautéed first, to prevent escape of much juice. Vegetables are often cooked with the meat. The temperature should be kept low. It is an excellent way for cooking spareribs, brisket, rump, shoulder or chuck roast. Besides stewing or boiling, it is an excellent way to prepare the tough cuts.
Pan frying in just enough fat to brown the foods nicely and keep them from sticking to the pan is called sautéing. Fish, steaks, chops and potatoes are cooked by this method.
Meat for a stew, such as neck, clod, shank, brisket or chuck, can be cut in small pieces, browned to hold in juices before cooking in the boiling water; or, omitting that process, put directly in a small amount of hot water and cooked at a low temperature for a long time. All nutriment is retained in the meat.
For this method of cooking, an iron kettle is best. Half fill the kettle with fat and place over fire; melt and, when a slight blue vapor arises, test with a small cube of bread. If bread browns in one minute, the temperature is right for uncooked mixtures (doughnuts). If it browns in forty seconds, it is right for cooked materials (croquettes). The temperature of the fat should average 350-400 degrees F. Keep the temperature even; if too cool, the food will soak fat; if too hot, both fat and material to be cooked will burn. Foods cooked in deep fat should be drained on brown paper.

Dredge the roast with flour. Rub skillet with suet and, when pan is hot, quickly sear roast on all sides. Add seasonings, except salt. Roast in hot oven for fifteen minutes, sprinkle with salt, lower heat and cook slowly until tender. Baste every twenty minutes, adding a little boiling water if necessary.

Cut the suet and bacon fine and fry. Add the onion, garlic and green pepper chopped quite fine and fry. When beginning to brown, add the meat, turning it so that it will be well browned on all sides. Then add the hot water, tomatoes and the seasoning. Simmer gently for three hours, add 2 tsp. salt and a quarter tsp. pepper at the end of an hour and a half. Half an hour before the meat is finished, boil the spaghetti till tender, drain it and put it into the sauce surrounding the meat. Let cook 10 minutes. For serving, put the meat on a platter and the sauce in a dish, grating American cheese thickly over the top.
Wipe steak. Score across grain with sharp knife. Rub with flour and brown; sprinkle with salt and pepper. Spread one side with bread dressing, well seasoned. Roll up and fasten with skewers or tie with a cord. Place in a casserole, add one-fourth cup boiling water and let bake slowly until tender. Slice and serve with the gravy.
Wipe meat. Sear quickly to seal in juices. Sprinkle with salt and pepper. Cut garlic in two pieces and place on meat. Dredge both meat and bottom of pan with flour. Place roast on rack in roasting pan, and add hot water. Place in hot oven and baste every fifteen minutes. Lower gas after the first twenty minutes’ cooking, and cook slowly until tender. Keep meat covered and about three-fourths pint of water in the pan, as the steaming will help make the meat tender. Cook at low temperature.
Set ham on a rack in a baking pan and bake one-half hour in a hot oven, turning after the first fifteen minutes. Lower heat. Pour a cupful of cider over ham and let bake five hours, basting often with the liquid in the pan. Remove from the oven and skin. Insert cloves in the fat of the ham, from which the skin has been taken; press these into the ham in a symmetrical manner.[31] Mix half a cupful of brown sugar with half a teaspoon of pepper and half a cupful of fine cracker crumbs and sprinkle over the portion containing the cloves; return the ham to the oven for one hour.
Wipe beef, cut in two-inch pieces, and roll in flour. Cut salt pork in dice and fry until light brown. Add beef and cook until meat is well browned, stirring constantly. Add salt and enough boiling water to prevent burning, and cook slowly two hours or until tender. In another dish cook tomatoes, onion, chopped celery, bay leaf and cloves for thirty minutes. Add two tbsp. flour, mixed until smooth with two tbsp. cold water, and cook thoroughly. Add to meat. Remove meat to center of platter, surround it with potato slices and carrots cut in strips and cooked until tender in boiling salted water, and add the green pepper parboiled and cut in strips. Pour gravy over the meat; garnish with parsley.
Wipe meat with cloth wrung out of cold water. Remove superfluous fat and use to grease the broiler. Have broiler very hot. Place meat on broiler about three inches from the heat, which should be even, whether it is coal, gas or electricity. Turn meat every ten seconds at first, that the surface may be well seared and prevent the escape of the juices.
Steak 1½ inches thick will require 10 minutes if desired rare, 12 to 15 minutes if preferred well done.

Wipe steak, remove superfluous fat, and pan broil seven minutes. Grease an oak plank and arrange, close to the edge, a border of mashed potatoes, pressed through a pastry bag. Remove steak to plank, put into a hot oven, and bake until steak is cooked and potatoes are browned. Spread steak with butter, salt and pepper, and garnish with parsley, lemon and olives. Arrange beets and other vegetables, if desired, on the side.
Use the meat juices left from cooked meat or fowl, removing any excess fat. Extract of beef may be substituted for meat juices in gravy.
After removing meat and excess fat from the roasting pan or skillet, heat meat juices to boiling and thicken carefully. To avoid lumpy gravy, the best way is to mix the flour with a small amount of water, stirring until smooth, then gradually adding more cold water until the thickening is of the right consistency. Add gradually to the hot liquid, stirring constantly.
Allow mixture to cook ten minutes. Gravy should be cooked thoroughly to avoid any raw or starchy taste, too common to American gravies.
Season carefully, according to the meats gravy is to be served with. It is wise to taste before serving.
The distinctive touch French chefs are noted for in their meat and fish dishes is often due to the sauce accompanying them. Any careful American cook can acquire the same reputation for skill by following the suggestions to cook thoroughly and season distinctively.
| Thin | Sauce | 1 tbsp. fat, 1 tbsp. flour to ½ pt. liquid |
| Medium | “ | 2 tbsp. fat, 2 tbsp. flour to ½ pt. liquid |
| Thick | “ | 3 tbsp. fat, 3 tbsp. flour to ½ pt. liquid |
Method of Preparation—Melt fat, add flour, stir until smooth. Add liquid gradually, stirring constantly. Place over hot water until the starch is well cooked and the sauce is smooth and of the desired thickness. Season to taste.
The flesh of young fowl is smooth. The claws and feet are usually light yellow in color and are very supple. A breastbone which bends easily indicates young fowl. Fowl should be plump, but not over plump. If fowl is exceptionally fat at the crop, it indicates large inner organs. They weigh heavily, and therefore are poor purchases.
Care should be taken that the fowl is drawn and thoroughly cleansed. This is often attended to by the local butcher, but special care and attention is also needed in the home.
The pin feathers must all be removed and the fowl singed. All blood clots, portions of lungs, etc., should be removed. Hold fowl under faucet, and let water from faucet rush through it to remove any clinging portions.
Chicken and turkey being dry meat, require frequent bastings. The grease which accumulates in the roasting of geese must be poured off from time to time. This should be clarified and carefully saved for use in pastries and as spreads. Strips of salt pork or bacon if placed across turkey or chicken baste the fowl as well as flavor it.
Older fowl is best when stewed. The fowl should be put into boiling water, seasoning added, and gently cooked at the simmering point for several hours before the vegetables are added. Cook until the meat is very tender. Add dumplings the last twenty minutes.
Fowl that is to be broiled should be brushed well with oil and allowed to stand in cool place some time before broiling. Sprinkling with lemon juice also tends to make it tender as well as flavors the fowl. Strips of bacon laid across the top baste the fowl. Turn frequently to insure thorough cooking.
Select young fowl for frying. Long, slow cooking is needed to thoroughly cook the fowl. The portions are dipped in egg and crumbs to protect them from the high heat of the pan and so keep them tender. Use a shallow griddle and add bacon fat as necessary.
In order that the legs, wings, and neck of fowl will not dry out, it is well to truss the fowl for roasting.
Fold back the wings so that they form a “V” on the back. Fold the neck back so that it fits beneath the wings. Fasten with twine. Bend back legs and fasten them close to the rump. Also fasten joints close to the body. If dressing is to be used, stuff in body and then sew up the openings. A trussing or darning needle threaded with twine makes the matter of trussing quite simple.
If fowl is purchased frozen, thaw in pan of cold water or place in refrigerator for six hours and then dress in the usual manner. Frozen fowl handled by a nationally recognized food organization has been carefully selected and possesses a delicate flavor.
Fowl may be fried or stewed in the pressure cooker. The foods are made ready as in the ordinary method and are placed in the bottom of the cooker. Vegetables or cereals may be placed on the rack above and cooked at the same time. The lid is then adjusted and the pressure raised to about 18 pounds and then kept there for thirty minutes. Fowl that is old is quickly cooked tender in a pressure cooker.
Fricassee, creamed chicken, chicken à la king, croquettes, soufflé of fowl, timbales, en casserole, salad, pilaff, patties, cold jellied loaf with vegetables, club sandwiches, hot chicken sandwiches, fritters, dumplings, pot pie, cottagers’ pie, pan roast, boned stuffed chicken, soup, country fried, pressed chicken, forcemeat, blanketed, curry, cutlets, gumbo, scalloped, stew.

Salads are combinations of meat, fish, eggs, vegetables, or fruits and nuts with a dressing.
Mayonnaise should not be added to salad until just before serving, as it may liquefy. It is most satisfactory to mix each ingredient in a fruit or vegetable salad with the dressing separately and combine at the last moment.
Green vegetables, such as lettuce, should not have dressing added until just before serving.
The flavor of meat and fish salads is improved by marinating in French dressing before combining with other materials.
Wash and pick over carefully as soon as brought from garden or market. Wrap in a wet tea towel or in salad bag and place on the ice or in cold place to keep fresh.
To keep parsley or other garnishes fresh, place in a fruit jar, sprinkle with cold water and cover tightly. The greens will remain fresh as long as there is moisture in the jar.
A mixture of salad oil, two parts, with one part vinegar and salt and pepper to taste.—Suitable for almost all salads.
To a French dressing add one part of one of the stronger varieties of cheese, crumbled.—Suitable for lettuce salad.
Salad oil, eggs, a small amount of lemon juice, or vinegar and seasoning whipped together to form a thick dressing.—Suitable for chicken, Waldorf, cream cheese, fruit, Macedoine, asparagus, celery and other salads.
Milk, eggs, mustard, vinegar and seasonings cooked together to form a dressing of the consistency of soft custard.—Suitable for potato or cabbage salad, and salads where oil dressing is not liked.
To one cup of boiled dressing add one-fourth cup of ground ham, 2 tablespoons of caviar, 1 tablespoon of shallots, horseradish and grape juice, and season with sour cream, sugar, pepper and salt.—Suitable for vegetable salads.
A mayonnaise dressing to which is added pimento, green peppers, chili sauce, Worcestershire sauce, pickles and whipped cream.—Suitable for lettuce, endive, and watercress.
Whipped cream added to a small proportion of boiled dressing or mayonnaise dressing. Use—For fruit salad, chicken salad, and other meats of delicate flavor.
| MATERIALS | DRESSING | WHEN TO SERVE |
| FRUIT | ||
Waldorf—Apple, celery, nuts and dressing |
Whipped cream dressing | Luncheon, dinner or light dinner |
Half pear filled with chopped fruit |
“ | Luncheon or heavy dinner |
Mixed fruits—orange, pineapple, dates, banana |
“ | Luncheon or to replace dessert for dinner |
| CHEESE | ||
American cheese cut in cubes, peas, gherkins |
Boiled dressing | Main luncheon dish or light dinner |
Celery stuffed with cream cheese |
French dressing | Luncheon or course dinner |
Cheese and nut balls lettuce |
“ | “ |
Lettuce, grated cheese |
Mayonnaise | “ |
Pineapple slice with cheese ball |
French dressing | Serve with baked ham dinner |
| FISH | ||
Tuna and diced celery |
Mayonnaise | Main luncheon dish or with light dinner |
Fresh watercress, minced onion, shredded finnan haddie |
French dressing | “ |
Salmon en mayonnaise—asparagus tips |
French dressing | “ |
| VEGETABLE | ||
Any vegetable fresh, canned or cooked |
French dressing or mayonnaise dressing | Luncheon, dinner or to replace second vegetable at dinner |

Although hens’ eggs are more commonly in use, the eggs of ducks, geese, guinea fowl and turkeys are all used as food.
The various uses of eggs in cooking may be listed as follows:
In cooking eggs, heat produces a change in both color and in firmness, the firmness, or hardness, depending on the temperature and length of time cooked. The change which takes place in the egg albumen is called coagulation. A high temperature for any continued length of time will produce a leathery consistency, which necessitates a longer time for digestion.
Soft-cooked eggs digest more quickly and more satisfactorily than do eggs prepared any other way.
The margin is slight, however, and the stomach takes care of all kinds of cooked eggs.
| Hours to Digest | |||
| 1 Boiled— | Soft | 3 | |
| Hard | 3½ | ||
| 2 Poached | 2½ | ||
| 3 Scrambled | 3½ | ||
| 4 Fried | 3½ | ||
| 5 Baked or Shirred | 2¼ | ||
| 6 Raw | 1¼ | ||
As there is a harvest time for eggs, it is necessary to insure eggs for year around use by preserving a supply for winter release.
Preserve only fresh clean eggs in the spring and early summer when they are cheap and plentiful. They may be preserved in any of the following ways:
1 Commercial cold storage is the most satisfactory method of preserving eggs.
2 Pack in sawdust, salt, bran or sand, with small end down.
3 Cover with salt brine, limewater or water glass.
4 Coat with lard, oil or paraffin.
Cheese is sufficiently cooked when melted. Protein is toughened by a high temperature, therefore a low temperature process should always be used in preparing cooked cheese dishes.
Cheese should be kept dry and covered, but never wholly exclude the air. If spread with melted paraffin, it will keep moist. Soft cheese should be kept in the ice box. The receptacle for cheese should be thoroughly sterilized before new cheese is placed in it.
Cheese gives character to many nourishing but indistinct-flavored foods.
| Uncooked Cheese— | Sandwiches | |
| Grated in Soups | ||
| Salad | ||
| With Pie or Pudding | ||
| With Crackers and Coffee | ||
| Cooked— | In Scalloped Dishes | |
| Rarebit | ||
| Sauces | ||
| Croquettes | ||
| Soufflés and Fondues | ||
| Biscuits, Muffins, Cheese Sticks | ||
| Topping for Baked Dishes |
Melt the oleomargarine, add the flour and when well mixed add gradually the scalded milk. Then add salt, cayenne and cheese. Remove from the fire and add the yolks of eggs, beaten until lemon colored. Cool the mixture and fold into the whites, beaten until stiff. Pour into a buttered baking dish and cook twenty minutes in a slow oven. Serve at once. Cheese soufflé is suitable as the main dish for luncheon, dinner or supper.
Make a medium white sauce. To each cup of sauce add half a cup of grated cheese and cook in double boiler until melted.
Use as a sauce over macaroni, spaghetti, rice, hominy, escalloped vegetable dishes, over toast as mock rarebit, or as a foundation for cream of cheese soup.

Fresh vegetables should be whole and sound when purchased. Roots and tubers require special care as to cleanliness. Perishable vegetables should be used as soon as purchased. If kept for any length of time, they should be stored in a cool, dry place. From time to time, they should be looked over and those which show signs of decay, removed.
The first step is cleansing. Wash thoroughly in cold water and then pick over or scrub with a vegetable brush to thoroughly remove any small portions of dirt that may be embedded in the outer covering or hidden among the leaves. Remove all leaves, tops, etc. The ideal way, from a food value standpoint, is to cook potatoes with the skins on, for, if pared, the valuable mineral salts escape into the water. Vegetables that are pared before cooking should be pared very thin. Between the skin and outer layers of the vegetable lies a layer containing much nutritive material, and, unless the parings are thin, this material is lost. Water in which pared vegetables are cooked should be saved and used as soup stock.
Vegetables should be cooked in boiling water. Strong smelling vegetables, such as cabbage, onions, etc., will not give off strong odors if cooked in plenty of water and uncovered. Other vegetables should be cooked in just enough water to cover and the kettle should be covered. Salt, however, toughens the fiber and, for this reason, is only used in the cooking of young, tender shoots. For the older vegetables the salt may be added just before serving.
Steaming is a very satisfactory method of cooking vegetables. The vegetables are placed on racks in the steamer and cooked until tender. None of the juices are lost, and the fiber is not toughened, and the appearance and shape of the vegetables are preserved.
Vegetables may be washed, and baked in a moderate oven until the skin bursts. This method of cooking is satisfactory in that no nutriment is lost. The vegetables classed as roots, such as turnips, parsnips, etc., may be baked, but are less suited to this method of cooking.
Garnishes of vegetables are often used to give a colorful touch to meat dishes. A little sprig of parsley is often sufficient decoration. Clever garnishes are made by means of vegetable cutters. These are attractive additions when used as a border around a meat dish.
Lettuce is used extensively as a garnish. It is used most commonly as a garnish for cold meats.
Method: Pare the potatoes. Cut in two lengthwise. Parboil for fifteen minutes, drain and lay in baking dish. Spread with butter, sprinkle with salt and pepper, sugar and cinnamon. Add a few tablespoonfuls of hot water and bake until tender, basting often with the sauce in the pan.
ASPARAGUS BAKED WITH CHEESE
Wash and tie the asparagus in a bunch and cook in boiling salted water until tender. Drain and save the liquor for soup. Make a sauce of the butter, flour, seasoning, stock and evaporated milk; add the yolks and two tablespoonfuls of cheese. Stir the sauce until the cheese melts but do not boil. Put the asparagus in a buttered baking dish and cover with sauce. Cover with cracker crumbs and put in an oven and bake until brown.
| Classification | Shortening | Sugar | *Eggs | Liquid | Baking Powder or Soda | Flour | Salt | Flavoring | Other Ingredients | Method |
| PLAIN CAKE for layer or loaf | ¼ c. Butter or Oleomargarine | 1 c. | 2 | ½ c. Diluted Evaporated †Milk | 2½ tsp. B. P. | 1½ c. Sifted twice | ⅛ tsp. | ½ tsp. Vanilla | Cream butter, add sugar gradually and cream well, add beaten egg and mix. Mix and sift flour, baking powder and salt. Add the dry ingredients and the first mixture. Mix with as little stirring as possible. | |
| SPICE CAKE | 1 c. Bacon Drippings | 1½ c. Light Brown | 3 | 1 c. Sour Milk | 1 tsp. Soda | 2 c. Sifted twice | ⅛ tsp. | 5 tsp. Mixed Spices | Currants and Nuts | |
| GINGER CAKE | 4 tbsp. Drippings | 1 c. Molasses | 1 | ½ c. Hot Water | 1 tsp. Soda | 2 c. Sifted twice | ⅛ tsp. | 2 tsp. Ginger | ||
| DEVIL’S FOOD | ½ c. Drippings or Oleomargarine | 2 c. Light Brown | 4 | 1 c. Diluted Evaporated Milk | 5 tsp. B. P. | 2⅔ c. Sifted twice | ⅛ tsp. | ½ tsp. Vanilla | 4 squares Melted Chocolate | Variations: Add fruit and nuts with dry ingredients. When whites and yolks are beaten separately, mix the yolk with the butter, and cut and fold in the whites last. |
| POUND CAKE | 1 c. Butter or Nut Margarine | 1½ c. Powdered Sugar | 4 | ½ c. Diluted Evaporated Milk | 2 tsp. B. P. | 2 c. Sifted twice | ⅛ tsp. | 1 tsp. Almond Ext. | ||
| LADY BALTIMORE | 1 c. Butter | 2 c. Granulated | 6 whites | 1 c. Diluted Evaporated Milk | 2 tsp. B. P. | 2 c. Sifted twice | 1 tsp. Rosewater or Almond | |||
| FRUIT CAKE Dark |
2 c. Oleomargarine or Drippings | 1 c. Molasses, 2 c. dk. brn. Sugar | 2 | 1 c. Diluted Evaporated Milk | 1 tsp. Soda | 5 c. Sifted Flour | ½ tsp. | 1 tsp. Allspice 2 tsp. Cinnamon 1 tsp. Cloves |
1 lb. Raisins, ½ lb. Citron, 1 lb. Currants, ½ c. Maraschino Cherries | |
| FRUIT CAKE White |
½ c. Oleomargarine or Butter | 1 c. Sugar | 5 whites | 1 tsp. B. P. | 1¾ c. Sifted Flour | ½ tsp. Almond Extract | ⅓ cup Blanched Alm’ds ½ cup Cocoanut ½ cup Citron |
SPONGE CAKE Beat yolks until thick and lemon colored. Add sugar gradually and continue beating, using Dover beater. Add lemon juice and water. Cut and fold in whites of egg alternately with flour. |
||
| SPONGE CAKE | 1 c. Granulated | 5 | 1 c. Pastry Flour | ¼ tsp. | 1 tsp. Lemon Juice | |||||
| SPONGE DROPS | ⅓ c. Powdered | 2 yolks 3 whites |
⅓ c. Pastry Flour | ⅛ tsp. | ¼ tsp. Vanilla | Variations: Sponge Drops should be dropped from teaspoon on oil paper. |
||||
| ORANGE CAKE | 2 c. Powdered | 5 yolks 4 whites |
2 c. Pastry Flour | ½ tsp. | Orange Frosting 2 tsp. Cream of Tartar |
Cake is judged by its delicate flavor, fine grain or texture, evenly baked crust, and appearance. Special pastry flour assures a more delicate texture than bread flour in cake making.

Salt is used to bring out flavor. Quantity used should be according to amount of butter present. When nuts are used, the amount of salt should be increased slightly to bring out flavor. When chocolate or cocoa is used, decrease the amount of fat, as there is a certain amount of fat in the cocoa and chocolate.

In plain pastry the shortening is mixed into the flour by chopping or with tips of fingers. All ingredients and utensils should be cold. When the lard is thoroughly chilled a large amount of ice-water can be incorporated, which, when converted into steam, acts as a leavening agent and makes the pastry light and fluffy.
In puff paste the shortening is worked into a paste of flour and water by folding and rolling. Equal parts by weight of flour and shortening are used.
Pure leaf lard is the ideal shortening for pastry making. It makes a light colored, soft, tender crust. Pure leaf lard is made only of leaf fat rendered in open kettles by a special process which makes the resulting product extremely rich and delicate.
Vegetole may be successfully used, following the same methods as with lard. Vegetole is an absolutely pure vegetable fat, processed to proper cooking consistency without anything being added. It may be secured in a sanitary pail in convenient size for home use.
Butter and oleomargarine are especially desirable for puff paste. A fine pastry or cake flour will absorb moisture least and is therefore one of the first requisites to pastry making. A small quantity of baking powder insures lightness to pie paste, but is not an essential to the product of an expert.
Everything must be cold, handled lightly and quickly and baked in a hot oven, to assure delicate pastry. To prevent escape of juice, mix cornstarch or flour with sugar and sprinkle lightly over the fruit before covering with the top crust. Press the edges of the upper and lower crusts tightly together. A cone of paper or piece of macaroni may be put into the slit of the crust to allow the escape of steam.
French pastries are nationally popular and are very attractive for tea or fancy dessert service. The maker has wide scope for the display of individuality in devising and decorating pastries. Slices of jelly roll, loaf or sponge cake may be spread with mocha frosting to form individual cakes. Fruit-filled tarts, topped with a bit of meringue, are always popular. The real French pastry is made of puff paste, very tender and flaky, and filled with fruit.
Baking powder, soda and eggs are used as leavening agents; this is to make the cake light. If the number of eggs is increased in the cake recipe, decrease the amount of baking powder. One egg is equivalent to one teaspoon baking powder in leavening. Egg and milk together should not exceed 1½ cups liquid with three cups flour.
A large amount of fat makes a cake close-grained; a small amount makes it porous, but it dries out easily. With too much fat, the cake crumbles and it maybe heavy. If melted fat is used in a cake, add it cool. If added hot, the cake will be tough, coarse in grain and less light.
If water is substituted for milk, use seven-eighths cup of water where one cup of milk is called for. If Veribest Evaporated Milk is substituted for whole milk, use one-third cup of evaporated milk and two-thirds cup of water. If cream is substituted for milk, lessen the shortening and use more cream than the milk called for.
Soda and acid both act on gluten and tend to make it tender, so cakes made with sour milk or buttermilk will be more tender than those made with water or sweet milk. One scant teaspoonful of soda is necessary to neutralize a cup of buttermilk or milk of the same sourness as buttermilk. An excess of soda gives the product an unpleasant flavor and, if present in too large a quantity, is injurious as well.
Sour evaporated milk is very useful in cookery. Dilute it as when sweet and add the necessary amount of soda to the product in which it is to be used.
Muffins, griddle cakes and biscuits are better made with sour milk than with sweet milk. Every bit of sour evaporated milk may be used in this way.
Evaporated milk does not sour quickly because of the thorough sterilization in heating to the temperature necessary for evaporation.
A quality grade of evaporated milk will keep after being open some four days before souring in warm weather and over a week in cold weather.
Foods made with sour milk are characterized by a particular softness of texture.

Cereals are economical, contain unusually good proportions of necessary food ingredients with small proportion of refuse, are readily prepared for the table, palatable, digestible, compact, and easily preserved without deterioration.
Rolled oats is perhaps the best-known of the cereals and lends itself to the greatest variety of dishes, aside from its popular use as a breakfast food.
Corn flakes are manufactured of the best pure white corn, thoroughly toasted and ready to serve. Wheat flakes are the whole wheat berry, flaked and toasted.
Macaroni, spaghetti, and egg noodles are made from Durum wheat semolina, ground fine. Eggs are added to the cereal for noodles.
Hominy grits and whole hominy are favorite American breakfast cereals and combine well with other foods as the main dish for the meal.
Among the staple food products, rice is one of the least expensive and should appear frequently on the family bill of fare.
Thorough cooking is the secret of the tasty and easily digested dish of cereal. Cereals in bread, muffins, cookies, cakes, croquettes, and in casseroles with cheese, fish, or left-over meat; in the baking dish with a slice of ham, or with a vegetable, they give variety to the menu and make the preparation of the everyday dishes more interesting.
| Kind | Quantity | Water | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rolled Oats | 1 c. | 2 c. | 20 min. |
| Corn Meal | 1 c. | 3½ c. | 2 hrs. |
| Hominy (Fine) | 1 c. | 4 c. | 1 hr. |
| Hominy (Whole, canned) | 1 can | heat in own liquid | 15 min. |
| Rice (Steamed) | 1 c. | 2 to 3 c. | 45 min. |
| Wheat Cereals | 1 c. | 2¾ c. | 30 min. |
| Macaroni | 1 c. | 2 qts. | 20 min. |
| Spaghetti | 1 c. | 2 qts. | 20 min. |
Stir cereals gradually into required quantity of boiling water, allowing one teaspoon salt to each cup of cereal. Fine granular cereals may be mixed first with a small amount of cold water to prevent lumping, then add boiling water. Stir flaky cereals with a fork. Cook rapidly at first over flame five or ten minutes, then in double boiler. For prepared cereals, allow plenty of time to cook thoroughly as their palatability and ease of digestion depend largely on this.
For variety, stir figs, dates or marmalade into cereals before serving. Serve with canned fruits, baked apples, or fresh fruits sliced over the cereal.
Cold cooked cereals may be sliced, dipped in flour, or in eggs and crumbs and fried. In preparing corn meal mush for frying, a little flour added to the corn meal will make it slice more easily.
During the season when fruits are plentiful serve them plain, uncooked and well ripened. Small fruits and berries should be thoroughly chilled. All fruits should be washed and drained or wiped before serving. To wash berries, place in a colander and pour water over them, handling as little as possible. If washed under the faucet turn to a small stream. Wash strawberries before removing the stems, otherwise they will become water soaked.
Serve canned fruits with their juices as a dessert for luncheon and dinner, as an appetizer for breakfast, in cocktails for dinner, and in various desserts in which fruit is used as a base. The flavor of canned fruit is improved by removing from the can to a dish and allowing to stand in the air one hour before using. The juice which is not served with the fruit should be used in fruit gelatins, sauces, or drinks. Do not waste any fruit juice.
Certain fruit juices contain a neutral substance called pectin, which, when properly cooked, causes them to solidify or jell. In this form much of our excess fruit and juices are preserved. Apples, grapes, currants, cranberries, and plums are the best known jell makers.
In preparing grapefruit to serve, chill the fruit thoroughly, cut in two crosswise, remove the seeds with a sharp pointed knife, remove the center, and, slipping the knife down between rind and pulp, loosen all around without cutting the tissue.
Bread can be made out of flour, water, yeast, and salt, but usually a little fat and sugar are added to give additional food value and flavor. Milk when used in place of water makes a more nutritious bread, and the crust has a more appetizing appearance.
Hard wheat flour, which is made from spring wheat and contains a high percentage of gluten, is best for bread making. Winter or soft wheat flour is used where a lighter, more flaky product is desired.
Good bread is sometimes described as porous or containing a large number of holes, all about the same size and shape. A loaf of bread should be light in weight according to its size and should be elastic and have a symmetrical form and an unbroken golden crust.
1. Use dependable materials and correct utensils.
2. Cleanliness. Exactness of proportions, measuring, mixing and molding.
3. Set bread to rise in a warm place. Keep it warm while rising.
4. Adjust oven temperature high at first to form crust, then medium and steady.
5. Cool loaves without steaming.
Baking bread (1) kills the ferment (2) makes starch soluble (3) drives off the alcohol and carbon dioxide (4) forms brown crust of pleasant flavor. Bread should be baked 45 minutes-1 hour in a moderate oven at a temperature of 350°-400°. If the oven is too hot, the crust will brown too quickly before the center of the bread is baked. The first fifteen minutes of the baking, the loaves should continue rising, then should brown and continue browning for the next twenty minutes. The last fifteen minutes should finish the baking.
After baking, the loaves should be removed from the pans at once, and turned on their side on a wire bread or cake cooler. If a soft crust is desired, brush with butter and cover; if a crisp crust is preferred, allow the bread to cool without covering.
Pour two cups of scalded milk (or part milk and part water) over one cup and a half of rolled oats, add two tablespoons of sugar or molasses. When cooled to lukewarm, add one-third a cake of compressed yeast, softened and mixed with half a cup of lukewarm water, three cups of whole wheat flour and two of white flour. Mix with a knife to a dough, adding as much more flour as is required to make a dough that may be kneaded. Knead until smooth and elastic. Wash and butter the mixing bowl; in it put the dough, carefully cover and set aside out of draughts. When the dough is doubled in bulk, cut down and shape into two loaves. When again nearly doubled in bulk bake one hour.
| Points | ||||
| 1. General appearance | — | Shape | 5 | |
| Smoothness of crust | 5 | |||
| Depth and evenness | 5 | |||
| 2. Lightness | 10 | |||
| 3. Crust | — | Thickness | 5 | |
| Quality (crispness and elasticity) | 5 | |||
| Color | 10 | |||
| Texture (size uniformity of cells, thinness of cell walls) | 15 | |||
| 4. Crumb—Elasticity (softness, springiness) | 15 | |||
| 5. Flavor (taste and odor) | 25 | |||
| Total | 100 | |||
Boil potatoes, drain and press through colander. Add enough water to liquor drained from the potatoes to make four cups of liquid. Add to this one yeast cake dissolved in one-fourth cup of lukewarm water, add lard, salt, hominy, and enough white flour to knead.
Knead and let rise until double its size. Knead again, shape into loaves, put into pans, and let rise again. Bake in a moderate oven forty-five minutes to one hour.
Bread and Bread Making in the Home by Caroline L. Hunt and Hanna L. Wessling. Farmer’s Bul. 807, U. S. Dept. of Ag. 1917. Bread Making—H. Atwater. Va. Agric. Dept. B. Bul. 109-16. Some Points in Making and Judging Bread by Isabelle Bevier, Univ. of Ill. Bul. Vol. X: No. 25-1916.

Cook onion and pepper with oleomargarine five minutes; add tomatoes, mushrooms, and olives and cook two minutes, then add brown sauce. Bring to boiling point and serve hot. This can accompany fish, meat or vegetables.
This is a most delicate and palatable way of cooking chicken. After cleaning the young chicken, split down the back and dredge with salt and pepper. Put a tablespoonful of lard into the frying pan, and, when it is hot, add the chicken. Cook over slow fire fifteen minutes, then add a half cup of water, and set back on the stove, and let it simmer gently and steadily for about an hour. Serve with a garnish of chopped parsley. Some smother the chicken in butter, but this is according to taste.
Put the corn through a food chopper; add the well-beaten eggs, flour, seasoning and baking powder. Mix well and fry on a well-greased hot griddle or in deep fat.
Stir the flour and add the salt, mixing thoroughly; then add the lard, and blend by rubbing through the hands till not a lump remains in the flour. Now add gradually the water or milk, or the milk and water combined, using half and half of each, and knead all together till the dough, which must not be too soft, but rather stiff, is formed. Then lay the dough on a biscuit board on a block, and beat for a half hour with a rolling pin. Knead lightly, and beat again for a full ten minutes, till from every portion of the surface and sides the air bubbles or “blisters” form. A special biscuit beater simplifies this process. Roll to quarter of an inch thick and cut round with round cutter, or square with a knife, and stick here and there with a fork. Bake in a moderate oven for about ten or fifteen minutes, till a delicate brown above and below.
Scald the cornmeal with boiling water, add butter, and stir. Beat the yolks of the eggs very, very light. Add the cornmeal and melted butter and the salt, and beat until very light, moistening with the milk. Then add the whites of the eggs, beaten to a stiff froth. Beat all well together. Pour into shallow tins and bake quickly. This is the real creole corn bread, so highly praised by all tourists through Louisiana. The secret of the exquisite flavor depends upon the proper beating of the eggs, as well as on the rising of the corn bread itself. If the eggs are well beaten, the corn bread will need neither soda nor baking powder to make it rise properly. Some add a tablespoonful of sugar when they wish to have sweetened corn bread. Corn bread, to be delicious, should always be served hot and generously buttered.

The sandwich plays such an important part in the diet that its food value from the standpoint of balanced ration is of interest. A sandwich, being composed of slices of bread filled with meat or fruit and salad dressing, constitutes a meal when coupled with a beverage. All food principles are present and in the right proportions. A sandwich embodies protein, carbohydrate, mineral matter and fat.
Bread for sandwiches should be twenty-four hours old. Remove all outside crusts or not, as desired, before slicing. Slice very thin, for sandwiches should be dainty. Always cream the butter. It not only goes farther, but spreads more easily.
Cold sliced meats form dainty sandwiches of fine flavor. Chopped pickles, olives, capers or other adjuncts improve meat sandwiches by adding a tart, spicy flavor.
Butter is often mixed with creamed cheese, chopped anchovies, or other material of like nature, to form sandwich pastes for filling. An ordinary sized loaf of sandwich bread should make between two and three dozen dainty sandwiches. One-half pound of butter is allowed for spreading this number of sandwiches.
Star ham, mayonnaise, chopped pickles, lettuce. Cold chopped veal, mayonnaise, chopped peppers, pimentos. Cold chopped pork, mayonnaise, chopped parsley, lettuce. Star ham, Thousand Island dressing, lettuce. Cold chopped pork, boiled dressing, chopped olives.
Cream cheese, chopped nuts, green chopped olives, lettuce. Chopped almonds, Thousand Island dressing, lettuce.
Grated American cheese, mayonnaise, chopped green peppers. Chopped liver sausage, mayonnaise, chopped chives, lettuce. Sliced tongue, lettuce. Chopped egg and cress, lettuce. Bean paste, and chopped ham and pickles.
Chopped figs, mayonnaise, chopped prunes. Chopped orange peel, mayonnaise. Chopped cherries, nuts, mayonnaise. Cucumber and tomato, mayonnaise, lettuce. Tomato, mayonnaise. Cottage cheese and cress, boiled dressing.
Cold sliced chicken, mayonnaise, lettuce. Chopped ham and egg, boiled dressing, lettuce. Deviled turkey, parsley, boiled dressing.
Star Summer Sausage, lettuce. Caserta Peperoni chopped with green peppers. Cooked sweetbreads, chopped, dressing, lettuce. Strassburg liver pudding, lettuce.
Corned beef, lettuce. Chopped dry sausage, pimento, boiled dressing. Loin roll, tomato ketchup. Smoked ham, lettuce.
Waste has no place in the substantial American home. The wise home manager uses every bit of wholesome edible product for food. She makes tasty dishes of all left-over foods. A bit of extract of beef adds just the flavor necessary to make many left-over meat and vegetable dishes favorites with the family.
Left-over egg yolks are rich in fat and may be used with skimmed milk in making custards, pudding sauces, salad dressings, noodles and in soups or drinks. Left-over whites may be used to clear coffee, consommé or bouillon.
Left-over bits of cheese are excellent as garnishes and as flavoring for soups and milk sauces; they not only add a great deal of fat, but some protein also. Cheese may be grated, added to white sauce and served on toast. This makes a fine, tasty luncheon dish.


The fundamental principle in child feeding is the gradual development of the digestive powers.
A normal child fed upon his mother’s milk doubles in weight in the first six months of his life, largely because his food is adapted to his needs. Never will he double his weight so rapidly again.
Cow’s milk is the safe staple throughout the second year. Milk is easily assimilated; its protein furnishes nitrogen in the best form for muscle building, and its fat provides the valuable vitamines. The mineral salts, so necessary to bone formation, are also found in this valuable food. Great care must be exercised to maintain clean, pure milk.
Eggs, cereals, orange juice, tomato juice, or other mild fruit juices (a few spoonfuls at a time), round out the diet.
When the teeth are cut, stale bread or dry toast should be added to the diet, to train the child to masticate.
When the children grow older they should be gradually given a variety in diet and, above all, trained to eat what is put before them without comment. Avoid monotony; children as well as adults enjoy change in the form in which food is served.
A normal child three to four years old needs 1100-1400 calories of food per day; at the age of five, 1435-1517 calories are required; at the age of six, 1530-1575 calories; and at seven, 1600-1700 calories, according to weight.
Milk and eggs continue to supply the necessary protein, even after green vegetables are introduced, and a plain, simple dessert may be served at the end of a meal.
Each day’s menus should contain some protective foods. Breakfast is an important meal for the school child and should be given early so the child is not hurried or worried by fear of being late. Many children do poor work in school because they are not sufficiently nourished, and frequently the meager breakfast is at fault. A regular meal schedule should now be established and strictly adhered to. Irregularity is a grave error in child feeding.
Milk, to the extent of a quart a day, should be continued up to the twelfth year. Evaporated milk contains all the food properties of fresh milk.
“Diet for the school child”—Health Education No. 2; United States Bureau of Education, Washington, D. C. “Diet for school children”—Purdue Agricultural Exp. Station Leaflet No. 103, LaFayette, Indiana. “Feeding a child from 9 months to 2 years”—Iowa Ag. Ext.
Much waste of food is due to carelessness in handling after it is delivered in the home. Thus the benefits of the elaborate care exercised in bringing the food to the consumer are sometimes lost by the carelessness of the housewife.
Few of us realize the patient care and ofttimes burdensome labor incident to food production. The long hours of labor necessary to produce food in any form should give us a wholesome respect for it when it comes into our kitchen all ready to form a part of the family diet.
In case of vegetable foods, the preparation of the soil, selection of seed, the planting, care while growing, harvesting and perhaps threshing, all demand great care and much labor upon the part of the farmer and his family.
The food product ready, it is put to one of two uses—fed to the live stock from which we obtain our milk, butter, cheese, meat and meat products, or it is sent to factories where by means of much more labor and care it is further prepared for our table. By canning, as in case of fruits and vegetables, by milling of grains, or, if the product is a meat animal, by the many complicated processes of packing, the food is prepared for transportation.
Perishable foods must be cared for in cold storage and transported in refrigerator cars, all of which occupies the time and energy of thousands of people.
Next, the retailer adds his services, and the article which has cost so much in money and energy is finally delivered in the home in good condition.
It is the duty of the housewife to unpack and properly put away all foods as soon as they are delivered.
Place butter, milk, oleomargarine, shortenings, and frying mediums, eggs, and meat, as well as other perishables, in appropriate receptacles and put them in the refrigerator. Meat should be unwrapped, placed on a plate and set in the refrigerator, but never directly on ice. Fresh salad materials should be cleaned, wiped dry, and put in a salad bag, in a cool place.
Place cereals, syrups, coffee, tea, spices, baking powder, salt, extracts and all canned foods upon the pantry shelf or in the convenient kitchen cabinet.

To observe the rules given for maid service when without a maid, would be an unnecessary tax upon one’s time and strength. The serving can be done nicely if attention be paid to certain points.
To avoid disturbance and frequent rising from the table, all foods which the temperature of the rooms will not affect should be placed upon the table or the serving table.
It is a good plan to have some young member of the family circle perform what service is required. For this kind of service it is permissible to remove plates or dishes two at a time, one in each hand, and to leave a person without a plate. This is, of course, contrary to conventional service.
1. Pass and place everything from the left, except beverages and extra silver belonging on the right.
2. Place and remove plates one at a time. To save time, two plates may be brought to the dining room. Place one on the serving table and the other on the dining table; return to the serving table for the second plate, rather than to the pantry.
3. Use a folded napkin in the hand under all dishes served which contain food.
4. Use a tray only when passing or removing more than one article, as cream and sugar, or salt and pepper.
5. In removing a course, first take all dishes containing food, then soiled plates and silver.
6. Special watchfulness should be given by the maid that each person’s needs are attended to.
7. Two pieces of silver placed on a platter containing food to be served are more convenient than one, for the person serving himself.
8. No sound of preparation should come from the pantry.
9. Hot dishes must come to the table hot and served on hot plates. Cold dishes must be cold and served on cold plates.
10. A maid should always wear a clean fresh dress and apron.
The great majority of the American housewives do their own work.
A bit of hourly help now and then is the extent of help in thousands of representative homes.
To be able to prepare a perfect meal, have the house in order, the children happy and spotless, the table attractively set, and to serve the meal oneself at the same time retaining one’s poise, occupying the hostess’ place at the table, directing the conversation and creating a feeling of true hospitality is, perhaps, the greatest test of one’s generalship.
These suggestions will help make the accomplishments a pleasure.
1. Plan menu and do all buying excepting fresh salad materials.
2. Prepare as much as possible of the company meal.
3. Put the house in order.
4. See that all silver, china, glassware and linen is in perfect condition.
1. Set the children at an interesting game early in the day where they will be free to romp. They will then want a rest at your busy time.
2. Think what a joy these guests are to be and how happy you want to make everyone.
3. Do necessary finishing touches, arranging decorations, and rest ten minutes, enjoying your anticipated pleasure before beginning the actual preparation of the meal.
4. Manage a rest period of twenty minutes before dressing for dinner, and call to mind a few amusing incidents to relate.
The ideal hostess is never tired or worried and has a fund of interesting conversation.
1. The Russian Service is most formal. No food is on the table except candy and nuts. All serving is done from the pantry or the serving table. The food is attractively arranged upon suitable dishes from which each person helps himself; or portions may be arranged upon plates, one of which is placed before each person. The former method is preferable.
2. The English Service is informal. The food is placed upon the table and served by those seated at the head and the foot. If one has a maid, the passing is done by her; if not, by those sitting at the table.
3. The Mixed Service is a combination of the two mentioned and requires the service of a waitress. Some of the courses are served “from the side” (Russian), and some “from the table” (English). Frequently the meat is served from the table and the accompanying vegetables served from the side (Russian).
The body needs food to keep it warm, to furnish energy for the activities of daily life; to build and repair tissue and to regulate the body process.
Proteins, fats, carbohydrates, mineral matter, and water, are the chief classes of food. The chief work of proteins is to build and repair tissue. Meat and milk are the principal sources of protein. Nuts, vegetables and some cereals also supply this element.
Carbohydrates are the starches and sugars. They are found in vegetables, cereals, and fruits and give heat and energy to the body. Fats give two and a half times as much energy as any other food.
Mineral matters enter into the composition of the body tissues and blood. They act as regulators, preserving the alkalinity of the body. They are found in varying proportions in all foods, but milk contains all the essential ones.
Vitamines are necessary for growth and are abundant in leafy vegetables and milk. Foods rich in vitamine content are known as protective foods. They prevent the development of deficiency and old age diseases.
Water is necessary as a carrier and regulator. It aids digestion, removes waste, and keeps the temperature normal.
A general balance of food should be maintained in each day’s diet: 1/5th meat or meat alternatives, 1/5th fat, and 3/5ths carbohydrates, with a serving of fruits and vegetables and plenty of liquid, completes the necessary variety.
Before assimilation, the food we eat must be oxidized or burned. The heat resulting from this oxidation is measured in terms of calories, or heat units.
While the number of calories supplied by the diet is important, the proper balance as to the classification of the food is of prime importance. We cannot build up the diet on calorie values alone without consideration of the food elements.
| Man at light work | 2500 to 2800 | Calories | per | day |
| Man at moderate work | 3000 to 3500 | “ | “ | “ |
| Man at very hard work | 4000 to 5000 | “ | “ | “ |
| Woman at light work | 1800 to 2400 | “ | “ | “ |
| Woman at moderate work | 2400 to 2800 | “ | “ | “ |
| Child from two to six | 1200 to 1800 | “ | “ | “ |
| Child from six to fifteen | 1800 to 2500 | “ | “ | “ |
| Aged Man | 1800 to 2000 | “ | “ | “ |
| Aged Woman | 1600 to 1800 | “ | “ | “ |
The responsibility for the correct development of a family rests more and more surely at the door of the one who plans and cooks the meals for that family.
Nutrition experts are continually making careful tests and giving us valuable information through the newspapers and women’s national publications. With such easy access to the fundamentals of correct eating, it comes close to criminal negligence for a mother to feed her family improperly; the present percentage of under-nourished children is appalling, and many of these are in the homes of the well-to-do.
The most important “food finding” of the year has been the information given the public regarding Protective Foods, sometimes called dietetic ferments or the foods rich in the vitamines that promote growth and those rich in the vitamines that protect one from deficiency diseases such as scurvy, beriberi, pellagra and less dangerous skin diseases.
Milk and its products, butter and cheese, are foremost growth promotors. In this class comes also the yolk of eggs, glandular meats, and grains with the living germ still intact. Leafy vegetables, such as spinach, lettuce, cabbage, chard, cauliflower, kale, all greens, water cress, onions, string beans, and a few others are classed with protective foods.
While Professor McCullom does not yet definitely list the tomato under protective foods, it is found to have valuable protective qualities, often being substituted for orange juice in preventing scurvy in baby feeding. The protective substance of the tomato is not easily destroyed.
Experiments are continually being completed which add new foods to this important group.



Accurate measuring of materials, heat and time are primary factors in successful cooking. Every kitchen should have a weighing scale and a measuring cup.
| 3 teaspoons | 1 tablespoon |
| 16 tablespoons | 1 cup |
| 2 tablespoons butter | 1 oz. |
| 4 tablespoons flour | 1 oz. |
| 1 square Baker’s chocolate | 1 oz. |
| ⅓ cup chopped almonds | 1 oz. |
| 2 cups | 1 pint |
| 4 cups flour | 1 lb. |
| 2⅔ cups corn meal | 1 lb. |
| 2 cups gran. sugar | 1 lb. |
| 2⅔ cups brown sugar | 1 lb. |
| 2¾ cups powdered sugar | 1 lb. |
| 4¾ cups rolled oats | 1 lb. |
| 2 cups finely chopped meat | 1 lb. |
| c.—cup |
| tbsp.—tablespoon |
| tsp.—teaspoon |
| 4 saltspoonfuls | = | 1 teaspoonful |
| 4 teaspoonfuls dry | = | 1 tablespoonful dry |
| 3 tsp. liquid | = | 1 tablespoonful liquid |
| 16 tablespoonfuls | = | 1 cupful dry ingredients |
| 12 tablespoonfuls | = | 1 cupful wet ingredients |
| 2 cupfuls | = | 1 pint |
| 2 pints | = | 1 quart |
| 4 quarts | = | 1 gallon |
| 8 quarts | = | 1 peck |
| 1 lb. cornstarch | = 3 | cups - 2 tbsp. | ||
| 1 lb. butter | = 2 | cups - 2 tbsp. | ||
| 1 lb. lard | = 2 | cups - 2 tbsp. | ||
| 1 lb. bran | = 9 | cups - 2 tbsp. | ||
| 1 lb. rice | = 2 | cups - ½ tbsp. | ||
| 1 lb. rye flour | = 3⅞ | cups | ||
| 1 lb. pastry flour | = 4 | cups | ||
| 1 lb. bread flour | = 4 | cups | ||
| 1 lb. confectioner’s sugar | = 2⅞ | cups | ||
| 1 lb. light brown sugar | = 2¾ | cups | ||
| 1 lb. pulverized coffee | = 5½ | cups | ||
| 1 lb. graham flour | = 3¾ | cups | ||
| 1 lb. entire wheat flour | = 3½ | cupfuls plus 1 tablespoonful | ||
| 1 lb. granulated corn meal | = 3 | cupfuls plus 1 tablespoonful | ||
| 1 lb. granulated sugar | = 2 | cupfuls | ||
| c.—cup |
| tbsp.—tablespoon |
| tsp.—teaspoon |
It will not be long before thermometers will be generally used as kitchen appliances. Until then we must show how we may know when a food is cooked, instead of stating the exact number of minutes required. It is better in most cases to subject foods to a moderate heat for a long time, than to intense heat for a shorter period. The shape and size of the article to be cooked and the variety and age of fruit or vegetables must be considered.
| SLOW | MODERATE | HOT OR QUICK | VERY HOT |
| 250°-350° | 350°-400° | 400°-425° | 425°-500° |
| Custards | Bread | Biscuits | Roast Meat |
| Meringues | Cakes | Cookies | Roast Poultry |
| Pastry | Pastry, Tarts | ||
| Rolls | Puff Paste |
| Biscuits, baking powder | 15 | minutes |
| Bread (1 lb. loaf) white | 60 | “ |
| Bread (1 lb. loaf) graham | 40 | “ |
| Rolls or biscuits (raised) | 20 | “ |
| Gems or muffins | 30 | “ |
| Corn bread (thin) | 20 | “ |
| Corn bread (thick) | 35 | “ |
| Sponge cake | 45 to 60 | “ |
| Layer cake | 20 to 30 | “ |
| Loaf cake | 40 to 60 | “ |
| Pound cake | 1¼ to 2 | hours |
| Indian or plum pudding | 2 to 3 | “ |
| Muffins, fritters, doughnuts | 3 to 5 | minutes |
| Croquettes and fish balls | 1 | “ |
| Potatoes, cut thick | 10 | “ |
| Breaded chops | 5 to 8 | “ |
| Fillet of fish | 5 to 10 | “ |
| Small fish | 5 | “ |
| Steak (1 inch thick) | 10 to 12 | min. |
| Steak (2 in. thick) | 15 to 20 | “ |
| Pork chops (cook slow) | 30 to 40 | “ |
| Mutton chops | 7 to 10 | “ |
| Fish | 15 to 20 | “ |
| Beef roast (rare) | 15 | min. | to | warm | through | 12 | min. | per | lb. | |
| Beef roast (well done) | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 15 | “ | “ | “ | |
| Mutton leg | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 10 to 15 min. per lb. | ||||
| Mutton shoulder | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 15 | min. | per | lb. | |
| Lamb roast | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 18 | “ | “ | “ | |
| Veal roast | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 18 | “ | “ | “ | |
| Pork roast | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 30 | “ | “ | “ | |
| Chicken | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 15 to 18 min. | ||||
| Goose | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 18 | min. | per | lb. | |
| Duck | “ | “ | “ | “ | “ | 18 | “ | “ | “ | |
| Turkey, large | Roast in slow oven | 4 to 5 hours | ||||||||
| Turkey, small | Roast in slow oven | 3½ to 4 hours | ||||||||
| Ham, medium weight | Moderate oven | 4 to 5 hours | ||||||||
| BREADS | |
|---|---|
| PAGE | |
| Baking bread | 39 |
| Beaten biscuit, recipe | 40 |
| Corn fritters, recipe | 40 |
| Good bread, qualities of | 39 |
| Hominy bread, recipe | 39 |
| How to judge bread | 39 |
| Points to remember in bread making | 39 |
| References regarding bread | 39 |
| Rolled oats bread, recipe | 39 |
| Southern egg bread, recipe | 40 |
| CEREALS | |
| Cold cooked cereals | 38 |
| How to serve cereals | 38 |
| Table for cooking cereals | 38 |
| Use of cereals in the diet | 38 |
| CHARTS AND TABLES | |
| Balanced rations, food classification for | 27 |
| Beef, dishes, cuts, and ways to use | 12 |
| Beef, retail cuts, food value, cost, cooking, uses | 7 |
| Beef, standard retail cuts (illustrated) | 8 |
| Beef and veal, extra portions, food value, cost, uses | 15 |
| Cakes, recipes for making | 36 |
| Calorie requirements | 44 |
| Cereals, table for cooking | 38 |
| Cheese, how to use | 34 |
| Chicken, ways of serving | 13 |
| Cook books, popular list of | 28 |
| Cream sauces, foundation recipes for | 31 |
| Dependable products, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Eggs, uses and ways of cooking | 34 |
| Eggs, ways to serve | 18 |
| Family budget, example for apportionment | 5 |
| Family budget, form for | 6 |
| Fats, chemical composition of Armour’s | 22 |
| Fats, smoking point, calories, how to use | 22 |
| Foods, list of equivalents in | 46 |
| Fruits to serve with meats | 23 |
| Ham and bacon, ways to serve | 16-17 |
| Household equipment | 45 |
| Lamb and mutton, extra portions, food value, cost, uses | 15 |
| Lamb dishes, variety and cuts for same | 14 |
| Lamb, retail cuts, food value, cost, cooking, uses | 9 |
| Measures, list of equivalents in | 46 |
| Menus for unexpected demands | 27 |
| Oven temperatures | 46 |
| Pantry supplies | 27 |
| Pork dishes, variety of, and cuts for same | 14 |
| Pork, extra portions, food value, cost, cooking, uses | 15 |
| Pork, retail cuts, food value, cost, cooking, uses | 9 |
| Sauces and garnishes for various cuts of beef | 12-40 |
| Sausages, varieties of | 19-20 |
| Time for baking, broiling, frying, roasting | 46 |
| Veal, retail cuts, food value, cost cooking, uses | 9 |
| Vegetables to serve with meals | 23 |
| Weights and measures | 46 |
| DAIRY PRODUCTS | |
| Butter in cold storage | 10 |
| Cheese, how to cook and keep | 34 |
| Cheese, how to use, cooked and uncooked | 18 |
| Cheese sauce, recipe | 34 |
| Cheese soufflé, recipe | 34 |
| Dairy products, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Milk as a food | 17 |
| Milk, evaporated | 17 |
| Milk, evaporated, uses of | 17 |
| DIET | |
| Balanced diet chart | 27 |
| Calories | 44 |
| Children, food for | 42 |
| Elements of foods | 44 |
| Food in the home, care of | 42 |
| EGGS | |
| Eggs in cold storage | 10 |
| Eggs, how to preserve | 34 |
| Eggs, uses of | 34 |
| Eggs, value in the diet | 18 |
| Eggs, ways to serve | 18 |
| Eggs, ways of cooking, time required to digest | 34 |
| FATS | |
| Chemical composition of Armour Fats | 22 |
| Clarifying fats | 22 |
| Fats, how to use (chart) | 22 |
| Fats, use of drippings | 22 |
| Foods that soak fats | 22 |
| Salad oils in cooking | 22 |
| Shortenings and frying mediums, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Test for frying fats | 22 |
| FISH | |
| Cream sauces | 31 |
| Creole sauce, recipe | 40 |
| Fish in the menu | 14 |
| FRUITS | |
| Canned fruits | 38 |
| Fresh fruits, serving | 38 |
| Fruits to serve with various meats | 23 |
| Fruits, value in diet | 23 |
| HOUSEHOLD EQUIPMENT | |
| Bread making equipment | 45 |
| Cleaning purposes equipment | 45 |
| Dessert making equipment | 45 |
| Fish cooking equipment | 45 |
| General kitchen equipment | 45 |
| Meat cookery equipment | 45 |
| Popular cook books | 28 |
| Salad making equipment | 45 |
| Sundry equipment | 45 |
| Vegetable cooking equipment | 45 |
| LEFT-OVERS | |
| Uses of left-overs | 39 |
| Ways of serving left-over fowl | 32 |
| MEATS | |
| Bacon, how to select | 16 |
| Bacon, ways to serve | 16 |
| Beef extract | 20 |
| Beef sauces and garnishes | 12 |
| Beef, ways to serve | 12 |
| Boiling meats | 29 |
| Braising meats | 29 |
| Broiling meats | 29 |
| Canned meats, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Creole sauce, recipe | 40 |
| [48]Deep frying of meats | 29 |
| Fresh meats, how to select | 11 |
| Gov’t inspection of meats | 10 |
| Ham and bacon sauces | 17 |
| Ham, baked, recipe | 30 |
| Ham, baked, ways to serve | 16 |
| Ham, boiled, ways to serve | 16 |
| Ham, how to select | 16 |
| Hungarian Goulash, recipe | 31 |
| Jellied loaves | 20 |
| Loaf meats, list of Armour’s | 20-26 |
| Luncheon meats, list of Armour’s | 20-26 |
| Pan broiling meats | 29 |
| Pot roast of beef with spaghetti, recipe | 30 |
| Pot roasting meats | 29 |
| Roast chuck, recipe | 30 |
| Roast shoulder of mutton, recipe | 30 |
| Roasting and baking meats | 29 |
| Rolled flank steak, recipe | 30 |
| Sauces and gravy for meats, recipes | 31 |
| Sautéing meats | 29 |
| Smoked meats, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Steak, rump, planked, recipe | 31 |
| Steak, sirloin, broiled, recipe | 31 |
| Stewing meats | 29 |
| MENUS | |
| Christmas dinner | 40 |
| For unexpected demands | 27 |
| Southern dishes | 40 |
| Thanksgiving dinner | 40 |
| MINCE MEAT | |
| Food value of mince meat | 23 |
| List of Armour’s mince meat | 26 |
| Variety of uses of mince meat | 23 |
| PANTRY SUPPLIES | |
| Cereals and flour | 27 |
| Condiments and seasonings | 27 |
| Flavoring extracts and baking powder | 27 |
| Fruits, canned | 27 |
| Miscellaneous articles | 27 |
| Plum pudding (Veribest) | 26 |
| Products easily served | 27 |
| Quality products for the pantry shelf (illustrated) | 24-25 |
| Sea Foods, canned | 27 |
| Soups, canned | 27 |
| Spreads, shortenings and frying mediums | 27 |
| Vegetables, canned | 27 |
| Vegetables, fresh | 27 |
| POULTRY | |
| Chicken, smothered, recipe | 40 |
| Chicken, ways to serve | 13 |
| Fowl, preparation of | 32 |
| Fowl, pressure cooking of | 32 |
| Fowl, roasting, stewing, broiling, frying and dressing | 32 |
| Fowl, serving left-over | 32 |
| Poultry in cold storage | 10 |
| Poultry, how to select | 13-32 |
| Poultry, how to thaw frozen | 13 |
| Poultry, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Poultry, U. S. Dept. of Ag. bulletins | 13 |
| SALADS | |
| Care of materials | 33 |
| Cheese salad dressing, recipe | 33 |
Dressings, boiled, cheese, French, mayonnaise, Russian, Thousand Island, whipped cream, recipes | 33 |
| Fish salad, recipe | 33 |
| Fruit salad, recipe | 33 |
| Lettuce salad, recipe | 33 |
| Vegetable salad, recipe | 33 |
| When to serve salads | 33 |
| SANDWICHES | |
| Brown bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Graham bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Nut bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Raisin bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Rye bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Sandwiches, how to prepare | 41 |
| White bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| Whole wheat bread sandwich, recipe | 41 |
| SAUCES | |
| Varieties of | 12-17, 31-34 |
| SAUSAGES | |
| Sausage, dry, how to serve | 19 |
| Sausages, dry, smoked and unsmoked, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Sausages, fresh and smoked, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Sausage, pork, fresh, how to serve | 19 |
| Sausage, smoked, how to serve | 19 |
| Sausages, varieties of | 20 |
| SOUPS | |
| Soups, canned | 28 |
| Soups, preparing | 28 |
| SPREADS | |
| Butter as a spread | 21 |
| Nut margarine as a spread | 21 |
| Oleomargarine as a spread | 21 |
| Peanut butter as a spread | 21 |
| Peanut butter, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Peanut butter, uses of | 18 |
| Spreads, list of Armour’s | 26 |
| Spreads, proper fat for every cookery use | 21 |
| TABLE SERVICE | |
| Care of the table | 43 |
| Russian, English and mixed service | 43 |
| Standard rules | 43 |
| VEGETABLES | |
| Asparagus, baked with cheese, recipe | 35 |
| Beans, value in the diet | 18 |
| Boiling, steaming and baking vegetables | 35 |
| Candied sweet potatoes, recipe | 35 |
| Cream sauces | 31 |
| Creole sauce, recipe | 40 |
| Garnishes of vegetables | 35 |
| Vegetables, composition of | 23 |
| Vegetables, selection of | 35 |
| Vegetables to serve with various meats | 23 |
| Ways of serving vegetables | 35 |
Obvious punctuation errors repaired. Consistent unusual spellings were retained such as “Peperoni” and “vitamines.”
Page 16, “Amercan” changed to “American” (foods in the American)
Page 17, “effected” changed to “affected” (affected by the process)
Page 25, “knobloch” changed to “knoblach” (Garlic or Knoblach Sausage)
Page 39, “by” removed from italics to match rest of text’s usage (in Making and Judging Bread by)